Effects of Different Pretreatment on Curcumin-mediated Photodynamic Inactivation and Preservation of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea)
-
摘要: 为了阐明不同预处理方式对姜黄素介导的水产品光动力灭活(photodynamic inactivation,PDI)保鲜效果的影响,本研究首次系统对比研究了喷洒姜黄素水溶液后再孵育、喷洒后不孵育、浸泡后再孵育和浸泡后不孵育,即4种不同预处理方式下对大黄鱼(Larimichthys crocea)的PDI保鲜效果。结果表明:在10 mmol/L姜黄素水溶液中浸泡再孵育30 min的预处理方式下对大黄鱼进行PDI处理,相比于其它3种预处理方式,其经4 ℃冷藏8 d后大黄鱼保持了较高的感官可接受度,又能够有效保持冷藏大黄鱼的色泽。同时,该处理条件下大黄鱼的细菌总数(TVC)、pH和总挥发性盐基氮(TVB-N)含量最小,分别为5.82±0.07 lg CFU/g、7.07±0.02和17.45±0.35 mg/100 g,说明此预处理方式可通过有效抑制TVC、pH和TVB-N含量的增加,高效保持冷藏大黄鱼品质,进而延长其货架期。因此,采用姜黄素水溶液浸泡再孵育的水产品预处理方式,是获得姜黄素介导的高效PDI保鲜的重要前提。Abstract: In order to investigate the effect of different pretreatment methods on the preservation efficacy of curcumin-mediated photodynamic inactivation (PDI) for aquatic products, four pretreatment methods were evaluated for their PDI preservation effect on Larimichthys crocea, including incubation after spraying curcumin solution, no incubation after spraying, incubation after soaking, and no incubation after soaking. The results demonstrated that PDI treatment was performed on L. crocea after soaking in the curcumin aqueous solution of 10 mmol/L and incubating for 30 min, resulted in higher sensory acceptability compared to the other three pretreatment methods after 8 days of refrigeration at 4 ℃. Additionally, this treatment effectively preserved the color of refrigerated L. crocea. Meanwhile, the total viable count (TVC), pH, and total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) content of L. crocea under this treatment were the smallest, which were 5.82±0.07 lg CFU/g, 7.07±0.02, and 17.45±0.35 mg/100 g, respectively. This pretreatment method could effectively inhibit the increase of TVC, pH and TVB-N content, thereby preserving the quality of refrigerated L. crocea and extending the shelf life. Therefore, the pretreatment method of immersion followed by incubation in curcumin aqueous solution was an essential prerequisite for obtaining efficient PDI preservation of aquatic products mediated by curcumin.
