Preparation of Cod Gelatin Antifreeze Peptides and Its Application of Frozen-Thawed Surimi
-
摘要: 为优化高活性鳕鱼明胶抗冻多肽(DcAFPs)的制备方法,明确鳕鱼明胶多肽对鱼糜的冷冻保护效果,本研究将鳕鱼明胶多肽添加至鱼糜中,以冷冻后鱼糜肌原纤维蛋白含量为考察指标,通过单因素和正交试验进行工艺优化。通过测定DcAFPs分子量分布和氨基酸组成,分析其基本性质;通过测定鱼糜肌原纤维蛋白含量,并运用内源荧光光谱和SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳技术,评估DcAFPs对反复冻融循环后鱼糜的保护效果。结果表明,DcAFPs的最优制备工艺是:使用复合蛋白酶、底物浓度为3.5%(w/v)、酶底比为5%(w/w)、水解pH为8、水解温度为55 ℃、水解时间为2 h。DcAFPs分子量主要集中在185~3081 Da,Gly、Ala和Glu的含量最高。DcAFPs能有效防止鱼糜在冻融过程中肌原纤维蛋白含量的减少,抑制肌原纤维蛋白结构和组成的变化,延缓蛋白变性,其总体效果优于商业抗冻剂。综上所述,DcAFPs对反复冻融的鱼糜显示出显著的冷冻保护效果。Abstract: To optimize the preparation method of highly active cod gelatin antifreeze peptides (DcAFPs) and clarify its cryoprotective effects on surimi, this study added cod gelatin peptides to surimi. The myofibrillar protein content in the surimi after freezing was used as an evaluation index, and the process was optimized through single-factor and orthogonal experiments. By determining the molecular weight distribution and amino acid composition of DcAFPs, their basic properties were analyzed. Additionally, the protective effects of DcAFPs on surimi subjected to repeated freeze-thaw cycles were assessed by measuring myofibrillar protein content and utilizing intrinsic fluorescence spectroscopy and SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis techniques. The results showed that the optimal preparation process for DcAFPs involved using compound protease, with a substrate concentration of 3.5% (w/v), an enzyme-to-substrate ratio of 5% (w/w), a hydrolysis pH of 8, a hydrolysis temperature of 55 ℃, and a hydrolysis time of 2 hours. The molecular weight of DcAFPs was primarily concentrated between 185 and 3081 Da, with glycine (Gly), alanine (Ala), and glutamic acid (Glu) being the most abundant amino acids. DcAFPs effectively prevented the reduction of myofibrillar protein content during freeze-thaw cycles, inhibited changes in the structure and composition of myofibrillar proteins, and delayed protein denaturation. In conclusion, DcAFPs exhibited significant cryoprotective effects on surimi that subjected to repeated freeze-thaw cycles and outperformed commercial antifreeze agents.
-
Keywords:
- cod fish gelatin /
- antifreeze peptides /
- surimi /
- myofibrillar proteins /
- antifreeze activity
-
鱼糜因其味道鲜美、营养价值高而在世界范围内需求量大。鱼糜在常温下易腐败,冷冻保存是维持其品质的重要手段。然而,鱼糜的高水分含量在冷冻过程中易形成冰晶[1],这些冰晶在存储和运输过程中的生长和反复冻结会对细胞和肌肉组织造成损害,破坏蛋白质结构,导致鱼糜品质下降。为了减轻这种损害,添加抗冻剂成为了一种有效的策略[2]。目前,商业上常用的抗冻剂是山梨醇和蔗糖的混合物,它们已被证实能有效抑制鱼糜在冻融过程中的品质劣化[2−3]。但这种传统抗冻剂可能会给鱼糜带来额外的热量和甜味,不符合现代消费者对低糖低热量食品的需求[3]。因此,开发“低糖、低卡”的绿色抗冻剂成为了冷冻鱼糜加工领域的研究热点。
