Post-harvest Epidermal Wax of Grapes and Fruit Storage Quality
-
摘要: 为探究不同品种葡萄采后表皮蜡质变化规律及其与耐贮性关系,本研究以夏黑葡萄及阳光玫瑰葡萄为试验材料,分别采用SEM与GC-MS分析葡萄表皮蜡质微观结构与蜡质组分,分析贮藏期间果实失重率、硬度、MDA、总酚等品质指标变化,研究表皮蜡质对葡萄果实营养品质及贮藏保鲜效果的影响。结果表明:两种葡萄表皮蜡质含量变化规律呈现“W”趋势,夏黑葡萄表皮蜡质含量极显著高于阳光玫瑰葡萄(P<0.01),贮藏末期分别为36.66 mg/100 g和26.90 mg/100 g;SEM结果显示夏黑葡萄表皮蜡质结构呈堆叠片状晶体,孔隙较多,阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮蜡质在贮藏过程中晶体孔径较小或不存在孔径,结构分布均匀;两种葡萄表皮蜡质成分含量与其贮藏品质相关性呈现不同规律,蜡质主要成分为脂肪酸、伯醇、酯类、醛类、烷烃,分别占49.84%~81.00%、0.10%~11.68%、0~9.41%、0.43%~8.83%、0.90%~6.66%。贮藏过程中,果实失重率、脱粒率、MDA含量上升,硬度及还原糖、总酚、维生素C含量下降,贮藏品质降低;相关性分析表明,夏黑葡萄表皮蜡质中脂肪酸含量高,可加速果实细胞脂质过氧化,与失重率、MDA含量等呈显著正相关(P<0.05)结果相一致,不利于维持果实营养品质;阳光玫瑰表皮蜡质中酯类含量与维生素C、总酚含量呈显著负相关(P<0.05),显著降低果实抗氧化能力。本研究为葡萄表皮蜡质在不同品种葡萄贮藏保鲜中的应用方向提供了理论依据和技术指导。Abstract: To investigate the changes of epidermal wax and its relationship with storage tolerance in harvested grapes, Summer Black grapes and Shine Muscat grapes were selected as the grapes models. The microstructures of the grapes epidermal wax were detected by SEM, and the compositions of the epidermal wax were detected by GC-MS. The changes of fruit weight loss rate, hardness, MDA, total phenol and other quality indexes during storage were analyzed, the effects of epidermal wax on the nutritional quality and storage preservation of grape fruits were studied. The results showed that the content of epidermal wax in the two kinds of grapes showed a "W" trend. The epidermal wax content in Summer Black grapes was significantly higher than that in Shine Muscat grapes (P<0.01), and the contents were 36.66 mg/100 g and 26.90 mg/100 g at the end of storage, respectively. The SEM results showed that the epidermal waxy structure of Summer Black grapes was stacked flake crystal with pores, while the one of Shine Muscat grapes had more uniform structure distribution with small or even no pores during storage. The correlation between the compositions content of the epidermal wax and the storage quality of the two grapes showed different rules. The main compositions of epidermal waxy were fatty acids (49.84%~81.00%), primary alcohols (0.10%~11.68%), esters (0~9.41%), aldehydes (0.43%~8.83%) and alkanes (0.90%~6.66%). With the increase of storage time, the weight loss rate, threshing rate, and MDA content of grapes were increased, while the hardness, the contents of reducing sugar, total phenol and vitamin C were decreased, the storage quality of grapes were reduced. Correlation analysis results showed that high fatty acid content in epidermal wax of Summer Black grapes accelerated lipid peroxidation in fruit cells, which was consistent with a significant positive correlation (P<0.05) between weight loss rate, MDA content, and other factors, which was not conducive to maintaining the fruit nutritional quality. The content of esters in the epidermal wax of Shine Muscat grapes was significantly negatively correlated with vitamin C and total phenol content (P<0.05), significantly reducing the antioxidant capacity of the fruit. This study provides theoretical basis and technical guidance for the application of grape epidermal wax in the storage and preservation of different varieties of grapes.
