Analysis of Flavor and Quality Differences in Black Tea from Different Geographical Origins in Fujian
-
摘要: 为进一步探究福建不同地区红茶风味品质特征,本研究以福建省5个不同产地共30份红茶样本为研究材料,通过感官评估、生化成分和香气物质检测结合化学计量学方法分析比较福建不同产地红茶的风味品质成分差异。研究结果表明,福建红茶以薯香、花香和甜香为主,滋味上以醇、甜为主,不同产地红茶风味品质成分有较大差异,武夷红茶茶多酚(17.65%)和茶褐素(7.57%)含量最高,福安红茶可溶性糖(16.45 mg/g)、总黄酮(12.81 mg/g)及茶黄素(0.43%)含量高于其他产地,政和红茶的总儿茶素(21.56 mg/g)及游离氨基酸含量(6.66%)高于其他地区,尤溪红茶茶黄素含量(0.19%)最低。样品中共鉴定出81种香气物质,醇类和酯类是主要的香气化合物,其中芳樟醇、苯乙醇、橙花醇、香叶醇、β-紫罗兰酮、棕榈酸甲酯、香叶基丙酮、水杨酸甲酯和(3E)-3,7-二甲基辛-1,3,6-三烯等9种成分是武夷红茶花果香的关键物质,茉莉酮酸甲酯和α-紫罗兰酮是福安红茶浓郁花香和甜香的赋香成分,正癸醛是福鼎红茶的特征性香气物质,苯甲醛是政和红茶特征性赋香物质。本研究结果综合分析了福建不同产地红茶的风味品质差异成分,进一步丰富了福建红茶风味品质特征的研究理论。
-
关键词:
- 福建红茶 /
- 风味品质 /
- 香气特征 /
- 顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱联用仪(HS-SPME-GC-MS) /
- 气味活性值(OAV)
Abstract: To further explore the flavor and quality characteristics of black tea from different regions of Fujian, with 30 samples of black tea sourced from 5 distinct regions within Fujian Province as research material, this study of the differences in flavor quality components of black tea from distinct regions in Fujian conducted a comprehensive analysis employing sensory evaluation, biochemical profiling, and aroma compound detection coupled with chemometric methodologies. The findings revealed that Fujian black tea was predominantly characterized by the aroma of potatoes, floral bouquets, and sweetness, with a taste profile that leant towards a mellow and sweet flavor. Notably, significant disparities existed in the flavor quality components of black tea across different regions. For instance, Wuyi black tea exhibited the highest levels of tea polyphenols (17.65%) and theabrownin (7.57%), whereas Fu'an black tea exhibited elevated concentrations of soluble sugars (16.45 mg/g), total flavonoids (12.81 mg/g), and theaflavin (0.43%) compared to its counterparts. Moreover, Zhenghe black tea exhibited higher levels of total catechins (21.56 mg/g) and free amino acids (6.66%) relative to other regions, whereas Youxi black tea presented the lowest theaflavin content (0.19%) among the samples. A total of 81 aroma compounds were identified across the samples, with alcohols and esters emerging as the primary aroma constituents. Notable contributors to the floral and fruity aroma of Wuyi black tea included linalool, phenylethanol, nerol, geraniol, β-ionone, methyl palmitate, geranyl acetone, methyl salicylate, and (3E)-3,7-dimethyl octa-1,3,6-triene. Fu'an black tea, on the other hand, derived its rich floral and sweet aroma from methyl jasmonate and α-ionone. Characteristic aroma substances were also observed, with n-decanal distinguishing Fuding black tea and benzaldehyde characterizing Zhenghe black tea. Overall, this study provides a comprehensive analysis of the flavor qualitative and chemical variations in Fujian black tea across different regions, thereby enhancing the understanding of its quality components. -
红茶因具有香气高扬,滋味甜爽的独特品质特征[1],受到广大消费者的喜爱,福建作为世界红茶的发源地[2],盛产名优红茶,如武夷山正山小种、金骏眉、政和工夫、白琳工夫、坦洋工夫及尤溪红茶等,受区域环境条件、加工方式及品种等因素的影响[3],福建不同地区的红茶综合品质呈现出较大差异,不同区域红茶具有自己的品牌特色,进一步明确不同地区红茶的风味品质差异成分对建设区域红茶品牌具有重要作用。
茶叶滋味和香气在五项因子感官审评中分别占比30%和25%,是决定茶叶品质风味特征的重要因子[4]。据前人研究,武夷红茶花果香浓郁兼具蜜香、滋味甘爽甜醇[5]。白琳工夫以其外形细长秀丽、金毫显、滋味鲜浓醇的品质特征而闻名于世[6]。政和工夫外形乌黑油润,毫芽显呈金黄色,汤色红艳,滋味醇厚[7]。林洁鑫等[8]对福安坦洋工夫和尤溪红茶进行了滋味特征分析研究,认为黄酮类物质和氨基酸成分差异显著是造成福安坦洋工夫红茶醇厚鲜爽,尤溪红茶甘醇的主要原因。目前针对福建单一地区红茶品质特征及差异成分的研究较多,但对于福建省多个不同主要红茶产区样本的具体风味差异物质的研究报道还较少。
目前在茶叶香气研究领域中,检测方法多样[9],其中,顶空固相微萃取(headspace solid-phase microextraction,HS-SPME)技术在萃取富集香气过程中,具有便捷、高效的优势,其与气相色谱-质谱(gas chromatography-mass spectrometry,GC-MS)联用可对茶叶香气成分含量进行更加高效准确的检测和鉴定[10−12],宋加艳[13]对不同产区红茶进行研究,发现不同地区红茶香气含量和物质成分上存在较大的差异, KANG等[14]对世界具有代表性的四大红茶进行了香气检测研究,分析发现不同区域红茶香气成分差异显著,差异香气物质促成了世界不同地区红茶的香气特征。但前人在红茶品质研究上,大多数集中在不同茶树品种、加工工艺及世界和全国范围不同产区上的香气差异研究,而对于福建不同产地红茶风味品质差异成分的研究相对较少。
为进一步综合探究福建不同产地红茶风味品质差异,本研究以福建5个不同产地(武夷山、福安、政和、尤溪和福鼎)共30份红茶为试材,通过感官审评、生化成分及香气成分检测,结合化学计量学及气味活性值(odor activity value, OAV)等分析方法,进一步明确不同地区红茶间风味品质成分差异,为福建不同产地红茶风味品质特征的判别和区域红茶品牌的建设提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
红茶样品 取自福建省5个主要红茶产区(武夷山市、福安市、政和县、尤溪县,福鼎市),原料采摘一芽一二叶初展,均按照红茶工艺(鲜叶-萎凋-揉捻-发酵-干燥)制得[15],具体信息见表1。每份茶样分为2份,一份采用铝箔袋密封,常温避光保存用于感官审评,另外一份按照国家标准GBT 8303-2013进行磨样,过40目筛,茶粉置于−4 ℃冰箱保存待测。
表 1 红茶样品信息Table 1. Black tea samples information样品编号 样品数量 产地 收样年份 品种 WY 6 武夷山市 2022 菜茶 FA 6 福安市 2022 金牡丹 ZH 6 政和县 2022 福安大白 YX 6 尤溪县 2022 梅占 FD 6 福鼎市 2022 福鼎大毫 癸酸乙酯(色谱纯)、儿茶素类、茶黄素类标准品(纯度≥99%) Sigma-Aldrich 公司;蒽酮、福林酚、茚三酮 分析纯,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;甲醇、乙腈、冰乙酸 色谱级,德国默克公司;二水合磷酸二氢钠、硫酸、正丁醇、无水乙醇、磷酸二氢钾、碳酸氢钠 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;植物可溶性糖检测试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所。
固相微萃取SPME手柄 上海安谱实验科技股份有限公司;TRACR 1300 ISQQD 型气质联用仪 赛默飞世尔科技有限公司;DB-5 MS(30 m×0.25 mm,0.25 μm)色谱柱 美国Agilent公司;e2695高效液相色谱仪 美国Waters公司;Infinite M200 PRO多功能酶标仪 奥地利Tecan公司;YS6060台式分光测色仪 深州市三恩时科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 感官审评
根据国家标准GB/T 23776-2018《茶叶感官审评方法》进行审评,由实验室7位茶叶审评专家(4女3男),对福建5个产地红茶进行外形、汤色、滋味、香气和叶底五项因子审评,综合得分=外形×25%+汤色×10%+香气×25%+滋味×30%+叶底×10%,最后计算均分。同时参考曾亮等[16]的方法并进行一定修改,由7名审评专家组成定量描述分析法(quantitative descriptive analysis,QDA)评价小组,筛选保留薯香、花香、果香、嫩香、甜香、木香和火攻香7个出现频率较高的香气属性词,苦、涩、鲜爽、甜、酸、回甘、醇和浓厚8个滋味属性词,各因子评分范围 0~10分,其中,0未察觉,1~2微弱,3~4弱,5~6一般,7~8较强,9强,10极强。
1.2.2 色差值测定
色差值L*、a*、b*参照GB/T 23776-2018进行茶汤制备,冷却至室温后采用分光测色仪进行测定,每个样品进行3次重复。
1.2.3 生化成分测定
水浸出物含量测定参照GB/T 8305-2013《茶 水浸出物测定》;游离氨基酸总量测定参照 GB/T 8314-2013《茶 游离氨基酸总量的测定》;可溶性总糖含量根据植物可溶性糖检测试剂盒说明书步骤测定;总黄酮含量测定参照WANG等[17]的方法,为三氯化铝比色法;茶红素、茶褐色含量测定参照 NY/T 3675-2020《红茶中茶红素和茶褐素含量的测定 分光光度法》;茶多酚含量及儿茶素组分测定参照GB/T 8313-2018《茶叶中茶多酚和儿茶素类含量的检测方法》;茶黄素组分测定参照王坤波等[18]及ISO/TC 34/SC 8N 2016(E)《Tea-Determination of theaflavins in black tea-Method using high performance liquid chromatography》方法。
1.2.4 挥发性物质测定
参照戴浩民等[19]的方法并做一定的调整,称取0.5 g的茶粉置于20 mL顶空瓶中,加入5 mL沸水和30 μL质量浓度为8.62 μg/mL的癸酸乙酯内标,加盖混匀平衡10 min,后置于100 ℃的磁力加热台上加热。将已老化的萃取头插入萃取40 min。萃取结束后,将萃取头插入气相色谱仪的进样口,在250 ℃下热解析5 min。
1.2.4.1 GC条件