磷酸盐类抗冻剂目前也被广泛关注。它们由磷酸与金属离子反应生成,因其出色的保水能力[4]和成本效益而在鱼糜抗冻领域备受青睐。尽管磷酸盐类抗冻剂能够提升鱼糜的持水能力,维持其冷冻品质,但过量摄入可能会影响人体对钙的吸收,对健康造成潜在风险[5]。抗冻蛋白是一类能够降低体系冰点并抑制冰晶生长的蛋白质[6],添加到鱼糜中可增加鱼糜营养价值,但由于制备过程复杂和资源有限,目前尚未广泛应用于食品工业。因此,探索新的、可商业化的抗冻蛋白资源具有重要意义。
通过酶解技术从食源性蛋白中筛出高活性抗冻多肽是解决抗冻蛋白资源短缺的有效途径[7]。食源性抗冻多肽原料丰富,生产工艺可控,便于工业化生产和应用[8]。与传统的商业抗冻剂(4%山梨醇+4%蔗糖)和磷酸盐类物质相比,抗冻多肽不仅具有相当的冷冻保护效果,还能提升食品的营养价值[2]。此外,与资源有限、制备复杂的抗冻蛋白相比,抗冻多肽的成本更低,物理化学性质更稳定[3],对鱼糜的感官品质影响较小,有望成为新型绿色抗冻剂。例如,KHAN等[9]的研究表明,通过将酶解海洋鱼废料得到的蛋白水解产物添加至鱼糜中,可抑制肌原纤维蛋白ATP酶活性和鱼糜凝胶持水性的下降,有效维持冷冻鱼糜品质。
鳕鱼作为一种深海冷水鱼类,其耐寒特性可能与其体内含有的抗冻蛋白有关,使其有望成为抗冻剂制备的优质原料[10]。鱼明胶,作为鱼加工副产品的再利用产物,富含亲水性氨基酸[11],具有高安全性,是制备抗冻肽的理想原料[12]。鳕鱼明胶(由鳕鱼的鱼皮、鱼骨等制备而成的明胶)不仅来源丰富、可持续生产,还能减少食品加工中的废弃物,提高资源利用率。研究表明相对于大分子的蛋白,小分子的肽更具有生物活性[9,13]。LIU等[13]将鳕鱼酶解成多肽后显示出显著的抗氧化活性,能够有效抑制鲜切马铃薯片的褐变。然而目前尚未发现有关于鳕鱼明胶多肽作为鱼糜抗冻剂的报道。因此,本研究以鳕鱼明胶为原料,通过单因素实验和正交试验优化鳕鱼明胶抗冻多肽(DcAFPs)的制备工艺条件,并对DcAFPs进行分子量分布和氨基酸组成的性质表征。进一步地,将DcAFPs添加至鱼糜中,通过冻融处理后分析肌原纤维蛋白的含量,并采用电泳和荧光光谱技术评估DcAFPs在鱼糜中的冷冻保护效果。这些研究成果为DcAFPs在冷冻鱼糜中的应用提供了理论依据,有望推动新型绿色抗冻剂的开发和应用。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
鳕鱼明胶 江西福美泰生物科技有限公司;复合蛋白酶(≥120 units/mg)、蔗糖、山梨醇、1 mol/L Tris-HCl(pH7.4) 北京索莱宝生物科技有限公司;其他试剂均为国产分析纯。
U-2910型紫外-可见光光度计、D-2000HSM型高效液相色谱仪 日本HITACHI公司;L-8080型全自动氨基酸分析仪 日本日立公司;F6/10手持式匀浆机 上海净信实业发展有限公司;H2050R台式高速冷冻离心机 湖南湘仪仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 DcAFPs的制备工艺优化
1.2.1.1 鳕鱼明胶多肽制备
配制一定浓度的鳕鱼明胶溶液,根据单因素设置条件利用NaOH或HCl调节溶液pH。随后,添加不同剂量的复合蛋白酶[14]在不同温度下水解不同时间。水解结束后,将样品置于100 ℃水浴中煮沸15 min,以终止酶的活性。待样品冷却至室温后,在10000 r/min条件下离心10 min[15] ,取上清液并冻干,冻干物于−80 ℃冰箱贮藏备用。
1.2.1.2 单因素实验
以鱼糜冷冻后的肌原纤维蛋白含量为指标,对DcAFPs水解工艺进行单因素实验。单因素实验中使用复合蛋白酶,依次按照酶底比、水解温度、水解pH、底物浓度、水解时间的筛选进行实验,每次实验严格控制单一变量。筛选酶底比时设置酶解初始条件为:底物浓度3%(w/v),水解温度为50 ℃,水解时间为4 h,水解pH为7,基于每次筛选所得的结果,对初始条件中的相应因素进行替换,随后继续进行后续的因素筛选工作。各因素的变量为:酶底物比为1%、3%、5%、7%、9%(w/w);水解温度为30、40、50、60、70 ℃;水解pH为5、6、7、8;底物浓度1%、2%、3%、4%、5%(w/v);水解时间为0.5、1、2、4、6 h。
1.2.1.3 正交试验设计
基于单因素实验结果,选择结果影响最为显著的三个因素:底物浓度、水解时间、水解温度为试验因素,以多肽加入鱼糜冷冻5 d后的肌原纤维蛋白含量为指标进行正交试验设计。并通过正交软件设计三因素三水平的L9(34)试验方案,优化DcAFPs的制备工艺。设计方案如表1所示。
表 1 正交试验设计因素与水平Table 1. Factors and level of orthogonal experiment design水平 因素 A水解温度(℃) B水解时间(h) C底物浓度(%) 1 55 1 2 2 60 2 3 3 65 3 3.5 1.2.1.4 鱼糜制备及抗冻多肽抗冻活性测定
将新鲜杀好的白鲢鱼体洗净,取鱼肉中的白肉部分。将所取得的白肉绞成肉糜,随后将肉糜放入清水中漂洗(鱼肉:水=1:3),漂洗过程中慢速搅拌10 min,之后用纱布过滤,此过程重复2次。之后再用0.5%氯化钠溶液漂洗(鱼肉:0.5%氯化钠溶液=1:3,w/v),纱布过滤。最后再于离心机中离心脱水(4000 r/min,15 min,4 ℃),所得沉淀即为鱼糜[16]。将冻干后的样品以4%的重量比添加到鱼糜中,并将混合后的鱼糜于−20 ℃的条件下冷冻5 d。冷冻后,测定鱼糜中的肌原纤维蛋白含量。此含量将作为评价多肽抗冻活性的指标。鉴于工艺优化周期较长,且不同批次鱼会因季节以及生长环境不同导致鱼糜初始肌原纤维蛋白含量有所差异[17−18],因此工艺优化过程中优化同一条件时均使用同一批鱼进行鱼糜制备及加样以确保准确优化出最佳条件。
1.2.1.5 肌原纤维蛋白提取及其含量测定
肌原纤维蛋白提取方法参考张霞[19]的方法,并在此基础上作出适当的修改。取2 g鱼糜于50 mL离心管中,加入20 mL的Tris-HCl缓冲液(10.00 mmol/L,pH7.0),均质2 min(12000 r/min,每次均质30 s后停20 s),在12000 r/min、4 ℃条件下离心15 min。弃上清液,加入20 mL的Tris-HCl缓冲液(10.00 mmol/L,pH7.0),均质30 s(12000 r/min)将沉淀悬浮,之后在12000 r/min、4 ℃条件下离心15 min。弃上清液,在沉淀中加入20 mL的Tris-HCl 缓冲液(0.60 mol/L NaCl,10.00 mmol/L Tris-HCl缓冲液,pH7.0)。充分均质30 s后,放置在4 ℃冰箱中浸提1 h。提取完后在12000 r/min、4 ℃下离心15 min,离心后所得的上清液即为鱼糜的肌原纤维蛋白溶液。以牛血清白蛋白为标准,采用Bradford法测定蛋白含量。
1.2.2 DcAFPs分子量分布
将DcAFPs配制成2 mg/mL的水溶液,根据高效液相色谱法测定DcAFPs分子量分布。使用标准品细胞色素C、抑肽酶、L-还原谷胱甘肽和羟脯氨酸绘制校准曲线,并根据相对分子质量校正曲线方程(y=0.16848x+6.46562,R2=0.99577)计算出样品的分子质量分布范围[20]。
1.2.3 DcAFPs氨基酸组成
参照KETNAWA等[21]的方法对样品进行前处理,并参考GB 5009.124-2016《食品中氨基酸的测定》中方法采用L-8080型全自动氨基酸分析仪对样品进行氨基酸测定[22]。
1.2.4 鱼糜冻融循环及肌原纤维蛋白提取和含量测定
鱼糜制备方法同1.2.1.4。将新鲜制备好的鱼糜分为6组,分别添加CC(商业抗冻剂:4%蔗糖和4%山梨醇混合物)、0%、2%、4%、6%、8% DcAFPs。未添加抗冻剂组为阴性对照(Control),添加商业抗冻剂组为阳性对照。对每组样品进行5次冻融循环实验(−20 ℃冷冻5 d后于25 ℃解冻1 h),并进行冻融0次和冻融5次循环后鱼糜肌原纤维蛋白含量的提取和测定(方法同1.2.1.5)。
1.2.5 肌原纤维蛋白内源荧光光谱分析
用0.6 mol/L氯化钠溶液将鱼糜冻融0次和冻融5次后所提取的肌原纤维蛋白溶液稀释至0.5 mg/mL,并于荧光分光光度计中进行光谱扫描。采用激发波长为290 nm,扫描范围300~400 nm,扫描速度为1200 nm/min[23]。
1.2.6 肌原纤维蛋白SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳
将鱼糜冻融0次和冻融5次后所提取的肌原纤维蛋白溶液用0.6 mol/L氯化钠溶液稀释至1 mg/mL,将稀释得到的蛋白溶液与上样缓冲液4:1比例混匀。100 ℃煮沸变性10 min后于12000 r/min离心3 min,取上清液20 μL进行上样。实验中选择12%的分离胶和5%的浓缩胶。将电压设置为90 V,运行30 min,待样品离开浓缩胶后,再将电压调整为120 V,继续运行60 min,直到溴酚蓝指示剂到达分离胶的底部。最后将凝胶于考马斯亮蓝染色液中染色30 min,再经脱色液脱色后于扫描仪中拍照成像[24]。
1.3 数据处理
所有测试至少经过3次独立重复实验,数据采用平均值±标准差表示,利用SPSS 27.0软件进行数据处理和分析,ANOVA进行显著性分析(P<0.05表示数据之间有显著性差异),利用Origin 2021或GraphPad Prism 9进行作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素结果分析
肌原纤维蛋白是一种盐溶性蛋白,占鱼糜蛋白质含量的50%~60%,是鱼糜蛋白质主要成分[25],也是构成鱼糜凝胶的主要成分[26],其含量是影响鱼糜凝胶化能力的主要因素之一。而鱼糜在冷冻过程中,冰晶生长会破坏肌原纤维蛋白质构象,蛋白发生变性聚集,导致其含量下降[27]。所以抑制鱼糜冷冻后肌原纤维蛋白含量下降可准确体现该物质的抗冻能力。因此,本研究以鱼糜冷冻5 d后肌原纤维蛋白含量为指标进行工艺优化,筛选出对鱼糜具有冷冻保护效果的多肽。
2.1.1 酶底比对鳕鱼明胶多肽抗冻活性的影响
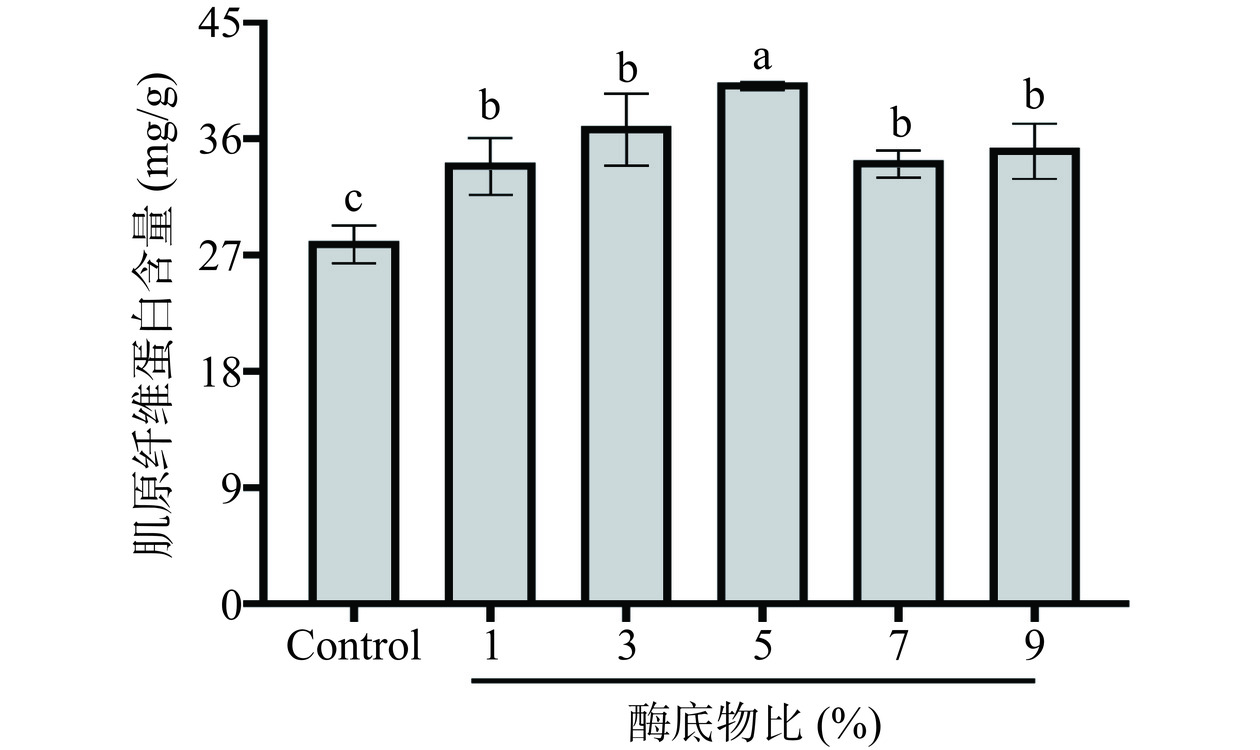
不同酶底比(1%、3%、5%、7%、9%(w/w))对明胶多肽抗冻活性的影响如图1所示。随着酶底比增加,鳕鱼明胶多肽抑制鱼糜冷冻后肌原纤维蛋白含量下降能力呈现先上升后下降的趋势。这可能是由于酶底比过低时,水解度不足,无法产生足够的抗冻活性肽段,多肽的抗冻活性较低;而酶底比过高时,水解度增加,但最佳肽段会进一步被分解为更小的片段,从而降低多肽的抗冻活性[15]。而当酶底比为5%时,鳕鱼明胶能够产生足够的抗冻活性肽段。故选择酶底比为5%进行后续的实验。
2.1.2 水解温度对鳕鱼明胶多肽抗冻活性的影响
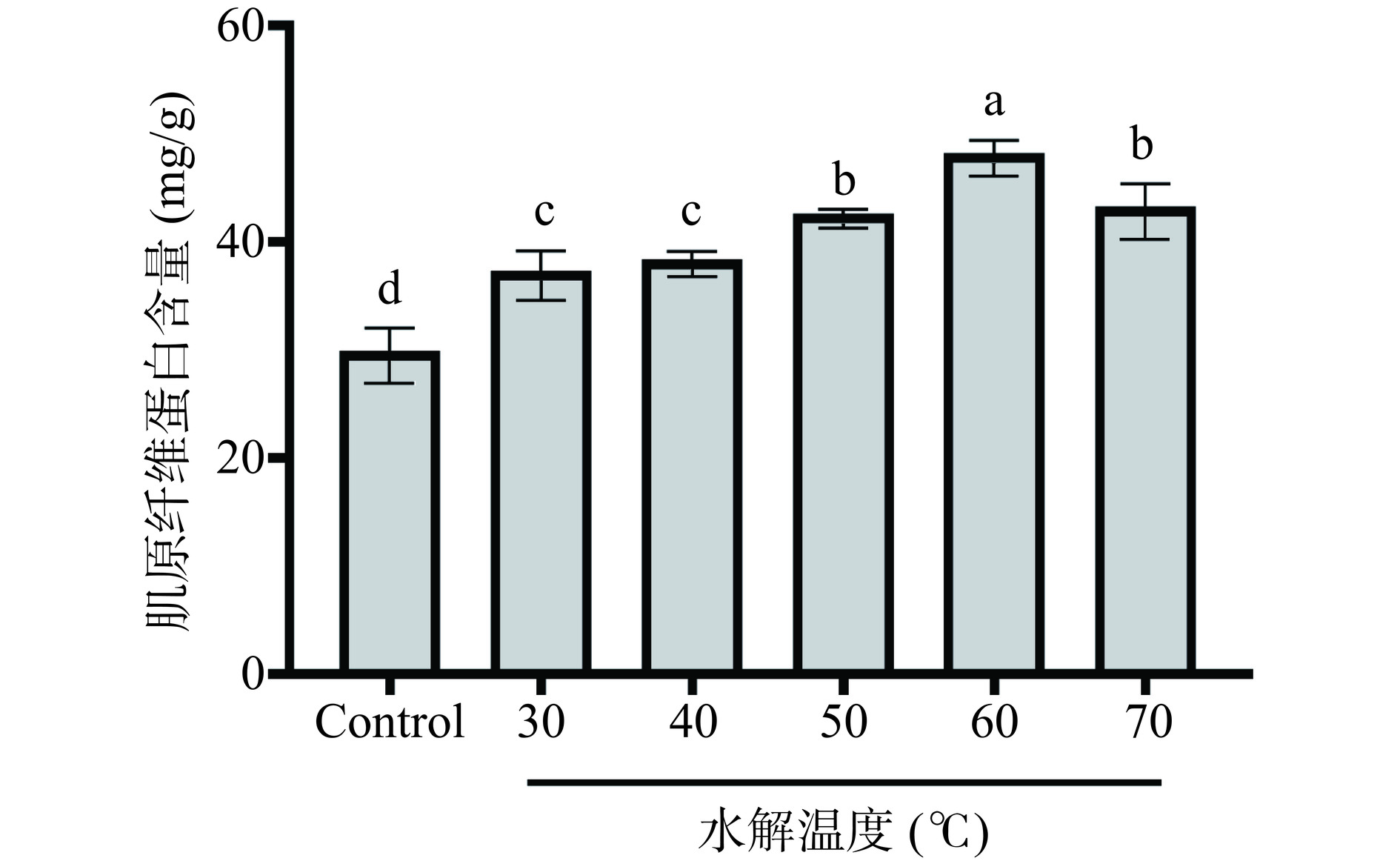
水解温度对明胶多肽抗冻活性的影响如图2所示。随着水解温度增加,多肽抑制鱼糜冷冻后肌原纤维蛋白含量下降能力均呈现先上升后下降的趋势,当水解温度为60 ℃时抗冻活性最佳。这可能是由于水解温度过低或过高会影响复合蛋白酶活性[28],导致鳕鱼明胶水解不够彻底,从而产生较少抗冻活性肽段。而当温度达到60 ℃时,鳕鱼明胶水溶性大幅提高,增加了其与复合蛋白酶的接触面积,从而更易产生抗冻活性肽段[29],达到最佳多肽抗冻活性。故选择水解温度为60 ℃进行后续实验。
2.1.3 水解pH对鳕鱼明胶多肽抗冻活性的影响
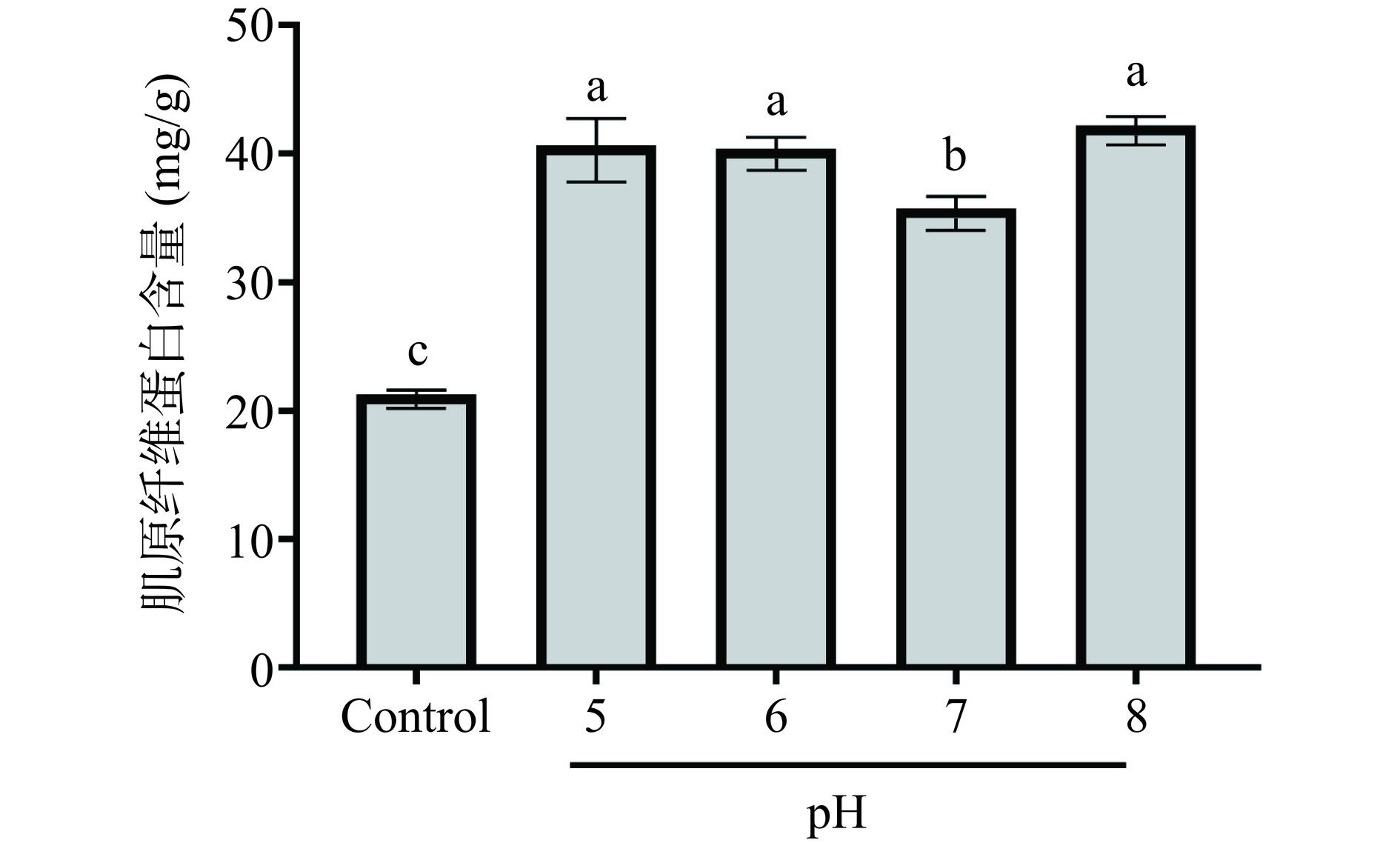
水解pH对明胶多肽抗冻活性的影响如图3所示。基于复合蛋白酶pH作用范围为5~8,因此选择pH为5、6、7、8进行优化。结果显示,随着水解pH增加,多肽抑制鱼糜冷冻后肌原纤维蛋白含量下降能力均呈现先下降后上升的趋势。这可能是由于鳕鱼明胶在60 ℃时溶解性较好,在弱酸环境下水解能有效促进其进一步降解,生成更多具有抗冻活性的肽段。因此,多肽在偏酸环境中的抗冻活性较为优越。而复合蛋白酶主要含有碱性蛋白酶,在pH为8的弱碱环境中活性最佳,可促进鳕鱼明胶水解产生更多的抗冻活性肽段[28],使得多肽抗冻活性最佳。因此,考虑到多肽的最优活性和复合蛋白酶的高效利用,后续实验选择pH为8进行实验。
2.1.4 底物浓度对鳕鱼明胶多肽抗冻活性的影响
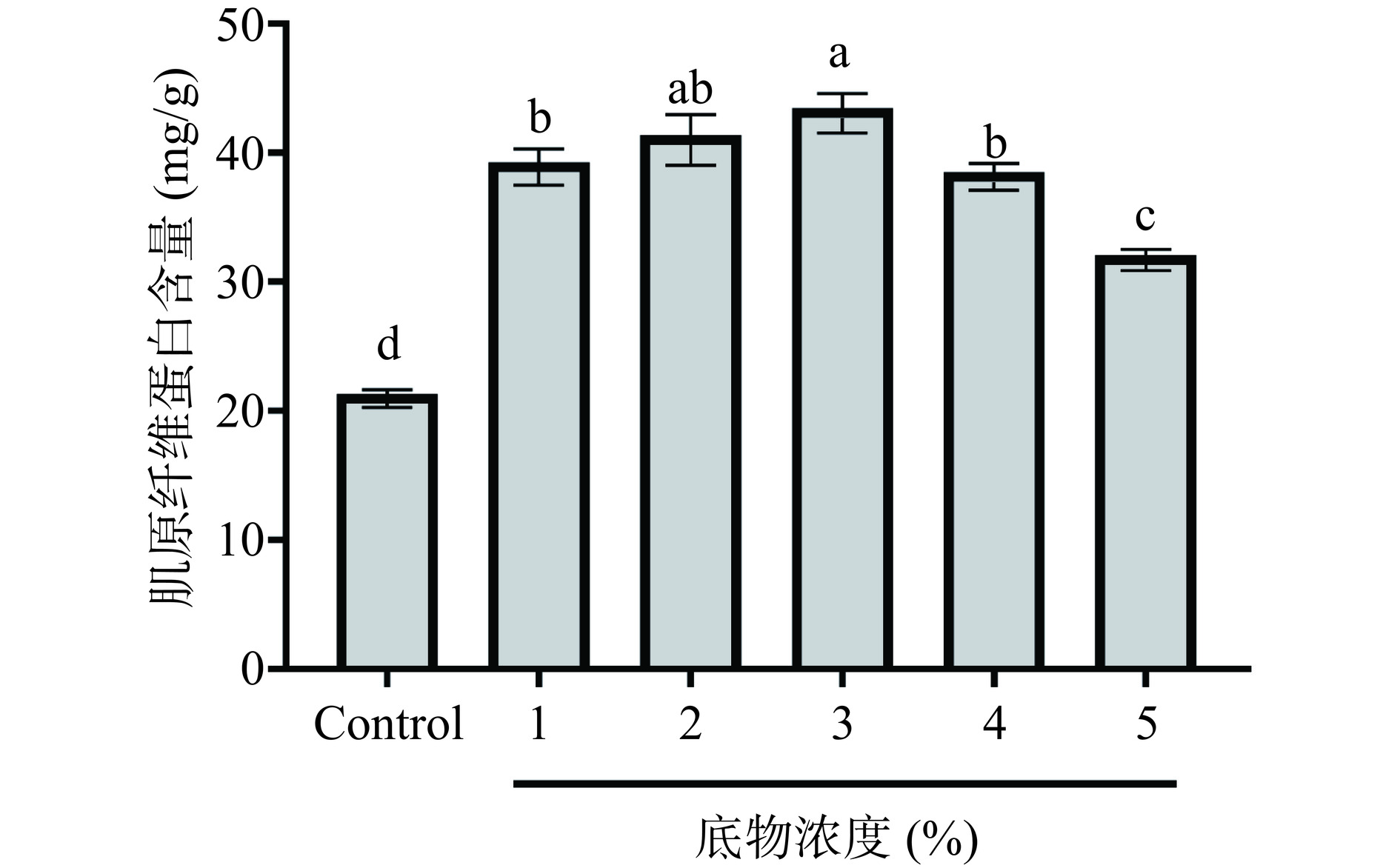
底物浓度对明胶多肽抗冻活性的影响如图4所示。随着底物浓度增加,多肽抑制鱼糜冷冻后肌原纤维蛋白含量下降能力呈现先上升后下降的趋势。这可能是由于一定范围内底物浓度越高与酶反应越充分[30],从而进一步促进鳕鱼明胶水解,而当底物浓度为3%时更利于复合蛋白酶水解产生足够的抗冻活性肽段[15]。故选择底物浓度为3%进行后续的实验。
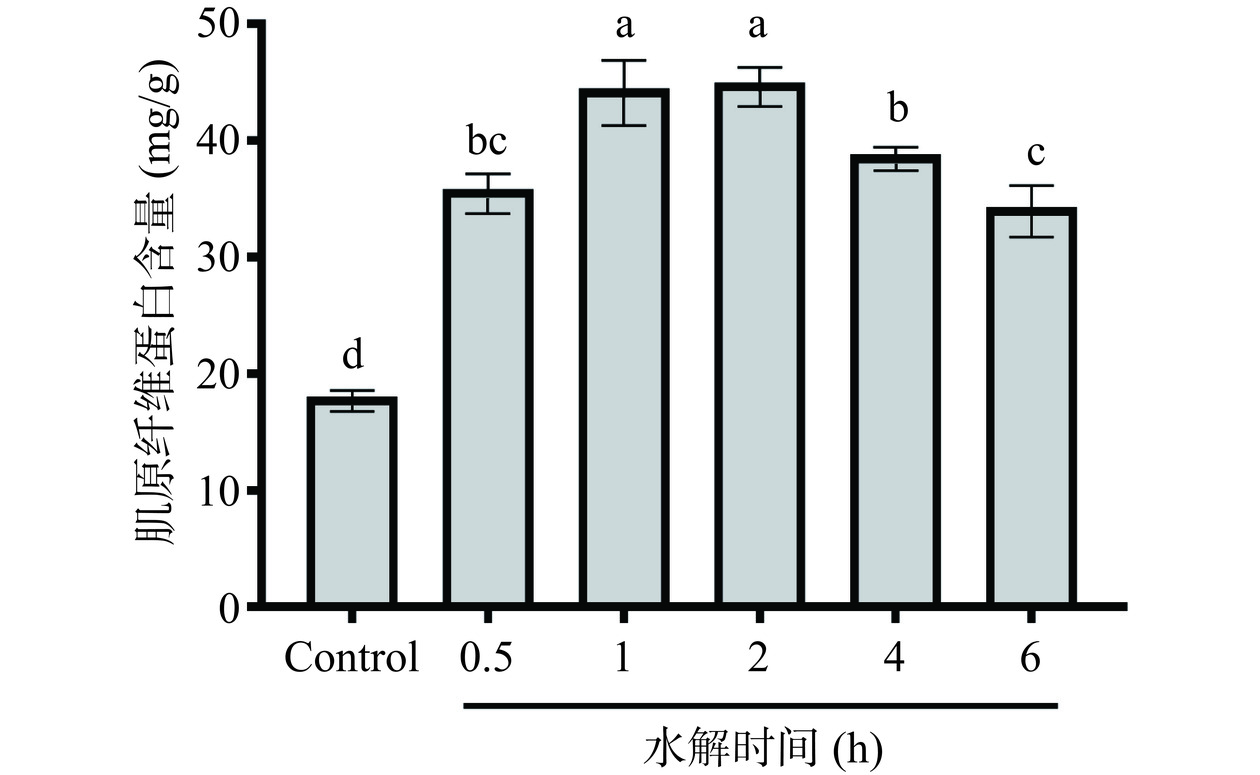
2.1.5 水解时间对鳕鱼明胶多肽抗冻活性的影响
水解时间对明胶多肽抗冻活性的影响如图5所示。随着水解时间增加,多肽抑制鱼糜冷冻后肌原纤维蛋白含量下降能力呈现先上升后下降的趋势。这可能是由于在水解初期已产生最佳肽段,具有较好的抗冻性能。随着时间的延长,多肽过度水解,产生的最佳肽段会被进一步分解,而不具有良好的抗冻性能。水解时间过短则不足以产生足够的抗冻活性肽段。结果显示,当水解时间为1 h和2 h时,多肽的抗冻活性相近。
2.2 高活性明胶抗冻多肽制备正交试验优化
2.2.1 正交试验结果
基于上述单因素实验结果,选择对抗冻活性影响最为显著的三个因素:水解温度、水解时间、底物浓度,固定酶添加量为5%、水解pH为8进行正交试验。正交试验结果如表2所示,可知对鱼糜冷冻后肌原纤维蛋白含量影响顺序为:水解温度>底物浓度>水解时间。最优条件为A1B2C3,即水解温度55 ℃、水解时间2 h、底物浓度3.5%。
表 2 正交试验结果Table 2. Results of orthogonal experiment处理组 A水解温度 B水解时间 C底物浓度 空白 肌原纤维蛋白含量
(mg/g)A1B1C1 1 1 1 1 34.06 A1B2C2 1 2 2 2 33.60 A1B3C3 1 3 3 3 35.53 A2B1C2 2 1 2 3 33.52 A2B2C3 2 2 3 1 36.67 A2B3C1 2 3 1 2 32.71 A3B1C3 3 1 3 2 29.37 A3B2C1 3 2 1 3 27.77 A3B3C2 3 3 2 1 26.08 K1 103.19 96.94 94.54 96.81 K2 102.90 98.05 93.20 95.69 K3 83.22 94.32 101.57 96.82 k1 34.40 32.31 31.51 32.27 k2 34.30 32.68 31.07 31.90 k3 27.74 31.44 33.86 32.27 极差R 6.65 1.24 2.79 0.37 主次顺序 水解温度>底物浓度>水解时间 最优条件 A1 B2 C3 最优组合 55 ℃、2 h、3.5% 2.2.2 正交条件验证
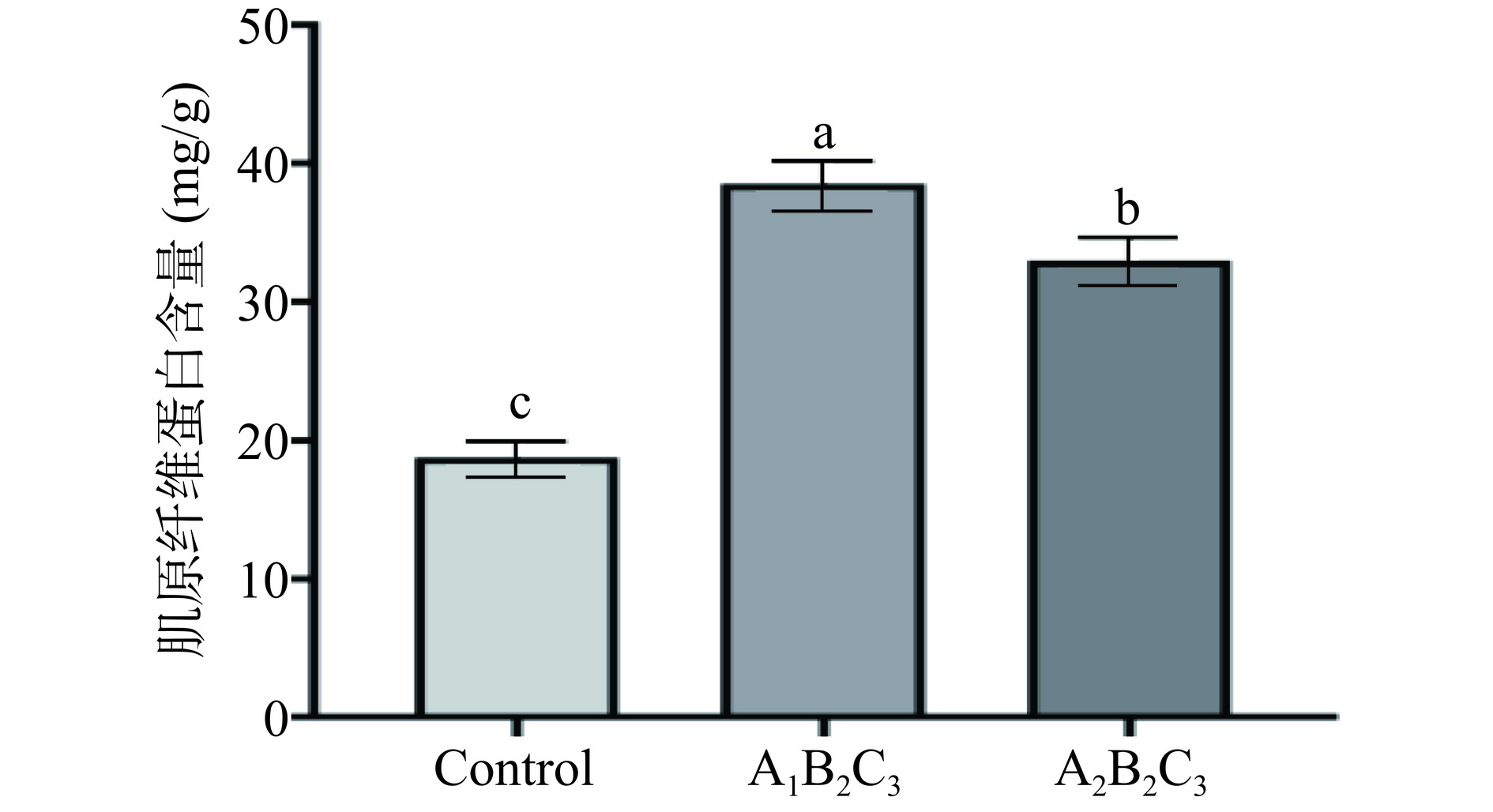
图6为正交试验验证的结果。A1B2C3为正交试验所得最优组合,A2B2C3为正交试验中抑制鱼糜冷冻后肌原纤维蛋白含量下降效果最佳的组合。结果显示同等条件下,A1B2C3条件下制备的抗冻多肽加入鱼糜冷冻5 d后肌原纤维蛋白含量为38.49 mg/g,而添加A2B2C3条件制备的抗冻多肽肌原纤维蛋白含量为32.96 mg/g,可证明正交试验所得结果正确。因此确定制备DcAFPs条件为:使用复合蛋白酶、底物浓度为3.5%(w/v)、酶底比为5%(w/w)、水解pH为8、水解温度为55 ℃、水解时间为2 h。而在工艺优化试验中存在优化后蛋白含量相较优化前蛋白含量偏低的现象,这可能与不同批次鱼原本的品质不同导致鱼糜中初始蛋白含量不同有关[15,18],重复工艺优化实验后所得结果一致。
2.3 DcAFPs基本性质分析
2.3.1 DcAFPs分子量分布
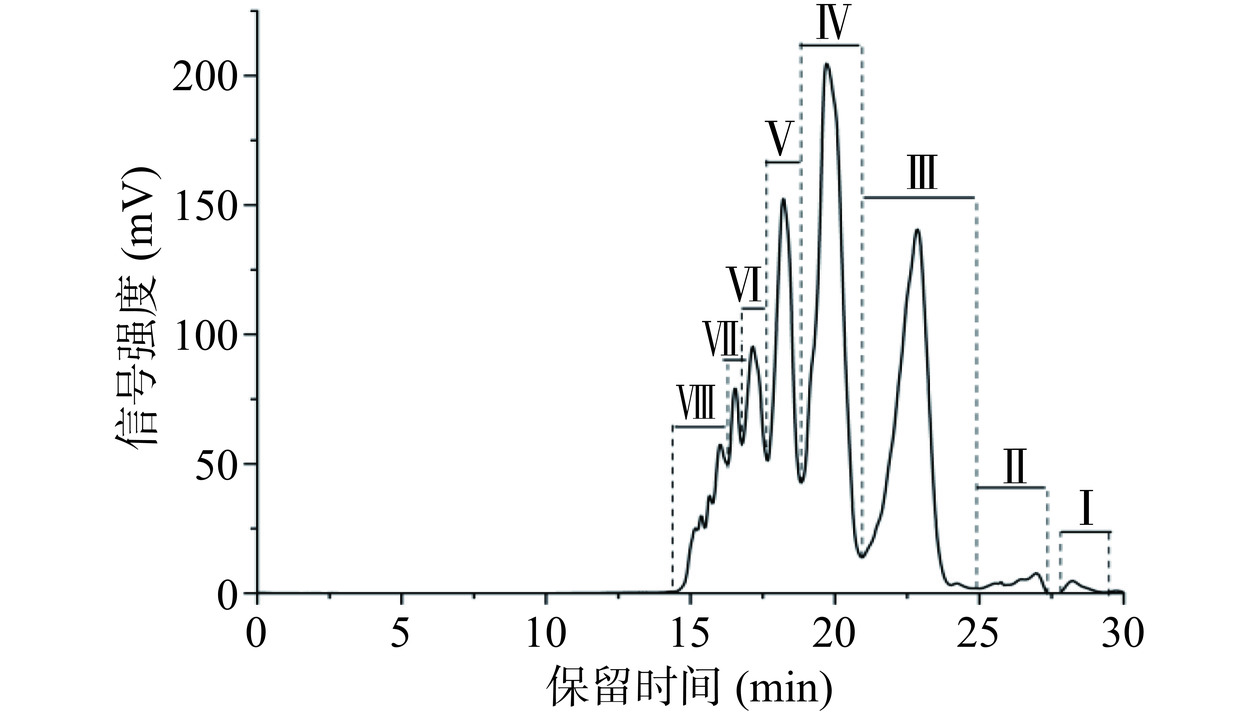
多肽的相对分子量与其生物活性密切相关,分子量较小的多肽通常比分子量更大的肽更具有亲水性、柔和性和热稳定性,更容易吸附在冰晶上,可显示更好的抗冻活性[7]。图7为DcAFPs分子量分布图,结果显示DcAFPs主要包括8个组分,分子量主要集中在185~3081 Da之间,占总量的76.20%(表3),说明DcAFPs主要成分是2~10个氨基酸的小肽。该结果与国内外对具有抗冻活性的多肽分子量分布趋势一致[3,31−32]。分子量较低的抗冻多肽更容易与冰晶结合,抑制冰晶生长;同时也更容易与水结合,抑制大冰晶的产生[33−35]。CHEN等[3]从猪皮胶原蛋白中水解得到的抗冻多肽,其分子量集中在180~3000 Da,研究发现其可显著提高鱼糜冻融后的蛋白含量维持冷冻鱼糜品质;ZHAI等[36]从银鲤鱼肉水解得到三个不同分子量分布的组分:UF-1:>10 kDa、UF-2:3~10 kDa、UF-3:<3 kDa,研究发现UF-3组分抗冻活性最佳。
表 3 DcAFPs的分子量分布Table 3. Molecular weight distribution of DcAFPs组分 分子量范围(Da) 相对含量(%) Ⅰ 31~60 0.5 Ⅱ 71~185 1.45 Ⅲ 185~866 26.97 Ⅳ 866~1961 32.83 Ⅴ 1961~3081 16.4 Ⅵ 3081~4345 9.64 Ⅶ 4345~5277 4.73 Ⅷ 5277~11064 7.19 2.3.2 DcAFPs氨基酸组成分析
多肽氨基酸组成被认为是影响多肽抗冻活性的关键结构特征[37]。表4为DcAFPs氨基酸组成,其中亲水性氨基酸占52.49%,疏水性氨基酸占23.44%;Gly占比多(41.84%),其次为Ala、Glu、Ser、Asp、Arg、Pro。DAMODARAN等[15]和ZHANG等[38]研究发现,抗冻蛋白或冰结构蛋白的抗冻活性与其氨基酸含量密切相关,特别是Gly、Ala和Thr,Gly和Ala的柔软侧链结构使其能够与水分子形成多种氢键,可抑制冰晶重结晶[7];Thr与水分子和冰表面发生相互作用,增强抗冻肽的抗冻活性[39]。DcAFPs中Gly、Ala和Thr占56.02%,这一结果表明DcAFPs抗冻活性可能与其氨基酸组成中Gly、Ala和Thr的丰度密切相关。
表 4 DcAFPs氨基酸组成Table 4. Composition of DcAFPs amino acids氨基酸 相对含量(%) 氨基酸 相对含量(%) Asp 5.94±0.01 Ile** 1.13±0.00 Thr* 2.83±0.01 Leu** 2.01±0.00 Ser* 7.26±0.06 Tyr* 0.33±0.00 Glu 8.85±0.03 Phe** 1.26±0.00 Gly* 41.84±0.04 Lys 3.42±0.01 Ala** 11.35±0.00 His 0.81±0.00 Cys* 0.23±0.02 Arg 5.05±0.00 Val** 1.97±0.01 Pro** 4.53±0.00 Met** 1.20±0.02 注:*表示亲水性氨基酸,**表示疏水性氨基酸。 2.4 DcAFPs 抗冻活性研究
2.4.1 DcAFPs对鱼糜反复冻融后肌原纤维蛋白含量的影响
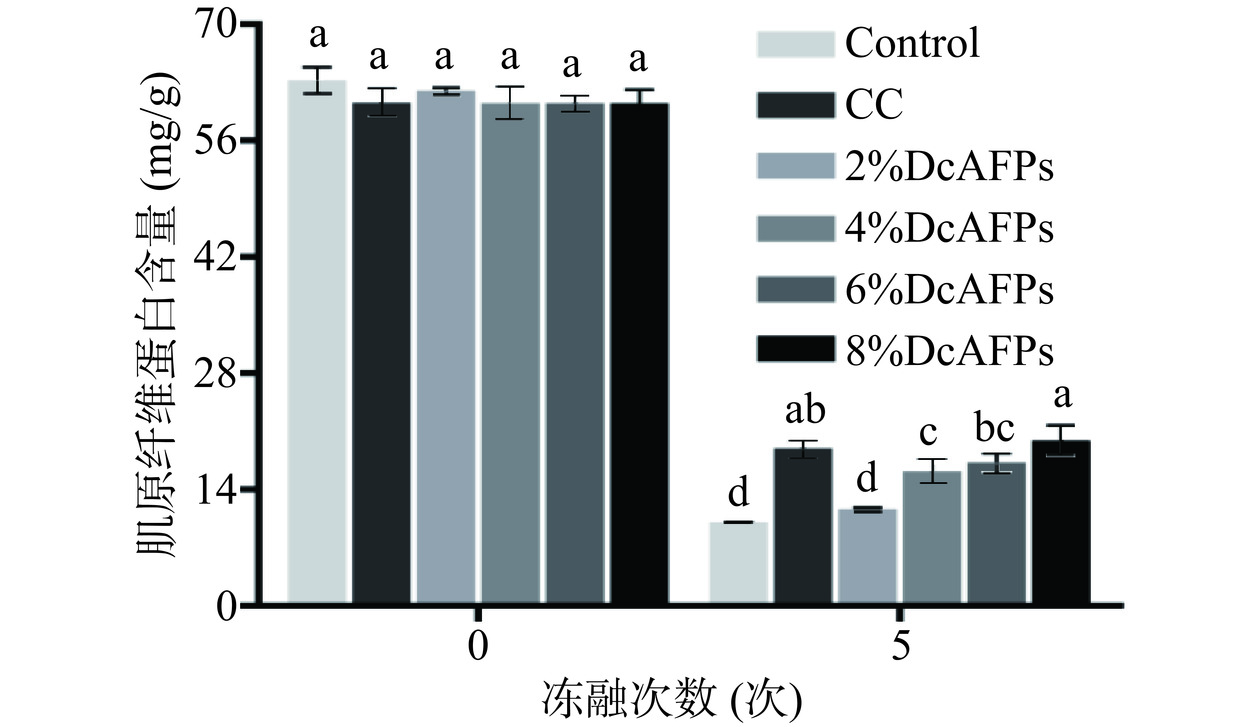
为明确DcAFPs对鱼糜反复冻融后的冷冻保护效果,鱼糜冻融5次后的肌原纤维蛋白含量结果如图8所示,在新鲜鱼糜中,各组鱼糜肌原纤维蛋白含量无显著性差异(P>0.05),说明添加DcAFPs不影响鱼糜肌原纤维蛋白含量。经过5次冻融循环后各组鱼糜肌原纤维蛋白含量均低于新鲜鱼糜,其中添加8%和6%DcAFPs和添加商业抗冻剂抑制鱼糜冻融后肌原纤维蛋白含量下降效果相似。这可能是因为DcAFPs中的疏水氨基酸可与蛋白表面的疏水区域相互作用,阻止蛋白冷冻过程中聚集,DcAFPs中的亲水性氨基酸可与水形成氢键,降低冰晶形成的速率和减小冰晶的尺寸,减少冰晶对蛋白的机械损伤,进而防止蛋白变性[7,39]。
2.4.2 DcAFPs对鱼糜冻融后肌原纤维蛋白三级结构的影响
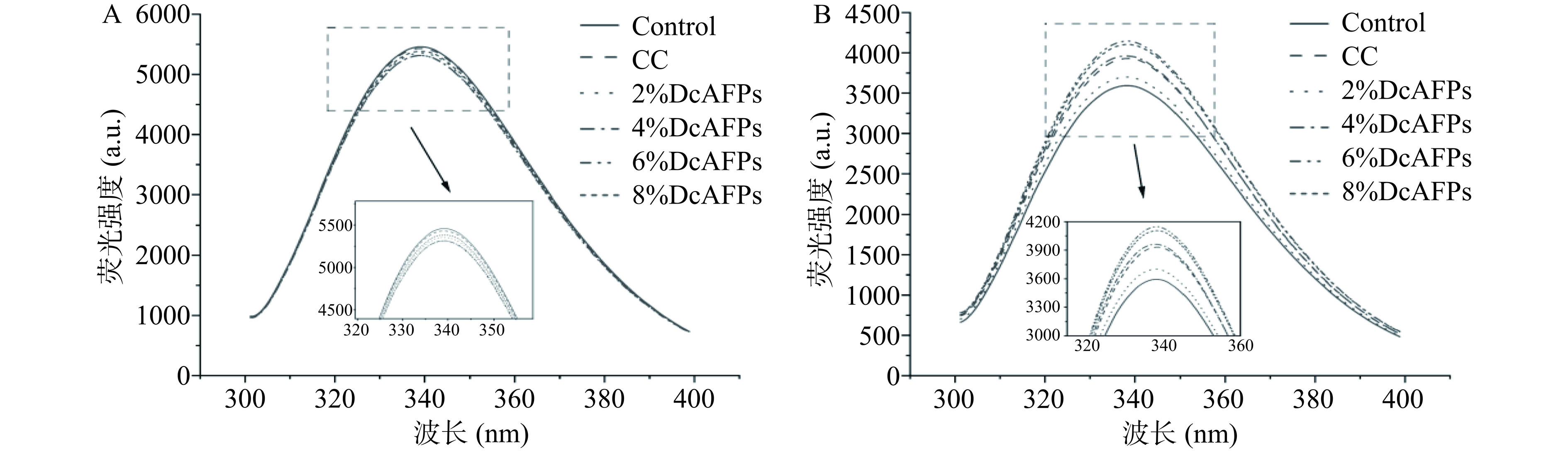
色氨酸残基位于肌原纤维蛋白的核心,当肌原纤维蛋白处于正常折叠状态时可显现较高的荧光强度,当蛋白发生变性时,内部的色氨酸残基容易暴露于极性环境中而发生淬灭[40−41]。荧光光谱技术可以通过检测色氨酸残基的状态进而监测蛋白三级结构的变化[42]。
鱼糜冻融0次和鱼糜冻融5次后肌原纤维蛋白荧光强度变化如图9所示。当鱼糜未冻融时,各组的肌原纤维蛋白荧光强度无显著差异(图9A),表明添加抗冻剂不会影响鱼糜肌原纤维蛋白色氨酸残基变化及蛋白三级结构变化。当鱼糜冻融5次后,各组蛋白荧光强度均下降(图9B),这表明冻融对蛋白色氨酸残基变化影响较大。这可能与反复冻融后色氨酸残基容易发生氧化损伤[43]有关。且冻融过程中冰晶生长和融化导致蛋白结构发生变化,埋藏于蛋白内部的色氨酸容易暴露于极性环境中而发生淬灭[40]。其中阴性对照组蛋白荧光强度下降最为剧烈,4% DcAFPs组达到和商业抗冻剂组抑制鱼糜冻融后蛋白荧光强度下降相似效果,6%和8%DcAFPs组效果最好。DcAFPs具有较好的抗冻效果,可能是因为DcAFPs较小的分子量更容易与冰晶结合从而抑制冰晶生长,进而阻止蛋白因受大冰晶的挤压而发生结构变化[7];同时DcAFPs可以与蛋白表面的水分子结合而保护蛋白的空间结构[44]。
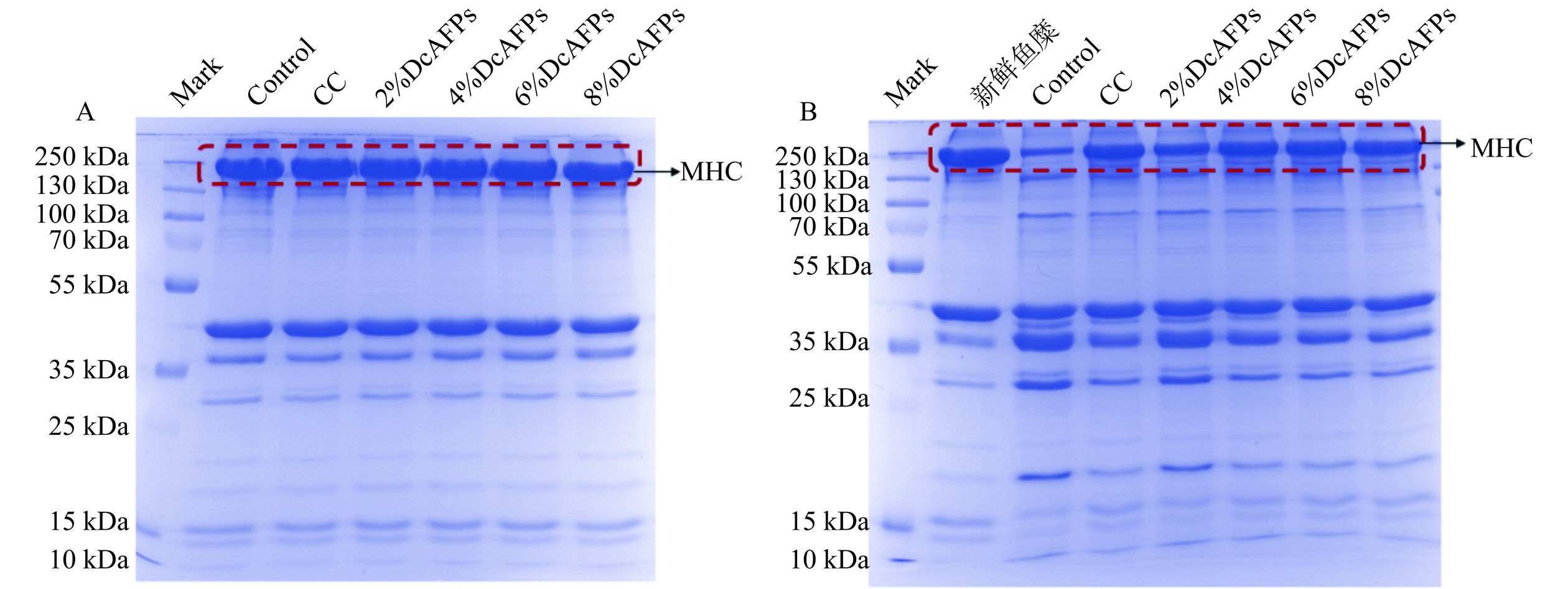
2.4.3 DcAFPs对鱼糜冻融后肌原纤维蛋白组成的变化
肌原纤维蛋白主要由肌球蛋白重链(MHC,200 kDa)和肌动蛋白(48 kDa)组成[45],其中MHC与鱼糜凝胶过程密切相关,在提升鱼糜物理化学品质中发挥关键作用[46]。在新鲜鱼糜中各组电泳条带无明显变化(图10A),表明抗冻剂加入不影响鱼糜肌原纤维蛋白的蛋白组成。当鱼糜冻融后MHC条带明显浅于新鲜鱼糜,且明显新增了新的电泳条带(70~100 kDa、35~55 kDa)及部分条带变深(图10B),表明鱼糜冻融后损伤了蛋白结构导致MHC发生降解。而加入了抗冻剂组的MHC降解程度明显低于阴性对照组,且仅添加4%DcAFPs达到和商业抗冻剂相似效果。结果表明,添加DcAFPs能够维持鱼糜冻融过程中肌原纤维蛋白结构及其组成发生变化,延缓蛋白变性。
3. 结论
本研究以鳕鱼明胶为原料,旨在优化DcAFPs的制备工艺,以提高鱼糜在冻融处理中肌原纤维蛋白的稳定性。通过以鱼糜冷冻后的肌原纤维蛋白含量为评价指标,确定了DcAFPs的最佳制备条件:使用复合蛋白酶、底物浓度为3.5%(w/v)、酶底比为5%(w/w)、水解pH为8、水解温度为55 ℃、水解时间为2 h。所得DcAFPs的分子量主要集中在185~3081 Da范围内,占比达到总量的76.20%,且富含具有抗冻肽特征氨基酸。通过分析DcAFPs在鱼糜反复冻融过程中的抗冻效果,发现DcAFPs的添加显著抑制了鱼糜在反复冻融后肌原纤维蛋白含量下降,有效延缓了鱼糜冻融过程中肌原纤维蛋白色氨酸残基暴露于极限环境,并减缓了肌原纤维蛋白中肌球蛋白重链发生降解过程。同时,与商业抗冻剂相比,DcAFPs展现出更优的冷冻保护效果。总而言之,本研究不仅为鳕鱼明胶制备DcAFPs提供了科学依据,还揭示了DcAFPs作为蛋白质源多肽在冷冻食品保护领域的广泛应用潜力。这些发现为开发新型绿色抗冻剂提供了新的思路,有助于推动冷冻食品加工技术的进步。
-
表 1 正交试验设计因素与水平
Table 1 Factors and level of orthogonal experiment design
水平 因素 A水解温度(℃) B水解时间(h) C底物浓度(%) 1 55 1 2 2 60 2 3 3 65 3 3.5 表 2 正交试验结果
Table 2 Results of orthogonal experiment
处理组 A水解温度 B水解时间 C底物浓度 空白 肌原纤维蛋白含量
(mg/g)A1B1C1 1 1 1 1 34.06 A1B2C2 1 2 2 2 33.60 A1B3C3 1 3 3 3 35.53 A2B1C2 2 1 2 3 33.52 A2B2C3 2 2 3 1 36.67 A2B3C1 2 3 1 2 32.71 A3B1C3 3 1 3 2 29.37 A3B2C1 3 2 1 3 27.77 A3B3C2 3 3 2 1 26.08 K1 103.19 96.94 94.54 96.81 K2 102.90 98.05 93.20 95.69 K3 83.22 94.32 101.57 96.82 k1 34.40 32.31 31.51 32.27 k2 34.30 32.68 31.07 31.90 k3 27.74 31.44 33.86 32.27 极差R 6.65 1.24 2.79 0.37 主次顺序 水解温度>底物浓度>水解时间 最优条件 A1 B2 C3 最优组合 55 ℃、2 h、3.5% 表 3 DcAFPs的分子量分布
Table 3 Molecular weight distribution of DcAFPs
组分 分子量范围(Da) 相对含量(%) Ⅰ 31~60 0.5 Ⅱ 71~185 1.45 Ⅲ 185~866 26.97 Ⅳ 866~1961 32.83 Ⅴ 1961~3081 16.4 Ⅵ 3081~4345 9.64 Ⅶ 4345~5277 4.73 Ⅷ 5277~11064 7.19 表 4 DcAFPs氨基酸组成
Table 4 Composition of DcAFPs amino acids
氨基酸 相对含量(%) 氨基酸 相对含量(%) Asp 5.94±0.01 Ile** 1.13±0.00 Thr* 2.83±0.01 Leu** 2.01±0.00 Ser* 7.26±0.06 Tyr* 0.33±0.00 Glu 8.85±0.03 Phe** 1.26±0.00 Gly* 41.84±0.04 Lys 3.42±0.01 Ala** 11.35±0.00 His 0.81±0.00 Cys* 0.23±0.02 Arg 5.05±0.00 Val** 1.97±0.01 Pro** 4.53±0.00 Met** 1.20±0.02 注:*表示亲水性氨基酸,**表示疏水性氨基酸。 -
[1] TOLSTOREBROV I, EIKEVIK T M, BANTLE M. Effect of low and ultra-low temperature applications during freezing and frozen storage on quality parameters for fish[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration,2016,63:37−47. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2015.11.003
[2] CHEN X, LI X Z, YANG F J, et al. Effects and mechanism of antifreeze peptides from silver carp scales on the freeze-thaw stability of frozen surimi[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,396:133717. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133717
[3] CHEN X, WU J H, LI X Z, et al. Investigation of the cryoprotective mechanism and effect on quality characteristics of surimi during freezing storage by antifreeze peptides[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,371:131054. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131054
