Analysis of Fungal Diversity and Isolation and Identification of Yeast in High-temperature and Medium-high-temperature Daqu Using Three Generation Sequencing Technology
-
摘要: 为明确不同类型大曲真菌多样性及可培养酵母菌的差异,本研究采用三代测序技术对高温和中高温大曲的真菌类群进行了解析,并结合传统微生物纯培养方法和分子生物学技术对其蕴含的酵母菌资源进行挖掘。α多样性分析结果表明,2种类型大曲真菌群落丰富度和多样性上存在显著差异(P<0.05);种属分析结果表明,高温大曲主要以疏棉状嗜热霉(Thermomyces lanuginosus)为主,平均相对含量为73.81%,中高温大曲主要以多育曲霉(Aspergillus proliferans)为主,平均相对含量为52.58%;β多样性分析结果表明,高温和中高温大曲真菌群落结构存在非常显著的差异(P<0.01);LEfSe分析表明,嗜热真菌属(Thermomyces)和曲霉科(Aspergillaceae)可以分别作为高温和中高温大曲的生物标志物;纯培养技术结果表明,从10份大曲样品中共分离得到18株酵母菌,高温和中高温大曲的优势分离株均为扣囊复膜孢酵母(Saccharomycopsis fibuligera)。由此可见,高温和中高温大曲真菌多样性上存在明显差异。Abstract: To elucidate the variations in fungal diversity and cultivable yeast in different types of Daqu, third-generation sequencing technology was employed to analyze the fungal communities in high-temperature and medium-high-temperature Daqu. Additionally, traditional microbial pure culture methods and molecular biology techniques were utilized to investigate the yeast resources within Daqu. Alpha diversity analysis revealed significant differences (P<0.05) in the richness and diversity of fungal communities between the two types of Daqu. The sequencing data indicated that Thermomyces lanuginosus predominated in high-temperature Daqu, with an average relative content of 73.81%, while medium-high-temperature Daqu was primarily composed of Aspergillus proliferans, representing an average relative content of 52.58%. Beta diversity analysis demonstrated a notable distinction in the fungal community structure between high-temperature and medium-high-temperature Daqu (P<0.01). Moreover, the LEfSe analysis identified Thermomyces and Aspergillaceae as potential biomarkers for high-temperature and medium-high-temperature Daqu, respectively. Pure culture results revealed 18 yeast strains isolated from 10 Daqu samples, with Saccharomycopsis fibuligera identified as the dominant yeast strain in both high-temperature and medium-high-temperature Daqu. These findings underscore pronounced differences in fungal diversity between high-temperature and medium-high-temperature Daqu.
-
