Inhibition Mechanism of Pleurotus citrinipileatus Sing. Ergothioneine on Pancreatic Lipase Activity
-
摘要: 为探究金顶侧耳麦角硫因的降脂作用机理,采用酶动力学、紫外吸收、内源荧光、同步荧光、三维荧光等多光谱和分子对接技术研究了其与胰脂肪酶之间的相互作用。结果表明:金顶侧耳麦角硫因对胰脂肪酶具有可逆非竞争型抑制作用,其半抑制浓度为15.29 mg/mL。紫外光谱显示随着加样浓度的升高,胰脂肪酶的肽键C=O基团产生π→π*跃迁现象,疏水性减弱,亲水性变强,极性增大。荧光光谱揭示它能改变胰脂肪酶的空间结构,以静态方式有效猝灭其内源荧光,在298 K下结合常数Ka达到1.55×103 L/mol,位点数约为1。两者结合的热力学参数焓变ΔH和熵变ΔS分别为−8.57 kJ/mol与2.55 J/(mol·K),主要以氢键与静电作用互作;同步和三维荧光发现,随着样品浓度增加,最大吸收峰分别红移6和3 nm,荧光强度分别下降32.2%和25.6%,进一步证实两者结合使胰脂肪酶分子微环境疏水性减弱,极性增强。分子对接表明,麦角硫因分子可在酶催化活性中心外以氢键、电荷吸引及范德华力结合在残基位点上,从而抑制该酶活性。本研究有助于从分子水平上深入了解金顶侧耳麦角硫因的胰脂肪酶抑制作用,为后续该类食品资源加工提供基础。Abstract: The interaction between Pleurotus citrinipileatus Sing. ergothioneine (PCEGT) and pancreatic lipase (PL) was studied by analyzing multiple spectroscopies including enzyme kinetics, ultraviolet absorption (UV), fluorescence spectroscopy, synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy and 3D fluorescence spectroscopy as well as the PCEGR-PL interaction mechanism by molecular docking in order to clarify its inhibitory mechanism. The results showed that the inhibition process of PCEGT on PL was reversible non-competitive with 15.29 mg/mL of the half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50). The UV spectrum indicated there was a π→π* transition produced by the peptide bond C=O group of PL as the mass concentration of PCEGT increased, which could reflect the reinforcement of polarity and hydrophilicity. Fluorescence spectra data revealed PCEGT could efficiently static-quench the intrinsic fluorescence of PL by changing its space structure. Based on the Lineweaver-Burk equation, the binding constants (Ka) under three different temperatures were obtained. Among them the Ka value was estimated to be 1.55×103 L/mol with approximately 1 binding site at 298 K. The thermodynamic parameters including enthalpy change and enthopy change calculated by Van't Hoff's law were to be −8.57 kJ/mol and 2.55 J/(mol·K), respectively. PCEGT might combine with the amino acid residues of PL via hydrogen bonding and electrostatic force. With the increase of the concentration of PCEGT, synchronous fluorescence intensity and 3D fluorescence spectra demonstrated that the failing hydrophobicity and incremental polarity of PL could be achieved evidencing by obvious redshifts of maximum absorption peaks (6 and 3 nm) and descent fluorescence intensities (32.2% and 25.6%). Molecular docking results further reinforced that PCEGT interacted with amino acids outside catalytic site of PL via hydrogen bonding, charge attraction and van der waals' force, resulting in the inhibition of PL. This study was beneficial for the deep understanding the hyperlipidemia of PCEGT from molecular mechanism and boosted the future health food processing of Pleurotus citrinipileatus Sing..
-
现如今肥胖越来越成为危害人类健康,导致人体生理代谢异常的主要原因。在人肠道脂肪的消化过程中,胰脂肪酶扮演着至关重要的角色,它负责水解和吸收肠腔内大部分总膳食脂肪,是脂肪分解的关键酶可使膳食中油分解成甘油,脂肪酸等小分子,这些物质又被人体吸收并参与代谢过程[1]。因此,抑制小肠内胰脂肪酶活性减少脂质的吸收,可有效预防或减少肥胖症状[2−3]。奥利司他作为常见的抑制剂会导致胃肠排气增加和脂肪泻等不良反应的发生。随着人们健康意识的不断提高,用天然型抑制剂代替合成型抑制剂已成为食品和添加剂行业发展的大势所趋。
胰脂肪酶作为重要的脂肪分解酶,包含有449个氨基酸残基的两个折叠单元,其催化活性中心是由Asp177-His264-Ser153形成的酯解位点三联结构域,它位于双缠绕平行β-折叠的C端边缘[4]。近年来,已有很多研究者针对该脂肪酶的结构区特点,开发出抑制效果较好的化学修饰的小分子或天然抑制剂。天然小分子尤其是氨基酸类物质被证实对胰脂肪酶具有显著的抑制作用。例如,三个驼血蛋白肽均能占据胰脂肪酶活性袋,其中肽段ALERMFLGF可与C端活性中心周围Asp206发生静电作用,与Asn213发生氢键作用,与Ala179、Pro181发生疏水作用。另一条肽段GQPAVPVRF也可与C端活性中心点His264发生氢键作用[5]。坛紫菜多肽NAPPP,主要含有Glu、Asp、Arg和Gln等氨基酸,可直接通过氢键、范德华力和π键与胰脂肪酶的催化三联体结合达到抑制作用[6]。米佳等[7]研究发现以刺囊酸为先导化合物,通过C-3和C-16位上乙酰化,C-28位上引入氨基酸甲酯,可显著增强与胰脂肪酶的结合力,即取代基上的氨基酸残基与胰脂肪酶上的活性位His264、Phe237及Arg248作用,另外疏水性氨基酸比例增大有效防止了蛋白酶N端的翻转,从而发挥降脂作用。这些均为寻找新型天然氨基酸类抑制剂提供可能。
金顶侧耳(Pleurotus citrinipileatus Sing.)被誉为“真菌之花”,具有较好的抗氧化、抗肿瘤、增强免疫力、降血脂等生物活性[8],是一种极具开发价值的食用菌资源。它含有活性多糖、蛋白质、糖脂、氨基酸、微量元素等多种功能成分,营养价值高,在保健品与食品行业中展现出巨大的成长空间。其中富含一种天然氨基酸-麦角硫因(ergothioneine,EGT),属于硫醇化修饰后的组氨酸衍生物,在自然界中存在硫醇和硫酮两种形式的异构体。在生理pH条件下,它以硫酮形式存在,其氧化还原电势为−0.06 V,比其他抗氧化剂稳定且具有硫醚的特性,正是这些特殊化学性质使其具有较好的生物活性,该成分已被证明具有强抗氧化作用,可清除羟基、四氯化碳过氧化物、叠氮化合物等,促进VC再生并诱导生育酚和生育醌转化为VE,可抑制各种降血糖、血脂等疾病,被看作是一种重要维生素,可被用来作为一种膳食功能性食品的组成部分[9],2018年Bruce Ames已提议将其归类为“长寿维生素”[10]。已有研究表明金顶侧耳提取物具有降脂等功能[9],然而该天然成分如何参与降血脂功能,尤其与胰脂肪酶的抑制作用机理尚未见报道。本研究以国内广泛种植的金顶侧耳为原料,通过高效分离纯化,获得高纯度金顶侧耳麦角硫因,借助酶动力学研究该天然氨基酸类物质对胰脂肪酶的抑制作用,又利用荧光光谱、紫外光谱及分子对接技术,进一步揭示它与胰脂肪酶的分子互作机理,为阐明金顶侧耳中麦角硫因功效成分的减肥降脂活性,摸清天然氨基酸类抑制剂的结构特征,以及开发金顶侧耳为降脂功能食品资源提供数据基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
金顶侧耳(PL.C0003) 杭州众芝康菇生物技术有限公司提供;月桂酸4-硝基苯酯(4-Nitrophenyl laurate,p-NPL)、三羟甲基氨基甲烷、二甲亚砜、溴化钾 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;麦角硫因标准品(L-(+)-麦角硫因,编号:E7521,CAS号:497-30-3,EC号:207-843-5,纯度≧98%)、猪胰脂肪酶(30~90 units/mg) 默克sigma公司;无水乙醇(分析纯) 生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司。
Varioskan Flash酶标仪 赛默飞世尔科技公司;SCI280-Pro磁力搅拌器 美国赛洛捷克公司;2019 Discovery studio软件 创腾科技;UV-2802紫外分光光度计 尤尼柯(上海)仪器有限公司;F-4600荧光光谱仪 日立分析仪器(上海)有限公司;Eppendorf mini span离心机 德国艾本德;Labscale TFF System小型切向流超滤系统 密理博中国有限公司;Prep100制备色谱系统 上海赛梵科分离技术有限公司;Ultimate 3000高效液相色谱仪 美国Thermo公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 金顶侧耳麦角硫因的精制
将金顶侧耳子实体洗净,放置在通风处晾干,然后在50 ℃烘箱中烘12 h,粉碎并过60目筛,按料液比1:50取30 g金顶侧耳干粉加入65%乙醇,于50 ℃恒温水浴提取30 min。提取液随后加入4倍95%乙醇沉淀12 h,6000 r/min离心20 min。参考姜文侠等[11]的方法,对麦角硫因粗提液以5 kDa超滤膜进行超滤,并收集超滤透过液,并进行真空浓缩。再用中压制备色谱系统进一步纯化,色谱柱为Sepfocus-C18A(20 mm×250 mm),采用等度洗脱,流动相为乙腈-水,体积比85:15,流速40 mL/min,检测波长和收集波长分别为280 nm和254 nm,根据紫外检测光谱图,对分离的每个色谱峰的对应物进行收集,利用高效液相色谱检测,浓缩和干燥含有麦角硫因的组分进行液相和红外光谱[12]检测,计算金顶侧耳中麦角硫因的纯度,纯度计算公式如式(1)所示:
麦角硫因纯度(%)=c×v×nm×100 (1) 式中:m为金顶侧耳质量,mg;c为样品麦角硫因质量浓度,mg/mL;v为样品溶液总体积,mL;n为稀释倍数。
1.2.2 红外光谱测定
将 1 mg麦角硫因样品及100 mg KBr颗粒在研钵中均匀研磨成粉,压片后形成透明圆片。在FT-IR变换红外光谱仪器上扫描测定红外光谱,扫描波长段4000~750 cm−1,扫描次数32次,分辨率为4 cm−1。
1.2.3 金顶侧耳麦角硫因对胰脂肪酶的抑制作用
参考廖家乐等[13]的方法,配制5 mmol/L的Tris-HCl缓冲液500 mL,用60 mL Tris-HCl缓冲液溶解0.6 g胰脂肪酶,混匀后将其在冰水浴条件下置于转速900 r/min的磁力搅拌器上搅拌30 min后离心,取上清液,于4 °C保存,得到胰脂肪酶溶液,用40 mL二甲亚砜溶液溶解0.0102 g p-NPL,得到0.8 mmol/L p-NPL溶液。
分别制备不同质量浓度的金顶侧耳麦角硫因溶液(0、5、10、15、20 mg/mL),往96孔板中依次添加20 µL溶液、60 µL胰脂肪酶溶液、40 µL Tris-HCI缓冲液。实验空白组为未添加胰脂肪酶体系,对照组为不加麦角硫因提取物,对照空白组则为未添加胰脂肪酶及提取物。37 ℃预热15 min,向每个孔中加入80 µL p-NPL溶液,配平至200 µL,使96孔板在37 ℃下避光摇床中轻微振荡混匀,反应30 min,用酶标仪测405 nm处吸光值,各重复三次,具体实验反应体系如表1。
表 1 胰脂肪酶活性测定反应体系Table 1. Reaction system for the determination of pancreatic lipase activity组别 缓冲液(μL) 抑制剂(μL) 酶液(μL) p-NPL(μL) 对照试验组(A) 60 0 60 80 对照空白组(a) 120 0 0 80 样品试验组(B) 40 20 60 80 样品空白组(b) 100 20 0 80 1.2.4 金顶侧耳麦角硫因抑制类型测定
控制p-NPL底物浓度为0.8 mmol/L不变,金顶侧耳麦角硫因提取物浓度为10 mg/mL,改变胰脂肪酶的质量浓度(0、1、5、10、15 mg/mL)。以胰脂肪酶质量浓度为横坐标,以反应初速率(V)为纵坐标绘制曲线,由图判断抑制作用类型[14]。
