Research Progress of ROS-Mitochondrial Pathway on Cardiovascular Protection of Tea Polyphenols
-
摘要: 心血管疾病是全球首要致死病因,其中活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)失衡和线粒体功能障碍是导致其发生的重要机制。线粒体是ROS产生的主要场所,也是ROS攻击的靶点。大量研究证实,茶多酚能够调控ROS生成和保护线粒体结构与功能,对心血管具有显著的保护作用。因此,本文在介绍ROS的来源及其危害的基础上,概括了ROS-线粒体与心血管疾病发生和发展的内在联系以及茶多酚对ROS的清除作用,并重点对近年来茶多酚通过ROS-线粒体途径对心血管保护作用的研究进展展开综述。从ROS-线粒体视角阐明了茶多酚主要通过调控线粒体融合与分裂蛋白的表达、降低线粒体膜通透性转换孔的开放程度、维持细胞钙稳态、减轻线粒体DNA损伤以及调控线粒体凋亡的信号转导以改善心血管疾病,并进一步对茶多酚的应用前景进行展望,旨在为相关领域的研究和应用提供参考。Abstract: Reactive oxygen species (ROS) imbalance and mitochondrial dysfunction played critical roles in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases which are the leading cause of death worldwide. Mitochondrion is the main ROS production, which is also the vulnerable target for ROS attack. Compelling evidence has been provided that tea polyphenols could regulate ROS generation and protect mitochondrial structure and function, contributing to its beneficial health effects on cardiovascular protection. Hence, the article introduces the sources and detrimental effects of ROS, then the intrinsic connections between ROS, mitochondria, and the development of cardiovascular diseases, as well as the ROS-scavenging effects of tea polyphenols are summarized. From the perspective of ROS-mitochondrial pathway, the article elucidates how tea polyphenols behaved the beneficial effects against cardiovascular diseases by modulating the expression of mitochondrial fusion and fission proteins, reducing the opening of mitochondrial membrane permeability transition pore, maintaining cellular calcium homeostasis, mitigating mitochondrial DNA damage and regulating mitochondrial apoptosis signaling pathways. Correspondingly, the potential applications of tea polyphenols are discussed, aiming to provide valuable insights for research and application in related fields.
-
心血管疾病是危及人类健康的“头号杀手”[1]。近年来,因肥胖现象盛行以及人口老龄化加剧,罹患心血管疾病风险的人群规模呈不断上升趋势[2]。世界卫生组织发布的《2019年全球卫生估计报告》统计发现缺血性心脏病是非传染性疾病中最大的致死病因,占总死亡人数的16%[3]。心血管疾病是心脏疾病和血管疾病的统称,包括冠心病、心肌炎、心律失常和心力衰竭等,是一种世界范围内严重威胁人类健康的主要疾病[4]。ROS的过量生成是人类疾病元凶,与心血管疾病、神经退行性疾病、糖尿病和癌症的发生发展密切相关[5]。生物体内的ROS可在线粒体、细胞膜、内质网和核膜等位点伴随着机体新陈代谢而产生。线粒体作为细胞的“能量工厂”,在氧化磷酸化代谢过程中不可避免地导致ROS生成,同时也成为了ROS攻击的主要靶点[6]。心脏是高能量需求器官,线粒体含量丰富,因此,维持线粒体的正常结构与功能及ROS的平衡对于确保心脏的正常运转具有重要意义[7]。
茶多酚是茶叶中最重要的生物活性成分,具有降血压、降血脂和抗动脉粥样硬化等心血管保护活性[8]。近年来,随着对茶多酚研究的深入,其在心血管保护方面的机制和应用得到了进一步的阐明和扩展。大量研究表明,茶多酚是较好的天然抗氧化剂,可以清除生物体内过剩的ROS,抑制氧化应激,保护线粒体结构与功能,避免生物体遭受ROS引起的氧化损伤[9−10]。由此可见,茶多酚对保护心血管和促进人体健康具有积极意义,在心血管疾病的防治方面具有广阔的开发和应用前景。本文从ROS-线粒体途径出发,综述了茶多酚在心血管保护作用方面的研究进展。期望推动茶多酚在食品工业中的广泛应用,为开发功能性食品和健康补充剂等提供科学依据,为茶多酚在食品工业中的应用与研究提供一定的参考。
1. ROS的来源与危害
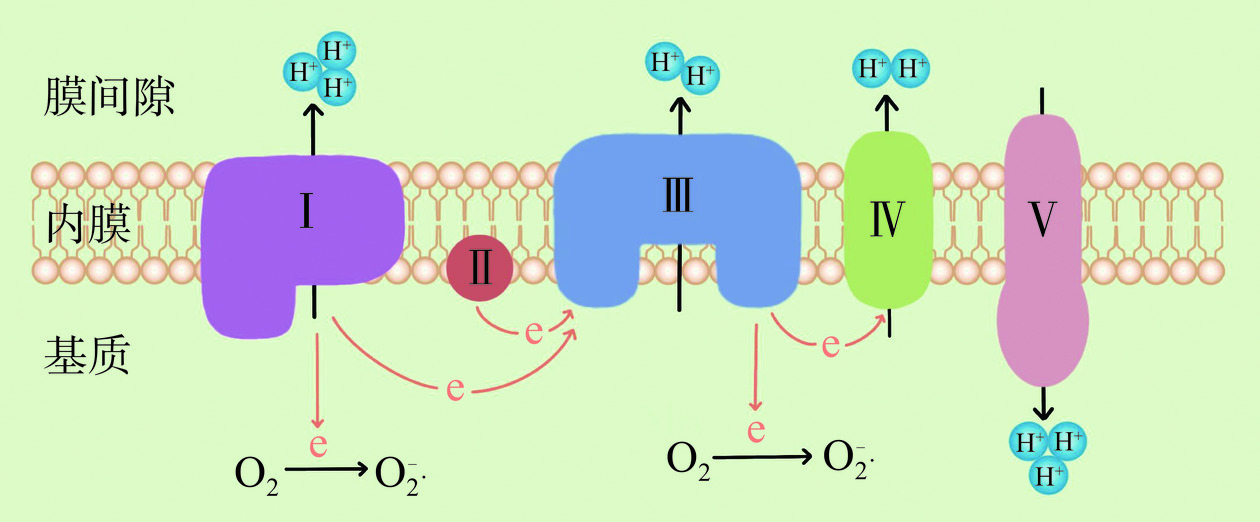
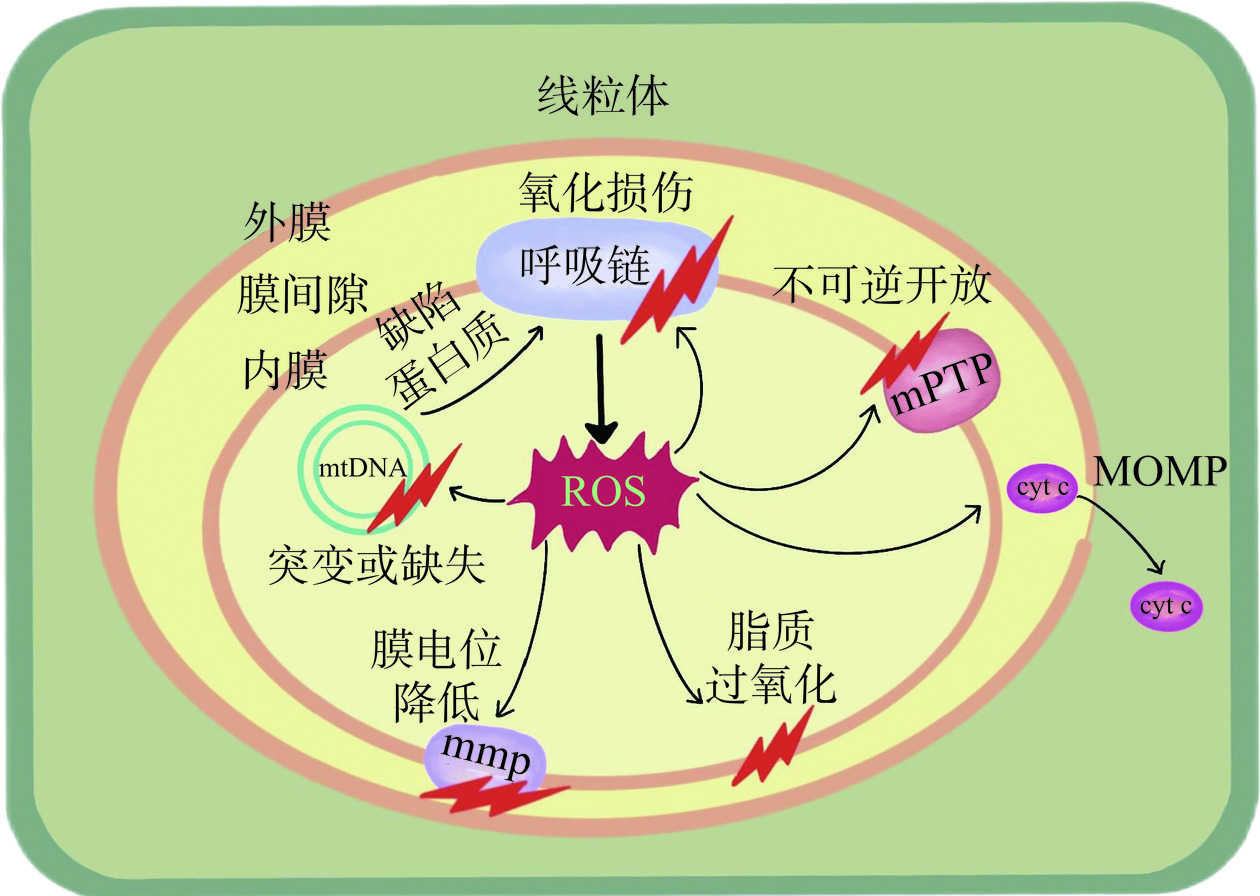