-
Keywords:
- Summer Black grapes /
- Shine Muscat grapes /
- epidermal wax /
- storage quality /
- microstructure
-
夏黑葡萄(Vitis vinifera ‘Summer Black’)与阳光玫瑰葡萄(Vitis labrusca×V. vinifera,‘Shine Muscat’)均属于欧美杂交品种。夏黑葡萄别名‘夏黑无核’,为早熟无核葡萄品种[1],于1998年引入中国。其紫黑色的成熟果实上覆盖较多表皮蜡质,具有果皮厚、果肉硬脆,酸甜的特点。阳光玫瑰葡萄又名‘晴王葡萄’,为中晚熟品种,于2009年引入种植[2]。其绿色果皮较薄,表皮蜡质较少,具有含糖量高、玫瑰香味等特点。两种葡萄均有优质、无核等优良特性,已成为我国南方葡萄产区主栽品种。
表皮蜡质是保护植物不受外界侵害的第一道屏障,由脂肪酸、烷烃、醛类、萜类、伯醇等组成,呈片状、棒状等结构,具有疏水性,可防止水分流失、抵抗外部恶劣环境、对抗外来虫害及细菌侵入[3]。Gabler等[4]研究发现42个品种葡萄的表皮蜡质含量高低与其抵抗灰霉病菌的能力呈正相关,即蜡质含量越高,抵御灰霉病能力越强,特别是蜡质中的n-脂肪醇成分可抑制灰霉病菌的萌发与生长[5]。Zhang等[6]将巨峰葡萄分别贮藏于低温(4 ℃)及常温(25 ℃)条件下,发现低温下贮藏的葡萄蜡质含量、保水性显著高于常温的,而蜡质中的烷烃含量则相反。Yang等[7]研究表明葡萄表皮蜡质的损失会加速果实失重、软化及褐变。王雨菲[8]则证实了葡萄表皮蜡质的存在能够减少活性氧积累,减弱细胞损伤,较好地维持果实采后品质。因此表皮蜡质在果实品质和采后贮藏方面发挥重要作用。然而针对葡萄在贮藏过程中表皮蜡质的变化规律及其与果实耐贮性的关系鲜有报道。
本研究以夏黑葡萄和阳光玫瑰葡萄为材料,通过对不同贮藏时间果实表皮蜡质含量、结构、成分及果实品质进行检测分析,了解不同品种葡萄表皮蜡质变化规律及与耐贮性关系,为培育采后耐贮的优良品种提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
夏黑葡萄、阳光玫瑰葡萄 采摘于湖南省常德市澧县张公庙葡萄园;OPP梯形透明带孔包装袋 义乌德进塑料包装袋厂;半乳糖醛酸 分析纯,湖南国伦美有限公司;葡萄糖、氢氧化钠、酒石酸钾钠、亚硫酸钠、结晶酚、甲醇、咔唑、二氯甲烷、14%三氟化硼-甲醇、正庚烷、氯化钠、3,5-二硝基水杨酸 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;盐酸、硫酸 分析纯,成都市科隆化学品有限公司;维生素C试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)试剂盒 索莱宝生物科技有限公司;无水乙醇 分析纯,天津市恒兴化学设计及制造有限公司;正己烷 色谱纯,上海易恩化学技术有限公司。
GY-2指针式水果硬度计 北京金科利达电子科技有限公司;SpectraMax i3X酶标仪 美国Molecular Devices公司;FE28台式pH计 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;RV10旋转蒸发仪 德国IKA集团;TESCAN MIRA LMS型扫描电子显微镜 捷克泰思肯公司;TQ8040气相色谱质谱(gas chromatography-mass spectrometry,GC-MS)联用仪 日本岛津公司。
1.2 实验方法
两种葡萄各选择30 kg表皮蜡质完整、无机械损伤、大小及成熟度一致的果实,阴凉处放置24 h去除田间热后,每串果穗装于OPP梯形透明带孔包装袋中冷藏(4±0.5 ℃)。分别在贮藏第0、10、20、30、40、50、60 d对葡萄蜡质含量、结构、成分及果实品质进行测定。
1.2.1 提取蜡质及含量计算
提取蜡质方法参考王雨菲[8]。提取方法如下:将每颗完好的葡萄从果穗上剪下,保留2 mm左右的果梗,防止果肉中脂溶性物质渗出。将150 g果实洗净晾干后称重,实际重量记为M,将果实浸泡于提取液(二氯甲烷:正己烷=3:1,液料比2:1 mL/g)中7.5 min,期间用玻璃棒轻轻搅拌。称取洁净的培养皿重量记为m1。将提取液采用旋转蒸发仪(40 ℃)进行浓缩,当浓缩液体积约为培养皿体积时停止旋转蒸发,将其倒入培养皿中自然挥发得到白色粉末即为蜡质,存在蜡质的培养皿重量记为m2。蜡质含量结果以mg/100 g表示,计算公式如下:
1.2.2 葡萄表皮蜡质微观结构观察
方法参考楚文靖[9]并有所修改。用小刀割下葡萄赤道处6 mm×6 mm的表皮,放于冰箱−25 ℃冷冻区24 h,随后置于冷冻干燥机进行干燥。干燥的样品喷金后利用扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM)进行观察,放大倍数为5000倍。
1.2.3 蜡质成分的GC-MS测定
具体蜡质组分及含量的测定结果以相对含量(%)表示,方法参考王雨菲[8]。称取蜡质粉末50 mg,加入5 mL 14%三氟化硼-甲醇溶液,同时加入100 μL 0.2 mg/mL甲基异丁基甲醇作内标(矫正仪器进样误差与响应误差),70 ℃水浴冷凝回流5 min,从冷凝管上端加入5 mL正庚烷,继续回流2 min,待烧瓶冷却至室温后,加5 mL饱和氯化钠溶液后,静置分层,吸取上清液经0.5 g无水硫酸钠除水后,取上清液过0.22 μm有机滤膜,待测。样品进样温度为260 ℃,辅助加热器为280 ℃,升温程序:初始温度50 ℃(1 min),以4 ℃/min升温至290 ℃(22 min),离子源温度为280 ℃,扫描范围为50~600 m/z。蜡质成分各组分经计算机谱库NIST 20.L检索进行定性分析,以甲基异丁基甲醇为内标,以测定组分峰面积与已知含量内标峰面积之比,利用内标法及峰面积归一法计算出蜡质中每一组分在总成分中百分比含量,进行相对定量。
1.2.4 失重率、脱粒率的测定
每个品种葡萄固定6串作为样品,采用称重法测定葡萄的失重率及脱粒率。计算公式如下:
1.2.5 硬度的测定
每个品种随机选取10粒葡萄,削掉果实赤道处表皮(6 mm×6 mm),硬度计垂直戳入果实内部后读取示数,结果以kg·cm−2表示。
1.2.6 还原糖、可滴定酸含量测定
参考曹建康等[10]方法,还原糖测定采用3,5-二硝基水杨酸法,可滴定酸采用氢氧化钠滴定法,结果以%表示。
1.2.7 总酚、维生素C含量测定
总酚的测定参考曹建康等[10]方法,结果以OD280/g表示。维生素C含量测定采用南京建成生物工程研究所试剂盒A009-1-1,结果以mg/100 g表示。
1.2.8 MDA含量测定
采用索莱宝生物科技有限公司的MDA试剂盒(BC0025)进行测定,结果以nmol/g表示。
1.2.9 果胶含量测定
参考曹建康等[10],采用咔唑比色法进行测定,结果以mg/g表示。
1.3 数据处理
以上指标均为3组生物学重复,使用SPSS 22.0分析处理数据(P<0.05即为具有显著性差异),使用Origin 2022绘制图表,使用ChiPlot网站绘制相关性图片。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 贮藏期间两种葡萄表皮蜡质含量变化
