Emulsifying Properties of Dietary Fiber from Different Sources
-
摘要: 本实验选取5种不同来源的膳食纤维(米糠、香蕉皮、苹果皮、燕麦麸皮以及柑橘皮)作为原料制备膳食纤维基水包油乳液。通过分析乳液的电位、粒径、乳析指数、Turbiscan稳定指数、流变特性等指标,探究不同浓度(1%、2%、3%)下各类膳食纤维稳定乳液的能力。结果表明:当纤维浓度从1%增加到3%时,所有乳液粒径均显著减小(P<0.05),其中米糠、香蕉皮、苹果皮、燕麦麸皮和柑橘膳食纤维乳液的D4,3值分别减小了49.94%、44.02%、33.68%、1.01%、0.17%。乳液Zeta电位绝对值和表观黏度随纤维浓度的增加而增大,且均在浓度为3%的米糠膳食纤维乳液中达到最大值(Zeta电位值:−59.45 mV;黏度:15.88 mPa·s)。贮藏稳定性结果显示,随着贮藏时间的延长,燕麦麸皮膳食纤维乳液和柑橘纤维稳定乳液出现明显的油水分离现象,乳化性能较其他各组更差;米糠、香蕉皮和苹果皮膳食纤维乳液底部出现明显的乳清层,且乳析指数随纤维浓度的增加而逐渐降低,当浓度达到3%时,米糠膳食纤维乳液贮藏5 d后的乳析指数最低(27.43%)、稳定性最高。综上,米糠膳食纤维在五种膳食纤维乳液中具有最佳的乳化性能,且浓度越大,乳液稳定性越高。本研究的结果证明了副产物膳食纤维在作为乳化剂稳定预乳化液方面的优良潜力,有望作为脂肪替代物应用于食品体系。Abstract: Five kinds of dietary fibers (rice bran, banana peel, apple peel, oat bran and citrus peel) from different sources were selected as row materials to prepare dietary fiber-based O/W emulsions and the ability of various types of dietary fibers to stabilize emulsions at different concentrations (1%, 2%, 3%) were investigated by analyzing Zeta potential, particle sizes, creaming index, Turbiscan stability index and rheological properties. The results showed that when the fiber concentration increased from 1% to 3%, the particle size D4,3 of all emulsions decreased significantly (P<0.05) by 49.94%, 44.02%, 33.68%, 1.01% and 0.17%, respectively, for rice bran, banana peel, apple peel, oat bran and citrus dietary fiber emulsions. The absolute value of Zeta potential and apparent viscosity increased with increasing fiber concentration, and both reached the maximum value in the rice bran dietary fiber emulsion with fiber concentration of 3% (Zeta potential value: −59.45 mV; viscosity: 15.88 mPa·s). The results of storage stability suggested that with the extension of storage time, oat bran dietary fiber emulsion and citrus fiber emulsion showed obvious oil-water layered, and the emulsification ability was lower than that of other groups. There was obvious clear layer shown at the bottom of rice bran, banana peel and apple peel dietary fiber emulsion, and the creaming index decreased gradually with the increase of fiber concentration. When the concentration reached 3%, the rice bran dietary fiber emulsion after 5 d of storage showed the lowest (27.43%) creaming index and the highest stability. In conclusion, rice bran dietary fiber exhibited the best emulsifying property among the five dietary fiber emulsions, and the higher the concentration, the higher the stability of the emulsion. This study demonstrates the excellent potential of by-product dietary fiber as an emulsifier to stabilize pre-emulsion, which is expected to be used as a fat substitute in food system.
-
Keywords:
- dietary fiber /
- emulsifier /
- emulsifying properties /
- stability
-
乳液是两种互不相溶的相借助特定的乳化剂而形成的乳化体系,通常包含水相和油相[1−2]。乳液目前已被广泛应用在食品和药品体系中,如牛奶、冰淇淋、配制乳膏以及凝胶等产品[3]。乳液属于热力学不稳定体系,随着时间延长它们会由于液滴聚集、聚结、分层、相转变、物理不稳定、氧化和水解等物理和化学不稳定现象而絮凝分层[4−5]。因此,食品工业中常添加乳化剂等以提高乳液体系的稳定性,从而延长其保质期[6]。目前,高分子量乳化剂/稳定剂(蛋白质、多糖)和小分子表面活性剂都可被用来稳定乳液。然而在某些条件下,较高的成本和有限的乳化效果会限制其在实际生产加工中的应用[7]。因此寻找低成本、乳化性能较好的乳化剂是食品行业的研究热点。
膳食纤维由于其降低慢性疾病的发生风险和促进健康的生理活性功能而被认定为人体必需的“第七大营养素”,研究表明其具有控制血糖水平、降低胆固醇、预防肥胖以及促进肠道蠕动等作用[8−9]。此外,添加在食品中的膳食纤维还可改善食品的品质特性:张华等[10]将竹笋膳食纤维加入面团中,显著提高了面团的弹性、黏性,增强了面团的持水能力;有研究将马铃薯膳食纤维添加在猪肝酱中加工出了具有较好的质地、风味和颜色的肝酱[11];Choi等[12]将米糠膳食纤维添加在法兰克福香肠中,不仅降低了香肠的脂肪含量,而且证实了含有米糠纤维的法兰克福香肠具有较好的质地和风味。因膳食纤维结构中含有较多的亲水基团而具有较好的水合特性,近年来吸引了很多科研人员的关注[13]。已有部分研究证明以植物基膳食纤维作乳化剂稳定的食品乳液具有较好的稳定性:栗俊广等[14]采用鹰嘴豆膳食纤维制备水包油乳液,发现当鹰嘴豆膳食纤维浓度达到2%时,乳液在贮藏72 h后未发生乳析现象,具有较好的稳定性。何康慧[15]采用竹笋膳食纤维稳定水包油Pickering乳液,结果表明当竹笋纤维的含量高达0.05wt%时,放置一个月后乳液粒径大小几乎不发生变化,且受温度、pH等环境的影响较小。然而,在谷物类和果蔬行业中,高达40%以上的果皮、残渣以及农业加工副产品等被丢弃或用作低成本的动物饲料。这不仅给产业带来了巨大的处理成本,而且造成了严重的资源浪费[16]。这些果皮残渣以及副产品中往往存在较高含量的膳食纤维、维生素、矿物质等营养成分,对人体健康有利。因此,加快实现农业以及果蔬副产物的高附加值利用至关重要。米糠,是稻米加工的副产物,富含膳食纤维、维生素、矿物质等多种营养成分,其中膳食纤维的含量高达约40%[17]。香蕉皮占香蕉总质量的比例高达30%,且香蕉皮、苹果皮和柑橘皮中均富含纤维素、半纤维素、无机盐等多种营养物质以及生物活性物质[18−21];燕麦麸皮是燕麦加工的主要副产物,热量低,富含膳食纤维,然而燕麦麸皮主要被用于畜禽饲料,利用率低[22−23]膳食纤维优异的乳化性能和生理功能已被广泛应用于各种乳液的稳定以及食品加工行业中。
基于此,本研究选取了五种膳食纤维含量丰富的、具有高附加值的米糠膳食纤维(Rice bran dietary fiber,RF)、香蕉皮膳食纤维(Banana peel dietary fiber,BF)、苹果皮膳食纤维(Apple peel dietary fiber,AF)、燕麦麸皮膳食纤维(Oat bran dietary fiber,OF)和柑橘纤维(Citrus dietary fiber,CF),用于制备不同浓度的膳食纤维-大豆油乳液,通过测定乳液电位、粒径、贮藏稳定性、Turbiscan稳定指数 (Turbiscan stability index,TSI)和表观黏度对不同膳食纤维稳定的水包油乳液的稳定性进行评价,以揭示副产物膳食纤维在食品乳液中的应用价值。以期揭示膳食纤维在食品乳液中的应用前景。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
天然米糠膳食纤维(灰分:7.83%;蛋白质:4.42%;脂肪:1.26%;淀粉2.45%;总膳食纤维:79.52%)、苹果皮膳食纤维(灰分:3.22%;蛋白质:8.42%;脂肪3.24%;总膳食纤维:62.6%) 陕西沐菲生物科技有限公司;香蕉皮膳食纤维(灰分:12.5%;蛋白质:9.33%;脂肪:7.87%;总膳食纤维:60.88%)、燕麦麸皮膳食纤维(灰分:5.15%;蛋白质:3.42%;脂肪:3.39%;膳食纤维:66.14%) 兰州沃特莱斯生物科技有限公司;柑橘皮膳食纤维(灰分:2.97%;蛋白质:6.53%;脂肪:2.35%;膳食纤维:61.26%) 西安宜珺生物科技有限公司;金龙鱼大豆油 益海嘉里金龙鱼粮油食品有限公司;无水乙醇 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;所有试剂均为分析纯。
160目检验筛 绍兴上虞圣超仪器设备有限公司;Shimadzu AUY 120分析天平 日本岛津公司;SANYO制冰机(SIM-F124) 日本三洋公司;IKA C-MAG HS7 磁力搅拌器、Ultra Turrax T-25 Basic 高速匀浆机 德国IKA公司;Malvern Mastersizer 3000 激光粒度仪、Zetasizer Nano ZS 90 zeta电位仪 英国马尔文仪器有限公司;Turbiscan多重光散射仪 法国Formulaction有限公司;Anton Paar动态剪切流变仪 安东帕有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 五种不同来源的膳食纤维的傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(Fourier transform infrared spectrometer,FTIR)分析
将所有干燥后的膳食纤维与色谱级KBr粉末以1:100比例混合研磨后,用压片机制成透明片,置于傅里叶变换红外光谱仪上测定。每个样品均在4000~400 cm−1波数范围内进行扫描,分辨率设置为4 cm−1。
1.2.2 膳食纤维-大豆油预乳化液制备方法
首先将天然米糠膳食纤维(RF)、香蕉皮膳食纤维(BF)、苹果皮膳食纤维(AF)、燕麦麸皮膳食纤维(OF)和柑橘皮膳食纤维(CF)五种膳食纤维过160目筛子,与超纯水分别以0.1:10(W/V)、0.2:10(W/V)和0.3:10(W/V)的比例混合,磁力搅拌过夜水合后,得到质量浓度为1%、2%和3%的膳食纤维水溶液。将大豆油与不同浓度的5种膳食纤维水溶液按1:4(V/V)比例混合,冰浴中以15000 r/min均质乳化40 s,均质3次,得到浓度为1%、2%和3%的膳食纤维预乳化液,分别记为1%-RF、1%-BF、1%-AF、1%-OF、1%-CF乳液、2%-RF、2%-BF、2%-AF、2%-OF、2%-CF乳液和3%-RF、3%-BF、3%-AF、3%-OF、3%-CF乳液。对照组乳液为大豆油与超纯水按1:4(V/V)比例混合并均质后得到。
1.2.3 膳食纤维-大豆油乳液电位的测定
参考Gao等[24]的方法,采用Zetasizer Nano-ZS 90 电位仪测定乳液的电位。新鲜制备的膳食纤维-大豆油预乳化液超纯水稀释50倍后进行分析测定,所有测试均在室温下进行。
1.2.4 膳食纤维-大豆油乳液粒径大小及其分布的测定
参考Liu等[17]的方法并略加以修改。不同乳液的平均粒径和粒度分布采用Mastersizer 3000激光粒度仪进行分析测定。将新鲜制备的乳液立即滴入样品池,以防止聚集和絮凝。激光遮挡范围为10%~20%;颗粒折射率和吸收率分别设置为1.436和0.001;分散剂为水,分散剂折射率为1.330。
1.2.5 膳食纤维-大豆油乳液贮藏稳定性的测定
将制备好的乳化液立即转移到有盖玻璃瓶中,密封,在4 ℃下保存5 d,观察乳液分层情况。乳液将分离成上部乳化层和下部乳清层(第1 h内间隔30 min记录一次H2,随后间隔3 h记录一次,24 h后记录时间间隔为1 d)。乳液的乳析指数(Creaming index,CI)为乳清层高度与乳液总高度的比值,计算公式如式(1)所示[25−26]。
CI(%)=H2H1×100 (1) 式中:H1为乳液总高度(cm);H2为乳清层的高度(cm)。
1.2.6 膳食纤维-大豆油乳液TSI的测定
TSI可以反映乳液的动力学稳定性。参考Mengual等[27]的方法,采用多重光散射仪测定乳液的TSI值。取新鲜制备的乳液约20 mL于专用玻璃瓶中进行扫描测试,近红外光(880 nm)从乳液底部向上部扫描,时间间隔为110 s,扫描时间为12 h,测试温度设定为25 ℃。TSI的计算如式(2)所示:
TSI=∑i∑h|scani(h)-scani-1(h)|H (2) 式中:scani为第i次扫描的平均后向散射强度,scani-1为第(i-1)次扫描的平均后向散射强度,h为乳液在仪器中的扫描高度;H为整个测试的扫描次数。
1.2.7 膳食纤维-大豆油乳液表观黏度的测定
乳液的表观黏度参考赵颖颖等[28]的方法,并进行适当修改。表观黏度的大小由Anton Paar动态剪切流变仪通过稳态剪切测试测得。将新鲜制备的样品均匀放置于50 mm平板上,防止产生气泡。测试使用PP50不锈钢平板;测试参数为:测试温度设置为25 ℃;间隙设置为1 mm,剪切速率范围为0.1~100 s−1。
1.3 数据处理
采用Excel 2010和SPSS 26.0进行数据统计学分析。采用单因素ANOVA分析和Duncan's多重比较法对不同处理组间差异进行统计分析。所有图形均由GraphPad Prism 9.5绘制。所有实验均进行三次及以上。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 五种不同来源的膳食纤维的FTIR分析
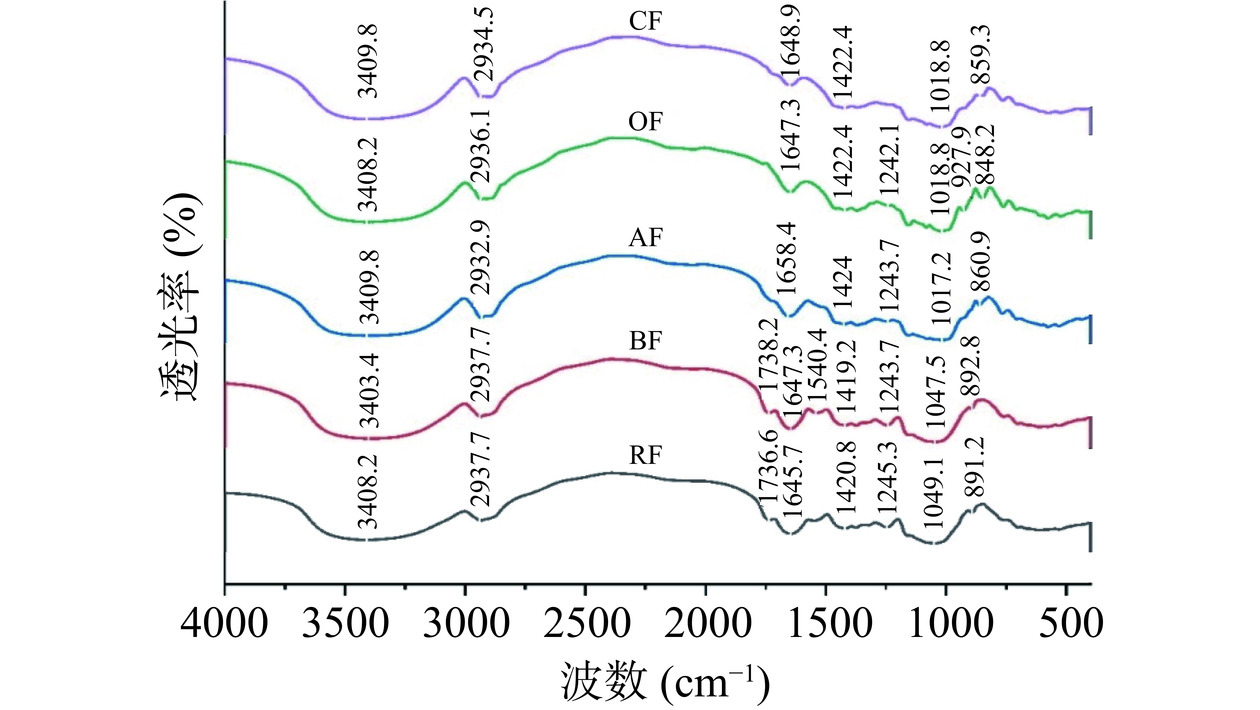
采用FTIR光谱对五种不同来源的膳食纤维的分子结构和官能团进行分析(图1),并与相关文献数据进行了比较[23,29−31]。在五种膳食纤维的FTIR光谱图中,接近3400、2930、1640、1400、1000~1100和800~900 cm−1的吸收峰是共享波段。3400 cm−1处较宽的吸收峰对应于O-H的伸缩振动。2930 cm−1处的谱带与纤维素中的甲基或亚甲基的C-H的张力和弯曲振动有关。RF和BF在1730 cm−1处吸收峰的强度高于AF、OF和CF。RF和CF也共享1730和1540 cm−1处的波段。其中1730和1540 cm−1处的峰分别归因于半纤维素中乙酰基和糖醛酯基团和木质素中芳香环C=O的振动[32]。纤维素中的特征吸收峰位于1640和1018 cm−1处。根据Tibolla等[33]的研究,该区域(1240 cm−1)的谱带可能与半纤维素的组成有关。处于800~1000 cm−1的峰通常与α-吡喃糖有关。其中,接近890 cm−1处的峰可能表明RF和BF中存在葡萄糖的β构型[34]。
2.2 膳食纤维来源及浓度对乳液Zeta电位的影响
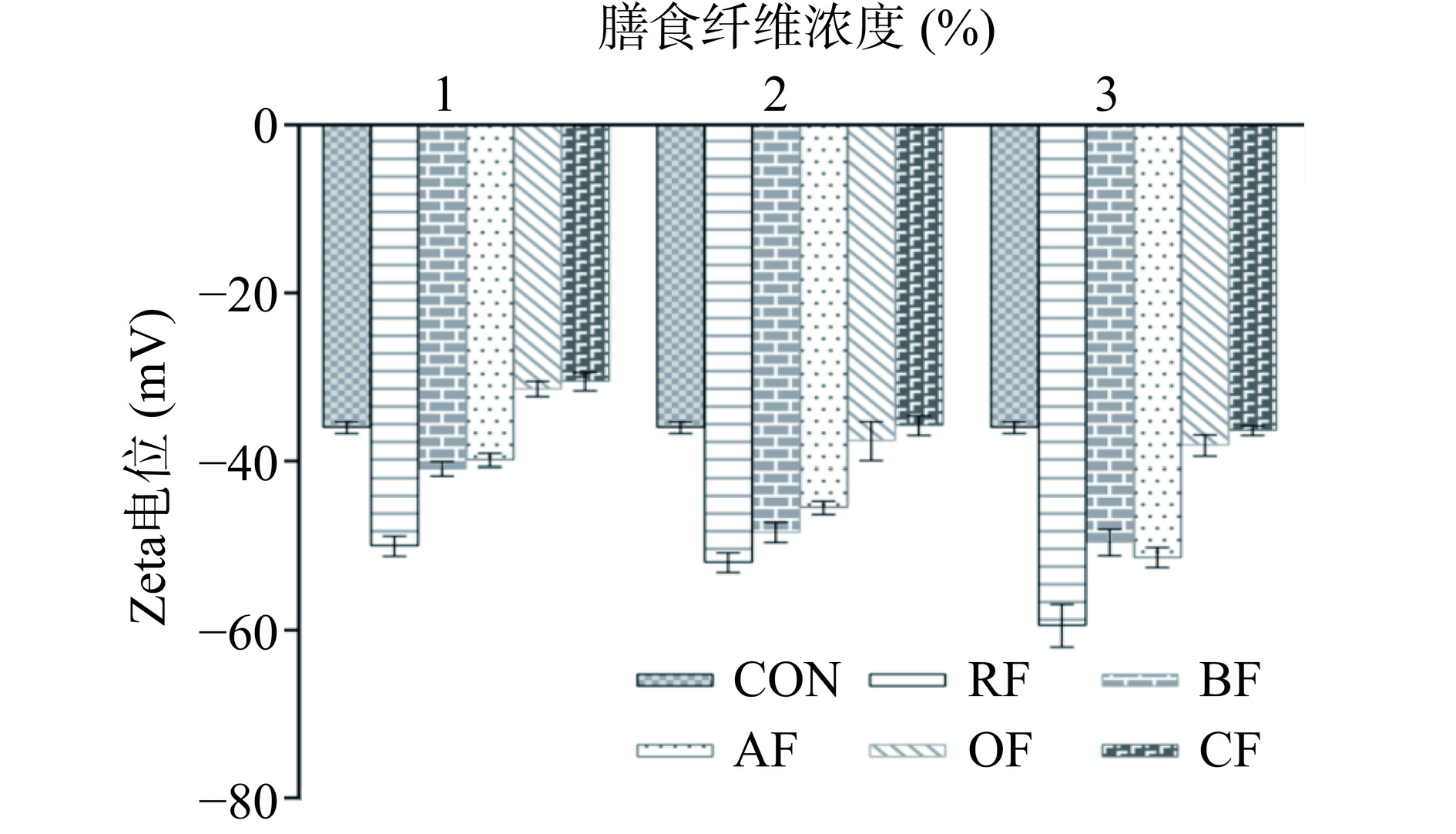
Zeta电位可以衡量乳液液滴在分散体系中的稳定性,反映液滴间的静电相互作用和空间位阻效应[35−36]。通常,大多数胶体体系通过静电排斥作用维持稳定的,胶体粒子之间的排斥力越大,它们发生聚集或者絮凝的可能性就越低,抗聚结稳定性越高[37]。一般认为,Zeta电位绝对值小于30 mV的乳液具有较弱的稳定性,而高于30 mV的乳液因存在较高的静电斥力而较为稳定[38]。图2为膳食纤维(RF、BF、AF、OF、CF)在不同浓度下(1%、2%、3%)制备的膳食纤维-大豆油乳液的Zeta电位值图。由图可知,所有处理组的Zeta电位值均为负值,说明乳液中的五种纤维粒子均带负电荷;且Zeta电位绝对值均高于30 mV,说明乳液均具有较好的稳定性。对于同种膳食纤维,随着膳食纤维浓度的增加,乳液的Zeta电位绝对值增大,表明较高浓度的膳食纤维稳定的水包油乳液液滴之间的静电斥力和空间位阻更大,阻碍或减缓了液滴的聚集,从而提高乳液体系的稳定性。另外,纤维浓度的增加使得乳液体系中的负电荷增多,从而提高乳液的Zeta电位绝对值。综上,在相同的膳食纤维浓度条件下(1%、2%、3%),由不同膳食纤维稳定的水包油乳液稳定性顺序为:RF乳液>BF乳液>AF乳液>OF乳液>CF乳液,且随着纤维浓度的增加,不同乳液的Zeta电位均逐渐减小;当纤维浓度为3%时,RF乳液的Zeta电位值最小(−59.45±2.32 mV),稳定性最佳。在不同膳食纤维浓度条件下,RF、AF和BF乳液的Zeta电位均小于对照组(−36.02±0.64 mV);OF乳液的Zeta电位在1%浓度时高于对照组,浓度为2%和3%时低于对照组;而不同浓度的CF稳定的乳液Zeta电位与对照组均无显著差异(P>0.05),且1%浓度时高于对照组,表明CF乳液较差的稳定性。
2.3 膳食纤维来源及浓度对乳液粒径的影响
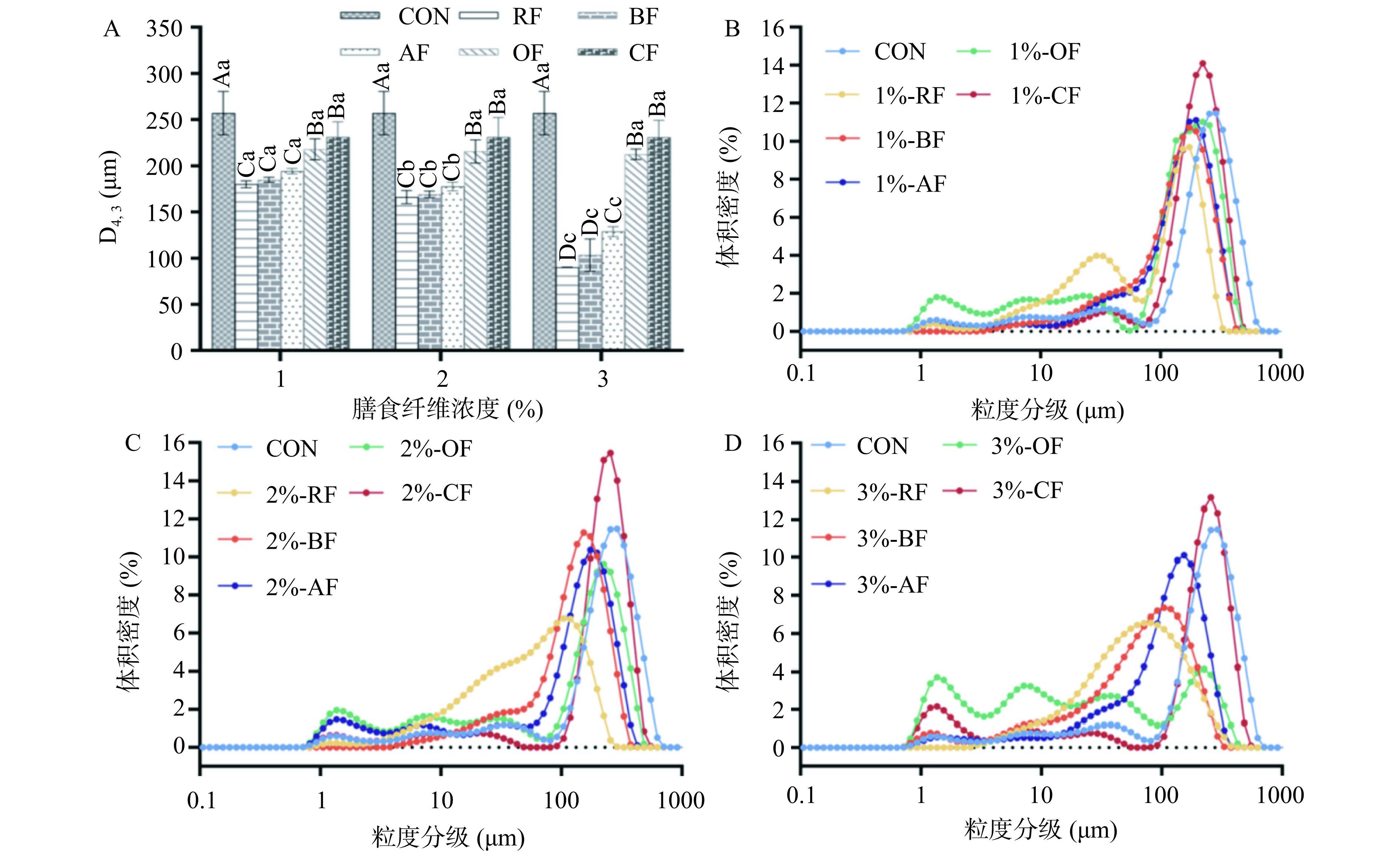
