| [1] |
王鸿泽, 赵聪颖, 兰海铭, 等. 鳕鱼排加工工艺的研究[J]. 食品安全导刊,2018,203(12):149−150.
|
| [2] |
Toppe J, Albrektsen S, Hope B, et al. Chemical composition, mineral content and amino acid and lipid profiles in bones from various fish species[J]. Comparative Biochemistry Physiology B Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,2007,146(3):395−401. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2006.11.020
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
刘伯业. 小麦蛋白低苦味肽的制备及其脱苦机理研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2017: 5−10.
|
| [5] |
Kukman I L, Zelenik-blatnik M, Abram V. Isolation of low-molecular-mass hydrophobic bitter peptides in soybean protein hydrolysates by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,1995,704(1):113−120. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(95)00014-E
|
| [6] |
Shinoda I, Tada M, Okai H, et al. Bitter taste of h-pro-phe-pro-gly-pro-ile-pro-oh corresponding to the partial sequence (positions 61-67) of bovine b-casein, and related peptides[J]. Journal of Agricultural Chemical Society of Japan,1986,50(5):1247−1254.
|
| [7] |
Liu H, Li Y, Diao X, et al. Effect of porcine bone protein hydrolysates on the emulsifying and oxidative stability of oil-in-water emulsions[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2018,538:757−764. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.11.061
|
| [8] |
Fan, W W, Tan X Y, Xu X B, et al. Relationship between enzyme, peptides, amino acids, ion composition, and bitterness of the hydrolysates of Alaska pollock frame[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry 2019, 43(4): e12801.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
中华人民共和国卫生部. GB 5009.5-2010 食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2010: 2−6.
|
| [11] |
Burton L J, Rivera M, Hawsawi O, et al. Muscadine grape skin extract induces an unfolded protein response-mediated autophagy in prostate cancer cells: A TMT-based quantitative proteomic analysis[J]. PLoS One,2016,11(10):e0164115. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164115
|
| [12] |
白艳红, 张相生, 赵电波, 等. 分步酶解猪骨粉提取猪骨素的工艺研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2012,28(12):1696−1699.
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
Dauksas E, Slizyte R, Rustad T, et al. Bitterness in fish protein hydrolysates and methods for removal[J]. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology,2004,13(2):101−114. doi: 10.1300/J030v13n02_09
|
| [15] |
曾晓房. 鸡骨架酶解及其产物制备鸡肉香精研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2007: 5−10.
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
吴莉莉, 陈俊香. 双酶法降解核酸生产核苷酸食品增鲜剂: 酵母深加工高附加值产品[J]. 甘蔗糖业,2000(3):32−36, 41.
|
| [18] |
Chobert J M, Unklesbay N, Hsieh F H, et al. Hydrophobicity of bitter peptides from soy protein hydrolysates[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry,2004,52(19):5895−5901.
|
| [19] |
Matoba T, Hata T. Relationship between bitterness of peptides and their chemical structures[J]. Agricultural & Biological Chemistry,2004,36(8):1423−1431.
|
| [20] |
Ishibashi N, Ono I, Kato K, et al. Role of the hydrophobia amino acid residue in the bitterness of peptides[J]. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry,1988,52(1):91−94.
|
| [21] |
Zhao J, Xiong Y L. Interfacial peptide partitioning and undiminished antioxidative and emulsifying activity of oxidatively stressed soy protein hydrolysate in an O/W emulsion[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2015,61(2):322−329. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2014.12.022
|
| [22] |
Agboola S O, Singh H, Munro P A, et al. Destabilization of oil-in-water emulsions formed using highly hydrolyzed whey proteins[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,1998,46(1):84−90. doi: 10.1021/jf970365b
|
| [23] |
Slattery H, Fitzgerald R J. Functional properties and bitterness of sodium caseinate hydrolysates prepared with a bacillus proteinase[J]. Journal of Food Science,2008,63(3):418−422.
