Gel Formation Mechanism of κ-Carrageenan in Co-solute Field and Its Application in 3D Printing
-
摘要: κ-卡拉胶因其优异的胶凝能力而被广泛用于食品行业中。共溶质场是指蛋白或多糖等高分子材料溶胶-凝胶转变时所处的环境不是仅含高分子组分的水溶液环境,同时溶液中还含有蔗糖、乳化剂、多元醇等单一或多种小分子共溶物(即共溶质)。共溶质对κ-卡拉胶的凝胶化进程有重要影响,其相关作用机制包含以下三种假说:共溶质引起“水的结构化”、高分子对共溶质的“排离效应”、共溶质与高分子的“结合效应”,但目前尚没有统一的结论。此外,本文还综述了κ-卡拉胶在3D打印食品中的应用,包括κ-卡拉胶作为3D打印用凝胶基质材料、以及κ-卡拉胶作为添加剂以调控不同食材体系的3D打印特性。Abstract: κ-Carrageenan is widely used in the food industry due to its excellent gelling ability. The co-solute field refers to the environment in which the sol-gel transformation of polymer materials, such as proteins or polysaccharides, occurs. This environment is not a simple aqueous solution containing only polymer components, it also includes one or more small molecule co-solutes such as sucrose, emulsifiers, and polyols. Co-solutes significantly impact the gelation process of κ-carrageenan. Three main hypotheses explain this mechanism: The ''structure of water" effect induced by co-solutes, the "expulsion effect" of polymers on co-solutes, and the "binding effect" between co-solutes and polymers. However, there is no unified conclusion yet. Additionally, this article reviews the application of κ-carrageenan in 3D printed food, including its use as a gel matrix material for 3D printing and as an additive to regulate the 3D printing characteristics of different food systems.
-
Keywords:
- κ-carrageenan /
- co-solute /
- gel formation mechanism /
- 3D printing
-
卡拉胶通常是从角叉菜、麒麟菜、杉藻及沙菜等多种红藻中提取的一种天然硫酸盐线性多糖[1]。它是由β-D-半乳糖与3,6-内醚-α-D-半乳糖交替连接形成线形高分子聚合物,其硫酸基团含量为15%~40%,平均分子量通常在100 kDa以上[2]。根据硫酸基团的数量和位置的不同,卡拉胶可分为:κ-卡拉胶、ι-卡拉胶、λ-卡拉胶、θ-卡拉胶、υ-卡拉胶、ζ-卡拉胶、γ-卡拉胶等七种类型[3−4]。目前食品工业上使用较为广泛的卡拉胶主要有三种:κ-(Kappa)型、ι-(Iota)型和λ-(Lamda)型[5],其中κ-卡拉胶具有优异的增稠性能、可逆的溶胶-凝胶转变特性、以及调节质构、改善口感等多重作用,在食品工业中应用最为广泛,是凝胶态食品的重要胶基[6]。