色谱柱DB-5 MS(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm),氦气(纯度>99.999%);升温程序:初温50 ℃,保持5 min,以5 ℃/min升至210 ℃,保持3 min,再以15 ℃/min升至250 ℃,保持1 min。采用不分流模式进样,载气恒定流速1 mL/min,进样口温度250 ℃,进样量10 μL。
1.2.4.2 MS条件
离子源EI,离子源和接口温度为230 ℃,电离能量70 eV,全扫描模式,质量扫描范围40~500 m/z。
1.2.4.3 挥发性物质定性定量
对气相色谱/质谱联用测得红茶样本挥发性有机物的总离子色谱图,经标准谱图(NIST08和NIST08 s)检索匹配,同时根据正构烷烃出峰时间来计算各挥发物保留指数并通过查阅文献,对挥发物的化学结构、名称等进行进一步的定性。用内标癸酸乙酯定量各挥发性组分,定量计算公式如下:
待测物浓度(μg/kg)=待测物峰面积×癸酸乙酯质量浓度癸酸乙酯峰面积 1.2.5 气味活性值(OAV)计算方法
通过计算OAV来评判香气成分对红茶样本贡献程度的大小。计算公式如下:
OAVi=CiOTi 式中,Ci为香气物质i的样本浓度;OTi表示香气物质i在水中的阈值,单位均为:μg/kg。
1.3 数据处理
采用Microsoft Excel 2022绘制雷达图,SPSS 26进行相关性检验和单因素方差分析,SIMCA 14.1软件进行正交偏最小二乘判别分析(orthogonal partial least squares-discrimination analysis,OPLS-DA),Origin 2021绘制柱形图,Cytoscape制作相关网络图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同产地红茶感官品质分析
感官审评结果见表2,福建5个产地红茶整体品质较优,感官综合得分均在93分以上,武夷红茶>福安红茶>福鼎红茶>尤溪红茶>政和红茶,武夷红茶感官综合得分显著高于其他地区(P<0.05),综合感官品质较好。这5个产地红茶原料较嫩,叶底细嫩柔软,汤色明亮,以橙红、橙黄为主,滋味以甜醇为主,在香气上,以花香、甜香为主。QDA感官审评结果显示(图1),福建红茶以薯香、花香和甜香为主,滋味上以醇、甜及浓厚为主。其中武夷红茶的薯香和果香强于其他地区,福鼎红茶的嫩香、甜香和木香较强,政和和福安红茶则花香明显。政和红茶滋味上苦、涩强于其他地区,福安红茶和武夷红茶浓厚、醇及回甘强度均高于其他地区,福鼎红茶则酸度强于其他地区,尤溪红茶在香气和滋味上整体表现较为平和。
表 2 福建不同区域红茶感官品质评价Table 2. Sensory quality evaluation of black tea in different areas of Fujian编号 外形(25%) 汤色(10%) 香气(25%) 滋味(30%) 叶底(10%) 综合得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 WY 紧细,乌润,金毫显 95.00±0.41a 橙黄明亮 94.50±0.58ab 花香薯香 96.75±0.29a 甜醇爽口 95.13±0.85a 细嫩,较
软亮94.75±0.29a 95.20±0.44a FA 乌润匀整 92.88±1.11b 橙黄明亮 94.75±0.29a 甜香带
花香95.00±0.41ab 较甜醇 94.13±0.63ab 柔软较亮较匀 92.00±0c 93.88±0.41b ZH 紧结乌润
金毫显94.00±0.82ab 红艳较
明亮93.00±1.15b 薯香带
花香93.13±0.25b 甜醇较
爽口92.88±0.25b 细嫩匀亮,带花青 92.75±0.65bc 93.25±0.4b YX 紧细,
金毫显95.00±1.08a 浅橙红,
较亮91.00±1.63c 甜香稍带火香,略有花香 93.00±2.71b 甜醇带
薯味93.00±1.22b 细嫩红匀较亮 94.13±0.75ab 93.41±0.91b FD 乌润金毫显,较匀整 94.88±0.25a 橙黄较
明亮94.00±0.82ab 甜花香显,微带薯香 93.25±0.96b 较甜,醇厚 93.00±1.83b 细嫩,
较红匀93.13±1.03bc 93.64±0.83b 注:表中数值为平均值±标准差,同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表3同。 2.2 不同产地红茶茶汤色差值比较分析
对供试样品进行色差值测定分析,L*代表明亮度值,a*值代表红绿值,b*值代表黄蓝值。L*值越小,样品的透光性越差,色泽越深[20]。结果如表3,尤溪红茶L*值高于其他地区,其汤色亮度较高,与福安红茶和政和红茶差异显著(P<0.05),a*值和b*值均最低,说明样本色泽饱和度相对较低,颜色相对较浅,而政和红茶L*值(83.89)最小,显著低于其他地区(P<0.05),色泽较深,a*值、b*值均高于其余地区,说明样本色泽饱和度较高,推测其茶汤可溶性物质含量较多,使得其颜色较深。
表 3 福建不同产地红茶L*、a*、b*值的对比Table 3. Comparison of L*, a*, and b* values of black tea from different areas in Fujian茶样 L* a* b* WY 86.89±2.34ab 2.25±1.89bc 59.68±8.28bc FA 86.56±0.17b 3.33±0.05ab 61.47±1.87ab ZH 83.89±0.5c 4.55±0.31a 68.79±0.89a YX 88.75±3.06a 1.03±2.5c 52.31±14.04c FD 87.96±0.49ab 1.9±0.64bc 62.49±2.44ab 2.3 不同产地红茶生化成分比较分析
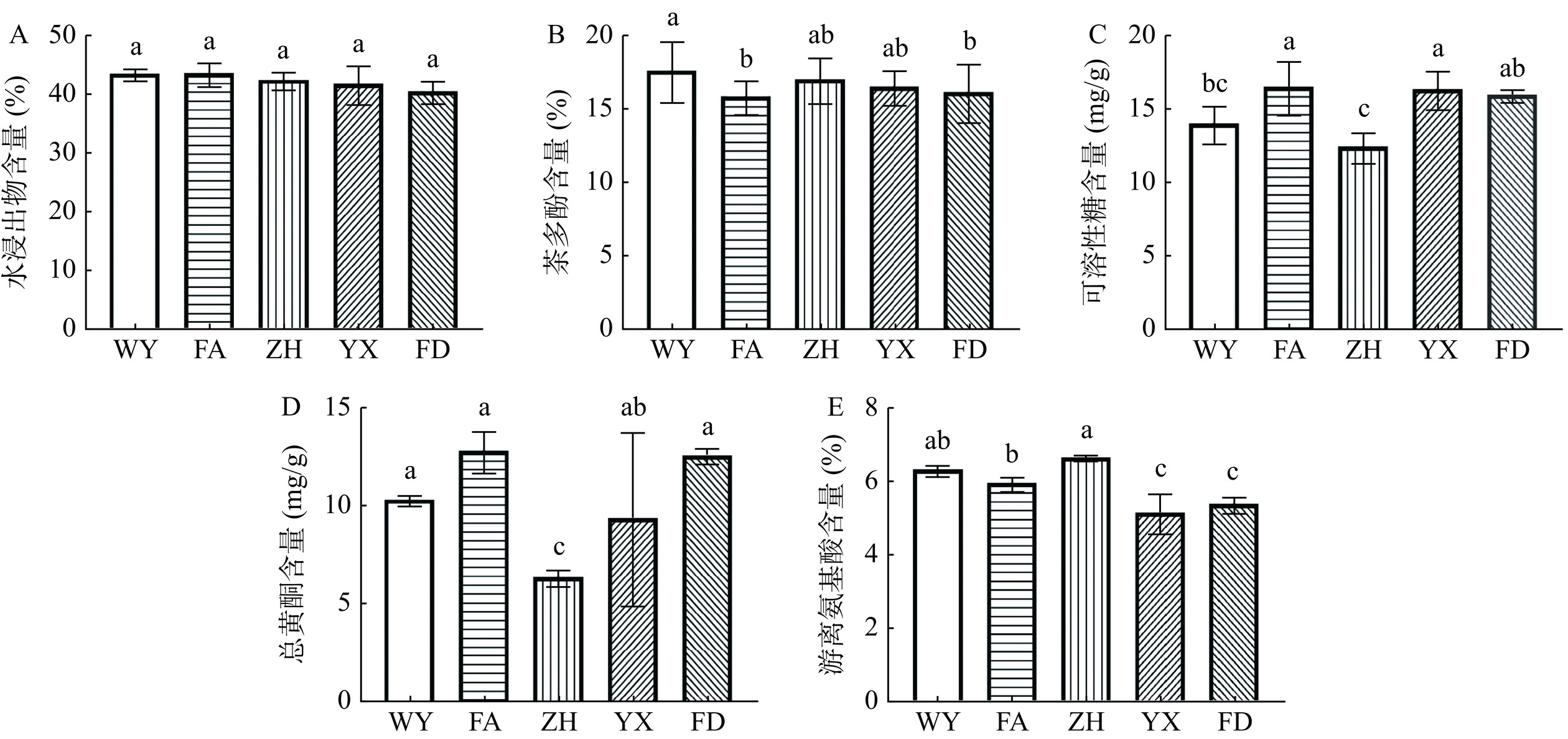
对福建5个不同产地红茶进行生化成分检测,结果如图2和图3所示,不同地区红茶成分差异明显。图2显示,水浸出物含量福安红茶(43.55%)最高,但地区之间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。茶多酚作为茶叶中重要的呈味物质之一,表现为苦涩且具有收敛性,含量的多少决定着茶汤苦涩程度[21],武夷红茶茶多酚含量(17.65%)显著高于福安和福鼎地区(P<0.05),是其茶汤收敛性较强的重要物质。可溶性糖是茶汤呈现甜味的重要成分[22],福安红茶(16.45 mg/g)和尤溪红茶(16.31 mg/g)的可溶性糖含量显著高于武夷红茶(13.96 mg/g)和政和红茶(12.39 mg/g)(P<0.05)。黄酮是组成茶汤色泽的重要成分之一,也是茶汤呈现苦涩味的重要成分[23]。政和红茶的总黄酮含量(6.38 mg/g)与福鼎红茶(12.58 mg/g)和福安红茶(12.81 mg/g)之间具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。游离氨基酸是促进茶汤呈现鲜爽的重要物质[24],不同地区之间的游离氨基酸含量具有较大的差异,政和红茶游离氨基酸含量(6.66%)显著高于尤溪红茶(5.17%)和福鼎红茶(5.33%)(P<0.05),促进了政和红茶的滋味鲜爽度。
![]() 图 3 福建不同地区红茶生化成分含量对比注:TF-3-G:Theaflavin-3-gallate茶黄素-3-没食子酸酯;TF-3'-G:Theaflavin-3'-gallate茶黄素-3'-没食子酸酯;TF-3,3'-G:Theaflavin-3,3'-digallate茶黄素-3,3'-双没食子酸酯;TF:Theaflavin简单茶黄素;EGCG:(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯;ECG:(-)-Epicatechin gallate表儿茶素没食子酸酯;GCG:Galocatechin gallate没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯。Figure 3. Comparison of the contents of the main biochemical components in black tea from different areas in Fujian
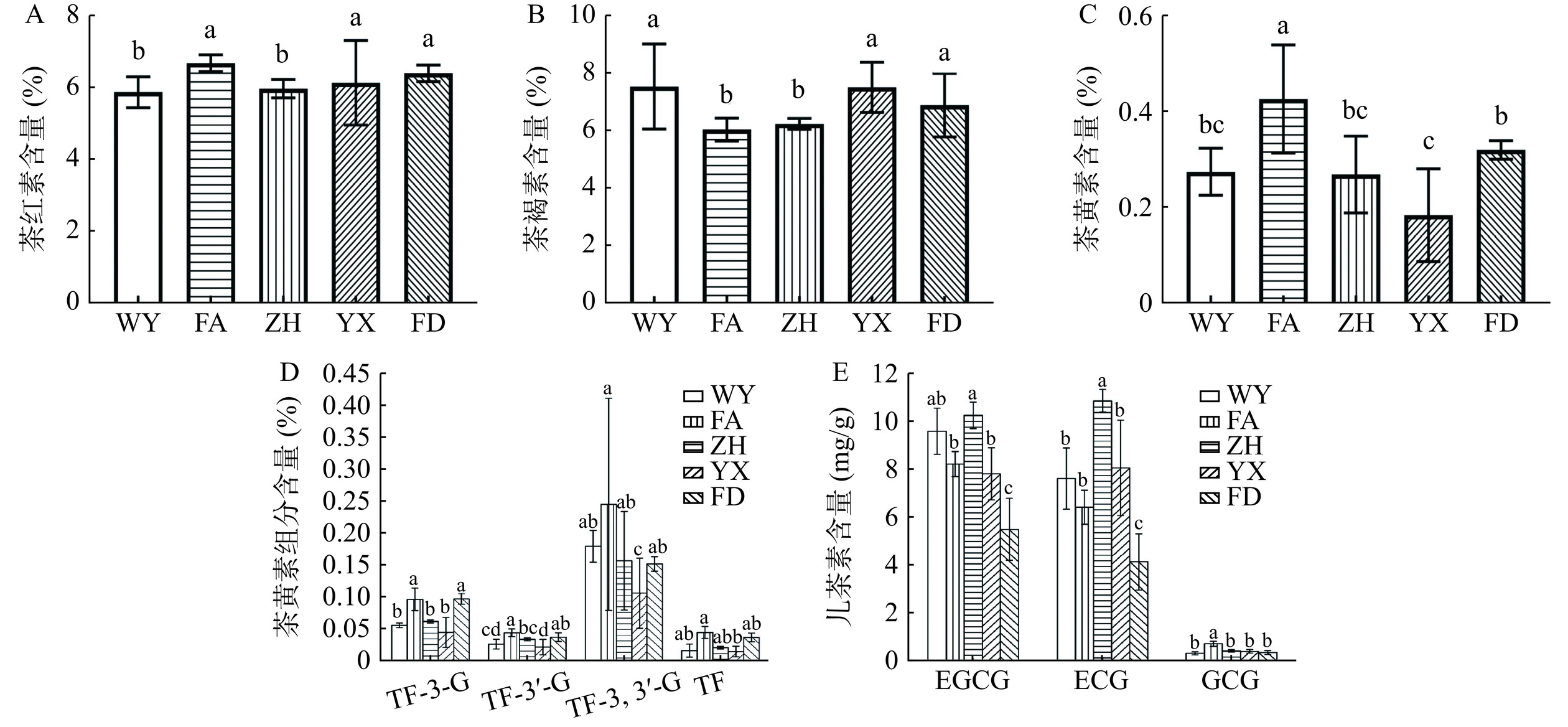
图 3 福建不同地区红茶生化成分含量对比注:TF-3-G:Theaflavin-3-gallate茶黄素-3-没食子酸酯;TF-3'-G:Theaflavin-3'-gallate茶黄素-3'-没食子酸酯;TF-3,3'-G:Theaflavin-3,3'-digallate茶黄素-3,3'-双没食子酸酯;TF:Theaflavin简单茶黄素;EGCG:(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯;ECG:(-)-Epicatechin gallate表儿茶素没食子酸酯;GCG:Galocatechin gallate没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯。Figure 3. Comparison of the contents of the main biochemical components in black tea from different areas in Fujian茶红素和茶褐素为酚类氧化物,茶红素能够增强茶汤滋味醇厚度,与品质呈正相关关系,而茶褐素与茶汤色泽则呈负相关[25−26]。福建不同产地红茶茶红素和茶褐素含量测定结果(图3A、B)显示,茶红素含量范围在(5.93%~6.74%),福安、福鼎和尤溪地区红茶茶红素含量显著高于武夷和政和红茶(P<0.05),在茶褐素含量范围在(6.08%~7.57%)之间,武夷山、福鼎及尤溪红茶茶褐素含量显著高于政和和福安红茶(P<0.05)。茶黄素对红茶汤色和滋味品质具有正向调控作用[27],结果如图3C所示,福安红茶含量(0.43%)显著高于其他地区(P<0.05),尤溪红茶含量(0.19%)最低,两地之间呈现出显著差异性(P<0.05),茶黄素组分含量结果(图3D)显示,福安红茶的TF-3-G、TF-3’-G、TF-3,3’-G以及TF各组分含量均显著高于尤溪红茶(P<0.05),推测认为茶黄素对福安红茶滋味特征的形成具有重要作用。总体上,福安红茶茶黄素、茶红素含量高于其他地区,茶褐素含量低于其他地区,这与福安红茶茶汤呈现橙黄明亮的品质特征结果一致。
儿茶素是茶叶中主要功能性成分,是茶汤中呈现涩味重要物质之一[28]。对样本中主要的3类酯型儿茶素(EGCG、GCG及ECG)含量进行检测,结果如图3E所示,不同地区之间EGCG含量差异较大,政和红茶含量(10.26 mg/g)最高,福鼎红茶含量(5.51 mg/g)最低,二者具有显著性差异(P<0.05);ECG含量中,政和红茶含量(10.86 mg/g)最高,约是福鼎红茶含量(4.15 mg/g)的2.6倍;福安红茶GCG含量(0.74 mg/g)最高,其他四个地区样本间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。综上,福鼎红茶儿茶素总含量(3.344 mg/g)低于其他地区,政和红茶高于其他地区,这与审评滋味上政和红茶涩感、收敛性强于其他地区的结果是一致的。
2.4 不同产地红茶挥发性物质成分差异分析
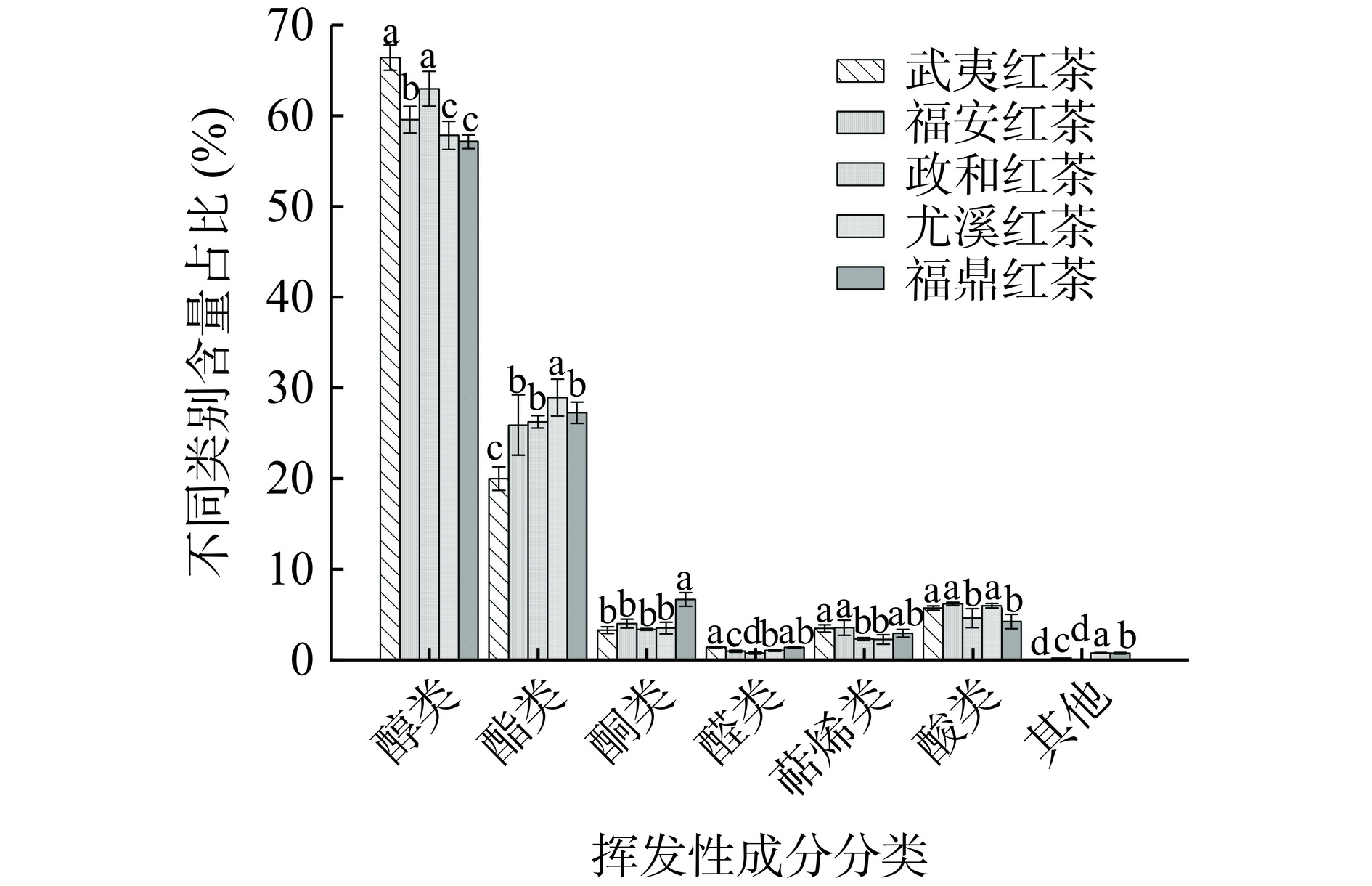
由表4可知,共检测鉴定出81种香气物质,其中醇类16 种、酯类35种、酮类8种、醛类5种、酸类5种、萜烯类化合物10种和其他3种,每类挥发性成分含量占比结果如(图4),5个地区红茶醇类化合物含量占比最高,均超过50%,其次是酯类(24.71%)、酸类(5.48%)和酮类(3.77%)。武夷红茶中醇类物质占比(66.44%)最高,尤溪红茶则酯类(28.90%)和酸类物质(5.91%)含量高于其他地区,而福鼎红茶则酮类(6.60%)和萜烯类物质(2.87%)含量占比较高,尤其是酮类物质显著高于其他地区(P<0.05)。检测出的16种醇类化合物中有10种共有成分,其中芳樟醇、香叶醇、苯乙醇、橙花醇及反式-橙花叔醇等含量均较高,这与前人研究的红茶呈现甜香、花香的主要基调结果相符合[29];酯类化合物呈现出怡人的果香[30],其在各地区茶样中含量占比:尤溪(28.90%)>福鼎(27.23%)>政和(26.23%)>福安(25.87%)>武夷山(19.93%),尤溪红茶酯类含量显著高于其他地区(P<0.05)。醇类和酯类在五个地区红茶中的总量占比均较高,是构成福建红茶具有花香、果香的主体成分。香叶醇作为红茶中重要的醇类物质,具有浓烈的蔷薇、玫瑰类花香[31],从表4可知,在福建5个产区中含量占比均较高,含量占比排序为:武夷红茶(51.86 %)>政和红茶(41.68 %)>尤溪红茶(40.69 %)>福安红茶(37.01 %)>福鼎红茶(31.47 %),可认为香叶醇是福建红茶呈现花香、甜香的重要的物质成分。