|
| [24] |
Fitz Gerald R J, O’Cuinn G. Enzymatic debittering of food protein hydrolysates[J]. Biotechnology Advances,2006,24(2):234−237. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2005.11.002
|
| [25] |
Kim H O, Li-Chan E C Y. Quantitative structure-activity relationship study of bitter peptides[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2006,54(26):10102−10111. doi: 10.1021/jf062422j
|






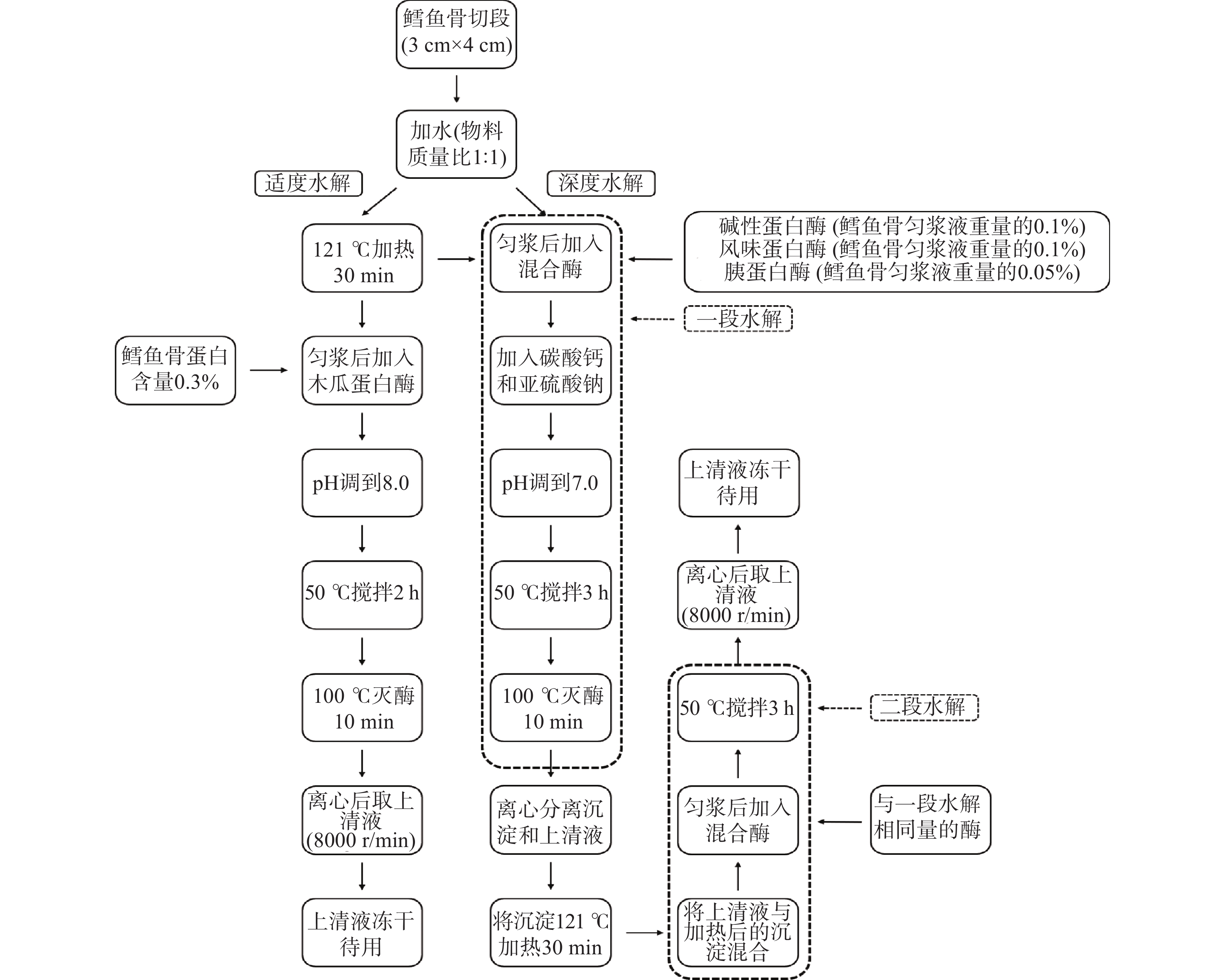




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: