Effects of Different Extraction Methods on Structure and Functional Characteristics of Almond Protein
-
摘要: 为提高杏仁蛋白(Almond protein,AP)的利用率,本研究使用等电点沉淀法(Alkaline extraction by isoelectric precipitation,AI)、热碱法(Thermal-alkaline,TA)和盐析法(Salt extraction,SE)提取AP,分别为AIAP、TAAP和SEAP,探究提取方法对蛋白质结构和功能特性的影响。结果表明,不同提取方法对AP的结构和功能特性具有显著影响。SEAP的提取率(55.94%)和纯度(88.21%)最高,AIAP的纯度最低(75.06%),TAAP的提取率最低(50.71%)。AIAP表面粗糙且结构疏松,而TAAP和SEAP的结构致密,AIAP的β-折叠含量(44.97%)和表面疏水性高于TAAP和SEAP。相较于TAAP和SEAP,AIAP的持水性和持油性较高。SEAP和TAAP的溶解度显著高于AIAP,且乳化特性和起泡特性较好。本研究为杏仁蛋白在食品工业的应用提供一定的理论参考。Abstract: The objective of this study was to increase the utilization rate of almond protein (AP). In this study, the alkaline extraction by isoelectric precipitation (AI), thermal alkaline (TA) and salt extraction (SE) were used to extract AP, namely AIAP, TAAP and SEAP were to explore the effects of extraction methods on protein structure and functional properties. The results showed that the structure and function of AP were affected by different extraction methods. SEAP exhibited the highest protein extraction rate (55.94%) and purity (88.21%), while AIAP had the lowest protein purity (75.06%), and the extraction rate of TAAP was the lowest (50.71%). The surface of AIAP was rough and the structure was loose, while the structure of TAAP and SEAP was dense, and the β-sheet content of AIAP (44.97%) and surface hydrophobicity of AIAP were higher than that of TAAP and SEAP. Compared with TAAP and SEAP, AIAP showed higher water holding and oil holding capacity. The solubility of SEAP and TAAP was significantly higher than that of AIAP, and the protein exhibited superior emulsification and foaming properties. This study provides a theoretical reference for the application of almond protein in food industry.
-
Keywords:
- extraction method /
- almond protein /
- structural /
- functional characteristics
-
杏仁的营养价值较高,其蛋白质含量约为19%~27%[1],具有祛痰平喘、止咳润肺的功效。杏仁粕是杏仁榨油后的副产物,富含的杏仁蛋白(Almond protein,AP)约为40%~50%[1],蛋白质变性程度小,是重要的蛋白资源。AP主要以杏仁储存蛋白为主,称为Amandin,占总可溶性蛋白质的65%~70%[2]。Amandin是一种经典的球蛋白,其特征在于沉降系数为14S,分子量为360 kDa,具有由6个亚基组成的六聚体结构,每个亚基的分子量为60~66 kDa[3]。AP富含人体所需的18种氨基酸,其中,8种必需氨基酸占比与1973年联合国粮食和农业组织(FAO)/联合国世界卫生组织(WHO)修正的标准模式谱[4]接近,因此AP可作为优质的植物蛋白源。
不同方法提取的蛋白表现出不同的结构和功能特性[5]。目前常见的AP提取方法主要包括等电点沉淀法(Alkaline extraction by isoelectric precipitation,AI)、热碱法(Thermal-alkaline,TA)和盐析法(Salt extraction,SE)等[6]。AI是工业中提取蛋白质常用的方法,蛋白质在碱性环境溶解,酸性环境沉淀,最后经过离心、洗沉淀及冷冻干燥等处理得到蛋白质。解春艳等[6]利用AI提取的AP含量为43.79 mg/g,AI提取的蛋白具有较好的持水性和持油性。该方法操作简单,提取率高,但提取的蛋白质易变性[7],且溶解度较低。SE是将蛋白质溶于稀盐溶液中,再通过添加盐离子使提取液达到一定的饱和浓度,从而析出蛋白质,SE提取的蛋白质纯度较高,结构不易被破坏[8]。刘凯等[9]通过盐法提取AP,提取率达到72.00%,提取的蛋白质具有较好的乳化特性及起泡特性[10-11]。TA是在AI的基础上对提取液进行加热以提高蛋白质的溶解度,碱性环境破坏蛋白质结构,有效释放出蛋白质[12],随后加入盐离子使蛋白质析出。TA提高了蛋白质的提取率,提取的蛋白具有较好的功能特性,但操作繁琐,不适用于工业生产。
因此,本文选择AI、TA和SE提取杏仁蛋白,探究不同提取方法对AP的提取率、蛋白质纯度以及结构和功能特性的影响,以期为杏仁蛋白在食品工业的应用提供一定的理论参考。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 材料及仪器