样品质量浓度分别为0、10、20、40 mg/mL,胰脂肪酶浓度为10 mg/mL,p-NPL浓度为0.6、0.8、2、4 mmol/L时,测定酶催化剂的初始速度。绘制底物浓度的倒数(1/[S])与反应速率的倒数(1/V)之间的Lineweaver-Burk双倒数曲线,以确定反应的最大速率(Vmax)、米氏常数(Km)和抑制常数(Ki)的数值。x轴与曲线的截距为1/Km,而y轴与曲线的截距则为1/Vmax,将底物浓度倒数(1/[S])作为x轴,以初始速度的倒数(1/V)为y轴,获得Lineweaver-Burk双倒数曲线,得到最大反应速率(Vmax),米氏常数(Km)和抑制常数(Ki)[15−16]。
1.2.5 紫外光谱测定
准确移取1 mg/mL胰脂肪酶溶液和3 mL 0、5、10、15、20 mg/mL金顶侧耳麦角硫因溶液,均匀混合,室温下静置5 min,取2 mL混合液用紫外光谱扫描200~300 nm[17]。
1.2.6 荧光发射光谱分析
1.2.6.1 荧光光谱测定
将1 mL 0、5、10、15、20 mg/mL的金顶侧耳麦角硫因溶液和3 mL胰脂肪酶液(1 mg/mL)混合均匀,在反应温度298、303和310 K下,静置10 min,分别移取2 mL进行荧光光谱测定,激发波长在290 nm,发射波长在300~500 nm之间扫描,狭缝宽为5 nm[18]。
1.2.6.2 荧光猝灭机理与结合常数计算
金顶侧耳麦角硫因与胰脂肪酶基于上述所得的荧光光谱峰值绘制298、303、310 K三种温度下胰脂肪酶Stern-Volmer曲线[19]。对比加入它的荧光强度(F)与未加入强度(F0),借助公式(2)绘制以F0/F为纵坐标、[Q]为横坐标的图,其中斜率为Stern-Volmer猝灭常数Ksv。利用公式(3)推算双分子碰撞时的猝灭常数Kq。其中τ0为生物分子的荧光寿命大小为10−8 s[20]。
F0F=1+Ksv[Q] (2) Kq=KSVτ0 (3) 1.2.6.3 同步荧光光谱测定
移取金顶侧耳麦角硫因溶液不同质量浓度1 mL和3 mL 1 mg/mL的酶液,将其混合均匀,在298 K静置10 min,并使用同步荧光光谱在250~350 nm范围扫描。激发波长与发射波长之差Δλ设为15 nm与60 nm[21]。
1.2.6.4 三维荧光光谱测定
移取1 mL 5 mg/mL的金顶侧耳麦角硫因溶液和3 mL 1 mg/mL的酶液,将其进行充分混合后,室温静置20 min,进行三维荧光光谱的扫描,设置激发波长范围为200~350 nm、发射波长范围为200~500 nm,间隔为5 nm、激发狭缝为10 nm[22]。
1.2.6.5 分子对接
胰脂肪酶的晶体结构(PDB ID:1GPL)来自蛋白质数据库Protein Data Bank,麦角硫因分子3D结构采用ChemBioDraw14.0软件绘制,并用MM2能量最小化后转成.pdb文件,采用Auto Dock-vina软件进行分子对接模拟,力场选择CHARMM36,实行前先去除蛋白质晶体结构中的杂原子和水分子、加氢等操作[23],最后用Discovery Studio 2019软件显示对接结果。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验数据重复3次,表示为平均值±标准差(x±s),采用IBM SPSS Statistics19.0软件进行ANOVA差异性显著分析(P<0.05),使用Origin2021软件进行荧光数据处理、制图及曲线拟合。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 金顶侧耳麦角硫因分离纯化
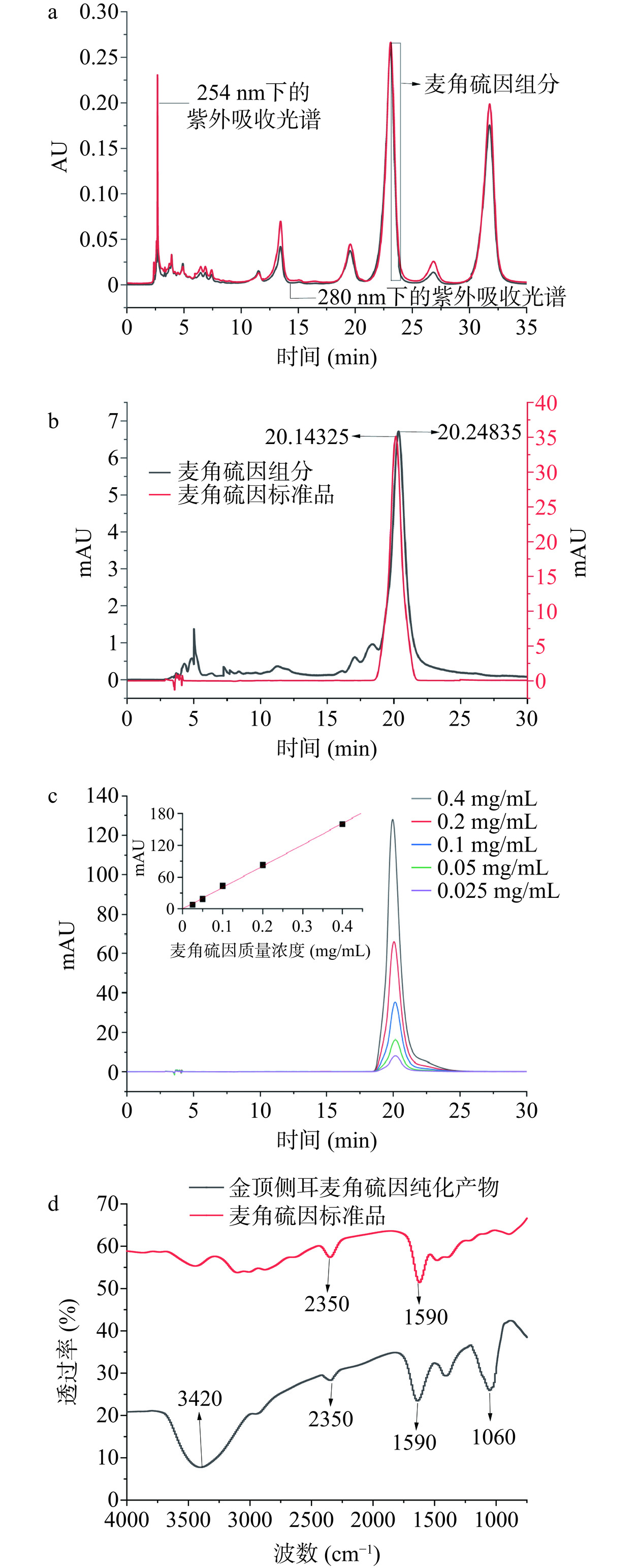
金顶侧耳子实体经过65%乙醇提取,95%乙醇沉淀,可去除大部分蛋白质、多糖及无机盐类杂质,提取液离心后用5 kDa超滤膜进一步分离去除大分子杂质,收集超滤透过液,浓缩后再利用中压反向色谱柱Sepfocus-C18A(10 mm×250 mm)对金顶侧耳麦角硫因提取物进行纯化,洗脱收集到五个主要组分,其中第三个组分(保留时间在22.9~23.4 min),峰形均一,其峰面积占五个组分峰面积的比值为48.7%(图1a)。收集纯化后的第三洗脱组分,进行浓缩、冻干,利用高效液相色谱法发现该组分在保留时间为24.25 min出现单一峰,且与标准品的保留时间接近,可判定其为麦角硫因化合物(图1b)。其纯度进一步利用麦角硫因标准曲线计算。本研究选取麦角硫因标准品系列浓度为0.025、0.05、0.1、0.2、0.4 mg/mL,以浓度为横坐标,色谱峰面积为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线,得到的回归方程为y=403.12x+0.1215(R2=0.9984),线性相关性良好。麦角硫因检测结果见图1c,纯度为91.7%。红外光谱吸收峰的特征变化可表征分子中官能团的振动和蛋白质的二级结构,波数的变化显示了分子结构的变化,如图1d所示,为金顶侧耳麦角硫因纯化产物以及麦角硫因标准品的红外光谱图,麦角硫因标准品主要在1590 cm−1和1390 cm−1处有明显的特征吸收峰,分别代表了COO反对称和对称伸缩振动,2340 cm−1处为NH2+伸缩振动[24];而纯化后的金顶侧耳麦角硫因除了以上氨基酸类特有的吸收峰以外,还在3420 cm−1处可见-OH伸缩振动吸收峰,1060 cm−1的吡喃糖环特征吸收峰,说明了纯化后的麦角硫因仍含有少量低聚糖类化合物。
![]() 图 1 麦角硫因的中压制备分离(a)、高效液相色谱检测(b)、不同质量浓度下的标准曲线及其液相色谱图(c)、傅里叶红外光谱图(d)Figure 1. Profile of ergothioneine separated by medium pressure preparative chromatography (a), HPLC profile (b), standard curves at different mass concentrations and their liquid chromatograms (c) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (d)
图 1 麦角硫因的中压制备分离(a)、高效液相色谱检测(b)、不同质量浓度下的标准曲线及其液相色谱图(c)、傅里叶红外光谱图(d)Figure 1. Profile of ergothioneine separated by medium pressure preparative chromatography (a), HPLC profile (b), standard curves at different mass concentrations and their liquid chromatograms (c) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (d)2.2 金顶侧耳麦角硫因对胰脂肪酶的抑制作用
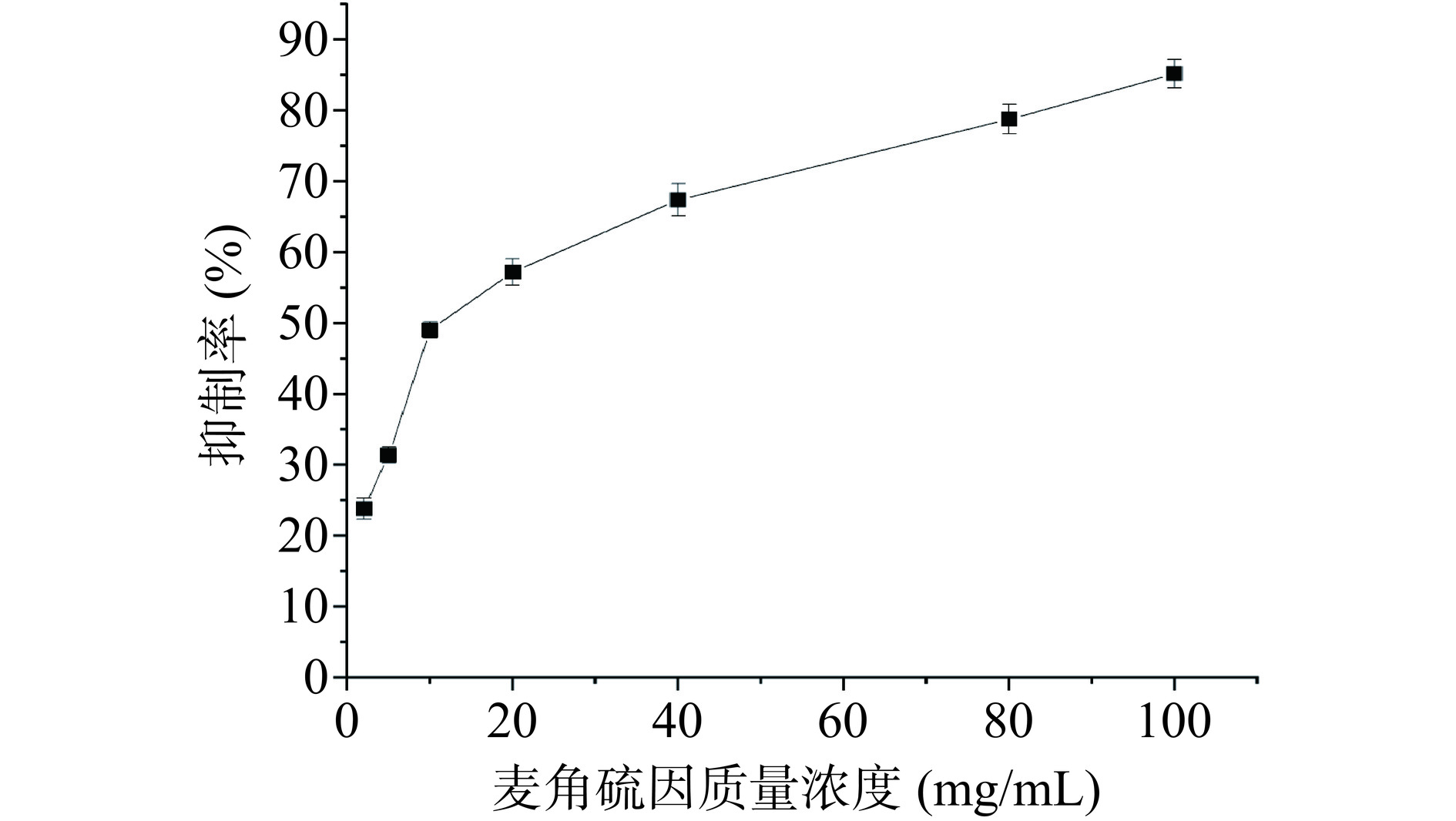
图2表明了金顶侧耳麦角硫因对胰脂肪酶的活性抑制,在麦角硫因质量浓度为0~20 mg时,抑制率显著上升,后趋于平缓上升,其半抑制率通过多元非线性拟合曲线,求得IC50为15.29 mg/mL。研究者也报道了其他活性多肽同样具有胰脂肪酶抑制效果。例如:麦胚多肽5 mg/mL时胰脂肪酶活性抑制率为33.54%[25];苹果种子分离蛋白水解90 min后得到的短肽,在1.5 mg/mL时对胰脂肪酶抑制率为31.08%[26];蛋白核小球藻中筛选出一种五肽分子FLGPF,在8 mg/mL时的胰脂肪酶抑制率为50.12%[27]。