ROS是生物体内与氧代谢有关的,或环境中由氧组成的,含氧且具有不成对电子的原子、分子、离子或原子团。ROS的种类很多,按来源可分为内源性和外源性两大方面[11]。外源性ROS来源于食物添加剂、农药、辐射、吸烟和酒精等外来因素,内源性ROS来源于线粒体、NADPH氧化酶、中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞等[12]。在人类通过摄入食物获取能量的过程中,ROS在线粒体、细胞膜、内质网和核膜等位点,伴随着碳水化合物、蛋白质和脂质的氧化磷酸化不可避免地产生[13]。线粒体是为细胞提供能量的细胞器,作为细胞的“能量工厂”,绝大部分的碳水化合物、蛋白质和脂质最终都是在线粒体内进行氧化磷酸化生成能量ATP[14]。因此,线粒体作为细胞内重要细胞器,既是ROS的主要生产者,同时也是ROS攻击的靶点。线粒体通过转移电子释放氧气,从而产生ATP形式的能量,并产生水。但是机体并非总能把4个电子都转移释放氧气变成水,这其中有1%~2%的电子会逸出,由此产生出“ROS”[15]。这一过程主要发生在线粒体内膜的呼吸链上,特别是其中的复合物Ⅰ和复合物Ⅲ,复合物Ⅰ产生约20%的O2−·,复合物Ⅲ产生约80%的O2−·[16],机制如图1所示。因此,ROS是细胞正常代谢过程中的产物,在线粒体能量代谢过程中,ROS的产生是无可避免的[17]。然而,过量的ROS会攻击线粒体,导致线粒体膜通透性转换孔(mitochondrial permeability transition pore,mPTP)不可逆开放,伴随着离子流失,线粒体膜电位无法继续维持,线粒体DNA(mitochondrial DNA,mtDNA)受损,线粒体结构与功能障碍,无法合成ATP,从而不能满足细胞对能量的需求[18−19],导致细胞损伤或死亡[20−21]。同时,过量的ROS还可与线粒体膜间隙和基质中存在的多种促凋亡因子相互影响,从而诱导细胞凋亡[22]。ROS对线粒体的损伤机制如图2所示。
2. ROS与心血管疾病
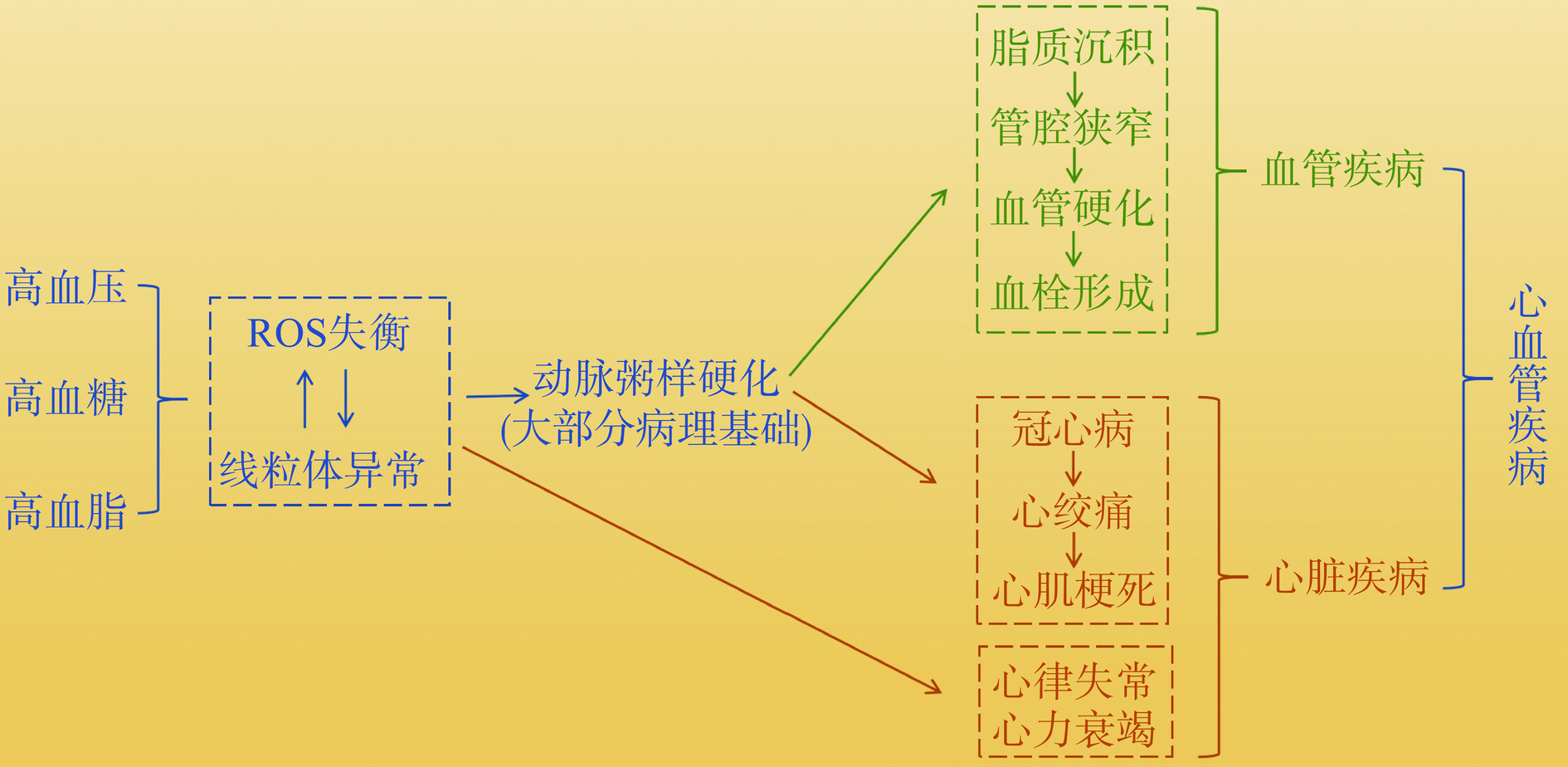
长期以来,ROS一直被认为对人体有害。大量研究表明,过高的ROS水平会破坏氧化还原稳态,导致氧化应激、细胞凋亡和炎症反应,对细胞膜、蛋白质和DNA等造成损伤[23]。然而事实上,当ROS处于正常生理水平时,它可以作为信号分子,参与细胞增殖与分化、损伤修复、信号转导和免疫应答等多种生理过程[24-25]。ROS是细胞正常代谢过程中的副产物,其产生与消除均受到严格的调控,以确保ROS平衡。当细胞受到病理性因素刺激时,可导致ROS产生过量,攻击线粒体等细胞器,进而诱导一系列与氧化应激有关的信号级联反应[17,26−27]。大量基础研究显示,高血脂时体内ROS的产生和清除平衡被破坏,超氧化物歧化酶等抗氧化酶类活性降低,导致大量脂质过氧化物的产生。脂质过氧化物的产物丙二醛极易修饰低密度脂蛋白形成氧化型低密度脂蛋白,被单核细胞衍生的巨噬细胞和中膜平滑肌细胞摄取形成泡沫细胞使得脂质进一步沉积,推动动脉粥样硬化及心血管疾病的发展[28−29]。心肌急剧的暂时缺血与缺氧可以诱导ROS爆炸性释放,造成心脏功能的损伤。缺血再灌注损伤释放大量的ROS,促使细胞发生脂质过氧化反应,加重ROS的细胞毒性作用,在线粒体内出现独特的“ROS诱导的ROS释放”现象,形成恶性循环[30],加速心肌损伤和动脉粥样硬化形成[31−32]。由此可见,ROS是导致心血管疾病发生发展的重要因素,其相关性如图3所示。心脏是体内连续工作的器官,心肌细胞内含有大量线粒体,大约占据细胞体积的40%。据统计,一个心肌细胞中大约有6000个线粒体,平均每天能够产生6 kg ATP[33]。因此,控制ROS的适量生成以及维持线粒体的正常形态与功能,对于维系心脏的能量需求和循环系统的正常运作等具有重要意义。
3. 茶多酚对ROS的清除作用
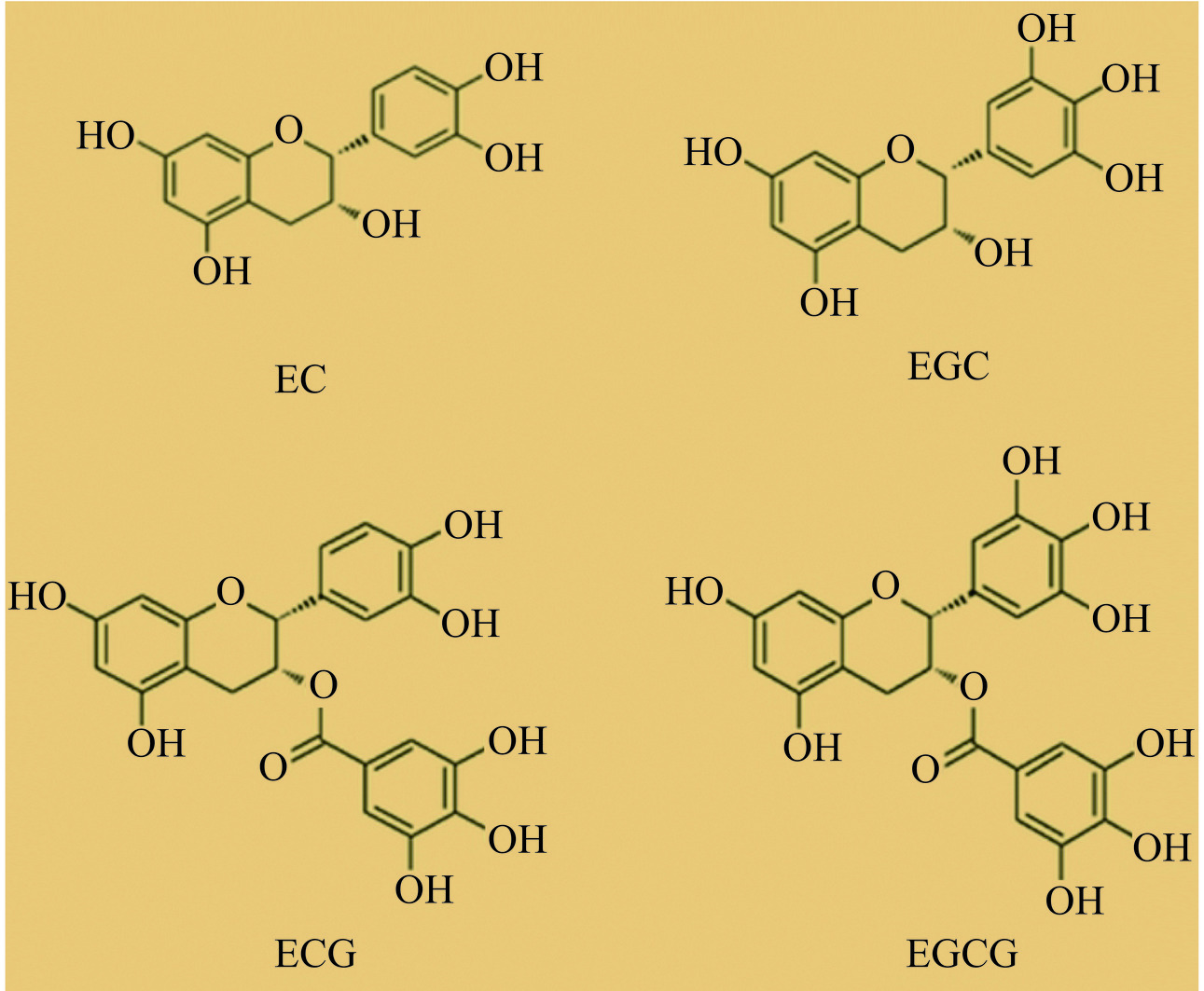
研究证实,茶多酚具有较好的抗氧化、降血压、抗动脉粥样硬化和降血脂等心血管保护作用。茶多酚是茶叶中重要的活性成分,是茶叶中30多种酚性成分的统称,主要包括黄烷醇、黄酮醇、酚酸和花青素等,在干茶叶中的质量分数为12%~25%[34]。儿茶素为黄烷醇的衍生物,在众多茶多酚类物质中质量分数最高,约为70%~80%。根据化学结构可将儿茶素类分为四种(图4):表儿茶素(epicatechin,EC);表没食子儿茶素(epigallocatechin,EGC);表儿茶素没食子酸酯(epigallocatechin gallate,ECG)和表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(epigallocatechin-3-gallate,EGCG),其中,EGCG含量最高,占儿茶素的50%左右[35]。众所周知,茶多酚是一种天然抗氧化剂,抗氧化能力比2,6-二叔丁基对甲酚等合成抗氧化剂高许多,是维生素E和维生素C的数倍,可有效清除机体内过剩的ROS,保护线粒体功能。研究报道,茶多酚清除ROS的主要机制有:茶多酚中儿茶素因其具有连或邻苯酚基的特殊结构,可直接清除ROS,并表现出比一般的非自由酚性或单酚羟基类抗氧化剂更高的抗氧化活性;茶多酚是较好的质子或中子供体,可显著增强体内抗氧化酶的活性,增强抗氧化防御能力,发挥间接清除ROS的作用;茶多酚能与金属离子发生络合反应,降低产生ROS所必需的铁离子含量,从而减少ROS的生成[36−37]。
4. 基于ROS-线粒体途径的茶多酚对心血管的保护作用
在正常细胞中,线粒体参与能量产生和生物合成、维持氧化还原平衡、调节钙稳态和细胞凋亡等 [39]。同时,当细胞内抗氧化系统与氧化系统失去平衡,大量ROS不断积聚就会导致线粒体氧化应激,造成线粒体损伤,从而诱发心血管疾病[40]。线粒体氧化应激不仅会降低呼吸链酶活性,导致电子传递速度减慢,还会促进ROS的产生。同时,它还会上调解偶联蛋白表达,这种过度表达是引起线粒体功能障碍的关键机制之一[41]。此外,氧化应激还能触发链式脂质过氧化级联反应,破坏线粒体膜的通透性,进一步削弱呼吸链酶活性,形成恶性循环。这一系列反应最终导致心肌细胞走向凋亡或坏死,对心脏健康造成严重影响[42−44]。研究表明,线粒体氧化应激在动脉粥样硬化、心力衰竭和心肌缺血后再灌注损伤(myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury,MIRI)等多种心血管系统疾病的发生与发展中扮演关键角色[45]。在动脉粥样硬化病理状态中,线粒体功能发生障碍,产生过多的ROS,呼吸链酶活性降低、线粒体膜电位去极化,mtDNA损伤或突变,从而导致心脏组织细胞功能受损[46]。心肌缺血后再灌注过程中产生的过量ROS也是导致MIRI的主要原因,其中线粒体是产生ROS的重要来源[44]。由上可知,调控ROS-线粒体信号级联反应对于预防和治疗心血管疾病至关重要。茶多酚通过多种不同的机制,如降血压、降血脂、抗动脉粥样硬化和抗心律失常等,对心血管具有较好的保护作用[8]。目前已有大量研究揭示了茶多酚对心血管疾病的保护作用机制与调节ROS生成及线粒体保护有关。根据心血管疾病的发展程度不同,茶多酚的保护作用机制不同,但保护机制的一个共同点是从源头上减少ROS产生,避免细胞氧化应激,从而保证线粒体结构与功能正常,起到保护心血管的作用。