通常情况下,食品体系是多种物质共存的复杂体系。共溶质场指食品蛋白或多糖高分子溶胶-凝胶转变过程所处的环境并非仅含高分子组分的水溶液环境,同时存在小分子糖[7]、多元醇[8]、氨基酸[9]等单一或多元小分子共溶质,共溶质的分子量虽远小于蛋白或多糖分子质量,但可改变蛋白或多糖高分子在溶液中的折叠和缠结,并影响到溶胶-凝胶转变过程的相行为、流变性质和微观结构形成,进而影响到产品的质构或风味等品质特性[10]。因此,深入理解共溶质对κ-卡拉胶凝胶形成的影响及调控机制,对实现κ-卡拉胶凝胶基质食品物性的精准调控有重要意义,但目前这方面的综述还未见报道。
此外,κ-卡拉胶具有优异的凝胶特性,在食品3D打印领域应用广泛,其主要应用于两个方面:一是作为3D打印凝胶基质食品的原料;二是作为添加剂调控食品的3D打印特性和产品品质。小分子共溶质在食品3D打印过程中对κ-卡拉胶的溶胶-凝胶转变及打印品质具有重要影响,但目前这方面的研究还非常少。
总体而言,本文首先论述了共溶质对κ-卡拉胶溶胶-凝胶转变过程及凝胶特性的影响机制。随后,进一步讨论了κ-卡拉胶在食品3D打印中的影响及其调控特性。该文可对深入理解共溶质场中κ-卡拉胶的凝胶形成机制及其在食品3D打印领域的应用提供参考。
1. κ-卡拉胶及其凝胶机制
1.1 κ-卡拉胶的结构与特性
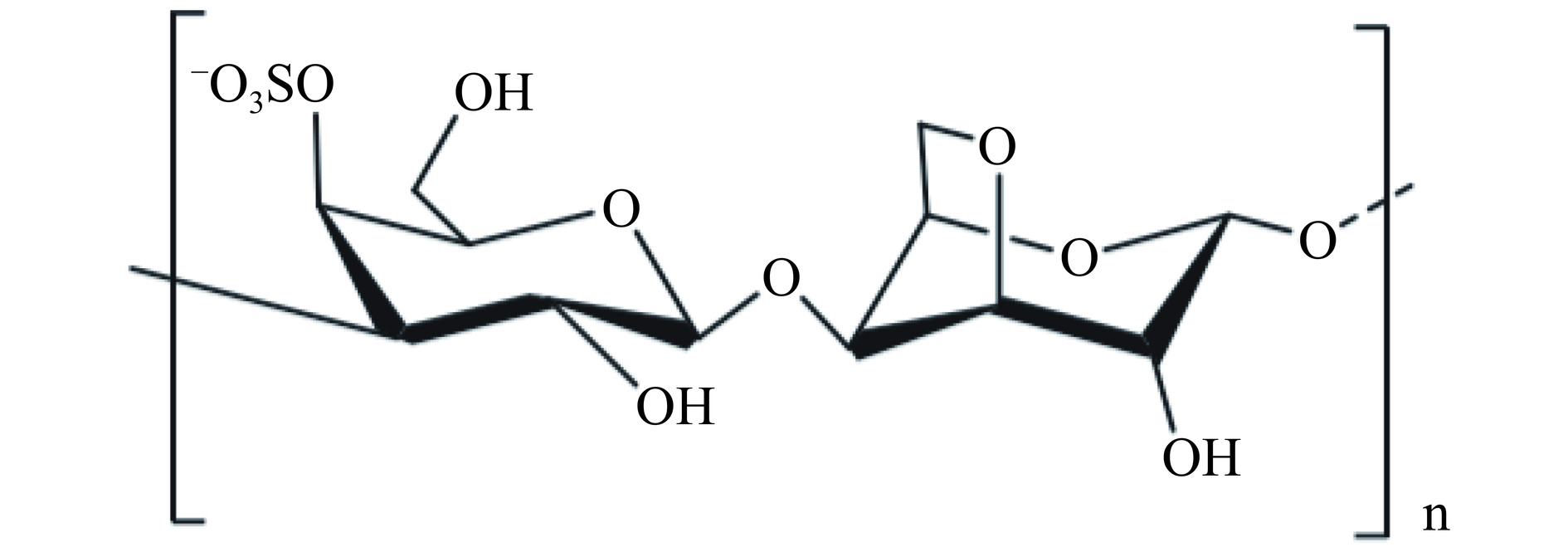
κ-卡拉胶是一种热可逆凝胶,由重复的α(1→3)-D-半乳糖-4-硫酸盐和β(1→4)-3,6-脱水-D-半乳糖二糖单元所组成(图1)[11],其凝胶特性主要与其化学组成、结构和分子大小密切相关。κ-卡拉胶还具有优良的物理性质,如亲和性、高分散性、持水性及独特的抗蛋白凝聚性等[12]。κ-卡拉胶在食品工业中应用广泛,可作为增稠剂、悬浮剂、乳化剂和稳定剂添加于乳制品、饮料、糖果、冰激凌及肉制品中[13−15]。然而,尽管κ-卡拉胶单独使用即可形成凝胶,且表现出良好的凝胶性能,但仍存在脆性大、弹性小的缺点[16]。此外,它对钾离子较为敏感,因此其凝胶性能容易受其影响。
1.2 κ-卡拉胶的凝胶机理分析
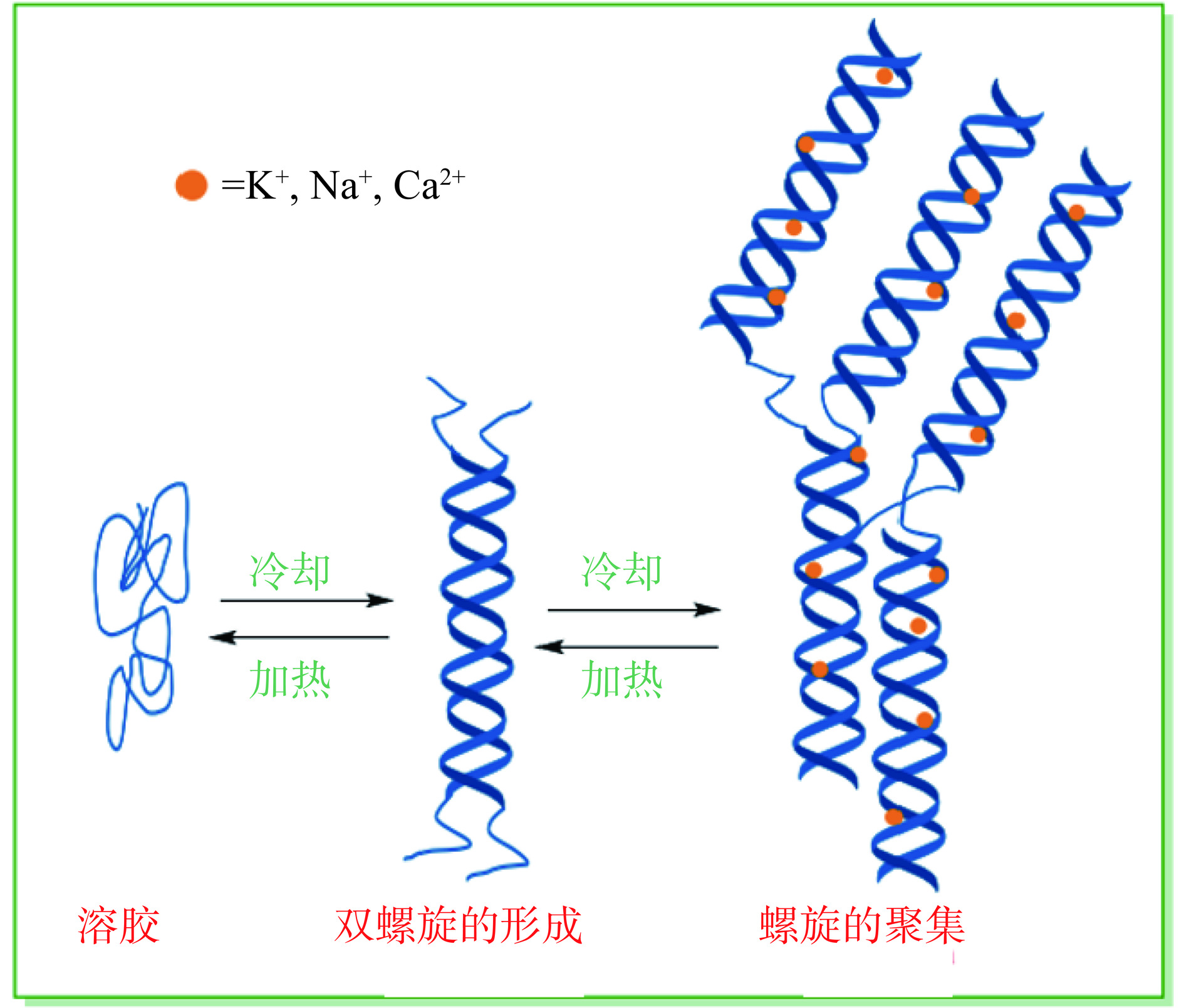
κ-卡拉胶分子链在水溶液中主要存在两种构象:双螺旋结构(有序状态)和无规则线团(无序状态)[17]。目前,普遍接受的κ-卡拉胶的凝胶机理是“二步”形成机理,形成过程分两步进行:第一步从无规则线团形成螺旋,第二步指螺旋聚集并形成凝胶。即在凝胶形成过程中,较高温度下κ-卡拉胶分子在水溶液中以无规则线团的形式存在,当冷却至某一温度时,无规则线团逐渐聚集形成单螺旋,然后单螺旋随之缔合为双螺旋,双螺旋再聚集并与水形成具有一定形态和硬度的凝胶;升温则发生可逆过程,加热到一定温度后凝胶结构破坏,有序的三维网络结构又逐渐变回无规则线团结构,并形成溶胶(图2)[18−20]。
κ-卡拉胶的凝胶化除受温度影响外,还受阳离子(如K+、Na+、Ca2+)、小分子糖和多元醇等共溶质的影响[21]。κ-卡拉胶作为一种阴离子多糖,对阳离子非常敏感,在无阳离子存在的条件下,κ-卡拉胶不能形成凝胶,而且不同阳离子对κ-卡拉胶凝胶强度产生不同的影响[22]。在一定范围内,κ-卡拉胶的凝胶强度随阳离子浓度增加而增强,且与其他阳离子相比,K+的调控效应更强[23−24]。如有研究报道,由κ-卡拉胶形成的凝胶的储能模量G′随K+浓度的增加而增加,且比其它阳离子影响更为显著,如Ca2+[25−26]。此外,κ-卡拉胶的凝胶特性也会受到糖、糊精、多元醇等共溶质的显著影响,其已被广泛用于调控κ-卡拉胶的凝胶特性及稳定性[11,27]。关于共溶质如何在分子水平影响κ-卡拉胶的凝胶特性将在下一部分进行讨论。
2. 共溶质场中κ-卡拉胶的凝胶形成机制
共溶质场指蛋白或多糖等高分子凝胶形成过程中所处的环境并非是仅含高分子组分的水溶液环境,而是同时存在小分子糖、多元醇、氨基酸等单一或多元小分子共溶质。共溶质的分子量虽远小于蛋白或多糖分子,但可显著影响其凝胶特性、流变行为和热力学特性等[10,28]。目前,关于共溶质如何影响高分子溶胶-凝胶转变的观点主要有以下三种,即共溶质引起“水的结构化”[29]、高分子对共溶质的“排离效应”[30−31]、共溶质与高分子间的“结合效应”[31],具体阐述如下。
2.1 共溶质引起“水的结构化”