2.3 金顶侧耳麦角硫因对胰脂肪酶的抑制作用类型
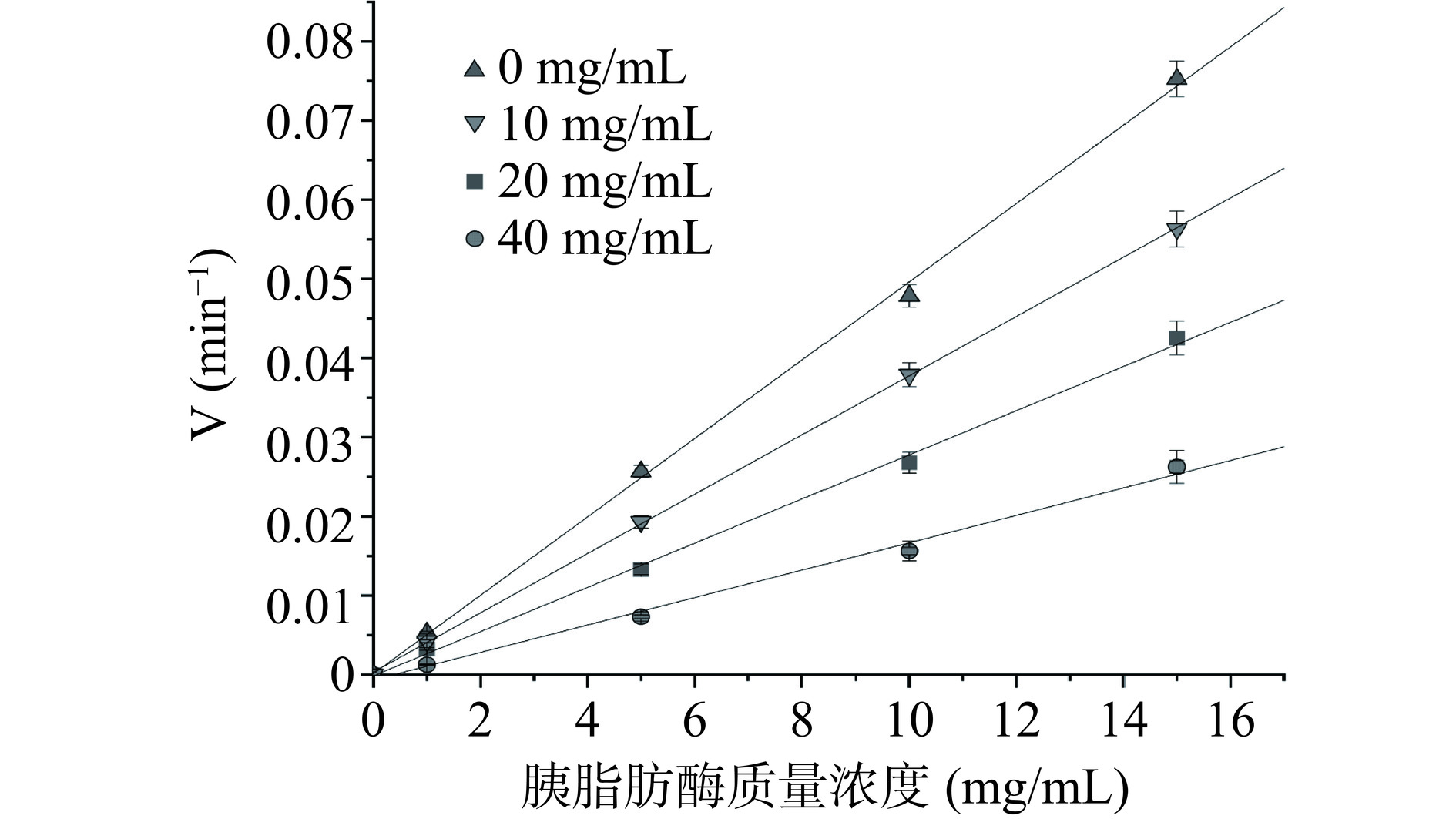
胰脂肪酶抑制类型一般可划分为两种:可逆性抑制和不可逆性抑制[28]。当包含抑制剂的曲线和不包含抑制剂的曲线在原点相交时,添加抑制剂后斜率变小,为可逆型抑制[29]。由图3可见,三个不同浓度下的抑制曲线均通过原点,且与无抑制剂组相比,加入抑制剂组曲线斜率随浓度增大而变小,表明金顶侧耳麦角硫因对胰脂肪酶的抑制类型为可逆抑制。
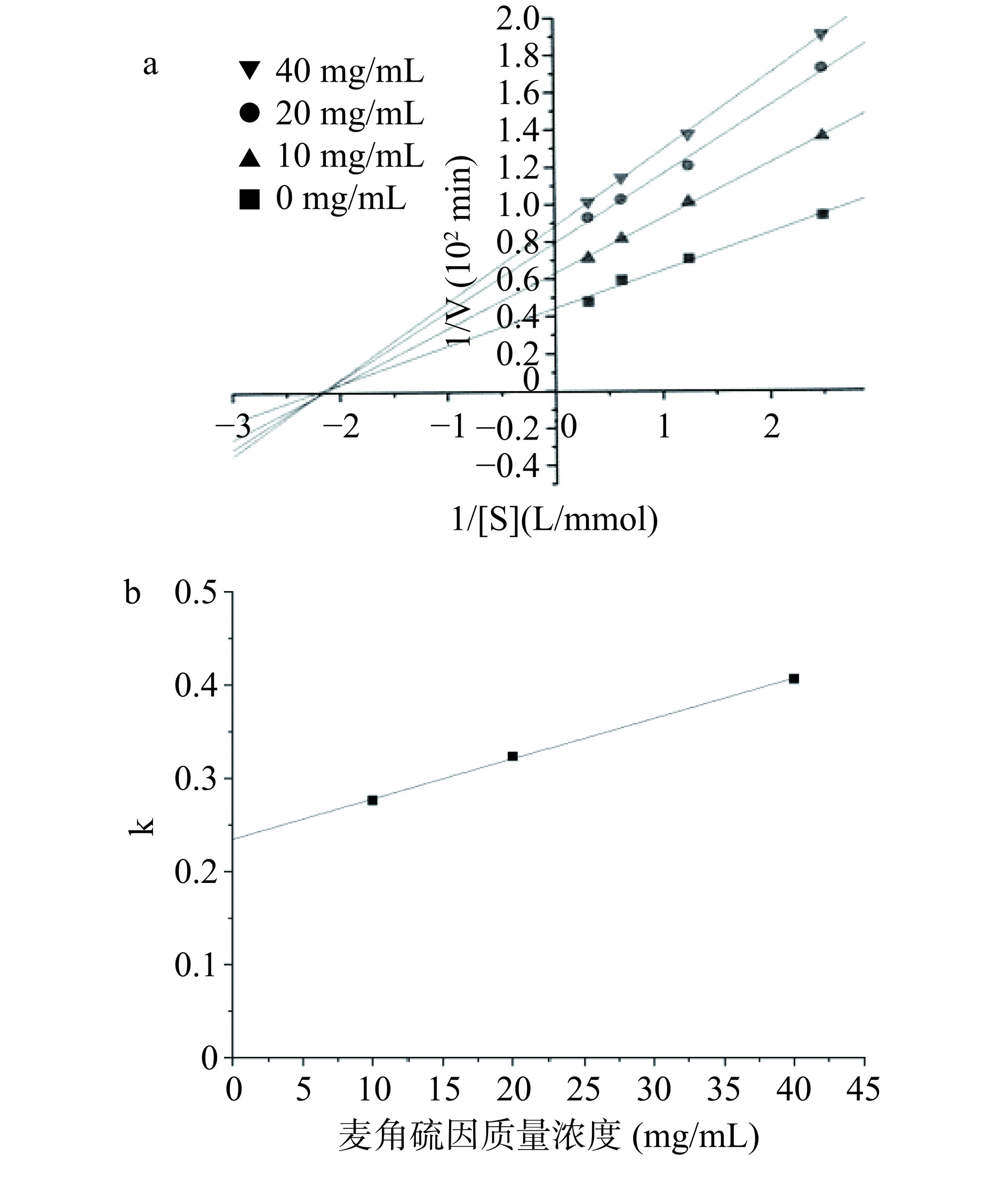
而可逆型抑制作用又分为竞争性、非竞争性和混合性抑制[30−32],前者指抑制剂与底物竞争过程中,跟胰脂肪酶活性中心的可逆型结合,从而降低胰脂肪酶发挥作用的可能性,导致其活性下降,表现为Km增大,Vmax不变;非竞争性抑制指抑制剂与胰脂肪酶非活性中心部位可逆型结合,表现为Vmax降低的,Km保持恒定;后者指两种方式都存在。由图4可看出p-NPL浓度在0.6~4 mmol/L范围,不同浓度的金顶侧耳麦角硫因组和无抑制剂组的Lineweaver-Burk曲线拟合延长交于x轴,横轴上截距不变,直线斜率增加,即Km保持不变,Vmax降低,这表明金顶侧耳麦角硫因对胰脂肪酶具有非竞争性抑制作用,各个酶动力学参数和半抑制浓度见表2。
表 2 半抑制浓度和动力学参数Table 2. Half inhibitory concentration and kinetic parameters组别 IC50(mg/mL) Vmax(min−1) Km(mg/mL) Ki(mg/mL) 对照组 2.09 0.45 36.32 40 mg/mL麦角硫因 15.29 0.98 0.45 36.32 20 mg/mL麦角硫因 15.29 1.08 0.45 36.32 10 mg/mL麦角硫因 15.29 1.41 0.45 36.32 2.4 麦角硫因对胰脂肪酶的紫外吸收影响
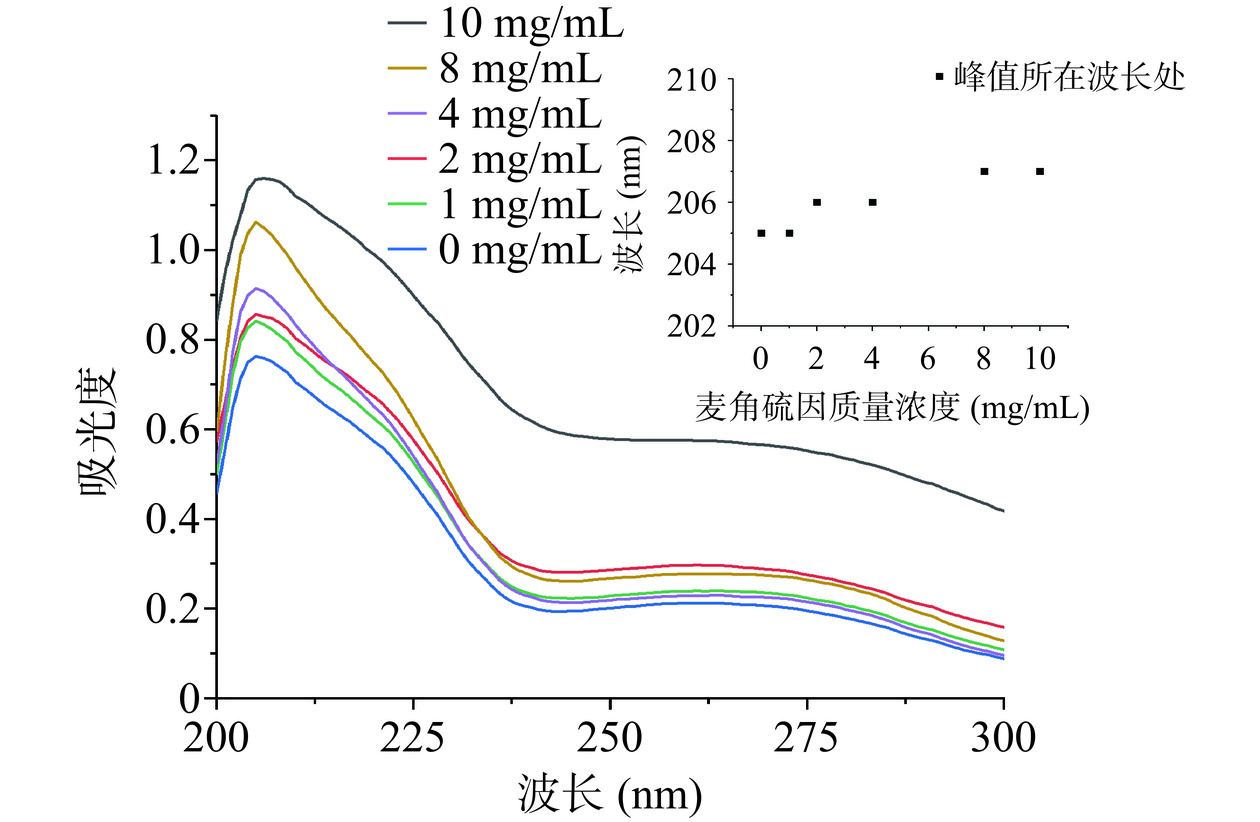
通过蛋白质在紫外光谱中的吸收峰强度和波长的变化,可确定出其基团所处微环境的状态。由图5可看出随着金顶侧耳麦角硫因浓度不断增大,胰脂肪酶的最大紫外吸收峰向长波微弱移动(205 nm→207 nm),而样品间峰形并没发生较大变化。说明可能是胰脂肪酶中色氨酸和酪氨酸残基与金顶侧耳中麦角硫因分子通过静电相互作用结合形成复合物,使胰脂肪酶的肽键C=O基团发生π→π*跃迁,且疏水性减弱,亲水性变强,极性增大,并且胰脂肪酶中α-螺旋含量升高[18]。
2.5 麦角硫因与胰脂肪酶的荧光光谱分析
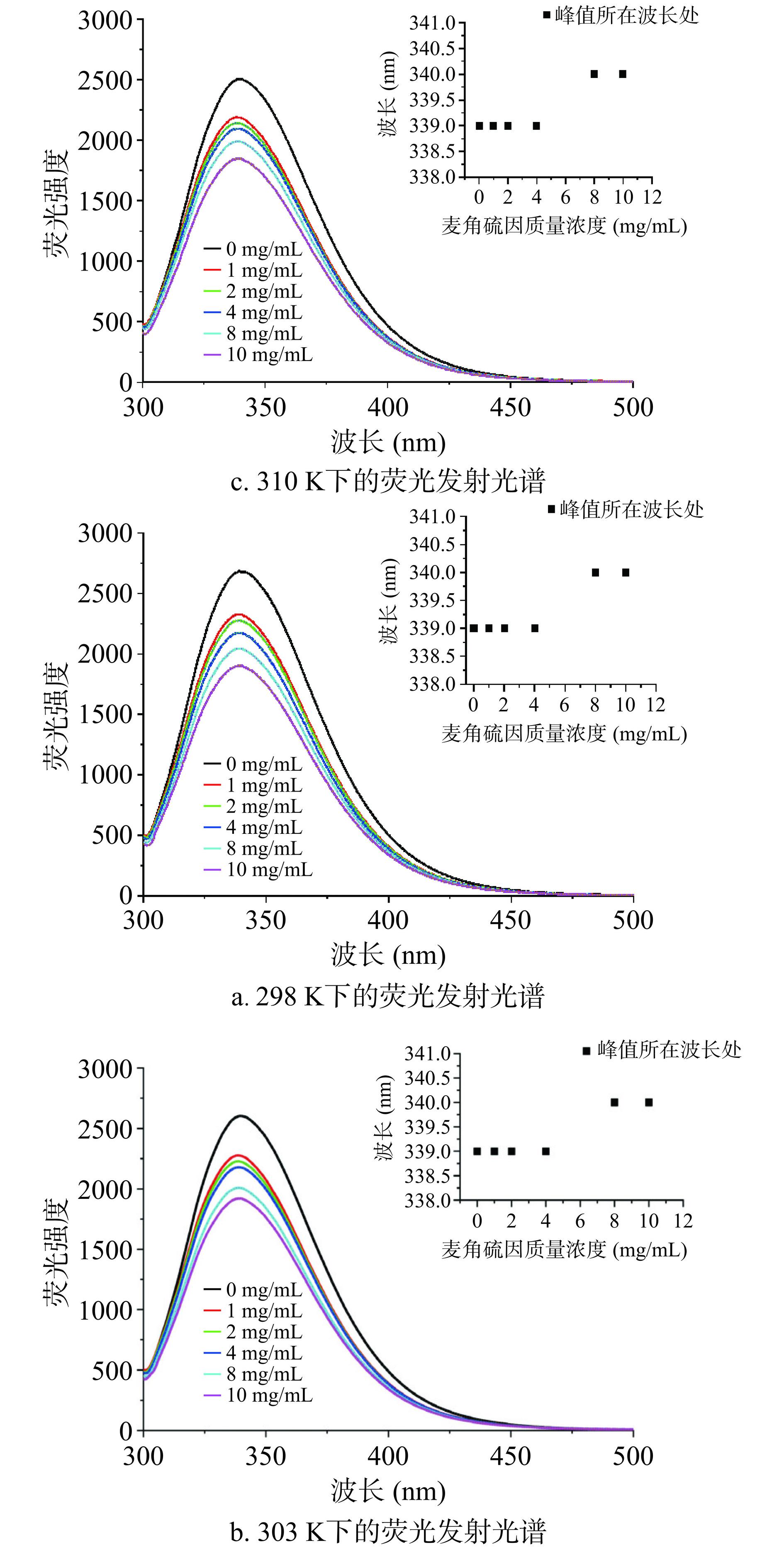
胰脂肪酶因含有苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸和色氨酸残基存在内源荧光,在三种温度298、303和310 K下,它与金顶侧耳麦角硫因相互作用的荧光光谱见图6。可知随着样品质量浓度的增加,胰脂肪酶的荧光吸收峰值逐渐减弱,峰形位置基本不变。当金顶侧耳麦角硫因浓度超过8 mg/mL时,该蛋白质的发射波长发生由339 nm向340 nm红移1 nm的微弱偏移,该荧光峰偏移可能是由于胰脂肪酶内疏水基团暴露,造成疏水作用加强和极性降低,而周围极性降低将导致红移现象,使得周围环境成为一个更疏水的环境,导致胰脂肪酶空间位置发生了变化[33],进一步验证了金顶侧耳麦角硫因对胰脂肪酶具有一定的抑制作用。
2.5.1 麦角硫因与胰脂肪酶相互作用的荧光猝灭机理
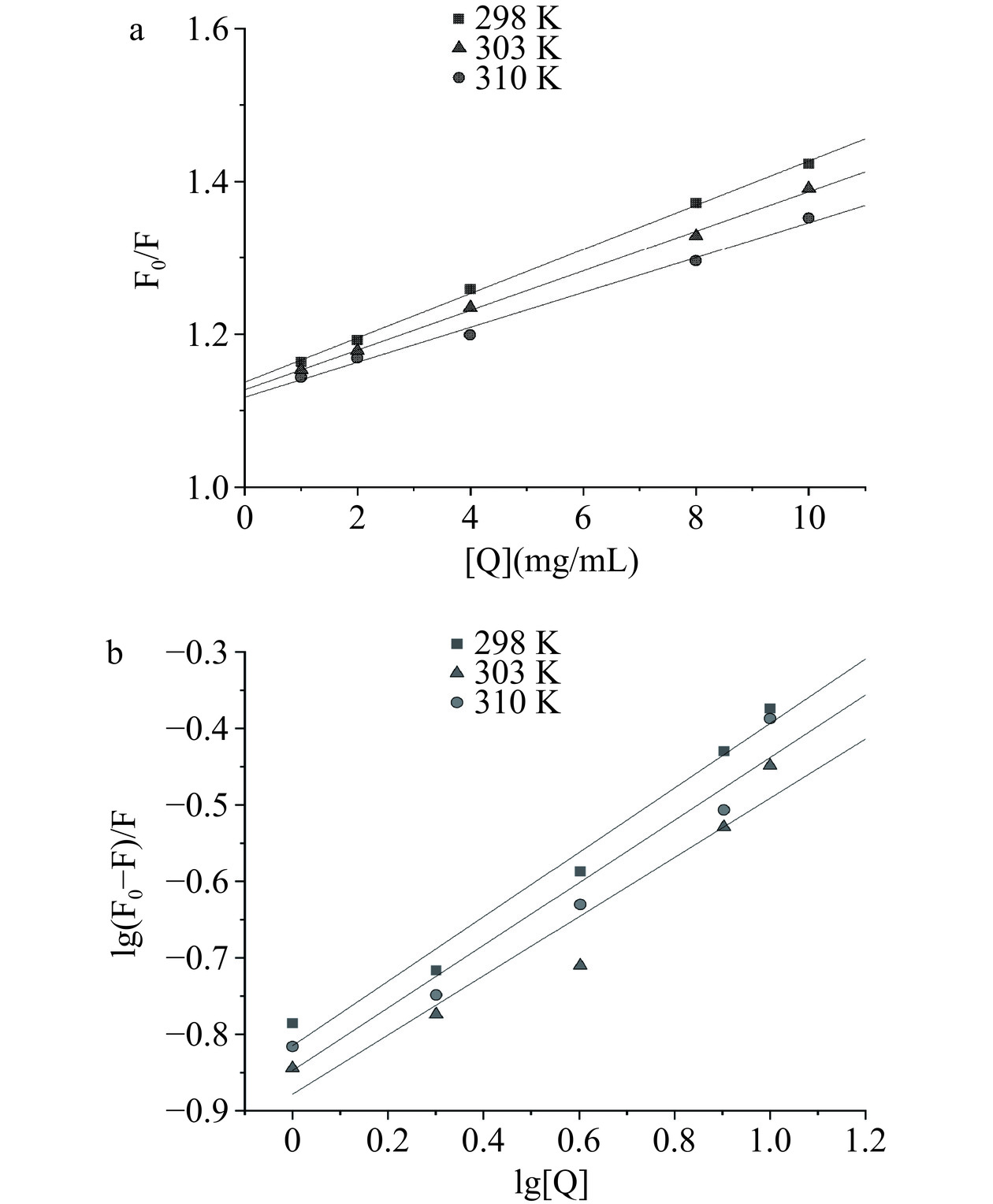
荧光猝灭种类可以分静态猝灭、动态猝灭和混合猝灭,根据金顶侧耳麦角硫因在298、303和310 K对胰脂肪酶荧光猝灭的Stern-Volmer 曲线[34](图7a),猝灭常数Ksv和Kq值可由斜率获得。它对胰脂肪酶荧光猝灭常数Ksv均随着三种温度的上升而降低,满足静态猝灭的特性[35],且三个Kq值(1012数量级)均远大于生物分子最大分散碰撞猝灭常数(2×1010 L/(mol·s)),以上结果表明它对胰脂肪酶的猝灭方式为静态猝灭。根据公式(4),利用Lineweaver-Burk双倒数曲线方程对它们的结合方式进行分析(图7b)。
lgF0−FF=lgKa+nlg[Q] (4) 由表3可知,三种温度下金顶侧耳麦角硫因与胰脂肪酶结合的Ka值均较大,尤其是298 K时达到了1.55×103 L/mol,且随着温度的升高而减少,形成的复合物稳定性下降,证实了两者结合属于静态猝灭[36]。
表 3 不同温度条件下金顶侧耳麦角硫因与胰脂肪酶相互作用的猝灭常数Table 3. Quenching constants of interaction between PCEGT and pancreatic lipase at different temperatures温度(K) Ksv(×104 L/mol ) Kq(×1012 L/(mol·s)) R2 Ka(L/mol ) n 298 3.75 3.75 0.9986 1.55×103 0.31 303 3.49 3.49 0.9984 1.38×103 0.37 310 3.28 3.28 0.9940 1.32×103 0.40 2.6 热力学参数及作用力类型
根据公式(5)~(7)计算焓变(∆H)、熵变(∆S)和吉布斯自由能变(∆G):
ΔH=lnKa2Ka11T1−1T2×R (5) ΔS=ΔH−ΔGT (6) ΔG=−RTlnK (7) 式中,R:气体常数,8.314 J/(mol·K);Ka1:293 K下的结合常数,L/mol;Ka2:310 K下的结合常数,L/mol。
从热力学角度,化合物与蛋白质之间的结合反应能否自发进行,是由吉布斯自由能的变化所决定的,若ΔG<0,说明有可能自发反应,再根据反应前后热力学焓变ΔH和熵变ΔS的相对值,确定化合物与生物大分子之间主要作用力类型的规律[33]。由表4可知,金顶侧耳麦角硫因与胰脂肪酶相互作用时ΔH<0并且ΔS>0,表明它与胰脂肪酶之间的结合是放热反应,而且两者相互作用力主要为氢键与静电作用力。
表 4 在不同温度下金顶侧耳麦角硫因与胰脂肪酶反应的热力学分析Table 4. Thermodynamic analysis of the interaction between PCEGT and pancreatic lipase at different temperatures温度(K) ΔH(kJ/mol) ΔG(kJ/mol) ΔS(J/(mol·K)) 298 −8.57 −18.20 2.55 303 −18.21 2.51 310 −18.51 2.45 2.7 同步荧光光谱
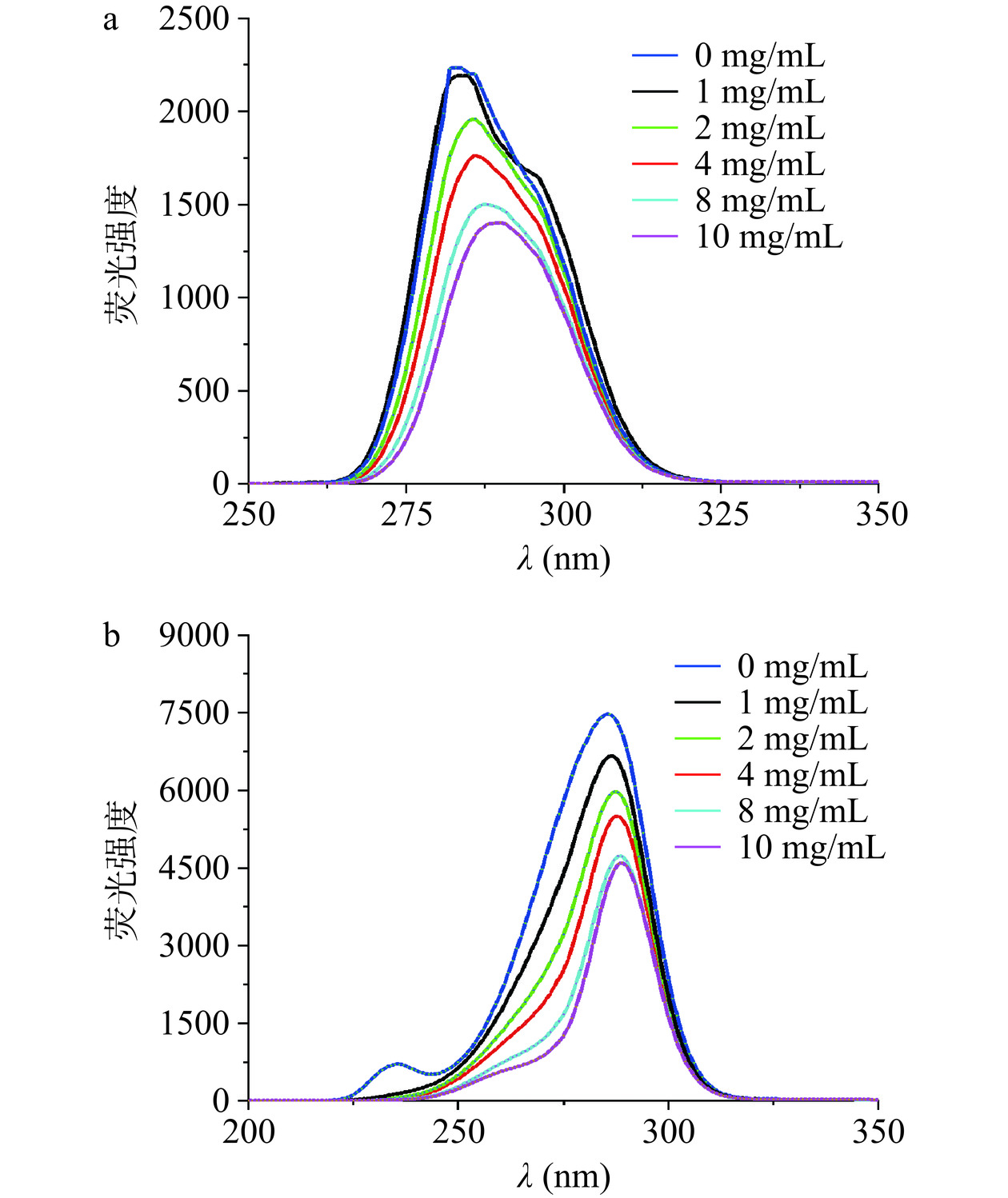
同步辐射荧光光谱可同时监测激发与发射光谱,其中两个固定波段Δλ=15 nm和Δλ=60 nm,可分别揭示抑制剂作用于蛋白质后,其酪氨酸与色氨酸残基的微环境信息[37],依据最大发射波长与强度的改变可得到蛋白质中相关氨基酸残基微环境极性的变化,可显示药物的小分子性在蛋白质结构中的变化的作用程度[38]。由图8可知随着麦角硫因浓度的增加,两种氨基酸残基的荧光强度都逐渐减弱,且发生明显的红移。当Δλ=15 nm时,酪氨酸荧光峰值从284 nm红移至290 nm(约6 nm),强度减少了40.9%;当Δλ=60时,色氨酸峰值从286 nm 红移至289 nm(约3 nm),强度减少了35.3%。说明随着金顶侧耳中麦角硫因分子与胰脂肪酶中Ser152-His263-Asp176催化三联体活性中心区域外的残基结合,导致蛋白质整体构象发生变化,疏水性减弱,极性增强。
2.8 三维荧光光谱分析
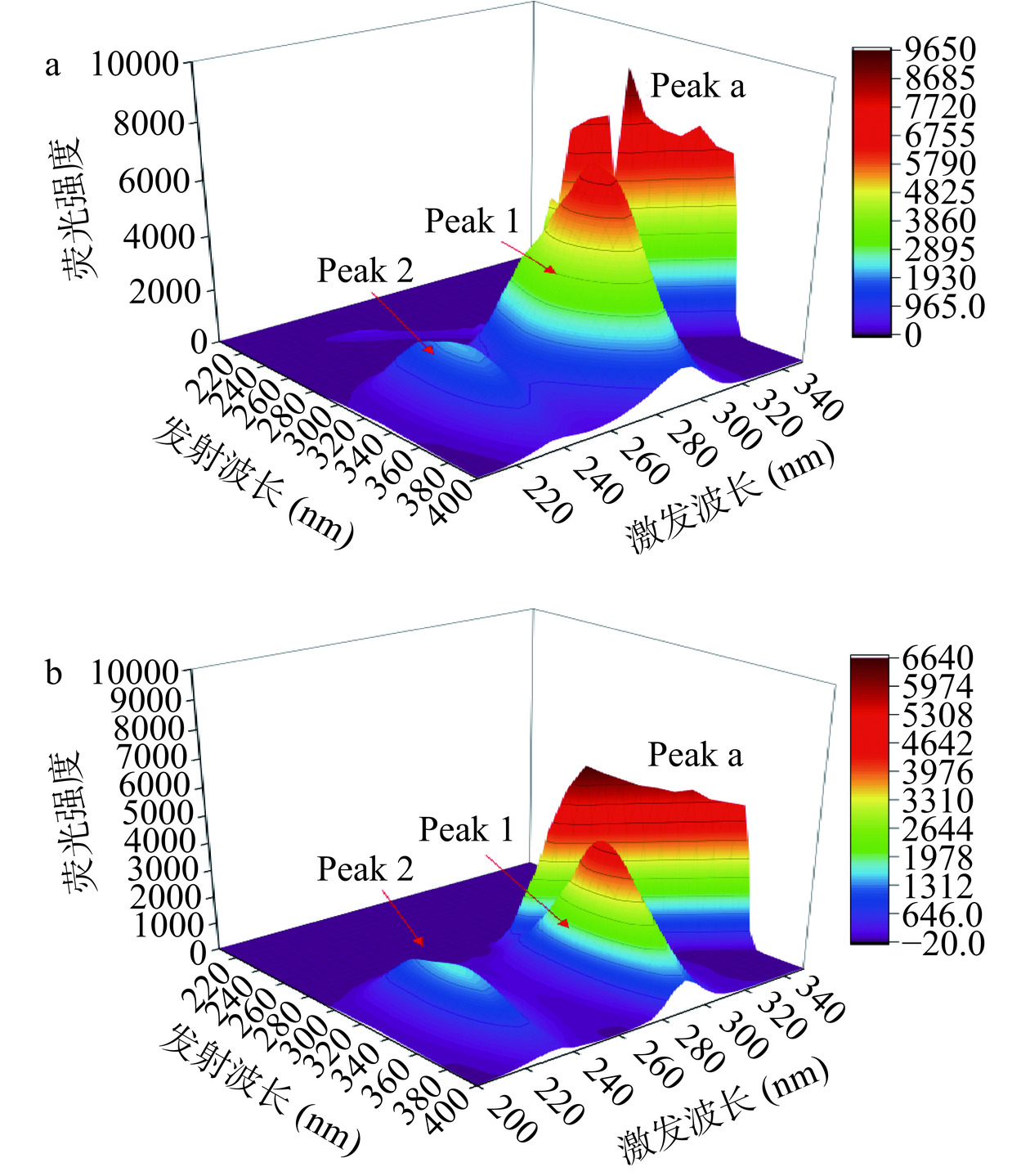
三维荧光光谱在获取激发波长与发射波长变化信息的同时还能够获取其荧光强度变化,常用来表征蛋白质的微观结构和构象是否发生变化[39]。胰脂肪酶三维光谱图中,Peak a为瑞丽散射峰(λex=λem,F),Peak 1和Peak 2为荧光特征峰(2λex=λem,F)分别是Tyr/Trp残基的荧光特征峰及多肽骨架结构荧光特征峰。麦角硫因对胰脂肪酶作用前后的3D荧光光谱如图9所示。由图9知,加入麦角硫因后,Peak 1由(285.0 nm/340.0 nm,7279)变化为(285.0 nm/345.0 nm,4933),Peak 2由(235.0 nm/330.0 nm,2207)变化为(235.0 nm/335.0 nm,1641)。即Peak 1和Peak 2各红移5 nm,荧光强度分别下降32.2%和25.6%,表明胰脂肪酶多肽链发生了折叠,导致胰脂肪酶Tyr/Trp残基微环境发生了变化,进而胰脂肪酶的构象发生了变化。此外,Peak a的荧光强度降低,可能是胰脂肪酶表面的保护水层分子分散程度增大,分子粒径减小,散射效应减弱,导致荧光强度降低。
2.9 分子对接结果分析
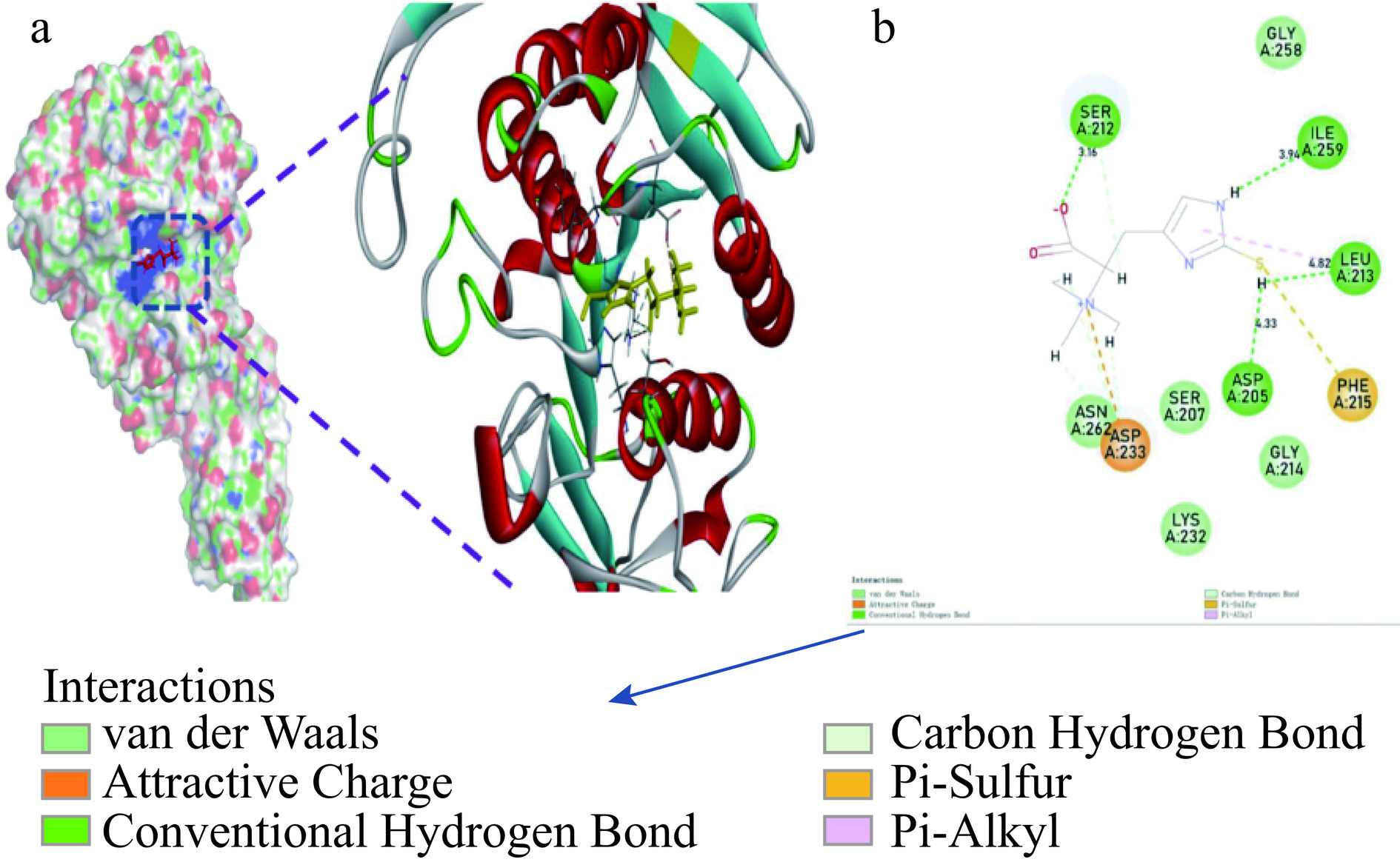
分子对接技术能在微观上表达配体-受体之间的结合部位及结合部位构象,从而帮助研究它们之间的作用机制,解释酶的抑制特性[40],酶和抑制剂分子之间的作用有助于从微观角度对其抑制特性进行研究。由分子对接图10a可知,金顶侧耳中麦角硫因分子可与胰脂肪酶的催化中心外围疏水区域结合,从而形成与底物p-NPL非竞争的结合,这与上述同步荧光光谱分析相一致。本研究中显示该分子不仅通过巯基SH与Asp 205、Leu 213形成氢键,键长分别为4.33和4.82 Å;而且自身羧基氧和杂环氮上的氢与Ser 212、Ile 259残基也形成氢键,键长分别为3.16和3.94 Å,这对维持胰脂肪酶结构非常重要。另外,它的巯基与Phe215形成Pi-碳离子键,与残基Ser 207、Lys 232、Gly 214、Gly 258形成弱的范德华力,与Asp 233通过电荷相互吸引。这些结合力的存在进一步揭示,若小分子含有与作用靶点类似的氨基酸或部分官能团化学修饰后,可显著提升其生物活性。麦角硫因作为一种天然化学修饰的氨基酸类物质,不仅含有与胰脂肪酶活性位点相似的组氨酸,其硫醇官能团显著抑制催化中心。该研究进一步从分子角度揭示了作为一种特殊的天然修饰氨基酸物质,金顶侧耳麦角硫因可与胰脂肪酶紧密结合形成复合物,从而猝灭其内源荧光,发挥降脂生物活性的作用,为金顶侧耳资源的深度开发提供基础。
3. 结论
本实验以金顶侧耳子实体为原料分离纯化后,金顶耳中麦角硫因纯度达到91.7%,利用酶动力学曲线,发现它对胰脂肪酶有一定的抑制作用,作用类型为非竞争型可逆抑制,米氏常数Km为0.45 mg/mL,抑制常数Ki为36.32 mg/mL。紫外和荧光光谱结果均显示,随着金顶侧耳麦角硫因质量浓度的增大,它可与胰脂肪酶形成复合物并发生红移,使蛋白分子疏水性减弱,亲水性变强,极性增大;金顶侧耳中麦角硫因分子以静态方式有效猝灭其内源荧光,利用Lineweaver-Burk曲线求得三种温度下两者的结合常数Ka,其结合位点均为1。根据Van’t Hoff定律计算得到热力学参数焓变ΔH和熵变ΔS,两者间的主要作用力为氢键与静电作用力;同步和三维荧光测得酪氨酸和色氨酸残基的最大吸收峰发生红移,荧光强度均下降,说明麦角硫因可使胰脂肪酶分子微环境改变。分子对接表明该分子主要是通过范德华力,吸引电荷,氢键等非竞争结合到酶催化活性中心以外的部位。以上研究结果从分子机理上阐释了金顶侧耳麦角硫因对胰脂肪酶的抑制作用,可为其开发成降脂功能食品提供理论依据,此外天然提取、化学合成以及生物合成方式得到的麦角硫因对胰脂肪酶活性的抑制作用的异同可作为后续研究的重点。
-
图 1 麦角硫因的中压制备分离(a)、高效液相色谱检测(b)、不同质量浓度下的标准曲线及其液相色谱图(c)、傅里叶红外光谱图(d)
Figure 1. Profile of ergothioneine separated by medium pressure preparative chromatography (a), HPLC profile (b), standard curves at different mass concentrations and their liquid chromatograms (c) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (d)
表 1 胰脂肪酶活性测定反应体系
Table 1 Reaction system for the determination of pancreatic lipase activity
组别 缓冲液(μL) 抑制剂(μL) 酶液(μL) p-NPL(μL) 对照试验组(A) 60 0 60 80 对照空白组(a) 120 0 0 80 样品试验组(B) 40 20 60 80 样品空白组(b) 100 20 0 80 表 2 半抑制浓度和动力学参数
Table 2 Half inhibitory concentration and kinetic parameters
组别 IC50(mg/mL) Vmax(min−1) Km(mg/mL) Ki(mg/mL) 对照组 2.09 0.45 36.32 40 mg/mL麦角硫因 15.29 0.98 0.45 36.32 20 mg/mL麦角硫因 15.29 1.08 0.45 36.32 10 mg/mL麦角硫因 15.29 1.41 0.45 36.32 表 3 不同温度条件下金顶侧耳麦角硫因与胰脂肪酶相互作用的猝灭常数
Table 3 Quenching constants of interaction between PCEGT and pancreatic lipase at different temperatures
温度(K) Ksv(×104 L/mol ) Kq(×1012 L/(mol·s)) R2 Ka(L/mol ) n 298 3.75 3.75 0.9986 1.55×103 0.31 303 3.49 3.49 0.9984 1.38×103 0.37 310 3.28 3.28 0.9940 1.32×103 0.40 表 4 在不同温度下金顶侧耳麦角硫因与胰脂肪酶反应的热力学分析
Table 4 Thermodynamic analysis of the interaction between PCEGT and pancreatic lipase at different temperatures
温度(K) ΔH(kJ/mol) ΔG(kJ/mol) ΔS(J/(mol·K)) 298 −8.57 −18.20 2.55 303 −18.21 2.51 310 −18.51 2.45 -
[1] BIALECKA-FLORJANCZYK E, FABISZEWSKA A U, KRZYCZKOWSKA J, et al. Synthetic and natural lipase inhibitors[J]. Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry,2018,18(8):672−683. doi: 10.2174/1389557516666160630123356