4.1 调控线粒体融合与分裂蛋白的表达
线粒体是一个不断变化的动态细胞器,它会根据细胞内外部环境变化,自身不断地进行融合与分裂。线粒体分裂时,片段化程度加强,呈粒状或线状等结构;而线粒体融合时,网络化程度加强,呈管状或网状结构。在正常细胞内,线粒体融合与分裂始终处于动态平衡[47−48]。线粒体融合与分裂需要多种蛋白质参与。线粒体外膜的融合需要线粒体融合蛋白1(mitofusin 1,Mfn1)和线粒体融合蛋白2(mitofusin 2,Mfn2)参与,线粒体内膜的融合需要视神经萎缩蛋白1(optic atrophy 1,Opa1)参与;线粒体分裂离不开动力相关蛋白1(dynamin-related protein 1,Drp1)的参与。此外,分裂蛋白1(fission protein 1,Fis1)、线粒体蛋白18(mi-tochondrial protein 18 kDa,MPT18)和线粒体分裂因子(mitochondrial fission factor,Mff)等均是参与线粒体分裂的重要蛋白质[49−51]。ROS介导的线粒体氧化应激可影响上述蛋白表达水平和这些蛋白的翻译后修饰,导致线粒体融合与分裂失衡,引发线粒体的破裂与细胞凋亡[52]。
研究表明,茶多酚可以通过调节线粒体融合与分裂蛋白的表达,来改善ROS介导的线粒体损伤,使线粒体的融合与分裂始终保持动态平衡。Pletjushkina等[53]用过氧化氢处理细胞来模拟氧化应激,实验中观察到线粒体在过氧化氢处理后,开始不断分裂,从网管状向点状变化,线粒体片段化程度加强,而抗氧化剂处理后,这一现象得以缓解。Chen等[54]通过体外和体内蛛网膜下腔出血(SAH)模型研究了EGCG在抑制细胞死亡后挽救线粒体功能障碍和线粒体动力学的能力。结果发现EGCG通过调节Drp1、Fis1、OPA1、Mfn1和Mfn2蛋白的表达,改善了氧合血红蛋白(OxyHb)诱导的线粒体动力学损伤,并且EGCG使SAH后OxyHb组线粒体碎片和mtDNA拷贝数的增加恢复到几乎正常的水平。在舒周伍[55]研究中,通过对人主动脉平滑肌细胞(human aortic smooth muscle cells,HASMC)培养,并给予不同浓度(20、50、100 μmol/L)的EGCG进行干预,实验结果发现50 μmol/L 浓度的EGCG能够显著抑制HASMC增殖,同时Mfn2蛋白的表达明显上调,表明EGCG可能通过上调Mfn2的表达来抑制HASMC增殖,进而抑制动脉粥样硬化的形成。
4.2 降低线粒体mPTP的开放程度
线粒体膜通透性转换孔,是一组存在于线粒体内外膜间隙中的蛋白复合体,它是一种非特异性通道,容许相对分子质量<1500的溶质分子(如H+、Ca2+、细胞色素c及谷胱甘肽等)通过,在细胞的生存和凋亡中起重要作用。在生理状态下,mPTP呈间断、可逆性开放,这有利于Ca2+的流通,从而维持细胞内钙稳态[56]。心肌细胞在受到不良病理因素刺激时,会产生大量ROS,诱导mPTP不可逆开放,导致大量离子流失,线粒体膜电位无法维持,ATP合成减少。mPTP的不可逆开放又能诱导心肌细胞产生更多的ROS,形成恶性循环,进一步加重线粒体损伤[57]。此外,mPTP不可逆开放会使线粒体内膜通透性显著增加,导致还原型谷胱甘肽从线粒体内流出,同时伴随大量超氧阴离子的生成。这些变化进一步引起线粒体基质渗透压升高,线粒体吸水而变得明显肿胀。最终,线粒体外膜因无法承受内部压力而破裂,释放出位于内外膜间隙中的细胞色素c(cytochrome c,Cytc)和凋亡诱导因子等,触发一系列复杂的生物化学反应,包括与细胞骨架、细胞膜及细胞核相关的蛋白质切割水解,从而介导细胞凋亡或坏死。这一过程与多种疾病的发生发展密切相关[58−59]。Ma等[60]用雄性SD大鼠研究茶黄素对缺血再灌注心脏的保护作用及机制。结果发现,与对照组相比,茶黄素组对缺血再灌注后心脏功能的恢复效果较好,且呈剂量依赖性;再灌注15 min时给药的线粒体mPTP开启剂白术苷完全消除了茶黄素对心脏的保护作用。这些结果表明,茶黄素可通过抑制线粒体mPTP的开放从而保护大鼠心脏免受缺血再灌注损伤。Zhou等[61]通过血管紧张素II(angiotensin II,Ang-II)诱导人脐静脉内皮细胞(human umbilical vein endothelial cells,HUVEC)凋亡,研究EGCG在其中能否发挥保护作用。结果发现:Ang II处理增加了HUVEC中ROS产生、mPTP开放和Cytc释放,激活了caspase-3/9,从而诱导线粒体相关细胞凋亡。然而,用EGCG处理HUVEC后,这些由Ang II引发的现象被抑制,减缓了氧化应激和细胞凋亡引起的细胞损伤。
4.3 维持细胞钙稳态
线粒体在心肌细胞钙稳态的调节过程中发挥重要作用。事实上,线粒体呼吸代谢氧化磷酸化的过程与线粒体对细胞内钙稳态的调节过程紧密联系,在呼吸链进行电子传递的同时,线粒体膜电位形成,这有利于促进线粒体对Ca2+的摄取;而线粒体内的Ca2+又能提高氧化磷酸化过程中脱氢酶的活性,从而促进氧化磷酸化过程合成ATP,为细胞提供能量。简而言之,线粒体的电子传递与钙离子的相互作用共同调节着细胞的能量生产过程[62−63]。研究表明,ROS可通过影响呼吸链复合物的活性、诱导mPTP 开放以及改变线粒体膜电位等导致线粒体内Ca2+紊乱,引起心肌细胞线粒体功能障碍[20]。Li等[64]通过Ang-II诱导血管内皮细胞损伤来揭示茶多酚对心血管疾病保护作用,结果表明,茶多酚能明显改善Ang-II诱导的细胞内钙浓度和线粒体膜电位的变化,以维持心肌细胞线粒体的正常生理功能。Chen等[65]用过氧化氢处理大鼠心肌细胞(H9C2)创造氧化应激病理状态。对照组中细胞内Ca2+水平为0.15 μm,过氧化氢组细胞内Ca2+水平上升至0.3 μm,过氧化氢和EGCG共同处理组细胞内Ca2+水平不到0.15 μm。结果表明EGCG能显著降低细胞内Ca2+水平,从而起到保护线粒体功能的作用。Devika等[66]用异丙肾上腺素(isoproterenol,ISO)建立老鼠心肌梗死模型,来探讨EGCG对心肌梗死保护作用。实验过程中发现ISO可以增加细胞对Ca2+摄取,导致细胞内Ca2+过载,ATP酶过度激活,损伤线粒体的氧化磷酸化能力,使ATP合成减少。EGCG组结果显示ISO处理的大鼠心脏细胞线粒体中Ca2+的水平降低并增强了ATP水平。故EGCG可能是通过调控ISO产生的氧化应激而清除过量ROS,恢复线粒体中Ca2+和ATP水平,从而减轻线粒体损伤。
4.4 减轻mtDNA损伤
ROS介导的线粒体氧化应激会导致mtDNA损伤,线粒体功能下降,缺失形式的mtDNA在心肌细胞中积累会导致心脏肥大和心力衰竭等疾病[43]。线粒体是一种半自主细胞器,mtDNA是其遗传物质,由于mtDNA缺乏组蛋白和DNA 结合蛋白的保护,且直接暴露于线粒体呼吸代谢产生的高ROS环境中,故其极易受到ROS的攻击而导致氧化损伤。再加上它缺乏有效的修复系统,故氧化损伤后很容易导致突变,随着突变程度累积到一定阈值,便会出现线粒体功能障碍相关疾病的症状,这便是线粒体基因突变的阈值效应[67−69]。Chen等[70]通过对雄性老鼠进行腹主动脉缩窄(TAC)手术,建立左心室肥大模型作为实验组,对照组进行假手术。实验组腹腔注射EGCG,对照组腹腔注射缓冲水,总共持续21 d。实验结果显示mtDNA拷贝数(mtDNA与18rRNA的比例)在TAC组中减少26%,这与ROS的增加相一致。与假手术组相比,用EGCG处理TAC老鼠后,mtDNA拷贝数又恢复到正常水平,且线粒体功能的损伤也发生了逆转。此外,线粒体呼吸链中由mtDNA基因编码的部分复合物I、III和IV的酶活性在TAC后显著降低,而完全由核DNA编码的复合物II的酶活性在TAC后没有改变。这些数据表明mtDNA拷贝数减少和线粒体功能受损之间的关系,同时也说明EGCG对TAC诱导的左心室肥大的抑制作用可能部分是因为预防由ROS介导的线粒体mtDNA损伤和功能障碍。
5. 茶多酚调控线粒体凋亡的信号转导机制
当心肌细胞内ROS产生过量时,会造成线粒体氧化损伤,从而释放凋亡诱导因子,引发心肌细胞凋亡级联反应[71]。细胞凋亡又称细胞程序性死亡,它通过选择性去除老化、受损或不需要的细胞来维持生物体稳态,在维持内环境稳定、组织生长、胚胎发育以及机体防御等多种生理过程中发挥重要作用[72]。细胞凋亡是一个由特定的蛋白酶——半胱氨酸蛋白酶(cysteinyl aspartate specific proteinase,Caspase)介导的精密过程。Caspase作为细胞凋亡的关键执行者,能够与多种底物作用,触发凋亡细胞发生一系列独特的生物化学和形态学变化,包括线粒体外膜通透性改变、DNA断裂和细胞骨架重排等,这些形态特征上的改变在凋亡体形成时达到最高点,最终凋亡体被吞噬细胞识别和清除,这一过程对于维持机体内环境稳态至关重要[73−74]。根据激活路径不同,凋亡途径可分为死亡受体途径、内质网途径和线粒体途径[75]。其中,线粒体途径包括两类,第一类需要激活Caspase通路,线粒体在一系列凋亡诱导因素的刺激下,把Cytc释放至胞质中,与凋亡酶激活因子1和凋亡起始分子Caspase-9结合形成凋亡小体,Caspase-9被激活从而继续激活下游的凋亡执行分子Caspase-3、Caspase-6和Caspase-7等,从而诱发细胞凋亡的级联反应;第二类是不依赖于Caspase途径,由凋亡诱导因子(apoptosis inducing factor,AIF)介导的细胞凋亡。正常情况下,AIF位于线粒体内部,当细胞受到内部凋亡因子刺激时,AIF可从线粒体转运至胞质,进入细胞核,破坏核DNA,导致细胞死亡[76−78]。在真核生物中,细胞信号通路是一个十分复杂的网络。细胞可能选择性地走其中的一条、两条甚至全部,它们之间既相互独立又相互交织,形成一个复杂的网络[79−80]。线粒体因参与多种细胞凋亡信号通路而被称为凋亡通路中的“门卫”,在其中发挥重要枢纽作用,各种死亡通路之间的相互交叉使线粒体成为凋亡通路中最关键的部分[81−82]。因此,在心血管疾病的预防和治疗过程中,通过调控线粒体凋亡途径从而减少心脏细胞凋亡是最为有效的办法之一。
Adikesavan等[83]通过将小鼠暴露于吸烟的环境中12周,建立心肌损伤模型。实验组显示线粒体脂质过氧化显著增加,抗氧化酶如谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶和三羧酸循环酶的活性显著降低,线粒体氧化应激,释放Cytc进入胞质,激活Caspase-3和Caspase-9,并显著下调抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2,同时上调促凋亡蛋白Bax,促进小鼠心肌细胞凋亡。EGCG给药组显示线粒体脂质过氧化水平显著降低,抗氧化酶活性增加,表明EGCG对保护线粒体功能具有较好的效果。实验中进一步观察到EGCG处理可以抑制Cytc释放至胞质,从而抑制Caspase-3和Caspase-9的激活,下调Bax和上调Bcl-2,结果显著抑制模型组小鼠心肌细胞凋亡。研究结果表明,EGCG可以通过清除过量的ROS,减少氧化应激的产生,并调控线粒体介导的凋亡信号通路对吸烟诱导的心肌损伤起到保护作用。Chen等[65]用过氧化氢处理大鼠心肌细胞H9C2,建立MIRI模型。实验过程中发现,过氧化氢可以诱导细胞中聚磷酸肌醇磷酸酶4B表达、进而减少PI(3,4)P2水平、抑制pASKT(s473)磷酸化和增加pGSK-3β磷酸化,还可以通过淋巴细胞中的PI3K依赖通路触发AktT308磷酸化,激活MAPK级联反应,从而促进细胞凋亡。经过实验研究,确定了EGCG对心脏的保护作用是通过调节PIP2、PIP3合成,激活Akt/GSK-3β通路,抑制GSK-3β介导的心脏细胞损伤达到的。Chen等[70]通过对雄性老鼠进行腹主动脉缩窄手术,建立左心室肥大模型。实验组心脏细胞内ERK2,p38和JNK1的活性显著增加,NF-κB和AP-1被激活,而EGCG可以直接或间接阻断MAPK途径,减弱NF-κB和AP-1的活性,抑制心脏肥大,从而起到心脏保护作用。Hirai等[84]用Krebs-Henseleit(KH)溶液对豚鼠的心脏建立缺血后再灌注损伤模型,然后检测Caspase-3活性,观察心脏细胞凋亡情况。对照组1是心脏缺血1 h后用正常的KH溶液灌注30 min,而对照组2则是用无药物溶液灌注5 h。实验组是EGCG或GCG在缺血前施用4 min,并在整个再灌注期间施用5 h。对照组和实验组中使用相同的冷冻组织,并用TUNEL方法测量Caspase-3活性。实验结果发现,EGCG或GCG处理会降低Caspase-3活性,从而抑制心脏细胞凋亡。
6. 结论与展望
线粒体是ROS产生的主要场所,也是ROS 攻击的重要靶点,二者之间关系非常密切,互为因果。线粒体是细胞的“能量工厂”,心脏是能量需求极高的器官,其线粒体含量最为丰富。在各种内外部不利因素的刺激下,ROS产生异常,导致线粒体结构与功能受损,在一系列心血管相关疾病的发生与发展中发挥关键性作用。茶多酚是茶叶中重要的活性成分,可通过调控ROS-线粒体途径,发挥心血管保护作用。研究表明,茶多酚对ROS-线粒体途径的调控,与线粒体分裂与融合、mPTP的开放、细胞钙水平及mtDNA密切相关。对ROS-线粒体途径相关的线粒体调亡信号转导的调控作用,是茶多酚发挥心血管保护作用的重要机制。总之,随着国内外学者研究的不断深入,茶多酚在心血管疾病的预防和治疗中必将有更广阔的发展和应用前景。未来的研究应进一步探索茶多酚的推荐摄入标准、特异性、效力、可行性以及长期使用对人体是否有副作用等问题[5,27,85]。
-
-
[1] 张瑾怡, 张世忠. 心血管疾病与心理疾病流行病学及相关机制研究新进展[J]. 中国全科医学,2024,27(8):893−899. [ZHANG J Y, ZHANG S Z. Advances in epidemiology and related mechanisms of cardiovascular diseases and mental illness[J]. Chinese General Practice,2024,27(8):893−899.] ZHANG J Y, ZHANG S Z. Advances in epidemiology and related mechanisms of cardiovascular diseases and mental illness[J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(8): 893−899.
[2] 杨继, 张垚, 马腾, 等. 1990~2019年中国心血管疾病流行现状、疾病负担及发病预测分析[J]. 中国全科医学,2024,27(2):233−244,252. [YANG J, ZHANG Y, MA T, et al. Epidemic status, disease burden and prediction of cardiovascular diseases in China, 1990-2019[J]. Chinese General Practice,2024,27(2):233−244,252.] YANG J, ZHANG Y, MA T, et al. Epidemic status, disease burden and prediction of cardiovascular diseases in China, 1990-2019[J]. Chinese General Practice, 2024, 27(2): 233−244,252.
[3] World Health Organization. 前十位死亡原因 [EB/OL]. (2020-12-09)[2024-04-10]. https://www.who.int/zh/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death. [4] KELLER A, WALLACE T C. Tea intake and cardiovascular disease:An umbrella review[J]. Annals of Medicine,2021,53(1):929−944. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1933164
[5] CHENG X M, HU Y Y, YANG T, et al. Reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress in vascular-related diseases[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2022,2022:7906091.
[6] ZOROV D B, JUHASZOVA M, SOLLOTT S J. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ros) and ros-induced ros release[J]. Physiological Reviews,2014,94(3):909−950. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00026.2013
[7] NICOLAS-AVILA J A, LECHUGA-VIECO A V, ESTEBAN-MARTINEZ L, et al. A network of macrophages supports mitochondrial homeostasis in the heart[J]. Cell,2020,183(1):94−109. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.031
[8] 李露, 吕佳倩, 江承佳, 等. 茶多酚对心血管保护作用的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(19):283−288. [LI Lu, LÜ Jiaqian, JIANG Chengjia, et al. Advances in research on protective effect of polyphenols in cardiovascular disease[J]. Food Science,2016,37(19):283−288.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201619047 LI Lu, LÜ Jiaqian, JIANG Chengjia, et al. Advances in research on protective effect of polyphenols in cardiovascular disease[J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(19): 283−288. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201619047
[9] 陈志云, 李杰, 冯雨, 等. 茶多酚生物活性及作用机制研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(13):333−341. [CHEN Zhiyun, LI Jie, FENG Yu, et al. Research progress on bioactivity and Mechanism of tea polyphenols[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(13):333−341.] CHEN Zhiyun, LI Jie, FENG Yu, et al. Research progress on bioactivity and Mechanism of tea polyphenols[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(13): 333−341.
[10] 张文娟, 刘雪娜, 李丽维, 等. 茶多酚生理机制及其保健食品研发进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2023,44(5):217−224. [ZHANG Wenjuan, LIU Xuena, LI Liwei, et al. Physiological mechanism of tea polyphenols and development of their health food[J]. Food Research and Development,2023,44(5):217−224.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2023.05.031 ZHANG Wenjuan, LIU Xuena, LI Liwei, et al. Physiological mechanism of tea polyphenols and development of their health food[J]. Food Research and Development, 2023, 44(5): 217−224. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2023.05.031
[11] ZHAO R Z, JIANG S, ZHANG L, et al. Mitochondrial electron transport chain, ROS generation and uncoupling (review)[J]. International Journal of Molecular Medicine,2019,44(1):3−15.
[12] 丁洪基, 李龙龙, 王灿, 等. 活性氧与疾病关系的研究进展[J]. 临床与实验病理学杂志,2023,39(2):212−215. [DING H J, LI L L, WNAG C, et al. Research progress on the relationship between reactive oxygen species and disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical and Experimental,2023,39(2):212−215.] DING H J, LI L L, WNAG C, et al. Research progress on the relationship between reactive oxygen species and disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical and Experimental, 2023, 39(2): 212−215.
[13] 马淇, 刘垒, 陈佺. 活性氧、线粒体通透性转换与细胞凋亡[J]. 生物物理学报,2012,28(7):523−536. [MA Q, LIU L, CHEN Q. Reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial permeability transition and apoptosis[J]. Acta Biophysica Sinica,2012,28(7):523−536.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1260.2012.20103 MA Q, LIU L, CHEN Q. Reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial permeability transition and apoptosis[J]. Acta Biophysica Sinica, 2012, 28(7): 523−536. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1260.2012.20103
[14] KARIMI M, SADEGHI R, KOKINI J. Human exposure to nanoparticles through trophic transfer and the biosafety concerns that nanoparticle-contaminated foods pose to consumers[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2018,75:129−145.
[15] HERNANSANZ-AGUSTIN P, ENRIQUEZ J A. Generation of reactive oxygen species by mitochondria[J]. Antioxidants,2021,10(3):415. doi: 10.3390/antiox10030415
[16] 李良德, 王定锋, 吴光远. 线粒体内活性氧产生靶标位点研究进展[J]. 生命科学研究,2015,19(6):530−535. [LI L D, WANG D F, WU G Y. Progresses on Producing Sites of Reactive Oxygen Species in Mitochondria[J]. Life Science Research,2015,19(6):530−535.] LI L D, WANG D F, WU G Y. Progresses on Producing Sites of Reactive Oxygen Species in Mitochondria[J]. Life Science Research, 2015, 19(6): 530−535.
[17] CHEN Y R, ZWEIER J L. Cardiac mitochondria and reactive oxygen species generation[J]. Circulation Research,2014,114(3):524−537. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.300559
[18] BERTERO E, MAACK C. Calcium signaling and reactive oxygen species in mitochondria[J]. Circulation Research,2018,122(10):1460−1478. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.310082
[19] DUNN J D, ALVAREZ L A J, ZHANG X, et al. Reactive oxygen species and mitochondria:A nexus of cellular homeostasis[J]. Redox Biology,2015,6:472−485. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.09.005
[20] PEOPLES J N, SARAF A, GHAZAL N, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in heart disease[J]. Experimental and Molecular Medicine,2019,51(12):1−13.
[21] 李泽君, 呼丹, 熊克朝, 等. 活性氧与线粒体损伤研究概述[J]. 中南药学,2014,12(10):989−993. [LI Z J, HU D, XIONG K Z, et al. A brief overview between reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial injury[J]. Central South Pharmacy,2014,12(10):989−993.] LI Z J, HU D, XIONG K Z, et al. A brief overview between reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial injury[J]. Central South Pharmacy, 2014, 12(10): 989−993.
[22] REDZA-DUTORDOIR M, AVERILL-BATES D A. Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species[J]. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Molecular Cell Research,2016,1863(12):2977−2992. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.09.012
[23] LUSHCHAK V I. Free radicals, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and its classification[J]. Chemico-Biological Interactions,2014,224:164−175. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.10.016
[24] RAUF A, KHALIL A A, AWADALLAH S, et al. Reactive oxygen species in biological systems:Pathways, associated diseases, and potential inhibitors-A review[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2024,12(2):675−693.
[25] YU Y F, LIU S Z, YANG L C, et al. Roles of reactive oxygen species in inflammation and cancer[J]. MedComm,2024,5(4):e519. doi: 10.1002/mco2.519
[26] 孙伊人, 杨子琪, 王欣然, 等. 硫氧还蛋白-1:预防心脏相关活性氧损伤的潜在靶点[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2023,30(12):1779−1783. [SUN Y R, YANG Z Q, WANG X R, et al. Thioredoxin-1:A potential target for prevention of heart-related reactive oxygen species injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery,2023,30(12):1779−1783.] SUN Y R, YANG Z Q, WANG X R, et al. Thioredoxin-1: A potential target for prevention of heart-related reactive oxygen species injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 2023, 30(12): 1779−1783.
[27] CHEN Q S, WANG Q W, ZHU J H, et al. Reactive oxygen species:key regulators in vascular health and diseases[J]. British Journal of Pharmacology,2018,175(8):1279−1292. doi: 10.1111/bph.13828
[28] FORRESTER S J, KIKUCHI D S, HERNANDES M S, et al. Reactive oxygen species in metabolic and inflammatory signaling[J]. Circulation Research,2018,122(6):877−902. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311401
[29] 高萍萍, 宋湘. 氧化应激对心血管疾病影响的研究进展[J]. 心血管康复医学杂志,2023,32(2):163−166. [GAO P P, SONG X. Research progress of influence of oxidative stress on cardiovascular diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Cardiovascular Rehabilitation,2023,32(2):163−166.] GAO P P, SONG X. Research progress of influence of oxidative stress on cardiovascular diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Cardiovascular Rehabilitation, 2023, 32(2): 163−166.
[30] SHAITO A, ARAMOUNI K, ASSAF R, et al. Oxidative stress-induced endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Frontiers in Bioscience-Landmark,2022,27(3):105. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2703105
[31] SENONER T, DICHTL W. Oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases:Still a therapeutic target?[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(9):2090−2090. doi: 10.3390/nu11092090
[32] SNEZHKINA A V, KUDRYAVTSEVA A V, KARDYMON O L, et al. ROS generation and antioxidant defense systems in normal and malignant cells[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2019,2019(2019):6175804.
[33] 王佳慧, 梁欢, 方典, 等. 抑制线粒体活性氧自由基可减轻高糖诱导的心肌细胞焦亡和铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2021,41(7):980−987. [WANG J H, LIANG H, FANG D, et al. Inhibition of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species reduces high glucose-induced pyroptosis and ferroptosis in H9C2 cardiac myocytes[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University,2021,41(7):980−987.] WANG J H, LIANG H, FANG D, et al. Inhibition of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species reduces high glucose-induced pyroptosis and ferroptosis in H9C2 cardiac myocytes[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(7): 980−987.
[34] YAHFOUFI N, ALSADI N, JAMBI M, et al. The immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory role of polyphenols[J]. Nutrients,2018,10(11):1618. doi: 10.3390/nu10111618
[35] RANA A, SAMTIYA M, DHEWA T, et al. Health benefits of polyphenols:A concise review[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2022,46(10):e14264.
[36] YAN Z M, ZHONG Y Z, DUAN Y H, et al. Antioxidant mechanism of tea polyphenols and its impact on health benefits[J]. Animal Nutrition,2020,6(2):115−123. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2020.01.001
[37] MUSIAL C, KUBAN-JANKOWSKA A, GORSKA-PONIKOWSKA M. Beneficial properties of green tea catechins[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2020,21(5):1744−1744. doi: 10.3390/ijms21051744
[38] XING L J, ZHANG H, QI R L, et al. Recent advances in the understanding of the health benefits and molecular mechanisms associated with green tea polyphenols[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019,67(4):1029−1043. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06146
[39] 杜赐杰, 陈宝丹, 王孟飞, 等. 线粒体与细胞命运调控[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报,2024,46(1):79−89. [DU C J, CHEN B D, WANG M F, et al. Mitochondria and cell fate regulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology,2024,46(1):79−89.] DU C J, CHEN B D, WANG M F, et al. Mitochondria and cell fate regulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Cell Biology, 2024, 46(1): 79−89.
[40] 韩晓婷, 宋海燕. 线粒体功能障碍在糖尿病心肌病中的作用研究进展[J]. 心血管康复医学杂志,2024,33(1):94−97. [HAN X T, SONG H Y. Research progress of role of mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy[J]. Chinese Journal of Cardiovascular Rehabilitation,2024,33(1):94−97.] HAN X T, SONG H Y. Research progress of role of mitochondrial dysfunction in diabetic cardiomyopathy[J]. Chinese Journal of Cardiovascular Rehabilitation, 2024, 33(1): 94−97.
[41] 王道鑫, 张添光, 缪朝玉. 血管内皮细胞线粒体氧化应激与动脉粥样硬化[J]. 药学实践与服务,2023,41(6):329−334,388. [WANG Daoxin, ZHANG Tianguang, MIAO Chaoyu. Mitochondrial oxidative stress in vascular endothelial cell and atherosclerosis[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service,2023,41(6):329−334,388.] WANG Daoxin, ZHANG Tianguang, MIAO Chaoyu. Mitochondrial oxidative stress in vascular endothelial cell and atherosclerosis[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice and Service, 2023, 41(6): 329−334,388.
[42] CHISTIAKOV D A, SHKURAT T P, MELNICHENKO A A, et al. The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiovascular disease:A brief review[J]. Annals of Medicine,2018,50(2):121−127. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2017.1417631
[43] BAYEVA M, GHEORGHIADE M, ARDEHALI H. Mitochondria as a therapeutic target in heart failure[J]. Journal of the American College of Cardiology,2013,61(6):599−610. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.08.1021
[44] WANG J, ZHOU H. Mitochondrial quality control mechanisms as molecular targets in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B,2020,10(10):1866−1879. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.03.004
[45] DUBOIS-DERUY E, PEUGNET V, TURKIEH A, et al. Oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Antioxidants,2020,9(9):864−864. doi: 10.3390/antiox9090864
[46] 王雪梅, 王怡婷, 曹莹, 等. 线粒体功能调控动脉粥样硬化的研究进展[J]. 心血管病学进展,2022,43(11):1016−1020,1049. [WANG X M, WANG Y T, CAO Y, et al. Atherosclerosis mediated by mitochondrial function[J]. Advances in Cardiovascular Diseases,2022,43(11):1016−1020,1049.] WANG X M, WANG Y T, CAO Y, et al. Atherosclerosis mediated by mitochondrial function[J]. Advances in Cardiovascular Diseases, 2022, 43(11): 1016−1020,1049.
[47] 楚魏, 马洪月, 朴钟源, 等. 线粒体动力学对肿瘤、神经、心血管系统疾病的影响及中药干预[J]. 中医学报,2023,38(11):2274−2281. [CHU W, MA H Y, PU Z Y, et al. Effects of mitochondrial dynamics on tumors, neurological and cardiovascular diseases and research progress of Chinese medicine intervention[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine,2023,38(11):2274−2281.] CHU W, MA H Y, PU Z Y, et al. Effects of mitochondrial dynamics on tumors, neurological and cardiovascular diseases and research progress of Chinese medicine intervention[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine, 2023, 38(11): 2274−2281.
[48] PERNAS L, SCORRANO L. Mito-Morphosis:Mitochondrial fusion, fission, and cristae remodeling as key mediators of cellular function [M]. Julius D. Annual Review of Physiology, 2016:505−531.
[49] GIACOMELLO M, PYAKUREL A, GLYTSOU C, et al. The cell biology of mitochondrial membrane dynamics[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology,2020,21(4):204−224. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0210-7
[50] TILOKANI L, NAGASHIMA S, PAUPE V, et al. Mitochondrial dynamics:overview of molecular mechanisms [M]. Garone C, Minczuk M. Mitochondrial Diseases, 2018:341−360.
[51] ADEBAYO M, SINGH S, SINGH A P, et al. Mitochondrial fusion and fission:The fine-tune balance for cellular homeostasis[J]. [J]. FASEB Journal,2021,35(06):e21620.
[52] JEZEK J, COOPER K F, STRICH R. Reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial dynamics:The yin and yang of mitochondrial dysfunction and cancer progression[J]. Antioxidants,2018,7(1):13. doi: 10.3390/antiox7010013
[53] PLETJUSHKINA O Y, LYAMZAEV K G, POPOVA E N, et al. Effect of oxidative stress on dynamics of mitochondrial reticulum[J]. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Bioenergetics,2006,1757(5−6):518−524. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2006.03.018
[54] CHEN Y, CHEN J J, SUN X X, et al. Evaluation of the neuroprotective effect of EGCG:A potential mechanism of mitochondrial dysfunction and mitochondrial dynamics after subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. Food & Function,2018,9(12):6350−6360.
[55] 舒周伍. EGCG对人主动脉平滑肌细胞增殖的影响及其机制研究[D]. 汕头:汕头大学, 2014. [SHU Z W. Effect and Mechanisms of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate on the Proliferation of Human Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells[D]. Shantou:Shantou University, 2014.] SHU Z W. Effect and Mechanisms of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate on the Proliferation of Human Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells[D]. Shantou: Shantou University, 2014.
[56] 连婷, 张瑞君, 熊晓兰, 等. 线粒体通透性转换孔在锌缺乏模型大鼠心肌缺血/再灌注损伤中的作用[J]. 基础医学与临床,2022,42(3):389−394. [LIAN T, ZHANG R J, XIONG X L, et al. Role of mitochondrial permeability transition pore in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat models with zinc deficiency[J]. Basic and Clinical Medicine,2022,42(3):389−394.] LIAN T, ZHANG R J, XIONG X L, et al. Role of mitochondrial permeability transition pore in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat models with zinc deficiency[J]. Basic and Clinical Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 389−394.
[57] 向仕钊, 张萌, 江波. 线粒体膜通透性转换孔对缺血/再灌注损伤心肌细胞的影响[J]. 中国分子心脏病学杂志,2016,16(6):1940−1944. [XIANG Shizhao, ZHANG Meng, JIANG Bo. The affection from mitochondrial permeability transition pore on cardiomyocytes induced-by ischemia reperfusion injury[J]. Molecular Cardiology of China,2016,16(6):1940−1944.] XIANG Shizhao, ZHANG Meng, JIANG Bo. The affection from mitochondrial permeability transition pore on cardiomyocytes induced-by ischemia reperfusion injury[J]. Molecular Cardiology of China, 2016, 16(6): 1940−1944.
[58] 金曼, 吴娟, 黎笔熙. 线粒体膜通透性转换孔在细胞凋亡中的作用[J]. 医学研究生学报,2019,32(11):1222−1227. [JIN Man, WU Juan, LI Bixi. The role of mitochondrial membrane permeability transition pore in apoptosis[J]. Journal of Medical Research & Combat Trauma,2019,32(11):1222−1227.] JIN Man, WU Juan, LI Bixi. The role of mitochondrial membrane permeability transition pore in apoptosis[J]. Journal of Medical Research & Combat Trauma, 2019, 32(11): 1222−1227.
[59] 何芸岸, 廖显军, 张艳, 等. 细胞色素C功能及应用的研究进展[J]. 华西药学杂志,2023,38(4):464−467. [HE Yun'an, LIAO Xianjun, ZHANG Yan, et al. Research progress on function and application of cytochrome C[J]. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,2023,38(4):464−467.] HE Yun'an, LIAO Xianjun, ZHANG Yan, et al. Research progress on function and application of cytochrome C[J]. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2023, 38(4): 464−467.
[60] MA H J, HUANG X L, LI Q, et al. ATP-dependent potassium channels and mitochondrial permeability transition pores play roles in the cardioprotection of theaflavin in young rat[J]. Journal of Physiological Sciences,2011,61(4):337−342. doi: 10.1007/s12576-011-0148-9
[61] ZHOU X L, LIANG L W, ZHAO Y, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate ameliorates angiotensin II-Induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells through the activation of Nrf2/Caspase-3 signaling[J]. Journal of vascular research,2017,54(5):299−308. doi: 10.1159/000479873
[62] 郑曦, 陈世蓉, 熊挺淋, 等. 乌头提取物通过调控蛋白激酶C信号通路对心力衰竭大鼠钙转运及心肌线粒体呼吸功能的影响[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志,2023,18(1):62−67. [ZHENG Xi, CHEN Shirong, XIONG Tinglin, et al. Effects of Aconitum carmichaelii extract on calcium transport and myocardial mitochondrial respiratory function in rats with heart failure by regulating pkc signaling pathway[J]. World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine,2023,18(1):62−67.] ZHENG Xi, CHEN Shirong, XIONG Tinglin, et al. Effects of Aconitum carmichaelii extract on calcium transport and myocardial mitochondrial respiratory function in rats with heart failure by regulating pkc signaling pathway[J]. World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2023, 18(1): 62−67.
[63] MARCHI S, PATERGNANI S, MISSIROLI S, et al. Mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum calcium homeostasis and cell death[J]. Cell Calcium,2018,69:62−72. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2017.05.003
[64] LI M G, MA G X, HAN L, et al. Regulating effect of tea polyphenols on endothelin, intracellular calcium concentration, and mitochondrial membrane potential in vascular endothelial cells injured by angiotensin II[J]. Annals of Vascular Surgery,2014,28(4):1016−1022. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2013.11.003
[65] CHEN W C, HSIEH S R, CHIU C H, et al. Molecular identification for epigallocatechin-3-gallate-mediated antioxidant intervention on the H2O2-induced oxidative stress in H9c2 rat cardiomyoblasts[J]. Journal of Biomedical Science,2014,21(1):56. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-21-56
[66] DEVIKA P T, PRINCE P S M. (-)Epigallocatechingallate protects the mitochondria against the deleterious effects of lipids, calcium and adenosine triphosphate in isoproterenol induced myocardial infarcted male Wistar rats[J]. Journal of Applied Toxicology,2008,28(8):938−944. doi: 10.1002/jat.1357
[67] 吕宇璇, 倪艳辉, 刘立天, 等. 线粒体DNA对心血管疾病作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2023,25(10):1112−1114. [LÜ Y X, NI Y H, LIU L T, et al. Research progress on the mechanism of mitochondrial DNA in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Geriatric Heart Brain and Vessel Diseases,2023,25(10):1112−1114.] LÜ Y X, NI Y H, LIU L T, et al. Research progress on the mechanism of mitochondrial DNA in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Geriatric Heart Brain and Vessel Diseases, 2023, 25(10): 1112−1114.
[68] 孙伟, 王倩怡, 张璐莎, 等. 线粒体DNA与心肌梗死后的炎症反应[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志,2022,14(10):1267−1270. [SUN W, WANG Q Y, ZHANG L S, et al. Mitochondrial DNA and inflammatory response after myocardial infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Evidence-Based Cardiovascular Medicine,2022,14(10):1267−1270.] SUN W, WANG Q Y, ZHANG L S, et al. Mitochondrial DNA and inflammatory response after myocardial infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Evidence-Based Cardiovascular Medicine, 2022, 14(10): 1267−1270.
[69] 周园媛, 杨莹. 线粒体DNA变异与2型糖尿病发生的研究进展[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2023,15(1):66−70. [ZHOU Yuanyuan, YANG Ying. Advances of mitochondrial DNA variation in type2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chinese Journal of the Frontiers of Medical Science (Electronic Version),2023,15(1):66−70.] ZHOU Yuanyuan, YANG Ying. Advances of mitochondrial DNA variation in type2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Chinese Journal of the Frontiers of Medical Science (Electronic Version), 2023, 15(1): 66−70.
[70] CHEN D D, DONG Y G, LIU D, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate attenuates cardiac hypertrophy in hypertensive rats in part by modulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signals[J]. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology,2009,36(9):925−932. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2009.05173.x
[71] COJOCARU K A, LUCHIAN I, GORIUC A, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and therapeutic strategies in diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease[J]. Antioxidants,2023,12(3):658. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030658
[72] DADSENA S, KING L E, GARCIA-SAEZ A J. Apoptosis regulation at the mitochondria membrane level[J]. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Biomembranes,2021,1863(12):183716. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2021.183716
[73] 杨涛, 费振海, 钟兴明. Caspase家族与细胞凋亡的研究进展[J]. 浙江医学,2018,40(18):2083−2087,2091. [YANG T, FEI Z H, ZHONG X M. Research progress of Caspase family and apoptosis[J]. Zhejiang Medical Journal,2018,40(18):2083−2087,2091.] doi: 10.12056/j.issn.1006-2785.2018.40.18.2017-950 YANG T, FEI Z H, ZHONG X M. Research progress of Caspase family and apoptosis[J]. Zhejiang Medical Journal, 2018, 40(18): 2083−2087,2091. doi: 10.12056/j.issn.1006-2785.2018.40.18.2017-950
[74] LOSSI L. The concept of intrinsic versus extrinsic apoptosis[J]. Biochemical Journal,2022,479(3):357−384. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20210854
[75] 李帅, 张炳东. 细胞凋亡途径的研究进展[J]. 山东医药,2017,57(37):103−106. [LI S, ZHANG B D. Advances in the study of apoptosis pathways[J]. Shandong Medical Journal,2017,57(37):103−106.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2017.37.036 LI S, ZHANG B D. Advances in the study of apoptosis pathways[J]. Shandong Medical Journal, 2017, 57(37): 103−106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2017.37.036
[76] 向军军, 赖菁菁, 胡跃强. 近3年线粒体介导细胞凋亡的研究进展[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2016,14(13):1497−1499. [XIANG J J, LAI J J, HU Y Q. Research progress of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in recent 3 years[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Disease,2016,14(13):1497−1499.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1349.2016.13.018 XIANG J J, LAI J J, HU Y Q. Research progress of mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in recent 3 years[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Disease, 2016, 14(13): 1497−1499. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1349.2016.13.018
[77] 赵微, 王帅. 线粒体相关内质网膜-细胞凋亡途径在动脉粥样硬化发病中的作用[J]. 中医学报,2023,38(11):2287−2292. [ZHAO W, WANG S. Research progress on mitochondrial associated endoplasmic reticulum membrances-apoptosis pathway in atherosclerosis[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine,2023,38(11):2287−2292.] ZHAO W, WANG S. Research progress on mitochondrial associated endoplasmic reticulum membrances-apoptosis pathway in atherosclerosis[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine, 2023, 38(11): 2287−2292.
[78] DAVIDSON, SEAN M. Mitochondrial and mitochondrial-independent pathways of myocardial cell death during ischaemia and reperfusion injury[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine,2020,24(7):3795−3806. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15127
[79] 梁炜杰, 张耀伟, 王永佳, 等. 线粒体相关细胞凋亡诱导因子3通过调控STAT3信号通路影响结直肠癌细胞增殖与迁移[J]. 实用医学杂志,2022,38(7):821−827. [LIANG Weijie, ZHANG Yaowei, WANG Yongjia, et al. AIFM3 interferes the proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells by regulating STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. The Journal of Practical Medicine,2022,38(7):821−827.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2022.07.009 LIANG Weijie, ZHANG Yaowei, WANG Yongjia, et al. AIFM3 interferes the proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells by regulating STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. The Journal of Practical Medicine, 2022, 38(7): 821−827. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2022.07.009
[80] 高苑, 刘振兵. 细胞凋亡在心肌缺血再灌注损伤中的研究进展[J]. 临床医学研究与实践,2023,8(14):195−198. [GAO Yuan, LIU Zhenbing. Research progress of apoptosis in myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury[J]. Clinical Research and Practice,2023,8(14):195−198.] GAO Yuan, LIU Zhenbing. Research progress of apoptosis in myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury[J]. Clinical Research and Practice, 2023, 8(14): 195−198.
[81] BOCK F J, TAIT S W G. Mitochondria as multifaceted regulators of cell death[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology,2020,21(2):85−100. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0173-8
[82] VAKIFAHMETOGLU-NORBERG H, OUCHIDA A T, NORBERG E. The role of mitochondria in metabolism and cell death[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2017,482(3):426−431. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.11.088
[83] ADIKESAVAN G, VINAYAGAM M M, ABDULRAHMAN L A, et al. (-)-Epigallocatechin-gallate (EGCG) stabilize the mitochondrial enzymes and inhibits the apoptosis in cigarette smoke-induced myocardial dysfunction in rats[J]. Molecular Biology Reports,2013,40(12):6533−6545. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2673-5
[84] HIRAI M, HOTTA Y, ISHIKAWA N, et al. Protective effects of EGCg or GCg, a green tea catechin epimer, against postischemic myocardial dysfunction in guinea-pig hearts[J]. Life Sciences,2007,80(11):1020−1032. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2006.11.032
[85] KANWAR J, TASKEEN M, MOHAMMAD I, et al. Recent advances on tea polyphenols[J]. Frontiers in bioscience (Elite edition),2012,4(1):111−131.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



