Progress on the Mechanism of Action of Probiotics in Alleviating Cow's Milk Allergy
-
摘要: 牛乳过敏是由牛乳中蛋白质引起的不良免疫介导反应,多发于人类生命早期,常涉及皮肤、呼吸系统和消化系统,现已成为婴幼儿时期最主要的食物过敏问题,若不及时治疗对婴幼儿的生长发育有一定影响,严重者可引发全身过敏性休克甚至死亡。目前,服用益生菌成为缓解牛乳过敏的重要方法,然而,益生菌调节牛乳过敏的机制相对复杂,尚无明确具体的结论。本文综述了牛乳过敏的免疫机制、肠道微生物群与牛乳过敏的相关性,并从调节肠道菌群、增强肠道屏障、促进肠黏膜免疫和分解牛乳过敏原蛋白等方面重点阐述了益生菌缓解牛乳过敏的作用机制。本研究将有助于探索益生菌在胃肠道功能和代谢中的抗过敏作用,以期为食物过敏的预防及治疗提供新的思路。Abstract: Cow's milk allergy is an immune-mediated response induced by the proteins found in cow's milk, which occurs early in human life and frequently affects the skin, respiratory system, and digestive system. It has now become the most common food allergy problem in infants and young children. If cow's milk allergy is not treated promptly, it will have an impact on infants' and young children's growth and development, and in severe cases, it may result in systemic anaphylactic shock or even death. Currently, probiotics have become an essential tool for treating cow's milk allergy; nevertheless, the mechanism by which probiotics regulate cow's milk allergy is somewhat complex, with no clear and precise conclusion. In this paper, the immune mechanism of cow's milk allergy, the relationship between gut microbiota and cow's milk allergy, and the mechanism of probiotics to alleviate cow's milk allergy in terms of gut flora regulation, intestinal barrier enhancement, intestinal mucosal immunity promotion, and cow's milk allergenic protein catabolism are reviewed. This study will help to explore the anti-allergic role of probiotics in gastrointestinal function and metabolism, with a view to providing new ideas for the prevention and treatment of food allergy.
-
近年来,食物过敏越来越普遍,影响着全球约4%的成年人和10%的儿童,与成年人相比,婴幼儿及儿童食物过敏的患病率更高,且多以牛乳过敏(Cow's milk allergy,CMA)为主[1]。牛乳过敏的发生往往与肠道菌群有关,正常情况下,肠道菌群的组成和比例保持相对稳定,当肠道菌群受到外界等多种因素影响时这种动态平衡就会被破坏导致肠道微生态紊乱,继而造成肠道菌群代谢活动和免疫应答偏移,引发过敏反应[2]。此外,牛乳过敏患儿在成长的不同阶段,伴发其他过敏性疾病的风险增高,严重过敏可以危及生命,甚至造成死亡。据流行病学调查,在发展中国家,3 岁以下婴幼儿的牛乳过敏比例高达8%,且呈逐年上升趋势。有15%的牛乳过敏患者存在终身过敏的风险。目前,牛乳过敏尚无根治疗法,饮食回避法是患者的最佳选择,但完全避免牛乳的摄入往往会导致婴幼儿营养素缺失等问题。因此探究更加安全有效的防治方法对CMA具有重要意义[3−4]。
越来越多的证据表明,CMA与肠道菌群失衡和免疫系统过度反应有关,且益生菌对食物过敏的改善具有显著效果。Cukrowska等[5]研究评估了益生菌ŁOCK菌株的混合制剂在CMA儿童中的疗效。通过给予CMA患者益生菌制剂或安慰剂,发现益生菌组表现出对牛乳蛋白的耐受性明显高于安慰剂组。本文以牛乳过敏为切入点,综述牛乳过敏的免疫机制、肠道微生物群与牛乳过敏的相关性,并从调节肠道菌群、增强肠道屏障、促进肠黏膜免疫以及分解牛乳过敏原蛋白等方面重点阐述益生菌缓解牛乳过敏的作用机制。
1. 牛乳中的致敏性蛋白
牛乳中含有30 多种蛋白质,如α-乳白蛋白(α-Lactalbumin,α-La)、β-乳球蛋白(β-Lactoglobulin,β-Lg)、乳铁蛋白、牛血清白蛋白及酪蛋白等,都具有潜在致敏性[6]。通过酶法切割、肽芯片、合成重叠肽等技术可以确定乳蛋白的免疫球蛋白E(ImmunoglobulinE,IgE)表位以及免疫球蛋白G(ImmunoglobulinG,IgG)表位,甚至定位到表位的关键残基[13]。
目前普遍认为α-La、β-Lg及酪蛋白是牛乳中的主要过敏原[7](表1)。其中,α-La是一种属于溶菌酶家族的钙结合金属蛋白,具有4 个二硫键和1 个钙离子结合位点,能与钙离子形成高亲和力的稳定结构[8]。研究发现肽段AA7-18、AA51-61和AA89-108为α-La的IgG结合表位,α-La的肽段AA5-18可与IgE高度结合[9−10]。在牛乳过敏患者中,约有27.6%~62.8%的人群对α-乳白蛋白过敏[11]。β-Lg是一种脂质运载蛋白,在天然状态下以36 kDa二聚体的形式存在,具有2 个二硫键和1 个游离半胱氨酸。β-Lg的高度结构化使其具有耐酸和耐蛋白酶水解特性,即使在人体消化过程中,β-Lg仍能保持其完整性或产生具有致敏作用的肽段,引发过敏反应[12]。在β-Lg表位研究中,AA41~60、AA102~124和 AA149~162为重要的线性表位,可以被高达89%~97%的牛乳过敏患者的血清样本所识别[13]。酪蛋白主要以交联的聚集体形式存在于牛乳中,形成的胶束会覆盖部分过敏原表位,但当人体摄入牛乳时,酪蛋白胶束结构易被破坏,导致过敏原表位重新暴露,增强了酪蛋白的致敏性[14]。由于人乳中不存在αs1-酪蛋白,因此人类对致敏原αs1-酪蛋白非常敏感。αs1-酪蛋白具有AA19~30、AA86~103、AA141~150等3个IgE/IgG免疫重叠区,其中AA86~103的致敏性最强,约有65%的牛奶过敏患者对其产生过敏反应[15−16]。AA69~78、AA173~194片段可以与持续性牛乳过敏患者的血清发生IgE特异性结合,有助于预测牛乳过敏患者的自然病程[17]。
蛋白质 分子量(kDa) 牛乳中的含量(g/kg) 氨基酸数(个) 抗原表位 α-乳白蛋白 14.2 1.1 123 1~16、13~26、45~78、93~102;7~18、51~61、89~108;5~18 β-乳球蛋白 18.4 3.0 162 21~40、41~60、102~124、127~141;149~162 αs1-酪蛋白 23.6 12.7 199 19~30、69~78、86~103、123~132;141~150、173~194 2. 牛乳过敏机制
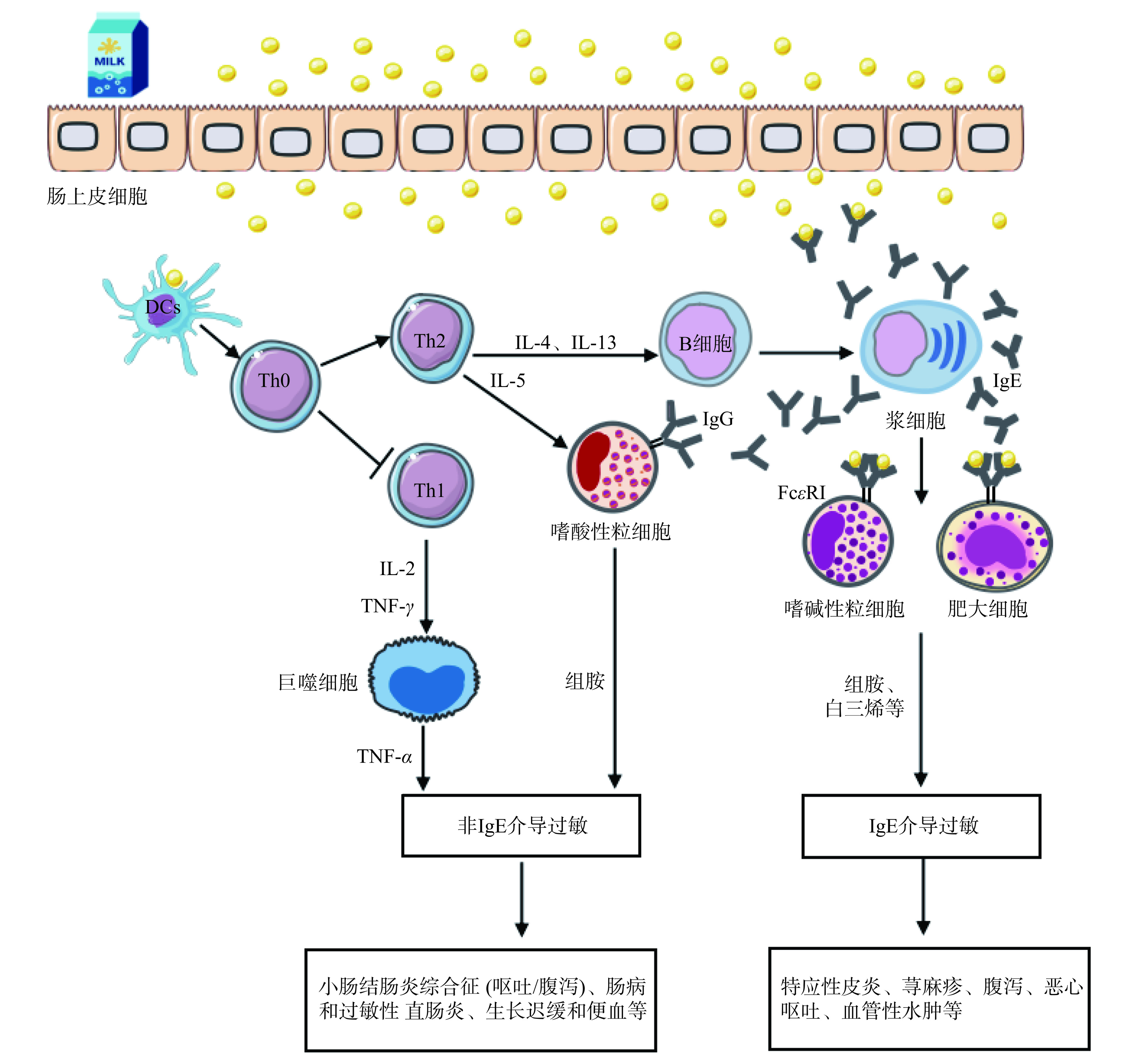
研究发现,大部分CMA是由非IgE途径介导,但IgE途径介导研究较多。欧洲研究显示非IgE和IgE介导的CMA占比分别为56.3%、43.7%[18]。而国内研究显示只有27.0%的CMA患儿是由IgE介导的免疫反应[19]。IgE和非IgE介导的牛乳过敏机制如图1所示。
IgE介导的牛乳过敏反应为速发型,其发病机制分为两个阶段:一是致敏阶段,首先,乳过敏原进入机体后,抗原呈递细胞进行传递,随后T细胞(Th0)被活化,生成较少的Th1和大量的Th2[20]。以Th2途径为主,Th2细胞分泌细胞因子IL-4、IL-13,并刺激B细胞发生抗体类别转换,诱导浆细胞释放IgE和少量的IgG[21]。IgE的Fc段会与血液中肥大细胞或嗜碱性粒细胞上表达的高亲和力受体(FcεRI)结合,使机体处于致敏状态[22]。若长期避免与过敏原接触,这种致敏状态将会慢慢消失;二是效应阶段,当同一乳过敏原再次进入处于致敏状态的机体时,会与附着在肥大细胞和嗜碱性粒细胞表面上的IgE交联,促发信号级联反应,导致肥大细胞等效应器细胞脱颗粒,释放组胺、白三烯等生物活性介质,引起局部或全身性过敏反应[23]。
非IgE介导的牛乳过敏通常在摄入乳蛋白数小时至数天后出现,属于迟发型反应,此过程Th1和Th2都有参与。当机体摄入乳过敏原后,抗原呈递细胞进行传递,随后 T细胞(Th0)被活化,Th1细胞产生IL-2和肿瘤坏死因子,激活巨噬细胞产生免疫应答。同时,Th2细胞分泌的IL-5刺激嗜酸粒细胞,分泌的IL-4、IL-13刺激B细胞发生抗体类别转换,产生IgG抗体。经过血液循环,IgG附着到嗜酸粒细胞上,刺激其产生组胺,导致非lgE介导过敏发生[16]。
3. 牛乳过敏患者肠道菌群的变化
研究表明,牛乳过敏人群与健康人群的肠道菌群组成存在显著差异,这些差异在婴儿和儿童中更为明显(表2)。Bunyavanich等[25]对不同年龄组的CMA患儿进行粪便样本分析,发现226 例儿童中,128 例儿童8 岁时牛奶过敏消退。3~6 个月时的肠道微生物组成与8 岁时牛奶过敏的缓解有关,即在3~6 个月大的样本中,8 岁牛奶过敏消退者的婴儿肠道微生物群中富含厚壁菌门和梭状芽孢杆菌门,而8 岁牛奶过敏未消退者的肠道微生物群中富含拟杆菌门和肠杆菌门。Roberto等[26]研究发现CMA 肠道菌群失调是由拟杆菌属和另枝菌属聚集驱动的,且CMA 两种介导途径的肠道菌群失调具有重叠特征,即拟杆菌属的富集呈现出显著性增高。另一项研究表明,肠杆菌科(Enterobacteriaceae)和拟杆菌科(Bacteroidaceae)的比值(E/B)可以被视为肠道菌群成熟度的指标。正常情况下,健康婴儿肠杆菌科和拟杆菌科的比值(E/B)随着年龄的增长而逐渐降低,说明肠道菌群成熟度越高,而CMA患儿肠杆菌科和拟杆菌科的比值(E/B)升高,表明肠道菌群成熟延迟,这可能是预测CMA的一个重要因素[27]。Mauras等[28]研究表明,与健康婴儿相比,患有CMA的婴儿肠道双歧杆菌在出生时即低于正常,并且毛螺菌科丰度增加,随后将 CMA婴儿的肠道菌群移植至正常小鼠内,发现双歧杆菌/毛螺菌科比例较低的婴儿微生物群使小鼠免疫系统倾向于Th2特应性特征,增强了过敏的临床症状。
表 2 牛奶过敏患者肠道菌群的变化Table 2. Changes in intestinal flora in patients with cow's milk allergy研究对象 年龄 牛奶过敏患者肠道菌群的变化 参考文献 226 名过敏婴儿 3~16 个月 拟杆菌门、肠杆菌门↑ [25] 46 名过敏婴儿和23 名健康婴儿 1~26 个月 拟杆菌属、另枝菌属↑ [26] 166 名过敏婴儿 0~12个月 肠杆菌科/拟杆菌科↑、瘤胃球菌科↓ [27] 5 名过敏婴儿和6 名健康婴儿 9~10 个月 双歧杆菌↓、毛螺菌科及其艾森伯格氏菌属↑ [28] 6 名过敏儿童和8 名健康儿童 5~8 岁 厚壁菌门、芽孢杆菌纲、疣微菌科↑、变形菌门↓ [29] 50 名过敏婴儿和20 名健康婴儿 0~12 个月 放线菌门↓、厚壁菌门↑、双歧杆菌及产丁酸菌群↑ [30] 18 名过敏婴儿和6 名健康婴儿 1~6 个月 拟杆菌门↓、双歧杆菌属、伊格尔兹氏菌属、丁酸弧菌属、另枝菌属↓、长双歧杆菌、丁酸梭菌、鼠李糖乳杆菌↓、假链状双歧杆菌↑ [31] 24 名过敏婴儿和26 名健康婴儿 0~6 个月 厚壁菌门、变形菌门↑、放线菌门↓、链球菌属、肠杆菌属、柠檬酸杆菌属、狭义梭菌属-1、葡萄球菌属↑、双歧杆菌属↓ [32] 注:↑:增加;↓:减少。 国内学者也对CMA患儿肠道菌群的变化进行了研究。董艳如[29]应用 16S rDNA 基因测序研究肠道菌群的多样性和差异性,结果表明,同健康儿童相比,CMA患儿的厚壁菌门、芽孢杆菌纲、疣微菌科丰度明显升高,变形菌门丰度降低。通过动态监测分析CMA患儿临床治疗过程中牛奶蛋白耐受和肠道菌群的变化情况,李心悦等[30]发现同健康儿童相比,CMA组放线菌门的相对丰度明显降低,厚壁菌门相对丰度提高。同时,在建立免疫耐受过程中,CMA患儿肠道中双歧杆菌及产丁酸菌群相对丰度升高。王丽婷[31]研究表明,牛奶过敏组和健康对照组在门、属、种的组成结构存在统计学差异。门水平上,CMA组拟杆菌门丰度低于对照组;属水平上,双歧杆菌属、伊格尔兹氏菌属、丁酸弧菌属、另枝菌属等丰度也低于对照组;种水平上,长双歧杆菌、丁酸梭菌、鼠李糖乳杆菌丰度低于对照组,而假链状双歧杆菌丰度高于对照组。罗光月[32]对CMA患儿的肠道菌群进行了详细分析,结果显示,在门水平,CMA 组厚壁菌门、变形菌门丰度百分比较健康组高,而放线菌门则低。在属水平,CMA 组链球菌属、未分类的肠杆菌属、柠檬酸杆菌属、狭义梭菌属-1、葡萄球菌属丰度百分比较健康组高,双歧杆菌属则低。总结以上研究可知,CMA的发生与肠道菌群的失调密切相关,CMA患者肠道菌群的普遍特征表现在肠杆菌科与拟杆菌科比例的升高、厚壁菌门的增加以及双歧杆菌属的减少。因此,通过人体肠道菌群的变化可有效预测并预防CMA。
