Effects of White Quinoa Polysaccharide on Regulation of Glucolipid Metabolism in Type 2 Diabetic Mice
-
摘要: 为了研究白藜麦多糖(White quinoa polysaccharide,WQP)对糖尿病模型小鼠的降糖降脂作用,将小鼠分成模型组,多糖组(800 mg/kg),空白对照组三组。试验期间测定小鼠体重、空腹血糖(Fasting blood glucose,FBG)和口服糖耐量(Oral glucose tolerance text,OGTT)。连续饲喂四周后解剖,测定小鼠的血清指标、肝脏指标和短链脂肪酸(Short-chain fatty acids,SCFAs),通过16S rRNA测序技术分析小鼠肠道内容物。结果表明,与糖尿病组小鼠相比摄入WQP可以显著抑制糖尿病小鼠的体重和血糖升高,改善糖耐量异常,缓解胰岛素抵抗,同时使糖尿病小鼠的总胆固醇(Total cholesterol,TC)含量下降19%,低密度脂蛋白(Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)含量下降33%。WQP的摄入也使糖尿病小鼠的白介素-1β(Interleukin-1β,IL-1β)和肿瘤坏死因子-α(Tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)分别下降了21%和22%,并且使过氧化氢酶(Catalase,CAT)和谷胱甘肽(Glutathione,GSH)含量分别上调了20%和24%,丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)含量下调了25%。此外摄入WQP后使糖尿病小鼠的短链脂肪酸含量显著(P<0.05)上升。16S rRNA测序结果发现,在门水平上,摄入WQP使糖尿病小鼠肠道中拟杆菌门(Bacteroidota)上升,厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)下降,在属水平上摄入WQP可以提高阿克曼菌属(Akkermansia)的丰度。因此,WQP可通过提高2型糖尿病小鼠的抗氧化能力、调节肠道菌群结构进而发挥降糖降脂作用。Abstract: To investigate the hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering effects of white quinoa polysaccharide (WQP) in type 2 diabetic model mice, the mice were divided into model group, polysaccharide group (800 mg/kg) and normal control group. During the experiment, body weight, fasting blood glucose (FBG), and oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) were measured. After four weeks of continuous feeding, the mice were dissected, and the serum indexes, liver indexes, and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) of the mice were determined. The intestinal contents of the mice were analyzed by 16S rRNA sequencing technology. Results showed that compared with diabetic mice, WQP intake could significantly inhibit the increase of body weight and FBG, improve OGTT, and alleviate insulin resistance in diabetic mice. At the same time, the total cholesterol (TC) content of diabetic mice decreased by 19%, and the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) content decreased by 33%. The intake of WQP also reduced interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) by 21% and 22%, respectively. The contents of catalase (CAT) and glutathione (GSH) were increased by 20% and 24%, respectively. The content of malondialdehyde (MDA) was decreased by 25%. In addition, the intake of WQP significantly increased the content of SCFAs in diabetic mice (P<0.05). The results of 16S rRNA sequencing revealed that the intake of WQP led to an increase in the abundance of the Bacteroidota and a decrease in the Firmicutes in the intestines of diabetic mice. At the genus level, the intake of WQP increased the abundance of Akkermansia genus. Therefore, WQP plays a hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering role by improving the antioxidant capacity and regulating the gut microbiota structure of type 2 diabetic mice.
-
糖尿病是以慢性高血糖为主要临床表现的慢性代谢疾病,能够导致患者体内脂肪类、蛋白质和碳水化合物代谢失去平衡,同时会使患者其他并发症的发病概率增加[1]。预计到2040年,糖尿病患者人数将达到6亿[2]。当下,临床上确诊的糖尿病患者约90%为2型糖尿病患者,而肥胖被认为是糖尿病发展的主要驱动因素之一[3]。多糖主要存在于动植物体和微生物细胞壁中,且具有良好的生物活性,受到许多研究者的关注[4]。最近,从自然资源中提取的多糖显示出控制葡萄糖和脂质代谢的潜力,一些已经通过胰岛素增强和靶向β细胞功能障碍来研究其抗糖尿病作用[5]。来自自然资源的多糖已被证明可以调节肠道菌群,产生有益的代谢产物短链脂肪酸(Short-chain fatty acids,SCFAs)[6]。因此,多糖对肠道菌群的调节被认为是治疗糖尿病的潜在靶点[7]。
藜麦是一年生藜科草本作物,有“营养黄金”之美誉,由于其强大的环境适应性,可以在不同的气候和地区种植[8]。近几年,藜麦在我国多地区种植,而目前青海海西天然的生态环境可以生产出最优质的藜麦,所产藜麦品质可以与南美洲产品媲美[9],而藜麦多糖也因其良好的生物活性受到国内外学者的广泛关注,杨敏等[10]发现,将藜麦通过超声提取工艺得到的藜麦多糖有很强的体外抗氧化活性。高娟等[11]对藜麦多糖的提取工艺和活性进行分析,发现藜麦多糖有抗肿瘤和抗氧化的生物活性,此外也有一些国外的研究人员发现补充藜麦多糖可以改善高脂饮食诱导的高血糖症和高血脂症[12−14]。诸多试验表明藜麦多糖有多种较强的生物活性,然而其对于糖尿病小鼠的降血糖机制尚不明确。因此本试验研究了白藜麦多糖(White quinoa polysaccharide,WQP)在高脂饮食(High-fat diet,HFD)和链脲佐菌素(Streptozotocin,STZ)诱导的糖尿病动物模型中的降血糖、降血脂特性。此外,通过16S rRNA分析了WQP对糖尿病小鼠肠道菌群结构的影响。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
雄性SPF级C57BL/6小鼠(6周龄,20±2 g) 辽宁长生生物技术有限公司,许可证号:SCXK(辽)2020-0001;高脂饲料 沈阳茂华生物科技有限公司;白藜麦 格尔木纳木蓝商贸有限公司;链脲佐菌素(Streptozotocin,STZ) 美国Sigma公司;血清胰岛素(Serum insulin,INS)、总胆固醇(Total cholesterol,TC)、甘油三酯(Triglyceride,TG)、高密度脂蛋白(High-density lipoprotein cholesterol,HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白(Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)、白介素-1β(Interleukin-1β,IL-1β)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(Tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、过氧化氢酶(Catalase,CAT)、丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)、谷胱甘肽(Glutathione,GSH)试剂盒 南京建成生物科技公司;其他化学试剂均为分析纯。
ALC-310电子天平 赛多利斯科学仪器(北京)有限公司;PerkinElmer VICTOR Nivo酶标仪 上海珀金埃尔默企业管理有限公司;G25磨粉机 永康市得能工贸有限公司;KQ-250E型超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;5424高速离心机 美国Eppendorf股份公司;LPHA冷冻干燥机 德国Christ公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 白藜麦多糖提取工艺
参考任益平[15]的提取方法并稍加修改。以白藜麦全粒为原料,粉碎过80目筛,用石油醚浸泡5 h进行脱脂;过滤,加入95%乙醇室温浸泡24 h去除杂质,过滤,将固体在50 ℃下干燥备用;将处理后的样品以1:10的比例与蒸馏水混合,并在室温下浸泡2 h。将样品转移到超声装置中,60 ℃超声51 min,离心(8000×g,10 min)上清液中加入蛋白酶37 ℃水浴30 min、90 ℃水浴30 min进行除蛋白及灭酶;调节pH至4.5静置24 h后离心(8000×g,10 min),上清液加入4倍体积无水乙醇,将混合物在4 ℃下放置24 h醇沉,离心(4000×g,10 min),取沉淀物加少量蒸馏水,蒸发浓缩后,冷冻干燥得到WQP。
1.2.2 2型糖尿病小鼠模型建立及分组
选取6周龄的SPF级C57BL/6小鼠21只,适应性饲养1周,自由饮食饮水。在整个试验过程中,所有的动物试验操作都得到了黑龙江八一农垦大学动物伦理委员会的批准。随机选择7只作为空白组对照(Normal control,NC组)饲喂基础饲料,剩余14只小鼠作为试验组饲喂HFD。4周后,小鼠空腹6 h,试验组小鼠在30 min内腹腔注射新鲜的STZ缓冲液(生理盐水缓冲液配制,50 mg/kg),NC组小鼠注射同等体积和同等浓度的生理盐水缓冲液。1周后测定空腹血糖(Fasting blood glucose,FBG),FBG值大于11.1 mmol/L被认为造模成功[16],将其随机分成模型组(Diabetic mice,DM组)、多糖组(WQP组,800 mg/kg),每组7只,整个动物试验期间NC组的健康小鼠饲喂基础饲料,DM组饲喂HFD,WQP组饲喂混合白藜麦多糖的高脂饲料,每周记录小鼠的体重及FBG。
1.2.3 小鼠口服糖耐量测定
在试验第4周进行口服糖耐量(Oral glucose tolerance text,OGTT)测定[17]。小鼠禁食6 h灌胃葡萄糖溶液(2.0 g/kg),分别在灌胃0、30、60、90、120 min时取小鼠尾部静脉血,测定其血糖值,并计算OGTT曲线下面积(Area under the curve,AUC)。
1.2.4 小鼠血清指标测定
4周后小鼠注射麻药,麻醉解剖,腹主动脉取血、收集小鼠心脏、肝脏、肾脏、胰腺等组织备用,血液静置30 min,离心(3000×g,10 min),取血清,使用相应试剂盒测定INS、TC、TG、HDL-C、LDL-C、IL-1β、TNF-α。胰岛素抵抗指数(Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance,HOMA-IR)=(INS×FBG)/22.5。
1.2.5 小鼠肝脏指标测定
称取一定重量的肝脏以1:9的比例加入生理盐水,制备肝脏匀浆,离心(3000×g,10 min)取上清液,使用相应试剂盒测定CAT、GSH、MDA水平。
1.2.6 小鼠肠道短链脂肪酸含量测定
取小鼠盲肠内容物0.2 g,加入0.24 mL的硫酸溶液(2.5 mmol/L)酸化样品,振动捣碎样品提取挥发性脂肪酸,5000×g离心10 min,取上清液,0.04 mL加入25%的偏磷酸溶液,充分混匀后冷冻。完全解冻后,12000×g离心10 min,吸取上清液经水相滤膜过滤进行高效液相色谱法分析测定SCFAs的含量[18]。色谱条件:有机酸专用色谱柱(7.8 mm×300 mm,5 um粒径),温度60 ℃;流动相:2.5 mmol/L 硫酸水溶液(5%乙腈)流速:0.50 mL/min;检测器:差折光检测器;检测器池体温度:30 ℃。
1.2.7 16S rRNA分析
每组取3只小鼠结肠内容物进行肠道菌群微生物分析,并用琼脂糖凝胶电泳法测定其完整性。用条形码引物扩增菌群中16S rRNA基因的V3~V4区域。纯化的扩增子在平台上按上海美吉的标准方案进行等摩尔和配对端测序。原始的16S rRNA基因测序用Fastp(https://github.com/OpenGene/fastp,version 0.20.0)软件进行质控,然后用FLASH(http://www.cbcb.umd.edu/software/flash,version 1.2.7)软件进行合并。使用UPARSE(http://drive5.com/uparse/,version 7.1)软件对具有97%相似性截断的操作分类单位进行聚类(OUT,Operational taxonomic units)[19]。使用http://www.majorbio.com对16S rRNA数据库进行分类分析,置信阈值为0.7。
1.3 数据处理
试验数据以平均数±标准差表示,使用SPSS 23.0分析数据,用单因素方差分析方法进行显著性分析,P<0.05表示差异显著,用Origin 21软件作图。
2. 结果与分析
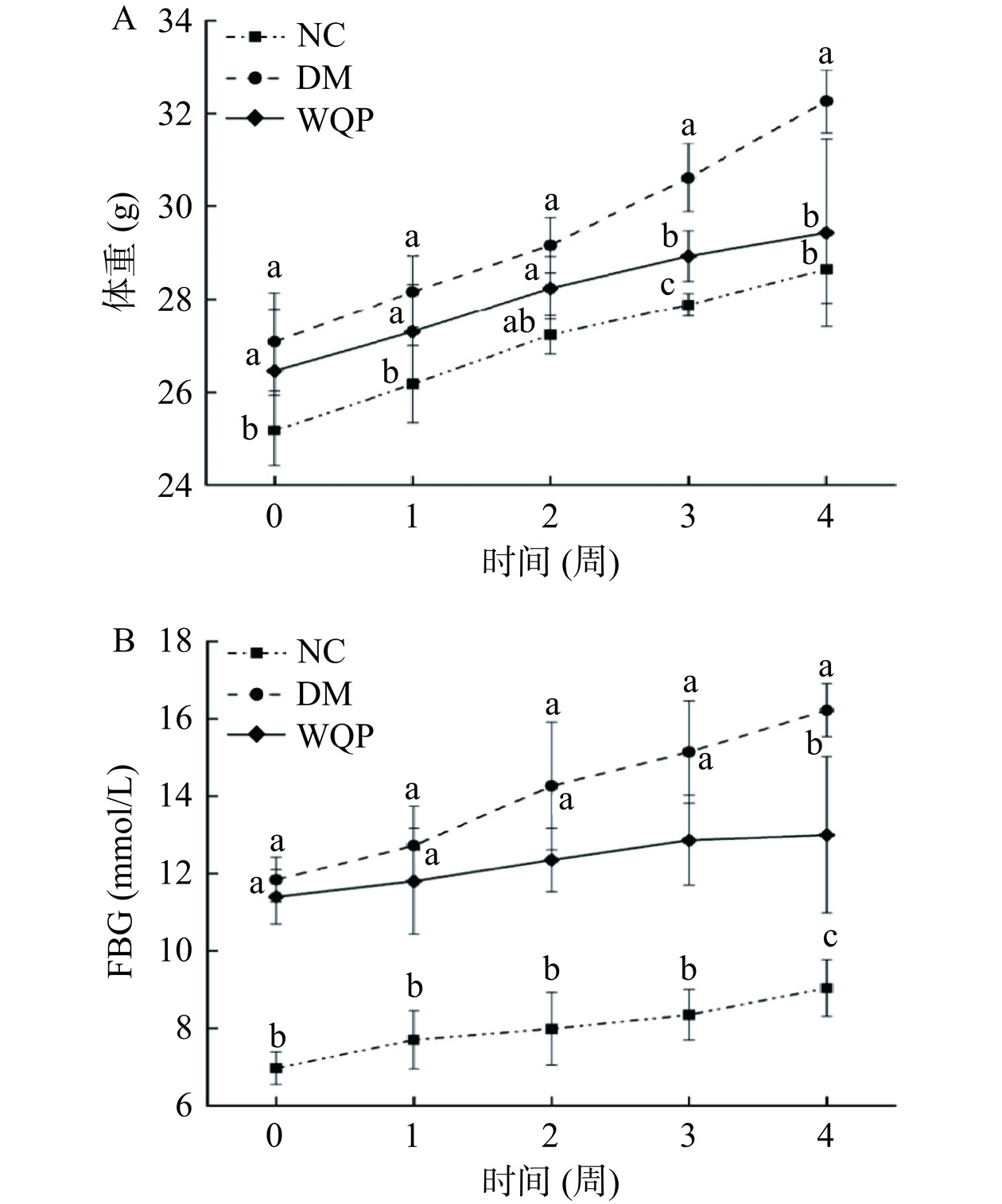
2.1 WQP对2型糖尿病小鼠体重和空腹血糖影响
糖尿病患者的表现为多饮、多尿、多食和体重下降[20],然而在本研究中,如图1A所示第0周开始所有小鼠体重均有上升趋势,并且在第4周时DM组体重上升了19%,WQP组体重上升了11%,可能是因为持续饲喂高脂饮食导致糖尿病小鼠的体重上涨。摄入WQP后,与DM组小鼠相比,WQP组小鼠体重上升缓慢(P<0.05),可能因为WQP能够抑制糖尿病小鼠的食欲,延缓了食物的消化速度并且产生饱腹感。
FBG是判断糖尿病是否发生的指标之一[21],为了判定WQP降糖效果,可以通过观察糖尿病小鼠的血糖水平变化情况。如图1B所示三组小鼠血糖水平均不同程度上升,WQP组血糖的上升趋势(14%)显著低于DM组(36%)(P<0.05),表明WQP能抑制糖尿病小鼠血糖上升。
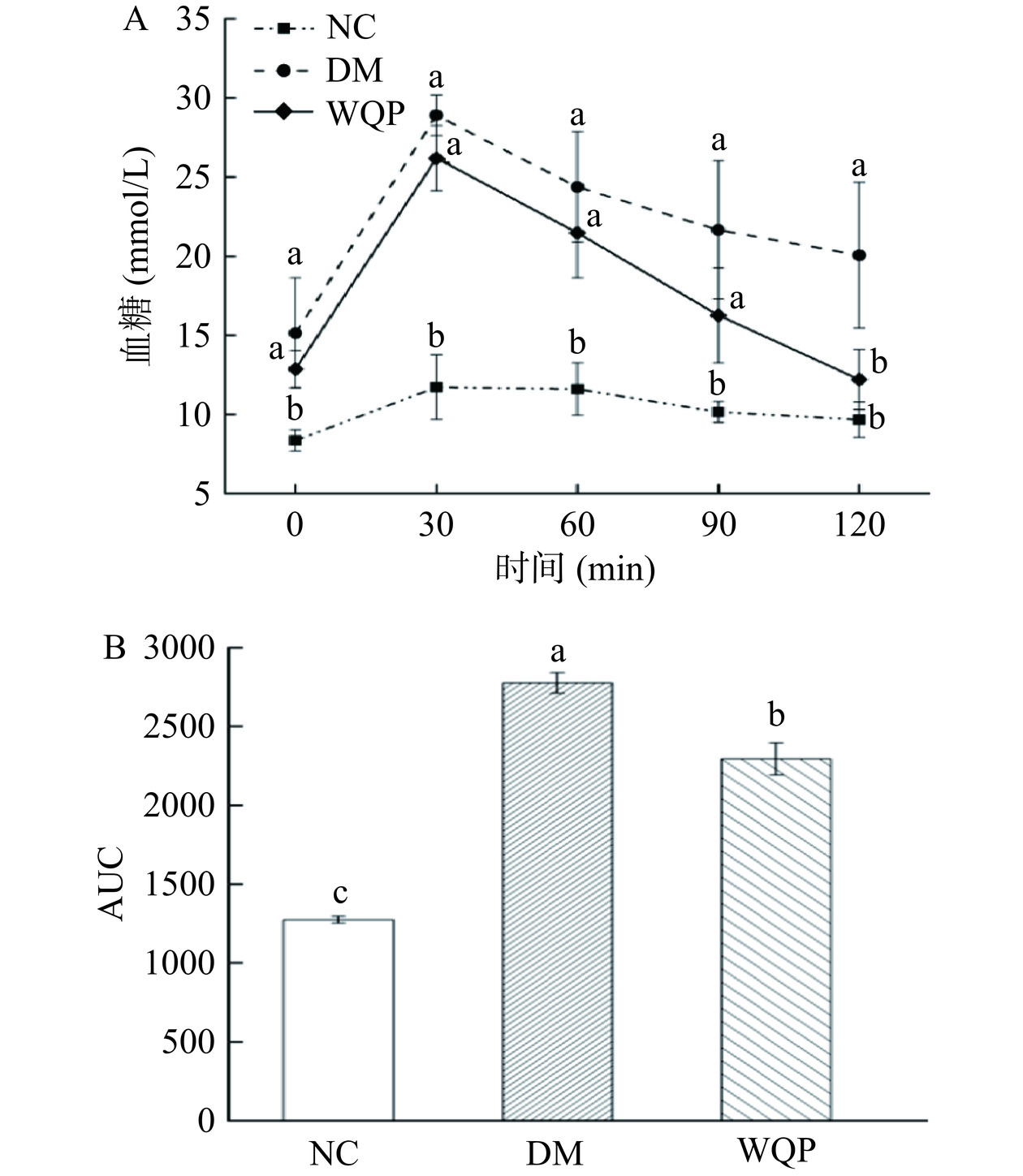
2.2 WQP对糖尿病小鼠OGTT的影响
OGTT是诊断糖尿病的重要方法,特别是对早期糖尿病和轻度糖尿病的诊断有重要作用[17]。如图2A和图2B所示,灌胃葡萄糖溶液后,各组的血糖水平在30 min内达到峰值然后开始下降。此外,在每个时间点DM组小鼠血糖值均显著高于NC组,说明糖尿病小鼠糖耐量发生异常,而与DM组小鼠相比,WQP组小鼠血糖浓度降低,WQP组曲线下面积也显著(P<0.05)低于DM组,表明WQP能够改善糖尿病小鼠糖耐量异常情况。
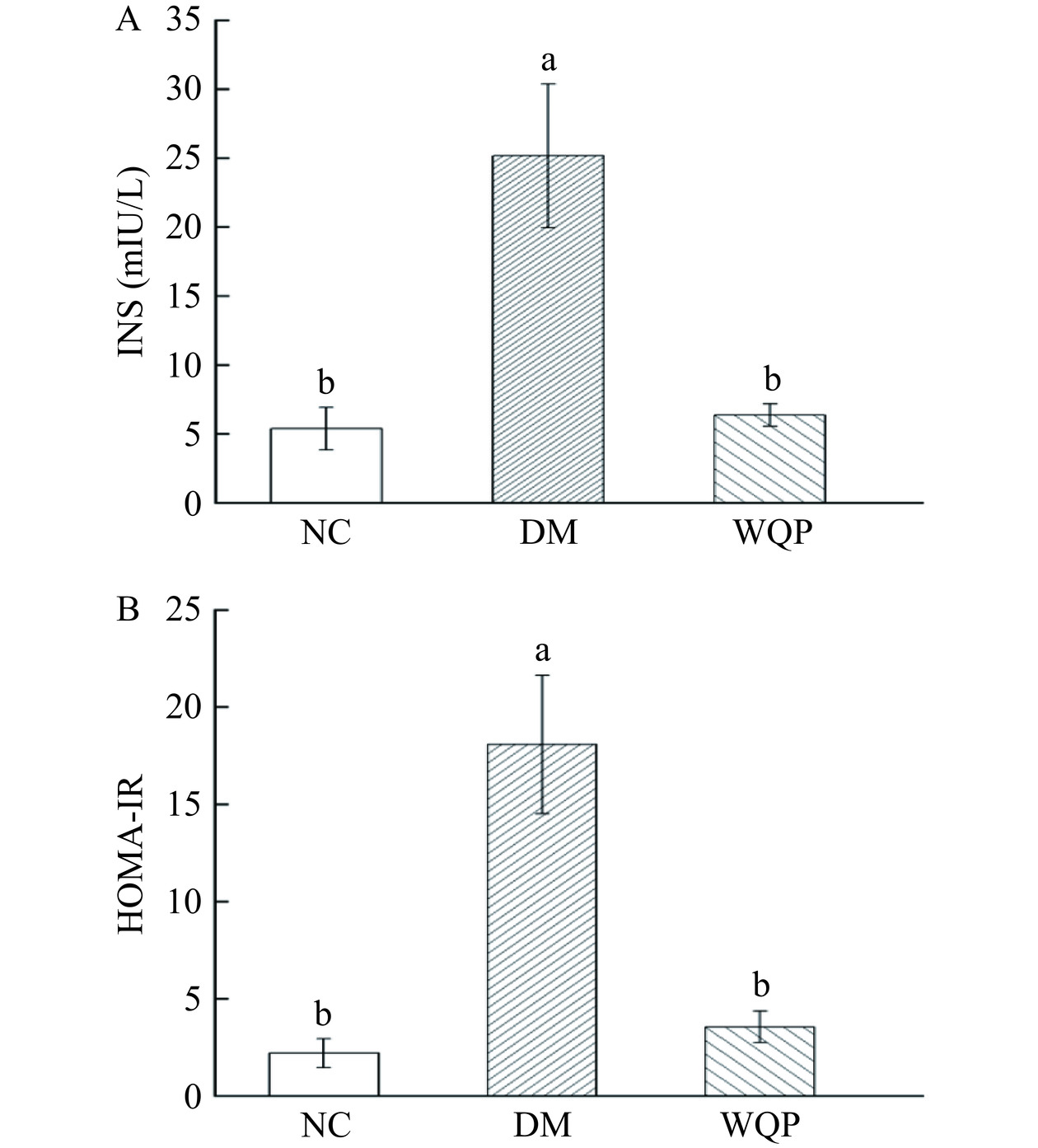
2.3 WQP对糖尿病小鼠血清胰岛素的影响
胰岛素是唯一能降低血糖的激素,糖尿病患者发病初期,血糖升高刺激胰岛素含量上升,随着病情发展患者的胰岛功能逐渐病变,最终出现胰岛素抵抗,胰岛素抵抗会损害外周组织并诱发其他并发症[22]。如图3所示,与NC组相比,DM组INS含量显著上升(P<0.05),并且胰岛素抵抗指数也显著上升(P<0.05),说明糖尿病小鼠的胰岛素敏感性下降,发生了胰岛素抵抗,给予WQP干预后糖尿病小鼠INS含量从25.16±5.21 mIU/L下降到6.36±0.81 mIU/L(P<0.05),胰岛素抵抗指数从18.07±3.50下降到3.55±0.80(P<0.05),与史岩等[23]对红豆杉多糖对糖尿病小鼠肝肾抗氧化作用的研究有相似的结果。表明WQP的摄入对糖尿病小鼠高胰岛素有明显的缓解作用,并且可以改善胰岛素抵抗。
2.4 WQP对糖尿病小鼠血脂指标的影响
许多研究证实血脂水平与糖尿病的联系非常紧密,可以通过改善血脂水平来改善糖尿病[24]。如表1所示与NC组相比DM组的TC、TG、和LDL-C水平均显著升高(P<0.05),HDL-C水平显著下降(P<0.05),给予WQP后可不同程度的改善该症状,其中TC和LDL-C水平显著下降,TG和HDL-C水平变化虽不显著但也有正向的趋势,与Zhu等[25]研究的黄菊花多糖对尿病小鼠的降血脂作用有相同研究结果,上述结果表明WQP的摄入可以改善糖尿病小鼠的血脂异常。
表 1 WQP对糖尿病小鼠血脂指标的影响Table 1. Effects of WQP on blood lipids level in diabetic mice组别 TC(mmol/L) TG(mmol/L) LDL-C(mmol/L) HDL-C(mmol/L) NC组 1.92±0.21c 0.88±0.01b 3.72±0.24b 1.20±0.11a DM组 3.27±0.20a 0.93±0.02a 6.16±0.69a 0.76±0.05b WQP组 2.64±0.22b 0.90±0.03a 4.07±0.34b 0.97±0.18b 注:同一列不同字母表示不同组间有差异显著性(P<0.05)。 2.5 WQP对糖尿病小鼠炎症因子水平的影响
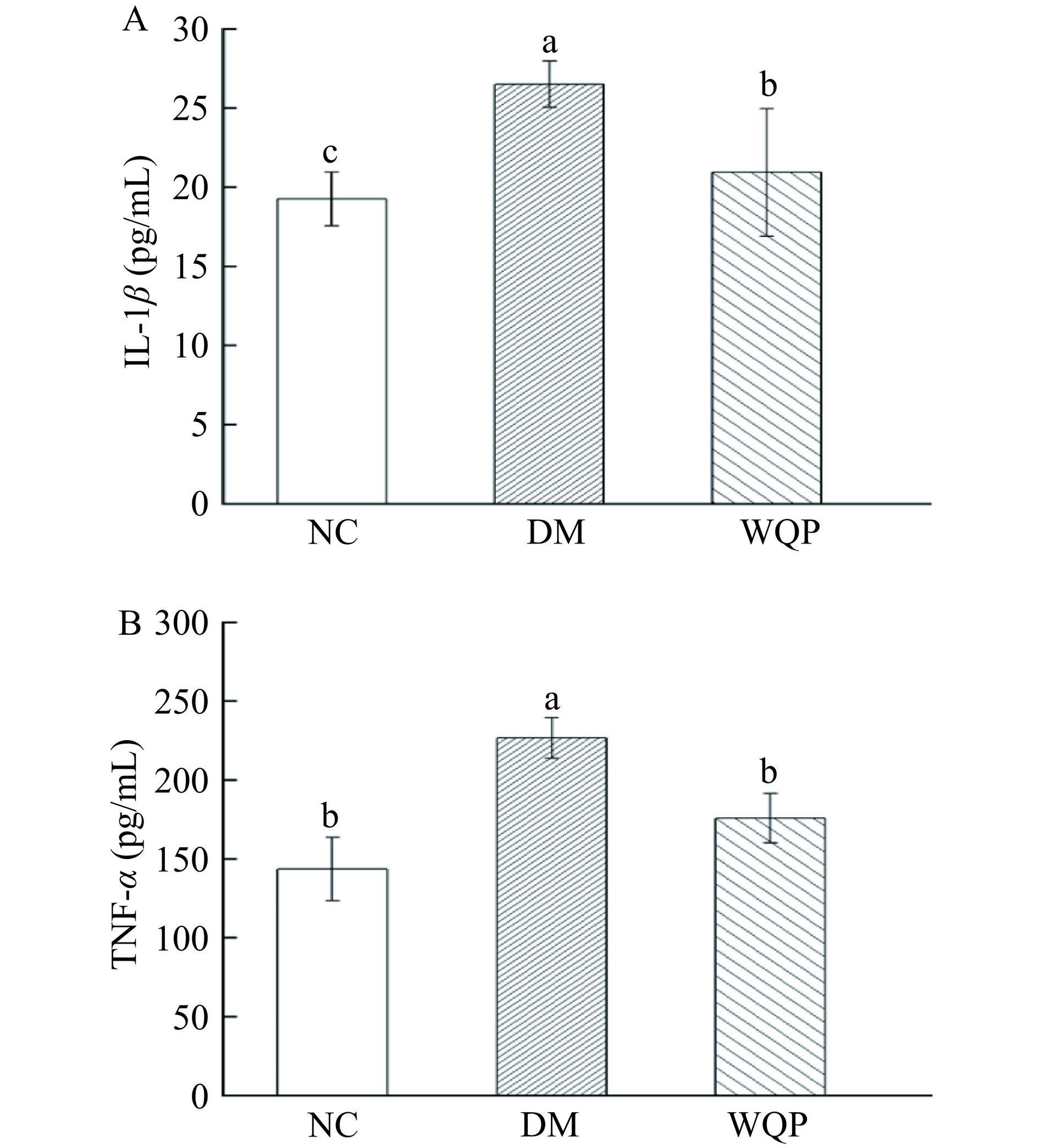
越来越多的报道表明,慢性炎症与糖尿病的发生和预防显著相关[26]。IL-1β、TNF-α是两种炎症因子,参与炎症反应,可以用来了解体内炎症的发展[27]。如图4所示,与NC组小鼠相比,DM组小鼠的IL-β和TNF-α水平都显著上升(P<0.05),说明糖尿病小鼠的体内发生了炎症。而经过WQP干预四周后,可以看到WQP组小鼠的IL-β和TNF-α水平分别下降了21%和22%(P<0.05),说明WQP的摄入可以抑制糖尿病小鼠体内促炎因子的升高。
2.6 WQP对糖尿病小鼠氧化应激指标的影响
氧化与糖尿病之间存在着不可分割的联系,这种联系会增强氧化应激,从而导致糖尿病及其病发症的进展,因此,抗氧化、清除自由基可能是对糖尿病有效的治疗途径[18,28]。CAT、GSH、MDA是反应机体氧化应激水平的主要指标。由表2可知与NC组相比,DM组的CAT和GSH水平均显著降低(P<0.05),MDA水平显著升高(P<0.05),说明糖尿病小鼠发生了氧化应激。而WQP的摄入逆转了这一情况,说明摄入WQP可以缓解糖尿病小鼠的氧化应激。贺映侠等[29]也提出了糖尿病的治疗作用与多糖减轻体内氧化应激有关,本研究与之有相似的结果。
表 2 WQP对糖尿病小鼠肝脏CAT、GSH和MDA水平的影响Table 2. Effects of WQP on CAT, GSH and MDA levels in liver of diabetic mice组别 CAT(U/mL) GSH(μmol/g prot) MDA(nmol/L) NC组 1.12±0.15a 6.90±0.55a 0.45±0.14b DM组 0.75±0.13b 5.10±0.89b 0.69±0.10a WQP组 0.90±0.16a 6.31±0.36a 0.52±0.03b 注:同一列不同字母表示不同组间有差异显著性(P<0.05)。 2.7 WQP对糖尿病小鼠肠道短链脂肪酸含量影响
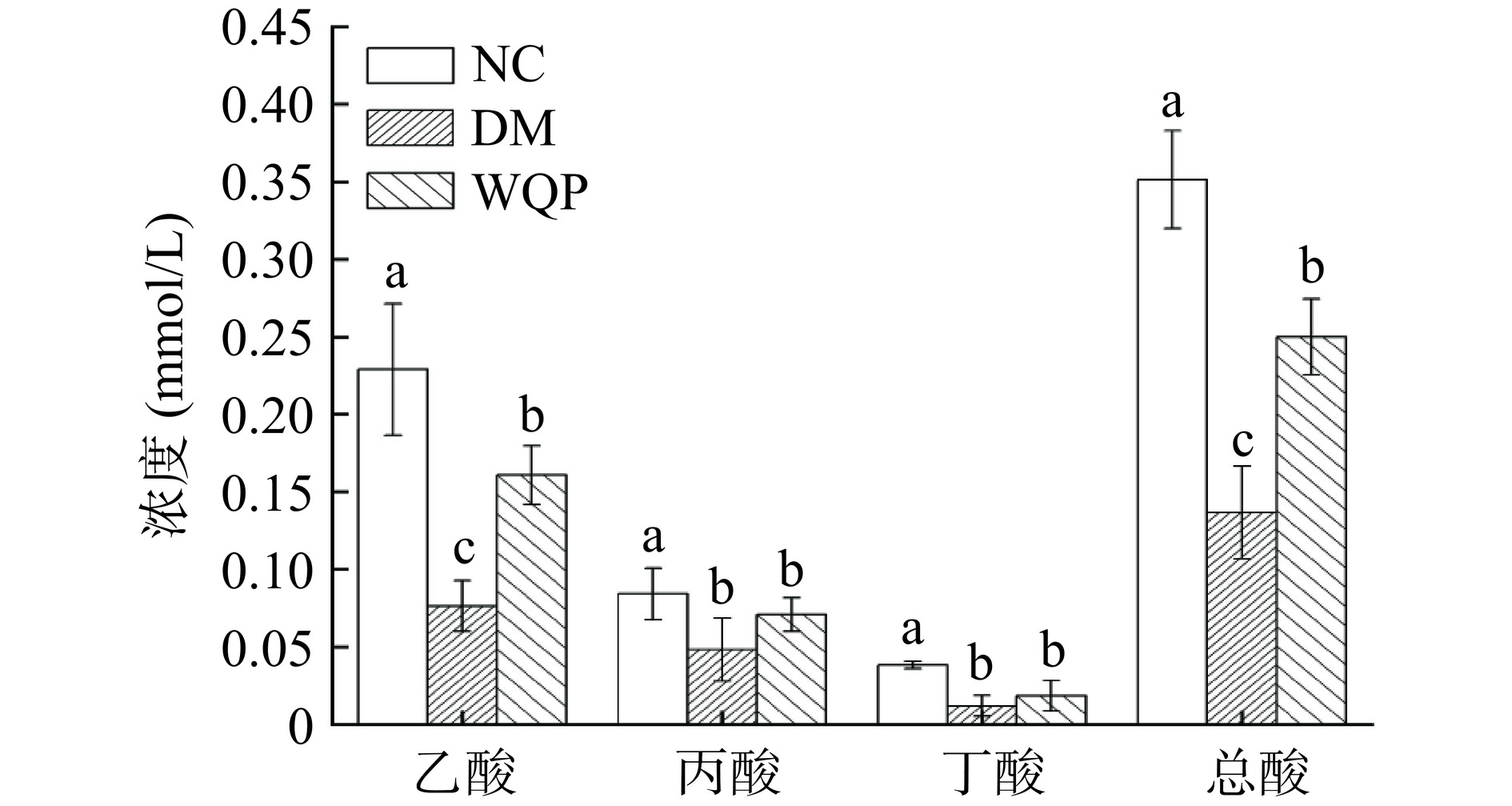
SCFAs是肠道微生物群的主要产物[18],通过分析小鼠肠道中的SCFAs含量,以进一步研究WQP对糖尿病小鼠的影响。由图5可知与NC组相比,DM组小鼠的乙酸、丙酸、丁酸和总酸含量显著下降(P<0.05),摄入WQP后糖尿病小鼠的乙酸和总酸含量显著上升(P<0.05),丙酸和丁酸含量变化不显著但也有上升趋势,结果表明摄入WQP可以促进糖尿病小鼠短链脂肪酸的生成。
2.8 WQP对糖尿病小鼠肠道菌群影响
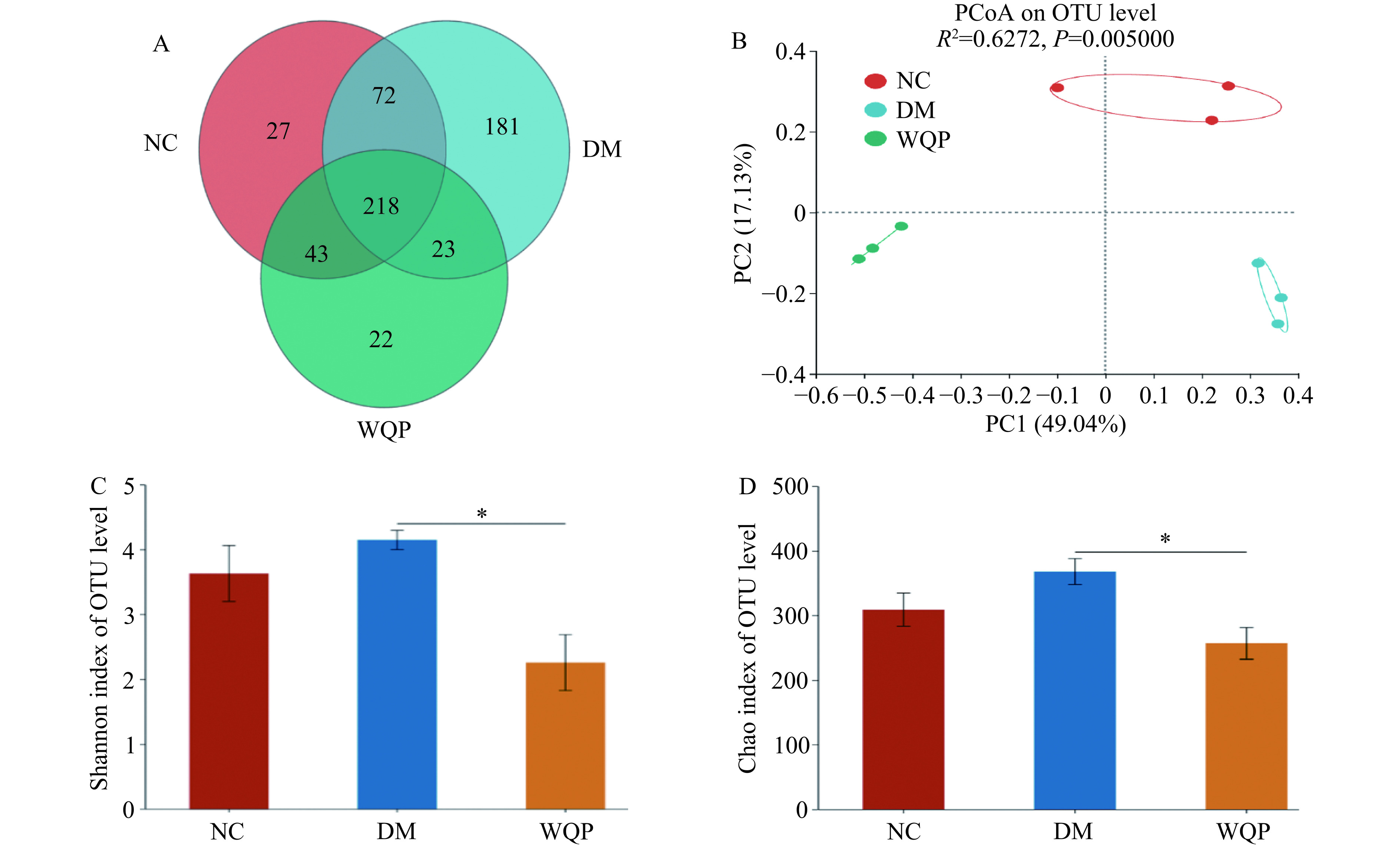
为了进一步了解WQP对糖尿病小鼠肠道菌群结构和组成的影响,进行了β-多样性分析和α-多样性分析。如图6A所示,各组共同OTU数为218,NC组、DM组和WQP组的OTU数分别为27个、181个和22个。Chao指数和Shannon指数可以分别用来表示物种的丰富度和菌群的丰度[25]。如图6C和图6D所示,与NC组相比,DM组的Shannon指数和Chao指数升高。在主坐标分析中,如图6B所示,PCoA结果显示,各组在不同区域呈聚类。说明糖尿病小鼠肠道菌群已经被破坏,可能是因为糖尿病小鼠血糖升高,刺激细胞产生大量血清素,破坏了肠道菌群,给予WQP后,WQP组的Chao指数和Shannon指数向NC组靠近,宋巧英等[30]研究了瓜蒌籽多糖减轻Ⅱ型糖尿病诱导的小鼠肝肾损伤及对肠道菌群的调节作用,本文与之有相同的研究结果。
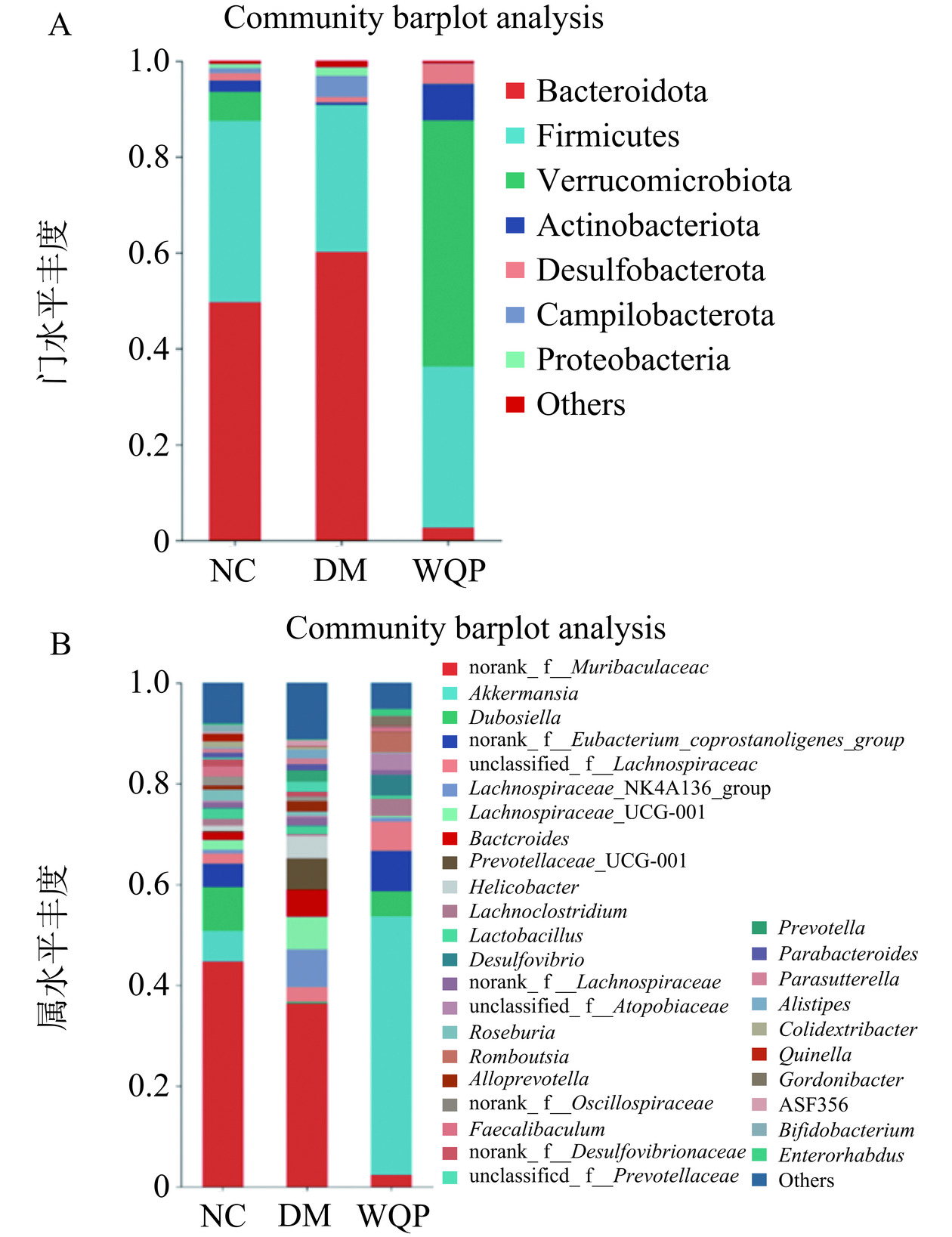
如图7A所示,在门水平上,拟杆菌门(Bacteroidota)和厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)所占比例最高。相关研究表明,肥胖和糖尿病的发生与这两种细菌门的丰度变化有关但尚未有统一的研究结果[31]。有研究发现,在肥胖或糖尿病小鼠中,拟杆菌门丰度较低,厚壁菌门丰度较高,或肥胖小鼠肠道中厚壁菌门与拟杆菌门相对丰度之比Firmicutes/Bacteroidota(F/B)升高,经饮食或药物干预后降低[32]。然而,其他研究显示,2型糖尿病患者中拟杆菌门的丰度要明显高于糖耐量正常或糖尿病前期患者[33]。在本研究中,糖尿病小鼠厚壁菌门丰度下降,拟杆菌门丰度增加,F/B下降,而给予WQP干预后可以改善该症状,使肠道菌群向健康小鼠方向发展。
如图7B所示,在属水平上,DM组杜氏杆菌属(Dubosiclla)、阿克曼菌属(Akkemansia)和的含量明显降低,而毛螺菌属(Lachnospiraccae)和拟杆菌属(Bacteroides)的相对丰度较高。朱升龙等[34]发现使用杜氏杆菌属喂食HFD诱导的肥胖小鼠可使小鼠的各种异常指标恢复正常,改善肠道菌群紊乱,提高免疫能力,减少细菌感染。有研究者发现,毛螺菌属会在不同疾病的受试者中增加[35]。拟杆菌属与肠炎、厌食、肥胖、糖尿病、腹胀、慢性肾病等相关,可以引发人类或动物疾病,并且存在足够的预防或治疗方法[36]。值得注意的是,WQP组的阿克曼菌属丰度很高,有研究证明,膳食纤维通过增加阿克曼菌的相对丰度,延缓了代谢性疾病的发展,减弱了免疫反应[37]。上述结果表明,WQP对糖尿病小鼠的肠道菌群丰度有一定的正向调节作用。
3. 讨论
本研究的目的是探究WQP对糖尿病小鼠的降糖降脂作用及机制,经HFD和STZ诱导后的小鼠体重和血糖显著升高,发生胰岛素抵抗,符合2型糖尿病的前期症状,证明2型糖尿病小鼠的造模是成功的,经WQP干预4周,糖尿病小鼠的体重和血糖得到抑制。糖尿病的并发症以血脂异常为特征,并且有研究表明高血脂可以引发胰岛素抵抗,高水平的TC、TG和LDL-C可能导致肠内皮功能障碍,并加重动脉粥样硬化的发生和进展[24]。在本研究中,糖尿病小鼠的TC、TG、LDL-C和HDL-C都发生了异常,而给予WQP后糖尿病小鼠的TC和LDL-C水平显著降低,表明摄入WQP可以降低血脂水平缓解胰岛素抵抗。研究表明,氧化与糖尿病密不可分,CAT是过氧化物酶体的标志酶,在肝脏中高度存在,GSH可以催化脂质过氧化物以防止MDA的形成[28],MDA的变化可以反映出机体抗氧化能力的变化,自由基产生等情况[29]。本研究中与健康小鼠相比,糖尿病小鼠的CAT和GSH水平显著降低,MDA水平显著升高,说明糖尿病小鼠发生了严重的氧化应激,这些指标均在给予WQP后恢复,表明糖尿病小鼠的氧化应激得到改善。炎症介质可以预测糖尿病的发生,所以调节炎症反应能在一定程度上改善糖尿病[38],经WQP干预后,IL-1β和TNF-α两种炎症因子的水平都显著下降。
许多研究表明,糖尿病与肠道菌群有密切关系,SCFAs是肠道内的重要产物,可以通过多种途径来参与机体代谢[31]。SCFAs主要包括乙酸、丙酸、丁酸,在本研究中摄入WQP会使糖尿病小鼠的短链脂肪酸含量增加,乙酸、丙酸和丁酸的升高与摄入WQP对糖尿病小鼠高甘油三酯、高血糖和高胆固醇的缓解作用相对应。肠道菌群的一些组分是炎症反应的活化因子,因此WQP可以通过改善肠道菌群结构来改善炎症因子水平从而降低血糖[39]。给予WQP后能发现糖尿病小鼠的肠道菌群结构发生变化,其结构更趋向于NC组小鼠。并且在属水平上可以观察到,WQP组小鼠的阿克曼菌属丰度升高,阿克曼菌属参与糖脂代谢、免疫反应和炎症疾病等多种生理过程,并有很大潜力成为疾病早期治疗的靶点[26]。因此,摄入WQP可以富集糖尿病小鼠肠道内的有益菌群从而来改善糖尿病。
4. 结论
综上所述,本试验以HFD结合STZ诱导建立2型糖尿病小鼠模型,研究了WQP对2型糖尿病小鼠的降糖降脂作用。结果表明,口服WQP可以有效抑制2型糖尿病小鼠的体重和血糖上升,通过下调TC和LDL-C含量来降低血脂。WQP的摄入还可以上调糖尿病小鼠的CAT和GSH水平,下调MDA水平来改善氧化应激,降低炎症因子IL-1β和TNF-α来修复肝脏炎症损伤,提高短链脂肪酸含量,此外,还可以改善糖尿病小鼠的肠道菌群结构。因此WQP有潜力作为功能性食品的降血糖成分,为其开发利用提供理论基础。
-
表 1 WQP对糖尿病小鼠血脂指标的影响
Table 1 Effects of WQP on blood lipids level in diabetic mice
组别 TC(mmol/L) TG(mmol/L) LDL-C(mmol/L) HDL-C(mmol/L) NC组 1.92±0.21c 0.88±0.01b 3.72±0.24b 1.20±0.11a DM组 3.27±0.20a 0.93±0.02a 6.16±0.69a 0.76±0.05b WQP组 2.64±0.22b 0.90±0.03a 4.07±0.34b 0.97±0.18b 注:同一列不同字母表示不同组间有差异显著性(P<0.05)。 表 2 WQP对糖尿病小鼠肝脏CAT、GSH和MDA水平的影响
Table 2 Effects of WQP on CAT, GSH and MDA levels in liver of diabetic mice
组别 CAT(U/mL) GSH(μmol/g prot) MDA(nmol/L) NC组 1.12±0.15a 6.90±0.55a 0.45±0.14b DM组 0.75±0.13b 5.10±0.89b 0.69±0.10a WQP组 0.90±0.16a 6.31±0.36a 0.52±0.03b 注:同一列不同字母表示不同组间有差异显著性(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 赵丹. 益生菌补充对2型糖尿病患者血糖控制和血脂代谢的影响[J]. 山西大同大学学报(自然科学版),2024,40(1):93−95. [ZHAO D. Effect of probiotic supplementation on blood glucose control and lipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Journal of Shanxi Datong University (Natural Science Edition),2024,40(1):93−95.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0874.2024.01.018 ZHAO D. Effect of probiotic supplementation on blood glucose control and lipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Journal of Shanxi Datong University (Natural Science Edition), 2024, 40(1): 93−95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0874.2024.01.018
[2] 方晨茜, 孙丽雅, 刘研, 等. 糖尿病肾脏疾病非经典临床类型与病理变化综述[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版),2023,54(6):1074−1079. [FANG C Q, SUN L Y, LIU Y, et al. Review of non-classical clinical types and pathological changes of diabetic kidney disease[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Medical Edition),2023,54(6):1074−1079.] doi: 10.12182/20231160102 FANG C Q, SUN L Y, LIU Y, et al. Review of non-classical clinical types and pathological changes of diabetic kidney disease[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Medical Edition), 2023, 54(6): 1074−1079. doi: 10.12182/20231160102
