Effect of Hydrostatic Pressure Processing Combined with DMDC and Nisin Treatment on the Quality of Bayberry Juice during Storage
-
摘要: 为增强超高压处理对杨梅汁的杀菌效果,比较了热杀菌(Thermal sterilization,TS)(90 ℃,5 min)、超高压(Hydrostatic pressure processing,HPP)杀菌(500 MPa,5 min)、HPP联合抑菌剂处理(HPP联合二烷酸二甲酯(Dimethyl dicarbonate,DMDC)处理、HPP联合乳酸链球菌素(Nisin)处理以及HPP联合DMDC和Nisin处理)对杨梅汁4 ℃贮藏过程中微生物数量、色度、花色苷、聚合色素、褐变度、总黄酮、总酚、挥发性化合物的影响。结果表明,单独HPP处理对杨梅汁杀菌效果有限,在贮藏10 d后,杨梅汁中菌落总数超过食品安全国家标准规定的100 CFU/mL。TS处理与HPP联合抑菌剂处理的杨梅汁,4 ℃贮藏40 d,微生物数量仍符合食品安全国家标准。在贮藏过程中,不同处理组杨梅汁的花色苷含量呈下降趋势,聚合色素、褐变度呈上升趋势,总黄酮、总酚含量先下降后上升,色差变化不明显,其中TS处理组贮藏过程中聚合色素、总花色苷、褐变度、总酚含量均低于HPP处理组和HPP联合抑菌剂处理组,而4组非热杀菌的杨梅汁各项指标无明显差异。在贮藏40 d后,各组挥发性化合物含量相比于未杀菌杨梅汁均减少,其中热杀菌组和非热杀菌组含量没有显著差异,但非热杀菌更好地保留了杨梅汁中芳樟醇(玫瑰花香)与2-戊基呋喃(蔬菜味青香)这两种积极风味物质。贮藏40 d后的热处理组总香气活力值低于HPP处理组和HPP联合抑菌剂处理组,香气损失较大。通过主成分分析(PCA),能够区分原汁、热杀菌组与非热杀菌组挥发性物质的差异性,而4组非热杀菌杨梅汁彼此之间距离接近,表明抑菌剂的使用不会对贮藏后期的杨梅汁风味产生明显影响。综上所述,HPP联合DMDC和Nisin可以提升HPP对杨梅汁的杀菌效果,延长杨梅汁货架期,且能较好地保留杨梅汁的品质。该研究结果可为杨梅汁的非热加工提供理论依据。Abstract: In order to enhance the sterilization effect of hydrostatic pressure processing (HPP) on bayberry juice, the effects of thermal sterilization (90 ℃, 5 min), HPP treatment (500 MPa, 5 min), HPP combined antimicrobial agent treatment (HPP combined with dimethyl dicarbonate (DMDC), HPP combined with nisin, and HPP combined with both DMDC and nisin) on microbial population, chromaticity, anthocyanin, polymeric pigment, browning degree, total flavonoid, total phenolics, and volatile compounds of bayberry juice during storage at 4 ℃ were compared. The results showed that HPP treatment alone had limited sterilizing effect on bayberry juice. After 10 d of storage, the total number of colonies in bayberry juice exceeded 100 CFU/mL, which violated the national food safety standard. The quantity of microorganisms of bayberry juice treated with TS and HPP combined antimicrobial agent still met the national standard of food safety after 40 d storage at 4 ℃. During the storage, the anthocyanin content of bayberry juice in different treatment groups showed a decreasing trend, whereas the polypigment and browning degree kept increasing. Meanwhile, the total flavonoid and total phenolic contents decreased first and then increased, while the color difference did not change significantly. The polymerized pigment, total anthocyanin, browning degree, and total phenolic content of TS group were lower than those of the HPP treatment group and the HPP combined antimicrobial agent treatment group during 40 d storage, and no obvious difference was observed among the parameters of the non-thermal-sterilized groups. After 40 d of storage, the content of volatile components decreased in all groups compared to unpasteurized bayberry juice, with no significant difference between thermal sterilization group and the non-thermal-sterilized groups. However, the non-thermal-sterilized bayberry juice better retained two positive flavor substances namely linalool (rose aroma) and 2-pentylfuran (green aroma). The total OVA contribution in the heat-treated group after 40 d of storage was lower than that in the HPP treated group and the HPP combined antimicrobial agent treated group, indicating greater loss of aroma due to thermal treatment. Principal component analysis (PCA) allowed the distinguishment of differences in volatiles among the original juice, heat-sterilized group and non-heat-sterilized group. And the four groups of non-thermal-sterilized bayberry juice were close to each other, indicating that the use of antimicrobial agents did not significantly affect the flavor of bayberry juice in the later stages of storage. In summary, DMDC and nisin can improve the sterilizing effect of HPP on bayberry juice, extending its shelf life, and better maintaining the quality of bayberry juice. The results can provide theoretical basis for non-thermal processing of bayberry juice.
-
Keywords:
- hydrostatic pressure processing /
- bayberry juice /
- DMDC /
- nisin /
- anthocyanin /
- volatile compounds /
- odor activity value
-
杨梅(Morella rubra Lour.)是杨梅科杨梅属的常绿乔木植物,又名龙晴、朱红,因其形似水杨子,味道似梅子,所以名叫杨梅。杨梅起源于中国,在两千年前就有人工栽培的记载[1]。杨梅主要生长于我国的亚热带地区,云南、广西、广东、浙江均有种植,其果实颜色鲜艳、酸甜适中、风味独特,含有花青素和黄酮醇等生物活性成分,具有抗炎、抗肿瘤、抗菌、预防心血管疾病等多种健康功效,具有较高的食用、经济价值[2]。但杨梅成熟期集中,鲜果供应时间短,且果肉不具有果皮保护,极易腐败变质,贮藏期短。对杨梅进行精深加工,可以减少采后损失,提升附加值。将杨梅加工成果汁,可在短期内大量消耗杨梅,延长产业链;而果汁既可以作为终端产品直面消费者,也可以作为饮料、果酒等加工产品的中间原料,具有较好的市场前景。