4. 益生菌缓解牛乳过敏的机制
4.1 益生菌在牛乳过敏中的应用
大量动物实验和人群研究表明,益生菌的摄入可以改善牛乳过敏的发生与发展(如表3所示)。益生菌在缓解牛乳过敏中的应用主要集中在维持肠道菌群平衡、改善肠道屏障功能、维持Th1/Th2细胞平衡等方面。通过给予不同过敏个体益生菌疗法和补充剂,可有效缓解牛乳过敏症状。
表 3 益生菌在缓解牛乳过敏中的应用Table 3. Probiotics in the alleviation of cow's milk allergy研究对象 种类 疗法和补充剂 结果 参考文献 人 鼠李糖乳杆菌GG 水解酪蛋白配方治疗,同时或不补充LGG(4.5×107~8.5×107 CFU/g),持续6 个月 通过影响婴儿肠道的菌株水平的细菌群落结构,促进牛奶过敏婴儿的耐受性 [26] 人 长双歧杆菌婴儿亚种M-63、长双歧杆菌长亚种 BB536和短双歧杆菌M-16V 以3.5×109 CFU/剂量给药,每天2次,持续30 d 长双歧杆菌婴儿亚种M-63在CMA婴儿肠道中的长期定植与阿克曼氏菌和瘤胃球菌的增加有关 [33] 人 两歧双歧杆菌TMC3115 每天口服2 mL的两歧双歧杆菌TMC3115(1×109 cells/mL) 和0.85%
生理盐水溶液,持续6个月TMC3115降低了婴儿的过敏评分和血清IgE水平,增加了IgG2水平。同时增加了益生菌属比例,降低了病原体比例 [34] 人 鼠李糖乳杆菌GG 每日口服1×109 CFU LGG,持续4 周 鼠李糖乳杆菌GG株对牛乳过敏婴儿的治疗具有积极作用,可明显改善婴儿牛乳过敏的相关症状 [35] 小鼠 嗜酸乳杆菌LaVK2和双歧杆菌BbVK3 乳清蛋白致敏前7 d,饲喂5 g益生菌混合物 Th1产生的细胞因子增加,Th2产生的IL-4细胞因子下降,可通过增强Th1型免疫反应抑制Th2型免疫反应 [36] 小鼠 副干酪乳杆菌L9 灌服2×109 CFU副干酪乳杆菌L9,1次/d,
共35 dL9可以提高过敏小鼠体内Foxp3+ Treg细胞数量,调节过敏小鼠淋巴细胞的Th1/Th2失衡 [37] 小鼠 唾液乳杆菌LA307
长双歧杆菌亚种LA308
鼠李糖乳杆菌LA305109 CFU/g,持续6 周 LA307能阻断Th1和Th2反应并可能诱导Treg细胞。LA308促进Th1细胞因子的增加,抑制Th2细胞的增殖,LA305调控并促进Th1反应 [38] 4.2 益生菌调节牛乳过敏的作用机制
4.2.1 调节肠道菌群
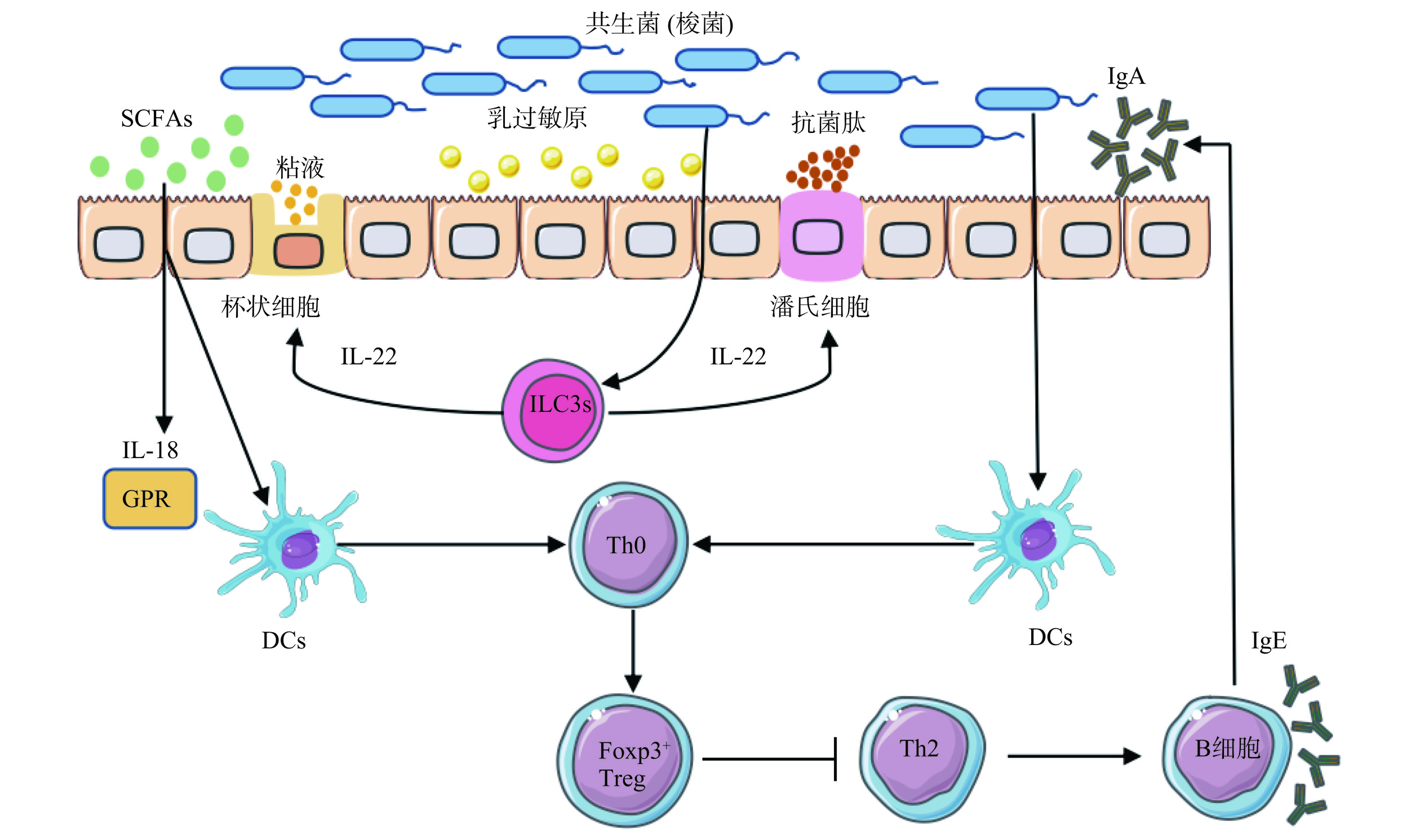
由于过敏人群和健康人群的肠道菌群在种类和丰度上存在显著差异,因此调节肠道菌群是控制牛乳过敏反应的一种有效策略。当营养物质受限时,益生菌与肠壁内有害菌竞争定殖位点并争夺营养物质,益生菌可利用自身合成的消化酶分解消化道内未完全水解吸收的营养物质[39]。正常生理状态下远端小肠和近端结肠内乳酸杆菌的含量较高,而远端结肠内双歧杆菌的数量占据优势。故添加乳酸杆菌或双歧杆菌可有效降低其他微生物对营养物质的消耗[40]。同时,双歧杆菌还能促进胃肠道黏膜上皮分泌黏液和调节胃肠激素水平。益生菌与黏液及肠道上皮细胞的黏附作用,不仅赋予菌株竞争优势,同时也抑制致病菌对肠上皮细胞的黏附[41]。如双歧杆菌借助脂壁磷酸的黏附作用,在肠上皮细胞中合成细胞外糖苷酶,以降解潜在的致病菌并形成肠道保护屏障,从而有效地防止致病菌的入侵、黏附和定植[42−43]。
国内外许多临床研究证明益生菌的摄入是调节宿主肠道菌群的最直接方式,在缓解牛乳过敏症状方面发挥着重要作用[44]。如采用广泛水解酪蛋白配方(Extensively hydrolyzed casein formula,EHCF)辅以鼠李糖乳杆菌GG(Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG,LGG)对19 名CMA婴儿进行治疗,发现与健康婴儿相比,颤螺菌是唯一丰度不同的微生物,且大多数耐受婴儿的粪便丁酸盐水平显著增加,而在这些样本中显著富集的菌群布劳特氏菌和罗斯氏菌,在耐受婴儿和过敏婴儿中表现出特定的菌株水平界限。这说明使用EHCF联合LGG治疗可通过影响婴儿肠道菌落结构提高CMA婴儿的耐受性[26]。Mennini等[33]发现长双歧杆菌婴儿亚种M-63的长期定植,增加了CMA婴儿肠道中阿克曼氏菌和瘤胃球菌的丰度,促进肠道菌群的有益调节。长双歧杆菌婴儿亚种M-63可能具有治疗CMA婴儿的生物学合理性。国外学者在探究双歧杆菌TMC3115对CMA婴儿的干预实验中发现,双歧杆菌、乳杆菌、螺旋杆菌和拟杆菌是干预组最优势的门,而对照组最优势的门为厚壁菌门。摄入双歧杆菌TMC3115降低了CMPA婴儿的过敏评分,改善了抗炎反应[34]。一项以0~12月龄的CMA婴儿为研究对象的实验表明,连续4 周每天食用鼠李糖乳杆菌GG可明显改善婴儿过敏症状如血便、腹泻、腹胀等,但对腹痛、便秘和皮肤炎症状的改善并不明显[35]。综上所述,益生菌摄入对肠道菌群调节的有益影响可以提高CMA婴儿的耐受性,改善过敏症状。虽然许多益生菌被证明具有抗过敏特性,但随着多菌株益生菌制剂的大量上市,在进行临床研究之前,应评估其特定益生菌在肠道中的定植和持久性,以获得更好的治疗效果。
4.2.2 增强肠道屏障
肠道屏障是一个由机械、化学、免疫和菌群屏障组成的动态系统,这4 个屏障协同作用,可有效抵抗病原体,阻止过敏原的渗透和吸收。机械屏障由肠道上皮细胞及细胞间的紧密连接构成,细胞间的这种紧密连接可选择性的转运物质,防止过敏原及炎性介质进入肠黏膜。益生菌可通过上调宿主肠上皮细胞对紧密连接蛋白的表达,有效维持黏膜完整性[45]。化学屏障主要由肠道杯状细胞分泌的消化液和益生菌分解的抗菌物质组成。研究发现,梭菌及其他共生菌可与3型天然淋巴细胞(ILC3s)相互作用产生白细胞介素-22(IL-22),诱导潘氏细胞产生抗菌肽,促进杯状细胞分泌粘液,从而调节乳过敏原的摄取[46](图2)。肠道菌群结构形成一种相互依赖并相互制约的微生态系统,其生态平衡形成了人体肠道的菌群屏障。菌群屏障主要通过益生菌的竞争性机制和分泌的代谢产物调节肠道屏障功能,是益生菌群的综合屏障,不仅具有免疫增强作用,而且能进一步降解致敏蛋白[47]。当婴儿摄入致敏蛋白后,对应蛋白酶消化功能较弱,致使牛乳的部分蛋白难以消化,加之肠道屏障功能尚未发育完善,所以过敏蛋白分子易透过婴儿肠道进入体内,或在婴幼儿肠道菌群失调的情况下,有害菌也可引起肠黏膜通透性的变化而使过敏蛋白进入肠道,从而导致过敏[7]。而益生菌定植后,可使肠黏膜表面形成保护膜,既修复并强化了肠黏膜的屏障功能,同时也对菌群平衡起到调节作用,促使免疫屏障得以巩固[48]。综上所述,益生菌可以调节肠道屏障功能,且其参与的肠道屏障的增强作用可能是阻止牛乳过敏原进入的关键。