“水的结构化”是指小分子共溶质可以增强自身以及高分子周围的水分子之间的氢键网络,从而提升高分子自身的疏水效应并诱发凝聚[29−31]。该观点中的疏水效应被认为是影响高分子溶胶-凝胶转变的主要作用,疏水效应是由于与疏水溶质相邻的水分子之间氢键的增强而引起的熵增驱动的结果。疏水溶质周围水分子间增强的氢键网络会提升高分子间的疏水效应。Nishinari等[32]通过差示扫描量热法(DSC)分析不同糖对κ-卡拉胶凝胶热性能的影响,发现卡拉胶的融化温度随添加糖的增加而提高,主要因素是水的结构化或糖与κ-卡拉胶的羟基之间的相互作用。Oakenfull[33]通过计算机模拟表明糖的加入改变了糖自身周围水分子间的氢键网络,同时也改变了高分子之间的疏水相互作用,且认为糖对周围水分子状态的影响是控制高分子凝胶化的主要因素。
2.2 高分子对共溶质的“排离效应”
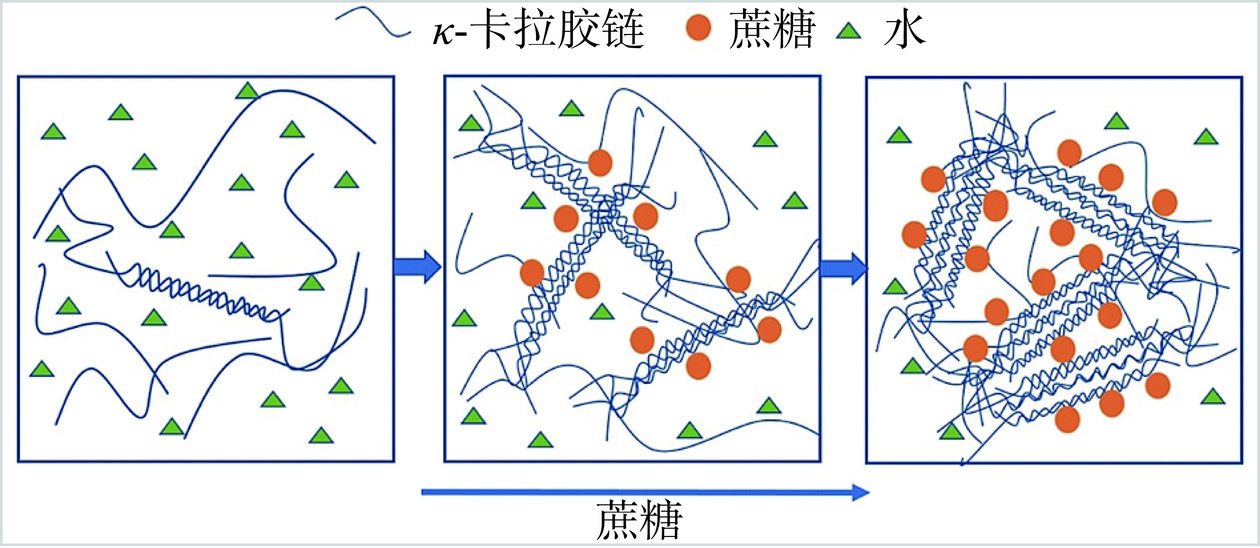
该观点认为高度水合的共溶质被排离高分子周围,因此减少了高分子周围水分子的数量,间接提高了高分子的浓度并促进其凝聚[30−31]。Shimizu等[30]认为促进凝胶化的是高分子对共溶质的排离,而不是高分子周围水的结构化。Russ等[34]发现,添加蔗糖/海藻糖可提升琼脂糖-黄原胶/海藻酸钠复合体系的凝胶化温度,这是因为小分子糖的加入会通过与多糖高分子之间竞争结合水分子,间接提高了高分子浓度,从而增加了凝胶形成的可能性。Yang等[35]表明蔗糖的加入提高了κ-卡拉胶的凝胶化温度和熔融温度,这与蔗糖在水溶液中的高度水合作用有关,高度的水合效应驱使蔗糖分子远离卡拉胶分子,使得卡拉胶周围的水分子含量降低,间接提升了卡拉胶浓度并促进凝胶形成(见图3)。Huang等[36]发现加入到κ-卡拉胶溶液中的木糖醇和麦芽糖醇在水相中具有高度水合作用,多元醇的加入降低了κ-卡拉胶链周围的平均水分子数量,从而提高了凝胶化温度,且随着木糖醇和麦芽糖醇浓度的增加,κ-卡拉胶的复合模量G*值增加,弛豫指数降低,这表明多元醇的加入改善了κ-卡拉胶的凝胶网络。此外,Yang等[37]研究了添加乙醇对κ-卡拉胶凝胶性能的影响,发现由于乙醇在水相中的高度水合作用会间接将水分子从κ-卡拉胶分子的周围排离,导致κ-卡拉胶分子周围的水分子的数量减少,间接提升了κ-卡拉胶浓度。与糖和多元醇不同,环糊精是环状低聚糖,研究表明环糊精对κ-卡拉胶凝胶形成的影响主要发生在溶胶状态:一是在溶胶状态下,环糊精与水分子的结合效应会导致卡拉胶周围水的浓度下降;二是环糊精会对溶胶态下κ-卡拉胶的分子重排产生影响,促进卡拉胶分子间螺旋结构的形成,并最终形成三维网络结构[38]。基于以上讨论可知,由于共溶质优异的水合能力,它们在溶液状态下会优先与水分子结合并远离高分子周围,从而间接导致高分子周围水分子浓度的下降,最终促进高分子间的结合和凝胶网络的形成。
2.3 共溶质与高分子间的“结合效应”
共溶质与高分子间的“结合效应”是指在凝胶过程中,共溶质分子会与高分子通过羟基产生氢键相互作用,促进凝胶形成[31]。在凝胶状态下,高分子与小分子共溶质结合是影响共溶质诱导的高分子凝胶化的重要因素。研究发现,蔗糖和κ-卡拉胶分子通过羟基产生氢键相互作用,促进凝胶形成,使得κ-卡拉胶凝胶网络强度和稳定性都得到了显著改善[35]。Liu等[39]通过宽带介电光谱研究葡萄糖诱导κ-卡拉胶的凝胶化,结果表明葡萄糖虽不会影响溶胶态下κ-卡拉胶的分子构象,但会影响其凝胶态下的分子构象;而在凝胶状态下,葡萄糖分子通过氢键与κ-卡拉胶分子结合,并影响凝胶特性。任艳艳[40]认为魔芋葡甘聚糖与κ-卡拉胶的协同增效机理是在升温过程中,魔芋葡甘聚糖分子链展开,κ-卡拉胶暴露的半酯式硫酸基与魔芋葡甘聚糖分子链上的羟基形成氢键相互作用,当温度降低时,魔芋葡甘聚糖与κ-卡拉胶之间形成大量的结合位点,促进三维网络结构的形成。另有研究发现,乙醇的羟基基团和κ-卡拉胶分子之间可形成氢键,促进κ-卡拉胶凝胶的形成,随着乙醇浓度的增加,κ-卡拉胶会发生更多的自结合和螺旋转变,形成大的连接或聚集体,从而形成更致密、更坚固的凝胶网络[37]。多元醇同样可与κ-卡拉胶之间通过氢键发生相互作用,且麦芽糖醇对κ-卡拉胶的影响比木糖醇更强,这是因为麦芽糖醇中所含羟基基团更多[35]。此外,环糊精可与凝胶状态的κ-卡拉胶通过氢键结合,提高凝胶强度和稳定性,由于环糊精的特殊结构,其对κ-卡拉胶的凝胶性质和稳定性的影响大于糖[38]。Yuan等[41]发现功能性糊精与κ-卡拉胶通过羟基相互作用形成氢键,从而促进凝胶形成,且加入糊精后κ-卡拉胶凝胶强度增强、结构更均匀。以上研究表明,共溶质的加入可促进κ-卡拉胶分子的聚集,并通过与其形成氢键相互作用增强凝胶强度和稳定性。
总体而言,关于共溶质如何影响κ-卡拉胶的溶胶-凝胶转变以及相应的凝胶特性方面并没有统一的结论,何种效应占据主导作用、不同效应之间是否有协同作用以及如何协同等方面都尚不清楚,需要进一步深入研究,以实现基于共溶质调控的κ-卡拉胶凝胶特性的分子设计及调控。
3. κ-卡拉胶在3D打印食品中的应用
食品3D打印是一种新兴的食品制造技术,可以生产复杂和定制化的食物,近年来越来越受到人们的关注[42]。挤出型3D打印技术具有适用范围广、成本低、易操作等优点,目前在食品领域应用最为广泛[43]。用于挤出3D打印的食品材料应具有适当的流变特性,使食品材料易于从喷嘴中挤出,且还必须具有足够的机械强度,以最大限度地减少打印后的变形[44]。但受限于大多数天然食品材料打印性能差,材料体系多样,物料性质会显著影响3D打印效果。为提高3D打印食材的适印性和稳定性,保证食品材料能够顺利挤出,并在3D打印后保持形状,通常会添加一些食品添加剂以改善物料的流变特性和加工特性[45]。κ-卡拉胶因优异的增稠、冷固化、热可逆和剪切稀化性能而在食品3D打印领域应用广泛[46]。根据κ-卡拉胶在调控3D打印材料特性方面所起作用的不同,可分为以下两类:即κ-卡拉胶作为凝胶基质和κ-卡拉胶作为添加剂。
3.1 κ-卡拉胶作为凝胶基质在3D打印食品中的应用
κ-卡拉胶通常表现出剪切稀化行为的非牛顿流体特征,且由于κ-卡拉胶是一种热可逆凝胶,在较高的温度下往往呈现溶胶状态,具有很好的流动性以保证3D打印的顺利挤出,同时在温度降低时会发生凝胶化使材料的机械性能上升以提高3D打印的成型性和结构稳定性,因此具有良好的可打印性,常被用作凝胶食品的胶基[47−48]。κ-卡拉胶凝胶食品通常在3D打印过程中会经历溶胶-凝胶转变,这一特性不仅影响油墨的可打印性(即油墨从喷嘴尖端挤出的能力),还决定了食品油墨的自支撑性以及印刷后形状的稳定性,而共溶质会影响其溶胶-凝胶转变特性,进而影响3D打印性能和产品的质量[48]。
由于κ-卡拉胶在食品中单独使用可能导致凝胶食品出现脆性增加、弹性小、易析水等缺陷[49],因此通常在κ-卡拉胶体系中加入小分子糖类、氨基酸、多元醇等共溶质改善κ-卡拉胶的凝胶特性,或将其与蛋白质、其他水胶体(如黄原胶和明胶)等进行协同复配以提升凝胶机械性能、减少析水,从而确保实现成功的3D打印。如Zhu等[50]通过在挤出、形成和自支撑阶段揭示了基于果糖影响下的κ-卡拉胶溶胶-凝胶转变与3D打印性能的相关性(图4),果糖的加入促进κ-卡拉胶溶胶-凝胶转变,原因是果糖共溶质被排离κ-卡拉胶的周围,导致κ-卡拉胶周围水分子数量减少,从而促进κ-卡拉胶链之间的聚集,其次是果糖通过与κ-卡拉胶分子之间的交联氢键结合以促进凝胶的形成;并且添加果糖后,κ-卡拉胶的凝胶时间缩短,G′增加,有助于油墨在挤出后的迅速固化,同时提高了打印结构的自支撑机械强度。Avallone等[51]表明κ-卡拉胶凝胶强度随黄原胶浓度呈指数级增加,两种网络之间存在协同作用,且蔗糖共溶质能够通过氢键与κ-卡拉胶结合,从而促进κ-卡拉胶螺旋在κ-卡拉胶/黄原胶和糖的三元水溶液中的形成和聚集,高糖浓度可以提高凝胶的打印适应性和形状保真度。
总体来看,共溶质的加入可调控κ-卡拉胶的溶胶-凝胶转变特性以及3D打印品质,加快3D打印挤出后的凝胶化速率,提升打印结构的稳定性。但目前这方面的研究还非常少,对于共溶质通过何种效应来影响κ-卡拉胶3D打印特性的机理研究尚不清楚。此外,关于共溶质对高分子凝胶机理的研究都是基于传统的凝胶制备过程,而3D打印过程中物料会经历复杂的剪切、压力、温度等物理场变化,这很可能会对共溶质场中高分子的凝胶机理产生影响,然而研究者对此关注较少。因此,在3D打印过程中,共溶质对κ-卡拉胶凝胶机理还需进一步深入研究,以拓展κ-卡拉胶在3D打印领域的应用。
3.2 κ-卡拉胶作为添加剂调控食品3D打印特性
κ-卡拉胶通常会被添加到一些无明显温度响应特性浆状食品材料(如果蔬、鱼糜、肉糜凝胶体系)中以调节物料的流变特性或温度响应特性,并进而提高3D打印的成型性和结构稳定性[52]。κ-卡拉胶的胶凝性可以使豌豆、胡萝卜和白菜等蔬菜泥的微观结构更致密,同时添加κ-卡拉胶使油墨屈服应力显著增加,可以更好地保持打印结构的形状,改善其3D打印性能[53]。κ-卡拉胶有助于增加土豆泥的表观粘度和G′,原因是添加κ-卡拉胶的土豆泥形成了更强的氢键以维持其网络结构,使物料具有优异的适印性和良好的机械强度,从而获得良好的自支撑性能[54]。据报道,添加κ-卡拉胶可促进复合鱼糜中的蛋白质分子在3D打印和固化过程中与水分子和其他蛋白质形成交联,形成均匀紧凑的凝胶网络,从而产生更优良的凝胶强度、质构特性和持水性,并减少了蒸煮损失,且κ-卡拉胶以最佳量1.5wt%加入时,3D打印样品的机械强度、一致性、成型性和保形性均达到最佳[55]。另有研究发现,增加κ-卡拉胶的浓度可显著提高猪肉糜的屈服应力、粘度和剪切应力,在添加κ-卡拉胶的样品中,蛋白质和κ-卡拉胶能够通过静电相互作用形成凝胶状结构,进而增强猪肉糜的稳定性,改善猪肉糜的流变性能和3D打印性能[56]。
此外,使用含有κ-卡拉胶的浓缩橙汁、小麦淀粉共混物打印的物体对目标几何形状具有最大的保真度和良好的承载能力,添加κ-卡拉胶显著提高了凝胶强度和弹性性能,这可能是因为κ-卡拉胶能够与淀粉分子相互作用[57]。适量的κ-卡拉胶还可以促使淀粉体系在打印时固化,且随着胶体含量的增多可加快固化速度和增强固化强度,打印产品形成良好的空心结构,且卡拉胶固化性能优于结冷胶[58]。最近,有研究发现κ-卡拉胶和L-赖氨酸对黄桃凝胶3D打印性能具有协同作用,黄桃中含有一定量的果糖,果糖分子通过分子间氢键与κ-卡拉胶分子连接,从而使凝胶更稳定、更具支撑性,同时L-赖氨酸作为一种小分子共溶质,可能通过与κ-卡拉胶结合产生更多的氢键,从而增加黄桃凝胶的弹性并降低凝胶内部粘性,提高最大挤出压力和3D打印精度[59]。
由此可见,利用κ-卡拉胶的凝胶性对制造加工可食性凝胶食品至关重要,如图5是添加κ-卡拉胶3D打印的样品。在3D打印过程中,共溶质的存在会引起κ-卡拉胶溶胶-凝胶转变,从而间接影响食品3D打印性能。然而,目前关于κ-卡拉胶作为食品3D打印添加剂时,共溶质与κ-卡拉胶之间协同作用的研究还非常有限。
4. 结论与展望
本文综述了共溶质对κ-卡拉胶溶胶-凝胶转变及凝胶特性的影响,主要有以下三种观点,即共溶质引起“水的结构化”、高分子对共溶质的“排离效应”、共溶质与高分子间的“结合效应”。然而,目前对于这些效应的具体作用机制仍存在争议,特别是尚不明确哪种效应起主导作用以及三种效应之间是否存在协同作用,需要进一步深入研究,以实现基于共溶质调控的κ-卡拉胶凝胶特性的分子设计。
此外,κ-卡拉胶由于其优异的增稠特性、成胶特性、热可逆及剪切稀化等特性在3D打印食品领域应用广泛,其中共溶质的存在会显著影响κ-卡拉胶的溶胶-凝胶特性,而目前关于这些共溶质在分子水平上如何增强凝胶化的研究仍然十分欠缺。且尚没有学者深入研究共溶质在3D打印过程中剪切、压力、温度等多因素协同作用下对κ-卡拉胶凝胶特性的调控效应及机理,亟需进一步深入研究。
-
-
[1] GEONZON L C, DESCALLAR F B A, DU L, et al. Gelation mechanism and network structure in gels of carrageenans and their mixtures viewed at different length scales-A review[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,108:106039. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106039
[2] DONG Y, WEI Z H, XUE C H. Recent advances in carrageenan-based delivery systems for bioactive ingredients:A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,112:348−361.
[3] 尚旭珂, 朱斯亮, 郑宝东, 等. 体外模拟消化环境中消化酶对κ-卡拉胶/酪蛋白复合体系流变学特性及微观结构的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(4):33−41. [SHANG X K, ZHU S L, ZHENG B D, et al. Effects of digestive enzymes on rheological properties and microstructure of κ-carrageenan/casein composite systems in vitro simulated digestion environment[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(4):33−41.] SHANG X K, ZHU S L, ZHENG B D, et al. Effects of digestive enzymes on rheological properties and microstructure of κ-carrageenan/casein composite systems in vitro simulated digestion environment[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(4): 33−41.
[4] YUAN C, DU L, ZHANG G J, et al. Influence of cyclodextrins on texture behavior and freeze-thaw stability of kappa-carrageenan gel[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,210:600−605. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.05.014
[5] GEONZON L C, ZHUANG X, SANTOYA A M, et al. Gelation mechanism and network structure of mixed kappa carrageenan/lambda carrageenan gels studied by macroscopic and microscopic observation methods[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,105:105759. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105759
[6] 徐东彦. 环糊精对卡拉胶/魔芋胶复配凝胶凝胶特性的影响及应用[D]. 济南:齐鲁工业大学, 2019. [XU D Y. Effect of cyclodextrins on the gelling properties of carrageenan/konjac glucommanan and its applications[D]. Jinan:Qilu University of Technology, 2019.] XU D Y. Effect of cyclodextrins on the gelling properties of carrageenan/konjac glucommanan and its applications[D]. Jinan: Qilu University of Technology, 2019.
[7] YANG D Y, GAO S A, YANG H S. Effects of sucrose addition on the rheology and structure of iota-carrageenan[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,99:105317. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105317
[8] BAYDIN T, AARSTAD O A, DILLE M J, et al. Long-term storage stability of type A and type B gelatin gels:The effect of Bloom strength and co-solutes[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,127:107535. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107535
[9] WEN C R, WANG N, DONG Y Y, et al. Calcium-induced-gel properties for L-carrageenan in the presence of different charged amino acids[J]. LWT,2021,146:111418. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111418
[10] 朱建华, 邹秀容, 刘日斌, 等. 超声对蔗糖共溶质场中大豆分离蛋白/魔芋胶共混体系流变及凝胶性质的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2019,34(9):46−52. [ZHU J H, ZOU X R, LIU R B, et al. Effects of ultrasonication on the rheological and gel properties of soybeanlsolated protein/konjac gum blend under sucrose cosolute environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Grain and Oil,2019,34(9):46−52.] ZHU J H, ZOU X R, LIU R B, et al. Effects of ultrasonication on the rheological and gel properties of soybeanlsolated protein/konjac gum blend under sucrose cosolute environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Grain and Oil, 2019, 34(9): 46−52.
[11] 王艳丽, 刘亚伟, 袁超, 等. 肉桂精油/羟丙基-β-环糊精包合物对κ-卡拉胶质构和流变特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(20):61−65. [WANG Y L, LIU Y W, YUAN C, et al. Influence of cinnamon essential oil/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex on texture and rheological properties of к-carrageenan[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(20):61−65.] WANG Y L, LIU Y W, YUAN C, et al. Influence of cinnamon essential oil/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex on texture and rheological properties of к-carrageenan[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(20): 61−65.
[12] 桑璐媛, 袁超, 刘亚伟, 等. 不同盐离子对κ-卡拉胶凝胶质构及流变学性质的影响[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2017(2):65−69. [SANG L Y, YUAN C, LIU Y W, et al. Effect of various salt ions on gel texture and rheological properties of kappa-carrageenan[J]. China Food Additives,2017(2):65−69.] SANG L Y, YUAN C, LIU Y W, et al. Effect of various salt ions on gel texture and rheological properties of kappa-carrageenan[J]. China Food Additives, 2017(2): 65−69.
[13] 李鑫江, 赵善贞, 何启煜, 等. κ-卡拉胶的高温高压法降解工艺和降解机制研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(13):4242−4249. [LI X J, ZHAO S Z, HE Q Y, et al. Study on the degradation process and degradation mechanism of κ-carrageenan by high temperature and high pressure method[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022,13(13):4242−4249.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.13.spaqzljcjs202213022 LI X J, ZHAO S Z, HE Q Y, et al. Study on the degradation process and degradation mechanism of κ-carrageenan by high temperature and high pressure method[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2022, 13(13): 4242−4249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.13.spaqzljcjs202213022
[14] RUPERT R, RODRIGUES K F, THIEN V Y, et al. Carrageenan from Kappaphycus alvarezii (Rhodophyta, Solieriaceae):Metabolism, structure, production, and application[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2022,13:859635. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.859635
[15] PRADHAN B, KI J S. Biological activity of algal derived carrageenan:A comprehensive review in light of human health and disease[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2023,238:124085. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124085
[16] 桑璐媛. 环糊精对κ-卡拉胶凝胶特性的影响及其应用研究[D]. 郑州:河南工业大学, 2018. [SANG L Y. Influence of cyclodextrins on the gel properties of κ-carrageenan and its applications[D]. Zhengzhou:Henan University of Technology, 2018.] SANG L Y. Influence of cyclodextrins on the gel properties of κ-carrageenan and its applications[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2018.
[17] 张建丰. κ-卡拉胶基功能性水凝胶的构建[D]. 太原:中北大学, 2023. [ZHANG J F. Construction of κ-carrageenan based functional hydrogel[D]. Taiyuan:North University of China, 2023.] ZHANG J F. Construction of κ-carrageenan based functional hydrogel[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2023.
[18] LIU S J, CHAN W L, LI L. Rheological properties and scaling laws of κ-carrageenan in aqueous solution[J]. Macromolecules,2015,48(20):7649−7657. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.5b01922
[19] LIU S J, HUANG S, LI L. Thermoreversible gelation and viscoelasticity of κ-carrageenan hydrogels[J]. Journal of Rheology,2016,60(2):203−214. doi: 10.1122/1.4938525
[20] MIRZAEI A, ESMKHANI M, ZALLAGHI M, et al. Biomedical and evironmental applications of carrageenan-based hydrogels:A review[J]. Journal of Polymersand the Environment,2022,31(5):1679−1705.
[21] TAO H T, GUO L, QIN Z, et al. Textural characteristics of mixed gels improved by structural recombination and the formation of hydrogen bonds between curdlan and carrageenan[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,129:107678. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107678
[22] 苏一帆, 钱志强, 刘忠. 无机盐对κ-卡拉胶凝胶行为影响的机理[J]. 盐科学与化工,2021,50(8):16−20,33. [SU Y F, QIAN Z Q, LIU Z. Gelation mechanisms of κ-carrageenan in solutions under the influence of inorganic salts[J]. Journal of Salt Science and Chemical Industry,2021,50(8):16−20,33.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3408.2021.08.005 SU Y F, QIAN Z Q, LIU Z. Gelation mechanisms of κ-carrageenan in solutions under the influence of inorganic salts[J]. Journal of Salt Science and Chemical Industry, 2021, 50(8): 16−20,33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3408.2021.08.005
[23] 袁超, 桑璐媛, 刘亚伟. κ-卡拉胶的功能特性及其应用研究进展[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2016,37(4):118−123. [YUAN C, SANG L Y, LIU Y W. Research progress in the functional characteristics of kappa-carrageenan and its applications[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2016,37(4):118−123.] YUAN C, SANG L Y, LIU Y W. Research progress in the functional characteristics of kappa-carrageenan and its applications[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 37(4): 118−123.
[24] MAKSHAKOVA O N, FAIZULLIN D A, ZUEV Y F. Interplay between secondary structure and ion binding upon thermoreversible gelation of κ-carrageenan[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,227:115342. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115342
[25] 袁超, 付腾腾, 朱新亮, 等. 卡拉胶的性质及在食品中的应用[J]. 粮食与油脂,2016,29(6):5−8. [YUAN C, FU T T, ZHU X L, et al. Functions and application of carrageenan in food industry[J]. Cereals& Oils,2016,29(6):5−8.] YUAN C, FU T T, ZHU X L, et al. Functions and application of carrageenan in food industry[J]. Cereals& Oils, 2016, 29(6): 5−8.
[26] NGUYEN B T, NICOLAI T, BENYAHIA L, et al. Synergistic effects of mixed salt on the gelation of κ-carrageenan[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,112:10−15. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.05.048
[27] WANG Y L, YUAN C, LIU Y W, et al. The influence of a hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin composite on the gelation of kappa-carrageenan[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,90:276−284. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.12.037
[28] 朱建华, 邹秀容, 刘日斌, 等. 蔗糖共溶质体系中明胶-变性淀粉共混凝胶相行为、质构及微观结构研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2017,33(12):16−22,88. [ZHU J H, ZOU X R, LIU R B, et al. Phase behavior, texture, and microstructure properties of gelatin-modified starch blend gels in co-solute of sucrose[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2017,33(12):16−22,88.] ZHU J H, ZOU X R, LIU R B, et al. Phase behavior, texture, and microstructure properties of gelatin-modified starch blend gels in co-solute of sucrose[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2017, 33(12): 16−22,88.
[29] BORAL S, BOHIDAR H B. Effect of water structure on gelation of agar in glycerol solutions and phase diagram of agar organogels[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2012,116(24):7113−7121. doi: 10.1021/jp3022024
[30] SHIMIZU S, MATUBAYASI N. Gelation:The role of sugars and polyols on gelatin and agarose[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2014,118(46):13210−13216. doi: 10.1021/jp509099h
[31] STENNER R, MATUBAYASI N, SHIMIZU S. Gelation of carrageenan:Effects of sugars and polyols[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2016,54:284−292. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.10.007
[32] NISHINARI K, WATASE M. Effects of sugars and polyols on the gel-sol transition[J]. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry,1992,206:149−162.
[33] OAKENFULL D. Solvent structure and gelation of polysaccharides in concentrated solutions of simple sugars[J]. Gums and Stabilisers for the Food Industry, 2000:277-284.
