Optimization of Wall-disruption Process of Rose Bee Pollen and Comparison of Physiological Activities of Its Ethanol Extracts
-
摘要: 玫瑰蜂花粉气味芳香、口感清甜,富含多酚等活性物质,是极具营养价值和开发潜力的天然保健品。本研究以玫瑰蜂花粉为研究对象,旨在优化其酶解破壁工艺条件,并比较不同乙醇提取物的生理活性及主要成分含量,以期筛选抗炎和抗良性前列腺增生(Benign prostatic hyperplasia,BPH)活性最佳的玫瑰蜂花粉提取物。结果显示,玫瑰蜂花粉双酶解法破壁最优工艺参数是料液比为1:30、温度55 ℃、pH6、复合酶体系添加量2.0%(纤维素酶:复合蛋白酶=7:5),反应9 h,可得最佳破壁率为73.13%;90%乙醇提取的活性物质能显著(P<0.01)降低脂多糖诱导的RAW264.7细胞炎症因子释放水平(20 μg/mL时,与造模组相比,一氧化氮、白细胞介素-6和肿瘤坏死因子-α分别降低了67.04%、16.74%、21.74%)并对BPH-1细胞活力和增殖有最明显的抑制作用,因此具有最佳的抗炎和抗BPH效果。本研究为明确玫瑰蜂花粉中的活性成分及进一步开发其深加工产品提供了理论依据。Abstract: Rose bee pollen has a pleasant aroma and a sweet taste, and it is rich in polyphenols and other bioactive substances, making it a highly nutritious and promising natural health product. To optimize the enzymatic hydrolysis process for rose bee pollen and to systematically compare the physiological activities and primary component profiles of its different ethanolic extracts. This was done with the aim of discerning the most efficacious extract that possessed significant anti-inflammatory and anti-benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) effects. The results demonstrated that the optimal enzymatic hydrolysis process parameters for rose bee pollen were a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:30, a temperature of 55 °C, pH6, a composite enzyme system addition of 2.0% (cellulase comprising a ratio of 7:5 with composite protease), and a reaction time of 9 h, resulting in the highest wall-disruption rate of 73.13%. The active substances extracted with 90% ethanol could significantly (P<0.01) reduce the release level of inflammatory factors induced by lipopolysaccharide in RAW264.7 cells (at 20 μg/mL, compared with the model group, nitric oxide, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α decreased by 67.04%, 16.74% and 21.74% respectively), and had the most obvious inhibitory effect on the activity and proliferation of BPH-1 cells, thus exhibiting optimal anti-inflammatory and anti-BPH effects. This research provides a theoretical basis for identifying the active ingredients in rose bee pollen and further developing value-added processed products.
-
蜂花粉(Bee pollen)是蜜蜂将采集的蜜源植物花粉球与花蜜及唾液等自身的腺体分泌物互相掺杂后形成的不规则扁圆形颗粒物[1−2]。蜂花粉既源于植物的生殖细胞,又是蜜蜂的重要营养来源,富含生命所需的各类营养成分和功能因子[3],因此有着“天然微型全能营养库”之称。研究发现,蜂花粉具有突出的抗氧化[4−6]、抗炎[7]、抗癌[8]、免疫调节[9]以及改善前列腺疾病[10−11]等多种活性功能,是一种极具营养价值的天然保健品,有巨大的潜力应用于疾病辅助治疗,保障人民生命健康。玫瑰蜂花粉是我国产量较大的一种蜂花粉,其富含蛋白质[12]、多酚[13]等活性物质的同时,相比其他蜂花粉具有独特的风味和上乘的口感,十分适用于营养保健品的开发。
然而,蜂花粉外层的花粉壁具有较强抗生物分解特性,使机体对其内容物的消化吸收较为困难,影响蜂花粉功效。因此,开发有效的破壁方法,提取蜂花粉中活性物质,最大程度发挥蜂花粉功效,是推动蜂花粉功能性产品开发的必要手段。蜂花粉的常用破壁方式有物理法、化学法、生物法以及复合破壁法[14]。其中,生物法破壁效应好,反应条件温和,对活性成分影响小,还可以将大分子化合物降解为利于人体消化吸收的小分子化合物[15]。当前尚未有文章报道玫瑰蜂花粉的破壁提取工艺,这极大地限制了对玫瑰蜂花粉生物活性的开发利用。
良性前列腺增生(Benign prostatic hyperplasia,BPH)是一种多发于50岁以上中老年男性的泌尿系统慢性病,其特征是下尿路症状、不受控制的增生和前列腺扩大[16−17],因高发病率、高治疗成本而给公众健康造成巨大负担。尽管BPH的确切发病机制尚未完全阐明,但多项研究表明慢性炎症在BPH的病程中起着重要的推动作用,大多数BPH组织样本中均存在炎性浸润,这可能与前列腺组织中细胞凋亡与增殖的失衡有关[18−19]。
多项研究证实蜂花粉具有改善良性前列腺增生的功效[20],然而尚未有关于玫瑰蜂花粉活性成分的抗炎和抗BPH效果的报道。因此本研究旨在通过优化破壁工艺和提取分离方法从玫瑰蜂花粉中高效地提取活性物质,并探究验证其抗炎和抗BPH作用,为推动玫瑰蜂花粉的功能性产品开发,促进其辅助应用于BPH的治疗,提供相应的理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
玫瑰蜂花粉 上海森蜂园蜂业有限公司;纤维素酶(10000 U/g) 上海麦克林生化试剂有限公司;复合蛋白酶(BR,120 U/mg) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;EdU-488细胞增殖检测试剂盒、NO检测试剂盒 上海碧云天生物技术有限公司;小鼠TNF-α ELISA试剂盒、小鼠IL-6 ELISA试剂盒 上海纪宁生物科技有限公司;CCk-8检测试剂盒 上海世泽生物科技有限公司;所有化学试剂均为分析纯;人前列腺增生上皮细胞(BPH-1) 上海通蔚实业有限公司提供;小鼠单核巨噬细胞白血病细胞(RAW264.7) 由武汉尚恩生物技术有限公司提供;培养基为DMEM-HG(添加10%胎牛血清和1%双抗),在37 ℃,含95%空气和5% CO2恒温培养箱中培养。
Multiskan GO酶标仪 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;SW-CJ-1F超净工作台 苏州安泰空气技术有限公司;F90(HT)恒温培养箱 上海齐欣科学技术有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品前处理与缓冲液的配制
将玫瑰蜂花粉用高速粉碎机粉碎,并过60目筛;准确称取1.0 g左右蜂花粉于50 mL离心管,然后向管中加入一定量柠檬酸盐缓冲液以调节pH。每个水平设置3个重复试验。
1.2.2 玫瑰蜂花粉双酶解法破壁单因素实验
1.2.2.1 纤维素酶与复合蛋白酶添加比例的确定
在pH5,温度为45 ℃,料液比1:20(g/mL)的条件下,向玫瑰蜂花粉-缓冲液体系中分别添加体积比为0.6%~1.8%的纤维素酶,并在最佳纤维素酶添加量的基础上添加0.2%~1.2%的复合蛋白酶并测定破壁率。
1.2.2.2 pH对玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率的影响
按照料液比1:20和体积分数1.5%向蜂花粉中加入缓冲液和复合酶体系,分别在pH3、4、5、6、7,温度为45 ℃的条件下振荡水浴加热9 h;反应结束后,立即测定玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率。
1.2.2.3 复合酶添加量对玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率的影响
控制pH5,温度为45 ℃,料液比1:20(g/mL),向蜂花粉中分别加入1.0%、1.5%、2.0%、2.5%、3.0%的复合酶体系反应9 h并测定玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率。
1.2.2.4 温度对玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率的影响
向pH5,料液比1:20(g/mL)的缓冲液中加入1.5%的复合酶,分别在温度为40、45、50、55、60 ℃的条件下振荡水浴9 h并测定玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率。
1.2.2.5 料液比对玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率的影响
分别按照料液比1:20、1:30、1:40、1:50、1:60(g/mL)向蜂花粉中加入缓冲液,调节pH5并加入1.5%的复合酶,45 ℃振荡水浴9 h;测定玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率。
1.2.2.6 时间对玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率的影响
向pH5,料液比1:20(g/mL)的缓冲液中加入1.5%的复合酶,45 ℃分别振荡水浴加热6、9、12、15、18 h并测定玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率。
1.2.3 破壁率的测定
吸取适量破壁蜂花粉液,制成玻片,在10×20倍的光学显微镜下观察并计数,每个组别的破壁率随机取5个视野下的破壁率求平均值。
破壁率(%)=视野中破壁蜂花粉数量视野中蜂花粉总数×100 1.2.4 正交试验设计
在单因素实验基础上,进行三因素三水平L9(34)的正交试验,并通过极差分析获得玫瑰蜂花粉双酶解法最优破壁条件。设计表见表1。
表 1 玫瑰蜂花粉破壁影响因素正交试验设计Table 1. Orthogonal experimental design of influencing factors on wall-breaking of rose bee pollen试验号 A温度(℃) B酶添加量(%) C pH 1 1(50) 1(1.5) 1(4) 2 1 2(2.0) 2(5) 3 1 3(2.5) 3(6) 4 2(55) 1 2 5 2 2 3 6 2 3 1 7 3(60) 1 3 8 3 2 1 9 3 3 2 1.2.5 超声辅助提取活性物质
参考文献[11]中的提取方法,破壁玫瑰蜂花粉按1:30(g/mL)的料液比加入不同浓度乙醇溶液(50%、70%、90%),以50 ℃、频率53 Hz超声提取30 min后,离心收集上清,将沉淀以同一方式再提取1次,合并两次上清液,抽滤得醇提液。减压浓缩除去乙醇并进行真空冷冻干燥后,即得玫瑰蜂花粉醇提物。
1.2.6 CCK-8法检测细胞活力
BPH-1细胞按照约每孔5000个、RAW264.7细胞按照约每孔3×104个分别在96孔板中培养24 h和12 h后,向BPH-1细胞培养板中以100 μg/mL浓度分别加入3种醇提物,RAW264.7细胞培养板中加入不同浓度的3种玫瑰蜂花粉醇提物或LPS,分别孵育24 h;然后按照10 μL/孔加入CCK-8试剂,37 ℃孵育2 h后450 nm下测定吸光值。
1.2.7 NO含量检测
RAW264.7细胞设置NC组、LPS组(1 μg/mL LPS)、蜂花粉提取物组(1 μg/mL LPS+10~30 μg/mL 3种蜂花粉提取物),孵育24 h后取各组培养基上清,按照NO试剂盒方法测定NO含量。
1.2.8 炎症因子IL-6、TNF-α含量检测
RAW264.7细胞设置NC组、LPS组和高低剂量蜂花粉提取物组(10 μg/mL和20 μg/mL),孵育24 h后取各组培养基上清,按照ELISA试剂盒说明检测IL-6、TNF-α含量。
1.2.9 EdU法检测BPH-1细胞增殖情况
BPH-1细胞经相应处理后加入EdU标记2 h,然后进行固定、Alexa Fluor 488染色、Hoechst 33342染色,通过倒置荧光显微镜定性观察和流式细胞仪定量检测EdU阳性细胞。
1.2.10 总酚含量的检测
采用王晶[21]的方法:以没食子酸为标品,制得标准曲线(y=0.0087x+0.0727,R2=0.999);取100 μL适当稀释的提取液,加入250 μL福林酚、250 μL 15% Na2CO3溶液和400 μL去离子水,混匀。40 ℃水浴1 h,静置冷却至室温后在778 nm下检测吸光值。
1.2.11 黄酮含量的检测
参照GB/T 30359-2013进行蜂花粉中黄酮类化合物的测定[22]。以芦丁为标品,制得标准曲线(y=0.8145x+0.0488,R2=0.997)。
1.2.12 总糖含量的检测
参考张萍等[23]的方法。以葡萄糖为标品,制得标准曲线(R2=0.999);取1 mL适当稀释的样品溶液,加入0.5 mL 5%苯酚溶液、2.5 mL浓H2SO4,混合均匀后静置30 min,测定497 nm处的吸光值,制得标准曲线(y=8.6559x+0.07641,R² = 0.999)。
1.2.13 可溶性糖含量的检测
参考李文砚等[24]的方法,以葡萄糖为标品,绘制标准曲线(y=3.7073x+0.1309,R² = 0.999);取样品溶液1 mL,加入5 mL蒽酮检测试剂,混匀后沸水浴10 min,冷却,620 nm测定吸光度。
1.3 数据处理
绘图、数据处理和统计分析使用Origin 2018和IBM SPSS Statistics 26软件进行。实验均进行3次重复,数据以均值±标准差(mean±SD)表示,并使用T检验分析样本差异。P<0.05时认为有统计学差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 双酶解法对玫瑰蜂花粉的破壁效果评价
2.1.1 纤维素酶与复合蛋白酶添加比例的确定
纤维素酶可以水解玫瑰蜂花粉内壁中的主要成分—纤维素[25],复合蛋白酶则可分解花粉壁和萌发孔的重要构成之一的蛋白质[26]。为了确定两种酶在体系中的添加比例,首先探究纤维素酶添加量对玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率的影响。
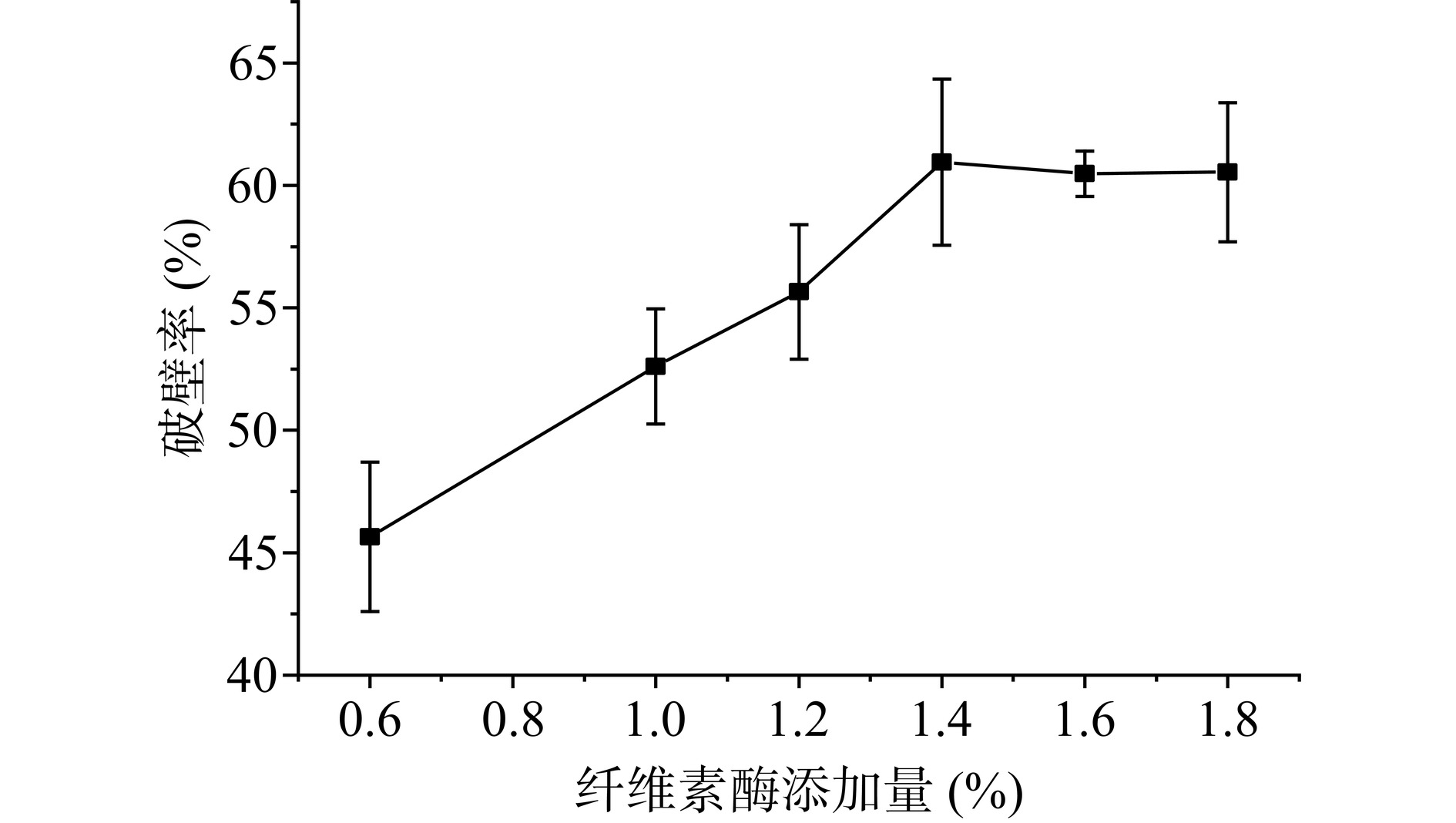
如图1所示,破壁率随着纤维素酶含量的上升而提高,但当纤维素酶添加量高于1.4%后,破壁率变化缓慢,综合成本等因素考虑,选择1.4%的纤维素酶添加量进行后续实验。
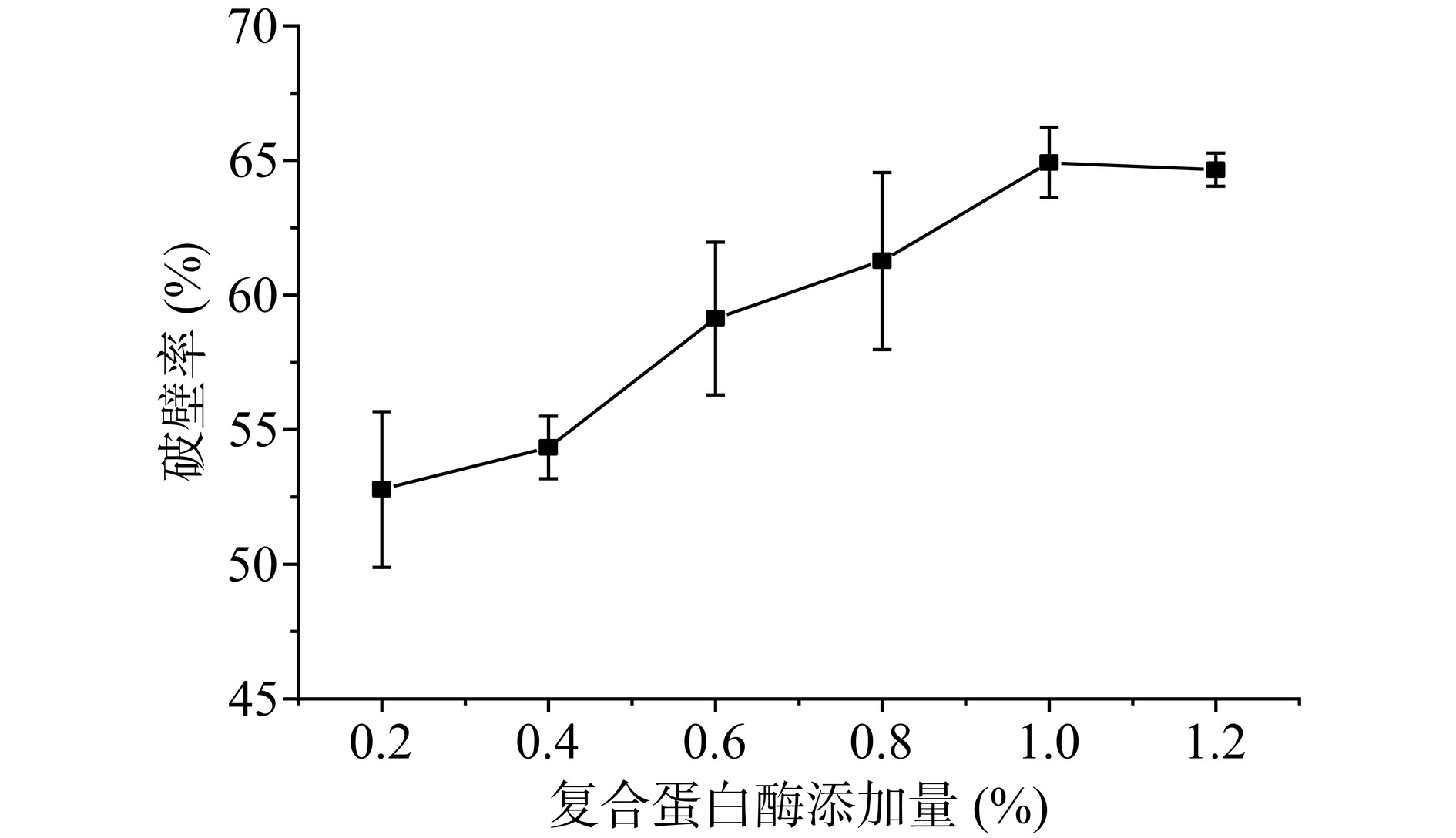
在确定了最佳纤维素酶添加量的基础上,分别添加不同比例的复合蛋白酶,其对破壁率的影响如图2所示。在复合蛋白酶的添加量小于1.0%时,玫瑰蜂花粉的破壁率提高明显,而添加量大于1.0%后,破壁率几乎没有变化,因此选择1.0%为复合蛋白酶的最佳添加量。此时纤维素酶与复合蛋白酶的添加比例为7:5。
2.1.2 pH对玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率的影响
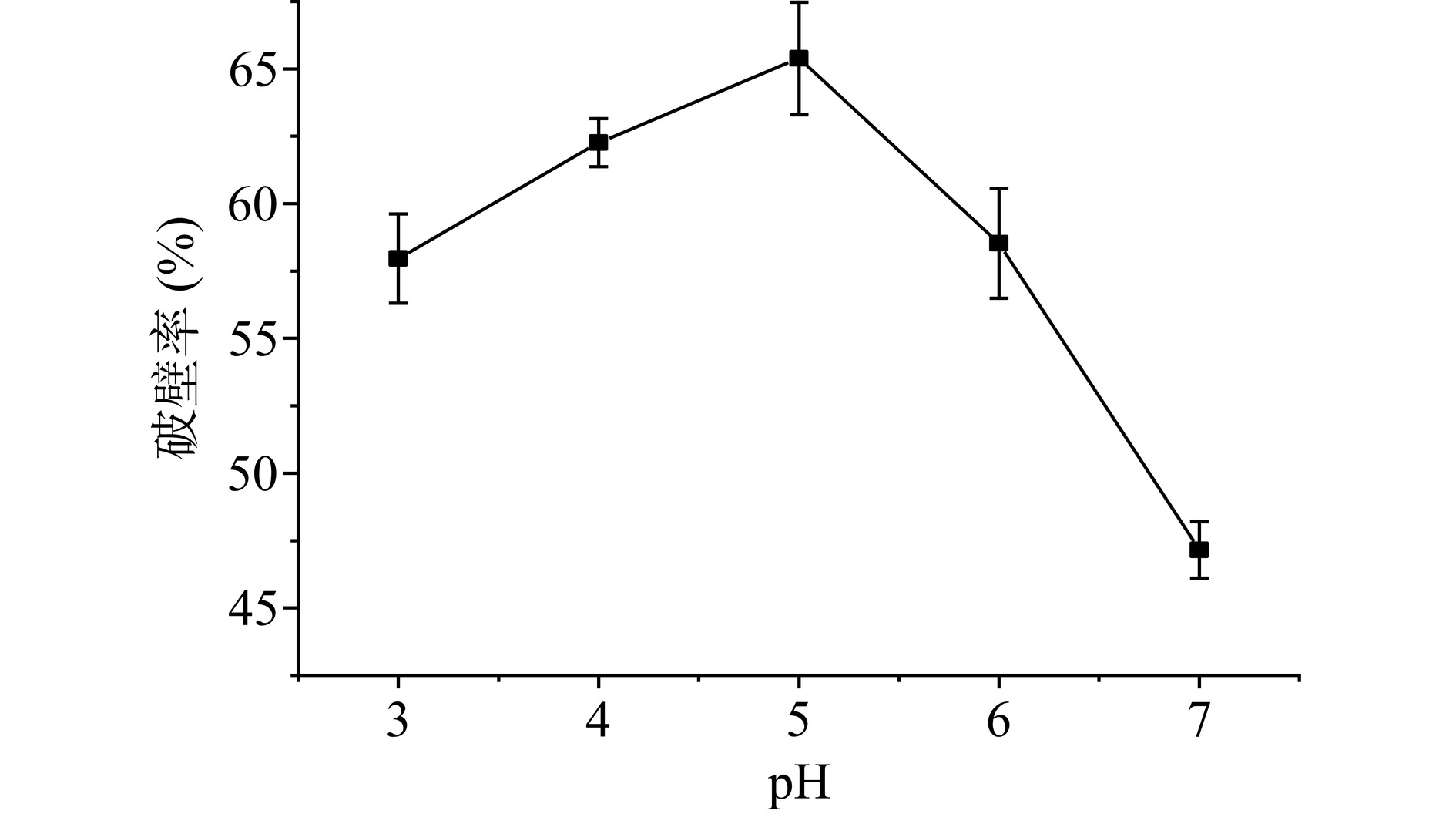
pH对酶活有较大影响,合适的pH能够促进酶与底物结合[27] ,因实验选择的两种生物酶最适pH不同,因此实验探究了在建议pH范围内破壁率的变化。由图3可知,控制其他因素不变,当pH在3~5时,蜂花粉的破壁率逐渐提高,当pH在5~7时,破壁率随着pH的增大迅速下降。这可能是因为在pH不合适的情况下,酶分子的部分氨基酸侧链上的质子化状态会发生改变,影响其空间构象,致使酶的催化中心与底物结合的概率减小或者酶活性降低。基于本实验结果,确定复合酶体系最适的酶解pH为5。
2.1.3 复合酶添加量对玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率的影响
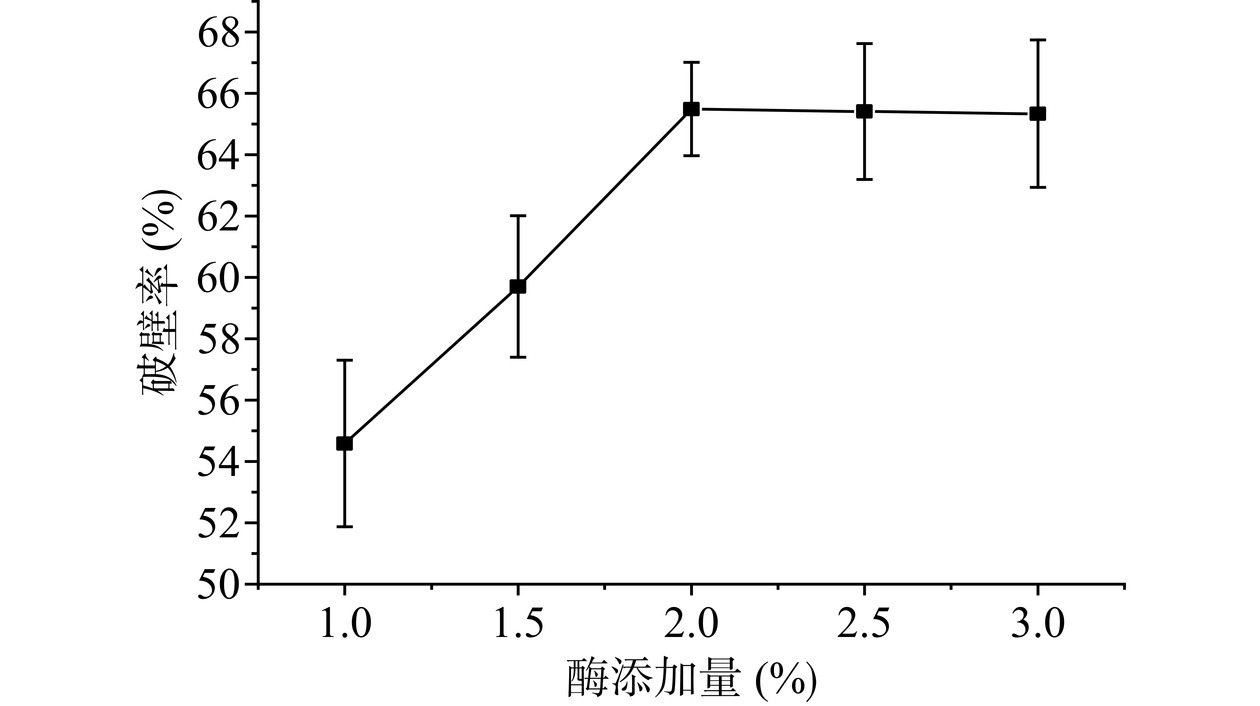
根据2.1.1中结果,纤维素酶与复合蛋白酶添加比例为7:5时破壁率较高,而酶使用量是限制生物酶法实际生产应用的关键[28],因此实验探究了在这一比例下,不同复合酶添加量对破壁率的影响,以降低酶使用量。如图4所示,当复合酶添加量小于2.0%时,随着酶含量的增加,破壁率有着明显的提高;而当加酶量大于2.0%后,破壁率略有降低。这可能因为随着酶浓度的提高,酶解速率也逐渐提高,但酶浓度饱和后,体系的反应速率已经达到峰值,继续提高酶添加量,反而可能会导致反应成本的增加,甚至削弱酶解效果。因此,2.0%为复合酶的最佳添加量。
2.1.4 温度对玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率的影响
温度显著影响酶活力,进而影响玫瑰蜂花粉的破壁率,因此复合酶的最适温度需要进行探究。如图5所示,随着温度的升高,破壁率先上升后下降,在55 ℃时破壁率最高。这是由于过高的温度会改变酶分子的空间构象,从而使酶的活性降低甚至失去催化活性[29],进而影响2种酶对玫瑰蜂花粉花粉壁成分的分解效果。所以本实验的最佳水浴温度是55 ℃。
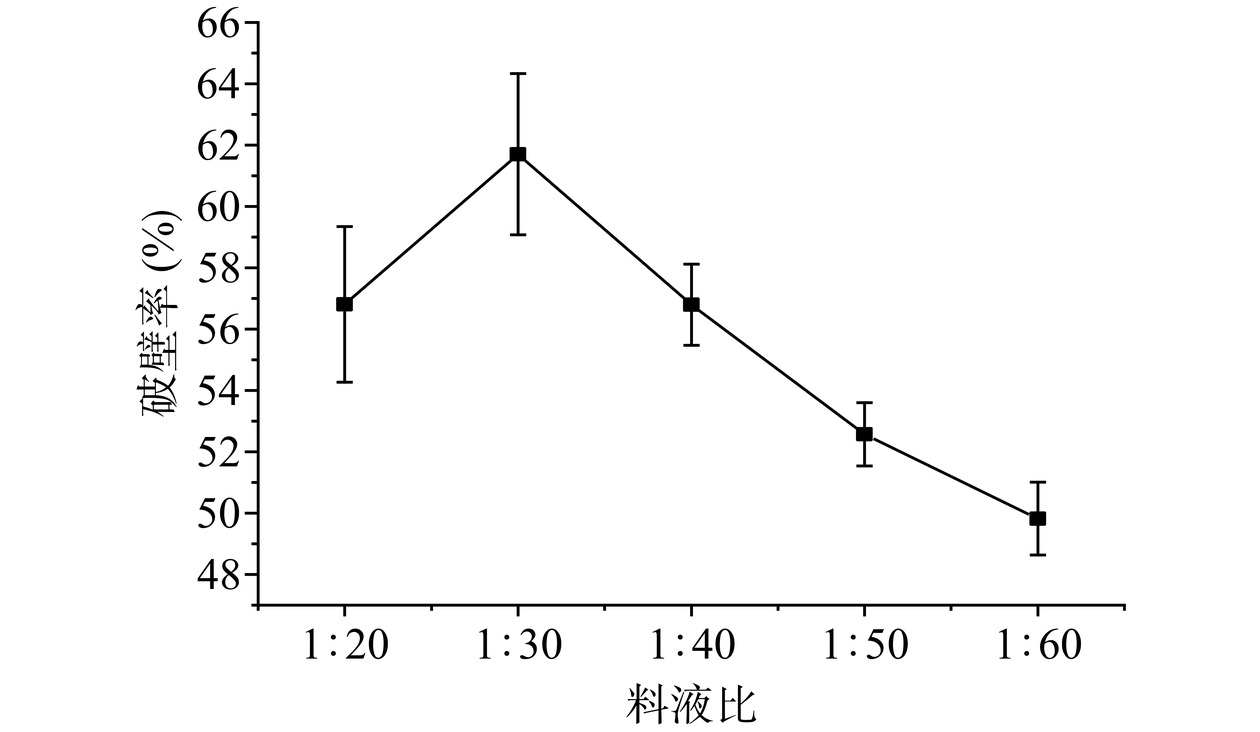
2.1.5 料液比对玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率的影响
蜂花粉溶液的浓度直接影响蜂花粉与酶的接触几率,进而影响酶的催化反应和破壁效率。如图6所示,其他条件不变,玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率随着缓冲液比例的增加先提高后降低,在1:30时,破壁率达到最大值。这是因为随着溶剂体积的增多,酶与蜂花粉的接触越来越充分,破壁率随之上升;而当料液比进一步增加,单位体积内的蜂花粉越来越少,酶与底物的有效碰撞频率也越来越小,导致破壁率的下降[30]。因此,料液比选择1:30为宜。
2.1.6 时间对玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率的影响
随着酶解反应时间的延长,底物被消耗殆尽,反应速率逐渐降低,此时反应时间已经充分[27]。由图7可知,当酶解时间达到9 h后,蜂花粉破壁率趋于平缓,继续增加时间无法再明显提高破壁率。因此,从实际生产需要出发,最优酶解时间为9 h。
2.1.7 正交试验优化结果分析
上述结果反映了单因素对玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率的影响,但实际实验过程中,破壁率是同时受各种因素交互影响的,因此在单因素实验的基础上,以破壁率为指标,取酶解温度、复合酶添加量、pH作为考察因素,设计正交试验。结果见表2。
表 2 玫瑰蜂花粉破壁影响因素正交试验结果Table 2. Orthogonal experimental results of influencing factors on wall-breaking of rose bee pollen试验号 A温度(℃) B酶添加量(%) C pH 破壁率(%) 1 1(50) 1(1.5) 1(4) 57.83 2 1 2(2.0) 2(5) 68.07 3 1 3(2.5) 3(6) 72.08 4 2(55) 1 2 59.10 5 2 2 3 73.13 6 2 3 1 69.36 7 3(60) 1 3 57.38 8 3 2 1 64.26 9 3 3 2 59.50 k1 65.99 58.10 63.82 k2 67.20 68.49 62.22 k3 60.38 66.98 67.53 R 6.82 10.38 5.31 由表2可知,3个因子影响主次顺序依次为:B>A>C,即酶添加量>温度>pH。实验结果表明,玫瑰蜂花粉达到最佳破壁效果的条件为A2B2C3,即反应时间为9 h,料液比为1:30,复合酶添加量为2.0%,pH为6,温度为55 ℃。在此条件下,玫瑰蜂花粉破壁率为73.13%。相较于单一的纤维素酶破壁工艺[31],本法使用纤维素酶-复合蛋白酶体系对玫瑰蜂花粉进行破壁,大幅降低了酶添加量,同时细化了反应pH的要求,具有一定的参考意义。
2.2 玫瑰蜂花粉3种醇提物的体外抗炎活性比较