[2] LI S, PAN J H, HU X, et al. Kaempferol inhibits the activity of pancreatic lipase and its synergistic effect with orlistat[J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 2020, 72: 1−11.
[3] DECHAKHAMPHU A, WONGCHUM N. Investigation of the kinetic properties of Phyllanthus chamaepeuce Ridl. extracts for the inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity[J]. Journal of Herbal Medicine,2022,32:100508. doi: 10.1016/j.hermed.2021.100508
[4] 孙茹欣, 吉日木图, 伊丽. 驼血蛋白胰脂肪酶抑制肽的分离纯化及鉴定[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(5):128−136. [SUN Ruxin, JIRIMUTU, YI Li. Purification and identification of camel blood protein pancreatic lipase inhibitory peptide[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(5):128−136.] SUN Ruxin, JIRIMUTU, YI Li. Purification and identification of camel blood protein pancreatic lipase inhibitory peptide[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2021, 46(5): 128−136.
[5] 王雪. 刺囊酸衍生物的制备及抑制胰脂肪酶活性研究[D]. 长春:吉林农业大学, 2019. [WANG Xue. Studies on the synthesis of echinocystic acid derivatives and their lipases inhibition activities[D]. Changchun:Jilin Agricultural University, 2019.] WANG Xue. Studies on the synthesis of echinocystic acid derivatives and their lipases inhibition activities[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2019.
[6] 冷檬. 坛紫菜胰脂肪酶抑制肽制备及其作用机理研究[D]. 厦门:集美大学, 2022. [LENG Meng. Preparation and interaction mechanism of pancreatic lipase inhibitory peptide from Porphyra haitanensis[D]. Xiamen:Jimei University, 2022.] LENG Meng. Preparation and interaction mechanism of pancreatic lipase inhibitory peptide from Porphyra haitanensis[D]. Xiamen: Jimei University, 2022.
[7] 米佳, 张渌淘, 禄璐, 等. 中压制备色谱法分离黑果枸杞中2个矮牵牛素花色苷及其对胰脂肪酶的抑制活性[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(22):16−23. [MI Jia, ZHANG Lutao, LU Lu, et al. Separation and pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity of two Petunidin anthocyanins from Lycium ruthenicum Murr. by preparative medium-pressure liquid chromatography[J]. Food Science,2023,44(22):16−23.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20221111-125 MI Jia, ZHANG Lutao, LU Lu, et al. Separation and pancreatic lipase inhibitory activity of two Petunidin anthocyanins from Lycium ruthenicum Murr. by preparative medium-pressure liquid chromatography[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(22): 16−23. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20221111-125
[8] 宋鸽. 金顶侧耳营养成分评价及药理活性的研究[D]. 长春:吉林农业大学, 2013. [SONG G. Evaluation of nutritional components and pharmacological activities of Pleurotus ostreatus[D]. Changchun:Jilin Agricultural University, 2013.] SONG G. Evaluation of nutritional components and pharmacological activities of Pleurotus ostreatus[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2013.
[9] GRIGAT S. Probing the substrate specificity of the ergothioneine transporter with methimazole, hercynine, and organic carbon[J]. Biochemical Pharmacology, 2007, 74(2):309−316.
[10] AMES B N. Prolonging healthy aging:longevity vitamins and proteins[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(43):10836−10844.
