Effects of Solid Fermentation of Aspergillus niger on Release of Bound Phenols and Antioxidant Activity of By-products of Pueraria thomsonii
-
摘要: 为提高粉葛加工副产物的利用价值,阐明结合态酚类的释放规律,采用黑曲霉对粉葛皮及粉葛渣进行固态发酵,对发酵过程中结合态酚类物质含量、纤维素酶、β-葡萄糖苷酶活力变化进行测定,利用高效液相色谱考察发酵后释放的结合态酚类物质的种类与含量,并对发酵过程中两种粉葛副产物发酵产物提取液抗氧化活性进行测定。结果表明,黑曲霉发酵可以有效释放粉葛副产物中的结合态酚类物质,且随发酵时间增加,结合态酚类释放含量显著提高(P<0.05)。发酵7 d时,测得粉葛皮中结合态酚含量为1.63±0.11 mg/g,粉葛渣中结合态酚含量为0.93±0.05 mg/g。粉葛皮纤维素酶活力在发酵第6 d达到最大,为662.74±17.06 U/g;β-葡萄糖苷酶活力在发酵第7 d时最高,为332.64±26.52 U/g;粉葛渣纤维素酶活力在发酵第7 d达到最大,为885.79±66.06 U/g;β-葡萄糖苷酶活力在发酵第3 d时最高,为354.63±9.45 U/g。发酵过程中酚类物质释放量与纤维素酶、β-葡萄糖苷酶活力呈正相关。液相结果表明发酵产物提取液中含3’-羟基葛根素、对羟基苯甲酸、葛根素、大豆苷元等物质。发酵产物提取液对DPPH·和ABTS+·清除能力随发酵时间增加而增强。表明黑曲霉固态发酵粉葛副产物,能够促进结合态酚类物质释放,提高发酵产物提取液抗氧化活性。Abstract: In order to improve the utilization value of the by-products from the Pueraria thomsonii and clarifie the release law of bound phenols, Aspergillus niger was used for solid state fermentation of kudzu peel and kudzu dregs. The contents of bound phenols, activities of cellulase and β-glucosidase were measured during fermentation. The types and contents of bound phenols released after fermentation were investigated by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The antioxidant activities of two by-products extracting solution of Pueraria thomsonii were measured during fermentation. The results showed that the fermentation of Aspergillus niger could effectively release the bound phenols in the by-products of Pueraria thomsonii, and the content of the released bound phenolic substances increased significantly with the increase of fermentation time (P<0.05). After fermentation for 7 days, the bound phenols content in the kudzu peel and kudzu dregs was 1.63±0.11 mg/g and 0.93±0.05 mg/g respectively. The maximum cellulase activity of kudzu peel was 662.74±17.06 U/g on the 6th day of fermentation and the highest β-glucosidase activity was 332.64±26.52 U/g on the 7th day of fermentation. The maximum cellulase activity of kudzu dregs was 885.79±66.06 U/g on the 7th day of fermentation and the highest β-glucosidase activity was 354.63±9.45 U/g on the 3rd day of fermentation. There was a positive correlation between the release of phenols and the activities of cellulase and β-glucosidase during fermentation. The liquid phase results showed that 3'-hydroxypuerarin, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, puerarin and daidzein were contained in the fermentation product extract solution. The scavenging ability of fermentation product extract solution for DPPH· and ABTS+· increased with the increase of fermentation time. The results showed that the by-products of Pueraria thomsonii solid fermented by Aspergillus niger could promote the release of bound phenols and improve the antioxidant activity of fermentation solution.
-
粉葛为葛属植物甘葛藤的干燥根,多用于生产葛粉,粉葛皮及粉葛渣为葛粉加工的副产物,产量巨大,通常作为废弃物填埋或焚烧,利用价值低且易造成环境污染。研究表明,粉葛渣中含有淀粉、蛋白质、膳食纤维等营养成分,还含有酚类、黄酮类及多糖等多种生物活性成分[1−3],可添加于面包、饼干等食品中,改善产品口味及理化性质[4−5];同时,葛粉加工副产物中富含结合态酚类物质[6],有研究表明,葛渣中含有32.41 mg/g的总黄酮和42.21 mg/g的葛根素[7],这些酚类物质多与纤维素紧密结合,具有抗氧化、抗炎、抑菌、抗肿瘤等多种生物活性[8−10]。
目前多采用化学法提取植物中结合酚,主要为酸、碱水解法,其中以碱水解法为主,通过破坏糖苷键与脂键释放结合态多酚[11−12],水解效率与结合酚得率较高,但此类方法化学试剂消耗大,易造成环境污染,且不适用于食品中结合酚的提取。而微生物发酵通过生成一系列酶,释放基质中结合酚,污染小且有助于改善风味、增强生物活性[13]。通过微生物发酵过程中产生的纤维素水解酶、木质素水解酶、β-葡萄糖苷酶等的水解作用,可释放植物体中的结合态酚类物质,进而增强抗氧化等生物活性[14]。Wang等[15]研究发现,纤维素酶及β-葡萄糖苷酶可显著提高番石榴叶中结合态酚类物质的释放,其中槲皮素和山奈酚含量分别提高了3.5倍和2.2倍,且抗氧化活性显著提升。王懿文等[16]利用黑曲霉对金银花进行固体发酵,发酵后其抗氧化能力、结合态酚含量、总黄酮含量等均得到提升。表明微生物发酵过程中可产生复合酶系,促进结合态酚类的释放,并增强发酵产物相关生物活性。
由于固态发酵具有操作简便、微生物易生长、酶系丰富且酶活力高等特点,目前已广泛应用于植物中结合酚的提取中,但尚未见固态发酵应用于粉葛加工副产物结合酚提取的相关报道。由于粉葛加工副产物以纤维素为主,且黑曲霉又被证明是纤维素酶产量最高的菌株之一[17]。因此,为进一步提高粉葛废弃物的资源利用和相关产品的开发,本研究利用黑曲霉对粉葛加工副产物进行固态发酵,探讨发酵过程对粉葛加工副产物中结合态多酚的释放及抗氧化性能的影响,旨在为粉葛加工副产物的深度开发利用提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
粉葛加工副产物 江西中横葛业大健康产业有限公司,为‘赣葛2号’粉葛提取完葛粉后的加工副产物,分别收集粉葛皮和粉葛渣,冻干后备用;黑曲霉(Aspergillus niger) 南昌大学食品学院,分离自江西特香型大曲(GenBank accession number:MZ707664),编号为NCUF413.1[18];正己烷、甲醇 分析纯,西陇科学股份有限公司;碳酸纳、过硫酸钾 分析纯,上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司;没食子酸、福林-酚试剂、1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼、2,2-联氮-二(3-乙基-苯并噻唑-6-磺酸)二铵盐均为分析纯、马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂培养基 北京索莱宝科技有限公司。
SCIENTZ-18N真空冷冻干燥机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;TOX-100AH超声波清洗机 山东新华医疗器械股份有限公司;NACHTC-15R高速冷冻离心机 杰懋万得福(中山)生物科技有限公司;UV-5500PC紫外可见分光光度计 上海元析仪器有限公司;AKSW-V-1G实验室超纯水机 成都唐氏康宁科技发展有限公司;Spectrum 3珀金埃尔默傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 美国Perkin Elmer;Multiskan FC酶标仪 赛默飞世尔(上海)仪器有限公司;Waters 2695高效液相色谱仪 美国沃特世;Leica TCS SP5激光扫描共聚焦显微镜 德国徕卡公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 粉葛皮及粉葛渣中脂肪及游离态酚类物质的去除
参考顿倩[19]的方法并略作修改,取冻干后的粉葛皮及粉葛渣,分别加正己烷浸没,于超声波清洗机中超声30 min,随后倾去上清液,加入80%甲醇(含0.1% HCl)浸没。超声提取30 min后6000 r/min离心5 min,去除上清液,将残渣按照同样的方法重复提取5次,直至上清液用福林酚法检测不含酚类物质。收集残渣,分别冷冻干燥后备用。
1.2.2 粉葛加工副产物固态发酵及样品制备
参考王懿文等[16]的方法并略作修改,将黑曲霉孢子菌粉接种于马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂(PDA)斜面培养基上,30 ℃恒温培养7 d,用无菌的生理盐水洗下孢子,制备成1.0×107 CFU/mL的孢子悬液备用。经脱脂与去除游离酚后的粉葛皮与粉葛渣,粉碎过60目筛,各称取2 g于100 mL的三角瓶中,制备2份样品分别用于结合态酚及酶液的提取。加入5 mL无菌水,于121 ℃灭菌30 min,冷却后备用。接入1 mL黑曲霉孢子菌悬液,混匀后置于培养箱30 ℃培养,每份样品设置3组平行,分别于1、2、3、4、5、6、7 d 取样用于后续酚类含量、抗氧化活性及酶活力的测定,空白组加入等量无菌水。
1.2.3 发酵释放的结合态酚类物质提取与测定
分别取2 g空白组与发酵不同天数的样品,以料液比1:30(g/mL)加入80%甲醇溶液,超声提取30 min,超声结束后8000 r/min离心10 min,收集上清液,重复3次后合并上清液粉葛皮及粉葛渣结合态酚类物质发酵提取液,进行结合态酚含量测定。
1.2.3.1 标准曲线的绘制
根据王振宇[20]的方法略作修改,没食子酸120 ℃烘干至恒重,配制成20、40、60、80、100、120、140 μg/mL的系列标准溶液,分别吸取500 μL标准液加入500 μL福林酚试剂,静置6 min后加入5 mL 7%的Na2CO3溶液,随后加入超纯水10 mL,室温下静置90 min,于760 nm下测定吸光度,根据吸光度和浓度绘制出标准曲线。y表示吸光度值;x表示没食子酸浓度(μg/mL),得回归方程y=0.003x+0.02,R2=0.9987。
1.2.3.2 结合态酚类物质含量的测定
分别取粉葛皮及粉葛渣结合态酚类物质提取液,依次加入500 μL福林酚试剂,静置6 min后加入5 mL 7%的Na2CO3溶液,随后加入超纯水10 mL,室温下静置90 min,于760 nm下测定吸光度,根据标准曲线的回归方程计算提取液中结合态酚的含量,并按下式计算粉葛加工副产物残渣中结合态酚类物质得率。
式中:C为没食子酸溶液质量浓度,μg/mL;V为溶液体积,mL;N为稀释倍数;m为样品残渣质量,g。
1.2.4 发酵过程中酶活力测定
分别取2 g空白组与发酵不同天数的样品,以料液比1:30(g/mL)加入生理盐水,于摇床30 ℃、180 r/min 振荡提取30 min,8000 r/min离心5 min,收集上清液,重复3次,即得粗酶提取液。酶活测定方法参考阎欲晓等[21]的方法,并加以修改。
1.2.4.1 纤维素酶(羧甲基纤维素酶)活力测定
在25 mL试管中加入粗酶液0.5 mL和羧甲基纤维素钠悬溶液1 mL,50 ℃水浴30 min后,立即加入3 mL 3,5-二硝基水杨酸试剂,沸水浴5 min。冷却后定容到20 mL,于540 nm波长处测定吸光度。根据葡萄糖标准方程计算葡萄糖质量(以加入沸水浴5 min后灭活0.5 mL粗酶液为空白对照)。1 g发酵基质,在酶最适反应条件下,每小时分解纤维素产生1 μmol葡萄糖所需的酶量定义为1个酶活力单位,用U/g表示。
1.2.4.2 β-葡萄糖苷酶活力测定
取160 μL的磷酸盐缓冲液(pH5.5)和20 μL 20 mmol/L的p-NPG溶液混匀后,30 ℃预热2 min,加入20 μL的粗酶液,反应20 min,加入50 μL 2 mol/L Na2CO3溶液终止酶反应,测定OD405 nm。采用p-NPG为标准品绘制标准曲线(以加入20 μL沸水浴5 min后失活的酶液作为空白对照)。1 g发酵基质(干质量),在酶最适反应条件下,每小时水解p-NPG释放1 μmol p-NPG所需的酶量定义为1个酶活力单位,用U/g表示。
1.2.5 粉葛加工副产物残渣发酵前后红外光谱表征
分别取未发酵与黑曲霉发酵7 d后的粉葛皮、粉葛渣样品1 mg与溴化钾粉末按1:100混合,研磨压片,扫描4000~400 cm−1红外光谱,采集分辨率为4 cm−1,扫描次数16次。
1.2.6 激光扫描共聚焦扫描显微镜观察
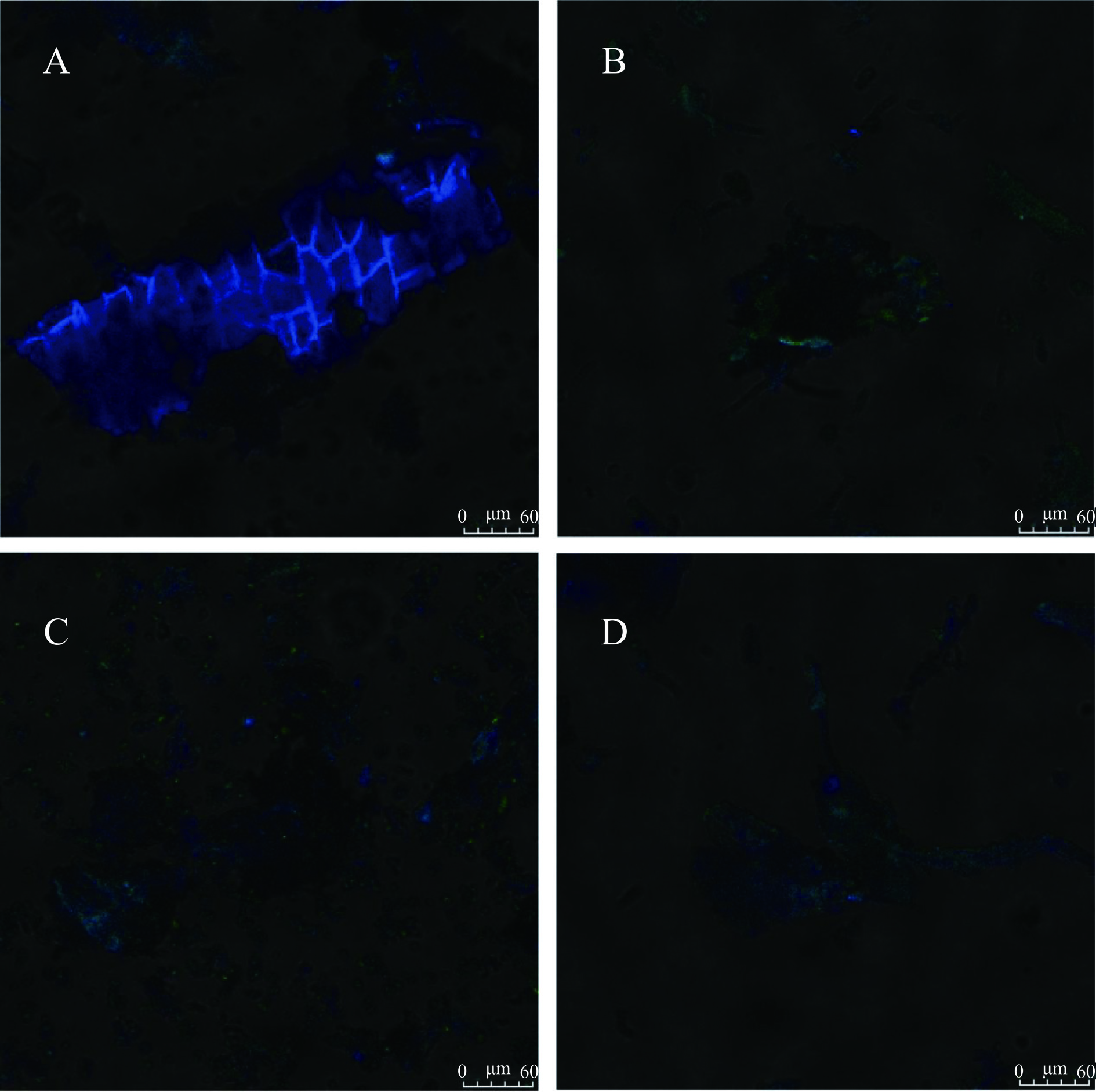
采用激光扫描共聚焦显微镜(Confocal laser scanning microscope,CLSM)观察未发酵与黑曲霉发酵7 d后粉葛皮与粉葛渣微观结构和酚类物质的分布变化,酚类化合物具有天然荧光,通过CLSM可以观察结合酚的分布情况。在405、488 nm氩激光源下测定,发射波长分别为440~470 nm及500~545 nm,在明场和荧光场中分别收集同一视角和倍数下的图像,叠加明场和荧光场的图像观察结合酚的分布情况。
1.2.7 粉葛加工副产物发酵产物提取液中酚类物质的定量分析
采用高效液相分别对发酵7 d后粉葛皮及粉葛渣发酵产物提取液进行定量分析,采用外标法计算发酵产物提取液中3’-羟基葛根素、对羟基苯甲酸、葛根素、大豆苷元四种物质含量。HPLC检测条件:ACE Excel 5 C18 色谱柱(250 mm);柱温25 ℃,进样量10 μL;检测波长:254 nm。流动相为乙睛(A)和0.1%磷酸水(B);洗脱程序;0~10 min,10%~15%A,90%~85%B;10~20 min,15%~30%A,85%~70%B;20~25 min,30%~50%A,70%~50%B;25~30 min,50%~10%A,50%~90%B。
1.2.8 发酵产物提取液抗氧化活性测定
1.2.8.1 DPPH·清除能力的测定
参考Dżugan等[22]的方法进行调整,在96孔板上依次将200 μL DPPH溶液(0.1 mmol/L)和10 μL发酵产物提取液混合,于室温避光反应30 min,用酶标仪在510 nm处测定吸光度,平行测定3次。Trolox溶液标准曲线浓度为78.125~12500 μmol/L,测定结果以Trolox为参考标准,结果以mol Trolox(TE)/g干重(mol TE/g DW)表示。
1.2.8.2 ABTS+·清除能力的测定
参考Xue等[23]的方法并优化。0.2 mL 7.4 mmol/L的ABTS溶液和0.2 mL 2.6 mmol/L的过硫酸钾溶液混合反应12 h得ABTS工作液母液,稀释母液至734 nm处的吸光值为0.70±0.05,此稀释液为工作液。向96孔板中依次加入200 μL的ABTS工作液和10 μL发酵产物待测样液,37 ℃避光反应15 min后于734 nm下用酶标仪测定其吸光度,平行测定3次。Trolox溶液标准曲线浓度为78.125~12500 μmol/L,测定结果以mol Trolox(TE)/g干重(mol TE/g DW)表示。
1.3 数据处理
所有数据以平均值±标准差(n=3)表示。采用SPSS 23.0软件对实验数据进行统计分析,Origin 2018软件作图,并采用SPSS 23.0进行单因素方差分析,P<0.05表示差异显著。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 粉葛加工副产物发酵过程结合态酚类物质释放量的变化
黑曲霉固态发酵粉葛加工副产物过程中结合酚含量变化如图1所示。粉葛加工副产物经过黑曲霉发酵后,所释放出的结合酚含量明显提高,其中粉葛皮中结合酚含量较粉葛渣中更高,主要原因是作为保护组织的外皮需要应对更多的机械损伤、昆虫侵袭、紫外辐射等,而酚类物质可有效抵御外界胁迫[24],因此,粉葛皮中结合态酚类物质含量相对粉葛渣更高。固态发酵过程中黑曲霉代谢产生的复合水解酶系的作用,改变了粉葛加工副产物中纤维的致密结构,促进了多酚释放。经过黑曲霉发酵处理的1~4 d内,两者结合酚含量均显著增加(P<0.05),分别由0.93±0.03 mg/g和0.34±0.07 mg/g升高至1.51±0.09 mg/g和0.77±0.02 mg/g;发酵4~7 d,结合酚含量增长趋于平缓,并于第7 d达到最高分别为1.63±0.11 mg/g 和0.93±0.05 mg/g。这与王懿文等[16]的研究结果一致,原因可能是粉葛加工副产物中碳源被耗尽,黑曲霉代谢速率减缓,致使结合态酚类物质释放减慢,含量增长趋于平缓。李丹青等[25]通过黑曲霉发酵麦麸,发现发酵至第3 d时,麦麸中结合态酚含量达到最大值,结合态酚含量增加了1.4 mg/g。葛渣主要由纤维素、半纤维素和木质素组成,而黑曲霉主要分泌纤维素酶、半纤维素酶等[26],黑曲霉发酵使葛渣微观结构更为疏松多孔,利于结合态酚类物质的释放[27]。
2.2 粉葛加工副产物发酵过程中酶活力的变化
在发酵过程中黑曲霉通过产生纤维素酶等,可有效将与纤维素结合的酚类物质释放。为阐明粉葛加工副产物发酵过程中,黑曲霉产生的纤维素酶、β-葡萄糖苷酶与结合酚释放的关系,对发酵过程中产生的纤维素酶活力和β-葡萄糖苷酶活力进行了跟踪测定,结果如图2~图3所示。粉葛皮与粉葛渣在黑曲霉固态发酵过程中均能产生一定量的纤维素酶和β-葡萄糖苷酶,且粉葛渣中纤维素酶与β-葡萄糖苷酶活力均高于粉葛皮,可能原因是作为营养组织的粉葛渣具有较保护组织的粉葛皮更多的营养成分,包括淀粉、多糖等,更有利于黑曲霉的生长与产酶。从种类上看纤维素酶活力明显高于β-葡萄糖苷酶活力。随着发酵时间的增加,纤维素酶活力不断增加,粉葛皮在第6 d达最大值,为662.74±17.06 U/g,随后略有下降但并不显著,粉葛渣中纤维素酶活力在第7 d达最大值,为885.79±66.06 U/g,高于王懿文等[16]采用黑曲霉固态发酵金银花的结果。β-葡萄糖苷酶活力活性呈先增加后平缓的变化趋势,两种粉葛加工副产物均在1~3 d内酶活力显著增强(P<0.05),随后4 d酶活力趋于平缓无显著增加(P>0.05)。粉葛皮β-葡萄糖苷酶活力在发酵第7 d达到最大值,为332.64±26.52 U/g,粉葛渣则在第3 d达到最大值,为354.63±9.45 U/g,随后活力略有下降但并不显著,酶活力变化趋势与谢欢等[26]研究结果一致。与图1相比,发酵过程中产生的水解酶系与酚类物质释放的变化趋势基本保持一致,均为先显著增加后趋于平稳,推测粉葛加工副产物中结合态酚类物质的释放与黑曲霉固态发酵过程中产生的水解酶系有密切的关系。
2.3 粉葛加工副产物经黑曲霉固态发酵前后红外光谱特征
如图4所示,粉葛加工副产物粉葛渣、粉葛皮固态发酵前后的红外光谱特征相似。在3400 cm−1均出现宽而强的特征峰,是由粉葛加工副产物中纤维素与半纤维素的O-H基团的伸缩振动引起的[28],2920 cm−1处为糖类亚甲基中C-H的伸缩振动峰[29],1400 cm−1范围内的吸收峰是由纤维素葡萄糖单元H-C-H弯曲和伸缩振动引起的[30]。1155 cm−1是半纤维素和纤维素C-O-C基团的特征峰[31]。粉葛渣、粉葛皮发酵前后,峰形无明显变化,表明发酵前后粉葛渣及粉葛皮官能团均未出现明显变化,但1155 cm−1处半纤维素和纤维素特征峰的吸收减弱,说明黑曲霉固态发酵能够破坏粉葛加工副产物纤维素、木质素等的化学键,并释放与之结合的酚类物质,这与Eisheekh等[32]和赵一帆等[33]的研究结果一致。
![]() 图 4 粉葛加工副产物发酵前后的红外光谱图注:A.粉葛皮;B.黑曲霉发酵后粉葛皮;C.粉葛渣;D.黑曲霉发酵后粉葛渣;图5同。Figure 4. Infrared spectrogram of Pueraria thomsonii processing by-products residue before and after solid state fermentation
图 4 粉葛加工副产物发酵前后的红外光谱图注:A.粉葛皮;B.黑曲霉发酵后粉葛皮;C.粉葛渣;D.黑曲霉发酵后粉葛渣;图5同。Figure 4. Infrared spectrogram of Pueraria thomsonii processing by-products residue before and after solid state fermentation2.4 激光共聚焦显微镜
共聚焦显微镜(CLSM)可直观观察酚类物质分布。粉葛加工副产物中结合酚分布情况如图5所示(为相同视野、相同放大倍数下,样品在明场和荧光场的叠加图)。绿色荧光主要是由于阿魏酸的存在,其在405 nm激发波长下可显示明亮的绿色[34];蓝色荧光主要由羟基肉桂酸的存在,其在488 nm激发波长下可显示蓝色,此外,黄酮类、黄酮醇类及其衍生物在500~545 nm范围内也可显示蓝色或绿色荧光[35]。由图5A、5C可知相较于粉葛渣,粉葛皮中荧光分布更加广泛且亮度更高,这表明粉葛皮中含有更多的酚类物质,与之前实验结论一致[36]。由图5B、5D可知,两种粉葛加工副产物经黑曲霉发酵后荧光范围缩小,荧光强度降低。特别是粉葛皮,对比图5A、5B两图,蓝绿色荧光强度在发酵后明显降低,表明所含酚类物质减少,说明结合酚在黑曲霉固态发酵过程中被释放。
2.5 粉葛加工副产物中发酵产物提取液中结合态酚类物质的组成及含量鉴定
以粉葛皮与粉葛渣为原料,通过黑曲霉固态发酵后结合酚得率分别为化学法的32.10%和36.61% [36]。利用高效液相色谱测定粉葛加工副产物发酵产物提取液中结合态酚类物质的组成,以标准品的保留时间确定结合酚种类,结果图6所示,发酵产物提取液中主要含有对3’-羟基葛根素、羟基苯甲酸、葛根素和大豆苷元,根据标准曲线(表1)计算其含量,详细结果见表2。在粉葛皮发酵后3’-羟基葛根素397.42±6.76 μg/g、对羟基苯甲酸47.99±0.62 μg/g、葛根素474.75±4.25 μg/g、大豆苷元361.69±4.11 μg/g;粉葛渣发酵后对羟基苯甲酸24.93±0.13 μg/g、葛根素370.03±3.21 μg/g、大豆苷元89.47±0.93 μg/g。表明粉葛加工副产物中葛根素含量最高,相较于粉葛渣,粉葛皮发酵产物提取液中具有3’-羟基葛根素而粉葛渣中并未检测到。粉葛皮与粉葛渣发酵产物提取液中结合态酚含量分别为1.63±0.11 mg/g及0.93±0.05 mg/g,其中粉葛皮发酵产物提取液中葛根素、3’-羟基葛根素、大豆苷元,分别占结合态酚含量的29.07%、24.34%及22.15%,是粉葛皮结合酚中主要的三种酚类物质。粉葛渣发酵产物提取液中葛根素、大豆苷元,分别占结合态酚含量的39.79%及9.62%,是粉葛渣结合酚中主要的两种酚类物质。已有研究表明[37]葛根中的酚类主要有葛根素、3’-羟基葛根素、大豆苷元、3-甲氧基葛根素和大豆苷等,且葛根素为粉葛中主要酚类物质,与本实验结果一致。
表 1 酚酸标准曲线Table 1. Standard curves of phenolic acid标准品名称 出峰时间(min) 标准曲线方程 3’-羟基葛根素 8.933 Y=60756X−118473,R2=0.999 对羟基苯甲酸 11.168 Y=86084X−9549,R2=0.999 葛根素 12.283 Y=75468X−5471,R2=0.999 大豆苷元 25.282 Y=75468X−5471,R2=0.999 表 2 两种粉葛加工副产物固态发酵后释放的主要结合酚Table 2. Main bound phenols released by solid state fermentation of two by-products of Pueraria thomsonii样品 3’-羟基葛根素(μg/g) 对羟基苯甲酸(μg/g) 葛根素(μg/g) 大豆苷元(μg/g) 粉葛皮 397.42±6.76 47.99±0.62 474.75±4.25 361.69±4.11 粉葛渣 / 24.93±0.13 370.03±3.21 89.47±0.93 2.6 发酵产物提取液的抗氧化活性
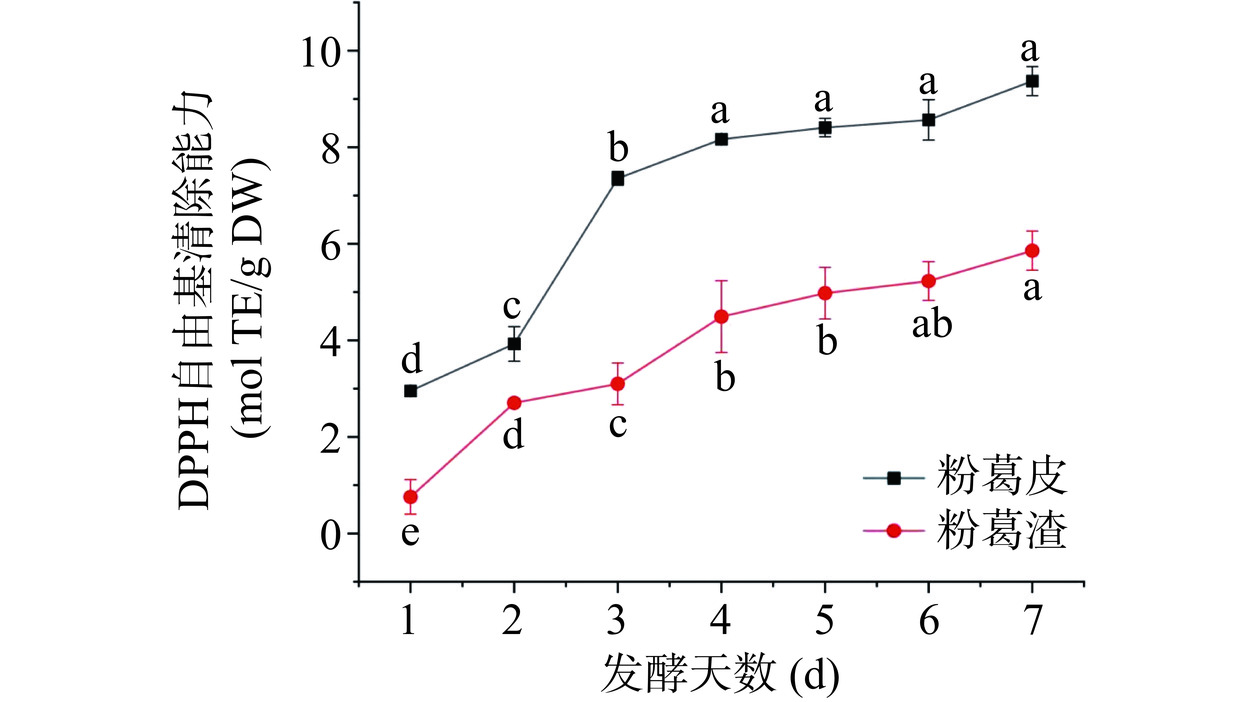
2.6.1 DPPH自由基清除能力
黑曲霉固态发酵过程中粉葛加工副产物提取液DPPH·清除能力变化见图7。粉葛加工副产物经发酵后,抗氧化能力得到显著提高。随着发酵进程的进行,粉葛渣与粉葛皮DPPH·清除能力分别由0.76±0.39(mol TE/g DW)和2.95±0.03(mol TE/g DW)提升至5.86±0.41(mol TE/g DW)和9.37±0.30 (mol TE/g DW)。粉葛皮发酵产物提取液DPPH·清除能力始终高于粉葛渣发酵产物提取液,与Wei等[38]研究结果一致。Fu等[39]同样发现杜仲叶提取过程中随着结合态酚含量的增加,其抗氧化活性显著增强,两者变化密切相关。王懿文等[16]使用黑曲霉发酵金银花,随着发酵天数的增加结合态酚含量由76.60 mg/g增加到95.09 mg/g,DPPH自由基清除率由61.25%稳定提升至84.57%。粉葛加工副产物结合态酚含量与抗氧化活性变化也呈正相关关系。
2.6.2 ABTS+自由基清除能力
如图8所示,副产物粉葛渣及粉葛皮发酵产物提取液有较强的ABTS+·清除能力,且随着发酵天数的增加,发酵产物提取液对ABTS+·清除能力逐渐增强。粉葛皮与粉葛渣ABTS+自由基清除能力分别由2.46±0.04(mol TE/g DW)和0.81±0.11(mol TE/g DW)提升至4.56±0.15(mol TE/g DW)和2.66±0.14(mol TE/g DW)。粉葛皮发酵产物提取液ABTS+自由基清除能力同样始终强于粉葛渣发酵产物提取液,与结合态酚含量趋势一致。Leónmedina等[40]通过黑曲霉固态发酵辅助提取卡斯蒂亚玫瑰中的多酚,并用ABTS法对提取的化合物进行抗氧化活性评价,发现抑制率达94.34%。Xi等[41]发现在黑曲霉发酵的蓝莓果渣中,所有花青素均呈上升趋势,且经固态发酵后蓝莓果渣ABTS+自由基清除率提高了33.56%,均表明抗氧化活性与结合态酚含量密切相关。
酚类物质抗氧化能力取决于酚类化合物的化学结构、羟基的数量、位置以及羟基结构糖基化,同时多酚的疏水性、溶解度都会对最终结果造成一定影响[42]。通过微生物发酵过程中产生的复合酶系的水解作用,粉葛加工副产物中的酚类物质与其他物质之间的共价作用或非共价作用解除,使其中的酚类物质,如对羟基苯甲酸、3’-羟基葛根素、葛根素、大豆苷向游离态转化,增加了可利用的酚类物质含量,特别是3’-羟基葛根素已被证实为具有高抗氧化能力,其抗氧化能力甚至优于维生素C[43]。此外,在复合酶系的水解作用下,糖苷分子去糖基化降解为苷元,有研究表明黄酮苷元清除人体氧自由基的生物活性明显优于黄酮糖苷[44]。这也为黑曲霉发酵提高粉葛加工副产物抗氧化活性提供了依据。
2.7 相关性分析
结合态酚含量、抗氧化能力、酶活力相关性分析结果如图9所示。粉葛皮与粉葛渣中结合态酚含量与纤维素酶活力及葡萄糖苷酶活力显著相关。在粉葛皮中结合态酚类物质含量与纤维素酶、β-葡萄糖苷酶活力的相关系数分别为0.87和0.90,粉葛渣中结合态酚类物质含量与纤维素酶、β-葡萄糖苷酶活力的相关系数分别为0.96和0.77,表明酶活力越强,越有利于粉葛加工副产物中酚类物质的释放。这与阎欲晓等[21]的研究结果一致。此外,结合态含量与抗氧化能力也呈显著相关。发酵产物提取液作为一种复杂体系,不仅有酚类物质,还包括了多糖、蛋白及其他物质,虽然通常情况下酚类物质被认为是抗氧化能力的主要贡献者,但实际上抗氧化活性还会受到体系中其他物质的影响,因此抗氧化活性的变化与酚类含量变化并不总是一致的,但根据相关性分析可以看出,结合态酚含量和抗氧化活性均随发酵的进行不断增强,且具有显著相关性。这表明发酵后的粉葛加工副产物的抗氧化活性增强主要归因于结合态酚类物质的释放。
3. 结论
本研究通过黑曲霉固态发酵两种粉葛加工副产物粉葛皮及粉葛渣,采用液相色谱法对发酵后发酵产物提取液中释放的结合酚进行含量测定,并对两种粉葛加工副产物抗氧化活性进行测定。结果表明,随着黑曲霉固态发酵两种粉葛加工副产物,其结合酚释放量不断增加。发酵过程中两者结合态酚含量、DPPH自由基清除能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力、纤维素酶活力、β-葡萄糖苷酶活力均显著提高。经固态发酵后粉葛皮中释放出1.63±0.11 mg/g酚类物质,粉葛渣中释放出0.93±0.05 mg/g酚类物质,抗氧化活性显著提升,粉葛渣与粉葛皮发酵产物提取液DPPH自由基清除能力分别达到5.86±0.41(mol TE/g DW)和9.37±0.30(mol TE/g DW),ABTS+自由基清除能力达2.66±0.14(mol TE/g DW)和4.56±0.15(mol TE/g DW)。相关性分析表明,结合态酚含量与酶活力及抗氧化能力呈显著相关(P<0.05),表明黑曲霉固态发酵粉葛渣可有效促进结合态酚类物质的释放,进而提高其抗氧化活性。本研究为葛加工副产物固态发酵及开发利用提供了一定的理论基础和依据。
-
图 4 粉葛加工副产物发酵前后的红外光谱图
注:A.粉葛皮;B.黑曲霉发酵后粉葛皮;C.粉葛渣;D.黑曲霉发酵后粉葛渣;图5同。
Figure 4. Infrared spectrogram of Pueraria thomsonii processing by-products residue before and after solid state fermentation
表 1 酚酸标准曲线
Table 1 Standard curves of phenolic acid
标准品名称 出峰时间(min) 标准曲线方程 3’-羟基葛根素 8.933 Y=60756X−118473,R2=0.999 对羟基苯甲酸 11.168 Y=86084X−9549,R2=0.999 葛根素 12.283 Y=75468X−5471,R2=0.999 大豆苷元 25.282 Y=75468X−5471,R2=0.999 表 2 两种粉葛加工副产物固态发酵后释放的主要结合酚
Table 2 Main bound phenols released by solid state fermentation of two by-products of Pueraria thomsonii
样品 3’-羟基葛根素(μg/g) 对羟基苯甲酸(μg/g) 葛根素(μg/g) 大豆苷元(μg/g) 粉葛皮 397.42±6.76 47.99±0.62 474.75±4.25 361.69±4.11 粉葛渣 / 24.93±0.13 370.03±3.21 89.47±0.93 -
[1] 陈慧, 何绍浪, 王馨悦, 等. 葛渣综合利用研究进展[J]. 江西农业学报,2023,35(9):162−168. [CHEN H, HE S L, WANG X Y, et al. Research progress in comprehensive utilization of Radix pueraria residues[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi,2023,35(9):162−168.] CHEN H, HE S L, WANG X Y, et al. Research progress in comprehensive utilization of Radix pueraria residues[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2023, 35(9): 162−168.
[2] 岳世彦, 周荣荣, 南铁贵, 等. 粉葛与葛根中主要化学成分的含量比较[J]. 中国中药杂志,2022,47(10):2689−2697. [YUE S Y, ZHOU R R, NAN T G, et al. Comparison of major chemical components in Puerariae thomsonii radix and Puerariae lobatae radix[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2022,47(10):2689−2697.] YUE S Y, ZHOU R R, NAN T G, et al. Comparison of major chemical components in Puerariae thomsonii radix and Puerariae lobatae radix[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2022, 47(10): 2689−2697.
[3] HAN X, SONG K, YU H, et al. Extraction and characterisation of kudzu root residue lignin based on deep eutectic solvents[J]. Phytochemical Analysis:PCA,2024,35(4):786−798. doi: 10.1002/pca.3328
[4] WEN C, YU J S, MING C F, et al. Wheat bran, as the resource of dietary fiber:A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2021,62(26):21−28.
[5] NIU Y, FANG H, HUO T, et al. A novel fat replacer composed by gelatin and soluble dietary fibers from black bean coats with its application in meatballs[J]. LWT,2020,122:109000. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.109000