果汁加工常用的杀菌方式有热杀菌和非热杀菌。传统热杀菌(Thermal sterilization,TS)对热敏性果汁中天然成分、生物活性成分以及挥发性成分影响较大,如王正东等[3]研究发现热杀菌(72 ℃,20 min)处理的杨梅汁,花色苷含量减少了34.5%,而非热杀菌对果汁的营养成分、色泽、风味和新鲜度等保持较好。超高压(Hydrostatic pressure processing,HPP)技术是典型的非热杀菌技术,产业化程度最高[4],但也存在一定缺陷,比如对于耐压菌杀菌效果较差[5]、后期活而不可培养(Viable but non-culture,VBNC)态细菌的复苏[6]、钝酶效果有限[7]等。杨梅热敏性较强,热杀菌易造成色泽和风味变化,而单一的超高压杀菌效果有限。为了应对这种现象,有学者提出HPP+技术的概念,将HPP灭菌技术联合其他非热杀菌技术一起使用,如联合二氧化碳[8]、乳酸链球菌素(Nisin)[9]、月桂酰精氨酸乙酯抗菌膜[10]处理,提高杀菌效果,降低HPP的加工强度(时间或压力)[10],减少能耗。Nisin是唯一被允许用作食品添加剂的细菌素,其本质是一种多肽类物质,能够被水解为氨基酸,对革兰氏阳性菌杀灭效果较革兰氏阴性菌好。超高压能够破坏细菌外膜屏障,增强Nisin的抗菌活性[9]。二烷酸二甲酯(Dimethyl dicarbonate,DMDC)又名维果灵,是我国食品添加剂使用标准中允许使用的一种果蔬饮料防腐剂,对酵母灭活效果较好,其机理是通过亲和基团与微生物中的关键酶相互作用使酶失活,从而导致细胞死亡[11]。DMDC在水中极易分解,生成微量的甲醇和二氧化碳,对人体无害。可见,Nisin和DMDC均具有较高的安全性,将其与超高压联合使用,很有可能提升超高压对杨梅汁的杀菌效果,但目前尚无相关报道。
因此,本研究比较了TS、HPP以及HPP联合抑菌剂(DMDC与Nisin)处理对贮藏过程中的杨梅汁品质的影响,以期为高品质杨梅汁的生产提供科学指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
杨梅 购买于水果批发市场,置于−20 ℃冷冻;DMDC、乳酸链球菌素Z(Nisin Z)、芦丁、福林酚 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;柠檬酸、氯化钾、亚硝酸钠、氢氧化钠、碳酸钠 福晨(天津)化学试剂有限公司;PCA(Plate count agar)培养基、孟加拉红(虎红)培养基 广东环凯微生物科技有限公司;氯化钠 天津市风船化学试剂科技有限公司;盐酸 广州化学试剂厂;无水乙酸钠、偏重亚硫酸钾、没食子酸 天津大茂化学试剂厂;冰醋酸、无水乙醇、无水甲醇 天津市富宇精细化工有限公司;磷酸(色谱级)、九水合硝酸铝 天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;乙腈(色谱级) 天津市彪仕奇科技发展有限公司;矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷(Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside,C3G) 成都钠钶锂生物科技有限公司;环己酮 色谱纯,上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司。
PBJ-S02E破壁料理机 江门市贝尔斯顿电器有限公司;SHHP-57DZM-600超高压设备 山西三水河科技股份有限公司;FE28型pH计 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;D3024R台式高速冷冻离心机 美国赛洛捷克SCILOGEX公司;UV-1900i紫外可见分光光度计、LC-20AT高效液相色谱仪 日本岛津公司;CR-400色彩色差计 日本Chroma Meter;DB-5非极性毛细管色谱柱(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm) 美国Restek;7890B-5977B型气相色谱-质谱联用仪、PAL自动进样器系统 美国Agilent科技公司;57329-U型三相固相微萃取头(DVB/CAR/PDMS) 美国Supelco公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 杨梅汁的制备
将冰冻杨梅于室温下解冻3 h,去核、打浆,200目滤布过滤,得杨梅汁。
热杀菌处理:将杨梅汁加热至90 ℃后,灌装于玻璃瓶中。然后将玻璃瓶置于90 ℃水浴灭菌5 min,随后倒置冷却。记为TS组。
超高压灭菌处理:灌装后进行超高压灭菌处理(500 MPa、5 min),记为H处理组。
超高压联合抑菌剂处理:向杨梅汁中分别添加DMDC(200 mg/L)与Nisin(150 mg/L),以及同时添加DMDC(200 mg/L)和Nisin(150 mg/L)[12]。灌装后进行超高压灭菌处理(500 MPa、5 min)。分别添加DMDC和Nisin记为HD和HN处理组。同时添加DMDC和Nisin记为HDN处理组。
灭菌完成后统一放置于4 ℃冷库中避光贮藏40 d。
1.2.2 微生物指标的测定
参考GB 4789.2-2022《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定》与GB 4789.15-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 霉菌和酵母计数》。测定杨梅汁中总好氧菌数(Total aerobic bacteria,TAB)、霉菌数(Yeasts,Y)、酵母数(Molds,M)。
1.2.3 色度值的测定
参考徐亦秀[13]的方法并稍作修改。将杨梅汁倒入5 cm×1 cm×5.2 cm的透明比色皿,使用手持色差仪测定。测定前使用白色标准板对颜色进行校正。色度值、色调角(h°)与色差按下列公式计算。
色度值=√(a∗2+b∗2) 色调角=arctan(b∗a∗) 色差=√ΔL∗2+Δa∗2+Δb∗2 1.2.4 总花色苷含量的测定
采用pH示差法测定[14]。取0.2 mL杨梅汁于5 mL离心管中,分别添加2.8 mL的pH1.0的缓冲盐溶液和pH4.5的缓冲盐溶液。静置10 min后,于5000 r/min下离心5 min。然后将上清液倒入比色皿中,以纯水为空白,分别测定510、700 nm下的吸光值A,按下列公式计算总花色苷含量。
花色苷含量(mg/L)=ΔA×Mw×DF×1000ε×1 式中:∆A=(A510 nm−A700 nm)pH1.0−(A510 nm−A700 nm)pH4.5;Mw表示矢车菊素3-葡萄糖苷的相对分子质量,449.2;DF表示稀释倍数,15;ε表示矢车菊素3-葡萄糖苷的摩尔消光系数,26900;1为比色皿光程。
1.2.5 单体花色苷的测定
使用酸化乙醇(乙醇:水:盐酸=50:49.5:0.5)提取杨梅汁中的花色苷(料液比1:9),超声提取10 min,于5000 r/min离心10 min,取上清,过0.22 μm尼龙膜,装入液相瓶待测。单体花色苷含量测定采用高效液相色谱法,参照曾丹等[15]的方法进行测定。
1.2.6 聚合色素含量的测定
聚合色素测定参考张正伟[16]的方法稍作修改。将1 mL的杨梅汁与2 mL的pH为3.0的醋酸/NaCl缓冲盐溶液于5 mL离心管中混合,于8000 r/min下离心5 min,取全部上清,倒入另一支5 mL的离心管,加入160 μL 0.36 mol/L的偏重亚硫酸钾溶液,静置反应10 min,随后测定其510 nm的吸光度值,记为聚合色素含量。
1.2.7 褐变度、总黄酮、总酚含量的测定
褐变度测定参考徐亦秀[13]的方法并稍作修改。将杨梅汁与无水乙醇1:1混合,超声提取10 min,于5000 r/min下离心10 min,取上清倒入比色皿,测定其420 nm下的吸光值。以其吸光度值作为褐变度值。
总黄酮测定参考李镜浩等[17]的方法并稍作修改。取褐变度提取液0.2 mL,加入0.8 mL的无水乙醇。再加入0.1 mL的10%亚硝酸钠溶液,静置反应5 min,随后加入0.1 mL的10%硝酸铝溶液,静置反应5 min,再加入0.8 mL 4% NaOH溶液,静置反应15 min,随后测定其510 nm下的吸光度值。结果以芦丁当量表示。
采用Folin-Ciocalteu比色法[17]测定杨梅汁中的总酚含量。使用酸化甲醇(甲醇:水:盐酸=80:19:1)提取总酚(料液比1:9),超声提取10 min,于8000 r/min离心10 min,取上清,用水稀释5倍后,取1 mL稀释液,加入1 mL福林酚试剂,避光反应5 min,再加入1 mL 15% Na2CO3溶液,避光反应1 h,测定其760 nm下的吸光度值。结果以没食子酸当量表示。
1.2.8 挥发性成分测定
顶空固相微萃取(HS-SPME)条件参照程焕[18]的方法:准确称取4.00 g杨梅汁和1.4 g氯化钠于萃取瓶中,再加入环己酮内标物(47.5 μg/g)。使用PAL自动进样器系统进行前处理,于50 ℃平衡10 min,吸附30 min,250 ℃下解析5 min。
GC-MS分析条件:毛细管柱为DB-5MS弹性毛细管柱(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm);载气为氦气,流速为1.0 mL/min;升温程序:起始温度为40 ℃,保持5 min,以5 ℃/min的速度升温至180 ℃,保持1 min,再以10 ℃/min的速度升温至240 ℃,保持4 min。不分流进样模式。质谱条件:采用全扫描模式采集信号,电离方式EI,电子轰击能量为70 eV;接口温度280 ℃,离子源温度为230 ℃,四级杆温度为150 ℃,扫描质量范围为35~350 amu;扫描速度为5.2次/s。
挥发性成分定性、定量分析:与标准信息库NIST 14进行比对,选择匹配度高于80的检测结果;参考程焕[18]的内标法对化合物进行定量,挥发性物质的相对含量=待求成分物质峰面积×内标物含量/内标物峰面积。
香气活度值(Odor activity value,OAV)的计算公式如下:
OAV=CiOTi 式中:Ci为香气成分的含量;OTi为查阅到的香气成分的香气阈值。
1.3 数据处理
除微生物测定外,所有实验均重复测定3次,使用Microsoft office Excel 2023和Origin2022进行统计、主成分分析和绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 杨梅汁贮藏期间微生物的变化情况