-
Keywords:
- curcumin /
- photodynamic inactivation /
- pretreatment method /
- Larimichthys crocea /
- cold storage
-
大黄鱼(Larimichthys crocea)色泽金黄、肉质鲜嫩,富含蛋白质、二十二碳六烯酸(DHA)、二十碳五烯酸(EPA)和维生素,是我国十分重要的高产量海洋经济鱼类[1]。目前,大黄鱼主要以冰鲜、冷冻贮藏和腌制加工为主[2−3]。但大黄鱼富含水分和营养物质,极易在加工、贮藏及流通过程中出现腐败变质,不仅影响风味与口感,还会严重影响食用安全性。因此,高效控制大黄鱼体微生物对保证其新鲜度和食用安全性具有重要意义。光动力灭活(photodynamic inactivation,PDI)作为一种新型、环保的非热杀菌技术,具有广谱灭活、不产生耐药性等诸多优势[4]。其利用光激发后的激发态光敏剂敏化周围氧气或进行能量传递而产生单线态氧(1O2)或活性氧物种(·OH、O2−·、H2O2),氧化破坏微生物的蛋白质、脂质及核酸等生物分子而起到灭活作用[5]。
在众多光敏剂中,姜黄素(curcumin)作为一种绿色安全的天然多酚类光敏剂,近年来在水产品PDI领域颇具应用研究前景[6]。目前,基于姜黄素介导的水产品PDI保鲜研究,主要集中在PDI工艺条件的优化(姜黄素工作液浓度、工作液与水产品共孵育时间、辐照时间),不同水产品的PDI保鲜效果、目标食源性致病菌PDI效果及机制,以及PDI处理后水产品的新鲜度监测等方面[7−17]。如刘丽芳等[16]发现,通过浸泡孵育方式,在姜黄素浓度50 μmol/L、超声波功率600 W及声光动力处理时间60 min的条件下,对牡蛎的保鲜效果明显。林以琳等[15]研究发现,通过喷洒30 mg/L姜黄素水溶液,避光孵育40 min、LED照射40 min,对南美白对虾起到了较好的PDI杀菌效果。这些已报道的PDI研究,为水产品非热杀菌技术提供了重要的理论与光动力工艺参数指导。另外,适当的预处理方式和PDI条件可以显著提高水产品的PDI保鲜效果。这包括优化预处理条件,如光敏剂浓度、光照时间,以及添加协同增效剂与处理技术等。然而,本文作者发现,上述工作在水产品的PDI预处理过程中,姜黄素工作液对水产品的处理方式有较大不同,主要为喷洒和浸泡两种预处理方式,两者均是通过让姜黄素与大黄鱼表面接触,再进行PDI保鲜处理。但它们的主要差异在于鱼体表面的姜黄素覆盖方式和附着量。此外,本文作者前期预实验发现,不同预处理方式对后续水产品冷藏保鲜效果有较大影响。
目前,针对水产品的不同PDI预处理方式,特别是姜黄素工作液喷洒后直接孵育或喷洒后不孵育、浸泡后孵育或浸泡后不孵育等预处理方式对姜黄素介导的水产品PDI保鲜效果的对比影响研究,还未见文献报道。基于此,本研究选取大黄鱼(Larimichthys crocea)作为模式水产品,重点探究姜黄素水溶液的喷洒和浸泡预处理方式对PDI保鲜效果的影响。具体通过测定PDI处理后冷藏大黄鱼的感官评分、色差、菌落总数(TVC)、pH和挥发性盐基氮(TVB-N)含量等典型新鲜度指标,探究预处理方式在姜黄素介导的PDI保鲜中的重要作用和必要性。旨在为指导不同水产品的PDI工艺优化、提升PDI保鲜效果提供重要参考。
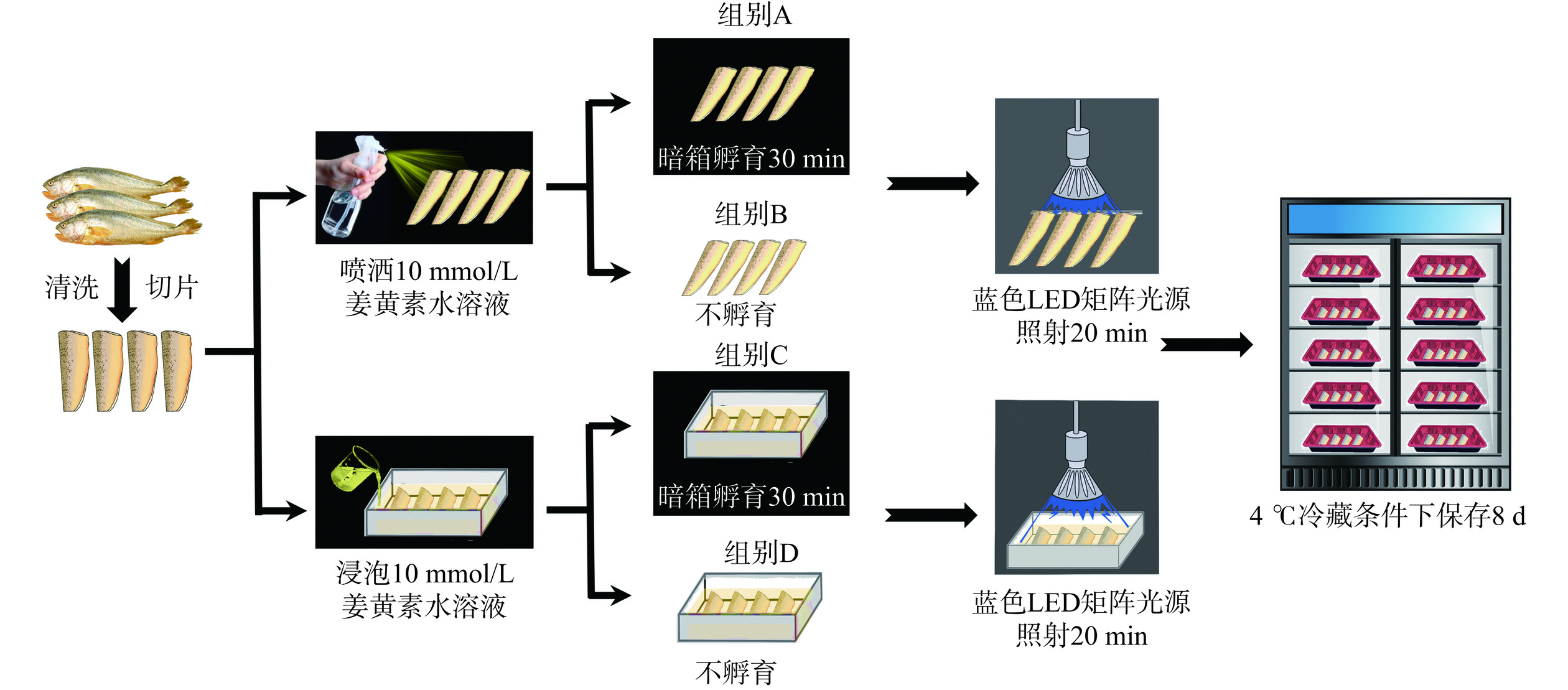
