Screening and Characteristics of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Cheese in Yili Area
-
摘要: 为筛选出传统发酵食品中具有优良功能特性的乳酸菌,对伊犁地区奶疙瘩中的乳酸菌进行分离鉴定,并对其益生特性和功能特性进行研究。从奶疙瘩中分离出乳酸菌菌株并进行分子生物学鉴定,通过耐酸、耐胆盐、自聚集、疏水性和模拟胃肠液耐受性等益生特性指标对菌株筛选,并测定菌株的自由基清除能力和α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率等功能特性。结果表明:从奶疙瘩样品中分离出的8株乳酸菌均表现出耐酸和耐胆盐能力,其中乳酸片球菌KT-7疏水率最高(77.2%),KT-7在胃液存活率最高(109.7%),副干酪乳杆菌KT-2在肠液存活率最高(103.4%);发酵上清液抗氧化实验中,KT-2的DPPH自由基清除率最高(79.8%),戊糖片球菌KT-8对羟基自由基清除率最高(96.8%),抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性实验中,菌株KT-2、KT-7、KT-8对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制率在20.0%以上,其中KT-8抑制率最高(34.9%)。因此,从伊犁地区奶疙瘩中筛选出的3株乳酸菌副干酪乳杆菌KT-2、乳酸片球菌KT-7、戊糖片球菌KT-8具有良好的益生特性与功能特性,可作为功能发酵食品的潜在菌株。Abstract: In order to screen out lactic acid bacteria with excellent functional properties in traditional fermented food, in this study, the lactic acid bacterias in Yili cheese were effectively isolated and identified, as well as evaluation of their probiotic and functional characteristics. The lactic acid bacteria strains from Yili cheese were firstly isolated, followed by been identified by molecular biology techniques. Then, the lactic acid bacteria strains were screened based on several probiotic characteristics including acid tolerance, bile salt tolerance, auto-aggregation, hydrophobicity, and simulated gastrointestinal fluids tolerance. The functional characteristics of screened strains were further evaluated through determination of the free radical scavenging ability and α-glucosidase inhibition rate. The results showed that all isolated lactic acid bacteria strains (8 strains) from Yili cheese exhibited high acid and bile salt tolerance. In addition, the highest hydrophobicity (77.2%), the highest survival rate in gastric fluid (109.7%), and the highest survival rate in intestinal fluid (103.4%) could be found in Pediococcus acidilactici KT-7, KT-7 and Lactobacillus paracasei KT-2 strains, respectively. The antioxidant tests in fermentation supernatants showed that the KT-2 and Pediococcus pentosaceus KT-8 strains exhibited the best free radical scavenging ability for DPPH (79.8%) and hydroxyl radical (96.8%), respectively. The KT-2 and KT-7 strains provided high α-glucosidase activity inhibition rate more than 20%, still less than inhibition rate induced by KT-8 strain (34.9%). These findings provide three promising potential lactic acid bacteria strains (Lactobacillus paracasei KT-2, Pediococcus acidilactici KT-7, and Pediococcus pentosaceus KT-8) in functional fermented foods, mainly screened from Yili cheese with satisfied probiotic and functional characteristics.
-
奶疙瘩是新疆哈萨克族的传统发酵乳制品[1]。哈萨克族人制作奶疙瘩时,将牛奶自然发酵后倒入锅中熬煮,然后装入布袋挤干水分,捏成小块,放至木席晒干即成。奶疙瘩富含多种营养成份,具有健胃、消食等特点,受到哈萨克族人民的喜爱[2]。奶疙瘩多采用自然发酵,其中微生物种质资源的应用和保护应予以重视,故亟需对奶疙瘩中优良微生物资源开发和利用[3]。
乳酸菌(Lactic acid bacteria,LAB)指一类可利用碳水化合物发酵产生大量乳酸的细菌[4]。近年来,许多学者从传统发酵食品中分离出各种功能的乳酸菌。赵玉娟等[5]从东北酸菜筛选出的植物乳植杆菌YJ132和肠膜明串珠菌肠膜亚种UA107能快速降解亚硝酸盐;李雪菲等[6]从传统发酵酸肉中分离筛选出两株益生潜力较强的乳酸菌,分别为香肠伴生乳杆菌(Companilactobacillus farciminis)KLMM196和植物乳植杆菌(Lactiplantibacillus plantarum)KLMM198。杨旭洲等[7]从传统发酵浆水中分离得到五株乳酸菌的抗氧化能力较高,对DPPH自由基清除率>30.0%、羟自由基清除率>50.0%、超氧阴离子自由基清除率>40.0%。此外,乳酸菌通过抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性,达到潜在降血糖作用。Zeng等[8]发现7株乳杆菌具有抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性的作用,Panwar等[9]证明人肠道中的乳杆菌能抑制葡糖苷酶活性,并且可以降低体内血糖反应[10]。刘顺等[11]筛选出的植物乳杆菌OD2其上清液对α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率为33.2%,并且部分学者通过动物实验,发现乳酸菌对Ⅱ型糖尿病有一定的改善作用[12−13]。因此,通过α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制实验筛选具有降血糖作用的乳酸菌是切实可行的。
本研究以伊犁地区奶疙瘩为样品,从中分离出乳酸菌菌株,利用16S rDNA测序技术对乳酸菌进行鉴定,通过测定菌株的生长特性、耐酸耐胆盐能力、菌株的自聚集、疏水性及胃肠液耐受等益生特性指标,筛选出益生特性良好的菌株并进一步研究其自由基清除能力和降血糖作用等功能特性,本研究不仅对新疆伊犁奶疙瘩中的优良菌株进行深度挖掘,而且可为进一步研究开发降血糖作用等功能性乳酸菌产品提供一定的理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
奶疙瘩 采集自新疆维吾尔自治区伊犁哈萨克自治州少数民族牧民家,传统方法发酵制得,输送途中用冰袋保藏,在实验室中4 ℃保存;MRS培养基、牛胆盐 青岛海博生物技术有限公司;二甲苯、盐酸、氯化钠、30%过氧化氢 上海国药集团化学试剂有限公司;硫酸亚铁、邻菲罗啉 分析纯,天津市致远化学试剂有限公司;DPPH(2,2-联苯基-1-苦基肼基,纯度≥97.0%)、胃蛋白酶(3000 U/mg)、胰蛋白酶(1500 U/mg)、PNPG、α-葡萄糖苷酶(100 U/mg)、阿卡波糖 上海源叶生物科技有限公司。
LC-HN-25BS恒温培养箱 上海力辰仪器科技有限公司;TU-1810紫外可见分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司;PTX FA210电子天平 上海力辰仪器科技有限公司;LDZF-30L型立式高压灭菌锅 上海三申医疗器械厂;ECLIPSE E200MV R光学显微镜 日本尼康公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 奶疙瘩中微生物分离与鉴定
1.2.1.1 乳酸菌的分离
将奶疙瘩样品与无菌生理盐水按1:9稀释后,混匀备用。梯度稀释培养液,在MRS琼脂培养基上涂布200 μL 10−4、10−5、10−6稀释液,于37 ℃倒置培养36 h[14],采用平板划线法对菌落进行分离与纯化。挑取纯化后的单菌落经过结晶紫初染、碘液媒染、乙醇脱色、番红复染等步骤进行革兰氏染色和过氧化氢酶试验[15]。
1.2.1.2 菌株形态鉴定
菌体形态:挑取单菌落,经过革兰氏染色后将玻片置于显微镜1000×下,观察染色结果和菌体细胞形态特征。
1.2.1.3 菌株的16S rDNA鉴定
将纯化后的菌株送北京博迈德基因技术有限公司进行菌株16S rDNA序列测定,16S rDNA基因的PCR扩增引物采用通用引物27F(5'-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3')。
1.2.2 菌株生长特性研究
参照焦媛媛等[16]的方法并适当优化,将菌株按体积比2.0%接种于MRS液体培养基,37 ℃培养24 h,以MRS液体培养基为空白对照,每2 h于波长600 nm处测定菌液OD值。
1.2.3 菌株益生特性研究
1.2.3.1 菌株对酸的耐受性分析
将菌株按体积比2.0%接种于pH为1.5、2.5、3.5、4.5、5.5、6.5的MRS液体培养基中,以接种0 h时OD600 nm值为对照,37 ℃培养18 h后测定菌液OD600 nm值。
1.2.3.2 菌株对胆盐的耐受性分析
将菌株按体积比2.0%接种于牛胆盐浓度为0.0%、0.1%、0.3%、0.5%的MRS液体培养基中,以接种0 h时OD600 nm值为对照,37 ℃培养18 h后测定菌液OD600 nm值。
1.2.3.3 菌株的自聚集率分析
参考Ruiz-Moyano等[17]的方法,并适当优化。将活化3代后的菌液用磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS,pH7.2)洗涤2次,调整菌悬液的OD600 nm值为0.8±0.05,室温静置3 h后,取上清液测定OD600 nm值,自聚集率计算按式(1)所示:
自聚集率(%)=(A0−A3h)A0×100 (1) 式中:A0:0 h菌悬液OD600 nm值;A3 h:静置3 h后OD600 nm值。
1.2.3.4 菌株对二甲苯的疏水性
参考Lin等[18]的方法,并适当优化。将活化3代后的菌液用磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS,pH7.2)洗涤2次,调整菌悬液的OD600 nm值为0.8±0.05。将菌悬液与二甲苯按照3:1(V:V)涡旋混合,室温静置20 min,取下层水相测定OD600 nm值,疏水性计算按式(2)所示:
疏水性(%)=(A0−At)A0×100 (2) 式中:A0:0 h时菌悬液OD600 nm值;At:加入二甲苯静置20 min后OD600 nm值。
1.2.3.5 菌株对模拟胃肠液的耐受能力
消化道环境耐受能力参考云月英等[19]的方法,适当优化。
模拟胃液:NaCl 2 g/L、胃蛋白酶3.5 g/L,HCl调整pH为3.0,过0.22 μm滤膜除菌备用。
模拟肠液:a液:重碳酸钠11 g/L、NaCl 2 g/L、胰蛋白酶1 g/L,用NaOH调整pH为8.0,过0.22 μm滤膜除菌备用;b液:牛胆盐18 g/L,用NaOH调整pH为8.0,过0.22 μm滤膜除菌备用;将a液和b液以2:1(V/V)混合即为人工模拟肠液。
取1 mL菌悬液加到9 mL模拟胃液中,充分混合均匀后37 ℃下培养2 h,分别在0 h和2 h取样进行平板计数,计算各菌株对模拟胃液的耐受能力。在9 mL模拟肠液中加入1 mL经过模拟胃液处理2 h的菌液,37 ℃下培养6 h,在6 h取样稀释涂布,在37 ℃培养48 h后进行平板计数,按照公式(3)计算菌株对模拟胃肠液的耐受能力。
存活率(%)=NN0×100 (3) 式中:N表示经过模拟胃肠液处理后的活菌数,CFU/mL;N0表示未经过模拟胃肠液处理的活菌数,CFU/mL。
1.2.4 菌株功能特性研究
1.2.4.1 菌株发酵上清自由基清除能力测定
将活化后的菌株接入培养基中,在37 ℃培养18 h后,于6000 r/min离心8 min,上层溶液即为发酵上清液。参照杨旭洲等[7]的方法,并适当优化后对乳酸菌发酵上清液DPPH和羟自由基清除率进行测定。
DPPH自由基清除能力测定:取2 mL样品与2 mL的0.2 mmol/L DPPH-无水乙醇溶液充分混匀,避光反应30 min,测定OD517 nm值。按公式(4)计算DPPH自由基清除能力。
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=(1−Ar−AsAt)×100 (4) 式中:Ar表示样品+DPPH-无水乙醇溶液的OD517 nm值;As表示样品+无水乙醇的OD517 nm值;At表示蒸馏水+DPPH-无水乙醇的OD517 nm值。
羟基自由基清除能力测定:在试管中加入1 mL样品,再逐次加入1 mL的2.5 mmol/L邻菲罗啉、PBS缓冲液、2.5 mmol/L FeSO4溶液和20 mmol/L H2O2,将其充分混匀后在37 ℃反应90 min,测定OD536 nm值。按公式(5)计算羟基自由基清除能力。
羟基自由基清除率(%)=Ak−AiAj−Ai×100 (5) 式中:Ak表示样品的OD536 nm值;Aj表示蒸馏水代替样品和H2O2的OD536 nm值;Ai表示蒸馏水代替样品的OD536 nm值。
1.2.4.2 菌株发酵上清液抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性测定
参考闫芬芬等[20]方法并适当优化,取酶标板,50 μL发酵上清液与50 μL PNPG混合;37 ℃保温10 min,再加入100 μL α-葡萄糖苷酶;37 ℃反应15 min,最后加入50 μL Na2CO3溶液终止反应,1 mg/mL阿卡波糖为对照,于波长405 nm处使用酶标仪检测吸光度。计算按式(6)所示:
抑制率(%)=(1−A−BC−D)×100 (6) 式中:A:样品+2.5 mmol/L PNPG+0.2 U/mL α-葡萄糖苷酶+1 mol/L Na2CO3;B:样品+2.5 mmol/L PNPG+PBS(0.1 mol/L,pH6.8)+1 mol/L Na2CO3;C:PBS+2.5 mmol/L PNPG+0.2 U/mL α-葡萄糖苷酶+1 mol/L Na2CO3;D:PBS+2.5 mmol/L PNPG+PBS+1 mol/L Na2CO3。
1.3 数据处理
每个实验做3组平行,实验结果表示为“平均值±标准差”的形式。使用SPSS 27软件中的单因素方差分析和Duncan多重比较法进行数据间的分析,显著性水平设定为0.05。使用Excel 2019制作三线表;Origin 2021绘制图形。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 奶疙瘩中菌株的分离
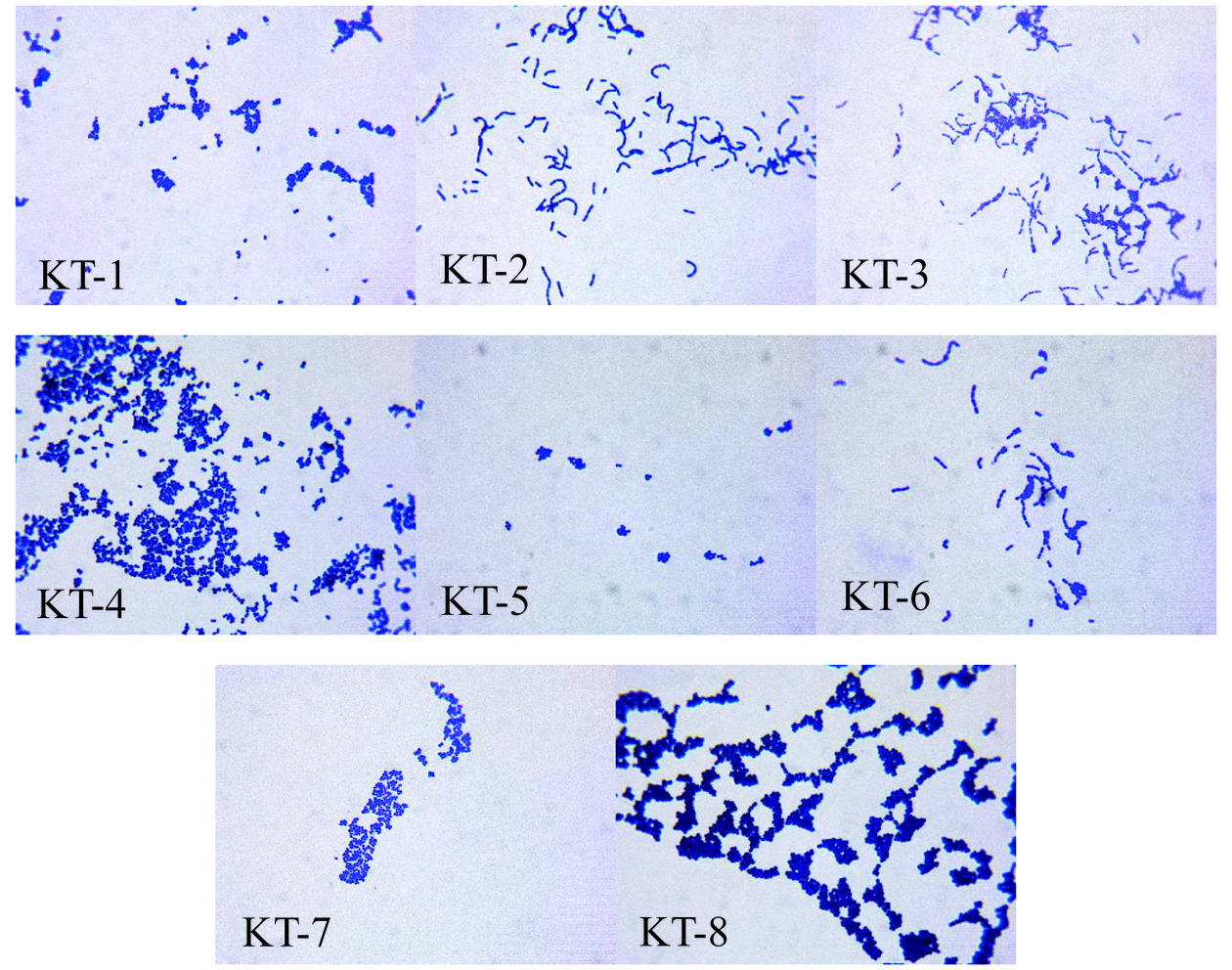
从伊犁地区奶疙瘩中分离出菌株并进行形态学观察,符合乳酸菌形态学鉴定要求菌株17株,筛选出滴加过氧化氢不产气泡且显微镜下观察革兰氏染色结果为紫色的菌株8株;图1为显微镜下8株细菌形态图片,8株菌株形态有所不同。其中,KT-2、KT-3、KT-6为杆菌,KT-1、KT-4、KT-5、KT-7、KT-8为球菌。从8份伊犁奶疙瘩样品中筛选出3株杆菌,5株球菌,推测球菌可能是奶疙瘩中的主要菌属。
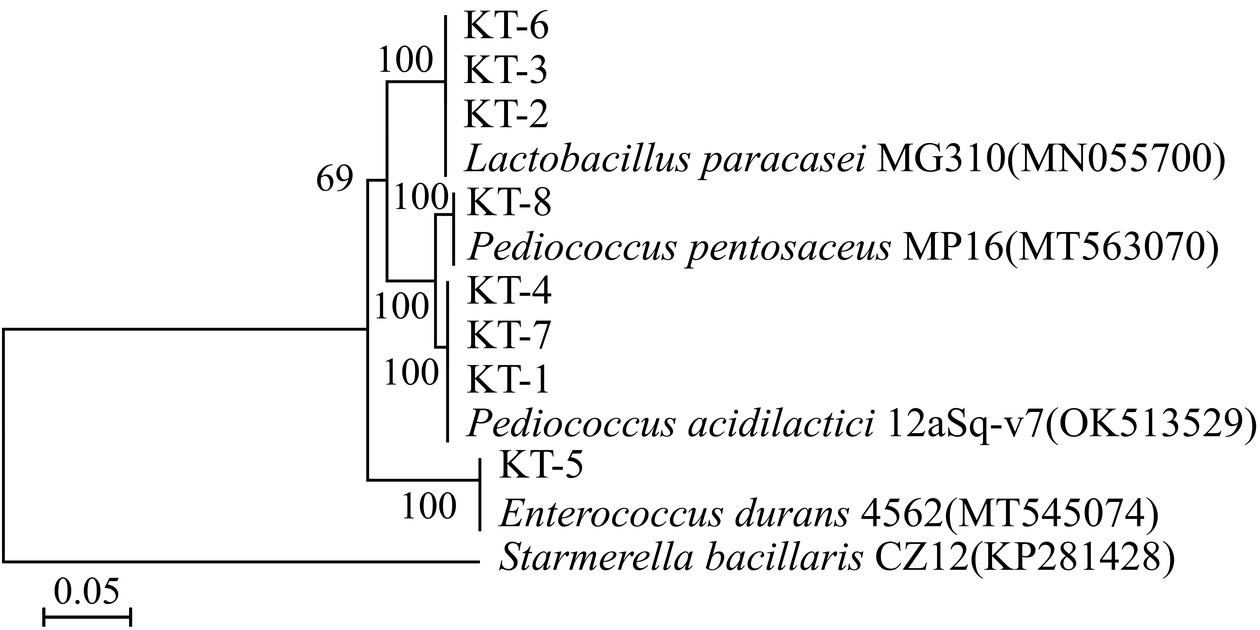
2.2 菌株分子生物学鉴定
将菌株的16S rDNA序列提交到NCBI数据库,利用BLAST进行比对,用MEGA 11软件构建系统发育树。由图2可知,菌株KT-1、KT-4、KT-7为乳酸片球菌(Pediococcus acidilactici);菌株KT-2、KT-3、KT-6为副干酪乳杆菌(Lactobacillus paracasei);菌株KT-5为耐久肠球菌(Enterococcus durans);菌株KT-8为戊糖片球菌(Pediococcus pentosaceus)。
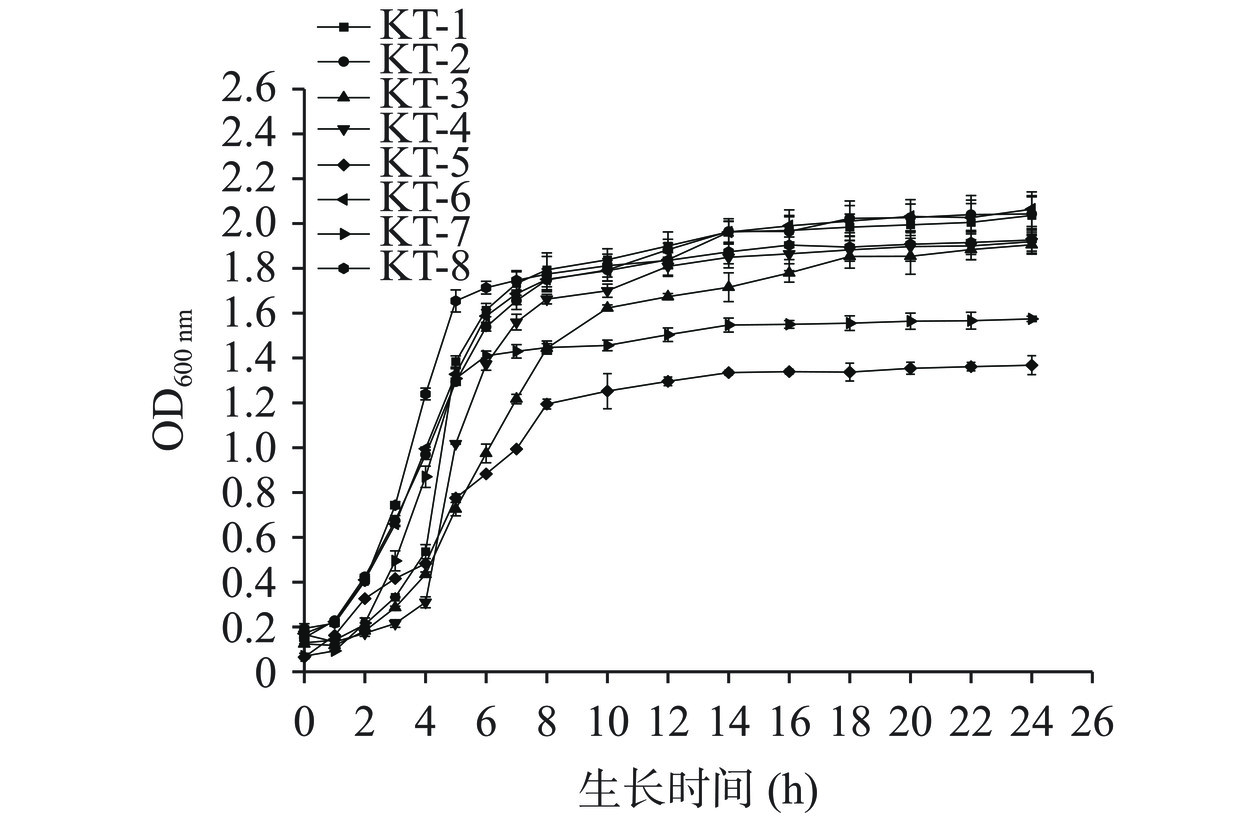
2.3 菌株的生长特性
生长能力强的乳酸菌能够缩短发酵时间[21],减少发酵过程中杂菌生长,提高产品的生产速度。由图3可知,不同菌株的生长状况有所不同,整体上,菌株的生长曲线呈现S型,可以直观地看出菌株生长的各个阶段。从OD600 nm值来看,菌株延滞期均在1 h内,说明从奶疙瘩中筛选出的乳酸菌具有较好的环境适应力,对数期在2~8 h,期间菌株生长迅速,随后趋于平稳进入稳定期,此时大部分菌株吸光度值达到了1.8以上,菌株KT-5、KT-7吸光度值偏低,可能是工业化制作的MRS培养基中氮源不适合这两株乳酸菌的生长需要。
2.4 菌株的益生特性
2.4.1 菌株对酸的耐受性分析
乳酸菌对于酸性环境的耐受性是筛选优良乳酸菌的一个重要因素[22],测得正常MRS液体培养基pH为6.5,由表1可知,随着环境pH升高,乳酸菌的生长呈现上升趋势。说明酸性环境对乳酸菌的生长具有一定程度的抑制,相较于0 h的菌液吸光度值,各菌液的吸光度值均有不同程度的升高,表明分离出的8株乳酸菌在酸性环境下均具有生长活性,但因环境pH的不同,故表现出的生长活性强弱有所不同,这与吕欣然等[23]结果一致,因此本实验中8株乳酸菌对酸性环境具有一定耐受性。
表 1 菌株耐酸性Table 1. Acid tolerance of strains菌株 对照 pH 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5 5.5 6.5 KT-1 0.069±0.006Dde 0.082±0.001De 0.095±0.001Df 0.121±0.001De 0.149±0.003Cf 1.181±0.011Be 1.984±0.058Aab KT-2 0.094±0.003Ea 0.11±0.002Eb 0.125±0.002Eb 0.157±0.009Db 0.194±0.002Cc 1.544±0.038Ba 2.023±0.078Aa KT-3 0.061±0.007Ff 0.097±0.002Ec 0.110±0.002Ed 0.13±0.001Dd 0.153±0.002Cef 1.402±0.019Bc 1.853±0.053Ac KT-4 0.073±0.003Gcd 0.115±0.004Fa 0.131±0.002Ea 0.172±0.007Da 0.218±0.011Cb 1.346±0.019Bd 1.882±0.041Abc KT-5 0.024±0.005Gg 0.09±0.002Fd 0.111±0.001Ed 0.126±0.003Dde 0.158±0.003Cde 0.351±0.006Bg 1.337±0.04Ae KT-6 0.078±0.003Fbc 0.115±0.002Ea 0.124±0.002Eb 0.162±0.002Db 0.244±0.004Ca 1.452±0.022Bb 2.011±0.069Aa KT-7 0.061±0.003Gef 0.088±0.002Ed 0.105±0.002Ee 0.129±0.001De 0.152±0.002Cef 0.29±0.004Bh 1.556±0.033Ad KT-8 0.085±0.005Gb 0.108±0.002Fb 0.117±0.003Ec 0.14±0.004Dc 0.163±0.002Cd 1.045±0.058Bf 1.895±0.063Abc 注:同行A~G表示相同菌株不同pH环境下差异显著(P<0.05);同列a~h表示相同pH环境下不同菌株差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.4.2 菌株对胆盐的耐受性分析
乳酸菌要在肠道中定植,必须对胆盐有一定程度的耐受性,胆盐会造成细胞外渗透压过高[24],会对乳酸菌细胞的存活造成影响。人体小肠中胆盐含量在0.03%~0.5%,通常为0.3%左右,适应人体小肠中的胆盐胁迫是益生菌发挥益生功能的重要前提[25]。
由表2可知,随着胆盐浓度的增加,对乳酸菌生长抑制作用增强,相较于接种0 h菌液的吸光度值,经过不同胆盐浓度处理18 h后菌液的吸光度值均有不同程度的增加,整体呈现上升趋势,表明在高浓度胆盐胁迫下可能是由于伊犁地区奶疙瘩为酸凝型发酵乳制品,且制作过程中会加入适量的盐,在奶疙瘩源乳酸菌生长发酵过程中,已适应了环境的胁迫,因此表现出良好的耐受能力。
表 2 菌株的胆盐耐受性Table 2. Bile salt tolerance of strains菌株 对照 胆盐浓度(%) 0.5 0.3 0.1 0 KT-1 0.069±0.006Ede 0.087±0.005Dc 0.101±0.003Cc 0.708±0.005Bc 1.984±0.058Aab KT-2 0.094±0.003Ea 0.109±0.003Db 0.141±0.006Ca 0.311±0.001Bf 2.023±0.078Aa KT-3 0.061±0.007Ef 0.079±0.003Dc 0.085±0.006Cd 0.148±0.002Bh 1.853±0.053Ac KT-4 0.073±0.003Dcd 0.083±0.003Dc 0.106±0.003Cc 0.37±0.003Be 1.882±0.041Abc KT-5 0.024±0.005Eg 0.036±0.005Dd 0.044±0.003Ce 0.292±0.002Bg 1.337±0.04Ae KT-6 0.078±0.003Ebc 0.125±0.004Da 0.137±0.004Cab 0.886±0.011Bb 2.011±0.069Aa KT-7 0.061±0.003Eef 0.11±0.007Db 0.133±0.002Cb 0.913±0.012Ba 1.556±0.033Ad KT-8 0.085±0.005Db 0.128±0.006Ca 0.132±0.004Cb 0.455±0.013Bd 1.895±0.063Abc 注:同行A~E表示相同菌株不同胆盐浓度环境下差异显著(P<0.05);同列a~h表示相同胆盐浓度环境下不同菌株差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.4.3 菌株的自聚集率
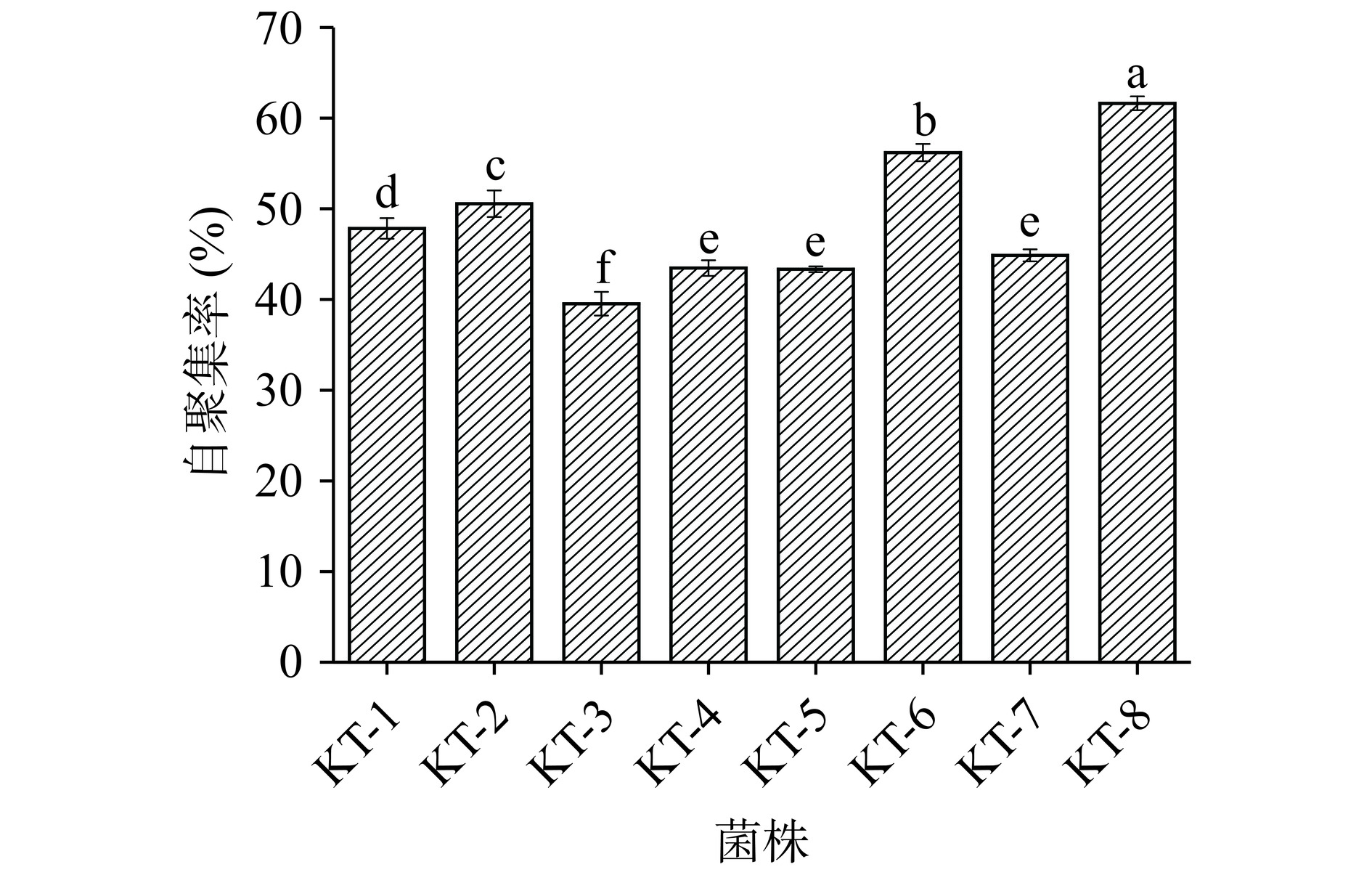
自聚集是菌体自行聚集成团的现象,用于衡量菌株的黏附性能[26]。自聚集率高的菌株不仅有利于其在肠道中定植,还能有效阻止病原体与宿主结合,从而阻止病原菌定植于胃肠道。