醇提法是较为常见的活性物质的提取方法,本实验选50%、70%、90%乙醇溶液作为溶剂,利用其不同的极性从而提取分离出不同的活性组分,并采用对组分破坏小、操作简单的超声波法辅助,提高提取效率。然后对三种醇提物的体外抗炎活性进行比较。
慢性炎症可能是BPH发生及临床进展的重要影响因素[32],其中巨噬细胞的异常活跃会导致大量炎症介质释放。因此通过玫瑰蜂花粉3种醇提物对RAW264.7细胞的影响来探究其抗炎活性。
2.2.1 细胞活性
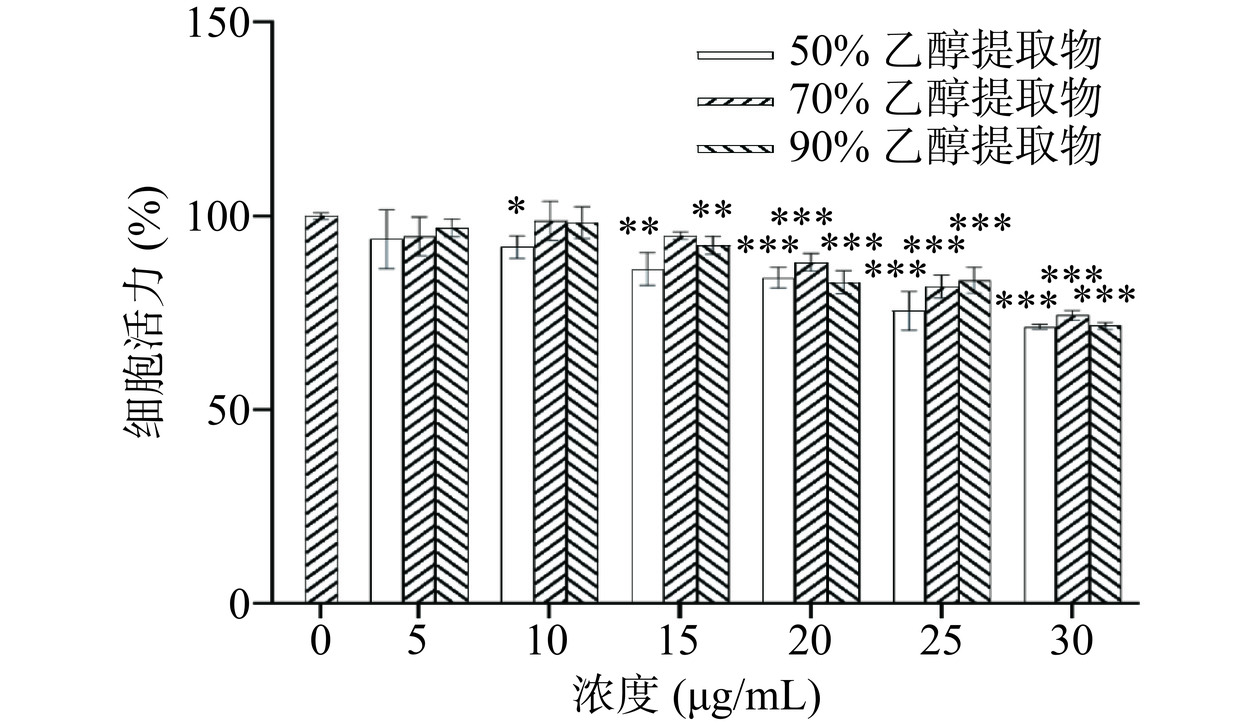
为了确定用于探究体外抗炎活性的合适的醇提物浓度,采用CCK-8法测定不同浓度的3种醇提物对RAW264.7细胞活力的影响,结果如图8所示。浓度为5 μg/mL时,与对照组相比,三种提取物处理下RAW264.7细胞活力无显著差异;实验浓度下,各提取物对RAW264.7细胞活力的抑制作用呈现出剂量依赖性,当提取物浓度为20 μg/mL时,50%、70%和90%乙醇提取物组细胞活力均大于80%,分别为84.1%、88.1%和83.0%,3种提取物的细胞毒性较低。因此,后续以10和20 μg/mL作为低、高剂量组探究蜂花粉醇提物的抗炎效果。
2.2.2 LPS诱导的细胞NO释放水平
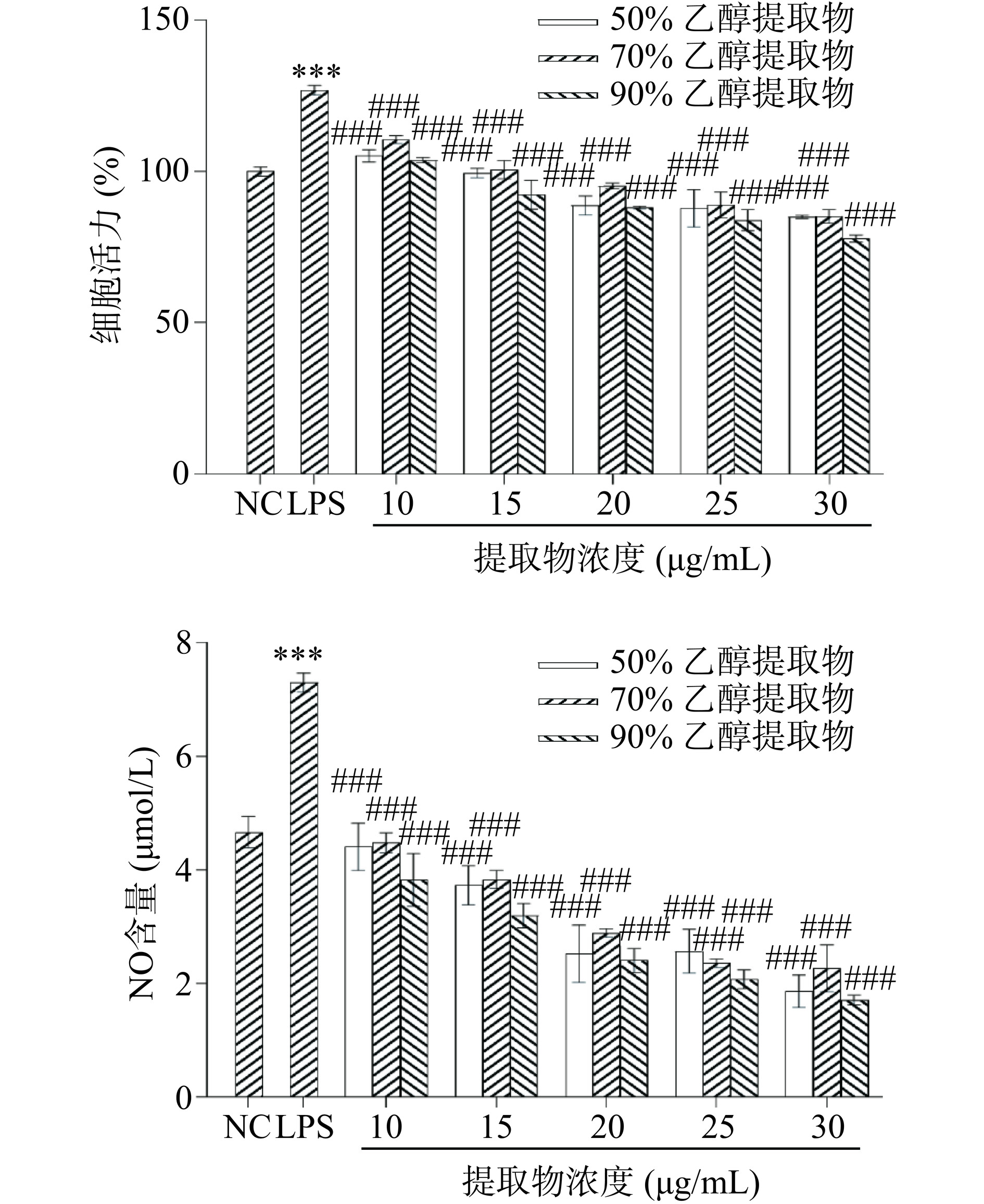
图9展示了3种醇提物对LPS诱导的RAW264.7细胞存活率和NO水平的影响。结果显示,与NC组相比,LPS处理诱导了RAW264.7细胞的过度激活,而3种蜂花粉提取物均能逆转这一趋势。在10~30 μg/mL时,各组提取物对RAW264.7细胞活性的抑制效果呈现剂量依赖性,其中,90%乙醇提取物在各个浓度下对RAW264.7细胞过度激活的抑制效果优于50%和70%乙醇提取物。
![]() 图 9 3种醇提物对LPS诱导的RAW264.7细胞活性和NO水平的影响注:#号表示与模型组相比差异显著,其中#,P<0.05;##,P<0.01;###,P<0.001,图10同。Figure 9. Effects of three alcoholic extracts on LPS-induced activity and NO levels in RAW264.7 cells
图 9 3种醇提物对LPS诱导的RAW264.7细胞活性和NO水平的影响注:#号表示与模型组相比差异显著,其中#,P<0.05;##,P<0.01;###,P<0.001,图10同。Figure 9. Effects of three alcoholic extracts on LPS-induced activity and NO levels in RAW264.7 cells巨噬细胞活化导致NO释放水平升高是LPS刺激RAW264.7细胞炎症模型的典型反应[32]。如图9右图所示,LPS处理显著增加了RAW264.7细胞释放的NO水平(P<0.001),这可能是由于LPS激活巨噬细胞,诱导局部炎症和抗体的产生,影响体内iNOS的表达,进而影响NO释放量。在实验浓度下,3种醇提物处理显著抑制NO释放量,且在相同浓度下,与50%和70%乙醇提取物相比,90%乙醇提取物可以使NO水平下降至更低水平。
2.2.3 LPS诱导的细胞IL-6和TNF-α释放量
巨噬细胞能够分泌多种炎症因子[33],为了研究三种蜂花粉醇提物对炎症因子产生的影响,通过ELISA测定RAW264.7细胞分泌IL-6和TNF-α的水平。结果如图10所示,高低剂量的3种醇提物都能够显著抑制LPS刺激介导的两种细胞因子的增加(P<0.05),并使其恢复至对照组水平(P>0.05),其中90%乙醇提取物的效果更好。
2.3 玫瑰蜂花粉3种醇提物对BPH-1细胞增殖情况的影响
在验证蜂花粉酶解提取物的抗炎活性后,比较了3种醇提物对人前列腺增生上皮细胞(BPH-1)增殖情况的影响。
2.3.1 细胞活性
相同浓度的50%、70%、90%乙醇提取物分别处理BPH-1细胞24 h后,采用CCK-8法检测细胞活力。结果如图11所示,当提取物浓度小于80 μg/mL时,3种醇提物对细胞活力均没有显著影响,当玫瑰蜂花粉醇提物浓度在100~500 μg/mL时,随着其浓度的增加,三种醇提物均显著降低BPH-1细胞的活力,并且50%、70%、90%乙醇提取的活性物质对BPH-1细胞增殖抑制效果依次增强,其中90%醇提物抑制效果最好。
2.3.2 细胞增殖
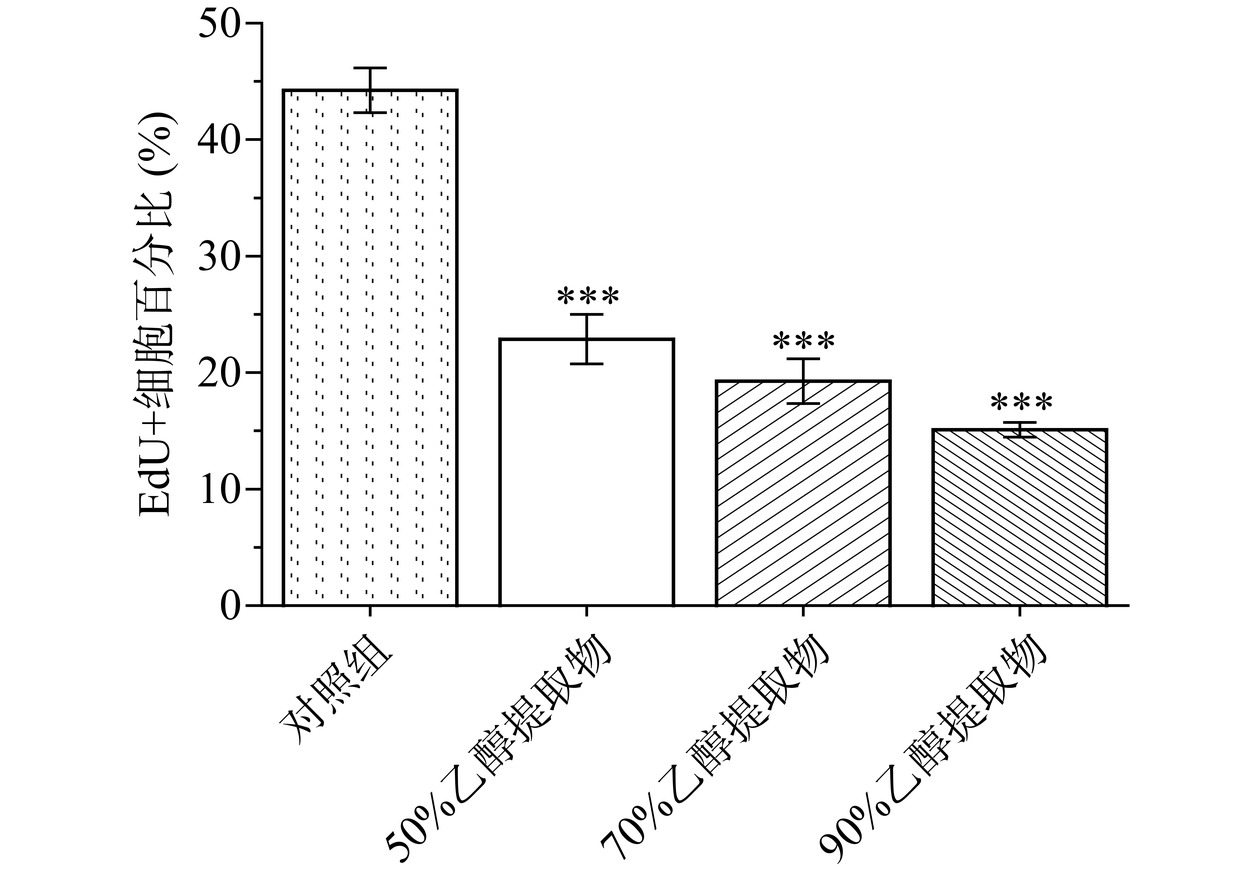
EdU是一种胸腺嘧啶脱氧核苷类似物,当细胞处于DNA合成期时,它可以进入到新合成的DNA中,利用流式测定被荧光标记的EdU含量,就能准确检测出新增殖细胞的占比。如图12所示,可以看出与对照组相比,50%、70%、90%乙醇的提取物刺激下BPH-1细胞的新增殖的细胞数量明显降低,且90%乙醇提取的活性物质抑制增殖效果最好。
2.4 玫瑰蜂花粉3种醇提物主要成分含量比较
根据上述结果,破壁玫瑰蜂花粉90%醇提物具备最显著的抗炎和抑制BPH-1细胞增殖的作用,故对其主要活性成分进行检测和比较,结果见表3。通过总糖和可溶性糖含量的测定,发现醇提物中的糖主要为可溶性糖,其中90%乙醇提取物中的可溶性糖约占总糖含量的92.7%,说明90%醇提物中多糖含量较少,这主要是因为多糖难溶于乙醇;90%醇提物还含有最丰富的酚类物质,其中黄酮含量占总酚含量的82.31%,其最优的抗炎和抑制BPH-1细胞增殖的作用可能与高含量的酚类物质有关。