4.2.3 促进肠黏膜免疫
研究发现婴儿CMA的发生与免疫系统的功能密切相关,益生菌可通过促进肠黏膜免疫来缓解牛乳过敏。由于婴儿肠黏膜免疫系统发育尚未完全,分泌型免疫球蛋白A(Secretory immunoglobulin A,SIgA)的分泌量较少,故无法避免乳过敏原的接触或控制机体的免疫过度反应[7]。此外,益生菌及其产物可激活免疫细胞,促进SlgA的分泌。SlgA在肠道黏液层可与过敏原结合来减缓过敏的发生,防止过敏原从肠道进入血液[49]。Shandilya等[36]以嗜酸乳杆菌LaVK2和双歧杆菌BbVK3为食物原料,对乳清蛋白过敏的小鼠进行喂养,发现益生菌组小鼠Th1产生的细胞因子增加,Th2产生的IL-4细胞因子下降,可见益生菌可通过增强Th1 型免疫反应抑制因过敏反应过度的Th2型免疫反应,从而调节Th1/Th2的免疫平衡而抑制过敏。杨景[37]利用细胞和动物模型评价了副干酪乳杆菌L9对小鼠牛乳蛋白过敏反应的缓解作用,结果表明,副干酪乳杆菌可有效改善过敏,其主要作用是调节细胞因子的分泌而维持过敏小鼠体内的Th1/Th2平衡。Neau等[38]研究了唾液乳杆菌LA307、长双歧杆菌亚种LA308、鼠李糖乳杆菌LA305三种菌株对β-乳球蛋白过敏小鼠的作用,结果发现,唾液乳杆菌LA307菌株具有很强的免疫抑制作用,可以阻断Th1和Th2反应,并可能诱导Treg细胞。而长双歧杆菌亚种LA308菌株促进Th1细胞因子的增加,抑制Th2细胞的增殖,鼠李糖乳杆菌LA305菌株可调控并促进Th1反应。可见这三种菌株有助于Th1/Th2免疫平衡的恢复,缓解牛乳过敏。
研究表明,肠道菌群诱导CD4+ FoxP3+ Treg细胞的特定亚群,这些细胞也表达RORγt+,即Th17细胞的特定转录因子。这种新型调节性T细胞被称为3型Treg[50]。为了进一步探索其能力,研究人员给予牛乳过敏小鼠灌胃干酪乳杆菌BL23,发现可诱导小鼠局部和全身FoxP3+ RORγt+ 3型Treg细胞,这些细胞可参与干酪乳杆菌BL23对牛乳过敏的免疫增强作用[51]。此外,益生菌代谢产物短链脂肪酸(SCFAs)可与宿主或病原体直接相互作用,向宿主传递信号,调节免疫反应。SCFAs通过G蛋白偶联受体作用于DCs,产生白细胞介素-18(Interleukin-18,IL-18),不仅可以修复上皮细胞损伤,还能促进Foxp3+ Treg细胞的自我增殖[52]。Foxp3+ Tregs可通过白细胞介素-10(Interleukin-10,IL-10)、白细胞介素-35(Interleukin-35,IL-35)、转化生长因子β(Transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)等抑制炎症反应,维持牛乳口服耐受。Sardecka-Milewska等[53]研究表明,Foxp3 mRNA表达的增加可以使CMA婴儿更快地获得耐受性。Foxp3+ Treg细胞还能促进B细胞分泌更多的免疫球蛋白A(ImmunoglobulinA,IgA)、IgG抗体,抑制Th2细胞和IgE抗体的产生,进而缓解牛乳过敏[54](图2)。
4.2.4 分解牛乳过敏原蛋白
益生菌可通过分解牛乳过敏原蛋白而降低其致敏性。Zhao等[55]最新研究发现酪丁酸梭菌株Z816对牛奶过敏原β-Lg表现出优异的降解能力,可有效降低其致敏性,改善牛奶过敏症状。β-LG的降解可能是由于酪丁酸梭菌株Z816产生蛋白酶,细胞通透性改善了底物蛋白与蛋白酶之间的接触,从而达到更好的降解效率。Micael等[56]在体外模拟胃肠道消化过程中,发现德氏乳杆菌保加利亚亚种CRL 454的预水解对β-乳球蛋白的消化有积极作用,可减轻过敏反应。此外,益生菌还可以通过发酵降解大分子的过敏原蛋白,破坏其抗原表位,降低牛乳过敏原的致敏性[4]。利用干酪乳杆菌LcY单独发酵可使α-乳白蛋白、β-乳球蛋白的免疫原性下降,经模拟消化后其过敏原致敏性显著降低[57]。而瑞士乳杆菌与嗜热链球菌的复合发酵也能显著降低α-乳白蛋白和β-乳球蛋白的抗原性,且复合菌株间存在一定的协同效应[58−59]。对于酪蛋白,Biscola等[57]研究发现在粪肠球菌VB63F发酵超高温瞬时杀菌(Ultra high temperature treated,UHT)脱脂乳的过程中产生的蛋白酶可以有效水解过敏原αs1-酪蛋白、αs2-酪蛋白和β-酪蛋白,降低其致敏能力。这进一步证明了益生菌分解牛乳过敏原蛋白并调控CMA的潜力。
5. 结论与展望
益生菌作为对宿主有益的活性微生物,在预防和改善各种食物过敏中起着关键作用,但其作用机制研究还不够深入。本文梳理了牛乳过敏的免疫机制、肠道微生物群与牛乳过敏的相关性,从调节肠道菌群、增强肠道屏障、促进肠黏膜免疫以及分解牛乳过敏原蛋白等方面重点阐述了益生菌缓解牛乳过敏的作用机制。然而,益生菌抗敏性的研究仍存在着许多不足之处。虽然益生菌抗过敏的疗效不断增强,但益生菌治疗食物过敏的研究规模仍然较小,并不是所有的菌株都有预防和治疗的效果,不同的菌株分泌不同的细胞因子,产生的作用也不同,因此必须充分考虑其安全性和有效性问题。
目前国内外对益生菌的研究多关注于其自身,对其与宿主之间的相互关系缺乏深入研究。探索益生菌在分子结构上是如何与肠道内的其他微生物群体进行交流,并通过交换遗传物质来建立起复杂的共生关系是必要的。同时,应拓展益生菌在代谢紊乱中的临床研究,具体研究益生菌在宿主脑-肠轴的作用,筛选出优势益生菌作为益生菌补充剂的基本原料,并明确这些益生菌补充剂如何改善宿主健康。对于具有更强安全性的后生物制剂,目前的大多数报告都是关于它们治疗食物过敏的潜力,相关研究并没有考虑使用后生物制剂的准确剂量。因此,未来仍需要进一步研究肠道微生物在CMA乃至食物过敏中的作用和机制,选择更有效的菌株进行治疗和预防,构建以肠道微生态为基础的CMA调控新途径。
-
蛋白质 分子量(kDa) 牛乳中的含量(g/kg) 氨基酸数(个) 抗原表位 α-乳白蛋白 14.2 1.1 123 1~16、13~26、45~78、93~102;7~18、51~61、89~108;5~18 β-乳球蛋白 18.4 3.0 162 21~40、41~60、102~124、127~141;149~162 αs1-酪蛋白 23.6 12.7 199 19~30、69~78、86~103、123~132;141~150、173~194 表 2 牛奶过敏患者肠道菌群的变化
Table 2 Changes in intestinal flora in patients with cow's milk allergy
研究对象 年龄 牛奶过敏患者肠道菌群的变化 参考文献 226 名过敏婴儿 3~16 个月 拟杆菌门、肠杆菌门↑ [25] 46 名过敏婴儿和23 名健康婴儿 1~26 个月 拟杆菌属、另枝菌属↑ [26] 166 名过敏婴儿 0~12个月 肠杆菌科/拟杆菌科↑、瘤胃球菌科↓ [27] 5 名过敏婴儿和6 名健康婴儿 9~10 个月 双歧杆菌↓、毛螺菌科及其艾森伯格氏菌属↑ [28] 6 名过敏儿童和8 名健康儿童 5~8 岁 厚壁菌门、芽孢杆菌纲、疣微菌科↑、变形菌门↓ [29] 50 名过敏婴儿和20 名健康婴儿 0~12 个月 放线菌门↓、厚壁菌门↑、双歧杆菌及产丁酸菌群↑ [30] 18 名过敏婴儿和6 名健康婴儿 1~6 个月 拟杆菌门↓、双歧杆菌属、伊格尔兹氏菌属、丁酸弧菌属、另枝菌属↓、长双歧杆菌、丁酸梭菌、鼠李糖乳杆菌↓、假链状双歧杆菌↑ [31] 24 名过敏婴儿和26 名健康婴儿 0~6 个月 厚壁菌门、变形菌门↑、放线菌门↓、链球菌属、肠杆菌属、柠檬酸杆菌属、狭义梭菌属-1、葡萄球菌属↑、双歧杆菌属↓ [32] 注:↑:增加;↓:减少。 表 3 益生菌在缓解牛乳过敏中的应用
Table 3 Probiotics in the alleviation of cow's milk allergy
研究对象 种类 疗法和补充剂 结果 参考文献 人 鼠李糖乳杆菌GG 水解酪蛋白配方治疗,同时或不补充LGG(4.5×107~8.5×107 CFU/g),持续6 个月 通过影响婴儿肠道的菌株水平的细菌群落结构,促进牛奶过敏婴儿的耐受性 [26] 人 长双歧杆菌婴儿亚种M-63、长双歧杆菌长亚种 BB536和短双歧杆菌M-16V 以3.5×109 CFU/剂量给药,每天2次,持续30 d 长双歧杆菌婴儿亚种M-63在CMA婴儿肠道中的长期定植与阿克曼氏菌和瘤胃球菌的增加有关 [33] 人 两歧双歧杆菌TMC3115 每天口服2 mL的两歧双歧杆菌TMC3115(1×109 cells/mL) 和0.85%
生理盐水溶液,持续6个月TMC3115降低了婴儿的过敏评分和血清IgE水平,增加了IgG2水平。同时增加了益生菌属比例,降低了病原体比例 [34] 人 鼠李糖乳杆菌GG 每日口服1×109 CFU LGG,持续4 周 鼠李糖乳杆菌GG株对牛乳过敏婴儿的治疗具有积极作用,可明显改善婴儿牛乳过敏的相关症状 [35] 小鼠 嗜酸乳杆菌LaVK2和双歧杆菌BbVK3 乳清蛋白致敏前7 d,饲喂5 g益生菌混合物 Th1产生的细胞因子增加,Th2产生的IL-4细胞因子下降,可通过增强Th1型免疫反应抑制Th2型免疫反应 [36] 小鼠 副干酪乳杆菌L9 灌服2×109 CFU副干酪乳杆菌L9,1次/d,
共35 dL9可以提高过敏小鼠体内Foxp3+ Treg细胞数量,调节过敏小鼠淋巴细胞的Th1/Th2失衡 [37] 小鼠 唾液乳杆菌LA307
长双歧杆菌亚种LA308
鼠李糖乳杆菌LA305109 CFU/g,持续6 周 LA307能阻断Th1和Th2反应并可能诱导Treg细胞。LA308促进Th1细胞因子的增加,抑制Th2细胞的增殖,LA305调控并促进Th1反应 [38] -
[1] 时丽霞. 肠道菌群与婴幼儿食物过敏相关性的研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(12):4959−4963. [SHI L X. Research progress on the correlation between gut microbiota and food allergies in infants and young children[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Testing,2021,12(12):4959−4963.] SHI L X. Research progress on the correlation between gut microbiota and food allergies in infants and young children[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Testing, 2021, 12(12): 4959−4963.
[2] MARTINIS M D, SIRUFO M M, SUPPA M, et al. New perspectives in Food Allergy[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2020,21(4):1474. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041474
[3] 程伟. 多酚氧化酶交联牛乳α-乳白蛋白的结构变化及其消化性与过敏原性的评估[D]. 南昌:南昌大学, 2012. [CHENG W. Structural changes of polyphenol oxidase cross-linked milk α-lactalbumin and its evaluation of digestibility and allergenism[D]. Nanchang:Nanchang University, 2012.] CHENG W. Structural changes of polyphenol oxidase cross-linked milk α-lactalbumin and its evaluation of digestibility and allergenism[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2012.
[4] 曲也直, 苏米亚, 陈文亮, 等. 牛乳过敏与肠道微生物相关性研究进展[J]. 乳业科学与技术,2023,46(2):50−58. [QU Y Z, SU M Y, CHEN W L, et al. Research progress on the correlation between milk allergy and intestinal microbiota[J]. Dairy Science and Technology,2023,46(2):50−58.] QU Y Z, SU M Y, CHEN W L, et al. Research progress on the correlation between milk allergy and intestinal microbiota[J]. Dairy Science and Technology, 2023, 46(2): 50−58.