微生物指标是果汁安全的重要指标。未杀菌的杨梅汁菌落总数为1.205×106 CFU/mL,酵母总数为1.13×106 CFU/mL,霉菌未检出。经热杀菌后,杨梅汁中的菌落总数降低至10 CFU/mL,符合GB 7101-2022《食品安全国家标准 饮料》要求的可接受水平限量值100 CFU/mL,且在40 d贮藏过程中,其菌落总数均未超标(表1)。研究发现,500 MPa、5 min超高压灭菌处理能够将杨梅汁中的菌落总数降低至95 CFU/mL,但在10、20、30、40 d贮藏期间,杨梅汁菌落总数均超标。而超高压联合抑菌剂灭菌处理后,杨梅汁在贮藏期间菌落总数均低于100 CFU/mL,表明超高压联合DMDC、Nisin处理具有较好的杀菌效果。这与林怡[19]的500 MPa、5 min处理杨梅汁菌落总数贮藏过程中不超过100 CFU/mL的研究结果不同,这可能与杨梅汁中的初始菌群及前处理不同有关,果汁中耐压菌群的存在会影响超高压灭菌的效果[5],此外,经过超高压胁迫,细菌处于假死(VBNC)状态,在贮藏过程中,能够复苏[6]。因此,对于耐压菌群和处于VBNC状态的细菌,需要利用其他栅栏因子来灭活。
表 1 杨梅汁中微生物数量随贮藏时间的变化(CFU/mL)Table 1. Changes of microbial population in bayberry juice with storage time (CFU/mL)贮藏时间(d) 组别 TS H HD HN HDN 1 TAB 10.00±
14.1495.00±
7.0770.00±
0.0030.00±
14.1445.00±
21.21Y − − − − − M − − − − − 10 TAB 10.00±
14.14105.00±
7.0755.00±
7.0760.00±
14.1455.00±
21.21Y − − − − − M − 5.00±
7.07− − − 20 TAB 5.00±
7.07110.00±
14.1445.00±
35.3650.00±
14.1475.00±
7.07Y − − 5.00±
7.07− − M − − − − − 30 TAB 15.00±
7.07105.00±
7.0765.00±
21.2160.00±
14.1460.00±
0.00Y − − − − − M − − − − − 40 TAB 30.00±
0.00110.00±
14.1475.00±
7.0755.00±
7.0740.00±
0.00Y − − − − − M − − − − − 注:“−”表示未检出;根据GB 7101-2022要求,饮料中菌落总数需低于100 CFU/mL,酵母总数需低于20 CFU/mL,霉菌总数需低于20 CFU/mL。 2.2 杨梅汁贮藏期间的色度变化情况
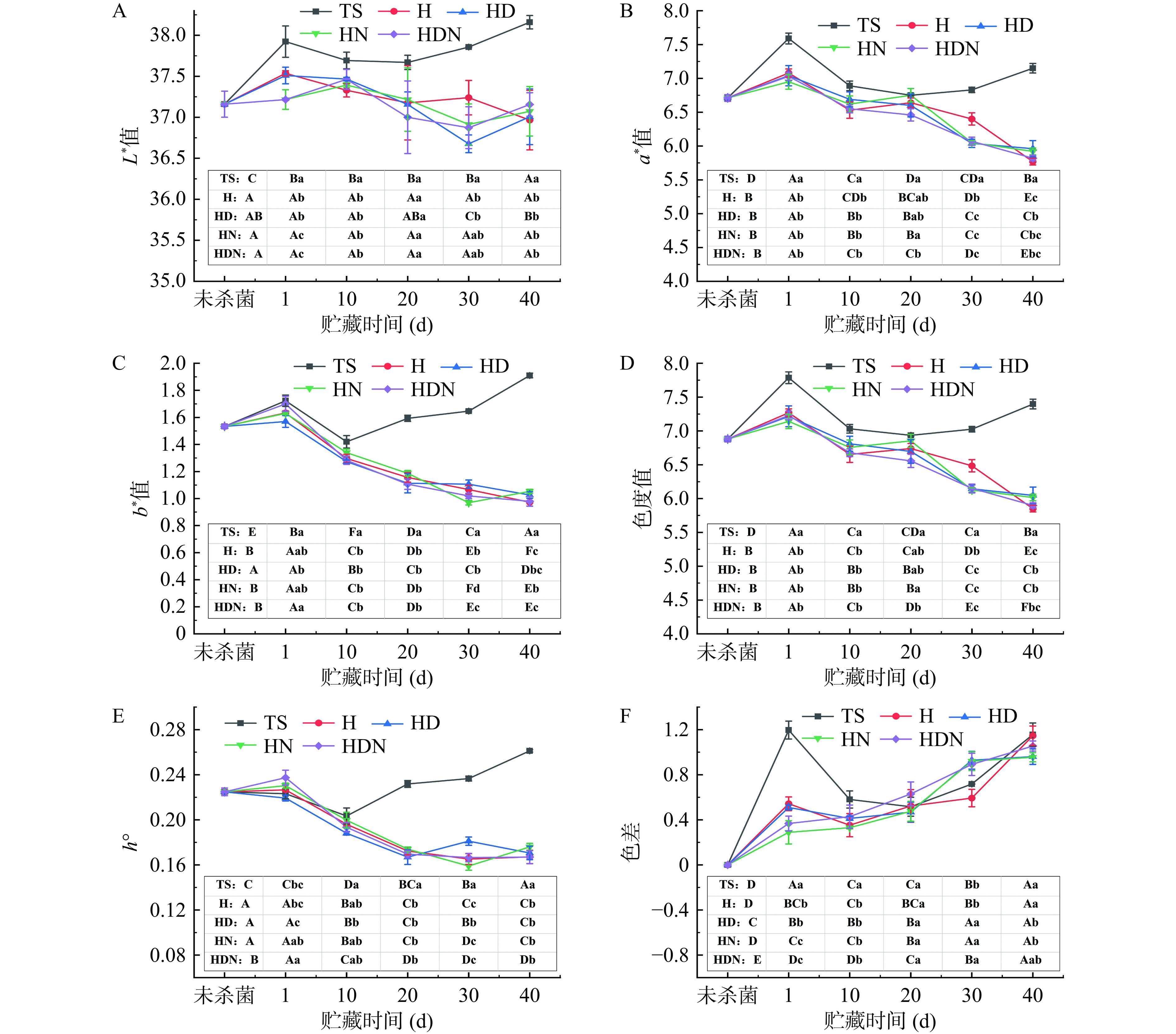
从图1可以看出,热杀菌的杨梅汁色泽略微偏暗。贮藏过程中杨梅汁色度的变化如图2所示,初始色度L*=37.16,a*=6.71,b*=1.53,贮藏过程中,非热杀菌组L*值、a*值、b*值色度值和色调角低于热杀菌组。热杀菌后杨梅汁的色差值增加至1.2,而在贮藏至第40 d时,各组的色差值ΔE无明显差异。
L*值由大到小表示由白变黑、a*值由大到小表示由红变绿,b*值由大到小表示由黄变蓝,色度值表示色彩的饱和度,其值越大表示颜色越丰富,色调角越接近于0度代表颜色越红。褐变的增加会导致颜色更深,L*值更低[20],这与贮藏期间非热杀菌组的褐变度高于热杀菌组的结果一致。红色是杨梅汁最重要的颜色,贮藏期间,热杀菌组a*值高于非热杀菌组,表明热杀菌组红色程度更高,但非热杀菌组的色调角值却更接近0度,表明非热杀菌组红色程度更高。这两种结果互相矛盾,这可能是由于非热杀菌组与热杀菌组二者红色相差程度很小,导致这两种评价方法具有相反的结果。
色差用来衡量颜色之间的差别,其值越大表示差别越大。杨梅汁经过热杀菌后,色差值先增加后降低,这是由于L*值与a*值贮藏过程中先增加后降低。相似的趋势在Yu等[21]的研究中也被报道。在贮藏期间,各处理组总体色差值均小于2,表明颜色变化不明显[20]。由此可见,添加抑菌剂DMDC、Nisin不会对杨梅汁贮藏期间的色泽产生明显影响。
2.3 杨梅汁贮藏期间总花色苷、单体花色苷含量及聚合色素含量变化情况
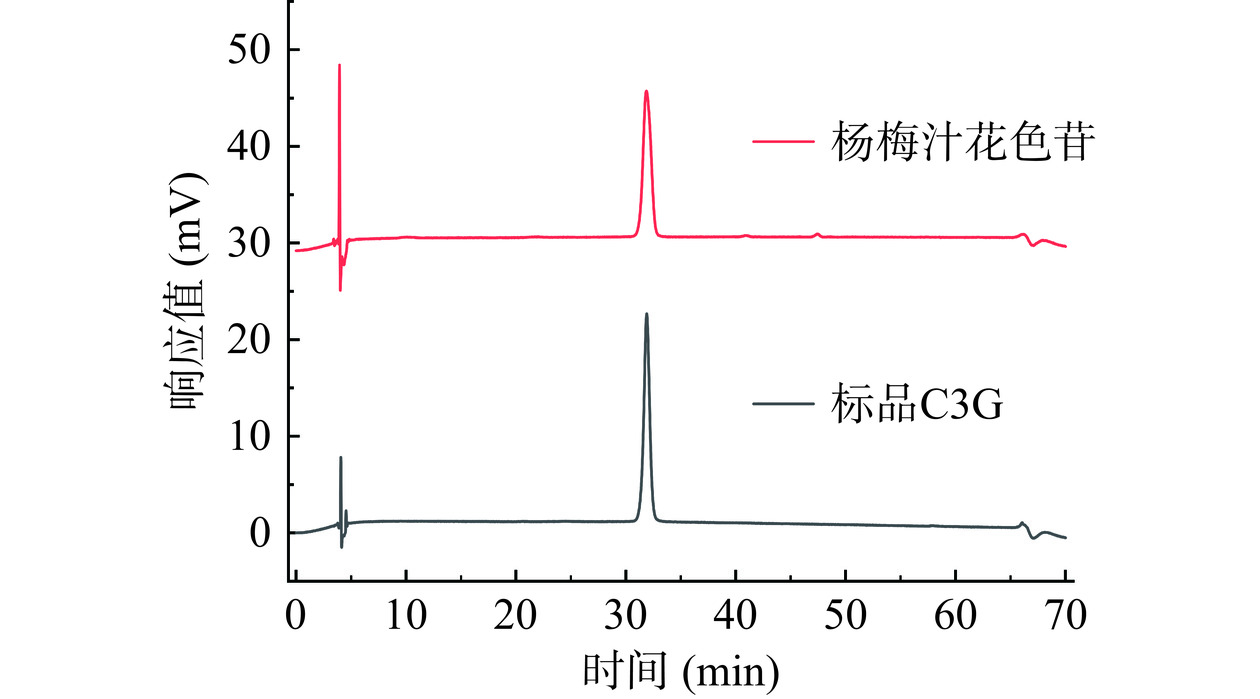
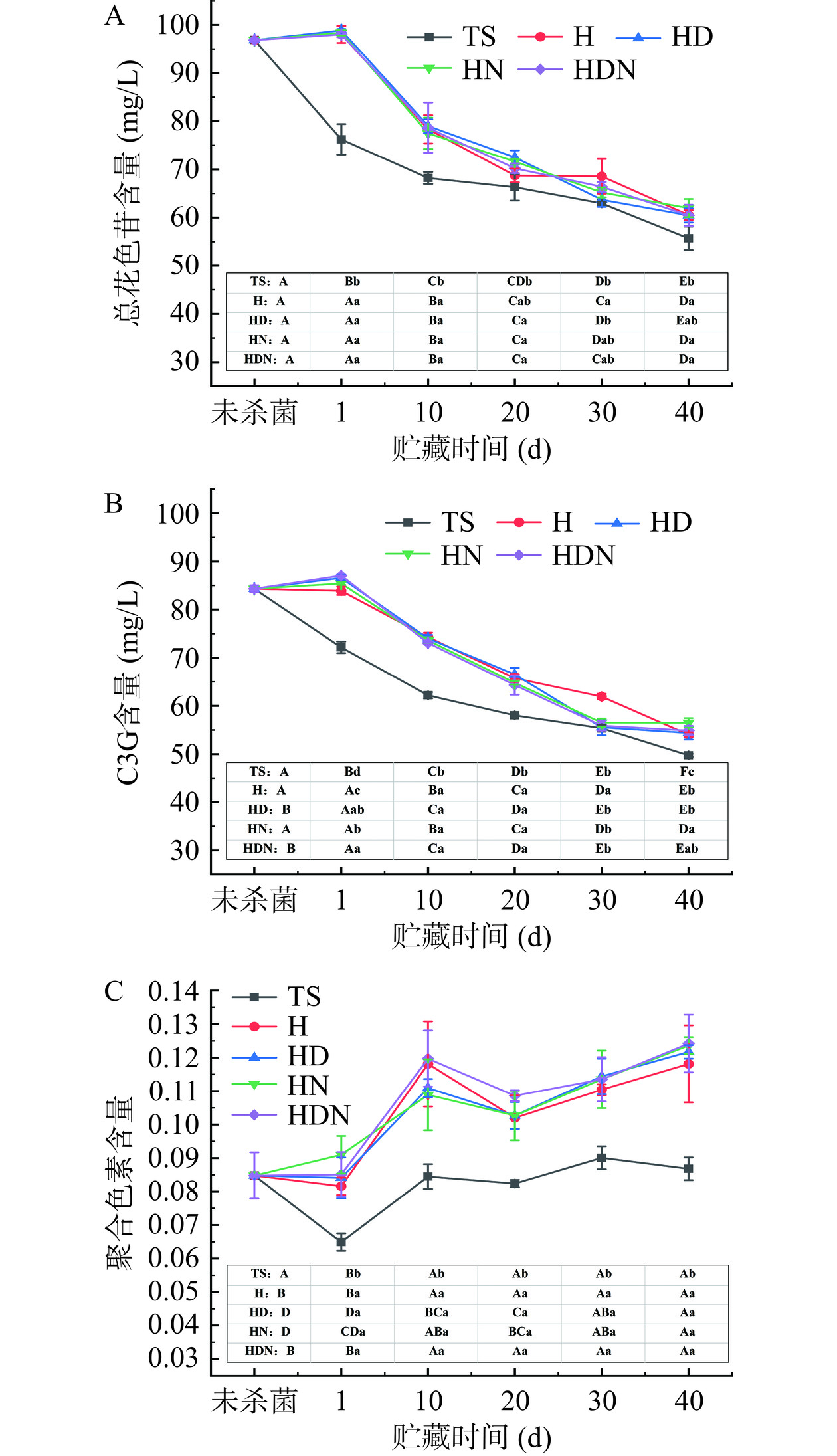
花色苷是植物中主要的水溶性色素,其中矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷分布最广泛[16]。如图3所示,通过液相色谱分析,在520 nm波长下,仅仅观察到一个峰,通过与C3G标准品的保留时间比对,确定其为C3G。杨梅原汁的总花色苷含量为96.85 mg/L(图4A),C3G含量为84.30 mg/L(图4B),占总花色苷的87%,表明C3G是杨梅汁的主要花色苷,这与杜琪珍等[22]的研究结果一致。
杨梅汁经超高压处理后,总花色苷含量略微提高了1.2%~1.5%,而经热杀菌处理后,总花色苷含量降低了21.29%;在前10 d贮藏过程中,非热杀菌处理组杨梅汁始终高于热杀菌处理组,在贮藏10 d后,部分非热杀菌组与热杀菌组总花色苷含量无显著性差异。贮藏过程中C3G变化趋势与总花色苷一致(图4A~B)。由图4C可知,杨梅汁经热杀菌后,聚合色素含量下降,而4组非热杀菌处理组无显著性差异;贮藏过程中,所有处理组的聚合色素含量不断增加,与总花色苷和C3G的变化趋势呈负相关。
研究表明,果汁中花色苷不稳定,对温度、光照等敏感,可与黄烷醇等物质发生缩合反应,生成更稳定的聚合色素[16]。热处理导致的花色苷和聚合色素的下降,可能与花色苷和部分黄烷醇分解从而减少了聚合反应底物有关。而非热处理组贮藏初始阶段花色苷含量较高,但贮藏过程中降解较快,这可能与超高压钝酶效果较弱有关[23],果汁中多酚氧化酶等会加速杨梅汁贮藏过程中花色苷的降解。
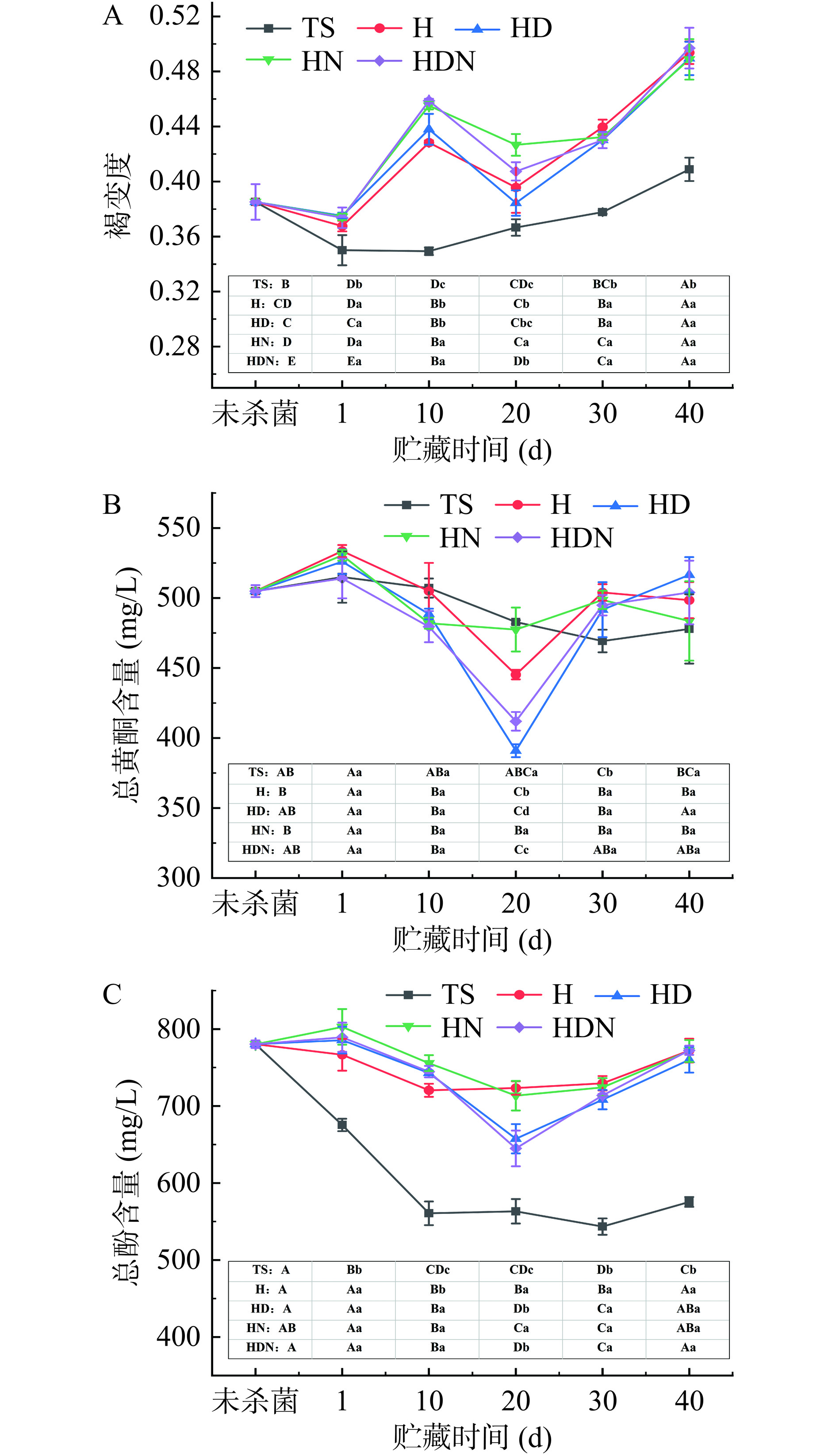
2.4 杨梅汁贮藏过程中褐变度、总黄酮、总酚含量变化情况
由图5A可知,经灭菌后,热杀菌组杨梅汁相比于非热杀菌组的褐变度显著降低(P<0.05),而在贮藏过程中,非热杀菌组杨梅汁褐变度的增加大于热杀菌组。由图5B可知,所有处理组的黄酮含量均呈现先下降后上升的波动趋势,非热杀菌组的总黄酮含量在第20 d达到最低,热杀菌组在第30 d达到最低。由图5C可知,杨梅汁经过热杀菌后,总酚含量降低了13%,而非热杀菌处理则较好地保留了酚类物质;在贮藏过程中,热处理组总酚含量在贮藏前10 d呈下降趋势,后趋于稳定,超高压处理组在贮藏前20 d总酚含量均有不同程度的下降,随后上升;但在整个贮藏过程中,所有非热处理组的总酚含量均显著高于热杀菌处理组(P<0.05)。
热杀菌处理的杨梅汁褐变度低于非热杀菌组,可能与花色苷在420 nm具有一定吸光度有关,与非热处理相比,热杀菌会导致更多的花色苷被降解,使得其在420 nm下测得的吸光度降低。此外,热处理能够使杨梅汁中的酶失活,因此贮藏过程中的褐变主要与非酶褐变有关[24],而超高压处理钝酶效果较弱[23],可能还存在酶促褐变。花色苷是杨梅中主要的类黄酮,在贮藏过程中,热杀菌组花色苷含量均低于非热杀菌组,但黄酮含量却接近,这可能是花色苷降解产物仍具有黄酮母核结构有关,该结果这与李国林等[25]报道的杨梅汤在贮藏过程中的花色苷、类黄酮含量变化情况相似。花色苷等多酚类物质具有热不稳定性,在加热过程中易降解,而超高压以及超高压联合抑菌剂处理在常温下进行,因此,对多酚类物质破坏作用较小。然而,在贮藏后期总酚含量有所增加,可能与果汁中新形成的还原性物质有关[26]。类似的结果在桑葚汁中[27]也有相关报道。
2.5 杀菌前及杀菌贮藏后杨梅汁挥发性成分比较
2.5.1 挥发性物质种类、数量及含量比较
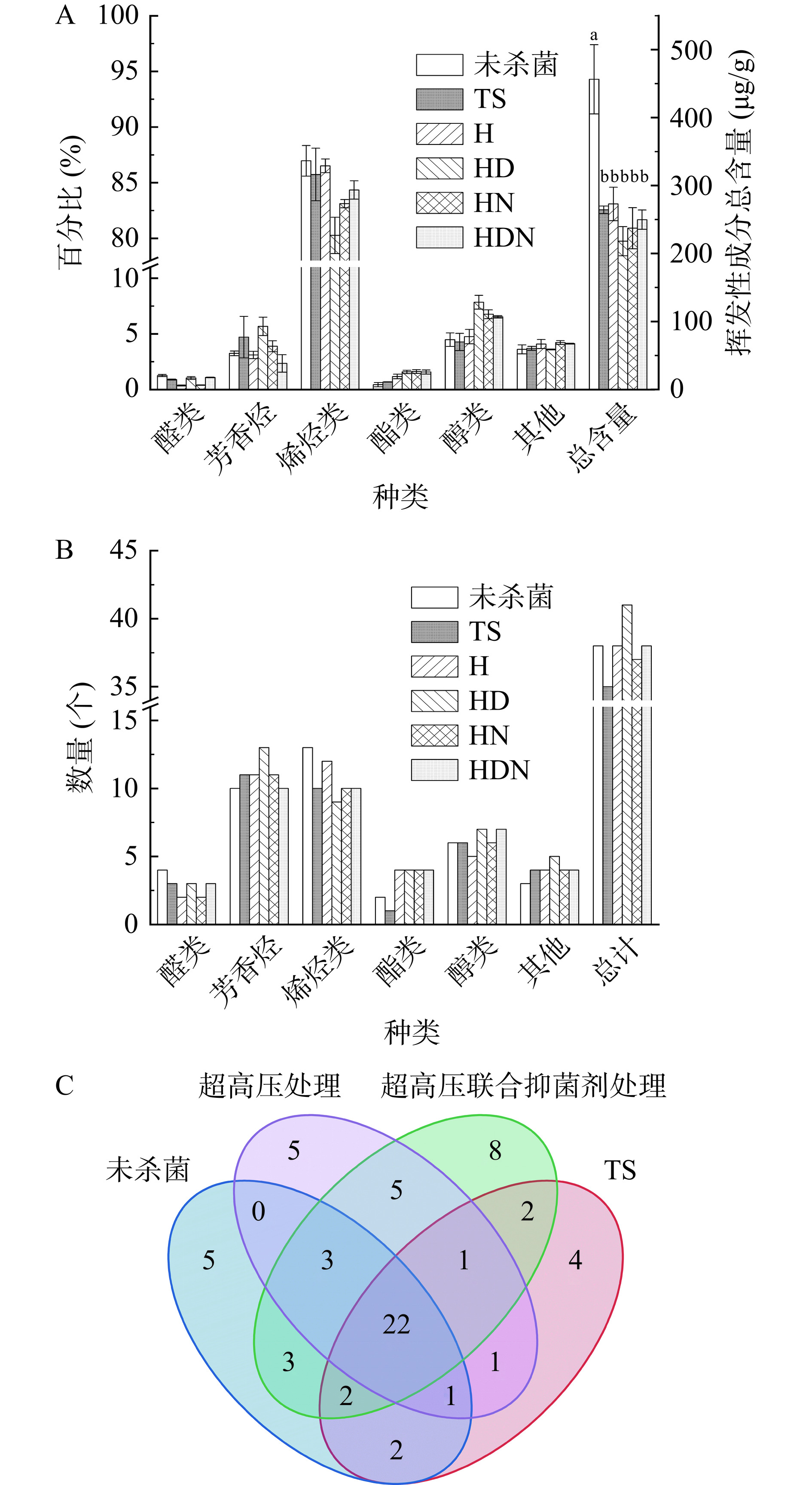
通过HS-SPME-GC-MS分析未杀菌和杀菌后贮藏40 d的杨梅汁中的挥发性成分,结果由图6A所示,原汁中挥发性成分总含量为456.27 μg/g,杀菌贮藏后各组含量显著降低(P<0.05),其中热杀菌组为264.26 μg/g,H组为272.89 μg/g,HD组为218.14 μg/g,HN组为237.61 μg/g,HDN组为249.74 μg/g。灭菌贮藏40 d后,非热杀菌组与热杀菌组挥发性成分含量没有显著差异(P>0.05)。
从杨梅汁中共检测到64种挥发性化合物,其中原汁38种,贮藏40 d后的热杀菌组35种,H组38种,HD组41种,HN组37种,HDN组38种(图6B)。由图6C可知,非热杀菌组独有的风味物质有18种,其中超高压联合抑菌剂处理组(HD、HN、HDN组)独有的风味物质有8种。非热杀菌组与原汁共有挥发性成分有31种,占原汁挥发性成分种类的82%,热杀菌组与原汁共有挥发性成分有27种,占原汁挥发性成分种类的71%。以上结果表明非热杀菌相比于热杀菌能更好保持其感官品质,使其接近新鲜果汁。
2.5.1.1 醛类物质比较
在所有样品中,共检出醛类6种,分别是己醛、壬醛、十一醛、(Z)-2-壬烯醛、反式-2-壬烯醛、反,反-2,4-壬二烯醛。由图6可知,6组样品中醛类物质含量占比均低于2%,表明其并不是杨梅汁中的主要挥发性物质。结合总含量分析,杨梅汁经杀菌贮藏之后,醛类挥发性物质含量降低。由表2可知,非热杀菌组杨梅汁相比于热杀菌组具有更高含量的己醛、反,反-2,4-壬二烯醛。
表 2 未杀菌及杀菌贮藏后杨梅汁挥发性物质含量Table 2. Content of volatile components in bayberry juice before sterilization and after sterilization and storage挥发性成分 分类 含量(μg/g) 未杀菌 TS H HD HN HDN 己醛 醛类 0.64±0.02a 0.38±0.02b 0.70±0.07a 0.74±0.07a 0.62±0.07a 0.65±0.07a 壬醛 1.72±0.23a 1.91±0.10a − 1.18±0.05b − − 十一醛 0.11±0.02a 0.09±0.00a − − − − (Z)-2-壬烯醛 − − − − − 1.72±0.05a 反式-2-壬烯醛 3.25±0.23a − − − − − 反,反-2,4-壬二烯醛 − − 0.29±0.02a 0.32±0.08a 0.30±0.02a 0.33±0.01a 间二甲苯 芳香烃 − − 0.11±0.03a − − − 对二甲苯 − − 0.43±0.09ab 0.43±0.05ab 0.50±0.09a 0.23±0.14b 邻乙基甲苯 2.22±0.91a 1.62±0.57ab 1.37±0.26ab 0.96±0.42ab 0.84±0.51ab 0.44±0.22b 均三甲苯 − 2.57±3.17a − 3.26±1.73a 1.84±1.42a 1.41±1.76a 1,2,3-三甲苯 3.11±1.68a − − 1.48±1.02a 2.17±1.63a − 3-丙基甲苯 0.83±0.24a 0.72±0.06ab 0.56±0.06bc 0.47±0.02c 0.38±0.05c 0.35±0.04c 5-乙基-3,5-二甲基苯 1.24±0.40a 1.01±0.13ab 0.69±0.06bc − 0.46±0.05c 0.43±0.03c 1-甲基-2-丙基苯 0.34±0.09a 0.27±0.03a − − − − 2-乙基对二甲苯 0.77±0.20a 0.74±0.22a 0.45±0.05a 0.82±0.76a 0.46±0.37a 0.56±0.22a 1,3-二甲基-4-乙基苯 − 0.67±0.06a − 0.41±0.02b − 0.33±0.04b 邻异丙基甲苯 − − 1.11±0.39a 0.93±0.34a − − 间异丙基甲苯 1.94±0.63a − − 0.67±0.43b − − 对异丙基甲苯 − − − − 0.62±0.08a − 均四甲苯 2.08±0.32ab 2.76±0.54a 0.70±0.54b 1.39±0.39b 0.99±0.95b 1.21±0.29b 1,2,3,4-四甲基苯 − − 1.63±0.69a − − − 1-甲基-4-仲丁苯 − 0.26±0.03a − − − − 4-甲基茚满 1.22±0.55a 0.92±0.45ab 0.72±0.31ab 0.76±0.24ab 0.53±0.21b 0.40±0.03b 萘 1.04±0.20a 0.87±0.11a 0.68±0.03b 0.64±0.04b 0.54±0.06b 0.55±0.04b 2-蒎烯 烯烃类 − 0.15±0.00a − − − − 萜品烯 1.06±0.16a 0.90±0.03a 0.84±0.08a − − − 萜品油烯 − − − − 0.11±0.02a − 3-乙基-2-甲基-(Z)-1,3-己二烯 − − 4.09±0.17a − − − β-波旁烯 1.05±0.10a 0.55±0.04bc 0.70±0.06b 0.49±0.09c 0.62±0.09bc 0.64±0.07bc β-缆香烯 2.96±0.35a 1.04±0.13b 1.07±0.08b 0.77±0.10b 0.92±0.17b 0.98±0.12b 异石竹烯 34.08±6.09a 18.25±1.78b 20.33±2.24b 16.43±3.30b 19.12±2.58b 20.33±1.73b β-石竹烯 330.29±41.45a 198.30±5.82b 187.10±16.68b 146.07±16.57b 164.34±21.57b 176.08±8.26b 9-epi-β石竹烯 − − − − − 0.76±0.44a (+)-香橙烯 − − − − 1.02±0.03a − 4,11,11-三甲基-8-亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一碳-3-烯 5.92±0.32a 3.42±0.27b 3.24±0.24b 1.96±0.37c 2.31±0.36c 2.43±0.14c (Z,Z)-α−法尼烯 1.27±0.05a − − − − − 佛术烯 0.38±0.00a − 0.27±0.01b − − 0.21±0.02c Β-瑟林烯 3.39±0.38a 1.70±0.06b 1.67±0.13b 1.22±0.24b 1.42±0.24b 1.59±0.22b α-瑟林烯 3.95±0.40a 1.91±0.05b − 1.39±0.26b 1.61±0.27b 1.71±0.13b α-石竹烯 − − 9.54±1.41a − − − α-紫穗槐烯 0.39±0.02a − − − − − 氧化石竹烯 11.37±1.60a − 7.04±1.25b 6.17±0.79b 6.14±0.94b 5.88±0.73b (+)-喇叭烯 − 0.34±0.17a − − − − 去氢白菖烯 − − 0.24±0.02a − − − 2-异丙烯基-4a,8-二甲基-1,2,3,4,4a,5,6,7-八氢萘 1.15±0.12a − − − − − 正己酸乙酯 酯类 − − 0.61±0.09a 0.70±0.09a 0.67±0.09a 0.60±0.15a γ−戊基丁内酯 1.68±0.53b 1.81±0.04ab 2.19±0.30ab 2.24±0.20ab 2.42±0.08a 2.50±0.10a 9-十六碳烯酸乙酯 − − 0.07±0.02b 0.09±0.02ab 0.11±0.00ab 0.13±0.02a 十六酸乙酯 0.24±0.06b − 0.30±0.11b 0.40±0.12b 0.61±0.05a 0.70±0.15a 芳樟醇 醇类 5.08±0.33a 2.34±0.08b 4.68±0.25a 4.81±0.34a 4.46±0.30a 4.45±0.11a 正辛醇 − 0.38±0.01a − − − − 苯乙醇 0.29±0.15a − − − − − 3,6-(E,Z)-壬二烯-1-醇 醇类 − − − 0.54±0.05a 0.60±0.01a 0.60±0.02a (-)-4-萜品醇 2.70±0.29b 3.71±0.05a 3.15±0.37a 3.40±0.21a 3.29±0.13a 3.43±0.06a 顺-3-壬烯-1-醇 − 1.09±0.02b 1.51±0.10a − − − alpha-松油醇 − − − 1.14±0.05a 1.10±0.09a 1.13±0.02a 石竹烯醇 0.68±0.15a 0.55±0.04ab 0.61±0.06ab 0.44±0.03b − 0.43±0.02b 10,10-二甲基-2,6-二亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一烷-5β−醇 1.61±0.03a 3.25±2.14a 3.09±3.24a 1.12±0.12a 1.10±0.14a 1.07±0.11a 11,11-二甲基-4,8-二亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一烷-3-醇 9.88±0.22a − − 5.48±0.64b 5.42±0.66b 5.19±0.55b 10,10-二甲基-2,6-二亚甲基二环[7.2.0]十一烷 烷烃类 12.51±0.39a 7.65±0.57b 7.30±0.56b 4.69±0.84c 5.49±0.89c 5.87±0.33c 正十四烷 − − − 0.13±0.04a − − 正十七烷 0.17±0.12a 0.21±0.03a 0.19±0.10a 0.16±0.08a 0.15±0.09a 0.12±0.08a 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 其他类 − 1.14±0.17b 1.42±0.27ab 1.43±0.17ab 1.76±0.14a 1.66±0.09a 2-戊基呋喃 3.66±0.38a 0.79±0.05c 2.19±0.34b 2.41±0.25b 2.59±0.09b 2.64±0.03b 注:−表示未检出;同行不同小写字母表示组间差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.5.1.2 烃类物质比较
在所有样品中,共检出芳香烃类18种,烯烃类21种、烷烃3种。由图6可知,杨梅汁中烯烃类物质占到总含量的80%以上,其中β-石竹烯含量占总挥发性化合物含量的70%左右,表明其是杨梅汁最主要的挥发性化合物,这与程焕[18]的研究结果一致。由表2可知,贮藏40 d后,非热杀菌组杨梅汁中的β-石竹烯含量略低于热杀菌组杨梅汁,但无显著性差异(P>0.05)。
2.5.1.3 酯类物质比较
与未杀菌组及热杀菌组相比,非热杀菌组具有更高的酯类占比(图6)。非热杀菌组杨梅汁中的酯类物质含量高于原汁及热杀菌组杨梅汁(表2),表明非热杀菌能更好地保留杨梅汁中的酯类物质。本研究共检出正己酸乙酯、γ-戊基丁内酯、9-十六碳烯酸乙酯、十六酸乙酯4种酯类物质。李镜浩等[17]研究报道,DMDC处理荔枝汁后,会产生微量的碳酸二甲酯。但本研究中未检测到此物质,这可能是其在贮藏过程中分解。这也表明DMDC处理对果汁风味影响很小。
2.5.1.4 醇类及其他类物质比较
除了烃类、醛类、酯类物质,杨梅汁中还有醇类等其他物质。所有样品中,共检出醇类10种。由图6可知,超高压联合抑菌剂处理组(HD、HN、HDN组)相比于其他组,具有更高的醇类占比。进一步分析发现,非热杀菌组芳樟醇含量较高(表2),表明超高压及超高压联合抑菌剂处理能更好地保留这种风味物质。
本研究中,还检出2,4-二叔丁基苯酚和2-戊基呋喃2种物质。由表2可知,2,4-二叔丁基苯酚在经灭菌贮藏后检出,表明其可能是在灭菌或贮藏过程中产生的物质。2-戊基呋喃在经灭菌贮藏后含量减少,但非热杀菌组的含量高于热杀菌组,说明非热杀菌相能更好地保留这种风味物质。
2.6 未杀菌及杀菌贮藏后杨梅汁挥发性成分风味贡献比较
挥发性成分含量的高低并不能真实反映出单个成分对整体香气的贡献大小,为了比较TS、HPP以及HPP联合抑菌剂(DMDC与Nisin)处理对贮藏后杨梅汁的整体香气影响,对各组杨梅汁挥发性成分进行了风味贡献分析。比较表3中杨梅汁的OAV总贡献值大小,未杀菌杨梅汁具有最强烈的风味,其次是非热杀菌组,OAV总贡献值由高到低为未杀菌组、HDN组、HD组、HN组、H组、TS组。