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大黄鱼 采购于浙江舟山国际水产城,加冰保鲜处理,随机取15条,质量为374.82±11.83 g,体长为31.43±0.86 cm;姜黄素(纯度98%) 安徽泽升科技股份有限公司;轻质氧化镁(纯度98.5%) 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;平板计数琼脂培养基 青岛高科技工业园海博生物技术有限公司;本研究所用的化学试剂均为分析级试剂,实验用水均为超纯水。
蓝光LED矩阵光源(波长450±10 nm,功率12 W) 中山芝米光源有限公司;CS-210精密色差仪 杭州彩谱科技有限公司;FE28FiveEasy Plus pH计 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;KDN-19A挥发性盐基氮测定仪 上海纤检测仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 大黄鱼前处理
随机抽取的15条冰鲜大黄鱼,平均分成五组,每组3条。除去大黄鱼的鱼鳞、鱼头以及内脏,剔除主骨后,切成两大片大黄鱼鱼片试样,用去离子水冲洗、沥干后备用。
1.2.2 PDI预处理方式
使用超纯水配制姜黄素水溶液(10 mmol/L),避光备用。其中,喷洒组:使用35 mL的母液均匀喷洒在大黄鱼表面及切面。浸泡组:1:1的料液比浸泡在浓度为10 mmol/L的姜黄素溶液中。不同PDI预处理方式见图1,即A组:避光下,将姜黄素水溶液喷洒于大黄鱼体表面,然后避光孵育30 min。B组:避光下,将姜黄素水溶液喷洒于大黄鱼体表面,不孵育。C组:避光下,将大黄鱼浸泡于姜黄素水溶液中,避光孵育30 min。D组:避光下,将大黄鱼浸泡于姜黄素水溶液中,不孵育。同时,设置对照组(Control):不对大黄鱼进行光敏剂孵育或是光照处理,只用超纯水洗净后,进行对照实验。
1.2.3 PDI过程
将上述不同预处理后的大黄鱼置于蓝光LED光源下,进行20 min辐照处理(图1)。辐照结束后,将大黄鱼置于已灭菌的塑料生鲜保鲜盒中,密封袋密封后置于4 °C冰箱冷藏保存。并在0、2、4、6、8 d进行采样分析,检测TVC、色差、pH和TVB-N含量等典型新鲜度指标,并对大黄鱼进行感官评价。
1.2.4 TVC检测
参考GB 4789.2-2022《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定》方法,测定平板计数琼脂的TVC,结果以lg CFU/g表示。即将10.00±0.01 g大黄鱼肉与90 mL生理盐水(0.85%)混合,然后使用数字高速均质机在8000 r/min均质30 s。将得到的均质液在0.85% NaCl(1 mL均质液或稀释的均质液+9 mL NaCl溶液)中连续稀释,将每个梯度1 mL溶液置于平板计数琼脂上。在培养箱中在30 ℃下培养72 h后,选择具有30~300个菌落的培养皿进行计数和统计。
1.2.5 感官评价
参考唐智鹏等[17]感官评价方法并加以修改,评价PDI处理后大黄鱼的颜色、气味、质地、形态和黏液等感官特征,最后取各指标相加后的平均得分值。评估小组由8名来自水产品实验室的专业从事感官训练的工作人员组成(男女比例1:1,年龄区间20~40岁)。感官评价标准如表1所示,喜好得分为每项10分,范围为0~10分。其中,7分作为人类消费可接受的新鲜度下限。
表 1 大黄鱼感官评价标准Table 1. Sensory evaluation criteria of L. crocea感官指标 感官评分 9~10分 7~8分 5~6分 3~4分 0~2分 颜色 非常明亮,有金色的光泽 明亮,呈黄色 轻微暗淡,淡黄色 暗淡的,非常淡的黄色 非常暗淡,白色 气味 气味清新,海水鱼味浓郁 气味清新,腥味较弱 气味正常,腥味稍强 腥味明显 腥味较重,腐败味明显 质地 紧密且有弹性 柔软但有弹性 稍软且弹性较小 柔软且没有弹性 完全松散 形态 鱼完好无损 相对完整 较少部分松散 比较松散 皮肉分离 黏液 光滑无黏液 黏液稀薄 黏液较多 黏液多且浑浊 黏液多且很浓稠 1.2.6 色差测定
使用色差仪测定冷藏后大黄鱼皮肤和鱼肉的颜色差,记录亮度(L*)、红绿色度(a*)和黄蓝色度(b*)。白度(W)采用如下公式进行计算:
W=100−√(100−L∗)2+a∗2+b∗2 1.2.7 pH测定