杏仁粕 购自河北承德露露有限公司;正己烷、磷酸缓冲溶液、磷酸盐、硫酸铵、氢氧化钠(NaOH)、盐酸(HCl)、8-苯胺-1-萘磺酸(ANS)、十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)、苯酚、葡萄糖标准品 均购自上海源叶生物科技有限公司;其他试剂均属于分析纯。
JA200电子天平 上海精密科学仪器有限公司;TP-350S智能数显磁力加热搅拌器 杭州米欧仪器有限公司;FE28 pH计 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;TGL-16M高速冷冻离心机 上海卢湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;FD-1A-50真空冷冻干燥机 北京博医康实验仪器有限公司;GZX-9030MBE电热鼓风干燥箱 上海博旭医疗生物仪器股份有限公司;D-500高剪切分散均质机 德国维根技术(北京)有限公司;U120 Pro紫外可见光分光光度计 翱艺仪器(上海)有限公司;Synergy HTX多功能酶标仪 美国博腾公司;Zetasizer Lab纳米粒度及Zate电位分析仪 英国Malvern Panalytical公司;NICOLET IS50傅里叶红外光谱仪 德国Thermo Scientific公司;SU3800扫描电子显微镜、F7100荧光分光光度计 日本Hitachi公司;CS-580A色差仪 彩谱科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 杏仁蛋白的制备
1.2.1.1 杏仁粕脱脂处理
将杏仁粕磨碎,过80目筛,按1:5(w/v)加入正己烷,磁力搅拌12 h。将上层正己烷倒出,沉淀在通风橱挥发剩余正己烷,干燥24 h,得到脱脂杏仁粕。
1.2.1.2 等电点沉淀法制备杏仁蛋白(AIAP)
等电点沉淀法参照糟龙[4]的方法并作修改,制备AIAP。按照1:10(w/v)的比例,将脱脂杏仁粕溶解在蒸馏水中,搅拌12 h。用1.0 mol/L的NaOH调pH至9.0,室温搅拌1 h。4 ℃以4000 r/min的速度离心20 min,取上清液,用蒸馏水多次洗涤沉淀,离心,合并上清液。用1.0 mol/L HCl将上清液的pH调至4.6,在4 ℃下以4000 r/min的速度离心20 min,冷冻干燥,得到AIAP。
1.2.1.3 热碱法制备杏仁蛋白(TAAP)
热碱法参照陈一等[13]的方法并略作修改,制备TAAP。按照1:30(w/v)的比例,将脱脂杏仁粕溶于磷酸缓冲溶液(pH7.0)中,搅拌12 h。用1.0 mol/L的NaOH调pH至9.0,45 ℃搅拌1 h。在4 ℃以4000 r/min的速度离心20 min,取上清液,沉淀洗涤两次,离心合并上清液。添加(NH4)2SO4使上清液中饱和浓度达到25%,静置12 h。4 ℃以4000 r/min的速度离心20 min,取上清液,加(NH4)2SO4使溶液的饱和浓度达到60%,静置12 h,4 ℃以4000 r/min的速度离心20 min,取沉淀。使沉淀溶于磷酸缓冲溶液中,用8~15 kDa的透析袋透析2 d,冷冻干燥得到TAAP。
1.2.1.4 盐析法制备杏仁蛋白(SEAP)
盐析法参照宋艳丽等[14]的方法制备SEAP,并略作修改。按照1:30(w/v)的比例,将脱脂杏仁粕溶解在磷酸缓冲溶液(pH7.0)中,搅拌12 h。4 ℃以4000 r/min的速度离心20 min,取上清液。后面步骤同1.2.1.3中(NH4)2SO4沉淀蛋白方法一致,得到SEAP。
1.2.2 AP提取率和AP纯度
参照GB 5009.5-2016,采用半自动凯氏定氮法,计算出含氮量,并通过杏仁蛋白的转换系数(5.18),得到蛋白质含量,即AP纯度,根据公式计算AP提取率:
AP提取率(%)=B×m2A×m1×100 式中,A表示脱脂杏仁粕中的蛋白质含量,g/100 g;B表示提取的AP蛋白含量,g/100 g;m1表示脱脂杏仁粕的质量,g;m2为提取的AP质量,g。
1.2.3 AIAP、TAAP和SEAP色度分析
采用色差仪对原料和三种蛋白测定颜色参数。先将色差仪分别进行白校准和黑校准,通过色差仪记录L*、a*、b*。白度值根据公式计算:
W=100−√(100−L∗)2+(a∗)2+(b∗)2 式中,W表示白度值;L*表示亮度;a*表示红绿;b*表示黄蓝。
1.2.4 原料、AIAP、TAAP和SEAP基本成分的测定
1.2.4.1 粗蛋白质的测定
参照GB 5009.5-2016,采用半自动凯氏定氮法,计算出含氮量,并通过杏仁蛋白的转换系数(5.18),转化为蛋白质的含量。
1.2.4.2 水分的测定
参照GB 5009.3-2016,将原料和AIAP、TAAP和SEAP放在105 ℃的烘箱中烘干24 h,直到样品恒重。
1.2.4.3 粗脂肪的测定
参照GB 5009.6-2016,通过索氏抽提的方法测定原料和AIAP、TAAP和SEAP中脂肪的含量。
1.2.4.4 灰分的测定
参照GB 5009.4-2016,将原料和AIAP、TAAP和SEAP炭化后,放入马弗炉中,550 ℃灰化6 h,直至恒重。
1.2.4.5 总糖的测定
总糖含量参考Zhou等[15]的方法测定,葡萄糖标准溶液加入蒸馏水,配制不同浓度梯度的溶液,随后加入5%苯酚溶液1.0 mL和浓硫酸溶液5 mL混匀,静置20 min后在波长490 nm处测定其吸光度值,蒸馏水作为空白对照。以葡萄糖浓度为横坐标(x),吸光度值为纵坐标(y),绘制葡萄糖标准曲线。将25 mL浓硫酸和10 mL蒸馏水加入AIAP、TAAP和SEAP,水浴加热1 h进行水解,4 ℃以4000 r/min的速度离心20 min,滤液定容至250 mL,按上述操作测定吸光度值,带入葡萄糖标准曲线,计算总糖质量浓度,根据公式计算总糖浓度:
总糖浓度(%)=a×VW×100 式中,a表示多糖浓度,mg/mL;V表示多糖溶液体积,mL;W表示AP质量,mg。
1.2.5 AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的红外分析
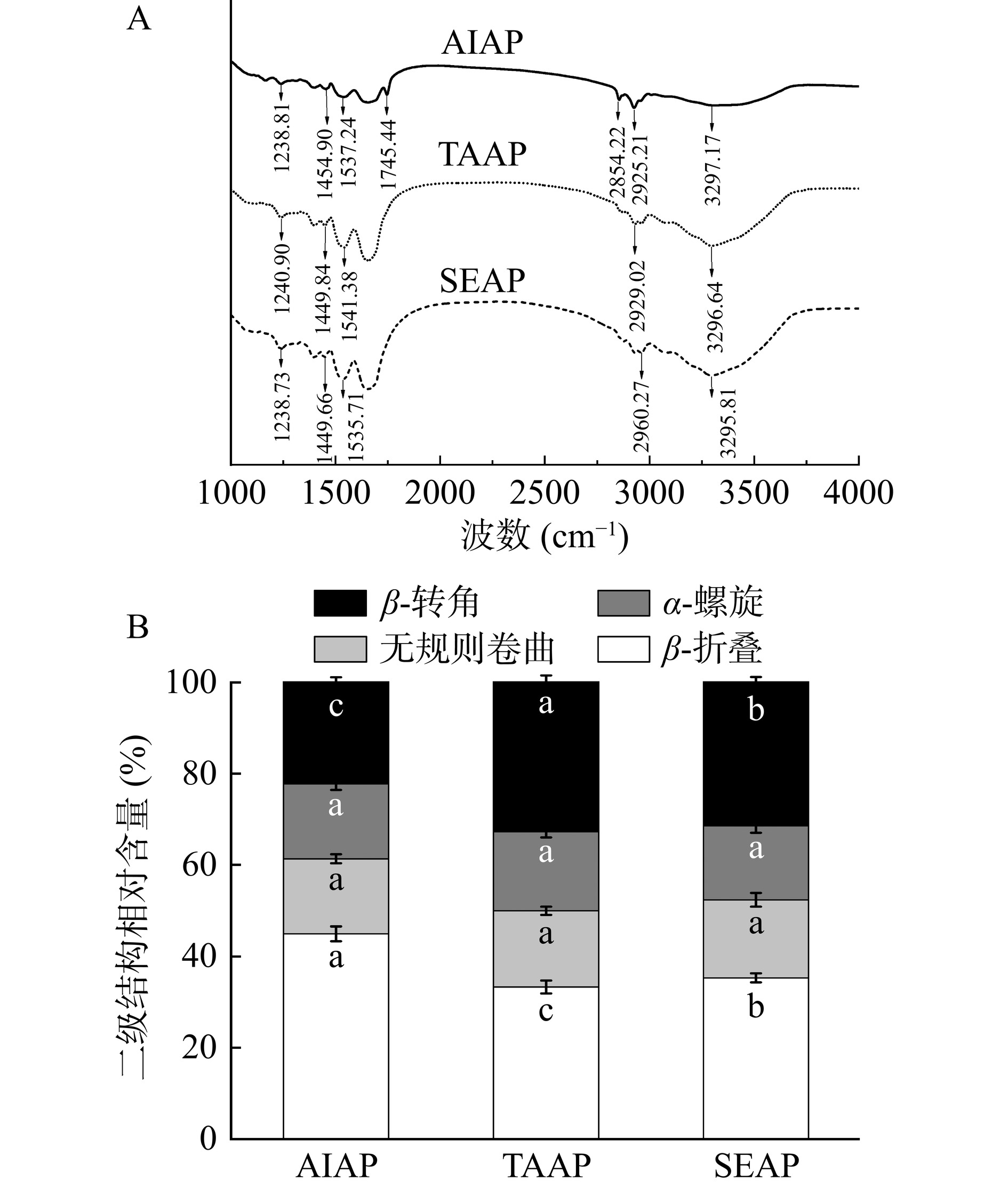
将干燥的样品按1:100(w/w)的比例与KBr混合后研磨成粉末,压成薄片,使用傅里叶红外光谱仪进行扫描。扫描范围为4000~1000 cm−1,以4 cm−1的分辨率共扫描16次。通过红外光谱仪扫描可得到红外光谱图谱,对蛋白质特征吸收峰波数为1700~1600 cm−1的红外光谱图进行采用 Peakfit 4.12 软件基线校正、去卷积、二阶求导及曲线拟合处理。根据蛋白中各二级结构的波段位置和对应特征吸收峰的面积大小来反映蛋白质分子中各二级结构含量的变化规律。
1.2.6 AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的微观结构
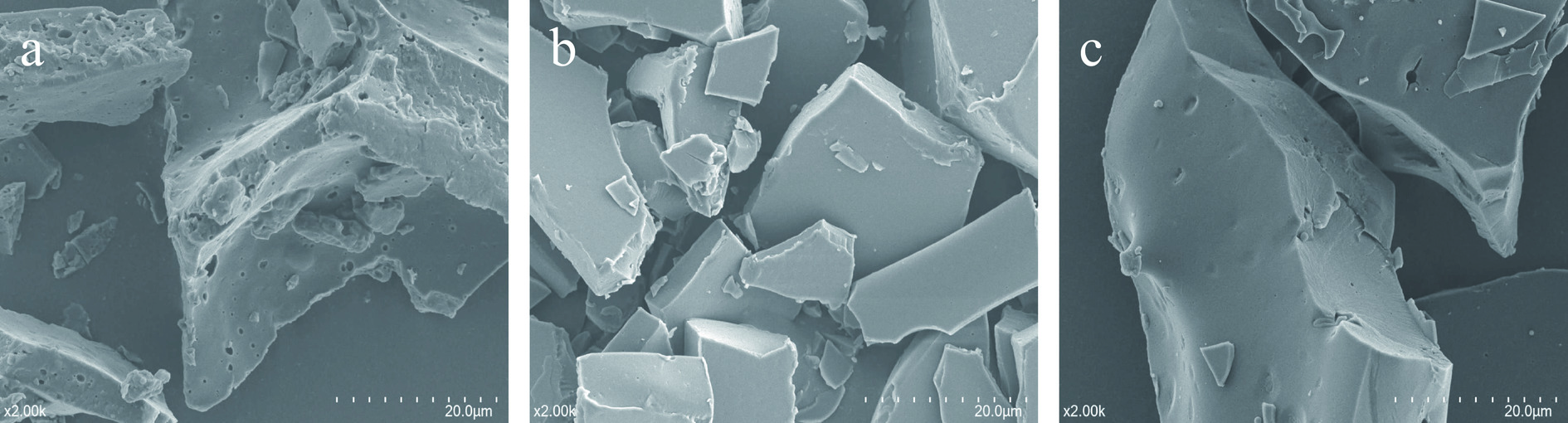
根据Hu等[16]的方法并作修改。用扫描电子显微镜观察AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的微观结构。将三种提取方法的蛋白质真空冷冻干燥,随后将蛋白质粉碎,用导电胶将蛋白粉沫粘在圆柱形铝支架上,随后使用溅射工艺在样品涂金,并使用扫描显镜在5 kV加速电压下拍摄蛋白质表面图像。选择放大2000倍数的显微照片作为每个样品的代表。
1.2.7 AIAP、TAAP和SEAP粒径和Zeta电位的测定
分别称取AIAP、TAAP和SEAP溶于磷酸缓冲溶液(pH 7.0),制备0.1 mg/mL蛋白质溶液,分别将蛋白质溶液pH调至3、5、7、9,采用纳米粒径电位仪测定,选择Size模式和Zeta模式,每组运行20次,平行3组。
1.2.8 AIAP、TAAP和SEAP表面疏水性的测定
表面疏水性使用荧光分光光度计测定,根据Zhang等[17]的方法并略作修改。将蒸馏水分别调至为pH3、5、7、9,将AIAP、TAAP和SEAP分别稀释至不同的五个浓度梯度,随后将20 μL的8.0 mmol/L ANS与4 mL的蛋白溶液混合,于室温下避光反应10 min,荧光分光光度计在激发波长为390 nm,扫描范围为400~600 nm,狭缝宽度为5 nm的条件下测量样品的荧光强度。根据不同蛋白质浓度下的荧光强度建立线性回归方程进行曲线拟合,计算的斜率为样品的表面疏水性。
1.2.9 AIAP、TAAP和SEAP溶解度的测定
溶解度参照王立博等[18]的方法测定并略作修改。将AIAP、TAAP和SEAP制成1 mg/mL溶液,搅拌12 h。蛋白溶液的pH分别调为3、5、7、9,室温溶解后,6000 r/min离心20 min,取上清液。采用考马斯亮蓝法测定上清液的蛋白质含量,根据公式计算溶解度:
溶解度(%)=m2m1×100 式中,m1表示蛋白质含量,g;m2表示测定上清液的蛋白质含量,g。
1.2.10 AIAP、TAAP和SEAP持水性和持油性的测定
持水性和持油性参照卢秋玲等[19]的方法略作修改后测定。称取一定量的AIAP、TAAP和SEAP于离心管中,持水性加入1 mL蒸馏水,分别将pH调至3、5、7、9,静置30 min,持油性加入1 mL大豆油,搅拌,充分振荡,于室温6000 r/min离心20 min,弃去离心管上层水分/油,滤纸吸取管壁上的水分/油,称重离心管和沉淀的重量。根据公式计算持水性和持油性:
持水性/持油性(%)=m3−m2−m1m2×100 式中,m1表示离心管的重量,g;m2表示称取AP的质量,g;m3表示离心管和沉淀的重量,g。
1.2.11 AIAP、TAAP和SEAP乳化性和乳化稳定性的测定
称取蛋白溶于蒸馏水中,制备1 mg/mL的AIAP、TAAP和SEAP溶液,按油相比3:2加入大豆油,10000 r/min高速剪切2 min,取100 μL的乳液,加入1 mg/mL 1%的SDS溶液稀释50倍,充分混匀后,用紫外分光光度计在500 nm处测定吸光度值A0,静置30 min,测定吸光度值A30。根据公式计算乳化性和乳化稳定性:
乳化性(m2/g)=2×2.303C×(1−ϕ)×104×A0×D 乳化稳定性(min)=A0A0−A30×t 式中,D表示稀释系数;C表示蛋白质浓度,g/mL;ϕ表示0.01,光程;t表示时间,min。
1.2.12 AIAP、TAAP和SEAP起泡性和起泡稳定性的测定
称取AIAP、TAAP和SEAP溶解于蒸馏水中,制备1 mg/mL蛋白质溶液,高速剪切机切1 min,读取泡沫高度和液体高度,静置30 min后,再次读取泡沫高度和液体高度,根据公式计算起泡性和起泡稳定性:
起泡性(%)=h1h2×100 起泡稳定性(%)=h3h4×100 式中,h1为1 min时泡沫高度,cm;h2为1 min时液体高度,cm;h3为30 min时泡沫高度,cm;h4为30 min时液体高度,cm。
1.3 数据处理
每个实验重复三次,实验结果采用SPSS 25.0进行显著性检验(P<0.05)分析,采用Origin 2018软件绘图,结果用平均数±标准差(SD)表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同提取方法对蛋白质提取率和纯度的影响
AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的提取率和纯度如图1所示。SEAP的纯度最高(88.21%),TAAP其次(87.58%),AIAP的纯度最低(75.06%),该结果与Stone等[20]的研究结果一致。在盐析过程中,蛋白质与蛋白质之间存在强烈的疏水相互作用,排除了蛋白质与非蛋白质物质的相互作用[5],因此SEAP的纯度高。在AI提取过程中,大部分蛋白质溶于碱性环境,pH在等电点附近时,蛋白质溶解度降低,导致蛋白质析出[21]。TA通过碱性环境和加热条件促进了蛋白质的溶解,因此蛋白质纯度比AI高。SE通过加入无机盐使蛋白质的表面电荷被中和,表面结合水减少,水化膜被破坏,蛋白质溶解度降低,导致蛋白质析出[8],因此SEAP的杂质少且蛋白质纯度高。
![]() 图 1 不同提取方法AP提取率及AP纯度注:不同小写字母代表不同方法提取的蛋白质间差异显著(P<0.05);图3同。Figure 1. AP extraction rate and AP purity of the different extraction methods
图 1 不同提取方法AP提取率及AP纯度注:不同小写字母代表不同方法提取的蛋白质间差异显著(P<0.05);图3同。Figure 1. AP extraction rate and AP purity of the different extraction methods2.2 不同提取方法对AP色度的影响
AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的色度如表1所示。由表1可知,AIAP、TAAP及SAAP的色度差异显著(P<0.05),且TAAP和SEAP的白度值(W)高于AIAP。AIAP的a*和b*显著高于TAAP和SAAP(P<0.05),且均为正值,表明AP的颜色加深。如图2所示,AIAP的颜色偏黄,与白瓜籽蛋白的研究结果一致[22],可能与酸碱环境中蛋白质变性[22]及酚类物质的氧化[23]有关。
表 1 AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的色度Table 1. Chromaticity of AIAP, TAAP and SEAP样品名称 L* a* b* W AIAP 32.87±0.04c 1.19±0.01a 10.31±0.02a 32.08±0.03b TAAP 33.66±0.01a 0.32±0.01b 7.60±0.02b 33.23±0.01a SAAP 33.50±0.03b 0.24±0.01c 6.16±0.03c 33.21±0.03a 注:同列不同小写字母代表不同方法提取的蛋白质间差异显著(P<0.05);表2同。 2.3 不同方法提取AP的基本成分
原料杏仁粕、脱脂杏仁粕以及AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的基本组成如表2所示。原料杏仁粕中脂质的含量较高,为28.75%,蛋白质含量为41.30%,可作为丰富的植物蛋白质资源。杏仁粕经过正己烷脱脂后,脂质的含量显著降低(28.75% vs 7.41%)(P<0.05),蛋白质含量显著提高(41.30% vs 48.85%),与Shi等[1]的研究结果相符。
表 2 杏仁粕、脱脂杏仁粕和AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的基本组成Table 2. Basic composition of almond meal, defatted almond meal and AIAP, TAAP and SEAP样品名称 蛋白质(%) 水分(%) 脂质(%) 灰分(%) 总糖(%) 杏仁粕 41.30±0.83d 3.94±0.51b 28.75±0.04a 4.02±0.26b 5.05±0.01a 脱脂杏仁粕 48.85±0.11c 5.83±0.30a 7.41±0.19b 5.19±0.15a 4.93±0.03a AIAP 75.06±3.96b 2.32±0.56d 2.84±0.07c 2.73±0.07d 1.21±0.28c TAAP 87.58±0.39a 4.28±0.26b 0.44±0.20d 3.09±0.26c 2.88±0.23b SEAP 88.21±0.25a 2.89±0.03c 0.56±0.15d 2.49±0.02e 1.50±0.21c 如表2所示,TA(87.58%)和SE(88.21%)提取的蛋白质含量显著高于AI(75.06%),在其他蛋白(大麻蛋白[5]、豌豆蛋白[20]、白瓜籽蛋白[22])中也发现了类似的高提取率。不同提取方法对杏仁粕中其它成分(脂质、糖类等)的去除效果不同,这些成分会影响蛋白质的溶解度和稳定性,从而引起蛋白质含量的差异[24]。TAAP的水分比AIAP和SEAP的水分高,这可能与透析时间及冻干条件有关。在脂质含量方面,AIAP>SEAP>TAAP,是因为少量的脂质溶解于碱性提取液。三种方法提取蛋白质的灰分含量差异显著(P<0.05),在透析过程中有残留的盐离子导致TAAP灰分含量较高[25]。
2.4 不同提取方法对AP二级结构的影响
红外二阶导数图谱中各二级结构的波段位置和对应特征吸收峰的面积大小能够反映蛋白质分子中各二级结构含量的变化规律[4]。AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的红外光谱以及二级结构分布图如图3所示。2850 cm−1附近的峰代表酰胺B带,可能与C-H和NH2拉伸振动有关[26];蛋白质中C=O的拉伸振动对应于酰胺I带(1700~1600 cm−1),平面内N-H弯曲对应于酰胺II带(1546~1541 cm−1),以及N-H弯曲和C-N拉伸振动对应于酰胺III带(1386~1240 cm−1)[27]。从图3A中看出,三种蛋白质官能团的峰值位置不同,表明三种蛋白质结构存在差异。二级结构中,α-螺旋结构成紧密而无空腔结构,α-螺旋结构含量越多蛋白质结构越稳定,而β-折叠、β-转角以及无规则卷曲结构的稳定性低于α-螺旋结构的稳定性[4]。由图3B可知,三种蛋白质的α-螺旋没有显著差异,但AIAP的β-折叠(44.93%)显著高于TAAP(33.28%)和SEAP(35.29%)(P<0.05),AIAP的β-转角(22.25%)显著低于TAAP(32.78%)和SEAP(31.47%)(P<0.05),β-折叠与β-转角这两个结构之间发生了转化,表明AIAP蛋白结构展开程度更高,TAAP和SEAP蛋白结构更加紧密[28],与2.5节微观结构结果一致。
2.5 不同提取方法对AP微观结构的影响
AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的微观结构如图4所示。AIAP蛋白表面粗糙,孔隙较大且密集,结构稍松散,呈层状结构,表面有小颗粒聚集。TAAP表面较AIAP光滑,孔隙较少,结构紧密,表面有少量颗粒聚集。SEAP表面光滑,结构致密,孔隙较少。AI提取AP过程中,强碱强酸环境导致AP变性,使其结构发生变化,因此AIAP结构松散。SE使用盐离子增加蛋白质溶液的浓度,使蛋白质凝聚析出,蛋白质的结构不易变性,因此SEAP的结构较完整。Fang等[5]的研究表明,表面越光滑的蛋白质溶解度越好,因此,表面光滑的SEAP和TAAP的溶解度比表面粗糙的AIAP高,该结果与2.8中AP溶解度结果一致。
2.6 不同提取方法在不同pH条件下对AP粒径和Zeta电位的影响
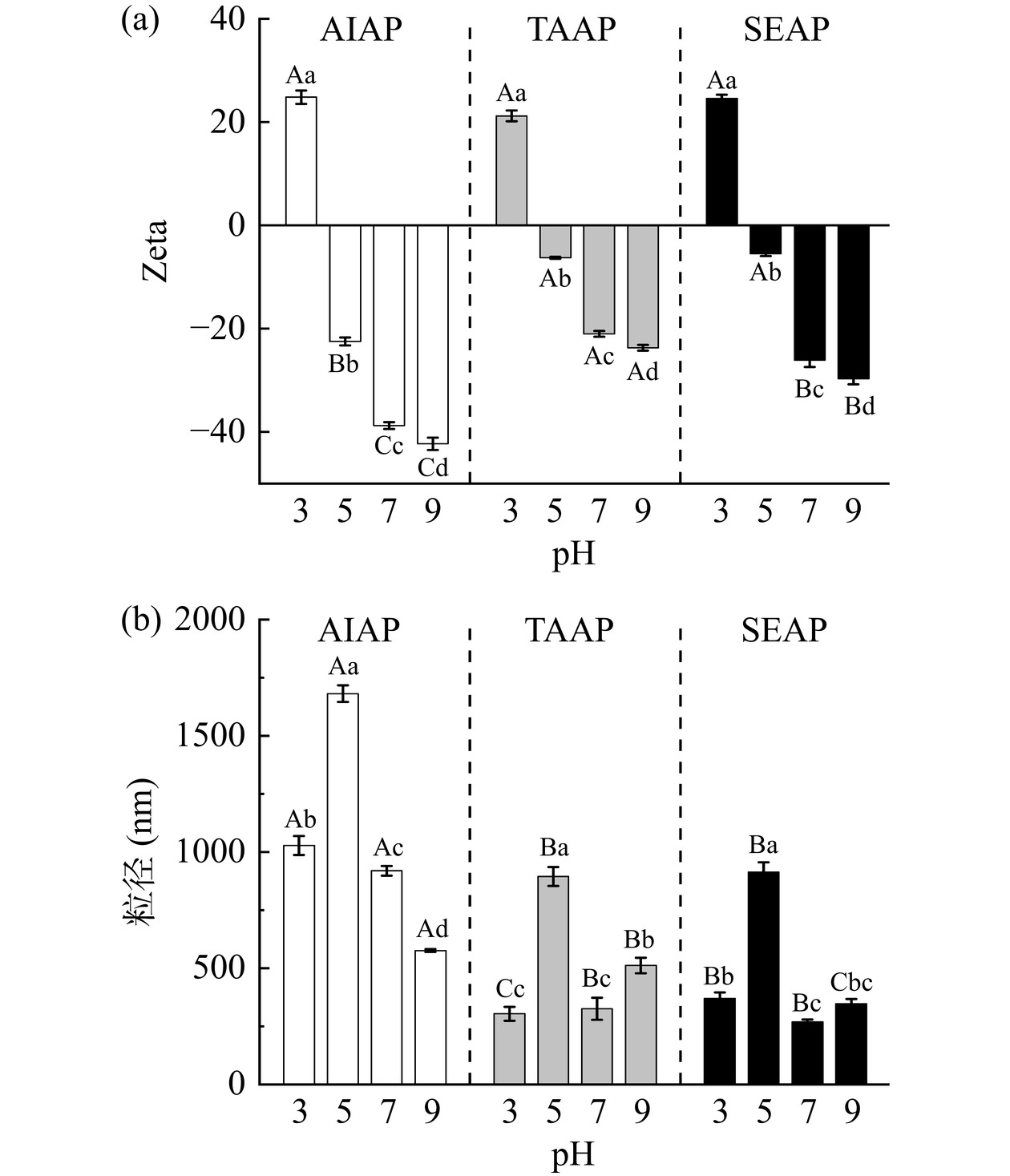
Zeta电位的绝对值越大,表明溶液中蛋白质之间的静电排斥作用力越强,蛋白质分子在溶液中的分散就越稳定,反映蛋白质溶液的稳定性[29]。AIAP、TAAP和SEAP在不同pH下的Zeta电位和粒径如图5所示。AP的等电点在4~5之间,当pH低于等电点时蛋白质溶液电荷带正电,高于等电点时带负电。Zeta电位绝对值大于25 mV时,溶液较稳定,当pH为3时,三种蛋白质的Zeta电位相近,则AIAP、TAAP和SEAP溶液稳定性相近。当pH>4时,AIAP提取蛋白质的Zeta绝对值大于TAAP和SEAP,且绝对值大于25 mV,AIAP溶液更稳定。