液滴大小和粒度分布是影响乳液稳定性的重要参数,通常乳液液滴越小,乳液的稳定性越好[39−40]。D4,3对乳液中大颗粒的存在较为敏感,更能反映聚结等失稳现象。乳状液液滴的大小受到诸多因素的影响,如膳食纤维颗粒的浓度、油的类型及含量等。如图3A,同种膳食纤维稳定的水包油乳液的D4,3随着膳食纤维浓度的增加而减小,这是因为有更多的膳食纤维来稳定更大的界面面积所致[14],且不同浓度的RF、BF、AF、OF和CF乳液的粒径均显著(P<0.05)小于对照组(257±20.94 μm)。此外,由于较高浓度的膳食纤维稳定的水包油乳液具有较高的Zeta电位绝对值,静电斥力和空间位阻较大,导致液滴之间难以聚结或絮凝,从而减小了液滴粒径。这一变化趋势与对纤维素纳米晶和微纤化纤维素稳定乳液的粒径结果相似:即随着纤维素浓度的增大,乳液液滴变小[41]。另外,乳液液滴的大小也受到膳食纤维类型的影响,当膳食纤维浓度相同时,由不同种类膳食纤维稳定的水包油乳液的D4,3值从小到大依次为:RF乳液、BF乳液、AF乳液、OF乳液、CF乳液。其中3%的RF乳液的粒径最小(90.10±0.19 μm),表明RF乳液具有最好的稳定性。图3B~图3D分别为浓度1%、2%和3%的五种膳食纤维稳定的水包油乳液的粒径分布曲线。由粒径分布图可知,纤维浓度为1%的RF乳液的粒径呈双峰分布,较小的峰可能反映油滴尺寸,而较大的峰可能为悬浮液中的不溶性膳食纤维[16],随着纤维浓度增加到2%和3%,双峰逐渐向单峰转变,表明RF添加量的增加使得体系产生了粒径更小更均匀的乳液液滴[42−43];而由BF、AF、OF和CF稳定的乳液则呈现多峰行为。对于同一种膳食纤维稳定的乳液,随着纤维浓度从1%增加到3%,乳液的总体粒径分布峰整体向左偏移,这与D4,3结果相对应。当膳食纤维浓度相同时,RF乳液的体积分布峰值均处于粒径较小的一方,且粒径越小,黏度越大,流动性越差,因此乳液体系稳定性越高[44]。综上,3%的RF乳液粒径最小,表现出最佳的乳液稳定性,且五种膳食纤维稳定的水包油乳液稳定性顺序与Zeta电位结果相一致。
2.4 膳食纤维来源及浓度对乳液贮藏稳定性的影响
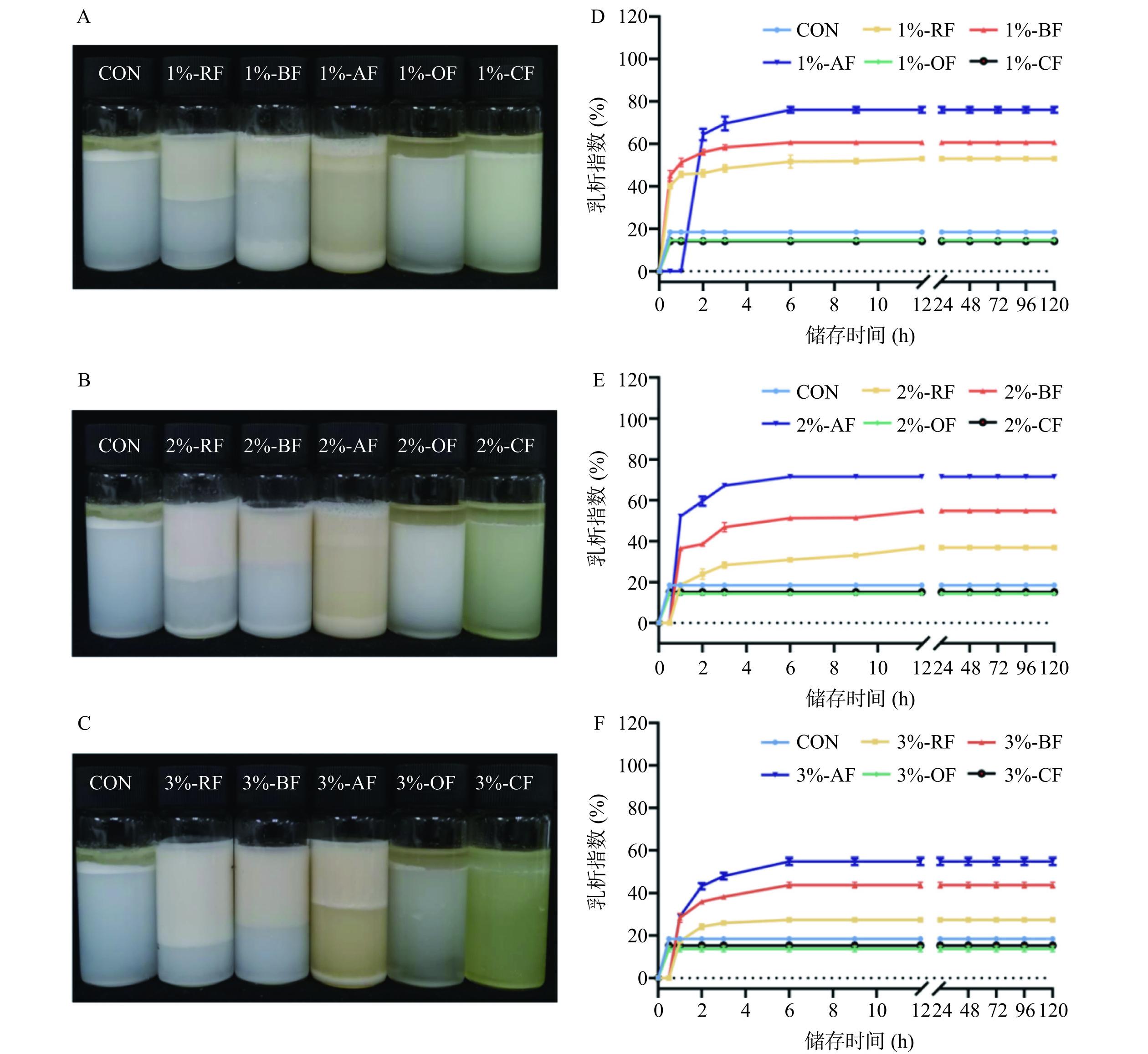
乳析指数可以间接反映乳液在贮藏期间的聚集和絮凝程度,是评估乳液贮藏稳定性的关键指标之一[45]。乳析指数越小,代表乳液透明乳清层的高度越小,乳液越稳定[46]。图4分别表示浓度为1%(A)、2%(B)和3%(C)的5种膳食纤维-大豆油乳液贮藏5 d后的外观状态,以及浓度为1%(D)、2%(E)和3%(F)的5种膳食纤维-大豆油乳液在贮藏5 d过程中的乳析指数变化。由图4 A~图4C可知,5种膳食纤维-大豆油乳液贮藏5 d后均出现不同的分层现象:RF乳液底部出现了明显的澄清层;BF乳液和AF乳液底部均出现了沉淀物,中间为澄清的乳清层,且随着浓度从1%增加到3%,底部沉淀物逐渐减少;OF乳液和CF乳液上层出现明显的油水分离现象,与对照组现象相一致,表明燕麦麸皮膳食纤维和柑橘皮膳食纤维颗粒不能很好的吸附在油水界面稳定乳液,从而导致乳液在贮藏较短时间内即发生明显的相分离现象。RF、BF和AF的乳化效果均优于OF、CF和对照组。对于同种膳食纤维(除了OF和CF),随着膳食纤维浓度从1%增加到3%,乳清层的高度逐渐减小,乳析指数逐渐减小(图4D~图4F),表明膳食纤维-大豆油乳液在贮藏5 d内的分层稳定性随着膳食纤维浓度增加而增加,且在不同的纤维浓度下,贮藏5 d后RF乳液的乳析指数均为最小(1%:53.08%±0.92%;2%:36.86%±0.33%;3%:27.43%±0.52%),表现出最好的分层稳定性。乳液分层稳定性的提高也可能与乳液液滴粒径相关,较小的液滴尺寸会增加连续相之间的黏度,进而阻止大量液滴的迁移。赵强忠等[46]在探究不同浓度的大豆纤维稳定的玉米油水包油乳液的研究中得出了相似的结论,随着大豆纤维浓度从0.125%增加到0.75%,大豆纤维乳液的乳析指数逐渐降低。在不同浓度的条件下,虽然OF乳液、CF乳液的乳析指数最小,但由于燕麦麸皮膳食纤维和柑橘皮膳食纤维颗粒未能很好的包裹住油滴,从而在上层析出油相,表现出较差的乳液稳定性。
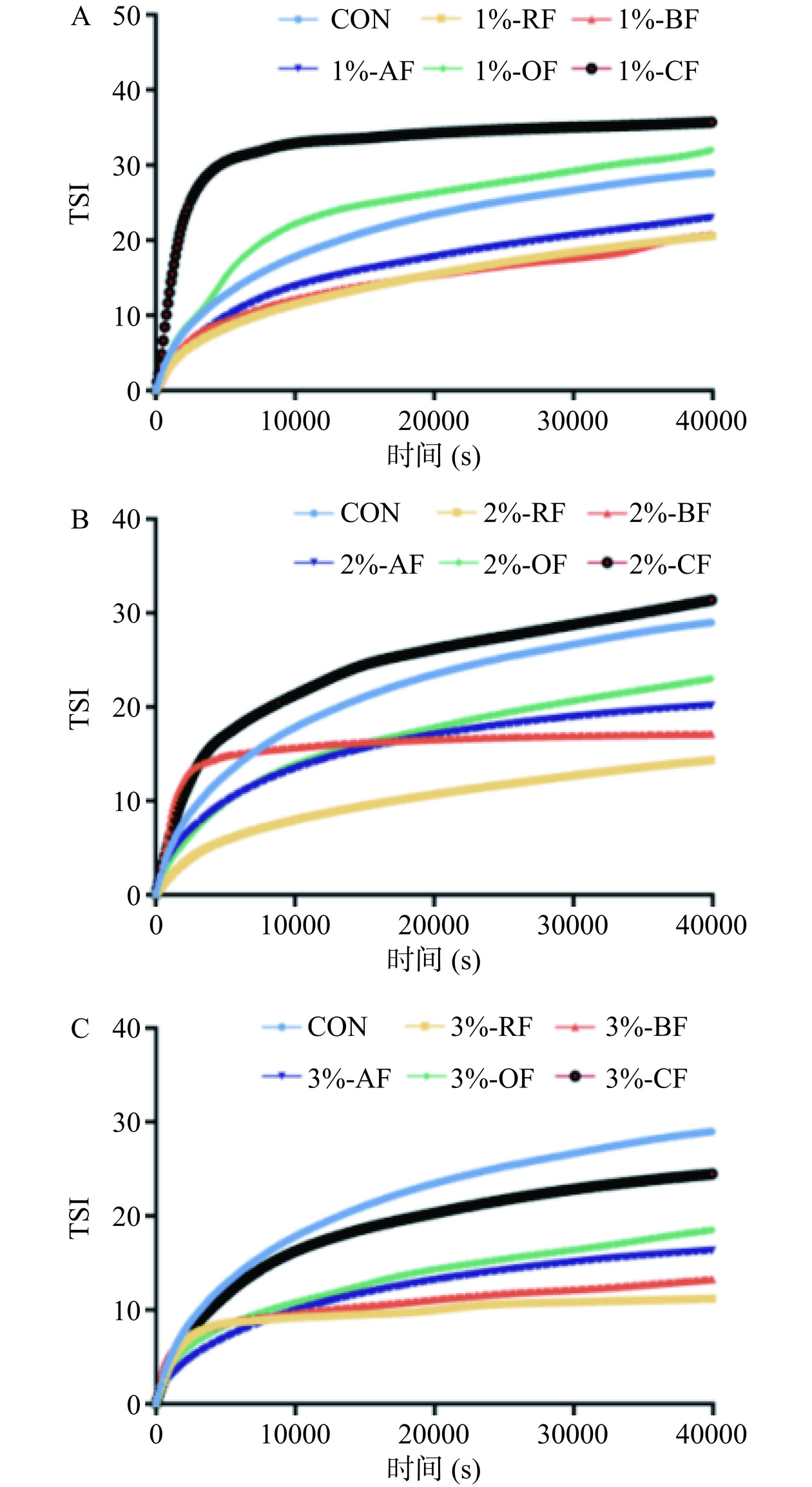
2.5 膳食纤维来源及浓度对乳液Turbiscan稳定指数(TSI)的影响
TSI可以用来表征乳液的稳定性,较小的TSI值表明乳液体系较高的稳定性[47]。如图5所示,全部乳液的TSI值随着扫描时间的延长先逐渐增大后逐渐趋于平稳。对于同种膳食纤维,纤维浓度的增加会提高乳液体系的稳定性。而对于相同浓度的纤维制备的乳液,RF稳定的水包油乳液的TSI值均最小,表明RF稳定乳液的能力最佳;其中,当纤维浓度为2%时,CF乳液的TSI值高于对照组,表明柑橘皮纤维不具备较好的乳化性能,这一结果与贮藏稳定性变化情况相对应。综上,浓度为3%的RF乳液TSI值最小,表现出最佳的乳液稳定性。
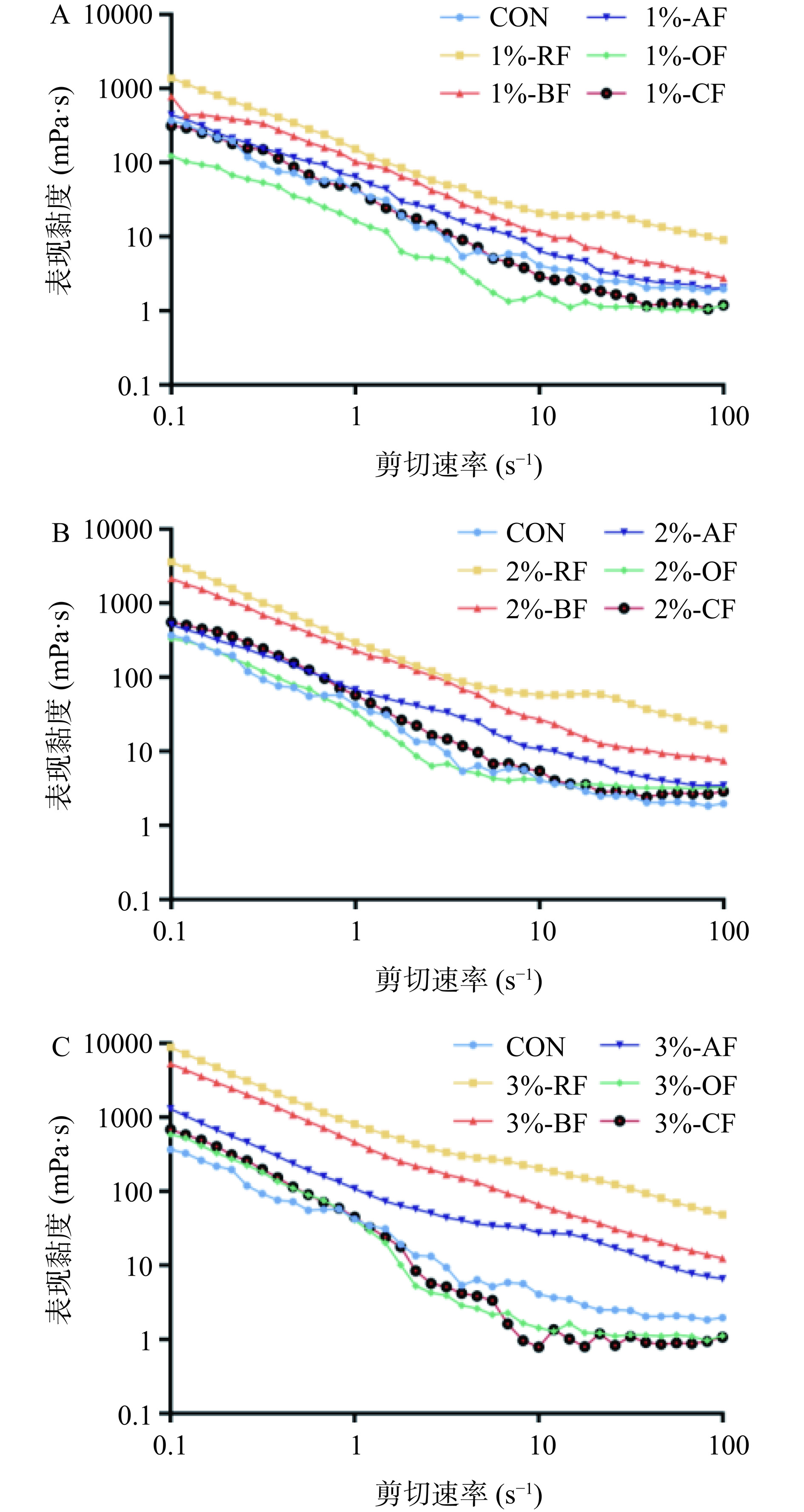
2.6 膳食纤维来源及浓度对乳液表观黏度的影响
