Effect of Whole Wheat Noodles on Biochemical Indexes and Histopathology of Type 2 Diabetic Rats
-
摘要: 目的:探究全麦面条对2型糖尿病(T2DM)大鼠生化指标及病理组织学的影响。方法:SD大鼠连续喂养8周后,随机分为正常组和高脂组,高脂组一次性腹腔注射链脲佐菌素(STZ)溶液建立2型糖尿病大鼠模型,然后分别用低、中、高剂量的全麦面条饲料干预糖尿病大鼠8周,定期测定大鼠的体重、饮食饮水量;并采用尾部采血法测定空腹血糖值,采用试剂盒测定血脂生化指标及血清氧化应激水平;大鼠解剖后取出肝脏、肾脏和胰腺组织,测定脏器指数,进行切片染色后生物显微镜观察脏器病理组织学形态变化。结果:与模型组相比,全麦面条干预能显著减缓糖尿病大鼠体重减轻的症状(P<0.05),减少糖尿病大鼠的饮食饮水量(P<0.01),降低糖尿病大鼠的血糖值(P<0.01),高剂量组效果最好,血糖值降低44.87%;使大鼠血清中总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)和低密度脂蛋白(LDL-C)含量极显著降低(P<0.01),高剂量分别降低53.09%、79.58%和45.11%,高密度脂蛋白HDL-C含量增加,高剂量组显著增加21.83%(P<0.05);T-AOC、SOD活性、GSH-Px活性、CAT活性显著增加(P<0.05),MDA含量极显著降低(P<0.01);肝脏和肾脏系数极显著降低(P<0.01),高剂量组分别下降19.92%和16.42%,胰腺系数没有显著性差异(P>0.05);肝细胞炎症细胞浸润现象改善,肾小球基底膜均质性增厚及肾小球系膜基质增多情况改善,胰岛形态更加完整,自溶现象改善。结论:全麦面条对2型糖尿病具有较好的干预效果,可以通过减缓体重减轻,降低血糖值,调节脂质代谢及机体的氧化应激水平,消除脏器炎症水肿,恢复脏器细胞损伤多个方面进行改善。Abstract: Objective: To investigate the effects of whole wheat noodles on biochemical indexes and histopathology of type 2 diabetic (T2DM) rats. Methods: SD rats were fed continuously for 8 weeks and then randomly divided into normal and high-fat groups. The high-fat group was injected intraperitoneally with streptozotocin (STZ) solution at one time to establish a type 2 diabetic rat model. Then, the diabetic rats were intervened with low, medium, and high doses of whole wheat noodles feed for 8 weeks, respectively. The body weights, dietary intake, and drinking volume of the rats were measured regularly. Fasting glucose value was measured by the tail blood sampling method, and the kit was used to measure the blood lipid biochemical indexes and serum oxidative stress levels. Rats were dissected, and liver, kidney, and pancreas tissues were removed to determine the organ indexes. Section staining was performed, followed by biomicroscopic observation of organ histopathological changes. Results: Compared with the model group, whole wheat noodles intervention significantly slowed down the symptoms of weight loss in diabetic rats (P<0.05), reduced dietary and water intake in diabetic rats (P<0.01), and lowered blood glucose values in diabetic rats (P<0.01), with the best effect in the high-dose group, with a reduction of blood glucose values by 44.87%. It also extremely significantly reduced the serum levels of total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C) (P<0.01), with reductions of 53.09%, 79.58%, and 45.11%, respectively, in the high-dose group. Additionally, it increased the content of high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C), with a significant increase of 21.83% in the high-dose group (P<0.05). The total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity, glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activity, and catalase (CAT) activity significantly increased (P<0.05), while the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) extremely significant decreased (P<0.01). Liver and kidney coefficients were extremely significant decreased (P<0.01), by 19.92% and 16.42% in the high-dose group, respectively, and pancreas coefficients showed no significant difference (P>0.05). The phenomenon of inflammatory cell infiltration in hepatocytes improved, homogeneous thickening of glomerular basement membranes and the increase in the stroma of glomerular tethered membranes were ameliorated, and the morphology of islets showed improvement with reduced autolysis phenomenon. Conclusion: Whole wheat noodle has a significant intervention effect on type 2 diabetes mellitus, manifested in slowing down weight loss, lowering blood glucose values, regulating lipid metabolism and oxidative stress levels in the body, eliminating inflammatory edema in the organs, and restoring cellular damage of the organs in several ways.
-
Keywords:
- whole wheat noodles /
- type 2 diabetes /
- blood lipids /
- oxidative stress /
- histopathology
-
糖尿病是一种由胰岛素分泌不足或胰岛素抵抗所导致的以高血糖为主要特征的代谢性疾病[1],已经成为继心血管疾病和癌症之后,危害我国居民健康的第三大疾病[2−3]。2型糖尿病(T2DM)占所有糖尿病的90%~95%[4],主要表现为胰岛素抵抗所导致的血糖升高[5−6]、脂质代谢异常[7−8]、机体氧化应激状态[9−10]以及脏器损伤[11−12]等,长期以往会导致微血管并发症、大血管并发症及心力衰竭[13−15]等,引起了人们的广泛关注。目前2型糖尿病治疗药物以胰岛素和西药为主,副作用大,易导致低血糖,在有效降糖的同时还会加重胰岛细胞损伤,增加胰岛素抵抗等[16−19]。通过饮食调节来降低2型糖尿病的发病率已成为研究的热点。
全麦食品由于富含膳食纤维、维生素、矿物质以及生物活性物质等,与心血管疾病、2型糖尿病和各种癌症(尤其是结直肠癌)风险的降低存在着良好的关系[20]。多项研究表明,全麦粉可以作为功能性食物成分,通过增强磷脂酰肌醇3磷酸激酶/蛋白激酶B和腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶途径来缓解T2DM,这与全麦粉含有大量的麸皮和胚芽组织有关[21],麸皮中富含的酚类物质具有良好的自由基清除能力,能对抗糖尿病所导致的机体氧化应激状态,胚芽中富含的亚麻酸对于降低胆固醇,调节脂质代谢有重要作用[22]。张丽娜等[23]研究表明,全麦粉可降低糖尿病大鼠血糖水平和血红蛋白含量,增加肝糖原含量。蔡梦迪[24]对石墨全麦挂面的研究表明,其膳食纤维含量显著高于小麦挂面,且血糖生成指数较低,在抗氧化活性及控制血糖方面具有优势。侯梦雅等[25]以不同比例的全麦粉制备面包,通过人体血糖值测试表明,全麦比例为90%、100%的全面面包为低GI食品,稳糖效果更好。
小麦是世界上35%~40%人群主要的粮食作物,当小麦以全谷物形式食用时,更好地保留了存在于麸皮和胚芽部分的膳食纤维、微量营养素和活性成分,因此全麦面条不仅食用方便,而且具有功能性[26]。本文通过高脂饲料喂养联合STZ腹腔注射诱导建立 T2DM 大鼠模型,以全麦面条进行饮食干预,探究全麦膳食对于2型糖尿病大鼠生化指标及脏器组织的改善效果,从而为2型糖尿病患者的健康饮食提供参考依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
全麦粉 山东龙脉科技发展有限公司提供,平均粒径77.95±1.06 μm,基础营养成分含量:水分10.38%,蛋白质12.15%,粗脂肪1.55%,总膳食纤维9.928%,灰分1.80%;雄性SPF级SD大鼠(150~180 g,6~8周) 成都达硕实验动物有限公司,许可证号:SCXK(川)2020-0030,实验方案经重庆第二师范学院重庆市功能性食品工程技术研究中心实验动物伦理委员会审批(202101006B);STZ 德国Biofroxx公司;TC测定试剂盒、TG测定试剂盒、LDL-C测定试剂盒、HDL-C测定试剂盒、总抗氧化能力(T-AOC)测定试剂盒、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)测定试剂盒、过氧化氢酶(CAT)测定试剂盒、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)测定试剂盒、丙二醛(MDA)测定试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所。
5KSM3311XCFG多功能搅拌和面机 凯膳怡贸易有限责任公司;FKM-200俊媳妇压面机 永康市富康电器有限公司;TGL-20高速冷冻离心机 四川蜀科仪器有限公司;金稳+三诺血糖仪 三诺生物传感股份有限公司;INFINITE 200多功能酶标仪 奥地利帝肯有限责任公司;T18 IKA数显型分散机 艾卡仪器设备有限公司;VOKTEX-5涡旋振荡器 海门市其林贝尔仪器制造有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 全麦面条制备
称取全麦粉,加入41%水、1.5%食用盐,和面机搅打4 min、在4 ℃条件下醒发16 h,放入压面机压成1.0 mm厚的面片,再切成2.0 mm宽的面条,−18 ℃条件下储存备用。60 ℃烘干,水分含量为13.64%±0.23%,打成粉末,加入饲料中。
1.2.2 动物实验及分组
雄性SPF级SD大鼠50只(10只/组)适应性喂养1周,试验期间保持温度25±0.5 ℃和相对湿度60%±5%,12 h明暗交替环境。
将大鼠分为正常组(N)和高脂组(F),连续喂养8周后,高脂组腹腔一次性注射1%STZ溶液(35 mg/kg·bw, 溶于0.1 mmol/L柠檬酸缓冲液(pH4.5)),正常组注射同等剂量的柠檬酸缓冲液。注射3 d后,测定空腹血糖值(FBG),FBG值大于11.10 mmol/L,且出现多食、多饮、多尿及体重减轻,视为建模成功[27]。将建模成功的糖尿病大鼠分为4组,分别为模型组(M)、全麦面条低(W-L)、中(W-M)、高(W-H)剂量组,每组10只。正常组和模型组继续给予基础维持饲料和高脂饲料,饲料由成都达硕实验动物有限公司提供;全麦面条受试组将高脂饲料中碳水化合物来源玉米粉和标准小麦粉替换为全麦面条粉(每100 g饲料中低剂量组用30 g全麦面条替换30 g小麦粉,中剂量组用45 g全麦面条替换30 g小麦粉和15 g玉米粉,高剂量组用60 g全麦面条替换30 g小麦粉和30 g玉米粉),蛋白质、脂质来源与高脂饲料无差异,由成都达硕实验动物有限公司制作成饲料,连续干预8周,期间自由饮食饮水。