[3] 沈玉玲, 李芬, 朱碧帆, 等. 2型糖尿病预防及治疗项目干预效果研究综述[J]. 中国初级卫生保健,2022,36(4):45−50. [SHEN Y L, LI F, ZHU B F, et al. Review of intervention effects of prevention and treatment programs for type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Primary Health Care in China,2022,36(4):45−50.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-568X.2022.04.0013 SHEN Y L, LI F, ZHU B F, et al. Review of intervention effects of prevention and treatment programs for type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Primary Health Care in China, 2022, 36(4): 45−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-568X.2022.04.0013
[4] 张慧慧, 李灿, 刘会平, 等. 肉桂多糖的提取纯化及体外抗氧化和降血糖活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(7):15−24. [ZHANG H H, LI C, LIU H P, et al. Extraction and purification of cinnamon polysaccharide and analysis of antioxidant and hypoglycemic activity in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(7):15−24.] ZHANG H H, LI C, LIU H P, et al. Extraction and purification of cinnamon polysaccharide and analysis of antioxidant and hypoglycemic activity in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(7): 15−24.
[5] LI M X, WANG J H, YE Y F, et al. Structural characterization and anti-inflammatory activity of a pectin polysaccharide AP2-c from the lignified okra[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2022,46(9):e14380.
[6] YANG C F, LAI S S, CHEN Y H, et al. Anti-diabetic effect of oligosaccharides from seaweed sargassum confusum via JNK-IRS1/PI3K signalling pathways and regulation of gut microbiota[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2019(131):110−562.
[7] WU Jianjun, SHI Songshan, WANG Huijun, et al. Mechanisms underlying the effect of polysaccharides in the treatment of type 2 diabetes:A review[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016(144):474−494.
[8] REN Yiping, LIU Shuxing. Effects of separation and purification on structural characteristics of polysaccharide from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa willd)[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2019,522(2):286−291.
[9] TENG Cong, SHI Zhenxing, YAO Yang, et al. Structural characterization of quinoa polysaccharide and its inhibitory effects on 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation[J]. Foods (Basel, Switzerland),2020,9(10):1511.