曲为酒之骨,大曲是在开放条件下经自然发酵而产生的一种块状物,集微生物菌系和酶系为一体,为白酒的生产提供糖化剂、发酵剂和生香剂[1]。在大曲发酵过程中,根据品温的不同,大曲可分为低温大曲(40~50 ℃)、中温大曲(50~55 ℃)、中高温大曲(55~60 ℃)和高温大曲(60~65 ℃)等[2],对白酒风格和品质的形成产生影响,“曲定酒型”的说法也由此而来,可见大曲在白酒酿造中具有极其重要的地位。目前已有许多研究人员对不同类型大曲的微生物进行了研究,例如张清玫等[3]对不同类型酒曲中微生物群落结构发现,低温大曲特征菌群以产酯真菌属毕赤酵母属(Pichia)组成,而高温大曲特征真菌属为丝衣霉菌属(Byssochlamys)和曲霉属(Aspergillus)。XIAO等[4]对高温大曲和中温大曲微生物多样性研究发现,相较于高温大曲,中温大曲中Aspergillus显著富集(P<0.05)。由此可见,不同类型的大曲微生物群落结构存在明显差异。因此,对不同类型的大曲微生物群落结构进行解析显得尤为必要。
近年来,以Pacific Biosciences(PacBio)公司的单分子实时测序技术(single-molecule real-time,SMRT)为代表的三代测序技术,通过利用菌株基因组序列之间的特异性实现对样品群落结构、物种多样性和丰富度的研究[5]。相较于二代测序,三代测序技术可以使研究人员进一步获得样品在种水平的物种组成,得到更细致的注释分辨率,具有高效、高速和高质量等特点[6],已被广泛应用于大曲微生物群落结构的研究中。例如ZHANG等[7]使用SMRT技术对不同成熟期的高温大曲样品进行解析发现,在真菌种类水平上Rasamsonia composticola和橙色嗜热子囊菌(Thermoascus aurantiacus)在熟化3个月和6个月大曲间存在显著差异(P<0.05)。HAN等[8]使用SMRT技术对合格和劣质汾酒大曲微生物群落结构进行研究发现,合格汾酒大曲样品扣囊复膜孢酵母(Saccharomycopsis fibuligera)和总状横梗霉菌(Lichtheimia ramosa)显著高于劣质汾酒大曲样品(P<0.05)。由此可见,运用三代测序技术对大曲微生物真菌群落多样性进行研究,揭示大曲样品微生物群落结构,进而对不同样品之间的差异进行挖掘具有可行性。
作为白酒发酵过程中极其重要的一类微生物,酵母菌主要负责酒化和酯化,其含量和种类直接关系到产酒率和风味物质的产生[9]。由于高温和中高温大曲的制曲温度一般在55 ℃左右,尤其是高温大曲,其最高品温甚至可达65 ℃以上[2],而酵母菌普遍对温度耐受性较差,导致成品曲中酵母菌含量很少,所以酱香型白酒需要通过堆积发酵来捕获空气中的酵母菌[10],为入窖后酒精发酵提供足够的动力。因此分离筛选耐高温且具有优良发酵性能的酵母菌菌株,从而通过外源接种来实现酱香型和浓香型白酒酿造中酵母菌的富集具有重要意义。平板分离纯化及分子生物学鉴定技术是传统微生物纯培养技术的典型代表,通过不同的筛选培养基将微生物进行保藏[11],该技术仍是白酒酿造微生物研究的一个重要手段。例如FAN等[12]采用平板分离法,从古井贡大曲分离并筛选出一株在最优条件下产乙酸乙酯量能够达到16.92 g/L的异常威克汉姆酵母(Wickerhamomyces anomalus)Y3604。
本研究采用三代测序技术对高温和中高温大曲的真菌类群进行了解析,并结合传统微生物纯培养方法和分子生物学技术对其蕴含的酵母菌资源进行挖掘,以期为具有优良发酵性能酵母菌菌株的筛选提供支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
TGuide S96磁珠法土壤/粪便基因组脱氧核糖核酸(deoxyribo nucleic acid,DNA)提取试剂盒 天根生化科技(北京)有限公司;KOD OneTM PCR Master Mix、KOD FX Neo 北京百灵克生物科技有限责任公司;Agencourt AMPure XP核酸纯化试剂盒 贝克曼库尔特有限公司;Qubit dsDNA HS测定试剂盒 美国赛默飞世尔公司;ExKubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit荧光定量检测试剂盒 上海吉泰依科赛生物科技有限公司;SMRTbell Template Prep Kit建库试剂盒 PacBio公司;马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂(potato dextrose agar,PDA)合成培养基 中国医药集团有限公司;大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)top10 实验室保存。
LRH-150生化培养箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;QYC-2102C全温培养摇床 上海新苗医疗器械制造有限公司;ECLIPSE Ci生物显微镜 日本Nikon公司;Qubit 4.0荧光计 美国赛默飞世尔公司;Veriti96-Well梯度基因扩增仪 美国Applied Biosystems公司;BioTek Synergy HTX酶标仪 基因有限公司;164-5050基础电泳仪 美国Bio-Rad公司;UVPCDS8000凝胶成像分析系统 美国UVP公司;Sequel II测序仪 PacBio公司;R930机架式服务器 美国DELL公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品收集
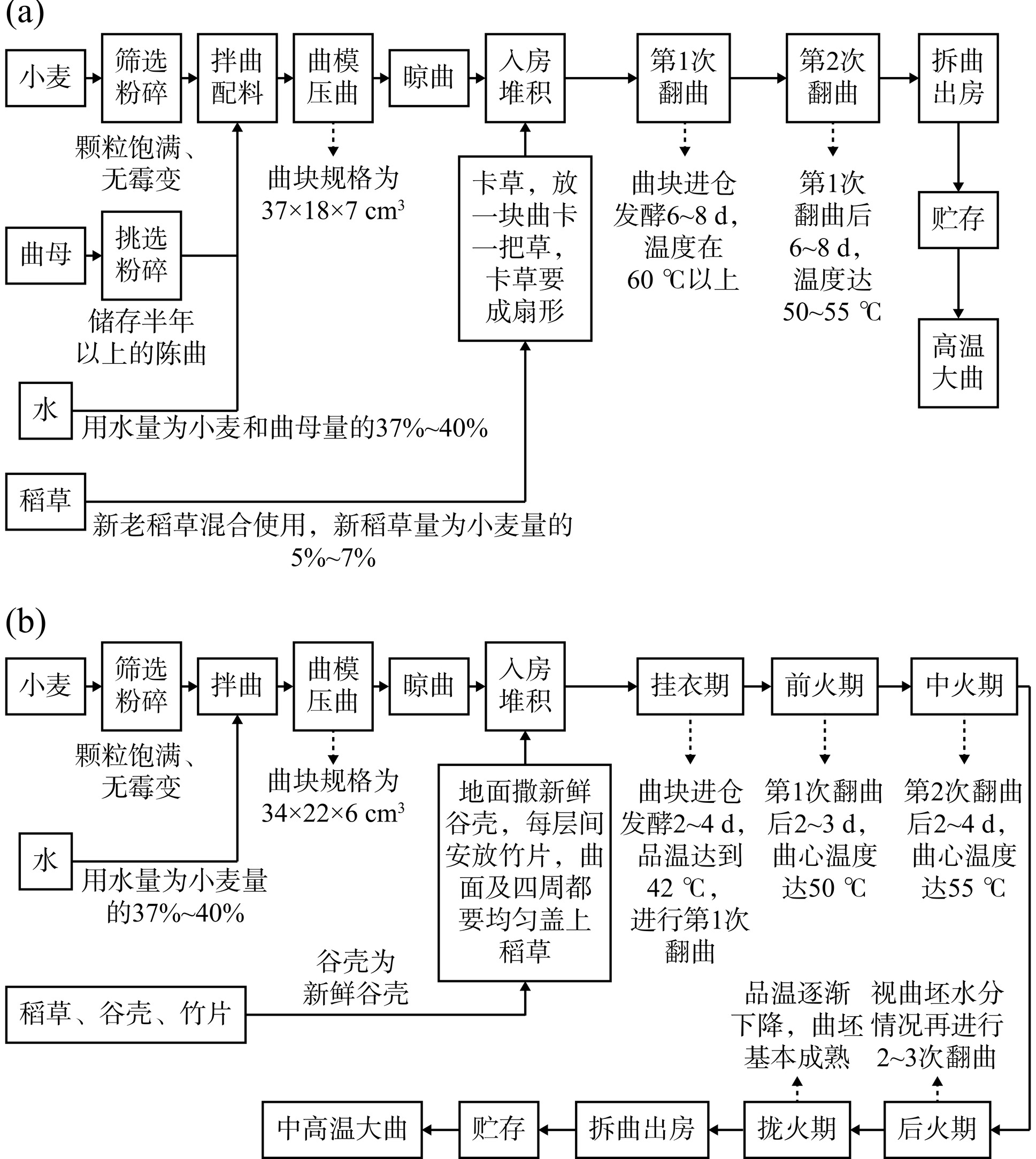
