Protective Effect of Black Soybean-Whey Blended Protein on Duodenal Barrier Injury and Liver Injury in Rats
-
摘要: 为了探究黑豆-乳清双蛋白(Black soybean-Whey blended Protein,B-WP)对大鼠十二指肠屏障损伤和肝损伤的保护作用机制,本研究选用低、中、高剂量B-WP喂食大鼠28 d,最后一天腹腔注射2.5 mg/kg脂多糖(Lipopolysaccharide,LPS)。采用酶联免疫试剂盒检测十二指肠组织中的丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)、超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide Dismutase,SOD)、谷胱甘肽(Glutathione,GSH)水平,Western Blot检测十二指肠中NF-κB p65、NF-κB p-p65、JAK2和STAT3的蛋白表达水平,并通过HE染色、酶联免疫法和实时荧光定量PCR对检测肝脏的组织形态、谷丙转氨酶(Alanine Aminotransferase,ALT)和谷草转氨酶(Aspartate Aminotransferase,AST)含量以及Toll样受体4(Toll-like Receptor 4,TLR4)、髓样分化因子88(Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response protein 88,MyD88)基因mRNA表达进行分析。结果表明:LPS会引起十二指肠氧化应激,激活NF-κB/JAK2/STAT3通路和肝损伤,进而造成十二指肠屏障损伤;低、中、高剂量B-WP膳食干预均能够调节氧化应激,其中中剂量膳食干预效果最为显著(P<0.01),具体表现为MDA含量减少34.93%,SOD活力提高61.16%,GSH含量增加48.48%;不同剂量B-WP膳食干预均能够下调NF-κB p65、NF-κB p-p65、JAK2和STAT3的蛋白含量,中剂量膳食干预效果最好,使NF-κB p65、NF-κB p-p65、JAK2和STAT3蛋白含量显著降低35.06%、42.53%、45.88%和44.32%(P<0.01);不同剂量的B-WP膳食对肝损伤程度均有所改善,以中剂量膳食干预效果最为显著(P<0.01),使ALT和AST水平分别降低47.07%和41.79%,TLR4和MyD88的mRNA含量分别降低48.87%和45.46%。综合来看,B-WP对LPS诱导的十二指肠屏障损伤的保护作用可能是通过调节氧化应激、抑制NF-κB/JAK2/STAT3通路的活化和改善肝损伤来实现,并且中剂量B-WP膳食的保护效果最佳。
-
关键词:
- 黑豆-乳清蛋白 /
- 十二指肠屏障 /
- 氧化应激 /
- NF-κB/JAK2/STAT3通路 /
- 肝脏
Abstract: To investigate the protective mechanism of black soybean-whey blended protein (B-WP) against duodenal barrier and liver injury in rats, the rats were fed with low, medium, and high doses of B-WP for 28 days. On the last day, they received an intraperitoneal injection of 2.5 mg/kg lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits were used to detect the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and glutathione (GSH) levels in the duodenal tissues. Western blot analysis was used to detect the protein expression levels of NF-κB p65, NF-κB p-p65, JAK2, and STAT3. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and quantitative real-time PCR were used to detect liver tissue morphology, alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) levels, and mRNA expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88 (MyD88) genes. The results showed that LPS induced duodenal oxidative stress, activated NF-κB/JAK2/STAT3 pathway, and caused liver injury, subsequently leading to duodenal barrier injury. Dietary intervention with low, medium, and high doses of B-WP regulated oxidative stress, with the medium dose showing the most significant effect (P<0.01), as evidenced by a 34.93% decrease in MDA content, a 61.16% increase in SOD activity, and a 48.48% increase in GSH content. Dietary intervention with different doses of B-WP could reduce the protein contents of NF-κB p65, NF-κB p-p65, JAK2 and STAT3, and the medium dose dietary intervention showed the best effect. The protein content of NF-κB p65, NF-κB p-p65, JAK2, and STAT3 significantly decreased by 35.06%, 42.53%, 45.88% and 44.32%, respectively (P<0.01). Furthermore, dietary intervention with B-WP at varying doses exhibited differential improvements in liver injury, with the medium-dose intervention exerting the most substantial effect (P<0.01). This was evidenced by a significant decrease in alanine ALT and AST levels by 47.07% and 41.79%, respectively, along with a reduction in TLR4 and MyD88 mRNA levels by 48.87% and 45.46%, respectively. In summary, the protective effects of B-WP against LPS-induced duodenal barrier injury are attributed to its regulation of oxidative stress, inhibition of the NF-κB/JAK2/STAT3 pathway activation, and amelioration of liver damage. Notably, the medium dose B-WP diet exhibits the most potent protective effects. -
肠屏障是指肠道黏膜的生物学屏障[1],它由物理、化学、微生物和免疫四种屏障构成。这些屏障均具有各自的结构和功能,其共同作用是防止有害物质和病原体进入肠道,它们相互协调,相互影响,共同维持肠道屏障功能的完整性。脂多糖(Lipopolysaccharide,LPS)又被称为细菌内毒素[2],腹腔注射LPS也已被证实能增加促炎性细胞因子的分泌[3−5],可作为构建肠屏障炎症模型的一种方式[6]。LPS进入机体后,会引发氧化应激,使其体内累积过量的活性氧,进而导致细胞大分子损伤,最终导致肠屏障受损[7−8]。有文献表明肠黏膜屏障的破坏与NF-κB通路活化有关,并且LPS的刺激会激活JAK2,诱导下游的STAT3蛋白发生磷酸化,进而导致肠屏障损伤[9−10],因此JAK2/STAT3通路的激活状况可用JAK2和STAT3的磷酸化水平来表示[11]。另外,肠道与肝脏的功能是相互影响的[12],称其为肠-肝轴。经过研究发现,肠-肝轴的一个重要组成部分是完整的肠屏障[13],肠屏障的多层防御都会遭到LPS的破坏,因此可以推断维持肠屏障的完整性对预防肝损伤是具有积极作用的。
乳清蛋白营养价值丰富,氨基酸比例合理,接近人体所需比例,且富含甲硫氨酸,具有高蛋白、高生物利用率等特点[14−15],Chaithanya等[16]发现乳清蛋白能够改善肠屏障功能。但是单一乳清蛋白并不能完全满足机体对营养的需求,且乳清蛋白需求的增多会造成兽药残留、环境压力增大等负面问题[17],因此选取植物蛋白代替部分乳清蛋白,可以减少对乳清蛋白的需求量。豆类蛋白是植物蛋白的主要来源之一,其中大豆蛋白的应用最为广泛,因此为了开发更多高附加值产品以及扩大其他豆类蛋白在食品中应用,课题组前期试验筛选了五种豆类蛋白,最终发现黑豆蛋白具有较高的营养价值和体外消化率[18]。以此为基础,本课题组以黑豆-乳清双蛋白(Black soybean-Whey blended Protein,B-WP)为研究对象进行了多项试验,证明了B-WP可以改善肠道微生物组成、提升机体免疫能力,同时能够维护肠屏障的完整性[19−21]。因此推测B-WP可能是通过缓解氧化应激,抑制炎症通路的活化以及改善肝损伤来维护肠屏障完整性,进而提升机体免疫能力。由前人研究结果可知,以β-伴大豆球蛋白为主的植物蛋白可以通过提高肠道紧密连接蛋白的基因表达量改善肠屏障[22−23],同时也有研究结果表明,以酪蛋白为主的动物蛋白可以通过提高分泌型免疫球蛋白A的含量从而增强肠道局部的免疫功能,改善肠屏障[24],但是对于双蛋白改善肠屏障的作用机制尚不清楚。
因此本研究采用B-WP对大鼠进行膳食干预,探讨B-WP是否可以通过调节氧化应激,抑制NF-κB/JAK2/STAT3通路以及改善肝损伤来保护LPS诱导引起的SD大鼠十二指肠屏障损伤,本实验结果可以为双蛋白应用于肠屏障损伤的膳食干预奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
清洁级雌性SD大鼠 7周龄,64只,体重120±10 g,购于长春市亿斯实验动物技术有限责任公司,生产许可证号:SCXK(吉)2023-0002;黑豆蛋白(纯度:90.30%) 西安恒基化工有限公司;乳清蛋白(纯度:90.66%) 郑州龙生化工有限公司;大鼠维持基础饲料(AIN-93G) 长春市亿斯实验动物技术有限责任公司,生产许可证号:SCXK-(吉)2020-0001;LPS 西格玛奥德里奇(上海)贸易有限公司;1×磷酸盐缓冲液(Phosphate Buffered Saline,PBS) 北京兰杰柯科技有限公司;超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide Dismutase,SOD)活性测试盒、谷胱甘肽(Glutathione,GSH)活性测试盒、丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)活性测试盒、谷丙转氨酶(Alanine Aminotransferase,ALT)活性测试盒、谷草转氨酶(Aspartate Aminotransferase,AST)活性测试盒 上海朗顿生物科技有限公司;RIPA裂解缓冲液、二辛可宁酸(BCA)蛋白质检测试剂盒、聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)膜 Millipore公司;兔抗信号转导子与转录激活子3(STAT3)抗体、兔抗肌动蛋白(Actin)抗体、鼠抗NF-κB p65抗体、鼠抗磷酸化NF-κB p65(NF-κB p-p65)抗体 Servicebio公司;兔抗Janus激酶2(JAK2)抗体 Affinity公司;4%多聚甲醛通用型组织固定液 Biosharp公司;RNA提取试剂(RNAiso Plus)、反转录试剂盒(PrimeScript™ RT reagent Kit) 北京宝日医生物技术有限公司;荧光定量PCR预混液(Hieff qPCR SYBR Green Master Mix) 上海翌圣生物科技股份有限公司;引物 北京擎科生物科技股份有限公司。