[5] CUKROWSKA B, CEREGRA A, MACIORKOWSKA E, et al. The effectiveness of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus casei strains in children with atopic dermatitis and cow's milk protein allergy:A multicenter, randomized, double blind, placebo controlled study[J]. Nutrients,2021,13(4):1169. doi: 10.3390/nu13041169
[6] 刘一璇, 鲁丁强, 刘丹阳, 等. 牛乳蛋白生物脱敏技术研究进展[J]. 中国乳品工业,2023,51(2):40−48. [LIU Y X, LU D Q, LIU D Y, et al. Research progress on biological desensitization technology of bovine milk protein[J]. China Dairy Industry,2023,51(2):40−48.] LIU Y X, LU D Q, LIU D Y, et al. Research progress on biological desensitization technology of bovine milk protein[J]. China Dairy Industry, 2023, 51(2): 40−48.
[7] 陈境, 张晓宁, 霍麒文, 等. 婴幼儿牛乳蛋白过敏机制及解决方法研究进展[J]. 中国食品学报,2020,20(7):289−298. [CHEN J, ZHANG X N, HUO Q W, et al. Research progress on the mechanism and solution of milk protein allergy in infants[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2020,20(7):289−298.] CHEN J, ZHANG X N, HUO Q W, et al. Research progress on the mechanism and solution of milk protein allergy in infants[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2020, 20(7): 289−298.
[8] 胡永芯, 谭宏凯, 胡巍, 等. 牛乳乳清中主要过敏原的B细胞表位定位[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(20):148−156. [HU Y X, TAN H K, HU W, et al. Localization of B cell epitopes of major allergens in milk and whey[J]. Food Science,2022,43(20):148−156.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20211111-143 HU Y X, TAN H K, HU W, et al. Localization of B cell epitopes of major allergens in milk and whey[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(20): 148−156. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20211111-143
[9] JARVINEN K, CHATCHATEE P, BARDINA L, et al. IgE and IgG binding epitopes on α-lactalbumin and β-lactoglobulin in cow’s milk allergy[J]. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology,2001,126(2):111−118. doi: 10.1159/000049501
[10] ADAMS S L, BARNETT D, WALSH B J, et al. Human IgE-binding synthetic peptides of bovine β-lactoglobulin and α-lactalbumin. In vitro cross-reactivity of the allergens[J]. Immunology and Cell Biology,1991,69(3):191−197. doi: 10.1038/icb.1991.28
[11] 河北农业大学. 可特异性识别α-乳白蛋白的核酸适配体及其应用:CN202111418490.3[P]. 2022-04-12. [Hebei Agricultural University. Aptamers that can specifically recognize α-lactalbumin and their applications:CN202111418490.3[P]. 2022-04-12.] Hebei Agricultural University. Aptamers that can specifically recognize α-lactalbumin and their applications: CN202111418490.3[P]. 2022-04-12.
[12] 杨晶晶, 赵树静, 刘甜甜, 等. 降低牛乳中β-乳球蛋白致敏性方法的研究进展[J]. 中国油脂,2021,46(5):75−81. [YANG J J, ZHAO S J, LIU T T, et al. Research progress on methods for reducing β-lactoglobulin allergenicity in milk[J]. China Oils and Fats,2021,46(5):75−81.] YANG J J, ZHAO S J, LIU T T, et al. Research progress on methods for reducing β-lactoglobulin allergenicity in milk[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2021, 46(5): 75−81.
