Effects of Separation and Purification on the Structure and Lipid-lowering Activity in Vitro of Tremella fuciformis Polysaccharide
-
摘要: 本研究采用热水浸提法提取银耳粗多糖(TFP),并利用DEAE-52纤维素柱进行纯化获得TFP-1,比较分析了纯化前后多糖的组成、结构及体外降血脂活性的变化。研究结果显示,相比于TFP,TFP-1中的总糖含量提高至78.19%,糖醛酸含量提高至31.39%,黏度降低为108.33 mPa·s;TFP的分子量范围分布更广,具有更多的线性大分子;纯化前后单糖组成保持不变,摩尔比例略有变化,TFP和TFP-1单糖组成都为甘露糖、木糖、岩藻糖、葡萄糖醛酸、葡萄糖、半乳糖和盐酸氨基葡萄糖,其摩尔比分别是0.51:0.212:0.182:0.076:0.013:0.006:0.001和0.552:0.193:0.132:0.103:0.014:0.004:0.003;并且纯化后多糖的微观结构由平滑的片状结构变为粗糙的纤维状。体外降脂实验显示,TFP在10 mg/mL浓度下的胆固醇结合率为32.64%,在15 mg/mL时的胰脂肪酶抑制率为61.51%,均显著高于TFP-1(P<0.05);而TFP-1在10 mg/mL时的胆汁酸结合率为27.43%,显著高于TFP(P<0.05)。这表明分离纯化改变了银耳多糖的部分结构性质,进而影响其降血脂活性。研究结果为开发具有降脂功能的银耳多糖相关食品提供了理论依据。Abstract: In this study, Tremella fuciformis crude polysaccharide (TFP) was extracted using hot water extraction and refined to yield TFP-1 using a DEAE-52 cellulose column. This study evaluated the pure and unpurified polysaccharides' composition, structure, and in vitro hypolipidemic action. The total sugar content of TFP-1 grew to 78.19%, the uronic acid content increased to 31.39%, and the viscosity reduced to 108.33 mPa·s in comparison to TFP, according to the data. TFP had more linear macromolecules and a broader variety of molecular weights. Before and after purification, the composition of monosaccharides did not change, but the molar ratio did. Mannose, xylose, fucose, glucuronic acid, glucose, galactose, and glucosamine hydrochloride made up the monosaccharide composition of TFP and TFP-1. Their molar ratios were 0.51:0.212:0.182:0.076:0.013:0.006:0.001 and 0.552:0.193:0.132:0.103:0.014:0.004:0.003. Furthermore, the smooth, flat microscopic structure of the refined polysaccharides gave way to a rough, fibrous structure. The results of in vitro lipid-lowering tests demonstrated that TFP had a considerably greater cholesterol binding rate (32.64%) at 10 mg/mL and pancreatic lipase inhibition rate (61.51%) at 15 mg/mL compared to TFP-1 (P<0.05). At 10 mg/mL, TFP-1's bile acid binding rate was 27.43%, substantially greater than TFP's (P<0.05). This suggested that Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide's separation and purification altered some of its structural characteristics, which in turn had an impact on its hypolipidemic action. The findings offered a theoretical foundation for the creation of foods related to Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide that had the ability to decrease cholesterol.
-
银耳是担子菌类真菌的子实体,又名雪耳、白色木耳[1]。含有多糖、膳食纤维、蛋白质和氨基酸等丰富的营养成分。其中多糖作为存在于银耳子实体、菌丝体和发酵液中的一种主要的活性物质,约占银耳干重的65%~71%。目前的研究表明,银耳多糖由甘露糖、木糖和葡萄糖醛酸通过α-1,3-糖苷键连接而成,侧链由半乳糖、阿拉伯糖和岩藻糖组成[2],具有抗肿瘤、抗氧化、降血糖、降血脂等多种生物活性功能[3]。因此,银耳多糖作为一个天然活性物质,常被研究用来治疗或预防糖尿病、高脂血症等慢性疾病。
高脂血症作为血管疾病的主要危险因素之一,对人体健康构成严重威胁[4]。通常通过使用降脂药物如烟酸、他汀类和贝特类来调节脂质代谢和降低血脂水平,但这些药物会产生副作用如肝炎、皮疹和便秘等[5]。因此利用饮食中的天然活性物质降低血脂水平成为了人们关注的热点。多糖作为广泛存在于食品中的生物大分子,已被证明是控制高脂血症的重要物质。研究表明多糖可以通过分子间氢键和相互作用结合胆汁酸来调节胆固醇代谢,并抑制胆固醇在肠道中的吸收[6]。此外,高分子量多糖容易形成复合凝胶,增加胃肠道的黏度,从而阻止脂质和脂肪酶的扩散[7]。因此,高黏度和大分子量是影响多糖降脂活性的关键因素[8]。银耳多糖作为一种大分子量及高黏特性的酸性杂多糖,已有研究发现可以促进胆汁酸和胆固醇的排泄,原因可能是多糖分子中含有大量的羟基、羧基和氨基,可以吸附脂类并与胆固醇发生作用,从而阻止脂类的吸收[9]。然而银耳多糖较大的分子量以及在水溶液中较高的黏度,制约了其分离纯化,影响了对其结构与功能关系的认识。通过对银耳多糖的分离纯化,可以更好地解析其结构对活性的影响,例如在对沙棘多糖的研究中,发现多糖中的降脂活性与富含糖醛酸密切相关[10]。但也有研究表明,体外降脂活性的差异可能与多糖中的其他基团有关,例如,香菇多糖中含有蛋白质基团可能会提高其生物活性[11]。因此可以通过对比分析纯化前后多糖的结构和活性的变化,可以更好地表明多糖的结构与功能之间的关系,更好地理解多糖的功能性及其应用潜力。
本文通过水提法提取银耳粗多糖,并经DEAE-52纤维素柱进行分离纯化;采用高效液相色谱与多角度光散射联用的方法和离子色谱法测定分子质量与单糖组成;并通过刚果红和碘化钾实验进一步表征纯化后的多糖分子特性。利用体外实验探索纯化前后的银耳多糖结构与降脂活性的关系,为提高银耳多糖的开发利用水平提供参考依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
鲜银耳 购于福建省宁德市古田县;苯酚、浓硫酸、正丁醇 均为分析纯,成都市科龙化工试剂厂;脂肪酶(20000 U/g)、DEAE-52填料 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;胆固醇试剂盒、胆汁酸试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;16种单糖标品(甘露糖、鼠李糖、半乳糖醛酸、半乳糖、葡萄糖、葡萄糖醛酸、阿拉伯糖、木糖、岩藻糖、盐酸氨基葡萄糖、N-乙酰-D-氨基葡萄糖、D-果糖、D-核糖、氨基半乳糖盐酸盐、L-古罗糖醛酸、D-甘露糖醛酸) 色谱纯,博睿糖生物技术有限公司。
RE-52AA型旋转蒸发器 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;DAWN HELEOS II 18角度激光光散射凝胶色谱联用仪 WYATT技术公司;ICS500离子色谱仪 ThermoFisher;lo-vi粘度计 艾卡(广州)仪器设备有限公司;光栅型多功能微孔板检测仪 奥地利TECAN公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 银耳多糖的制备与纯化
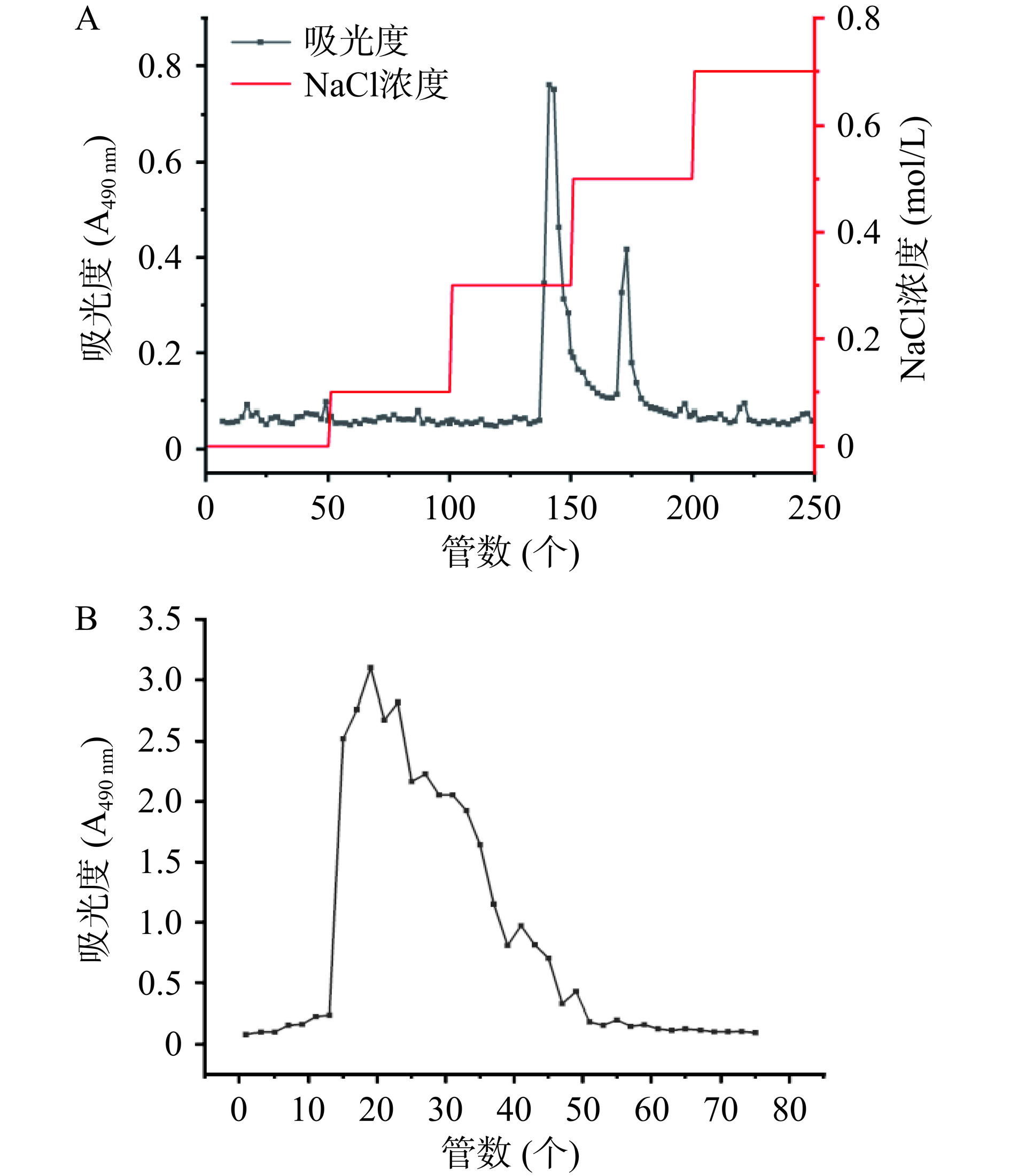
根据陈丽娟[12]的方法适当修改。银耳多糖的提取采用热水浸提法,将新鲜银耳洗净后擦净表面水分,测定其水分含量。然后将银耳撕碎,加入蒸馏水使料液比为1:10,在90 ℃下,浸提170 min。然后过滤,上清液旋蒸浓缩,加入4倍体积的95%无水乙醇,然后在4 ℃沉淀12 h,取沉淀。使用Sevage试剂(三氯甲烷:正丁醇=3:1,v/v)除去游离蛋白,后用8000~14000 Da的透析袋在纯水中透析48 h,然后真空冷冻干燥,得银耳粗多糖(TFP),根据公式计算其得率。进一步将TFP制备为5 mg/mL水溶液样品,通过DEAE-52纤维素色谱柱进行纯化。用蒸馏水、0.1、0.3、0.5和0.7 mol/L NaCl溶液以1.5 mL/min的流速梯度洗脱样品,每10 mL收集一管。在苯酚硫酸法的监测下收集与峰相对应的纯化馏分。将所得的2个组分,分别命名为TFP-1、TFP-2,用8000~14000 Da的透析袋透析48 h,然后经过冷冻干燥,做进一步分析。将TFP-1配制为2 mg/mL的水溶液并通过Sephacryl S-400凝胶柱(1.6 cm×80 cm)进一步纯化。使用蒸馏水作为洗脱液,流速为0.3 mL/min,收集样品每5 mL一管。然后对洗脱液进行浓缩和冻干,所得样品命名为TFP-1-1。其中纯化后多糖的回收率是过柱后多糖组分经透析冻干后的质量与过柱前多糖上样质量的比值。银耳粗多糖(TFP)得率计算公式如下:
Y(%)=M1×AM2×100 (1) 式中,Y表示粗多糖得率,%;A表示粗多糖中的多糖含量,%;M1表示冻干后的粗多糖质量,g;M2表示银耳干物质重量,g。
1.2.2 多糖化学组分及黏度测定
TFP和TFP-1的总糖含量通过苯酚硫酸法[13]测定,以0.1 mg/mL葡萄糖为标样,标准曲线方程:y=0.5293x−0.0062,R2=0.9949;蛋白质含量采用BCA法用试剂盒测定,标准曲线方程:y=1.1668x−0.1332,R2=0.9961;糖醛酸含量采用间羟基联苯法测定[14],以0.5 mg/mL葡萄糖醛酸为标样,标准曲线方程:y=1.9211x−0.0555,R2=0.9927。使用数字粘度计测定TFP和TFP-1的黏度,转速控制在60 r/min。黏度值以 mPa·s为单位记录。
1.2.3 单糖组成测定
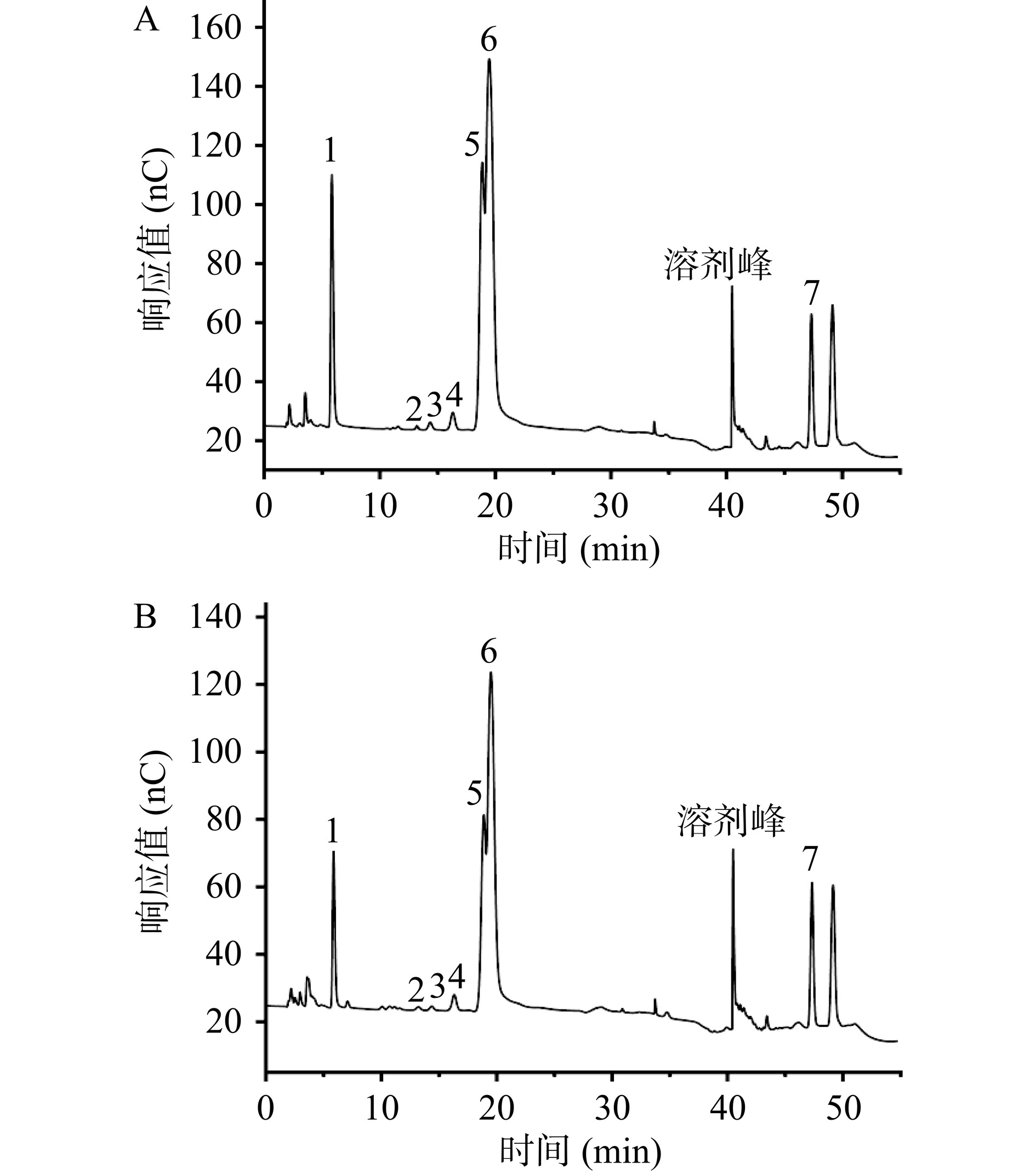
根据Jiang等[15]的方法,通过离子色谱法测定单糖组成。准确称量5 mg TFP和TFP-1置于安瓿瓶中,加入2 mL 3 mol/L三氟乙酸(TFA)密封,120 ℃烘箱热水解3 h。将水解液转移至试管中氮气吹干,加入5 mL水混匀后,吸取50 µL并加入950 µL去离子水混匀后,在15000×g下离心5 min,取上清进离子色谱仪分析。色谱条件为:采用Dionex™ CarboPac™ PA20(150 mm×3.0 mm,10 μm)液相色谱柱;流动相A:H2O,流动相B:15 mmol/L NaOH,流动相C:15 mmol/L NaOH和100 mmol/L NaAc;流速:0.3 mL/min;进样量:25 µL;柱温:30 ℃。16种单糖标准品为参照,分别为岩藻糖(Fuc)、氨基半乳糖盐酸盐(GalN)、鼠李糖(Rha)、阿拉伯糖(Ara)、盐酸氨基葡萄糖(GlcN)、半乳糖(Gal)、葡萄糖(Glc)、N-乙酰-D氨基葡萄糖(GlcNAc)、木糖(Xyl)、甘露糖(Man)、果糖(Fru)、核糖(Rib)、半乳糖醛酸(GalA)、古罗糖醛酸(GulA)、葡萄糖醛酸(GlcA)、甘露糖醛酸(ManA)。
1.2.4 分子量测定
根据Song等[16]的方法稍作修改,采用凝胶渗透色谱-多角度激光光散射-示差检测联用(GPC-RI-MALLS)测定银耳多糖的分子量。GPC-RI-MALLS 系统由液相系统、示差折光检测器Optilab rEX和多角度光散射器DAWN HELEOS(激光波长λ=658 nm)组成。流动相为超纯水,流速为0.5 mL/min。TFP和TFP-1用超纯水配制成1 mg/mL溶液通过0.45 μm过滤器过滤进样。多糖溶液的示差折光指数增量(dn/dc)为0.138 mL/g,使用Astra 1.4软件(Wyatt)计算重均分子量(Mw)和数均分子量(Mn)以及数均分子半径(Rn)和均方根回转半径(Rz)。
1.2.5 红外光谱及紫外光谱测定
称取干燥后的2 mg TFP和TFP-1与干燥的溴化钾以1:50混合压片后进行红外扫描,扫描范围为4000~400 cm−1。制备2 mg/mL的TFP和TFP-1溶液,用紫外分光光度计在200~600 nm的波长范围内扫描样品溶液,以验证样品溶液中是否含有蛋白质。
1.2.6 扫描电镜测定
将干燥的TFP和TFP-1用双胶粘剂放置在工作台上。喷金处理后,通过扫描电子显微镜仪器,在1000×和5000×的放大倍率下记录样品的表观特征。工作电压为15.0 kV。
1.2.7 刚果红实验
多糖的三螺旋结构测定采用刚果红法,并略有修改[17]。分别吸取2.0 mL浓度为1 mg/mL的TFP和TFP-1溶液,与2.0 mL 90 μmol/L的刚果红溶液混合,并逐滴向混合物中加入1 mol/L NaOH溶液,使NaOH的浓度分别达到0、0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4和0.5 mol/L。室温平衡10 min。于400~700 nm可见光区范围内进行波长扫描,并记录最大吸收波长。
1.2.8 碘-碘化钾实验
碘-碘化钾测定用于多糖的分支度分析[18]。取2 mL 1 mg/mL的TFP和TFP-1溶液与1.2 mL碘试剂(含0.02% I的0.2% KI溶液)混合,在300~700 nm的紫外可见光范围内进行扫描。
1.2.9 体外降脂活性测定
1.2.9.1 胆汁酸结合试验
根据Kahlon等[19]的方法,并稍作修改。用0.1 mol/L PBS(pH6.8)制备含有9 mmol/L甘胆酸、9 mmol/L糖代氧胆酸、9 mmol/L糖基氧胆酸、4.5 mmol/L牛磺酸和4.5 mmol/L牛磺脱氧胆酸的混合胆汁酸储备液,将储备溶液储存在−20 ℃,并在每次测定前用PBS稀释为0.72 μmol/mL的工作液。以蒸馏水作为空白对照,考来烯胺为阳性对照。分别加入1 mL 10 mg/mL的TFP、TFP-1和考来烯胺溶液,然后再加入1 mL,0.01 mol/L的HCl,于37 ℃,120 r/min模拟胃的酸性消化2 h。然后用NaOH将样品pH调节至7~7.5。向每个待测样品中加入4 mL胆汁酸工作液(0.72 μmol/mL)和5 mL 10 mg/mL的胰酶,于37 ℃,120 r/min条件下模拟体外肠消化2 h。混合物在6000 r/min的条件下离心20 min,取上清液用胆汁酸试剂盒测定其含量。胆汁酸结合率计算公式如下:
B1(%)=C1−C0C1×100 (2) 式中,B1表示胆汁酸结合率,%;C1表示空白组上清液中胆汁酸浓度,mmol/L;C0表示样品组上清液中胆汁酸浓度,mmol/L。
1.2.9.2 对胆固醇胶束的作用
根据文献报道的方法稍作修改来测定[20]。胆固醇胶束的配制:利用超声波将脂质胆固醇、油酸、卵磷脂充分溶解于10 mL甲醇溶液中,在室温下用氮气干燥,向溶液中加入含有牛黄胆酸钠的pH7.4磷酸缓冲溶液,然后用超声波处理,在37 ℃条件下将处理后的溶液培养12 h成胆固醇溶液。即配成每1 mL含10 mmol/L牛磺胆酸钠、2 mmol/L胆固醇、5 mmol/L油酸和卵磷脂、132 mmol/L氯化钠、15 mmol/L的磷酸缓冲液的胆固醇胶束。以2、5、10 mg/mL的考来烯胺为阳性对照,蒸馏水为空白对照。分别取1 mL的2、5、10 mg/mL的TFP和TFP-1溶液,加入3 mL胆固醇胶束溶液,在37 ℃条件振荡培养2 h,离心取上清液,用胆固醇试剂盒测定胆固醇浓度。胆固醇结合率计算公式如下:
B2(%)=D1−D0D1×100 (3) 式中,B2表示胆固醇结合率,%;D1表示空白组上清液中胆固醇浓度,mmol/L;D0表示样品组上清液中胆固醇浓度,mmol/L。
1.2.9.3 胰脂肪酶活性抑制作用
根据Cai等[21]的方法,并稍作修改。本实验所用的缓冲液为pH为7.6的100 mmol/L Tris缓冲液。将胰脂肪酶溶解在缓冲液中,浓度为2 mg/mL,然后以10000×g离心5 min,取上清液用于实验。以PNPB为反应底物,用缓冲液配制为0.1%(w/v)。以奥利司他为阳性对照,然后分别将50 μL不同浓度的TFP、TFP-1和奥利司他溶液(2、5、7.5、10、15 mg/mL)与50 μL缓冲溶液和50 μL酶溶液混合,在37 ℃下孵育15 min,然后加入100 μL PNPB溶液,在37 ℃条件下反应20 min后,在405 nm处测定吸光度值。样品对照组用Tris缓冲液代替胰脂肪酶溶液;空白组用纯水代替样品;空白对照组用纯水代替样品、缓冲液代替胰脂肪酶溶液。胰脂肪酶抑制率计算公式如下:
I(%)=(1−B−B0A−A0)×100 (4) 式中,I表示胰脂肪酶抑制率,%;A表示空白管吸光度;A0 表示空白管对照吸光度;B表示样品管吸光度;B0表示样品对照管吸光度。
1.3 数据处理