Model 680型酶标仪 美国BIO-RAD公司;TGL-16型高速台式冷冻离心机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司;DK-98-1型电热恒温水浴锅 天津市泰斯特仪器有限公司;Mini Vortexer型旋涡混合振荡器 Henry Troemner LLC公司;DS-3D100型多功能型摇床、SVE-2型垂直电泳仪、SVT-2型转印电泳仪 Servicebio公司;6100型化学发光仪 CLINX公司;ViiA7型荧光定量PCR仪 ABI公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 B-WP饲料的制备
1985年世界粮农组织/世界卫生组织(FAO/WHO)提出蛋白质推荐摄入量不分男女每天均为0.75 g/kg因大鼠与人类的等效剂量换算系数为6.25[25],进而得知大鼠每天蛋白质摄入量应为4.6875 g/kg,将此剂量设为中剂量,另按照低、中、高剂量比为1:2:3分别计算低、高剂量,得出低剂量为2.3438 g/kg,高剂量为7.0313 g/kg。后取64只大鼠平均体重180 g计算,最终可分别确定低剂量、中剂量、高剂量的每天蛋白质摄入量(后期B-WP摄入量随大鼠体重变化做出相应调整)。课题组前期研究结果表明当黑豆蛋白:乳清蛋白=1:2时体外消化率最高,所以按该比例混合黑豆蛋白和乳清蛋白并将其掺入已打碎的大鼠基础饲料中作为最终的B-WP饲料。
1.2.2 实验动物分组及处理
将购买的64只雌性大鼠按照动物保护道德准则和黑龙江八一农垦大学动物使用规则饲养(动物实验伦理学审批号:SPXY2023016),控制环境恒温恒湿(23±2 ℃,50%~60%),适应性饲养1周后随机分成8组,每组8只,自由饮食、饮水。分组设置为空白组(Blank)、脂多糖组(LPS)、低剂量B-WP(L)、中剂量B-WP(M)、高剂量B-WP(H)、低剂量B-WP干预+LPS(L-LPS)、中剂量B-WP干预+LPS(M-LPS)、高剂量B-WP干预+LPS(H-LPS)。
适应性饲养结束后,对Blank组、LPS组大鼠继续正常饲喂基础饲料(AIN-93G),其余六组根据其体重及进食量来确定B-WP饲料量,共持续28 d。其中B-WP摄入量按照1.2.1中最终确定的低、中、高剂量进行计算。最后一天对Blank组、L组、M组、H组大鼠进行腹腔注射生理盐水(剂量按体质量计1 mL/100 g),对LPS组、L-LPS组、M-LPS组、H-LPS组大鼠进行腹腔注射LPS(浓度按2.5 mg/kg计,为课题组前期实验所得结果),8组大鼠腹腔注射结束后,对其禁食禁水12 h,随后立即用过量的异氟烷处死并解剖各组大鼠,采集十二指肠组织和肝脏用于后续实验。十二指肠组织放置于冻存管中,先用液氮快速冷冻十二指肠组织,再放置于−80 ℃冰箱备用;肝脏组织需分为两部分储存,一部分立即放入4%多聚甲醛固定液中储存,用于病理学检测,另一部分肝脏放置于冻存管中,先用液氮快速冷冻肝脏,再放置于−80 ℃冰箱备用。
1.2.3 酶联免疫法检测大鼠十二指肠组织MDA、SOD、GSH水平
酶联免疫法参照赵芳芳等[26]的方法并稍作修改。从−80 ℃冰箱中取出备用的十二指肠组织,4 ℃解冻,称取1 g十二指肠组织,加入9 mL的PBS(pH7.4),用组织捣碎机10000 r/min研磨制成10%组织匀浆,取匀浆液于3000 r/min,4 ℃离心20 min,取上清液,按照酶联免疫试剂盒说明书,分别对MDA、SOD、GSH进行测定。
1.2.4 Western Blot检测NF-κB p65、NF-κB p-p65、JAK2、STAT3蛋白表达
参照冯文静等[27]的方法并稍作修改。用含有苯甲磺酰氟和磷酸酶抑制剂的RIPA裂解液裂解十二指肠组织,4 ℃、12000 r/min离心10 min,收集上清液即为抽提得到的细胞核蛋白。取未变性的蛋白溶液,用BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒测蛋白浓度,等量蛋白灭活后上样。按照需求配制不同浓度的SDS-PAGE胶进行电泳。将蛋白转在PVDF膜(将转印完的膜放入装有TBST的孵育槽中),5%的脱脂牛奶(0.5%TBST配),在脱色摇床上室温封闭30 min;按照抗体说明书,进行一抗稀释p65(1:1000)、p-p65(1:1000)、JAK2(1:1000)、STAT3(1:1000),4 ℃孵育过夜;二抗后进行化学发光显色,暗盒显影。采用Image J软件分析条带光密度值。
1.2.5 HE染色观察肝脏组织病理学变化
HE染色方法参照Zou等[28]的方法并稍作修改。将放置于4%多聚甲醛固定的肝组织采用石蜡包埋,乙醇脱水,切片2~3 μm,光学显微镜下观察各组大鼠肝脏的病理学变化,并进行图像采集。
1.2.6 酶联免疫法检测大鼠肝脏组织ALT、AST水平
酶联免疫法参照赵芳芳等[26]的方法并稍作修改。从−80 ℃冰箱中取出备用的肝脏组织,4 ℃解冻,称取1 g肝脏组织,加入9 mL的PBS(pH7.4),用组织捣碎机10000 r/min研磨制成10%组织匀浆,取匀浆液于3000 r/min,4 ℃离心20 min,取上清液并且按照酶联免疫试剂盒说明书,分别对ALT、AST进行测定。
1.2.7 实时荧光定量PCR(qPCR)检测肝脏组织TLR4、MyD88 mRNA表达
参照马成军等[29]和张文将等[30]的方法并稍加修改。取100 mg肝脏样品至研钵中,加入液氮研磨至粉末状,将其转移到装有1 mL RNAiso Plus的2 mL离心管中,振荡混匀后室温静置约5 min,加入0.2 mL氯仿,振荡混匀后室温静置3 min,放于12000 r/min,4 ℃离心15 min并转移水相至2 mL离心管中,加入0.5 mL异丙醇,混匀后室温静置10 min,放于12000 r/min,4 ℃离心10 min,弃上清液,加入75%乙醇,混匀后放于7500 r/min,4 ℃离心5 min,弃上清液,空气干燥RNA沉淀约5 min,加入适量焦碳酸二乙酯溶解RNA沉淀,并用分光光度计测定RNA浓度和纯度,再利用Takara反转录试剂盒获取cDNA,随后进行qPCR扩增反应,95 ℃预变形5 min,三步循环法反应(95 ℃变性10 s,60 ℃退火延伸30 s),40个循环,得到TLR4和MyD88的Ct值,GAPDH为内参,通过2−∆∆Ct法[31]计算mRNA表达。目的基因及引物序列见表1。