本研究于2023年12月从湖北省宜昌市(E 29°56'~31°34',N 110°15'~112°04')某酒厂采集到高温大曲5份和中高温大曲5份,共计10份样品,高温大曲编号为G1~G5,中高温大曲编号为Z1~Z5。采集的所有大曲样品均为该企业生产,具体生产工艺流程如图1所示。将采集的高温和中高温大曲曲块装入自封袋,在低温条件下迅速运回实验室,随后将其进行粉碎过筛,−20 ℃冰箱保存备用。
1.2.2 DNA提取、PCR扩增和PacBio SMRT测序
按照试剂盒说明书约束的实验步骤进行样本DNA的提取,使用Qubit dsDNA HS测定试剂盒和Qubit 4.0荧光计测量样品的DNA浓度。将检测合格的DNA使用ITS全长(ITS1F/ITS4)引物进行PCR扩增,使用Agencourt AMPure XP核酸纯化试剂盒纯化PCR产物,使用Qubit dsDNA HS测定试剂盒和Qubit 4.0荧光计对PCR产物进行定量,将检测合格的PCR产物送往北京百迈客生物科技有限公司进行测序。
1.2.3 序列质控和生物信息学分析
参照吴成等[13]的方法首先使用SMRT-Link(v8.0)软件对样品真菌群落的DNA序列进行环形一致性序列(circular consensus sequencing,CCS)的筛选,标准为:目标片段重复次数≥5;最低预测准确率≥90%。使用lima(v1.7.0)软件将CCS序列分配给相应的样本,然后通过识别正向和反向引物并使用Cutadapt软件进行质量控制。使用UCHIME算法去除嵌合体序列,利用USEARCH将上述有效数据中以97%的一致性将序列聚类为分类操作单元(operational taxonomic units,OTU),并过滤重丰度<0.005%的OTU。随后选取OTU的代表性序列使用BLAST与UNITE数据库进行序列比对,对代表性序列进行物种注释。使用R软件计算α和β多样性指数,并进行可视化。
1.2.4 高温和中高温大曲样品中酵母菌的分离与纯化
称取10 g大曲粉末加入含有90 mL生理盐水的250 mL锥形瓶内,28 ℃振荡混匀30 min,随后进行10倍梯度稀释,高温大曲取10−1、10−2和10−3稀释液100 μL进行涂布,中高温大曲取10−2、10−3和10−4稀释液100 μL进行涂布,然后将涂布完成的培养皿正置于28 ℃培养箱内培养3 d。挑选单菌落进行纯化,使用甘油管藏法将纯化的单菌落进行保藏。
1.2.5 高温和中高温大曲样品中酵母菌的鉴定
采用十六烷基三甲基溴化铵法对酵母菌分离株的DNA进行提取,随后对其进行PCR扩增。将经过1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测合格的PCR产物进行连接转化,然后将经1.5%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测合格的克隆子送往上海桑尼生物科技有限公司进行测序,并将测序公司返回的序列在美国国立生物技术信息中心网站(NCBI,https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)上进行比对,并将分离株序列与模式菌株序列一起构建系统发育树。
1.3 数据分析
10份大曲样本各测定一次,数据分析完成后,使用R软件进行α多样性小提琴图、β多样性的主坐标分析(principal co-ordinates analysis,PCoA)图、无度量多维标定法(non-metric multidimensional scaling,NMDS)图、非加权组平均法(unweighted pair - group method with arithmetic means,UPGMA)聚类图和优势属与种柱状堆积图的绘制,使用Galaxy网站(http://huttenhower.sph.harvard.edu/galaxy/)进行LEfSe的绘制,使用Past3软件Mann-Whitney检验法对优势真菌属和种进行显著性分析,使用MEGA 5.0进行系统发育树的构建。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 高温和中高温大曲真菌菌群α多样性分析
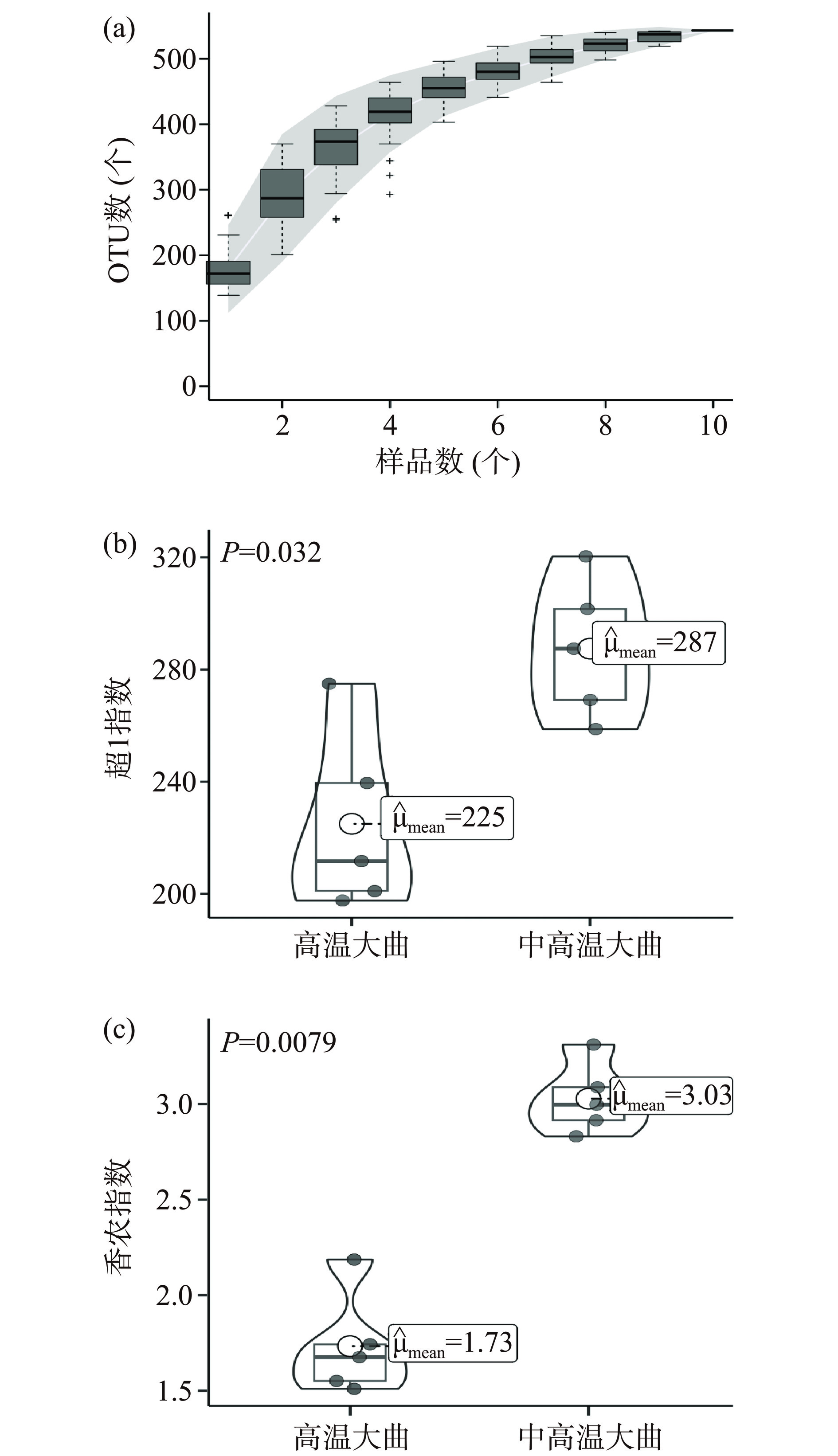
测序结果显示,纳入本研究的10份大曲样品测序后共获得130728条ITS序列,其中高温和中高温大曲平均每个样品分别得到13035和13111条序列。按照100%和97%的一致性将ITS序列进行聚类共得到543个OTU,其中高温和中高温大曲平均每个样品分别得到342和386个OTU。选取OTU的代表性序列与UNITE数据库对ITS序列进行物种注释后,本研究首先对α多样性指数进行计算,结果如图2所示。
由图2(a)可知,随着测序深度的增加,大曲样品真菌的物种累计曲线逐渐趋于平缓,说明本研究的测序合理,测序深度覆盖了高温和中高温大曲样品的大部分真菌群落。由图2(b)和图2(c)可知,高温大曲真菌群落的超1指数和香农指数平均值分别为225和1.73,中高温大曲分别为287和3.03,经Mann-Whitney检验发现,两者之间存在显著差异(P<0.05)。据报道,生产区域、制曲季节和发酵方式等对大曲的微生物群落结构存在影响,而温度是影响微生物生长更替的重要参数之一[14],决定了物种的丰富度和多样性。由此可见,随着发酵温度的升高,大曲中不耐高温的真菌群落生长则会受到抑制,从而导致高温大曲真菌群落的丰富度和多样性明显低于中高温大曲。
2.2 高温和中高温大曲真菌菌群结构分析
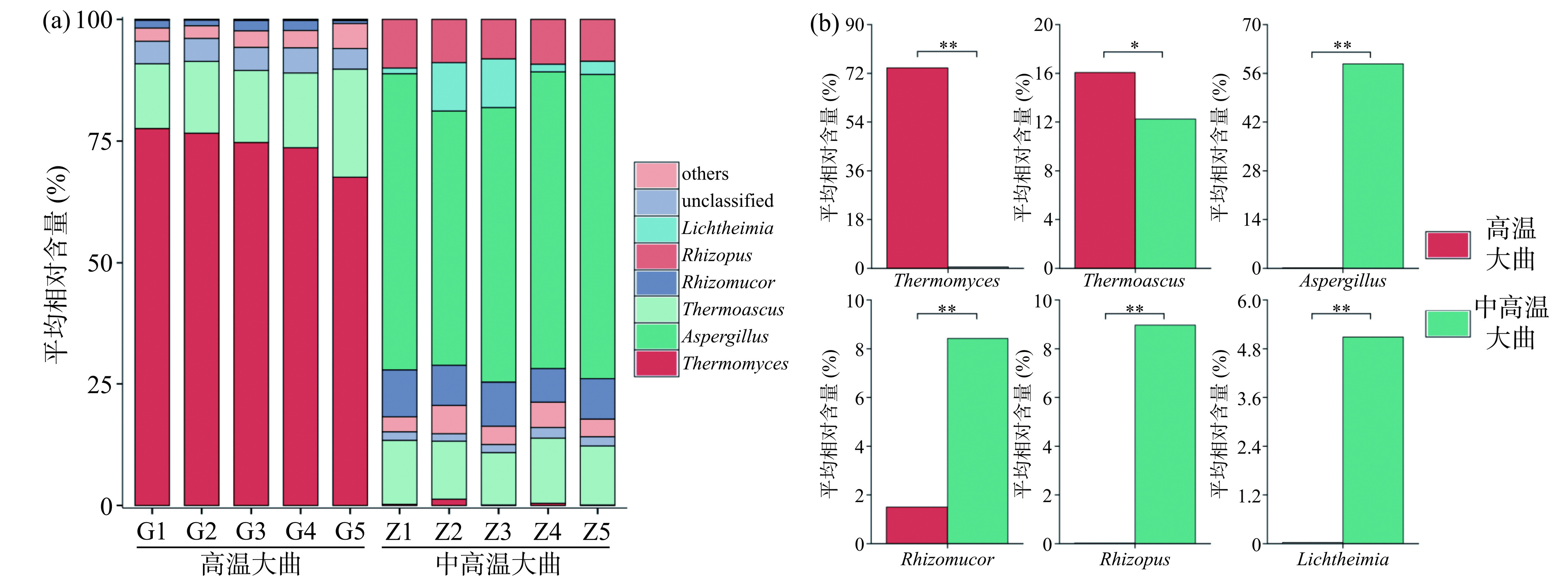