表 4 福建不同产地红茶挥发性香气成分Table 4. Volatile aroma components of black tea from different origins in Fujian序号 香气物质 英文名 CAS RI 含量(μg/kg) WY FA ZH YX FD 1 顺-a,a-5-三甲基-5-乙烯基四氢化呋喃-2-甲醇 Cis-alpha,alpha,5-trimethyl-5-vinyl tetrahydrofuran-2-methanol 5989-33-3 1028 100.12±64.44a 74.41±72ab 39.65±6.05b 31.69±16.49b 25.92±9.94b 2 芳樟醇 Linalool 78-70-6 1070 1220.44±939.55a 888.93±637.8a 451.27±63.23a 315.64±256.1a 543.26±92.44a 3 二氢芳樟醇 3,7-Dimethyl-1,5,7-Octatrien-3-ol 29957-43-5 1112 − − − 44.7±26.1a − 4 苯甲醇 Benzyl alcohol 100-51-6 1117 68.99±29.66a 34.41±3.1b 34.34±1.85b 35.45±18.19b 33.47±5.36b 5 壬醇 1-Nonanol 143-08-8 1142 − 12.3±0b 18.55±0.07a − 22.96±6.83a 6 苯乙醇 Phenylethyl alcohol 60-12-8 1058 6877±422.58a 105.11±29.12b 268.48±42.95b 124.66±5.84b 148.98±63.41b 7 橙花醇 Cis-3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienol 106-25-2 1212 295.94±189.31a 73.5±62.72b 61.67±7b 66.95±73.31b 36.26±7.96b 8 香叶醇 Geraniol 106-24-1 1250 11390.25±7247.64a 6289.44±2840.92ab 4979.18±566.77ab 4921.08±5156.61ab 2084.78±289.14b 9 反式-橙花叔醇 (±)-Trans-nerolidol 40716-66-3 1558 636.15±296ab 757.86±221.27a 645.1±60.84ab 376.02±194.15ab 246.18±66.1b 10 Α-毕橙茄醇 α-Cadinol 481-34-5 1651 92.77±50.39a 42.08±24.42b 16.84±2.78b 18.77±6.4b 15.14±9.97b 11 异植物醇 Isophytol 505-32-8 1944 66.53±26.14a 53.55±3.62ab 30.67±3.23bc 24.67±18.19c 15.71±5.2c 12 植物醇 Phytol 150-86-7 2125 35.21±4.62c 1562±476.05a 900.73±103.49ab 808.54±740.44ab 581.19±164.16bc 13 (-)-异雪松醇 (3R,3aS,6S,7R)-3,6,8,8-Tetramethyloctahydro-1H-3a,7-methanoazulen-6-ol 19903-73-2 1602 − 47.65±21.93ab 70.99±7.41a 22.63±18.58bc 28.7±9.29bc 14 香叶基香叶醇 Geranylgeraniol 24034-73-9 1849 − 18.53±0.31a − − 3.38±0.67b 15 T-杜松醇 T-cadinol 5937-11-1 1483 − 14.88±0a 9.54±1.5b 8.52±0.85b − 16 2,2,6-三甲基-6-乙烯基四氢-2H-呋喃-3-醇 2H-Pyran-3-ol,6-ethenyltetrahydro-2,
2,6-trimethyl-14049-11-7 1149 − 146.97±7.35b − 196.29±62.1a − 醇类(16种) 14593.97±9215.2a 10121.63±2933.86ab 7527.01±663.37ab 6995.6±6688.02ab 3785.91±558.16b 17 水杨酸甲酯 Methylsalicylate 119-36-8 1172 388.99±218.3a 342.05±166.85a 159.59±11.51a 204.25±129.27a 194.12±27.37a 18 癸酸乙酯 Ethyldecanoate 110-38-3 1392 528.5±32.45ab 533.71±53.34ab 566±72.88a 517.8±0ab 451.49±34.71b 19 (Z)-己酸-3-己烯酯 (Z)-Hexanoicacid-3-hexenylester 31501-11-8 1376 24.21±9.28b 122.06±88.91a 1.42±0.14b 21.56±20.97b 82.16±38.24ab 20 N-己酸(反-2-己烯基)酯 Trans-2-hexenylhexanoate 53398-86-0 1385 18.31±4.08a − − − − 21 2,5-十八碳二炔酸
甲酯2,5-Octadecadiy-
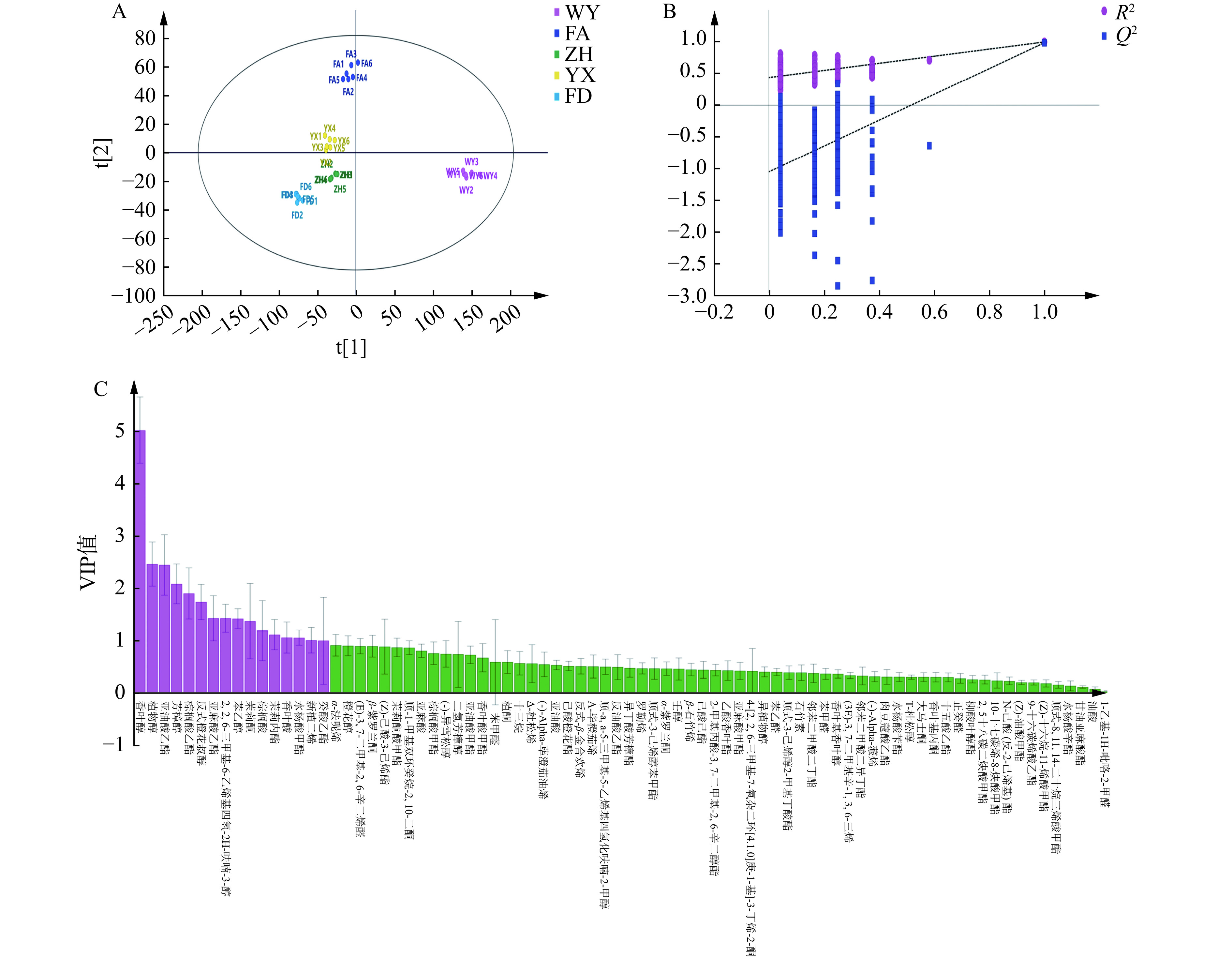
noicacidmethylester57156-91-9 1111 12.08±4.95a − − 5.49±0.83b − 22 茉莉内酯 Jasminlactone 25524-95-2 1645 − 176.62±3.54a − − 7.8±0.59b 23 己酸橙花酯 Nerylhexanoate 68310-59-8 1747 − − 21.14±2.88a − − 24 茉莉酮酸甲酯 Methyljasmonate 1211-29-6 1749 − 103.85±3.94a − − 19.07±0.96b 25 棕榈酸甲酯 Methylhexadecanoate 112-39-0 1924 294.36±148.95a 184.06±33.27ab 137.54±10.89b 143.55±47.42b 72.8±13.02b 26 棕榈酸乙酯 Palmiticacidethylester 628-97-7 1993 1290.87±153.55a 794.7±187b 1055.92±58.24ab 836.77±237.17b 3475±107.04c 27 9-十六碳烯酸乙酯 Ethyl9-hexadecenoate 54546-22-4 1970 1.49±0.14c 9.95±0.3a 2.9±0.36bc 4.91±2.32b 1.48±0.76c 28 邻苯二甲酸二异丁酯 Diisobutylphthalate 84-69-5 1854 34.81±18.64a 14.32±2.61b 22.88±4.4ab 8.7±3.45b 7.42±5.57b 29 水杨酸苄酯 Benzylsalicylate 118-58-1 1864 − 16.34±6.44a 9.12±0.97b 8.4±0.51b − 30 (Z)-油酸甲酯 Methyloleate 112-62-9 2126 106.56±39.98a 13.96±0.48b 4.93±0.68b 8.79±2.32b 6.99±3.6b 31 亚油酸甲酯 (Z,Z)-9,12-Octadecadienoicacid 112-63-0 2127 99.75±44.92a 62.89±15.16ab − 55.08±12.51b 32.5±1bc 32 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯 Dibutylphthalate 84-74-2 1949 46.34±15.15a 23.82±10.21bc 41.05±9.3ab 20.68±4.81c 9.3±4.83c 33 亚麻酸甲酯 MethylLinolenate 301-00-8 2134 106.36±54.56a 68.79±13.73bc 64.27±13.83bc 56.83±15.01bc 42.75±7.28c 34 反油酸乙酯 Elaidicacidethylester 6114-18-7 2143 53.07±10.64a 51.68±8.48a 56.34±6.47a 66.93±8.08a 29.08±14.9b 35 亚麻酸乙酯 Ethyl linolenate 1191-41-9 2168 1011.05±302.92a 828.32±50.36ab 864.45±119.57ab 844.26±338.77ab 443.98±143.01b 36 肉豆蔻酸乙酯 Ethyl myristate 124-06-1 1792 − − 9.42±5.68ab 13.74±1.44a 5.86±3.32b 37 甘油亚麻酸酯 1-α−Linolenoylglycerol 18465-99-1 2219 − 1.86±0.85a − 1.61±0.66a − 38 乙酸香叶酯 Geranylacetate 105-87-3 1374 − − 18.42±3.15a − 8.61±0.07b 39 10-十七碳烯-8-炔酸甲酯 10-Heptadecen-8-antiacid,methyl ester,(E)- 16714-85-5 1215 − − − 4.39±1.59a − 40 (Z)-十六烷-11-烯酸甲酯 (Z)-Methylhexadec-11-enoate 822-05-9 1861 − − − 2.58±0.46a − 41 2-甲基丙酸-3,7-二甲基-2,6-辛二醇酯 Geranylisobutyrate 2345-26-8 1553 54.92±39.59a − − − − 42 顺式-3-己烯醇2-甲基丁酸酯 (Z)-Hex-3-enyl2-methylbutyrat 53398-85-9 1211 − 22.3±4.23a − − − 43 柳酸叶醇酯 (Z)-3-Hexenylsalicylate 65405-77-8 1523 − 10.09±0.41a − − − 44 异丁酸芳樟酯 Linalylisobutyrate 78-35-3 1226 56.79±26.49a 27.56±6.93b 25.16±2.09b − 14.58±2.63bc 45 香叶酸甲酯 Methylgeranate 1189-09-9 1315 143.47±110.35a 41.35±2b 33.75±4.02b − 14.91±1.4b 46 己酸己酯 Hexylhexanoate 6378-65-0 1382 26.66±6.22b 33.47±0.56a − − − 47 顺式-3-己烯醇苯甲酸酯 Cis-3-hexenylbenzoate 25152-85-6 1567 78.24±62.53a 47±24.64ab 25.79±1.12ab 15.62±9.43b 5.45±0.5b 48 十五酸乙酯 N-Penyadecanoicacidethylester 41114-00-5 1893 − 12.51±1.06a 12.99±1.71a 8.2±1.19b 3.18±1.63c 49 水杨酸辛酯 2-Ethylhexylsalicylate 118-60-5 1812 − − − − 2.88±1.05a 50 顺式-8,11,14-二十烷三烯酸甲酯 Cis-8,11,14-eicosatrienoicacid 1783-84-2 1136 − − − 1.92±0.35a − 51 亚油酸乙酯 Ethyl linoleate 544-35-4 2164 − 851.86±106.56a − 643.32±348.15a − 酯类(35种) 4376.84±1042.57a 4395.12±219.23a 3133.07±211.66ab 3495.37±1345.04a 1803.96±318.62b 52 大马士酮 Beta-damascenone 23726-93-4 1398 − 16.9±0.64a 7.36±0.56b 19±0.01a 9.02±4.56b 53 α-紫罗兰酮 α-Ionone 127-41-3 1416 − 40.98±1.7a 14.45±0.91bc 11.65±8.26c 21.62±3.1b 54 香叶基丙酮 Geranylacetone 3796-70-1 1442 36.27±29.29a 24.57±3.2a 29.36±3.72a 17.56±6.47a 15.85±1.84a 55 茉莉酮 Jasmone 488-10-8 1383 140.93±43.83ab 158.1±24.03ab 39.28±4.02b 44.82±42.19b 227.18±162a 56 β-紫罗兰酮 β-Ionone 79-77-6 1471 156.92±97.95a 122.67±12.4a 14.91±0b 75.57±55.35ab 81.17±15.03ab 57 4-[2,2,6-三甲基-7-氧杂二环[4.1.0]庚-1-基]-3-丁烯-2-酮 4-(2,2,6-Trimethyl-7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]hept-1-yl)-3-buten-2-one 23267-57-4 1475 − − − 15.47±11.77a − 58 顺-1-甲基双环癸烷-2,10-二酮 Cis-1-Methylbicyclodecane-2,10-dione 83406-41-1 1651 278.97±139.65a 244.74±58.51a 223.27±20.13a 208.5±92.37ab 67.38±11.39b 59 植酮 