[11] 姜文侠, 刘琦, 王洪宇, 等. 麦角硫因的提取及纯化方法:天津, CN104774182A8[P]. 2018-01-09. [JIANG Wenxia, LIU Qi, WANG Hongyu, et al. Extraction and purification method of ergothioneine:Tianjin, CN104774182A8[P]. 2018-01-09.] JIANG Wenxia, LIU Qi, WANG Hongyu, et al. Extraction and purification method of ergothioneine: Tianjin, CN104774182A8[P]. 2018-01-09.
[12] 梅洁, 李芳, 王晓雯, 等. 核桃谷蛋白多肽及其肽锌螯合物的分离纯化、鉴定与结合位点分析[J]. 食品科学,2024,45(22):2208−2216. [MEI Jie, LI Fang, WANG Xiaowen, et al. Isolation, purification, identification and binding site analysis of walnut glutelin peptide and its peptide zinc chelate[J]. Food Science,2024,45(22):2208−2216.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20231201-005 MEI Jie, LI Fang, WANG Xiaowen, et al. Isolation, purification, identification and binding site analysis of walnut glutelin peptide and its peptide zinc chelate[J]. Food Science, 2024, 45(22): 2208−2216. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20231201-005
[13] 廖家乐, 方甜, 范艳丽. 枸杞叶黄酮对胰脂肪酶活性的抑制作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(5):43−53. [LIAO Jiale, FANG Tian, FAN Yanli. Inhibitory effects of Lycium barbarum leaves flavonoids on pancreatic lipase activity[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(5):43−53.] LIAO Jiale, FANG Tian, FAN Yanli. Inhibitory effects of Lycium barbarum leaves flavonoids on pancreatic lipase activity[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22(5): 43−53.
[14] 辛相余. 黑豆芽多酚体外模拟消化的生物可及性及其对消化酶的抑制作用研究[D]. 西安:陕西师范大学, 2021. [XIN Xiangyu. Studies on the bioaccessibility of black bean sprouts polyphenols for simulated digestionin vitro and their inhibitory effect on digestive enzymes[D]. Xi'an:Shaanxi Normal University, 2021.] XIN Xiangyu. Studies on the bioaccessibility of black bean sprouts polyphenols for simulated digestion in vitro and their inhibitory effect on digestive enzymes[D]. Xi'an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2021.
[15] ELSHIHAWY H, HELAL M A, SAID M, et al. Design, synthesis, and enzyme kinetics of novel benzimidazole and quinoxaline derivatives as methionine synthase inhibitors[J]. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry,2014,22(1):550−558.
[16] 陈永丽, 黄俊僮, 王玲, 等. 桑叶多糖的化学组成及其对胰脂肪酶的抑制作用研究[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(3):162−166. [CHEN Yongli, HUANG Juntong, WANG Ling, et al. Chemical composition of mulberry leaf polysaccharide and its inhibitory effect on pancreatic lipase[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(3):162−166.] CHEN Yongli, HUANG Juntong, WANG Ling, et al. Chemical composition of mulberry leaf polysaccharide and its inhibitory effect on pancreatic lipase[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2021, 46(3): 162−166.
[17] 张楠, 胡童霞, 朱鑫麗, 等. 紫外和荧光光谱法研究油菜蜂花粉多酚对胰脂肪酶的作用过程[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(22):36−42. [ZHANG Nan, HU Tongxia, ZHU Xinli, et al. Study on the interaction process between rape bee pollen polyphenols and pancreatic lipase by ultraviolet and fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(22):36−42.] ZHANG Nan, HU Tongxia, ZHU Xinli, et al. Study on the interaction process between rape bee pollen polyphenols and pancreatic lipase by ultraviolet and fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(22): 36−42.
