Optimization of Preparation Technology of Matcha Hickory Kernel and Study on Antioxidant and Lipid-lowering Activities
-
摘要: 为了优化抹茶山核桃仁制作工艺并考察其抗氧化和降脂活性,本研究以感官评分作为评价指标,通过单因素与响应面试验确定抹茶山核桃仁最佳加工工艺;通过测定1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯基(1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)和羟自由基的清除能力,牛磺胆酸钠和甘氨胆酸钠的结合能力以及对3T3-L1脂肪细胞模型中细胞内总胆固醇、甘油三酯水平的影响来评价抹茶山核桃仁抗氧化和降脂活性。结果表明,抹茶山核桃仁的最佳加工工艺为:白砂糖添加量15%、抹茶浸泡液浓度8%、烘烤时间30 min和烘烤温度130 ℃,感官评分88.40分。抹茶山核桃仁对DPPH和羟自由基的清除能力IC50分别为0.50 mg/mL和0.42 mg/mL;在0.10 g/mL时,抹茶山核桃仁对甘氨胆酸钠和牛磺胆酸钠的结合率分别达到56.25%和53.06%;在200 μg/mL时,抹茶山核桃仁能够极显著降低3T3-L1脂肪细胞内的总胆固醇和甘油三酯含量(P<0.001)。本实验确定的工艺简单易行,体外和细胞实验表明抹茶山核桃仁具有一定的抗氧化能力和降脂活性。Abstract: This study aimed to optimize the production process of matcha hickory kernel and investigate its antioxidant activity and lipid-lowering potential. Sensory scores were utilized as the evaluation criterion to identify the optimal processing technique for matcha hickory kernel via single-factor and response surface experiments. The antioxidant and lipid-lowering activities of matcha hickory kernel were assessed using various methods, including the scavenging abilities of 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and hydroxyl radicals, the binding capacities of sodium taurocholate and sodium glycocholate, and the impact on total cholesterol and triglyceride levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The findings indicated that the most effective processing technique for matcha hickory kernel included the following parameters: White sugar content at 15%, matcha infusion concentration at 8%, baking time of 30 min, baking temperature set at 130 ℃, and a sensory score of 88.40 points. IC50 values for the scavenging abilities of DPPH and hydroxyl radicals by matcha hickory kernel were 0.50 mg/mL and 0.42 mg/mL, respectively. At a concentration of 0.10 g/mL, the binding rates of matcha hickory kernel with sodium glycocholate and sodium taurocholate were found to be 56.25% and 53.06%, respectively. At a concentration of 200 μg/mL, matcha hickory kernel demonstrated an extremely significant reduction in the levels of total cholesterol and triglycerides in 3T3-L1 adipocytes (P<0.001). The process established in this experiment is straightforward and feasible, in vitro and cellular studies have demonstrated that matcha hickory kernel possesses significant antioxidant and lipid-lowering activities.
-
山核桃(Carya cathayensis Sarg.)是胡桃科山核桃属的植物,又称小胡桃,主要分布于我国浙江省天目山区以及安徽省皖南山区和大别山区[1]。山核桃果仁风味与营养俱佳,富含脂肪、膳食纤维、植物蛋白和矿物质等物质[2],其中的多酚和黄酮类物质表现出一定的清除ABTS+、DPPH自由基以及羟自由基的能力[3]。研究表明,坚果由于含有丰富的不饱和脂肪酸、多酚类、生育酚、植物甾醇及矿质元素等,在预防和管理肥胖方面具有潜在的益处[4]。Domínguez-Avila等[5]通过给大鼠饲喂添加山核桃油、山核桃多酚及整个山核桃仁的高脂饲料发现,添加整个山核桃仁组对大鼠的改善作用最强,能够有效预防高瘦素血症并降低了TC。
抹茶是一种经过蒸汽、杀青、干燥和研磨等加工工艺制成的微粉状茶产品[6]。与传统绿茶相比,抹茶能更好地保留绿茶的清香和色泽,并且能够较好地保留绿茶中的功能活性成分,例如茶多酚、咖啡碱、游离氨基酸、叶绿素、蛋白质、维生素以及各种微量元素[7]。据报道,抹茶在调节肥胖相关代谢综合征方面具有突出的潜力[8]。抹茶中的茶多酚能够改变淀粉结构,阻碍消化酶与淀粉的相互作用,从而影响淀粉的消化过程。这意味着抹茶中的茶多酚对糖尿病具有潜在的预防和治疗作用[9]。此外,抹茶中的不溶性纤维和纤维结合酚类物质还能减少小鼠血清中脂质和葡萄糖的上升[10]。
随着人们健康意识的增强,越来越多的人开始关注食品中的抗氧化和降脂成分。山核桃仁作为一种富含多种营养成分的坚果,具有较高的营养价值和市场价值[11]。然而,目前对抹茶山核桃仁在抗氧化和降脂方面的研究还比较有限,因此有必要对其制作工艺进行优化,并探讨其抗氧化和降脂活性。本研究以山核桃仁和抹茶为主要原料,通过单因素和响应面试验确定抹茶山核桃仁的最佳加工工艺;通过测定1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯基(1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)和羟自由基的清除能力来评价不同加工处理对山核桃仁的抗氧化性能的影响。同时,为评价抹茶山核桃仁的体外降脂活性,本研究分别测定了抹茶山核桃仁对甘氨胆酸钠、牛磺胆酸钠的结合能力,以及对胰岛素、地塞米松和3-异丁基-1-甲基黄嘌呤(3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine,IBMX)三种物质联合诱导的3T3-L1高脂细胞模型中细胞内总胆固醇和甘油三酯的含量的影响。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
山核桃仁 浙江省杭州市临安区创辉食品厂;抹茶 贵州铜仁贵茶茶叶股份有限公司;氢氧化钠(97%) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;无水乙醇(99.8%)、1,1-二苯-2-苦基肼(DPPH)(98%) 上海凌锋化学试剂有限公司;人工胃液/SGF(除菌,USP)、人工小肠液(无菌) 北京百奥莱博科技有限公司;3T3-L1脂肪细胞 湖南丰辉生物科技有限公司;胰岛素(来源于猪胰腺)、3-异丁基-1-甲基黄嘌呤(99%)、地塞米松(98%) 上海阿拉丁生化科技有限公司;超敏型细胞增殖检测试剂(CCK-8)试剂盒、总胆固醇测定试剂盒、甘油三酯测定试剂盒 南京建成科技有限公司。
KQD60F-F1嵌入式烤箱 宁波方太厨具有限公司;C21-WT2116多功能电磁炉 广东省美的生活电器制造有限公司;XMTD-8222水浴锅 上海精宏实验设备有限公司;ME103E/02电子天平 瑞士梅特勒-托利多有限公司;PHS-3C pH计 上海雷磁有限公司;SpectraMax M2酶标仪 美国Molecular Devices公司;SW-CJ-1FD超净工作台 苏州集团安泰空气技术有限公司;311 CO2恒温培养箱 美国赛默飞世尔科技公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 工艺流程
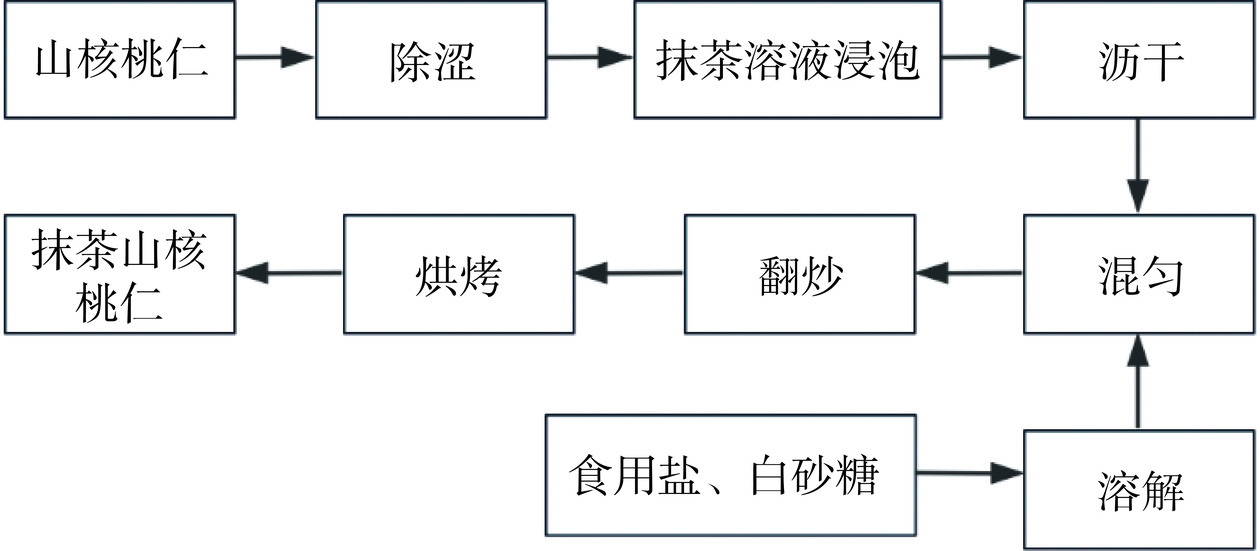
抹茶山核桃仁制作流程图见图1。
1.2.2 操作要点
1.2.2.1 原料选择
选择新鲜成熟的山核桃,去壳后取出山核桃仁。
1.2.2.2 除涩处理
将山核桃仁浸泡在65 ℃的5%碳酸钠溶液中进行除涩处理[12],除涩总时长为100 min。
1.2.2.3 抹茶溶液浸泡
抹茶与水按照质量比进行配制。除涩后的山核桃仁在抹茶溶液中浸泡2 h,每隔30 min搅拌一次。
1.2.2.4 翻炒处理
在锅中加入20 mL水、0.9%的食用盐和适量白砂糖,加热至白砂糖和食用盐完全溶解后,放入山核桃仁,继续翻炒直至山核桃仁表面无水分。
1.2.2.5 烘烤处理
将翻炒后的核桃仁放入烤箱中,以适当温度和时间进行烘烤,保持其内部营养成分。
1.2.3 单因素实验设计
设定不同白砂糖添加量、抹茶浸泡液浓度、烘烤时间和烘烤温度共四个指标进行单因素实验。参考刘杰梅等[13]的实验方法绘制感官评价得分表(表1)作为评价标准,选定10名具有食品相关背景的人员进行品尝打分,取他们的平均得分作为最终的感官评分。具体实验步骤如下。
表 1 感官评价标准Table 1. Sensory evaluation criteria指标 评分标准 得分 色泽(20分) 金黄色,抹茶色分布均匀 14~20 淡黄色,抹茶色分布不均匀 7~13 抹茶色太深或烤焦 0~6 气味(20分) 无异味,有抹茶的特殊香味 14~20 略有焦糊味,抹茶香味略淡 7~13 焦糊味严重,无香气 0~6 滋味(30分) 无涩味,甜味适宜 21~30 微涩,甜味稍重或稍淡 11~20 涩味很重 0~10 咀嚼性(30分) 口感酥脆,软硬适中 21~30 口感酥脆性较差,稍软或稍硬 11~20 口感过软或过硬 0~10 1.2.3.1 不同白砂糖添加量的选择
固定抹茶浸泡液浓度为10%,烘烤时间为30 min,烘烤温度130 ℃,研究不同添加量(5%、10%、15%、20%和25%)白砂糖对抹茶山核桃仁品质的影响,通过感官评分筛选出最佳白砂糖添加量。
1.2.3.2 不同抹茶浸泡液浓度的选择
固定白砂糖添加量为10%,烘烤时间为30 min,烘烤温度130 ℃,研究不同浓度(5%、10%、15%、20%和25%)抹茶浸泡液对抹茶山核仁桃品质的影响,通过感官评分筛选出最佳抹茶浸泡液浓度。
1.2.3.3 不同烘烤时间的选择
固定白砂糖添加量为10%,抹茶浸泡液浓度为10%,烘烤温度130 ℃,研究不同烘烤时间(10、20、30、40和50 min)对抹茶山核桃仁品质的影响,通过感官评分筛选出最佳烘烤时间。
1.2.3.4 不同烘烤温度的选择
固定白砂糖添加量为10%,抹茶浸泡液浓度为10%,烘烤时间为30 min,研究不同烘烤温度(110、120、130、140和150 ℃)对抹茶山核桃仁品质的影响,通过感官评分筛选出最佳烘烤温度。
1.2.4 响应面试验设计
在前期单因素实验基础上,运用Design-Expert 13软件进行响应面设计(表2),以感官评分为响应值,设计4因素3水平的试验方案。
表 2 响应面试验因素与水平设计Table 2. Response surface experimental factors and level design水平 因素 A白砂糖添
加量(%)B抹茶浸泡液
浓度(%)C烘烤时间
(min)D烘烤温度
(℃)−1 10 5 20 120 0 15 10 30 130 1 20 15 40 140 1.2.5 体外抗氧化性能测定
1.2.5.1 DPPH自由基清除能力测定
依据Rumpf等[14]的方法并稍加修改,用无水乙醇配制浓度分别为0.05、0.15、0.25、0.35、0.45 mg/mL的鲜山核桃仁、传统山核桃仁(未添加抹茶,140 ℃烤20 min)和抹茶山核桃仁溶液,配制好的溶液与0.2 mmol/L的DPPH溶液按照1:3的体积比进行混合,室温避光静置30 min后使用酶标仪测定其在517 nm处吸光度值。DPPH自由基清除率计算公式如下:
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=A0−(A1−A2)A0×100 (1) 式中:A1为样品组吸光度值(样品+DPPH);A2为对照组吸光度值(样品+无水乙醇);A0为样品空白组吸光度值(DPPH+无水乙醇)。
1.2.5.2 羟自由基清除能力测定
依据Lin等[15]的方法并稍加修改,分别取浓度分别为0.05、0.15、0.25、0.35、0.45 mg/mL的鲜山核桃仁、传统山核桃仁和抹茶山核桃仁溶液1.0 mL,加入1 mL 9 mmol/L水杨酸钠溶液,1 mL 9 mmol/L七水硫酸铁溶液,50 µL过氧化氢溶液(0.025%,v/v)。37 ℃孵育30 min,反应结束后在510 nm处测定吸光度值。羟自由基清除率计算公式如下:
羟自由基清除率(%)=A0−(A1−A2)A0×100 (2) 式中:A1为样品组吸光度值(样品+H2O2);A2为对照组吸光度值(样品+蒸馏水);A0为空白组吸光度值(蒸馏水+H2O2)。
1.2.5.3 半数清除率(IC50)的计算
以样品浓度与其对自由基清除率作图并进行线性拟合,得到线性回归方程,根据方程计算清除50%自由基时所需样品浓度(mg/mL),即IC50值。
1.2.6 胆酸盐结合能力测定
胆酸盐结合能力测定参考刘淑敏[16]的方法。配制浓度分别为0、0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5 mmol/L的胆酸盐(牛磺胆酸钠、甘氨胆酸钠)标准溶液,取2.5 mL标准溶液于具塞试管中,加入质量分数为60%的硫酸溶液7.5 mL,混匀,70 ℃水浴加热20 min,迅速冷却后,紫外可见分光光度法于387 nm波长处测定吸光度。以吸光度为纵坐标,胆酸盐含量为横坐标,绘制标准曲线。
称取2.0 g山核桃仁粉末置于锥形瓶中,加入20 mL蒸馏水,用柠檬酸调节pH至6.5,加入1 mL α-淀粉酶溶液(酶活75 U/mL)后置于37 ℃水浴振荡10 min,8000 r/min离心10 min,取1.0 mL上清液于10 mL具塞试管中,加入1 mL人工胃液,在37 ℃恒温振荡消化1 h。用0.1 mol/L氢氧化钠调节pH为6.8,随后加入4 mL人工小肠液,37 ℃恒温振荡消化1 h。消化液中加入4 mL 1.0 mmol/L胆酸盐溶液,其余操作与标准曲线绘制的方法一致。根据标准曲线,计算消化液上清液中胆酸盐含量,即为未结合胆酸盐含量。胆酸盐结合能力按照以下公式进行计算:
胆酸盐结合率(%)=胆酸盐总量−未结合胆酸盐含量胆酸盐总量×100 (3) 1.2.7 抹茶山核桃仁对3T3-L1脂肪细胞的影响
1.2.7.1 细胞传代及培养
细胞培养于含10%胎牛血清(FBS)和1%双抗(青霉素-链霉素溶液)的高糖培养基中,并置于37 ℃、5% CO2的细胞培养箱中培养,隔天换一次培养基。待细胞密度长至约瓶壁的80%,用0.25%胰蛋白酶消化,按照1:3比例传代。
1.2.7.2 细胞毒性
根据1.2.6中的操作步骤,制备抹茶山核桃仁体外消化液,并设置0(对照组)、25、50、100、200、400和800 μg/mL 7个浓度梯度进行实验。使用CCK-8法测定山核桃仁对3T3-L1脂肪细胞增殖毒性的影响[17],以确定最佳的给药剂量,该给药剂量将用于后续实验。
1.2.7.3 3T3-L1细胞的诱导分化与总胆固醇、甘油三酯含量测定
参考陈超等[18]的方法建立高脂细胞模型。将3T3-L1脂肪细胞接种于6孔培养板,生长至接触抑制状态后继续培养48 h;换液后使用包含0.5 mmol/L IBMX、1 μmol/L地塞米松、1 μg/mL胰岛素的高糖培养基继续培养48 h;换用含有1 μg/mL胰岛素的高糖培养基继续培养48 h;最后,将细胞转移至高糖培养基中继续培养,直至超过90%的细胞分化为成熟脂肪细胞。将3T3-L1成熟脂肪细胞以5×105个/mL的浓度接种于6孔细胞培养板上,每孔2 mL。CO2培养箱中培养24 h后,将细胞分成以下4组:模型组(在完全培养液中培养24 h);抹茶山核桃仁低剂量组(细胞在含50 µg/mL抹茶山核桃仁体外消化液的完全培养基中培养24 h);抹茶山核桃仁中剂量组(细胞在含100 µg/mL抹茶山核桃仁体外消化液的完全培养基中培养24 h);抹茶山核桃仁高剂量组(细胞在含200 µg/mL抹茶山核桃仁体外消化液的完全培养基中培养24 h)。未经诱导的3T3-L1脂肪细胞作为对照组(在完全培养液中培养24 h)。细胞培养完成之后收集细胞上清液,按照试剂盒操作步骤测定细胞内的总胆固醇和甘油三酯含量。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验均进行三次平行实验,数据分析结果以平均值和标准差(Mean±SD)表示,P<0.05表示具有显著差异,P<0.01表示差异极显著。采用GraphPad Prism 9.0进行组间单因素方差分析,并使用GraphPad Prism 9.0进行统计图的绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
