Differences in Metabolites of Different Varieties from Xinjiang Large-fruit Sea Buckthorn as Analyzed by Non-targeted Metabolomics
-
摘要: 为探究不同品种新疆大果沙棘代谢产物的差异性,采用超高效液相色谱-质谱联用技术(UPLC-QTOF-MS)结合多元统计分析法和通路富集分析对6种新疆大果沙棘样品(‘混果’、‘巨人’、‘深秋红’、‘无刺丰’、‘向阳’和‘状元黄’)进行非靶向代谢组学研究。结果表明,代谢组学分析共得到334种代谢产物。依据log2FC绝对值≥1和错误发现率(FDR)<0.05分析,‘混果’与‘巨人’共筛选出112种差异代谢物;‘混果’与‘深秋红’间筛选出118种差异代谢物;‘混果’和‘无刺丰’共筛选出67种差异代谢物;‘混果’和‘向阳’共筛选出160种差异代谢物;‘混果’和‘状元黄’共筛选出126种差异代谢物。代谢通路富集分析表明,不同大果沙棘的差异代谢物主要富集在不饱和脂肪酸生物合成、脂肪酸生物合成、色氨酸代谢、黄酮和黄酮醇生物合成等通路上。基于VIP值>1、log2FC绝对值≥1和FDR<0.05筛选标准,发现共有差异代谢物5种,且大果沙棘中脂质和类脂质分子、苯丙烷及聚酮类化合物的总体丰度较高,占比分别在38%~81%和15%~49%之间,其中芥酸酰胺、亚油酸、棕榈酸、水仙苷、异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷、芦丁等可能是鉴别不同新疆大果沙棘的关键代谢物。非靶向代谢组学可从整体水平上阐明不同品种新疆大果沙棘的代谢差异,为新疆大果沙棘品种选育和加工利用提供了科学依据。
-
关键词:
- 新疆大果沙棘 /
- 非靶向代谢组学 /
- 差异代谢物 /
- 超高效液相色谱-质谱联用技术
Abstract: This experiment aimed to investigate the differences in metabolites of different varieties from Xinjiang large-fruit sea buckthorn, ultra high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF-MS) coupled with multivariate statistical analysis and pathway enrichment analysis were used to characterize the metabolites of six Xinjiang large-fruit sea buckthorn species ('Mixed Fruit', 'Giant', 'Shenqunhon', 'Wucifeng', 'Xiangyang' and 'Zhuangyuan Yellow') were subjected to non-targeted metabolomics study. The results showed that a total of 334 metabolites were obtained from the metabolomic analysis. Based on log2FC absolute value≥1 and FDR<0.05 analysis, a total of 112 differential metabolites were screened between 'Mixed Fruit' and 'Giant'. 'Mixed Fruit' and 'Shenqunhon' screened a total of 118 differential metabolites. 'Mixed Fruit' and 'Wucifeng' screened a total of 67 differential metabolites. A total of 160 differential metabolites were screened between 'Mixed Fruit' and 'Xiangyang' and a total of 126 differential metabolites were screened between 'Mixed Fruit' and 'Zhuangyuan Yellow'. The metabolic pathway enrichment analysis showed that the differential metabolites of different large-fruit sea buckthorns were mainly enriched in the pathways of unsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis, fatty acid biosynthesis, tryptophan metabolism, and flavonoid and flavonol biosynthesis. Based on the VIP value>1, log2FC absolute value≥1 and FDR<0.05 screening criteria, a total of five differential metabolites were found, and overall high abundance and lipid-like molecules, phenylpropanes and polyketides were found in sea buckthorn, ranging from 38% to 81% and 15% to 49%, respectively, among which erucic acid amide, linoleic acid, palmitic acid, narcissin, isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside, rutin, etc. might be the key metabolites to identify different Xinjiang large-fruit sea buckthorn. Non-targeted metabolomics can elucidate the metabolic differences of different varieties of Xinjiang large-fruit sea buckthorn at the overall level, which provides scientific basis for the selection and breeding of Xinjiang large-fruit sea buckthorn varieties and their processing and utilization. -
沙棘(Hippophae rhamnoides L.)是一种耐旱的落叶灌木,属于胡颓子科沙棘属[1]。沙棘浆果富含黄酮、脂肪酸、有机酸、酰基脂质等生物活性物质,具有抗氧化、免疫调节、抗动脉粥样硬化、抗应激、肝保护、辐射保护和组织修复等作用[2−4]。沙棘原产于欧洲西北部,经中亚至阿尔泰山脉、中国西部和北部以及喜马拉雅山北部,在我国主要分布于新疆、西藏和内蒙古等地[5−6]。按其栽培方式可分为野生沙棘(中国沙棘和西藏沙棘)和栽培沙棘(大果沙棘),其中大果沙棘具有极强的抗逆能力、果实营养丰富、适宜加工等特点,已在新疆、黑龙江等地区广泛栽培[7−8]。现主栽大果沙棘品种主要有‘深秋红’、‘状元黄’、‘无刺丰’、‘向阳’和‘巨人’等[9−10],加工产品有沙棘原浆、沙棘汁、沙棘粉、沙棘油、沙棘护肤品和沙棘复方栓剂等[10]。新疆阿勒泰地区的大果沙棘作为国家地理标志产品,具有产量高、活性含量高的资源优势[9],但目前对大果沙棘质量评价研究不足,仅集中在总黄酮[11]、总酚[12]、维生素C[13]等有限指标类别评价上,导致目前企业无法有针对性地科学选品、加工及调控大果沙棘品质,从而影响大果沙棘产品的品质提升。
代谢组学分析是通过从生物样本中检测和筛选具有生物学意义和统计学差异的代谢物[14]。其代谢差异物是鉴别不同样品之间理化性质差异的表达产物,也是品质调控的重要衡量指标。因此,代谢组学的研究对提高食品品质具有重要意义。现已应用于蓝莓[15]、番茄[16]、蔓越莓[17]等果蔬研究上,但在沙棘方面的相关研究较少。郑文惠[18]通过代谢组学分析沙棘不同部位(果实、枝、叶)共鉴定出34种代谢物,沙棘叶和果实之间的代谢成分差异显著,主要差异物为黄酮类化合物。丁健等[19]采用代谢组学分析了不同成熟度沙棘果肉,共筛选出124个显著差异代谢物,并发现成熟度与脂类、黄酮和5-羟色胺合成代谢之间具有相关性。而对不同品种沙棘代谢物差异对比分析研究尚未见报道。为了更好地了解不同大果沙棘品种之间的整体差异,本研究运用非靶向代谢组学技术,以5种新疆大果沙棘(‘深秋红’、‘状元黄’、‘巨人’、‘无刺丰’和‘向阳’)主栽品种为研究对象(‘混果’为对照),对其代谢产物及其差异物进行鉴定与分析,明确区分不同新疆大果沙棘品种和预测产品品质性状的关键差异代谢物,以期为新疆大果沙棘后续加工生产与品质调控提供理论和数据支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
本实验选择新疆阿勒泰清河县(85°31′E~44°59′N)生长的6种大果沙棘样品,‘深秋红’沙棘(简称GS)、‘状元黄’沙棘(简称GZ)、‘巨人’沙棘(简称GJ)、‘无刺丰’沙棘(简称GW)、‘向阳’沙棘(简称GX)、‘混果’(简称GH) 由新疆慧华沙棘生物科技有限公司提供,如图1所示,样品均为成熟度相当,无病虫害无损伤的大果沙棘,将采摘的浆果液氮速冻后保存在−20 ℃ 冰箱待测;甲醇、乙腈、乙酸铵 均为色谱级,德国MERK公司。
SCIEX ExionLC AD超高效液相色谱系统、Triple TOF 6600型质谱仪 美国 SCIEX公司;Centrifge5810R型高速冷冻离心机 德国Eppendorf公司;IKA MS3 漩涡混合器 德国 IKA 公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品制备
将准备好的冻干样品研磨成粉,分别取样本各80 mg与甲醇/乙腈/水预冷溶液(比例为2:2:1,v/v)涡旋混合1 min后,在−20 ℃下超声功率30 min,低温静置15 min,在4 ℃下14000×g离心20 min后取上清液为待测样品,质谱分析时加入100 μL乙腈水溶液(乙腈:水=1:1,v/v)复溶,涡旋,4 ℃,14000×g离心15 min,取上清液进样分析。
1.2.2 UPLC-QTOF-MS分析
参考胡谦等[20]的方法并略作修改。色谱柱为Kinetex C18柱(2.1 mm×100 mm,2.6 µm)。流动相A为水(0.5%甲酸,25 mmol/L乙酸铵),流动相B为甲醇;进样量2 μL;柱温40 ℃ ;流速0.3 mL/min;洗脱梯度依次为:0.0~1.0 min,95% A,5% B;1.0~14.0 min,95%~2% A,5%~98% B;14.0~16.0 min,2% A,98% B;16.0~16.2 min,2%~95% A,98%~5% B;16.2~18.0 min,95% A,5% B。
采用配备DuoSpray离子源的串联QTOF质谱进行检测。离子源温度550 ℃ ;喷雾电压分别为+5500 V和−4500 V;气帘气、雾化气、辅助加热气分别设置为30 psi、50 psi、50 psi;去簇电压±80 V。扫描TOF MS:滞留时间为250 ms,质量扫描范围在m/z 100~1200之间。MS/MS模式:碰撞能量和扩展碰撞能量分别为±35、15 eV;滞留时间为50 ms;质量扫描范围在m/z 50~1200之间。
1.3 数据处理
运用 R XCMS(V3.12.0)软件包进行峰检测、过滤和对齐处理,得到代谢物定量列表;采用总峰面积归一化的方法进行数据矫正。使用SIMCA软件对鉴定的代谢物数据进行对数和中心化处理,建立主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA)模型和正交偏最小二乘判别分析(orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis,OPLS-DA)模型;通过变量投影重要度(variable importance in the projection,VIP)值、P值筛选差异物。当VIP≥1和P<0.05时,代谢物分子的统计学显著差异。代谢通路富集分析采用Origin 2021软件绘图并利用京都基因与基因组百科全书(Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes,KEGG)富集数据库进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 离子色图谱分析
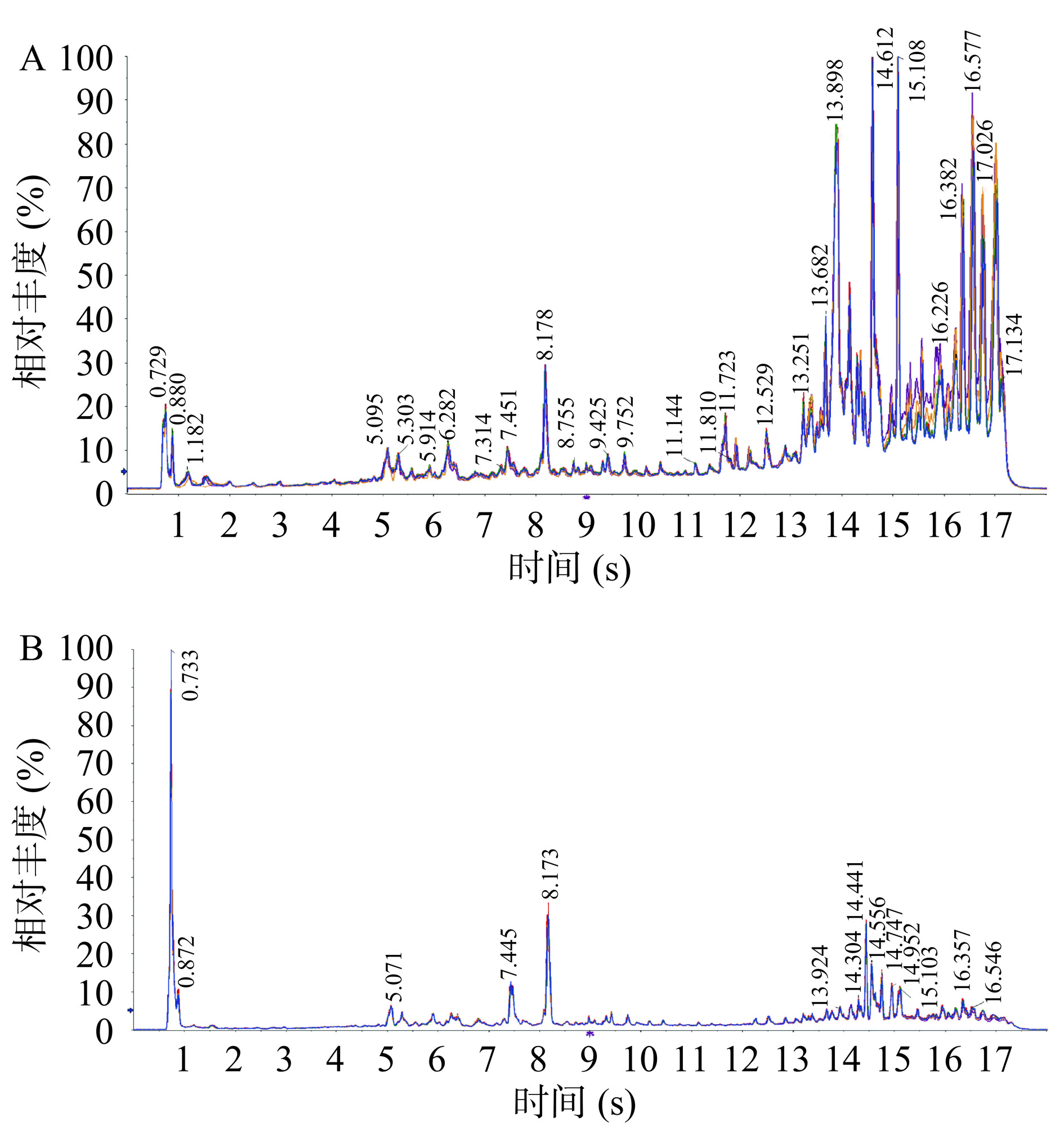
质量控制(QC)样品正、负离子模式下的总离子流(total ion current,TIC)色谱结果如图2所示,所有QC样品的峰面积和保留时间的重叠度均较高,说明仪器稳定性强,实验数据质量高。研究表明,6种大果沙棘的正、负离子色谱结果共鉴定出334种代谢物。
2.2 不同大果沙棘代谢物的分类统计
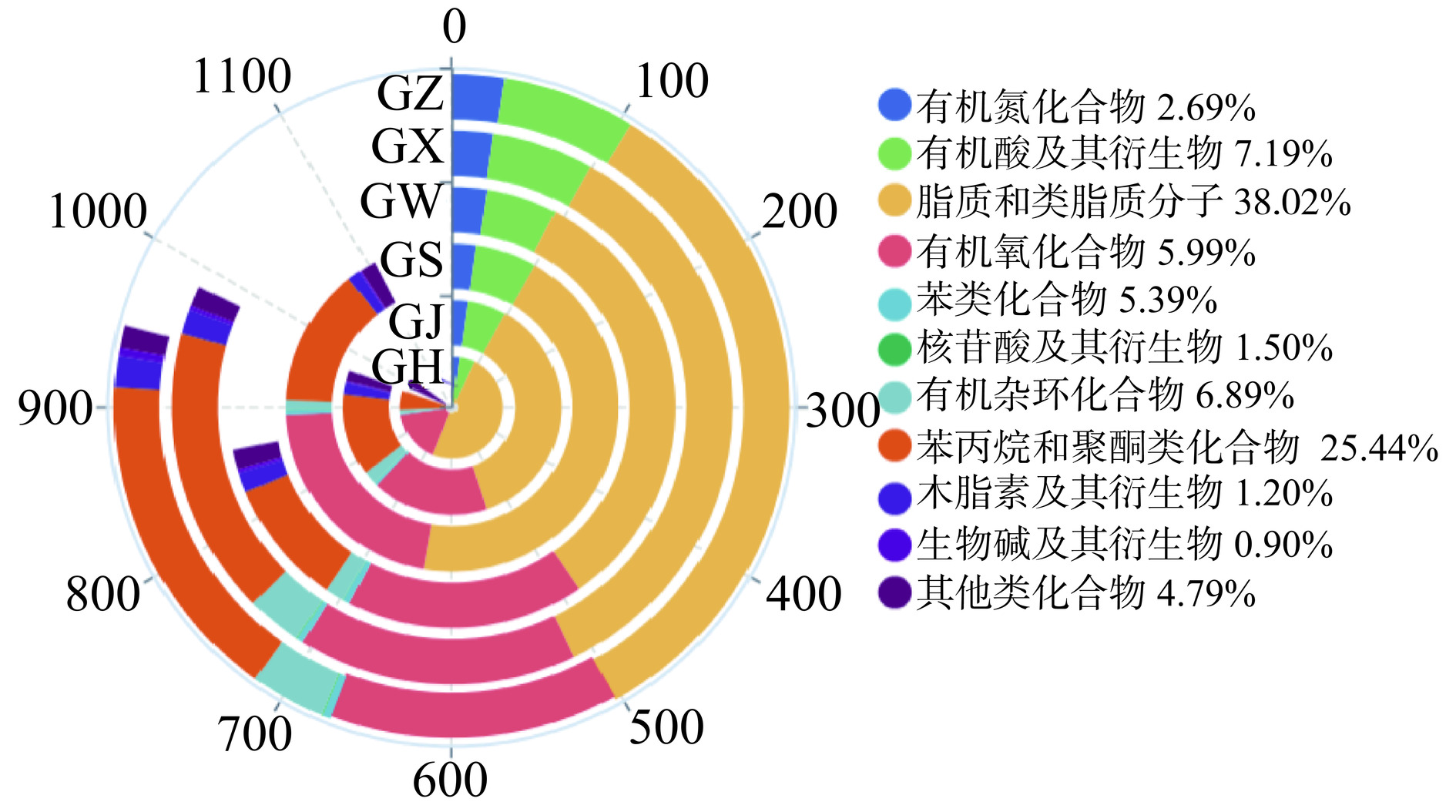
通过构建兼具条形图与环形图特点的玉玦图,对6种大果沙棘样品中提取的代谢物进行全面评估,直观反映了不同类别化合物的占比信息。正负离子模式下分别鉴定出188种和146种代谢物。共334种代谢物的化学分类及数量占比如图3显示,主要包括9种有机氮化合物、24种有机酸及其衍生物、127种脂质和类脂质分子、20种有机氧化合物、18种苯类化合物、5种核苷酸及其衍生物、23种有机杂环化合物、85种苯丙烷和聚酮类化合物、4种木质素及其衍生物、3种生物碱及其衍生物和16种其他类化合物。由此可知,大果沙棘中代谢物种类较多的化合物为脂质和类脂质分子(38.02%)、苯丙烷和聚酮类化合物(25.44%),占大果沙棘总代谢物的63.46%。
2.3 不同大果沙棘代谢物的化学型差异
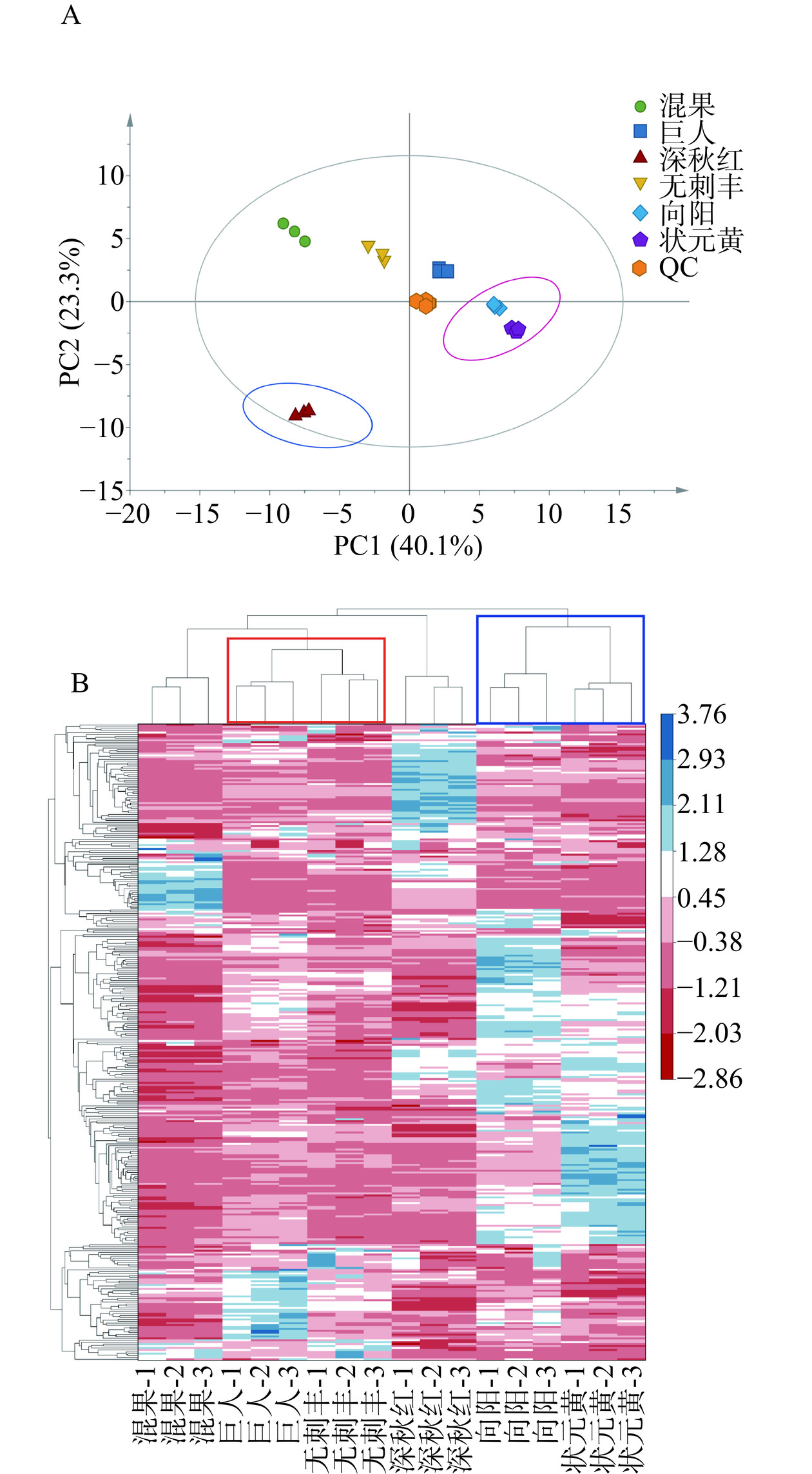
主成分分析(principal component analysis, PCA)是用于进行组学分析以识别组间和组内潜在因素并使数据尽可能可视化地保留原始数据中信息的技术[21]。对不同品种的大果沙棘代谢物进行PCA分析,如图4A所示,第一主成分(PC1)可解释原始数据集40.1%的特征,第二主成分(PC2)可解释原始数据集23.3%的特征,因此该PCA能够保留原始数据63.4%的差异。各QC样本成分聚类在一起,表明各QC样本变异度低,且进一步说明仪器操作稳定。图4A中‘巨人’沙棘分布在第一象限,‘混果’和‘无刺丰’沙棘品种分布在第二象限,‘深秋红’沙棘在第三象限,并与其他沙棘果实区分明显,这可能与不同大果沙棘品种的遗传背景和种植栽培方式等有关[22],‘状元黄’和‘向阳’沙棘品种主要分布在第四象限,且两者相近,说明其代谢物含量及组成相似。与PCA相比,聚类热图可直观呈现多代谢物在不同大果沙棘中表达量聚类关系的作用,图中的色块代表代谢物的丰度高低,颜色从深蓝色到红色代表样品的代谢物丰度由高到低。图4B上方中的树形图可得,不同品种大果沙棘根据接近度或相似性进行分组,其存在明显的分组模式,‘巨人’和‘无刺丰’的代谢物种类与含量较为接近,聚为同一类;‘向阳’和‘状元黄’聚为同一类,且与其他品种差异较大。结合PCA和聚类分析表明,不同大果沙棘具有不同的代谢特征,需进一步分析。
2.4 基于OPLS-DA模型的差异代谢物筛选
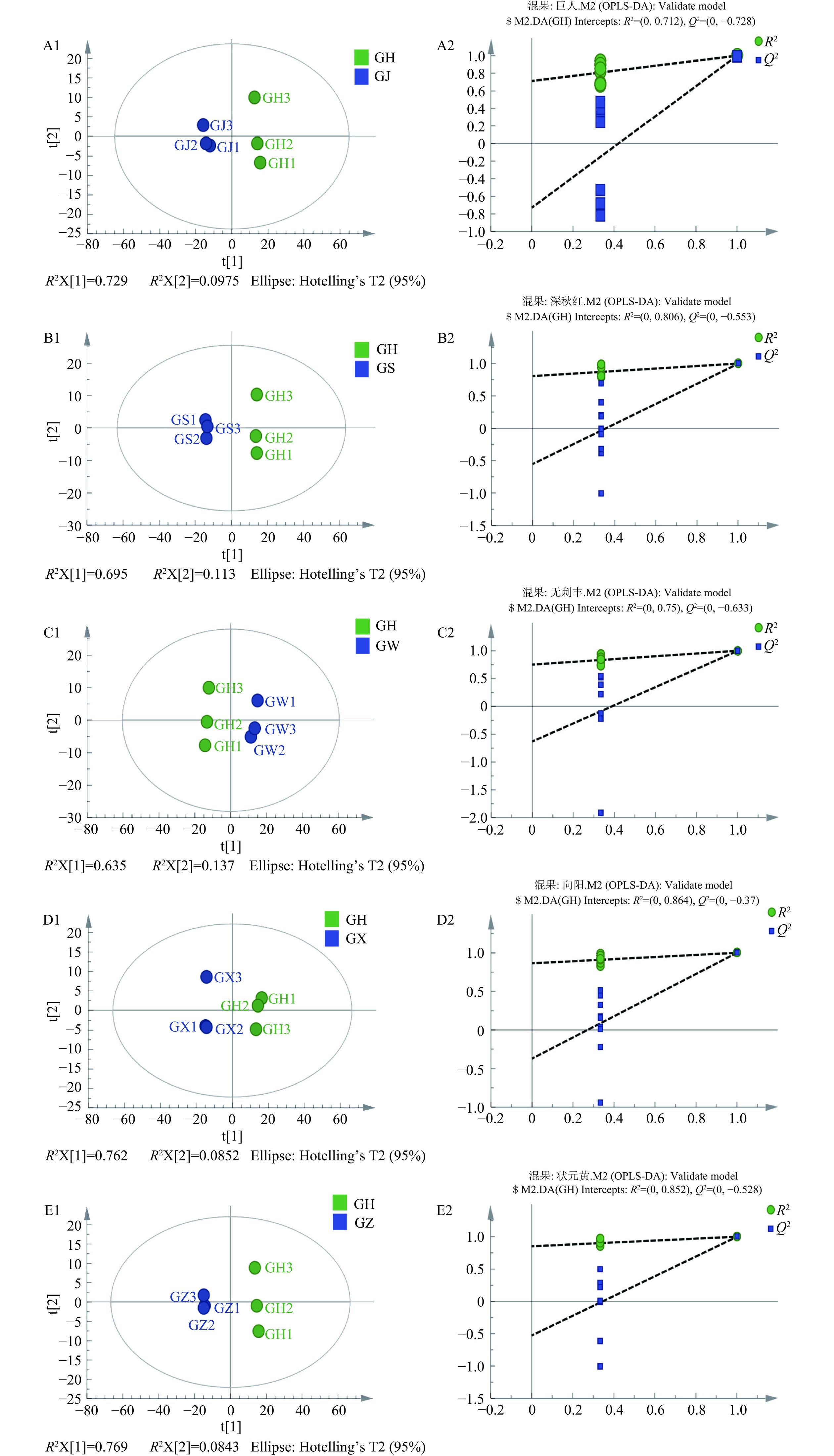
OPLS-DA是一种有监督的判别分析统计方法[23],采用SIMCA软件分别建立不同大果沙棘品种的OPLS-DA模型。如图5所示,为了更好地了解6种大果沙棘之间的代谢物差异,广泛针对大果沙棘果实中‘混果’和其他5种大果沙棘的代谢组学进行研究,分别为GH vs GJ、GH vs GS、GH vs GW、GH vs GX和GH vs GZ,并采用OPLS-DA进一步对数据进行分析和置换检验。图中5组样品分布在置信区间的左右两侧,且每组样本全部处于95%置信区间内,表明每组代谢物的差异显著,判别效果明显,可用于后续差异代谢物分析。通过置换检验随机模型得到所有R2点的数值按顺序从左到右递减,直至低于最右侧的原始R2点;所有Q2点的数值均在原始Q2点之下;此外,点的回归线与横坐标交叉或小于0,说明OPLS-DA模型具有可靠性,能够有效解释两组样本之间的差异。综上表明,这5组原始模型具有良好的稳定性,未发现过拟合问题,可用于进一步筛选差异代谢物。
2.5 不同大果沙棘差异代谢物的鉴定与分析
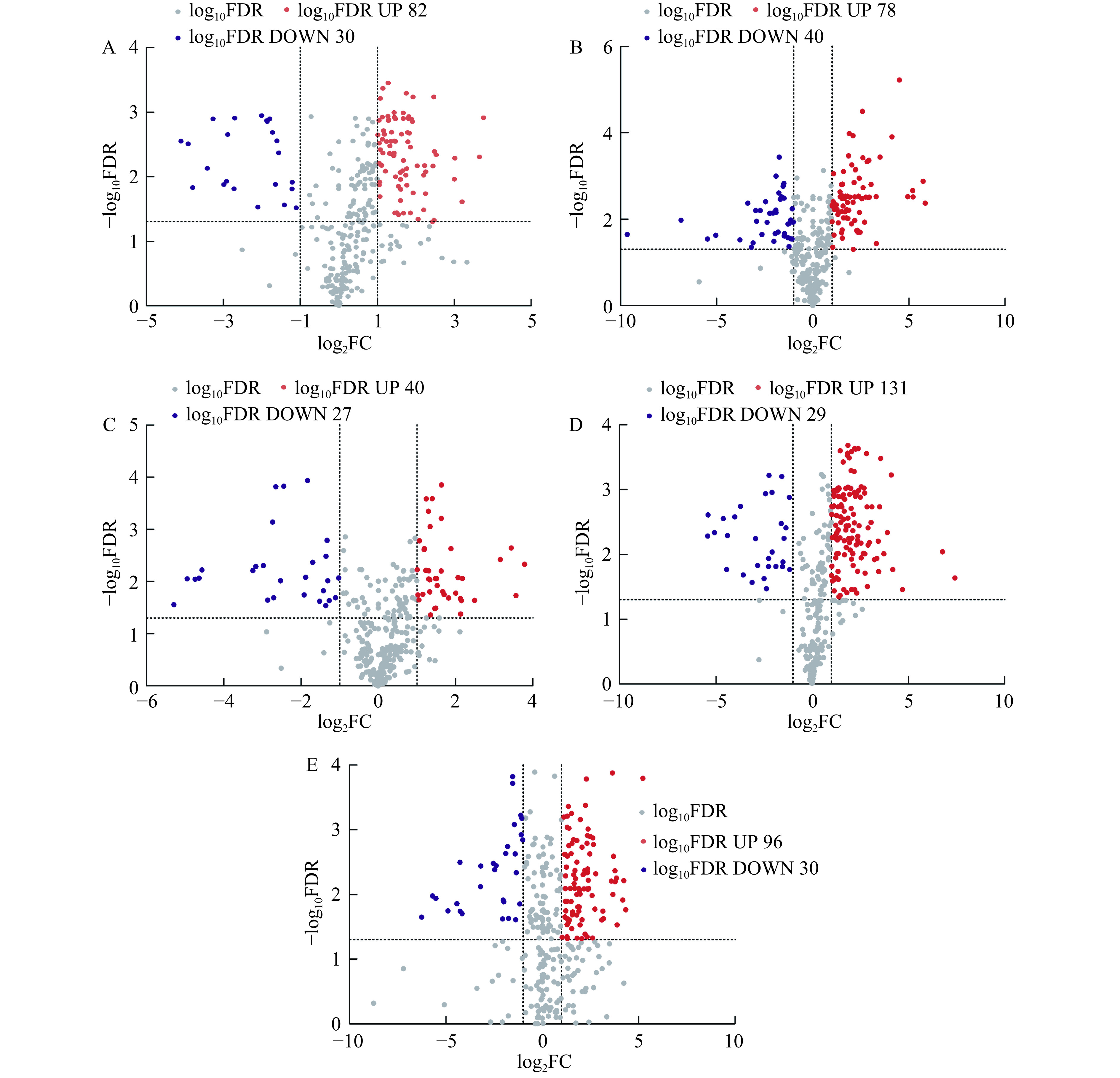
基于表达量比值的双倍对数log2FC绝对值≥1和错误发现率(FDR)<0.05的筛选标准,对分组样本的差异代谢物进行筛选。图6火山图中红色为上调代谢物,蓝色为下调代谢物,灰色为未显代谢物。火山图表明,‘混果’和‘巨人’之间存在112种差异代谢物,其中‘巨人’对于‘混果’上调代谢物82个,下调代谢物30个;‘混果’和‘深秋红’之间存在118种差异代谢物,其中‘深秋红’对于‘混果’上调代谢物78个,下调代谢物40个;‘混果’和‘无刺丰’之间存在67种差异代谢物,其中‘无刺丰’对于‘混果’上调代谢物40个,下调代谢物27个;‘混果’和‘向阳’之间存在160种差异代谢物,其中‘向阳’对于‘混果’上调代谢物131个,下调代谢物29个;‘混果’和‘状元黄’之间存在126种差异代谢物,‘向阳’对于‘混果’上调代谢物96个,下调代谢物30个。由此可见,‘向阳’的差异代谢物数量最多,表明‘向阳’的品质较其他品种与‘混果’的差异最大。
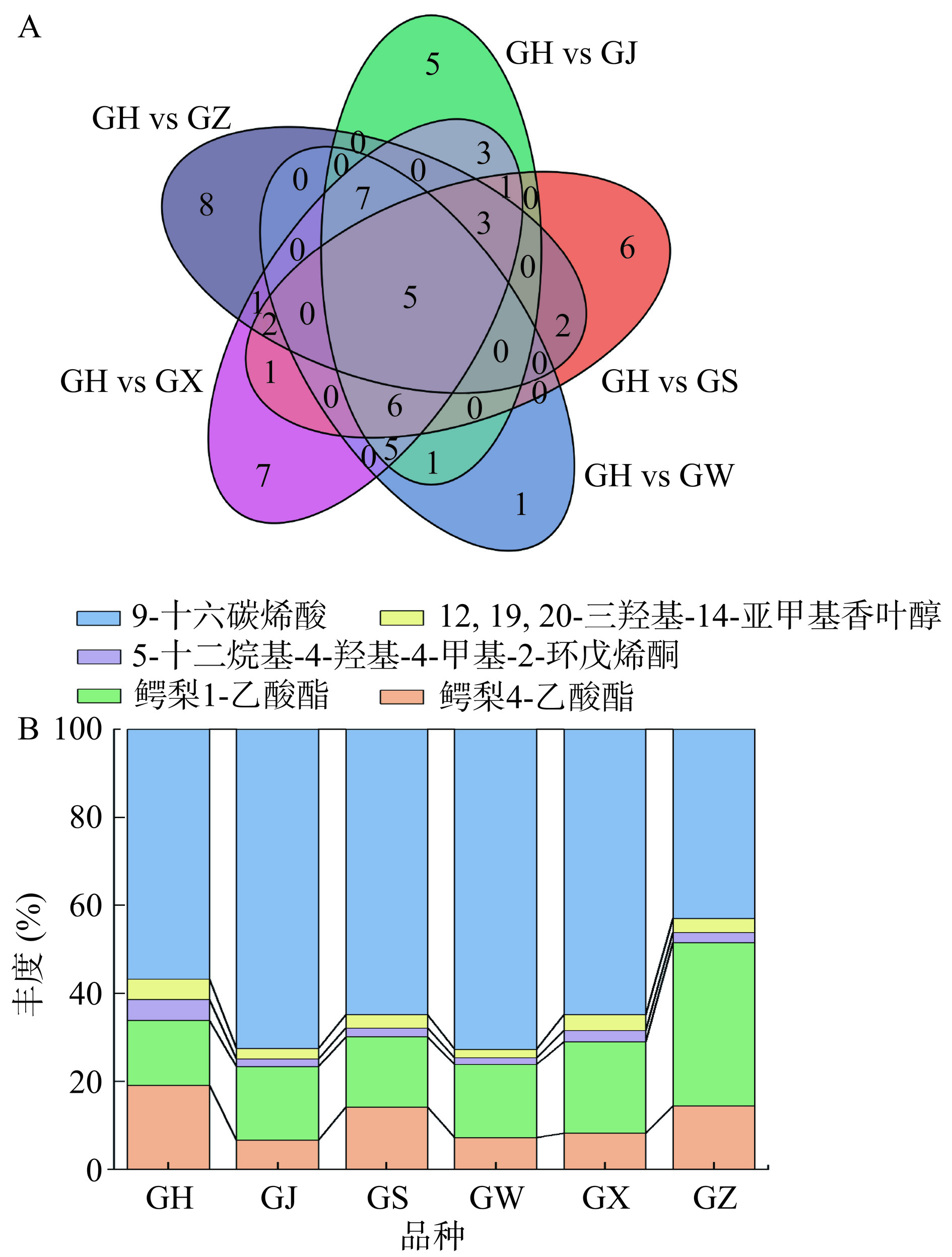
结合OPLS-DA模型的VIP值>1和火山图筛选得到的差异代谢物得到韦恩图(图7),如图所示,特有差异代谢物以GH vs GJ有5种;GH vs GS有6种;GH vs GW中只有1种特有差异代谢物,为圣草酚-7-O-葡糖苷;GH vs GX有7种;GH vs GZ有8种,代谢物的分布差异可能与大果沙棘的代谢化合物形成途径有关,且不同组内之间的差异可能受这些关键代谢物的调控。从5组中筛选出共有差异物5种,分别为3种脂质和类脂质分子(鳄梨 4-乙酸酯、鳄梨 1-乙酸酯、9-十六碳烯酸),2种其他类代谢化合物(5-十二烷基-4-羟基-4-甲基-2-环戊烯酮、12,19,20-三羟基-14-亚甲基香叶醇)。由百分比图可见,不同大果沙棘果实中这3种脂质和类脂质分子化合物的丰度均高于其他类化合物,说明不同大果沙棘中这些化合物占主导地位。 Yang等[24]采用气相色谱技术分析不同地区沙棘中的脂肪酸差异发现其含量高低与沙棘(亚)种、海拔、采摘时期等因素有关,且脂肪酸通常以酯的形式参与各种脂质的组成。9-十六碳烯酸(又称棕榈油酸)的占比(43%~73%)最高,可作为不饱和脂肪酸具有降低糖尿病风险的能力,且酯化后的棕榈油酸是一种源自脂肪细胞的有益脂质激素(脂质因子),它的释放可防止过多的非酯化脂肪酸对全身葡萄糖代谢的有害影响[25]。Yang等[26]研究发现沙棘果实中的棕榈油酸含量最高,与上述研究基本一致。因此,棕榈油酸可作为不同大果沙棘果实中共有的营养关键代谢物。
2.6 差异代谢物的KEGG分析
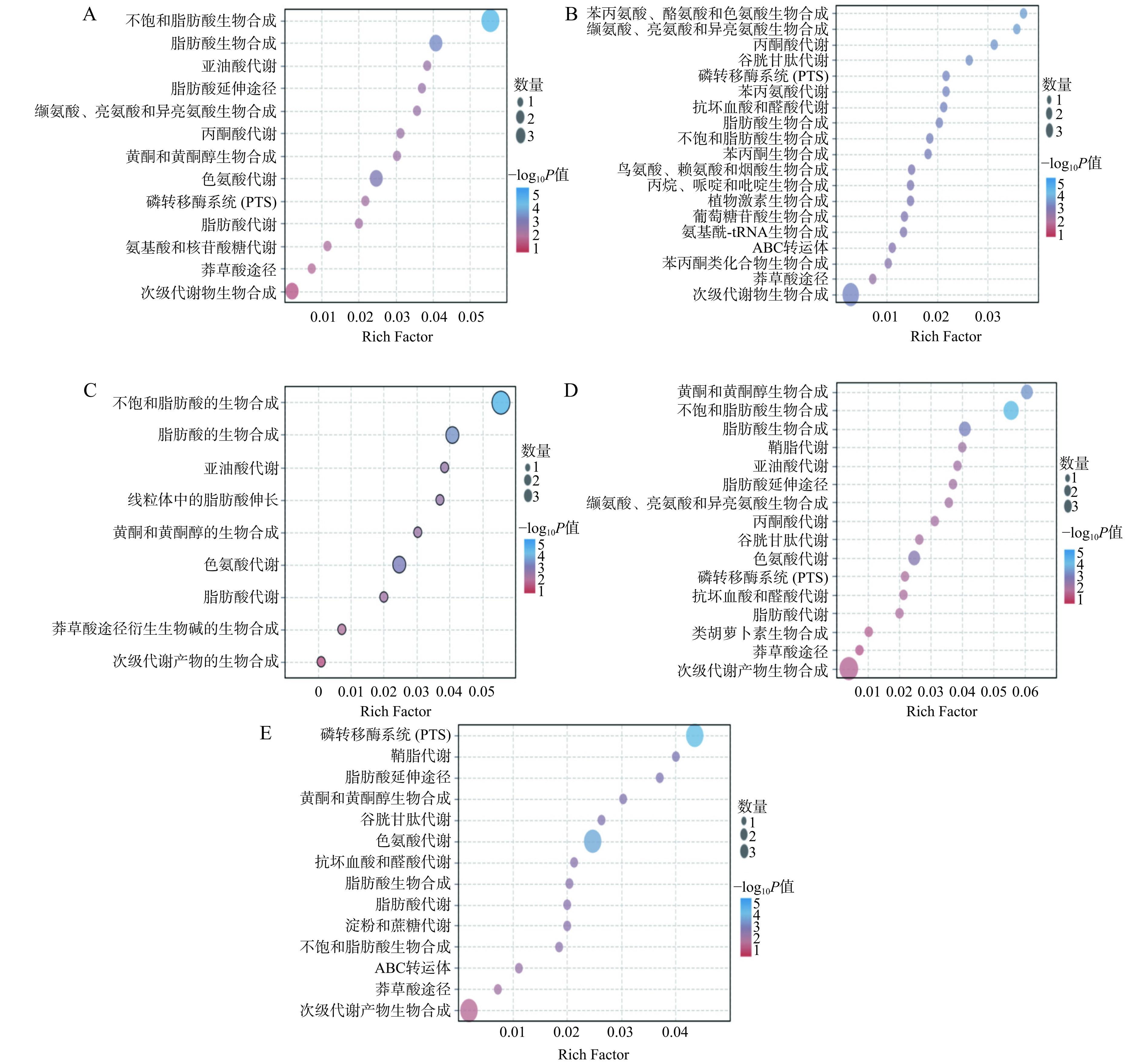
通过KEGG数据库对不同大果沙棘中筛选出来的差异代谢物进行通路富集,并对P值最小的前3条通路进行分析。KEGG分析发现(图8),在GH vs GJ中的差异代谢物被注释到13条代谢通路中,其中被注释的差异代谢物数目排前3的KEGG通路类型分别为不饱和脂肪酸生物合成、脂肪酸生物合成及色氨酸代谢,主要参与的代谢物为5-羟色胺、亚油酸、棕榈酸和油酸;GH vs GS的差异代谢物被注释到19条代谢通路中,其中,KEGG通路类型中排前3的差异代谢物分别为苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸和色氨酸生物合成,缬氨酸、亮氨酸和异亮氨酸生物合成,丙酮酸代谢。3条通路中涉及的代谢物为苯丙氨酸和2-异丙基苹果酸。本研究发现,含有苯丙氨酸代谢物的代谢通路占总代谢通路的63%,说明映射出来的该差异代谢物对通路的影响较大。苯丙氨酸代谢物可通过莽草酸途径转化产生羟基肉桂酸,在羟基肉桂酸侧链缩短后,形成羟基苯甲酸,有效抑制食品中的微生物,延缓食品变质[27]。GH vs GW中差异代谢物被注释到9条代谢通路中,其中被注释的差异代谢物数目排前3的KEGG通路类型分别为不饱和脂肪酸生物合成、脂肪酸生物合成和色氨酸代谢,参与的代谢物分别为5-羟色胺、吲哚-3-乙醛、亚油酸、棕榈酸和油酸;GH vs GX的显著差异代谢物被注释到19条代谢通路中,其中被注释的差异代谢物数目排前3的KEGG通路类型分别为不饱和脂肪酸生物合成、黄酮和黄酮醇生物合成、脂肪酸生物合成,参与的代谢物为芦丁、异槲皮素、亚油酸、棕榈酸和油酸;GH vs GZ中的差异代谢物被注释到14条代谢通路中,其中被注释的差异代谢物数目排前3的KEGG通路类型分别为磷转移酶系统(PTS)、鞘脂代谢和色氨酸代谢途径,参与的主要代谢物为海藻糖、抗坏血酸、吲哚-3-乙醛和植物鞘氨醇。
2.7 不同大果沙棘的营养关键代谢物
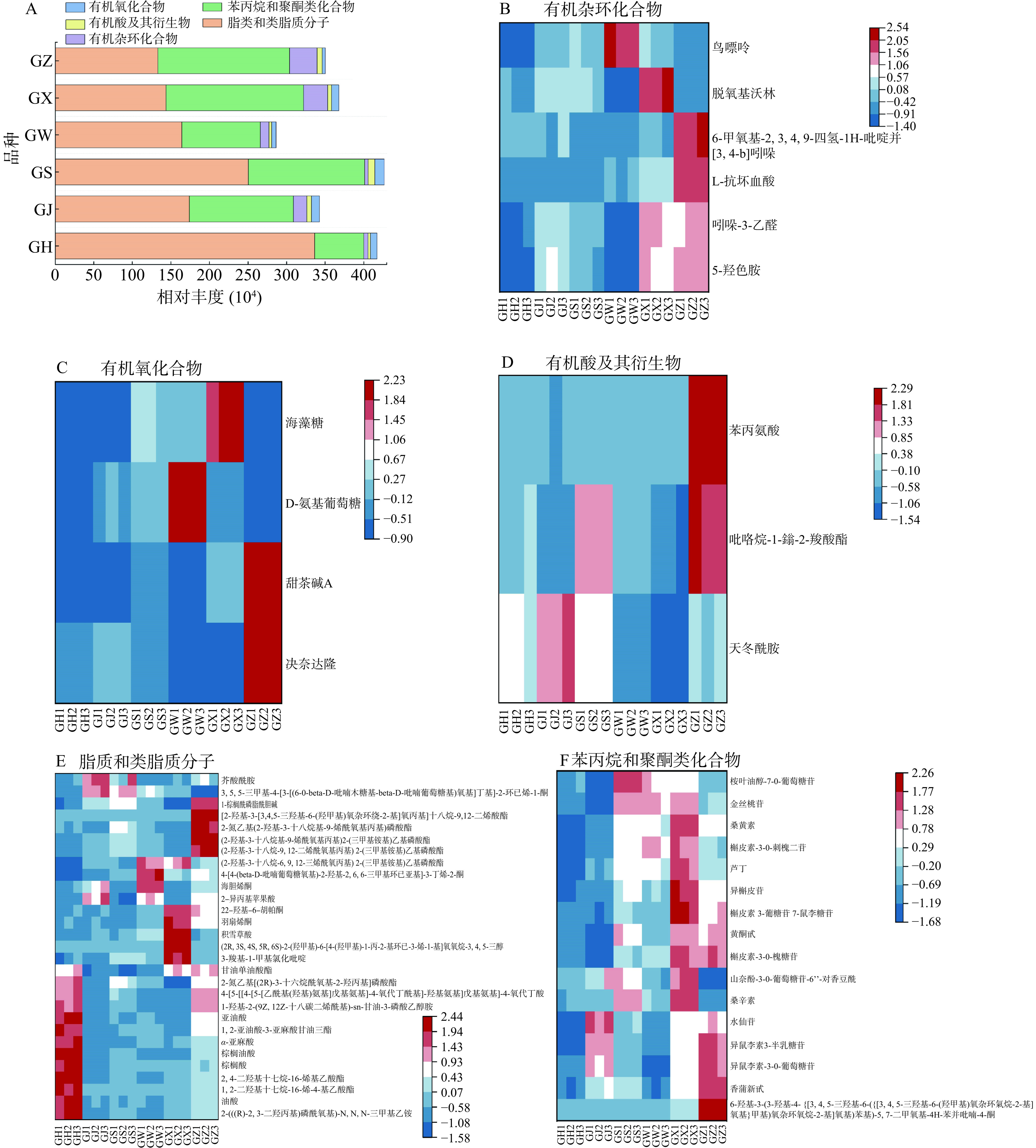
根据基于VIP值>1、log2FC绝对值≥1和FDR<0.05的筛选标准,在不同大果沙棘中共鉴定出66种对样品贡献较大的代谢物。这些化合物对影响大果沙棘的品质特性至关重要,主要属于有机杂环化合物、有机氧化合物、有机酸及其衍生物、脂质和类脂质分子及苯丙烷和聚酮类化合物这5种类别。由主要代谢物分类柱状图(图9A)可见,所有大果沙棘中脂质和类脂质分子的占比较大,在38%~81%之间;其次是苯丙烷和聚酮类化合物,占比在15%~49%之间,说明它们在塑造大果沙棘果实品质方面发挥着重要作用。
杂环化合物是最大和最多样化的有机化合物家族,因具有抗癌、抗病毒、抗炎和抗高血压等生物活性,在药物中发挥着重要作用[28]。本研究显示,贡献较大的有机杂环化合物有6种,其中5-羟色胺、吲哚-3-乙醛和L-抗坏血酸的丰度较高。5-羟色胺能够使大脑产生愉悦情绪,从而起到治疗抑郁症的效果,还具有缩减癌变范围和干扰肿瘤生长的作用[29]。5-羟色胺主要由色氨酸代谢通路在代谢过程中部分色氨酸经过氧化脱羧转变而成[30]。图中在‘状元黄’沙棘中丰度较高,其次是‘向阳’沙棘。以上两种沙棘果实中的5-羟色胺的丰度较高,可能与较高的槲皮素有关(图9B),其可抑制受体活性,从而增加5-羟色胺水平[31]。鸟嘌呤仅在‘深秋红’沙棘中丰度较高,6-甲氧基-2,3,4,9-四氢-1H-吡啶并[3,4-b]吲哚在‘状元黄’沙棘中相对较低。有机氧化合物是指含有碳和氧元素的化合物,本研究中4种有机氧化合物的贡献度均高,分别为3种碳水化合物(D-氨基葡萄糖、海藻糖、甜茶碱A)和1种羰基化合物(决奈达隆)。其中决奈达隆主要用于治疗心律失常[32],在‘深秋红’沙棘中相对较高。而沙棘果实中富含丰富的碳水化合物,可作为蛋白质和细胞的组成部分,具有重要的生物学功能[33]。研究发现,碳水化合物和有机化合物的浓度与温度相关,且较低的温度会诱导还原糖和有机化合物的积累[34]。因此,初步推断沙棘品种之间的差异还与采摘地的温度差异有关。有机酸及其衍生物有3种,为天冬酰胺、吡咯烷-1-鎓-2-羧酸酯和苯丙氨酸,每组中天冬酰胺的丰度均为最高。Ciesarov等[35]也发现天冬酰胺是沙棘中的主要氨基酸,其在治疗肝脏和神经系统中有良好作用[36]。
由图9E可知,不同沙棘果实中大多数差异化合物为脂质和类脂质分子,其中贡献度较大的有28种,包含3种戊二烯醇脂质类、12种脂肪酰基类,4种烯醇酮脂类、6种甘油磷脂类、2种甘油糖脂类和1种甘油脂。丰度较高的代谢化合物主要为芥酸酰胺、亚油酸、棕榈酸、棕榈油酸和油酸,上述代谢化合物具有去除羟自由基、增强细胞免疫和体液免疫,并促进NK细胞活性的功效[37−38]。Ercisli等[39]通过研究不同土耳其沙棘品种的化学成分发现所有沙棘中占据优势的脂肪酸为棕榈油酸、棕榈酸、油酸和亚油酸,这与本研究一致。亚油酸能降低胆固醇含量,与棕榈酸相互作用后有效增加高密度脂蛋白、降低低密度脂蛋白和降血压[40],图中‘混果’中棕酮酸和亚油酸的丰度最高,其次是‘深秋红’沙棘。芥酸酰胺是沙棘果实中贡献度较高的脂肪酰基类,具有抑菌、抗焦虑和抗抑郁等作用[41],在‘巨人’沙棘中丰度最高。而不同大果沙棘之间的差异可能与基因型有关[26]。
苯丙烷和聚酮类化合物是一大类具有多种生物学功能的植物次生代谢产物[42]。图9F中贡献度高的化合物有16种,既黄酮类化合物(15种)和异黄酮类(1种),其中水仙苷、异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷、芦丁、异槲皮苷、异鼠李素3-半乳糖苷的丰度较高。研究发现,黄酮类化合物拥有较好的生理作用,如提高人体的抵抗力、降低血液中胆固醇含量,并具有明显的抗肿瘤、抗炎和抗衰老等作用,且黄酮类化合物能够与反应性羰基或二羰基相结合,从而竞争性抑制天冬酰胺和葡萄糖之间的美拉德反应[43]。沙棘富含黄酮类化合物,当中山奈素、异鼠李素、槲皮素是主要母核,其C-3或C-7位羟基易与芸香糖、鼠李糖、槐糖等糖基结合生成糖苷,具有抗氧化、抗癌及治疗和预防慢性疾病等的多种生物活性作用和有益健康的功效[44]。根据差异热图可得,16种差异代谢物在‘向阳’沙棘果中的丰度较高,这可能与其高丰度的苯丙氨酸有关,苯丙氨酸是黄酮类化合物合成的前体物质,可通过不同的分支合成途径合成黄酮类成分[36]。在‘深秋红’沙棘中异鼠李素-3-O-芸香糖苷(别名水仙苷)的丰度较高,‘巨人’沙棘中桉叶油醇-7-O-葡萄糖苷和金丝桃苷丰度较高;‘状元黄’中香蒲新甙、异鼠李素3-半乳糖苷、异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷等丰度较高。本研究表明,水仙苷是大果沙棘果实中丰度最高的黄酮类化合物,这与王琬宁[45]研究的一致,说明该化合物可能是影响沙棘果实黄酮含量的代谢标志物,对果实品质上起着重要作用。
综上所述,不同大果沙棘果实主要差异代谢物为脂质和类脂质分子、苯丙烷和聚酮类这两大类化合物的数量较多,后续可在此基础上深入挖掘加工过程中的关键活性物质变化,从而有针对性地对沙棘产品品质进行合理调控。66种差异代谢物的种类和比例共同构成了各大果沙棘在活性物质上的差异性,同时也赋予了大果沙棘果实丰富的营养品质和独特滋味,如‘状元黄’和‘向阳’沙棘中5-羟色胺丰度较高,则表明这两个品种更适合5-羟色胺的提取;‘向阳’沙棘中富含丰富的苯丙氨酸和黄酮类化合物,说明该品种较适宜黄酮类化合物的提取。
3. 结论
本研究采用非靶向代谢组学系统地揭示了不同品种新疆大果沙棘的代谢物差异。共检测出代谢产物334种,总共分为11类,主要为脂质和类脂质分子(38.02%)、苯丙烷和聚酮类化合物(25.44%)等。大果沙棘基本具有不同的代谢特征,研究发现的差异代谢物可分别作为区分‘混果’与‘巨人’、‘深秋红’、‘无刺丰’、‘向阳’、‘状元黄’的不同大果沙棘品种的主要代谢物。且棕榈油酸在共有的代谢物中占比最高,在43%~73%之间,可作为营养关键代谢物为机体提供更多的能量。与‘混果’相比,‘巨人’、‘深秋红’、‘无刺丰’、‘向阳’和‘状元黄’沙棘的差异代谢物分别富集在13、19、9、19和14条代谢通路上,主要参与的代谢物有5-羟色胺、亚油酸和苯丙氨酸等。鉴定出66种对样品贡献较大的代谢物,主要属于脂质和类脂质分子、苯丙烷和聚酮类化合物等,发现的差异代谢通路和主要代谢物为新疆大果沙棘品种的鉴别和加工品质调控提供了应用新思路。当前研究仅分析了不同品种新疆大果沙棘的主要代谢物分析,后期可在此基础上,进一步对新疆大果沙棘产品不同加工工段中主要差异代谢物的变化规律开展精准靶向研究,为深入应用靶向代谢组学分析大果沙棘关键营养代谢物的合成机制提供理论依据。
-
-
[1] ADIL H, HUSSAIN A S, QURATULAIN S, et al. A supernatural multipurpose plant Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.):An updated overview of its folk traditional uses, phytochemical profile and biological activities[J]. Journal of Berry Research,2023,13(1):21−66. doi: 10.3233/JBR-220055
[2] WEI D, JIAN D, SHUNGUANG L, et al. Identification of the key flavonoid and lipid synthesis proteins in the pulp of two sea buckthorn cultivars at different developmental stages[J]. BMC Plant Biology,2022,22(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03688-5
[3] JI M, GONG X, LI X, et al. Advanced research on the antioxidant activity and mechanism of polyphenols from Hippophae species-A Review[J]. Molecules,2020,25(4):917. doi: 10.3390/molecules25040917
[4] OLAS B, SKALSKI B, ULANOWSKA K. The anticancer activity of sea buckthorn (Elaeagnus rhamnoides (L.) A. Nelson)[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2018,9:232. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00232
[5] SINGH S, SHARMA P C. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based metabolome diversity of Seabuckthorn (H. rhamnoides L.) berries originating from two geographical regions of Indian Himalayas[J]. Food Analytical Methods,2021,prepublish:1−15.
[6] 陶翠, 王捷, 姚玉军, 等. 沙棘中白雀木醇表征方法及其分布规律[J]. 北京林业大学学报,2020,42(1):121−126. [TAO C, WANG J, YAO Y J, et al. Characterization method of white sparrow wood alcohol in sea buckthorn and its distribution pattern[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University,2020,42(1):121−126.] TAO C, WANG J, YAO Y J, et al. Characterization method of white sparrow wood alcohol in sea buckthorn and its distribution pattern[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 2020, 42(1): 121−126.
[7] 劳斐, 李杰, 王翻红. 阿勒泰地区大果沙棘营养成分研究[J]. 食品安全导刊,2021,21(21):122−123. [LAO F, LI J, WANG F H. Nutritional composition of sea buckthorn in Altay region[J]. Food Safety Journal,2021,21(21):122−123.] LAO F, LI J, WANG F H. Nutritional composition of sea buckthorn in Altay region[J]. Food Safety Journal, 2021, 21(21): 122−123.
[8] 王官, 韩有志, 安雄韬, 等. 不同品种大果沙棘叶片与果实特征的研究[J]. 山西林业科技,2013,42(1):32−34. [WANG G, HAN Y Z, AN X T, et al. Research on leaf and fruit characteristics of different varieties of sea buckthorn[J]. Shanxi Forestry Science and Technology,2013,42(1):32−34.] WANG G, HAN Y Z, AN X T, et al. Research on leaf and fruit characteristics of different varieties of sea buckthorn[J]. Shanxi Forestry Science and Technology, 2013, 42(1): 32−34.
[9] 李珍, 李杰, 张湖林, 等. 阿勒泰地区大果沙棘质量分析研究[J]. 饮料工业,2023,26(2):48−51. [LI Z, LI J, ZHANG H L, et al. Quality analysis of sea buckthorn in Altay region[J]. Beverage Industry,2023,26(2):48−51.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7871.2023.02.009 LI Z, LI J, ZHANG H L, et al. Quality analysis of sea buckthorn in Altay region[J]. Beverage Industry, 2023, 26(2): 48−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7871.2023.02.009
[10] 姚娜娜, 车凤斌, 李永海, 等. 沙棘的营养价值及综合开发利用概述[J]. 保鲜与加工,2020,20(2):226−232. [YAO N N, CHE F B, LI Y H, et al. Overview of the nutritional value and comprehensive development and utilization of sea buckthorn[J]. Freshness and Processing,2020,20(2):226−232.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6221.2020.02.038 YAO N N, CHE F B, LI Y H, et al. Overview of the nutritional value and comprehensive development and utilization of sea buckthorn[J]. Freshness and Processing, 2020, 20(2): 226−232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6221.2020.02.038
[11] 韩蓉, 马燕, 敖羽, 等. 基于多元分析法综合评价新疆不同品种大果沙棘汁品质特性及加工适宜性[J/OL]. 食品工业科技:1−17[2024-11-23]. [HAN R, MA Y, AO Y, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of quality characteristics and processing suitability of different varieties of sea buckthorn juice in Xinjiang based on multivariate analysis[J/OL]. Food Industry Science and Technology:1−17[2024-11-23].] HAN R, MA Y, AO Y, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of quality characteristics and processing suitability of different varieties of sea buckthorn juice in Xinjiang based on multivariate analysis[J/OL]. Food Industry Science and Technology: 1−17[2024-11-23].
[12] 方贵平, 毕金峰, 刘春海, 等. 中国四个地区代表性沙棘果实综合品质评价[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(21):249−260. [FANG G P, BI J F, LIU C H, et al. Comprehensive quality evaluation of representative sea buckthorn fruits from four regions in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering,2022,38(21):249−260.] doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.21.029 FANG G P, BI J F, LIU C H, et al. Comprehensive quality evaluation of representative sea buckthorn fruits from four regions in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(21): 249−260. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.21.029
[13] 乌仁斯庆, 姚玉军, 张宇, 等. 不同产地和品种沙棘果品质研究[J]. 食品安全导刊,2022,23:80−85,125. [WU R S Q, YAO Y J, ZHANG Yu, et al. Comparative study on fruit quality of Seabuckthorn from different producing habitats and varieties[J]. Food Safety Journal,2022,23:80−85,125.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0270.2022.13.spaqdk202213039 WU R S Q, YAO Y J, ZHANG Yu, et al. Comparative study on fruit quality of Seabuckthorn from different producing habitats and varieties[J]. Food Safety Journal, 2022, 23: 80−85,125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0270.2022.13.spaqdk202213039
[14] JIANG L, LU M, RAO T, et al. Comparative analysis of fruit metabolome using widely targeted metabolomics reveals nutritional characteristics of different rosa Roxburghii genotypes[J]. Foods,2022,11(6):850. doi: 10.3390/foods11060850
[15] LI Y, LI H, WANG S, et al. Metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses of the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway in blueberry (Vaccinium spp.)[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2023,14:1082245. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1082245
[16] CAI W Q, JIANG P F, LIU Y, et al. Distinct changes of taste quality and metabolite profile in different tomato varieties revealed by LC-MS metabolomics[J]. Food Chemistry,2024,442:138456. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.138456
[17] WANG Y, VORSA N, HARRINGTON P D B, et al. Nontargeted metabolomic study on variation of phenolics in different cranberry cultivars using UPLC-IM–HRMS[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(46):12206−12216. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b05029
[18] 郑文惠. 沙棘不同部位的代谢组学分析及抗炎活性研究[D]. 兰州:兰州大学, 2020. [ZHENG W H. Metabolomic analysis and anti-inflammatory activity of different parts of sea buckthorn[D]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University, 2020.] ZHENG W H. Metabolomic analysis and anti-inflammatory activity of different parts of sea buckthorn[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2020.
[19] 丁健, 阮成江, 杨红, 等. 基于UPLC-MS技术分析沙棘果肉成熟过程中生物活性成分差异[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(22):276−286. [DING J, RUAN C J, YANG H, et al. Differences in bioactive components of sea buckthorn pulp during ripening based on UPLC-MS[J]. Food Science,2023,44(22):276−286.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220904-038 DING J, RUAN C J, YANG H, et al. Differences in bioactive components of sea buckthorn pulp during ripening based on UPLC-MS[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(22): 276−286. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220904-038
[20] 胡谦, 张九凯, 韩建勋, 等. 基于UPLC-QTOF-MS技术的压榨和浸出油茶籽油甘油酯组成比较分析[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(2):235−240. [HU Q, ZHANG J K, HAN J X, et al. Comparative analysis of glyceride composition of pressed and leached Camellia sinensis oil based on UPLC-QTOF-MS[J]. Food Science,2021,42(2):235−240.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200115-182 HU Q, ZHANG J K, HAN J X, et al. Comparative analysis of glyceride composition of pressed and leached Camellia sinensis oil based on UPLC-QTOF-MS[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(2): 235−240. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200115-182
[21] 张蓝月, 孙万成, 罗毅皓. 基于非靶向代谢组学分析不同地区羊肉代谢物的差异[J]. 现代食品科技,2023,39(7):91−101. [ZHANG L Y, SUN W C, LUO Y H. Analysis of differences in lamb metabolites in different regions based on untargeted metabolomics[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2023,39(7):91−101.] ZHANG L Y, SUN W C, LUO Y H. Analysis of differences in lamb metabolites in different regions based on untargeted metabolomics[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2023, 39(7): 91−101.
[22] 王珊珊, 张萍, 张冰冰, 等. 寒地沙棘种质资源果实品质分析与综合评价[J]. 农业工程学报,2023,39(13):281−289. [WANG S S, ZHANG P, ZHANG B B, et al. Fruit quality analysis and comprehensive evaluation of cold-land sea buckthorn germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering,2023,39(13):281−289.] doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202303150 WANG S S, ZHANG P, ZHANG B B, et al. Fruit quality analysis and comprehensive evaluation of cold-land sea buckthorn germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39(13): 281−289. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.202303150
[23] 欧阳红军, 刘义军, 袁源, 等. HS-SPME-GC-MS结合OPLS-DA分析提取方法对牛油果油挥发性香气化合物的影响[J]. 南方农业学报,2021,52(3):779−788. [OUYANG H J, LIU Y J, YUAN Y, et al. Effect of HS-SPME-GC-MS combined with OPLS-DA analytical extraction method on volatile aroma compounds of avocado oil[J]. Southern Agricultural Journal,2021,52(3):779−788.] OUYANG H J, LIU Y J, YUAN Y, et al. Effect of HS-SPME-GC-MS combined with OPLS-DA analytical extraction method on volatile aroma compounds of avocado oil[J]. Southern Agricultural Journal, 2021, 52(3): 779−788.
[24] YANG B R, KALLIO H. Effects of harvesting time on triacylglycerols and glycerophospholipids of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berries of different origins[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Chemistry,2002,15(2):143−157. doi: 10.1006/jfca.2001.1041
[25] GRZEGORZ D, SYLWESTER C, MARCIN S, et al. Composition of flesh lipids and oleosome yield optimization of selected sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) cultivars grown in Poland[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,369:130921. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130921
[26] YANG, KALLIO, H P. Fatty acid composition of lipids in sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berries of different origins[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2001,49(4):1939−1947. doi: 10.1021/jf001059s
[27] YING C, YUNFEI C, KE W, et al. Bioactive compounds in sea buckthorn and their efficacy in preventing and treating metabolic syndrome[J]. Foods (Basel, Switzerland),2023,12(10):1985.
[28] ASIF M, IMRAN M. Antimicrobial activities of various thiazine based heterocyclic compounds:A mini-review[J]. Mini-Reviews in Organic Chemistry,2022,19(2):166−172. doi: 10.2174/1570193X18666210629102447
[29] 王申萌. 黑果腺肋花楸花青素纯化及益生菌对果汁品质的影响研究[D]. 黑龙江:东北林业大学, 2023. [WANG S M. Study on the effect of anthocyanin purification and probiotics on juice quality of Rowania nigra[D]. Heilongjiang:Northeast Forestry University, 2023.] WANG S M. Study on the effect of anthocyanin purification and probiotics on juice quality of Rowania nigra[D]. Heilongjiang: Northeast Forestry University, 2023.
[30] 刘晶晶, 邓高文, 胡嘉亮, 等. 基于非靶向代谢组学的不同菌种强化发酵浏阳豆豉的代谢差异分析[J]. 食品科学,2024,45(1):42−49. [LIU J J, DANG G W, HU J L, et al. Analysis of metabolic differences between different strains of fortified fermented Liuyang tempeh based on untargeted metabolomics[J]. Food Science,2024,45(1):42−49.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230227-246 LIU J J, DANG G W, HU J L, et al. Analysis of metabolic differences between different strains of fortified fermented Liuyang tempeh based on untargeted metabolomics[J]. Food Science, 2024, 45(1): 42−49. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230227-246
[31] KHADEEJA K, KALAM A N, MOHD A. A natural phenolic compound quercetin showed the usefulness by targeting inflammatory, oxidative stress markers and augment 5-HT levels in one of the animal models of depression in mice[J]. Drug Research, 2019, 69(7):392−400.
[32] Dobutamine/dronedarone/insulin[J]. Reactions Weekly, 2024, 2005(1):330.
[33] 谭亮, 赵静, 马家麟, 等. 青海玉树沙棘不同部位营养成分分析与营养价值评价[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2018,30(5):807−816,899. [TAN L, ZHAO J, MA J L, et al. Analysis of nutrient composition and evaluation of nutritional value of different parts of sea buckthorn from Yushu, Qinghai[J]. Natural Products Research and Development,2018,30(5):807−816,899.] TAN L, ZHAO J, MA J L, et al. Analysis of nutrient composition and evaluation of nutritional value of different parts of sea buckthorn from Yushu, Qinghai[J]. Natural Products Research and Development, 2018, 30(5): 807−816,899.
[34] JUNG Y, LEE J, KIM H K, et al. Metabolite profiling of curcuma species grown in different regions using 1H NMR spectroscopy and multivariate analysis[J]. The Analyst,2012(137):5597−5606.
[35] CIESAROV Z , MUEKOVIC M , CEJPEK K , et al. Why is sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) so exceptional? A review[J]. Food Research International, 2020, 133 (prepublish):109170.
[36] 邹丽秋, 王彩霞, 匡雪君, 等. 黄酮类化合物合成途径及合成生物学研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志,2016,41(22):4124−4128. [ZOU L Q, WANG C X, KUANG X J, et al. Advances in the synthesis pathway and synthetic biology of flavonoids[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2016,41(22):4124−4128.] ZOU L Q, WANG C X, KUANG X J, et al. Advances in the synthesis pathway and synthetic biology of flavonoids[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 41(22): 4124−4128.
[37] 蔡永国, 袁江玲, 朱国强, 等. 沙棘果油提高小鼠免疫功能的实验研究[J]. 疾病预防控制通报,2020,35(1):1−4. [CAI Y G, YUAN J L, ZHU G Q, et al. Experimental study on the enhancement of immune function in mice by sea buckthorn fruit oil[J]. Bulletin of Disease Control and Prevention,2020,35(1):1−4.] CAI Y G, YUAN J L, ZHU G Q, et al. Experimental study on the enhancement of immune function in mice by sea buckthorn fruit oil[J]. Bulletin of Disease Control and Prevention, 2020, 35(1): 1−4.
[38] TUDOR C, BOHN T, IDDIR M, et al. Sea buckthorn oil as a valuable source of bioaccessible xanthophylls[J]. Nutrients,2019,12(1):76. doi: 10.3390/nu12010076
[39] ERCISLI S, OTHAN E, OZDEMIR O, et al. The genotypic effects on the chemical composition and antioxidant activity of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) berries grown in Turkey[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2007,115(1):27−33.
[40] HIRAOKA-YAMAMOTO J, IKEDA K, NEGISHI H, et al. Serum lipid effects of a monounsaturated (palmitoleic) fatty acid-rich diet based on macadamia nuts in healthy, young Japanese women[J]. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, 2005, 31Suppl 2(s2):S37−S38.
[41] QI D, ZOU L, ZHOU D, et al. Taxonomy and broad-spectrum antifungal activity of Streptomyces sp. SCA3-4 isolated from rhizosphere soil of opuntia stricta[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2019,10:1390. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01390
[42] ARIMBOOR R, KUMAR K S, ARUMUGHAN C. Simultaneous estimation of phenolic acids in sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) using RP-HPLC with DAD[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2007,47(1):31−38.
[43] SHAO X, BAI N, HE K, et al. Apple polyphenols, phloretin and phloridzin:New trapping agents of reactive dicarbonyl species [J]. Chemical Research in Toxicology,2008,21(10):2042−2050. doi: 10.1021/tx800227v
[44] REN R, LI N, SU C, et al. The bioactive components as well as the nutritional and health effects of sea buckthorn[J]. RSC Advances,2020,10(73):44654−44671. doi: 10.1039/D0RA06488B
[45] 王琬宁. 沙棘果实中黄酮类物质的分析[D]. 哈尔滨:东北农业大学, 2020. [WANG W N. Analysis of flavonoids in sea buckthorn fruit[D]. Harbin:Northeast Agricultural University, 2020.] WANG W N. Analysis of flavonoids in sea buckthorn fruit[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2020.






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