由图4可知,本实验中的菌株都表现出较好的自聚集率,且不同菌株间自聚集率差异显著(P<0.05),菌株KT-3自聚集率最低为39.5%,KT-2、KT-6、KT-8表现出的自聚集率大于50.0%,其中KT-8自聚集率最高为61.6%,邹思博等[27]从东北酸菜中分离出的乳酸菌自聚集率为27.3%,说明从奶疙瘩中筛选出的菌株KT-8对肠上皮细胞有较好的黏附作用。
2.4.4 菌株的疏水性
益生菌生物膜疏水性越高[28],越容易黏附于人体胃肠道表面,进而发挥益生作用[29]。疏水性小于30.0%时菌株表现为亲水,疏水性处于30.0%~60.0%的菌株表现为中度疏水,疏水性大于60.0%的菌株表现为高度疏水。
由图5可知,不同菌株对二甲苯的疏水性有所不同,可能是因为不同的菌株细胞壁表面蛋白质结构有所区别。菌株KT-1、KT-4疏水性小于30.0%,表现为亲水,其余6个菌株疏水性均大于30.0%,表现出良好的疏水性,其中菌株KT-5、KT-6、KT-7疏水性大于60.0%,为高度疏水,且菌株KT-7疏水性最高为77.2%,推测菌体表面细胞壁上与肠道上皮细胞的结合位点较多,更易与肠上皮细胞结合[30],能更好地黏附于肠道上皮细胞,说明本研究从奶疙瘩中筛选得到的乳酸菌具有良好的疏水性。
2.4.5 菌株对模拟胃肠液的耐受能力
胃液中的低pH和肠液中的胆盐胁迫会影响菌株通过消化道后的活性,而菌株的存活情况是发挥其益生特性的重要基础[31]。人体胃液的pH通常在3左右,食物在胃部消化,这一过程中胃液和肠液中的酶类会破坏菌株细胞壁表面膜结构,使大多数微生物致死。因此,消化道耐受能力是评价微生物是否具有益生潜力的重要指标。
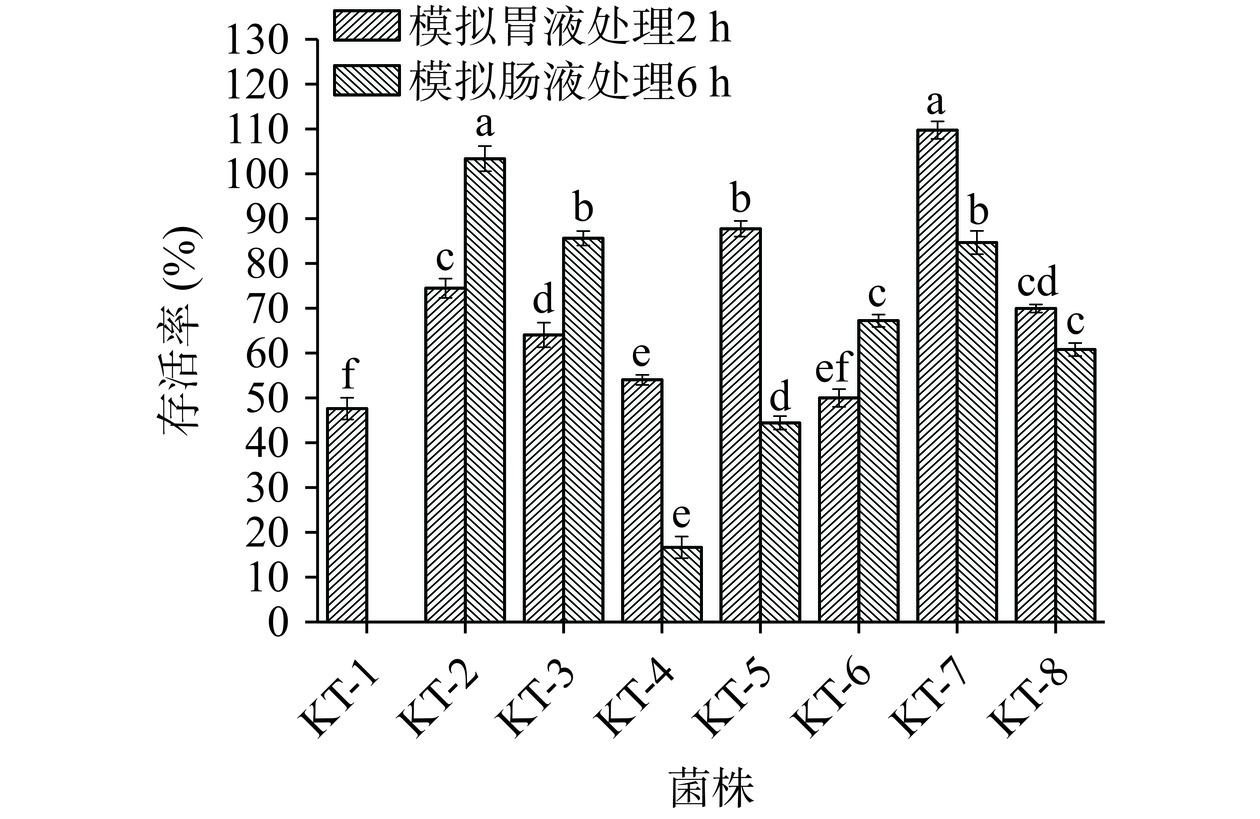
如图6可知,菌株经pH为3的模拟胃液处理2 h后,存活率为47.6%~109.7%,不同菌株间在模拟胃液存活率差异显著(P<0.05),菌株KT-1存活率低于50.0%,其余株菌存活率大于50.0%,其中KT-7在模拟胃液表现出较好的耐受性,存活率为109.7%,再经模拟肠液处理6 h,菌株存活率在0.0%~103.4%之间,不同菌株在模拟肠液耐受能力有所区别。其中,菌株KT-1存活率为0.0%,表明KT-1无法适应模拟肠液环境,可能是肠液中的碱性环境和蛋白酶造成菌体细胞壁裂解导致菌体死亡,KT-2、KT-3、KT-6、KT-7、KT-8在模拟肠液存活率大50.0%,表现出较好的耐受性,KT-2存活率最高为103.4%。陈佩等[32]研究发现干酪乳杆菌CCFM0412在pH8的人工肠液中存活8 h后存活率90.98%。可能是菌株在接收到轻微的环境胁迫信号后,通过基因的选择性表达,在胞内分泌某种激素后刺激菌株代谢速度,促进菌株生长,与覃志成等[33]结果一致。通过模拟胃肠液,发现KT-2、KT-3、KT-6、KT-7、KT-8表现出在模拟胃肠液较好的耐受性,选取自聚集率大于30.0%、疏水性大于30.0%、胃肠液中存活率大于50%的菌株进一步通过对自由基清除率测定,评价其抗氧化能力。
2.5 菌株发酵上清液的自由基清除能力
DPPH是一种稳定的有机氮自由基,能吸收抗氧化物的电子而引起样品颜色改变。羟基自由基是一种氧化性很强的自由基,它可以使生物细胞大分子损伤[34]。
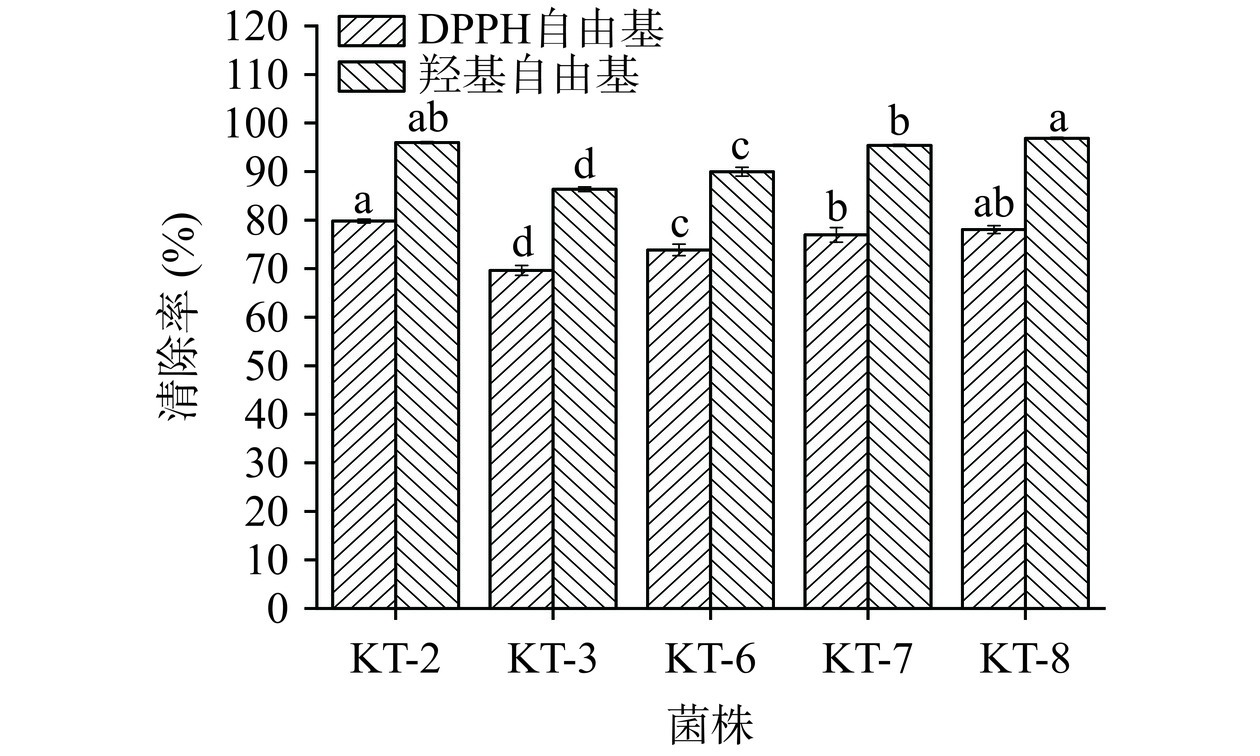
由图7可知,通过上文筛选得到的5株菌DPPH自由基和羟基自由基的清除能力有所不同。不同菌株的DPPH自由基和羟基自由基清除率有显著差异(P<0.05),5株乳酸菌发酵上清液清除DPPH自由基的能力为69.6%~79.8%,对羟基自由基清除率在86.4%~96.8%;KT-2、KT-7、KT-8对DPPH自由基清除率大于75.0%,对羟基自由基清除率大于90.0%。其中菌株KT-2对DPPH自由基清除率最高为79.8%,KT-8对羟基自由基清除率最高为96.8%,推测可能是乳酸菌通过细胞膜释放到外部环境的初级代谢产物中,多糖和有机酸这两类物质较多,多糖结构复杂,具有较多的自由基结合位点,而有机酸类物质则提供氢原子或电子转移,抢占自由基的结合位点,达到清除自由基的目的。综上可知,菌株KT-2、KT-7、KT-8具有较高的抗氧化能力。
2.6 菌株发酵上清液对α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性
α-葡萄糖苷酶是一种存在于小肠黏膜刷状缘的专门负责催化碳水化合物水解的水解酶[35]。因此,通过抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性,从而降低小肠对葡萄糖的吸收速度,控制餐后血糖升高已成为糖尿病临床干预的有效靶点[36]。
将抗氧化能力强的3株乳酸菌,进行抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性测定,由图8可知,不同菌株的抑制作用有所不同,菌株KT-2、KT-7、KT-8对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制率都在20.0%以上,说明三株乳酸菌具有较好的抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶的作用,其中KT-8对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制率最高为34.9%,说明菌株KT-8在一定程度上能有效抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性,具有潜在降血糖作用。有研究表明,乳酸菌代谢产生的多糖、有机酸等大分子物质释放在发酵上清液中[37]。乳酸菌发酵上清液中胞外多糖的含量与其降血糖活性呈正相关[38]。李向菲等[39]研究发现多糖和丁酸是乳酸菌发挥降血糖作用的相关因素。可见,乳酸菌发酵上清液对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用与菌株分泌到环境中的代谢物有关。
3. 结论