[10] 杨敏, 奚军伟. 黑藜麦多糖超声辅助提取工艺及其抗氧化活性、稳定性研究[J]. 湖北农业科学,2023,62(8):160−166. [YANG M, XI J W. Study on ultrasonic assisted extraction of polysaccharide from quinoa nigra and its antioxidant activity and stability[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2023,62(8):160−166.] YANG M, XI J W. Study on ultrasonic assisted extraction of polysaccharide from quinoa nigra and its antioxidant activity and stability[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 62(8): 160−166.
[11] 高娟, 焦斐, 郑炜, 等. 藜麦多糖的提取工艺及活性分析[J]. 中国食品,2022(22):145−147. [GAO J, JIAO F, ZHENG W, et al. Extraction technology and activity analysis of quinoa polysaccharide[J]. Chinese Food,2022(22):145−147.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1085.2022.22.051 GAO J, JIAO F, ZHENG W, et al. Extraction technology and activity analysis of quinoa polysaccharide[J]. Chinese Food, 2022(22): 145−147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1085.2022.22.051
[12] RONGAN C, NAN M, SUBRAMANIAN P, et al. Structural elucidation and immunostimulatory activities of quinoa non-starch polysaccharide before and after deproteinization[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment,2021,30(6):11−13.
[13] HU Y C, ZHANG J M, ZOU L, et al. Chemical characterization, antioxidant, immune-regulating and anticancer activities of a novel bioactive polysaccharide from chenopodium quinoa seeds[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2017:99622−99629.
[14] NG Chongyi, WANG Mingfu. The functional ingredients of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) and physiological effects of consuming quinoa:A review[J]. Food Frontiers,2021,2(3):329−356. doi: 10.1002/fft2.109
[15] 任益平. 藜麦多糖的提取纯化及其性质研究[D]. 西安:陕西科技大学, 2020. [REN Y P. Study on extraction, purification and properties of quinoa polysaccharide[D]. Xi’an:Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2020.] REN Y P. Study on extraction, purification and properties of quinoa polysaccharide[D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[16] ZHANG L, LIU Y X, KE Y, et al. Antidiabetic activity of polysaccharides from suillellus luridus in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2018:119134-119140.
[17] TAO X, LIANG S, CHE J Y, et al. Antidiabetic activity of acidic polysaccharide from schisandra chinensis in STZ-Induced diabetic mice[J]. Natural Product Communications,2019,14(6):1934578.
[18] WANG Z Y, LIN Y, LIU L, et al. Effect of lotus seed resistant starch on lactic acid conversion to butyric acid fermented by rat fecal microbiota[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2022,70(5):1525−1535. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c06000
[19] SHAO W M, XIAO C, YONG T Q, et al. A polysaccharide isolated from ganoderma lucidum ameliorates hyperglycemia through modulating gut microbiota in type 2 diabetic mice[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2021:19723−19738.
[20] CHAI Y Y, LUO J Y, BAO Y H. Effects of polygonatum sibiricum saponin on hyperglycemia, gut microbiota composition and metabolic profiles in type 2 diabetes mice[J]. Biomedicine Pharmacotherapy, 2021, 143(Pt A):112155.
[21] FEYISOLA A F, PRITI M, CHEE Y G, et al. Identification and characterization of cholesterol esterase and lipase inhibitory peptides from amaranth protein hydrolysates[J]. Food Chemistry:X, 2021, 12:100165.
[22] 洪凌, 杨振. 人参多糖对高脂饲料联合链脲菌素诱导糖尿病小鼠的影响[J]. 人参研究,2023,35(4):6−8. [HONG L, YANG Z. Effect of ginseng polysaccharide on diabetic mice induced by high fat diet combined with streptococcin[J]. Study on Ginseng,2023,35(4):6−8.] HONG L, YANG Z. Effect of ginseng polysaccharide on diabetic mice induced by high fat diet combined with streptococcin[J]. Study on Ginseng, 2023, 35(4): 6−8.
[23] 史岩, 祝丽玲, 郭丽娇, 等. 红豆杉多糖对糖尿病小鼠肝肾抗氧化作用的研究[J]. 黑龙江医药科学,2023,46(6):5−7. [SHI Y, ZHU L L, GUO L J, et al. Study on the antioxidant effect of Taxus polysaccharide on liver and kidney of diabetic mice[J]. Heilongjiang Medical Science,2023,46(6):5−7.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0104.2023.06.002 SHI Y, ZHU L L, GUO L J, et al. Study on the antioxidant effect of Taxus polysaccharide on liver and kidney of diabetic mice[J]. Heilongjiang Medical Science, 2023, 46(6): 5−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0104.2023.06.002
[24] YU X, GUO Y T, CENG Z, et al. Gallic acid and diabetes mellitus:its association with oxidative stress[J]. Molecules,2021,26(23):7115−7115. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237115
[25] ZHU Y Z, WANG D, ZHOU S B, et al. Hypoglycemic effects of Gynura divaricata (L.) DC polysaccharide and action mechanisms via modulation of gut microbiota in diabetic mice[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024.
[26] ZHANG Tingting, ZHAO Wenying, XIE Bin, et al. Effects of auricularia auricula and its polysaccharide on dietinduced hyperlipidemia rats by modulating gut microbiota[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,72:104038. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.104038
[27] 苑慧敏. 大豆异黄酮对2型糖尿病模型小鼠脂代谢及炎症因子的影响[D]. 太原:山西医科大学, 2021. [YUAN H M. Effects of soybean isoflavones on lipid metabolism and inflammatory factors in type 2 diabetic mice[D]. Taiyuan:Shanxi Medical University, 2021.] YUAN H M. Effects of soybean isoflavones on lipid metabolism and inflammatory factors in type 2 diabetic mice[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi Medical University, 2021.
[28] DONG J , LIANG Q X, NIU Y , et al. Effects of Nigella sativa seed polysaccharides on type 2 diabetic mice and gut microbiota[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020(159):725-738.
[29] 贺映侠, 朱虹. 黄芪多糖对2型糖尿病大鼠骨骼肌氧化应激水平及SIRT3表达的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2018,38(12):3023. [HE Y X, ZHU H. Effects of astragalus polysaccharides on oxidative stress level and SIRT3 expression in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology,2018,38(12):3023.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.12.079 HE Y X, ZHU H. Effects of astragalus polysaccharides on oxidative stress level and SIRT3 expression in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 2018, 38(12): 3023. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.12.079
[30] 宋巧英, 翁少亭, 张坤朋, 等. 瓜蒌籽多糖减轻Ⅱ型糖尿病诱导的小鼠肝肾损伤及对肠道菌群的调节作用[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2024,35(1):150−161. [SONG Q Y, WENG S T, ZHANG K P, et al. Effect of fructus trichosanthis polysaccharide on liver and kidney injury induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus and its regulatory effect on intestinal flora in mice[J]. Chinese Food Additives,2024,35(1):150−161.] SONG Q Y, WENG S T, ZHANG K P, et al. Effect of fructus trichosanthis polysaccharide on liver and kidney injury induced by type 2 diabetes mellitus and its regulatory effect on intestinal flora in mice[J]. Chinese Food Additives, 2024, 35(1): 150−161.
[31] DU Haiping, ZHAO Aiqing, WANG Qi, et al. Supplementation of inulin with various degree of polymerization ameliorates liver injury and gut microbiota dysbiosis in high fat-fed obese mice[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(3):779−787. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b06571
[32] GUY J L, FLORIAN C, REBECA M, et al. Beneficial effects on host energy metabolism of short-chain fatty acids and vitamins produced by commensal and probiotic bacteria[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2017, 16(1):79.
[33] ZHAO F Q, LIU Q B, CAO J, et al. A sea cucumber (Holothuria leucospilota) polysaccharide improves the gut microbiome to alleviate the symptoms of type 2 diabetes mellitus in goto-kakizaki rats[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2020(135):110886.
[34] 朱升龙, 陈永泉, 姜旋. 杜氏杆菌在预防和改善肥胖及其相关疾病中的应用:中国, CN111686133A[P/OL]. 2020-2-22. [ZHU S L, CHEN Y Q, JIANG X. Use of Duchenne in the prevention and improvement of obesity and related diseases:China, CN111686133A[P/OL]. 2020-2-22.] ZHU S L, CHEN Y Q, JIANG X. Use of Duchenne in the prevention and improvement of obesity and related diseases: China, CN111686133A[P/OL]. 2020-2-22.
[35] 洪昇杓, 南荣度, 林美泳, 等. 使用肠道微生物预测或诊断疾病风险的组合物、使用肠道微生物的诊断试剂盒、提供信息的方法以及筛选用于预防或治疗糖尿病的试剂的方法:中国, CN116261599A[P/OL]. 2023-06-13. [HONG S S, NAN R D, LIN M Y, et al. Compositions for predicting or diagnosing disease risk using gut microbes, diagnostic kits for using gut microbes, methods for providing information, and methods for screening reagents for the prevention or treatment of diabetes:China. CN116261599A[P/OL]. 2023-06-13.] HONG S S, NAN R D, LIN M Y, et al. Compositions for predicting or diagnosing disease risk using gut microbes, diagnostic kits for using gut microbes, methods for providing information, and methods for screening reagents for the prevention or treatment of diabetes: China. CN116261599A[P/OL]. 2023-06-13.
[36] 张宇航, 崔一民, 郑波, 等. 拟杆菌属肠道菌及其代谢相关物质在制备逆转氟尿嘧啶类药物耐药性的药物中的用途:中国, CN114028573B[P/OL]. 2023-02-24. [ZHANG Y H, CUI Y M, ZHENG B, et al. Bacteroidetes and their metabolism-related substances in the preparation of drugs to reverse resistance to fluorouracils:China, CN114028573B[P/OL]. 2023-02-24.] ZHANG Y H, CUI Y M, ZHENG B, et al. Bacteroidetes and their metabolism-related substances in the preparation of drugs to reverse resistance to fluorouracils: China, CN114028573B[P/OL]. 2023-02-24.
[37] SIMA G, AMIN A, MOHAMMAD-HOSSEIN S, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila:from its critical role in human health to strategies for promoting its abundance in human gut microbiome[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2022.
[38] 关敬, 哈森, 袁颢, 等. 小陷胸汤加味方对2型糖尿病大鼠肝损伤的保护作用及其机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(医学版),2023,49(3):608−616. [GUAN J, HA S, YUAN H, et al. Protective effect of Modified Xiao-Xian-Xiong Decoction on liver injury in rats with type 2 diabete mellitus and its mechanism[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition),2023,49(3):608−616.] GUAN J, HA S, YUAN H, et al. Protective effect of Modified Xiao-Xian-Xiong Decoction on liver injury in rats with type 2 diabete mellitus and its mechanism[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(3): 608−616.
[39] WU Jiasheng, YANG Kangping , FAN Hancheng, et al. Targeting the gut microbiota and its metabolites for type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Frontiers in endocrinology, 2023, 9(14):1114424.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