[34] RUSS N, ZIELBAUER B I, VILGIS T A. Impact of sucrose and trehalose on different agarose-hydrocolloid systems[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2014,41:44−52. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.03.020
[35] YANG Z, YANG H J, YANG H S. Effects of sucrose addition on the rheology and microstructure of κ-carrageenan gel[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,75:164−173. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.08.032
[36] HUANG M, MAO Y H, MAO Y Z, et al. Xylitol and maltitol improve the rheological property of kappa-carrageenan[J]. Foods,2021,11(1):51. doi: 10.3390/foods11010051
[37] YANG Z, YANG H J, YANG H S. Characterisation of rheology and microstructures of κ-carrageenan in ethanol-water mixtures[J]. Food Research International,2018,107:738−746. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.03.016
[38] YUAN C, SANG L Y, WANG Y L, et al. Influence of cyclodextrins on the gel properties of kappa-carrageenan[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,266:545−550. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.060
[39] LIU Y, ZHAO K S, MA Q. Insight into the glucose cosolvent induced gelation of κ-carrageenan by broadband dielectric spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids,2020,318:114268. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.114268
[40] 任艳艳. κ-卡拉胶/魔芋葡甘聚糖复合水凝胶机械性能强化与表征[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学, 2021. [REN Y Y. Enhancedment and characterization of κ-carrageenan/konjac glucomannan compound hydrogel[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021.] REN Y Y. Enhancedment and characterization of κ-carrageenan/konjac glucomannan compound hydrogel[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021.
[41] YUAN C, ZHAN W, CUI B, et al. Influence of two functional dextrins on the gel properties of kappa-carrageenan[J]. Food Research International,2020,138:109666. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109666
[42] HUSSAIN S, MALAKAR S, ARORA V K. Extrusion-based 3D food printing:Technological approaches, material characteristics, printing stability, and post-processing[J]. Food Engineering Reviews,2022,14(1):100−119. doi: 10.1007/s12393-021-09293-w
[43] CHENG Y T, WANG B, LÜ W Q, et al. Effect of xanthan gum on physicochemical properties and 3D printability of emulsion-filled starch gels[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2024,149:109613. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.109613
[44] LIU Z B, BHANDARI B, PRAKASH S, et al. Linking rheology and printability of a multicomponent gel system of carrageenan-xanthan-starch in extrusion based additive manufacturing[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,87:413−424. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.08.026
[45] 周莎莎, 杨晓溪, 李翠平, 等. 添加剂在食品3D打印中的应用现状[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(6):41−48. [ZHOU S S, YANG X X, LI C P, et al. Status of food additives in 3D food printing[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(6):41−48.] ZHOU S S, YANG X X, LI C P, et al. Status of food additives in 3D food printing[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(6): 41−48.
[46] UDO T, MUMMALETI G, MOHAN A, et al. Current and emerging applications of carrageenan in the food industry[J]. Food Research International,2023,173:113369. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113369
[47] 段松岐, 唐婷婷, 刘奕希, 等. 食品胶体对库拉索芦荟凝胶的3D打印特性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(23):116−122. [DUAN S Q, TANG T T, LIU Y X, et al. Effects of food colloids on the 3D printing properties of Aloe vera gel[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(23):116−122.] DUAN S Q, TANG T T, LIU Y X, et al. Effects of food colloids on the 3D printing properties of Aloe vera gel[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(23): 116−122.
[48] QIU L, ZHANG M, GHAZAL A F, et al. Development of 3D printed κ-carrageenan-based gummy candies modified by fenugreek gum:Correlating 3D printing performance with sol-gel transition[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2024,265:130865. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130865
[49] 吕明月, 吕健, 谢晋, 等. 多频脉冲超声对以赤藓糖醇为共溶质的桃浆-卡拉胶共混凝胶体系性质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(19):58−64. [LÜ M Y, LÜ J, XIE J, et al. Effect of multi-frequency pulsed ultrasound on the properties of peach pulp-carrageenan blend gel system with erythritol as cosolute[J]. Food Science,2023,44(19):58−64.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20221020-194 LÜ M Y, LÜ J, XIE J, et al. Effect of multi-frequency pulsed ultrasound on the properties of peach pulp-carrageenan blend gel system with erythritol as cosolute[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(19): 58−64. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20221020-194
[50] ZHU Y L, DI W, SONG M Y, et al. Correlating 3D printing performance with sol-geltransition based on thermo-responsive κ-carrageenan affected by fructose[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2023,340:111316. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2022.111316
[51] AVALLONE P R, RUSSO SPENA S, ACIERNO S, et al. Thermorheological behavior of κ-carrageenan hydrogels modified with xanthan gum[J]. Fluids,2023,8(4):119. doi: 10.3390/fluids8040119
[52] 刘振彬. 马铃薯泥及其淀粉混合凝胶体系的挤出型3D打印及后加工适应性研究[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2021. [LIU Z B. Study on extrusion 3D printing and post-processing adaptability of mashed potato and its starch mixed gel system[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2021.] LIU Z B. Study on extrusion 3D printing and post-processing adaptability of mashed potato and its starch mixed gel system[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021.
[53] PANT A, LEE A Y, KARYAPPA R, et al. 3D food printing of fresh vegetables using food hydrocolloids for dysphagic patients[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,114:106546. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106546
[54] LIU Z B, ZHANG M, BHANDARI B. Effect of gums on the rheological, microstructural and extrusion printing characteristics of mashed potatoes[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,117:1179−1187. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.06.048
[55] YU W Y, WANG Z M, PAN Y X, et al. Effect of κ-carrageenan on quality improvement of 3D printed Hypophthalmichthys molitrix-sea cucumber compound surimi product[J]. LWT,2022,154:112279. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112279
[56] XU J H, FAN Y H, CHEN Q, et al. Effects of κ-carrageenan gum on 3D printability and rheological properties of pork pastes[J]. Meat Science,2023,197:109078. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2022.109078
[57] AZAM R S M, ZHANG M, BHANDARI B, et al. Effect of different gums on features of 3D printed object based on vitamin-D enriched orange concentrate[J]. Food Biophysics,2018,13:250−262. doi: 10.1007/s11483-018-9531-x
[58] 张文海. 温敏型胶体对玉米淀粉3D打印固化性能的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(9):45−52. [ZHANG W H. Effect of temperature sensitive colloid on 3D printing and curing properties of corn starch[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(9):45−52.] ZHANG W H. Effect of temperature sensitive colloid on 3D printing and curing properties of corn starch[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(9): 45−52.
[59] SHI R, LIU Z B, YI J J, et al. The synergistic effect of κ-carrageenan and L-lysine on the 3D printability of yellow flesh peach gels:The importance of material elasticity in the printing process[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2024,254:127920. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127920





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