Phytone 502-69-2 1840 93.88±64.92a 60.7±4.09ab 65.87±0ab 25.35±14.7b 15.16±3.95b 酮类(8种) 706.98±358.12a 668.66±58.59a 394.5±26.57a 417.92±151.43a 437.38±143.83a 60 苯乙醛 Benzeneacetaldehyde 122-78-1 1120 93.98±43.73a 49.77±10.83ab 56.8±4.27ab 46.91±17b 45.25±21.56b 61 (E)-3,7-二甲基-2,6-辛二烯醛 (E)-3,7-Dimethyl-2,6-Octadienal 141-27-5 1261 202.17±72.22a 97.33±58.02b − 72.8±62.17b 31.35±6.33b 62 正癸醛 Decanal 112-31-2 1193 − − − − 10.66±0.78a 63 1-乙基-1H-吡咯-2-甲醛 1-Ethyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carbaldehyde 2167-14-8 1053 − 0.21±0.09a − − − 64 苯甲醛 Benzaldehyde 100-52-7 986 − 6.61±0.17b 27.24±13.76a − − 醛类(5种) 296.15±115.41a 153.92±47.21b 84.05±26.97b 119.7±46.6b 87.26±26.68b 65 β-石竹烯 (-)-β-Caryophyllene 87-44-5 1392 − 28.57±0.55a − − − 66 反式-β-金合欢烯 Trans-β-farnesene 18794-84-8 1401 41.64±12.49a 22.37±0.77b 30.43±1.91b − 10.45±0.08c 67 α-法呢烯 α-Farnesene 502-61-4 1476 − 138.89±2.09a − 23.88±16.38b 11.09±0.85bc 68 Δ-杜松烯 (+)-Delta-cadinene 483-76-1 1511 − − − 24.54±10.55a − 69 新植二烯 Neophytadiene 504-96-1 1859 454.15±182.01a 373.52±65.98ab 228.81±22.23b 202.86±167.79b 161.49±43.09b 70 (3E)-3,7-二甲基辛-1,3,6-三烯 (3E)-3,7-Dimethyl-1,3,6-Octatriene 3779-61-1 960 34.93±11.19a − − 7.45±9.03b − 71 (-)-Alpha-荜澄茄油烯 (-)-Alpha-clbebene 17699-14-8 1346 118±21.85a − − − − 72 罗勒烯 Ocimene 13877-91-3 998 58.8±40.52a 21.89±8.36b − − 7.01±2.68b 73 (-)-Alpha-蒎烯 Alpha-pinene 80-56-8 1516 41.95±11.12a 7.07±2.02b 9.46±2.86b 6.67±2.05b − 萜烯类(10种) 749.46±224.14a 592.31±60.42a 268.7±23.61b 265.4±196.18b 190.03±44.87b 74 香叶酸 Geranicacid 459-80-3 1359 388.34±225.1a 351.05±45.85ab 180.99±22.27abc 150.56±134.28bc 84.28±22.22c 75 棕榈酸 N-Hexadecanoicacid 57-10-3 1962 642.24±126.4a 506.56±68.41ab 280.3±121.57cd 412.75±124.04bc 140.32±58.46d 76 油酸 Oleicacid 112-80-1 1980 − − − 0.53±0.18a − 77 亚油酸 Linoleicacid 60-33-3 2141 110.22±27.09a 88.79±12.77a 81.6±15.85a 78.74±28.92a 23.34±9.85b 78 亚麻酸 α-Linolenicacid 463-40-1 2145 100.55±35.82a 91.99±13.88a − 72.18±28.92a 28.08±11.81b 酸类(5种) 1241.34±393.47a 1038.39±64.72ab 542.89±93.88cd 714.76±292.5bc 276.01±94.7d 79 2-正辛基呋喃 2-N-Octylfuran 4179-38-8 1740 − − − 85.58±18.03a − 80 石竹素 Caryophylleneoxide 1139-30-6 1276 − 21.94±5.47a − − − 81 十三烷 N-Tridecane 629-50-5 223 − − − − 44.85±4.79a 其他(3种) − 21.94±5.47a − 85.58±18.03a 44.85±4.79a 总量 21964.74±11311.48a 16991.97±3152.81ab 11950.21±773.01ab 12094.34±8533.91ab 6625.4±973.06b 注:表中数值为平均值±标准差,同行不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),−代表未检出。 为进一步分析福建不同产地红茶之间的香气差异物质,以81个香气物质作为因变量,5个不同产地作为自变量,通过正交偏最小二乘法判别分析(OPLS-DA),自变量拟合指数(R2X)为0.984,因变量拟合指数(R2Y=0.979),模型预测指数(Q2=0.929),模型拟合效果好[32]。经200次置换检验,结果如图5B所示,Q2回归线和纵轴相交点小于零,模型不存在过拟合情况,验证有效,该结果可用于这5个不同产地红茶香气的差异分析。
OPLS-DA结果(如图5A)所示,5个产地红茶能有效区分,说明不同产地红茶的香气成分具有明显差异。福鼎红茶、政和红茶和尤溪红茶的样本差异较小,这三个地区的红茶香气特征较为相似;福安红茶和武夷红茶的样本则差异较大,香气特征差异明显。如图5C所示,共有16种挥发性物质(VIP值>1)对不同产地福建红茶风味品质的区分起重要作用。香叶醇、植物醇、亚油酸乙酯、芳樟醇、棕榈酸乙酯、反式-橙花叔醇、亚麻酸乙酯、2,2,6-三甲基-6-乙烯基四氢-2H-呋喃-3-醇、苯乙醇、茉莉酮、棕榈酸、茉莉内酯、香叶酸、水杨酸甲酯、新植二烯、癸酸乙酯等特征挥发性物质含量差异是区分福建不同产地红茶的重要因子。此外,α-法呢烯、橙花醇、β-紫罗兰酮等也是不同产地红茶重要差异性香气物质。
2.5 不同产地红茶关键香气活性化合物的筛选
香气物质含量的高低直接影响茶叶香气类型,有些含量低但阈值高的物质对茶叶香气特征也有较大的贡献度。OAV是计算表征挥发性物质贡献度大小的物理量,表示单一的香气成分对整体香气的贡献度,通常认为OAV值>1的成分很大程度上对总体风味有直接影响[33]。表5显示, OAV值>1的香气化合物共18个,其中武夷红茶13个,福鼎红茶14个,福安红茶16个,政和红茶12个,尤溪红茶15个。其中OAV值>10的香气物质共15个,分别是芳樟醇、苯乙醇、橙花醇、香叶醇、水杨酸甲酯、茉莉酮酸甲酯、棕榈酸甲酯、α-紫罗兰酮、香叶基丙酮、β-紫罗兰酮、苯乙醛、正癸醛、苯甲醛、(3E)-3,7-二甲基辛-1,3,6-三烯及亚麻酸等。其中,具有冬青香、花香的水杨酸甲酯[34]在5个产地中的酯类占比并不高,但其OAV值在这5个产地中均大于3000,说明水杨酸甲酯对福建地区红茶香气的形成具有重要贡献作用。同一香气物质在不同样品中的OAV值差异较大,通常认为OAV值越大,贡献度越大[35]。其中,芳樟醇、苯乙醇、橙花醇、香叶醇、水杨酸甲酯、棕榈酸甲酯、香叶基丙酮、β-紫罗兰酮及(3E)-3,7-二甲基辛-1,3,6-三烯(OAV>100)等9种是武夷红茶重要赋香成分,对武夷红茶的贡献度高于其他茶样,这些成分共同构成了武夷红茶花香带有果香和薯香的特征,这进一步验证了武夷红茶在香气感官评分上高于其他地区,与刘菲等[36]评价武夷红茶其香气为花、果、薯、蜜等综合香型的结论一致。正癸醛(OAV>100)是福鼎红茶的重要香气物质,具有甜香、脂香和花香的正癸醛[37]对福鼎红茶的贡献度高于其他地区的红茶,与其他物质相结合共同构成福鼎红茶甜花香的品质特征。茉莉酮酸甲酯和α-紫罗兰酮(OAV>100)对福安红茶的贡献度高于其他茶样,是福安红茶呈现花香甜香浓郁的特征性香气成分。具有杏仁气味和焦糖甜香的苯甲醛对政和红茶的贡献度高于其他地区,是政和红茶重要的赋香物质。大马士酮(OAV>1)在尤溪红茶中的贡献度高于其他地区,与其他香气成分共同促成其花香甜香的特征。综上,花果香型的香气物质在福建5个产区的红茶中表现出较高强度,整体呈现出较强的花香、甜香和果香。
表 5 福建不同产地红茶挥发性有机物OAV值Table 5. OAV value of volatile organic compounds in black tea from different areas in Fujian序号 香气物质 OT(µg/kg) WY FD FA ZH YX 香气特征[38−41] 1 芳樟醇 0.58[42] 1905.93 966.84 1532.64 780.92 544.21 玉兰、百合等花香 2 苯乙醇 0.75[43] 833.54 214.94 140.14 354.23 166.21 玫瑰香、甜花香 3 橙花醇 0.3[43] 905.75 121.92 245.01 204.96 223.18 橙花香气 4 香叶醇 3.2[44] 3280.75 661.48 1965.45 1551.23 1537.84 玫瑰、蔷薇花香 5 反式-橙花叔醇 250[45] 2.38 0.94 3.03 2.50 1.50 橙花香,花香 6 水杨酸甲酯 0.04[43] 8987.26 5006.18 8551.22 3964.87 5106.26 冬青油味、花香 7 (Z)-己酸-3-己烯酯 16[46] 1.57 4.67 7.63 0.09 1.35 花香 8 茉莉酮酸甲酯 0.07[43] 0.00 275.57 1483.57 0.00 0.00 茉莉花香 9 棕榈酸甲酯 2[43] 138.07 36.29 92.03 65.67 71.78 轻微果香 10 大马士酮 10[45] 0.00 0.95 1.69 0.72 1.90 玫瑰香 11 α−紫罗兰酮 0.4[42] 0.00 53.15 102.46 35.84 29.13 甜花香 12 香叶基丙酮 0.186[47] 177.30 86.69 132.09 155.23 94.42 果香、淡花香 13 β−紫罗兰酮 0.021[42] 6890.02 3938.92 5841.49 709.94 3598.69 紫罗兰香、木香 14 苯乙醛 4[42] 21.73 12.49 12.44 14.03 11.73 花香,似蜜香 15 正癸醛 0.1[42] 0.00 105.71 0.00 0.00 0.00 脂香,甜香,花香 16 苯甲醛 3.5[43] 0.00 0.00 1.89 10.47 0.00 杏仁气味、焦糖甜香 17 (3E)-3,7-二甲基辛-1,3,6-三烯 0.034[47] 1035.22 0.00 0.00 0.00 219.20 − 18 亚麻酸 5[45] 19.18 5.84 18.40 0.00 14.44 − 2.6 不同产地红茶风味品质成分与感官特征相关性分析
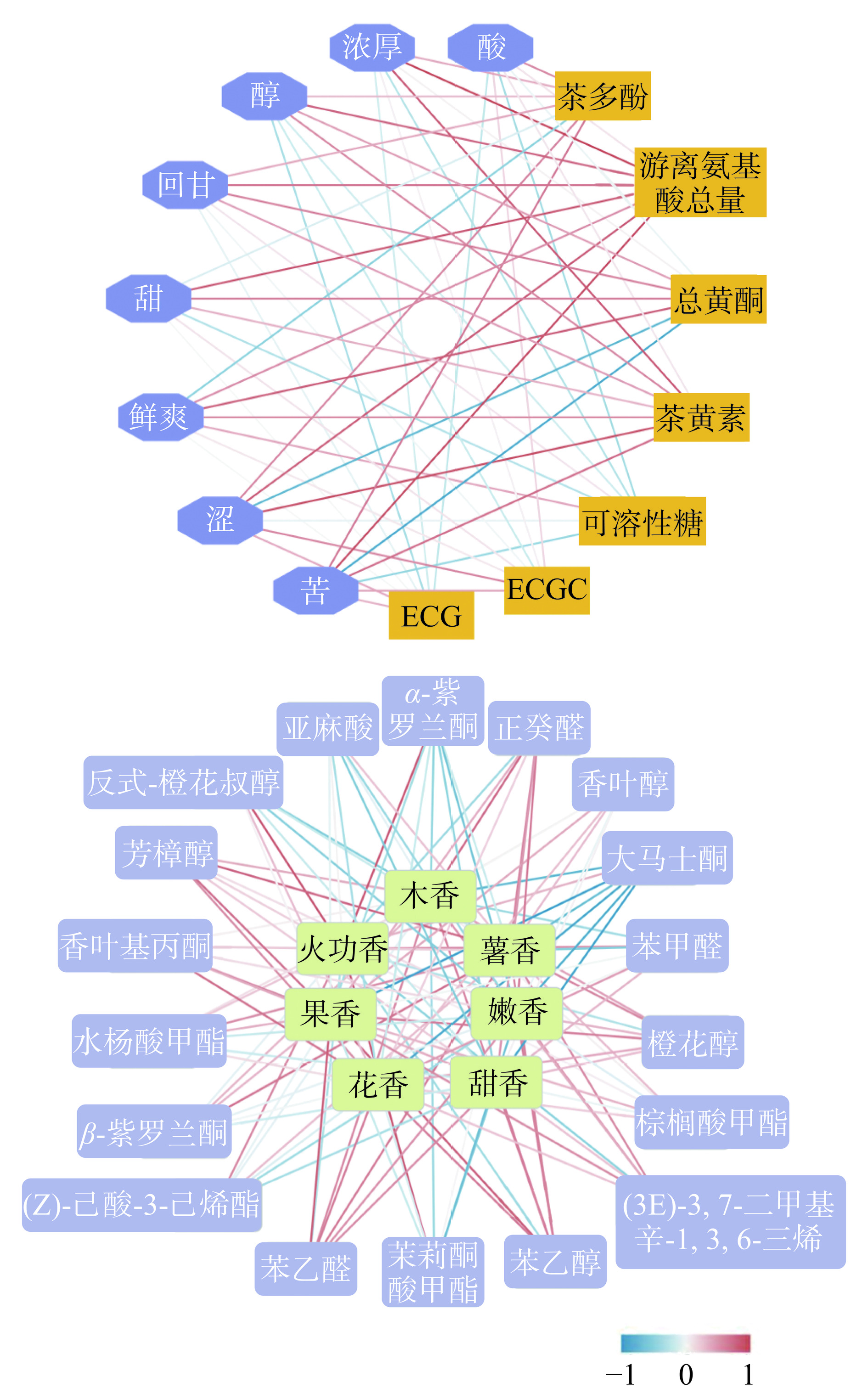
为进一步分析不同产地红茶风味品质的差异性,对主要滋味成分和香气(OAV>1)的18种挥发性物质与感官审评结果进行关联分析,如图6A所示,总黄酮、可溶性糖与苦、涩和酸呈负相关,游离氨基酸总量、茶黄素与苦、涩、酸、鲜爽、甜及醇、回甘和浓厚呈正相关,而EGCG和ECG与苦、涩呈正相关,与回甘、醇呈负相关。福安红茶可溶性糖、总黄酮及茶黄素含量均高于其他地区,可溶性糖中和总黄酮和茶黄素共同促成了福安红茶滋味甜醇爽口的特征。政和红茶则具有较高含量的游离氨基酸及儿茶素,可溶性糖和总黄酮含量较低,促进了政和红茶爽口收敛性强的感官特征。香气物质与感官相关联结果如图6B所示,芳樟醇与薯香、果香及花香的感官属性呈显著正相关(P<0.05),苯乙醇则与嫩香、甜香呈显著正相关(P<0.05),香叶基丙酮与花香呈正相关,这些物质促成了武夷红茶薯香甜香更显的品质特征。正癸醛和苯乙醛则与薯香、果香和木香呈正相关,这增强了福鼎红茶的花香和政和红茶的果香和甜香,而茉莉酮酸甲酯与火攻香呈正相关关系,其可能与其他香气成分联合增强了福安红茶的火攻香。这些物质对于各地区红茶不同香型的形成具有较大的促进作用,推测其可能是形成福建这5个不同产地红茶香型差异的重要成分。
3. 结论
本研究通过感官审评、国标法、顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱联用仪(HS-SPME-GC-MS)等方法,综合分析了福建5个地区(武夷山、福安、政和、尤溪和福鼎)红茶的风味品质特征,其中福安红茶可溶性糖、总黄酮、茶黄素及茶红素含量高于其他地区;政和红茶游离氨基酸总量和儿茶素总含量最高,福鼎红茶儿茶素含量低于其他地区,但总黄酮含量较高;尤溪红茶茶黄素含量明显低于其他地区,但可溶性糖含量仅次于福安红茶,这些差异较大的生化成分促进了福建不同地区红茶滋味特征的形成,同时在一定程度上可作为判断不同产地红茶品质的参考指标。