每组数据重复测定三次,结果以平均值±标准偏差表示。采用SPSS 20.0统计分析,通过方差分析(ANOVE)确定显著性差异,当P<0.05时,认为有显著性差异;Origin 2023软件作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 银耳多糖分离纯化
如图1所示,经DEAE-52洗脱获得2个洗脱峰,分别命名为TFP-1和TFP-2。透析冷冻干燥后,TFP-1回收率为63.2%,TFP-2回收率只有13.6%,总回收率为76.8%左右。由于TFP-2较低的糖含量(58%)及回收率,所以后续采用TFP-1凝胶柱继续纯化。TFP-1经凝胶柱纯化后所得的TFP-1-1,其多糖含量为67%左右,较TFP-1(多糖含量78.19%)显著下降(P<0.05),且由洗脱曲线可看出,无法将TFP-1按分子量分离开来。其原因可能是银耳多糖黏度较大,无法正常流入凝胶填料的孔隙且可能与填料发生相互作用,导致部分较大的多糖分子在凝胶基质中被保留,从而降低收集部分的整体多糖含量。因此,后续研究采用DEAE-52纯化后的TFP-1进行。
2.2 银耳多糖化学成分及黏度分析
银耳多糖的化学成分见表1。鲜银耳热水提取银耳多糖的得率有15.83%左右,此结果比Chen[22]从干银耳中用热水浸提银耳多糖得率3.08%要提高许多。原因可能为鲜银耳更有利于多糖的溶出。TFP的总糖含量为62.94%,经DEAE-52纤维柱纯化后得TFP-1总糖含量为78.19%,总糖含量显著升高(P<0.05),糖醛酸含量同样显著升高(P<0.05)。此外,粗多糖TFP有较高的黏度,经分离纯化后得到样品黏度显著降低(P<0.05)。可能因为多糖在提取过程中带有其他生物大分子、小分子、离子等杂质,经过纯化处理,这些杂质被去除,导致多糖分子之间的相互作用减少,从而降低了黏度[23]。还有可能是经过纯化使多糖的分子量分布变得更加单一,从而减小了分子间的相互作用,降低了黏度。
表 1 TFP和TFP-1化学成分、黏度及得率Table 1. Chemical composition, viscosity and yield of TFP and TFP-1样品 总糖(%) 蛋白质(%) 糖醛酸(%) 黏度(mPa·s) 得率(%) TFP 62.94±0.24b 3.09±0.04a 22.53±0.61b 526.16±5.11a 15.83±1.98b TFP-1 78.19±0.75a 1.83±0.02b 31.39±1.37a 108.33±2.52b 63.20±2.20a 注:同列不同的小写字母表示具有显著差异(P<0.05),表4同。 2.3 单糖组成测定
如图2和表2所示,在TFP和TFP-1中均检测到了甘露糖、木糖、岩藻糖、葡萄糖醛酸、葡萄糖、半乳糖和盐酸氨基葡萄糖,其摩尔比分别是0.51:0.212:0.182:0.076:0.013:0.006:0.001 和 0.552:0.193:0.132:0.103:0.014:0.004:0.003。结果表明银耳多糖是一种酸性多糖。银耳多糖经纯化后单糖组成未变,摩尔比例略有改变。相比于TFP,TFP-1的甘露糖、葡萄糖及葡萄糖醛酸的比例增加,而木糖与岩藻糖比例降低。与Xu等[24]研究的热水提取银耳粗多糖的单糖组成大致相似,摩尔占比有所差异,银耳多糖都含有大量的甘露糖,其次是木糖、岩藻糖、葡萄糖醛酸。
表 2 TFP和TFP-1的单糖组成Table 2. Monosaccharide composition of TFP and TFP-1样品 甘露糖 木糖 岩藻糖 葡萄糖
醛酸葡萄糖 半乳糖 盐酸氨基
葡萄糖TFP 0.51 0.212 0.182 0.076 0.013 0.006 0.001 TFP-1 0.552 0.193 0.132 0.103 0.014 0.004 0.003 2.4 银耳多糖分子量及分布分析
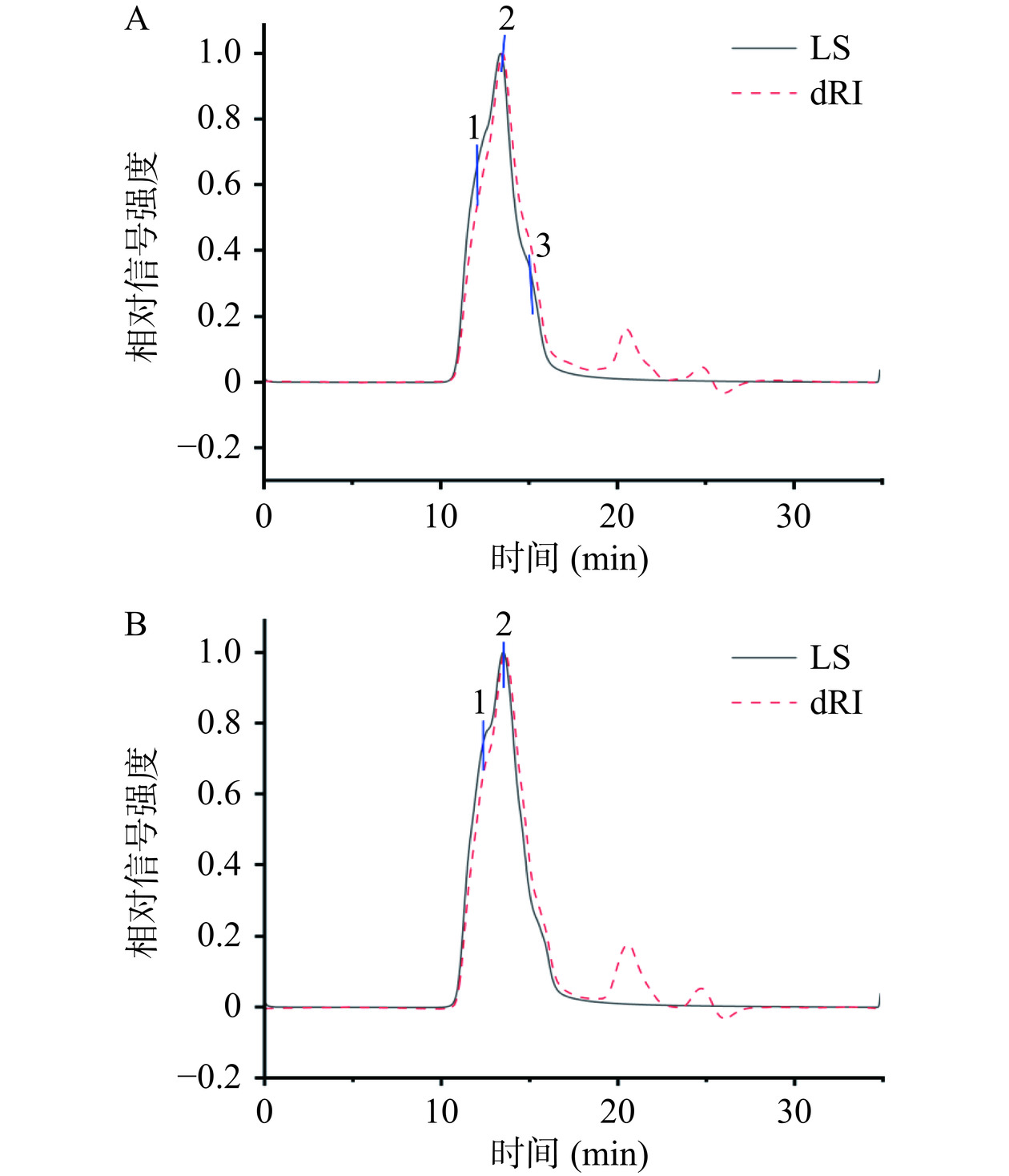
在本研究中,采用GPC-RI-MALLS对银耳多糖的重均分子量(Mw)、聚合物分散指数(Mn/Mw)、数均分子半径(Rn)和均方根回转半径(Rz)进行了详细分析。图3A和B显示了从MALLS检测器和RI检测器获得的色谱图,其中TFP与TFP-1两种多糖在10~17 min内均显示出较强的激光散射信号,在20~25 min范围内无明显的激光散射信号,表明是溶剂峰的特征。在LS色谱图中,TFP有三个峰值,Mw的分布范围是1.164×106~3.532×106 Da;进一步纯化的TFP-1呈现两个主峰,其中峰2的Mw为1.839×106 Da,约占峰面积的71.61%,是主要组分。从表3也可看出,TFP样品显示了显著的峰分布差异性,意味着其包含多种成分,并且某些成分具有较宽的分子量分布(较高的Mn/Mw值),这表明了成分的复杂性以及分子大小的多样性。TFP-1样品展现了两个相对接近的峰值且多分散指数(Mn/Mw)较小,反映了分子量分布相对较窄,分子量分布相对较均一。
表 3 通过GPC-RI-MALS计算的TFP 和TFP-1的分子量参数Table 3. Molecular weight parameters of TFP and TFP-1 calculated by GPC- RI-MALS参数 TFP TFP-1 峰1 峰2 峰3 峰1 峰2 含量(%) 29.88 52.07 18.05 28.39 71.61 Mn(Da) 3.223×106 1.561×106 1.154×106 2.723×106 1.787×106 Mw(Da) 3.532×106 1.647×106 1.164×106 2.761×106 1.839×106 Mn/Mw 1.096 1.055 1.009 1.014 1.029 Rn(nm) 160.7 114.2 106.0 151.1 123.2 Rz(nm) 176.9 119.8 106.1 153.3 126.6 Rz与线性分子的几何尺寸成正比,Rz较长的大分子在溶液中占据更大的空间[25]。在样品分析中,如果Rz值显著高于Rn(数均分子半径)和Rw(重均分子半径),这可能表明样品中含有相对较多的线性大分子。通常,Rn提供了关于小分子平均尺寸的信息,Rn越小说明样品中小分子的数量越多。如表3所示,TFP的Rz为106.1~176.9 nm,且显著高于Rn,这表明其主要由线性大分子组成,且这些大分子在尺寸上具有显著差异,反映了广泛的分子量分布。TFP-1样品的Rn和Rz值在不同的峰中较为均匀分布,且Rn与Rz接近,这与其较窄的分子量分布一致,表明分子尺寸分布相对均一。总的来说,TFP样品表现出更大的分子尺寸和更宽的分子量分布,这可能与其线性大分子的比例较高有关;而纯化后的TFP-1样品则显示出更均匀的分子量和分子尺寸的分布。
2.5 红外光谱与紫外可见光谱分析
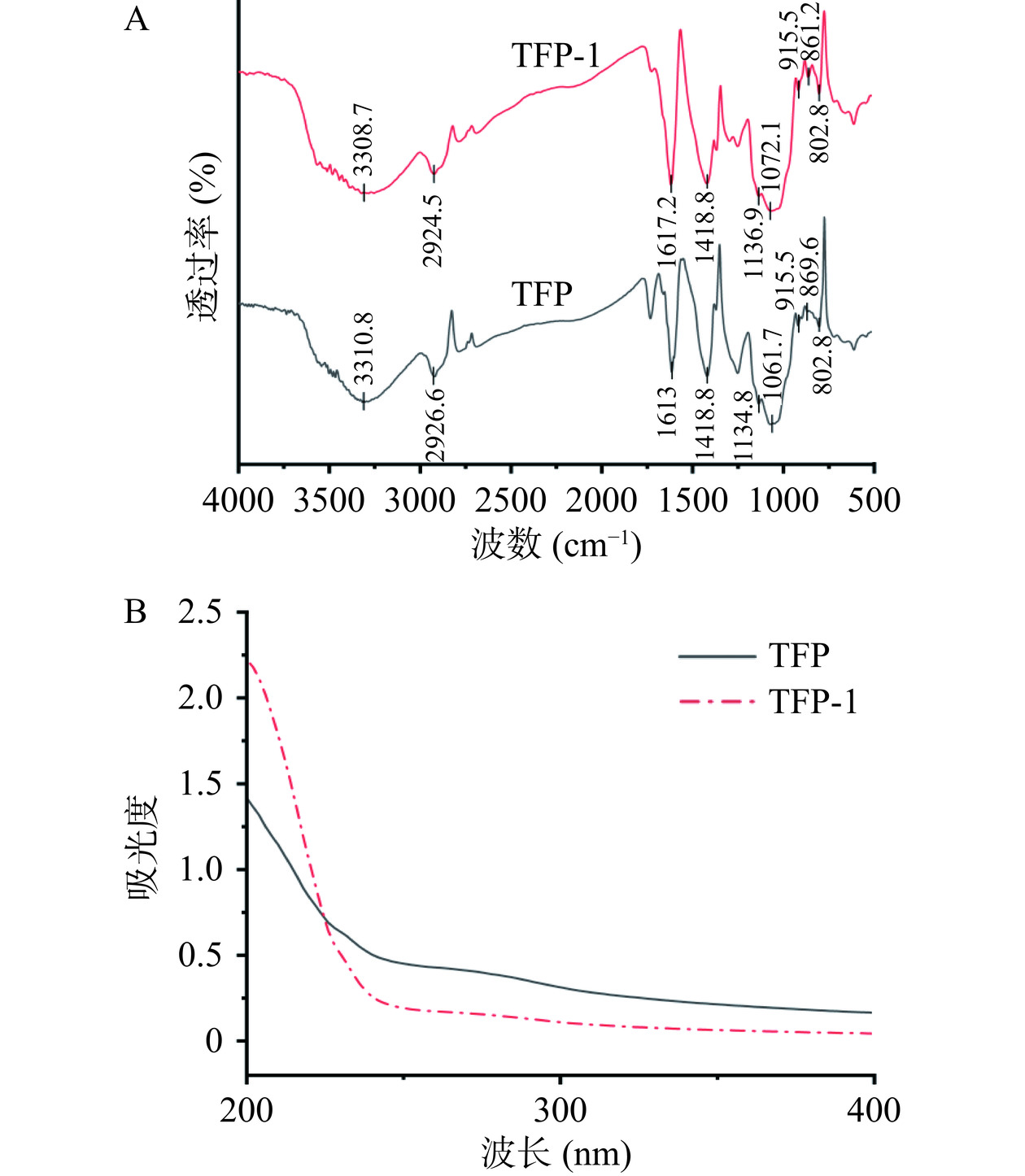
傅里叶变换红外光谱(FT-IR)因其高表征潜力而被用于分析多糖中的官能团。TFP和TFP-1的FT-IR扫描光谱如图4A所示。纯化后的多糖相比于粗多糖未出现新的结构峰,表明银耳多糖分离纯化过程中未产生新的官能团。两种多糖共有的吸收峰包括:3300 cm−1附近的宽峰是由多糖分子中的O-H拉伸振动引起的,表明多糖中存在分子间或分子内氢键。在2924 cm−1附近的吸收峰是C-H伸缩振动引起的,这两类都是多糖的特征吸收峰[26]。其次,在1613 cm−1和1617 cm−1附近的特征峰是C=O的伸缩振动,表明多糖样品中存在糖醛酸。在1134 cm−1附近和1062~1072 cm−1波长范围出现的吸收峰归因于吡喃糖环的C-O-H和C-O-C伸缩振动形成的吸收峰[27],表明银耳多糖纯化前后都存在吡喃环。此外,在 860 cm−1 与 915 cm−1 左右,TFP 与 TFP-1 样品都存在吸收峰,表明多糖样品中可能含有α-苷键与β-苷键[28]。与Shi等[29]报道的热水浸提后银耳多糖可能具有α和β糖苷键及吡喃糖环结构的结论一致。
此外,图4B紫外可见光谱表明,TFP和TFP-1在260 nm和280 nm处没有明显的吸收峰。表明这2种物质几乎不含游离蛋白质及核酸样物质。
2.6 SEM分析
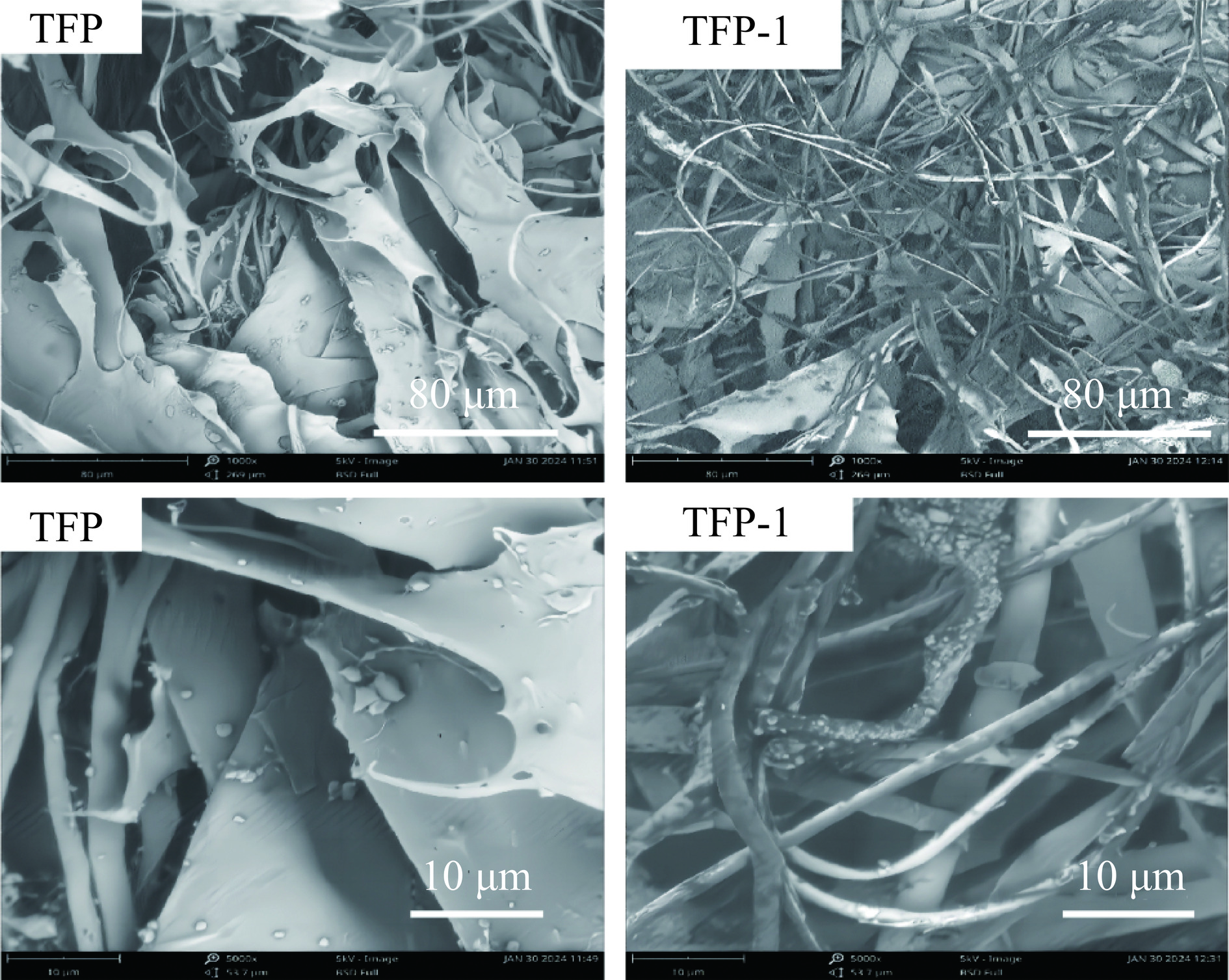
采用扫描电镜观察多糖的微观结构如图5所示。由图可知,纯化前后多糖的形状方面都呈现出不同的状态。TFP在1000×时,形貌呈现出致密、大片状结构。在5000×下,多糖片状结构更加清晰,并伴有一些折叠,它们可能提供了较大的表面积。这种结构可能表明了一种紧密堆叠的排列方式,这可能影响到它们的物理化学性质,如溶解度、吸附能力和交互作用的特性。而TFP-1在1000×下,展示了一个纤维状的网络结构,纤维交织,形成了复杂的多层结构,可能有利于与其他分子的相互作用。在更高的放大倍数下,纤维间的空间和连接点变得更加明显,这些结构可能对多糖与其他分子的相互作用具有重要作用。这种纤维网络结构可能会影响多糖在生物体中的功能,如与蛋白质的结合、细胞附着或作为药物递送系统的潜力。可以推断TFP有较平滑的表面和层状特征,TFP-1有明显的纤维结构,表明可能具有不同的表面相互作用潜力。Ren等[30]研究发现藜麦多糖未纯化前为多边形片状,表面光滑,经纯化后厚度更薄,层状结构更松散,可能是因为分离纯化降低了多糖分子之间的相互作用,从而导致多糖的一些物理性质发生了变化,此结论与本文研究发现一致。因此,可以说明银耳多糖纯化后微观结构发生了改变,可能会影响其物理特性。
2.7 刚果红实验与碘-碘化钾实验结果
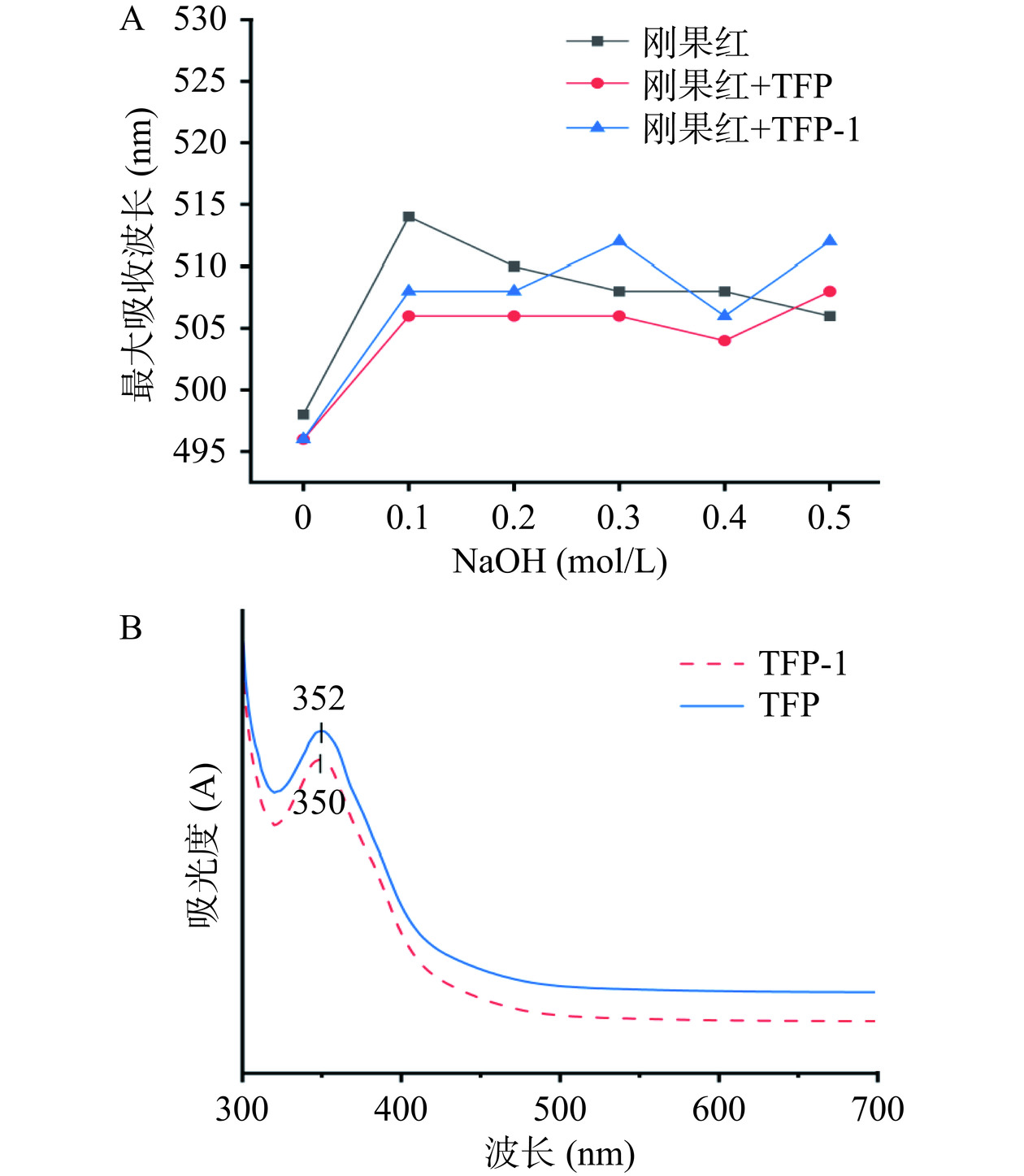
具有三螺旋结构的多糖与刚果红形成的络合物在适当的NaOH浓度下,最大吸收波长会发生红移,当NaOH浓度超过0.3 mol/L时则可能会破坏其结构,导致最大吸收波长减小[31]。从图6A可知,在弱碱溶液中,TFP和TFP-1样品的最大吸收峰的波长较刚果红对照样品,均发生蓝移,并且随着氢氧化钠浓度的增加,呈现出不规则的变化现象,当NaOH浓度逐渐变为0.5 mol/L时,最大吸收波长增加。说明TFP和TFP-1分子结构中不含有三螺旋构象。此外,碘-碘化钾实验一般用来判断多糖样品侧链的长短和支链的多少,具有较短侧链和少量分支的线性骨架的多糖可以与碘结合,在565 nm处形成吸收峰;而在350 nm处出现吸收峰,则表明分子中存在更长的侧链和更多的支链[32]。从图6B可以看到纯化前后银耳多糖的最大吸收峰在352 nm与350 nm,在565 nm附近没有观察到吸收峰,这说明TFP和TFP-1分子骨架上存在较长的侧链和较多的支链。因此,从多糖的这两个实验中均发现TFP和TFP-1的分子都不含有三螺旋结构,且都具有较长的侧链和较多的支链,表明纯化前后多糖的构象均未发生明显改变。
2.8 胆汁酸结合能力分析
考来烯胺作为一种增加胆汁酸消除和减少膳食胆固醇吸收的药物,被用来作为阳性对照[33]。银耳多糖纯化前后的胆汁酸结合能力如表4所示,在10 mg/mL的浓度下,考来烯胺的胆汁酸结合能力为66.47%±0.66%,纯化后的TFP-1的胆汁酸结合能力为27.43%±2.39%,显著高于粗多糖TFP(18.23%±0.71%)(P<0.05)。相对于考来烯胺,TFP和TFP-1的结合率分别为27.43%与41.27%,该结果表明,银耳多糖具有胆汁酸结合能力,纯化后的组分结合能力上升,该结果可能与本身的结构有关。胆汁酸和多糖之间的结合能力不仅与疏水相互作用、静电相互作用和流体动力学限制有关,还与多糖的单糖组成、大分子特性、黏度和胆汁酸的嵌入有关。根据扫描电镜结果显示,TFP-1的微观结构相比于TFP,更加疏松多孔,可能为胆汁酸结合提供了较多的活性位点,这与Zheng等[34]的研究结果一致。TFP-1的高胆汁酸结合能力也可能归因于其高糖醛酸含量。Yan等[35]也证实了这一观点,含有最高糖醛酸含量的样品,胆汁酸结合能力也最高。因此,TFP-1比TFP有较好的胆汁酸结合能力的原因可能是疏松多孔的结构暴露了与降血脂活性相关的分子链,增加了糖醛酸含量,可能为胆汁酸结合提供更多活性位点。
表 4 TFP和TFP-1的体外胆汁酸结合能力Table 4. In vitro bile acid binding ability of TFP and TFP-1样品 上清液中胆汁酸浓度(μmol/L) 胆汁酸结合率(%) 相对于考来烯胺结合率(%) TFP 36.96±0.32a 18.23±0.71c 27.43±1.06c TFP-1 32.81±1.08b 27.43±2.39b 41.27±3.6b 考来烯胺 15.16±1.02c 66.47±0.66a 100±0.99a 2.9 胆固醇结合能力分析
