Effects of Walnut Protein Peptides on Promotion of White Adipose Tissue Browning and Prevention of Obesity
-
摘要: 目的:探究核桃肽对促进白色脂肪棕色化及预防肥胖的作用。方法:在3T3-L1前脂肪细胞分化过程中加入核桃肽(0.25、1.00 mg/mL),分化成功后检测脂肪细胞脂质积累、线粒体数量、白色脂肪棕色化关键因子蛋白表达水平的变化。进一步,采用核桃肽(400 mg/kg BW)干预高脂饮食(High-fat diet,HFD)雄性C57BL/6小鼠8周后,监测体重、脂肪组织重量、血脂水平并进行口服葡萄糖耐量试验(Oral glucose tolerance test,OGTT),观察腹股沟白色脂肪组织形态变化,同时检测腹股沟白色脂肪组织中棕色化标志物的蛋白表达情况。结果:在细胞水平,核桃肽干预3T3-L1脂肪细胞后脂滴减小,脂质积累水平降低,线粒体数量增加,上调了解偶联蛋白1(Uncoupling protein 1,UCP1)、过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅激活因子1α(Peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α,PGC-1α)、PR结构域蛋白16(PR domain-containing 16,PRDM16)、过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α(Peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor α,PPARα)的蛋白表达。在动物水平,与HFD组小鼠相比,核桃肽干预8周显著缓解了体重过度增加,降低了白色脂肪组织(附睾脂肪、腹股沟脂肪)质量指数,降低了血清中甘油三酯(Triglyceride,TG)、总胆固醇(Total cholesterol,TC)、低密度脂蛋白(Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)的水平,增加了高密度脂蛋白(High-density lipoprotein cholesterol,HDL-C)水平,并增加了葡萄糖耐受能力。腹股沟脂肪组织苏木精-伊红染色(Hematoxylin-eosin staining,H&E)及免疫组化结果分析显示,核桃肽明显降低了HFD导致的平均脂肪细胞面积增加,并上调了UCP1阳性细胞数量。此外,核桃肽同样增加了腹股沟脂肪组织中棕色化关键因子UCP1、PGC-1α、PRDM16、PPARα的蛋白表达。结论:核桃肽具有促进白色脂肪棕色化的效果,能够预防由HFD引发的肥胖及代谢紊乱,具有作为抗肥胖功能性食品配料的潜力。Abstract: Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of walnut protein peptides (WPP) on the promotion of white adipose tissue (WAT) browning to prevent obesity. Methods: The 3T3-L1 preadipocytes were treated with WPP (0.25 mg/mL, 1.00 mg/mL) during the differentiation. Lipid accumulation, mitochondrial quantity, and the protein expression of key factors involved in WAT browning were detected in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes after differentiation. Furthermore, male C57BL/6 mice fed with high-fat diet (HFD) were treated with WPP (400 mg/kg BW) for 8 weeks. Body weight, adipose tissue weight and blood lipid levels were monitored, and oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) was performed. The morphological changes of inguinal WAT were observed, and the protein expression of key factors involved in WAT browning were detected. Results: WPP treatment decreased the size of lipid droplets, reduced lipid accumulation, and increased mitochondrial quantity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Western blot results showed that WPP significantly up-regulated the protein expression level of key factors involved in WAT browning uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1), peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), PR domain-containing 16 (PRDM16), and peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα). Compared with the HFD group, WPP intervention for 8 weeks significantly alleviated the body weight gain and reduced the WAT (epididymal fat, inguinal fat) mass index. WPP reduced the serum levels of triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in HFD mice, while increased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels and glucose tolerance. The results of H&E staining and UCP1 immunohistochemistry of inguinal WAT showed that WPP significantly reduced the increase in the average adipocyte area caused by HFD, and increased the number of UCP1 positive cells. In addition, compared with HFD group, WPP also increased the protein expression levels of UCP1, PGC-1α, PRDM16 and PPARα in inguinal WAT. Conclusions: WPP can promote the browning of WAT and prevent obesity and metabolic disorders induced by HFD, which provides potential as a functional food ingredient for preventing obesity.
-
Keywords:
- walnut protein peptides /
- high-fat diet /
- white adipose tissue browning /
- obesity
-
由于人们生活水平的提高,高脂、高糖饮食等不良饮食习惯易造成体内脂肪堆积,引起肥胖及相关代谢紊乱[1]。脂肪组织作为一种代谢器官,在调节机体能量方面发挥重要作用,主要分为白色脂肪组织(White adipose tissue,WAT)和棕色脂肪组织(Brown adipose tissue,BAT)两大类[2]。白色脂肪细胞主要以甘油三酯的形式存储能量,其过量积累和扩增会导致肥胖[3]。棕色脂肪细胞通过燃烧脂肪酸、葡萄糖等底物产热,从而消耗能量[1]。BAT的产热活性在很大程度上取决于位于线粒体内膜上的解偶联蛋白1(Uncoupling protein 1,UCP1)。UCP1能催化脂肪酸氧化呼吸链中的质子泄漏,最终通过氧化磷酸化作用解偶联释放能量[4]。 研究表明,在冷刺激、β3-肾上腺素受体、细胞/生长因子、营养因子等刺激下WAT中会出现表达UCP1并富含线粒体的脂肪细胞,这些细胞的特性介于白色脂肪细胞与棕色脂肪细胞之间,被称为“米色”脂肪细胞(Beige/brite adipocytes)[5]。米色脂肪细胞既可直接起源于米色前体脂肪细胞,也可由白色前体脂肪细胞分化或从白色脂肪细胞直接转化而来,这些过程称为“白色脂肪棕色化”[6]。多种转录因子参与白色脂肪棕色化的调控,如PR结构域蛋白16(PR domain-containing 16,PRDM16)在控制棕色脂肪基因程序中起着重要作用[7],能通过与棕色脂肪基因增强子结合,激活下游产热基因表达[8,9]。过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅激活因子1α(Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1-α,PGC-1α)是线粒体生物合成和线粒体功能的关键调节因子,白色脂肪细胞中PGC-1α的异位表达可诱导多种线粒体基因和产热基因的表达,如UCP1[10];而白色脂肪中PGC-1α的缺失会严重损害白色脂肪棕色化的进程[11]。核受体过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体α(Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α,PPARα)是米色/棕色脂肪标记物,其通过诱导脂肪组织中PGC-1α和PRDM16协作调节脂质分解代谢和产热能力[12]。在动物模型中,白色脂肪中UCP1和其他产热基因的表达能够改善肥胖、葡萄糖代谢紊乱和胰岛素抵抗[13]。因此,使用营养学干预诱导WAT的棕色化来促进能量消耗,是改善代谢健康的新策略之一。
中国是世界上核桃产量最大的国家[14]。核桃作为传统的健脑食品,是植物蛋白的宝贵来源,约含有18%~24%的蛋白质和丰富的必需氨基酸[15]。核桃蛋白是核桃油加工的主要副产物之一,通常被丢弃或用作动物饲料,造成蛋白质资源的浪费[16]。核桃蛋白及其生物活性肽具有抗肿瘤、降血糖、抗氧化、保护心血管、改善记忆等多种生理活性[17],同时核桃肽可以解决食品开发中核桃蛋白溶解性差等的技术瓶颈,基于核桃肽开发个性化健康食品具有广阔的市场前景。已有研究表明,核桃及其蛋白肽能够改善肥胖、糖尿病等相关代谢紊乱的发生和发展[17]。核桃干预6周能够调节高糖饮食雄性Wistar大鼠血浆和组织中脂肪酸代谢,提示其在预防和治疗代谢综合征方面的巨大潜力[18]。脱脂核桃粕提取物能够通过调节肠道菌群抑制糖尿病饮食和链脲佐菌素(Streptozotocin,STZ)药物对大鼠高血糖的影响,缓解胰岛素抵抗[19]。核桃源肽LPLLR通过抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶的活性,减轻肝脏HepG2细胞的胰岛素抵抗,从而达到抗糖尿病的作用[20]。核桃粕多肽能有效缓解高脂饮食对大鼠体重的增加,降低肝脏脂肪含量,改善脂质代谢水平[21]。然而,核桃肽是否能够通过调节白色脂肪棕色化预防肥胖尚不清楚。因此,本研究首先利用3T3-L1前脂肪细胞在体外探究核桃肽促进白色脂肪棕色化的作用;进一步利用高脂饮食小鼠模型,验证核桃肽在体内促进白色脂肪棕色化、预防肥胖的效果,为核桃肽在抗肥胖功能性食品开发中的应用提供理论依据与科学基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
3T3-L1前脂肪细胞 购自ATCC细胞库;健康SPF级C57BL/6J 雄性小鼠(30只),4周龄 购自郑州大学实验动物中心,生产许可证号:SCXK(豫)2021-0009;小鼠维持饲料(D12450H)、小鼠高脂饲料(D12451) 购自美国research diets公司;脱脂核桃粕 购自于大理云上普瑞农业有限责任公司;DMEM高糖培养基 购自美国HyClone公司;胎牛血清 购自以色列BI公司;青链霉素双抗溶液(100×)、0.05%胰蛋白酶(含EDTA)(1:250/L) 购自美国Gibco公司;噻唑蓝四唑蓝(3-(4,5-Dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide,MTT)试剂盒、油红O染液 购自南京建成生物工程研究所;胰岛素 购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司;地塞米松、3-异丁基-1-甲基黄嘌呤(3-Isobutyl-1-methyl-7H-xanthine,IBMX)、3,3',5-三碘 -L-甲腺原氨酸(3,3',5-Triiodo-L-thyronine,T3)、吲哚美辛、GW6471(PPARα抑制剂) 购自西格玛奥德里奇贸易有限公司;anti-UCP1、anti-PGC-1α、anti-PRDM16、anti-PPARα抗体 购自艾比玛特医药科技(上海)有限公司;anti-β-actin抗体 购自北京博奥森生物技术有限公司;Western及IP细胞裂解液、RIPA裂解液、蛋白酶磷酸酶抑制剂混合物、BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒、辣根过氧化物酶标记山羊抗兔IgG(H+L)、FITC标记山羊抗兔IgG(H+L)、一抗稀释液、MitoTracker Red、胎牛血清(Fetal bovine serum,FBS) 购自上海碧云天生物技术有限公司;TC、TG、HDL-C、LDL-C测试盒 购自南京建成生物工程研究所;PVDF膜(0.45 μm 和0.20 μm)、ECL化学发光底物 购自密理博中国有限公司;4%多聚甲醛通用型组织固定液 购自合肥Biosharop公司;所有其他无机、有机溶剂均为国产分析纯。
BS-420型全自动生化分析仪 深圳迈瑞有限公司;Varioskan LUX多功能酶标仪 美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司;DXY-2倒置荧光显微镜 上海缔伦光学仪器有限公司;Odyssey®双色红外激光成像系统 基因有限公司;TGL-16G低温高速离心机 上海安亭科学仪器厂;ME204分析天平 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;552BR伯乐小型垂直电泳槽 美国Rio-Rad公司;Forma™ II 3110水套式二氧化碳培养箱 Thermo公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 核桃肽的制备
参考Chen等[22]的方法并做以下修改。脱脂核桃粕经凯氏定氮法测定蛋白质含量并冷冻干燥。将脱脂核桃粕以5%的浓度溶于蒸馏水中,100 ℃沸水浴15 min,以底物与酶比为20:1(w/w)加入胰蛋白酶,pH8.0、55 ℃的条件下水解4 h。然后在100 ℃的沸水浴中加热15 min使酶失活,上清液调至中性,将样品以4000 r/min离心15 min,将上清液冷冻干燥。将酶解物于4 ℃中进行超滤分离,收集<3 kDa的组分并冻干,通过三氯乙酸-可溶性氮法测定该组分肽得率为82.86%。后续称取不同质量的冻干粉进行细胞及动物实验。
1.2.2 细胞的分化与培养
3T3-L1前脂肪细胞在加入含有10%胎牛血清(FBS)、1%双抗的高糖DMEM培养基于37 ℃、5% CO2,饱和湿度条件下培养。将3T3-L1前脂肪细胞以 2.5×104个/mL接种于6孔细胞培养板,待细胞达到汇合状态后培养2 d。弃去细胞培养液,使用含诱导分化培养基A(含10 μg/mL胰岛素、1 μmol/L地塞米松、500 μmol/L IBMX、10 nmol/L T3、0.125 mmol/L吲哚美辛)作用2 d;2 d后,换诱导分化培养基B(含10 μg/mL胰岛素、10 nmol/L T3)、10% FBS、1%双抗的高糖DMEM培养基)培养6 d。分化过程中每2 d更换一次培养基,至分化开始第8 d形成成熟的脂肪细胞,分别在第0、2、4、6 d加入终浓度为0.25、1.00 mg/mL的核桃肽干预,分化结束后分别进行油红O染色、Western blot等实验。
1.2.3 相对细胞存活率的测定
将细胞以2.5×104个/mL的密度接种至96孔板中,贴壁24 h后,加入不同终浓度(0.01~16.00 mg/mL)的核桃肽与细胞共同作用48 h,空白对照组添加等量PBS。培养结束后每孔加入20 μL MTT溶液(5.0 mg/mL),培养4 h后,取出。轻轻吸出孔板中的培养基,每孔加入180 μL DMSO溶液,在570 nm下检测吸光值(Absorbance value,Abs)。相对细胞存活率按下式计算:
相对细胞存活率(%)=Abs处理组Abs空白组×100 式中:Abs处理组代表核桃肽干预组的吸光值,Abs空白组代表空白对照组的吸光值。
1.2.4 油红O染色
将2.4 mL油红O原液与1.6 mL ddH2O混合后过滤,制成油红O溶液。使用PBS(pH7.4)洗涤细胞,使用4%多聚甲醛固定细胞1 h。固定完成后用60%异丙醇洗涤细胞,并在室温下用油红O溶液染色15 min,用显微镜观察染色细胞并进行拍照。除去油红O染料后,用PBS清洗细胞多次,向孔中加入200 μL的异丙醇,轻轻吹打均匀,随后将提取液逐孔转移至另一96孔板,并使用酶标仪检测510 nm 波长处吸光度(Optical density,OD)值。
1.2.5 线粒体数量的测定及细胞免疫荧光染色
将细胞6孔板内加入适量的培养基覆盖盖玻片进行爬片培养,根据1.2.2中的方法分化3T3-L1脂肪细胞,用4%多聚甲醛固定5 min,Triton X-100通透10 min。随后用5%牛血清白蛋白封闭30 min后,加入UCP1抗体(1:500)在4 °C下孵育过夜。用PBS洗涤细胞3次,用FITC标记山羊抗兔IgG(H+L)以1:500的稀释度孵育2 h。细胞核用Hoechst 33342 染色10 min后,用PBS冲洗3次。最后,用预热的Mito-Tracker Deep Red FM染色工作液在37 ℃培养条件下孵育30 min。染色结束后,用PBS冲洗细胞3次,使用新鲜培养液或缓冲液替换上述染色液,将其置于激光共聚焦显微镜下观察。利用Image J软件计算相对荧光强度。
1.2.6 Western blot测定UCP1、PGC-1α、PRDM16、PPARα相对蛋白表达量
对于细胞蛋白的提取,3T3-L1脂肪细胞在分化过程中分别利用核桃肽(0.25、1.00 mg/mL)、GW6471 (PPARα 抑制剂)(10 μmol/L)干预,或利用 1.00 mg/mL 核桃肽和10 μmol/L的GW6471共同干预。分化结束后,在细胞培养皿中加入细胞裂解液及蛋白酶磷酸酶抑制剂,进行超声破碎,制备细胞裂解液。对于腹股沟脂肪组织蛋白的提取,利用匀浆机在添加蛋白酶磷酸酶抑制剂混合物的RIPA裂解液中均匀化脂肪组织,获得组织匀浆。将细胞裂解液或组织匀浆于 4 ℃、12000 r/min离心15 min取上清液,BCA法测定蛋白浓度。加入5×上样缓冲液和细胞裂解液调整各组蛋白浓度一致。蛋白样品用10%~15% SDS-PAGE电泳进行分离,利用湿转法于冰水浴中恒流 200 mA,转膜2 h。将PVDF膜放入5%脱脂乳中封闭1 h,随后分别转移到稀释后的一抗(anti-UCP1、anti-PGC-1α、anti-PRDM16、anti-PPARα抗体)溶液中4 ℃孵育过夜。1×TBST溶液洗5次,每次5 min,之后将PVDF膜放入稀释后的二抗溶液中孵育1 h,随后用1×TBST洗5次,每次5 min。将ECL发光液的A、B液等体积混合反应1 min后,均匀加到膜上,置于凝胶成像仪中进行发光检测并利用Image J软件进行光密度值分析。
1.2.7 高脂饮食肥胖小鼠模型的建立及分组
动物实验程序按照机构伦理委员会关于动物福利的规定进行,由郑州大学实验动物福利和伦理委员会批准(批准号:ZZU-LAC2022090607)。健康C57BL/6J雄性小鼠自由饮水摄食,在22±1 ℃、12 h:12 h日夜循环的环境中适应1周。之后,将小鼠随机分为3组,正常对照组(ND组,n=10)饲喂普通饲料,高脂饮食组(HFD组,n=10)饲喂高脂饲料。核桃肽组(WPP组,n=10)在高脂饮食的基础上灌胃400 mg/kg BW核桃肽[22−24],持续8周。当HFD组小鼠体重是ND组小鼠1.2倍以上时证明建模成功[25]。小鼠饲养期间每周记录体重及摄食量。实验结束后,将小鼠处死,收集血液及脂肪组织置于−80 ℃保存。根据脂肪组织重量与小鼠体重的比值计算脂肪指数。
1.2.8 血脂水平的测定
小鼠处死后血液于室温放置2 h,在1000×g下4 ℃离心20 min,分离上层血清,置于−80 ℃保存。采用全自动生化分析仪检测血清中TG、TC、HDL-C和LDL-C的浓度。
1.2.9 口服葡萄糖耐量(Oralglucose tolerance test,OGTT)的测定
小鼠采用核桃肽干预8周后,过夜禁食,灌胃葡萄糖(2.0 g/kg b.w.)。在灌胃葡萄糖之前(0 min)和灌胃葡萄糖之后30 、60、90及120 min尾尖采血,用血糖仪测定血糖水平。采用 GraphPad Prism 8.0软件计算曲线下面积(Area under curve,AUC)。
1.2.10 苏木精-伊红染色(Hematoxylin-eosin staining,H&E)及免疫组织化学(IHC)染色
取新鲜的腹股沟脂肪组织,用生理盐水冲洗,放入4%多聚甲醛内固定24 h,石蜡包埋。然后将固定的组织切片成5 μm的薄片,装在玻片上。切片去蜡,H&E染色进行形态学观察。此外,利用10%山羊血清室温封闭30 min,PBS清洗后用UCP1一抗(1:200)孵育过夜、二抗室温孵育1 h。DAB溶液显色,脱水,封片。使用Image Scope软件测定分析脂肪细胞面积,Image J软件分析代表UCP1表达量的IHC平均光密度值。
1.3 数据处理
结果表示为平均值±标准差。采用版本为23.0的SPSS软件进行统计分析。当多组数据间进行显著性分析时,使用单因素方差分析(One way ANOVA)伴随 Duncan多重比较,当P<0.05认为具有显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 核桃肽对3T3-L1相对细胞存活率及脂质积累的影响
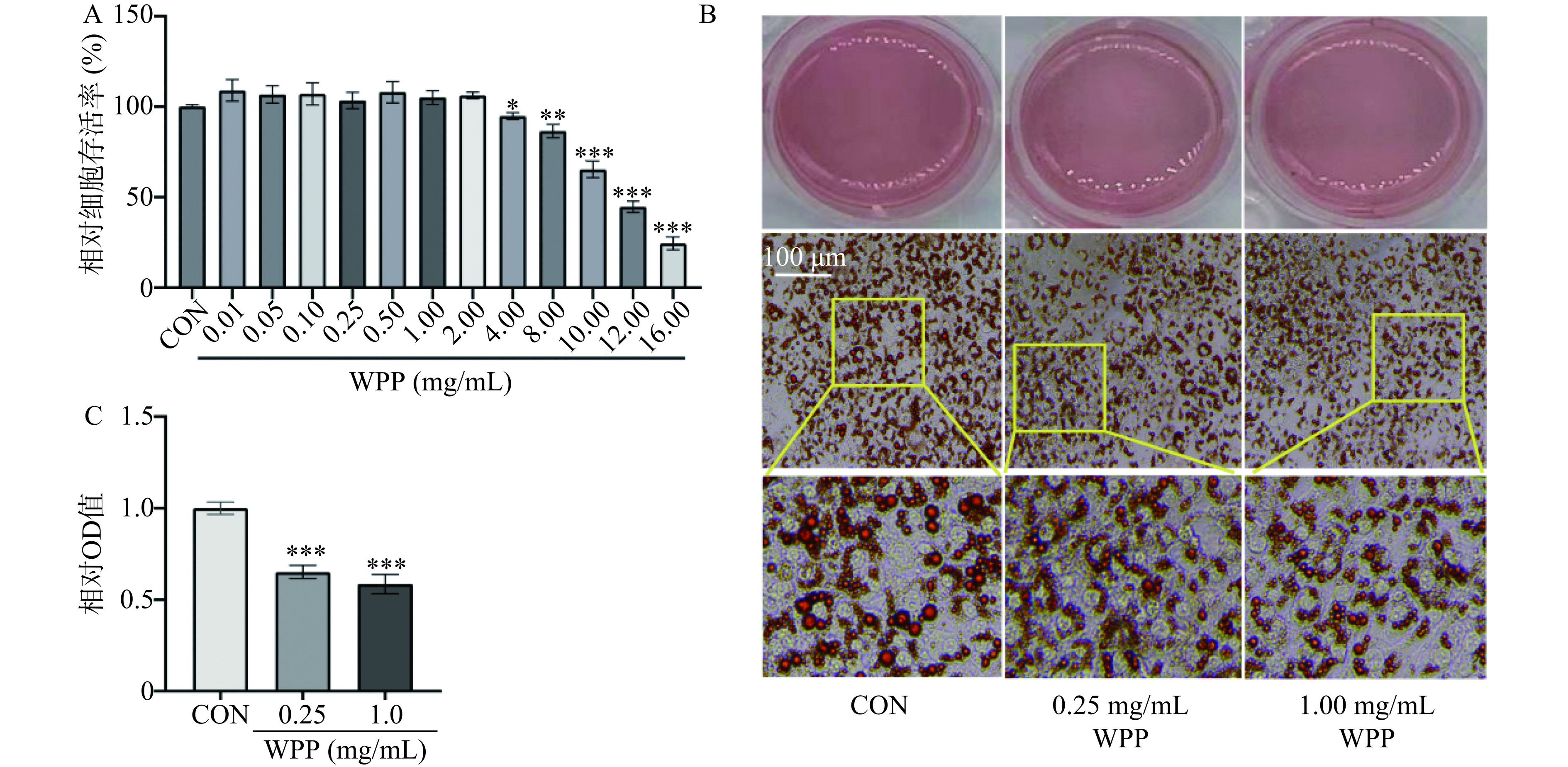
为了确定核桃肽的安全作用剂量,利用MTT法对相对细胞存活率进行检测。如图1A所示,相比于空白对照组细胞,0.01~2.0 mg/mL的核桃肽干预48 h后对相对细胞存活率没有显著影响(P>0.05);随着核桃肽浓度的增加(4.0~16.0 mg/mL),相对细胞存活率显著下降(P<0.05)。根据相关文献报道,核桃肽在0.10~1.00 mg/mL的浓度范围内对HT22细胞和RAW264.7细胞的相对细胞存活率没有影响[26−27]。因此,综合图1A的结果,后续实验中选择0.25 mg/mL和1.00 mg/mL的核桃肽进行研究。为了探究核桃肽对3T3-L1脂肪细胞脂质积累的影响,利用油红O染色法测定脂质水平。结果显示,在细胞分化的第8 d,与空白对照组相比,0.25和1.00 mg/mL的核桃肽干预能减少3T3-L1脂肪细胞的脂滴大小(图1B);分析油红O染色相对OD值结果显示,核桃肽组的相对OD值极显著降低(P<0.001),说明核桃肽降低了细胞脂质水平(图1C)。
![]() 图 1 核桃肽对3T3-L1脂肪相对细胞存活率及脂质积累的影响注:A. 相对细胞存活率;B. 油红O染色;C. 油红O染色相对OD值。与空白对照组比较,*表示差异显著,P<0.05,**表示差异非常显著,P<0.01,***表示差异极显著,P<0.001,图2同。Figure 1. Effects of walnut protein peptides on the cell viability and lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