表 3 玫瑰蜂花粉3种醇提物主要成分的含量Table 3. Content of the main components of three alcoholic extracts of rose bee pollen成分(mg/g) 50%乙醇提取物 70%乙醇提取物 90%乙醇提取物 总糖 80.50±1.94c 96.29±0.70b 109.52±0.95a 可溶性糖 76.11±1.05c 87.35±1.69b 103.27±1.97a 总酚 47.03±0.11c 52.65±1.46b 67.72±0.51a 黄酮 34.06±0.54c 36.59±0.70b 55.74±0.30a 注:同行不同字母表示组间有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 3. 讨论与结论
我国玫瑰蜂花粉产量丰富,开发潜力巨大[34],因此探究一种安全高效的活性物质提取工艺,并对提取物进行功能的验证,对于推动玫瑰蜂花粉功能性保健食品的开发、提升相关产业的效益和发展都具有一定的积极意义。酶解破壁条件温和,对活性成分的影响小,还能通过生物反应降解大分子物质,提高机体对其活性物质的利用[35]。因此,为了便于后续对蜂花粉活性物质的提取,本研究选取酶解法先进行蜂花粉破壁,促进有效物质的溶出,然后利用超声辅助醇提增加提取效率[36],最终确定了纤维素酶-复合蛋白酶破壁玫瑰蜂花粉的最佳工艺参数为料液比1:30、温度55 ℃、pH6、加入2%的复合酶体系(其中纤维素酶:复合蛋白酶=7:5)、反应时间9 h,蜂花粉内壁破壁率为73.13%。
同时,研究发现蜂花粉90%乙醇提取物的抗炎效果优于50%和70%乙醇提取物,且对BPH-1细胞增殖的抑制作用更为显著。进一步比较三者的主要成分后发现,90%醇提物含有更丰富的多酚和黄酮。本研究揭示了玫瑰蜂花粉不同醇提物中活性成分在化学成分和抑制炎症与BPH效果上的差异,这一发现为继续研究这些差异物质的具体结构和作用机制奠定了基础,为开发风味更佳、更具有针对性改善疾病效果的产品提供了方向。
多酚和黄酮据报道有多重生物功效[37]和突出的抗炎活性[38−39],有可能是蜂花粉抗BPH的关键活性成分。但是蜂花粉中还存在其他活性物质[40],如维生素、类胡萝卜素、谷胱甘肽,n-6/n-3多不饱和脂肪酸[41]和植物甾醇[42]等,在本研究中尚无法明确关键物质,还需更进一步的实验探究,以更好地为玫瑰蜂花粉开发利用提供指导。
-
图 9 3种醇提物对LPS诱导的RAW264.7细胞活性和NO水平的影响
注:#号表示与模型组相比差异显著,其中#,P<0.05;##,P<0.01;###,P<0.001,图10同。
Figure 9. Effects of three alcoholic extracts on LPS-induced activity and NO levels in RAW264.7 cells
表 1 玫瑰蜂花粉破壁影响因素正交试验设计
Table 1 Orthogonal experimental design of influencing factors on wall-breaking of rose bee pollen
试验号 A温度(℃) B酶添加量(%) C pH 1 1(50) 1(1.5) 1(4) 2 1 2(2.0) 2(5) 3 1 3(2.5) 3(6) 4 2(55) 1 2 5 2 2 3 6 2 3 1 7 3(60) 1 3 8 3 2 1 9 3 3 2 表 2 玫瑰蜂花粉破壁影响因素正交试验结果
Table 2 Orthogonal experimental results of influencing factors on wall-breaking of rose bee pollen
试验号 A温度(℃) B酶添加量(%) C pH 破壁率(%) 1 1(50) 1(1.5) 1(4) 57.83 2 1 2(2.0) 2(5) 68.07 3 1 3(2.5) 3(6) 72.08 4 2(55) 1 2 59.10 5 2 2 3 73.13 6 2 3 1 69.36 7 3(60) 1 3 57.38 8 3 2 1 64.26 9 3 3 2 59.50 k1 65.99 58.10 63.82 k2 67.20 68.49 62.22 k3 60.38 66.98 67.53 R 6.82 10.38 5.31 表 3 玫瑰蜂花粉3种醇提物主要成分的含量
Table 3 Content of the main components of three alcoholic extracts of rose bee pollen
成分(mg/g) 50%乙醇提取物 70%乙醇提取物 90%乙醇提取物 总糖 80.50±1.94c 96.29±0.70b 109.52±0.95a 可溶性糖 76.11±1.05c 87.35±1.69b 103.27±1.97a 总酚 47.03±0.11c 52.65±1.46b 67.72±0.51a 黄酮 34.06±0.54c 36.59±0.70b 55.74±0.30a 注:同行不同字母表示组间有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 何佳洁, 汪燕, 马振刚. 综述蜂花粉的广泛应用[J]. 蜜蜂杂志,2020,40(1):13−17. [HE J J, WANG Y, MA Z G. Review on the widespread application of bee pollen[J]. Journal of Bee,2020,40(1):13−17.] HE J J, WANG Y, MA Z G. Review on the widespread application of bee pollen[J]. Journal of Bee, 2020, 40(1): 13−17.