福建不同地区红茶在香气上虽有较多共有成分,但各有其特征性物质。鉴定的81种挥发性物质整理归类为醇类、酯类、酮类、醛类、酸类、萜烯类和其他7种类型,通过OPLS-DA建模结合香气活度值(OAV)分析,共筛选出16个(VIP值>1)和18种(OAV>1)特征性香气成分,其中芳樟醇、苯乙醇、橙花醇、香叶醇、水杨酸甲酯、棕榈酸甲酯、香叶基丙酮、β-紫罗兰酮及(3E)-3,7-二甲基辛-1,3,6-三烯等9种物质是武夷红茶的重要赋香物质。茉莉酮酸甲酯和α-紫罗兰酮等促成福安红茶花香甜香。正癸醛是福鼎红茶区别于其他产区的重要香气成分,而苯甲醛对政和红茶贡献度最高,而具有玫瑰花香的大马士酮则对尤溪红茶香气具有较大贡献作用,总体而言福建红茶以花香、果香及甜香物质为主。综上,本研究结果为福建不同地区红茶风味品质特征的研究提供一定的理论依据,后期可继续丰富不同等级、品种、季节等红茶样品,以更加全面科学分析福建红茶特征。
-
图 3 福建不同地区红茶生化成分含量对比
注:TF-3-G:Theaflavin-3-gallate茶黄素-3-没食子酸酯;TF-3'-G:Theaflavin-3'-gallate茶黄素-3'-没食子酸酯;TF-3,3'-G:Theaflavin-3,3'-digallate茶黄素-3,3'-双没食子酸酯;TF:Theaflavin简单茶黄素;EGCG:(-)-Epigallocatechin gallate表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯;ECG:(-)-Epicatechin gallate表儿茶素没食子酸酯;GCG:Galocatechin gallate没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯。
Figure 3. Comparison of the contents of the main biochemical components in black tea from different areas in Fujian
表 1 红茶样品信息
Table 1 Black tea samples information
样品编号 样品数量 产地 收样年份 品种 WY 6 武夷山市 2022 菜茶 FA 6 福安市 2022 金牡丹 ZH 6 政和县 2022 福安大白 YX 6 尤溪县 2022 梅占 FD 6 福鼎市 2022 福鼎大毫 表 2 福建不同区域红茶感官品质评价
Table 2 Sensory quality evaluation of black tea in different areas of Fujian
编号 外形(25%) 汤色(10%) 香气(25%) 滋味(30%) 叶底(10%) 综合得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 评语 得分 WY 紧细,乌润,金毫显 95.00±0.41a 橙黄明亮 94.50±0.58ab 花香薯香 96.75±0.29a 甜醇爽口 95.13±0.85a 细嫩,较
软亮94.75±0.29a 95.20±0.44a FA 乌润匀整 92.88±1.11b 橙黄明亮 94.75±0.29a 甜香带
花香95.00±0.41ab 较甜醇 94.13±0.63ab 柔软较亮较匀 92.00±0c 93.88±0.41b ZH 紧结乌润
金毫显94.00±0.82ab 红艳较
明亮93.00±1.15b 薯香带
花香93.13±0.25b 甜醇较
爽口92.88±0.25b 细嫩匀亮,带花青 92.75±0.65bc 93.25±0.4b YX 紧细,
金毫显95.00±1.08a 浅橙红,
较亮91.00±1.63c 甜香稍带火香,略有花香 93.00±2.71b 甜醇带
薯味93.00±1.22b 细嫩红匀较亮 94.13±0.75ab 93.41±0.91b FD 乌润金毫显,较匀整 94.88±0.25a 橙黄较
明亮94.00±0.82ab 甜花香显,微带薯香 93.25±0.96b 较甜,醇厚 93.00±1.83b 细嫩,
较红匀93.13±1.03bc 93.64±0.83b 注:表中数值为平均值±标准差,同列不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表3同。 表 3 福建不同产地红茶L*、a*、b*值的对比
Table 3 Comparison of L*, a*, and b* values of black tea from different areas in Fujian
茶样 L* a* b* WY 86.89±2.34ab 2.25±1.89bc 59.68±8.28bc FA 86.56±0.17b 3.33±0.05ab 61.47±1.87ab ZH 83.89±0.5c 4.55±0.31a 68.79±0.89a YX 88.75±3.06a 1.03±2.5c 52.31±14.04c FD 87.96±0.49ab 1.9±0.64bc 62.49±2.44ab 表 4 福建不同产地红茶挥发性香气成分
Table 4 Volatile aroma components of black tea from different origins in Fujian
序号 香气物质 英文名 CAS RI 含量(μg/kg) WY FA ZH YX FD 1 顺-a,a-5-三甲基-5-乙烯基四氢化呋喃-2-甲醇 Cis-alpha,alpha,5-trimethyl-5-vinyl tetrahydrofuran-2-methanol 5989-33-3 1028 100.12±64.44a 74.41±72ab 39.65±6.05b 31.69±16.49b 25.92±9.94b 2 芳樟醇 Linalool 78-70-6 1070 1220.44±939.55a 888.93±637.8a 451.27±63.23a 315.64±256.1a 543.26±92.44a 3 二氢芳樟醇 3,7-Dimethyl-1,5,7-Octatrien-3-ol 29957-43-5 1112 − − − 44.7±26.1a − 4 苯甲醇 Benzyl alcohol 100-51-6 1117 68.99±29.66a 34.41±3.1b 34.34±1.85b 35.45±18.19b 33.47±5.36b 5 壬醇 1-Nonanol 143-08-8 1142 − 12.3±0b 18.55±0.07a − 22.96±6.83a 6 苯乙醇 Phenylethyl alcohol 60-12-8 1058 6877±422.58a 105.11±29.12b 268.48±42.95b 124.66±5.84b 148.98±63.41b 7 橙花醇 Cis-3,7-dimethyl-2,6-octadienol 106-25-2 1212 295.94±189.31a 73.5±62.72b 61.67±7b 66.95±73.31b 36.26±7.96b 8 香叶醇 Geraniol 106-24-1 1250 11390.25±7247.64a 6289.44±2840.92ab 4979.18±566.77ab 4921.08±5156.61ab 2084.78±289.14b 9 反式-橙花叔醇 (±)-Trans-nerolidol 40716-66-3 1558 636.15±296ab 757.86±221.27a 645.1±60.84ab 376.02±194.15ab 246.18±66.1b 10 Α-毕橙茄醇 α-Cadinol 481-34-5 1651 92.77±50.39a 42.08±24.42b 16.84±2.78b 18.77±6.4b 15.14±9.97b 11 异植物醇 Isophytol 505-32-8 1944 66.53±26.14a 53.55±3.62ab 30.67±3.23bc 24.67±18.19c 15.71±5.2c 12 植物醇 Phytol 150-86-7 2125 35.21±4.62c 1562±476.05a 900.73±103.49ab 808.54±740.44ab 581.19±164.16bc 13 (-)-异雪松醇 (3R,3aS,6S,7R)-3,6,8,8-Tetramethyloctahydro-1H-3a,7-methanoazulen-6-ol 19903-73-2 1602 − 47.65±21.93ab 70.99±7.41a 22.63±18.58bc 28.7±9.29bc 14 香叶基香叶醇 Geranylgeraniol 24034-73-9 1849 − 18.53±0.31a − − 3.38±0.67b 15 T-杜松醇 T-cadinol 5937-11-1 1483 − 14.88±0a 9.54±1.5b 8.52±0.85b − 16 2,2,6-三甲基-6-乙烯基四氢-2H-呋喃-3-醇 2H-Pyran-3-ol,6-ethenyltetrahydro-2,
2,6-trimethyl-14049-11-7 1149 − 146.97±7.35b − 196.29±62.1a − 醇类(16种) 14593.97±9215.2a 10121.63±2933.86ab 7527.01±663.37ab 6995.6±6688.02ab 3785.91±558.16b 17 水杨酸甲酯 Methylsalicylate 119-36-8 1172 388.99±218.3a 342.05±166.85a 159.59±11.51a 204.25±129.27a 194.12±27.37a 18 癸酸乙酯 Ethyldecanoate 110-38-3 1392 528.5±32.45ab 533.71±53.34ab 566±72.88a 517.8±0ab 451.49±34.71b 19 (Z)-己酸-3-己烯酯 (Z)-Hexanoicacid-3-hexenylester 31501-11-8 1376 24.21±9.28b 122.06±88.91a 1.42±0.14b 21.56±20.97b 82.16±38.24ab 20 N-己酸(反-2-己烯基)酯 Trans-2-hexenylhexanoate 53398-86-0 1385 18.31±4.08a − − − − 21 2,5-十八碳二炔酸
甲酯2,5-Octadecadiy-
noicacidmethylester57156-91-9 1111 12.08±4.95a − − 5.49±0.83b − 22 茉莉内酯 Jasminlactone 25524-95-2 1645 − 176.62±3.54a − − 7.8±0.59b 23 己酸橙花酯 Nerylhexanoate 68310-59-8 1747 − − 21.14±2.88a − − 24 茉莉酮酸甲酯 Methyljasmonate 1211-29-6 1749 − 103.85±3.94a − − 19.07±0.96b 25 棕榈酸甲酯 Methylhexadecanoate 112-39-0 1924 294.36±148.95a 184.06±33.27ab 137.54±10.89b 143.55±47.42b 72.8±13.02b 26 棕榈酸乙酯 Palmiticacidethylester 628-97-7 1993 1290.87±153.55a 794.7±187b 1055.92±58.24ab 836.77±237.17b 3475±107.04c 27 9-十六碳烯酸乙酯 Ethyl9-hexadecenoate 54546-22-4 1970 1.49±0.14c 9.95±0.3a 2.9±0.36bc 4.91±2.32b 1.48±0.76c 28 邻苯二甲酸二异丁酯 Diisobutylphthalate 84-69-5 1854 34.81±18.64a 14.32±2.61b 22.88±4.4ab 8.7±3.45b 7.42±5.57b 29 水杨酸苄酯 Benzylsalicylate 118-58-1 1864 − 16.34±6.44a 9.12±0.97b 8.4±0.51b − 30 (Z)-油酸甲酯 Methyloleate 112-62-9 2126 106.56±39.98a 13.96±0.48b 4.93±0.68b 8.79±2.32b 6.99±3.6b 31 亚油酸甲酯 (Z,Z)-9,12-Octadecadienoicacid 112-63-0 2127 99.75±44.92a 62.89±15.16ab − 55.08±12.51b 32.5±1bc 32 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯 Dibutylphthalate 84-74-2 1949 46.34±15.15a 23.82±10.21bc 41.05±9.3ab 20.68±4.81c 9.3±4.83c 33 亚麻酸甲酯 MethylLinolenate 301-00-8 2134 106.36±54.56a 68.79±13.73bc 64.27±13.83bc 56.83±15.01bc 42.75±7.28c 34 反油酸乙酯 Elaidicacidethylester 