[4] WANG P, XU X L, ZHOU G H. Effects of meat and phosphate level on water-holding capacity and texture of emulsion-type sausage during storage[J]. Agricultural Sciences in China,2009,8(12):1475−1481. doi: 10.1016/S1671-2927(08)60361-2
[5] 吕金润, 戚勃, 杨贤庆, 等. 坛紫菜多糖对冻藏凡纳滨对虾品质维持的研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 1−12. [2024-11-19]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.039317. [LÜ Jinrun, QI Bo, YANG Xianqing, et al. Study on the effect of orphyra polysaccharides on the quality maintenance of frozen Litopenaeus vannamei [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 1−12. [2024-11-19]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.039317.] LÜ Jinrun, QI Bo, YANG Xianqing, et al. Study on the effect of orphyra polysaccharides on the quality maintenance of frozen Litopenaeus vannamei [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 1−12. [2024-11-19]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.039317.
[6] DAVIES P L. Ice-binding proteins:A remarkable diversity of structures for stopping and starting ice growth[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences,2014,39(11):548−555. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.09.005
[7] CHEN X, WU J H, CAI X X, et al. Production, structure-function relationships, mechanisms, and applications of antifreeze peptides[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2021,20(1):542−562. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12655
[8] YANG F J, CHEN X, HAUNG M C, et al. Molecular characteristics and structure–activity relationships of food-derived bioactive peptides[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture,2021,20(9):2313−2332.
[9] KHAN M A, HOSSAIN M A, HARA K, et al. Effect of enzymatic fish-scrap protein hydrolysate on gel-forming ability and denaturation of lizard fish surimi during frozen storage[J]. Fisheries Science,2003,69(6):1271−1280. doi: 10.1111/j.0919-9268.2003.00755.x
[10] JENKELUNAS P J, LI-CHAN E C Y. Production and assessment of Pacific hake hydrolysates as cryoprotectants for frozen fish mince[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,239:535−543. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.06.148
[11] ALVES A L, FRAGUAS F J, CARVALHO A C, et al. Characterization of codfish gelatin:A comparative study of fresh and salted skins and different extraction methods[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2022, 124.