[6] 张帅, 罗静怡, 唐婷范, 等. 固态发酵葛根渣制备葛根素[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,42(12):102−106. [ZHANG S, LUO J Y, TANG T F, et al. Puerarin preparation from Pueraria root residue through solid state fermentation[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,42(12):102−106.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.12.014 ZHANG S, LUO J Y, TANG T F, et al. Puerarin preparation from Pueraria root residue through solid state fermentation[J]. Food Research and Development, 2022, 42(12): 102−106. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.12.014
[7] 杨树平, 韩立军, 朱金卫, 等. 葛渣总黄酮提取及葛根素含量测定[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(14):303−306. [YANG S P, HAN L J, ZHU J W, et al. Optimization of total flavonoids extraction from Radix Puerariae and HPLC determination of puerarin[J]. Food Science,2011,32(14):303−306.] YANG S P, HAN L J, ZHU J W, et al. Optimization of total flavonoids extraction from Radix Puerariae and HPLC determination of puerarin[J]. Food Science, 2011, 32(14): 303−306.
[8] FULGENCIO S. Dietary fiber as a carrier of dietary antioxidants:An essential physiological function[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2011,59(1):43−49. doi: 10.1021/jf1036596
[9] 徐茂. 地榆游离酚与结合酚的提取纯化、抑菌活性及应用研究[D]. 南昌:南昌大学, 2023. [XU M. Study on the extraction, purification, antibacterial activity, andapplication of free phenol and combined phenol from Sanguisorba officinalis L[D]. Nanchang:Nanchang University, 2023.] XU M. Study on the extraction, purification, antibacterial activity, andapplication of free phenol and combined phenol from Sanguisorba officinalis L[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2023.
[10] 王浩毓, 赵惠玲, 李宏全. 马齿苋结合态多酚和自由态多酚抑制肝癌细胞HepG-2增殖及诱导细胞凋亡的研究[J]. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版),2019,39(4):70−78. [WANG H Y, ZHAO H L, LI H Q. The proliferation inhibition and apoptosis effects of bound polyphenol and free polyphenol from Portulaca oleracea L. on human hepatoma cell line HepG-2[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition),2019,39(4):70−78.] WANG H Y, ZHAO H L, LI H Q. The proliferation inhibition and apoptosis effects of bound polyphenol and free polyphenol from Portulaca oleracea L. on human hepatoma cell line HepG-2[J]. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 39(4): 70−78.
[11] 高艳艳, 祝琳琳, 李想, 等. 酸水解和酶水解在多糖研究中的应用进展[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2022,40(5):142−146. [GAO Y Y, ZHU L L, LI X, et al. Application progress of acid hydrolysis and enzyme hydrolysis in study of polysaccharides[J]. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2022,40(5):142−146.] GAO Y Y, ZHU L L, LI X, et al. Application progress of acid hydrolysis and enzyme hydrolysis in study of polysaccharides[J]. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 40(5): 142−146.
[12] TANYAWAN S, KRITTAPORN W, KANOKPHAT A, et al. Protein glycation inhibitory activity and antioxidant capacity of clove extract[J]. Journal of food Science and Technology,2015,52(6):3843−3850.