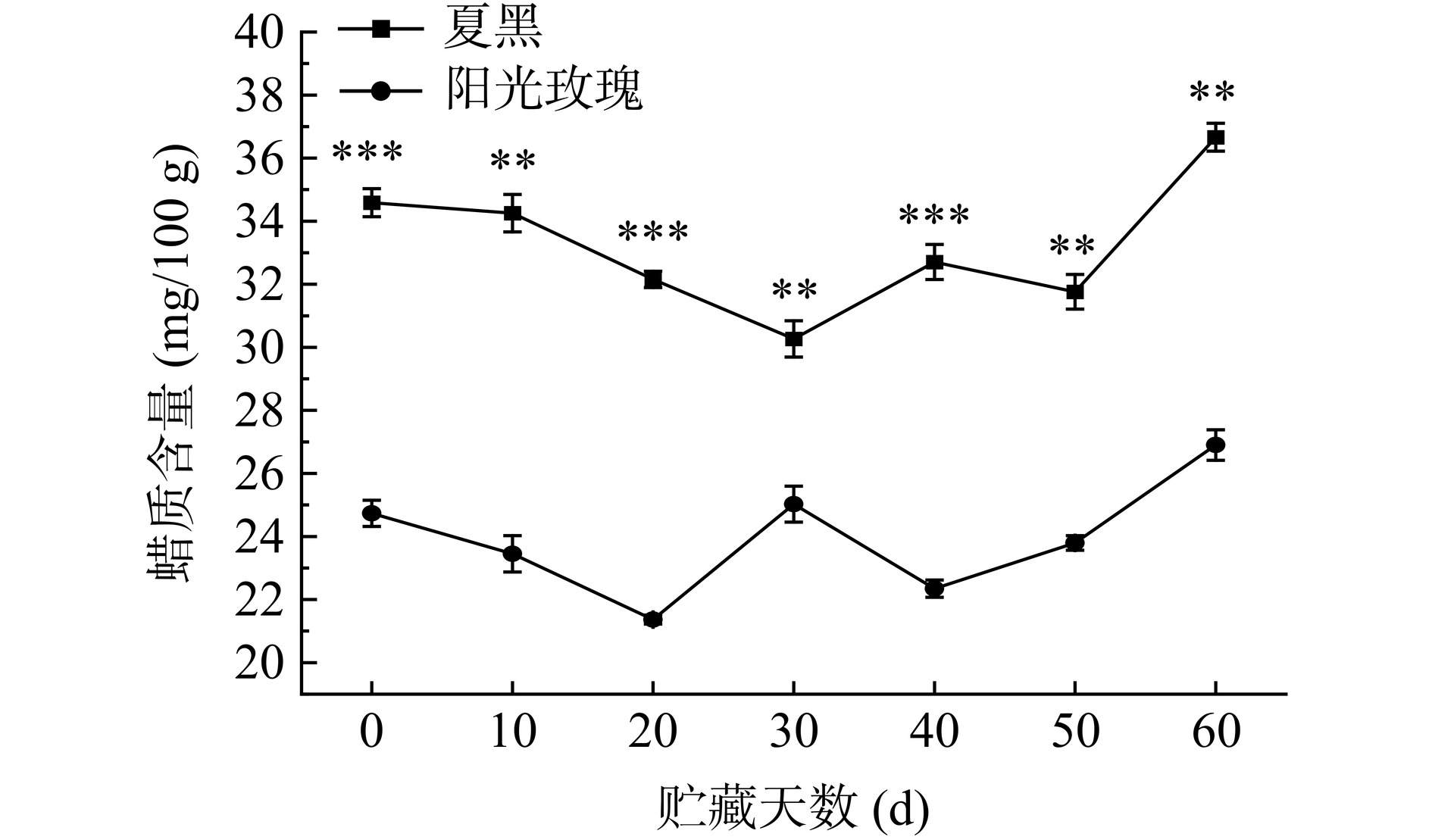
葡萄采后脱离母体,处于环境胁迫状态,此时表皮蜡质合成途径改变,含量因此发生变化[11]。由图1可知,在60 d的贮藏期内,两种葡萄蜡质含量呈现先下降后上升再下降再上升的“W”趋势,在同一贮藏时间下夏黑葡萄的蜡质含量均极显著高于阳光玫瑰葡萄(P<0.01)。夏黑葡萄贮藏初期表皮蜡质含量为34.59 mg/100 g,贮藏30 d下降到最低含量30.27 mg/100 g,贮藏末期达到含量最高值36.66 mg/100 g。阳光玫瑰葡萄贮藏初期表皮蜡质含量为24.73 mg/100 g,于贮藏20 d达到最低含量21.37 mg/100 g,此后含量上升再下降,贮藏结束时达到含量最高值26.90 mg/100 g。与其他研究者[6,12−13]结论一致,果实在贮藏前期损失部分表皮蜡质,导致其含量减少,而后期果实蜡质出现再生现象[12],使其含量增高。因此,葡萄表皮蜡质含量在贮藏期内存在一定波动性,夏黑葡萄蜡质含量高于阳光玫瑰葡萄。
2.2 贮藏期间两种葡萄表皮蜡质微观结构变化
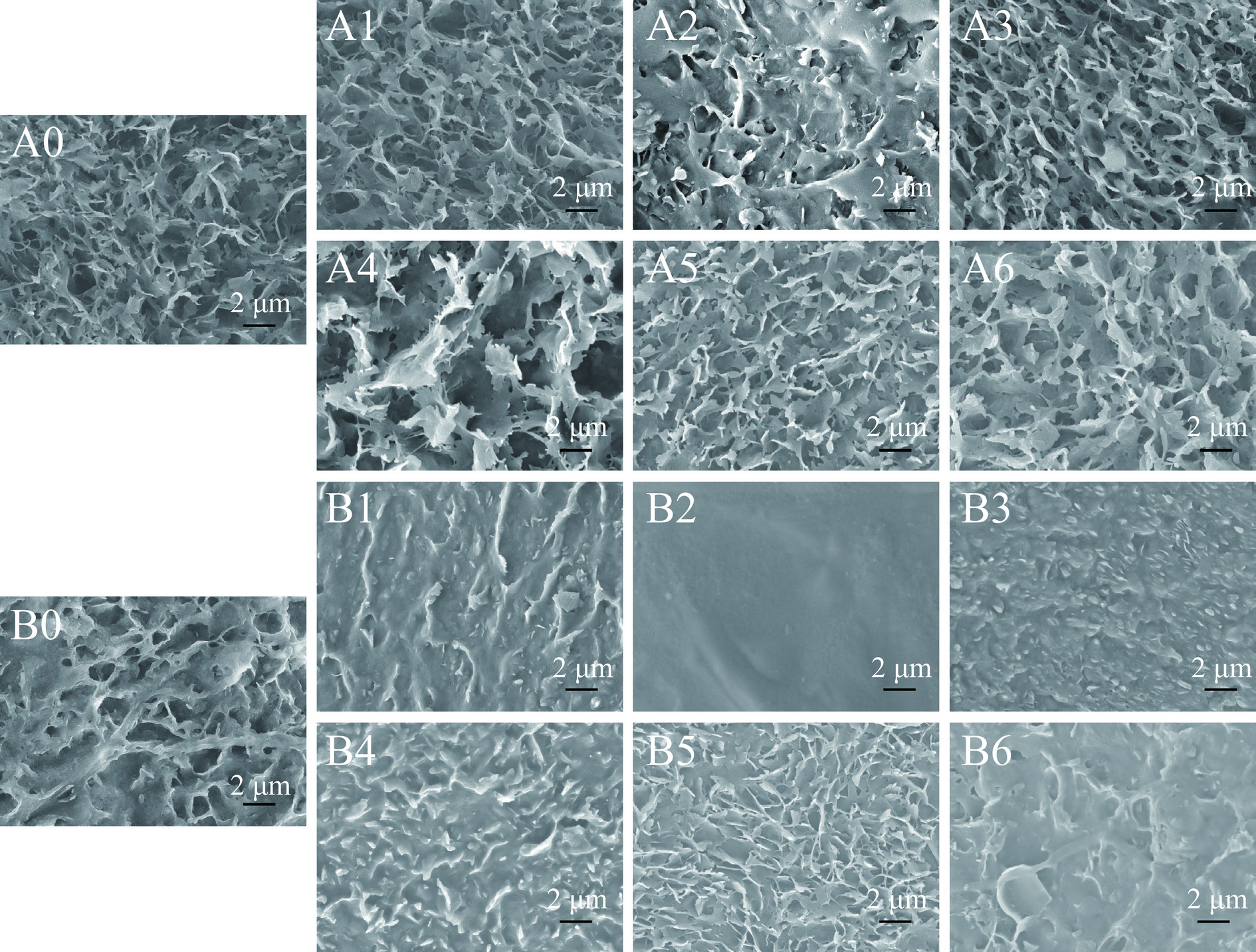
蜡质具有形态各异的结构,如蓝莓的管状晶体[9],金桔的血小板状晶体[12],苹果的片状及颗粒状晶体[13]等。由图2可知,在夏黑葡萄60 d的贮藏期内,表皮蜡质结构均呈现堆叠分散,为不规则的片状晶体,边缘粗糙,晶体间存在许多不均匀的空隙。贮藏20 d葡萄表皮蜡质结构塌陷,呈现破碎状的不规则凸起。于40 d时蜡质片状晶体破碎,晶体间孔径达到最大。而阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮蜡质结构较夏黑更稀疏,表现为茎状及不规则孔洞。贮藏10 d后,蜡质发生损耗,呈不连续凸起茎状。20 d蜡质呈平滑状,分布更紧密、均匀。贮藏30 d开始积累生成凹凸不平的点状蜡质晶体颗粒,50 d生成较多片状蜡质晶体,贮藏结束时(60 d)结构呈熔融状。
结合图1与图2可知,虽然阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮蜡质含量低于夏黑葡萄,但从微观结构可知,阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮蜡质表面趋于光泽,蜡质结构随贮藏时间的延长晶体间孔径较小或不存在孔径,分布更加均匀,表明阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮蜡质抵御外部环境能力可能优于夏黑葡萄,其蜡质晶体均匀覆盖果实表面,有利于果实的保水作用。Chai等[13]贮藏10个品种苹果,同样发现表皮蜡质微观结构表面趋于平滑的现象,蜡质均匀分布可显著减少果实水分流失。因此,表皮蜡质晶体的结构分布与果实采后失水率密切相关[14]。
2.3 贮藏期间两种葡萄表皮蜡质成分变化
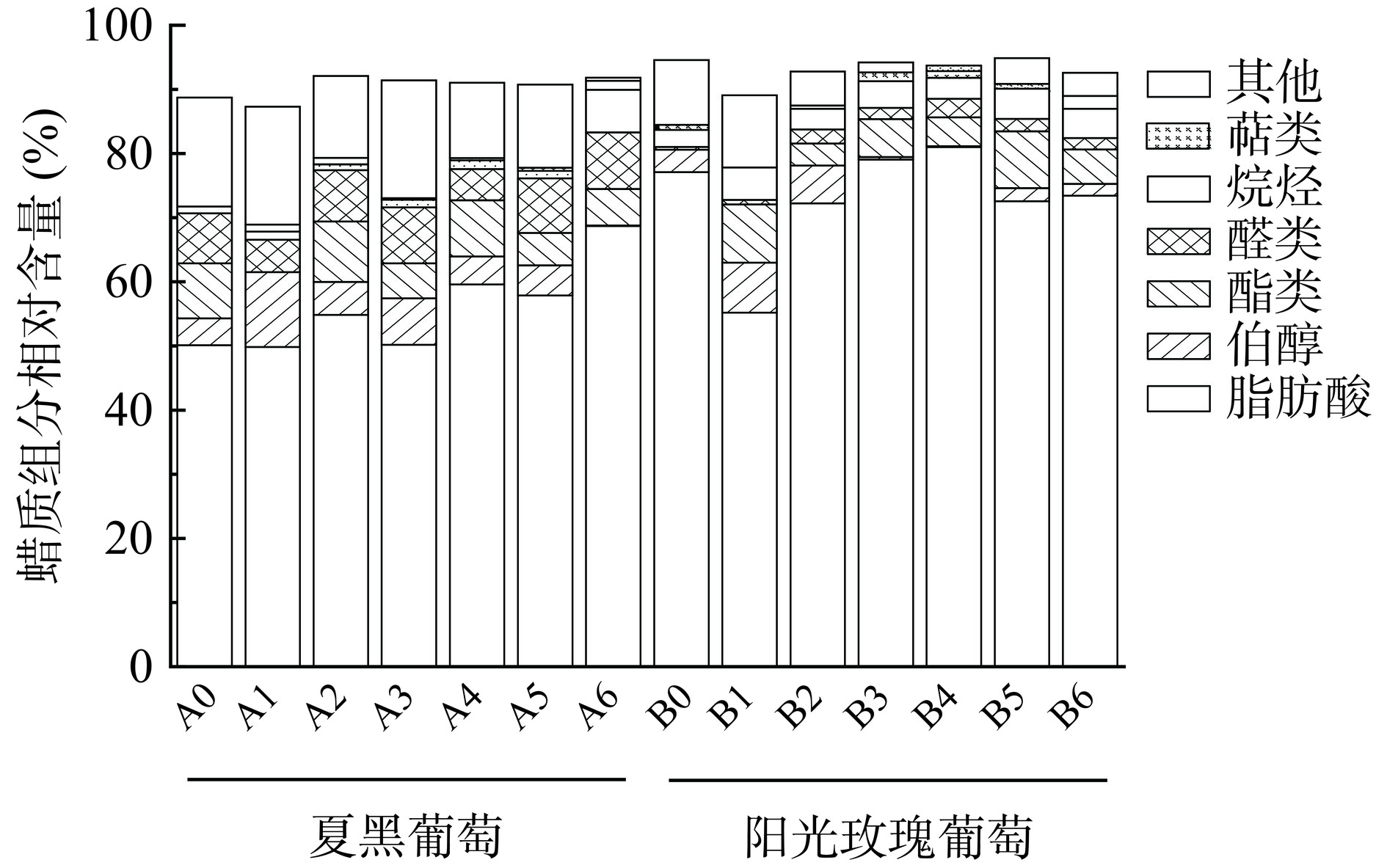
将GC-MS所测得的179种葡萄表皮蜡质成分,其中相对含量大于等于1%的组分汇总于表1。图3结合表1可知,GC-MS测得两种葡萄表皮蜡质成分主要是脂肪酸、伯醇类、酯类、醛类、烷烃,这与大多数水果类似,如苹果[13]、李[15]、橙子[16]、荔枝[17]等。
表 1 葡萄表皮蜡质成分Table 1. Compositions of grape epidermal wax序号 化合物 相对含量(%) A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 脂肪酸 1 亚油酸 0.75 − 1.19 0.83 − 1.21 1.32 0.39 0.8 0.76 1.32 0.95 − − 2 反-9-十八碳烯酸 1.06 1.57 1.76 1.35 1.48 1.59 2.15 0.53 1.01 0.69 0.59 0.47 1.07 1.74 3 二十烷酸 3.47 4.62 4.25 3.26 2.67 3.97 4.22 − − 2.13 3.34 2.26 3.19 5.67 4 蜡酸(二十六烷酸) 6.71 9.05 7.42 6.97 7.24 7.68 9.11 5.6 7.8 8.4 10.76 8.99 9.74 11.28 5 24-甲基蜡酸 1.22 1.86 − − − − − 0.77 1.46 1.41 1.84 1.61 1.8 1.81 6 二十八烷酸 17.25 0.64 18.36 18.17 18.22 19.04 22.02 19.9 1.14 21.45 1.51 24.59 1.38 1.26 7 二十九烷酸 2.46 3.38 2.45 2.45 2.6 2.59 2.7 1.7 2.71 2.03 3.15 2.38 3.22 2.9 8 蜂蜡酸(三十酸) 14.33 19.17 13.94 14.61 13.86 15.4 16.96 22.6 23.09 17.81 29.44 20.64 28.62 27.86 9 三十二烷酸 2.85 3.46 2.52 2.52 2.73 − 3.1 13.5 10.74 6.59 15.51 10.3 13.45 13.81 10 9,12-十八烷二烯酸 − 1.38 − − 1 − − − − − − − 1.49 3.22 11 硬脂酸(十八烷酸) − 4.71 2.95 − 2.51 3.38 2.84 2.7 − − 2.5 2.27 3.19 − 12 二十四烷酸 − − − − 7.27 − − 1.5 2.44 2.71 3.54 2.53 2.87 3.88 13 十二烷酸 − − − − − 2.99 − − − − − − − − 14 十六酸(棕榈酸) − − − − − − 4.27 5.2 − − 2.74 − − − 15 18-甲基十九碳酸 − − − − − − − 1.5 2.11 − − − − − 16 山嵛酸 − − − − − − − 1.2 1.89 2.08 2.81 1.9 2.55 − 17 14-甲基十五酸 − − − − − − − − − 3.67 − 2.11 − − 18 14-甲基十七酸 − − − − − − − − − 2.5 − − − − 总和 50.1 49.84 54.84 50.16 59.58 57.85 68.69 77.09 55.19 72.23 79.05 81 72.57 73.43 伯醇类 1 二十二烷醇 0.25 0.29 0.11 0.21 − − − 0.14 0.17 2.21 0.09 − 1.09 − 2 二十七烷醇 3.95 4.52 2.09 2.1 1.73 1.98 0.1 1.2 2.32 1.08 0.18 0.06 0.62 0.68 3 二十四烷醇 − 6.66 2.95 3.25 2.64 2.74 − 2 3.56 1.66 − − 0.09 1.14 4 二十八烷醇 − 0.21 − 1.7 − − − 0.17 1.74 0.94 0.12 0.08 0.23 − 总和 4.2 11.68 5.15 7.26 4.37 4.72 0.1 3.51 7.79 5.89 0.39 0.14 