图 1 核桃肽对3T3-L1脂肪相对细胞存活率及脂质积累的影响注:A. 相对细胞存活率;B. 油红O染色;C. 油红O染色相对OD值。与空白对照组比较,*表示差异显著,P<0.05,**表示差异非常显著,P<0.01,***表示差异极显著,P<0.001,图2同。Figure 1. Effects of walnut protein peptides on the cell viability and lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes2.2 核桃肽对3T3-L1脂肪细胞线粒体数量的影响
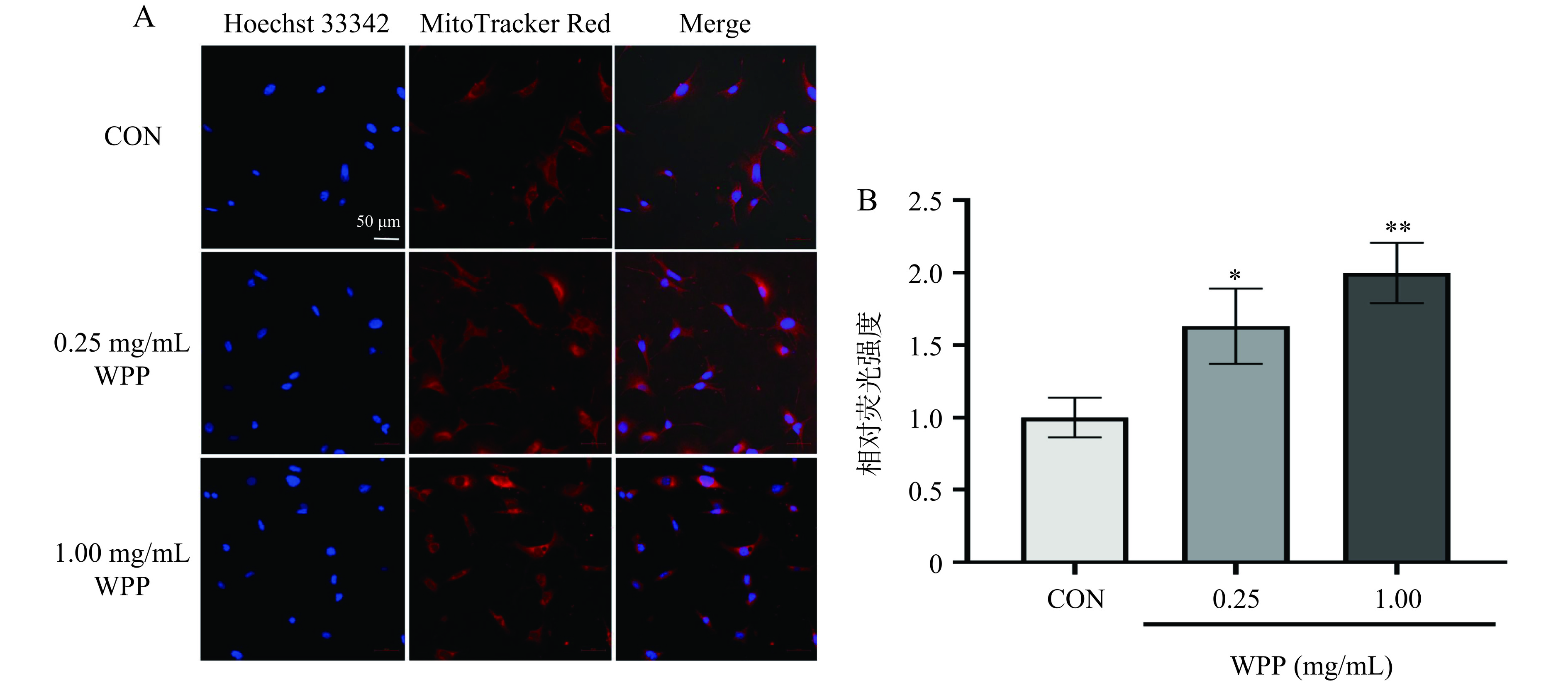
线粒体生物合成是细胞增加线粒体质量和线粒体DNA拷贝数的过程,对米色细胞的产热有重要影响[28]。代谢紊乱与线粒体丢失和功能障碍有关,通过营养及药理干预诱导线粒体增殖可改善胰岛素信号传导和能量代谢[29]。为了探究核桃肽对3T3-L1脂肪细胞线粒体数量的影响,利用红色荧光染料MitoTracker Red对线粒体进行染色,根据荧光强度的变化来表示线粒体数量的变化。如图2A、2B所示,相比于空白对照组细胞,0.25、1.00 mg/mL的核桃肽处理细胞至分化结束能够显著增加红色荧光强度(P<0.05或P<0.01);其中,1.0 mg/mL核桃肽干预组MitoTracker Red相对荧光强度相比空白对照组增加了99.88%±19.09%,说明核桃肽干预增加了3T3-L1脂肪细胞的线粒体数量。与本研究结果类似,Liu等[30]研究证明核桃小分子寡肽具有良好的抗疲劳作用,其机制可能与改善能量代谢、增强骨骼肌线粒体功能如增加线粒体生物合成、增加线粒体数量有关。
2.3 核桃肽对3T3-L1脂肪细胞棕色化标志物蛋白表达的影响
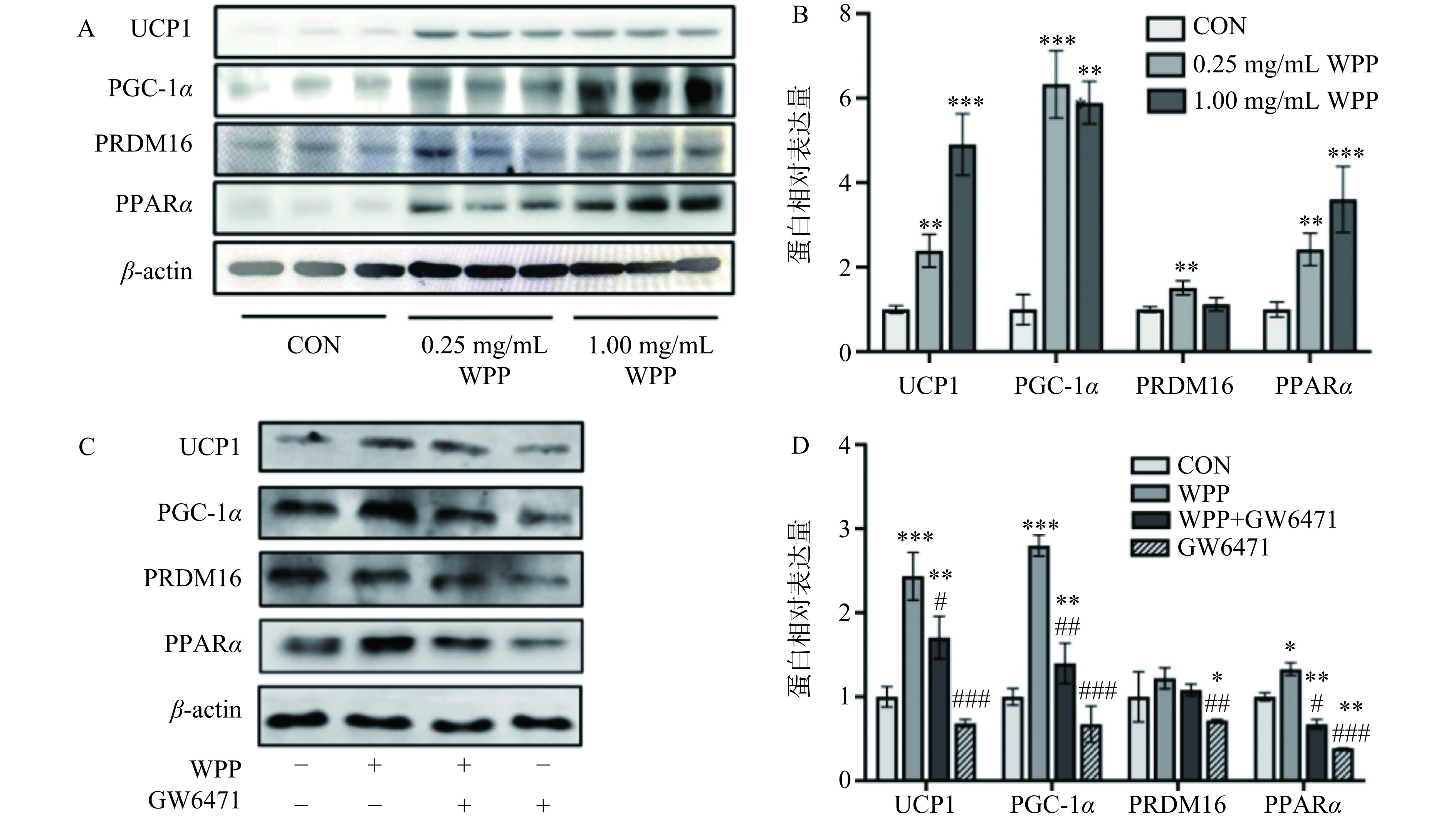
为了验证核桃肽是否可以促进3T3-L1前脂肪细胞的棕色化,测定了核桃肽对细胞中棕色化标志物(UCP1、PGC-1α、PRDM16、PPARα)蛋白表达的影响。如图3A、3B所示,与空白对照组细胞相比,0.25、1.00 mg/mL的核桃肽处理细胞至分化结束后,明显增加了3T3-L1细胞中UCP1、PGC-1α、PRDM16、PPARα的相对蛋白表达量,其中1.0 mg/mL的核桃肽处理使UCP1、PGC-1α、PPARα的表达量分别增加至4.90±0.73倍(P<0.001)、5.89±0.50倍(P<0.01)、3.60±0.78倍(P<0.001);0.25 mg/mL核桃肽处理使PRDM16的相对蛋白表达量增加至1.51±0.17倍(P<0.01)。
![]() 图 3 核桃肽对3T3-L1脂肪细胞棕色化关键因子蛋白表达的影响注:A. 免疫印迹图;B. 蛋白相对表达量;C. GW6471处理的免疫印迹图;D. GW6471处理的蛋白相对表达量。与空白对照组比较,*表示差异显著,P<0.05,**表示差异非常显著,P<0.01,***表示差异极显著,P<0.001;与WPP单独处理组比较,#表示差异显著,P<0.05,##表示差异非常显著,P<0.01,###表示差异极显著,P<0.001。Figure 3. Effect of walnut protein peptides on the protein expression of browning markers in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
图 3 核桃肽对3T3-L1脂肪细胞棕色化关键因子蛋白表达的影响注:A. 免疫印迹图;B. 蛋白相对表达量;C. GW6471处理的免疫印迹图;D. GW6471处理的蛋白相对表达量。与空白对照组比较,*表示差异显著,P<0.05,**表示差异非常显著,P<0.01,***表示差异极显著,P<0.001;与WPP单独处理组比较,#表示差异显著,P<0.05,##表示差异非常显著,P<0.01,###表示差异极显著,P<0.001。Figure 3. Effect of walnut protein peptides on the protein expression of browning markers in 3T3-L1 adipocytes研究表明,PPARα激动剂可诱导PGC-1α和PRDM16的转录,激活白色脂肪棕色化[31]。为了探究核桃肽是否通过激活PPARα发挥产热活性,采用PPARα抑制剂(GW6471)处理细胞,探究其对核桃肽介导的白色脂肪棕色化的影响。如图3C和3D所示,相比于空白对照组,核桃肽单独处理显著增加了UCP1、PGC-1α以及PPARα的蛋白表达(P<0.05,P<0.001)。而相比于核桃肽处理组,PPARα抑制剂GW6471的进一步加入则阻碍了核桃肽对UCP1、PGC-1α以及PPARα蛋白表达的促进作用(P<0.05,P<0.01)。多项研究表明长期补充PPARα激活剂能诱导WAT棕色化,减轻肥胖,改善代谢紊乱[32−33]。与本研究类似,许多食源多肽,如α-乳白蛋白酶解物[34]、荞麦球蛋白水解物[35]、糙米蛋白水解物等[36],都可以通过激活PPARα基因或蛋白表达预防和缓解高脂饮食造成的糖脂代谢紊乱。因此,推测核桃肽可能通过促进3T3-L1脂肪细胞中PPARα的表达,激活其下游白色脂肪棕色化标志物的表达。
2.4 核桃肽对肥胖小鼠体重及脂肪蓄积的影响
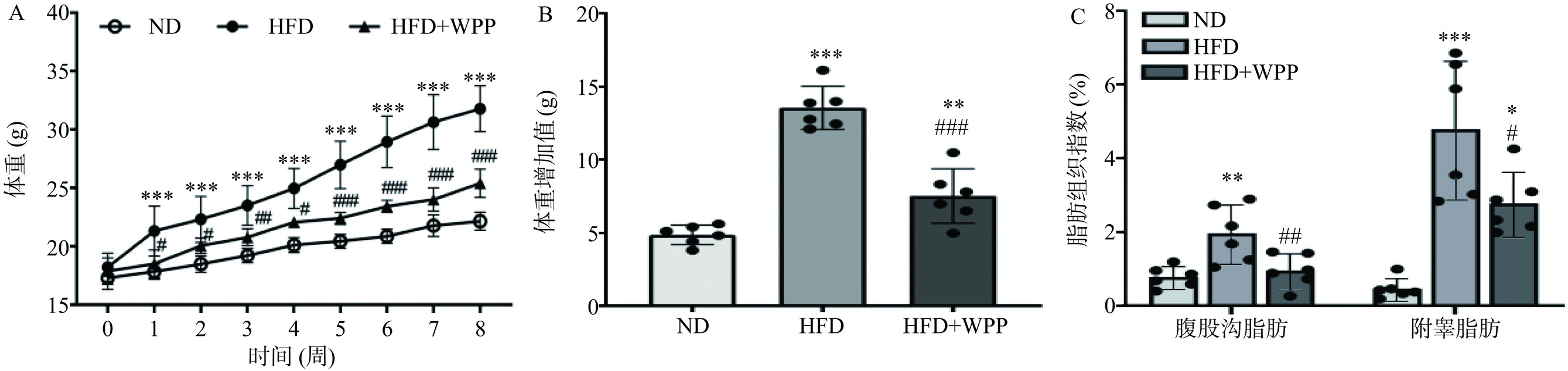
在明确了核桃肽在体外促进白色脂肪棕色化的效果后,进一步利用HFD建立C57BL/6J肥胖小鼠模型,探究核桃肽在体内的效果。如图4A所示,HFD干预前各组小鼠的体重没有显著性的差异,HFD干预8周后,与ND组小鼠相比,HFD极显著增加了小鼠体重至ND组小鼠的1.43倍(P<0.001),达到肥胖模型的标准[37]。如图4B所示,核桃肽干预8周后,小鼠体重增加值相比于HFD组极显著降低了44.17%±14.36%(P<0.001),说明核桃肽能够减轻肥胖小鼠的体重。肥胖通常伴随白色脂肪的蓄积,因此进一步测定了白色脂肪组织质量的变化。如图4C所示,与ND组相比,HFD显著增加了白色脂肪(腹股沟脂肪、附睾脂肪)指数(P<0.01,P<0.001),而核桃肽干预则显著降低了这些脂肪组织的质量,腹股沟、附睾脂肪指数相比HFD组分别降低了51.27%(P<0.01)和41.83%(P<0.05)。这些结果说明核桃肽干预能够缓解肥胖造成的体重增加以及白色脂肪蓄积。