通过测定乳液的稳态剪切行为,研究了不同浓度的膳食纤维稳定的水包油乳状液的表观黏度随剪切速率的变化规律。如图6所示,所有乳液的表观黏度均随剪切速率的增加而降低,表明这些乳液均为假塑性流体,并表现出典型的剪切变薄行为,这主要是乳液液滴之间的网络结构被破坏造成的[13]。对于同种膳食纤维,1%和2%浓度条件下制备的乳液的黏度均小于3%。有报道称[14]表观黏度的增大可能与体系中增加的粒子数有关,纤维浓度的提高会增加体系中的颗粒数,粒子间的相互作用和摩擦增强,从而使膳食纤维形成的网络结构更稳定,提高乳液体系之间的黏度。也有研究发现膳食纤维主要通过形成网络结构来稳定乳液,较低浓度的膳食纤维不足以形成基于纤维的网络或形成的网络结构刚性较弱,因此表观黏度更低[48]。这与栗俊广等[14]的研究结果相似,鹰嘴豆膳食纤维(CDF)乳液的表观黏度随着CDF浓度的增加而增加。综上,当膳食纤维浓度相同时,不同种膳食纤维稳定的乳液的表观黏度大小顺序为:RF乳液>BF乳液>AF乳液 >CF乳液>OF乳液,表明米糠膳食纤维稳定乳液的性能最佳,而OF乳液、CF乳液与对照组的表观黏度相近,乳化效果较差。
3. 结论
本实验验证了不同来源的副产物膳食纤维稳定大豆油乳液的能力。结果表明:在相同纤维浓度下,相较于BF乳液、AF乳液、OF乳液和CF乳液,RF乳液的粒径最小,Zeta电位值最小且乳液在12 h贮藏中TSI值变化最小,具有更高的抗聚结稳定性;而对于同种膳食纤维,纤维浓度的增加,会增强粒子间的静电斥力和空间位阻、降低乳液液滴的粒径、提高乳液体系的表观黏度,从而形成更强的纤维基网络结构,进一步提高了乳液体系的稳定性。因此,在五种膳食纤维中,浓度为3%的RF的乳化性最好,此研究证实了米糠膳食纤维是一种成本低、性能佳的天然乳化剂,同时揭示了副产物膳食纤维在稳定乳液方面的应用潜力,为其作为脂肪替代物在食品加工中的应用提供理论指导。然而RF乳液的整体稳定性依然不佳,因此后续研究中可进一步探究提高RF乳液稳定性的方法,如对米糠膳食纤维进行化学、物理或者生物改性等。
-
-
[1] FENG T, HU Z, WANG K, et al. Emulsion-based delivery systems for curcumin:Encapsulation and interaction mechanism between debranched starch and curcumin[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,161:746−754. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.088
[2] THAIWONG N, THAIUDOM S. Stability of oil-in-water emulsion influenced by the interaction of modified tapioca starch and milk protein[J]. International Journal of Dairy Technology,2021,74(2):307−315. doi: 10.1111/1471-0307.12766
[3] ASHAOLU T J, ZHAO G. Fabricating a pickering stabilizer from okara dietary fibre particulates by conjugating with soy protein isolate via maillard reaction[J]. Foods,2020,9(2):143. doi: 10.3390/foods9020143
[4] HONG X, ZHAO Q, LIU Y, et al. Recent advances on food-grade water-in-oil emulsions:Instability mechanism, fabrication, characterization, application, and research trends[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2023,63(10):1406−1436. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1964063
[5] LI J, WANG Q, MENG F, et al. Analysis of instability of starch-based Pickering emulsion under acidic condition of pH<4 and improvement of emulsion stability[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 261(Pt 2):129886.