[18] 周素珍, 邢莉, 范金波, 等. 分子对接结合荧光光谱法探究3种类胡萝卜素与HSA的相互作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2023,23(2):61−71. [ZHOU Suzhen, XING Li, FAN Jinbo, et al. Exploring the interaction between three carotenes and HSA by molecular docking and fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2023,23(2):61−71.] ZHOU Suzhen, XING Li, FAN Jinbo, et al. Exploring the interaction between three carotenes and HSA by molecular docking and fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 23(2): 61−71.
[19] 倪丹, 蒋新元, 唐玉莲, 等. 鞣花酸抑制酪氨酸酶的动力学、荧光光谱分析及分子对接[J]. 食品科学,2024,45(2):104−112. [NI Dan, JIANG Xinyuan, TANG Yulian, et al. Kinetics, fluorescence spectroscopy analysis and molecular docking of tyrosinase inhibition by ellagic acid[J]. Food Science,2024,45(2):104−112.] NI Dan, JIANG Xinyuan, TANG Yulian, et al. Kinetics, fluorescence spectroscopy analysis and molecular docking of tyrosinase inhibition by ellagic acid[J]. Food Science, 2024, 45(2): 104−112.
[20] 申炳俊, 柳婷婷. 光谱法和分子对接技术研究胡桃醌与人血清白蛋白的相互作用[J]. 分析化学,2020,48(10):1383−1391. [SHEN Bingjun, LIU Tingting. Spectroscopy and molecular docking technique for investigation of interaction between juglone and human serum albumin[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2020,48(10):1383−1391.] SHEN Bingjun, LIU Tingting. Spectroscopy and molecular docking technique for investigation of interaction between juglone and human serum albumin[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2020, 48(10): 1383−1391.
[21] 张孟丽, 陈慧慧, 郑世杰, 等. 鹅膏蕈氨酸与人血清蛋白相互作用机制的研究[J]. 化学研究与应用,2021,33(11):2222−2227. [ZHANG Mengli, CHEN Huihui, ZHENG Shijie, et al. Study on the mechanism of interaction between ibotenic acid and human serum albumin[J]. Chemical Research and Application,2021,33(11):2222−2227.] ZHANG Mengli, CHEN Huihui, ZHENG Shijie, et al. Study on the mechanism of interaction between ibotenic acid and human serum albumin[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2021, 33(11): 2222−2227.
[22] 张钊维, 宋雨欣, 王艺蓉, 等. 金纳米花的合成及其与人血清白蛋白相互作用的研究[J]. 化学通报,2022,85(4):490−495. [ZHANG Zhaowei, SONG Yuxin, WANG Yirong, et al. Study on the synthesis of gold nanoflower and its interaction with human serum albumin[J]. Chemistry,2022,85(4):490−495.] ZHANG Zhaowei, SONG Yuxin, WANG Yirong, et al. Study on the synthesis of gold nanoflower and its interaction with human serum albumin[J]. Chemistry, 2022, 85(4): 490−495.
[23] 李佳欣, 李道亮, 周鸿媛, 等. 荧光光谱法研究链格孢霉毒素TeA与血清白蛋白的互作机理[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(8):288−295. [LI Jiaxin, LI Daoliang, ZHOU Hongyuan, et al. Interaction mechanism between Alternaria mycotoxins TeA and serum albumin by fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(8):288−295.] LI Jiaxin, LI Daoliang, ZHOU Hongyuan, et al. Interaction mechanism between Alternaria mycotoxins TeA and serum albumin by fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(8): 288−295.
[24] 翁诗甫, 徐怡庄. 傅里叶变换红外光谱分析[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社, 2016:370−374. [WEN Shifu, XU Yizhuang. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy[M]. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press, 2016:370−374.] WEN Shifu, XU Yizhuang. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2016: 370−374.
[25] 李雨欣, 胡芸利, 刘聪, 等. 河套麦胚多肽的制备工艺优化及其体外降血脂活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(17):174−180. [LI Yuxin, HU Yunli, LIU Cong, et al. Preparation optimization of hetao wheat germ polypeptide and its in vitro hypolipidemic activity[J]. [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(17):174−180.] LI Yuxin, HU Yunli, LIU Cong, et al. Preparation optimization of hetao wheat germ polypeptide and its in vitro hypolipidemic activity[J]. [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(17): 174−180.
[26] MEHNAZA M A B, JAGMOHAN S A, ZUHAIB F B, et al. Multifunctional apple seed protein hydrolysates:Impact of enzymolysis on the biochemical, techno-functional and in vitro α-glucosidase, pancreatic lipase and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition activities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 257.
[27] 林娈, 柳雯郡, 黄俊媛, 等. 蛋白核小球藻胰脂肪酶抑制肽的分离纯化、鉴定及其降脂活性[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(24):155−163. [LIN Luan, LIU Wenjun, HUANG Junyuan, et al. Isolation, purification, identification and hypolipidemic activity of lipase inhibitory peptide from Chlorella pyrenoidosa[J]. Food Science,2023,44(24):155−163.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230302-021 LIN Luan, LIU Wenjun, HUANG Junyuan, et al. Isolation, purification, identification and hypolipidemic activity of lipase inhibitory peptide from Chlorella pyrenoidosa[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(24): 155−163. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230302-021
[28] 安欢, 叶云, 丁华杰, 等. 苦瓜多糖对胰脂肪酶抑制作用的研究[J]. 中国调味品, 2020, 45(2):27−31. [AN Huan, YE Yun, DING Huajie, et al. Study on the inhibitory effect of Momordica charantia polysaccharide on pancreatic lipase[J]. China Condiment, 2020, 45(2):27−31.] AN Huan, YE Yun, DING Huajie, et al. Study on the inhibitory effect of Momordica charantia polysaccharide on pancreatic lipase[J]. China Condiment, 2020, 45(2): 27−31.
[29] 曹叶霞, 李慧卿, 尹爱萍, 等. 韭菜提取物对胰脂肪酶抑制作用的研究[J]. 粮食与油脂,2023,36(4):141−144,159. [CAO Yexia, LI Huiqing, YIN Aiping, et al. Study on the inhibitory effect of leek extracts on pancreatic lipase[J]. Cereals & Oils,2023,36(4):141−144,159.] CAO Yexia, LI Huiqing, YIN Aiping, et al. Study on the inhibitory effect of leek extracts on pancreatic lipase[J]. Cereals & Oils, 2023, 36(4): 141−144,159.
[30] HUANG R, ZHANG Y, SHEN S, et al. Antioxidant andpancreatic lipase inhibitory effects of flavonoids from different citrus peel extracts:an in vitro study[J]. Food Chemistry, 2020, 326: 1−10.
[31] 纪慧杰, 朱彩平. 石榴皮多糖的提取及组成、体外降脂活性研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2023,49(4):161−168. [JI Huijie, ZHU Caiping. Study on the extraction and composition of pomegranate peel polysaccharide and hypolipidemic activity in vitro[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(4):161−168.] JI Huijie, ZHU Caiping. Study on the extraction and composition of pomegranate peel polysaccharide and hypolipidemic activity in vitro[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2023, 49(4): 161−168.
[32] 满子意, 凤怡, 吴祥庭. 儿茶素单体EGC对胰脂肪酶的抑制作用及其机理研究[J]. 茶叶科学,2022,42(6):863−874. [MAN Ziyi, FENG Yi, WU Xiangting. Inhibitory effect of catechin monomer EGC on pancreatic lipase and mechanism[J]. Journal of Tea Science,2022,42(6):863−874.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2022.06.010 MAN Ziyi, FENG Yi, WU Xiangting. Inhibitory effect of catechin monomer EGC on pancreatic lipase and mechanism[J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2022, 42(6): 863−874. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2022.06.010
[33] 胡慧娟, 闫巧丽, 卢晓刚, 等. 猪胰脂肪酶催化外消旋P-手性α-羟基磷酸酯类化合物的动力学拆分(英文)[J]. 有机化学,2023,43(8):2815−2825. [HU Huijuan, YAN Qiaoli, LU Xiaogang, et al. Kinetic resolution of racemic P-chiral α-hydroxymethylphos-phonates catalyzed by lipase from porcine pancreas[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry,2023,43(8):2815−2825.] doi: 10.6023/cjoc202212005 HU Huijuan, YAN Qiaoli, LU Xiaogang, et al. Kinetic resolution of racemic P-chiral α-hydroxymethylphos-phonates catalyzed by lipase from porcine pancreas[J]. Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2023, 43(8): 2815−2825. doi: 10.6023/cjoc202212005
[34] 玉叶, 廖娟, 文彬, 等. 光谱法研究牛磺酸与人血清白蛋白相互作用[J]. 量子电子学报,2023,40(6):827−835. [YU Ye, LIAO Juan, WEN Bin, et al. Study on interaction between taurine and human serum protein by spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics,2023,40(6):827−835.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5461.2023.06.003 YU Ye, LIAO Juan, WEN Bin, et al. Study on interaction between taurine and human serum protein by spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2023, 40(6): 827−835. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5461.2023.06.003
[35] YUE Y, LIU J, LIU R, et al. Binding of helicid to human serum albumin:A hybrid spectroscopic approach and conformational study[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2014,124:46−51. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2013.12.108
[36] 宝贵荣, 金亮, 包仓, 等. 胡椒酸己二醇单酯的降血脂作用及其与牛血清白蛋白相互作用研究[J]. 化学试剂,2022,44(11):1605−1609. [BAO Guirong, JIN Liang, BAO Cang, et al. Study on the antihyperlipidemic activity of 1.6-Hexanediol piperinic-monoester and its interaction with bovine serum albumin[J]. Chemical Reagents,2022,44(11):1605−1609.] BAO Guirong, JIN Liang, BAO Cang, et al. Study on the antihyperlipidemic activity of 1.6-Hexanediol piperinic-monoester and its interaction with bovine serum albumin[J]. Chemical Reagents, 2022, 44(11): 1605−1609.
[37] CHEN J H, WU X H, ZHOU Y, et al. Camellia nitidissima Chi leaf as pancreatic lipase inhibitors:Inhibition potentials and mechanism[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2021,45(9):e13837.
[38] HUANG S, LI H M, LIU Y, et al. Comparable investigation of in vitro interactions between three ruthenium (II) arene complexes with curcumin analogs and CT DNA[J]. Polyhedron,2019,167:51−61. doi: 10.1016/j.poly.2019.04.013
[39] ZHANG Q L, ZHU Z, NI Y N. Interaction between aspirin and vitamin C with human serum albumin as binary and ternary systems[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2020,236:118356. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2020.118356
[40] 黄欣莉, 吴伟杰, 陈杭君, 等. 桃仁中苦杏仁苷高效提取及其体外生物活性研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2023,23(4):146−156. [HUANG Xinli, WU Weijie, CHEN Hangjun, et al. High-efficiency extraction and in vitro bioactivity of amygdalin from peach kernel[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2023,23(4):146−156.] HUANG Xinli, WU Weijie, CHEN Hangjun, et al. High-efficiency extraction and in vitro bioactivity of amygdalin from peach kernel[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 23(4): 146−156.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