为明确不同类型大曲中真菌类群的结构特征,本研究将平均相对含量大于1%的属定义为优势真菌属,进一步对高温和中高温大曲优势真菌属的群落结构组成进行了分析,结果如图3所示。
![]() 图 3 高温和中高温大曲优势真菌属群落结构组成分析(a)及相对含量比较分析(b)注:图(b)中“*”表示P<0.05,差异显著;“**”表示P<0.01,差异极显著;图4(b)同。Figure 3. Analysis of community structure composition (a) and relative content comparison (b) of dominant fungal genera in high-temperature and medium-high-temperature Daqu
图 3 高温和中高温大曲优势真菌属群落结构组成分析(a)及相对含量比较分析(b)注:图(b)中“*”表示P<0.05,差异显著;“**”表示P<0.01,差异极显著;图4(b)同。Figure 3. Analysis of community structure composition (a) and relative content comparison (b) of dominant fungal genera in high-temperature and medium-high-temperature Daqu由图3(a)可知,从10份大曲样品中共检测到6个优势真菌属,其中高温大曲以嗜热真菌属(Thermomyces)和嗜热子囊菌属(Thermoascus)为主,平均相对含量分别为74.02%和16.06%。通过高通量技术,ZHOU等[15]对传统高温大曲研究发现Thermomyces富集明显,平均相对含量超过75%,与本研究结果一致。Thermomyces具有较高的耐热性,在高温条件下亦能产生高活力的纤维素酶和蛋白酶,保持稳定的催化效率,对产酒生香具有积极作用[16],且周会娴等[17]研究发现Thermomyces与谷氨酸和精氨酸的含量呈现显著正相关,而谷氨酸和精氨酸在生物体内的蛋白质代谢过程占重要地位,参与动物和微生物中的许多重要化学反应,亦是重要的呈味氨基酸,促进白酒品质的形成[18]。
由图3(a)亦可知,中高温大曲则以曲霉属(Aspergillus)、Thermoascus、根毛霉属(Rhizomucor)、根霉属(Rhizopus)和横梗霉属(Lichtheimia)为主,平均相对含量分别为58.72%、12.25%、8.42%、8.97%和5.09%。糖化靠霉菌,Aspergillus和Rhizomucor等霉菌能够参与糖酵解、乙醇代谢和丙酮酸代谢等途径,同时能够产生淀粉酶、蛋白酶、糖化酶、酯化酶等多种酶类[19],为白酒酿造前期对原料中淀粉等大分子物质的降解提供稳定动力,此外在霉菌的代谢过程中,亦会分泌一些呈香物质,这可能会对高温和中高温大曲风味的形成和微生物的演替起重要作用[20]。其中Aspergillus是酒曲中常见的优势霉菌,分泌的酶系也最为广泛,并且在这些酶的作用下,可以形成酵母菌便于利用的氨基酸,从而丰富白酒的口感[21]。Rhizopus和Lichtheimia能够分泌乙醛脱氢酶、甲醛脱氢酶等酶类,催化了苯乙醛的还原反应,进一步促进醛向长链或复杂醇的转化[22]。
由图3(b)可知,经Mann-Whitney检验发现,高温大曲中Thermomyces和Thermoascus的平均相对含量显著偏高(P<0.05),而Aspergillus、Rhizomucor、Rhizopus和Lichtheimia的平均相对含量极显著偏低(P<0.01),可能是高温和中高温大曲生产过程中生产工艺的差异导致的。然而无论是高温大曲还是中高温大曲都富集了更多的霉菌和耐热真菌,程伟等[23]发现低温大曲更多富集的是复膜孢酵母属(Saccharomycopsis)等酵母菌,而本研究酵母菌含量非常低,究其原因可能是高温和中高温大曲的制曲温度最高可达55 ℃以上,而大部分真菌的最适生长温度仅为20~30 ℃,所以仅一小部分能够耐受高温的嗜热真菌属和霉菌能够在高温和中高温大曲中占据优势。
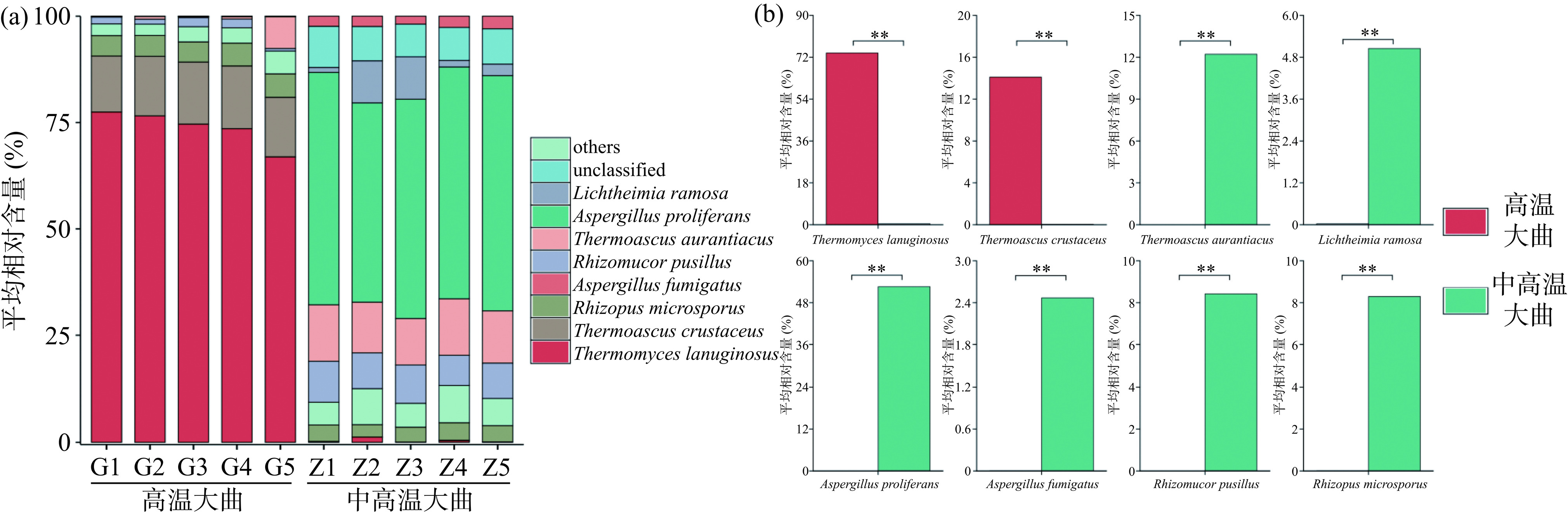
本研究将平均相对含量大于1%的种定义为优势真菌种,进一步对高温和中高温大曲优势真菌种的群落结构组成进行了分析,结果如图4所示。
由图4(a)可知,从10份大曲样品中共检测到8个优势真菌种,其中高温大曲主要以疏棉状嗜热霉(Thermomyces lanuginosus)和坚脆嗜热子囊菌(Thermoascus crustaceus)为主,平均相对含量分别为73.81%和14.10%,中高温大曲主要以多育曲霉(Aspergillus proliferans)和橙色嗜热子囊菌(Thermoascus aurantiacus)为主,平均相对含量分别为52.58%和12.21%。嗜热真菌属的真菌是可以耐受最高生长温度为50 ℃及以上的特殊真菌类群,而隶属于曲霉属的真菌大部分对高温不耐受,进一步证明高温大曲发酵时的温度更高,高温持续时间更长,抑制了对热不耐受真菌的生长,为嗜热真菌属提供了良好的生长繁殖环境。ZHENG等[24]采用高通量测序技术对北方大曲和南方大曲研究亦发现高温大曲中T. lanuginosus占主导地位,T. lanuginosus是一种嗜热丝状真菌,广泛运用于环境友好、低价格和高活性的脂肪酶生产中,以催化酯交换和酯化反应[25]。A. proliferans能产生高效纤维素降解酶[26],此外还被用于工业废水的脱色[27]。
由图4(b)可知,经Mann-Whitney检验发现,高温大曲中T. lanuginosus、T. crustaceus的平均相对含量极显著偏高(P<0.01),平均相对含量分别为73.81%和14.19%,中高温大曲中A. proliferans、T. aurantiacus、R. pusillus、R. microsporus、L. ramosa和A. fumigatus的平均相对含量极显著偏高(P<0.01)。但是同属于Thermoascus下的T. crustaceus和T. aurantiacus虽然亲缘关系较近,但在2种类型大曲中呈现相异的分布趋势,在高温大曲中含量更高的T. crustaceus在基因工程和酶工程等方面具有较大的运用价值,研究人员相继运用此菌种分离到木聚糖酶、阿魏酸酯酶等具有高耐热性的酶,并且这些酶的最适温度一般在55~70 ℃之间,接近高温大曲的发酵顶温[28−29]。在中高温大曲中占比更高的T. aurantiacus是嗜热木聚糖酶生产表达的研究对象[30],与其他嗜热真菌产生的酶相比,这种真菌的酶在解构木质纤维素方面具有更高的热稳定性和效率[31]。无论是高温大曲还是中高温大曲中均存在一定比例的未鉴定菌种,平均相对含量分别为5.07%和3.64%,这表明大曲的菌种群分布具有一定的品种特异性,菌种资源有待进一步挖掘。
2.3 高温和中高温大曲真菌群落结构差异解析
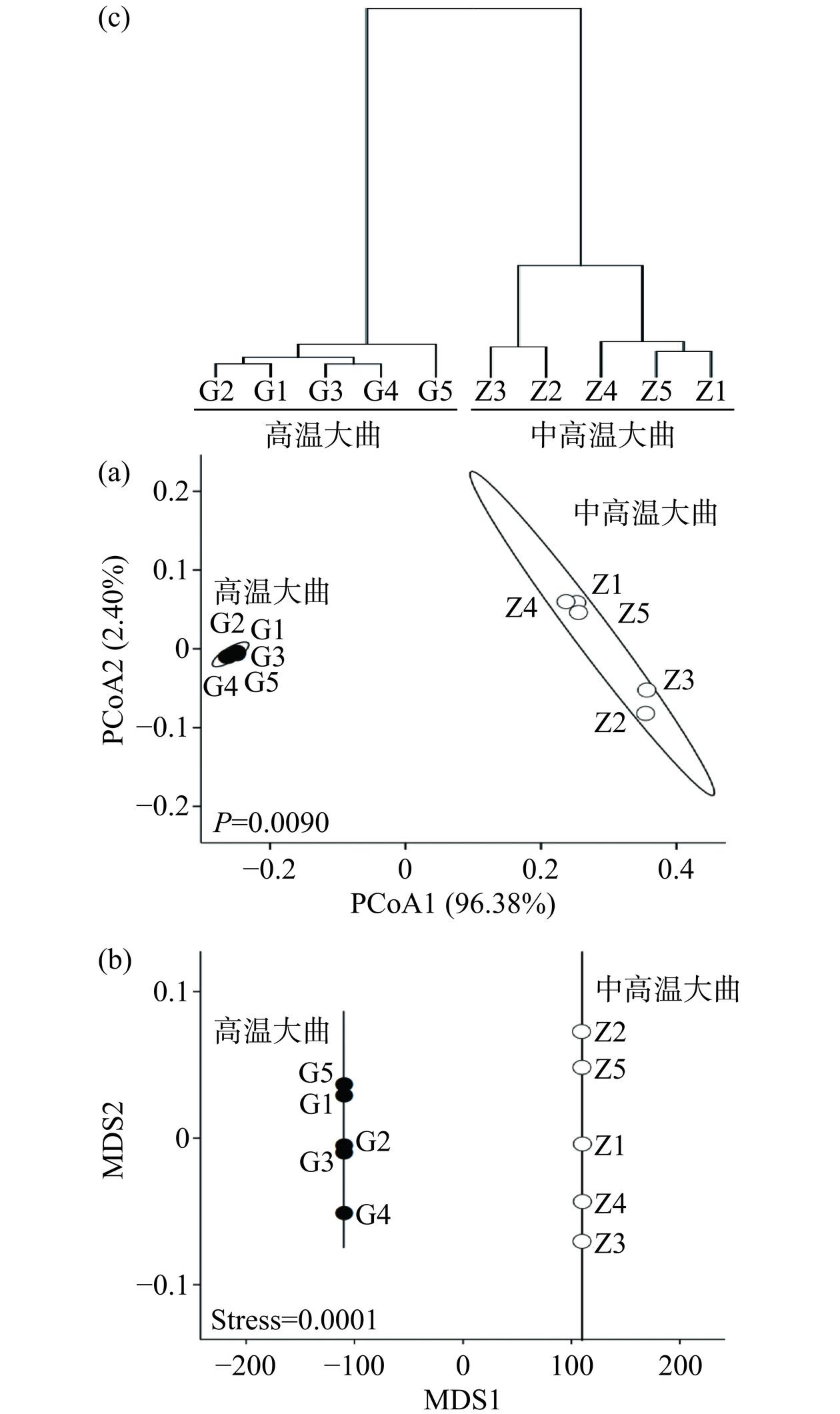
本研究进一步对高温和中高温大曲真菌类群的β多样性进行了分析,结果如图5所示。
由图5(a)可知,在PCoA分析中PC1为96.38%,PC2为2.40%,2种类型大曲在沿X轴上的排布呈现出明显的分离趋势,且高温大曲排布更为密集,同时经PERMANOVA检验发现,2种类型大曲样品在真菌菌群上存在极显著差异(P<0.01)。NMDS分析是对原始数据进行降维处理,研究不同组样本间群落构成的相似情况,作为描述指标的Stress值一般用于判断该图形是否准确反应数据排序的真实性。通常认为Stress<0.2时有一定的解释意义,当Stress<0.1时,可认为是一个好的排序,当Stress<0.05时,则具有很好的代表性[32]。由图5(b)可知,高温和中高温大曲真菌群落测序结果排序分析的Stress值为0.0001<0.05,排序结果良好,并且高温大曲与中高温大曲不存在重合现象,说明两者真菌菌群之间差异较大。由图5(c)可知,2种类型大曲亦存在明显的聚类趋势,其中高温大曲G1~G5形成一个聚类,中高温大曲Z1~Z5形成一个聚类,其结果与PCoA结果相一致。综上可知,2种类型大曲样品的真菌菌群结构间存在较大差异。
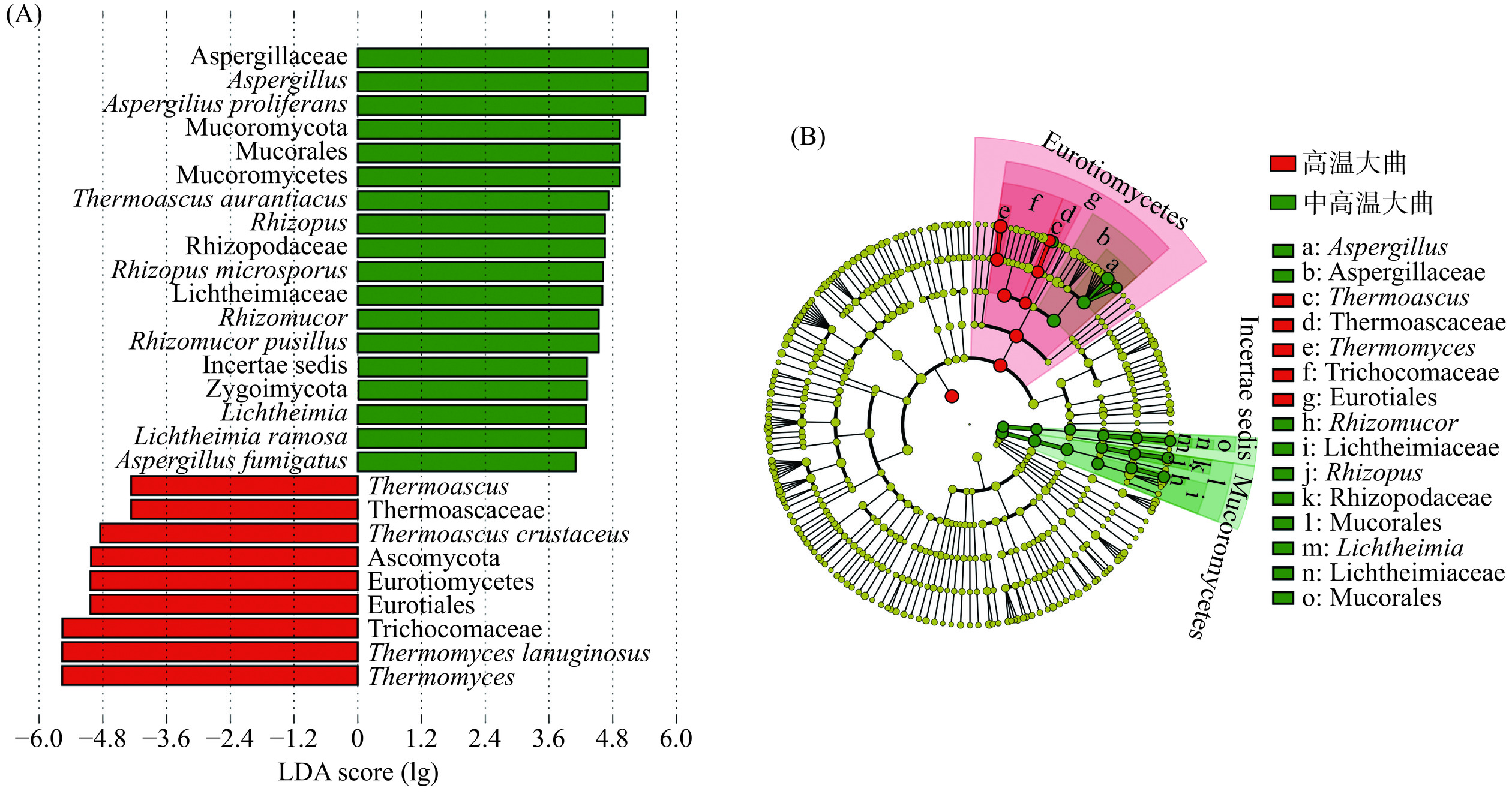
为进一步分析2种类型大曲真菌菌群的差异性,利用LEfSe对大曲样品之间的差异真菌进行甄别,结果如图6所示。
由图6可知,2种类型大曲中具有显著性差异的真菌菌群有28个(LDA阈值为4,P<0.05),9个为高温大曲的差异真菌菌群,除了优势物种Thermoascus、Thermomyces、T. lanuginosus、T. crustaceus,还有发菌科(Trichocomaceae)、散囊菌目(Eurotiales)、散囊菌纲(Eurotiomycetes)、子囊菌门(Ascomycota)、和嗜热子囊菌科(Thermoascaceae)。同样中高温大曲的19个差异真菌菌群,除了优势物种A. fumigatus、L. ramosa、R. pusillus、R. microsporus、T. aurantiacus和A. proliferan外,还有毛霉目(Mucorales)和接合菌门(Zygomycota)等。同时高温和中高温大曲中LDA分值最高的是生物标志物分别是Thermomyces和曲霉科(Aspergillaceae),因此可以分别作为高温和中高温大曲的生物标志物。进一步对比发现甄别到的28个差异真菌菌群中有8个为优势真菌种和6个优势细菌属,这与真菌菌群结构分析的结果一致。
2.4 高温和中高温大曲酵母菌的分离鉴定
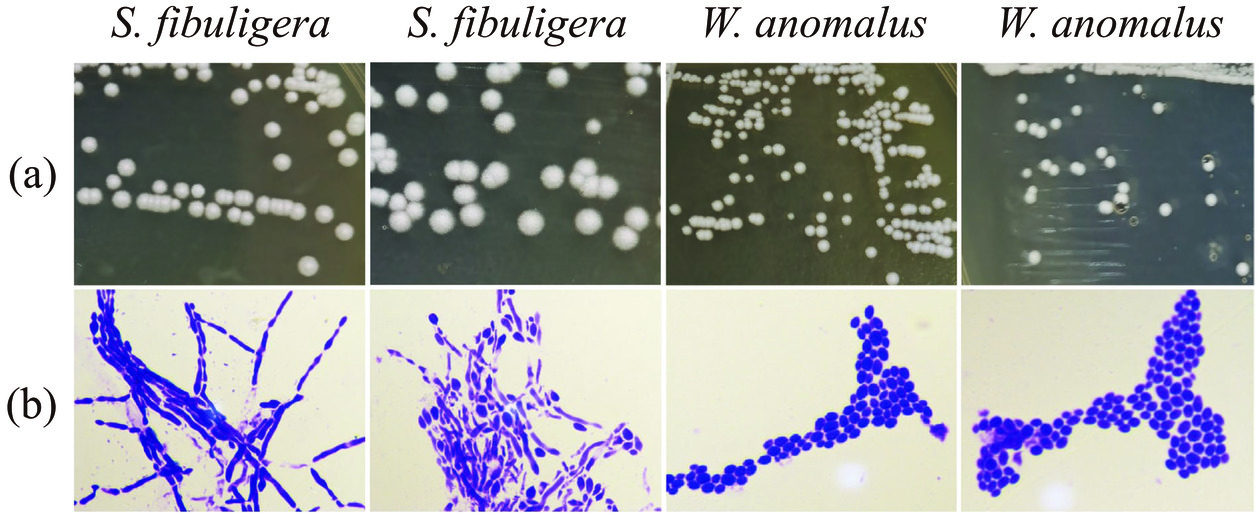
本研究采用微生物纯培养方法对高温和中高温大曲中的酵母菌菌株进行了分离鉴定,从10份大曲样品中共得到18株酵母菌,归属于2个属下的2个种,分别为隶属于复膜孢酵母属(Saccharomycopsis)下的S. fibuligera和隶属于威克汉姆酵母属(Wickerhamomyces)下的W. anomalus,部分菌株菌落形态及显微镜形态特征如图7所示。
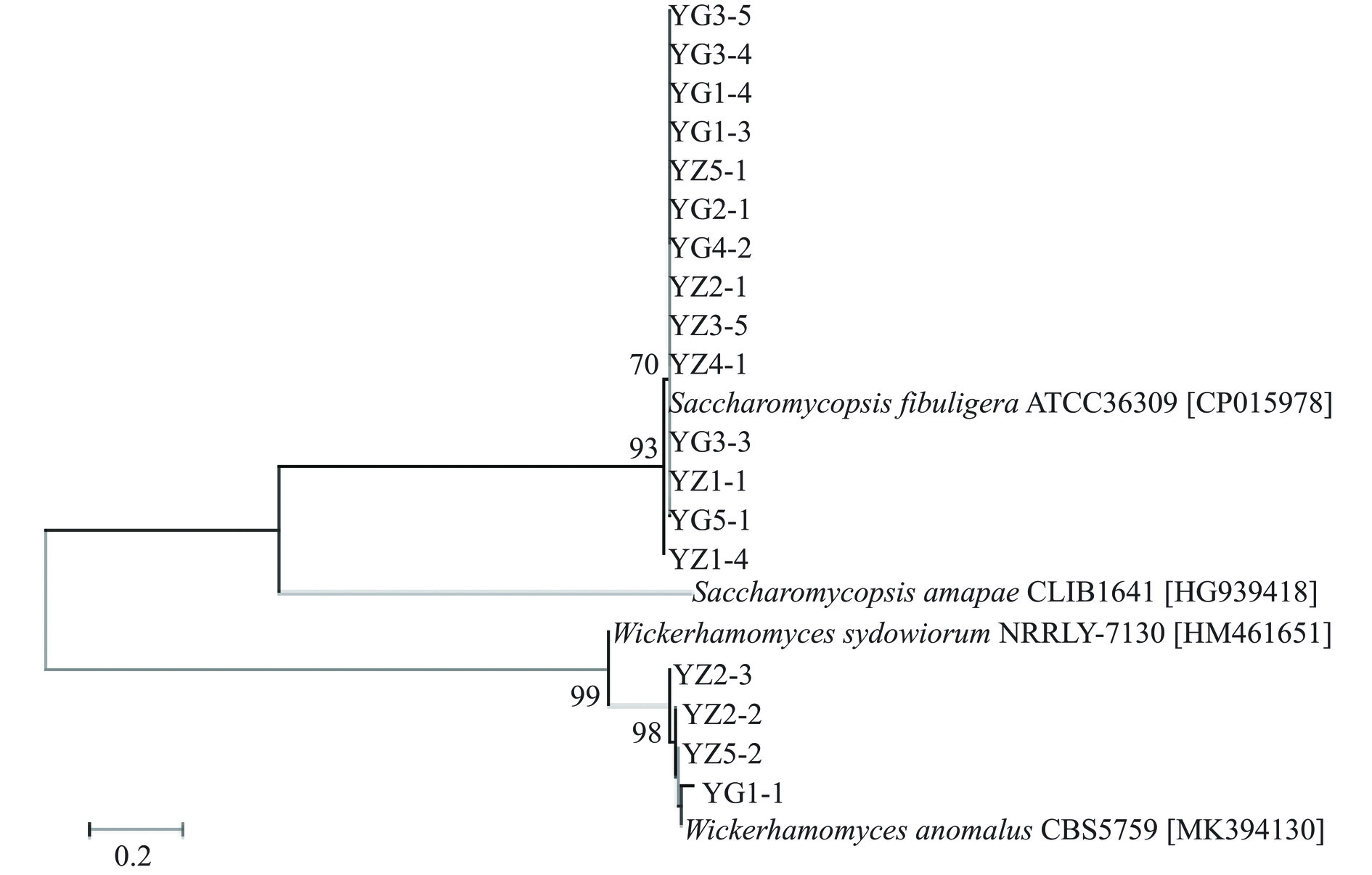
S. fibuligera在YPD平板上生长较快,一般为2 d,平板打开后有淡淡的酒香味,其在YPD培养基上形成的单菌落呈现规则的圆形,生长2 d后的直径大约为3~5 mm,白色,表面干燥,菌落表面一圈覆盖有细小的绒毛,边缘不规整,且与培养基紧密结合,接种环不易挑取。W. anomalus在YPD平板上亦生长较快,形成的单菌落呈现规则的圆形,生长2 d后的直径大约为1~2 mm,白色,表面湿润且光滑,边缘规整,接种环易挑取。由图7(b)可知,S. fibuligera在显微镜下观察形状多为椭圆,且多含有分支状的假菌丝,W. anomalus在显微镜下观察形状多为椭圆状的单细胞,未见有假菌丝存在。进一步将分离的18株酵母菌菌株与其模式菌株构建系统发育树,结果如图8所示。