表 3 未杀菌及杀菌贮藏后杨梅汁部分挥发性成分香气活度值Table 3. Odor activity value of some volatile components in bayberry juice before sterilization and after sterilization and storage挥发性成分 分类 阈值(μg/g) OAV 未杀菌 TS H HD HN HDN 己醛 醛类 0.21 3.05 1.81 3.33 3.52 2.95 3.10 壬醛 0.0035 491.43 545.71 − 337.14 − − 十一醛 0.014 7.86 6.43 − − − − (Z)-2-壬烯醛 0.003 − − − − − 573.33 反式-2-壬烯醛 0.000065 50000.00 − − − − − 反,反-2,4-壬二烯醛 0.00006 − − 4833.33 5333.33 5000.00 5500.00 间二甲苯 芳香烃 5.5 − − 0.02 − − − 对异丙基甲苯 0.0133 − − − − 46.62 − 萘 0.05 20.80 17.40 13.60 12.80 10.80 11.00 2-蒎烯 烯烃类 0.12 − 1.25 − − − − 萜品烯 2.65 0.40 0.34 0.32 − − − β-石竹烯 0.16 2064.31 1239.38 1169.38 912.94 1027.13 1100.50 α-石竹烯 0.16 − − 59.63 − − − 正己酸乙酯 酯类 0.0005 − − 1220.00 1400.00 1340.00 1200.00 γ-戊基丁内酯 1 1.68 1.81 2.19 2.24 2.42 2.50 十六酸乙酯 1.5 0.16 − 0.20 0.27 0.41 0.47 芳樟醇 醇类 0.0015 3386.67 1560.00 3120.00 3206.67 2973.33 2966.67 正辛醇 0.054 − 7.04 − − − − 苯乙醇 0.045 6.44 − − − − − alpha-松油醇 0.3 − − − 3.80 3.67 3.77 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 其他类 0.5[34] − 2.28 2.84 2.86 3.52 3.32 2-戊基呋喃 0.0048 762.50 164.58 456.25 502.08 539.58 550.00 OAV值总计 56745.30 3548.03 10881.13 11717.70 10950.048 11914.68 注:−表示未检出;除特殊标注外,化合物阈值信息来自《化合物香味阈值汇编(第二版)》[35],部分化合物阈值信息未能查阅到。 2.6.1 醛类物质比较
在原汁中反式-2-壬烯醛的OAV值高达50000,是原汁中的主要气味,但经杀菌贮藏后未检出,这可能是杨梅汁经灭菌贮藏后风味强度减少的主要原因。6种醛类物质OAV值均高于1,可以认为其对样品风味有贡献,壬醛具有肥皂、青草香[28],十一醛具有辛辣、甜味[29],己醛、反式-2-壬烯醛与反,反-2,4-壬二烯醛,均具有青草香、脂肪味[28]。相比于原汁,热杀菌组仅有壬醛这一种重要的醛类香气物质(OAV>10),而非热杀菌组具有OAV值更高的反,反-2,4-壬二烯醛,具有更强烈的青草香,这补充了原汁中反式-2-壬烯醛带来的青草香,对杨梅汁风味具有积极作用。
2.6.2 烃类物质比较
烃类一般具有较高的阈值,对整体香气贡献较小[30]。β-石竹烯属于萜烯类,具有油炸味、香料味[31],在杨梅汁中含量最高,由于其含量远超过阈值(0.16),对杨梅汁具有较高的香气贡献。杨梅汁经杀菌贮藏40 d后,β-石竹烯含量减少,OAV值对应降低。
2.6.3 酯类物质比较
由表3可知,酯类物质中,正己酸乙酯具有较高的香气贡献,具有菠萝味水果香[32]。酯类物质为非热杀菌组杨梅汁提供了独特的水果香。本研究中,贮藏40 d后的热杀菌组并不具有正己酸乙酯,缺少水果香气特征,对果汁风味具有一定影响。
2.6.4 醇类及其他类物质比较
表3中的4种醇类物质中,芳樟醇在所有样品中均检出,其OAV值高于10,可以认为其是重要香气物质,其香味特征为花香型/玫瑰香味[32],是杨梅汁香味的重要组成部分。正辛醇仅在热杀菌组杨梅汁中检出,其具有芳香味、油脂味[33]。苯乙醇具有玫瑰花香[32],其仅在原汁中检出,属于杨梅汁贮藏后损失的积极香味物质。
本研究中,还检出2,4-二叔丁基苯酚(OAV值高于1)和2-戊基呋喃(OAV值高于10)2种物质。2,4-二叔丁基苯酚对酒体中糊味贡献度较大[34]。其在未杀菌杨梅汁中未被检出,表明其可能是在灭菌或贮藏过程中产生的异味物质。2-戊基呋喃具有青香型/蔬菜味[32],是积极的重要香气物质,和芳樟醇类似,超高压杀菌相比于热杀菌能更好地保留这种风味物质,使其风味特征优于热杀菌组。
2.7 未杀菌及杀菌贮藏后杨梅汁贮藏后挥发性成分PCA分析
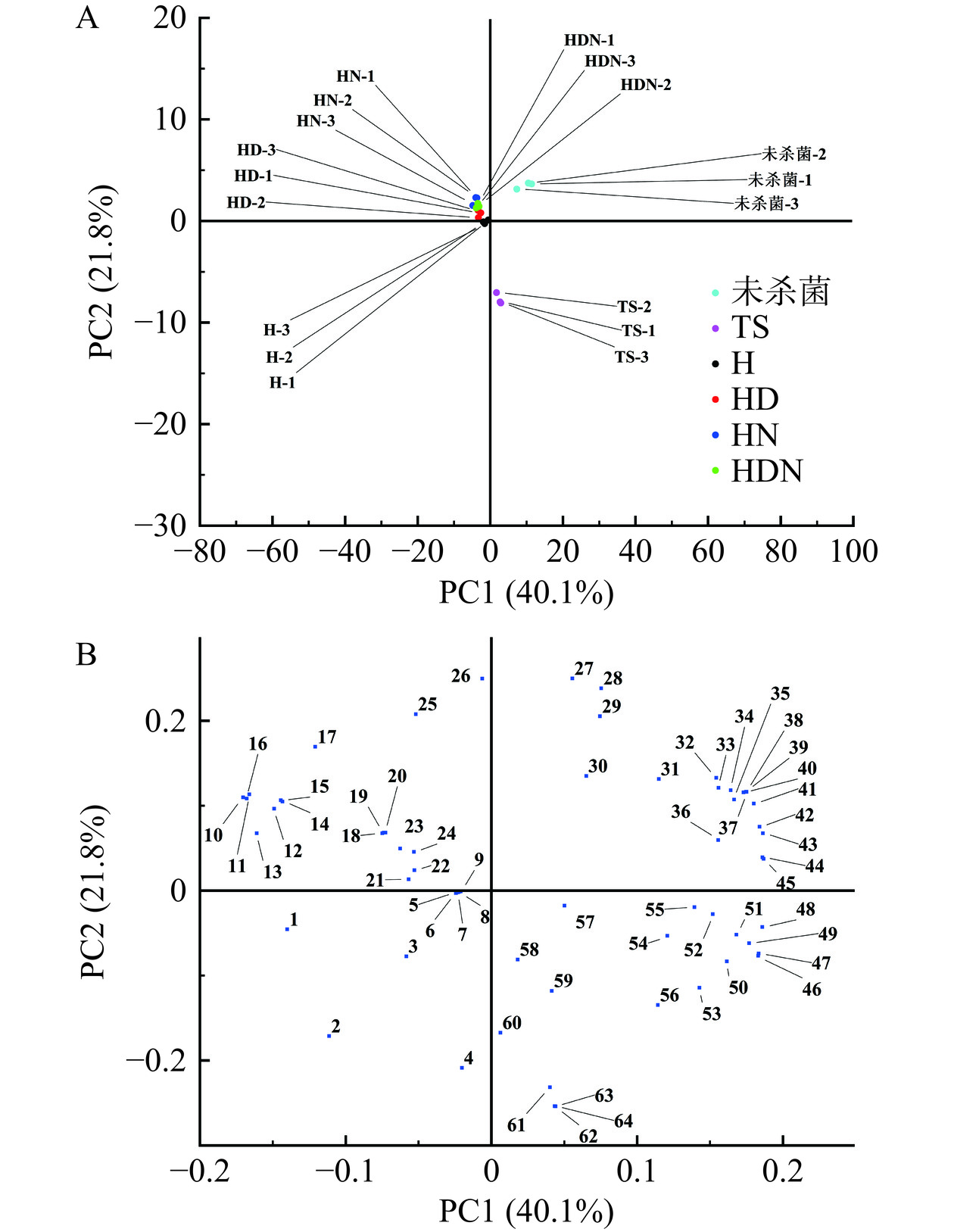
本研究采用主成分分析法对6种不同杨梅汁样品的挥发性组分进行分析,得到得分和载荷图(图7)。由表4可知,主成分分析结果中,前6个主成分累计方差贡献为92.6%,说明前6个主成分能够反映杨梅汁样本的主要特征。前两个主成分累计方差贡献仅为61.9%,这是由于非热杀菌组(H、HD、HN、HDN组)四组之间区分不明显,导致贡献率过低,这也表明抑菌剂的使用对风味影响不大。但原汁、热杀菌组与非热杀菌组挥发性物质种类和浓度之间具有差异性。超高压处理组位于第二、三象限边界处,超高压联合抑菌剂处理组位于第二象限,彼此之间距离接近,与热杀菌组相比,非热杀菌组与未处理组距离更接近,其香气品质更接近于新鲜产品[7]。可见,抑菌剂的使用不会对贮藏后期的杨梅汁风味产生明显的影响。
![]() 图 7 未杀菌及杀菌贮藏后杨梅汁PCA得分图(A)及载荷图(B)注:1.2,4-二叔丁基苯酚;2.(-)-4-萜品醇;3.均三甲苯;4.1,3-二甲基-4-乙基苯;5.3-乙基-2-甲基-(Z)-1,3-己二烯;6.去氢白菖烯;7.α-石竹烯;8.间二甲苯;9.1,2,3,4-四甲基苯;10.反,反-2,4-壬二烯醛;11.9-十六碳烯酸乙酯;12.对二甲苯;13.γ-戊基丁内酯;14.alpha-松油醇;15.3,6-(E,Z)-壬二烯-1-醇;16.正己酸乙酯;17.十六酸乙酯;18.(+)-香橙烯;19.对异丙基甲苯;20.萜品油烯;21.邻异丙基甲苯;22.正十四烷;23.(Z)-2-壬烯醛;24.9-epi-β石竹烯;25.己醛;26.芳樟醇;27.2-戊基呋喃;28.氧化石竹烯;29.11,11-二甲基-4,8-二亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一烷-3-醇;30.1,2,3-三甲苯;31.佛术烯;32.β-波旁烯;33.间异丙基甲苯;34.异石竹烯;35.苯乙醇;36.α-瑟林烯;37.2-异丙烯基-4a,8-二甲基-1,2,3,4,4a,5,6,7-八氢萘;38.反式-2-壬烯醛;39.α-紫穗槐烯;40.(Z,Z)-α-法尼烯;41.β-榄香烯;42.β-瑟林烯;43.β-石竹烯;44.10,10-二甲基-2,6-二亚甲基二环[7.2.0]十一烷;45.4,11,11-三甲基-8-亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一碳-3-烯;46.十一醛;47.1-甲基-2-丙基苯;48.萘;49.3-丙基甲苯;50.萜品烯;51.5-乙基-3,5-二甲基苯;52.邻乙基甲苯;53.壬醛;54.石竹烯醇;55.4-甲基茚满;56.均四甲苯;57.2-乙基对二甲苯;58.正十七烷;59.10,10-二甲基-2,6-二亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一烷-5β-醇;60.顺-3-壬烯-1-醇;61.(+)-喇叭烯;62.1-甲基-4-仲丁苯;63.2-蒎烯;64.正辛醇。Figure 7. Plots of PCA scores (A) and loadings (B) of bayberry juice before sterilization and after sterilization and storage表 4 主成分的特征值和贡献率Table 4. Characteristic values and contribution rates of principal components
图 7 未杀菌及杀菌贮藏后杨梅汁PCA得分图(A)及载荷图(B)注:1.2,4-二叔丁基苯酚;2.(-)-4-萜品醇;3.均三甲苯;4.1,3-二甲基-4-乙基苯;5.3-乙基-2-甲基-(Z)-1,3-己二烯;6.去氢白菖烯;7.α-石竹烯;8.间二甲苯;9.1,2,3,4-四甲基苯;10.反,反-2,4-壬二烯醛;11.9-十六碳烯酸乙酯;12.对二甲苯;13.γ-戊基丁内酯;14.alpha-松油醇;15.3,6-(E,Z)-壬二烯-1-醇;16.正己酸乙酯;17.十六酸乙酯;18.(+)-香橙烯;19.对异丙基甲苯;20.萜品油烯;21.邻异丙基甲苯;22.正十四烷;23.(Z)-2-壬烯醛;24.9-epi-β石竹烯;25.己醛;26.芳樟醇;27.2-戊基呋喃;28.氧化石竹烯;29.11,11-二甲基-4,8-二亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一烷-3-醇;30.1,2,3-三甲苯;31.佛术烯;32.β-波旁烯;33.间异丙基甲苯;34.异石竹烯;35.苯乙醇;36.α-瑟林烯;37.2-异丙烯基-4a,8-二甲基-1,2,3,4,4a,5,6,7-八氢萘;38.反式-2-壬烯醛;39.α-紫穗槐烯;40.(Z,Z)-α-法尼烯;41.β-榄香烯;42.β-瑟林烯;43.β-石竹烯;44.10,10-二甲基-2,6-二亚甲基二环[7.2.0]十一烷;45.4,11,11-三甲基-8-亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一碳-3-烯;46.十一醛;47.1-甲基-2-丙基苯;48.萘;49.3-丙基甲苯;50.萜品烯;51.5-乙基-3,5-二甲基苯;52.邻乙基甲苯;53.壬醛;54.石竹烯醇;55.4-甲基茚满;56.均四甲苯;57.2-乙基对二甲苯;58.正十七烷;59.10,10-二甲基-2,6-二亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一烷-5β-醇;60.顺-3-壬烯-1-醇;61.(+)-喇叭烯;62.1-甲基-4-仲丁苯;63.2-蒎烯;64.正辛醇。