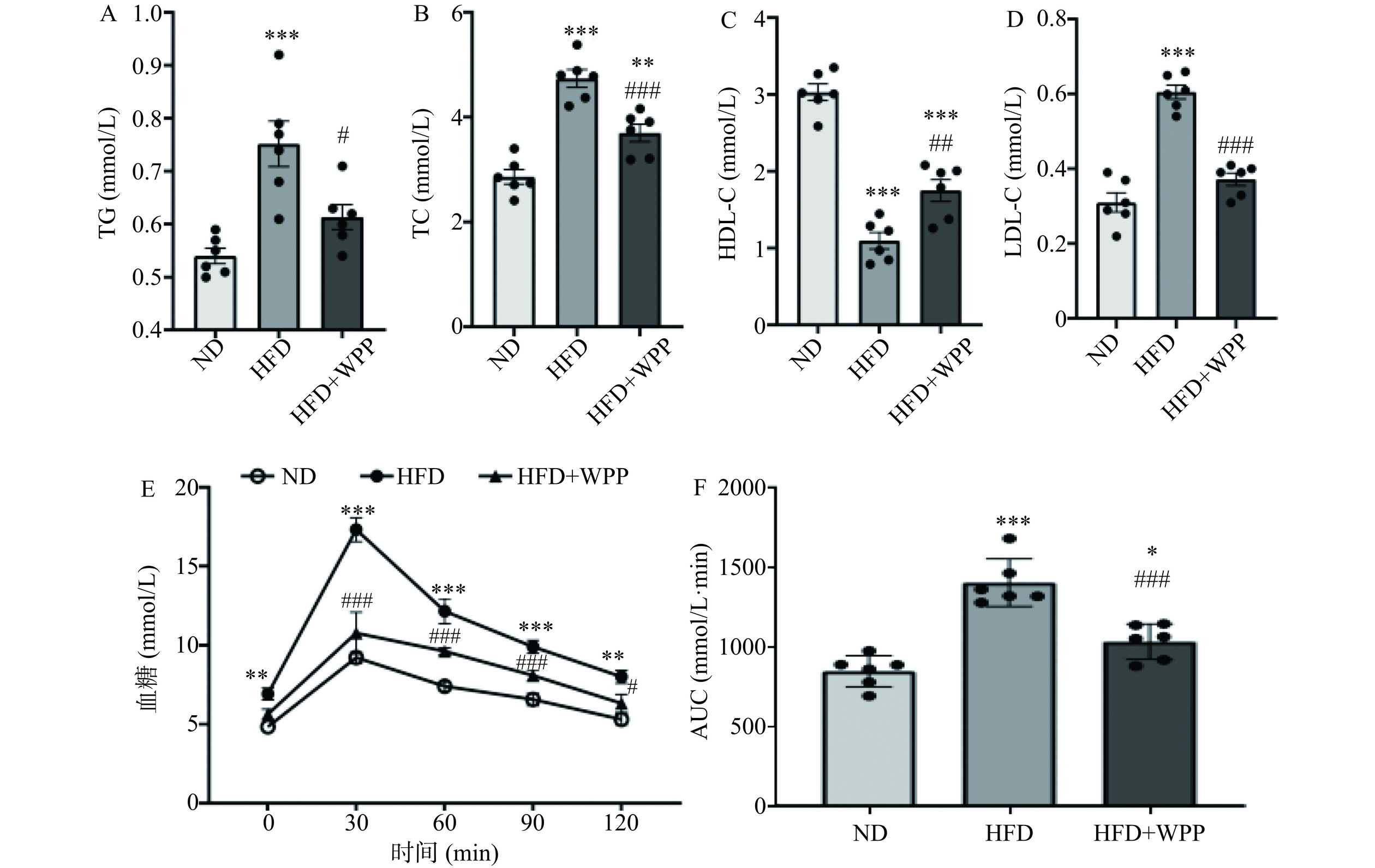
2.5 核桃肽对肥胖小鼠血脂水平及葡萄糖耐受能力的影响
已有研究表明,HFD造成的肥胖伴随着血清中脂质水平的紊乱及高血脂症的发生发展[38]。脂肪组织的蓄积能够进一步引发血脂异常,为了探究核桃肽对肥胖小鼠血脂水平的影响,测定了血清中TG、TC、HDL-C和LDL-C水平的变化。如图5A~D所示,相比于ND组小鼠,HFD组小鼠血清TG、TC、LDL-C的浓度水平极显著增加(P<0.001),HDL-C浓度水平极显著下降(P<0.001)。相比于HFD组,核桃肽干预后血清中TG、TC、LDL-C的浓度水平显著下降了18.40%±3.57%(P<0.05)、21.91%±2.87%(P<0.001)、38.57%±4.65%(P<0.001),HDL-C浓度水平非常显著增加至1.60±0.67倍(P<0.01)。与本研究结果一致,Yang等[21]研究发现饲喂核桃粕多肽可抵消高脂饲料引起的体重、附睾脂肪重量增加,并降低血清TG、TC和LDL-C的浓度。说明核桃肽改善了肥胖小鼠的血脂水平紊乱。
研究表明,肥胖会引起胰岛素抵抗和葡萄糖不耐受,最终导致2型糖尿病的发生[39]。在肥胖个体中,脂肪组织释放的游离脂肪酸、甘油、激素、促炎细胞因子等含量增加,激活炎症通路,引起胰岛素抵抗[40]。因此,为了探究核桃肽对肥胖小鼠葡萄糖耐受的作用,进行了口服葡萄糖耐量试验(OGTT)。如图5E,口服葡萄糖后,ND组小鼠的血糖在0~30 min内明显增高,随后逐渐下降,并在120 min时接近0 min血糖值水平。与ND组小鼠相比,HFD组小鼠在0、30、60、90和120 min各个时刻的血糖均显著升高(P<0.01,P<0.001),经过核桃肽处理后,小鼠血糖显著下降(P<0.05,P<0.001)。图5F所示为图5E的曲线下面积结果,可以看出与ND组小鼠(847.50±98.46 mmol/L·min)相比,HFD 组小鼠OGTT 的AUC(1404.75±150.21 mmol/L·min)极显著增(P<0.001),说明其葡萄糖耐受能力受损;而经过核桃肽干预后,AUC值极显著低于HFD组(P<0.001),说明核桃肽可以增强肥胖小鼠葡萄糖耐受能力。与本研究结果类似的是,李丽等[41]研究表明在2型糖尿病动物模型中核桃肽有良好的降糖活性,且核桃肽的降糖效果优于核桃蛋白。Hou等[42]利用链脲霉素联合HFD建立2型糖尿病小鼠模型,发现核桃衍生肽混合物(3~10 kDa)和核桃五肽LPLLR可降低血糖和空腹胰岛素水平,改善胰岛素抵抗和血脂异常。因此,本结果证明了核桃肽对肥胖相关糖脂代谢紊乱具有一定的改善作用。
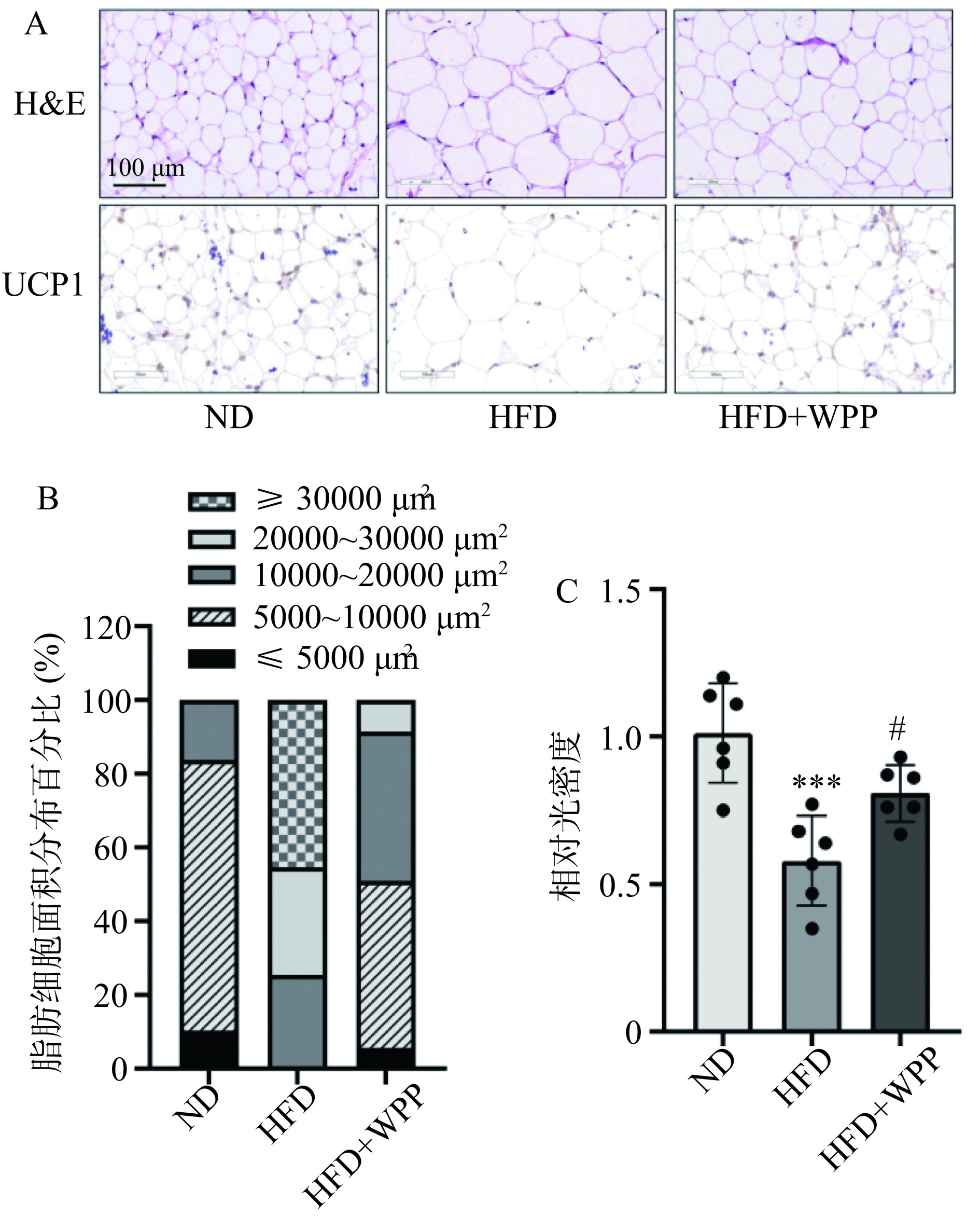
2.6 核桃肽对HFD小鼠腹股沟脂肪组织形态的影响
采用H&E染色观察脂肪细胞形态变化,并利用免疫组化技术分析表达棕色化标志物UCP1的阳性细胞数量,初步探究核桃肽对腹股沟白色脂肪棕色化的影响。如图6A 所示,相比于 ND 组,HFD 组增加了脂肪细胞的直径,而核桃肽干预能够明显降低脂肪细胞的直径。如图6B所示,按平均面积计算,ND组面积为5000~10000 µm2和10000~20000 µm2的脂肪细胞占比分别为73.43%和16.23%;HFD组脂肪细胞平均面积大于30000 µm2的细胞占比为45.34%;而核桃肽处理后,脂肪细胞平均面积降低,平均面积多分布在5000~10000 µm2(45.32%)和10000~20000 µm2(40.45%)之间。如图6C所示,HFD组腹股沟脂肪中UCP1阳性脂肪细胞的数量极显著低于ND组(P<0.001)。相比于HFD组,核桃肽干预肥胖小鼠显著增加了UCP1阳性细胞数量,平均光密度值增加至1.39倍(图6C)(P<0.05)。这些结果说明核桃肽能够缓解肥胖小鼠腹股沟脂肪细胞的扩增,并初步证明了核桃肽的促白色脂肪棕色化作用。
2.7 核桃肽对HFD小鼠腹股沟脂肪中棕色化标志物蛋白表达的影响
棕色脂肪和米色脂肪是小鼠适应性产热的主要部位,其活性可显著影响全身能量消耗;缺乏棕色脂肪的小鼠对于肥胖易感,而增加小鼠棕色/米色脂肪活性则能够缓解 HFD造成的代谢紊乱,如肥胖和胰岛素抵抗[43]。为了进一步探究核桃肽干预肥胖小鼠对腹股沟脂肪棕色化的影响,测定了棕色化标志物(UCP1、PGC-1α、PRDM16、PPARα)蛋白表达的变化。如图7A、7B所示,与ND组相比,HFD显著降低了腹股沟脂肪中UCP1、PGC-1α、PRDM16、PPARα的蛋白表达水平(P<0.05,P<0.001),而核桃肽干预则显著增加了PGC-1α、PRDM16、PPARα的蛋白表达水平,分别增加至1.31(P<0.01)、1.51(P<0.01)及2.07倍(P<0.001),且UCP1蛋白相对表达量有上升趋势(0.76±0.04 增加至0.88±0.10)。这些结果表明核桃肽干预肥胖小鼠促进了腹股沟白色脂肪的棕色化程度。与本研究类似,在一项研究中,核桃肽被证明能够增加衰老加速小鼠模型中腓肠肌组织中线粒体DNA含量,提高PGC-1α等的表达水平,从而改善线粒体功能[44]。此外,鲑鱼蛋白水解物能够促进血清中胆汁酸浓度升高,增加棕色脂肪组织中参与能量代谢和解偶联的基因Pgc-1α和Ucp1的表达,从而缓解饮食造成的肥胖及代谢综合征[45],说明了食源活性肽在改善能量代谢中具有潜在的益处。因此,本研究的结果进一步证明了核桃肽能够通过促进白色脂肪组织中棕色化关键蛋白的表达来预防高脂饮食造成的肥胖。
3. 结论
本研究利用3T3-L1脂肪细胞和HFD肥胖小鼠模型,对核桃肽促进白色脂肪棕色化、预防肥胖的作用进行探究。结果表明,核桃肽可降低3T3-L1脂肪细胞的脂质积累、增加线粒体数量,增加脂肪棕色化关键因子UCP1、PGC-1α、PRDM16、PPARα的蛋白表达水平。对于HFD肥胖小鼠,核桃肽可缓解体重过度增加、改善血清血脂水平和葡萄糖耐受能力;同时,核桃肽改善了HFD小鼠腹股沟白色脂肪的过度积累,降低平均脂肪细胞面积,增加UCP1阳性细胞数量,上调棕色化关键因子UCP1、PGC-1α、PRDM16、PPARα的蛋白表达水平。本实验通过以上研究,为核桃肽抗肥胖功能性产品的开发提供了科学依据,为进一步探讨其促进白色脂肪棕色化和能量代谢的作用机制提供了一定的理论基础。