6114-18-7 2143 53.07±10.64a 51.68±8.48a 56.34±6.47a 66.93±8.08a 29.08±14.9b 35 亚麻酸乙酯 Ethyl linolenate 1191-41-9 2168 1011.05±302.92a 828.32±50.36ab 864.45±119.57ab 844.26±338.77ab 443.98±143.01b 36 肉豆蔻酸乙酯 Ethyl myristate 124-06-1 1792 − − 9.42±5.68ab 13.74±1.44a 5.86±3.32b 37 甘油亚麻酸酯 1-α−Linolenoylglycerol 18465-99-1 2219 − 1.86±0.85a − 1.61±0.66a − 38 乙酸香叶酯 Geranylacetate 105-87-3 1374 − − 18.42±3.15a − 8.61±0.07b 39 10-十七碳烯-8-炔酸甲酯 10-Heptadecen-8-antiacid,methyl ester,(E)- 16714-85-5 1215 − − − 4.39±1.59a − 40 (Z)-十六烷-11-烯酸甲酯 (Z)-Methylhexadec-11-enoate 822-05-9 1861 − − − 2.58±0.46a − 41 2-甲基丙酸-3,7-二甲基-2,6-辛二醇酯 Geranylisobutyrate 2345-26-8 1553 54.92±39.59a − − − − 42 顺式-3-己烯醇2-甲基丁酸酯 (Z)-Hex-3-enyl2-methylbutyrat 53398-85-9 1211 − 22.3±4.23a − − − 43 柳酸叶醇酯 (Z)-3-Hexenylsalicylate 65405-77-8 1523 − 10.09±0.41a − − − 44 异丁酸芳樟酯 Linalylisobutyrate 78-35-3 1226 56.79±26.49a 27.56±6.93b 25.16±2.09b − 14.58±2.63bc 45 香叶酸甲酯 Methylgeranate 1189-09-9 1315 143.47±110.35a 41.35±2b 33.75±4.02b − 14.91±1.4b 46 己酸己酯 Hexylhexanoate 6378-65-0 1382 26.66±6.22b 33.47±0.56a − − − 47 顺式-3-己烯醇苯甲酸酯 Cis-3-hexenylbenzoate 25152-85-6 1567 78.24±62.53a 47±24.64ab 25.79±1.12ab 15.62±9.43b 5.45±0.5b 48 十五酸乙酯 N-Penyadecanoicacidethylester 41114-00-5 1893 − 12.51±1.06a 12.99±1.71a 8.2±1.19b 3.18±1.63c 49 水杨酸辛酯 2-Ethylhexylsalicylate 118-60-5 1812 − − − − 2.88±1.05a 50 顺式-8,11,14-二十烷三烯酸甲酯 Cis-8,11,14-eicosatrienoicacid 1783-84-2 1136 − − − 1.92±0.35a − 51 亚油酸乙酯 Ethyl linoleate 544-35-4 2164 − 851.86±106.56a − 643.32±348.15a − 酯类(35种) 4376.84±1042.57a 4395.12±219.23a 3133.07±211.66ab 3495.37±1345.04a 1803.96±318.62b 52 大马士酮 Beta-damascenone 23726-93-4 1398 − 16.9±0.64a 7.36±0.56b 19±0.01a 9.02±4.56b 53 α-紫罗兰酮 α-Ionone 127-41-3 1416 − 40.98±1.7a 14.45±0.91bc 11.65±8.26c 21.62±3.1b 54 香叶基丙酮 Geranylacetone 3796-70-1 1442 36.27±29.29a 24.57±3.2a 29.36±3.72a 17.56±6.47a 15.85±1.84a 55 茉莉酮 Jasmone 488-10-8 1383 140.93±43.83ab 158.1±24.03ab 39.28±4.02b 44.82±42.19b 227.18±162a 56 β-紫罗兰酮 β-Ionone 79-77-6 1471 156.92±97.95a 122.67±12.4a 14.91±0b 75.57±55.35ab 81.17±15.03ab 57 4-[2,2,6-三甲基-7-氧杂二环[4.1.0]庚-1-基]-3-丁烯-2-酮 4-(2,2,6-Trimethyl-7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]hept-1-yl)-3-buten-2-one 23267-57-4 1475 − − − 15.47±11.77a − 58 顺-1-甲基双环癸烷-2,10-二酮 Cis-1-Methylbicyclodecane-2,10-dione 83406-41-1 1651 278.97±139.65a 244.74±58.51a 223.27±20.13a 208.5±92.37ab 67.38±11.39b 59 植酮 Phytone 502-69-2 1840 93.88±64.92a 60.7±4.09ab 65.87±0ab 25.35±14.7b 15.16±3.95b 酮类(8种) 706.98±358.12a 668.66±58.59a 394.5±26.57a 417.92±151.43a 437.38±143.83a 60 苯乙醛 Benzeneacetaldehyde 122-78-1 1120 93.98±43.73a 49.77±10.83ab 56.8±4.27ab 46.91±17b 45.25±21.56b 61 (E)-3,7-二甲基-2,6-辛二烯醛 (E)-3,7-Dimethyl-2,6-Octadienal 141-27-5 1261 202.17±72.22a 97.33±58.02b − 72.8±62.17b 31.35±6.33b 62 正癸醛 Decanal 112-31-2 1193 − − − − 10.66±0.78a 63 1-乙基-1H-吡咯-2-甲醛 1-Ethyl-1H-pyrrole-2-carbaldehyde 2167-14-8 1053 − 0.21±0.09a − − − 64 苯甲醛 Benzaldehyde 100-52-7 986 − 6.61±0.17b 27.24±13.76a − − 醛类(5种) 296.15±115.41a 153.92±47.21b 84.05±26.97b 119.7±46.6b 87.26±26.68b 65 β-石竹烯 (-)-β-Caryophyllene 87-44-5 1392 − 28.57±0.55a − − − 66 反式-β-金合欢烯 Trans-β-farnesene 18794-84-8 1401 41.64±12.49a 22.37±0.77b 30.43±1.91b − 10.45±0.08c 67 α-法呢烯 α-Farnesene 502-61-4 1476 − 138.89±2.09a − 23.88±16.38b 11.09±0.85bc 68 Δ-杜松烯 (+)-Delta-cadinene 483-76-1 1511 − − − 24.54±10.55a − 69 新植二烯 Neophytadiene 504-96-1 1859 454.15±182.01a 373.52±65.98ab 228.81±22.23b 202.86±167.79b 161.49±43.09b 70 (3E)-3,7-二甲基辛-1,3,6-三烯 (3E)-3,7-Dimethyl-1,3,6-Octatriene 3779-61-1 960 34.93±11.19a − − 7.45±9.03b − 71 (-)-Alpha-荜澄茄油烯 (-)-Alpha-clbebene 17699-14-8 1346 118±21.85a − − − − 72 罗勒烯 Ocimene 13877-91-3 998 58.8±40.52a 21.89±8.36b − − 7.01±2.68b 73 (-)-Alpha-蒎烯 Alpha-pinene 80-56-8 1516 41.95±11.12a 7.07±2.02b 9.46±2.86b 6.67±2.05b − 萜烯类(10种) 749.46±224.14a 592.31±60.42a 268.7±23.61b 265.4±196.18b 190.03±44.87b 74 香叶酸 Geranicacid 459-80-3 1359 388.34±225.1a 351.05±45.85ab 180.99±22.27abc 150.56±134.28bc 84.28±22.22c 75 棕榈酸 N-Hexadecanoicacid 57-10-3 1962 642.24±126.4a 506.56±68.41ab 280.3±121.57cd 412.75±124.04bc 140.32±58.46d 76 油酸 Oleicacid 112-80-1 1980 − − − 0.53±0.18a − 77 亚油酸 Linoleicacid 60-33-3 2141 110.22±27.09a 88.79±12.77a 81.6±15.85a 78.74±28.92a 23.34±9.85b 78 亚麻酸 α-Linolenicacid 463-40-1 2145 100.55±35.82a 91.99±13.88a − 72.18±28.92a 28.08±11.81b 酸类(5种) 1241.34±393.47a 1038.39±64.72ab 542.89±93.88cd 714.76±292.5bc 276.01±94.7d 79 2-正辛基呋喃 2-N-Octylfuran 4179-38-8 1740 − − − 85.58±18.03a − 80 石竹素 Caryophylleneoxide 1139-30-6 1276 − 21.94±5.47a − − − 81 十三烷 N-Tridecane 629-50-5 223 − − − − 44.85±4.79a 其他(3种) − 21.94±5.47a − 85.58±18.03a 44.85±4.79a 总量 21964.74±11311.48a 16991.97±3152.81ab 11950.21±773.01ab 12094.34±8533.91ab 6625.4±973.06b 注:表中数值为平均值±标准差,同行不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),−代表未检出。 表 5 福建不同产地红茶挥发性有机物OAV值
Table 5 OAV value of volatile organic compounds in black tea from different areas in Fujian
序号 香气物质 OT(µg/kg) WY FD FA ZH YX 香气特征[38−41] 1 芳樟醇 0.58[42] 1905.93 966.84 1532.64 780.92 544.21 玉兰、百合等花香 2 苯乙醇 0.75[43] 833.54 214.94 140.14 354.23 166.21 玫瑰香、甜花香 3 橙花醇 0.3[43] 905.75 121.92 245.01 204.96 223.18 橙花香气 4 香叶醇 3.2[44] 3280.75 661.48 1965.45 1551.23 1537.84 玫瑰、蔷薇花香 5 反式-橙花叔醇 250[45] 2.38 0.94 3.03 2.50 1.50 橙花香,花香 6 水杨酸甲酯 0.04[43] 8987.26 5006.18 8551.22 3964.87 5106.26 冬青油味、花香 7 (Z)-己酸-3-己烯酯 16[46] 1.57 4.67 7.63 0.09 1.35 花香 8 茉莉酮酸甲酯 0.07[43] 0.00 275.57 1483.57 0.00 0.00 茉莉花香 9 棕榈酸甲酯 2[43] 138.07 36.29 92.03 65.67 71.78 轻微果香 10 大马士酮 10[45] 0.00 0.95 1.69 0.72 1.90 玫瑰香 11 α−紫罗兰酮 0.4[42] 0.00 53.15 102.46 35.84 29.13 甜花香 12 香叶基丙酮 0.186[47] 177.30 86.69 132.09 155.23 94.42 果香、淡花香 13 β−紫罗兰酮 0.021[42] 6890.02 3938.92 5841.49 709.94 3598.69 紫罗兰香、木香 14 苯乙醛 4[42] 21.73 12.49 12.44 14.03 11.73 花香,似蜜香 15 正癸醛 0.1[42] 0.00 105.71 0.00 0.00 0.00 脂香,甜香,花香 16 苯甲醛 3.5[43] 0.00 0.00 1.89 10.47 0.00 杏仁气味、焦糖甜香 17 (3E)-3,7-二甲基辛-1,3,6-三烯 0.034[47] 1035.22 0.00 0.00 0.00 219.20 − 18 亚麻酸 5[45] 19.18 5.84 18.40 0.00 14.44 − -