2.03 1.82 酯类 1 碳酸癸基十四烷基酯 5.79 − 5.03 5.44 3.95 − − − − 3.44 5.61 4.07 5 5.37 2 山嵛酸乙酯 2.78 − 2.48 − 2.26 2.65 2.52 − − − 0.19 0.15 0.13 − 3 花生酸乙酯 − − 1.9 − 2.54 2.41 0.4 − − − − 0.15 − − 4 木焦油酸乙酯 − − − − − − 2.74 − − − 0.12 0.13 − − 5 碳酸癸基十二烷基酯 − − − − − − − − 5.03 − − − − − 6 二十酸甲酯 − − − − − − − − 4.06 − − − 3.72 − 总和 8.57 0 9.41 5.44 8.75 5.06 5.66 0 9.09 3.44 5.92 4.5 8.85 5.37 醛类 1 正二十六烷醛 3.06 3.75 3.06 3.68 − 3.69 4.78 − − − − − − − 2 二十九醛 0.72 0.62 0.58 0.92 0.73 0.43 0.57 0.33 0.69 0.99 1.17 1.23 0.91 0.73 3 9Z-十八烯醛二甲基缩醛 1.32 − 1.29 − 1.27 3.21 1.84 − − 1.19 − 1.58 0.94 0.95 4 十二醛二甲缩醛 − 0.64 0.43 0.93 0.25 1.18 1.64 0.1 − − 0.56 0.06 0.1 0.12 5 二十八烷醛 2.71 − 2.65 3.22 2.63 − − − − − − − − − 总和 7.81 5.01 8.01 8.75 4.88 8.51 8.83 0.43 0.69 2.18 1.73 2.87 1.95 1.8 烷烃 1 正三十二烷 0.59 0.68 0.53 0.53 0.54 0.63 − 0.81 1.14 0.76 1.07 0.93 1.33 1.04 2 正四十烷 0.47 0.6 0.37 0.41 0.46 0.4 − 0.82 1.15 0.68 1.04 0.88 1.2 1 3 2-甲基二十六烷 − − − 0.24 − 0.13 − 0.62 1.91 1.1 1.18 0.83 1.32 1.28 4 二十二烷 − − − − 0.34 − − 0.4 0.86 0.68 0.89 0.66 0.85 1.21 5 正二十八烷 − − − − − − 6.66 − − − − − − − 总和 1.06 1.28 0.9 1.18 1.34 1.16 6.66 2.65 5.06 3.22 4.18 3.3 4.7 4.53 萜类 1 叶绿醇 − 1.11 0.89 0.26 0.22 0.3 1.25 0.8 − 0.35 0.86 0.47 − 0.63 2 1-甲氧基-3,7,11-三甲基-2,6,10-十二烷三烯 − − 0.12 − 0.15 0.18 0.16 − − 0.17 0.53 0.57 0.77 1.39 总和 0 1.11 1.01 0.26 0.37 0.48 1.41 0.8 0 0.52 1.39 1.04 0.77 2.02 其他类 1 1-十五烯 3.41 − 0.5 0.65 0.44 0.72 − − 0.17 − − − 0.09 − 2 (E)-5-二十碳烯 1.18 1.34 0.4 0.65 0.46 0.33 − 0.4 0.26 0.18 − − − − 3 1-十九烯 9.49 11.07 4.64 5.84 4.2 4.54 0.17 3.5 5.47 2.54 0.13 0.06 1.71 1.61 4 1-二十一(碳)烯 1.1 1.21 0.5 0.63 0.48 0.39 − 0.39 0.68 0.22 − − 0.12 0.13 5 1-十四烯 − 2.56 − − − − − − − − − − − − 6 1-十七碳烯 − − 3.44 4.5 3.06 3.14 − 2.2 3.69 1.06 − − 1.01 0.76 7 1-十八烯基甲基醚 1.81 2.21 1.79 2.12 1.83 2.16 − 1.1 0.98 1.3 1.41 0.82 1.09 1.11 8 三(2,4-二-叔丁基苯基)磷酸酯 − − 1.48 3.97 1.28 1.68 0.32 − − − − − − − 9 芥酸酰胺 − − − − − − − 2.5 − − − − − − 总和 16.99 18.39 12.75 18.36 11.75 12.96 0.49 10.09 11.25 5.3 1.54 0.88 4.02 3.61 注:−表示未检测到该物质;A0、A1、A2、A3、A4、A5、A6,B0、B1、B2、B3、B4、B5、B6分别为夏黑及阳光玫瑰葡萄于贮藏期中第0、10、20、30、40、50、60 d。 由表1可知,两种葡萄表皮蜡质成分及相对含量差异较大。其中,脂肪酸所占表皮蜡质比例最多,为49.84%~81.00%,这与王雨菲[8]的结果一致。贮藏期间阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮蜡质的脂肪酸相对含量高于夏黑葡萄。夏黑葡萄中相对含量最高的脂肪酸为二十八烷酸、蜂蜡酸,贮藏期间脂肪酸含量逐渐升高,在第60 d时脂肪酸积累达到峰值68.69%。而阳光玫瑰葡萄中相对含量最高的脂肪酸为蜂蜡酸、二十八烷酸以及三十二烷酸,贮藏期间脂肪酸含量呈先降后升再降的波动趋势,于第40 d达到其峰值81.00%。而18-甲基十九碳酸、山嵛酸、14-甲基十五酸、14-甲基十七酸仅在阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮蜡质中出现。根据GC-MS结果表明,阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮蜡质中饱和脂肪酸占比多于夏黑葡萄,推测其可能不易发生氧化现象,对于维持果实品质具有积极作用[18]。
伯醇占比在葡萄表皮蜡质中有先升后降的趋势,为0.10%~11.68%,主要成分为二十四烷醇与二十七烷醇。贮藏10 d,夏黑葡萄和阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮蜡质伯醇相对含量达到最高,分别为11.68%、7.79%,贮藏结束时,相对含量分别降至0.10%、1.82%。研究表明[19],伯醇成分可响应果实中非生物的胁迫作用,这可能是由于果实在贮藏前期需合成伯醇成分应对外部环境的改变,贮藏后期果实能量亏损[20],其成分占比减少。
酯类对于果实香气具有重要的贡献作用[21],然而当其作为表皮蜡质成分时,会对果实贮藏品质产生不利影响[22]。在60 d的贮藏中,两种葡萄表皮蜡质酯类相对含量为0~9.41%,处于规律的增减状态,相差较大。夏黑葡萄的酯类含量在大多贮藏期高于阳光玫瑰葡萄,两种葡萄表皮蜡质主要的酯类成分为碳酸癸基十四烷基酯,而碳酸癸基十二烷基酯与二十酸甲酯仅在阳光玫瑰葡萄中出现。