表 1 qPCR分析的引物序列Table 1. Primer sequence for qPCR基因名称 序列(5'~3') GAPDH 正向AGACAGCCGCATCTTCTTGT 反向TGATGGCAACAATGTCCACT TLR4 正向GAGGCAGCAGGTCGAATTGT 反向AGAAGATGTGCCTCCCCAGA MyD88 正向AGTTCTACCATCAAGGGGGC 反向CGTGCCACTACCTCATGCAA 1.3 数据处理
运用GraphPad Prism 9.0软件进行绘图及统计学分析,数据结果均以平均数±标准差表示,采用单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA)的Turkey’s检验检测差异的显著性,P<0.05定义为显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 B-WP对大鼠氧化应激的影响
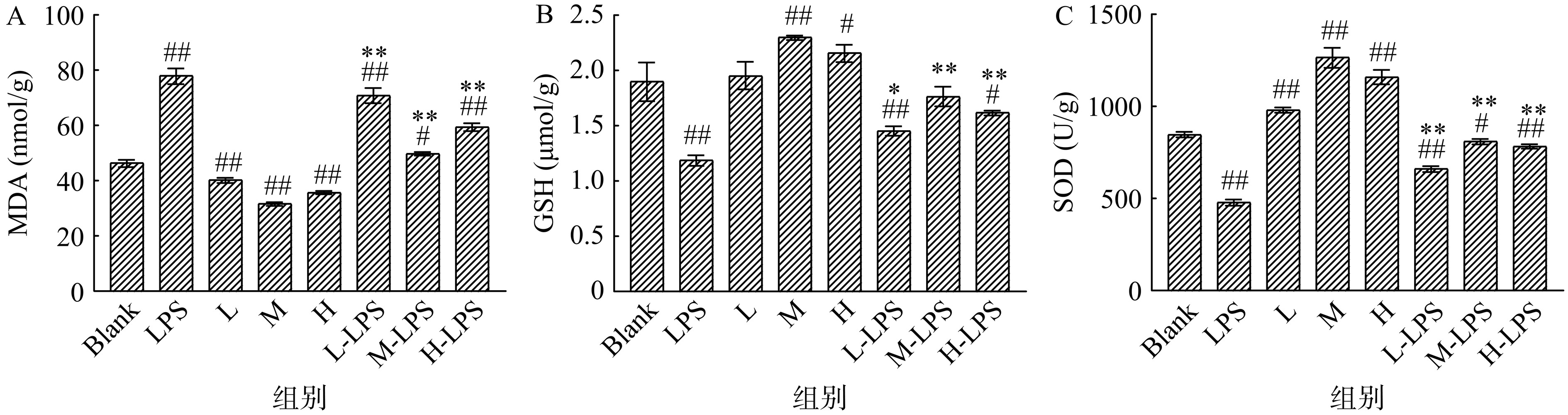
MDA为脂质过氧化的最终分解产物,能够反映机体过氧化程度,随着机体氧化应激程度的增强,MDA含量会逐渐上升。由图1A可以看出,与Blank组相比,LPS组的MDA的含量极显著增加67.91%(P<0.01),L、M、H组的MDA含量与Blank组相比差异极显著降低(P<0.01),分别降低了13.29%、31.82%和23.17%;与LPS组相比,L-LPS、M-LPS组、H-LPS组大鼠的MDA含量分别极显著降低了9.21%,34.93%和23.79%(P<0.01),且M-LPS的MDA含量更接近于Blank组,表明B-WP膳食干预能够有效降低MDA含量,且中剂量B-WP膳食干预缓解氧化应激效果最好。
SOD是体内重要的一种抗氧化酶,能够清除细胞内的自由基,当机体产生氧化应激时,SOD活力会下降;GSH是体内重要的一种抗氧化剂,能够清除机体过量的自由基和活性氧化合物,氧化应激发生后,GSH含量会明显降低,随着氧化应激的改善,GSH含量也会有一定程度的回升,而且SOD和GSH在维持机体氧化还原稳态中发挥重要作用[32−34]。由图1B可知,相比于Blank组,LPS组GSH含量极显著降低了37.47%,M组GSH含量极显著提高了21.05%(P<0.01),而M-LPS组相比较于LPS组极显著增加了48.48%(P<0.01)。由图1C可看出,与Blank组相比,LPS组SOD的活力极显著降低了43.29%(P<0.01),相比于LPS组,L-LPS、M-LPS和H-LPS组大鼠的SOD活力变化极显著,分别提高了37.98%、61.16%和54.88%(P<0.01)。
万祥[35]通过LPS诱导昆明小鼠急性肺损伤,探究驴乳清蛋白对急性肺损伤小鼠的保护作用,发现乳清蛋白组改善了肺组织中的氧化应激水平,证明了驴乳清蛋白能通过改善急性肺损伤小鼠氧化应激从而起到保护作用,这与本研究的结果相似。B-WP对大鼠氧化应激显著的缓解作用,一方面归功于蛋白质能够增强肠黏膜的修复能力和更新能力,提高肠粘液和抗菌蛋白产生,减少肠道致病菌的定植量,降低十二指肠组织的损伤程度[36];另一方面蛋白质中的氨基酸含有许多抗氧化性质的成分,例如谷氨酰胺和半胱氨酸都是含有硫元素的氨基酸,它们具有较强的抗氧化活性,能够清除过量的自由基,从而抑制了氧化应激的发生[37−38]。
2.2 B-WP对大鼠十二指肠组织NF-κB/JAK2/STAT3相关蛋白表达的影响
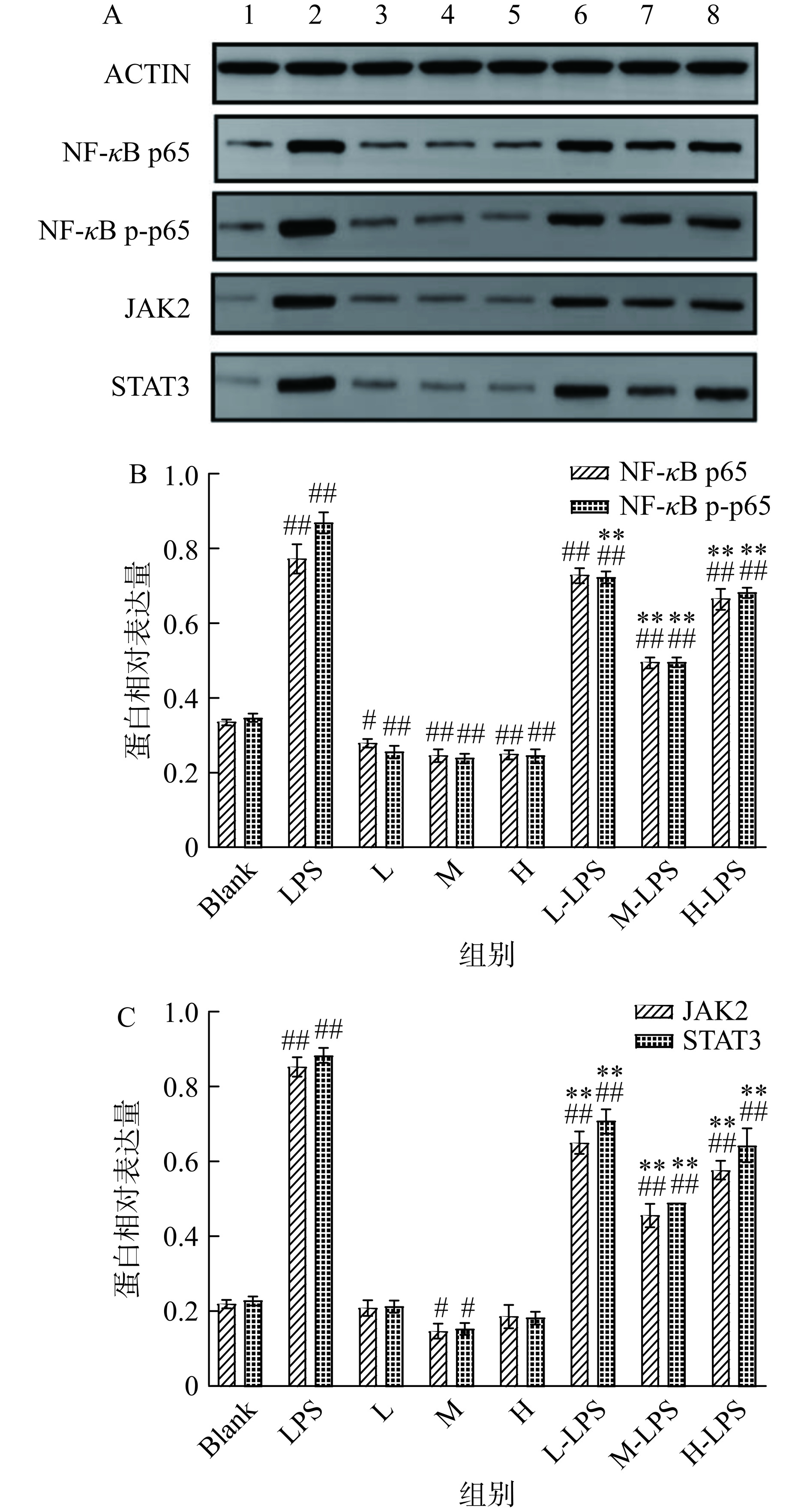
大鼠十二指肠组织NF-κB/JAK2/STAT3通路相关蛋白Western Blot电泳图见图2A。由图2B可知,与Blank组相比,LPS组NF-κB p65、NF-κB p-p65蛋白的相对表达量分别极显著地增加了1.26倍和1.48倍(P<0.01),证明了LPS能够通过激活NF-κB通路诱导十二指肠屏障损伤;M组和H组的NF-κB p65、NF-κB p-p65蛋白的相对表达量与Blank组相比差异均极显著(P<0.01),其中M组的效果最为明显,分别下降了26.47%和31.43%;相比于LPS组,M-LPS组和H-LPS组大鼠NF-κB p65、NF-κB p-p65蛋白的相对表达量差异均极显著降低(P<0.01),M-LPS组分别下降了35.06%和42.53%,H-LPS组分别下降了12.99%和21.84%。由图2C可知,与Blank组相比,L组和H组大鼠的JAK2、STAT3蛋白的相对表达量并没有发生显著改变(P>0.05),而M组JAK2、STAT3蛋白的相对表达量分别显著降低了31.82%和34.78%(P<0.05),LPS组大鼠JAK2、STAT3蛋白的相对表达量相比于Blank组分别极显著地提高了2.86倍和2.83倍(P<0.01);相比于LPS组,L-LPS、M-LPS和H-LPS组大鼠NF-κB p65,NF-κB p-p65蛋白的相对表达量差异均极显著降低(P<0.01),其中M-LPS组的效果最为明显,分别降低了45.88%和44.32%。
在本试验中,低剂量B-WP膳食干预未能产生最好的效果可能是因为机体自我修复功能中的新细胞生成需要蛋白质来完成[39],而低剂量B-WP并未修复完全受伤的肠黏膜,导致未能更好地缓解十二指肠屏障损伤;研究发现蛋白质进入机体必须经过分解消化,如果摄入过量蛋白质,机体就必须不断处理大量蛋白质,进而无法修补细胞,最终会导致机体损伤[40],这可能是高剂量B-WP膳食干预未能更好改善十二指肠屏障损伤的原因。但如果是适当的蛋白质进入肠道会经过消化等一系列反应将其转变成氨基酸,然后被肠黏膜吸收进入体内,继而被合成生产和修补免疫细胞和分子的原料,提高机体健康水平,增强人体的免疫功能[41]。
综合分析上述结果并结合2.1的结果来看,B-WP对十二指肠屏障损伤的拮抗作用可能是通过缓解机体的氧化应激反应;同时下调NF-κB p65、NF-κB p-p65、JAK2、STAT3的表达,进而抑制NF-κB/JAK2/STAT3信号通路的激活,减弱炎症反应程度,达到拮抗LPS诱导所致十二指肠屏障损伤的效果。
2.3 B-WP对肝脏的影响
2.3.1 B-WP对肝脏组织形态的影响
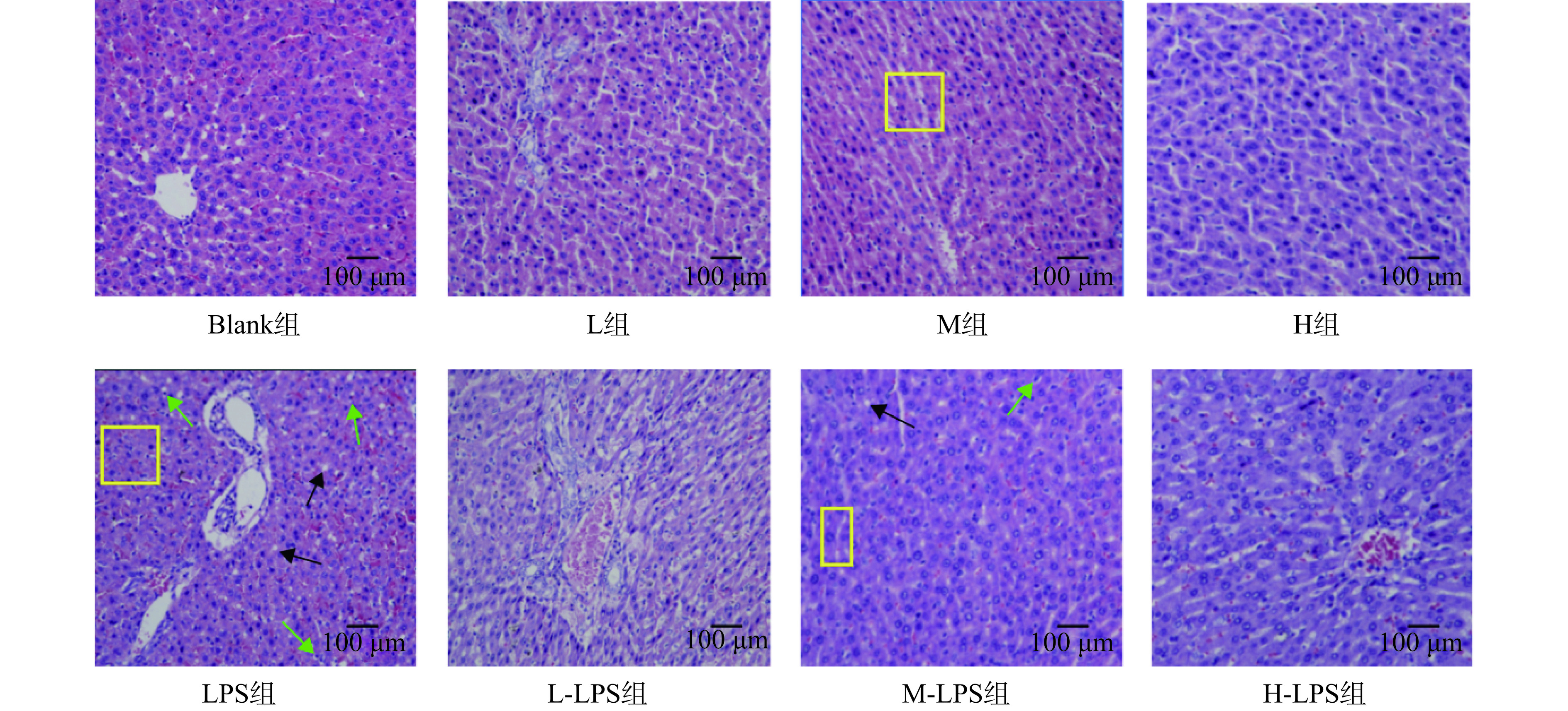
各组大鼠肝组织经过HE染色后的形态见图3,Blank组肝细胞组织形态正常,细胞核圆润且位于细胞中央,肝细胞索以中央静脉为中心呈放射状有序排列,无明显的脂肪空泡;LPS组大鼠肝小叶结构破坏严重,肝细胞明显变性且呈不规则式分布,细胞边缘模糊,可见明显的炎性细胞浸润,出现大量脂肪空泡、纤维组织增生。与Blank组相比,L、M、H三组大鼠均不同程度加强肝细胞排列,使其更加紧密,呈现规则的索状结构;L-LPS、M-LPS、H-LPS三组大鼠肝细胞可见明显的排列不整齐,脂肪空泡汇聚,同时出现不同程度的肝细胞坏死以及炎细胞浸润,但较LPS组有不同程度的改善。