参考GB 5009.237-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品pH值的测定》方法测定pH。即称取10.00 g大黄鱼鱼肉,搅碎后置于烧杯中,加入90 mL新煮沸后的冷却水,高速均质2 min,在4 ℃冰水浴中放置30 min。保留上清液,使用pH计测定其pH。
1.2.8 TVB-N含量测定
参考GB 5009.228-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定》方法,采用凯氏定氮法测定TVB-N值。即取10.00 g大黄鱼鱼肉,与75 mL超纯去离子水混合,使得样品在样液中均匀分散。然后置于冰水浴30 min后,加入1 g氧化镁。随后使用全自动凯氏定氮分析仪,按照预设好的程序进行测定。TVB-N含量按以下公式计算,结果以mg/100 g表示。
TVB-N(mg/100g)=(V1−V2)×C×14m×100 式中,V1和V2为样品组和空白组滴定所消耗的盐酸体积,mL;C为盐酸标准滴定溶液的浓度,mol/L;m为样品质量,g。
1.3 数据处理
每组测试样品设置3个平行,并进行3次独立重复实验后取平均值。通过Origin 8.5和SPSS 21.0对数据进行统计分析及作图;通过SPSS 21.0软件进行单因素方差分析,P<0.05表示具有显著性差异,且图中肩标不同小写字母表示相同贮藏时间点不同处理组间差异显著(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同预处理方式对大黄鱼TVC的影响
水产品富含多种营养物质,如非蛋白氮(NPN)、多不饱和脂肪酸以及维生素等,且水分含量较高,极易因腐败细菌寄生代谢而引起变质[18]。因此,通过对比5组大黄鱼在4 ℃冷藏过程中TVC值的变化情况,以直接评价不同预处理方式对大黄鱼的PDI效果影响,结果如图2所示。
从图2可以看出,贮藏第0 d,对照组的TVC值为4.08±0.04 lg CFU/g,而4个PDI处理组的细菌总数均有显著下降(P<0.05)。但其中,B组和D组的初始TVC值相对较高,分别为3.67±0.01 lg CFU/g和3.48±0.03 lg CFU/g。而A组和C组的初始TVC值均显著降低(P<0.05),分别为3.38±0.04 lg CFU/g和3.29±0.03 lg CFU/g,这可能是由于在对大黄鱼进行不同的前处理后,为保证大黄鱼的新鲜度,置于4 ℃冰箱暂时储存一定的时间,此时,组别A和C的孵育处理,使得姜黄素更好地与大黄鱼表面的微生物接触,从而提高PDI处理的杀菌效果。随着贮藏时间的延长,5组的TVC值呈现差异性升高。在贮藏第8 d,除对照组外,其他所有组别的TVC值均未超过生鲜鱼类可食用的最大限度值7 lg CFU/g[19]。这表明,4种不同PDI预处理方式对大黄鱼均有不同程度的PDI效果。但其中,B组TVC值最高,达到6.52±0.07 lg CFU/g。而C组TVC值为5.82±0.07 lg CFU/g,显著低于其它3组(P<0.05)。可见,大黄鱼浸泡于光敏剂中孵育30 min预处理后再进行蓝光LED光源辐照,能更好地抑制其贮藏过程中微生物的繁殖。
2.2 不同预处理方式对大黄鱼感官评分的影响
感官评分是鱼类品质新鲜度的重要参数[20]。因此,评价了不同PDI预处理方式对大黄鱼感官品质的影响,对比结果见图3。
从图3雷达网对比图可以看出,对照组和4个不同预处理组在第0 d所有参数的初始得分都在8分以上,说明随机抽取的大黄鱼样本品质较高。随着贮藏时间延长,5组大黄鱼感官指标呈现不同程度的降低。第2 d,对照组的感官评分为6.95(图3B),小于7分,因此认为该对照组样本不可食用。A组、B组、C组和D组的感官评分分别为7.925、7.625、8.675和8.15。贮藏第4 d,B组感官评分为5.83分(图3C),已远小于7分,鱼体表面光泽减弱、腥味加强、鱼体变软且弹性接近消失,即该样本也被视为不可食用;并且,除C组外,其余各组的感官评分均小于7分(图3C)。此外,与其他4组相比,C组在储存4 d内的感官评分明显呈缓慢下降的趋势,储存第6 d的感官评分才开始低于7分(图3D)。感官评价结果表明:C组,即大黄鱼浸泡于姜黄素水溶液中孵育30 min预处理后再进行蓝光LED光源辐照,在贮藏期间对大黄鱼外观、颜色和肌肉组织等感官指标具有一定的保护作用,可较好保持冷藏大黄鱼品质。