[13] SELO I, CLEMENT G, BEMARD H, et al. Allergy to bovine beta-lactoglobulin:Specificity of human IgE to tryptic peptides[J]. Clin Exp Allergy,1999,29(8):1055−1063. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.1999.00612.x
[14] 熊子奕, 马鑫, 陈红兵, 等. 牛乳主要过敏原酪蛋白的特性和分离纯化研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(20):391−399. [XIONG Z Y, MA X, CHEN H B, et al. Research progress on characterization and isolation and purification of casein, the main allergen of cow's milk[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(20):391−399.] XIONG Z Y, MA X, CHEN H B, et al. Research progress on characterization and isolation and purification of casein, the main allergen of cow's milk[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(20): 391−399.
[15] SPUERGIN P, MUELLER H, WALTER M, et al. Allergenic epitopes of bovine alpha S1-casein recognized by human IgE and IgG[J]. Allergy,1996,51(5):306−312.
[16] 党慧杰, 刘振民, 郑远荣. 牛乳主要过敏原及其检测技术研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(3):765−770. [DANG H J, LIU Z M, ZHENG Y R. Research progress on major allergens of milk and their detection techniques[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2020,11(3):765−770.] DANG H J, LIU Z M, ZHENG Y R. Research progress on major allergens of milk and their detection techniques[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2020, 11(3): 765−770.
[17] CHATCHATEE P, JÄRVINEN K M, BARDINA L, et al. Identification of IgE-and IgG-binding epitopes on α(s1)-casein:Differences in patients with persistent and transient cow's milk allergy[J]. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology,2001,107(2):379−383. doi: 10.1067/mai.2001.112372
[18] SCHOEMAKER A A, SPRIKKELMAN A B, GRIMSHAW K E, et al. Incidence and natural history of challenge-proven cow's milk allergy in European children--EuroPrevall birth cohort[J]. Allergy, 2015, 70(8):963-972.
[19] 梁敏, 张立文, 朱美华, 等. 血清IgE测定对牛奶过敏婴儿的临床意义[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志,2015,17(6):618−622. [LIANG M, ZHANG L W, ZHU M H, et al. Clinical significance of serum IgE determination in infants with cow's milk allergy[J]. CJCP,2015,17(6):618−622.] LIANG M, ZHANG L W, ZHU M H, et al. Clinical significance of serum IgE determination in infants with cow's milk allergy[J]. CJCP, 2015, 17(6): 618−622.
[20] 李丽娜. 关于IgE-Fc电化学受体传感器的研究[D]. 天津:天津商业大学, 2019. [LI L N. Research on IgE-Fc electrochemical receptor sensor[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University of Commerce, 2019.] LI L N. Research on IgE-Fc electrochemical receptor sensor[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Commerce, 2019.
[21] 党慧杰, 郑远荣, 刘振民, 等. 牛乳蛋白过敏及酶水解降低其致敏性的研究进展[J]. 中国乳品工业,2020,48(8):29−33,45. [DANG H J, ZHENG Y R, LIU Z M, et al. Research progress on milk protein allergy and enzymatic hydrolysis to reduce its allergenicity[J]. China Dairy Industry,2020,48(8):29−33,45.] DANG H J, ZHENG Y R, LIU Z M, et al. Research progress on milk protein allergy and enzymatic hydrolysis to reduce its allergenicity[J]. China Dairy Industry, 2020, 48(8): 29−33,45.
[22] ANVARI S, MILLER J, YEH C Y, et al. IgE-mediated food allergy[J]. Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology,2019,57(2):244−260.
[23] 曹婷, 赵丽娜, 陈庆学, 等. 益生菌改善牛乳蛋白过敏性的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(23):11−18. [CAO T, ZHAO L N, CHEN Q X, et al. Research progress on probiotics improving milk protein allergy[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(23):11−18.] CAO T, ZHAO L N, CHEN Q X, et al. Research progress on probiotics improving milk protein allergy[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(23): 11−18.
[24] GOLKAR A, MILANI J M, VASILJEVIC T. Altering allergenicity of cow's milk by food processing for applications in infant formula[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science & Nutrition,2019,59(1):159−172.
[25] BUNYAVANICH S, SHEN N, GRISHIN A, et al. Early-life gut microbiome composition and milk allergy resolution[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol,2016,138(4):1122−1130. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.03.041
[26] ROBERTO B C, FRANCESCA D F, RITA N, et al. Gut microbiota composition and butyrate production in children affected by non-IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy[J]. Entific Reports,2018,8(1):12500.
[27] DONG P, FENG J J, YAN D Y, et al. Early-life gut microbiome and cow’s milk allergy-a prospective case-control 6-month follow-up study[J]. Saudi Journal of Biological Scienences,2018,25(5):875−880. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.11.051
[28] MAURAS A, WOPEREIS H, YEOP I, et al. Gut microbiota from infant with cow’s milk allergy promotes clinical and immune features of atopy in a murine model[J]. Allergy,2019,74(9):1790. doi: 10.1111/all.13787
[29] 董艳如. 牛乳蛋白过敏儿童肠道菌群结构及短链脂肪酸分析[D]. 哈尔滨:东北农业大学, 2018. [DONG Y R. Structure of intestinal microbiota and analysis of short-chain fatty acids in children with bovine milk protein allergy[D]. Harbin:Northeast Agricultural University, 2018.] DONG Y R. Structure of intestinal microbiota and analysis of short-chain fatty acids in children with bovine milk protein allergy[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2018.
[30] 李心悦, 王硕, 张华, 等. 牛奶蛋白过敏婴儿肠道菌群动态变化特点[J]. 临床儿科杂志,2022,40(11):831−838. [LI X Y, WANG S, ZHANG H, et al. Dynamic changes of intestinal microbiota in infants with cow's milk protein allergy[J]. Journal of Clinical Pediatrics,2022,40(11):831−838.] doi: 10.12372/jcp.2022.21e1524 LI X Y, WANG S, ZHANG H, et al. Dynamic changes of intestinal microbiota in infants with cow's milk protein allergy[J]. Journal of Clinical Pediatrics, 2022, 40(11): 831−838. doi: 10.12372/jcp.2022.21e1524
[31] 王丽婷. 婴儿牛奶蛋白过敏中肠道菌群结构及多样性研究[D]. 广州:南方医科大学, 2020. [WANG L T. Study on the structure and diversity of intestinal microbiota in infant cow's milk protein allergy[D]. Guangzhou:Southern Medical University, 2020.] WANG L T. Study on the structure and diversity of intestinal microbiota in infant cow's milk protein allergy[D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2020.
[32] 罗光月. 不同喂养方式牛奶蛋白过敏患儿肠道菌群的多样性分析[D]. 遵义:遵义医科大学, 2022. [LUO G Y. Diversity analysis of intestinal microbiota in children with cow's milk protein allergy with different feeding methods[D]. Zunyi:Zunyi Medical University, 2022.] LUO G Y. Diversity analysis of intestinal microbiota in children with cow's milk protein allergy with different feeding methods[D]. Zunyi: Zunyi Medical University, 2022.
[33] MENNINI M, REDDEL S, CHIERICO F D, et al. Gut microbiota profile in children with IgE-mediated cow's milk allergy and cow's milk sensitization and probiotic intestinal persistence evaluation[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2021,22(4):1649. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041649
[34] JING W, LIU Q, WANG W. Bifidobacterium bifidum TMC3115 ameliorates milk protein allergy in by affecting gut microbiota:A randomized double-blind control trial[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2021,45(11):e13591.