[2] JOSÉ S S, ESTEFANÍA S R, SILVIA S D, et al. Bee products - chemical and biological properties[M]. Berlin:Springer International Publishing, 2017:221−277.
[3] VOLKAN A, SORAIA I. F, SEYMANUR E, et al. From the hive to the table:Nutrition value, digestibility and bioavailability of the dietary phytochemicals present in the bee pollen and bee bread[J]. [J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,109:464−481.
[4] 李岚涛, 王宏, 白卫东, 等. 蜂花粉活性成分、生物活性及破壁技术研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(23):408−417. [LI L T, WANG H, BAI W D, et al. Research progress on bioactive ingredients, biological activity and wall-breaking technology of bee pollen[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(23):408−417.] LI L T, WANG H, BAI W D, et al. Research progress on bioactive ingredients, biological activity and wall-breaking technology of bee pollen[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(23): 408−417.
[5] BARBIERI D, GABRIELE M, SUMMA M, et al. Antioxidant, nutraceutical properties and fluorescence spectral profiles of bee pollen samples from different botanical origins[J]. Antioxidants (Basel),2020,9(10):1001. doi: 10.3390/antiox9101001
[6] 周望庭, 米佳, 禄璐, 等. 枸杞蜂花粉主要化学成分与抗氧化作用[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(4):219−224. [ZHOU W T, MI J, LU L, et al. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of Chinese wolfberry bee pollen[J]. Food Science,2018,39(4):219−224.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201804033 ZHOU W T, MI J, LU L, et al. Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of Chinese wolfberry bee pollen[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(4): 219−224. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201804033
[7] RZEPECKA-STOJKO A, PILAWA B, RAMOS P, et al. Antioxidative properties of bee pollen extracts examined by EPR spectroscopy[J]. J Apic Sci,2012,56:23−31.
[8] WAN A, NUR A, NURDIANAH H, et al. Bee pollen extract of Malaysian stingless bee enhances the effect of cisplatin on breast cancer cell lines[J]. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine,2016,6(3):265−269. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.12.011
[9] PAGES, EL-BIALY B E, ABDEEN E E, EL-BORAI N B, et al. Experimental studies on some immunotoxicological aspects of aflatoxins containing diet and protective effect of bee pollen dietary supplement[J]. Pak J Biol Sci,2016,19(1):26−35.
[10] JIN B, JU J, NUGROHO A, et al. Carica papaya leaf extract inhibits prostatitis-associated prostatic hyperplasia via the TRAF6/TAK1/MEK/NF-κB pathway[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2021,135:111197.
[11] 达热卓玛, 饶剑, 徐德平. 油菜蜂花粉中抗前列腺增生的活性成分[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2018,37(1):38−43. [DARE Z M, RAO J, XU D P. Anti-prostatic hyperplasia activity and ingredient of rape bee pollen[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2018,37(1):38−43.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2018.01.007 DARE Z M, RAO J, XU D P. Anti-prostatic hyperplasia activity and ingredient of rape bee pollen[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2018, 37(1): 38−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2018.01.007
[12] 牛德芳, 刘萍, 张翠平, 等. 蜂花粉营养成分及其提取物抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(8):192−198. [NIU D F, LIU P, ZHANG C P, et al. Nutrient components and antioxidant activities of extracts from bee pollens[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(8):192−198.] NIU D F, LIU P, ZHANG C P, et al. Nutrient components and antioxidant activities of extracts from bee pollens[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2021, 46(8): 192−198.
[13] 黄新球, 杨有仙, 梁铖, 等. 十一种蜂花粉中总黄酮和总多酚含量分析[J]. 蜜蜂杂志,2017,37(11):3−6. [HUANG X Q, YANG Y X, LIANG C, et al. The contents of total flavonoids and polyphenols in eleven kinds of bee pollens[J]. Journal of Bee,2017,37(11):3−6.] HUANG X Q, YANG Y X, LIANG C, et al. The contents of total flavonoids and polyphenols in eleven kinds of bee pollens[J]. Journal of Bee, 2017, 37(11): 3−6.
[14] 褚珊珊, 左绍远. 蜂花粉破壁技术研究进展[J]. 蜜蜂杂志,2018,38(9):12−14. [CHU S S, ZUO S Y. Research progress on cell wall disruption method of bee pollen[J]. Journal of Bee,2018,38(9):12−14.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9139.2018.09.009 CHU S S, ZUO S Y. Research progress on cell wall disruption method of bee pollen[J]. Journal of Bee, 2018, 38(9): 12−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9139.2018.09.009
[15] 王凯, 任向楠, 董捷, 等. 多指标评价果胶酶对油菜蜂花粉的破壁作用[J]. 食品与机械,2015,31(6):164−168. [WANG K, REN X N, DONG J, et al. Effects of breaking cell wall on rape bee pollen treated with pectinase using multi-index evaluation[J]. Food & Machinery,2015,31(6):164−168.] WANG K, REN X N, DONG J, et al. Effects of breaking cell wall on rape bee pollen treated with pectinase using multi-index evaluation[J]. Food & Machinery, 2015, 31(6): 164−168.
[16] WU X Y, GU Y, LI L. The anti-hyperplasia, anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of Qing Ye Dan and swertiamarin in testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats[J]. Toxicology Letters,2017,265:9−16. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2016.11.011
[17] 刘丹, 白雪, 刘桂敏, 等. 前列腺增生症发病机制的研究进展[J]. 实用临床医药杂志,2021,25(5):112−117. [LIU D, BAI X, LIU G M, et al. Research progress on pathogenesis of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Journal of Clinical Medicine in Practice,2021,25(5):112−117.] doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20210021 LIU D, BAI X, LIU G M, et al. Research progress on pathogenesis of benign prostatic hyperplasia[J]. Journal of Clinical Medicine in Practice, 2021, 25(5): 112−117. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20210021
[18] JIANG M, STRAND D W, FRANCO O E, et al. PPARγ:A molecular link between systemic metabolic disease and benign prostate hyperplasia[J]. Differentiation,2011,82(4):220−236.
[19] EL-SHERBINY M, EL-SHAFEY M, EL-AGAWY M S E, et al. Diacerein ameliorates testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in rats:Effect on oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis[J]. International Immunopharmacology,2021,100:108082. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108082
[20] CHEN X, WU R Z, ZHU Y Q, et al. Study on the inhibition of Mfn1 by plant-derived miR5338 mediating the treatment of BPH with rape bee pollen[J]. Bmc Complementary & Alternative Medicine,2018,18(1):38−44.
[21] 王晶. 荞麦蜂花粉抗前列腺疾病与美白活性成分研究[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2017. [WANG J. Study on anti-prostate disease and whitening active ingredients of buckwheat bee pollen[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2017.] WANG J. Study on anti-prostate disease and whitening active ingredients of buckwheat bee pollen[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2017.
[22] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 国家标准化委员会. 蜂花粉:GB/T 30359-2013[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2013. [General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. Bee pollen:GB/T 30359-2013[S]. Beijing:China Standard Press, 2013.] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration. Bee pollen: GB/T 30359-2013[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2013.