Figure 7. Plots of PCA scores (A) and loadings (B) of bayberry juice before sterilization and after sterilization and storage表 4 主成分的特征值和贡献率Table 4. Characteristic values and contribution rates of principal components主成分 特征值 方差贡献率(%) 累计贡献率(%) PC1 25.683 40.129 40.129 PC2 13.945 21.789 61.918 PC3 9.673 15.115 77.033 PC4 4.217 6.589 83.622 PC5 3.703 5.785 89.404 PC6 2.063 3.223 92.631 由图7B可知,苯乙醇(35)、反式-2-壬烯醛(38)、β-石竹烯(43)、壬醛(53)等挥发性成分对PC1正半轴贡献较大,苯乙醇具有玫瑰花香[32],其余成分均具有青草味[28,31]。2,4-二叔丁基苯酚(1)、反,反-2,4-壬二烯醛(10)、正己酸乙酯(16)等挥发性成分对PC1负半轴贡献较大,2,4-二叔丁基苯酚的糊味是杨梅汁在贮藏期间产生的消极气味[34],反,反-2,4-壬二烯醛使非热杀菌组杨梅汁保留青草味[28],正己酸乙酯的水果香味[32]使非热杀菌组杨梅汁具有更好的积极气味。芳樟醇(26)、2-戊基呋喃(27)对PC2正半轴贡献较大,第二主成分将热杀菌组杨梅汁与原汁、非热杀菌组分开,芳樟醇具有玫瑰花香[32],2-戊基呋喃具有蔬菜味青香[32]。超高压处理能够保留这两种成分,从而维持杨梅汁的香气特征。正辛醇(64)等挥发性物质对PC2负半轴贡献较大,正辛醇具有芳香味、油脂味[33],这些物质使得热杀菌组杨梅汁产生区别于原汁的风味。
3. 结论
本实验探究了热、超高压以及超高压联合DMDC、Nisin处理对杨梅汁的杀菌效果及其品质的影响,结果表明,热杀菌以及超高压联合DMDC、Nisin处理对杨梅汁杀菌效果较好,4 ℃贮藏期可达40 d以上,明显高于超高压单独处理的杨梅汁(10 d)。在杨梅汁贮藏过程中,颜色变化不明显,矢车菊素3-葡萄糖苷含量不断下降,总黄酮、总酚含量先下降后上升,但热杀菌造成的花色苷、多酚损失更大。在杨梅汁中共检测出64种挥发性化合物,原汁中挥发性成分总含量为456.27 μg/g,贮藏40 d后明显减少,非热杀菌组与热杀菌组的挥发性成分含量没有显著差异。但通过香气活度计算及主成分分析,能够区分原汁、热杀菌组与非热杀菌组挥发性物质的差异性,非热杀菌组杨梅汁的香气品质更接近新鲜产品,能够更好地保留芳樟醇(玫瑰花香)与2-戊基呋喃(蔬菜味青香)这两种积极风味物质,DMDC和Nisin的使用不会对贮藏后期的杨梅汁风味产生明显影响。由此可见,超高压联合DMDC、Nisin处理能够在同等超高压处理强度下,提高杀菌效果,延长杨梅汁的货架期,保持其品质。本研究可为杨梅汁的非热加工提供理论支持。
然而,超高压联合抑菌剂处理对多酚氧化酶、过氧化物酶等酶的钝化效果较弱,在贮藏过程中花色苷降解速度较快,未来可以研究超高压联合酶抑制剂、超高压联合中温短时处理等对杨梅汁品质的影响,以进一步延长杨梅汁的货架期,减少花色苷的贮藏过程中的损失,提升产品品质。
-
图 7 未杀菌及杀菌贮藏后杨梅汁PCA得分图(A)及载荷图(B)
注:1.2,4-二叔丁基苯酚;2.(-)-4-萜品醇;3.均三甲苯;4.1,3-二甲基-4-乙基苯;5.3-乙基-2-甲基-(Z)-1,3-己二烯;6.去氢白菖烯;7.α-石竹烯;8.间二甲苯;9.1,2,3,4-四甲基苯;10.反,反-2,4-壬二烯醛;11.9-十六碳烯酸乙酯;12.对二甲苯;13.γ-戊基丁内酯;14.alpha-松油醇;15.3,6-(E,Z)-壬二烯-1-醇;16.正己酸乙酯;17.十六酸乙酯;18.(+)-香橙烯;19.对异丙基甲苯;20.萜品油烯;21.邻异丙基甲苯;22.正十四烷;23.(Z)-2-壬烯醛;24.9-epi-β石竹烯;25.己醛;26.芳樟醇;27.2-戊基呋喃;28.氧化石竹烯;29.11,11-二甲基-4,8-二亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一烷-3-醇;30.1,2,3-三甲苯;31.佛术烯;32.β-波旁烯;33.间异丙基甲苯;34.异石竹烯;35.苯乙醇;36.α-瑟林烯;37.2-异丙烯基-4a,8-二甲基-1,2,3,4,4a,5,6,7-八氢萘;38.反式-2-壬烯醛;39.α-紫穗槐烯;40.(Z,Z)-α-法尼烯;41.β-榄香烯;42.β-瑟林烯;43.β-石竹烯;44.10,10-二甲基-2,6-二亚甲基二环[7.2.0]十一烷;45.4,11,11-三甲基-8-亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一碳-3-烯;46.十一醛;47.1-甲基-2-丙基苯;48.萘;49.3-丙基甲苯;50.萜品烯;51.5-乙基-3,5-二甲基苯;52.邻乙基甲苯;53.壬醛;54.石竹烯醇;55.4-甲基茚满;56.均四甲苯;57.2-乙基对二甲苯;58.正十七烷;59.10,10-二甲基-2,6-二亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一烷-5β-醇;60.顺-3-壬烯-1-醇;61.(+)-喇叭烯;62.1-甲基-4-仲丁苯;63.2-蒎烯;64.正辛醇。
Figure 7. Plots of PCA scores (A) and loadings (B) of bayberry juice before sterilization and after sterilization and storage
表 1 杨梅汁中微生物数量随贮藏时间的变化(CFU/mL)
Table 1 Changes of microbial population in bayberry juice with storage time (CFU/mL)
贮藏时间(d) 组别 TS H HD HN HDN 1 TAB 10.00±
14.1495.00±
7.0770.00±
0.0030.00±
14.1445.00±
21.21Y − − − − − M − − − − − 10 TAB 10.00±
14.14105.00±
7.0755.00±
7.0760.00±
14.1455.00±
21.21Y − − − − − M − 5.00±
7.07− − − 20 TAB 5.00±
7.07110.00±
14.1445.00±
35.3650.00±
14.1475.00±
7.07Y − − 5.00±
7.07− − M − − − − − 30 TAB 15.00±
7.07105.00±
7.0765.00±
21.2160.00±
14.1460.00±
0.00Y − − − − − M − − − − − 40 TAB 30.00±
0.00110.00±
14.1475.00±
7.0755.00±
7.0740.00±
0.00Y − − − − − M − − − − − 注:“−”表示未检出;根据GB 7101-2022要求,饮料中菌落总数需低于100 CFU/mL,酵母总数需低于20 CFU/mL,霉菌总数需低于20 CFU/mL。 表 2 未杀菌及杀菌贮藏后杨梅汁挥发性物质含量
Table 2 Content of volatile components in bayberry juice before sterilization and after sterilization and storage
挥发性成分 分类 含量(μg/g) 未杀菌 TS H HD HN HDN 己醛 醛类 0.64±0.02a 0.38±0.02b 0.70±0.07a 0.74±0.07a 0.62±0.07a 0.65±0.07a 壬醛 1.72±0.23a 1.91±0.10a − 1.18±0.05b − − 十一醛 0.11±0.02a 0.09±0.00a − − − − (Z)-2-壬烯醛 − − − − − 1.72±0.05a 反式-2-壬烯醛 3.25±0.23a − − − − − 反,反-2,4-壬二烯醛 − − 0.29±0.02a 0.32±0.08a 0.30±0.02a 0.33±0.01a 间二甲苯 芳香烃 − − 0.11±0.03a − − − 对二甲苯 − − 0.43±0.09ab 0.43±0.05ab 0.50±0.09a 0.23±0.14b 邻乙基甲苯 2.22±0.91a 1.62±0.57ab 1.37±0.26ab 0.96±0.42ab 0.84±0.51ab 0.44±0.22b 均三甲苯 − 2.57±3.17a − 3.26±1.73a 1.84±1.42a 1.41±1.76a 1,2,3-三甲苯 3.11±1.68a − − 1.48±1.02a 2.17±1.63a − 3-丙基甲苯 0.83±0.24a 0.72±0.06ab 0.56±0.06bc 0.47±0.02c 0.38±0.05c 0.35±0.04c 5-乙基-3,5-二甲基苯 1.24±0.40a 1.01±0.13ab 0.69±0.06bc − 0.46±0.05c 0.43±0.03c 1-甲基-2-丙基苯 0.34±0.09a 0.27±0.03a − − − − 2-乙基对二甲苯 0.77±0.20a 0.74±0.22a 0.45±0.05a 0.82±0.76a 0.46±0.37a 0.56±0.22a 1,3-二甲基-4-乙基苯 − 0.67±0.06a − 0.41±0.02b − 0.33±0.04b 邻异丙基甲苯 − − 1.11±0.39a 0.93±0.34a − − 间异丙基甲苯 1.94±0.63a − − 0.67±0.43b − − 对异丙基甲苯 − − − − 0.62±0.08a − 均四甲苯 2.08±0.32ab 2.76±0.54a 0.70±0.54b 1.39±0.39b 0.99±0.95b 1.21±0.29b 1,2,3,4-四甲基苯 − − 1.63±0.69a − − − 1-甲基-4-仲丁苯 − 0.26±0.03a − − − − 4-甲基茚满 1.22±0.55a 0.92±0.45ab 0.72±0.31ab 0.76±0.24ab 0.53±0.21b 0.40±0.03b 萘 1.04±0.20a 0.87±0.11a 0.68±0.03b 0.64±0.04b 0.54±0.06b 0.55±0.04b 2-蒎烯 烯烃类 − 0.15±0.00a − − − − 萜品烯 