由图5(b)观察到,不同提取方法的粒径大小存在差异,其中,AIAP的粒径主要分布在500~1700 nm,TAAP和SEAP的粒径主要分布在300~900 nm。当pH为5时,这三种的蛋白质的粒径达到最大,分别为1681、894、913 nm,这是由于pH5接近等电点,蛋白质表面正负电荷相等,溶解度降低,蛋白质聚集,因此粒径变大。当远离等电点时,电荷的增多,静电斥力增加,蛋白质分子结构伸展,溶解度增加,因此粒径减小[30]。Zeta电位影响蛋白质的聚集程度,使蛋白质内部疏水基团的暴露程度不同,影响了AP的表面疏水性,从而影响蛋白质的功能特性[20]。
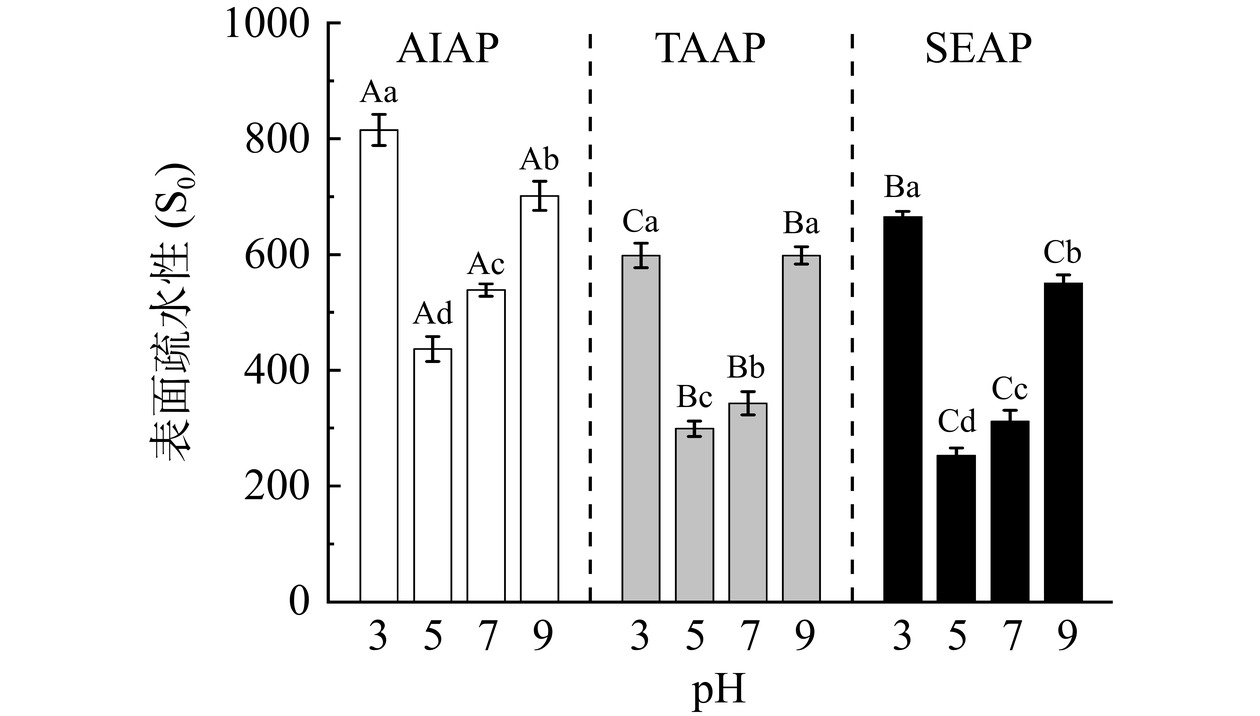
2.7 不同提取方法在不同pH条件下对AP表面疏水性的影响
表面疏水性是表明蛋白质内部结构和表面微环境变化的一个重要特征[31]。表面疏水性能够反映蛋白质疏水基团的暴露与包埋情况,以及不同条件下蛋白质间的疏水作用,表征蛋白质的分子折叠情况[4]。如图6所示,AIAP、TAAP 和 SEAP 的表面疏水性随pH的增大先降低后升高,经过pH处理后,AP发生了不同程度的变性,使蛋白质内部的疏水基团暴露。在pH5时表面疏水性最低(AIAP为436.30,TAAP为298.85,SEAP为252.72),这归因于pH5接近蛋白质的等电点,蛋白质聚集,疏水基团包裹在蛋白质的内部,此时表面疏水性最小。当pH为3和9时,蛋白质表面电荷增加,酸碱环境的变化导致蛋白质结构展开,内部的疏水集团暴露,表面疏水性增大。pH3时AP的表面疏水性最大,这归因于蛋白质的pH从等电点降低到pH3附近,蛋白质沉淀后复溶,其亚基折叠后舒展,位于α-螺旋内部的疏水氨基酸残基暴露,导致AP的疏水性增大[32]。
在不同pH条件下,AIAP的表面疏水性显著大于TAAP和SEAP(P<0.05),由二级结构和微观结构可知,AIAP变性导致结构疏松,内部的疏水基团暴露,表面疏水性增大,TAAP和SEAP的结构致密,暴露的疏水集团较少,因此疏水性较小。此外,球蛋白的表面疏水性比白蛋白高[20],表面疏水性差异归因于AIAP主要以球蛋白为主,TAAP和SEAP主要以白蛋白为主[5]。
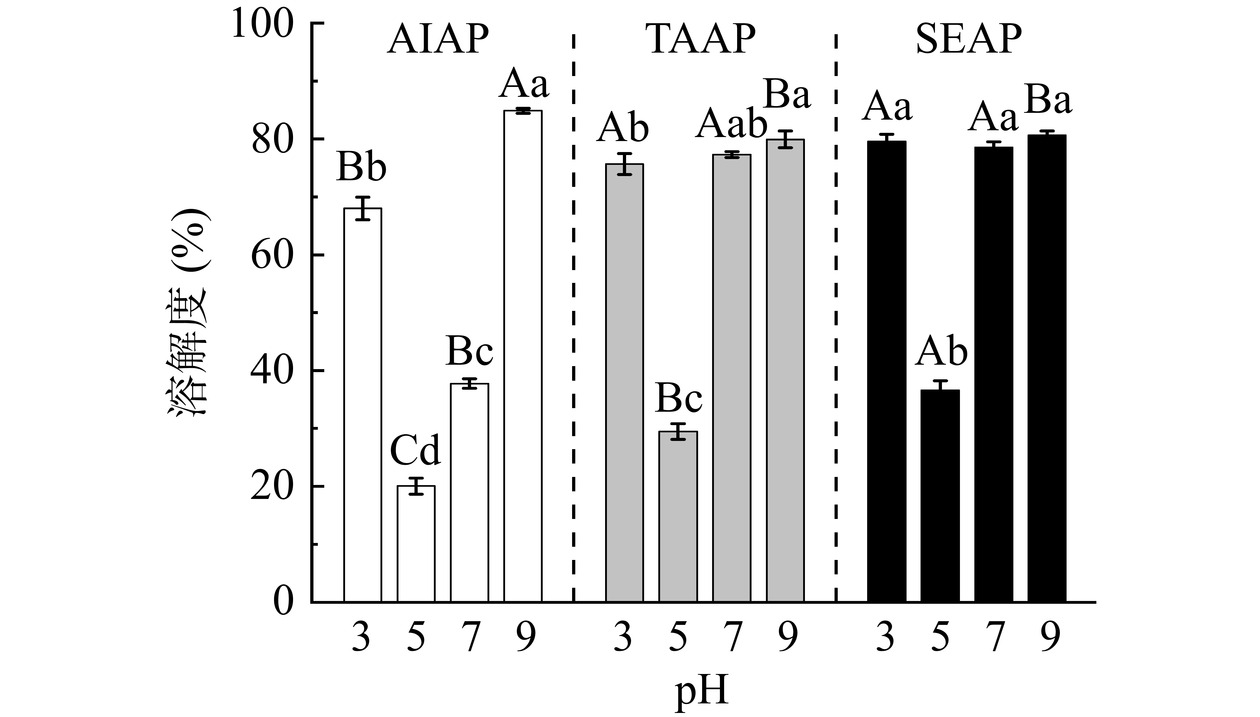
2.8 不同提取方法在不同pH条件下对AP溶解度的影响
AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的溶解度随pH的变化如图7所示。蛋白质的溶解度随pH的变化呈“V”型,符合蛋白质溶解度的特征。pH5的溶解度最低(AIAP为20.04%,TAAP为29.46%,SEAP为36.58%),这是由于接近AP的等电点(4.6),蛋白质的表面电荷为0,蛋白质聚集并形成沉淀。远离等电点时,蛋白质聚集程度降低,溶解度增加,因此pH3、7和9的溶解度增大。
在pH3、5、7条件下,SEAP和TAAP的溶解度高于AIAP,与Zhang等[33]的研究结果一致,这与蛋白质的表面疏水性和结构有关。疏水基团暴露导致了蛋白质之间的相互作用和不溶性[20],由2.7节可知,AIAP的表面疏水性大于TAAP和SEAP,蛋白质与蛋白质之间发生疏水相互作用,阻止了蛋白质与溶剂相互作用,AIAP的溶解度最低。此外,也可能是(NH4)2SO4保持杏仁蛋白和蛋白酶抑制剂的构象[33],使SEAP和TAAP的蛋白质表面结构比AIAP更光滑,结构更完整,因此SEAP的溶解度高于AIAP。
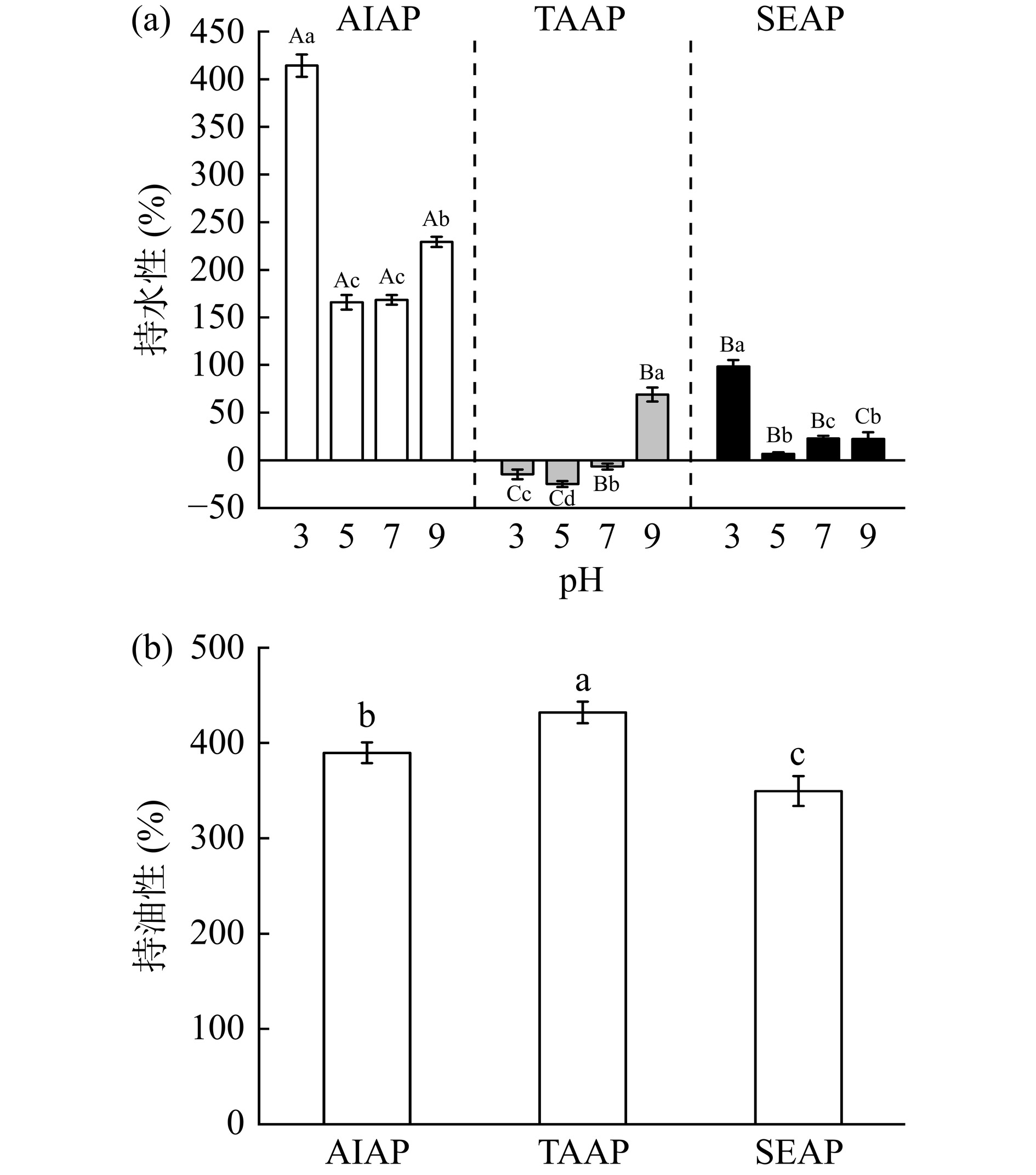
2.9 不同提取方法在不同pH条件下对AP持水性和持油性的影响
AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的持水性和持油性随pH的变化如图8所示。pH3至5时,三种蛋白质的持水性降低,其中TAAP为负值,蛋白质溶解至水中,不能体现出其持水性。而pH5到9时,蛋白质的持水性上升,蛋白质的持水性的变化呈“V”型。pH5时持水性最低,这是由于接近等电点(4.6),蛋白质表面的电荷为0,分子间的斥力最小,蛋白质逐渐絮凝[34]。远离等电点时蛋白质表面带正负电荷,与水分子结合较为紧密,因此持水性升高。
在不同pH条件下,AIAP的持水性显著高于TAAP和SAAP(P<0.05),这与AP的构成和表面结构有关,AIAP主要以不溶性谷蛋白为主[35],AIAP成层状结构,孔隙密集,表面粗糙,与水分结合紧密,因此AIAP能保留水分。而SEAP以白蛋白为主,易溶解,结构不规则,表面结构致密,孔隙少,因此持水性低。这进一步证实了等电点提取法中碱溶导致了AP的广泛构象变化、链展开和聚集[36],与二级结构的结果一致。
图8(b)观察到,TAAP的持油性最高(431.96%),其次是AIAP(389.70%),SEAP最低(349.53%),这与蛋白质的微观结构和表面疏水性有关。TAAP的表面粗糙,表面积比AIAP和SEAP大,AIAP多孔结构有突起,并且蛋白质表面疏水性较大[36],因此持油性比SEAP高。SEAP表面光滑,比其他两种蛋白质的表面积小,因此SEAP持油性最低。
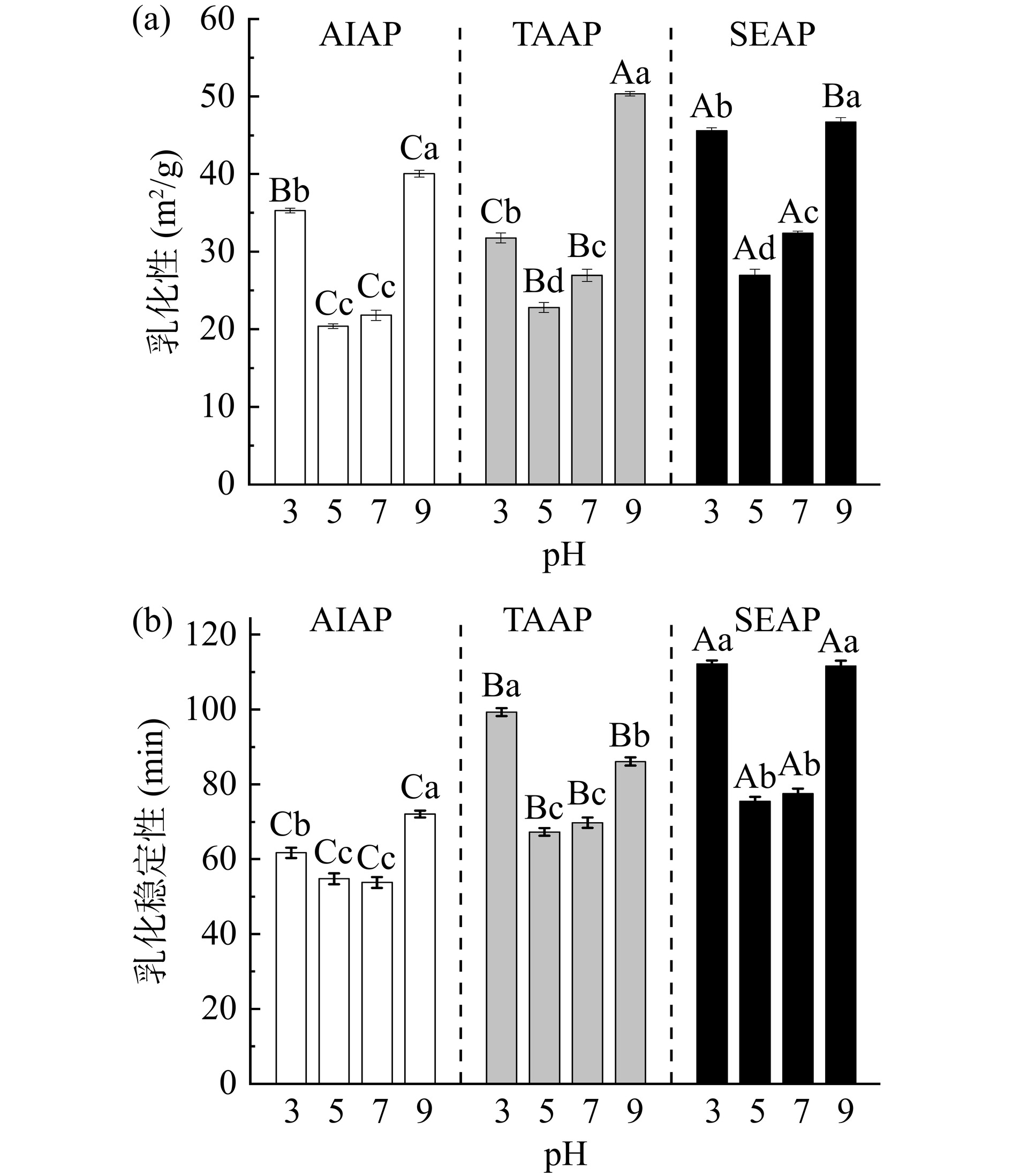
2.10 不同提取方法在不同pH条件下对AP乳化性和乳化稳定性的影响
AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的乳化性和乳化稳定性随pH的变化如图9所示。随pH的增大,AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的乳化性和乳化稳定性呈现降低后升高的趋势。pH5时三种蛋白质的乳化性和乳化稳定性最低(AIAP为20.38 m2/g,TAAP为22.80 m2/g,SEAP为26.95 m2/g),接近等电点蛋白质的表面电荷为0,蛋白质逐渐絮凝,溶解度最小,蛋白质颗粒无法在表面形成水化层,乳化粒子易絮凝聚集,因此乳化性最低。远离等电点时,分子间的相互作用力增加,使蛋白质向油/水界面的扩散能力增强,溶解度增加,因此乳化性和乳化稳定性提高[37]。不同pH条件下,SEAP的乳化性和乳化稳定性比AIAP和TAAP高,与三种蛋白质的溶解度趋势一致。
2.11 不同提取方法在不同pH条件下对AP起泡性和起泡稳定性的影响
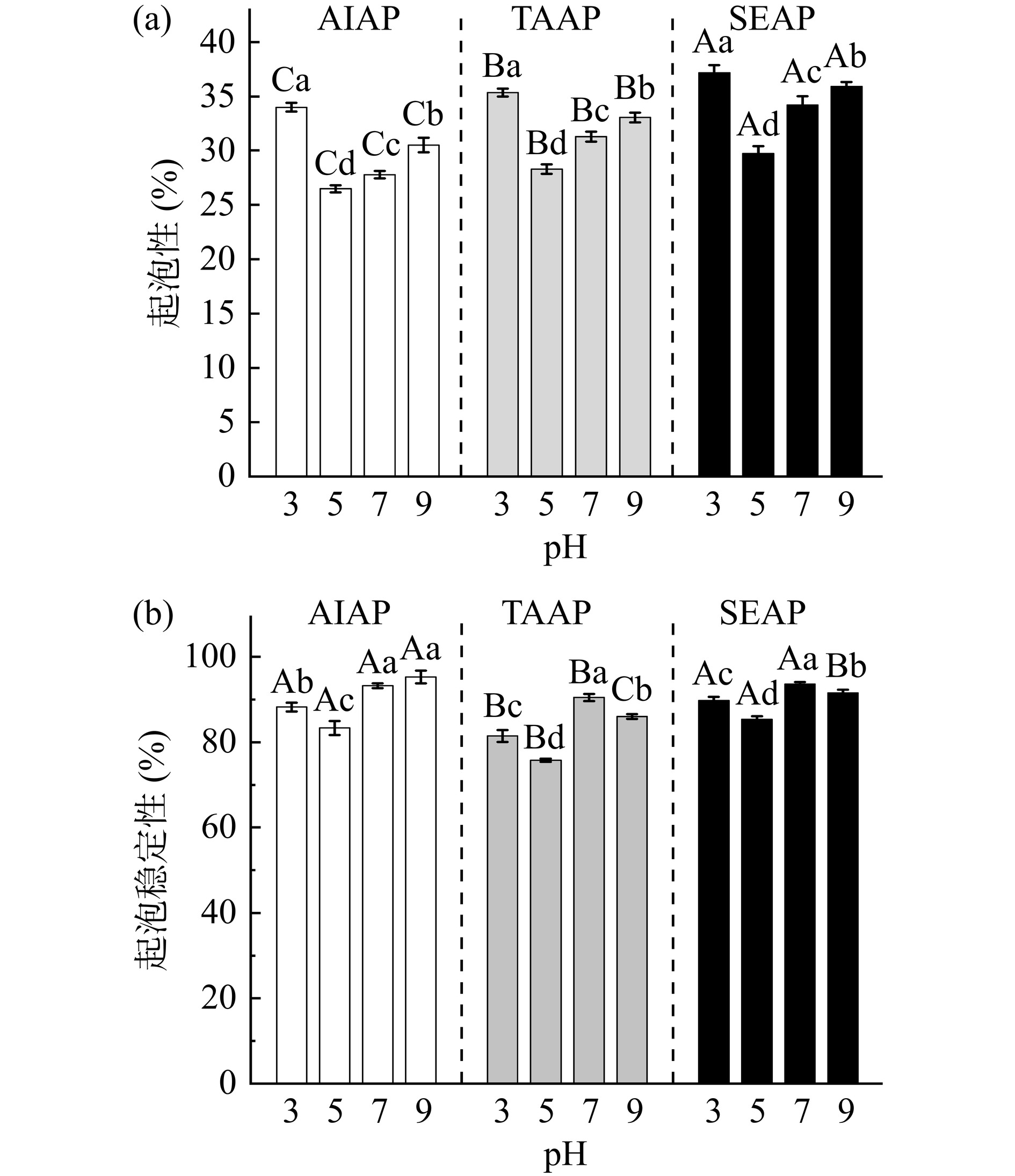
AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的起泡性和起泡稳定性随pH的变化如图10所示。AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的起泡性随pH的增大先降低后升高,pH5时起泡性最低(AIAP为26.47%,TAAP为28.28%,SEAP为29.71%),且AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的起泡稳定性随pH的增大先降低后升高再降低,与蛋白质的溶解度有关。在蛋白质等电点附近,溶解度降低,可用于形成泡沫的蛋白质减少,故起泡性降低。远离等电点时,蛋白质的溶解度增大,溶液中可溶性蛋白质含量增加,起泡性增大。