由图8可知,分离鉴定到的18株酵母菌中,从高温大曲中共分离鉴定得到9株酵母菌,其中8株为S. fibuligera,1株为W. anomalus,从中高温大曲中共分离鉴定得到9株酵母菌,其中6株为S. fibuligera,3株为W. anomalus,由此可见,高温和中高温大曲的优势酵母菌分离株主要为S. fibuligera。S. fibuligera具有较好的产β-葡萄糖苷酶和蛋白酶的能力,促进大曲或者酒醅等发酵底物的分解,提高酒精的产量[33],同时在酿造生香等方面具有较强的应用潜力,对β-苯乙醇、乙酸异戊酯和棕榈酸乙酯等挥发性风味的产生具有积极作用[34]。
相较于高温大曲,中高温大曲中W. anomalus的分离数量较多,陈丽花等[35]研究发现,当温度超过48 ℃时,W. anomalus的活力受到极大抑制,中高温大曲发酵品温通常在50 ℃左右,而高温大曲的品温可达60 ℃以上,所以推测W. anomalus在中高温大曲中的生存率高于高温大曲。WANG等[36]通过人工接种模拟白酒固态发酵发现,添加W. anomalus对固态发酵进行强化,可以明显提升乙酸乙酯的含量,同时亦会引起其他挥发性风味物质的变化,可能是W. anomalus的添加对整个固态发酵的微生物菌群结构产生了影响。综上,对大曲中的酵母菌进行分离鉴定,为丰富白酒年酿造酵母菌菌株和筛选具有耐高温、高产酒等优良性能的酵母菌菌株提供了支持。
3. 结论
本研究采用三代测序和传统微生物纯培养技术对高温和中高温大曲的真菌群落进行了研究,结果发现高温和中高温大曲真菌群落结构存在明显差异。高温大曲主要以Thermomyces lanuginosus和Thermoascus crustaceus为主,中高温大曲主要以Aspergillus proliferans和Thermoascus aurantiacus为主,并且高温大曲真菌菌群的多样性及丰富度显著低于中高温大曲。通过分离鉴定方法得到,高温和中高温大曲中优势酵母菌分离株主要为S. fibuligera。在后续工作中,可以进一步探寻真菌种之间的作用关系,以期更好地明确大曲呈现不同类型的原因,此外还可以对挖掘的酵母菌菌株进行筛选,重新接回大曲中,从而提升大曲品质。
-
图 3 高温和中高温大曲优势真菌属群落结构组成分析(a)及相对含量比较分析(b)
注:图(b)中“*”表示P<0.05,差异显著;“**”表示P<0.01,差异极显著;图4(b)同。
Figure 3. Analysis of community structure composition (a) and relative content comparison (b) of dominant fungal genera in high-temperature and medium-high-temperature Daqu
-
[1] 邹云曼, 邱树毅, 郑佳, 等. 基于原位培养和传统培养分析比较不同储存期酱香大曲的细菌群落[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2023,49(15):38−46. [ZOU Y M, QIU S Y, ZHENG J, et al. Comparative analysis of bacterial commumity of high-temperature Daqu with different storage periods based on in situ cultivation and traditional cultivation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(15):38−46.] ZOU Y M, QIU S Y, ZHENG J, et al. Comparative analysis of bacterial commumity of high-temperature Daqu with different storage periods based on in situ cultivation and traditional cultivation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2023, 49(15): 38−46.
[2] ZHAO Q S, YANG J G, ZHANG K Z, et al. Lactic acid bacteria in the brewing of traditional Daqu liquor[J]. Journal of the Institute of Brewing,2020,126(1):14−23. doi: 10.1002/jib.593
[3] 张清玫, 赵鑫锐, 李江华, 等. 不同香型白酒大曲微生物群落及其与风味的相关性[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(10):1−8. [ZHANG Q M, ZHAO X R, LI J H, et al. The relationship between microbial community and flavors of three types of Daqu[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(10):1−8.] ZHANG Q M, ZHAO X R, LI J H, et al. The relationship between microbial community and flavors of three types of Daqu[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(10): 1−8.