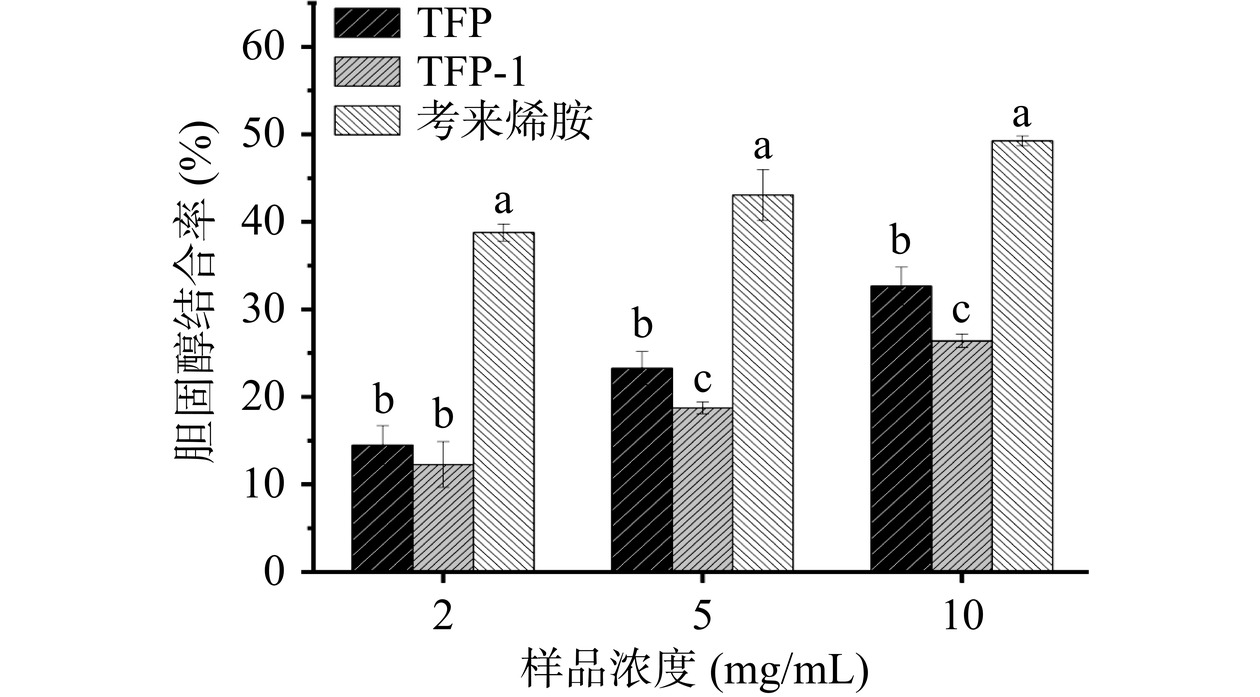
在肠道消化胆固醇的过程中,胆固醇胶束的形成是胆固醇吸收的关键。因此,胆固醇-胶束的破坏可以促进胆固醇从消化系统的吸收途径中逸出,从而降低体内的胆固醇水平。本实验模拟人体内的胃肠道环境,发现银耳多糖具有体外胆固醇结合能力,结果如图7所示。在2~10 mg/mL浓度下,TFP、TFP-1和考来烯胺的胆固醇结合能力呈一定的剂量趋势;当浓度为2 mg/mL时TFP、TFP-1和考来烯胺的胆固醇结合率分别为14.47%、12.26%和38.76%;当浓度升至10 mg/mL时,TFP、TFP-1和考来烯胺的胆固醇结合率分别为32.64%、26.39%和49.25%。在10 mg/mL浓度下,TFP和TFP-1相对于考来烯胺的胆固醇结合率分别为83.39%和77.17%,说明TFP和TFP-1都有较好的胆固醇结合能力,并且TFP的胆固醇结合能力显著高于TFP-1(P<0.05)。多糖纯化前后的胆固醇结合能力不相同的原因可能与其结构特征有关。有研究表明,多糖的体外结合能力与其表观黏度和分子量相关,这可能是由于胆固醇和多糖之间存在高疏水相互作用。TFP的胆固醇结合能力高于TFP-1,一方面可能是由于粗多糖较高的黏度以及较宽的高分子量分布,这与Nie等[36]研究发现秋葵多糖具有相对较高的胆固醇结合能力是由于其高分子量、宽分子量分布和高黏度一致;另一方面,TFP的黏度为526.16 mPa·s显著大于TFP-1的黏度(108.33 mPa·s)(P<0.05),当TFP浓度达到10 mg/mL时,溶液呈现凝胶状态,多糖凝胶的空间构型也可能提供了一种合适的环境,有利于胆固醇与凝胶相互作用,Huang等[37]发现可溶性膳食纤维的凝胶形成能力与其结合肠道中胆固醇并加速其提取的能力密切相关。因此,TFP具备胆固醇结合能力可能是其较宽及较高的分子量分布以及较大的表观黏度所致。这些结果证实了银耳多糖具有预防高脂血症的潜力。
![]() 图 7 TFP和TFP-1的胆固醇结合能力注:不同的小写字母表示相同浓度不同处理组具有显著差异(P<0.05),图8同。Figure 7. Cholesterol-binding capacity of TFP and TFP-1
图 7 TFP和TFP-1的胆固醇结合能力注:不同的小写字母表示相同浓度不同处理组具有显著差异(P<0.05),图8同。Figure 7. Cholesterol-binding capacity of TFP and TFP-12.10 胰脂肪酶抑制能力分析
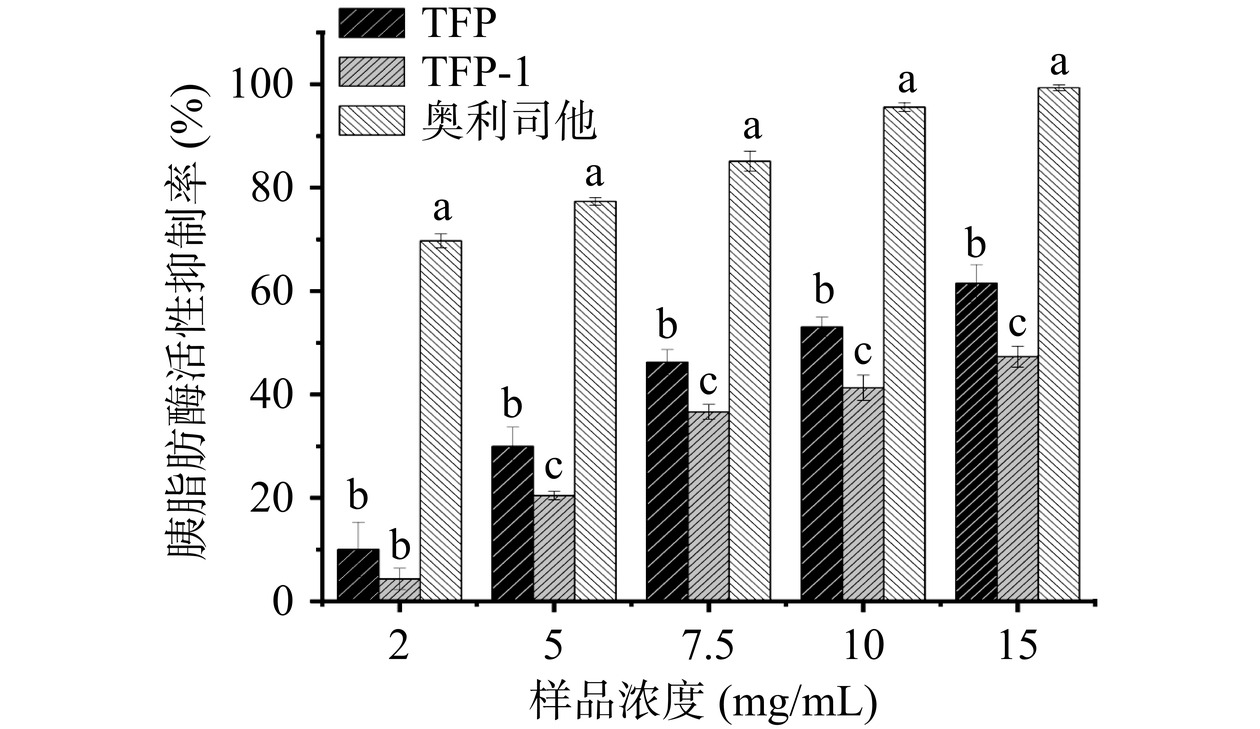
胰脂肪酶是肠道脂肪消化吸收的关键酶,其抑制活性是被用于评定天然产物降血脂潜力的参数之一。银耳多糖对胰脂肪酶抑制率的结果如图8所示。TFP、TFP-1及奥利司他在2~15 mg/mL的浓度下均对胰脂肪酶具有一定的抑制作用,在该浓度范围内三种样品表现出剂量依赖性。其中TFP在浓度为2 mg/mL时,抑制率为10%左右,当浓度上升至15 mg/mL,抑制率达到了61%,相对于奥利司他的抑制率为62%;经纯化后TFP-1的抑制率有所下降,在2 mg/mL的浓度下,抑制率为4%左右,当浓度为15 mg/mL时,抑制率为47%。结果表明TFP和TFP-1都对脂肪酶有抑制作用,且TFP的抑制能力更强。有研究表明高分子量的多糖可能更有效地抑制酶活性,因为较大的分子可以为酶提供物理屏障,阻止它们与底物相互作用[38]。因此,TFP对脂肪酶的抑制作用较好的原因可能是TFP具有更宽的高分子量分布。此外,黏度也是纯化前后银耳多糖的脂肪酶活性有差异的原因,TFP的黏度为526.16 mPa·s显著大于TFP-1样品(P<0.05)。有研究表明,高黏度的多糖可以形成黏稠的凝胶或溶液。当这种多糖存在于胃肠道中时,它们可能会在物理上阻碍脂肪酶进入脂质底物。这种阻塞会限制酶和脂肪分子之间的接触,降低脂肪消化和吸收的效率[39]。Guo等[40]也研究发现青稞中β-葡聚糖的脂肪酶抑制能力与黏度呈现正相关,与本研究发现一致。因此,TFP较好的脂肪酶抑制活性可能在于较高和较广的分子量分布,并且黏度也相对较高,可以阻碍酶与底物的结合;其次TFP具有较大的片状结构,有较大的表面积,提供更多的机会使得多糖与酶的活性位点发生相互作用。
在本文对胆固醇结合能力和胰脂肪酶抑制能力的测定中,粗多糖活性强于纯化后的多糖,这一结果与Qin等[41]对茶多糖纯化前后活性的研究以及常相娜[42]对苹果渣多糖活性的研究结果相似。从本文研究结果来看,银耳多糖的体外降脂活性主要取决于银耳多糖的黏度、高分子量以及糖醛酸的含量。其中,多糖黏度的改变影响了多糖与胆固醇化学结合能力;前文分析也表明,糖醛酸含量在影响胆汁酸结合能力方面起重要作用。此外,粗多糖分离纯化前含有分子量不同、结构性质不同的多种组分,有研究表明,具有多种结构特征的个体和组合会影响生物活性[43];且在分离纯化过程中,也可能会去除一些促进体外降脂活性的组分,例如蛋白质,从而导致活性下降[44]。本研究中,纯化后多糖的蛋白质含量有所降低,粗多糖中含有的可能是与糖结合的活性蛋白,从而表现出较高的降脂活性。目前,在开发具有降脂功能的食品时,不仅需要明确引起这些功能的物质,还需要满足绿色清洁加工的要求,表现出更强功能活性的粗提物更符合这一目的。
3. 结论
本研究采用热水浸提法从银耳子实体中提取银耳粗多糖,通过DEAE-52纤维素色谱柱从TFP中分离出组分TFP-1,并对银耳多糖纯化前后的结构特征和体外降脂活性能力进行了研究。TFP的Mw范围为1.164×106~3.532×106 Da,TFP-1主要Mw为1.839×106 Da,TFP分子量分布更广,含更多的线性大分子。单糖组成分析表明,纯化前后多糖的单糖组成未改变,摩尔比略有改变。TFP和TFP-1单糖组成都为甘露糖、木糖、岩藻糖、葡萄糖醛酸、葡萄糖、半乳糖和盐酸氨基葡萄糖,其摩尔比分别是0.51:0.212:0.182:0.076:0.013:0.006:0.001 和 0.552:0.193:0.132:0.103:0.014:0.004:0.003。并且FI-IR分析表明,银耳多糖分离纯化过程中未产生新的官能团,都是含有α和β糖苷键的吡喃糖。此外,纯化后多糖的微观结构从平滑的片状结构向粗糙的纤维状转变,并且两种多糖样品都不具有三螺旋结构,但有较长的侧链及较多的支链,其中TFP黏度最大。对比其体外降脂能力,其中粗多糖TFP具有更好的胆固醇结合能力和胰脂肪酶抑制能力,在10 mg/mL时胆固醇结合率为32.64%,在15 mg/mL时,胰脂肪酶抑制率为61.51%;而TFP-1在浓度为10 mg/mL时有相对较高的胆汁酸结合能力为27.43%。本文研究结果表明,银耳多糖纯化前后都具有体外降血脂能力,其化学结合能力的差异可能与其结构性质有关,如黏度、糖醛酸含量和表面微观结构。研究结果可为银耳多糖相关食品的开发及银耳多糖在功能食品工业中的应用提供了理论依据。