1.06±0.16a 0.90±0.03a 0.84±0.08a − − − 萜品油烯 − − − − 0.11±0.02a − 3-乙基-2-甲基-(Z)-1,3-己二烯 − − 4.09±0.17a − − − β-波旁烯 1.05±0.10a 0.55±0.04bc 0.70±0.06b 0.49±0.09c 0.62±0.09bc 0.64±0.07bc β-缆香烯 2.96±0.35a 1.04±0.13b 1.07±0.08b 0.77±0.10b 0.92±0.17b 0.98±0.12b 异石竹烯 34.08±6.09a 18.25±1.78b 20.33±2.24b 16.43±3.30b 19.12±2.58b 20.33±1.73b β-石竹烯 330.29±41.45a 198.30±5.82b 187.10±16.68b 146.07±16.57b 164.34±21.57b 176.08±8.26b 9-epi-β石竹烯 − − − − − 0.76±0.44a (+)-香橙烯 − − − − 1.02±0.03a − 4,11,11-三甲基-8-亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一碳-3-烯 5.92±0.32a 3.42±0.27b 3.24±0.24b 1.96±0.37c 2.31±0.36c 2.43±0.14c (Z,Z)-α−法尼烯 1.27±0.05a − − − − − 佛术烯 0.38±0.00a − 0.27±0.01b − − 0.21±0.02c Β-瑟林烯 3.39±0.38a 1.70±0.06b 1.67±0.13b 1.22±0.24b 1.42±0.24b 1.59±0.22b α-瑟林烯 3.95±0.40a 1.91±0.05b − 1.39±0.26b 1.61±0.27b 1.71±0.13b α-石竹烯 − − 9.54±1.41a − − − α-紫穗槐烯 0.39±0.02a − − − − − 氧化石竹烯 11.37±1.60a − 7.04±1.25b 6.17±0.79b 6.14±0.94b 5.88±0.73b (+)-喇叭烯 − 0.34±0.17a − − − − 去氢白菖烯 − − 0.24±0.02a − − − 2-异丙烯基-4a,8-二甲基-1,2,3,4,4a,5,6,7-八氢萘 1.15±0.12a − − − − − 正己酸乙酯 酯类 − − 0.61±0.09a 0.70±0.09a 0.67±0.09a 0.60±0.15a γ−戊基丁内酯 1.68±0.53b 1.81±0.04ab 2.19±0.30ab 2.24±0.20ab 2.42±0.08a 2.50±0.10a 9-十六碳烯酸乙酯 − − 0.07±0.02b 0.09±0.02ab 0.11±0.00ab 0.13±0.02a 十六酸乙酯 0.24±0.06b − 0.30±0.11b 0.40±0.12b 0.61±0.05a 0.70±0.15a 芳樟醇 醇类 5.08±0.33a 2.34±0.08b 4.68±0.25a 4.81±0.34a 4.46±0.30a 4.45±0.11a 正辛醇 − 0.38±0.01a − − − − 苯乙醇 0.29±0.15a − − − − − 3,6-(E,Z)-壬二烯-1-醇 醇类 − − − 0.54±0.05a 0.60±0.01a 0.60±0.02a (-)-4-萜品醇 2.70±0.29b 3.71±0.05a 3.15±0.37a 3.40±0.21a 3.29±0.13a 3.43±0.06a 顺-3-壬烯-1-醇 − 1.09±0.02b 1.51±0.10a − − − alpha-松油醇 − − − 1.14±0.05a 1.10±0.09a 1.13±0.02a 石竹烯醇 0.68±0.15a 0.55±0.04ab 0.61±0.06ab 0.44±0.03b − 0.43±0.02b 10,10-二甲基-2,6-二亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一烷-5β−醇 1.61±0.03a 3.25±2.14a 3.09±3.24a 1.12±0.12a 1.10±0.14a 1.07±0.11a 11,11-二甲基-4,8-二亚甲基双环[7.2.0]十一烷-3-醇 9.88±0.22a − − 5.48±0.64b 5.42±0.66b 5.19±0.55b 10,10-二甲基-2,6-二亚甲基二环[7.2.0]十一烷 烷烃类 12.51±0.39a 7.65±0.57b 7.30±0.56b 4.69±0.84c 5.49±0.89c 5.87±0.33c 正十四烷 − − − 0.13±0.04a − − 正十七烷 0.17±0.12a 0.21±0.03a 0.19±0.10a 0.16±0.08a 0.15±0.09a 0.12±0.08a 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 其他类 − 1.14±0.17b 1.42±0.27ab 1.43±0.17ab 1.76±0.14a 1.66±0.09a 2-戊基呋喃 3.66±0.38a 0.79±0.05c 2.19±0.34b 2.41±0.25b 2.59±0.09b 2.64±0.03b 注:−表示未检出;同行不同小写字母表示组间差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 3 未杀菌及杀菌贮藏后杨梅汁部分挥发性成分香气活度值
Table 3 Odor activity value of some volatile components in bayberry juice before sterilization and after sterilization and storage
挥发性成分 分类 阈值(μg/g) OAV 未杀菌 TS H HD HN HDN 己醛 醛类 0.21 3.05 1.81 3.33 3.52 2.95 3.10 壬醛 0.0035 491.43 545.71 − 337.14 − − 十一醛 0.014 7.86 6.43 − − − − (Z)-2-壬烯醛 0.003 − − − − − 573.33 反式-2-壬烯醛 0.000065 50000.00 − − − − − 反,反-2,4-壬二烯醛 0.00006 − − 4833.33 5333.33 5000.00 5500.00 间二甲苯 芳香烃 5.5 − − 0.02 − − − 对异丙基甲苯 0.0133 − − − − 46.62 − 萘 0.05 20.80 17.40 13.60 12.80 10.80 11.00 2-蒎烯 烯烃类 0.12 − 1.25 − − − − 萜品烯 2.65 0.40 0.34 0.32 − − − β-石竹烯 0.16 2064.31 1239.38 1169.38 912.94 1027.13 1100.50 α-石竹烯 0.16 − − 59.63 − − − 正己酸乙酯 酯类 0.0005 − − 1220.00 1400.00 1340.00 1200.00 γ-戊基丁内酯 1 1.68 1.81 2.19 2.24 2.42 2.50 十六酸乙酯 1.5 0.16 − 0.20 0.27 0.41 0.47 芳樟醇 醇类 0.0015 3386.67 1560.00 3120.00 3206.67 2973.33 2966.67 正辛醇 0.054 − 7.04 − − − − 苯乙醇 0.045 6.44 − − − − − alpha-松油醇 0.3 − − − 3.80 3.67 3.77 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 其他类 0.5[34] − 2.28 2.84 2.86 3.52 3.32 2-戊基呋喃 0.0048 762.50 164.58 456.25 502.08 539.58 550.00 OAV值总计 56745.30 3548.03 10881.13 11717.70 10950.048 11914.68 注:−表示未检出;除特殊标注外,化合物阈值信息来自《化合物香味阈值汇编(第二版)》[35],部分化合物阈值信息未能查阅到。 表 4 主成分的特征值和贡献率
Table 4 Characteristic values and contribution rates of principal components
主成分 特征值 方差贡献率(%) 累计贡献率(%) PC1 25.683 40.129 40.129 PC2 13.945 21.789 61.918 PC3 9.673 15.115 77.033 PC4 4.217 6.589 83.622 PC5 3.703 5.785 89.404 PC6 2.063 3.223 92.631 -
[1] LI J, CHEN J, LIU L, et al. Domestication history reveals multiple genetic improvements of Chinese bayberry cultivars[J]. Horticulture Research,2022,9:9−12.
[2] 胡子聪, 雷琳, 周晨光, 等. 杨梅的营养功效及其应用研究进展[J]. 果树学报,2023,40(9):1966−1979. [HU Zicong, LEI Lin, ZHOU Chenguang, et al. Research progress in nutritional benefit and application of Chinese bayberry fruit[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2023,40(9):1966−1979.] HU Zicong, LEI Lin, ZHOU Chenguang, et al. Research progress in nutritional benefit and application of Chinese bayberry fruit[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2023, 40(9): 1966−1979.