-
图 1 核桃肽对3T3-L1脂肪相对细胞存活率及脂质积累的影响
注:A. 相对细胞存活率;B. 油红O染色;C. 油红O染色相对OD值。与空白对照组比较,*表示差异显著,P<0.05,**表示差异非常显著,P<0.01,***表示差异极显著,P<0.001,图2同。
Figure 1. Effects of walnut protein peptides on the cell viability and lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
图 3 核桃肽对3T3-L1脂肪细胞棕色化关键因子蛋白表达的影响
注:A. 免疫印迹图;B. 蛋白相对表达量;C. GW6471处理的免疫印迹图;D. GW6471处理的蛋白相对表达量。与空白对照组比较,*表示差异显著,P<0.05,**表示差异非常显著,P<0.01,***表示差异极显著,P<0.001;与WPP单独处理组比较,#表示差异显著,P<0.05,##表示差异非常显著,P<0.01,###表示差异极显著,P<0.001。
Figure 3. Effect of walnut protein peptides on the protein expression of browning markers in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
-
[1] LIU X, ZHANG Z, SONG Y, et al. An update on brown adipose tissue and obesity intervention:Function, regulation and therapeutic implications[J]. Frontiers in Endocrinology,2023,13:1065263. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1065263
[2] PAN R, CHEN Y. Latest advancements on combating obesity by targeting human brown/beige adipose tissues[J]. Frontiers in Endocrinology,2022,13:884944. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.884944
[3] REYES-FARIAS M, FOS-DOMENECH J, SERRA D, et al. White adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity and aging[J]. Biochemical Pharmacology,2021,192:114723. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114723
[4] CHOUCHANI E T, KAZAK L, SPIEGELMAN B M. New advances in adaptive thermogenesis:UCP1 and beyond[J]. Cell Metabolism,2019,29(1):27−37. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.11.002
[5] MONTANARI T, POŠĆIĆ N, COLITTI M. Factors involved in white‐to‐brown adipose tissue conversion and in thermogenesis:A review[J]. Obesity Reviews,2017,18(5):495−513. doi: 10.1111/obr.12520
[6] KURYŁOWICZ A, PUZIANOWSKA-KUŹNICKA M. Induction of adipose tissue browning as a strategy to combat obesity[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2020,21(17):6241. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176241
[7] SEALE P, KAJIMURA S, YANG W, et al. Transcriptional control of brown fat determination by PRDM16[J]. Cell Metabolism,2007,6(1):38−54. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.06.001
[8] HARMS M J, ISHIBASHI J, WANG W, et al. Prdm16 is required for the maintenance of brown adipocyte identity and function in adult mice[J]. Cell Metabolism,2014,19(4):593−604. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.03.007
[9] IIDA S, CHEN W, NAKADAI T, et al. PRDM16 enhances nuclear receptor-dependent transcription of the brown fat-specific Ucp1 gene through interactions with Mediator subunit MED1[J]. Genes & Development,2015,29(3):308−321.