1.2.3 实验大鼠处理及指标测定
实验结束后,乙醚麻醉后摘眼球取血,并断颈处死后解剖,取出肝脏、肾脏及胰腺,将脏器切分,一份保存于-80 ℃冰箱中,另一份保存于组织固定液中。采集的血液样本在4 ℃冰箱中放置2 h后,4 ℃,3000 r/min冷冻离心10 min,取上层血清用于分析测定。
1.2.3.1 饮食、饮水量及体重测定
建模成功后,分别于第1、3、5、8周测定大鼠饮食、饮水量,分别于第0、2、4、6、8周测定大鼠体重。
1.2.3.2 血糖值测定
建模成功后,分别于第1、3、5、8周同一时间将大鼠禁食不禁水过夜(12 h),剪尾采血用血糖仪测定大鼠的FBG值。
1.2.3.3 脏器系数测定
大鼠解剖后取出肝脏、肾脏和胰腺组织,生理盐水漂洗干净,用滤纸吸干水分后称重。按照公式计算脏器系数:
脏器系数(%)=脏器质量体重×100 1.2.3.4 血脂测定
按照试剂盒说明测定TC、TG、HDL-C、LDL-C指标。
1.2.3.5 血清氧化应激水平测定
按照试剂盒说明测定血清的T-AOC、SOD活性、GSH-Px活性、CAT活性和MDA含量。
1.2.3.6 H&E染色实验
肝脏、肾脏及胰腺组织放入4%多聚甲醛组织固定液中浸泡24 h后脱水,然后进行透明、浸蜡、包埋和切片操作;将薄片脱蜡后用苏木精染液对切片染色至细胞核变蓝,再转入伊红染液染色后脱水透明、封片;用生物显微镜观察、拍片。
1.3 数据处理
实验结果均以平均值±标准偏差(mean±SD)表示,采用IBM SPSS Statistic 19.0进行不同组间的One-way ANOVE显著性分析,使用Origin 2017软件进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
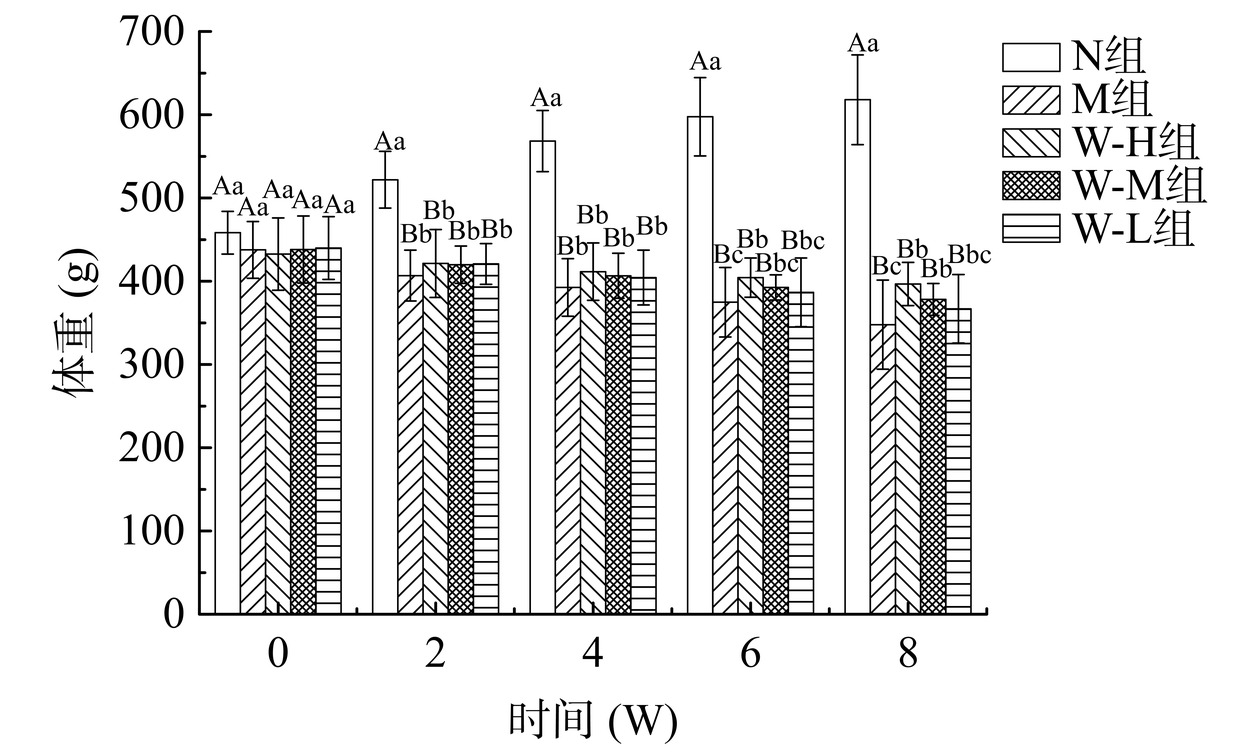
2.1 全麦面条对糖尿病大鼠体重的影响
体重减轻是糖尿病的典型症状之一。由图1可知,N组大鼠在整个试验期间体重持续增长,到实验末期体重达到618.03±19.84 g,与建模大鼠形成极显著性差异(P<0.01)。其余大鼠在建模后体重呈下降趋势,M组大鼠到实验末期体重降至347.78±12.23 g。W-H组、W-M组和W-L组大鼠的体重减轻症状得到了一定程度的缓解,分别为396.67±25.86、378.11±19.17和366.88±41.23 g,W-H和W-M组显著高于M组(P<0.05)。
2.2 全麦面条对糖尿病大鼠饮食饮水量的影响
除了体重减轻之外,“多饮多食”也是T2DM的典型症状,因此饮食饮水量的改变也是评价T2DM改善效果的关键因素。如表1所示,实验期间大鼠饮食饮水量N组无显著变化,M组持续增加,而全麦面条受试组增加趋势相对平缓;第3周时,大鼠的饮食饮水量W-H和W-M组极显著低于M组(P<0.01),W-L组显著低于M组(P<0.05);第8周时,大鼠的饮食饮水量W-H、W-M和W-L组都极显著低于M组(P<0.01)。说明全麦面条能显著改善T2DM大鼠“多饮多食”的症状。
表 1 不同组大鼠的饮食饮水量Table 1. Diet and water intake of rats in different groups指标 组别 1周 3周 5周 8周 饮食量
(g/100 g·bw)N组 5.62±0.69Bb 5.39±0.33Cd 5.79±0.31Cc 5.23±0.60De M组 9.13±1.14Aa 12.61±0.83Aa 15.10±0.84Aa 19.59±0.98Aa W-H组 9.05±1.16Aa 11.08±0.36Bc 11.12±0.58Bb 11.53±0.59Cd W-M组 9.22±1.60Aa 11.29±0.55Bc 11.65±0.33Bb 12.63±0.98Cc W-L组 9.24±1.11Aa 12.13±0.37Ab 11.96±0.82Bb 14.21±0.84Bb 饮水量
(mL/100 g·bw)N组 14.30±1.76Bb 12.99±2.25Dd 10.05±1.59De 11.08±1.26Ee M组 49.66±6.05Aa 63.46±4.18Aa 71.28±3.90Aa 90.23±7.94Aa W-H组 50.00±5.37Aa 56.87±4.35Cc 59.84±5.00Cd 64.72±5.20Dd W-M组 50.99±3.12Aa 57.41±5.00Cc 62.67±7.45Bc 70.43±4.94Cc W-L组 50.02±4.96Aa 58.54±3.81Bb 63.90±6.77Bb 80.37±5.90Bb 注:小写字母不同表示相同条件组间差异显著(P<0.05);大写字母不同表示相同条件组间差异极显著(P<0.01)。 2.3 全麦面条对糖尿病大鼠FBG值的影响
由图2可知,糖尿病(M、W-H、W-M、W-L)组FBG值极显著高于N组大鼠(P<0.01),且均大于11.1 mmol/L,说明通过腹腔注射STZ成功建立了大鼠糖尿病模型,且糖尿病各组大鼠之间无显著性差异。在整个实验过程中,M组大鼠的FBG值持续升高,到第8周时,其平均值达到21.84±2.54 mmol/L,与第1周相比,FBG值增加了30.15%。
通过喂食全麦面条饲料,FBG值得到了有效控制。到实验终期,W-H组、W-M组和W-L组大鼠FBG值相对于实验初期分别下降22.97%、15.12%、9.69%,并与M组大鼠形成极显著性差异(P<0.01),其中W-H组较M组降低了44.87%。说明全麦面条能明显降低糖尿病大鼠的空腹血糖,控制糖尿病病程的发展,并且高剂量的全麦面条表现出的降糖效果最好。
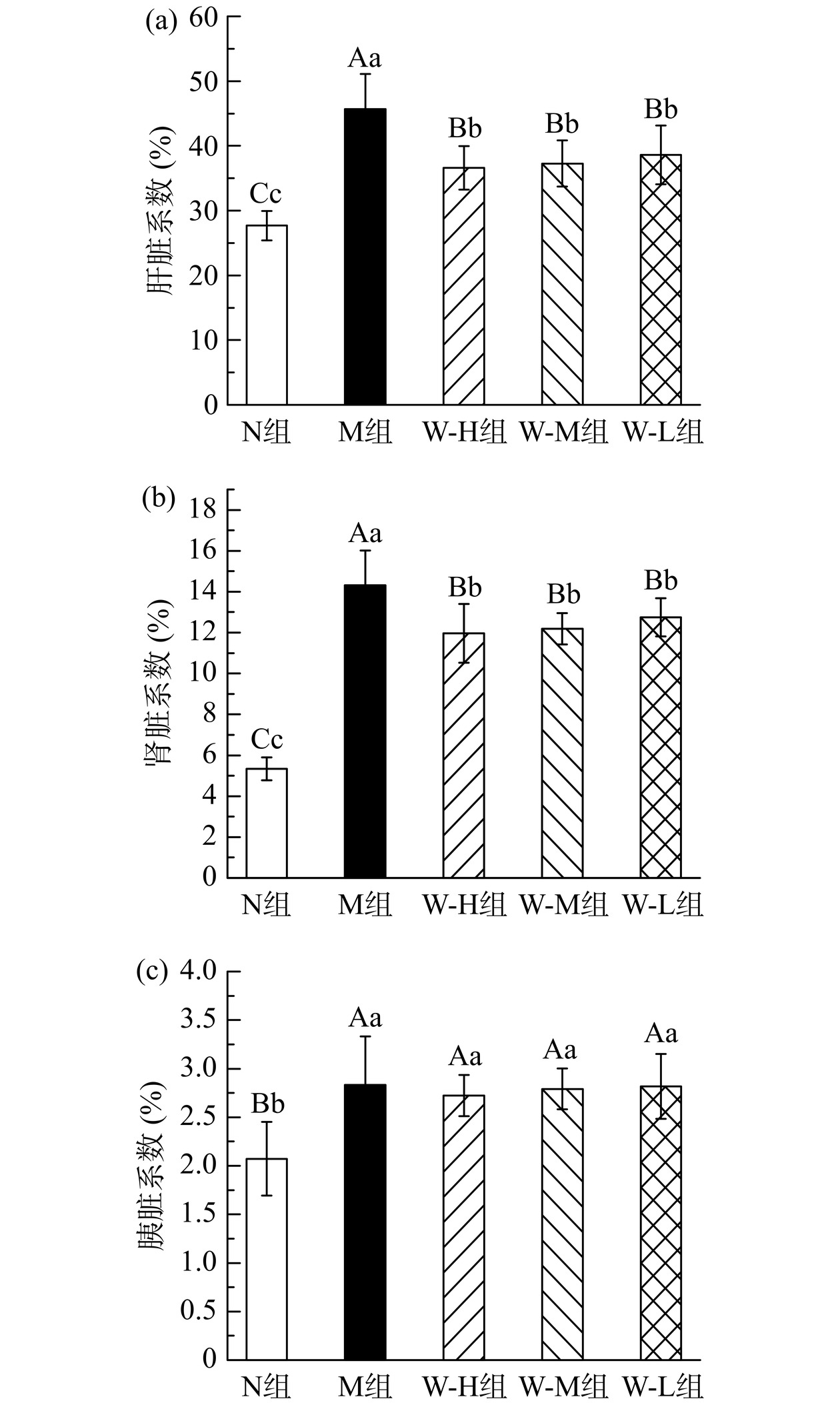
2.4 全麦面条对糖尿病大鼠脏器系数的影响
研究表明,脏器系数增大表示脏器出现了充血、水肿、肥大增生等异常变化;脏器系数减小表示脏器萎缩或其他退行性变化[28]。由于长期的高脂饲料喂养以及后期T2DM病程的发展所导致的炎症,会造成糖尿病大鼠的肝脏和肾脏脂肪堆积及肿大;而糖尿病对胰岛β细胞的破坏以及炎症作用,会导致胰腺组织的弥散和肿大[29]。
由图3(a)、(b)可知,糖尿病大鼠的肝脏系数和肾脏系数与N组相比都极显著增加(P<0.01),表示糖尿病大鼠的肝脏和肾脏都出现了脂肪堆积、肿大等症状。而与M组相比,全麦面条受试组肝脏系数和肾脏系数都极显著降低(P<0.01),且三组间不存在剂量差异。其中,W-H组大鼠的肝脏系数和肾脏系数相较于M组,分别下降了19.92%和16.42%;W-M组大鼠分别下降了18.45%和14.81%;W-L组大鼠分别下降了15.56%和10.90%。说明全麦面条能显著减轻肝脏和肾脏的脂肪堆积以及炎症引起的肿大,但剂量之间的差异不明显。
由图3(c)可知,相较于N组,糖尿病大鼠的胰腺系数也出现了极显著的增加(P<0.01),这表示糖尿病大鼠出现了胰腺组织肿大的症状。在4组糖尿病大鼠中,W-H组、W-M组、W-L组大鼠胰腺系数相较于M组有一定程度的下降,但各组数据间没有显著性差异(P>0.05)。说明全麦面条对于糖尿病大鼠胰腺肿大有一定的改善作用,但作用不明显。
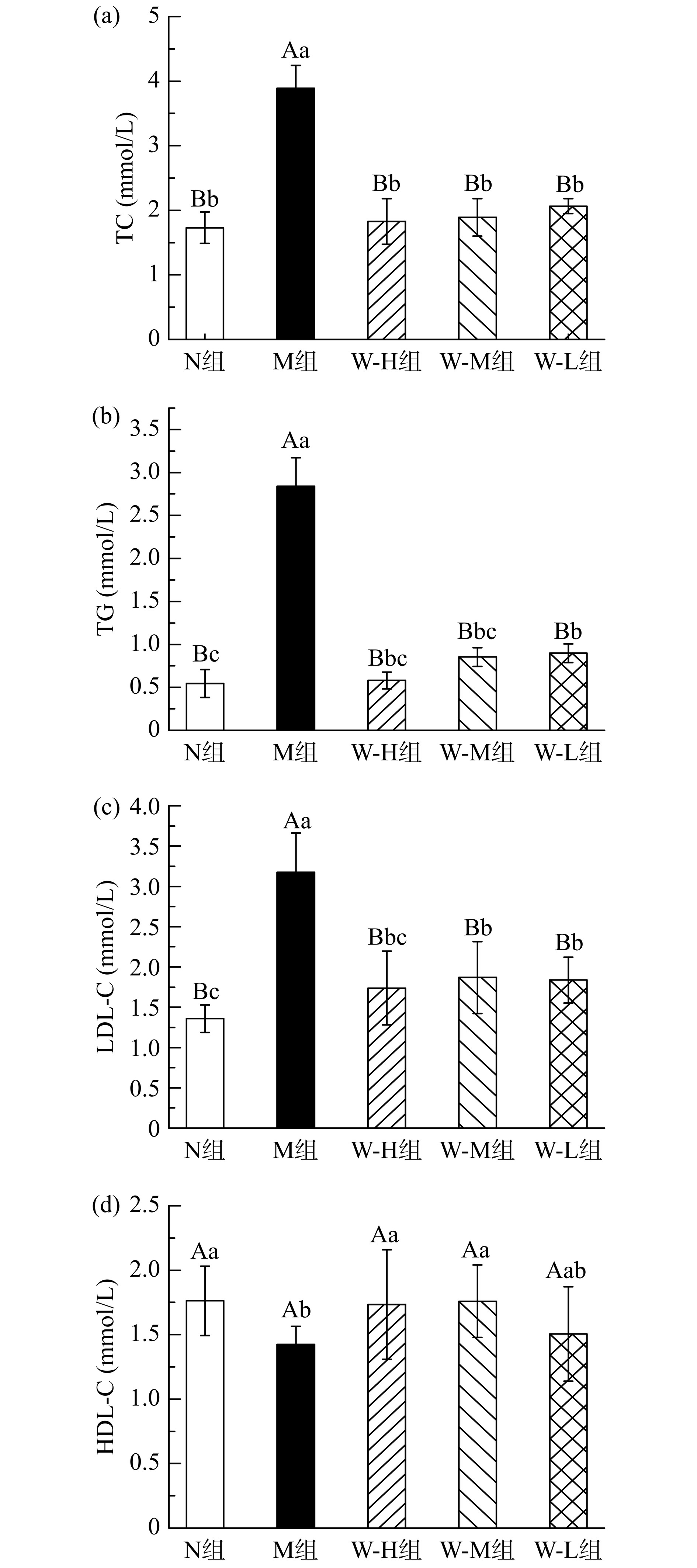
2.5 全麦面条对糖尿病大鼠血脂的调节作用
T2DM患者常常伴随着血脂异常,其原因在于血脂水平与胰岛素抵抗成正相关[30]。血脂异常表现为TC、TG、LDL-C升高及HDL-C降低。如图4所示,M组大鼠TC、TG、LDL-C含量均明显增加,相较于N组分别增加了1.25倍、4.26倍和1.33倍,与N组形成极显著性差异(P<0.01);而HDL-C含量减少了0.19倍,与N组形成显著性差异(P<0.05)。喂食全麦面条后,W-H组、W-M组、W-L组大鼠血脂异常现象得到了明显改善,其TC、TG及LDL-C含量相较于M组均极显著减少(P<0.01),其中W-H组最显著,TC含量减少了53.09%,TG含量减少了79.58%,LDL-C含量减少了45.11%;与N组相比,W-H组、W-M组、W-L组大鼠的TC含量恢复至无显著性差异,W-H组、W-M组大鼠的TG含量恢复至无显著性差异,W-H组大鼠的LDL-C含量恢复至无显著性差异。其次,与M组相比,W-H组和W-M组大鼠的HDL-C含量均显著增加(P<0.05),W-H组大鼠HDL-C含量增加最显著,为21.83%。说明全麦面条对于糖尿病所引起的血脂异常有明显的改善作用。
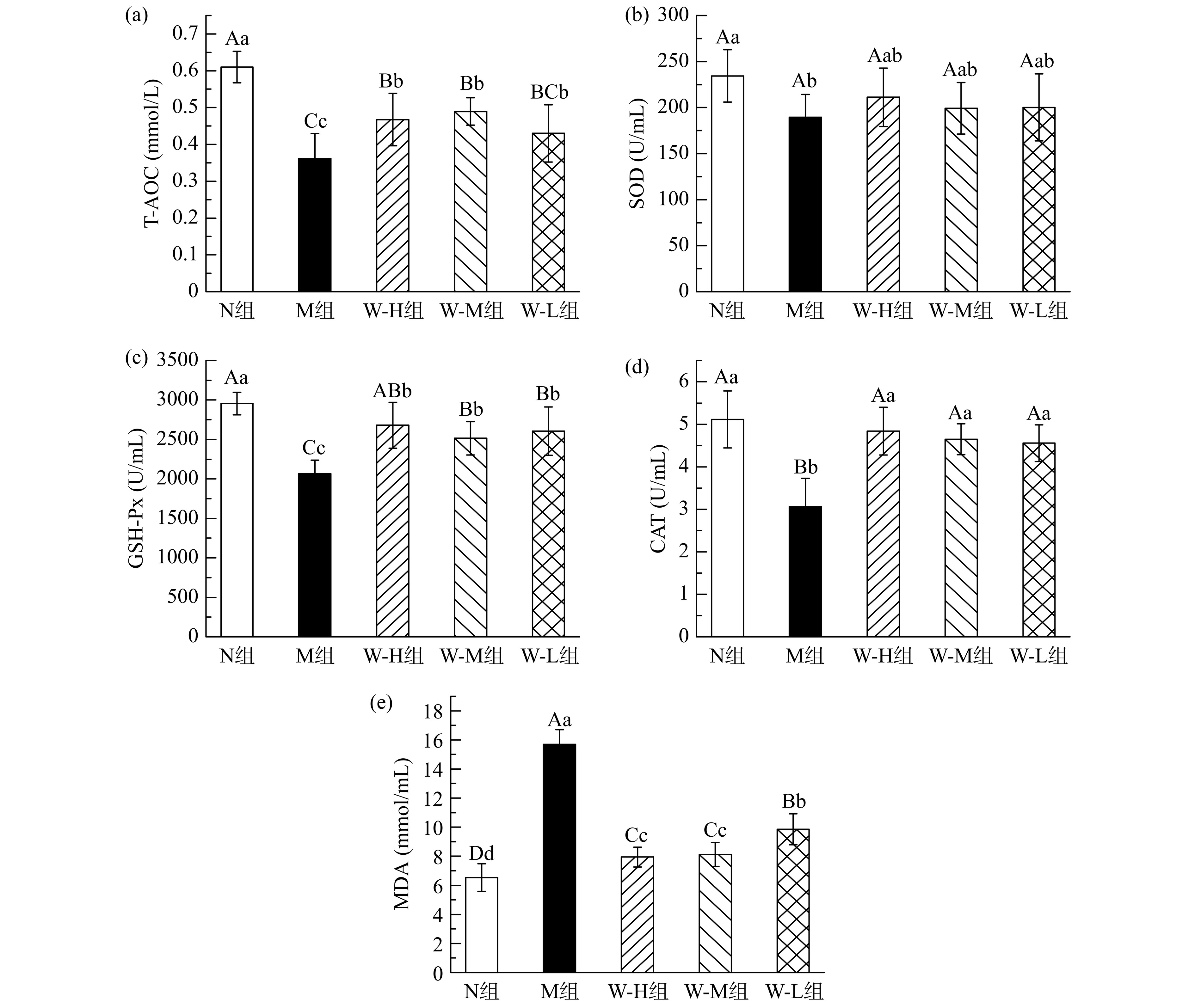
2.6 全麦面条对糖尿病大鼠血清抗氧化能力的影响