[4] XIAO Y, ZHOU W, DU Y K, et al. Difference of microbial community and gene composition with saccharification function between Chinese nongxiangxing daqu and jiangxiangxing daqu[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2023,103(2):637−647. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12175
[5] CHUL S S, HWAN A D, JIN K S, et al. Advantages of single-molecule real-time sequencing in high-GC content genomes[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(7):68824.
[6] SINGER E, BUSHNELL B, COLEMAN-DERR D, et al. Highresolution phylogenetic microbial community profiling[J]. The ISME Journal,2016,10(8):2020−2032. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.249
[7] ZHANG Y D, XU J G, JIANG Y L, et al. Microbial characteristics and metabolite profiles of high-temperature Daqu in different maturation stages[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology,2022,38(12):234.
[8] HAN P J, LUO L J, HAN Y, et al. Microbial community affects Daqu quality and the production of ethanol and flavor compounds in Baijiu fermentation[J]. Foods,2023,12(15):2936. doi: 10.3390/foods12152936
[9] WU Q, CHEN L Q, XU L. Yeast community associated with the solid state fermentation of traditional Chinese Maotai-flavor liquor[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2013,166(2):323−330. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.07.003
[10] DAI Y J, TIAN Z Q, MENG W N, et al. Microbial diversity and physicochemical characteristics of the Maotai-flavored liquor fermentation process[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology,2020,20(7):4097−4109. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2020.17522
[11] SENANAYAKE I C, RATHNAYAKA A R, MARASINGHE D S, et al. Morphological approaches in studying fungi:Collection, examination, isolation, sporulation and preservation[J]. Mycosphere,2020,11(1):2678−2754. doi: 10.5943/mycosphere/11/1/20
[12] FAN G S, TENG C, XU D, et al. Enhanced production of ethyl acetate using co-culture of Wickerhamomyces anomalus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering,2019,128(5):564−570.