本研究从伊犁地区奶疙瘩中分离出8株乳酸菌,通过耐酸耐胆盐、自聚集和疏水性及胃肠液的耐受等益生特性指标,筛选出具有良好益生特性的5株乳酸菌(其自聚集率大于30.0%、疏水性大于30.0%、在胃肠液中的存活率大于50.0%)。进一步通过菌株发酵上清液对自由基的清除能力和对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性抑制等实验,筛选出3株DPPH自由基清除率和羟基自由基清除率高的菌株,分别为副干酪乳杆菌(KT-2)、乳酸片球菌(KT-7)和戊糖片球菌(KT-8),其DPPH自由基清除率分别为79.8%、77.0%、78.0%,羟基自由基清除率分别为96.0%、95.4%、96.8%,测定3株乳酸菌对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性抑制率均大于20.0%(分别为23.2%、28.5%、34.9%),证明其均具有一定降血糖作用。研究结果表明,本实验筛选出的KT-2、KT-7、KT-8具有良好的益生特性与功能特性。因此,本文筛选出的3株乳酸菌副干酪乳杆菌(KT-2)、乳酸片球菌(KT-7)和戊糖片球菌(KT-8)具有制备益生菌制剂和降血糖功能性食品的潜力。
-
表 1 菌株耐酸性
Table 1 Acid tolerance of strains
菌株 对照 pH 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5 5.5 6.5 KT-1 0.069±0.006Dde 0.082±0.001De 0.095±0.001Df 0.121±0.001De 0.149±0.003Cf 1.181±0.011Be 1.984±0.058Aab KT-2 0.094±0.003Ea 0.11±0.002Eb 0.125±0.002Eb 0.157±0.009Db 0.194±0.002Cc 1.544±0.038Ba 2.023±0.078Aa KT-3 0.061±0.007Ff 0.097±0.002Ec 0.110±0.002Ed 0.13±0.001Dd 0.153±0.002Cef 1.402±0.019Bc 1.853±0.053Ac KT-4 0.073±0.003Gcd 0.115±0.004Fa 0.131±0.002Ea 0.172±0.007Da 0.218±0.011Cb 1.346±0.019Bd 1.882±0.041Abc KT-5 0.024±0.005Gg 0.09±0.002Fd 0.111±0.001Ed 0.126±0.003Dde 0.158±0.003Cde 0.351±0.006Bg 1.337±0.04Ae KT-6 0.078±0.003Fbc 0.115±0.002Ea 0.124±0.002Eb 0.162±0.002Db 0.244±0.004Ca 1.452±0.022Bb 2.011±0.069Aa KT-7 0.061±0.003Gef 0.088±0.002Ed 0.105±0.002Ee 0.129±0.001De 0.152±0.002Cef 0.29±0.004Bh 1.556±0.033Ad KT-8 0.085±0.005Gb 0.108±0.002Fb 0.117±0.003Ec 0.14±0.004Dc 0.163±0.002Cd 1.045±0.058Bf 1.895±0.063Abc 注:同行A~G表示相同菌株不同pH环境下差异显著(P<0.05);同列a~h表示相同pH环境下不同菌株差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 2 菌株的胆盐耐受性
Table 2 Bile salt tolerance of strains
菌株 对照 胆盐浓度(%) 0.5 0.3 0.1 0 KT-1 0.069±0.006Ede 0.087±0.005Dc 0.101±0.003Cc 0.708±0.005Bc 1.984±0.058Aab KT-2 0.094±0.003Ea 0.109±0.003Db 0.141±0.006Ca 0.311±0.001Bf 2.023±0.078Aa KT-3 0.061±0.007Ef 0.079±0.003Dc 0.085±0.006Cd 0.148±0.002Bh 1.853±0.053Ac KT-4 0.073±0.003Dcd 0.083±0.003Dc 0.106±0.003Cc 0.37±0.003Be 1.882±0.041Abc KT-5 0.024±0.005Eg 0.036±0.005Dd 0.044±0.003Ce 0.292±0.002Bg 1.337±0.04Ae KT-6 0.078±0.003Ebc 0.125±0.004Da 0.137±0.004Cab 0.886±0.011Bb 2.011±0.069Aa KT-7 0.061±0.003Eef 0.11±0.007Db 0.133±0.002Cb 0.913±0.012Ba 1.556±0.033Ad KT-8 0.085±0.005Db 0.128±0.006Ca 0.132±0.004Cb 0.455±0.013Bd 1.895±0.063Abc 注:同行A~E表示相同菌株不同胆盐浓度环境下差异显著(P<0.05);同列a~h表示相同胆盐浓度环境下不同菌株差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 王进, 张晶晶, 李晓晨, 等. 四种典型新疆奶疙瘩细菌多样性与气味特征探究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(20):285−290. [WANG J, ZHANG J J, LI X C, et al. Bacterial diversity and odor characteristics of four typical cheeses in Xinjiang[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(20):285−290.] WANG J, ZHANG J J, LI X C, et al. Bacterial diversity and odor characteristics of four typical cheeses in Xinjiang[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(20): 285−290.