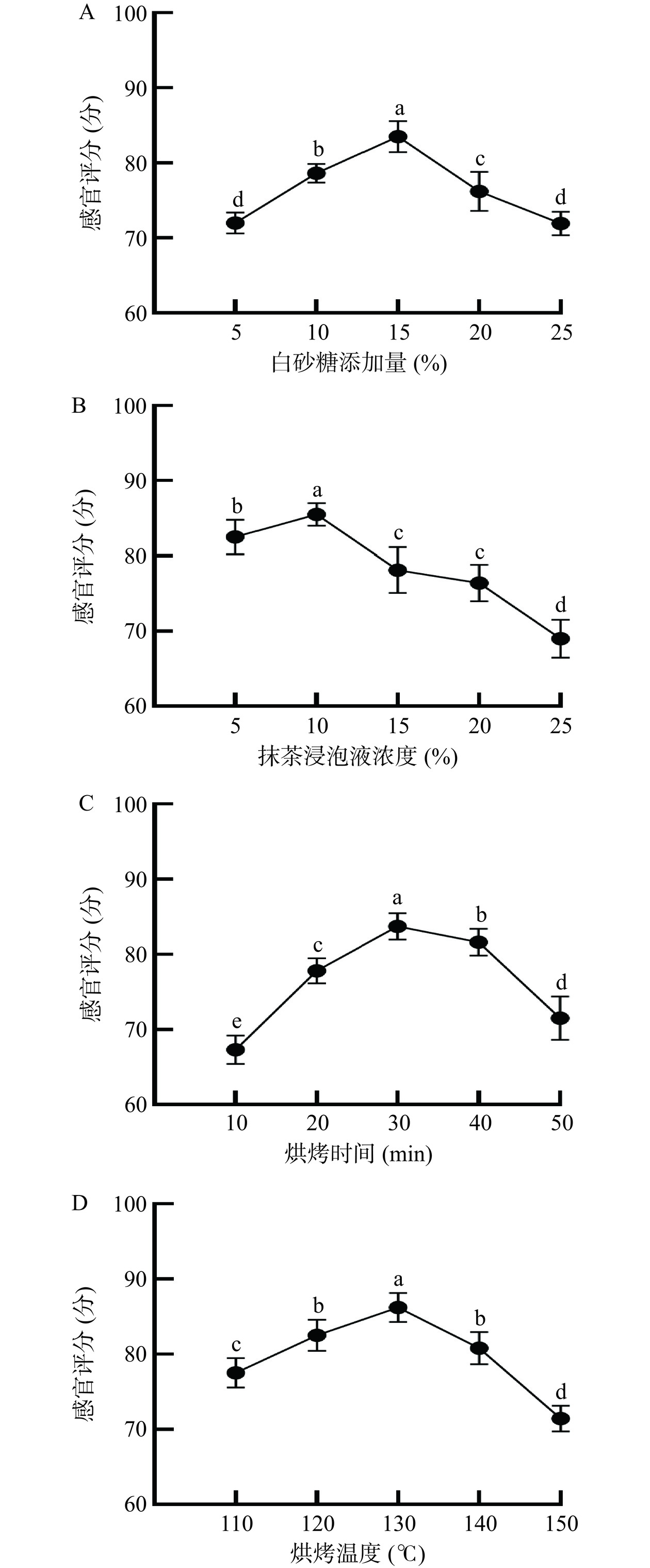
2.1.1 白砂糖添加量对抹茶山核桃仁感官品质的影响
由图2A可知,当白砂糖添加量逐渐增加至15%时,抹茶山核桃仁的感官评分最高,此时的山核桃仁口感香脆,甜度适宜。当白砂糖添加量低于10%时,山核桃仁的甜味会偏淡,与抹茶味不协调,整体风味不佳;当白砂糖添加量超过20%时,甜味会过于浓重,明显遮盖了山核桃仁本身的香气,同时焦糖色泽也会变得较深,整体风味也会变差。综上所述,白砂糖适宜添加量为15%。
2.1.2 抹茶浸泡液浓度对抹茶山核桃仁感官品质的影响
由图2B可知,随着抹茶浸泡液浓度的升高,感官评分呈现先缓慢上升,然后迅速下降的趋势。当抹茶浸泡液浓度为10%时,得分最高(85.5分),此时山核桃仁的抹茶色泽纯正,抹茶香突出,口感酥脆。然而,当抹茶浸泡液浓度低于5%时,抹茶色分布不均匀,茶香味较淡,口感一般;当抹茶的添加量超过15%时,抹茶的颜色会变得过于深沉,抹茶的味道也会逐渐显得更加浓烈。此外,口感也会变得较差,不够酥脆,这可能是由于抹茶中的多糖和果胶等物质阻碍了山核桃仁中水分的流失所致[19]。因此,抹茶浸泡液适宜浓度为10%。
2.1.3 烘烤时间对抹茶山核桃仁感官品质的影响
由图2C可知,当烘烤时间为30 min时,感官评分最高(83.7分),此温度下烘烤的山核桃仁表面没有焦糊,色泽纯正,口感酥脆可口。随着烘烤时间的增加,感官评分逐渐下降。烘烤时间过短会导致山核桃仁内部水分较多,焦香味不够浓郁,口感的酥脆度还有提升的空间。而烘烤时间过长则会使山核桃仁的色泽加深,同时风味中开始出现令人不悦的焦糊味,口感也变得过硬,这种现象可能是由于高温引起的蛋白质变性和水分流失所致[20]。因此,最佳烘烤时间为30 min。
2.1.4 烘烤温度对抹茶山核桃仁感官品质的影响
由图2D可知,烘烤温度对抹茶山核桃仁的品质有显著影响(P<0.05)。当烘烤温度为130 ℃时,感官评分最高(86.2分),在这个温度下,山核桃仁呈现明亮的黄褐色,焦香味适宜。烘烤温度过低会导致山核桃仁口感过软,酥脆性较差,香味不足,几乎没有焦香气味。而烘烤温度过高会使山核桃仁产生焦煳味,抹茶味不明显,从而降低感官评分。因此,最佳烘烤温度为130 ℃。
2.2 响应面分析
根据上述单因素实验结果,以白砂糖添加量(A)、抹茶浸泡液浓度(B)、烘烤时间(C)和烘烤温度(D)为自变量,以感官评分(Y)为响应值,通过Box Behnken试验进行预测,试验设计及结果如表3所示。
表 3 响应面试验结果Table 3. Results of response surface experiment试验号 A(%) B(%) C(min) D(℃) Y 感官评分(分) 1 10 5 30 130 82.4 2 20 5 30 130 85.9 3 10 15 30 130 74.7 4 20 15 30 130 72.1 5 15 10 20 120 77.4 6 15 10 40 120 77.5 7 15 10 20 140 70.8 8 15 10 40 140 76.5 9 10 10 30 120 80.9 10 20 10 30 120 79.1 11 10 10 30 140 74.9 12 20 10 30 140 71.7 13 15 5 20 130 74.1 14 15 15 20 130 72.3 15 15 5 40 130 81.9 16 15 15 40 130 70.7 17 10 10 20 130 79.4 18 20 10 20 130 71.8 19 10 10 40 130 78.7 20 20 10 40 130 77.7 21 15 5 30 120 80.1 22 15 15 30 120 75 23 15 5 30 140 75.3 24 15 15 30 140 68.6 25 15 10 30 130 87.2 26 15 10 30 130 88.2 27 15 10 30 130 89.8 2.2.1 响应面试验结果
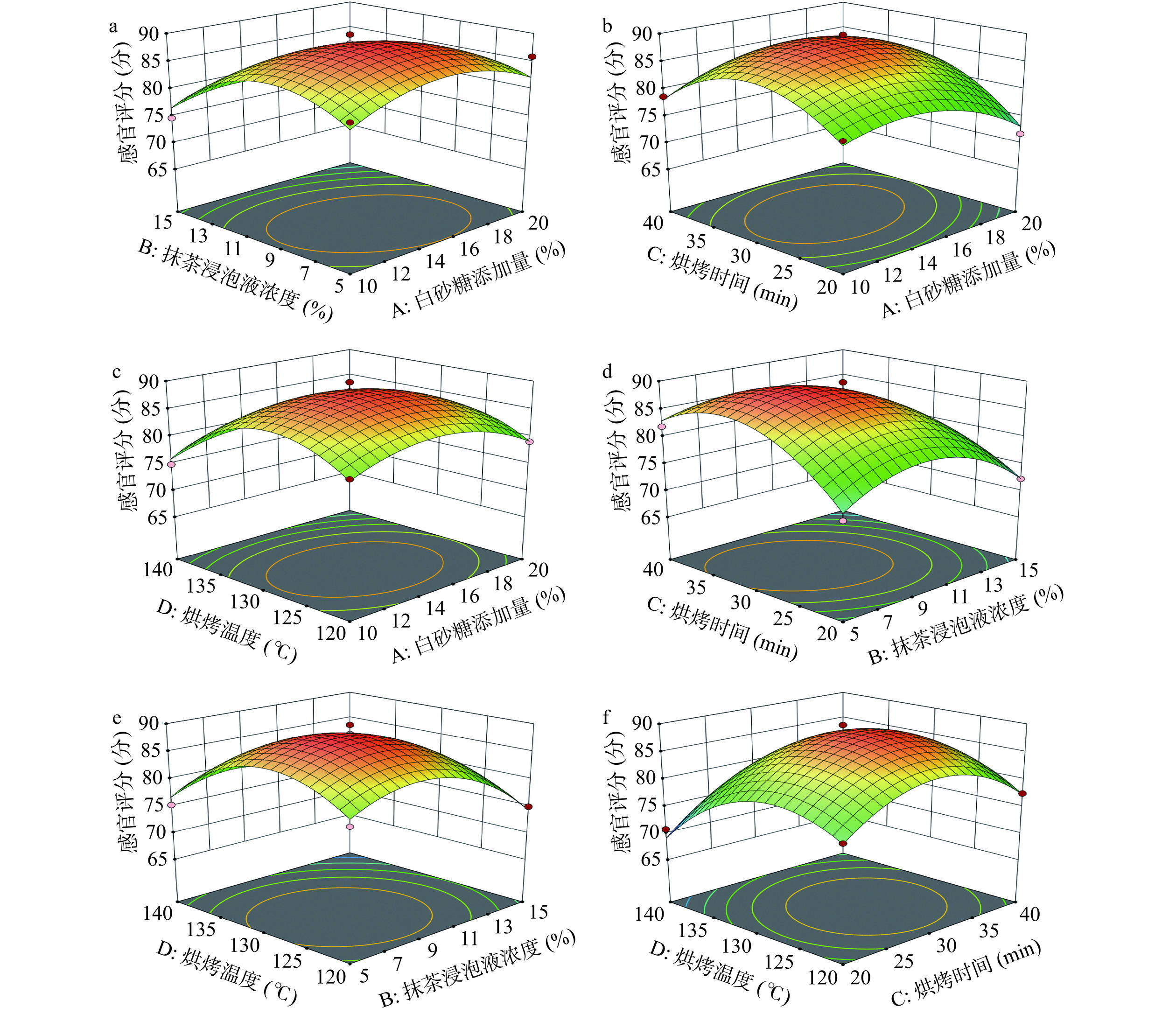
回归模型方差分析如表4所示,根据 Design-Expert 软件分析得到各因素水平与感官评分的二次多项回归方程:Y=88.40−1.06A−3.86B+1.43C−2.68D−1.53AB+1.65AC−0.35AD−2.35BC−0.4BD+1.40CD−4.27A2−6.29B2−6.83C2−6.95D2,其中P<0.0001说明模型极为显著,失拟项P=0.3353>0.05,为不显著,表明该模型具有较高的可信度;R2=0.9472,R2Adj=0.8856表明拟合程度好;根据F值可知,各因素对感官评分的影响程度由大到小依次为:抹茶浸泡液浓度(B)>烘烤温度(D)>烘烤时间(C)>白砂糖添加量(A)。此外,B、D、A2、B2、C2、D2对感官评分影响极显著(P<0.01),C、BC对感官评分影响显著(P<0.05)。
表 4 响应面模型方程方差分析结果Table 4. Response surface model equation and variance analysis results来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 786.67 14 56.19 15.38 <0.0001 ** A-白砂糖添加量 13.44 1 13.44 3.68 0.0792 B-抹茶浸泡液浓度 178.64 1 178.64 48.88 <0.0001 ** C-烘烤时间 24.65 1 24.65 6.75 0.0233 * D-烘烤温度 86.40 1 86.40 23.64 0.0004 ** AB 9.30 1 9.30 2.55 0.1366 AC 10.89 1 10.89 2.98 0.1099 AD 0.49 1 0.49 0.13 0.7206 BC 22.09 1 22.09 6.04 0.0301 * BD 0.64 1 0.64 0.18 0.6830 CD 7.84 1 7.84 2.15 0.1687 A² 97.09 1 97.09 26.57 0.0002 ** B² 211.12 1 211.12 57.77 <0.0001 ** C² 248.73 1 248.73 68.06 <0.0001 ** D² 257.92 1 257.92 70.58 <0.0001 ** 残差 43.85 12 3.65 失拟项 40.41 10 4.04 2.35 0.3353 纯误差 3.44 2 1.72 总和 830.52 26 注:*表示差异显著,P<0.05;**表示差异极其显著,P<0.01。 2.2.2 响应面分析
图3为不同因素的交互作用对抹茶山核桃仁的感官评分影响,响应面越陡峭,表明因素对感官评分影响越大。从图3 d可以看出,抹茶浸泡液浓度和烘烤时间的交互曲面陡峭,交互作用显著(P<0.05),且随着各因素的增加,抹茶山核桃仁的感官评分呈先升高后下降的趋势,而在其他交互作用的响应面中,感官评分随各因素水平的增加缓慢变化,交互作用不显著(P>0.05)。
2.2.3 响应面验证实验
根据响应面优化实验建立不同加工工艺对抹茶山核桃仁感官评分模型R,在Design-Expert 13中将感官评分最大值设为优化目标,得到最优实验条件:白砂糖添加量14.84%、抹茶浸泡液浓度8.39%、烘烤时间31.39 min和烘烤温度128.31 ℃。采用这一结果并根据实际情况,将工艺条件调整为:白砂糖添加量15%、抹茶浸泡液浓度8%、烘烤时间30 min和烘烤温度130 ℃。在此条件下进行3次验证性实验,得到的平均感官评分为88.40分,与预测值(89.37分)接近,说明该工艺准确可行。
2.3 不同山核桃仁的抗氧化性能比较
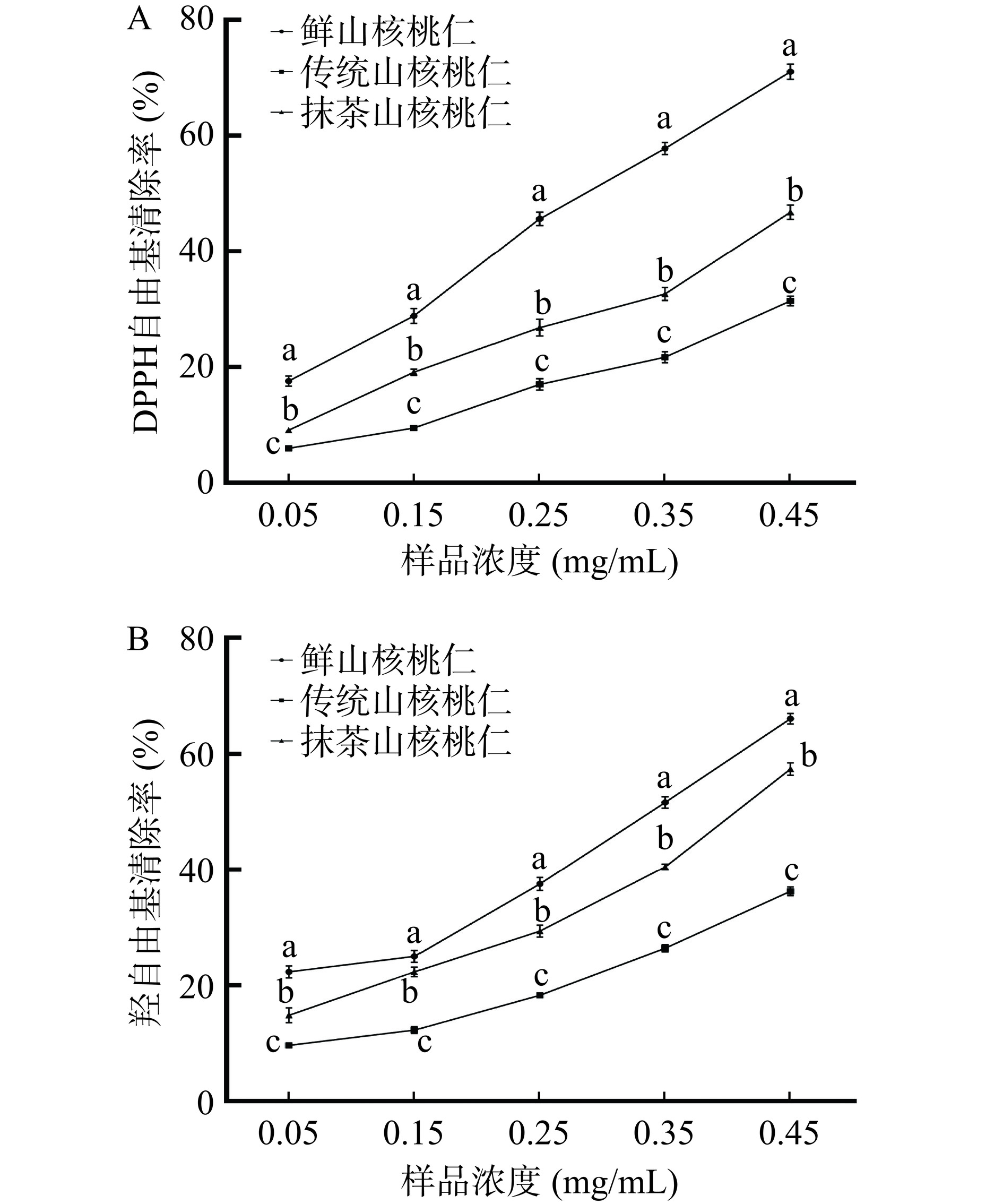
DPPH和羟自由基清除活性以及还原能力测定等方法,常用于评估化合物的抗氧化活性[21]。由图4A可以看出,山核桃仁提取液的DPPH自由基的清除能力在加工后均出现下降。传统山核桃仁、抹茶山核桃仁的IC50分别为0.77 mg/mL和0.50 mg/mL,存在极显著性差异(P<0.01)。
![]() 图 4 鲜山核桃仁、传统山核桃仁和抹茶山核桃仁自由基清除率注:(A)DPPH自由基清除率;(B)羟自由基清除率;不同小写字母表示处理组间存在显著性差异,P<0.05,图5同。Figure 4. Free radical scavenging rate of fresh hickory kernel, traditional hickory kernel and matcha hickory kernel
图 4 鲜山核桃仁、传统山核桃仁和抹茶山核桃仁自由基清除率注:(A)DPPH自由基清除率;(B)羟自由基清除率;不同小写字母表示处理组间存在显著性差异,P<0.05,图5同。Figure 4. Free radical scavenging rate of fresh hickory kernel, traditional hickory kernel and matcha hickory kernel山核桃仁对羟自由基的清除作用见图4B,各样品组对羟自由基均有一定的清除能力,并且随着样品浓度的升高而增强,呈现出一定的剂量效应。鲜山核桃仁对羟自由基的清除作用较为显著,当浓度为0.45 mg/mL时,清除率为66.04%,为同等质量浓度下传统山核桃仁和抹茶山核桃仁羟自由基清除率的182.32%和115.13%,传统山核桃仁和抹茶山核桃仁对羟自由基清除率的IC50值分别为0.69 mg/mL 和0.42 mg/mL,二者清除能力差异极显著(P<0.01)。
付田田[22]的研究发现三种茶制品(速溶绿茶、速溶红茶、抹茶)能够给予冻干米饭抗氧化能力和多种风味。张富[23]的研究发现焙烤温度过高或时间过长,儿茶素作为茶多酚主要成分也会加速异构化以及降解反应,造成茶曲奇饼干中的多酚含量降低,进而影响其抗氧化活性。本研究中,添加抹茶显著增强了山核桃仁的抗氧化活性,这种增强作用可能与抹茶中的茶多酚和维生素C有关。抹茶中的茶多酚是一类多酚化合物,根据GB 2760-2014《食品添加剂使用标准》[24],茶多酚可用于油脂、坚果、糕点、饮料等食品中,具有抗氧化功能。同时,抹茶中的VC含量大约是普通绿茶的两倍[25]。VC能够清除体内自由基,常常表现出抗氧化特性。
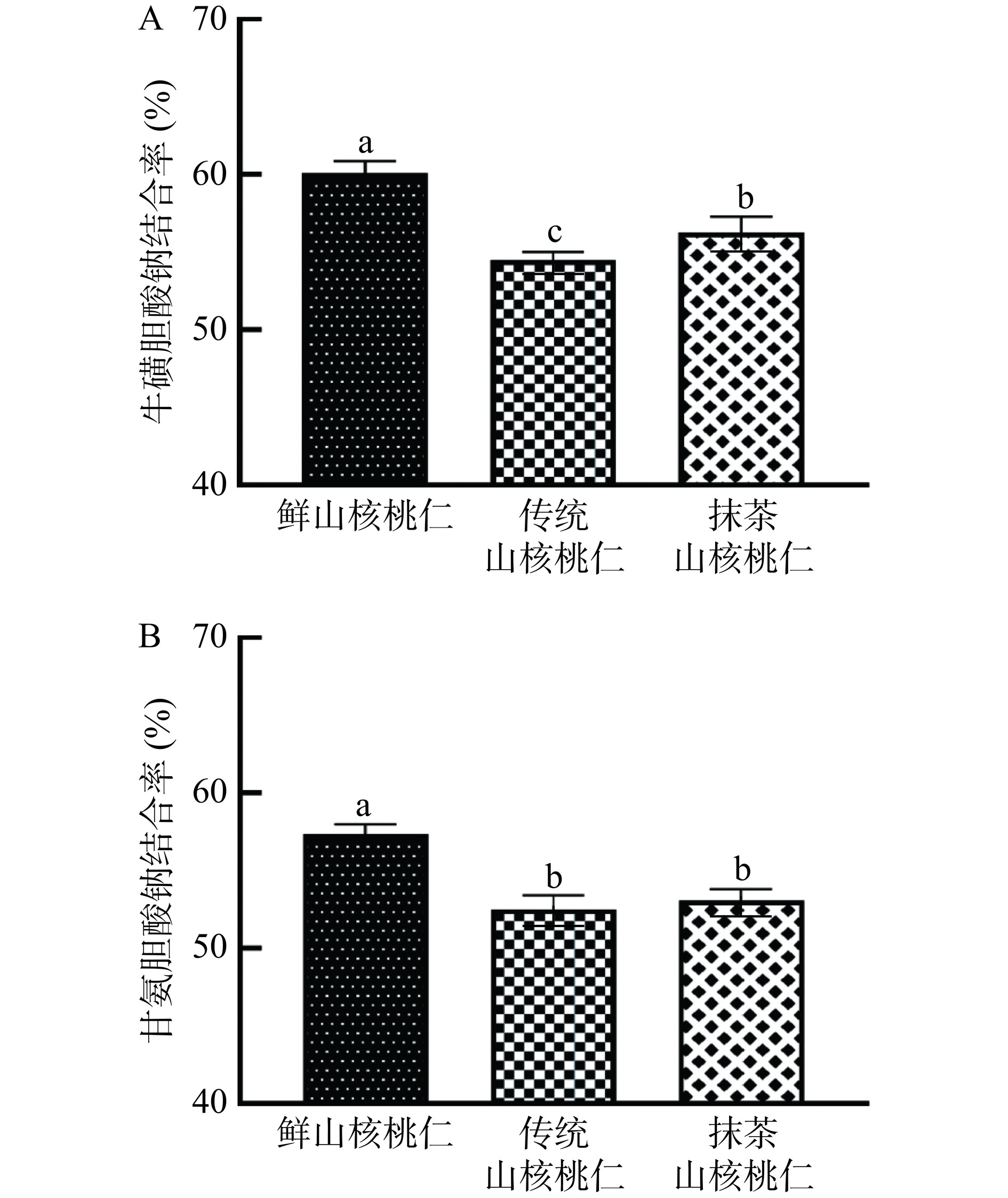
2.4 不同山核桃仁的胆酸盐结合能力比较
胆酸盐是胆汁酸的衍生物,具有乳化脂肪的能力,有助于小肠对脂肪的吸收。同时,胆酸盐也直接参与机体的脂类代谢过程,通过结合胆酸盐来降低其水平,可以有效缓解脂类的吸收[26]。由图5可知,不同山核桃仁对牛磺胆酸钠和甘氨胆酸钠均有一定的结合能力。当抹茶山核桃仁的浓度为0.10 g/mL时,对牛磺胆酸钠结合率为56.25%,与传统山核桃仁(54.48%)相比具有显著差异(P<0.05);对甘氨胆酸钠结合率为53.06%,与传统山核桃仁(52.52%)相比没有显著差异(P>0.05)。
2.5 抹茶山核桃仁对3T3-L1脂肪细胞的影响
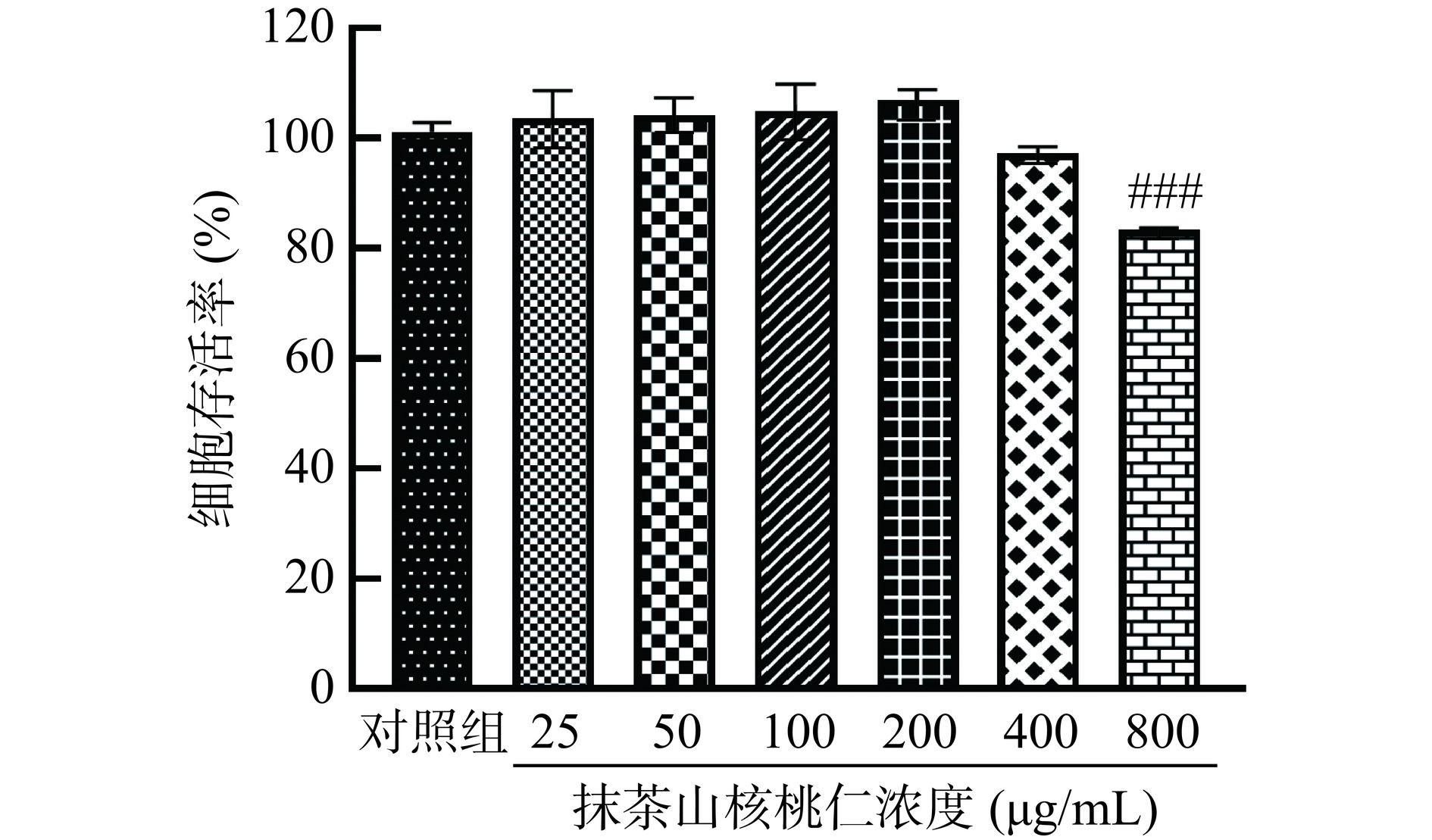
2.5.1 细胞毒性
根据图6的结果显示,在25~400 μg/mL浓度范围内,抹茶山核桃仁对3T3-L1脂肪细胞的存活率与对照组相比没有显著差异(P>0.05),并且细胞存活率保持在90%以上。然而,当样品浓度达到800 μg/mL时,细胞的存活率极显著下降至83.38%(P<0.001)。这些结果表明,在25~200 μg/mL浓度范围内,抹茶山核桃仁对3T3-L1脂肪细胞没有毒性,只有在高浓度下才表现出轻微的毒性[27]。因此,在后续实验中,选择50、100和200 μg/mL作为低、中和高剂量。
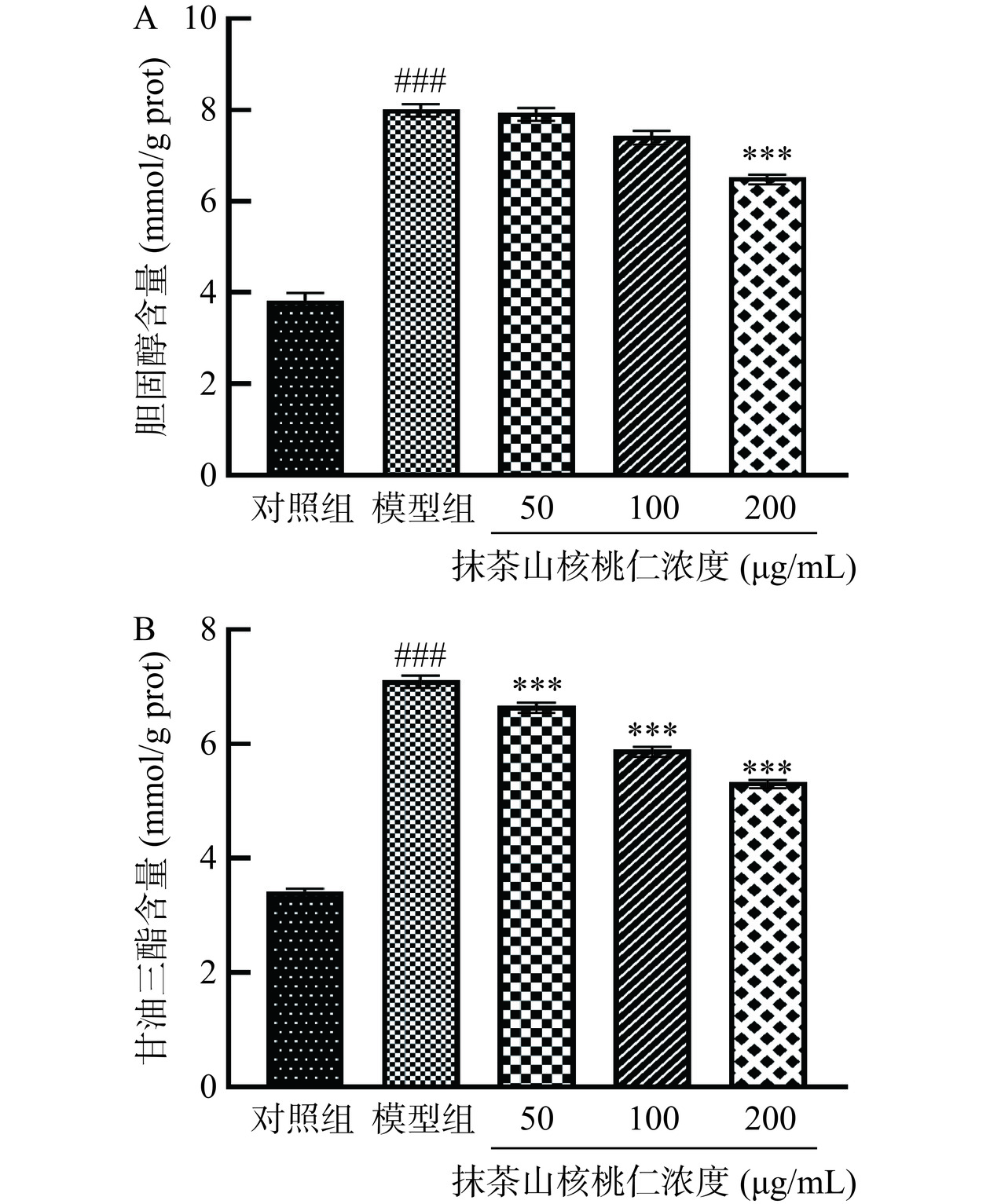
2.5.2 抹茶山核桃体仁外消化产物对3T3-L1脂肪细胞总胆固醇、甘油三酯水平的影响
脂质代谢紊乱导致肝细胞总胆固醇和甘油三酯的过度累积,是脂肪肝病发生的主要诱因,总胆固醇和甘油三酯的含量变化是临床常用的脂肪肝和高血脂症判断指标[28]。3T3-L1 细胞经过“鸡尾酒法”培养,能够在较短时间内分化成成熟的脂肪细胞[29]。根据图7显示的结果,模型组细胞内胆固醇和甘油三酯的积累明显增加,与对照组相比有极显著差异(P<0.001)。与模型组相比,抹茶山核桃仁的体外消化产物能够降低成熟的3T3-L1脂肪细胞内总胆固醇和甘油三酯的含量,并且这种降低的效果具有一定的剂量依赖性。当作用浓度为200 μg/mL时,抹茶山核桃仁组细胞内总胆固醇和甘油三酯的含量分别为模型组的81.46%和75.01%,与模型组相比有极显著差异(P<0.001)。Dominguez-avila等[5]发现将山核桃作为高脂肪饮食的一部分可以预防高瘦素血症、脂肪堆积和肝脂质过氧化。在油酸诱导的高脂HepG2细胞模型中,山核桃油可降低细胞内TC、TG的含量,表明山核桃油具有较好的降血脂功能活性[30],此结果与本文的实验发现总体上保持一致。同样地,抹茶及抹茶中的生物活性物质对2型糖尿病和代谢综合征的预防或改善作用已得到了广泛的研究[31]。抹茶中的多酚可以通过与TC的衍生物胆汁酸结合,能够促进其排除体外以及促进排便来使TG和TC不断分解外排[32]。Xu等[10]研究发现抹茶可以降低血清和肝脏的TC和TG水平,LDL-C水平和血糖水平,并提高小鼠的HDL-C水平。综上,高浓度的抹茶山核桃仁的体外消化产物能够极显著降低成熟的3T3-L1脂肪细胞内总胆固醇和甘油三酯的含量(P<0.001),表明抹茶山核桃仁有潜在的降脂作用。
3. 结论
本研究以抹茶和山核桃仁为主要原料,通过单因素和响应面优化试验确定抹茶山核桃仁的最佳加工工艺:白砂糖添加量15%、抹茶浸泡液浓度8%、烘烤时间30 min和烘烤温度130 ℃,感官评分达到88.40分。抹茶山核桃仁对DPPH和羟自由基清除能力IC50分别为0.50 mg/mL、0.42 mg/mL,具有一定的抗氧化性;在0.10 g/mL时,抹茶山核桃仁对甘氨胆酸钠和牛磺胆酸钠的结合率分别达到56.25%和53.06%;此外,抹茶山核桃仁当作用浓度为200 μg/mL时,细胞内总胆固醇和甘油三酯的含量分别为模型组的81.46%和75.01%,与模型组相比具有极显著差异(P<0.001),这表明抹茶山核桃仁具有一定的降脂作用。实验结果为山核桃仁和抹茶的综合利用提供了理论基础,也为开发山核桃仁降脂功能食品提供了一定的参考依据。
-
图 4 鲜山核桃仁、传统山核桃仁和抹茶山核桃仁自由基清除率
注:(A)DPPH自由基清除率;(B)羟自由基清除率;不同小写字母表示处理组间存在显著性差异,P<0.05,图5同。
Figure 4. Free radical scavenging rate of fresh hickory kernel, traditional hickory kernel and matcha hickory kernel
表 1 感官评价标准
Table 1 Sensory evaluation criteria
指标 评分标准 得分 色泽(20分) 金黄色,抹茶色分布均匀 14~20 淡黄色,抹茶色分布不均匀 7~13 抹茶色太深或烤焦 0~6 气味(20分) 无异味,有抹茶的特殊香味 14~20 略有焦糊味,抹茶香味略淡 7~13 焦糊味严重,无香气 0~6 滋味(30分) 无涩味,甜味适宜 21~30 微涩,甜味稍重或稍淡 11~20 涩味很重 0~10 咀嚼性(30分) 口感酥脆,软硬适中 21~30 口感酥脆性较差,稍软或稍硬 11~20 口感过软或过硬 0~10 表 2 响应面试验因素与水平设计
Table 2 Response surface experimental factors and level design
水平 因素 A白砂糖添
加量(%)B抹茶浸泡液
浓度(%)C烘烤时间
(min)D烘烤温度
(℃)−1 10 5 20 120 0 15 10 30 130 1 20 15 40 140 表 3 响应面试验结果
Table 3 Results of response surface experiment
试验号 A(%) B(%) C(min) D(℃) Y 感官评分(分) 1 10 5 30 130 82.4 2 20 5 30 130 85.9 3 10 15 30 130 74.7 4 20 15 30 130 72.1 5 15 10 20 120 77.4 6 15 10 40 120 77.5 7 15 10 20 140 70.8 8 15 10 40 140 76.5 9 10 10 30 120 80.9 10 20 10 30 120 79.1 11 10 10 30 140 74.9 12 20 10 30 140 71.7 13 15 5 20 130 74.1 14 15 15 20 130 72.3 15 15 5 40 130 81.9 16 15 15 40 130 70.7 17 10 10 20 130 79.4 18 20 10 20 130 71.8 19 10 10 40 130 78.7 20 20 10 40 130 77.7 21 15 5 30 120 80.1 22 15 15 30 120 75 23 15 5 30 140 75.3 24 15 15 30 140 68.6 25 15 10 30 130 87.2 26 15 10 30 130 88.2 27 15 10 30 130 89.8 表 4 响应面模型方程方差分析结果
Table 4 Response surface model equation and variance analysis results
来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 786.67 14 56.19 15.38 <0.0001 ** A-白砂糖添加量 13.44 1 13.44 3.68 0.0792 B-抹茶浸泡液浓度 178.64 1 178.64 48.88 <0.0001 ** C-烘烤时间 24.65 1 24.65 6.75 0.0233 * D-烘烤温度 86.40 1 86.40 23.64 0.0004 ** AB 9.30 1 9.30 2.55 0.1366 AC 10.89 1 10.89 2.98 0.1099 AD 0.49 1 0.49 0.13 0.7206 BC 22.09 1 22.09 6.04 0.0301 * BD 0.64 1 0.64 0.18 0.6830 CD 7.84 1 7.84 2.15 0.1687 A² 97.09 1 97.09 26.57 0.0002 ** B² 211.12 1 211.12 57.77 <0.0001 ** C² 248.73 1 248.73 68.06 <0.0001 ** D² 257.92 1 257.92 70.58 <0.0001 ** 残差 43.85 12 3.65 失拟项 40.41 10 4.04 2.35 0.3353 纯误差 3.44 2 1.72 总和 830.52 26 注:*表示差异显著,P<0.05;**表示差异极其显著,P<0.01。 -
[1] 章亭洲. 山核桃的营养、生物学特性及开发利用现状[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2006(4):90−93. [ZHANG T Z. The nutrition, biological characteristics, and development and utilization status of hickory[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2006(4):90−93.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-990X.2006.04.025 ZHANG T Z. The nutrition, biological characteristics, and development and utilization status of hickory[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2006(4): 90−93. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-990X.2006.04.025
[2] 姚佳伟, 刘彩琴. 山核桃生物活性研究进展[J]. 广州化工,2019,47(20):26−28. [YAO J W, LIU C Q. Research progress on biological activity of Carya cathayensi[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry,2019,47(20):26−28.] YAO J W, LIU C Q. Research progress on biological activity of Carya cathayensi[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2019, 47(20): 26−28.
[3] XIA W, GAO Y, FANG X, et al. Simulated gastrointestinal digestion of walnut protein yields anti-inflammatory peptides[J]. Food Chemistry,2024,445:138646.
[4] WU W, NIU B, PENG L, et al. Recent advances on the effect of nut consumption on cognitive improvement[J]. Food Frontiers,2023,4(4):1737−1746. doi: 10.1002/fft2.298
[5] DOMÍNGUEZ-AVILA J A, ALVAREZ-PARRILLA E, LÓPEZ-DÍAZ J A, et al. The pecan nut (Carya illinoinensis) and its oil and polyphenolic fractions differentially modulate lipid metabolism and the antioxidant enzyme activities in rats fed high-fat diets[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,168:529−537. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.092
[6] 刘智强, 燕飞, 王昕, 等. 超微茶粉在食品中应用的研究进展[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(7):82−87. [LIU Z Q, YAN F, WANG X, et al. Research progress on application of ultramicro tea powder in food[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(7):82−87.] LIU Z Q, YAN F, WANG X, et al. Research progress on application of ultramicro tea powder in food[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2020, 45(7): 82−87.