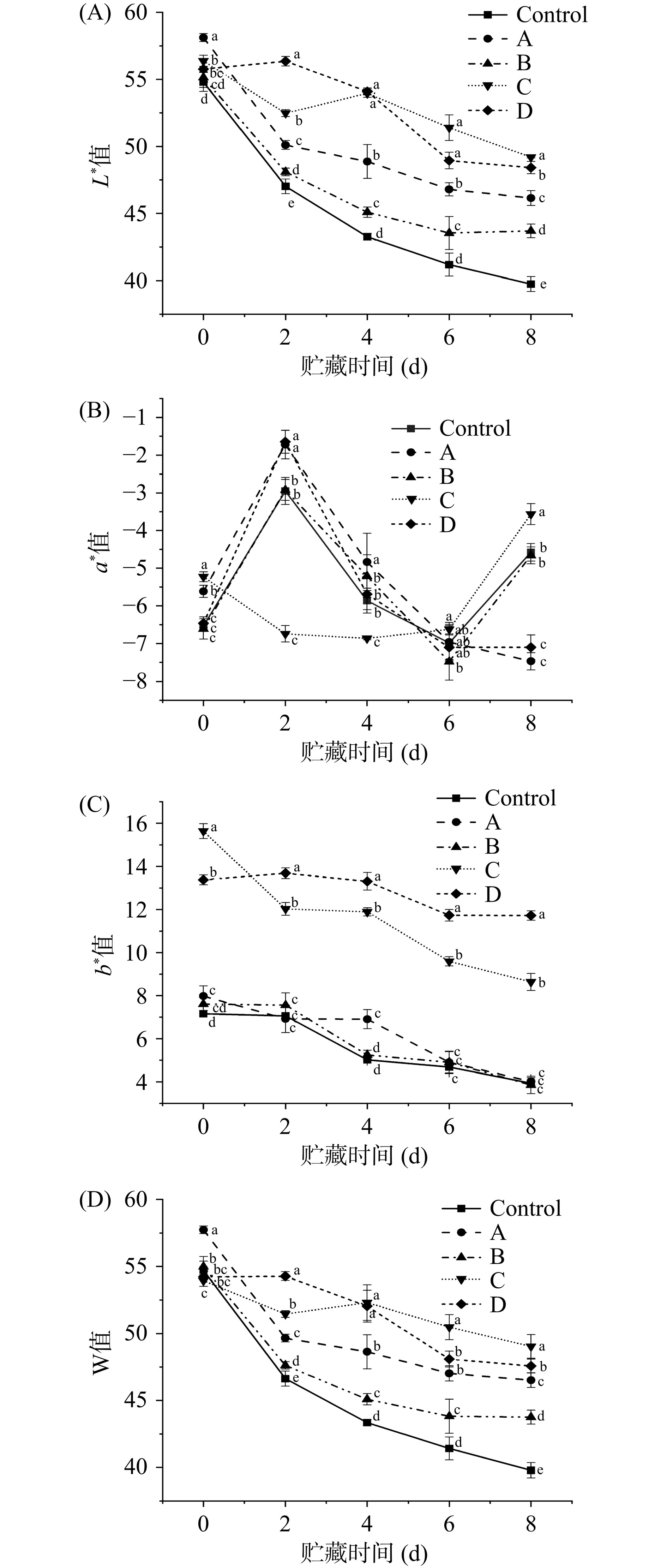
2.3 不同预处理方式对大黄鱼色差的影响
2.3.1 鱼体表面色差变化
色泽是水产品新鲜度的直观指标[21]。因此,测定并计算了不同PDI预处理方式对大黄鱼鱼体色泽的影响,结果如图4所示。
如图4所示,总体趋势而言,随着贮藏时间延长,各组大黄鱼鱼体的L*和b*值均降低,a*值变化无统计学意义。其中,贮藏第4 d,C组大黄鱼试样的L*值出现升高(图4A),这是由于大黄鱼经浸泡孵育预处理后,使得鱼表皮上姜黄素继续残留并可能扩散至鱼体细胞中。此外,鱼体会随着贮藏时间延长而逐渐变质,造成持水力下降,水分的流失使大黄鱼表面游离水含量增加,进而增加了光反射[22]。另外,在贮藏后期对照组和4个处理组的b*值下降变缓,其变化趋势与Hong等[23]报道的结果相似,即颜色损失可能是因为蛋白质和脂肪的氧化变质、鱼肉持水力下降。这也可以解释W值和L*值下降的原因。但是,与对照组相比,经过PDI处理后的大黄鱼鱼体的L*值和W值,呈现明显的延缓下降趋势。此外,A组初始L*值较于其它3组显著增加(P<0.05),这是由于A组的预处理方式是喷洒姜黄素并孵育后再光照,该方式使姜黄素充分覆盖在大黄鱼鱼体表面而致初始L*值较高。最后,贮藏8 d后,C组和D组的L*、b*和W值均显著高于A组和B组(P<0.05)。上述鱼体表面色差变化结果表明,经姜黄素浸泡再孵育的PDI处理组具有更好的大黄鱼鱼体护色效果。
2.3.2 肌肉色差变化
与此同时,对不同PDI预处理方式下大黄鱼鱼肉的色泽也进行了对比分析,结果如图5所示。
总体趋势可以看出,随着冷藏时间延长,对照组和4个预处理组大黄鱼鱼肉的L*、a*和W值均降低,b*值升高。鱼肉颜色变化趋势与文献报道的冷藏大黄鱼颜色变化趋势相似[24]。在贮藏期间鱼肉颜色损失可归因于蛋白质溶解、汁液流失,以及脂肪和蛋白质氧化等因素,使得色素和肌肉蛋白结合,从而导致鱼肉颜色发生变化,与上述非姜黄素残留导致的鱼体表面色泽发生变化的原因相同[25−26]。其中,a*值下降的另一个原因可能是鱼肉中存在的Fe2+被氧化为Fe3+,导致黄绿色出现[27]。C组的a*值显著高于其它4组(P<0.05),表明经姜黄素水溶液浸泡再孵育的PDI处理组,可能表现出较好地降低蛋白质氧化的效果。而b*值变化主要归因于氧化引起的褐变反应。贮藏8 d后,C组的a*和L*值均显著高于A、B和D组(P<0.05),同时,与对照组相比差异显著(P<0.05),W值损失率仅为9.01%,而对照组和A、B、D组的W值损失率分别为19.39%、17.73%、17.54%和16.78%。由此可见,经姜黄素浸泡再孵育预处理方式的PDI过程,能够有效抑制贮藏期间大黄鱼脂肪氧化以及内源性和微生物酶的活性,进而有效维持大黄鱼鱼肉色泽和减缓大黄鱼腐败变质。
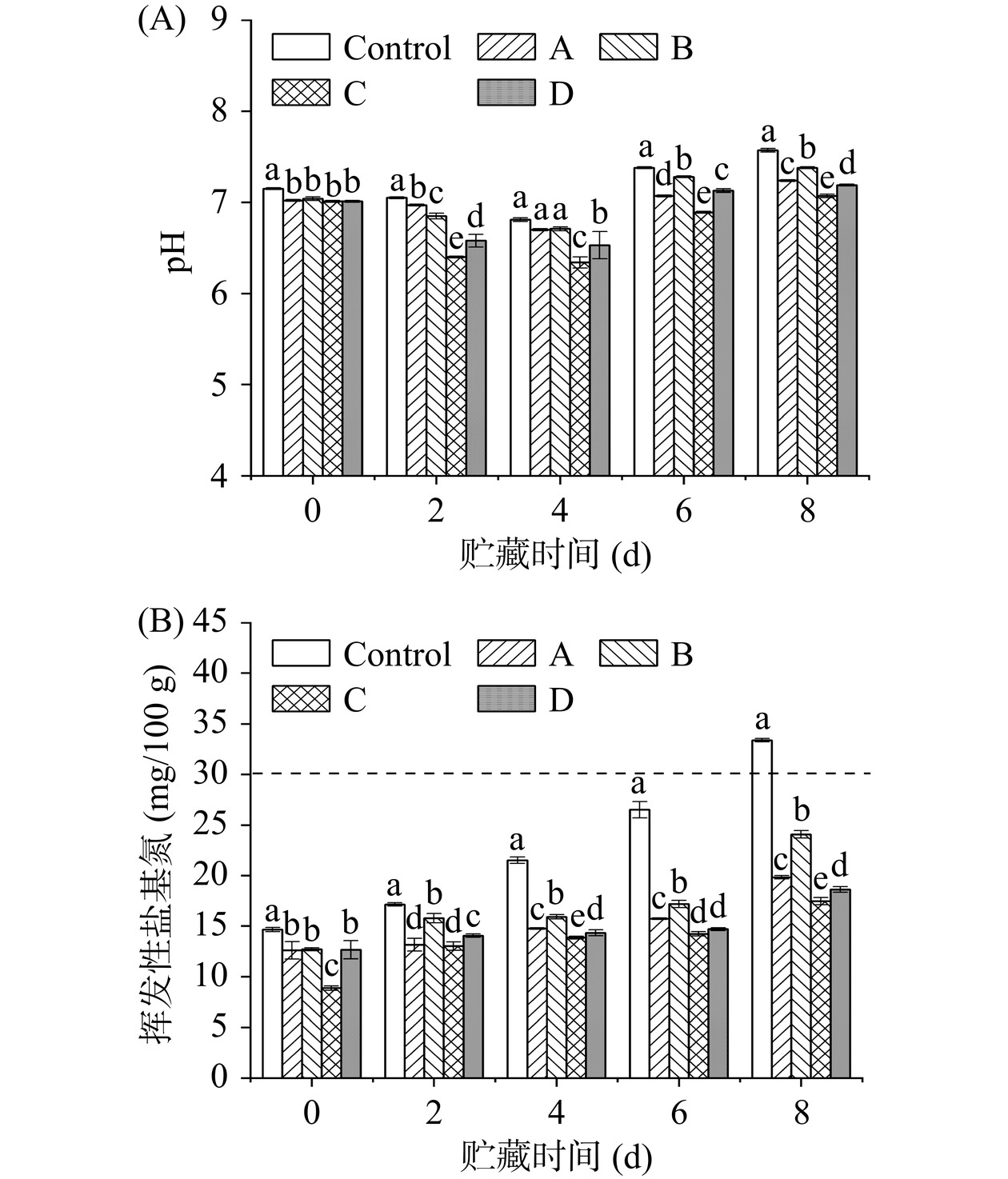
2.4 不同PDI预处理方式对大黄鱼pH和TVB-N含量的影响
测定了不同PDI预处理方式下冷藏大黄鱼的pH和TVB-N含量的变化情况,结果如图6所示。
从图6A可以看出,对照组及4组不同预处理方式的大黄鱼样品,在整个贮藏过程中鱼肉pH均呈现先降低后升高的趋势。5组大黄鱼样品的初始pH在7.00~7.15之间,表明大黄鱼新鲜度较好[28]。随着贮藏时间延长,pH逐渐降低,在第4 d达到最低值。该现象归因于大黄鱼鱼肉内部糖原分解产生的乳酸和ATP相关化合物分解的磷酸等酸类物质积累,导致pH逐渐下降[29]。但在贮藏后期,pH均逐渐升高,这主要与贮藏期间挥发性盐基氮含量增加,以及其它蛋白质在微生物作用下分解产生碱性化合物有关[30]。在整个贮藏期间,对照组的pH明显高于经过PDI处理的组别。贮藏第6 d,PDI处理组与对照组的pH差异显著(P<0.05);其中,A和C组的pH显著低于B组和D组(P<0.05)。此外,贮藏第2~8 d,C组的pH始终显著低于其他组别(P<0.05)。由此可见,经姜黄素水溶液浸泡再孵育预处理方式的PDI过程,可有效控制贮藏期间pH升高、保持鱼肉品质。