[2] 李墨钊, 热米拉·阿扎提, 郑晓冬, 等. 新疆特色奶疙瘩的菌群分析与抗衰老研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(7):149−156. [LI M Z, REMILA A Z T, ZHENG X D, et al. Microflora analysis and anti-aging research of Xinjiang milk knot[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(7):149−156.] LI M Z, REMILA A Z T, ZHENG X D, et al. Microflora analysis and anti-aging research of Xinjiang milk knot[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2021, 21(7): 149−156.
[3] 王进. 新疆奶疙瘩细菌多样性与风味解析及菌株的应用[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学, 2021. [WANG J. Analysis of bacterial diversity and flavor and application of strains in Xinjiang cheese[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University, 2021.] WANG J. Analysis of bacterial diversity and flavor and application of strains in Xinjiang cheese[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2021.
[4] GIRAFFA G, CHANISHVILI N, WIDYASTUTI Y. Importance of Lactobacillus in food and feed biotechnology[J]. Research in Microbiology,2010,161(6):480−487. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2010.03.001
[5] 赵玉娟, 刘才子, 高岩松, 等. 东北酸菜发酵乳酸菌的筛选及评价[J]. 现代食品科技,2024,40(3):121−130. [ZHAO Y X, LIU C Z, GAO Y S, et al. Screening and evaluation of lactic acid bacteria for Dongbei Suancai fermentation[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2024,40(3):121−130.] ZHAO Y X, LIU C Z, GAO Y S, et al. Screening and evaluation of lactic acid bacteria for Dongbei Suancai fermentation[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2024, 40(3): 121−130.
[6] 李雪菲, 潘琼, 罗慧婷, 等. 传统发酵酸肉中微生物的分离鉴定及其益生潜力评价[J]. 食品科学,2024,45(14):75−84. [LI X F, PAN Q, LUO H T, et al. Isolation, identification and probiotic potential evaluation of microorganisms from traditional fermented sour meat[J]. Food Science,2024,45(14):75−84.] LI X F, PAN Q, LUO H T, et al. Isolation, identification and probiotic potential evaluation of microorganisms from traditional fermented sour meat[J]. Food Science, 2024, 45(14): 75−84.
[7] 杨旭洲, 陈佩瑶, 张富新. 抗氧化乳酸菌的筛选及其益生特性评价[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2023,49(10):17−23. [YANG X Z, CHEN P Y, ZHANG F X. Screening of antioxidant lactic acid bacteria and evaluation of their probiotic properties[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(10):17−23.] YANG X Z, CHEN P Y, ZHANG F X. Screening of antioxidant lactic acid bacteria and evaluation of their probiotic properties[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2023, 49(10): 17−23.
[8] ZENG Z, LUO J Y, ZUO F L, et al. Screening for potential novel probiotic Lactobacillus, strains based on high dipeptidyl peptidase IV and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2016,20(1):486−495.
[9] PANWAR H, CALDERWOOD D, GRANT I R, et al. Lactobacillus strains isolated from infant faeces possess potent inhibitory activity against intestinal alpha- and beta-glucosidases suggesting anti- diabetic potential[J]. European Journal of Nutrition,2014,53(7):1465−1474. doi: 10.1007/s00394-013-0649-9
[10] AGUIREE F, BROWN A, CHO N H, et al. IDF diabetes atlas:Sixth edition[J]. International Diabetes Federation,2013,23(8):145−155.
[11] 刘顺, 谢远红, 张红星, 等. 具有潜在降血糖作用乳酸菌的筛选[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(16):255−259,273. [LIU S, XIE Y H, ZHANG H X, et al. Screening of lactic acid bacteria with potential hypoglycemic effect[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(16):255−259,273.] LIU S, XIE Y H, ZHANG H X, et al. Screening of lactic acid bacteria with potential hypoglycemic effect[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(16): 255−259,273.
[12] LI X, WANG E, YIN B. Effects of Lactobacillus casei CCFM419 on insulin resistance and gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice[J]. Beneficial microbes,2017,8(3):421−432. doi: 10.3920/BM2016.0167
[13] 蒋岚, 陈果, 高陈林, 等. 益生菌对T2DM患者肠道菌群和脂联素的影响[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2018,28(11):84−87. [JIANG L, CHEN G, GAO C L, et al. Curative efficacy of probiotics on intestinal microflora and adiponectin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. China Journal of Modern Medicine,2018,28(11):84−87.] JIANG L, CHEN G, GAO C L, et al. Curative efficacy of probiotics on intestinal microflora and adiponectin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. China Journal of Modern Medicine, 2018, 28(11): 84−87.
[14] 达菊庆, 武运, 吴聪, 等. 新疆昌吉奶疙瘩中乳酸菌的分离鉴定及发酵杏酱性能分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2024,50(12):84−91. [DA J Q, WU Y, WU C, et al. Isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria from cheese in Changji, Xinjiang and analysis of their fermentation performance in apricot jam[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2024,50(12):84−91.] DA J Q, WU Y, WU C, et al. Isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria from cheese in Changji, Xinjiang and analysis of their fermentation performance in apricot jam[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024, 50(12): 84−91.
[15] 林瑛兰, 张悦, 李阔, 等. 传统酸粥中乳酸菌的分离筛选及其体外抗氧化能力分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(20):126−134. [LIN Y L, ZHANG Y, LI K, et al. Screening lactic acid bacteria in traditional sour porridge and analysis of their antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(20):126−134.] LIN Y L, ZHANG Y, LI K, et al. Screening lactic acid bacteria in traditional sour porridge and analysis of their antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(20): 126−134.
[16] 焦媛媛, 杜丽平, 孙文, 等. 优良梨汁发酵乳酸菌的筛选与发酵性能分析[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(2):141−145. [JIAO Y Y, DU L P, SUN W, et al. Screening and fermentation characteristics of lactic acid bacteria for fermentation of pear juice[J]. Food Science,2019,40(2):141−145.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20171214-177 JIAO Y Y, DU L P, SUN W, et al. Screening and fermentation characteristics of lactic acid bacteria for fermentation of pear juice[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(2): 141−145. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20171214-177
[17] RUIZ-MOYANO S, GONÇALVES DOS SANTOS M, GALVAN A, et al. Screening of autochthonous lactic acid bacteria strains from artisanal soft cheese:Probiotic characteristics and prebiotic metabolism[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2019,114(1):108388.
[18] LIN Jiaxin, XIONG Tao, PENG Zhen, et al. Novel lactic acid bacteria with anti-hyperuricemia ability:Screening and in vitro probiotic characteristics[J]. Food Bioscience,2022,49(3):101840.
[19] 云月英, 徐娟, 张小利. 4株乳酸菌对模拟胃肠环境的耐受性及生长特性研究[J]. 中国酿造,2018,37(3):53−56. [YUN Y Y, XU J, ZHANG X L. Tolerance to simulated gastrointestinal environment and growth characteristics of four strains of lactic acid bacteria[J]. China Brewing,2018,37(3):53−56.] YUN Y Y, XU J, ZHANG X L. Tolerance to simulated gastrointestinal environment and growth characteristics of four strains of lactic acid bacteria[J]. China Brewing, 2018, 37(3): 53−56.
[20] 闫芬芬, 史佳鹭, 李娜, 等. 具有α-葡萄糖苷酶和二肽基肽酶Ⅳ抑制作用降糖益生菌的筛选[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(20):152−158. [YAN F F, SHI J L, LI N, et al. Screening for potential novel probiotic Lactobacillus strains with high dipeptidyl peptidase IV and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity[J]. Food Science,2019,40(20):152−158.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181106-069 YAN F F, SHI J L, LI N, et al. Screening for potential novel probiotic Lactobacillus strains with high dipeptidyl peptidase IV and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(20): 152−158. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181106-069
[21] 娄行行, 周万怡, 芦红云, 等. 黄酒酿造过程中氨基甲酸乙酯形成的细胞生物学基础及消减研究进展[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(10):406−413. [LOU H H, ZHOU W Y, LU H Y, et al. Research progress on cell biological basis and subtraction of ethyl carbamate formation in the process of rice wine brewing[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(10):406−413.] LOU H H, ZHOU W Y, LU H Y, et al. Research progress on cell biological basis and subtraction of ethyl carbamate formation in the process of rice wine brewing[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22(10): 406−413.