如图5(a)所示,M组、W-H组、W-M组、W-L组大鼠的血清T-AOC与N组形成极显著性差异(P<0.01),说明糖尿病建模对大鼠血清造成了抗氧化损伤。与M组相比,W-H组、W-M组、W-L组大鼠的血清T-AOC明显上升,W-H组、W-M组形成极显著性差异(P<0.01),W-L组形成显著性差异(P<0.05)。SOD、GSH-Px、CAT是广泛存在于机体内的抗氧化酶,随着机体氧化应激的发展,酶活性受到抑制。如图5(b)所示,M组大鼠SOD活性与N组相比显著降低(P<0.05),仅为189.38±11.32 U/mL,而喂食全麦面条的大鼠SOD活性较M组大鼠有所增加,其中W-H组大鼠的SOD活性最高,为211.17±5.47 U/mL。图5(c)、(d)是血清GSH-Px活性及血清CAT活性,M组大鼠的血清GSH-Px活性和CAT活性明显降低,与N组形成极显著性差异(P<0.01)。W-H组、W-M组、W-L组大鼠血清GSH-Px活性和CAT活性升高,与M组形成极显著性差异(P<0.01),其中W-H组大鼠血清GSH-Px活性恢复情况最好,但与N组相比还存在显著差异(P<0.05);全麦面条受试组大鼠血清CAT活性均恢复至与N组无显著性差异。MDA是脂质过氧化所产生的一种有害物质,能反映机体受氧化损伤程度。图5(e)反映了血清中MDA的含量,其中M组MDA含量达到了15.69±1.01 mmol/L,远高于其他组别,与其他组形成极显著差异(P<0.01),W-H组、W-M组、W-L组大鼠血清中的MDA含量明显下降,与M组形成极显著性差异(P<0.01),其中W-H组、W-M组效果更好。
因此,全麦面条能显著提高糖尿病大鼠血清的T-AOC、GSH-Px活性、CAT活性(P<0.05),并且极显著降低脂质过氧化所产生的MDA(P<0.01),对于T2DM引起的机体氧化应激状态有明显的缓解作用。其中高剂量的全麦面条对于大鼠氧化应激状态的改善效果更加显著。由于氧化应激与胰岛素抵抗之间存在正相关,所以随着机体氧化应激水平下降,大鼠胰岛素抵抗也随之减缓,从而改善糖尿病的发展。
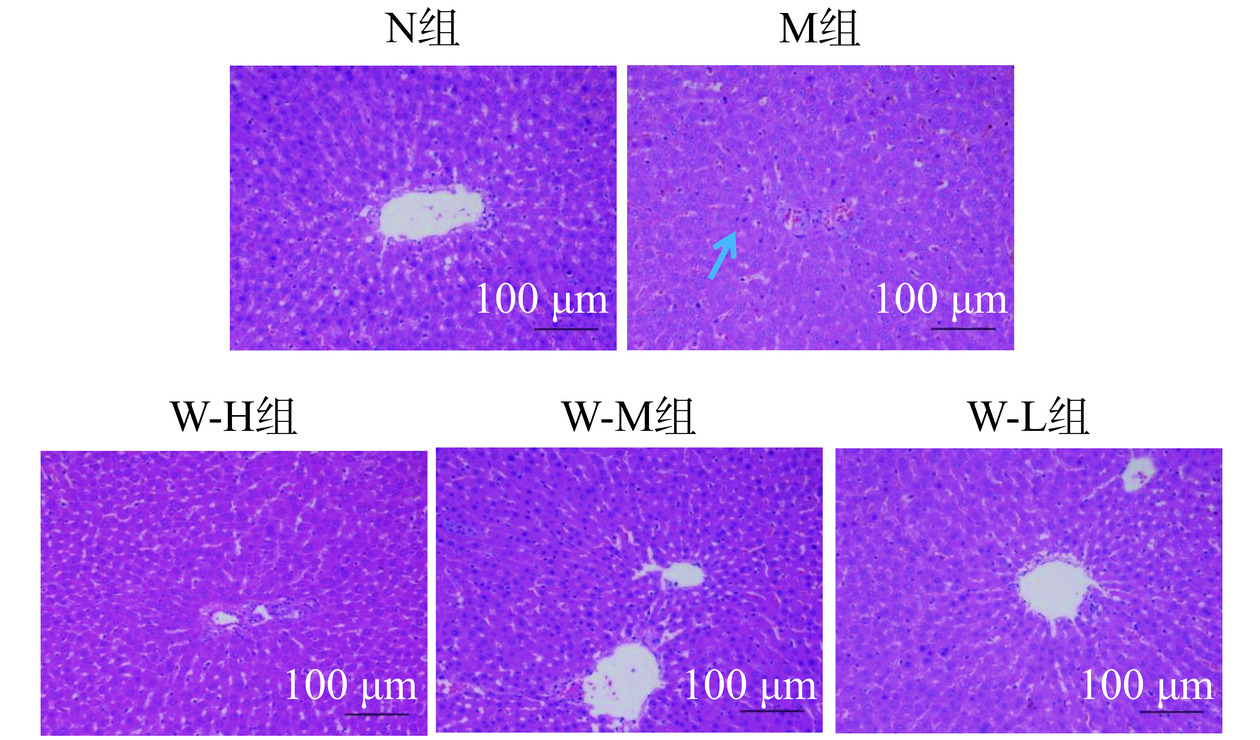
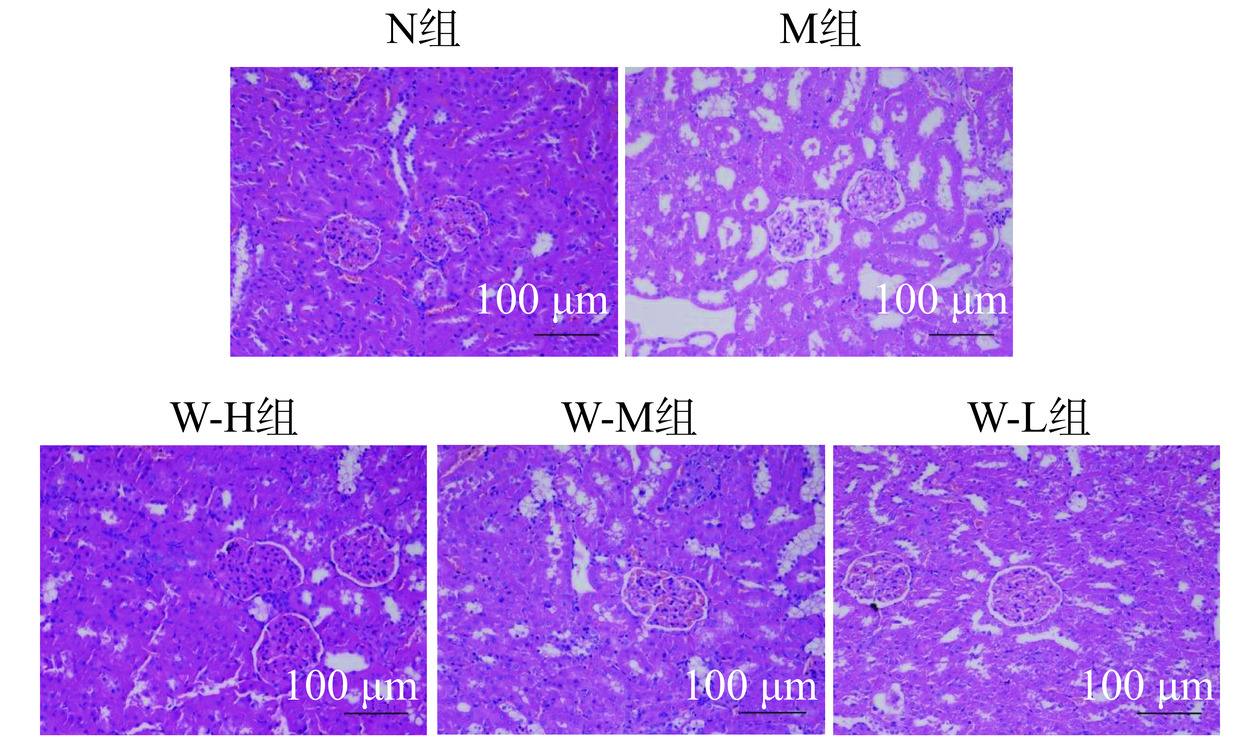
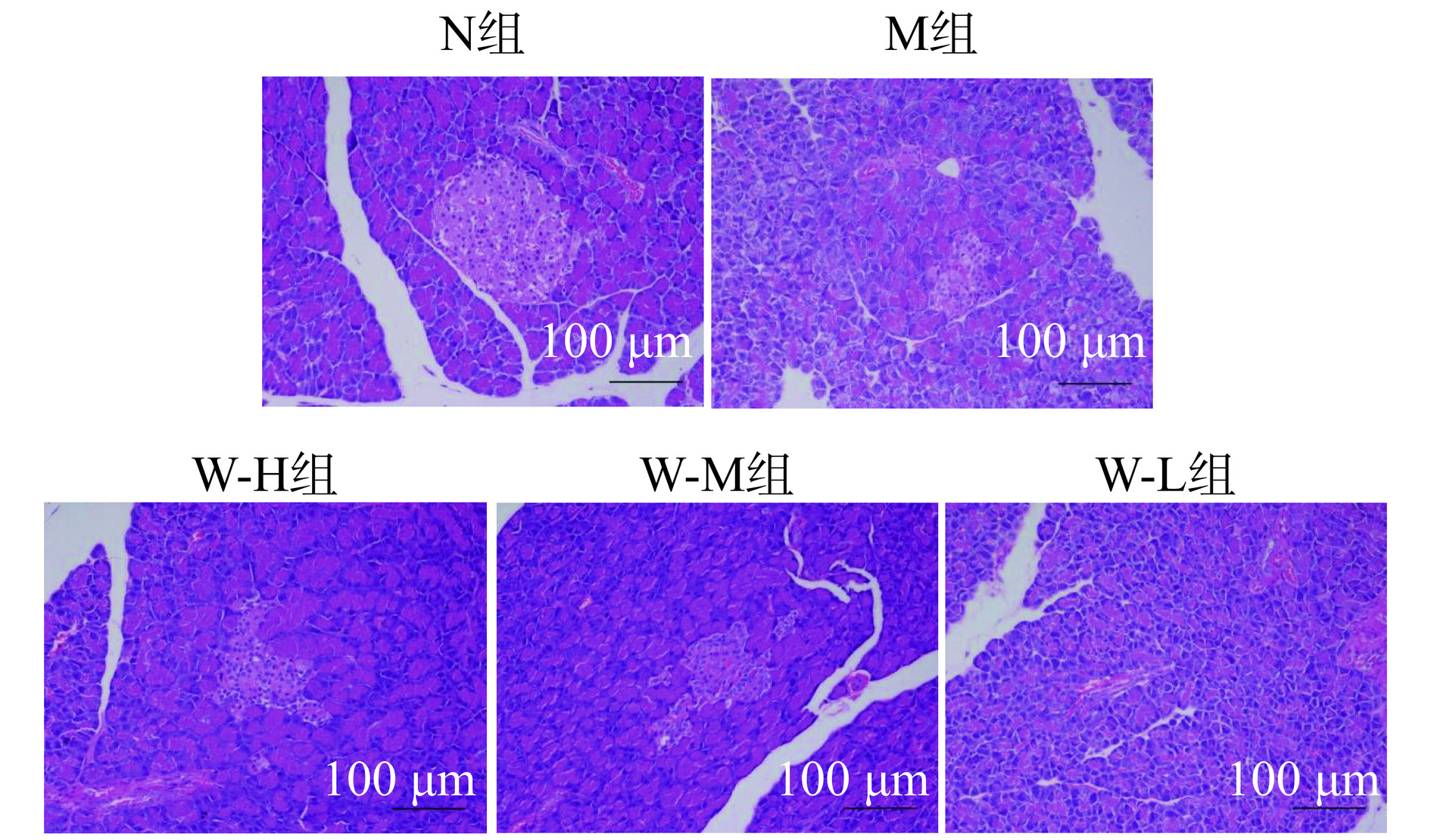
2.7 全麦面条对糖尿病大鼠脏器病理组织学的影响
2.7.1 全麦面条对糖尿病大鼠肝脏病理组织学的影响
由图6可知,N组大鼠肝脏未见明显病理性变化,肝索从中央静脉呈放射状整齐排列,肝血窦清晰明显,肝细胞形态正常,细胞核清晰圆润。M组大鼠肝脏细胞呈现碎片状坏死现象,存在炎症细胞浸润现象,肝索排列混乱,肝血窦减少,肝细胞膨胀肿大,形态异常,细胞核萎缩,着色浅,胞浆疏松且存在脂滴。W-H 组、W-M 组、W-L 组肝脏病变情况相较于 M组有所改善,其中W-H组效果最好,仅有少量点灶状细胞坏死,肝细胞形态基本正常,细胞核未见萎缩,肝索从中央静脉呈放射状排列,炎症细胞浸润现象有所改善;W-M组存在点灶状细胞坏死,炎症细胞浸润现象有所减轻,虽然细胞核数量较多,但存在萎缩现象,细胞核边界不清晰;W-L组存在碎片状细胞坏死和炎症细胞浸润,肝细胞形态异常,与M组相比改善不大。
2.7.2 全麦面条对糖尿病大鼠肾脏病理组织学的影响
由图7可知,N组大鼠的肾脏结构并未出现明显的病理变化,肾小球整体形态结构完整,未见有肾小球基底膜增厚及肾小球系膜基质增多,肾小球毛细血管清晰,未见有增生及变形。而M组大鼠肾脏H&E染色着色较浅,整体形态结构不清晰,肾小球增大,肾小球基底膜出现明显均质性增厚,肾小球系膜基质增多。W-L组、W-M组、W-H组肾脏病变情况逐渐变好,从低剂量组到高剂量组,肾小球整体形态结构越来越完整清晰,肾小球基底膜均质性增厚及肾小球系膜基质增多情况得到改善,W-H组肾脏整体形态结构更接近于N组。
2.7.3 全麦面条对糖尿病大鼠胰腺病理组织学的影响
由图8可知,N组大鼠胰岛结构完整清晰,胰岛细胞丰满充盈,排列整齐均匀,胰岛细胞核染色清晰可见。而M组相较于N组,胰岛严重坏死萎缩,胰岛边界不清晰,胰岛细胞发生自溶,排列松散,胰岛细胞核轻微着色。说明M组大鼠随着病程发展,胰岛细胞受到了严重破坏。相较于M组,W-H组、W-M组、W-L组大鼠的胰岛形态更加完整,胰岛边界更加清晰,胰岛细胞数目增加,自溶现象有所改善,胰岛细胞核着色明显,但相较于N组,胰岛萎缩情况并未得到较好恢复。
3. 结论
通过动物实验,研究了全麦面条对于T2DM大鼠的改善效果,结果表明全麦面条能明显降低糖尿病大鼠的FBG值,减少糖尿病大鼠的饮食饮水量并且改善糖尿病大鼠体重减轻的症状,说明全麦面条能明显改善糖尿病“三多一少”的症状。并且相较于模型组,全麦面条受试组大鼠的血清中TC、TG和LDL-C含量极显著降低(P<0.01),良性脂蛋白HLD-C含量增加,T-AOC、GSH-Px活性、CAT活性相较于模型组显著增加(P<0.05),MDA含量极显著降低(P<0.01),肝脏、肾脏及胰腺三种脏器系数较模型组明显降低,肝细胞炎症细胞浸润现象改善,肾小球基底膜均质性增厚及肾小球系膜基质增多情况改善,胰岛形态更加完整,自溶现象改善,说明全麦面条能够改善糖尿病大鼠的脂质代谢情况,对于脏器炎症水肿有缓解作用,能够改善脏器损伤,并可以通过改善机体的氧化应激水平来改善2型糖尿病。