从图6B可以看出,大黄鱼的初始TVB-N含量均小于15 mg/100 g。从第2 d开始,对照组TVB-N含量显著高于PDI处理组(P<0.05)。随着贮藏时间延长,TVB-N含量呈上升趋势,这与水产品易受到微生物和酶促反应影响而分解产生含胺类物质有关[31]。贮藏第8 d,与对照组相比(TVB-N含量已超30 mg/100 g),PDI预处理组的大黄鱼TVB-N含量显著减少(P<0.05),虽然均已超过15 mg/100 g,但均未超过海水鱼的限量值30 mg/100 g[32],仍属于合格水产品。这表明,4组不同预处理方式下姜黄素介导的PDI过程,均能有效地抑制冷藏大黄鱼TVB-N含量的增加,进而不同程度延缓大黄鱼的腐败变质。但其中,B组TVB-N含量显著高于A、C和D组(P<0.05),达到了24.08±0.37 mg/100 g。而C组大黄鱼TVB-N含量最低,仅为17.74±0.35 mg/100 g。因此,C组预处理方式下的PDI过程,有效减少了大黄鱼冷藏过程中TVB-N形成,进而提高了PDI保鲜效果。此结果与上述新鲜度分析结果相符。
3. 结论
本研究采用姜黄素介导的光动力技术对大黄鱼进行非热杀菌后保鲜处理,与4 ℃贮藏条件下无任何处理的保鲜组作比较,研究了4种不同的预处理方式对大黄鱼保鲜过程中菌落总数和理化指标的影响。结果表明,大黄鱼经10 mmol/L姜黄素水溶液浸泡再孵育30 min的预处理方式、再进行蓝色LED光源辐照20 min的PDI处理过程,相比于喷洒再孵育、喷洒不孵育以及浸泡不孵育的3种预处理方式,能更好地维持冷藏大黄鱼的感官指标和色泽,控制TVC值、pH和TVB-N含量的上升,从而有效保持冷藏大黄鱼品质,进而延长其货架期。通过对比分析预处理方式对PDI保鲜效果的影响,为水产品高效PDI保鲜处理工艺提供重要参考和实验支撑。后续研究将重点围绕不同预处理方式下,姜黄素分子与鱼体的相互作用,如姜黄素与蛋白质或脂肪相互作用与PDI保鲜效果的作用关系,进一步探讨PDI保鲜过程中的作用机理,为水产品的PDI保鲜技术提供重要理论基础。
-
表 1 大黄鱼感官评价标准
Table 1 Sensory evaluation criteria of L. crocea
感官指标 感官评分 9~10分 7~8分 5~6分 3~4分 0~2分 颜色 非常明亮,有金色的光泽 明亮,呈黄色 轻微暗淡,淡黄色 暗淡的,非常淡的黄色 非常暗淡,白色 气味 气味清新,海水鱼味浓郁 气味清新,腥味较弱 气味正常,腥味稍强 腥味明显 腥味较重,腐败味明显 质地 紧密且有弹性 柔软但有弹性 稍软且弹性较小 柔软且没有弹性 完全松散 形态 鱼完好无损 相对完整 较少部分松散 比较松散 皮肉分离 黏液 光滑无黏液 黏液稀薄 黏液较多 黏液多且浑浊 黏液多且很浓稠 -
[1] 黄莉, 胡颜寓, 任中阳, 等. 腌制时间对大黄鱼鱼肉理化性质和烤制品品质的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2024,24(1):209−219. [HUANG L, HU Y Y, REN Z Y, et al. Effect of salting time on physicochemical properties and roasting quality of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea)[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2024,24(1):209−219.] HUANG L, HU Y Y, REN Z Y, et al. Effect of salting time on physicochemical properties and roasting quality of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea)[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2024, 24(1): 209−219.