[3] 王正东, 戚向阳, 曹少谦. 脉冲强光处理对杨梅汁中酚类物质、色泽及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 果树学报,2012,29(4):661−667. [WANG Zhengdong, QI Xiangyang, CAO Shaoqian. Effect of pulsed light treatment on polyphenols, color and antioxidant activities of bayberry juice[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2012,29(4):661−667.] WANG Zhengdong, QI Xiangyang, CAO Shaoqian. Effect of pulsed light treatment on polyphenols, color and antioxidant activities of bayberry juice[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2012, 29(4): 661−667.
[4] 米璐, 徐贞贞, 刘鹏, 等. 食品超高压加工技术合规化历程与展望[J]. 包装与食品机械,2022,40(1):99−105. [MI Lu, XU Zhenzhen, LIU Peng, et al. History of compliance polices and prospect of high pressure processing technology[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery,2022,40(1):99−105.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1295.2022.01.017 MI Lu, XU Zhenzhen, LIU Peng, et al. History of compliance polices and prospect of high pressure processing technology[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery, 2022, 40(1): 99−105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1295.2022.01.017
[5] HUANG J, WANG S, ZHANG L, et al. Isolation and identification of high pressure-resistant bacteria naturally contaminating strawberry pulp[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2012,47(12):2620−2626.
[6] DONG K, PAN H, YANG D, et al. Induction, detection, formation, and resuscitation of viable but non-culturable state microorganisms[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2019,19(1):149−183.
[7] 徐樱樱, 罗琪, 潘鑫, 等. 超高压果蔬汁香气品质研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(20):378−389. [XU Yingying, LUO Qi, PAN Xin, et al. Research progress on aroma quality of high-pressure processing fruit and vegetable juices[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(20):378−389.] XU Yingying, LUO Qi, PAN Xin, et al. Research progress on aroma quality of high-pressure processing fruit and vegetable juices[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(20): 378−389.
[8] BU Z, LUO W, WEI J, et al. Impacts of Thermal processing, high pressure, and CO2-assisted high pressure on quality characteristics and shelf life of durian fruit puree[J]. Foods,2022,11(17):11−24.
[9] YANG D, JIANG Z, MENG Q, et al. Analyzing the pressure resistant, sublethal injury and resuscitable viable but non-culturable state population of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum under high pressure processing[J]. Food Research International,2023,173:113336. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113336
[10] LI T, CHEN J, DUAN X, et al. Combined antimicrobial effect of high pressure processing and ethyl lauroyl arginate (LAE)-containing films and its application in coconut water preservation[J]. Food Control, 2024, 155−165.
[11] CHENG M R, CHUREY J J, WOROBO R W. Inactivation of Salmonella enterica and spoilage microorganisms in orange juice treated with dimethyl dicarbonate (DMDC)[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2018,285:152−157.
[12] 郝森林, 余元善, 陈卫东, 等. 榴莲泥的超高压杀菌工艺研究[J]. 热带作物学报,2018,39(7):1447−1451. [HAO Senlin, YU Yuanshan, CHEN Weidong, et al. Sterilization of durian puree by ultra high pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2018,39(7):1447−1451.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2018.07.027 HAO Senlin, YU Yuanshan, CHEN Weidong, et al. Sterilization of durian puree by ultra high pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2018, 39(7): 1447−1451. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2018.07.027
[13] 徐亦秀. 杨梅浊汁风味劣变和非酶褐变的形成及控制研究[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2013. [XU Yixiu. Study on formation and control of flavour deterioration and non-enzymatic browning of cloudy bayberry juice[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2013.] XU Yixiu. Study on formation and control of flavour deterioration and non-enzymatic browning of cloudy bayberry juice[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2013.
[14] GIUSTI M M, WROLSTAD R E. Characterization and measurement of anthocyanins by UV-Visible spectroscopy[M]. New York:John Wiley & Sons, 2001:63−69.
[15] 曾丹, 邹波, 徐玉娟, 等. 蓝莓成熟过程中花色苷组分的变化[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(23):86−90. [ZENG Dan, ZOU Bo, XU Yujuan, et al. Changes in anthocyanin components of blueberry during ripening process[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(23):86−90.] ZENG Dan, ZOU Bo, XU Yujuan, et al. Changes in anthocyanin components of blueberry during ripening process[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2016, 37(23): 86−90.
[16] 张正伟. 杨梅酒颜色劣变与花色苷降解机理的研究[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2021. [ZHANG Zhengwei. Mechanisms of the color deterioration and anthocyanin degradation in Chinese bayberry wine[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2021.] ZHANG Zhengwei. Mechanisms of the color deterioration and anthocyanin degradation in Chinese bayberry wine[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021.
[17] 李镜浩, 肖更生, 徐玉娟, 等. 中温联合二甲基二碳酸盐对荔枝原汁品质的影响[J]. 现代食品科技,2023,39(9):233−243. [[LI Jinghao, XIAO Gengsheng, XU Yujuan, et al. Effects of mild heat combined with dimethyl dicarbonateon the quality of litchi juice[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2023,39(9):233−243.] [LI Jinghao, XIAO Gengsheng, XU Yujuan, et al. Effects of mild heat combined with dimethyl dicarbonateon the quality of litchi juice[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2023, 39(9): 233−243.
[18] 程焕. 杨梅风味特征组分鉴定及变化规律的研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2017. [CHENG Huan. Study on the flavor characteristics and changes of Chinese bayberry (Myrica. rubra)[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2017.] CHENG Huan. Study on the flavor characteristics and changes of Chinese bayberry (Myrica. rubra)[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017.
[19] 林怡. 超高压加工技术对杨梅汁品质的影响[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2013. [LIN Yi. Effect of high pressure processing on quality of Chinese bayberry juice[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2013.] LIN Yi. Effect of high pressure processing on quality of Chinese bayberry juice[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013.
[20] XU B, FENG M, CHITRAKAR B, et al. Multi-frequency power thermosonication treatments of clear strawberry juice:Impact on color, bioactive compounds, flavor volatiles, microbial and polyphenol oxidase inactivation[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2023, 84−94.
[21] YU Y, LIN Y, ZHAN Y, et al. Effect of high pressure processing on the stability of anthocyanin, ascorbic acid and color of Chinese bayberry juice during storage[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2013,119(3):701−706. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.06.036
[22] 杜琪珍, 姜华, 徐渊金. 杨梅中主要花色苷的组成与结构[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2008(8):48−51,55. [DU Q Z, JIANG H, XU J Y. The structure composition analysis and elucidation of anthocyanins in waxberry[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2008(8):48−51,55.] DU Q Z, JIANG H, XU J Y. The structure composition analysis and elucidation of anthocyanins in waxberry[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2008(8): 48−51,55.
[23] 吴新怡, 孟梓怡, 朱吟非, 等. 超高静压对非浓缩还原杨梅果汁中氧化酶的钝化作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2022,38(4):155−160. [WU Xinyi, MENG Ziyi, ZHU Yinfei, et al. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure treatment on inactivation of oxidase in non-concentrated bayberry juice[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2022,38(4):155−160.] WU Xinyi, MENG Ziyi, ZHU Yinfei, et al. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure treatment on inactivation of oxidase in non-concentrated bayberry juice[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2022, 38(4): 155−160.
[24] CAMINITI I M, NOCI F, MUÑOZ A, et al. Impact of selected combinations of non-thermal processing technologies on the quality of an apple and cranberry juice blend[J]. Food Chemistry,2011,124(4):1387−1392. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.07.096
[25] 李国林, 李丹丹, 王成有, 等. 两种不同加工方式杨梅汤抗氧化及风味品质比较[J]. 现代食品科技,2024,40(5):212−220. [[LI Guolin, LI Dandan, WANG Chengyou, et al. Comparison of antioxidant and flavor quality of bayberry soup produced by two different processing methods[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2024,40(5):212−220.] [LI Guolin, LI Dandan, WANG Chengyou, et al. Comparison of antioxidant and flavor quality of bayberry soup produced by two different processing methods[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2024, 40(5): 212−220.
[26] ESCARPA A, GONZÁLEZ M C. Approach to the content of total extractable phenolic compounds from different food samples by comparison of chromatographic and spectrophotometric methods[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta,2001,427(1):119−127. doi: 10.1016/S0003-2670(00)01188-0
[27] ZOU H, LIN T, BI X, et al. Comparison of high hydrostatic pressure, high-pressurecarbon dioxide and high-temperature short-time processing on quality of mulberry juice[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2015,9(2):217−231.
[28] 廖鹏飞, 王松, 王哲, 等. 同时蒸馏萃取结合GC-MS分析酿酒五粮原料蒸煮香气成分[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(6):235−243. [LIAO Pengfei, WANG Song, WANG Zhe, et al. Analysis of aroma components of five steamed grains for production of Nongxiangxing Baijiu by simultaneous distillation and extraction combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2023,44(6):235−243.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220609-091 LIAO Pengfei, WANG Song, WANG Zhe, et al. Analysis of aroma components of five steamed grains for production of Nongxiangxing Baijiu by simultaneous distillation and extraction combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(6): 235−243. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220609-091
[29] 张文玉, 李雅, 马赫, 等. 气相色谱-质谱联用结合化学计量法分析不同干燥方式对芫荽风味物质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2024,50(4):294−301. [ZHANG Wenyu, LI Ya, MA He, et al. Analysis of effects of different drying methods on flavor substances of coriander using GC-MS combined with stoichiometric method[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2024,50(4):294−301.] ZHANG Wenyu, LI Ya, MA He, et al. Analysis of effects of different drying methods on flavor substances of coriander using GC-MS combined with stoichiometric method[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024, 50(4): 294−301.
[30] GONZÁLEZ-ROMPINELLI E M, RODRÍGUEZ-BENCOMO J J, GARCÍA-RUIZ A, et al. A winery-scale trial of the use of antimicrobial plant phenolic extracts as preservatives during wine ageing in barrels[J]. Food Control,2013,33(2):440−447. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.03.026
[31] 程玉娇, 李贵节, 欧阳祝, 等. 基于气相色谱-质谱/脉冲火焰检测器和主成分分析对不同品种柚汁挥发性风味组分的分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(10):255−263. [CHENG Yujiao, LI Guijie, OUYANG Zhu, et al. Analysis of aroma compounds in different varieties of pomelo juice based on gas chromatography-mass spectrometry/pulsed flame photometric detector and principal component analysis method[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(10):255−263.] CHENG Yujiao, LI Guijie, OUYANG Zhu, et al. Analysis of aroma compounds in different varieties of pomelo juice based on gas chromatography-mass spectrometry/pulsed flame photometric detector and principal component analysis method[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(10): 255−263.
[32] 袁婕俐, 金晓玲, 张峥, 等. 紫花含笑不同开花时期花被片的挥发性成分分析[J]. 园艺学报,2023,50(5):1095−1109. [YUAN Jieli, JIN Xiaoling, ZHANG Zheng, et al. Volatility components of Michelia crassipes tepals at different flowering stages[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2023,50(5):1095−1109.] YUAN Jieli, JIN Xiaoling, ZHANG Zheng, et al. Volatility components of Michelia crassipes tepals at different flowering stages[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2023, 50(5): 1095−1109.
[33] 李祥雨, 熊雅婷, 滕建文, 等. 基于气相色谱-质谱技术与多元统计分析咸蛋黄热加工中的异味组分[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(16):292−300. [LI Xiangyu, XIONG Yating, TENG Jianwen, et al. Analysis of odor components in salted egg yolk during thermal processing using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and multivariate statistical analysis[J]. Food Science,2023,44(16):292−300.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220919-175 LI Xiangyu, XIONG Yating, TENG Jianwen, et al. Analysis of odor components in salted egg yolk during thermal processing using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and multivariate statistical analysis[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(16): 292−300. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220919-175
[34] WANG J, ZHANG B, WU Q, et al. Sensomics-assisted flavor decoding of coarse cereal Huangjiu[J]. Food Chemistry, 2022, 381−395.
[35] 里奥, 范海默特. 化合物香味阈值汇编(第二版)[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 2015. [VAN GEMERTL L J. Compilations of flavour threshold values in water and other media (2nd ed)[M]. Beijng:Science Press, 2015.] VAN GEMERTL L J. Compilations of flavour threshold values in water and other media (2nd ed)[M]. Beijng: Science Press, 2015.





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