[1] 范捷, 王秋霜, 秦丹丹, 等. 红茶品质及其相关生化因子研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(3):246−253. [FAN J, WANG Q S, QIN D D, et al. Recent progress in black tea quality and related biochemical factors[J]. Food Science,2020,41(3):246−253.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190217-077 FAN J, WANG Q S, QIN D D, et al. Recent progress in black tea quality and related biochemical factors[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(3): 246−253. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190217-077
[2] 廖泽明, 黄雅雯, 郭雅玲. 福建红茶产业优势与发展思考[J]. 福建茶叶,2017,39(3):1−3. [LIAN Z M, HUANG Y W, GUO Y L. Thoughts on the advantages and development of Fujian black tea industry[J]. Tea in Fujian,2017,39(3):1−3.] LIAN Z M, HUANG Y W, GUO Y L. Thoughts on the advantages and development of Fujian black tea industry[J]. Tea in Fujian, 2017, 39(3): 1−3.
[3] XU Y M, QIAO F B, HUANG J K. Black tea markets worldwide:are they integrated?[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture,2022,21(2):552−565. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(21)63850-9
[4] 中华全国供销合作总社杭州茶叶研究院. 茶叶感官审评方法:GB/T 23776-2018[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2018. [Hangzhou Tea Research Institute, China Cooperation. Methodology of sensory evaluation of tea:GB/T 23776-2018[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2018.] Hangzhou Tea Research Institute, China Cooperation. Methodology of sensory evaluation of tea: GB/T 23776-2018[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018.
[5] 林燕萍, 张渤, 张见明, 等. 不同萎凋方式对武夷红茶‘金骏眉’品质的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(19):78−85. [LIN Y P, ZHANG B, ZHANG J M, et al. Effects of different withering methods on the quality of bohea tea 'Jinjunmei'[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(19):78−85.] LIN Y P, ZHANG B, ZHANG J M, et al. Effects of different withering methods on the quality of bohea tea 'Jinjunmei'[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(19): 78−85.
[6] 张磊, 杨如兴. 福建红茶的生产现状与技术创新[J]. 茶叶科学技术,2011(2):12−15. [ZHANG L, YANG R X. Production status and technological innovation of Fujian black tea[J]. Tea Science and Technology,2011(2):12−15.] ZHANG L, YANG R X. Production status and technological innovation of Fujian black tea[J]. Tea Science and Technology, 2011(2): 12−15.
[7] 陈荣冰. 福建红茶的发展历程及其品质特征[J]. 福建茶叶,2010,33(Z2):14−16. [CHEN R B. The development process of Fujian black tea and its quality characteristics[J]. Tea in Fujian,2010,33(Z2):14−16.] CHEN R B. The development process of Fujian black tea and its quality characteristics[J]. Tea in Fujian, 2010, 33(Z2): 14−16.
[8] 林洁鑫, 王鹏杰, 金珊, 等. 基于广泛靶向代谢组学的不同产地红茶代谢产物比较分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(2):9−19. [LIN J X, WANG P J, JIN S, et al. Comparative analysis of black tea metabolites from different origins based on extensively targeted metabolomics[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(2):9−19.] LIN J X, WANG P J, JIN S, et al. Comparative analysis of black tea metabolites from different origins based on extensively targeted metabolomics[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(2): 9−19.
[9] ZHAI X T, ZHANG L, MICHAEL G, et al. Flavor of tea (Camellia sinensis):A review on odorants and analytical techniques[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2022,21(5):3867−3909. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12999
[10] 梁轶琳, 张灵枝, 戴浩民, 等. 基于HS-SPME-GC-MS分析不同茶树品种所制武夷岩茶呈香挥发性物质 [J/OL]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2024:1−12. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1751.TS.20240407.1349.002.html. [LIANG Y L, ZHANG L Z, DAI H M, et al. Analysis of aroma volatile compounds in wuyi rock tea produced from different tea plant varieties based on HS-SPME-GC-MS [J/OL]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2024:1−12. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1751.TS.20240407.1349.002.html.] LIANG Y L, ZHANG L Z, DAI H M, et al. Analysis of aroma volatile compounds in wuyi rock tea produced from different tea plant varieties based on HS-SPME-GC-MS [J/OL]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2024: 1−12. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1751.TS.20240407.1349.002.html.
[11] 罗学平, 李丽霞, 练学燕, 等. 响应面法优化顶空固相微萃取条件结合气相色谱-质谱法测定四川红茶挥发性成分[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(16):6472−6479. [LUO X P, LI l X, LIAN X Y, et al. Determination of volatile components in Sichuan black tea by response surface optimized headspace solid phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2021,12(16):6472−6479.] LUO X P, LI l X, LIAN X Y, et al. Determination of volatile components in Sichuan black tea by response surface optimized headspace solid phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2021, 12(16): 6472−6479.
[12] 王亚, 袁旺生, 姚婷, 等. 顶空-固相微萃取结合气质联用技术鉴定红茶挥发性香气组分[J]. 食品安全导刊,2021(34):49−52. [WANG Y, YUANG W S, YAO T, et al. Identification of volatile aroma components of black tea by headspace solid phase microextraction combined with GC/MS[J]. China Food Safety Magazine,2021(34):49−52.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0270.2021.34.spaqdk202134025 WANG Y, YUANG W S, YAO T, et al. Identification of volatile aroma components of black tea by headspace solid phase microextraction combined with GC/MS[J]. China Food Safety Magazine, 2021(34): 49−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0270.2021.34.spaqdk202134025
[13] 宋加艳. 不同产地英红9号红茶加工中香味物质代谢组学研究[D]. 长沙:湖南农业大学, 2021. [SONG J Y. Study on metabonomics of flavor substances in the processing of yinghong 9 black from different places[D]. Changsha:Hunan Agricultural University, 2021.] SONG J Y. Study on metabonomics of flavor substances in the processing of yinghong 9 black from different places[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2021.