[10] SHARP L Z, SHINODA K, OHNO H, et al. Human BAT possesses molecular signatures that resemble beige/brite cells[J]. PloS One,2012,7(11):e49452. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049452
[11] KLEINER S, MEPANI R J, LAZNIK D, et al. Development of insulin resistance in mice lacking PGC-1α in adipose tissues[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2012,109(24):9635−9640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1207287109
[12] HONDARES E, ROSELL M, DÍAZ-DELFÍN J, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) induces PPARγ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) gene expression and contributes to thermogenic activation of brown fat:Involvement of PRDM16[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2011,286(50):43112−43122. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.252775
[13] CHENG L, WANG J, DAI H, et al. Brown and beige adipose tissue:A novel therapeutic strategy for obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Adipocyte,2021,10(1):48−65. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2020.1870060
[14] CHAUHAN A, CHAUHAN V. Beneficial effects of walnuts on cognition and brain health[J]. Nutrients,2020,12(2):550. doi: 10.3390/nu12020550
[15] WEN C, ZHANG Z, CAO L, et al. Walnut protein:A rising source of high-quality protein and its updated comprehensive review[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2023,71(28):10525−10542. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c01620
[16] KONG X, ZHANG L, SONG W, et al. Separation, identification and molecular binding mechanism of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides derived from walnut (Juglans regia L.) protein[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,347:129062. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129062
[17] LIU D, GUO Y, MA H. Production, bioactivities and bioavailability of bioactive peptides derived from walnut origin by-products:A review[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2023,63(26):8032−8047. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2054933
[18] ZEC M M, KRGA I, TAKIĆ M, et al. Walnut consumption induces tissue-specific omega-6/omega-3 decrease in high-fructose-fed Wistar rats[J]. ACS Omega,2020,5(43):28136−28145. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03784
[19] LI Y, CHEN D, ZHANG F, et al. Preventive effect of pressed degreased walnut meal extracts on T2DM rats by regulating glucolipid metabolism and modulating gut bacteria flora[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,64:103694. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103694
[20] WANG J, WU T, FANG L, et al. Anti-diabetic effect by walnut (Juglans mandshurica Maxim.)-derived peptide LPLLR through inhibiting α-glucosidase and α-amylase, and alleviating insulin resistance of hepatic HepG2 cells[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,69:103944. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.103944
[21] YANG X Y, ZHONG D Y, WANG G L, et al. Effect of walnut meal peptides on hyperlipidemia and hepatic lipid metabolism in rats fed a high-fat diet[J]. Nutrients,2021,13(5):1410. doi: 10.3390/nu13051410
[22] CHEN H, ZHAO M, LIN L, et al. Identification of antioxidative peptides from defatted walnut meal hydrolysate with potential for improving learning and memory[J]. Food Research International,2015,78:216−223. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2015.10.008
[23] LI W, ZHAO T, ZHANG J, et al. Comparison of neuroprotective and cognition-enhancing properties of hydrolysates from soybean, walnut, and peanut protein[J]. Journal of Chemistry,2016,2016:9358285.
[24] YUAN Y, WANG X, WANG Y, et al. The gastroprotective effect of walnut peptides:Mechanisms and impact on ethanol-induced acute gastric mucosal injury in mice[J]. Nutrients,2023,15(23):4866. doi: 10.3390/nu15234866
[25] JISUN P, YVETTE F, ROLF D, et al. Effects of murine norovirus infection on a mouse model of diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance[J]. Comparative Medicine,2010,60(3):189−195.
[26] ZHANG Z, SHANG Y, LI S, et al. Molecular docking revealed the potential anti-oxidative stress mechanism of the walnut polypeptide on HT22 cells[J]. Foods,2023,12(7):1554. doi: 10.3390/foods12071554
[27] WANG Q, ZHI T, HAN P, et al. Potential anti-inflammatory activity of walnut protein derived peptide leucine-proline-phenylalanine in lipopolysaccharides-irritated RAW264.7 cells[J]. Food and Agricultural Immunology,2021,32(1):663−678. doi: 10.1080/09540105.2021.1982870
[28] ZHAO B, LIU M, LIU H, et al. Zeaxanthin promotes browning by enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis through the PKA pathway in 3T3-L1 adipocytes[J]. Food & Function,2021,12(14):6283−6293.
[29] ZENG C, CHEN M. Progress in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:SIRT family regulates mitochondrial biogenesis[J]. Biomolecules,2022,12(8):1079. doi: 10.3390/biom12081079
[30] LIU R, WU L, DU Q, et al. Small molecule oligopeptides isolated from walnut (Juglans regia L.) and their anti-fatigue effects in mice[J]. Molecules,2018,24(1):45. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010045
[31] LI T, DU M, WANG H, et al. Milk fat globule membrane and its component phosphatidylcholine induce adipose browning both in vivo and in vitro[J]. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2020,81:108372. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108372
[32] RACHID T L, PENNA-DE-CARVALHO A, BRINGHENTI I, et al. Fenofibrate (PPARalpha agonist) induces beige cell formation in subcutaneous white adipose tissue from diet-induced male obese mice[J]. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology,2015,402:86−94. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.12.027
[33] GOTO T, HIRATA M, AOKI Y, et al. The hepatokine FGF21 is crucial for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α agonist-induced amelioration of metabolic disorders in obese mice[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2017,292(22):9175−9190. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.767590
[34] GAO J, SONG J, DU M, et al. Bovine α-lactalbumin hydrolysates (α-LAH) attenuate high-fat diet induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating hepatic lipid metabolism in C57BL/6J mice[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2019,54:254−262. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.01.027
[35] ZHOU Y, WANG T, SHE X, et al. Pretreatment of buckwheat globulin by ultra-high pressure:Effects on enzymatic hydrolysis and final hydrolysate lipid metabolism regulation capacities[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,379:132102. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132102
[36] ZHANG H, BARTLEY G E, MITCHELL C R, et al. Lower weight gain and hepatic lipid content in hamsters fed high fat diets supplemented with white rice protein, brown rice protein, soy protein, and their hydrolysates[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2011,59(20):10927−10933. doi: 10.1021/jf202721z
[37] 杨兴文, 姚诗炜, 卢红伶, 等. 金松酸对高脂饮食诱导的肥胖小鼠肝脏脂质代谢的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(6):304−312. [YANG Xingwen, YAO Shiwei, LU Hongling, et al. Effect of sciadonic acid on hepatic lipid metabolism in obese mice induced by a high-fat diet[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry ,2024,45(6):304−312.] YANG Xingwen, YAO Shiwei, LU Hongling, et al. Effect of sciadonic acid on hepatic lipid metabolism in obese mice induced by a high-fat diet[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry , 2024, 45(6): 304−312.
[38] HOSOMI K, SAITO M, PARK J, et al. Oral administration of Blautia wexlerae ameliorates obesity and type 2 diabetes via metabolic remodeling of the gut microbiota[J]. Nature Communications,2022,13(1):4477. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32015-7
[39] NAGAOKA S, TAKEUCHI A, BANNO A. Plant-derived peptides improving lipid and glucose metabolism[J]. Peptides,2021,142:170577. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2021.170577
[40] KAHN S E, HULL R L, UTZSCHNEIDER K M. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes[J]. Nature,2006,444(7121):840−846. doi: 10.1038/nature05482
[41] 李丽, 黄雪梦, 杨璐嘉, 等. 采用2种降糖模型考察核桃蛋白及多肽的降糖作用[J]. 食品科技, 2017, 42(4):218−221. [LI Li, HUANG Xuemeng, YANG Lujia, et al. Comparison of blood glucose model of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and animal[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2017, 42(4):218−221.] LI Li, HUANG Xuemeng, YANG Lujia, et al. Comparison of blood glucose model of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and animal[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2017, 42(4): 218−221.
[42] HOU W, ZHAO F, FANG L, et al. Walnut-derived peptides promote autophagy via the activation of AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 pathway to ameliorate hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic mice[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2023,71(8):3751−3765. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c07112
[43] HERZ C T, KIEFER F W. Adipose tissue browning in mice and humans[J]. Journal of Endocrinology,2019,241(3):R97−R109. doi: 10.1530/JOE-18-0598
[44] FAN R, HAO Y, DU Q, et al. Beneficial effects of walnut oligopeptides on muscle loss in senescence-accelerated mouse prone-8 (SAMP8) mice:Focusing on mitochondrial function[J]. Nutrients,2022,14(10):2051. doi: 10.3390/nu14102051
[45] LIASET B, HAO Q, JØRGENSEN H, et al. Nutritional regulation of bile acid metabolism is associated with improved pathological characteristics of the metabolic syndrome[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2011,286(32):28382−28395. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.234732





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