2.3.2 B-WP对肝损伤炎性指标的影响
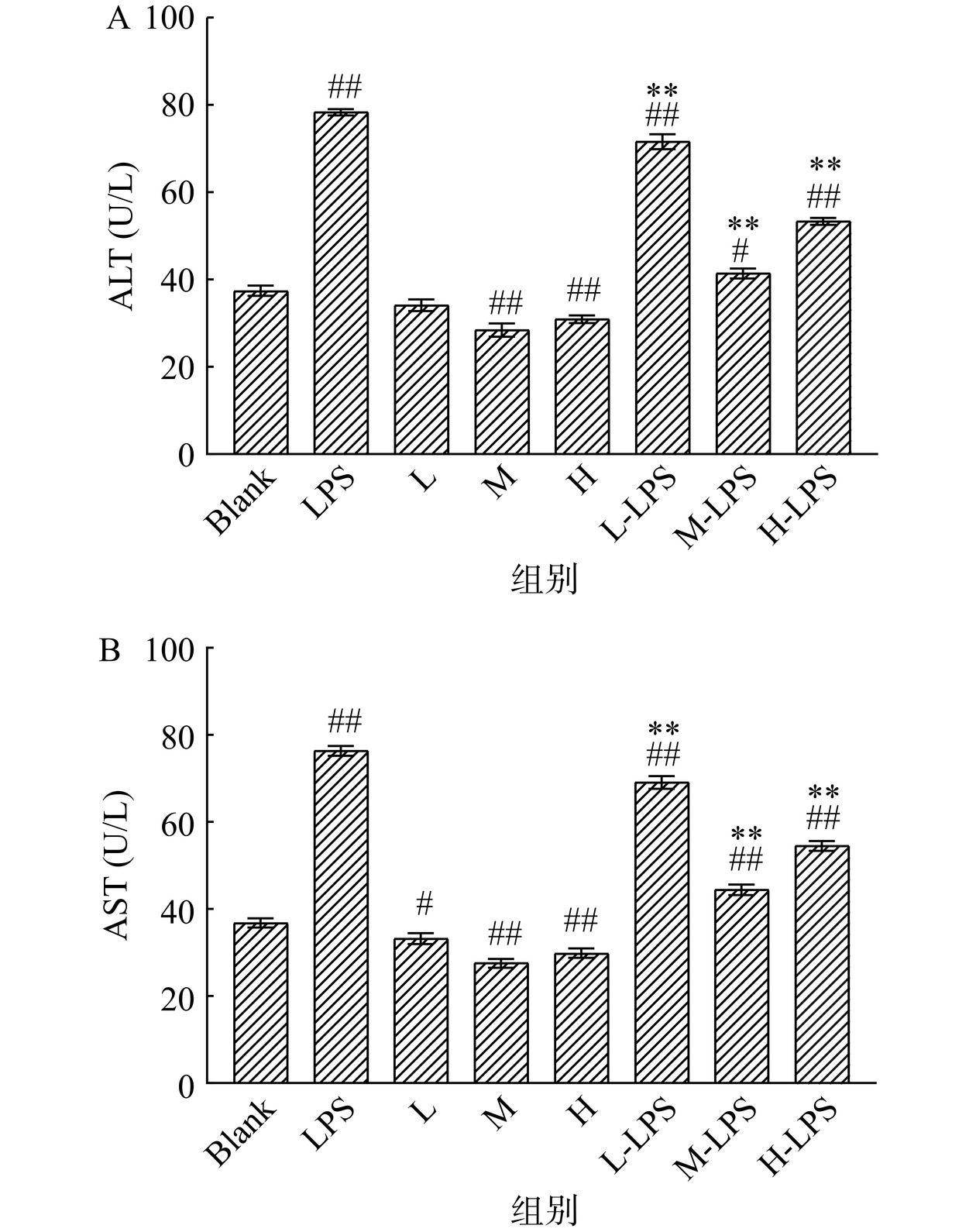
ALT主要分布于肝细胞浆中,AST主要存在于心肌、线粒体和肝细胞浆中,因此ALT和AST是常用来评价肝损伤的重要指标[42]。当肝脏受到损伤后,肝细胞中的转氨酶会进入血液中,进而造成ALT和AST含量随之升高。
本实验ALT、AST的水平测定结果见图4。LPS组大鼠肝脏ALT和AST水平极显著高于Blank组(P<0.01),分别增加了1.10倍和1.08倍,表明LPS会诱导大鼠肝脏功能受到损伤;与Blank组相比,M组和H组大鼠均极显著低于Blank组(P<0.01),其中M组的效果最为明显,分别降低了23.86%和24.90%,表明B-WP能够加强保护肝脏,降低ALT、AST水平。与LPS组大鼠相比,L-LPS、M-LPS和H-LPS组肝脏ALT和AST水平差异均极显著降低(P<0.01),其中M-LPS组的效果最为明显,分别降低了47.07%和41.79%。王丽等[43]采用驴乳清蛋白对C57BL/6 J小鼠进行干预后经腹腔注射乙酰氨基酚造成小鼠急性肝损伤,结果表明驴乳清蛋白对小鼠肝损伤具有保护作用,与本研究结果基本相符。
2.3.3 B-WP对肝脏TLR4、MyD88的mRNA表达的影响
LPS在肠屏障损伤后进入机体,Toll样受体4(Toll-like Receptors 4,TLR4)会激活髓样分化因子(Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response Protein 88,MyD88)依赖途径,下游信号分子就会进一步被激活,造成肝脏受到损伤[44−45]。而且目前阻断TLR4通路来抑制炎症反应已经成为干预肝脏疾病的有效途径之一[46]。
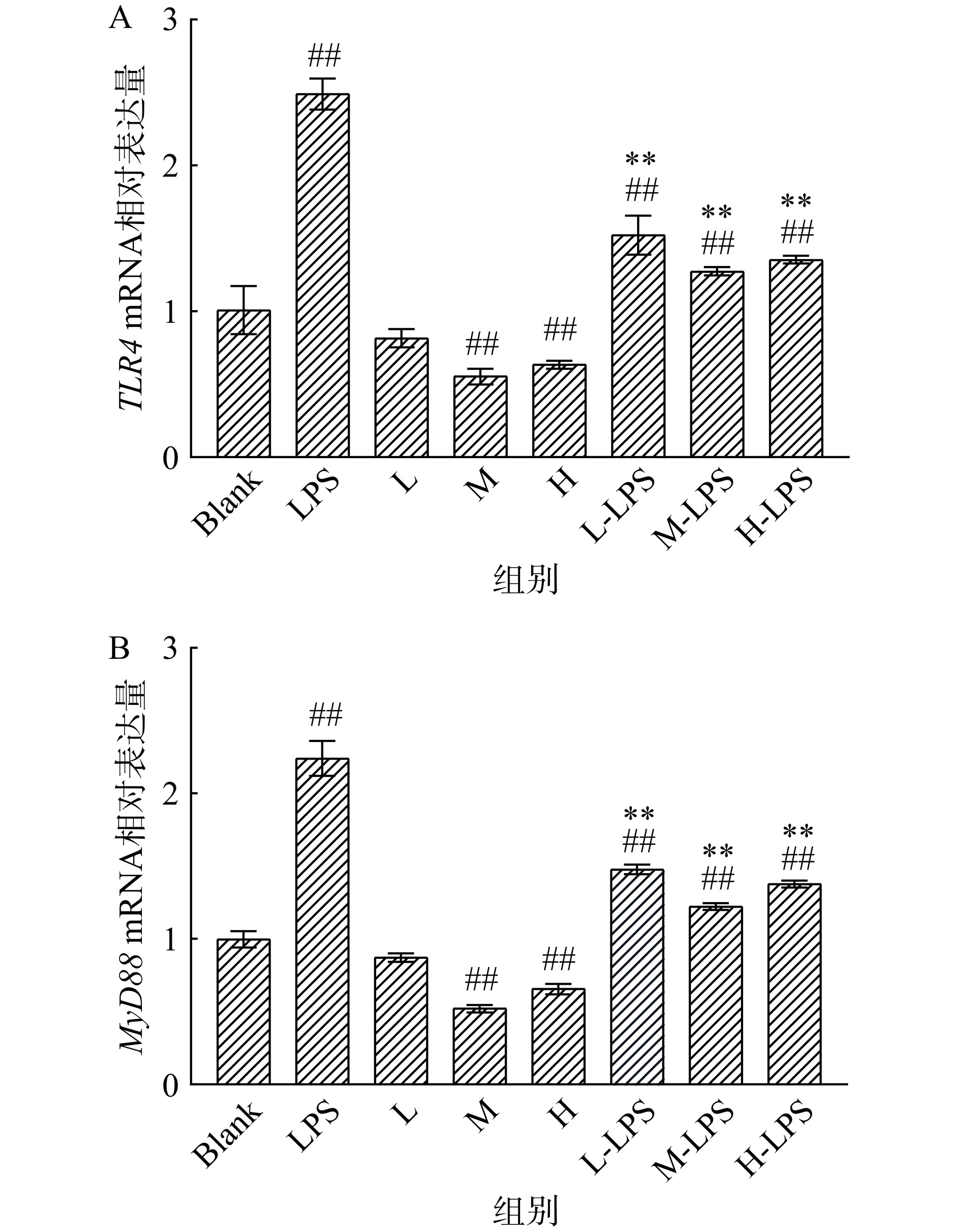
B-WP对大鼠TLR4、MyD88基因mRNA表达的影响如图5所示。相比于Blank组大鼠,L组大鼠TLR4和MyD88基因mRNA相对表达量差异不显著(P>0.05);M组大鼠TLR4和MyD88基因mRNA相对表达量分别降低了44.81%和47.48%,极显著低于Blank组(P<0.01);H组大鼠TLR4和MyD88基因mRNA相对表达量降低了36.91%和34.12%,极显著低于Blank组(P<0.01)。在注射LPS后,LPS组大鼠TLR4和MyD88基因mRNA相对表达量分别极显著高于Blank组1.47倍和1.24倍(P<0.01),而在B-WP膳食干预后,L-LPS、M-LPS和H-LPS组大鼠的TLR4和MyD88基因mRNA相对表达量均极显著低于LPS组大鼠(P<0.01),其中M-LPS组的效果最为明显,分别降低了48.87%和45.46%。
综合以上结果分析,B-WP通过改善肝脏组织形态,降低肝脏炎性指标ALT、AST水平,降低肝脏组织TLR4和MyD88基因mRNA相对表达量,进而达到对LPS诱导的肝损伤起到预防性的保护作用。研究表明TLR4和MyD88是TLR4/MyD88通路的关键基因[47],因此对这两个基因进行mRNA的测定可以从侧面验证TLR4/MyD88通路,但仍然缺乏其它mRNA的验证,因此有待进一步探究。B-WP对大鼠肝损伤显著的改善效果,一方面是因为蛋白质是肝细胞的重要组成成分,摄取适量的优质蛋白,会促进肝细胞的再生以替代损坏的肝细胞,进而有效的改善肝损伤[48−49];另一方面归功于蛋白质会参与构成多种生理活性物质,例如催化生化反应的酶,调节代谢平衡的激素和抵御病原微生物的抗体等[50],适量补充蛋白质可以促进人体内酶功能的发挥,有利于人体生理代谢和提高人体免疫力的提升。
综合2.1、2.2、2.3和他人试验结果分析,与单一蛋白相比,B-WP具有以下优势:a.乳清蛋白是快速消化吸收蛋白,其中的氨基酸会快速释放吸收,短时间内容易造成高氨基酸血症,而黑豆蛋白属于缓慢消化蛋白,氨基酸释放缓慢,能够延长氨基酸达到最高值的时间[51],因此B-WP可以在氨基酸释放上互补,摄入后能够较长时间的提供机体所需氨基酸;b.有研究表明大豆-乳清蛋白与单一蛋白相比能够显著降低MDA含量,提高SOD活力,进而增强机体抗氧化能力,这与本试验研究结果相似[52];c.研究发现双蛋白可以通过与肠道、肝脏等器官的协同作用改善机体营养状态,从而加强肠道和肝脏免疫能力增强,减轻肝损伤,维持肠道屏障的完整性,并且经过造血干细胞移植的白血病患者在摄入双蛋白后会有更低的感染率[53],证明双蛋白的独特作用优势。
3. 结论
本研究检测不同实验组大鼠十二指肠组织氧化应激和蛋白表达水平,以及肝脏组织的病理学变化、炎性指标和mRNA表达水平。结果发现相比于Blank组,M组大鼠的MDA含量极显著降低,SOD活力和GSH含量均极显著增加(P<0.01),且下调NF-κB p65、NF-κB p-p65、JAK2、STAT3的表达量;同时肝脏ALT和AST水平以及TLR4和MyD88的表达量均降低。与LPS组相比,不同剂量组B-WP膳食干预均能改善氧化应激,下调NF-κB p65、NF-κB p-p65、JAK2、STAT3的表达量,同时能够不同程度的降低肝脏ALT和AST水平以及TLR4和MyD88的表达量,且中剂量膳食干预效果较好。综上所述,推断B-WP可能是通过缓解氧化应激、抑制大鼠十二指肠组织NF-κB/JAK2/STAT3通路活化、改善肝损伤,进而改善十二指肠屏障损伤,为B-WP应用于肠道损伤营养干预提供理论基础。另外,虽已有充分证据证明肠屏障损伤和肝损伤之间紧密联系,但本研究并未深入探索该试验中的肝损伤和十二指肠屏障损伤的因果关系,并且缺乏肝损伤通路中其他mRNA的验证,因此有待进一步深入研究。
-
表 1 qPCR分析的引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequence for qPCR
基因名称 序列(5'~3') GAPDH 正向AGACAGCCGCATCTTCTTGT 反向TGATGGCAACAATGTCCACT TLR4 正向GAGGCAGCAGGTCGAATTGT 反向AGAAGATGTGCCTCCCCAGA MyD88 正向AGTTCTACCATCAAGGGGGC 反向CGTGCCACTACCTCATGCAA -
[1] KIRSTY M. Intestinal barrier protection[J]. Nature Reviews. Immunology,2022,22(3):144−145.