[35] BASTURK A, ISIK İ, ATALAY A, et al. Investigation of the efficacy of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in infants with cow’s milk protein allergy:A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial[J]. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins,2020,12:138−143. doi: 10.1007/s12602-019-9516-1
[36] SHANDILYA U K, SHARMA A, KAPILA R, et al. Probiotic Dahi containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum modulates immunoglobulin levels and cytokines expression in whey proteins sensitised mice[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2016,96(9):3180−3187. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.7497
[37] 杨景. 副干酪乳杆菌L9对小鼠牛乳蛋白过敏的缓解作用及机制研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学, 2016. [YANG J. Study on the alleviating effect and mechanism of Lactobacillus paracasei L9 on bovine milk protein allergy in mice[D]. Beijing:China Agricultural University, 2016.] YANG J. Study on the alleviating effect and mechanism of Lactobacillus paracasei L9 on bovine milk protein allergy in mice[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2016.
[38] NEAU E, DELANNOY J, MARION C, et al. Three novel candidate probiotic strains with prophylactic properties in a murine model of cow's milk allergy[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2016,82(6):1722−1733. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03440-15
[39] 蔡凯凯, 黄占旺, 叶德军, 等. 益生菌调节肠道菌群及免疫调节作用机理[J]. 中国饲料,2011(18):34−37. [CAI K K, HUANG Z W, YE D J, et al. Mechanisms of probiotics regulating intestinal flora and immunomodulation[J]. China Feed,2011(18):34−37.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3314.2011.18.012 CAI K K, HUANG Z W, YE D J, et al. Mechanisms of probiotics regulating intestinal flora and immunomodulation[J]. China Feed, 2011(18): 34−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3314.2011.18.012
[40] 孙笑非, 温俊. 益生菌调节肠道菌群的作用机制及研究进展[J]. 饲料研究,2010(4):56−58. [SUN X F, WEN J. Mechanism and research progress of probiotics regulating intestinal microbiota[J]. Feed Research,2010(4):56−58.] SUN X F, WEN J. Mechanism and research progress of probiotics regulating intestinal microbiota[J]. Feed Research, 2010(4): 56−58.
[41] 唐曼玉, 王晚晴, 强敬雯, 等. 益生菌与肠道菌群、免疫调节的相互作用与机制研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(16):486−493. [TANG M Y, WANG W Q, QIANG J W, et al. Research progress on the interaction and mechanism of probiotics with intestinal microbiota and immune regulation[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(16):486−493.] TANG M Y, WANG W Q, QIANG J W, et al. Research progress on the interaction and mechanism of probiotics with intestinal microbiota and immune regulation[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(16): 486−493.
[42] 刘延国, 张琳, 冯香安, 等. 益生菌在消化道中的抑菌作用[J]. 中国饲料,2011(16):9−12. [LIU Y G, ZHANG L, FENG X A, et al. Antibacterial effect of probiotics in digestive tract[J]. China Feed,2011(16):9−12.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3314.2011.16.005 LIU Y G, ZHANG L, FENG X A, et al. Antibacterial effect of probiotics in digestive tract[J]. China Feed, 2011(16): 9−12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3314.2011.16.005
[43] 赵胜娟, 孙文峰, 刘爱萍, 等. 益生菌对肠道微生态影响的研究现状[J]. 食品研究与开发,2008,29(4):182−185. [ZHAO S J, SUN W F, LIU A P, et al. Research status of the effects of probiotics on intestinal microecology[J]. Food Research and Development,2008,29(4):182−185.] ZHAO S J, SUN W F, LIU A P, et al. Research status of the effects of probiotics on intestinal microecology[J]. Food Research and Development, 2008, 29(4): 182−185.
[44] GU S, YANG D, LIU C, et al. The role of probiotics in prevention and treatment of food allergy[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2023,12(3):681−690. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.09.001
[45] 王超越, 韩瑨, 吴正钧, 等. 益生菌对宿主肠道屏障功能的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(15):309−315. [WANG C Y, HAN J, WU Z J, et al. Effect of probiotics on host intestinal barrier function[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022,48(15):309−315.] WANG C Y, HAN J, WU Z J, et al. Effect of probiotics on host intestinal barrier function[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2022, 48(15): 309−315.
[46] KULKARNI D H, GUSTAFSSON J K, KNOOP K A. et al. Goblet cell associated antigen passages support the induction and maintenance of oral tolerance[J]. Mucosal Immunol,2020,13(6275):271−282.
[47] 张鑫, 郭军. 益生菌与肠道黏膜免疫研究进展[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学,2017,38(11):58−64. [ZHANG X, GUO J. Progress in the study of probiotics and intestinal mucosal immunity[J]. Livestock and Feed Science,2017,38(11):58−64.] ZHANG X, GUO J. Progress in the study of probiotics and intestinal mucosal immunity[J]. Livestock and Feed Science, 2017, 38(11): 58−64.
[48] GAVROVIC-JANKULOVIC M, WILLEMSENILL L E M. Epithelial models to study food allergen-induced barrier disruption and immune activation[J]. Drug Discovery Today:Disease Models,2015,17:29−36.
[49] SPILJAR M, MERKLER D, TRAJKOVSKI M. The immune system bridges the gut microbiota with systemic energy homeostasis:Focus on TLRs, mucosal barrier, and SCFAs[J]. Frontiers in Immunology,2017,8:1353. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01353
[50] KLUGER M A, NOSKO A, RAMCKE T, et al. RORγt expression in Tregs promotes systemic lupus erythematosus via IL-17 secretion, alteration of Treg phenotype and suppression of Th2 responses[J]. Clinical & Experimental Immunology,2017,188(1):63−78.
[51] CORTES-PEREZ N G, LOZANO-OJALVO D, MAIGA M A, et al. Intragastric administration of Lactobacillus casei BL23 induces regulatory FoxP3+ RORγt+ T cells subset in mice[J]. Beneficial Microbes,2017,8(3):433−438. doi: 10.3920/BM2016.0174
[52] YANG H, QU Y, GAO Y, et al. Research progress on the correlation between the intestinal microbiota and food allergy[J]. Foods,2022,11(18):2913. doi: 10.3390/foods11182913
[53] SARDECKA-MILEWSKA I, O-RYCHARSK E, GAWRYJOLEK J, et al. Role of FOXP3 expression and serum vitamin D and C concentrations when predicting acquisition of tolerance in infants with cow's milk allergy[J]. Journal of Investigational Allergology & Clinical Immunology,2019,30(3):182−190.
[54] 张伟, 郭宏伟, 刘向增, 等. 肠道菌群与牛奶蛋白过敏及口服耐受关系研究进展[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志,2020,35(4):324−328. [ZHANG W, GUO H W, LIU X Z, et al. Research progress on the relationship between intestinal microbiota and cow's milk protein allergy and oral tolerance[J]. CJPP,2020,35(4):324−328.] ZHANG W, GUO H W, LIU X Z, et al. Research progress on the relationship between intestinal microbiota and cow's milk protein allergy and oral tolerance[J]. CJPP, 2020, 35(4): 324−328.
[55] ZHAO Q, WANG Y, ZHU Z, et al. Efficient reduction of β-lactoglobulin allergenicity in milk using Clostridium tyrobutyricum Z816[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2023,12(3):809−816. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.09.017
[56] MICAEL A, PESCUM A, ELVIRA M, et al. Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus CRL 454 cleaves allergenic peptides of β-lactoglobulin[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,170:407−414. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.08.086
[57] BISCOLA V, TULINI F L, CHOISET Y, et al. Proteolytic activity of Enterococcus faecalis VB63F for reduction of allergenicity of bovine milk proteins[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2016,99(7):5144−5154. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-11036
[58] MU G, ZHANG Z, WANG J, et al. Antigenicity and safety evaluation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum 7-2 screened to reduce α-casein antigen[J]. Foods,2021,11(1):88. doi: 10.3390/foods11010088
[59] BU G, LUO Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Effects of fermentation by lactic acid bacteria on the antigenicity of bovine whey proteins[J]. J Sci Food Agric,2010,90(12):2015−2020.
-
其他相关附件
-
PDF格式
EI Certificate 43KB
-





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