[13] 吴成, 程平言, 谢丹, 等. 酱香型白酒高温大曲发酵过程中真菌多样性研究[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2023,42(6):95−103. [WU C, CHENG P Y, XIE D, et al. Investigation on fungal diversity during high-temperature Daqu fermentation of sauce-flavor Baijiu[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2023,42(6):95−103.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2023.06.012 WU C, CHENG P Y, XIE D, et al. Investigation on fungal diversity during high-temperature Daqu fermentation of sauce-flavor Baijiu[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2023, 42(6): 95−103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2023.06.012
[14] 杨阳, 禄凌飞, 刘光钱, 等. 不同发酵顶温大曲中细菌群落结构的差异性分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2023,49(13):70−77. [YANG Y, LU L F, LIU G Q, et al. Difference analysis of bacterial community structure in Daqu with different peak temperatures achieved during fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(13):70−77.] YANG Y, LU L F, LIU G Q, et al. Difference analysis of bacterial community structure in Daqu with different peak temperatures achieved during fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2023, 49(13): 70−77.
[15] ZHOU Q F, MA K, SONG Y, et al. Exploring the diversity of the fungal community in Chinese traditional Baijiu daqu starters made at low-, medium-and high-temperatures[J]. LWT,2022,162(6):113408.
[16] LIU Y B, LI X, LI H D, et al. Taorong-type Baijiu starter:Analysis of fungal community and metabolic characteristics of middle-temperature Daqu and high-temperature Daqu[J]. PLoS One,2022,17(10):0274881.
[17] 周会娴, 熊琴琴, 刘志勇, 等. 中高温大曲发酵中小麦籽粒营养组分的动态变化分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2024,50(15):48−55. [ZHOU H X, XIONG Q Q, LIU Z Y, et al. Dynamic analysis of nutritional quality of wheat grain in medium-high temperature Daqu fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2024,50(15):48−55.] ZHOU H X, XIONG Q Q, LIU Z Y, et al. Dynamic analysis of nutritional quality of wheat grain in medium-high temperature Daqu fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024, 50(15): 48−55.
[18] DU P, JIAO G H, ZHANG Z Y, et al. Relationship between representative trace components and health functions of Chinese baijiu:A review[J]. Fermentation,2023,9(7):658. doi: 10.3390/fermentation9070658
[19] 夏玙, 罗惠波, 周平, 等. 不同处理方式的大曲真菌群落差异分析[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(22):166−172. [XIA Y, LUO H B, ZHOU P, et al. Comparison of fungal communities in Daqu with different treatments[J]. Food Science,2018,39(22):166−172.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201822026 XIA Y, LUO H B, ZHOU P, et al. Comparison of fungal communities in Daqu with different treatments[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(22): 166−172. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201822026
[20] ZHANG Y D, XU J G, DING F, et al. Multidimensional profiling indicates the shifts and functionality of wheat-origin microbiota during high-temperature Daqu incubation[J]. Food Research International,2022,156(6):111191.
[21] CHEN T, WU F H, GUO J J, et al. Effects of glutinous rice protein components on the volatile substances and sensory properties of Chinese rice wine[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(8):3297−3307. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10343
[22] DICKINSON J R, SALGADO L E J, HEWLINS M J E. The catabolism of amino acids to long chain and complex alcohols in Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2003,278(10):8028−8034.
[23] 程伟, 陈雪峰, 陈兴杰, 等. 基于高通量测序解析浓香型大曲真菌群落结构及其与质量指标的关联性分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(22):194−200,212. [CHENG W, CHEN X F, CHEN X J, et al. Analysis of fungal community structure based on high-throughput sequencing and its correlation with quality indicators of strong-flavor Daqu[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(22):194−200,212.] CHENG W, CHEN X F, CHEN X J, et al. Analysis of fungal community structure based on high-throughput sequencing and its correlation with quality indicators of strong-flavor Daqu[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(22): 194−200,212.
[24] ZHENG X W, YAN Z, NOUT M J, et al. Characterization of the microbial community in different types of Daqu samples as revealed by 16S rRNA and 26S rRNA gene clone libraries[J]. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology,2015,31(1):199−208.
[25] YANG X Y, ZHANG J X, DING Q Y, et al. Metabolites from two dominant thermophilic fungal species Thermomyces lanuginosus and Scytalidium thermophilum[J]. Chemistry & Biodiversity,2020,17(5):2000137.
[26] 王勇, 张育铭, 朱洪磊, 等. 高效纤维素降解菌的筛选及产酶活力测定[J]. 江苏农业科学,2020,48(23):255−260. [WANG Y, ZHANG Y M, ZHU H L, et al. Screening of high-efficiency cellulose-degrading bacteria and determination of enzyme-producing activity[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2020,48(23):255−260.] WANG Y, ZHANG Y M, ZHU H L, et al. Screening of high-efficiency cellulose-degrading bacteria and determination of enzyme-producing activity[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 48(23): 255−260.
[27] KANMANI P, R S K, YUVARAJ N, et al. Microbial decolorization of synthetic dyes and reactive dyes of industrial effluents by using a novel fungus Aspergillus proliferans[J]. Water Environment Research,2011,83(11):2099−2106.
[28] 李晓丽, 涂涛, 姚斌, 等. 嗜热子囊菌JCM12803来源的双功能木聚糖/纤维素酶[J]. 生物工程学报,2018,34(12):1996−2006. [LI X L, TU T, YAO B, et al. A novel bifunctional xylanase/cellulase TcXyn10A from Thermoascus crustaceus JCM12803[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology,2018,34(12):1996−2006.] LI X L, TU T, YAO B, et al. A novel bifunctional xylanase/cellulase TcXyn10A from Thermoascus crustaceus JCM12803[J]. Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2018, 34(12): 1996−2006.
[29] 罗艳, 涂涛, 姚斌, 等. 嗜热子囊菌JCM12803来源的阿魏酸酯酶FAE-2515酶学性质研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报,2018,20(9):57−64. [LUO Y, TU T, YAO B, et al. Studies on enzymatic properties of ferulic acid esterase FAE-2515 from Thermoascus crustaceus JCM12803[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology,2018,20(9):57−64.] LUO Y, TU T, YAO B, et al. Studies on enzymatic properties of ferulic acid esterase FAE-2515 from Thermoascus crustaceus JCM12803[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2018, 20(9): 57−64.
[30] PING L F, WANG M J, YUAN X L, et al. Production and characterization of a novel acidophilic and thermostable xylanase from Thermoascus aurantiacu[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,109(4):1270−1279.
[31] GABRIEL R, MUELLER R, FLOERL L, et al. CAZymes from the thermophilic fungus Thermoascus aurantiacus are induced by C5 and C6 sugars[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels,2021,14(8):1−13.
[32] NOVEAL R M, BURTON O T, WISE P, et al. A microbiota signature associated with experimental food allergy promotes allergic sensitization and anaphylaxis[J]. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology,2013,131(1):201−212. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.10.026
[33] 苏畅, 马莹莹, 杨建刚. 扣囊复膜酵母在酿酒中的应用研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2018, 39(1):205−209, 220. [SU C, MA Y Y, YANG J G, et al. Research progress of Saccharomycopsis fibuligera in Liquor-making industry[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 14(8):1−13.] SU C, MA Y Y, YANG J G, et al. Research progress of Saccharomycopsis fibuligera in Liquor-making industry[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 14(8): 1−13.
[34] MA R F, SUI L, ZHANG J S, et al. Polyphasic characterization of yeasts and lactic acid bacteria metabolic contribution in semi-solid fermentation of Chinese Baijiu (traditional fermented alcoholic drink)[J]. Towards the Design of a Tailored Starter Culture Microorganisms,2019,7(5):147.
[35] 陈丽花, 任丽霞, 李东娜, 等. 甜酒曲中优质酵母菌的分离鉴定及其产香特性分析[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(6):142−149. [CHEN L H, REN L X, LI D N, et al. Fermentation characteristics for flavor compounds production by quality yeast strains isolated from rice wine starters[J]. Food Science,2021,42(6):142−149.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191212-134 CHEN L H, REN L X, LI D N, et al. Fermentation characteristics for flavor compounds production by quality yeast strains isolated from rice wine starters[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(6): 142−149. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191212-134
[36] WANG W H, FAN G S, LI X T, et al. Application of Wickerhamomyces anomalus in simulated solid-state fermentation for Baijiu production:Changes of microbial community structure and flavor metabolism[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2020,11(11):598758.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