[6] MAPHOSA Y, IKHU-OMOREGBE D I, ADEYI O, et al. Effect of storage time and temperature on the stability and rheological properties of starch-soluble dietary fiber nanocomposite stabilized emulsion[J]. Chemistry Engineering Communications,2024,211(4):546−558. doi: 10.1080/00986445.2023.2261099
[7] CAI Y, HUANG L, CHEN B, et al. Effect of alkaline pH on the physicochemical properties of insoluble soybean fiber (ISF), formation and stability of ISF-emulsions[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,111:106188. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106188
[8] KETENOGLU O, MERT B, TEKIN A. Effects of microfluidized dietary fibers on stability properties of emulsions[J]. Journal of Texture Studies,2014,45(4):295−306. doi: 10.1111/jtxs.12074
[9] 姜龙波, 吕静, 张喜文, 等. 小米糠膳食纤维复合酶法改性工艺优化[J]. 轻工学报,2017,32(5):16−23. [JIANG Longbo, LÜ Jing, ZHANG Xiwen, et al. Process optimization of complex enzyme modification of millet bran dietary fiber[J]. Journal of Light Industry,2017,32(5):16−23.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1553.2017.5.003 JIANG Longbo, LÜ Jing, ZHANG Xiwen, et al. Process optimization of complex enzyme modification of millet bran dietary fiber[J]. Journal of Light Industry, 2017, 32(5): 16−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-1553.2017.5.003
[10] 张华, 李银丽, 李佳乐, 等. 竹笋膳食纤维对冷冻面团流变学特性、水分分布和微观结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(1):53−57. [ZHANG Hua, LI Yinli, LI Jiale, et al. Effect of bamboo shoot dietary fiber on rheological properties, moisture distribution and microstructure of frozen dough[J]. Food Science,2018,39(1):53−57.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201801008 ZHANG Hua, LI Yinli, LI Jiale, et al. Effect of bamboo shoot dietary fiber on rheological properties, moisture distribution and microstructure of frozen dough[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(1): 53−57. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201801008
[11] KAACK K, LÆRKE H N, MEYER A S. Liver pate enriched with dietary fibre extracted from potato fibre as fat substitutes[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2006,223(2):267−272. doi: 10.1007/s00217-005-0200-1
[12] CHOI Y S, KIM H W, HWANG K E, et al. Effects of fat levels and rice bran fiber on the chemical, textural, and sensory properties of frankfurters[J]. Food Science and Biotechnology,2015,24(2):489−495. doi: 10.1007/s10068-015-0064-5
[13] 张静. 燕麦膳食纤维复合物稳定的Pickering乳液对乳化香肠品质的影响[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学, 2023. [ZHANG Jing. Effect of pickering emulsions stabilized by oat dietary fiber complex on the quality of emulsified sausage[D]. Hohhot:Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2023.] ZHANG Jing. Effect of pickering emulsions stabilized by oat dietary fiber complex on the quality of emulsified sausage[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2023.
[14] 栗俊广, 马旭阳, 姜茜, 等. 鹰嘴豆膳食纤维的乳化性能[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(19):108−114. [LI Junguang, MA Xuyang, JIANG Xi, et al. Study on dietary fiber properties of chickpea[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(19):108−114.] LI Junguang, MA Xuyang, JIANG Xi, et al. Study on dietary fiber properties of chickpea[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(19): 108−114.
[15] 何康慧. 竹笋水不溶性膳食纤维稳定Pickering乳液及其应用[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学, 2021. [HE Kanghui. Water-insoluble dietary fiber of bamboo shoot stabilizing Pickering emulsion and its application[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021.] HE Kanghui. Water-insoluble dietary fiber of bamboo shoot stabilizing Pickering emulsion and its application[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021.
[16] WALLECAN J, MCCRAE C, DEBON S J J, et al. Emulsifying and stabilizing properties of functionalized orange pulp fibers[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,47:115−123. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.01.009
[17] LIU Z, SHEN R, YANG X, et al. Characterization of a novel konjac glucomannan film incorporated with Pickering emulsions:Effect of the emulsion particle sizes[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,179:377−387. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.02.188
[18] 邓艺杰, 张奕恺. 香蕉皮膳食纤维提取工艺优化及其应用研究[J]. 中国调味品,2023,48(8):131−134. [DENG Yijie, ZHANG Yikai. Optimization of extraction process of dietary fiber from banana peel and its application[J]. Chinese Condiments,2023,48(8):131−134].] DENG Yijie, ZHANG Yikai. Optimization of extraction process of dietary fiber from banana peel and its application[J]. Chinese Condiments, 2023, 48(8): 131−134].
[19] 崔芙蓉, 贝玉龙, 怀美玉, 等. 苹果皮膳食纤维饮料的开发[J]. 食品安全导刊, 2020(33):137, 139. [CUI Furong, BEI Yulong, HUAI Meiyu, et al. Development of apple peel dietary fiber beverage[J]. Food Safety Guide, 2020(33):137, 139.] CUI Furong, BEI Yulong, HUAI Meiyu, et al. Development of apple peel dietary fiber beverage[J]. Food Safety Guide, 2020(33): 137, 139.
[20] 焦孝平. 苹果副产物资源化利用调查研究[J]. 甘肃科技,2022,38(16):72−74,81. [JIAO Xiaoping. Investigation on resource utilization of apple by-products[J]. Gansu Science and Technology,2022,38(16):72−74,81.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0952.2022.16.019 JIAO Xiaoping. Investigation on resource utilization of apple by-products[J]. Gansu Science and Technology, 2022, 38(16): 72−74,81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0952.2022.16.019
[21] 周静, 魏春菊, 赵涛, 等. 物理法改性对不同品种柑橘皮渣纤维结构及理化功能特性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2024,50(22):176−185. [ZHOU Jing, WEI Chunju, ZHAO Tao, et al. Effects of physical modification on structural and physico-chemical functional propreties of fibers from different varieties of citrus peel pomace[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2024,50(22):176−185.] ZHOU Jing, WEI Chunju, ZHAO Tao, et al. Effects of physical modification on structural and physico-chemical functional propreties of fibers from different varieties of citrus peel pomace[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2024, 50(22): 176−185.