[2] PUTKER F, BOS M P, TOMMASSEN J. Transport of lipopolysaccharide to the Gram-negative bacterial cell surface[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews,2015,39(6):985−1002. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuv026
[3] 贾军峰. 栀子及其提取物对免疫应激仔猪及IPEC-J2细胞相关炎症通路的影响[D]. 大庆:黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2020. [JIA J F. Effects of gardenia and its extract on immune stress piglets and IPEC-J2 cell inflammatory pathways[D]. Daqing:Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2020.] JIA J F. Effects of gardenia and its extract on immune stress piglets and IPEC-J2 cell inflammatory pathways[D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2020.
[4] 阳金金, 杨芷, 杨雨, 等. 甜菜碱对脂多糖刺激仔鹅生长性能、器官指数、血清生化指标及脾脏炎性因子表达的影响[J]. 动物营养学报,2021,33(4):2044−2054. [YANG J J, YANG Z, YANG Y, et al. Effects of betaine on growth performance, organ indices, serum biochemical parameters and spleen inflammatory factor mRNA expression of geese challenged by lipopolysaccharide[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2021,33(4):2044−2054.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.04.024 YANG J J, YANG Z, YANG Y, et al. Effects of betaine on growth performance, organ indices, serum biochemical parameters and spleen inflammatory factor mRNA expression of geese challenged by lipopolysaccharide[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(4): 2044−2054. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2021.04.024
[5] 张柏林, 杨乾, 刘宁, 等. 饲粮添加L-谷氨酰胺对脂多糖刺激肉鸡血浆生化指标、免疫性能、肠道炎症因子表达及黏膜免疫的影响[J]. 动物营养学报,2020,32(6):2611−2623. [ZHANG B L, YANG Q, LIU N, et al. Effects of dietary L-glutamine supplementation on plasma biochemical parameters, immune performance, intestinal inflammatory factors expression and mucosal immune of broilers challenged by lipopolysaccharide[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2020,32(6):2611−2623.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2020.06.020 ZHANG B L, YANG Q, LIU N, et al. Effects of dietary L-glutamine supplementation on plasma biochemical parameters, immune performance, intestinal inflammatory factors expression and mucosal immune of broilers challenged by lipopolysaccharide[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2020, 32(6): 2611−2623. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2020.06.020
[6] NICOLE R, CAROLINE E, BARBARA D, et al. Endotoxin translocation and gut inflammation are increased in broiler chickens receiving an oral lipopolysaccharide (LPS) bolus during heat stress[J]. Toxins,2020,12(10):622. doi: 10.3390/toxins12100622
[7] 雷泓, 宋云林. 肠屏障功能障碍发病机制的研究进展[J]. 医学综述,2021,27(14):2715−2720. [LEI H, SONG Y L. Research progress in pathogenesis of intestinal barrier dysfunction[J]. Medical Recapitulate,2021,27(14):2715−2720.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2021.14.003 LEI H, SONG Y L. Research progress in pathogenesis of intestinal barrier dysfunction[J]. Medical Recapitulate, 2021, 27(14): 2715−2720. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2021.14.003
[8] 罗云彦, 高小童, 韦崇万, 等. 饲粮中添加白藜芦醇对“杜×长×大”猪空肠抗氧化能力及紧密连接蛋白表达的影响[J]. 饲料研究,2022,45(1):25−29. [LUO Y Y, GAO X T, WEI C W, et al[J]. Effects of dietary resveratrol on antioxidant capacity and tight junction protein expression in jejunum of 'Duroc×Landrace×Yorkshire' pigs[J]. Feed Research,2022,45(1):25−29.] LUO Y Y, GAO X T, WEI C W, et al[J]. Effects of dietary resveratrol on antioxidant capacity and tight junction protein expression in jejunum of 'Duroc×Landrace×Yorkshire' pigs[J]. Feed Research, 2022, 45(1): 25−29.
[9] 刘燕, 张晓翠, 邓芳. 脂多糖通过JAK2/STAT3通路诱导肾小球内皮细胞炎症反应的研究[J]. 安徽医科大学学报,2020,55(3):327−332. [LIU Y, ZHANG X C, DENG F. The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is involved in the inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide in glomerular endothelial cells[J]. Acta Universitatis Medicinalis Anhui,2020,55(3):327−332.] LIU Y, ZHANG X C, DENG F. The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is involved in the inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide in glomerular endothelial cells[J]. Acta Universitatis Medicinalis Anhui, 2020, 55(3): 327−332.
[10] 裴迅, 左新河, 赵勇, 等. 活血消瘿方含药血清对脂多糖诱导的甲状腺滤泡上皮细胞炎性损伤、凋亡及JAK2/STAT3通路的影响[J]. 中医药导报,2022,28(6):14−19. [PEI X, ZUO X H, ZHAO Y, et al. Effects of serum containing Huoxue Xiaoying Recipe on LPS induced inflammatory injury, apoptosis and JAK2/STAT3 pathway of thyroid follicular epithelial cells[J]. Guiding Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy,2022,28(6):14−19.] PEI X, ZUO X H, ZHAO Y, et al. Effects of serum containing Huoxue Xiaoying Recipe on LPS induced inflammatory injury, apoptosis and JAK2/STAT3 pathway of thyroid follicular epithelial cells[J]. Guiding Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2022, 28(6): 14−19.
[11] 刘剑锋, 陈杉杉, 冯伟, 等. 硫化氢通过JAK2/STAT3通路抑制脂多糖诱导的小胶质细胞M1型极化[J]. 中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志,2020,27(3):184−189,194. [LIU J F, CHEN S S, FENG W, et al. Hydrogen sulfide inhibits the M1 polarization of microglia induced by lipopolysaccharide through the JAK2/STAT3 pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Neuroimmunology and Neurology,2020,27(3):184−189,194.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2963.2020.03.004 LIU J F, CHEN S S, FENG W, et al. Hydrogen sulfide inhibits the M1 polarization of microglia induced by lipopolysaccharide through the JAK2/STAT3 pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Neuroimmunology and Neurology, 2020, 27(3): 184−189,194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2963.2020.03.004
[12] 王曼菲, 肖肽平, 赵好好, 等. 茵陈四苓汤对酒精性肝损伤大鼠肠黏膜屏障ZO-1及occludin的影响[J]. 中医药导报,2023,9(5):31−35. [WANG M F, XIAO T P, ZHAO H H, et al. Effect of Yin Chen Siling Decoctio on ZO-1 and occludin in intestinal barrier of rats with alcoholic liver injury[J]. Guiding Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy,2023,9(5):31−35.] WANG M F, XIAO T P, ZHAO H H, et al. Effect of Yin Chen Siling Decoctio on ZO-1 and occludin in intestinal barrier of rats with alcoholic liver injury[J]. Guiding Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2023, 9(5): 31−35.
[13] 蒋文浩. 紫锥菊多糖对小鼠肠道微生物及酒精性肝损伤的干预作用研究[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2022. [JIANG W H. Intervention of Echinacea purpurea polysaccharide on gut microbes and alcoholic liver injury in mice[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2022.] JIANG W H. Intervention of Echinacea purpurea polysaccharide on gut microbes and alcoholic liver injury in mice[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2022.