-
表 1 不同组大鼠的饮食饮水量
Table 1 Diet and water intake of rats in different groups
指标 组别 1周 3周 5周 8周 饮食量
(g/100 g·bw)N组 5.62±0.69Bb 5.39±0.33Cd 5.79±0.31Cc 5.23±0.60De M组 9.13±1.14Aa 12.61±0.83Aa 15.10±0.84Aa 19.59±0.98Aa W-H组 9.05±1.16Aa 11.08±0.36Bc 11.12±0.58Bb 11.53±0.59Cd W-M组 9.22±1.60Aa 11.29±0.55Bc 11.65±0.33Bb 12.63±0.98Cc W-L组 9.24±1.11Aa 12.13±0.37Ab 11.96±0.82Bb 14.21±0.84Bb 饮水量
(mL/100 g·bw)N组 14.30±1.76Bb 12.99±2.25Dd 10.05±1.59De 11.08±1.26Ee M组 49.66±6.05Aa 63.46±4.18Aa 71.28±3.90Aa 90.23±7.94Aa W-H组 50.00±5.37Aa 56.87±4.35Cc 59.84±5.00Cd 64.72±5.20Dd W-M组 50.99±3.12Aa 57.41±5.00Cc 62.67±7.45Bc 70.43±4.94Cc W-L组 50.02±4.96Aa 58.54±3.81Bb 63.90±6.77Bb 80.37±5.90Bb 注:小写字母不同表示相同条件组间差异显著(P<0.05);大写字母不同表示相同条件组间差异极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] SAEEDI P, PETERSOHN I, SALPEA P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045:Results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition[J]. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice,2019,157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
[2] SHARMA P K, RAJPAL N, UPADHYAY S, et al. Status of diabetes control and knowledge about diabetes in patients[J]. Endocrinologia, Diabetes y Nutricion,2021,68(10):716−727. doi: 10.1016/j.endinu.2020.12.006
[3] TANCET T. Diabetes:A dynamic disease[J]. Lancet,2017,389(10085):2163. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31537-4
[4] 练淑平, 张耀, 王振花. 氧化应激在糖尿病性心血管疾病中的研究进展[J]. 医学综述,2019,25(10):2029−2033. [LIAN S P, ZHANG Y, WANG Z H. Research progress of oxidative stress in diabetic cardiovascular disease[J]. Medical Recapitulate,2019,25(10):2029−2033.] LIAN S P, ZHANG Y, WANG Z H. Research progress of oxidative stress in diabetic cardiovascular disease[J]. Medical Recapitulate, 2019, 25(10): 2029−2033.
[5] VEGA-MORENO K D L, ROMERO-HERNÁNDEZ C B, RUÍZ-DANGÚ D G, et al. Glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) distribution on metabolic healthy obese (MHO) vs metabolic unhealthy obese (MUO)[J]. Metabolism,2020,104:154118.