[13] VINOD K, VIVEK A, SAURABH S, et al. Recent developments on solid-state fermentation for production of microbial secondary metabolites:Challenges and solutions[J]. Bioresource Technology,2020,323:124566.
[14] AJILA M C, GASSARA F, BRAR K S, et al. Polyphenolic antioxidant mobilization in apple pomace by different methods of solid-state fermentation and evaluation of its antioxidant activity[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2012,5(7):2697−2707. doi: 10.1007/s11947-011-0582-y
[15] WANG L, WU Y, LIU Y, et al. Complex enzyme-assisted extraction releases antioxidative phenolic compositions from guava leaves[J]. Molecules,2017,22(10):1648−1648. doi: 10.3390/molecules22101648
[16] 王懿文, 谢纯良, 朱作华, 等. 黑曲霉固态发酵对金银花多酚类物质释放及增效作用[J]. 食品研究与开发,2023,44(22):23−29. [WANG Y W, XIE C L, ZHU Z H, et al. Solid-state fermentation of Lonicerae japonica by Aspergillus niger:Effects on release of polyphenolsand improving function[J]. Food Research and Development,2023,44(22):23−29.] WANG Y W, XIE C L, ZHU Z H, et al. Solid-state fermentation of Lonicerae japonica by Aspergillus niger: Effects on release of polyphenolsand improving function[J]. Food Research and Development, 2023, 44(22): 23−29.
[17] 张熙, 韩双艳. 黑曲霉发酵产酶研究进展[J]. 化学与生物工程,2016,33(1):13−16. [ZHANG X, HAN S Y. Research progress on fermentation production of enzyme by Aspergillus niger[J]. Chemistry Bioengineering,2016,33(1):13−16.] ZHANG X, HAN S Y. Research progress on fermentation production of enzyme by Aspergillus niger[J]. Chemistry Bioengineering, 2016, 33(1): 13−16.
[18] GUI M F, WEN Q C, BIAO D, et al. Effects of Daqu inoculated with Aspergillus niger and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on microbial community, aroma compounds and physicochemical parameters of fermented grains during the brewing process of Chinese special-flavor Baijiu[J]. Journal of The Science of Food and Agriculture,2022,103(1):273−282.
[19] 顿倩. 黑豆膳食纤维结合的多酚构成和微生物代谢规律的研究[D]. 南昌:南昌大学, 2019. [DUN Q. Study on composition and microbial metabolism of bound phenolics binding to dietary fibre of black bean[D]. Nanchang:Nanchang University, 2019.] DUN Q. Study on composition and microbial metabolism of bound phenolics binding to dietary fibre of black bean[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2019.
[20] 王振宇. 莲子结合酚对3T3-L1细胞和肥胖小鼠脂质代谢的影响及作用机制的研究[D]. 福州:福建农林大学, 2019. [WANG Z Y. The effects and mechanism of lotus seeds bound phenolics on lipid metabolism in 3T3-L1 preadiposes and obese mice[D]. Fuzhou:Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2019.] WANG Z Y. The effects and mechanism of lotus seeds bound phenolics on lipid metabolism in 3T3-L1 preadiposes and obese mice[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2019.
[21] 阎欲晓, 粟桂娇, 何勇强. 黑曲霉固态发酵对甘蔗叶酚类物质释放及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(16):110−116. [YAN Y X, SU G J, HE Y Q. Effects of solid-state fermentation with Aspergillus niger on phenolics release and antioxidant activity of sugarcane leaves[J]. Food Science,2020,41(16):110−116.] YAN Y X, SU G J, HE Y Q. Effects of solid-state fermentation with Aspergillus niger on phenolics release and antioxidant activity of sugarcane leaves[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(16): 110−116.
[22] DZUGAN M, TOMCZYK M, SOWA P, et al. Antioxidant activity as biomarker of honey variety[J]. Molecules,2018,23(8):2069−2083. doi: 10.3390/molecules23082069
[23] XUE P Y, LIAO W, CHEN Y, et al. Release characteristic and mechanism of bound polyphenols from insoluble dietary fiber of navel orange peel via mixed solid-state fermentation with Trichoderma reesei and Aspergillus niger[J]. LWT,2022,161:113387−113397. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113387
[24] 邢晨, 王俐娟, 王晓琴. 可食用植物不同形态酚类化合物研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(5):266−275. [XING C, WANG L J, WANG X Q. Recent studies on free and bound phenolic compounds in edible plants:A review[J]. Food Science,2020,41(5):266−275.] XING C, WANG L J, WANG X Q. Recent studies on free and bound phenolic compounds in edible plants: A review[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(5): 266−275.
[25] 李丹青, 范娜. 黑曲霉发酵对麦麸多酚及其抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 商洛学院学报,2016,30(6):48−52. [LI D Q, FAN N. Effect of Aspergillus niger fermentation of polyphenols and antioxidant activity of wheat bran[J]. Journal of Shangluo University,2016,30(6):48−52.] LI D Q, FAN N. Effect of Aspergillus niger fermentation of polyphenols and antioxidant activity of wheat bran[J]. Journal of Shangluo University, 2016, 30(6): 48−52.
[26] 谢欢, 涂宗财, 张露, 等. 黑曲霉发酵制备高可溶性膳食纤维豆渣工艺优化及其水合性质研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2017,32(4):116−121. [XIE H, TU Z C, ZHANG L, et al. Process optimization of preparation of soluble dietary fiber bean dregs by Aspergilus niger and hydration properties[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2017,32(4):116−121.] XIE H, TU Z C, ZHANG L, et al. Process optimization of preparation of soluble dietary fiber bean dregs by Aspergilus niger and hydration properties[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2017, 32(4): 116−121.
[27] 符慧珍, 邓梅, 张名位, 等. 黑曲霉改性葛渣膳食纤维的工艺优化及其理化功能特性[J]. 中国农业科学,2023,56(12):2380−2394. [FU H Z, DENG M, ZHANG M W, et al. The optimal fermentation technique of Radix Puerariae residues by Aspergillus niger for dietary fiber modification and the consequent changes of physicochemical and functional properties of dietary fibers[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2023,56(12):2380−2394.] FU H Z, DENG M, ZHANG M W, et al. The optimal fermentation technique of Radix Puerariae residues by Aspergillus niger for dietary fiber modification and the consequent changes of physicochemical and functional properties of dietary fibers[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2023, 56(12): 2380−2394.
[28] PAMELA C. Renewable resources; reports outline renewable resources findings from metropolitan autonomous university (In vitro digestibility of ultrasound-treated corn starch)[J]. Ecology Environment & Conservation, 2017, 69(9-10).
[29] ACOSTA-ESTRADA A B, GUTIÉRREZ-URIBE A J, SERNA-SALDÍVAR O S. Bound phenolics in foods, a review[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,152:46−55. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.11.093
[30] 许涵婷, 唐语谦, 胡腾根, 等. 荔枝果渣可溶性膳食纤维去结合酚前后结构和功能性质的比较[J]. 现代食品科技,2023,39(8):206−212. [XU H T, TANG Y Q, HU T G, et al. Comparison of the structure and functional properties of soluble dietary fiber from lychee pomace before and after the removal of bound phenolics[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2023,39(8):206−212.] XU H T, TANG Y Q, HU T G, et al. Comparison of the structure and functional properties of soluble dietary fiber from lychee pomace before and after the removal of bound phenolics[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2023, 39(8): 206−212.