[14] 路膳远. 乳清蛋白发展概述[J]. 新农业,2023(24):68. [LU S Y. Overview of whey protein development[J]. New agriculture,2023(24):68.] LU S Y. Overview of whey protein development[J]. New agriculture, 2023(24): 68.
[15] 李云亮, 刘晓霜, 徐雅宣, 等. 乳清蛋白在临床肠内营养中的应用进展[J]. 中国乳品工业,2023,51(7):45−51. [LI Y L, LIU X X, XU Y X, et al. Application of whey protein in clinical enteral nutrition[J]. China Dairy Industry,2023,51(7):45−51.] LI Y L, LIU X X, XU Y X, et al. Application of whey protein in clinical enteral nutrition[J]. China Dairy Industry, 2023, 51(7): 45−51.
[16] CHAITHANYA C, JAEWANG G, HO S R. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications[J]. Experimental & Molecular Medicine,2018,50(8):103.
[17] SUN C X, FU J L, CHANG Y Y, et al. Structure design for improving the characteristic attributes of extruded plant-based meat analogues[J]. Food Biophysics,2021,17(2):137−149.
[18] 周荣荣, 庄柯瑾, 许庆鹏, 等. 优质豆类蛋白筛选及其与乳清蛋白最佳复配比例的研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2022,37(5):93−101. [ZHOU R R, ZHUANG K J, XU Q P, et al. Screening of high-quality legume protein and the optimum mixing ratio with whey protein[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2022,37(5):93−101.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.05.014 ZHOU R R, ZHUANG K J, XU Q P, et al. Screening of high-quality legume protein and the optimum mixing ratio with whey protein[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2022, 37(5): 93−101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.05.014
[19] ZHUANG K J, MENG W H, SHU X, et al. Fecal metabonomics combined with 16S rDNA sequencing to analyze the changes of gut microbiota in rats fed with different protein source diets[J]. European Journal of Nutrition,2023,62(6):2687−2703. doi: 10.1007/s00394-023-03168-y
[20] 梁得福, 孟维洪, 舒欣, 等. 黑豆-乳清双蛋白膳食对大鼠体内免疫的调节作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2024,40(1):1−9. [LIANG D F, MENG W H, SHU X, et al. Effects of black soybean-whey protein blend on immune regulation in rats[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2024,40(1):1−9.] LIANG D F, MENG W H, SHU X, et al. Effects of black soybean-whey protein blend on immune regulation in rats[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2024, 40(1): 1−9.
[21] 孟维洪, 李志明, 张家瑜, 等. 黑豆-乳清双蛋白膳食对脂多糖诱导肠屏障损伤大鼠的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技, 2025, 46(2):324−333. [MENG W H, LI Z M, ZHANG J Y, et al. Protective effect of black bean-whey double protein diet on intestinal barrier injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2025, 46(2):324−333.] MENG W H, LI Z M, ZHANG J Y, et al. Protective effect of black bean-whey double protein diet on intestinal barrier injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2025, 46(2): 324−333.
[22] 郑晶, 欧伟豪, 麦康森, 等. 植物蛋白质对海水养殖鱼类肠道健康的研究进展[J]. 动物营养学报,2019,31(3):1072−1080. [ZHENG J, OU W H, MAI K S, et al. Research progress of plant protein on intestinal health of mariculture fish[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2019,31(3):1072−1080.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2019.03.012 ZHENG J, OU W H, MAI K S, et al. Research progress of plant protein on intestinal health of mariculture fish[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2019, 31(3): 1072−1080. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2019.03.012
[23] SUNDH H, KVAMME B O, FRIDELL F, et al. Intestinal barrier function of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) post smolts is reduced by common sea cage environments and suggested as a possible physiological welfare indicator[J]. BMC Physiology,2010,10:22. doi: 10.1186/1472-6793-10-22
[24] 王永辉. 高蛋白膳食对限食大鼠肠屏障功能的保护作用及其机制研究[D]. 北京:中国人民解放军军事医学科学院, 2007. [WANG Y H. Study of protective effects of high protein diet on intestinal barrier in food restriction rats and the related mechanisms[D]. Beijing:Academy of Military Sciences, 2007.] WANG Y H. Study of protective effects of high protein diet on intestinal barrier in food restriction rats and the related mechanisms[D]. Beijing: Academy of Military Sciences, 2007.
[25] 章元沛. 药理学实验[M]. 2版. 北京:人民卫生出版社, 1996:238. [ZHANG Y P. Pharmacological experiments[M]. 2nd Edition. Beijing:People's Medical Publishing House. 1996:238.] ZHANG Y P. Pharmacological experiments[M]. 2nd Edition. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House. 1996: 238.
[26] 赵芳芳, 何文浩, 郭迪, 等. 槲皮素对断奶羔羊血清和肠道抗氧化指标及肠道屏障功能的影响[J]. 黑龙江八一农垦大学学报,2024,36(2):57−61. [ZHAO F F, HE W H, GUO D, et al. Effects of quercetin on serum and intestinal antioxidant indices and intestinal barrier function in weaned lambs[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University,2024,36(2):57−61.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2090.2024.02.009 ZHAO F F, HE W H, GUO D, et al. Effects of quercetin on serum and intestinal antioxidant indices and intestinal barrier function in weaned lambs[J]. Journal of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2024, 36(2): 57−61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2090.2024.02.009
[27] 冯文静, 穆静辉, 李彦泽, 等. MiR-320通过调节JAK2/STAT3和NF-κB信号通路对急性胰腺炎大鼠肠道损伤的影响[J]. 胃肠病学,2022,27(10):589−595. [FENG W J, MU J H, LI Y Z, et al. Effect of MiR-320 on Intestinal injury in rats with acute pancreatitis by regulating JAK2/STAT3 and NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology,2022,27(10):589−595.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7125.2022.10.003 FENG W J, MU J H, LI Y Z, et al. Effect of MiR-320 on Intestinal injury in rats with acute pancreatitis by regulating JAK2/STAT3 and NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. Chinese Journal of Gastroenterology, 2022, 27(10): 589−595. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7125.2022.10.003
[28] ZOU S P, WANG Y F, ZHOU Q, et al. Protective effect of Kinsenoside on acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia,2019,29(5):637−643. doi: 10.1016/j.bjp.2019.06.006
[29] 马成军, 闫丰喆, 杨丽霞, 等. 基于Nrf2/HO-1轴探讨大黄黄连泻心汤加味对2型糖尿病大鼠肝脏氧化应激损伤的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(24):121−130. [[MA C J, YAN F Z, YANG L X, et al. Based on Nrf2/HO-1 axis, the effects of supplemented Dahuang Huanglian Xiexin Decoction on liver oxidative stress injury in type 2 diabetic rats were studied[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2024,30(24):121−130.] [MA C J, YAN F Z, YANG L X, et al. Based on Nrf2/HO-1 axis, the effects of supplemented Dahuang Huanglian Xiexin Decoction on liver oxidative stress injury in type 2 diabetic rats were studied[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2024, 30(24): 121−130.
[30] 张文将, 段丽芳, 孟涛, 等. 基于TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB通路探讨茯砖茶改善ApoE~(-/-)小鼠非酒精性脂肪肝的作用[J]. 中成药,2023,45(10):3429−3432. [ZHANG W J, DUAN L F, MENG T, et al. To study the effect of Fuzhuan tea on ApoE~(-/-) non-alcoholic fatty liver in mice based on TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2023,45(10):3429−3432.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2023.10.046 ZHANG W J, DUAN L F, MENG T, et al. To study the effect of Fuzhuan tea on ApoE~(-/-) non-alcoholic fatty liver in mice based on TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2023, 45(10): 3429−3432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2023.10.046
[31] 刘晓云. 精氨酸对绵羊小肠上皮细胞氧化损伤、凋亡和屏障功能的影响机制研究[D]. 扬州:扬州大学, 2023. [LIU X Y. Effects of arginine on oxidative injury, apoptosis and barrier function of ovine intestinal epithelial cells[D]. Yangzhou:Yangzhou University, 2023.] LIU X Y. Effects of arginine on oxidative injury, apoptosis and barrier function of ovine intestinal epithelial cells[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2023.
[32] 马勤, 童鑫, 张名位, 等. 米糠酚类物质对高脂诱导的小鼠糖代谢异常及氧化应激的改善作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2024,24(1):119−125. [MA Q, TONG X, ZHANG M W, et al. Effect of rice bran phenolic extracts on abnormal glucose metabolism and oxidative stress induced by high-fat diet in mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2024,24(1):119−125.] MA Q, TONG X, ZHANG M W, et al. Effect of rice bran phenolic extracts on abnormal glucose metabolism and oxidative stress induced by high-fat diet in mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2024, 24(1): 119−125.