[7] 龙冬玲. 抹茶戚风蛋糕加工工艺研究[J]. 江苏调味副食品,2019(4):22−25. [LONG D L. Study on processing technology of matcha chiffon cake[J]. Jiangsu Condiment and Subsidiary Food,2019(4):22−25.] LONG D L. Study on processing technology of matcha chiffon cake[J]. Jiangsu Condiment and Subsidiary Food, 2019(4): 22−25.
[8] YILMAZ B, ACAR-TEK N. White tea:Its history, composition, and potential effects on body weight management[J]. eFood,2023,4(3):89. doi: 10.1002/efd2.89
[9] FU T, NIU L, LI Y, et al. Effects of tea products on in vitro starch digestibility and eating quality of cooked rice using domestic cooking method[J]. Food & Function,2020,11(11):9881−9891.
[10] XU P, YING L, HONG G, et al. The effects of the aqueous extract and residue of Matcha on the antioxidant status and lipid and glucose levels in mice fed a high-fat diet[J]. Food Function,2016,7(1):294−300. doi: 10.1039/C5FO00828J
[11] WEI H, CHEN Y, OUYANG Q, et al. Progress in comprehensive development and utilization of pecan resources[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science,2021,705(1):012032. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/705/1/012032
[12] 范思敏, 穆宏磊, 郜海燕, 等. 山核桃仁碱法脱涩工艺研究[J]. 浙江农业学报,2021,33(12):2381−2389. [FAN S M, MU H L, GAO H Y, et al. Study on alkaline deastringency of hickory kernel[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2021,33(12):2381−2389.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2021.12.18 FAN S M, MU H L, GAO H Y, et al. Study on alkaline deastringency of hickory kernel[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2021, 33(12): 2381−2389. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2021.12.18
[13] 刘杰梅, 李雪玲, 孙玥, 等. 核桃仁炒制工艺优化及其风味成分分析[J]. 中国粮油学报,2023(10):1−12. [LIU J M, LI X L, SUN Y, et al. Optimization of roasting process and analysis of flavor components of walnut[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2023(10):1−12.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2023.10.002 LIU J M, LI X L, SUN Y, et al. Optimization of roasting process and analysis of flavor components of walnut[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2023(10): 1−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2023.10.002
[14] RUMPF J, BURGER R, SCHULZE M. Statistical evaluation of DPPH, ABTS, FRAP, and Folin-Ciocalteu assays to assess the antioxidant capacity of lignins[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2023,233:123470. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123470
[15] LIN T Y, WU Y T, CHANG H J, et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects of polysaccharides extracted from unripe Carica papaya L. fruit[J]. Antioxidants (Basel),2023,12(8):1506. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081506
[16] 刘淑敏. 不同茶类浸提液及茶多酚的生物活性和机理研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2016. [LIU S M. Study on the biological activities and functional mechanisms of different tea extracts and tea polyphenols[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2016.] LIU S M. Study on the biological activities and functional mechanisms of different tea extracts and tea polyphenols[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2016.
[17] 吕迎兰, 程龙, 石璐, 等. 芦丁促进3T3-L1前脂肪细胞棕色化及其机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(5):137−143. [LÜ Y L, CHENG L, SHI L, et al. Rutin promotes browning of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2023,29(5):137−143.] LÜ Y L, CHENG L, SHI L, et al. Rutin promotes browning of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2023, 29(5): 137−143.
[18] 陈超, 黄平, 林若冰, 等. 绞股蓝总皂苷对3T3-L1前脂肪细胞棕色化和自噬活性的影响[J]. 中成药,2022,44(9):2817−2822. [CHEN C, HUANG P, LIN R B, et al. Effects of gypenosides on the browning and autophagy of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2022,44(9):2817−2822.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2022.09.012 CHEN C, HUANG P, LIN R B, et al. Effects of gypenosides on the browning and autophagy of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2022, 44(9): 2817−2822. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2022.09.012
[19] 顾宗珠. 超微茶粉面包的研制[J]. 食品科技,2003(4):58−60. [GU Z Z. Research on manufacturing of bread of ultramicrosome tea powder[J]. Food Science and Technology,2003(4):58−60.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2003.04.021 GU Z Z. Research on manufacturing of bread of ultramicrosome tea powder[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2003(4): 58−60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2003.04.021
[20] 彭祺, 边威, 王佳丽, 等. 不同加工工艺对临安山核桃营养成分的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2013,34(20):173−175,189. [PEN Q, BIAN W, WANG J L, et al. Effect of production techniques on nutrient content in Lin’an pecans[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2013,34(20):173−175,189.] PEN Q, BIAN W, WANG J L, et al. Effect of production techniques on nutrient content in Lin’an pecans[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2013, 34(20): 173−175,189.
[21] SHRIVASTAVA A K, SHRESTHA L, POKHREL B R, et al. LC-MS based metabolite profiling, in-vitro antioxidant and in-vivo antihyperlipidemic activity of Nigella sativa extract[J]. eFood,2023,4(4):107. doi: 10.1002/efd2.107
[22] 付田田. 茶制品对不同加工工艺米饭品质的影响[D]. 南昌:江西农业大学, 2021. [FU T T. Effects of tea products on the quality of cooked rice produced by the different processing[D]. Nanchang:Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2021.] FU T T. Effects of tea products on the quality of cooked rice produced by the different processing[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 2021.
[23] 张富. 绿茶曲奇工艺配方及其品质研究[D]. 广州:华南农业大学, 2018. [ZHANG F. Study on the process formula and quality of green tea cookies[D]. Guangzhou:South China Agricultural University, 2018.] ZHANG F. Study on the process formula and quality of green tea cookies[D]. Guangzhou: South China Agricultural University, 2018.
[24] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. 食品安全国家标准 食品添加剂使用标准 GB2760-2014[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2014. [National Health and Family Planning Commission. National food safety standard for use of food additives GB2760-2014[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2014.] National Health and Family Planning Commission. National food safety standard for use of food additives GB2760-2014[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2014.
[25] PHUAH Y Q, CHANG S K, NG W J, et al. A review on matcha:Chemical composition, health benefits, with insights on its quality control by applying chemometrics and multi-omics[J]. Food Research International, 2023:113007.
[26] 樊伟伟, 陈洁, 黄惠华, 等. 海南苦丁茶浸提液对胆酸盐结合能力及其降血脂作用的研究[J]. 粮食与食品工业,2018,25(4):31−33,37. [FAN W W, CHEN J, HUANG H H, et al. Study on bile salt-binding capacity and lipid-lowering effect of water extract from Hainan I. latifolia[J]. Cereal and Food Industry,2018,25(4):31−33,37.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5026.2018.04.009 FAN W W, CHEN J, HUANG H H, et al. Study on bile salt-binding capacity and lipid-lowering effect of water extract from Hainan I. latifolia[J]. Cereal and Food Industry, 2018, 25(4): 31−33,37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5026.2018.04.009
[27] SZLISZKA E, CZUBA Z P, DOMINO M, et al. Ethanolic extract of propolis (EEP) enhances the apoptosis-inducing potential of TRAIL in cancer cells[J]. Molecules,2009,14(2):738−754. doi: 10.3390/molecules14020738
[28] WANG M, ZHAO R, WANG W, et al. Lipid regulation effects of Polygoni Multiflori Radix, its processed products and its major substances on steatosis human liver cell line L02[J]. J Ethnopharmacol,2012,139(1):287−293. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.11.022
[29] ZEBISCH K, VOIGT V, WABITSCH M, et al. Protocol for effective differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells to adipocytes[J]. Analytical Biochemistry,2012,425(1):88−90. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2012.03.005
[30] 李晴. 山核桃油降血脂功能活性及其微胶囊化技术研究[D]. 舟山:浙江海洋大学, 2022. [LI Q. Study on hypolipidemic activity and microencapsulation technology of walnut oil[D]. Zhoushan:Zhejiang Ocean University, 2022.] LI Q. Study on hypolipidemic activity and microencapsulation technology of walnut oil[D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University, 2022.
[31] ZHOU J, LIN H, XU P, et al. Matcha green tea prevents obesity-induced hypothalamic inflammation via suppressing the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Food & Function,2020,11(10):8987−8995.
[32] WANG L, ZENG B, ZHANG X, et al. The effect of green tea polyphenols on gut microbial diversity and fat deposition in C57BL/6J HFA mice[J]. Food & Function,2016,7(12):4956−4966.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