[31] 郭天时. 米糖膳食纤维的微粉—酶法改性及其理化功能性质的变化研究[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨商业大学, 2017. [GUO T S. Micronized-enzymatic modification of rice bran dietary fibre and changes of its physicochemical and functional properties[D]. Harbin:Harbin University of Commerce, 2017.] GUO T S. Micronized-enzymatic modification of rice bran dietary fibre and changes of its physicochemical and functional properties[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Commerce, 2017.
[32] EISHEEKH M M, BEDAIWY M Y, EINAGAR A A, et al. Saccharification of pre-treated wheat straw via optimized enzymatic production using Aspergillus niger:Chemical analysis of Lignocellulosic matrix[J]. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation,2023,41(4):309−321. doi: 10.1080/10242422.2022.2087511
[33] 赵一帆, 罗磊, 马潇, 等. 基于黑曲霉固态发酵的绿豆皮降解及理化特性提升机理[J]. 中国粮油学报,2024,39(3):64−70. [ZHAO Y F, LUO L, MA X, et al. The mechanism of mung bean husk degradation and physicochemical characteristics improvement based on Aspergillus niger solid-state fermentation[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2024,39(3):64−70.] ZHAO Y F, LUO L, MA X, et al. The mechanism of mung bean husk degradation and physicochemical characteristics improvement based on Aspergillus niger solid-state fermentation[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2024, 39(3): 64−70.
[34] XU Z, XIONG X, ZENG Q, et al. Alterations in structural and functional properties of insoluble dietary fibers-bound phenolic complexes derived from lychee pulp by alkaline hydrolysis treatment[J]. LWT,2020,127:109335. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109335
[35] RAZGONOVA M P, ZINVHENKO Y N, KOZAK D K, et al. Autofluorescence-based investigation of spatial distribution of phenolic compounds in soybeans using confocal laser microscopy and a high-resolution mass spectrometric approach[J]. Molecules,2022,27(23):8228−8228. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238228
[36] 王胜宇, 杨梅, 胡鹤宇, 等. 粉葛加工副产物中结合态酚类物质的提取工艺优化、组成及抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(17):1−9. [WANG S Y, YANG M, HU H Y, et al. Optimization of extraction process, composition and antioxidant activity analysis of conjugated phenols from the by-product residue of Pueraria thomsonii[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(17):1−9.] WANG S Y, YANG M, HU H Y, et al. Optimization of extraction process, composition and antioxidant activity analysis of conjugated phenols from the by-product residue of Pueraria thomsonii[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(17): 1−9.
[37] 周礼仕, 潘小燕, 邱雯曦, 等. 粉葛与葛根HPLC指纹图谱[J]. 山东化工,2022,51(17):119−122. [ZHOU L S, PAN X Y, QIU W X, et al. Study on HPLC fingerprint of Pueraraiae thomsonii radix and Pueraraiae lobatae radix[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry,2022,51(17):119−122.] ZHOU L S, PAN X Y, QIU W X, et al. Study on HPLC fingerprint of Pueraraiae thomsonii radix and Pueraraiae lobatae radix[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2022, 51(17): 119−122.
[38] WEI Z L, XIAO L Z, XIAO Q H, et al. Effects of steam explosion pretreatment on the composition and biological activities of tartary buckwheat bran phenolics.[J]. Food & Function,2020,11(5):4648−4658.
[39] FU X, CHEN H. Air-steam explosion enhancing the extraction efficiency of chlorogenic acid from leaves of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2015,146:317−325. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2015.03.054
[40] LEÓNMEDINA D C J, SEPÚLVEDA L, MORLETTCHÁVEZ J, et al. Solid-state fermentation with Aspergillus niger GH1 to enhance polyphenolic content and antioxidative activity of Castilla rose (Purshia plicata)[J]. Plants (Basel, Switzerland),2020,9(11):1518−1518.
[41] XI Z T, FU Y L, XIU M L, et al. Effects of six different microbial strains on polyphenol profiles, antioxidant activity, and bioaccessibility of blueberry pomace with solid-state fermentation[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2023,10:1282438. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1282438
[42] JAKOBEK L, MATIĆ P. Non-covalent dietary fiber-polyphenol interactions and their influence on polyphenol bioaccessibility[J]. Trends in Food Science Technology,2018,83:235−83247.
[43] 黄再强, 王甜甜, 马逾英, 等. 基于多指标成分含量与抗氧化活性的葛根类药材质量评价研究[J]. 中草药,2018,49(7):1667−1676. [HUANG Z Q, WANG T T, MA Y Y, et al. Quality evaluation study of Pueraria Radix and Pueraria thomsonii by component contents and anti-oxidant activity[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2018,49(7):1667−1676.] HUANG Z Q, WANG T T, MA Y Y, et al. Quality evaluation study of Pueraria Radix and Pueraria thomsonii by component contents and anti-oxidant activity[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2018, 49(7): 1667−1676.
[44] HEIM E K, TAGLIFERRO R A, BOBILYA J D. Flavonoid antioxidants:Chemistry, metabolism and structure-activity relationships[J]. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2002,13(10):572−584. doi: 10.1016/S0955-2863(02)00208-5
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 刘影,庞富,陈佳鸿,陈炯葵,蔡烁仪. 本草清咽润喉糖的配方优化及抗氧化研究. 农产品加工. 2024(21): 41-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张敏君,段雪伟,王燕,杨慧文,刘冰,向文静,由天辉. 构树根皮活性成分乙醇提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2023(11): 196-203 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 王蕙雯. 豫西自然发酵柿子醋抗氧化性研究. 江苏调味副食品. 2023(03): 20-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 裴文清,吕泸楠,王靖宇,浦思琦,雷霜,王春丽. 木瓜皮多酚和黄酮提取工艺优化及酪氨酸酶与胰脂肪酶抑制活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2022(01): 188-195 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 周新崇,易灿,刘进兵. 微波辅助提取崀山脐橙皮总黄酮及生物活性研究. 邵阳学院学报(自然科学版). 2022(02): 87-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张清月,董姝慧,李胤豪,赵艳丽,史彬林,闫素梅. 诺丽果不同提取物抗氧化能力的比较研究. 中国粮油学报. 2022(05): 144-150 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 关随霞,王蕙雯,杨肖瑞,郭淑敏,张翅,张培杰,李道敏. 大青叶总黄酮提取工艺优化及抗氧化性研究. 中国食品添加剂. 2022(09): 138-144 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 陈慧玲,刘芳,钟恒勤,王伟枫. 超声波辅助乙醇提取百香果皮黄酮的工艺优化及黄酮抗氧化性测定. 宁德师范学院学报(自然科学版). 2022(03): 280-287 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 任海云,韩瑞,张磊. 基于Box-Behnken响应面法优化党参抗氧化活性组分提取工艺. 中医药信息. 2022(12): 5-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 赵雨晴,王宝庆,徐汉,刘楠楠. 醉鱼草总黄酮的提取及抗氧化活性研究. 化学试剂. 2021(07): 979-985 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 杨青青,龚吉军. 响应面法优化超声辅助葛根浸提工艺及浸提液抗氧化活性研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2021(13): 5409-5417 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)






 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