[22] 焦时阳, 王晓彤, 侯玉新, 等. 柿子醋醪中优良乳酸菌的筛选及其耐受性和功能性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(8):161−169. [JIAO S Y, WANG X T, HOU Y X, et al. Screening of superior lactic acid bacteria in persimmon vinegar broth and analysis of its tolerance and function[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(8):161−169.] JIAO S Y, WANG X T, HOU Y X, et al. Screening of superior lactic acid bacteria in persimmon vinegar broth and analysis of its tolerance and function[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(8): 161−169.
[23] 吕欣然, 李叙波, 佟鑫瑶, 等. 东北传统腌渍蔬菜中产γ-氨基丁酸乳酸菌的筛选及其生物特性研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2023,23(12):61−69. [LÜ X R, LI X B, TONG X Y, et al. Screening of lactic acid bacteria with production of γ-aminobutyric acid from traditional pickled vegetables in northeast China and their biological properties[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2023,23(12):61−69.] LÜ X R, LI X B, TONG X Y, et al. Screening of lactic acid bacteria with production of γ-aminobutyric acid from traditional pickled vegetables in northeast China and their biological properties[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 23(12): 61−69.
[24] YANG H, WANG D K, JIN Y, et al. Arginine deiminase pathway of Tetragenococcus halophilus contributes to improve the acid tolerance of lactic acid bacteria[J]. Food Microbiology,2023,113(2):104281.
[25] 麦日艳古·亚生, 伊力米热·热夏提, 努尔古丽·热合曼. 北疆传统发酵生奶酪中乳酸菌的耐受性及益生特性测定[J]. 微生物学通报,2023,50(5):2044−2062. [MAIRIYANGU Y S, YILIMIRE R X T, NVERGULI R H M. Tolerance and probiotic characteristics of lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented raw cheese in northern Xinjiang[J]. Microbiology China,2023,50(5):2044−2062.] MAIRIYANGU Y S, YILIMIRE R X T, NVERGULI R H M. Tolerance and probiotic characteristics of lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented raw cheese in northern Xinjiang[J]. Microbiology China, 2023, 50(5): 2044−2062.
[26] 李佳珣, 张秋香, 王瑞, 等. 乳杆菌表层蛋白对菌株表面特性和益生特性的影响[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(11):43−49,33. [LI J X, ZHANG Q X, WANG R, et al. Effects of surface proteins on the surface and probiotic properties of Lactobacillus species[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(11):43−49,33.] LI J X, ZHANG Q X, WANG R, et al. Effects of surface proteins on the surface and probiotic properties of Lactobacillus species[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2021, 37(11): 43−49,33.
[27] 邹思博, 赵明伟, 纪超凡, 等. 自然发酵东北酸菜中抗氧化乳酸菌的筛选及其益生性研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2023,14(1):42−50. [ZHOU S B, ZHAO M W, JI C F, et al. Screening of high antioxidant activity lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented Suancai of northeast China and its prebiotic studies[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2023,14(1):42−50.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2023.1.spaqzljcjs202301006 ZHOU S B, ZHAO M W, JI C F, et al. Screening of high antioxidant activity lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented Suancai of northeast China and its prebiotic studies[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2023, 14(1): 42−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2023.1.spaqzljcjs202301006
[28] 马丁, 秦双霞, 郝慧超, 等. 基于RBL-2H3细胞脱颗粒抑制作用的体外抗过敏活性益生菌的筛选及鉴定[J]. 食品科学,2024,45(6):55−63. [MA D, QIN S X, HAO H C, et al. Screening and identification of probiotics with in vitro anti-allergic activity based on the degranulation inhibition of RBL-2H3 cells[J]. Food Science,2024,45(6):55−63.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230613-098 MA D, QIN S X, HAO H C, et al. Screening and identification of probiotics with in vitro anti-allergic activity based on the degranulation inhibition of RBL-2H3 cells[J]. Food Science, 2024, 45(6): 55−63. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230613-098
[29] 郭志华, 王聪, 陈红玲. 红茶菌中降解亚硝酸盐乳酸菌的筛选、鉴定及其功能特性[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(8):309−316. [GUO Z H, WANG C, CHEN H L. Studies on screening, identification and functional properties of nitrite degrading lactic acid bacteria in kombucha[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(8):309−316.] GUO Z H, WANG C, CHEN H L. Studies on screening, identification and functional properties of nitrite degrading lactic acid bacteria in kombucha[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2021, 21(8): 309−316.
[30] REUBEN R C, ROY P C, SARKAR S L, et al. Characterization and evaluation of lactic acid bacteria from indigenous raw milk for potential probiotic properties[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2019,103(2):1223−1237.
[31] HU Y H, XIE Y, SU Q T, et al. Probiotic and safety evaluation of twelve lactic acid bacteria as future probiotics[J]. Foodborne Pathogens and Disease,2023,20(11):521−530. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2023.0039
[32] 陈佩, 党辉, 张秋香, 等. 1株具有潜在降糖作用的益生菌的筛选[J]. 中国食品学报,2014,14(11):27−33. [CHEN P, DANG H, ZAHNG Q X, et al. Screening for potential new probiotic based on antidiabetic effect[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2014,14(11):27−33.] CHEN P, DANG H, ZAHNG Q X, et al. Screening for potential new probiotic based on antidiabetic effect[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2014, 14(11): 27−33.
[33] 覃志成, 周笑犁, 吴承木, 等. 番茄发酵液中乳酸杆菌的分离鉴定及对模拟胃肠液耐受性研究[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2023,42(8):54−61. [QING Z C, ZHOU X L, WU C M, et al. Isolation and identification of Lactobacillus in tomato fermentation broth and investigation of its tolerance to simulated gastrointestinal environment[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2023,42(8):54−61.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2023.08.007 QING Z C, ZHOU X L, WU C M, et al. Isolation and identification of Lactobacillus in tomato fermentation broth and investigation of its tolerance to simulated gastrointestinal environment[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2023, 42(8): 54−61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2023.08.007
[34] 熊雯宇, 何君强, 刘斌. 灰树花水上清液中不同极性提取物的功能成分及其抗氧化活性[J]. 中国食品学报,2023,23(12):302−310. [XIONG W Y, HE J Q, LIU B. Functional components and antioxidant activities of different polarities extracts from the supernatant of Grifola frondosa[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2023,23(12):302−310.] XIONG W Y, HE J Q, LIU B. Functional components and antioxidant activities of different polarities extracts from the supernatant of Grifola frondosa[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 23(12): 302−310.
[35] ADEMILUYI A O, OBOTH G. Phenolic-rich extracts from selected tropical underutilized legumes inhibit α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and angiotensin I converting enzyme in vitro[J]. Journal of Basic and Clinic Physiology and Pharmacology,2012,23(1):17−25. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2011-0005
[36] 张会, 孙晓琛, 夏依旦·买买提, 等. 乳酸菌对羊乳酸奶体外降血糖和抗氧化功能的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(18):156−163. [ZHANG H, SUN X C, XIAYIDAN M M T, et al. Effects of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on hypoglycemic and antioxidant activities of goat yoghurt in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(18):156−163.] ZHANG H, SUN X C, XIAYIDAN M M T, et al. Effects of lactic acid bacteria fermentation on hypoglycemic and antioxidant activities of goat yoghurt in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(18): 156−163.
[37] GURUNATHAN S, THANGARAJ P, KIM J H. Postbiotics:Functional food materials and therapeutic agents for cancer, diabetes, and inflammatory diseases[J]. Foods,2023,13(1):89. doi: 10.3390/foods13010089
[38] 唐天培, 黄自伟, 张娜娜, 等. 酸面团发酵煎饼对2型糖尿病小鼠的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2023,23(6):121−131. [TANG T P, HUANG Z W, ZHANG N N, et al. Effects of pancake with sourdough fermentation on type 2 diabetic mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2023,23(6):121−131.] TANG T P, HUANG Z W, ZHANG N N, et al. Effects of pancake with sourdough fermentation on type 2 diabetic mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 23(6): 121−131.
[39] 李向菲, 沈丹, 黄俊凯, 等. 米糠功能活性成分及其功效的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(13):466−474. [LI X F, SHEN D, HUANG J K, et al. Research progress on functional active components and its efficacy in rice bran[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(13):466−474.] LI X F, SHEN D, HUANG J K, et al. Research progress on functional active components and its efficacy in rice bran[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(13): 466−474.





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