[6] DRAZNIN B, ARODA V R, GEORGE B, et al. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes:Standards of medical care in diabetes-2022 [J]. Diabetes Care, 2022, 45(Supplement 1):S15-S33.
[7] 黄文杰, 马建林, 李小蕤. 高甘油三酯血症与胰岛素抵抗关系的研究进展[J]. 中西医结合心血管病电子杂志,2019,7(8):14−15. [HAUAN W J, MA J L, LI X R. Research progress on the relationship between hypertriglyceridemia and insulin resistance[J]. Cardiovascular Disease Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine,2019,7(8):14−15.] HAUAN W J, MA J L, LI X R. Research progress on the relationship between hypertriglyceridemia and insulin resistance[J]. Cardiovascular Disease Journal of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, 2019, 7(8): 14−15.
[8] 尤丽, 党娅, 杨彬彦. 蓝莓花青素对2型糖尿病小鼠糖脂代谢的调节作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(9):381−388. [YOU L, DANG Y, YANG B Y. Regulation effects of blueberry anthocyanins on glucose-lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetic mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(9):381−388.] YOU L, DANG Y, YANG B Y. Regulation effects of blueberry anthocyanins on glucose-lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetic mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(9): 381−388.
[9] WANG K, LIANG Y T, SU Y, et al. Dhhp-6 ameliorates hepatic oxidative stress and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus through the PI3K/AKT and AMPK pathway[J]. The Biochemical Journal,2020,477(12):2363−2381. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200402
[10] OGUNTIBEJU O O. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, oxidative stress and inflammation:Examining the links[J]. International Journal of Physiology, Pathophysiology and Pharmacology,2019,11(3):45−63.
[11] DARYABOR G, ATASHZAR M R, KABELITZ D, et al. The effects of type 2 diabetes mellitus on organ metabolism and the immune system[J]. Frontiers in Immunology,2020,11:1582.
[12] ATKINSON M A, CAMPBELLTHOMPSON M, KUSMARTSEVA I, et al. Organisation of the human pancreas in health and in diabetes[J]. Diabetologia,2020,63(10):1966−1973. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05203-7
[13] STITT A W, CURTIS T M, CHEN M, et al. The progress in understanding and treatment of diabetic retinopathy[J]. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research,2016,51:156−186. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.08.001
[14] ZAKIN E, ABRAMS R, SIMPSON D M. Diabetic neuropathy[J]. Seminars in Neurology,2019,39(5):560−569.
[15] MARGOLIS S A. Diabetic foot-a global health challenge[J]. Australian Journal of General Practice,2020,49(5):237. doi: 10.31128/AJGP-05-20-1234e
[16] LI J, SHEN X P. Effect of rosiglitazone on inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress after intensive insulin therapy in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome,2019,11(1):35.
[17] EWIDS S F, SHABAAN A M H, ELDOMIATY H F, et al. Effect of insulin sensitizers and sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor on glycemic state and cardiovascular performance in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Qjm:An International Journal of Medicine, 2020, 113(Supplement1).
[18] HEBI M, EDDOUKS M. Leaf aqueous extract of Argania spiniosa exhibits antihyperglycemic effect in diabetic rats[J]. Cardiovascular & Hematological Agents in Medicinal Chemistry,2019,17:64−71.
[19] WANG S W, WU T, ZUO Z H, et al. Comparison of cardiovascular outcomes and cardiometabolic risk factors between patients with type 2 diabetes treated with sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors:A meta-analysis[J]. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology,2021,28(16):1840−1849.
[20] SHEWRY P R HEY S J. The contribution of wheat to human diet and health[J]. Food and Energy Security,2015,4:178−202. doi: 10.1002/fes3.64
[21] 李悦梅, 陈云志. 全麦食品的营养与保健功能的相关研究[J]. 食品安全导刊,2019,246(21):65. [LI Y M, CHEN Y Z. Research on the nutrition and health function of whole wheat food[J]. China Food Safety,2019,246(21):65.] LI Y M, CHEN Y Z. Research on the nutrition and health function of whole wheat food[J]. China Food Safety, 2019, 246(21): 65.
[22] 朱晓月, 黄志远, 马记红, 等. 全麦粉营养及生产工艺探讨[J]. 粮食加工,2014,39(1):12−14. [ZHU X Y, HUANG Z Y, MA J H, et al. Discuss of nutrition and production technology of the whole wheat flour[J]. Grain Processing,2014,39(1):12−14.] ZHU X Y, HUANG Z Y, MA J H, et al. Discuss of nutrition and production technology of the whole wheat flour[J]. Grain Processing, 2014, 39(1): 12−14.
[23] 张丽娜, 赵文红, 谢岩黎, 等. 全麦粉对实验型糖尿病大鼠血糖控制效应的影响[J]. 食品科技,2015,40(11):134−138. [ZHANG L N, ZHAO W H, XIE Y L, et al. Effects of whole wheat flour on the control of blood sugar of diabetic rats[J]. Food Science and Technology,2015,40(11):134−138.] ZHANG L N, ZHAO W H, XIE Y L, et al. Effects of whole wheat flour on the control of blood sugar of diabetic rats[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2015, 40(11): 134−138.
[24] 蔡梦迪. 石磨全麦挂面工艺及特性研究[D]. 绵阳:西南科技大学, 2023. [CAI M D. Study on the process and characteristics of stone-milled dried whole wheat noodles[D]. Mianyang:Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2023.] CAI M D. Study on the process and characteristics of stone-milled dried whole wheat noodles[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2023.
[25] 侯梦雅, 郭政利, 陈媚依, 等. 不同比例全麦粉全麦面包的感官品质和稳糖效果比较[J]. 现代食品科技,2023,39(12):29−34. [HOU M Y, GUO Z L, CHEN M Y, et al. Different proportions of whole wheat flour on the sensory quality and glycemic control of whole wheat bread[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2023,39(12):29−34.] HOU M Y, GUO Z L, CHEN M Y, et al. Different proportions of whole wheat flour on the sensory quality and glycemic control of whole wheat bread[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2023, 39(12): 29−34.
[26] 王梦倩, 任晨刚, 应剑, 等. 全麦粉营养及加工过程中影响血糖的主要因素分析[J]. 中国粮油学报,2021,36(9):185−193. [WANG M Q, REN C G, YING J, et al. Nutrition of whole wheat flour and analysis of main factors affecting blood glucose in processing[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2021,36(9):185−193.] WANG M Q, REN C G, YING J, et al. Nutrition of whole wheat flour and analysis of main factors affecting blood glucose in processing[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2021, 36(9): 185−193.
[27] NIU J M, XU G Y, JIANG S, et al. In vitro antioxidant activities and anti-diabetic effect of a polysaccharide from Schisandra sphenanthera in rats with type 2 diabetes[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,94:154−160. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.10.015
[28] QUESADA-MORUA M S, HIDALGO O, MORERA J, et al. Hypolipidaemic, hypoglycaemic and antioxidant effects of a tropical highland blackberry beverage consumption in healthy individuals on a high-fat, high-carbohydrate diet challenge[J]. Journal of Berry Research,2020,10(3):1−16.
[29] SUNEESH K, ANIL K C, ALLOUH M Z, et al. Epigenetic modifications in pancreas development, diabetes, and therapeutics[J]. Medicinal Research Reviews,2022,42(3):1343−1371. doi: 10.1002/med.21878
[30] ZHENG D Q, LI H B, AI F L, et al. Association between the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus among Chinese elderly:The Beijing longitudinal study of aging[J]. Bmj Open Diabetes Research & Care,2020,8(1):e811.





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