[23] 张萍, 陈燕, 王晓玲. 荞麦花粉多糖的提取工艺及抗氧化性能研究[J]. 食品科技,2011,36(7):169−173. [ZHANG P, CHEN Y, WANG X L. Extraction process and antioxidant properties of buckwheat pollen polysaccharides[J]. Food Science and Technology,2011,36(7):169−173.] ZHANG P, CHEN Y, WANG X L. Extraction process and antioxidant properties of buckwheat pollen polysaccharides[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2011, 36(7): 169−173.
[24] 李文砚, 韦持章, 孔方南, 等. 蒽酮法测定木奶果果实中可溶性糖含量的研究[J]. 中国园艺文摘,2015,31(12):7−8,28. [LI W Y, WEI C Z, KONG F N, et al. Determination of soluble sugar content in wood-nut fruits by anthrone method[J]. Chinese Horticulture Abstracts,2015,31(12):7−8,28.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0873.2015.12.003 LI W Y, WEI C Z, KONG F N, et al. Determination of soluble sugar content in wood-nut fruits by anthrone method[J]. Chinese Horticulture Abstracts, 2015, 31(12): 7−8,28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0873.2015.12.003
[25] 曹稳根, 方琪琪, 方思佩, 等. 响应面法优化纤维素酶-微波提取油菜蜂花粉总黄酮工艺[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(7):3190−3196. [CAO W G, FANG Q Q, FANG S P, et al. Optimisation of cellulase-microwave extraction of total flavonoids from rapeseed bee pollen by response surface methodology[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology,2020,39(7):3190−3196.] CAO W G, FANG Q Q, FANG S P, et al. Optimisation of cellulase-microwave extraction of total flavonoids from rapeseed bee pollen by response surface methodology[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2020, 39(7): 3190−3196.
[26] 王凌波, 朱松, 陈尚卫. 油菜蜂花粉蛋白酶法破壁提取及结构表征[J]. 食品与机械,2020,36(6):151−156. [WANG L B, ZHU S, CHEN S W. Enzymatic breaking-extraction and characterization of protein from rape bee pollen[J]. Food & Machinery,2020,36(6):151−156.] WANG L B, ZHU S, CHEN S W. Enzymatic breaking-extraction and characterization of protein from rape bee pollen[J]. Food & Machinery, 2020, 36(6): 151−156.
[27] 柯巧媚, 曾威, 帅雨桐, 等. 酒糟纤维素超声波辅助酶解工艺研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(8):196−203. [KE Q M, ZENG W, SHUAI Y T, et al. Study on ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis of distiller’s grains cellulose[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(8):196−203.] KE Q M, ZENG W, SHUAI Y T, et al. Study on ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis of distiller’s grains cellulose[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(8): 196−203.
[28] 余婷婷, 薛亚军. 纤维素酶水酶法提取茶籽油的条件优化及茶籽油成品分析[J]. 四川理工学院学报 (自然科学版),2019,32(5):1−7. [YU T T, XUE Y J. Optimization of conditions for the extraction of tea seed oil using cellulase and analysis of the tea seed oil[J]. Journal of Sichuan University of Science & Engineering (Natural Science Edition),2019,32(5):1−7.] YU T T, XUE Y J. Optimization of conditions for the extraction of tea seed oil using cellulase and analysis of the tea seed oil[J]. Journal of Sichuan University of Science & Engineering (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 32(5): 1−7.
[29] 王新娣, 马佰菁, 王信, 等. 紫斑牡丹花粉复合酶解破壁工艺的研究[J]. 甘肃医药,2023,42(6):533−535,560. [WANG X D, MA B Q, WANG X, et al. The broken-wall crafts for paeonia rockii pollen using multiple enzyme[J]. Gansu Medical Journal,2023,42(6):533−535,560.] WANG X D, MA B Q, WANG X, et al. The broken-wall crafts for paeonia rockii pollen using multiple enzyme[J]. Gansu Medical Journal, 2023, 42(6): 533−535,560.
[30] 李佳妮, 白宝清, 金晓第, 等. 酶解超声波协同提取藜麦多糖及体外活性评价[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(8):57−64. [LI J N, BAI B Q, JIN X D, et al. Synergistic extraction of chenopodium quinoa polysaccharide by enzyme-ultrasound and activity evaluation in vitro[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(8):57−64.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.08.010 LI J N, BAI B Q, JIN X D, et al. Synergistic extraction of chenopodium quinoa polysaccharide by enzyme-ultrasound and activity evaluation in vitro[J]. Food Research and Development, 2019, 40(8): 57−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.08.010
[31] 王悦, 徐元元, 杨二林, 等. 酶解结合高剪切破壁技术对蜂花粉酚类物质及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(2):313−320. [WANG Y, XU Y Y, YANG E L, et al. Effects of enzymatic hydrolysis combined with high-shear wall breaking technology on phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of bee pollen[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2021,37(2):313−320.] doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.2.036 WANG Y, XU Y Y, YANG E L, et al. Effects of enzymatic hydrolysis combined with high-shear wall breaking technology on phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of bee pollen[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2021, 37(2): 313−320. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.2.036
[32] BEGLEY L A, KASINA S, MACDONALD J, et al. The inflammatory microenvironment of the aging prostate facilitates cellular proliferation and hypertrophy[J]. Cytokine,2008,43(2):194−199. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2008.05.012
[33] 何冰心, 尚海, 李凌宇, 等. 异黄柏酮酸对LPS诱导RAW264.7细胞炎症的抑制作用[J]. 中成药,2023,45(5):1469−1475. [HE B X, SHANG H, LI L Y, et al. Inhibitory effects of isoflavonoic acid on LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2023,45(5):1469−1475.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2023.05.013 HE B X, SHANG H, LI L Y, et al. Inhibitory effects of isoflavonoic acid on LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2023, 45(5): 1469−1475. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2023.05.013
[34] 章振东. 蜂花粉篇[J]. 中国蜂业,2019,70(5):19. [ZHANG Z D. Bee Pollen[J]. Apiculture of China,2019,70(5):19.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0412-4367.2019.05.006 ZHANG Z D. Bee Pollen[J]. Apiculture of China, 2019, 70(5): 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0412-4367.2019.05.006
[35] 曹玉瑶, 董增, 曹稳根. 响应面优化纤维素酶法破壁提取油菜蜂花粉总黄酮的工艺[J]. 黄山学院学报,2017,19(3):53−57. [CAO Y Y, DONG Z, CAO W G. Response surface optimization of total flavonoids extracted from rape bee pollen by cellulase[J]. Journal of Huangshan University,2017,19(3):53−57.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-447X.2017.03.014 CAO Y Y, DONG Z, CAO W G. Response surface optimization of total flavonoids extracted from rape bee pollen by cellulase[J]. Journal of Huangshan University, 2017, 19(3): 53−57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-447X.2017.03.014
[36] 肖牧原. 低功率超声醇提薄荷总黄酮工艺优化及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国药业,2021,30(4):41−45. [XIAO M Y. Optimization of extraction process of total flavonoids from mentha haplocalyx by low-intensity ultrasound and its antioxidant activity[J]. China Pharmaceuticals,2021,30(4):41−45.] XIAO M Y. Optimization of extraction process of total flavonoids from mentha haplocalyx by low-intensity ultrasound and its antioxidant activity[J]. China Pharmaceuticals, 2021, 30(4): 41−45.
[37] KAŠKONIENĖ V, ADAŠKEVIČIŪTĖ V, KAŠKONAS P, et al. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of natural and fermented bee pollen[J]. Food Bioscience,2020,34(C):100532.
[38] YUAN K, ZHU Q Q, LU Q Y, et al. Quercetin alleviates rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting neutrophil inflammatory activities[J]. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2020,84:108454. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108454
[39] 付永平, 刘如明, 肖建辉. 植物源天然产物抗炎活性研究进展[J]. 医药导报,2020,39(5):666−671. [FU Y P, LIU R M, XIAO J H. Progress on anti-inflammatory activities of plant-derived natural products[J]. Herald of Medicine,2020,39(5):666−671.] doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1004-0781.2020.05.018 FU Y P, LIU R M, XIAO J H. Progress on anti-inflammatory activities of plant-derived natural products[J]. Herald of Medicine, 2020, 39(5): 666−671. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1004-0781.2020.05.018
[40] QIAO J T, ZHANG Y, HAUBRUGE E, et al. New insights into bee pollen:Nutrients, phytochemicals, functions and wall-disruption[J]. Food Research International,2024,2(178):113934.
[41] 耿越, 刘连亮, 胥保华, 等. 不同比例n-6/n-3多不饱和脂肪酸对小鼠良性前列腺增生和炎性细胞因子的影响[J]. 营养学报,2010,32(4):323−327. [GENG Y, LIU L L, XU B H, et al. Effects of varying n-6/n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids ratios on benign prostatic hyperplasia and inflammatory cytokines in mice[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica,2010,32(4):323−327.] GENG Y, LIU L L, XU B H, et al. Effects of varying n-6/n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids ratios on benign prostatic hyperplasia and inflammatory cytokines in mice[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica, 2010, 32(4): 323−327.
[42] ANANIAS P, SANDRA R, ALFREDO T, et al. Biological activities of commercial bee pollens:Antimicrobial, antimutagenic, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2014,1(63):233−239.





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