对于醛类而言,Zhu等[22]证实该成分与果实失重率呈正相关,与硬度呈负相关。在本研究中发现阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮蜡质所含醛类种类、相对含量均少于夏黑葡萄,前者相对含量为0.43%~2.87%,存在先升后降的趋势,于贮藏第40 d达到峰值,其主要成分为二十九醛;而后者相对含量为4.88%~8.83%,其主要成分是正二十六烷醛。因此,夏黑葡萄的失重率及果实软化可能与醛类成分有关。
在贮藏过程中两种葡萄烷烃相对含量相差不大,为0.90%~6.66%。阳光玫瑰葡萄中相对含量最高的烷烃为正三十二烷、正四十烷及2-甲基二十六烷,而夏黑葡萄表皮蜡质在贮藏中相对含量最高的烷烃为正二十八烷,其于第60 d出现,相对含量高达6.66%。另外,两种葡萄中相对含量较高的烷烃大多为直链烷烃,其平均链长与果实透水性呈负相关[23]。由表1可知,阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮蜡质中所含烷烃碳链更长,意味着其果实失水率可能低于夏黑葡萄。
2.4 贮藏期间两种葡萄失重率、脱粒率变化
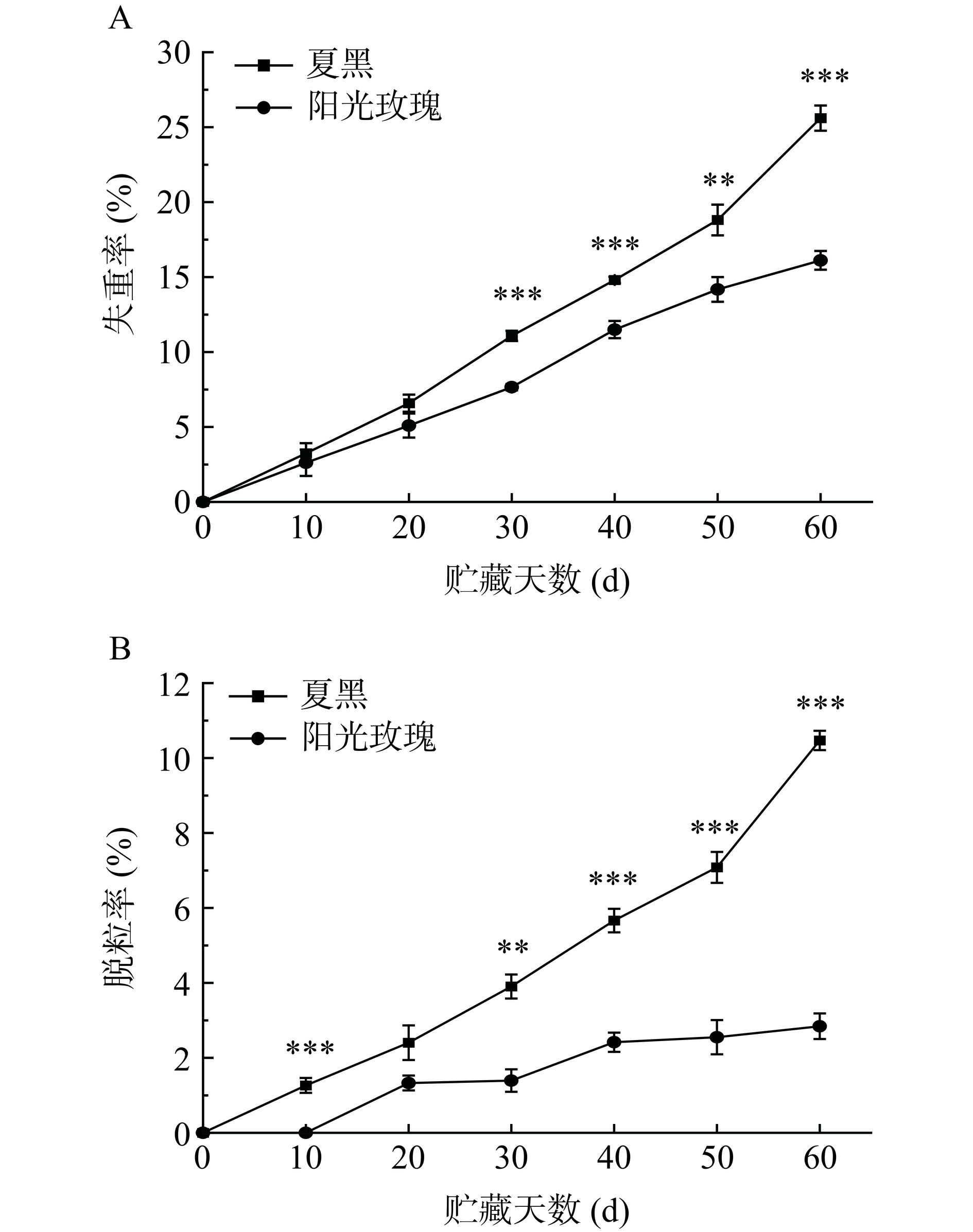
葡萄采后贮藏过程中,果实失水、脱粒可直观体现鲜食葡萄商品价值,是反映贮藏品质重要指标[24]。如图4A所示,两种葡萄的失重率随贮藏天数的延长而增加,这与Shi等[25]研究结果一致。而夏黑葡萄失重率在整个贮藏周期中均高于阳光玫瑰葡萄。至贮藏末期第60 d时,夏黑葡萄失重率高达25.6%,阳光玫瑰葡萄则为16.12%。如图4B所示,夏黑葡萄的脱粒率呈现上升趋势,于第10 d发生脱粒现象。阳光玫瑰葡萄脱粒呈现极为缓慢的增长趋势,于第20 d出现脱粒现象。贮藏60 d时,夏黑葡萄与阳光玫瑰葡萄的脱粒率分别为10.47%、2.84%。由于品种之间的差异,贮藏结束时夏黑葡萄失重率、脱粒率均极显著高于阳光玫瑰葡萄(P<0.001)。
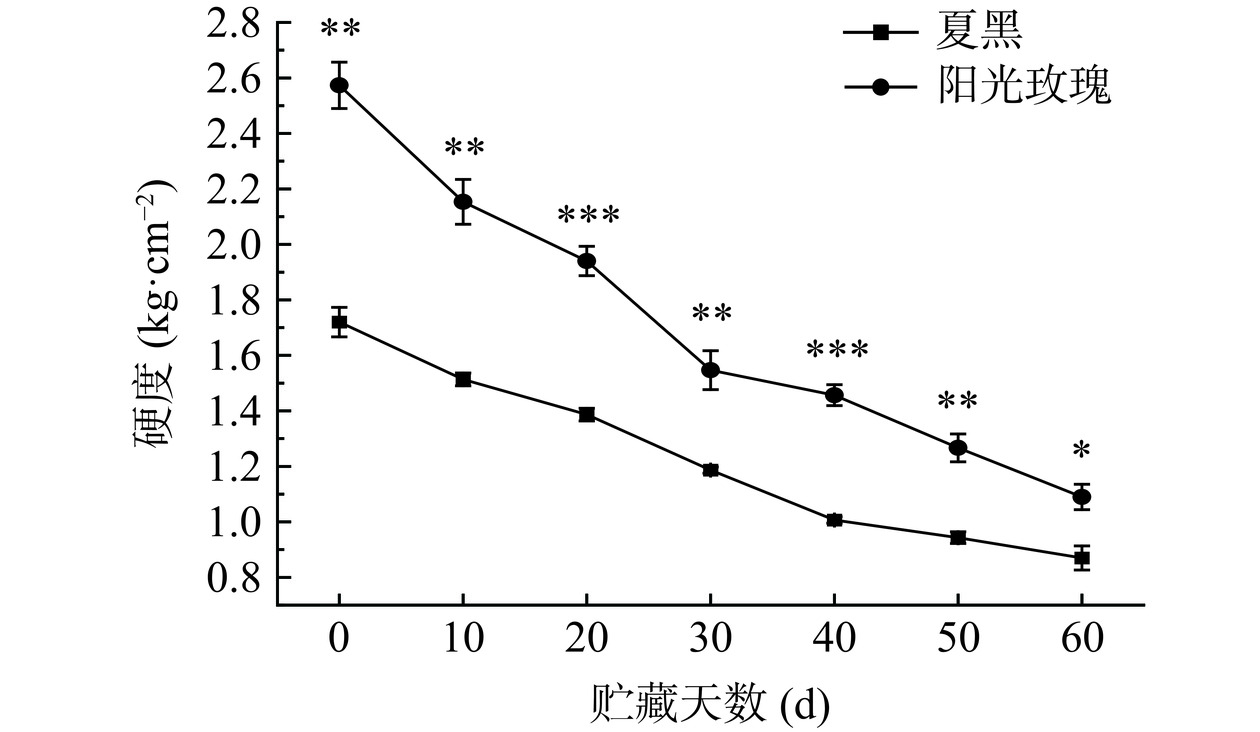
2.5 贮藏期间两种葡萄的硬度变化
果实硬度代表果实软化程度的多少,与果实中果胶含量及其降解程度有关[26]。如图5所示,两种葡萄果实硬度逐渐下降,阳光玫瑰葡萄初始硬度为2.57 kg·cm−2,贮藏30 d,阳光玫瑰葡萄硬度曲线斜率绝对值增大,表明阳光玫瑰果实软化速度在贮藏中期加快,贮藏结束后,其硬度降低至1.09 kg·cm−2,降低了57.59%。夏黑葡萄贮藏期间果实硬度下降平缓,且硬度显著低于阳光玫瑰葡萄(P<0.05),初始硬度1.72 kg·cm−2,贮藏60 d后降低至0.87 kg·cm−2,下降了49.42%。
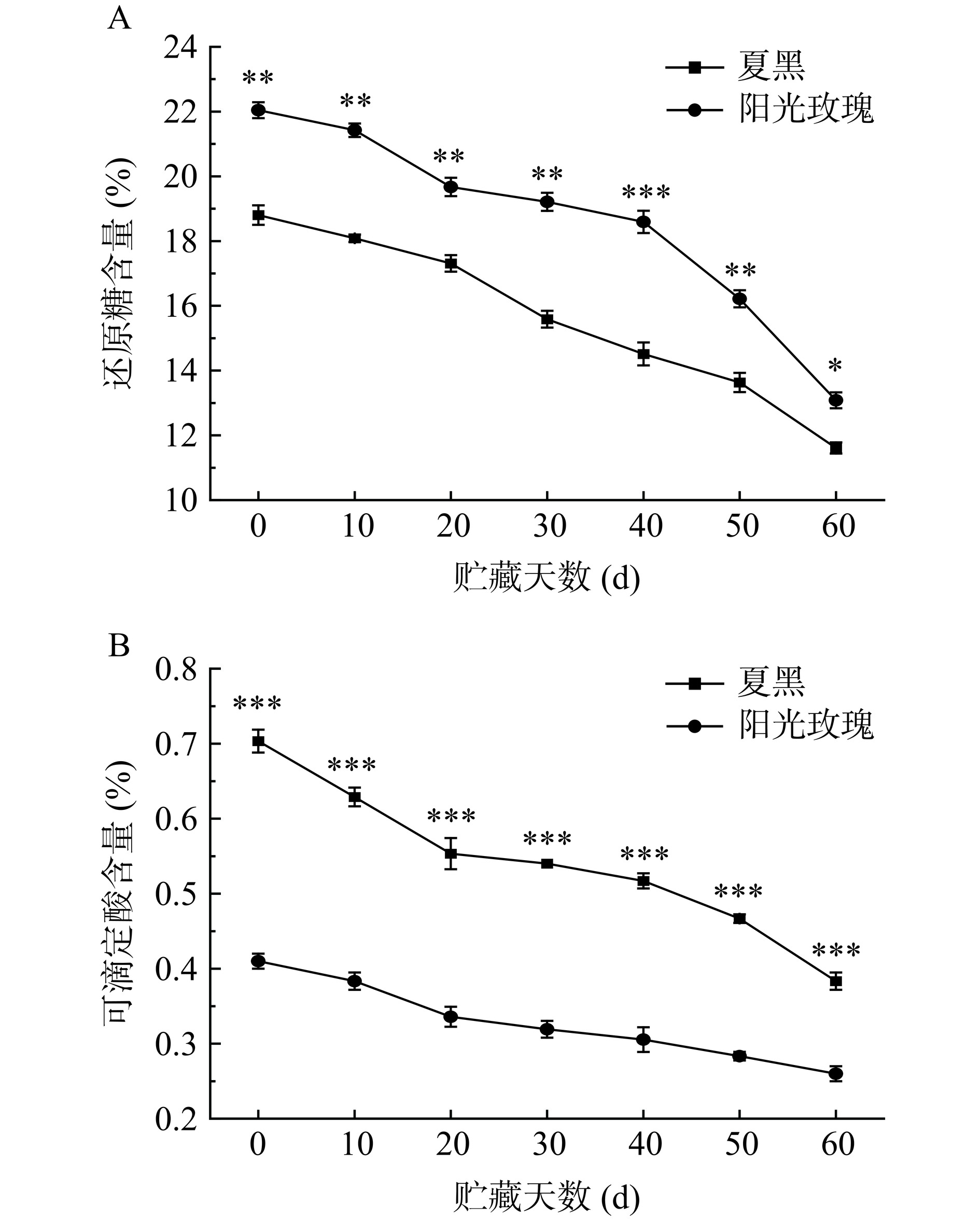
2.6 贮藏期间两种葡萄的还原糖、可滴定酸含量变化
还原糖与可滴定酸是果实中重要的营养成分,影响着果实的风味品质[27]。如图6所示,两种葡萄还原糖、可滴定酸含量随贮藏时间的延长而下降,结果与谭沙等[28]一致。如图6A所示,阳光玫瑰葡萄还原糖含量显著高于夏黑葡萄(P<0.05)。贮藏60 d,阳光玫瑰葡萄还原糖含量从初始的22.04%下降至13.08%,而夏黑葡萄从18.8%下降至11.61%,两种葡萄分别减少了8.96%、7.19%。如图6B所示,阳光玫瑰葡萄可滴定酸含量极显著低于夏黑葡萄(P<0.001),贮藏结束时阳光玫瑰葡萄与夏黑葡萄可滴定酸分别下降了0.15%、0.32%。结果表明,阳光玫瑰葡萄果实糖酸比明显高于夏黑葡萄,且维持得更好。
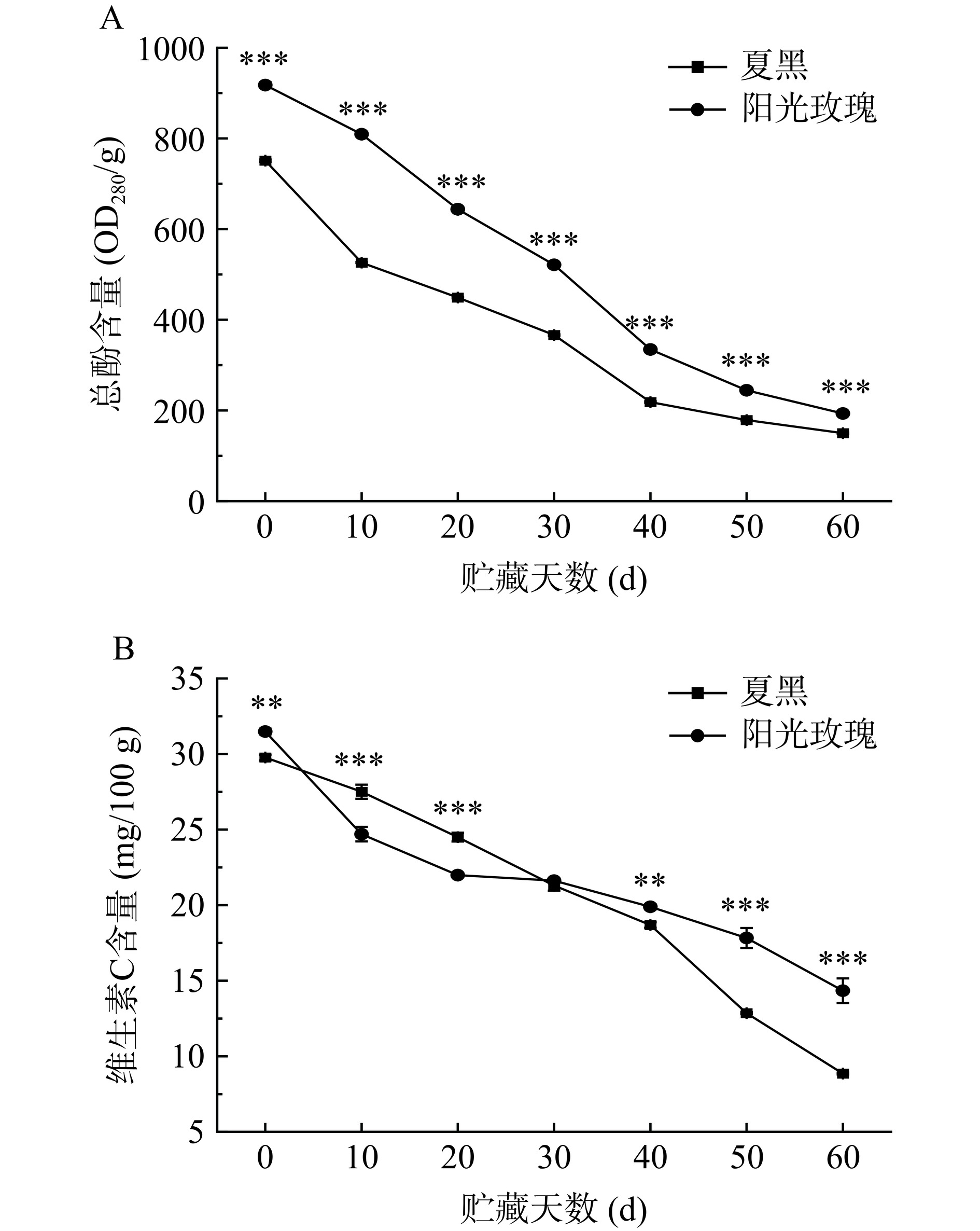
2.7 贮藏期间两种葡萄总酚、维生素C含量变化
果实采后仅靠自身能量维持生命活动,期间产生大量活性氧(ROS),攻击细胞组织,致使细胞发生严重损伤,加速果实衰老,缩短果实货架期[29]。总酚、维生素C作为植物细胞内非酶抗氧化活性成分,可将过量ROS清除,维持果实新鲜程度[30]。如图7所示,葡萄果实体内总酚、维生素C含量随贮藏时间的增加呈下降趋势。如图7A可知,阳光玫瑰葡萄总酚含量极显著高于夏黑葡萄(P<0.001),贮藏40 d内,两种葡萄果实的总酚含量快速下降,阳光玫瑰葡萄与夏黑葡萄总酚含量分别从917.63 OD280/g和751 OD280/g下降至334.43 OD280/g和218.53 OD280/g,贮藏后期总酚含量下降趋势平缓。前期总酚含量快速减少,其原因可能是果实采后急需清除积累的ROS,此时总酚发挥主要的抗氧化作用。这与王雨菲[8]的研究结果一致。如图7B所示,葡萄在贮藏过程中,维生素C含量呈现不同下降趋势,该结果与王晓晶等[24]一致。贮藏0 d,阳光玫瑰葡萄维生素C含量为31.49 mg/100 g,极显著高于夏黑葡萄维生素C含量 29.77 mg/100 g(P<0.01);贮藏20 d内,阳光玫瑰葡萄中维生素C含量快速下降,第20 d时为21.99 mg/100 g,极显著低于夏黑葡萄24.50 mg/100 g(P<0.01);贮藏40~60 d,夏黑葡萄维生素C含量极显著低于阳光玫瑰葡萄(P<0.01)。
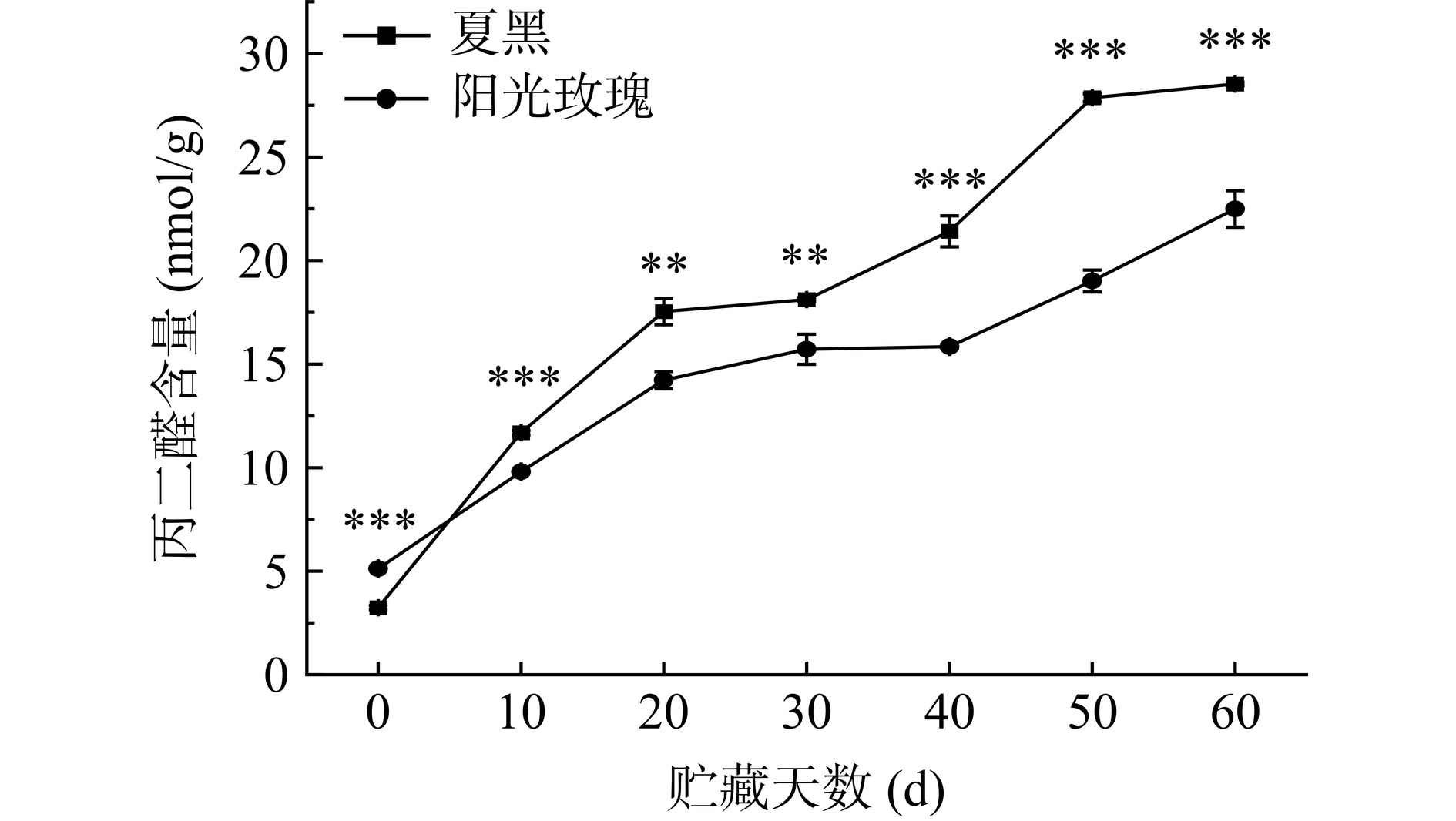
2.8 贮藏期间两种葡萄MDA含量变化
MDA是果实衰老过程中膜脂过氧化重要产物之一,其含量高低可评价膜脂过氧化程度及细胞受损程度[31]。如图8所示,贮藏过程中两种葡萄果实的MDA含量均呈上升趋势,这与孙思胜等[32]结果一致。贮藏第0 d时,夏黑葡萄MDA含量为3.24 nmol/g,极显著低于阳光玫瑰葡萄5.13 nmol/g(P<0.001);贮藏60 d,夏黑葡萄与阳光玫瑰葡萄MDA含量分别为28.53 nmol/g和22.50 nmol/g,各增长了7.81倍和3.39倍。结合图7与图8可知,夏黑葡萄果实抗氧化物质含量少于阳光玫瑰葡萄,前者MDA含量增长速率明显高于后者,表明贮藏过程中夏黑葡萄果实细胞破损程度大于阳光玫瑰葡萄,果实内部膜脂过氧化反应及衰老速度较快。
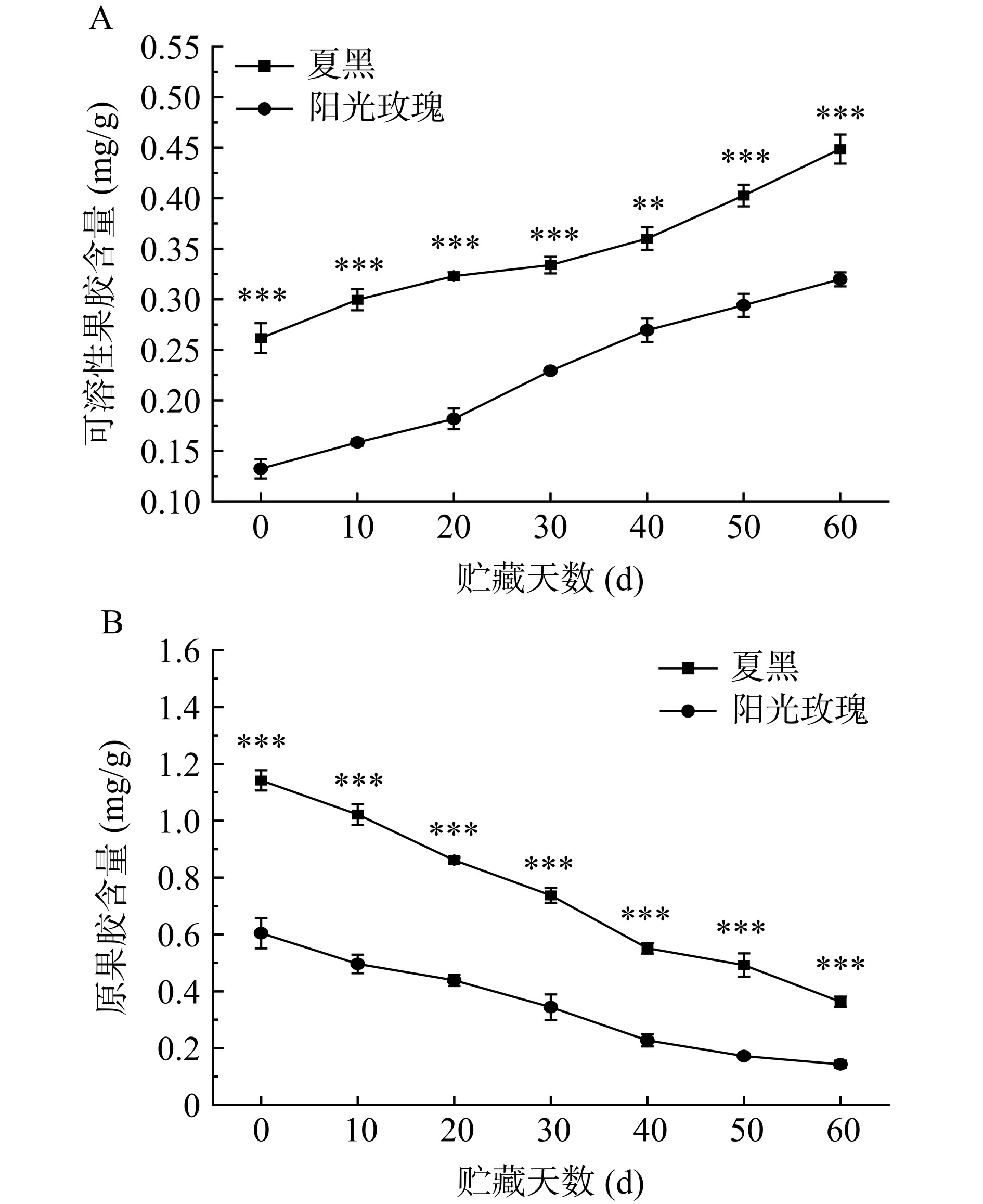
2.9 贮藏期间两种葡萄果胶含量变化
果胶分为不溶性原果胶与可溶性果胶,具有维持果实质地与细胞结构完整性作用,其含量变化显著影响果实硬度[33]。果实贮藏过程中,果胶酶将原果胶降解为可溶性果胶和果胶酸,导致细胞粘合力下降,细胞壁逐渐降解,果实质地软化[26]。由图9A可知,两种葡萄中原果胶含量随贮藏时间下降,原果胶降解后分解为可溶性果胶,故图9B显示可溶性果胶含量随贮藏时间逐渐增加。其中,夏黑葡萄原果胶及可溶性果胶含量极显著高于阳光玫瑰葡萄(P<0.01)。贮藏第0 d,夏黑葡萄与阳光玫瑰葡萄原果胶含量为1.14 mg/g和0.60 mg/g,可溶性果胶含量分别为0.26 mg/g和0.13 mg/g。贮藏60 d,夏黑葡萄与阳光玫瑰葡萄原果胶含量各减少了68.42%、76.67%,可溶性果胶含量分别增长了73.08%、146.15%。该结果与图5中两种葡萄硬度下降结果相对应。贮藏0 d时,阳光玫瑰葡萄原果胶所占果胶比例高于夏黑葡萄,因此其初始硬度高于夏黑葡萄。贮藏结束时,阳光玫瑰葡萄比贮藏第0 d产生更多可溶性果胶,其硬度降低了57.59%,大于夏黑葡萄的49.42%,然而由于其品种的差异性,其硬度仍然高于夏黑葡萄。
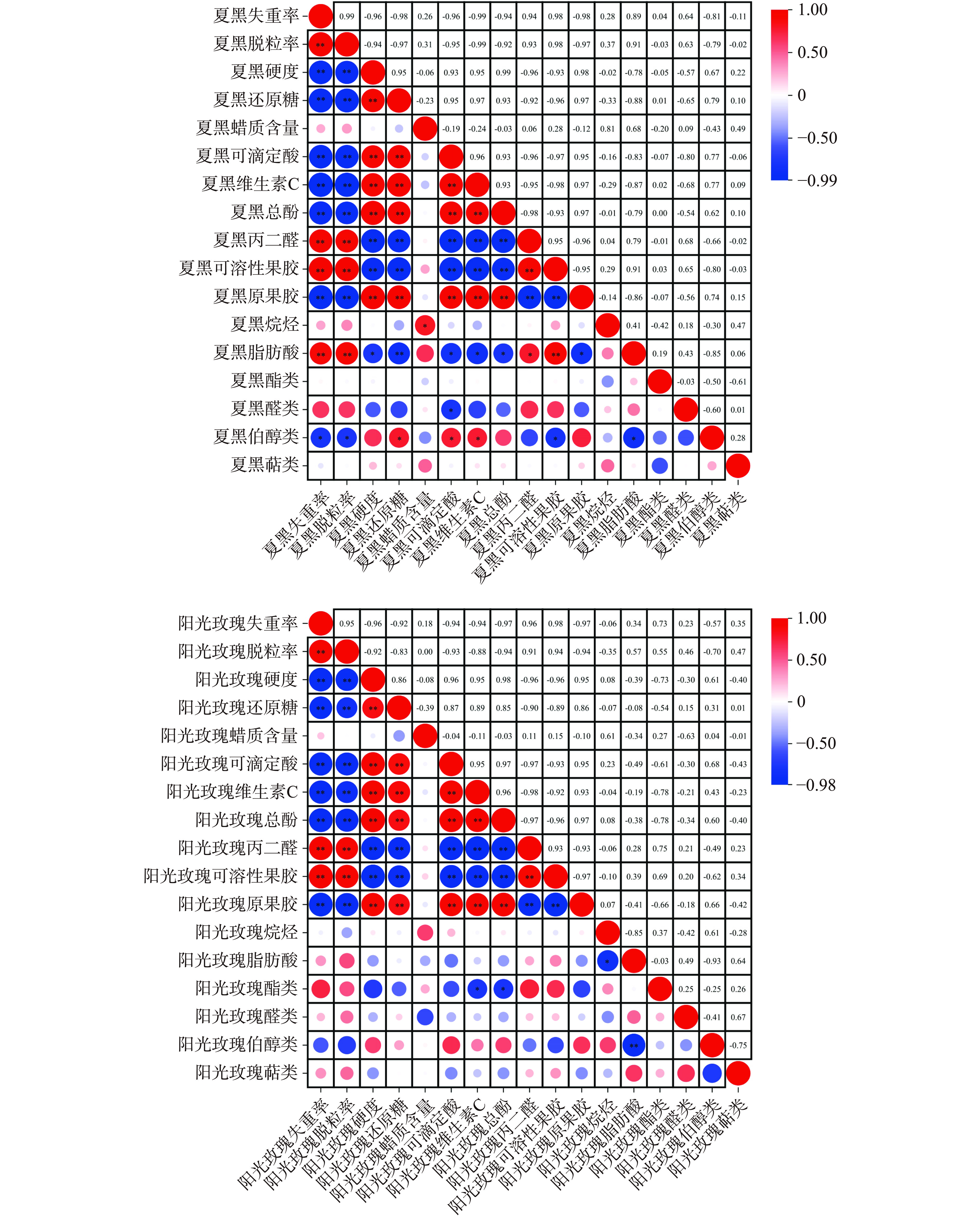
2.10 贮藏期间葡萄表皮蜡质与贮藏品质相关性分析
图10A结合图3可知,夏黑葡萄表皮蜡质中脂肪酸相对含量占比最大,其脂肪酸与果实失重率、脱粒率、可溶性果胶含量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与MDA含量呈显著正相关(P<0.05),与还原糖含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01),与硬度、可滴定酸、维生素C、总酚、原果胶呈显著负相关(P<0.05)。而夏黑葡萄蜡质伯醇相对含量与还原糖、可滴定酸、维生素C含量呈显著正相关(P<0.05),与失重率、脱粒率、可溶性果胶呈显著负相关(P<0.05)。研究表明[34],脂肪酸可抑制蜡质晶体的致密堆积,形成松散的网络结构,致使果实水分流失和软化,品质劣变,因此,表皮蜡质中的脂肪酸成分是降低果实耐贮性的重要因素。如图10B所示,阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮蜡质中,酯类成分与维生素C、总酚含量呈显著负相关(P<0.05)。结果表明,阳光玫瑰葡萄蜡质成分对果实质地影响较小,但对果实抗氧化能力影响较大,该结论与Thomai等[35]一致。
表皮蜡质是葡萄果实的第一层防线,能够抵御外界环境不利因素的干扰,对果蔬保鲜具有重要作用[36]。葡萄采后贮藏过程中,果实成熟、衰老均导致表皮蜡质含量、结构的变化[37],且不同品种葡萄果实表皮蜡质含量、结构及成分呈现多样性。果实蜡质中脂肪酸、酯类、醇类与果实保水能力显著相关[22]。本研究发现葡萄表皮蜡质的脂肪酸、酯类成分与失重率呈正相关(r夏黑脂肪酸=0.89;r阳光玫瑰脂肪酸=0.34;r夏黑酯类=0.04;r阳光玫瑰酯类=0.73),二者加速水分流失,不利于保持果实水分,与黄世安[15]、Yang等[12]研究结论一致。而表皮蜡质中的伯醇成分与果实失重率呈负相关(r夏黑=−0.81;r阳光玫瑰=−0.57),可有效减小果实水分蒸腾作用[37]。
葡萄蜡质能够有效延缓原果胶降解为可溶性果胶,延缓果实软化,对维持葡萄果实硬度具有正向作用[37−38]。本研究表明,果实硬度与可溶性果胶呈极显著负相关(r夏黑=−0.93;r阳光玫瑰=−0.96;P<0.01),且酯类与果实硬度呈负相关(r夏黑=−0.05;r阳光玫瑰=−0.73),与Liu等[39]结果相一致,表明酯类成分可能加速果实软化进程的发生。天然果实蜡质可维持果实的营养品质,保护抗氧化酶活性及减少抗氧化物含量的损失[37]。两种葡萄表皮蜡质的伯醇成分与维生素C(r夏黑=0.77;r阳光玫瑰=0.43)、总酚含量(r夏黑=0.62;r阳光玫瑰=0.60)呈正相关,该结果与黄世安[15]一致,因此,伯醇成分可能具有维持果实抗氧化能力的作用。
3. 结论
夏黑葡萄与阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮含有大量蜡质以保护果实,本研究通过对两种葡萄采后不同贮藏时间的蜡质含量、微观结构、成分及果实品质进行检测,并采用相关性分析探究蜡质成分对耐贮性的影响。结果表明,两种葡萄表皮蜡质在低温(4 ℃)贮藏条件下,蜡质含量均呈现反复先降后升的“W”趋势。且两种葡萄表皮蜡质微观结构随品种的不同而呈现不同的规律,在0~60 d贮藏过程中,阳光玫瑰葡萄表皮蜡质结构由茎状凸起变得平滑,贮藏中期形成颗粒,随后形成熔融状;夏黑葡萄则由堆叠片状转变为破碎片状晶体。葡萄表皮蜡质主要成分为脂肪酸、伯醇、酯类、醛类等,两种葡萄所含成分及相对含量差异较大。相关性分析结果表明,蜡质中脂肪酸、酯类成分的积累,导致果实失水率增加、软化,不利于维持果实耐贮性,而伯醇则对果实保鲜具有正向作用。后期可采用外源手段增加对果实贮藏有贡献成分的含量,或减少对贮藏不利成分的占比,以期为延长鲜食葡萄贮藏期提供理论基础。
-
表 1 葡萄表皮蜡质成分
Table 1 Compositions of grape epidermal wax
序号 化合物 相对含量(%) A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 B0 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 脂肪酸 1 亚油酸 0.75 − 1.19 0.83 − 1.21 1.32 0.39 0.8 0.76 1.32 0.95 − − 2 反-9-十八碳烯酸 1.06 1.57 1.76 1.35 1.48 1.59 2.15 0.53 1.01 0.69 0.59 0.47 1.07 1.74 3 二十烷酸 3.47 4.62 4.25 3.26 2.67 3.97 4.22 − − 2.13 3.34 2.26 3.19 5.67 4 蜡酸(二十六烷酸) 6.71 9.05 7.42 6.97 7.24 7.68 9.11 5.6 7.8 8.4 10.76 8.99 9.74 11.28 5 24-甲基蜡酸 1.22 1.86 − − − − − 0.77 1.46 1.41 1.84 1.61 1.8 1.81 6 二十八烷酸 17.25 0.64 18.36 18.17 18.22 19.04 22.02 19.9 1.14 21.45 1.51 24.59 1.38 1.26 7 二十九烷酸 2.46 3.38 2.45 2.45 2.6 2.59 2.7 1.7 2.71 2.03 3.15 2.38 3.22 2.9 8 蜂蜡酸(三十酸) 14.33 19.17 13.94 14.61 13.86 15.4 16.96 22.6 23.09 17.81 29.44 20.64 28.62 27.86 9 三十二烷酸 2.85 3.46 2.52 2.52 2.73 − 3.1 13.5 10.74 6.59 15.51 10.3 13.45 13.81 10 9,12-十八烷二烯酸 − 1.38 − − 1 − − − − − − − 1.49 3.22 11 硬脂酸(十八烷酸) − 4.71 2.95 − 2.51 3.38 2.84 2.7 − − 2.5 2.27 3.19 − 12 二十四烷酸 − − − − 7.27 − − 1.5 2.44 2.71 3.54 2.53 2.87 3.88 13 十二烷酸 − − − − − 2.99 − − − − − − − − 14 十六酸(棕榈酸) − − − − − − 4.27 5.2 − − 2.74 − − − 15 18-甲基十九碳酸 − − − − − − − 1.5 2.11 − − − − − 16 山嵛酸 − − − − − − − 1.2 1.89 2.08 2.81 1.9 2.55 − 17 14-甲基十五酸 − − − − − − − − − 3.67 − 2.11 − − 18 14-甲基十七酸 − − − − − − − − − 2.5 − − − − 总和 50.1 49.84 54.84 50.16 59.58 57.85 68.69 77.09 55.19 72.23 79.05 81 72.57 73.43 伯醇类 1 二十二烷醇 0.25 0.29 0.11 0.21 − − − 0.14 0.17 2.21 0.09 − 1.09 − 2 二十七烷醇 3.95 4.52 2.09 2.1 1.73 1.98 0.1 