[22] 白雪. 预处理燕麦麸皮改善肠道菌群和调节糖脂代谢作用机制研究[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学, 2023. [BAI Xue. Study on the mechanism of pretreated oat bran improving intestinal flora and glucolipid metabolism[D]. Hohhot:Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2023.] BAI Xue. Study on the mechanism of pretreated oat bran improving intestinal flora and glucolipid metabolism[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2023.
[23] 郭芸. 燕麦麸不溶性膳食纤维的酶法提取工艺及应用的研究[D]. 天津:天津大学, 2022. [GUO Yun. Study on enzymatic extraction technology and application of insoluble dietary fiber from oat bran[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University, 2022.] GUO Yun. Study on enzymatic extraction technology and application of insoluble dietary fiber from oat bran[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2022.
[24] GAO K, LIU T, CAO L, et al. Feasibility of pomelo peel dietary fiber as natural functional emulsifier for preparation of Pickering-type emulsion[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2022,102(11):4491−4499. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11804
[25] LOI C C, EYRES G T, BIRCH E J. Effect of mono- and diglycerides on physical properties and stability of a protein-stabilised oil-in-water emulsion[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2019,240:56−64. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.07.016
[26] WANG B, LI D, WANG L J, et al. Effect of concentrated flaxseed protein on the stability and rheological properties of soybean oil-in-water emulsions[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2010,96(4):555−561. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2009.09.001
[27] MENGUAL O, MEUNIER G, CAYRÉ I, et al. TURBISCAN MA 2000:Multiple light scattering measurement for concentrated emulsion and suspension instability analysis[J]. Talanta,1999,50(2):445−456. doi: 10.1016/S0039-9140(99)00129-0
[28] 赵颖颖, 李可, 王鹏, 等. 超声波处理对酪蛋白酸钠-大豆油预乳化液乳化稳定性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(3):75−80. [ZHAO Yingying, LI Ke, WANG Peng, et al. Effect of ultrasound treatment on the emulsion stability of pre-emulsified soybean oil with sodium caseinate[J]. Food Science,2017,38(3):75−80.] ZHAO Yingying, LI Ke, WANG Peng, et al. Effect of ultrasound treatment on the emulsion stability of pre-emulsified soybean oil with sodium caseinate[J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(3): 75−80.
[29] ZHANG Y, HU J, ZHONG Y, et al. Insoluble/soluble fraction ratio determines effects of dietary fiber on gut microbiota and serum metabolites in healthy mice[J]. Food & Function,2024,15(1):338−354.
[30] XIE F, ZHAO T, WAN H, et al. Structural and physicochemical characteristics of rice bran dietary fiber by cellulase and high-pressure homogenization[J]. Applied Sciences-Basel,2019,9(7):1270. doi: 10.3390/app9071270
[31] REN F, FENG Y, ZHANG H, et al. Effects of modification methods on microstructural and physicochemical characteristics of defatted rice bran dietary fiber[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,151:112161. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112161
[32] KHAWAS P, DEKA S C. Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanofibers from culinary banana peel using high-intensity ultrasonication combined with chemical treatment[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,137:608−616. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.020
[33] TIBOLLA H, PELISSARI F M, RODRIGUES M I, et al. Cellulose nanofibers produced from banana peel by enzymatic treatment:Study of process conditions[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2017,95:664−674. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.11.035
[34] WU X, LI F, WU W. Effect of rice bran rancidity on the structure and antioxidant properties of rice bran soluble dietary fiber[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2022,105:103469. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2022.103469
[35] CHEONG A M, TAN K W, TAN C P, et al. Kenaf Hibiscus cannabinus seed oil-in-water Pickering nanoemulsions stabilised by mixture of sodium caseinate, Tween 20 and β-cyclodextrin[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2016,52:934−941. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.09.005
[36] 高凯丽. 改性柚皮不溶性膳食纤维乳液的稳定机理及其对高脂饮食小鼠的健康调节作用[D]. 南昌:南昌大学, 2024. [GAO Kaili. Stabilization mechanism of modified grapefruit peel insoluble dietary fiber emulsion and its health-modifying effect on mice fed a high-fat diet[D]. Nanchang:Nanchang University, 2024.] GAO Kaili. Stabilization mechanism of modified grapefruit peel insoluble dietary fiber emulsion and its health-modifying effect on mice fed a high-fat diet[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2024.
[37] INES GUERRA-ROSAS M, MORALES-CASTRO J, ARACELI OCHOA-MARTINEZ L, et al. Long-term stability of food-grade nanoemulsions from high methoxyl pectin containing essential oils[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2016,52:438−446. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.07.017
[38] ZHAI X, LIN D, LIU D, et al. Emulsions stabilized by nanofibers from bacterial cellulose:New potential food-grade Pickering emulsions[J]. Food Research International,2018,103:12−20. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.10.030
[39] SHI J, XIAO J, LIU L, et al. Ultrasonic assisted oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by flaxseed protein isolate:influence of different oils[J]. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology,2022,43(12):1789−1800. doi: 10.1080/01932691.2021.1880923
[40] DYBOWSKA B E, KRUPA-KOZAK U. Stability of oil-in-water emulsions as influenced by thermal treatment of whey protein dispersions or emulsions[J]. International Journal of Dairy Technology,2020,73(3):513−520. doi: 10.1111/1471-0307.12689
[41] MIKULCOVA V, BORDES R, KASPARKOVA V. On the preparation and antibacterial activity of emulsions stabilized with nanocellulose particles[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2016,61:780−792. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.06.031
[42] 芒莱, 范方宇. OSA改性木薯淀粉基Pickering乳液制备及特性研究食品工业科技[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(22):63−71. [MANG Lai, FAN Fangyu. Preparation and characterization of OSA-modified tapioca starch-based Pickering emulsion[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(22):63−71.] MANG Lai, FAN Fangyu. Preparation and characterization of OSA-modified tapioca starch-based Pickering emulsion[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(22): 63−71.
[43] 景成童, 涂安, 赵春昊, 等. 玉米醇溶蛋白-假酸浆子胶二元复合物的制备及在Pickering乳液中的应用[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(9):91−98. [JING Chengtong, TU An, ZHAO Chunbao, et al. Preparation of zein-nicandra physaloides gum binary complex and its application in Pickering emulsions[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(9):91−98.] JING Chengtong, TU An, ZHAO Chunbao, et al. Preparation of zein-nicandra physaloides gum binary complex and its application in Pickering emulsions[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(9): 91−98.
[44] LIU C, LI M, HAN R, et al. Rheology of water-in-oil Emulsions with different drop sizes[J]. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology,2016,37(3):333−344. doi: 10.1080/01932691.2015.1010729
[45] WU J, XU F, WU Y, et al. Characterization and analysis of an oil-in-water emulsion stabilized by rapeseed protein isolate underpHand ionic stress[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(13):4734−4744. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10532
[46] 赵强忠, 周海媚. 大豆纤维稳定水包油型皮克林乳液的研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2016,32(10):39−44,8. [ZHAO Qiangzhong, ZHOU Haimei. Soybean fiber as particle stabilizers for oil-in-water Pickering emulsions[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2016,32(10):39−44,8.] ZHAO Qiangzhong, ZHOU Haimei. Soybean fiber as particle stabilizers for oil-in-water Pickering emulsions[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2016, 32(10): 39−44,8.
[47] VILLALOBOS-ESPINOSA J C, GARCIA-ARMENTA E, ALAMILLA-BELTRAN L, et al. Effect of pumping and atomisation on the stability of oil/water emulsions[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2022,327:111056. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2022.111056
[48] QI J R, SONG L W, ZENG W Q, et al. Citrus fiber for the stabilization of O/W emulsion through combination of Pickering effect and fiber-based network[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,343:128523. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128523
-
其他相关附件
-
PDF格式
EI Certificate 43KB
-





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