[14] KANG S Y, YAN H, ZHU Y, et al. Identification and quantification of key odorants in the world's four most famous black teas[J]. Food Research International,2019,121:73−83. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.03.009
[15] 夏涛. 制茶学[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2016, 208−218. [XIA T. Tea making[M]. Beijing:China Agriculture Press, 2016, 208−218.] XIA T. Tea making[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2016, 208−218.
[16] 曾亮, 张博闻, 魏芳, 等. 南川大树茶红茶QDA分析条件优化与风味轮建立[J]. 茶叶通讯,2023,50(2):141−152. [ZENG L, ZHANG B W, WEI F, et al. Optimization of QDA analysis conditions and flavor wheel establishment for Camellia nanchuanica black tea[J]. Journal of Tea Communication,2023,50(2):141−152.] ZENG L, ZHANG B W, WEI F, et al. Optimization of QDA analysis conditions and flavor wheel establishment for Camellia nanchuanica black tea[J]. Journal of Tea Communication, 2023, 50(2): 141−152.
[17] WANG Z H, LIANG Y L, GAO C X, et al. The flavor characteristics and antioxidant capability of aged Jinhua white tea and the mechanisms of its dynamic evolution during long-term aging[J]. Food Chemistry,2024,436:137705. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137705
[18] 王坤波 刘仲华, 黄建安, 等. 高效液相色谱法测定红茶中的茶黄素[J]. 色谱,2004(2):151−153. [WANG K B, LIU Z H, HUANG J A, et al. Determination of theaflavins in black tea by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Chromatography,2004(2):151−153.] WANG K B, LIU Z H, HUANG J A, et al. Determination of theaflavins in black tea by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Chromatography, 2004(2): 151−153.
[19] 戴浩民, 张灵枝, 梁轶琳, 等. 乌龙茶茶树品种制白茶的风味特征及特征组分分析[J]. 食品科学,2024,45(2):229−239. [DAI H M, ZHANG L Z, LIANG Y L, et al. Analysis of flavor characteristics and characteristic components of white tea made from Oolong tea cultivars[J]. Food Science,2024,45(2):229−239.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230303-035 DAI H M, ZHANG L Z, LIANG Y L, et al. Analysis of flavor characteristics and characteristic components of white tea made from Oolong tea cultivars[J]. Food Science, 2024, 45(2): 229−239. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230303-035
[20] 王家勤, 姚月凤, 袁海波, 等. 基于色差系统的工夫红茶茶汤亮度的量化评价方法研究[J]. 茶叶科学,2020,40(2):259−268. [WANG J Q, YAO Y F, YUAN H B, et al. A quantitative method for brightness evaluation of congou black tea infusions based on color difference analysis[J]. Journal of Tea Science,2020,40(2):259−268.] WANG J Q, YAO Y F, YUAN H B, et al. A quantitative method for brightness evaluation of congou black tea infusions based on color difference analysis[J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2020, 40(2): 259−268.
[21] 杨天铭, 马玉青, 梁名志. 不同杀青方式对茶叶中氟及主要呈味物质含量的影响[J]. 农产品加工,2022(22):19−22. [YANG T M, MA Y Q, LIANG M Z. Effects of different fixation methods on fluorine and mainly flavored substance content in tea[J]. Farm Products Processing,2022(22):19−22.] YANG T M, MA Y Q, LIANG M Z. Effects of different fixation methods on fluorine and mainly flavored substance content in tea[J]. Farm Products Processing, 2022(22): 19−22.
[22] 潘科, 方仕茂, 刘忠英, 等. 基于GC-MS/MS分析加工对古茶树红茶可溶性糖含量的影响[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版),2021,50(4):490−496. [PAN K, FANG S M, LIU Z Y, et al. Effects of processing on soluble sugar content of black tea from ancient tea tree based on GC-MS/MS[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University(Natural Science Edition),2021,50(4):490−496.] PAN K, FANG S M, LIU Z Y, et al. Effects of processing on soluble sugar content of black tea from ancient tea tree based on GC-MS/MS[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 50(4): 490−496.
[23] WANG H J, SHEN S, WANG J J, et al. Novel insight into the effect of fermentation time on quality of Yunnan congou black tea[J]. LWT,2022,155:112−939.
[24] 俞铮, 葛小通, 张佳汇, 等. 食品中鲜味的来源及其评价方法[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(19):338−347. [YU Z, GE X T, ZHANG J H, et al. Sources and evaluation methods of umami taste in foods[J]. Food Science,2022,43(19):338−347.] YU Z, GE X T, ZHANG J H, et al. Sources and evaluation methods of umami taste in foods[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(19): 338−347.
[25] DONG C W, LIANG G Z, HU B, et al. Prediction of congou black tea fermentation quality indices from color features using non-linear regression methods[J]. Scientific Reports,2018,8(1):10535. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28767-2
[26] YE J H, YE Y, YIN J F, et al. Bitterness and astringency of tea leaves and products:Formation mechanism and reducing strategies[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2022,123:130−143.
[27] 王伟伟, 乐婷, 杨刘艳, 等. 骏眉工艺红茶化学成分及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(10):3320−3327. [WANG W W, LE T, YANG L Y, et al. Study on the chemical constituents and antioxidant activity of black tea with Junmei technology[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022,13(10):3320−3327.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.10.spaqzljcjs202210035 WANG W W, LE T, YANG L Y, et al. Study on the chemical constituents and antioxidant activity of black tea with Junmei technology[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2022, 13(10): 3320−3327. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.10.spaqzljcjs202210035
[28] TAN J, DAI W, LU M, et al. Study of the dynamic changes in the non-volatile chemical constituents of black tea during fermentation processing by a non-targeted metabolomics approach[J]. Food Research International,2016,79:106−113. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2015.11.018
[29] WANG Q Q, QIN D D, HUANG G Z, et al. Identification and characterization of the key volatile flavor compounds in black teas from distinct regions worldwide[J]. Journal of Food Science,2022,87(8):3433−3446. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16248
[30] 王金源, 张佳慧, 庄莉萍, 等. HS-SPME-GC-TOF-MS结合ROAV分析花果香型红茶特征香气成分[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2023,35(12):2015−2026. [WANG J Y, ZHANG J H, ZHUANG L P, et al. Analysis of characteristic aroma compounds of black tea with flowery-fruity flavor by HS-SPME-GC-TOF-MS combined with ROAV[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2023,35(12):2015−2026.] WANG J Y, ZHANG J H, ZHUANG L P, et al. Analysis of characteristic aroma compounds of black tea with flowery-fruity flavor by HS-SPME-GC-TOF-MS combined with ROAV[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2023, 35(12): 2015−2026.
[31] 王梦琪, 朱荫, 张悦, 等. 茶叶挥发性成分中关键呈香成分研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(23):341−349. [WANG M Q, ZHU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. A review of recent research on key aroma compounds in tea[J]. Food Science,2019,40(23):341−349.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181015-132 WANG M Q, ZHU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. A review of recent research on key aroma compounds in tea[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(23): 341−349. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181015-132
[32] YUN J, CUI C J, ZHANG S H, et al. Use of headspace GC/MS combined with chemometric analysis to identify the geographic origins of black tea[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,360:130033. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130033
[33] 杨霁虹, 周汉琛, 刘亚芹, 等. 基于HS-SPME-GC-MS和OAV分析黄山地区不同茶树品种红茶香气的差异[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(16):235−241. [YANG J H, ZHOU H C, LIU Y Q, et al. Differences in aroma components of black tea processed from different tea cultivars in Huangshan by using headspace-solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and odor activity value[J]. Food Science,2022,43(16):235−241.] YANG J H, ZHOU H C, LIU Y Q, et al. Differences in aroma components of black tea processed from different tea cultivars in Huangshan by using headspace-solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and odor activity value[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(16): 235−241.
[34] 牛淼, 李雄宇, 杨洪焱, 等. 传统滇红工夫红茶与野生滇红工夫红茶香气特征分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(23):229−239. [NIU M, LI X Y, YANG H Y, et al. Analysis of aroma characteristics of traditional and wild Dianhong congou black tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(23):229−239.] NIU M, LI X Y, YANG H Y, et al. Analysis of aroma characteristics of traditional and wild Dianhong congou black tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(23): 229−239.
[35] DENG X, HUANG G, TU Q, et al. Evolution analysis of flavor-active compounds during artificial fermentation of Pu-erh tea[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,357:129783. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129783
[36] 刘菲, 赖凌凌, 张雪儿, 等. 不同冲泡条件对金骏眉感官品质的影响[J]. 茶叶学报,2023,64(4):21−28. [LIU F, LAI L L, ZHANG X E, et al. Sensory perception of Jinjunmei tea affected by brewing conditions[J]. Acta Tea Sinica,2023,64(4):21−28.] LIU F, LAI L L, ZHANG X E, et al. Sensory perception of Jinjunmei tea affected by brewing conditions[J]. Acta Tea Sinica, 2023, 64(4): 21−28.
[37] 刘霜, 彭思敏, 廖卢艳, 等. 茶油精炼过程中脂肪酸与风味物质变化研究[J]. 粮食与油脂,2023,36(7):69−72. [[LIU S, PENG S M, LIAO L Y, et al. Study on the changes of fatty acids and flavor substances in the refining process of Camellia oil[J]. Cereals & Oils,2023,36(7):69−72.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2023.07.016 [LIU S, PENG S M, LIAO L Y, et al. Study on the changes of fatty acids and flavor substances in the refining process of Camellia oil[J]. Cereals & Oils, 2023, 36(7): 69−72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2023.07.016
[38] WANG C, ZHANG C X, KONG Y W, et al. A comparative study of volatile components in dianhong teas from fresh leaves of four tea cultivars by using chromatography-mass spectrometry, multivariate data analysis, and descriptive sensory analysis[J]. Food Research International,2017,100(P1):267−275.
[39] 胡双明, 艾仄宜, 穆兵, 等. 基于电子鼻与HS-SPME-GC-MS技术的江苏红茶香气特征研究[J]. 南京农业大学学报,2024,47(4):760−771. [HU S M, AI Z Y, MU B, et al. Study on aroma characteristics of black tea in Jiangsu Province based on electronic nose and HS-SPME-GC-MS technology[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University,2024,47(4):760−771.] doi: 10.7685/jnau.202310025 HU S M, AI Z Y, MU B, et al. Study on aroma characteristics of black tea in Jiangsu Province based on electronic nose and HS-SPME-GC-MS technology[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2024, 47(4): 760−771. doi: 10.7685/jnau.202310025
[40] JIN L, LIAN X, CHEN L, et al. Characteristic aroma analysis and interaction study of key aroma compounds of Chuanhong congou black tea[J]. European food research and technology,2024,250(2):441−454. doi: 10.1007/s00217-023-04398-4
[41] 舒心, 高彦祥. 茶叶挥发性成分提取及其香气特征分析研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(15):469−480. [SU X, GAO Y X. Research progress on extraction of volatile compounds and analysis of aroma characteristics in tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(15):469−480.] SU X, GAO Y X. Research progress on extraction of volatile compounds and analysis of aroma characteristics in tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(15): 469−480.
[42] XUE J J, LIU P P, YIN J F, et al. Dynamic changes in volatile compounds of shaken black tea during its manufacture by GC×GC-TOFMS and multivariate data analysis[J]. Foods,2022,11(9):1228. doi: 10.3390/foods11091228
[43] 肖作兵, 王红玲, 牛云蔚, 等. 基于OAV和AEDA对工夫红茶的PLSR分析[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(10):242−249. [XIAO Z B, WANG H L, NIU Y W, et al. Analysis of aroma components in four Chinese congou black teas by odor active values and aroma extract dilution analysis coupled with partial least squares regression[J]. [J]. Food Science,2018,39(10):242−249.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201810037 XIAO Z B, WANG H L, NIU Y W, et al. Analysis of aroma components in four Chinese congou black teas by odor active values and aroma extract dilution analysis coupled with partial least squares regression[J]. [J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(10): 242−249. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201810037
[44] DIAS P M, CHANGARATH J, DAMODARAN A, et al. Compositional variation among black tea across geographies and their potential influence on endothelial nitric oxide and antioxidant activity[J]. Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2014,62(28):6655−6668. doi: 10.1021/jf501611w
[45] GEMERT L J V. Compilations of odour threshold values in air, water and other media[M]. Oliemans Punter&Partner BV, 2011.
[46] 石亚丽, 白艳, 马婉君, 等. 安吉白茶挥发性成分及关键呈香成分分析[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(20):261−268. [SHI Y L, BAI Y, MA W J, et al. Analysis of volatile components and key aroma-active compounds of Anjibaicha[J]. Food Science,2022,43(20):261−268.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20211207-091 SHI Y L, BAI Y, MA W J, et al. Analysis of volatile components and key aroma-active compounds of Anjibaicha[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(20): 261−268. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20211207-091
[47] 蒋容港, 黄燕, 金友兰, 等. 不同原料等级黄茶特征香气成分分析[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(16):89−98. [JIANG R G, HUANG Y, JIN Y L, et al. Analysis of characteristic aroma components of different grades of yellow tea[J]. Food Science,2021,42(16):89−98.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200709-137 JIANG R G, HUANG Y, JIN Y L, et al. Analysis of characteristic aroma components of different grades of yellow tea[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(16): 89−98. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200709-137





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