-
图 7 TFP和TFP-1的胆固醇结合能力
注:不同的小写字母表示相同浓度不同处理组具有显著差异(P<0.05),图8同。
Figure 7. Cholesterol-binding capacity of TFP and TFP-1
表 1 TFP和TFP-1化学成分、黏度及得率
Table 1 Chemical composition, viscosity and yield of TFP and TFP-1
样品 总糖(%) 蛋白质(%) 糖醛酸(%) 黏度(mPa·s) 得率(%) TFP 62.94±0.24b 3.09±0.04a 22.53±0.61b 526.16±5.11a 15.83±1.98b TFP-1 78.19±0.75a 1.83±0.02b 31.39±1.37a 108.33±2.52b 63.20±2.20a 注:同列不同的小写字母表示具有显著差异(P<0.05),表4同。 表 2 TFP和TFP-1的单糖组成
Table 2 Monosaccharide composition of TFP and TFP-1
样品 甘露糖 木糖 岩藻糖 葡萄糖
醛酸葡萄糖 半乳糖 盐酸氨基
葡萄糖TFP 0.51 0.212 0.182 0.076 0.013 0.006 0.001 TFP-1 0.552 0.193 0.132 0.103 0.014 0.004 0.003 表 3 通过GPC-RI-MALS计算的TFP 和TFP-1的分子量参数
Table 3 Molecular weight parameters of TFP and TFP-1 calculated by GPC- RI-MALS
参数 TFP TFP-1 峰1 峰2 峰3 峰1 峰2 含量(%) 29.88 52.07 18.05 28.39 71.61 Mn(Da) 3.223×106 1.561×106 1.154×106 2.723×106 1.787×106 Mw(Da) 3.532×106 1.647×106 1.164×106 2.761×106 1.839×106 Mn/Mw 1.096 1.055 1.009 1.014 1.029 Rn(nm) 160.7 114.2 106.0 151.1 123.2 Rz(nm) 176.9 119.8 106.1 153.3 126.6 表 4 TFP和TFP-1的体外胆汁酸结合能力
Table 4 In vitro bile acid binding ability of TFP and TFP-1
样品 上清液中胆汁酸浓度(μmol/L) 胆汁酸结合率(%) 相对于考来烯胺结合率(%) TFP 36.96±0.32a 18.23±0.71c 27.43±1.06c TFP-1 32.81±1.08b 27.43±2.39b 41.27±3.6b 考来烯胺 15.16±1.02c 66.47±0.66a 100±0.99a -
[1] 许欢怡, 李泉岑, 郑明锋, 等. 银耳多糖的结构、功能性及应用研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(4):362−370. [XU H Y, LI Q C, ZHENG M F, et al. Research progress on structure, function and application of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(4):362−370.] XU H Y, LI Q C, ZHENG M F, et al. Research progress on structure, function and application of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(4): 362−370.
[2] CHIU C, CHIU K, YANG L, et al. Amelioration of obesity in mice fed a high-fat diet with uronic acid-rich polysaccharides derived from Tremella fuciformis[J]. Polymers,2022,14(8):1514. doi: 10.3390/polym14081514
[3] 苏静. 古田银耳多糖体外消化特性及凝胶软糖产品开发[D]. 济南:山东农业大学, 2023. [SU J. Characteristics of in vitro digestion of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide from gutian and development of gel gummy products[D]. Jinan:Shandong Agricultural University, 2023.] SU J. Characteristics of in vitro digestion of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide from gutian and development of gel gummy products[D]. Jinan: Shandong Agricultural University, 2023.