由图10可知,三种蛋白质的起泡性,SEAP>TAAP>AIAP,与蛋白质溶解度的结果一致。AIAP起泡性低与蛋白质含量和溶解度低有关,也可能是因为球蛋白的表面变性较低,AIAP主要以球蛋白为主,因此起泡特性较低[22]。
3. 结论
本研究使用AI、TA和SE提取AP,探究提取方法对AP结构和功能特性的影响。结果表明,SEAP的蛋白质纯度最高(88.21%),AIAP的蛋白质纯度最低(75.06%),SEAP(55.94%)和AIAP(55.63%)提取率最高,TAAP的提取率最低(50.71%)。二级结构结果表明AIAP的β-折叠含量(44.97%)比SEAP和TAAP的高。微观结构结果表明,AIAP结构疏松,表面疏水性较高,SEAP和TAAP结构致密,其表面疏水性较低。AIAP的持水性高于TAAP和SEAP。TAAP和SEAP的溶解度高于AIAP,具有更好的乳化特性和起泡特性。
本文系统地研究了不同提取方法对AP结构和功能特性的影响。在未来的工作中将进一步优化AP的提取工艺,并结合AP的结构和功能特性开发相关的食品,为AP在食品工业的应用提供一定的理论参考。
-
图 1 不同提取方法AP提取率及AP纯度
注:不同小写字母代表不同方法提取的蛋白质间差异显著(P<0.05);图3同。
Figure 1. AP extraction rate and AP purity of the different extraction methods
表 1 AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的色度
Table 1 Chromaticity of AIAP, TAAP and SEAP
样品名称 L* a* b* W AIAP 32.87±0.04c 1.19±0.01a 10.31±0.02a 32.08±0.03b TAAP 33.66±0.01a 0.32±0.01b 7.60±0.02b 33.23±0.01a SAAP 33.50±0.03b 0.24±0.01c 6.16±0.03c 33.21±0.03a 注:同列不同小写字母代表不同方法提取的蛋白质间差异显著(P<0.05);表2同。 表 2 杏仁粕、脱脂杏仁粕和AIAP、TAAP和SEAP的基本组成
Table 2 Basic composition of almond meal, defatted almond meal and AIAP, TAAP and SEAP
样品名称 蛋白质(%) 水分(%) 脂质(%) 灰分(%) 总糖(%) 杏仁粕 41.30±0.83d 3.94±0.51b 28.75±0.04a 4.02±0.26b 5.05±0.01a 脱脂杏仁粕 48.85±0.11c 5.83±0.30a 7.41±0.19b 5.19±0.15a 4.93±0.03a AIAP 75.06±3.96b 2.32±0.56d 2.84±0.07c 2.73±0.07d 1.21±0.28c TAAP 87.58±0.39a 4.28±0.26b 0.44±0.20d 3.09±0.26c 2.88±0.23b SEAP 88.21±0.25a 2.89±0.03c 0.56±0.15d 2.49±0.02e 1.50±0.21c -
[1] SHI T, CAO J, CAO J, et al. Almond (Amygdalus communis L.) kernel protein:A review on the extraction, functional properties and nutritional value[J]. Food Research International,2023,167:112721. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112721
[2] DEVNANI B, ONG L, KENTISH S, et al. Structure and functionality of almond proteins as a function of pH[J]. Food Structure,2021,30:100229. doi: 10.1016/j.foostr.2021.100229
[3] ALBILLOS S M, JIN T, HOWARD A, et al. Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray characterization of prunin-1, a major component of the almond (Prunus dulcis) allergen amandin[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2008,56(13):5352−5358. doi: 10.1021/jf800529k
[4] 糟龙. 不同品种杏仁蛋白特性及即食豆腐开发研究 [D]. 阿拉尔:塔里木大学, 2022. [CAO L. Research on the characteristics of different varieties of almond protein and the development of instant tofu [D]. Alaer:TarimUniversity, 2022.] CAO L. Research on the characteristics of different varieties of almond protein and the development of instant tofu [D]. Alaer: TarimUniversity, 2022.
[5] FANG B, CHANG L, OHM J B, et al. Structural, functional properties, and volatile profile of hemp protein isolate as affected by extraction method:Alkaline extraction–isoelectric precipitation vs salt extraction[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,405:135001. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135001