[33] PISOSCHI A M, POP A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress:A review[J]. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2015,97:55−74. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.04.040
[34] POPRAC P, JOMOVA K, SIMUNKOVA M, et al. Targeting free radicals in oxidative stress-related human diseases[J]. Trends In Pharmacological Sciences,2017,38(7):592−607. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2017.04.005
[35] 万祥. 驴乳清蛋白对脂多糖诱导急性肺损伤小鼠的保护作用研究[D]. 塔里木:塔里木大学, 2023. [WAN X. Protective effect of donkey whey protein on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice[D]. Tarim:Tarim University, 2023.] WAN X. Protective effect of donkey whey protein on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice[D]. Tarim: Tarim University, 2023.
[36] HAMOSH M. Protective function of proteins and lipids in human milk[J]. BiolNeonate,1998,74(2):163−176.
[37] 高思惠, 马玉芯, 刘秀军, 等. 鱼鳔氨基酸组成分析及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 粮食与食品工业,2024,31(2):28−32. [GAO S H, MA Y X, LIU X J, et al. Analysis of amino acid composition and antioxidant activity of fish swim bladder[J]. Cereal & Food Industry,2024,31(2):28−32.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5026.2024.02.008 GAO S H, MA Y X, LIU X J, et al. Analysis of amino acid composition and antioxidant activity of fish swim bladder[J]. Cereal & Food Industry, 2024, 31(2): 28−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5026.2024.02.008
[38] 刘佳兴. 外源牛磺酸、半胱氨酸对卵形鲳鲹幼鱼生长、代谢、抗氧化及免疫功能的影响[D]. 大连:大连海洋大学, 2023. [LIU J X. Effects of exogenous taurine and cysteine on growth, metabolism, antioxidant and immune function of juvenile pomfret ovoides[D]. Dalian:Dalian Ocean University, 2023.] LIU J X. Effects of exogenous taurine and cysteine on growth, metabolism, antioxidant and immune function of juvenile pomfret ovoides[D]. Dalian: Dalian Ocean University, 2023.
[39] 吕珊. 浅析蛋白质与人体生命健康的关系[J]. 食品安全导刊,2023(11):152−154,158. [LÜ S. Analysis of the relationship between protein and human life and health[J]. China Food Safety Magazine,2023(11):152−154,158.] LÜ S. Analysis of the relationship between protein and human life and health[J]. China Food Safety Magazine, 2023(11): 152−154,158.
[40] 李明菊. 蛋白质的危害与合理膳食[J]. 攀枝花学院学报,2009,26(6):88−89. [LI M J. The harm of protein and rational diet[J]. Journal of Panzhihua University,2009,26(6):88−89.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0563.2009.06.025 LI M J. The harm of protein and rational diet[J]. Journal of Panzhihua University, 2009, 26(6): 88−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0563.2009.06.025
[41] 韩永霞. 食物蛋白质与人体免疫力[J]. 食品安全导刊, 2020(36):45, 47. [HAN Y X. Food protein and human immunity[J]. China Food Safety Magazine, 2020(36):45, 47.] HAN Y X. Food protein and human immunity[J]. China Food Safety Magazine, 2020(36): 45, 47.
[42] 姚文梅, 寇晨雨, 孙雨昕, 等. 全氟辛酸对肉鸡肝脏和十二指肠的损伤作用[J]. 中国兽医杂志,2024,60(2):9−17. [YAO W M, KOU C Y, SUN Y X, et al. Damaging effects of perfluorooctanoic acid on liver and duodenum of broilers[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine,2024,60(2):9−17.] YAO W M, KOU C Y, SUN Y X, et al. Damaging effects of perfluorooctanoic acid on liver and duodenum of broilers[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2024, 60(2): 9−17.
[43] 王丽, 杜冬华, 李忠浩, 等. 驴乳清蛋白通过抑制MAPK和NF-κB信号通路缓解对乙酰氨基酚诱导的小鼠急性肝损伤[J]. 中国兽医杂志,2023,59(7):76−81. [WANG L, DU D H, LI Z H, et al. Donkey whey protein alleviates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice through inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine,2023,59(7):76−81.] WANG L, DU D H, LI Z H, et al. Donkey whey protein alleviates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury in mice through inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2023, 59(7): 76−81.
[44] 杨玲, 周素芳, 路月红, 等. 基于LPS/TLR4信号通路探讨酒精性肝病大鼠疾病进展的相关机制[J]. 医学研究生学报,2022,35(1):35−40. [YANG L, ZHOU S F, LU Y H, et al. The exploration of the mechanism of progression in ALD rats based on LPS/TLR4 signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Medical Research & Combat Trauma Care,2022,35(1):35−40.] YANG L, ZHOU S F, LU Y H, et al. The exploration of the mechanism of progression in ALD rats based on LPS/TLR4 signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Medical Research & Combat Trauma Care, 2022, 35(1): 35−40.
[45] CHEN Q, WANG Y, JIAO F, et al. Betaine inhibits toll-like receptor 4 responses and restores intestinal microbiota in acute liver failure mice[J]. Sci Rep,2020,10(1):21850. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78935-6
[46] 农汝楠, 王竟静, 吴燕春, 等. 基于TLR4信号通路的中药抗肝脏疾病作用研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(16):201−212. [NONG R N, WANG J J, WU Y C, et al. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine on hepatic disease by inhibiting TLR4 signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2019,25(16):201−212.] NONG R N, WANG J J, WU Y C, et al. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine on hepatic disease by inhibiting TLR4 signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2019, 25(16): 201−212.
[47] 刘典. 大树蛙TLR2/TLR4及信号通路下游关键基因MyD88的克隆、结构及进化研究[D]. 新乡:河南师范大学, 2020. [LIU D. Cloning, structure and evolution of TLR2/TLR4 and the key MyD88 gene in the associated downstream signal pathway in Zhangixalus dennysi[J]Xinxiang:Henan Normal University, 2020.] LIU D. Cloning, structure and evolution of TLR2/TLR4 and the key MyD88 gene in the associated downstream signal pathway in Zhangixalus dennysi[J]Xinxiang: Henan Normal University, 2020.
[48] 孔凡真. 过多的摄取蛋白质对人体无益[J]. 山东食品科技,2002(7):29−33. [KONG F Z. Too much protein is not good for you[J]. Food and Drug,2002(7):29−33.] KONG F Z. Too much protein is not good for you[J]. Food and Drug, 2002(7): 29−33.
[49] 刘杰. 怎样合理调配重症患者的蛋白质摄入?[N]. 医药养生保健报, 2024-02-09(10). [LIU J. How to reasonably adjust the protein intake of severe patients? [N]. Medical Health Care Newspaper, 2024-02-09(10).] LIU J. How to reasonably adjust the protein intake of severe patients? [N]. Medical Health Care Newspaper, 2024-02-09(10).
[50] 熊祥玲. 漫话蛋白质[J]. 云南科技管理,2011,24(5):52. [XIONG X L. Rambling protein[J]. Yunnan Science and Technology Management,2011,24(5):52.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1168.2011.05.022 XIONG X L. Rambling protein[J]. Yunnan Science and Technology Management, 2011, 24(5): 52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1168.2011.05.022
[51] 武小亮. 双蛋白对异基因造血干细胞移植小鼠造血及免疫重建的功效评价研究[D]. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2020. [WU X L. Evaluation of the efficacy of double protein in hematopoiesis and immune reconstitution of mice after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020.] WU X L. Evaluation of the efficacy of double protein in hematopoiesis and immune reconstitution of mice after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020.
[52] REN G X, YI S Q, ZHANG H R, et al. Ingestion of soy-whey blended protein augments sports performance and ameliorates exercise-induced fatigue in a rat exercise model[J]. Food & Function,2017,8(2):670−679.
[53] 王靖, 张婧婕, 韩迪, 等. 双蛋白营养干预促进肠-肝-脾轴免疫互作[J]. 中国食品学报,2020,20(9):1−9. [WANG J, ZHANG J J, HAN D, et al. Dual protein nutritional intervention promotes immune interaction of intestine-liver-spleen axis[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2020,20(9):1−9.] WANG J, ZHANG J J, HAN D, et al. Dual protein nutritional intervention promotes immune interaction of intestine-liver-spleen axis[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2020, 20(9): 1−9.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 杨悦,刘梦圆,肖文军. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯与L-茶氨酸对乙醇脱氢酶和乙醛脱氢酶活性的体外协同作用. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(04): 260-265 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 丁树洽,谢昕雅,刘助生,廖贤军,刘仲华,蔡淑娴. 茶叶成分EGCG与L-theanine联合应用的神经保护作用研究. 茶叶科学. 2024(05): 779-792 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 韦柳花,赖兆荣,邓慧群,罗小梅,邱勇娟,诸葛天秋,黄金丽. 茶树良种紫鹃不同茶类适制性研究. 农业与技术. 2023(12): 4-6 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 薛璐,邢宇航,段志豪,陈绵鸿,周伟,李如一,李积华. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯与燕麦β-葡聚糖复合物的形成及表征. 食品工业科技. 2022(08): 124-132 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 吴颖,曲爱丽,纪荣全,王程安. 高花青素柏塘紫芽茶适制性的研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2022(12): 3875-3883 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 程倩,冯雪萍,陈昭,李春阳,张雪,张海波. 高效液相色谱法测定复合果汁饮品中茶氨酸的含量. 食品安全导刊. 2022(24): 87-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