[2] 饶从稳, 何亮银, 林志灯, 等. 大黄鱼的营养成分及其加工进展研究[J]. 食品科技,2023,48(12):113−118. [RAO C W, HE L Y, LIN Z D, et al. Research on nutritional composition and processing progress of Larimichthys crocea[J]. Food Science and Technology,2023,48(12):113−118.] RAO C W, HE L Y, LIN Z D, et al. Research on nutritional composition and processing progress of Larimichthys crocea[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2023, 48(12): 113−118.
[3] 刘迟, 李保国, 李亚伦, 等. 大黄鱼低温保鲜技术研究进展[J]. 包装与食品机械,2020,38(1):64−67. [LIU C, LI B G, LI Y L, et al. Progress in research of low temperature preservation technology of Pseudosciaena crocea[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery,2020,38(1):64−67.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1295.2020.01.014 LIU C, LI B G, LI Y L, et al. Progress in research of low temperature preservation technology of Pseudosciaena crocea[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery, 2020, 38(1): 64−67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1295.2020.01.014
[4] 檀茜倩, 麻冰, 玉王丹, 等. 光动力技术及其在生鲜食品保鲜中的应用研究进展[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2022,41(7):100−110. [TAN X Q, MA B, YU W D, et al. Research progress of photodynamic technology and its application in fresh food preservation[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2022,41(7):100−110.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2022.07.009 TAN X Q, MA B, YU W D, et al. Research progress of photodynamic technology and its application in fresh food preservation[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2022, 41(7): 100−110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2022.07.009
[5] 郑双芝, 林少玲, 曾绍校, 等. 光动力技术研究进展及其在食品工业中的应用前景[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2020,39(5):6−15. [ZHENG S Z, LIN S L, ZENG S X, et al. Photodynamic technology and its application in food industry[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2020,39(5):6−15.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2020.05.002 ZHENG S Z, LIN S L, ZENG S X, et al. Photodynamic technology and its application in food industry[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2020, 39(5): 6−15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2020.05.002
[6] 王晓迪, 郑双芝, 庞一, 等. 光动力技术对副溶血弧菌的灭活作用[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2024,50(3):119−125. [WANG X D, ZHENG S Z, PANG Y, et al. Inactivation effect of photodynamic technology on Vibrio parahaemolyticus[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2024,50(3):119−125.] WANG X D, ZHENG S Z, PANG Y, et al. Inactivation effect of photodynamic technology on Vibrio parahaemolyticus[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024, 50(3): 119−125.
[7] HUANG J M, CHEN B W, ZENG Q H, et al. Application of the curcumin-mediated photodynamic inactivation for preserving the storage quality of salmon contaminated with L. monocytogenes[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,359:129974. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129974
[8] GONG C, LI Y J, GAO R C, et al. Preservation of sturgeon using a photodynamic non-thermal disinfection technology mediated by curcumin[J]. Food Bioscience,2020,36:100594. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2020.100594
[9] SHERRILL W J, VINAYAK G, KIM M, et al. Antibacterial effect of 460 nm light-emitting diode in combination with riboflavin against Listeria monocytogenes on smoked salmon[J]. Food Control,2018,84:354−361. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.08.017
[10] 林以琳, 李世洋, 赖丹宁, 等. 姜黄素介导光动力减菌技术对缢蛏的保鲜效果[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(16):320−326. [LIN Y L, LI S Y, LAI D N, et al. Effects of curcumin-mediated of anti-microbial photodynamic technology on preservation of razor clam[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2020,36(16):320−326.] doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.16.038 LIN Y L, LI S Y, LAI D N, et al. Effects of curcumin-mediated of anti-microbial photodynamic technology on preservation of razor clam[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(16): 320−326. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.16.038
[11] WANG D H, ZHOU F, LAI D N, et al. Curcumin-mediated sono/photodynamic treatment preserved the quality of shrimp surimi and influenced its microbial community changes during refrigerated storage[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2021,78:105715. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105715
[12] 董冬丽, 林少玲, 孙崇臻, 等. 姜黄素光动力技术对水产食品霍利斯格里蒙特菌和溶藻弧菌的灭活作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(2):40−48. [DONG D L, LIN S L, SUN C Z, et al. Inactivation of curcumin photodynamic technology on Grimontia hollisae and Vibrio alginolyticus in aquatic food[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(2):40−48.] DONG D L, LIN S L, SUN C Z, et al. Inactivation of curcumin photodynamic technology on Grimontia hollisae and Vibrio alginolyticus in aquatic food[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22(2): 40−48.
[13] 檀利军, 胡钰梅, 陈博文, 等. 姜黄素介导的光动力技术对副溶血性弧菌与腐败希瓦氏菌的杀灭效果[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(3):83−91. [TAN L J, HU Y M, CHEN B W, et al. Inactivation of curcumin-mediated photodynamic technology on Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Shewanella putrefaciens[J]. Food Science,2022,43(3):83−91.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210121-224 TAN L J, HU Y M, CHEN B W, et al. Inactivation of curcumin-mediated photodynamic technology on Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Shewanella putrefaciens[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(3): 83−91. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210121-224
[14] 唐杰峰, 陈博文, 陈璐, 等. 姜黄素介导的光动力技术对牡蛎汁中副溶血性弧菌生物被膜的清除[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2024,50(17):31−38. [TANG J F, CHEN B W, CHEN L, et al. Inactivation effects of curcumin-mediated photodynamic technology on Vibrio parahaemolyticus biofilm formed in oyster juice[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2024,50(17):31−38.] TANG J F, CHEN B W, CHEN L, et al. Inactivation effects of curcumin-mediated photodynamic technology on Vibrio parahaemolyticus biofilm formed in oyster juice[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024, 50(17): 31−38.