[6] 解春艳, 李丛胜, 路艳霞, 等. 苦杏仁蛋白提取条件优化及加工特性研究[J]. 食品科技,2015,40(2):294−298. [XIE C Y, LI C S, LU Y X, et al. Extraction technique and characteristics of protein from bitter apricot kernel[J]. Food Science and Technology,2015,40(2):294−298.] XIE C Y, LI C S, LU Y X, et al. Extraction technique and characteristics of protein from bitter apricot kernel[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2015, 40(2): 294−298.
[7] 郑亚军, 郝利平, 李艳. 杏仁蛋白质的研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2006(11):208−211. [ZHENG Y J, HAO L P, LI Y. Research and advance of almond protein[J]. Food Research and Development,2006(11):208−211.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2006.11.067 ZHENG Y J, HAO L P, LI Y. Research and advance of almond protein[J]. Food Research and Development, 2006(11): 208−211. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2006.11.067
[8] 陈默. 珍珠油杏杏仁蛋白和抗氧化肽的制备及功能活性研究 [D]. 泰安:山东农业大学, 2022. [CHEN M. Preparation and functional activity of pearl oil apricot almond protein and antioxidant peptides [D]. Taian:Shandong Agricultural University, 2022.] CHEN M. Preparation and functional activity of pearl oil apricot almond protein and antioxidant peptides [D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2022.
[9] 刘凯, 梁俊玉, 肖引, 等. 磷酸盐法提取杏仁蛋白的工艺研究[J]. 武警医学,2013,24(9):783−785. [LIU K, LIANG J Y, XIAO Y, et al. Extracting process conditions from almond dregs by phosphate method[J]. Medical Journal of the Chinese People's Armed Police Force,2013,24(9):783−785.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3594.2013.09.015 LIU K, LIANG J Y, XIAO Y, et al. Extracting process conditions from almond dregs by phosphate method[J]. Medical Journal of the Chinese People's Armed Police Force, 2013, 24(9): 783−785. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3594.2013.09.015
[10] PENG D, HE Z, PAN X, et al. A comparative evaluation of the structure, functionality and volatile profiles of trichosanthes kirilowii seed protein isolates based on different extraction methods[J]. Food Chemistry,2024,443:138547. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.138547
[11] AMIRSHAGHAGHI Z, REZAEI K, HABIBI R M. Characterization and functional properties of protein isolates from wild almond[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2017,11(4):1725−1733. doi: 10.1007/s11694-017-9553-y
[12] 顾海洋. 热碱法提取制革污泥蛋白质及其阻燃应用研究 [D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2021. [GU H Y. Protein extraction from tannery sludge by thermo-alkali method and its application in flame retardant [D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2021.] GU H Y. Protein extraction from tannery sludge by thermo-alkali method and its application in flame retardant [D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021.