[4] PICARD F, STEG P G. Cardiovascular disease risk reduction in mild-moderate hypertriglyceridemia:Integrating prescription of Omega-3 with standard treatment[J]. Current Atherosclerosis Reports,2021,23(6):27. doi: 10.1007/s11883-021-00919-2
[5] LIU Y, XIANG Z, CHEN C, et al. Hypolipidemic and hepatoprotective effects of polysaccharides extracted from Liriope spicata var. prolifera in C57BL/6J mice with high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia[J]. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2020,2020:8013189.
[6] YANG Y, LIN L, ZHAO M, et al. The hypoglycemic and hypolipemic potentials of Moringa oleifera leaf polysaccharide and polysaccharide-flavonoid complex[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,210:518−529. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.04.206
[7] NAQASH F, MASOODI F A, RATHER S A, et al. Emerging concepts in the nutraceutical and functional properties of pectin-A review[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,168:227−239. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.03.058
[8] AGUILERA-ANGEL E, ESPINAL-RUIZ M, NARVAEZ-CUENCA C. Pectic polysaccharides with different structural characteristics as inhibitors of pancreatic lipase[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,83:229−238. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.05.009
[9] WU Y, WEI Z, ZHANG F, et al. Structure, bioactivities and applications of the polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis mushroom:A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,121:1005−1010. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.117
[10] LI Q, DOU Z, DUAN Q, et al. A comparison study on structure-function relationship of polysaccharides obtained from sea buckthorn berries using different methods:Antioxidant and bile acid-binding capacity[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2024,13(1):494−505. doi: 10.26599/FSHW.2022.9250043
[11] CHEUNG Y, SIU K, LIU Y, et al. Molecular properties and antioxidant activities of polysaccharide-protein complexes from selected mushrooms by ultrasound-assisted extraction[J]. Process Biochemistry,2012,47(5):892−895. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2012.02.004
[12] 陈丽娟. 银耳多糖快速提取及可控降解的研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2017. [CHENG L J. Study on rapid extraction and controlled degradation of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2017.] CHENG L J. Study on rapid extraction and controlled degradation of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017.
[13] 王迎香, 唐子惟, 彭腾, 等. 苯酚-硫酸法测定酒蒸多花黄精多糖含量的优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(18):308−316. [WANG Y X, TANG Z W, PENG T, et al. Optimization of phenol-sulfuric acid method for the determination of polysaccharide content of polygonum extract in wine steaming[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(18):308−316.] WANG Y X, TANG Z W, PENG T, et al. Optimization of phenol-sulfuric acid method for the determination of polysaccharide content of polygonum extract in wine steaming[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(18): 308−316.
[14] 陈巧巧, 万琴, 王振中, 等. 人参多糖中糖醛酸含量测定方法的建立[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2012,18(8):121−124. [CHENG Q Q, WANG Q, WANG Z Z, et al. Establishment of a method for determination of uronic acid in ginseng polysaccharide[J]. Journal of Chinese Experimental Formulae,2012,18(8):121−124.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9903.2012.08.038 CHENG Q Q, WANG Q, WANG Z Z, et al. Establishment of a method for determination of uronic acid in ginseng polysaccharide[J]. Journal of Chinese Experimental Formulae, 2012, 18(8): 121−124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9903.2012.08.038
[15] JIANG H, ZHU H, HUO G, et al. Oudemansiella raphanipies polysaccharides improve lipid metabolism disorders in murine high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Nutrients,2022,14(19):4092. doi: 10.3390/nu14194092
[16] SONG Y, ZHU M, HAO H, et al. Structure characterization of a novel polysaccharide from Chinese wild fruits (Passiflora foetida) and its immune-enhancing activity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,1(136):324−331.
[17] CHEN Juncheng, ZHANG Xia, HUO Da, et al. Preliminary characterization , antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of polysaccharides from Mallotus furetianus[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,215:307−315.
[18] GONG Y, MA Y, CHEUNG P C, et al. Structural characteristics and anti-inflammatory activity of UV/H2O2-treated algal sulfated polysaccharide from Gracilaria lemaneiformis[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2021,152:112157. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112157
[19] KAHLON T S, SMITH G E. In vitro binding of bile acids by blueberries (Vaccinium spp.), plums (Prunus spp.), prunes (Prunus spp.), strawberries (Fragariaa X ananass), cherries (Malpighia punicifolia), cranberries (Vaccinium macrocarpon) and apples (Malus sylvestris)[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,100(3):1182−1187. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.10.066
[20] FU Y, YUAN Q, LIN S, et al. Physicochemical characteristics and biological activities of polysaccharides from the leaves of different loquat (Eriobotrya japonica) cultivars[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,135:274−281. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.157
[21] CAI S, WANG O, WANG M, et al. In vitro inhibitory effect on pancreatic lipase activity of subfractions from ethanol extracts of fermented oats (Avena sativa L.) and synergistic effect of three phenolic acids[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2012,60(29):7245−7251. doi: 10.1021/jf3009958
[22] CHEN B. Optimization of extraction of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides and its antioxidant and antitumour activities in vitro[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2010,81(2):420−424. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.02.039
[23] ZHU X, CHEN J, WANG H, et al. Mechanism of viscosity reduction of okra pectic polysaccharide by ascorbic acid[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2022,284:119196. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119196
[24] XU X, CHEN A, GE X, et al. Chain conformation and physicochemical properties of polysaccharide (glucuronoxylomannan) from fruit bodies of Tremella fuciformis[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,245:116354. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116354
[25] YANG Y, ZHAO M, LIN L. Effects of extraction methods on structural characteristics and bile acid-binding capacities of Moringa oleifera leaf polysaccharide fractions[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2020,55(4):1539−1546. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.14430
[26] WANG Y, XIN Y, YIN J, et al. Revealing the architecture and solution properties of polysaccharide fractions from Macrolepiota albuminosa (Berk.) Pegler[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,368:130772.
[27] TANG H, CHEN C, WANG S, et al. Biochemical analysis and hypoglycemic activity of a polysaccharide isolated from the fruit of Lycium barbarum L[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,77:235−242. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.03.026
[28] ZHANG H, ZOU P, ZHAO H, et al. Isolation, purification, structure and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from pinecones of Pinus koraiensis[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,251:117078. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117078
[29] SHI X, FENG J, WANG S, et al. Primary structure, physicochemical properties, and digestive properties of four sequentially extracted polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2023,115:105005. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2022.105005
[30] REN Y, LIU S. Effects of separation and purification on structural characteristics of polysaccharide from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa willd)[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2020,522(2):286−291. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.10.030
[31] GU J, ZHANG H, WEN C, et al. Purification, characterization, antioxidant and immunological activity of polysaccharide from Sagittaria sagittifolia L.[J]. Food Research International,2020,136:109345. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109345
[32] WU C, ZHAO M, BU X, et al. Preparation, characterization, antioxidant and antiglycation activities of selenized polysaccharides from blackcurrant[J]. Rsc Advances,2020,10(54):32616−32627. doi: 10.1039/D0RA06462A
[33] WALLER J R. Drugs for lipid disorders, antiplatelet drugs and fibrinolytics[J]. Medicine,2022,50(7):460−464. doi: 10.1016/j.mpmed.2022.04.012
[34] ZHENG M, TIAN X, LI Z, et al. Effects of ultra-high pressure assisted extraction on the structure, antioxidant and hypolipidemic activities of Porphyra haitanensis polysaccharides[J]. Food Chemistry,2024,437(2):137856.
[35] YAN J, YU Y, WANG C, et al. Production, physicochemical characteristics, and in vitro biological activities of polysaccharides obtained from fresh bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.) via room temperature extraction techniques[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,337:127798.
[36] NIE X, LI H, DU G, et al. Structural characteristics, rheological properties, and biological activities of polysaccharides from different cultivars of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) collected in China[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,139:459−467. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.016
[37] HUANG Y, MA Y, TSAI Y, et al. In vitro hypoglycemic, cholesterol-lowering and fermentation capacities of fiber-rich orange pomace as affected by extrusion[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,124:796−801. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.249
[38] RAZAK N Q A, GAN C, SHAFIE M H. Unlocking the potential of Garcinia atroviridis fruit polysaccharides:A synergistic approach for obesity and hypertension management[J]. Food Bioscience,2024,57:103553. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2023.103553
[39] MCCLEMENTS D J. Food hydrocolloids:Application as functional ingredients to control lipid digestion and bioavailability[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,111:106404. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106404
[40] GUO H, LIN S, LU M, et al. Characterization, in vitro binding properties, and inhibitory activity on pancreatic lipase of β-glucans from different Qingke (Tibetan hulless barley) cultivars[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,120:2517−2522. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.023
[41] QIN H, HUANG L, TENG J, et al. Purification, characterization, and bioactivity of Liupao tea polysaccharides before and after fermentation[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,353:129419. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129419
[42] 常相娜. 酶解改性苹果渣中多糖的制备、结构解析及脂质代谢调控机制[D]. 西安:陕西科技大学, 2022. [CHANG X N. Preparation, structure analysis and lipid metabolism regulation mechanism of polysaccharides from apple residue modified by enzymatic hydrolysis[D]. Xi'an:Shannxi University of Science and Technology, 2022.] CHANG X N. Preparation, structure analysis and lipid metabolism regulation mechanism of polysaccharides from apple residue modified by enzymatic hydrolysis[D]. Xi'an: Shannxi University of Science and Technology, 2022.
[43] MAITY P, SEN I K, CHAKRABORTY I, et al. Biologically active polysaccharide from edible mushrooms:A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,172:408−417. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.081
[44] KHAN A A, YAO F, CUI F, et al. Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties and biological activities of crude polysaccharides isolated from selected Auricularia cornea strains[J]. Food Bioscience,2024,60:104486. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104486





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