[12] ZHU S C, JIN Y, YU J H, et al. Composition-antifreeze property relationships of gelatin and the corresponding mechanisms[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2024,268:131941. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131941
[13] LIU X, LU Y Z, YANG Q, et al. Cod peptides inhibit browning in fresh-cut potato slices:A potential anti-browning agent of random peptides for regulating food properties[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2018,146:36−42. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.08.001
[14] LI B, CHEN F, WANG X, et al. Isolation and identification of antioxidative peptides from porcine collagen hydrolysate by consecutive chromatography and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,102(4):1135−1143. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.07.002
[15] DAMODARAN S, WANG S Y. Ice crystal growth inhibition by peptides from fish gelatin hydrolysate[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,70:46−56. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.03.029
[16] CAO Y, ZHAO L Y, HUANG Q L, et al. Water migration, ice crystal formation, and freeze-thaw stability of silver carp surimi as affected by inulin under different additive amounts and polymerization degrees[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,124:107267. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107267
[17] JIANG Q, CHEN H, GAO P, et al. Seasonal variations in the channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus):Nutritional composition, texture, and physicochemical properties of myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Bioscience,2024,59:104034. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104034
[18] WANG X, FUKUDA Y, YUAN C, et al. Gel-forming properties and their seasonal changes of freshwater fish surimi[J]. Fisheries Science,2008,68(2):1533−1536.
[19] 张霞. 大豆低聚糖对淡水鱼糜的冷冻保护作用及其机制[D]. 长沙:中南林业科技大学, 2022. [ZHANG X. Protective effect of soybean oligosaccharides on freshwater surimi by freezing and its mechanism[D]. Changsha:Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2022.] ZHANG X. Protective effect of soybean oligosaccharides on freshwater surimi by freezing and its mechanism[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2022.
[20] 邓梅, 梅强根, 谢星, 等. 七种大宗淡水鱼酶解物抗氧化活性比较及其肽组成鉴定[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2024,50(16):110−117. [DENG M, MEI Q G, XIE X, et al. Comparison of antioxidant activities and peptide composition identification of enzymatic hydrolysates from seven common freshwater fishes[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2024,50(16):110−117.] DENG M, MEI Q G, XIE X, et al. Comparison of antioxidant activities and peptide composition identification of enzymatic hydrolysates from seven common freshwater fishes[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024, 50(16): 110−117.
[21] KETNAWA S, WICKRAMATHILAKA M, LICEAGA A M. Changes on antioxidant activity of microwave-treated protein hydrolysates after simulated gastrointestinal digestion:Purification and identification[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,254:36. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.133
[22] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药 品监督管理总局. GB 5009.124-2016食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.124-2016 National standard for food safety Determination of amino acids in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.124-2016 National standard for food safety Determination of amino acids in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[23] GAO W H, HUANG Y P, HE R X, et al. Synthesis and characterization of a new soluble soybean polysaccharide-iron(III) complex using ion exchange column[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,108:1242−1247. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.038
[24] XIE F, ZHENG W Q, FU T T, et al. Cryoprotective effect of tamarind seed polysaccharide on grass carp surimi:Characteristics, interactions, and mechanisms[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2024,153:110022. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2024.110022
[25] LI X X, FAN M C, HUANG Q L, et al. Effect of micro- and nano-starch on the gel properties, microstructure and water mobility of myofibrillar protein from grass carp[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,366:130579. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130579
[26] XIONG Z Y, SHI T, ZHANG W, et al. Improvement of gel properties of low salt surimi using low-dose L-arginine combined with oxidized caffeic acid[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,145:111303. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111303
[27] 杨贤庆, 袁悦, 赵永强, 等. 冷冻鱼糜绿色抗冻剂的研究进展[J]. 上海海洋大学学报,2018,27(5):789−796. [YANG X Q, YUAN Y, ZHAO Y Q, et al. Research progress on green antifreeze agents for frozen fish mince[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University,2018,27(5):789−796.] YANG X Q, YUAN Y, ZHAO Y Q, et al. Research progress on green antifreeze agents for frozen fish mince[J]. Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2018, 27(5): 789−796.
[28] 李军. 鲢鱼骨胶原多肽的制备及其抗氧化、钙螯合活性的研究[D]. 南昌:江西师范大学, 2020. [LI J. Preparation of silver carp bone collagen polypeptides and their antioxidant and calcium chelating activities[D]. Nanchang:Jiangxi Normal University, 2020.] LI J. Preparation of silver carp bone collagen polypeptides and their antioxidant and calcium chelating activities[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Normal University, 2020.
[29] 应宇斌. 鲤鱼鳞水解物对罗氏沼虾抗冻保护作用及其活性成分分析研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2022. [YING Y B. Study on antifreeze protection and active components of hydrolysate of common carp scales onMacrobrachium rosenbergii[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2022.] YING Y B. Study on antifreeze protection and active components of hydrolysate of common carp scales on Macrobrachium rosenbergii[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2022.
[30] 望天志, 刘义, 吴鼎泉, 等. 微量热法研究单底物酶促反应的热力学和动力学性质及过渡态的分析[J]. 化学学报,1998(7):625−630. [WANG T Z, LIU Y, WU D Q, et al. Study of thermodynamic and kinetic properties and transition state of enzymatic reaction of single substrate by microcalorimetry[J]. Acta Chemologica Sinica,1998(7):625−630.] WANG T Z, LIU Y, WU D Q, et al. Study of thermodynamic and kinetic properties and transition state of enzymatic reaction of single substrate by microcalorimetry[J]. Acta Chemologica Sinica, 1998(7): 625−630.
[31] CHEN X, LI L, YANG F J, et al. Effects of gelatin-based antifreeze peptides on cell viability and oxidant stress of during cold stage[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2020,136:11056.
[32] 李晓贞, 陈旭, 杨傅佳, 等. 白鲢鱼鳞抗冻多肽的制备及对冻融鱼糜凝胶特性的改善作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(1):242−252. [LI X Z, CHEN X, YANG F J, et al. Preparation of antifreeze peptides from silver carp scales and their improvement on the gel properties of frozen-thawed fish paste[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(1):242−252.] LI X Z, CHEN X, YANG F J, et al. Preparation of antifreeze peptides from silver carp scales and their improvement on the gel properties of frozen-thawed fish paste[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(1): 242−252.
[33] LIU Z L, YANG W E, WEI H M, et al. The mechanisms and applications of cryoprotectants in aquatic products:An overview[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,408:135202. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135202
[34] CAO L, MAJURA J J, LIU L, et al. The cryoprotective activity of tilapia skin collagen hydrolysate and the structure elucidation of its antifreeze peptide[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2023,179:114670. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2023.114670
[35] KIM J S, DAMODARAN S, YETHIRAJ A. Retardation of ice crystallization by short peptides[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry A,2009,113(16):4403−4407. doi: 10.1021/jp8110748
[36] ZHAI Y Y, PENG W Q, LUO W, et al. Component stabilizing mechanism of membrane-separated hydrolysates on frozen surimi[J]. Food Chemistry,2024,431:137114. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137114
[37] 张晓頔, 董烨, 张益奇, 等. 鱼糜副产物蛋白水解物的抗冻活性及对嗜热链球菌的抗冻效果及机制[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(7):39−47. [ZHANG X D, DONG Y, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Antifreeze activity of protein hydrolysates from fish mince by-products and their effects and mechanisms against thermophilic streptococcus[J]. Food Science,2023,44(7):39−47.] ZHANG X D, DONG Y, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Antifreeze activity of protein hydrolysates from fish mince by-products and their effects and mechanisms against thermophilic streptococcus[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(7): 39−47.
[38] ZHANG Y F, LIU K, LI K Y, et al. Fabrication of anti-icing surfaces by short α-helical peptides[J]. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(2):1957−1962.
[39] XUE B, ZHAO L S, QING X H, et al. Bioinspired ice growth inhibitors based on self-assembling peptides[J]. Acs Macro Letters,2019,8(10):1383−1390. doi: 10.1021/acsmacrolett.9b00610
[40] LI M M, HE S F, SUN Y Y, et al. Effectiveness of L-arginine/L-lysine in retarding deterioration of structural and gelling properties of duck meat myofibrillar protein during freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Food Bioscience,2023,51:102302. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2022.102302
[41] 李可, 张俊霞, 王欣瑶, 等. 不同超声波功率处理对类PSE鸡肉肌原纤维蛋白结构和乳化稳定性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(13):23−31. [LI K, ZHANG J X, WANG X Y, et al. Effects of different ultrasound power treatments on the structure and emulsification stability of PSE-like chicken myofibrillar proteins[J]. Food Science,2023,44(13):23−31.] LI K, ZHANG J X, WANG X Y, et al. Effects of different ultrasound power treatments on the structure and emulsification stability of PSE-like chicken myofibrillar proteins[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(13): 23−31.
[42] CAO Y G, TRUE A D, CHEN J, et al. Dual role (anti- and pro-oxidant) of gallic acid in mediating myofibrillar protein gelation and gel in vitro digestion[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2016,64(15):3054−3061. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00314
[43] TAN M T, YE J X, XIE J. Freezing-induced myofibrillar protein denaturation:Role of pH change and freezing rate[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,152:112381. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112381
[44] HU Y P, ZHANG L, YI Y W, et al. Effects of sodium hexametaphosphate, sodium tripolyphosphate and sodium pyrophosphate on the ultrastructure of beef myofibrillar proteins investigated with atomic force microscopy[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,338:12814.
[45] SUN X Y, LI Q, DING N, et al. Cryoprotective effect of fistular onion stalk polysaccharide on frozen surimi derived from bighead carp:Physicochemical properties and gel quality during storage[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2024,148:109404. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109404
[46] GAO W H, HUANG Y P, ZENG X A, et al. Effect of soluble soybean polysaccharides on freeze-denaturation and structure of myofibrillar protein of bighead carp surimi with liquid nitrogen freezing[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,135:839−844. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.186





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