[13] 陈一, 何晓叶. 热碱法提取杏仁粕分离蛋白的工艺研究[J]. 安徽:安徽农业科学,2012,40(32):15905−15907. [CHEN Y, HE X Y. Study on the technology of separating protein from almond meal by alkali-extraction[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2012,40(32):15905−15907.] CHEN Y, HE X Y. Study on the technology of separating protein from almond meal by alkali-extraction[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 40(32): 15905−15907.
[14] 宋艳丽, 王晓洁, 鲍诚, 等. 元宝枫籽油饼粕蛋白的提取工艺研究[J]. 鲁东大学学报(自然科学版),2023,39(3):258−263. [SONG Y L, WANG X J, BAO C, et al. Extraction technology of protein from acer truncatum seed oil cake[J]. Journal of Ludong University (Natural Science Edition),2023,39(3):258−263.] SONG Y L, WANG X J, BAO C, et al. Extraction technology of protein from acer truncatum seed oil cake[J]. Journal of Ludong University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 39(3): 258−263.
[15] ZHOU S, HUANG G, CHEN G. Extraction, structural analysis, derivatization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from chinese yam[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,361:130089. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130089
[16] HU H, FENG Y, ZHENG K, et al. The effect of subzero temperatures on the properties and structure of soy protein isolate emulsions[J]. Food Chemistry,2024,433:136829. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136829
[17] ZHANG S, HUANG W, ROOPESH M S, et al. Pre-treatment by combining atmospheric cold plasma and ph-shifting to prepare pea protein concentrate powders with improved gelling properties[J]. Food Research International,2022,154:111028. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111028
[18] 王立博, 陈静, 任艳娟, 等. 荞麦麸皮蛋白的制备及功能特性研究[J]. 中国调味品,2023,48(12):16−24. [WANG L B, CHEN J, REN Y J, et al. Preparation and functional properties of buckwheat bran protein[J]. China Condiment,2023,48(12):16−24.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2023.12.003 WANG L B, CHEN J, REN Y J, et al. Preparation and functional properties of buckwheat bran protein[J]. China Condiment, 2023, 48(12): 16−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2023.12.003
[19] 卢秋玲, 李琅, 杨敏, 等. 超声处理对文冠果种粕蛋白结构及性质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2024,50(20):79−87. [LU Q L, LI L, YANG M, et al. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on structure and properties of Xanthoceras sorbifolium Bunge seeds meal protein[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2024,50(20):79−87.] LU Q L, LI L, YANG M, et al. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on structure and properties of Xanthoceras sorbifolium Bunge seeds meal protein[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024, 50(20): 79−87.
[20] STONE A K, KARALASH A, TYLER R T, et al. Functional attributes of pea protein isolates prepared using different extraction methods and cultivars[J]. Food Research International,2015,76:31−38. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.11.017
[21] 郑俊. 燕麦、青稞营养组分、蛋白和多酚理化性质分析及加工方式对燕麦粉品质影响研究[D]. 南昌:南昌大学, 2016. [ZHENG J. Nutrional component analysis, properties of protein and polyphenol among oat varieties and hulless barley and the influence of processing on the quality of oat flour[D]. Nanchang:Nanchang University, 2016.] ZHENG J. Nutrional component analysis, properties of protein and polyphenol among oat varieties and hulless barley and the influence of processing on the quality of oat flour[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2016.
[22] OGUNBUSOLA E M, ALABI O O, ARAOYE K T, et al. Impact of extraction methods on the quality, physicochemical, and functional properties of white melon (Cucumeropsis mannii) seed protein concentrates[J]. Food Chemistry Advances,2022,1:100131. doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2022.100131
[23] JULAKANTI S, CHARLES A P R, ZHAO J, et al. Hempseed protein (Cannabis sativa L.):Influence of extraction pH and ball milling on physicochemical and functional properties[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2023,143:108835. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108835
[24] 杨洁茹, 刘海波, 李晴, 等. 油茶饼粕中多肽的分离纯化及抗氧化研究[J]. 粮食与食品工业,2022,29(05):4−9. [YANG J R, LIU H B, LI Q, et al. Separation and purification of polypeptides and antioxidant studies in Camellia oleifera cake meal[J]. Cereal and Food Industry,2022,29(05):4−9.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5026.2022.05.002 YANG J R, LIU H B, LI Q, et al. Separation and purification of polypeptides and antioxidant studies in Camellia oleifera cake meal[J]. Cereal and Food Industry, 2022, 29(05): 4−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5026.2022.05.002
[25] MIRANDA C G, SPERANZA P, KUROZAWA L E, et al. Lentil protein:Impact of different extraction methods on structural and functional properties[J]. Heliyon,2022,8(11):11775. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11775
[26] ZHENG L, WANG Z, KONG Y, et al. Different commercial soy protein isolates and the characteristics of chiba tofu[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,110:106115. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106115
[27] BECK T L, MCGREGOR P J, TAKAMI M, et al. Spatially resolved molecular hydrogen emission in the inner 200au environments of classical t tauri stars[J]. Astrophysical Journal,2008,122(888):241−247.
[28] 张倩, 陈复生. 反胶束萃取对大豆分离蛋白结构和特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(7):108−113. [ZHANG Q, CHEN F S. Effect of reverse micellar extraction on structure and physicochemical properties of soybean protein isolate[J]. Food Science,2019,40(7):108−113.] ZHANG Q, CHEN F S. Effect of reverse micellar extraction on structure and physicochemical properties of soybean protein isolate[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(7): 108−113.
[29] 朱乾乾. 超高压和酶法处理对苦杏仁蛋白结构和免疫反应性的影响[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2020. [ZHU Q Q. Effect of ultra-high pressure and enzymatic treatment on the structure and immunoreactivity of bitter apricot kernel protein[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2020.] ZHU Q Q. Effect of ultra-high pressure and enzymatic treatment on the structure and immunoreactivity of bitter apricot kernel protein[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2020.
[30] TANGER C, ENGEL J, KULOZIK U. Influence of extraction conditions on the conformational alteration of pea protein extracted from pea flour[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,107:105949. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105949
[31] FENG Y, WANG J, HU H, et al. Effect of oxidative modification by reactive oxygen species (ROS) on the aggregation of whey protein concentrate (WPC)[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,123:107189. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107189
[32] 曾琪, 胡淼, 王欢, 等. pH值处理对黑豆分离蛋白结构、流变特性及乳化性能的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(22):15−21. [ZENG Q, HU M, WANG H, et al. Effect of pH treatment on structure, rheological properties and emulsifying properties of black bean protein isolate[J]. Food Science,2020,41(22):15−21.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190906-080 ZENG Q, HU M, WANG H, et al. Effect of pH treatment on structure, rheological properties and emulsifying properties of black bean protein isolate[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(22): 15−21. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190906-080
[33] ZHANG D Q, MU T H, SUN H N, et al. Comparative study of potato protein concentrates extracted using ammonium sulfate and isoelectric precipitation[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2016,20(9-12):2113−2127.
[34] 温程程. 辽西山杏仁蛋白提取及功能特性研究[D]. 沈阳:沈阳农业大学, 2016. [WEN C C. Study on extraction and functional properties of western Liaoning mountain almond protein[D]. Shenyang:Shenyang Agricultural University, 2016.] WEN C C. Study on extraction and functional properties of western Liaoning mountain almond protein[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2016.
[35] 石宁蕙, 叶健明, 祖力皮亚·艾麦提, 等. 不同提取方法对甜杏仁蛋白形态及其功能性的影响[J]. 保鲜与加工,2020,20(2):6. [SHI N H, YE J M, ZU A, et al. Functional properties and characterization of almond protein obtained by different extraction methods[J]. Storage and Process,2020,20(2):6.] SHI N H, YE J M, ZU A, et al. Functional properties and characterization of almond protein obtained by different extraction methods[J]. Storage and Process, 2020, 20(2): 6.
[36] NOUSKA C, DELIGEORGAKI M, KYRKOU C, et al. Structural and physicochemical properties of sesame cake protein isolates obtained by different extraction methods [J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2024, 109757.
[37] 杜娟, 解春艳, 侯晓强, 等. 苦杏仁蛋白质功能特性的研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2018,9(7):1605−1610. [DU J, XIE C Y, HOU X Q, et al. Functional properties of bitter almond protein[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2018,9(7):1605−1610.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2018.07.024 DU J, XIE C Y, HOU X Q, et al. Functional properties of bitter almond protein[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2018, 9(7): 1605−1610. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2018.07.024






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