1.2 2.32 1.08 0.18 0.06 0.62 0.68 3 二十四烷醇 − 6.66 2.95 3.25 2.64 2.74 − 2 3.56 1.66 − − 0.09 1.14 4 二十八烷醇 − 0.21 − 1.7 − − − 0.17 1.74 0.94 0.12 0.08 0.23 − 总和 4.2 11.68 5.15 7.26 4.37 4.72 0.1 3.51 7.79 5.89 0.39 0.14 2.03 1.82 酯类 1 碳酸癸基十四烷基酯 5.79 − 5.03 5.44 3.95 − − − − 3.44 5.61 4.07 5 5.37 2 山嵛酸乙酯 2.78 − 2.48 − 2.26 2.65 2.52 − − − 0.19 0.15 0.13 − 3 花生酸乙酯 − − 1.9 − 2.54 2.41 0.4 − − − − 0.15 − − 4 木焦油酸乙酯 − − − − − − 2.74 − − − 0.12 0.13 − − 5 碳酸癸基十二烷基酯 − − − − − − − − 5.03 − − − − − 6 二十酸甲酯 − − − − − − − − 4.06 − − − 3.72 − 总和 8.57 0 9.41 5.44 8.75 5.06 5.66 0 9.09 3.44 5.92 4.5 8.85 5.37 醛类 1 正二十六烷醛 3.06 3.75 3.06 3.68 − 3.69 4.78 − − − − − − − 2 二十九醛 0.72 0.62 0.58 0.92 0.73 0.43 0.57 0.33 0.69 0.99 1.17 1.23 0.91 0.73 3 9Z-十八烯醛二甲基缩醛 1.32 − 1.29 − 1.27 3.21 1.84 − − 1.19 − 1.58 0.94 0.95 4 十二醛二甲缩醛 − 0.64 0.43 0.93 0.25 1.18 1.64 0.1 − − 0.56 0.06 0.1 0.12 5 二十八烷醛 2.71 − 2.65 3.22 2.63 − − − − − − − − − 总和 7.81 5.01 8.01 8.75 4.88 8.51 8.83 0.43 0.69 2.18 1.73 2.87 1.95 1.8 烷烃 1 正三十二烷 0.59 0.68 0.53 0.53 0.54 0.63 − 0.81 1.14 0.76 1.07 0.93 1.33 1.04 2 正四十烷 0.47 0.6 0.37 0.41 0.46 0.4 − 0.82 1.15 0.68 1.04 0.88 1.2 1 3 2-甲基二十六烷 − − − 0.24 − 0.13 − 0.62 1.91 1.1 1.18 0.83 1.32 1.28 4 二十二烷 − − − − 0.34 − − 0.4 0.86 0.68 0.89 0.66 0.85 1.21 5 正二十八烷 − − − − − − 6.66 − − − − − − − 总和 1.06 1.28 0.9 1.18 1.34 1.16 6.66 2.65 5.06 3.22 4.18 3.3 4.7 4.53 萜类 1 叶绿醇 − 1.11 0.89 0.26 0.22 0.3 1.25 0.8 − 0.35 0.86 0.47 − 0.63 2 1-甲氧基-3,7,11-三甲基-2,6,10-十二烷三烯 − − 0.12 − 0.15 0.18 0.16 − − 0.17 0.53 0.57 0.77 1.39 总和 0 1.11 1.01 0.26 0.37 0.48 1.41 0.8 0 0.52 1.39 1.04 0.77 2.02 其他类 1 1-十五烯 3.41 − 0.5 0.65 0.44 0.72 − − 0.17 − − − 0.09 − 2 (E)-5-二十碳烯 1.18 1.34 0.4 0.65 0.46 0.33 − 0.4 0.26 0.18 − − − − 3 1-十九烯 9.49 11.07 4.64 5.84 4.2 4.54 0.17 3.5 5.47 2.54 0.13 0.06 1.71 1.61 4 1-二十一(碳)烯 1.1 1.21 0.5 0.63 0.48 0.39 − 0.39 0.68 0.22 − − 0.12 0.13 5 1-十四烯 − 2.56 − − − − − − − − − − − − 6 1-十七碳烯 − − 3.44 4.5 3.06 3.14 − 2.2 3.69 1.06 − − 1.01 0.76 7 1-十八烯基甲基醚 1.81 2.21 1.79 2.12 1.83 2.16 − 1.1 0.98 1.3 1.41 0.82 1.09 1.11 8 三(2,4-二-叔丁基苯基)磷酸酯 − − 1.48 3.97 1.28 1.68 0.32 − − − − − − − 9 芥酸酰胺 − − − − − − − 2.5 − − − − − − 总和 16.99 18.39 12.75 18.36 11.75 12.96 0.49 10.09 11.25 5.3 1.54 0.88 4.02 3.61 注:−表示未检测到该物质;A0、A1、A2、A3、A4、A5、A6,B0、B1、B2、B3、B4、B5、B6分别为夏黑及阳光玫瑰葡萄于贮藏期中第0、10、20、30、40、50、60 d。 -
[1] 付镇芳, 何博, 顾群英. 塑料大棚夏黑葡萄早熟丰产栽培技术[J]. 农业科技与信息,2022(14):5−7. [FU Z F, HE B, GU Q Y. Plastic greenhouse Summer Black grape early maturity and yield cultivation technology[J]. Agricultural Science-Technology and Information,2022(14):5−7.] FU Z F, HE B, GU Q Y. Plastic greenhouse Summer Black grape early maturity and yield cultivation technology[J]. Agricultural Science-Technology and Information, 2022(14): 5−7.
[2] 孙明明, 丁玮琳, 常大勇, 等. 阳光玫瑰葡萄的果锈问题及防治措施[J]. 果树实用技术与信息,2023(8):43−45. [SUN M M, DING W L, CHANG D Y, et al. Fruit rust problems and control measures in Shine Muscat grapes[J]. Applied Technology and Information for Fruit Tree,2023(8):43−45.] SUN M M, DING W L, CHANG D Y, et al. Fruit rust problems and control measures in Shine Muscat grapes[J]. Applied Technology and Information for Fruit Tree, 2023(8): 43−45.
[3] LIU G S, LI H L, PENG Z Z, et al. Composition, metabolism and postharvest function and regulation of fruit cuticle:A review[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,411:135449. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.135449
[4] GABLER F M, SMILANICK J L, MANSOUR M, et al. Correlations of morphological, anatomical, and chemical features of grape berries with resistance to botrytis cinerea[J]. Phytopathology,2003,93(10):1263−1273. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO.2003.93.10.1263
[5] SILVA-MORENO E, BRITO-ECHEVERRÍA J, LÓPEZ M, et al. Effect of cuticular waxes compounds from table grapes on growth, germination and gene expression in botrytis cinerea[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology,2016,32(5):74. doi: 10.1007/s11274-016-2041-4
[6] ZHANG M, ZHANG P, LU S, et al. Comparative analysis of cuticular wax in various grape cultivars during berry development and after storage[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2021,8:817796. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.817796
[7] YANG M, LUO Z, LI D, et al. Role of epicuticular wax involved in quality maintenance of table grapes:Evidence from transcriptomic data[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2023,196:112155. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2022.112155
[8] 王雨菲. 木纳格葡萄表皮蜡质组分分析及其对果实耐贮性的影响[D]. 石河子:石河子大学, 2023. [WANG Y F. Analysis of the wax fractions of the epidermal skin of Munake grapes and their influence on the storage resistance of the fruit[D]. Shihezi:Shihezi University, 2023.] WANG Y F. Analysis of the wax fractions of the epidermal skin of Munake grapes and their influence on the storage resistance of the fruit[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2023.
[9] 楚文靖. 蓝莓蜡质对果实采后衰老的影响及机理研究[D]. 南京:南京农业大学, 2017. [CHU W J. Study on the effect and mechanism of blueberry wax on postharvest fruit senescence[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017.] CHU W J. Study on the effect and mechanism of blueberry wax on postharvest fruit senescence[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017.
[10] 曹建康, 姜微波, 赵玉梅. 果蔬采后生理生化实验指导[M]. 北京:中国轻工业出版社, 2007. [CAO J K, JIANG M W, ZHAO Y M. Experimental guidance on postharvest physiology and biochemistry of fruits and vegetables[M]. Beijing:China Light Industry Press, 2007.] CAO J K, JIANG M W, ZHAO Y M. Experimental guidance on postharvest physiology and biochemistry of fruits and vegetables[M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2007.
[11] RIEDERER M, SCHNEIDER G. The effect of the environment on the permeability and composition of citrus leaf cuticles:II. Composition of soluble cuticular lipids and correlation with transport properties[J]. Planta,1990,180(2):154−165.
[12] YANG L, HU W, LIU D, et al. Comparative analysis of the crystal morphology, chemical composition and key gene expression between two kumquat fruit cuticular waxes during postharvest cold storage[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2023,206:112550. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2023.112550
[13] CHAI Y, LI A, CHIT WAI S, et al. Cuticular wax composition changes of 10 apple cultivars during postharvest storage[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,324:126903. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126903
[14] GE S, WANG R, YANG L, et al. Transcriptomics and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry metabolomics reveal the mechanism of heat shock combined with 1-methylcyclopropene to regulate the cuticle wax of jujube fruit during storage[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,408:135187. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135187
[15] 黄世安. 李果实贮藏过程中蜡质变化规律及与耐贮性的关系[D]. 贵阳:贵州大学, 2023. [HUANG S A. Changes of wax regularity during storage of plum fruits and its relationship with storage resistance[D]. Guiyang:Guizhou University, 2023.] HUANG S A. Changes of wax regularity during storage of plum fruits and its relationship with storage resistance[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2023.
[16] LIU D, MA Q, YANG L, et al. Comparative analysis of the cuticular waxes and related gene expression between ‘Newhall’ and ‘Ganqi 3’ navel orange during long-term cold storage[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2021,167:1049−1060. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.09.032
[17] HUANG H, WANG L, XU X, et al. Morphological, chemical, and biosynthetic changes in pericarp waxes in response to the browning of litchi fruit during storage[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2022,191:111968. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2022.111968
[18] LARA I, BELGE B, GOULAO L F. The fruit cuticle as a modulator of postharvest quality[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2014,87:103−112. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2013.08.012
[19] WANG M, WANG Y, WU H, et al. Three TaFAR genes function in the biosynthesis of primary alcohols and the response to abiotic stresses in Triticum aestivum[J]. Scientific Reports,2016,6(1):25008. doi: 10.1038/srep25008
[20] 张群. 欧亚种提子类葡萄贮藏期间果实能量亏损与品质劣变机理研究[D]. 长沙:中南林业科技大学, 2019. [ZHANG Q. Study on mechanism of energy loss on quality deterioration of Vitis vinifera L. grape fruit during storage[D]. Changsha:Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2019.] ZHANG Q. Study on mechanism of energy loss on quality deterioration of Vitis vinifera L. grape fruit during storage[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2019.
[21] CHAI J, LIAO B, LI R, et al. Changes in taste and volatile compounds and ethylene production determined the eating window of ‘Xuxiang’ and ‘Cuixiang’ kiwifruit cultivars[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2022,194:112093. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2022.112093
[22] ZHU S, HUANG S, LIN X, et al. The relationships between waxes and storage quality indexes of fruits of three plum cultivars[J]. Foods,2023,12(8):1717. doi: 10.3390/foods12081717
[23] HUANG H, BURGHARDT M, SCHUSTER A C, et al. Chemical composition and water permeability of fruit and leaf cuticles of Olea europaea L.[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2017,65(40):8790−8797. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03049
[24] 王晓晶, 吴昊, 胡盼盼. 红枣多酚预涂膜对葡萄贮藏品质的影响[J]. 北方园艺,2023(24):89−95. [WANG X J, WU H, HU P P. The effect of red date polyphenol precoating film on grape storage quality[J]. Northern Horticulture,2023(24):89−95.] doi: 10.11937/bfyy.20232367 WANG X J, WU H, HU P P. The effect of red date polyphenol precoating film on grape storage quality[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2023(24): 89−95. doi: 10.11937/bfyy.20232367
[25] SHI H, ZHOU W H, XU Y Y, et al. Effect of calcium spray at flowering combined with post-harvest 1-MCP treatment on the preservation of grapes[J]. Heliyon,2023,9(9):e19918. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19918
[26] 海龙飞. 软/硬肉葡萄果实发育中细胞壁变化及VvPME19基因在果实软化中的功能分析[D]. 郑州:河南农业大学, 2023. [HAI L F. Cell wall changes in fruit development and the function of VvPME19 gene in fruit softening in soft/hard-fleshed grapes[D]. Zhengzhou:Henan Agricultural University, 2023.] HAI L F. Cell wall changes in fruit development and the function of VvPME19 gene in fruit softening in soft/hard-fleshed grapes[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2023.
[27] 帅良, 林德胜, 廖玲燕, 等. 不同贮藏温度对百香果果实糖酸组分变化的影响[J]. 核农学报,2023,37(12):2408−2416. [SHUAI L, LIN D S, LIAO L Y, et al. Effect of different storage temperatures on the changes of sugar and acid components of passion fruit[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2023,37(12):2408−2416.] doi: 10.11869/j.issn.1000-8551.2023.12.2408 SHUAI L, LIN D S, LIAO L Y, et al. Effect of different storage temperatures on the changes of sugar and acid components of passion fruit[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 37(12): 2408−2416. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.1000-8551.2023.12.2408
[28] 谭沙, 朱仁威. 不同保鲜处理方式对刺葡萄贮藏效果的影响[J]. 广东化工,2022,49(16):54−57,50. [TAN S, ZHU R W. Effect of different preservation treatments on the storage effect of Thorn grapes[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2022,49(16):54−57,50.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2022.16.018 TAN S, ZHU R W. Effect of different preservation treatments on the storage effect of Thorn grapes[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2022, 49(16): 54−57,50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2022.16.018
[29] ZHANG Z, XU J, CHEN Y, et al. Nitric oxide treatment maintains postharvest quality of table grapes by mitigation of oxidative damage[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2019,152:9−18. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.01.015
[30] 许蕙金兰, 吴培文, 陈仁驰, 等. 贮藏温度对巨峰葡萄采后生理和贮藏品质的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(21):192−197. [XU H L J, WU P W, CHEN R C, et al. Effects of storage temperature on postharvest physiology and storage quality of Kyoho grapes[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(21):192−197.] XU H L J, WU P W, CHEN R C, et al. Effects of storage temperature on postharvest physiology and storage quality of Kyoho grapes[J]. Food Research and Development, 2018, 39(21): 192−197.
[31] 冯叙桥, 关筱歆, 张鹏, 等. 1-MCP结合CIO2处理对冰温贮藏玫瑰香葡萄生理和品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2012,33(17):333−338. [FENG X Q, GUAN Y Y, ZHANG P, et al. Effects of 1-MCP combined with CIO2 treatment on physiology and quality of grapes stored at ice temperature[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2012,33(17):333−338.] FENG X Q, GUAN Y Y, ZHANG P, et al. Effects of 1-MCP combined with CIO2 treatment on physiology and quality of grapes stored at ice temperature[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2012, 33(17): 333−338.
[32] 孙思胜, 覃成, 张晓娟, 等. 不同浓度的川芎复方提取物对“夏黑”葡萄贮藏品质的影响[J]. 北方园艺,2024(16):80−86. [SUN S S, QIN C, ZHANG X J, et al. The effect of different concentrations of Chuanxiong compound extract on the storage quality of ‘Summer Black’ grapes[J]. Northern Horticulture,2024(16):80−86.] SUN S S, QIN C, ZHANG X J, et al. The effect of different concentrations of Chuanxiong compound extract on the storage quality of ‘Summer Black’ grapes[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2024(16): 80−86.
[33] 栗温新. 葡萄VvPGs/VvPLs基因家族鉴定及VvPL11在果实软化中的功能分析[D]. 郑州:河南农业大学, 2024. [LI W X. Identification of grapevine VvPGs/VvPLs gene family and functional analysis of VvPL11 in fruit softening[D]. Zhengzhou:Henan Agricultural University, 2024.] LI W X. Identification of grapevine VvPGs/VvPLs gene family and functional analysis of VvPL11 in fruit softening[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2024.
[34] WANG J, HAO H, LIU R, et al. Comparative analysis of surface wax in mature fruits between satsuma mandarin (Citrus unshiu) and ‘Newhall’ navel orange (Citrus sinensis) from the perspective of crystal morphology, chemical composition and key gene expression[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,153:177−185. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.12.021
[35] THOMAI T, SFAKIOTAKIS E, DIAMANTIDIS G, et al. Effects of low preharvest temperature on scald susceptibility and biochemical changes in ‘Granny Smith’ apple peel[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,1998,76(1):1−15.
[36] LI Z, HUANG J, CHEN H, et al. Sulfur dioxide maintains storage quality of table grape (Vitis vinifera cv ‘Kyoho’) by altering cuticular wax composition after simulated transportation[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,408:135188. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135188
[37] CHU W J, GAO H Y, CHEN H J, et al. Effects of cuticular wax on the postharvest quality of blueberry fruit[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,239:68−74. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.06.024
[38] DOMÍNGUEZ E, HEREDIA-GUERRERO J A, HEREDIA A. The biophysical design of plant cuticles:An overview[J]. New Phytologist,2011,189(4):938−949. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03553.x
[39] LIU R, SHANG F, NIU B, et al. Melatonin treatment delays the softening of blueberry fruit by modulating cuticular wax metabolism and reducing cell wall degradation[J]. Food Research International,2023,173:113357. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113357
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 张涛,周芷夷,邓文奇,张婷,马杰,王艺诺,于俊飞,周建中. 苦杏仁多肽/壳聚糖复合膜的制备及其对奶酪的保鲜效果. 食品与发酵工业. 2025(06): 232-238 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