[15] 林以琳, 李璟, 张江玲, 等. 姜黄素介导的光动力技术对生鲜南美白对虾品质的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2023,23(5):271−280. [LIN Y L, LI J, ZHANG J L, et al. Effect of curcumin-mediated photodynamic technology on the quality of fresh Penaeus vannamei[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2023,23(5):271−280.] LIN Y L, LI J, ZHANG J L, et al. Effect of curcumin-mediated photodynamic technology on the quality of fresh Penaeus vannamei[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 23(5): 271−280.
[16] 刘丽芳, 邱建清, 徐芳, 等. 声光动力联合杀菌技术对牡蛎的保鲜效果[J]. 农业工程学报,2023,39(5):232−240. [LIU L F, QIU J Q, XU F, et al. Preservation effect of oyster by sono-photodynamic sterilization technology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2023,39(5):232−240.] LIU L F, QIU J Q, XU F, et al. Preservation effect of oyster by sono-photodynamic sterilization technology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2023, 39(5): 232−240.
[17] 唐智鹏, 陈晨伟, 谢晶, 等. 聚乙烯醇活性薄膜对大黄鱼保鲜效果及品质动态监控[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(10):290−296. [TANG Z P, CHEN C W, XIE J, et al. Active poly(vinyl) alcohol film on the fresh-keeping effect and quality dynamic monitoring of Pseudosciaena crocea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(10):290−296.] TANG Z P, CHEN C W, XIE J, et al. Active poly(vinyl) alcohol film on the fresh-keeping effect and quality dynamic monitoring of Pseudosciaena crocea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(10): 290−296.
[18] CHEN Y, MIAO W H, LI X X, et al. The structure, properties, synthesis method and antimicrobial mechanism of ε-polylysine with the preservative effects for aquatic products[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2023,139:104131.
[19] WU T T, WU C G, FANG Z X, et al. Effect of chitosan microcapsules loaded with nisin on the preservation of small yellow croaker[J]. Food Control,2017,79:317−324. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.04.016
[20] 马晓宇, 索雅茹, 邹晨, 等. 臭氧冰的制备及其在大黄鱼保鲜中的应用评价[J]. 食品研究与开发,2023,44(11):100−105. [MA X Y, SUO Y R, ZOU C, et al. Preparation of ozone ice and its application in preservation of large yellow croaker[J]. Food Research and Development,2023,44(11):100−105.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2023.11.015 MA X Y, SUO Y R, ZOU C, et al. Preparation of ozone ice and its application in preservation of large yellow croaker[J]. Food Research and Development, 2023, 44(11): 100−105. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2023.11.015
[21] ZHANG M C, XIA X F, LIU Q, et al. Changes in microstructure, quality and water distribution of porcine longissimus muscles subjected to ultrasound-assisted immersion freezing during frozen storage[J]. Meat Science,2019,151:24−32. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.01.002
[22] JESSICA D O M, KENNYSON A D S, ANA C P V, et al. Clove and rosemary essential oils and encapsuled active principles (eugenol, thymol and vanillin blend) on meat quality of feedlot-finished heifers[J]. Meat Science,2017,130:50−57. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2017.04.002
[23] HONG H, LUO Y K, ZHOU Z Y, et al. Effects of low concentration of salt and sucrose on the quality of bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) fillets stored at 4 ℃[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,133:102−107. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.01.002
[24] ZHANG J Y, ZHOU G C, JI S Q, et al. Effect of pulse light on the quality of refrigerated (4 ℃ large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea)[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022,167:113855. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113855
[25] 何燕富, 黄卉, 李来好, 等. 低温贮藏的鱼肉品质变化及其影响因素的研究进展[J]. 大连海洋大学学报,2017,32(2):242−247. [HE Y F, HUANG H, LI L H, et al. Research progress of fish quality changes and influencing factors in low-temperature storage[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University,2017,32(2):242−247.] HE Y F, HUANG H, LI L H, et al. Research progress of fish quality changes and influencing factors in low-temperature storage[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2017, 32(2): 242−247.
[26] JIANG Q Q, NAHO N, HU Y Q, et al. Changes in quality properties and tissue histology of lightly salted tuna meat subjected to multiple freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,293:178−186. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.04.091
[27] WANG Y C, WANG Y, WANG Y G, et al. Antimicrobial blue light inactivation of pathogenic microbes:State of the art[J]. Drug Resistance Updates,2017,33-35:1−22. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2017.10.002
[28] LAN W Q, CHEN X N, ZHAO Y N, et al. The effects of ozonated slurry ice treatment on microbial, physicochemical, and quality of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) during cold-chain circulation[J]. Food Control,2023,145:109511. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2022.109511
[29] 黄佳珺, 李美锦, 陈亚楠, 等. EVOH-植酸复合活性包装膜对鲈鱼肉的保鲜效果[J]. 现代食品科技,2023,39(4):146−153. [HUANG J J, LI M J, CHEN Y N, et al. Preservation effect of EVOH-phytic acid composite packaging film on perch meat[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2023,39(4):146−153.] HUANG J J, LI M J, CHEN Y N, et al. Preservation effect of EVOH-phytic acid composite packaging film on perch meat[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2023, 39(4): 146−153.
[30] DONG Q F, YANG L, XIANG L W, et al. Development of electrospun fish gelatin film containing lauroyl arginate ethyl and its application in large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) preservation[J]. Food Control,2023,153:109959. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2023.109959
[31] XU W Y, MA Q Y, SUN J F, et al. Changes in quality characteristics of shrimp (Penaeus chinensis) during refrigerated storage and their correlation with protein degradation[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2022,114:104773. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104773
[32] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准鲜、冻动物性水产品:GB 2733-2015[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. National standards for food safety-fresh and frozen animal aquatic products:GB 2733-2015[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. National standards for food safety-fresh and frozen animal aquatic products: GB 2733-2015[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:



