Effect of Hydrothermal Treatment on Dissolution and Physical Properties of Polysaccharides from Tremella fuctiformis
-
摘要: 银耳多糖是银耳中的主要成分,其溶出规律影响多糖的物理特性。本文以Fick第二定律为基础构建常压热水浸提(HWE)及加压热水浸提(PHWE)银耳多糖的溶出动力学模型并解析相关参数,采用凝胶渗透色谱和流变仪对溶出过程中多糖的分子量和浸提液的黏度特性进行表征。结果表明,HWE和PHWE的多糖溶出率随着浸提温度升高和浸提时间的延长而增大,最大多糖溶出率分别为42.75%和62.03%。二者的溶出动力学参数:溶出速率常数k、有效扩散系数Ds与表观活化能Ea分别为0.0128~0.0175和0.057~0.1509 min−1、3.2532~4.4348和14.4428~38.2676 mm2/min、2.82~6.38和19.49~31.43 kJ/mol,动力学曲线线性决定系数R2均大于0.87,溶出动力学符合Fick 第二定律。此外,浸提温度的升高及浸提时间的延长均会降低多糖的分子量,且HWE的分子量分布范围明显大于PHWE的分子量分布范围,并表现出更高的表观黏度。Abstract: Tremella polysaccharide is the primary component of Tremella fuciformis, and its dissolution behavior significantly influences the physical properties of the polysaccharide. In this paper, utilizing Fick's second law as a foundation, dissolution kinetic models for hot water extraction (HWE) and pressurized hot water extraction (PHWE) were developed and the relevant parameters were analyzed. Subsequently, the molecular weight of the polysaccharides and the viscosity of the extracted solution were characterized using gel permeation chromatography and a rheometer. Results showed that the polysaccharide dissolution rates of both HWE and PHWE increased with higher extraction temperatures and longer extraction times. The maximum polysaccharide dissolution rates for HWE and PHWE were determined to be 42.75% and 62.03%, respectively. The dissolution kinetics parameters, including the dissolution rate constant (k), effective diffusion coefficient (Ds), and apparent activation energy (Ea), ranged from 0.0128 to 0.0175 min−1 and 0.057 to 0.1509 min−1, 3.2532 to 4.4348 mm2·min and 14.4428~38.2676 mm2/min, 2.82 to 6.38 kJ/mol, and 19.49 to 31.43 kJ/mol. The linear coefficient of determination (R2) of the kinetic curves for both HWE and PHWE exceeded 0.87, indicating that the dissolution process adhered to Fick's second law. Additionally, the molecular weight of polysaccharides decreased with increasing extraction temperature and prolonged extraction time, the molecular weight distribution range of HWE was significantly broader than that of PHWE, and exhibited a higher apparent viscosity.
-
Keywords:
- Tremella polysaccharides /
- dissolution /
- kinetic model /
- viscosity /
- molecular weight
-
银耳作为我国主要的食用菌品种之一,含有多糖、蛋白质、脂肪、粗纤维及少量的维生素,具有丰富的营养价值[1]。其中多糖约占银耳干重的65%~71.2%,是其主要活性成分[2]。除鲜销食用及干制品外,银耳深加工产品的主要形式是液体饮料,在该产品生产加工中通常涉及到银耳中多糖的溶出及热加工对产品品质及稳定性的影响[3−4]。但目前对银耳加工特性的研究侧重于干燥工艺[5−6]、银耳全粉的溶解度和流变学特性[7]以及特定结构的银耳多糖与其他原料配伍进行产品开发等方面[8−9],对加工过程中银耳多糖的溶出行为、理化性质及结构变化方面尚未有进一步认识。
银耳多糖是以甘露糖为主链的杂多糖,通常以α-(1,3)-糖苷键连接,侧链含有半乳糖、阿拉伯糖、葡萄糖、岩藻糖和果糖等,通常通过α-(1,2)-糖苷键连接至主链上,分子量约为0.8~6×106 Da[10−11]。银耳多糖具有多种生理活性功能,例如:银耳多糖可上调B淋巴细胞瘤的表达,抑制Bax的表达和细胞色素C的释放,通过caspase依赖的线粒体途径实现神经保护作用[12];银耳多糖可以清除DPPH自由基、羟基自由基和ABTS+自由基以及具有较强的Fe3+还原能力,具有较好的抗氧化活性[13];银耳多糖通过降低PPARγ、C/EBPα以及瘦素的mRNA表达抑制脂肪细胞的分化,且能够降低总胆固醇、甘油三酯和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇含量以及提高高密度脂蛋白胆固醇含量,具有良好的降血脂作用[14−15]。但这些生理活性的体现与在浸提过程中多糖的含量、相对分子质量分布以及在溶液中分子链的构象等密切相关,并在宏观上呈现为流变学特性的差异[16−18]。
目前银耳多糖的浸提主要采用水热法,利用在50~100 ℃的热水下浸提一定时间从而使细胞壁内的水溶性多糖溶出,具有成本低、操作方便的优势,但银耳的原料差异、浸提温度、时间、压力及溶出过程中多糖的浓度等均会影响多糖最终的溶出率、理化性质并表现出不同的生物活性[19−20]。因此,多糖溶出规律的研究一直是银耳多糖制备及以银耳多糖为主要成分的饮料加工中的关键问题,利用实验数据进行动力学模型的构建可更好地描述银耳多糖的溶出行为。一般而言,多糖的溶出是在渗透压作用下自发进行的,是一个非稳态扩散过程,主要包括溶剂从表面向内部扩散、溶质的溶解、溶质的内扩散以及溶质的外扩散[21]。目前主要利用Fick第二定律构建的球状模型和平板模型来描述多糖溶出行为[22−23]。利用该模型可以了解原料的溶胀情况、活性组分初始含量和扩散系数,得到多糖浸出液的浸泡剖面,从而达到控制生产条件以及预测生产结果的目的。但在实际生产过程中,多糖溶出并不是一个稳定持续的过程,还存在着溶解多糖分子结构的变化以及分子结构的降解,且溶出的机制与原料特性密切相关[24−25]。
因此,在了解对多糖溶出影响因素的基础上,本研究基于Fick第二定律构建不同温度与压力下的银耳多糖溶出动力学模型、解析各项动力学参数,并探讨多糖溶出过程中多糖含量及溶出率、分子量分布及流变学特性,为银耳多糖的提取及银耳饮料产品开发提供工艺参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
鲜银耳(银耳多糖含量占干物质的66.54%) 购于福建省宁德市古田县;葡聚糖标准品 色谱纯,美国Sigma公司;苯酚、浓硫酸 分析纯,成都市科龙化工试剂厂。
JULABO TW12恒温水浴锅 优莱博技术有限公司;ZM-100反压式高温灭菌锅 广州标际包装设备有限公司;INFINITE E PLEX光栅型多功能微孔板检测仪 奥地利TECAN公司;HAAKE-MARSⅢ 流变仪 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;Waters e2695高效液相凝胶渗透色谱 沃特世(Waters)科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 原料预处理
将鲜银耳用清水冲洗后擦净表面水分,切成5 cm×5 cm碎块备用,并测定得到鲜银耳的水分含量约为90%~92%。
1.2.2 样品制备
常压热水浸提(HWE):称取15 g鲜银耳碎片,分别按1:5、1:10、1:15 g/mL的料液比(m/V),在333、353、373 K下常压水浴浸提10、20、40、60、90、130与170 min,根据不同料液比处理样品分别记为HWE-5、HWE-10与HWE-15;加压热水浸提(PHWE):另称取15 g鲜银耳碎片,分别按1:5、1:10、1:15 g/mL的料液比(m/V),在压力为0.105、0.15、0.22 MPa(不同压力下对应的温度分别为374、384、394 K)的高压灭菌锅中浸提5、10、15、20、25与30 min,根据不同料液比处理样品分别记为PHWE-5、PHWE-10与PHWE-15。
1.2.3 浸提液多糖质量浓度的测定及多糖溶出率的计算
以0.1 mg/mL葡萄糖为标样,采用苯酚-硫酸法测定浸提液总糖质量浓度[26] ,得到标准曲线方程:y=0.00418+5.52289x,R2=0.99494。以1 mg/mL葡萄糖为标样,采用DNS法测定浸提液还原糖质量浓度[27],得到标准曲线方程:y=0.71083x−0.03432,R2=0.99903。采用NY/T 1676-2008《食用菌中粗多糖含量的测定》测定鲜银耳多糖含量。
银耳多糖溶出率计算公式如下:
Ct=C1−C2 (1) 多糖溶出率(%)=Ct×V15×(1−D)×66.54% (2) 式中,Ct表示任意时刻的浸提液多糖质量浓度,mg/mL;C1和C2分别表示浸提液的总糖质量浓度和还原糖质量浓度,mg/mL;V表示浸提液体积,mL;15为鲜银耳样品质量,g;D表示鲜银耳的水分含量;66.54%为银耳干物质中的多糖含量。
1.2.4 溶出动力学模型的构建
多糖的溶出分为三步,首先,溶剂与物料表面接触并向内渗透;其次,多糖溶解于溶剂,并从物料内部向物料外表面扩散(内扩散);最后,多糖从物料外表面渗出至溶剂主体并扩散(外扩散)。由于多糖溶出过程的速度不一致,是一个非稳态的扩散过程。因此可基于Fick 第二定律构建银耳多糖溶出的一阶动力学模型[22],并考虑在实际生产中所用到的鲜银耳通常为不规则的且有一定厚度的片状物料,因此,对银耳多糖溶出过程做出以下假设:a.将银耳看作是无厚度的薄板,且在溶出过程中形状不变;b.多糖的扩散主要沿垂直于薄板主面的轴进行;c.银耳表面的传质阻力忽略不计;d.溶出过程中,各成分在薄板内的分布是均匀一致的,并依据Stapley等[28]提出的当物料完全浸没于液体时,无限薄板在时间内溶出的动力学方程式可由式(3)表示:
C∞−C0C∞−Ct=∞∑n=1[(8n2(2n−1)2)exp(−(2n−1)2π24L2)Dst] (3) 式中,C∞为达到平衡时银耳多糖的质量浓度,mg/mL; L为物料边长的一半,cm;Ds为有效扩散系数,表示物质在介质中的扩散能力,mm2/min;t 为浸提时间,min。
由于多糖浓度的分布是一个无限序列,浓度的高次项趋近为零可以忽略不计,因此上式n=1时,则有:
C∞−C0C∞−Ct=∞∑n=1[8π2exp(−π24L2⋅Dst)] (4) 由于初始时刻C0=0,对式(4)两边取对数得:
ln(C∞C∞−Ct)=ln(π28)+π24L2⋅Dst=kt+b (5) 式中,k为表观速率常数,反映了物质在介质中扩散速率的快慢,min−1,且有k=π2Ds/4L2。
式(5)为银耳多糖的溶出动力学方程式,可反映多糖浓度与浸提时间、温度、料液比、银耳半径的变化关系。
1.2.5 浸提液分子量的分布
采用凝胶渗透色谱法测定不同热处理条件下银耳多糖的分子量。将多糖样品及5、12、25、80、410、670 kDa的葡聚糖标准品配制成1 mg/mL的溶液,并过0.45 μm的滤膜备用。
色谱条件:色谱柱使用TSK-GEL G4000PW XL凝胶柱(7.8×300 mm,10 μm),以 0.02 mol/L K2HPO4缓冲液作为流动相,流速为0.5 mL/min,在35 ℃柱温下洗脱40 min。然后以葡聚糖标准品的相对分子质量的对数值(lg Mw)为纵坐标,保留时间(min)为横坐标计算得到葡聚糖标准曲线方程:y=9.84095-0.31799x,R2=0.997。
1.2.6 浸提液流变学特性的测定
采用HAAKE流变仪,参照龙慧等[29]的方法并稍作修改。选择直径60 mm的平板,设定测量间距为1 mm,在25 ℃、0.1~1000 s−1的剪切速率范围内对浸提液的表观黏度进行测定。采用动态振荡模式,设置形变,在0.1~10 Hz的频率范围内对浸提液的储能模量G'和损耗模量G''进行测定。
1.3 数据处理
每组实验重复3次,数据结果以平均值±标准差表示。结果使用SPSS 26.0进行统计,比较ANOVA单因素方差分析,P<0.05,数据结果有统计学意义,Origin 2024 进行作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同溶出条件对浸提液多糖溶出率的影响
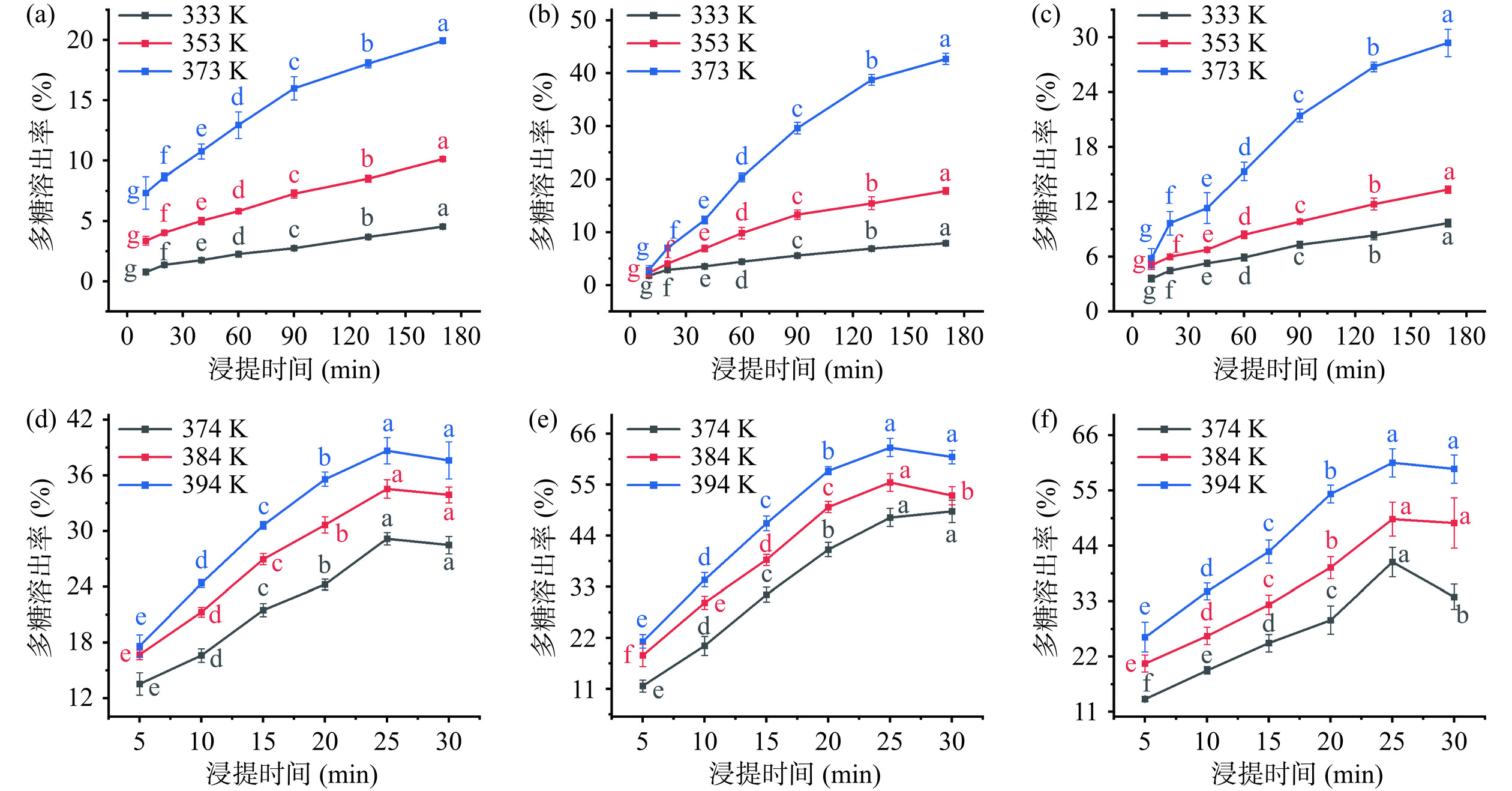
采用HWE和PHWE两种方法浸提鲜银耳,在不同的料液比和浸提温度下浸提液多糖溶出率的变化如由图1所示。由图1(a)~图1(c)可知,HWE浸提液的多糖溶出率随浸提时间、浸提温度的增大而升高。浸提温度为333 K和353 K时,HWE-5、HWE-10、HWE-15的多糖溶出率在60 min前增加速度较快,60 min后增加速度明显放缓,浸提达到平衡时多糖溶出率分别为4.75%和10.12%、7.92%和17.81%、9.67%和14.33%,原料中存在较多尚未溶出的多糖;浸提温度为373 K时,HWE-5、HWE-10、HWE-15的多糖溶出率在90 min前增加速度较快,90 min后增加速度变慢,浸提达到平衡时多糖溶出率分别为19.95%、42.75%、29.39%。多糖溶出率明显升高,说明提高浸提温度有助于多糖的溶出。以HWE-10为例,在333 K和373 K下浸提10~60 min时,多糖溶出率分别增加了2.60%和17.45%,浸提130~170 min时,多糖溶出率分别增加了1.04%和3.98%,溶出率增加缓慢,说明再延长浸提时间对多糖溶出的帮助有限。
由图1(d)~图1(f)可知,PHWE 浸提液的多糖溶出率同样随着浸提温度的升高而升高,PHWE-5、PHWE-10和PHWE-15的多糖溶出率分别为13.55%~38.68%、11.63%~62.03%和13.53%~60.5%,均高于HWE,说明多糖在加压条件下溶出的效率更高。实验结果表明,1:5料液比条件下浸提液的多糖溶出率均低于另外两个料液比,原因是多糖的溶出是在渗透压及热力共同作用下发生的,高料液比下溶液黏度大、体系内外浓度差小,渗透压作用减弱,使得原料内的多糖难以向溶液转移[30−31]。
2.2 银耳多糖溶出动力学
2.2.1 溶出速率常数k
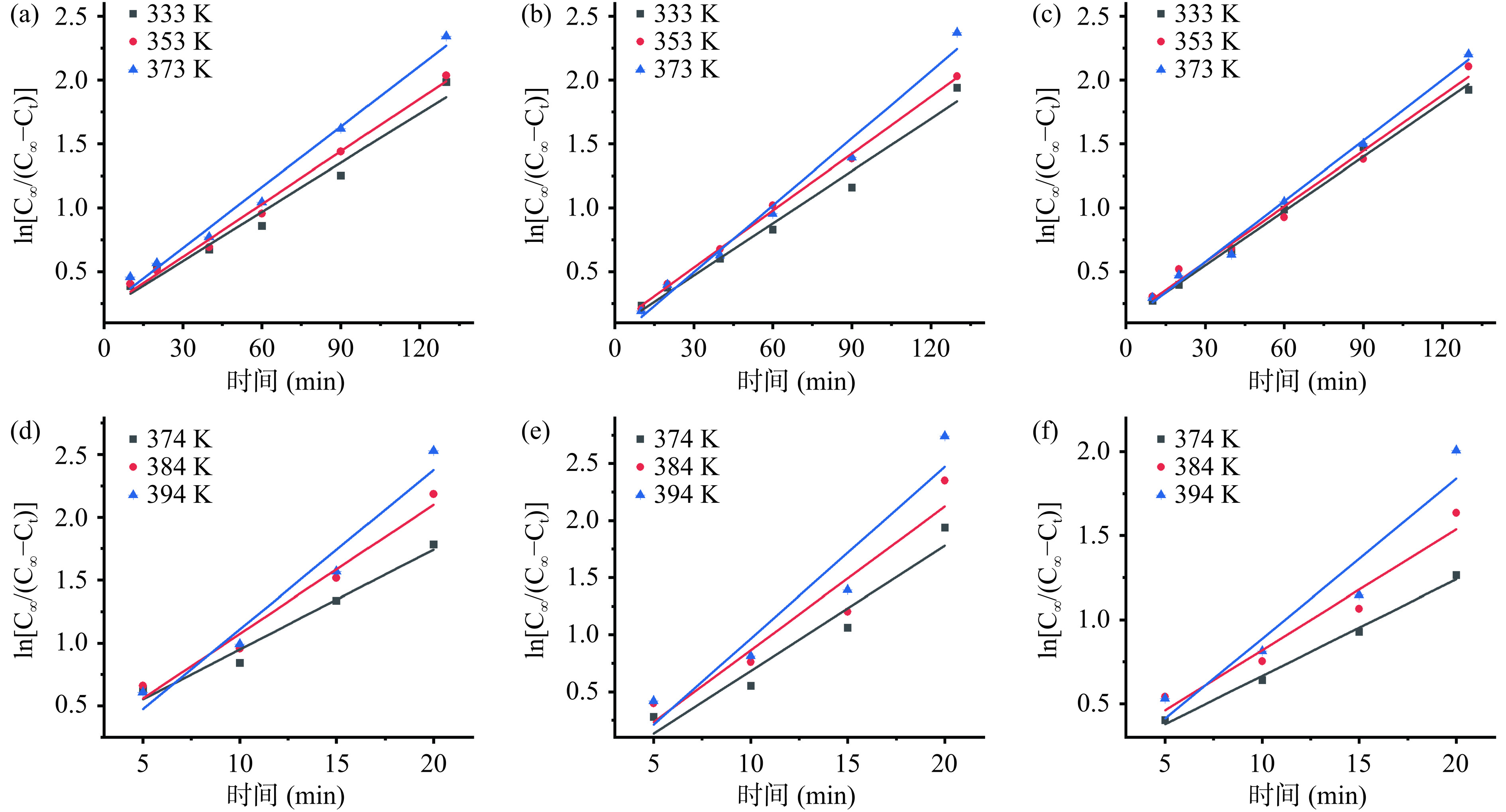
由图1可知,两种浸提方式下,浸提液的多糖溶出率随着浸提时间的增加而增加,最终达到浸提平衡,其中HWE与PHWE分别在浸提170 min与25 min时达到平衡。通过对不同浸提温度和料液比下ln[C∞/(C∞−Ct)]与浸提时间(t)的作图并拟合,可得到银耳多糖的溶出速率常数k,如表1及图2所示,拟合方程的线性决定系数R2均大于0.87,说明ln[C∞/(C∞−Ct)]与t 具有良好的线性关系,银耳多糖的溶出过程符合Fick 第二定律。研究发现,溶出速率常数k 随浸提温度的升高而增大,且PHWE的k值显著(P<0.05)高于HWE,说明较高的温度及适当加压有助于提高银耳多糖的扩散速度[32−34]。浸提温度相同时,k值的大小与料液比的关系为:HWE-5<HWE-15<HWE-10<PHWE-15<PHWE-5<PHWE-10,这可能是由于高料液比下银耳多糖在短时间内较快溶出,此时内外浓度差小,且高料液比下物料相互堆叠,与溶剂的接触不充分,不利于物料内部的多糖向溶剂继续扩散;低料液比时溶剂中多糖质量浓度低,且加压使得多糖降解速度加快,单位时间内溶剂中银耳多糖增加速度降低[32,35]。
表 1 不同热处理条件下银耳多糖动力学模型的各项参数Table 1. Parameters of the kinetic model of Tremella polysaccharides under different heat treatment conditions样品组 浸提温
度(K)平衡时
间(min)C∞ 线性模型 Ds 指数模型 拟合方程(ln[C∞/(C∞−Ct)]=kt+b) k R2 拟合方程(Y=a×expnt) R2 HWE-5 333 170 0.63 0.0128t+0.1989 0.0128 0.967 3.2532 0.7638exp−0.0111t 0.9771 353 170 1.35 0.0137t+0.2055 0.0137 0.9898 3.4839 0.7741exp−0.0125t 0.9873 373 170 2.65 0.0158t+0.2117 0.0158 0.984 4.0139 0.7469exp−0.0137t 0.9828 HWE-10 333 170 0.53 0.0136t+0.061 0.0136 0.979 3.4586 0.895exp−0.0124t 0.992 353 170 1.19 0.0149t+0.0862 0.0149 0.9976 3.773 0.9285exp−0.0152t 0.9968 373 170 2.84 0.0175t−0.0297 0.0175 0.9793 4.4348 0.918exp−0.0155t 0.9911 HWE-15 333 170 0.43 0.0142t+0.1263 0.0142 0.9949 3.5955 0.918exp−0.0149t 0.998 353 170 0.64 0.0145t+0.1411 0.0145 0.9847 3.6792 0.8258exp−0.0133t 0.9843 373 170 1.3 0.0158t+0.102 0.0158 0.9921 4.0164 0.9286exp−0.0131t 0.944 PHWE-5 374 25 3.88 0.0793t+0.1551 0.0793 0.9662 20.1174 0.792exp−0.0715t 0.9502 384 25 4.6 0.1026t+0.0464 0.1026 0.961 26.0254 0.8293exp−0.088t 0.9559 394 25 5.01 0.1267t−0.1588 0.1267 0.9598 32.1235 0.933exp−0.1024t 0.9612 PHWE-10 374 25 3.19 0.1098t−0.4151 0.1098 0.9139 27.8282 1.2183exp−0.0871t 0.9272 384 25 3.69 0.126t−0.3953 0.126 0.8783 31.9435 1.1133exp−0.0954t 0.9335 394 25 4.13 0.1509t−0.5442 0.1509 0.8811 38.2673 1.1644exp−0.1082t 0.9385 PHWE-15 374 25 1.81 0.057t+0.1033 0.057 0.996 14.4428 0.8867exp−0.0554t 0.9915 384 25 2.17 0.0724t+0.1013 0.0724 0.961 18.3679 0.8216exp−0.0625t 0.9374 394 25 2.78 0.0952t−0.6470 0.0952 0.8851 24.1364 0.8916xp−0.0770t 0.9217 注:C∞表示溶出达到平衡时浸提液银耳多糖的质量浓度,mg/mL;Ct表示任意时刻浸提液多糖的质量浓度,mg/mL;k表示银耳多糖的溶出速率常数,min−1;R2表示拟合方程的线性相关系数;Ds表示银耳多糖的表面扩散系数,mm2/min。 2.2.2 表面扩散系数Ds
表面扩散系数表示有效成分在物料内部的扩散速度,与溶出速率常数k和物料半径成正相关,实验结果如表1所示。两种热处理方式的Ds均随着浸提温度的升高而升高;在相同温度条件下,HWE-10和PHWE-10的Ds均大于其他两个料液比。对HWE-5而言,HWE-15的Ds更大,PHWE则相反,其原因可能是过高的料液比使得浸提液黏度较高,不利于多糖的溶出扩散,而温度较高并增加一定的压力会使浸提液黏度降低,银耳多糖的传质驱动力增加,此时高料液比的Ds高于低料液比[36−37]。
2.2.3 相对萃余率Y
相对萃余率Y=(C∞−Ct)/C∞ ,反映了溶出过程某一时刻的物料中还未溶出的有效成分与溶出达到平衡后溶剂中有效成分的比值。根据不同浸提温度和料液比的相对萃余率Y与浸提时间t作图并拟合,如图3及表1所示,拟合方程的决定系数R2均大于0.92,曲线拟合精度较好,说明银耳多糖的溶出过程符合指数模型。在不同的料液比与浸提温度下,HWE相对萃余率均在10~90 min内迅速下降,PHWE在5~10 min内迅速下降,说明该阶段多糖的溶出速率较快。在不同的料液比和浸提时间下,温度越高,相对萃余率的曲线斜率越大,多糖溶出效率越高。
2.2.4 活化能Ea
活化能(Ea)指分子进行能级跃迁时所需要的能量,可用于评价有效成分在特定条件下的溶出速率快慢,活化能越大,表明动力学溶出过程对温度越敏感。活化能与溶出速率常数k 以及浸提温度T 有关,遵循阿伦尼乌斯(Arrhenius)关系式[38]:
k=A⋅exp(−EaRT) (6) 式中:k为溶出速率常数,min−1;R=8.314 J·mol−1·K−1;A为指前因子;T为浸提温度,K;Ea为表观活化能,J/mol。
式(6)变形可得:
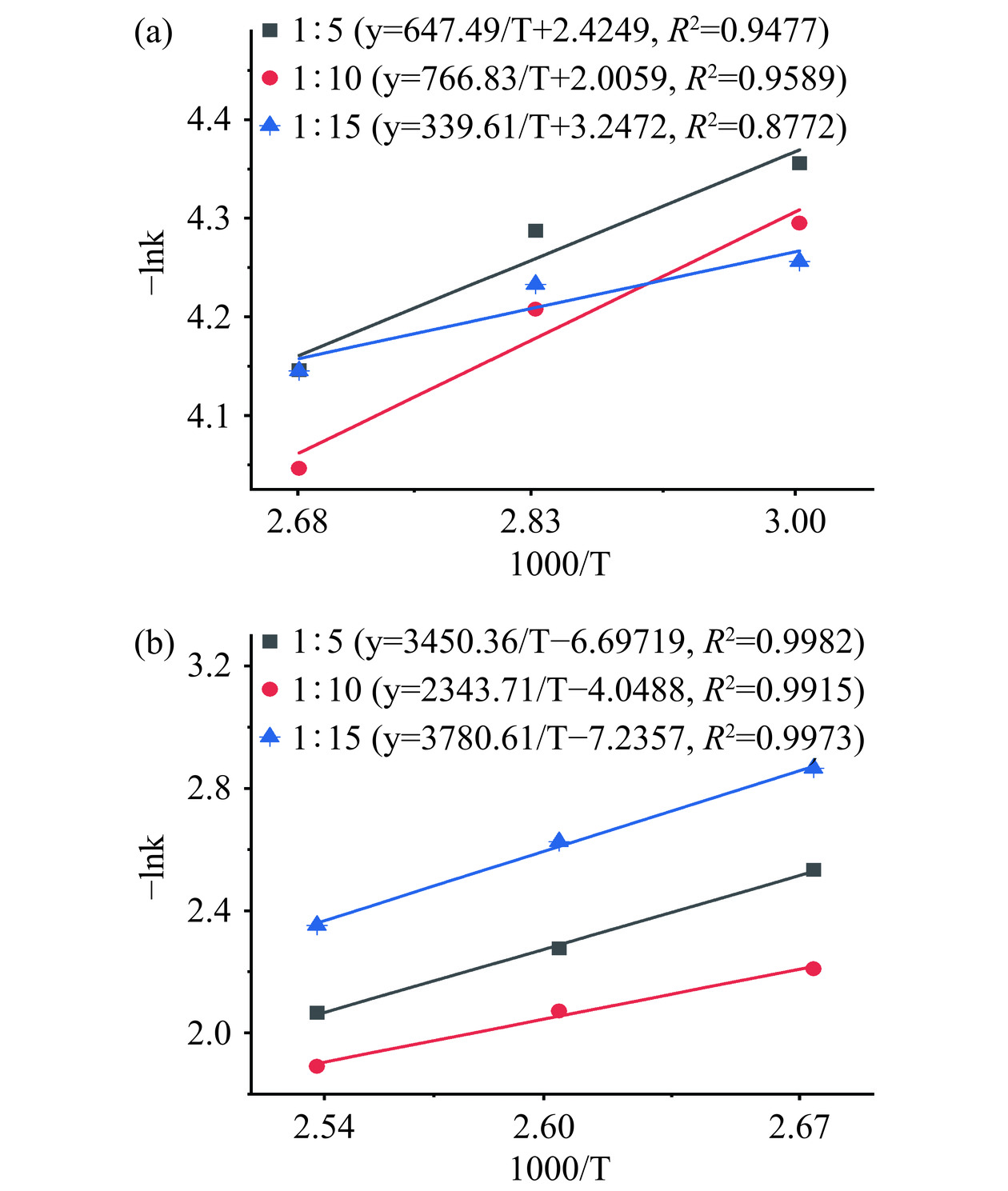
−lnk=−lnA+(EaRT) (7) 根据求得的速率常数k,对−lnk 与1000/T 作图并拟合,结果如图4 所示。
计算得到在料液比1:5、1:10、1:15时HWE与PHWE的活化能分别为:5.38、6.38、2.82 kJ/mol 与28.69、19.49、31.43 kJ/mol。PHWE样品的活化能及溶出速率常数k 均显著高于HWE样品,说明加压条件下银耳多糖溶出过程受温度的影响更大,更有利于银耳多糖的溶出,这与图1中多糖溶出率的结果相一致。有研究发现,颗粒状和片状紫菜多糖溶出过程的活化能分别为5.984 kJ/mol和1.406 kJ/mol[23],提取甘草多糖的活化能为8.0393~10.9168 kJ/mol[39],提取柑橘皮果胶的活化能为4.94~18.62 kJ/mol[40],基本低于本研究中银耳多糖溶出过程的活化能,这可能与银耳多糖在溶液中较大的黏度特性有关,多糖达到一定浓度会阻碍多糖进一步溶出。
因此,考虑到得率以及操作的便捷性,后续银耳多糖分子量及流变学特性的测定选取多糖溶出率较高且黏度较低的HWE-10和PHWE-10样品组进行。
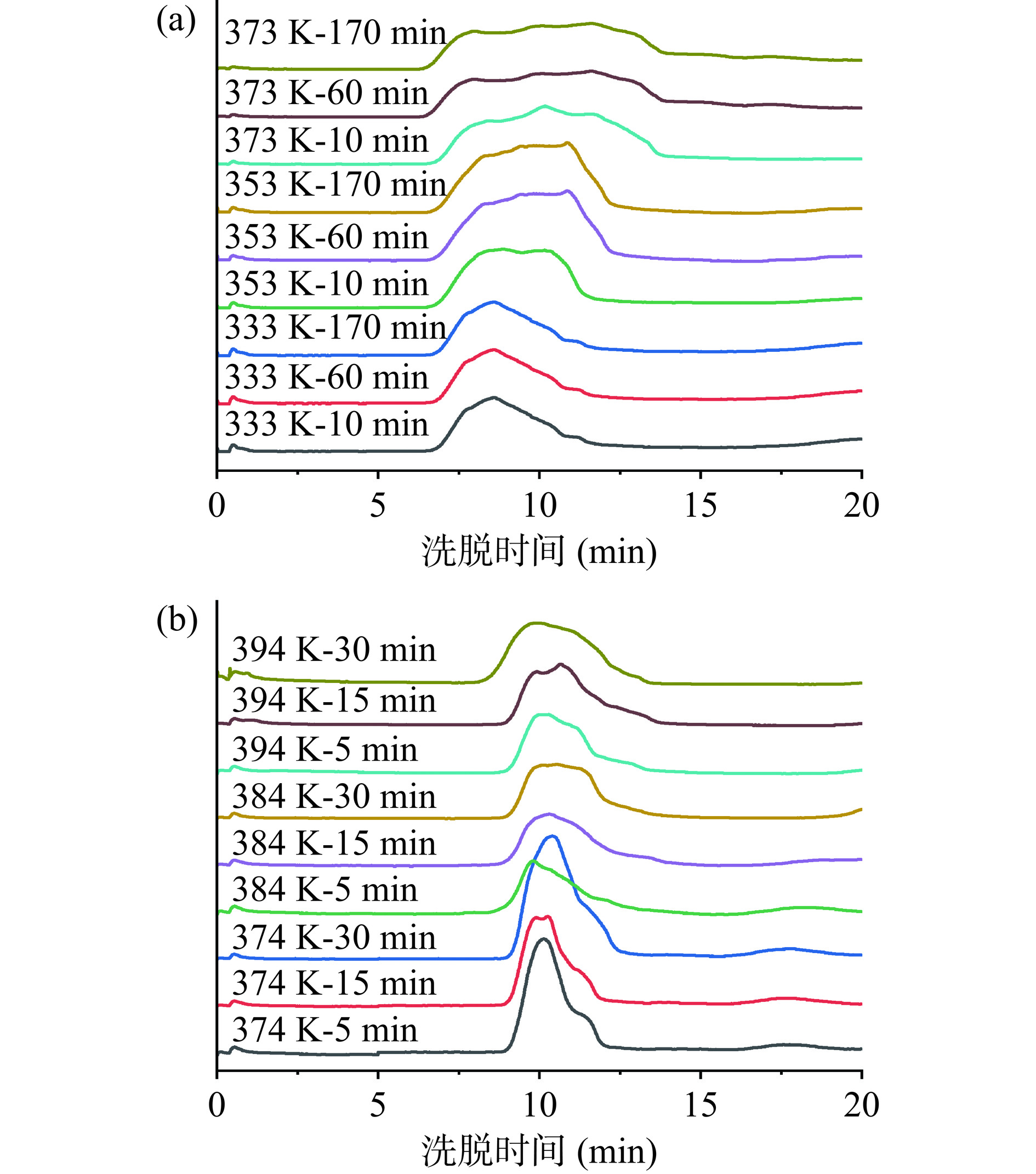
2.3 浸提液中多糖分子量的分布
为进一步了解两种水热处理方式对银耳多糖溶出及结构的影响,分别测定了HWE-10及PHWE-10在不同浸提时间与浸提温度下银耳多糖的分子量,多糖分子量的变化情况如图5 所示。由图5(a)可知,HWE-10多糖分子量在0.163~16.992×103 kDa 之间,分子量分布范围较广。浸提温度为333 K时,银耳多糖的分子量分布相似,未随着浸提时间的延长而发生变化,说明低温条件下浸提时间对银耳多糖的分子量分布无显著影响,低温能较好地保留银耳多糖的结构。随着浸提温度进一步升高及浸提时间的延长,大分子量的银耳多糖减少且出现了更小分子量的糖,分子量分布范围变大。由图5(b)可知,PHWE-10多糖分子量在0.072~3.271×103 kDa 之间,明显低于HWE-10。浸提温度为374 K时银耳多糖的分子量分布较为集中,随着浸提温度的升高和浸提时间的延长多糖分子量下降趋势明显,其原因可能是高温及压力使银耳多糖链断裂,大分子量的银耳多糖逐步降解为小分子量的糖[24,41]。
2.4 浸提液的流变学特性
2.4.1 静态流变学特性
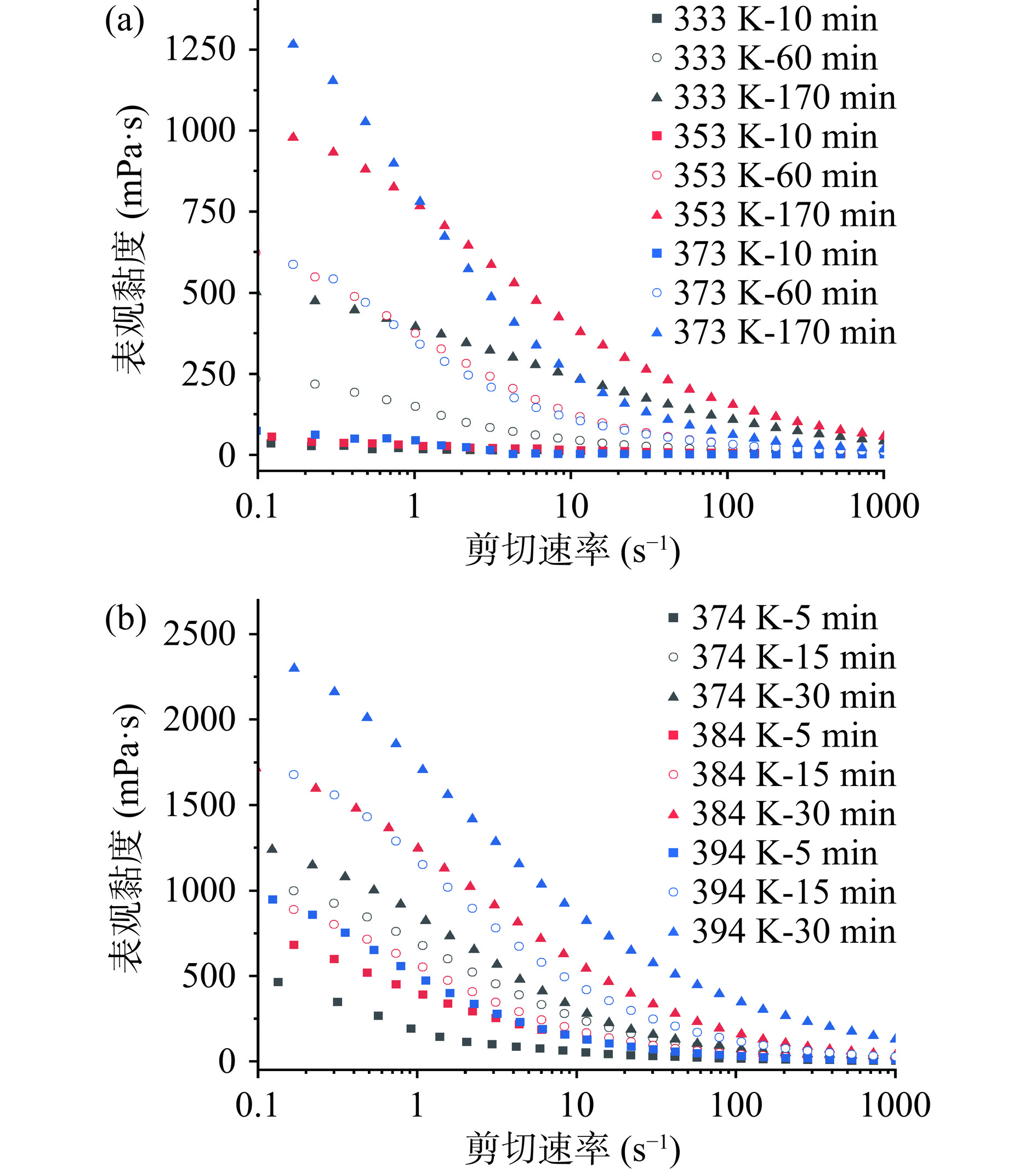
由图6可知,随着剪切速率的增大,多糖与水分子、多糖与多糖之间的相互作用力在剪切应力的作用下减弱,浸提液表观黏度逐渐减小直至趋于零,表现出剪切稀化的行为,呈现典型的非牛顿流体特征[42]。浸提温度相同时,浸提液的表观黏度随着浸提时间的延长而升高,这一变化主要与多糖质量浓度有关。其中,浸提温度为373 K的样品表观黏度在0~10 s−1的低剪切速率区域下降得更快,这是因为样品分子量分布较为分散,分子链结缠作用弱,多糖分子更容易被剪切力打散重排。多糖质量浓度相近时,HWE-10呈现出比PHWE-10更高的表观黏度(例如353 K-60 min与374 K-5 min),这是由于HWE-10的分子量显著大于PHWE-10,其在溶液中的重叠与纠缠程度更高,流体阻力增大,使得浸提液具有更高的黏度[43−44]。有研究发现多糖质量浓度相同时桑枝多糖与桑枝低聚糖相比具有更高的黏度,大粒车前子多糖及肉苁蓉多糖黏度也均随着分子量的减小而降低[45−47]。此外,溶液的黏度还可能与多糖分子的支化度、单糖组成及官能团有关[36,43,48]。
2.4.2 动态流变学特性
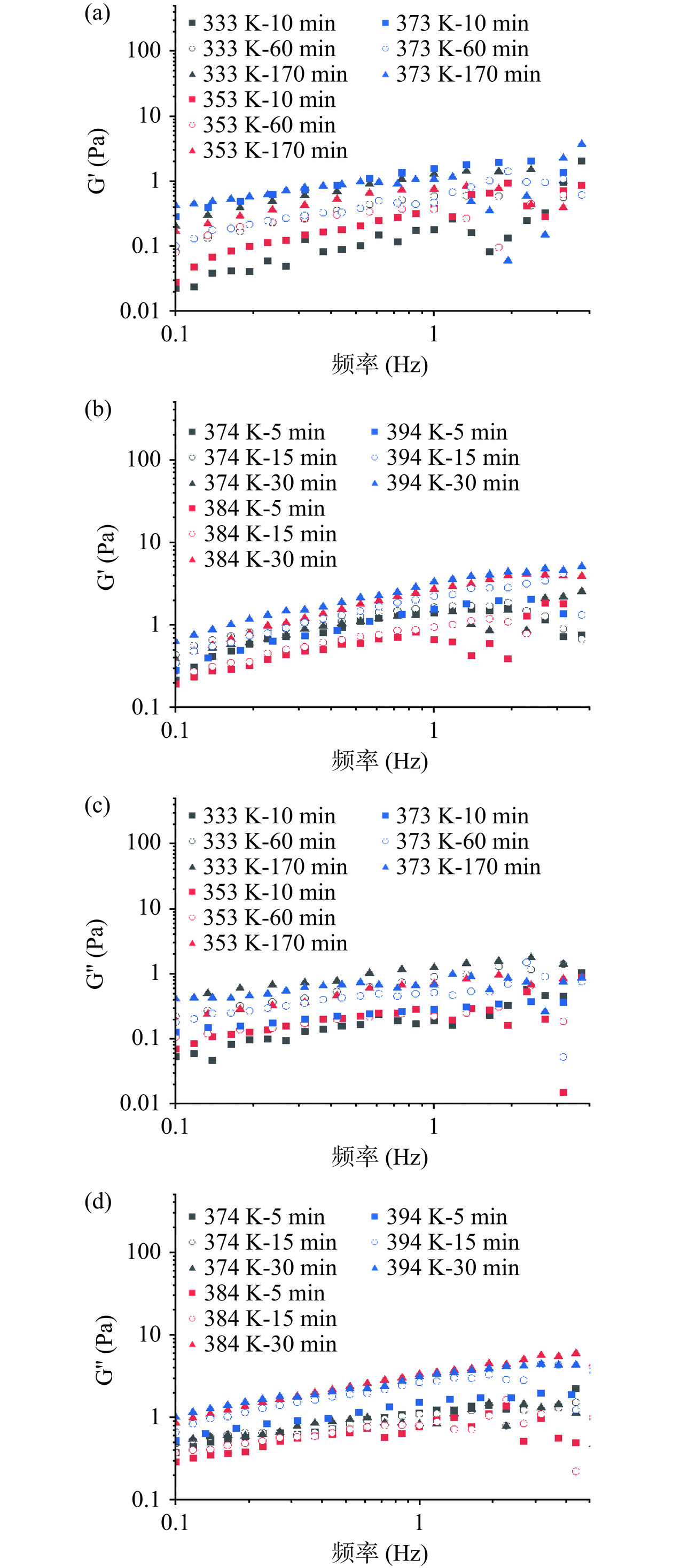
浸提过程中浸提液的动态流变学特性如图7及图8所示。实验结果表明,在低频率条件下,所有样品的储能模量G'均低于损耗模量G'',且数值与多糖质量浓度呈正比,说明浸提液在低频区域由黏性主导,呈现类液体属性[49]。随着振荡频率的增大,G'和G''逐渐增大,其中374 K-30 min及394 K-30 min的G'和G''始终呈有序排列(图7b、图7d),这可归因于高质量浓度所产生的强相互作用使得样品具有高稳定性[50]。373 K-170 min 也存在类似的现象(图7a、图7c),原因可能与该样品的分子量有关,大分子量的多糖在溶液中缠结程度更高,在单位浓度内可以形成更紧密的凝胶网络结构,使其与高质量浓度样品呈现相同状态[51]。
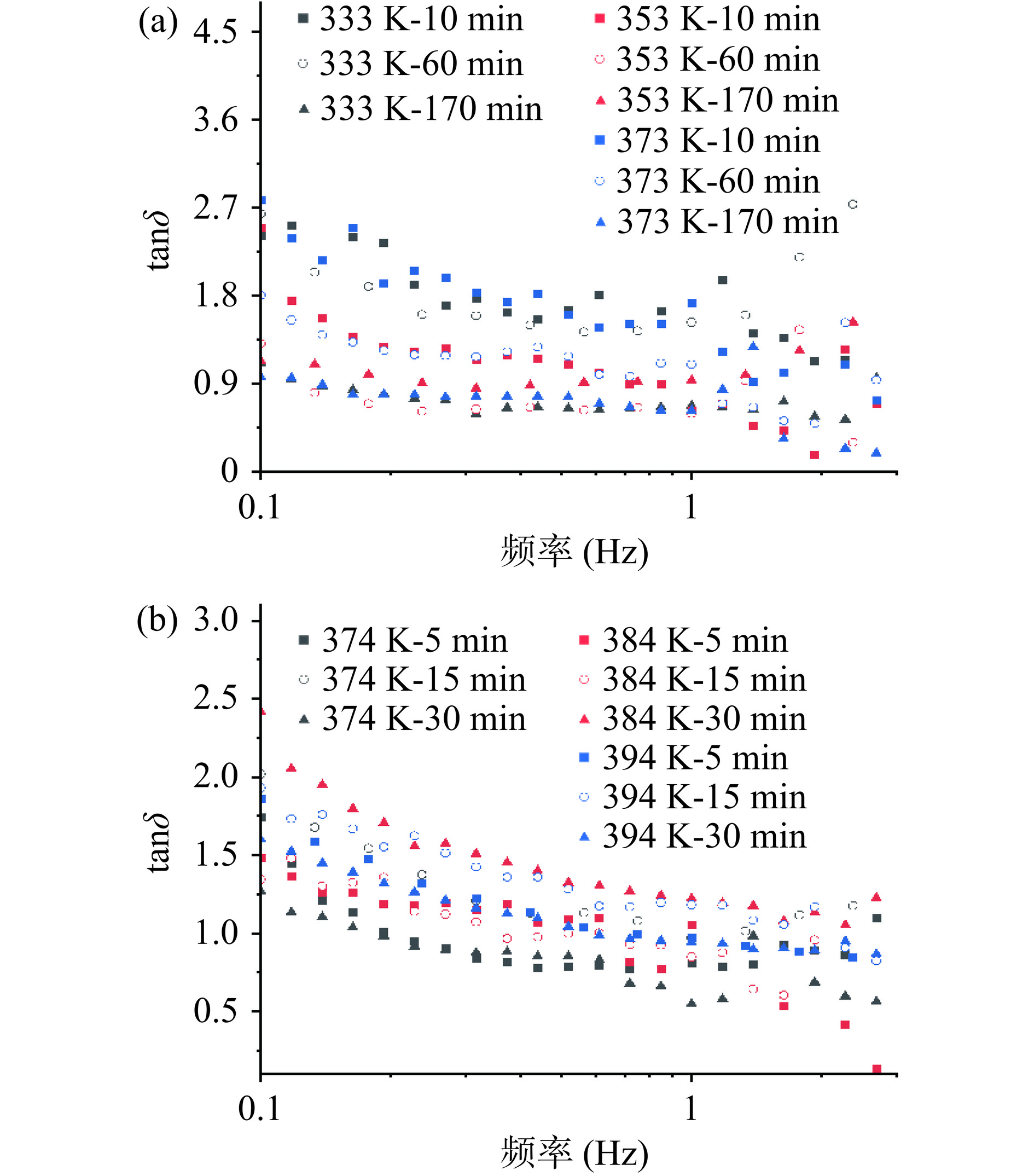
另外,流变学体系中还可以用tanδ(G''/G')解释溶液的流变行为,tanδ<0.1为强凝胶结构,0.1>tanδ>1为弱凝胶结构[52]。由图8可知,在低频区域,所有样品的tanδ均大于1,且其值与样品的多糖质量浓度成正比。随着振荡频率的增加,与HWE-10相比,PHWE-10的tanδ变化更为明显,其中多糖质量浓度最高的394 K-30 min的tanδ下降最为明显,说明凝胶结构的形成对多糖的质量浓度有强烈的依赖性,增大多糖质量浓度有助于浸提液形成更紧密的凝胶体系,以达到提高液体饮料稳定性的目的。
3. 结论
本研究以Fick第二定律为基础、片状银耳为原料构建了HWE及PHWE两个热处理条件下银耳多糖的溶出动力学模型并解析相关参数,测定了多糖浸提液的分子量及流变学特性。结果表明:浸提过程中,浸提液的多糖溶出率随浸提温度的升高及浸提时间的延长而增加,低料液比及高温条件下多糖溶出得更为充分。溶出过程中,银耳多糖的表观速率常数k和有效扩散系数Ds均随浸提温度的升高而增大,且PHWE高于HWE,提高浸提温度和加压有助于银耳多糖的溶出。HWE-10和PHWE-10浸提液的银耳多糖分子量分别为0.163~16.992×103 kDa 和0.072~3.271×103 kDa,浸提温度的升高及高温条件下延长浸提时间均会使多糖分子量降低。流变学特性表明,浸提液属于假塑性流体,在同一浸提温度下,浸提液的表观黏度随着浸提时间的延长而升高;多糖质量浓度相近时,HWE-10浸提液的表观黏度高于PHWE-10浸提液,说明浸提液的黏度与银耳多糖的质量浓度和分子量有关。本文通过建立动力学模型,研究不同热处理条件下以银耳多糖为主要成分的浸提液各项指标的变化情况,为银耳多糖在液体饮料中的开发应用提供理论依据。
-
表 1 不同热处理条件下银耳多糖动力学模型的各项参数
Table 1 Parameters of the kinetic model of Tremella polysaccharides under different heat treatment conditions
样品组 浸提温
度(K)平衡时
间(min)C∞ 线性模型 Ds 指数模型 拟合方程(ln[C∞/(C∞−Ct)]=kt+b) k R2 拟合方程(Y=a×expnt) R2 HWE-5 333 170 0.63 0.0128t+0.1989 0.0128 0.967 3.2532 0.7638exp−0.0111t 0.9771 353 170 1.35 0.0137t+0.2055 0.0137 0.9898 3.4839 0.7741exp−0.0125t 0.9873 373 170 2.65 0.0158t+0.2117 0.0158 0.984 4.0139 0.7469exp−0.0137t 0.9828 HWE-10 333 170 0.53 0.0136t+0.061 0.0136 0.979 3.4586 0.895exp−0.0124t 0.992 353 170 1.19 0.0149t+0.0862 0.0149 0.9976 3.773 0.9285exp−0.0152t 0.9968 373 170 2.84 0.0175t−0.0297 0.0175 0.9793 4.4348 0.918exp−0.0155t 0.9911 HWE-15 333 170 0.43 0.0142t+0.1263 0.0142 0.9949 3.5955 0.918exp−0.0149t 0.998 353 170 0.64 0.0145t+0.1411 0.0145 0.9847 3.6792 0.8258exp−0.0133t 0.9843 373 170 1.3 0.0158t+0.102 0.0158 0.9921 4.0164 0.9286exp−0.0131t 0.944 PHWE-5 374 25 3.88 0.0793t+0.1551 0.0793 0.9662 20.1174 0.792exp−0.0715t 0.9502 384 25 4.6 0.1026t+0.0464 0.1026 0.961 26.0254 0.8293exp−0.088t 0.9559 394 25 5.01 0.1267t−0.1588 0.1267 0.9598 32.1235 0.933exp−0.1024t 0.9612 PHWE-10 374 25 3.19 0.1098t−0.4151 0.1098 0.9139 27.8282 1.2183exp−0.0871t 0.9272 384 25 3.69 0.126t−0.3953 0.126 0.8783 31.9435 1.1133exp−0.0954t 0.9335 394 25 4.13 0.1509t−0.5442 0.1509 0.8811 38.2673 1.1644exp−0.1082t 0.9385 PHWE-15 374 25 1.81 0.057t+0.1033 0.057 0.996 14.4428 0.8867exp−0.0554t 0.9915 384 25 2.17 0.0724t+0.1013 0.0724 0.961 18.3679 0.8216exp−0.0625t 0.9374 394 25 2.78 0.0952t−0.6470 0.0952 0.8851 24.1364 0.8916xp−0.0770t 0.9217 注:C∞表示溶出达到平衡时浸提液银耳多糖的质量浓度,mg/mL;Ct表示任意时刻浸提液多糖的质量浓度,mg/mL;k表示银耳多糖的溶出速率常数,min−1;R2表示拟合方程的线性相关系数;Ds表示银耳多糖的表面扩散系数,mm2/min。 -
[1] 林钊. 不同银耳品系生理特性及品质分析研究[D]. 福州:福建农林大学, 2019. [LIN Z. Analysis of physiological characteristics and quality of different Tremella species[D]. Fuzhou:Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2019.] LIN Z. Analysis of physiological characteristics and quality of different Tremella species[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2019.
[2] 郑仕中. 银耳的化学成分和药理研究进展[J]. 中国药学杂志,1993(5):264−267. [ZHENG S Z. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacology of Tremella fuciformis[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal,1993(5):264−267.] ZHENG S Z. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacology of Tremella fuciformis[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal, 1993(5): 264−267.
[3] 刘健影. 银耳多糖提取工艺优化及其在饮料中的应用[D]. 长春:吉林农业大学, 2015. [LIU Z Y. Process optimization on the extraction of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide and its application in beverages[D]. Changchun:Jilin Agricultural University, 2015.] LIU Z Y. Process optimization on the extraction of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide and its application in beverages[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2015.
[4] 张姗姗, 吴琼, 王冰聪. 银耳多糖对花生蛋白饮料稳定性的影响[J]. 食品科技,2017,42(7):200−204. [ZHANG S S, WU Q, WANG B C. Effects of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides on stability of peanut protein beverage[J]. Food Science and Technology,2017,42(7):200−204.] ZHANG S S, WU Q, WANG B C. Effects of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides on stability of peanut protein beverage[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2017, 42(7): 200−204.
[5] LI Y B, CHEN J C, LAI P F, et al. Influence of drying methods on the physicochemical properties and nutritional composition of instant Tremella fuciformis[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,40(3):741−748. doi: 10.1590/fst.20519
[6] LI Y, LI J W, FAN L P. Effects of combined drying methods on physicochemical and rheological properties of instant Tremella fuciformis soup[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,396:133644. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133644
[7] ZHAO X Y, LIU H K, ZHANG X W, et al. Effect of pressure grinding technology on the physicochemical and antioxidant properties of Tremella aurantialba powder[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2018,42(12):e13833. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.13833
[8] KOUR H, KOUR D, KOUR S, et al. Bioactive compounds from mushrooms:An emerging bioresources of food and nutraceuticals[J]. Food Bioscience, 2022,50:102124.
[9] ZHANG L F, CHEN J, XU F, et al. Effect of Tremella fuciformis on dough structure and rheology, noodle flavor, and quality characteristics[J]. LWT,2022,172:114180. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.114180
[10] MA X, YANG M, HE Y, et al. A review on the production, structure, bioactivities and applications of Tremella polysaccharides[J]. International Journal of Immunopathology and Pharmacology,2021,35:1120256459.
[11] XU X Q, CHEN A J, GE X Y, et al. Chain conformation and physicochemical properties of polysaccharide (glucuronoxylomannan) from fruit bodies of Tremella fuciformis[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,245:116354. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116354
[12] JIN Y X, HU X Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Studies on the purification of polysaccharides separated from Tremella fuciformis and their neuroprotective effect[J]. Mol Med Rep,2016,13(5):3985−3992. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5026
[13] LI X G, ZHANG F Y, JIANG C X, et al. Structural analysis, in vitro antioxidant and lipid-lowering activities of purified Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide fractions[J]. Process Biochemistry,2023,133:99−108. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2023.06.005
[14] JEONG H J, YOON S J, PYUN Y R. Polysaccharides from edible mushroom Hinmogi (Tremella fuciformis) inhibit differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes by reducing mRNA expression of PPAR gamma, C/EBP alpha, and leptin[J]. Food Science and Biotechnology,2008,17(2):267−273.
[15] ZHANG S S, XU X, L CAO X, et al. The structural characteristics of dietary fibers from Tremella fuciformis and their hypolipidemic effects in mice[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2023,12(2):503−511. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.07.052
[16] LAN X Y, WANG Y H, DENG S, et al. Physicochemical and rheological properties of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide fractions by ethanol precipitation[J]. CYTA:Journal of Food,2021,19(1):645−655.
[17] LI J, LI B, GENG P, et al. Ultrasonic degradation kinetics and rheological profiles of a food polysaccharide (Konjac glucomannan) in water[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,70:14−19. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.03.022
[18] 张庆, 袁源, 邓扬龙, 等. 不同栽培方式银耳多糖单糖组成分析及体外抗氧化活性比较[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(8):54−60. [ZHANG Q, YUAN Y, DENG Y L, et al. Monosaccharide composition analysis and antioxidant activity comparison of polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis cultivated in different methods[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(8):54−60.] ZHANG Q, YUAN Y, DENG Y L, et al. Monosaccharide composition analysis and antioxidant activity comparison of polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis cultivated in different methods[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(8): 54−60.
[19] LI P, JIANG Z, SUN T, et al. Comparison of structural, antioxidant and immuno-stimulating activities of polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis in two different regions of China[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2018,53(8):1942−1953.
[20] SHI X D, FENG J W, WANG S Y, et al. Primary structure, physicochemical properties, and digestive properties of four sequentially extracted polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2023,115:105005. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2022.105005
[21] FARAKTE R A, YADAV G U, JOSHI B S, et al. Modeling of tea tnfusion kinetics incorporating swelling kinetics[J]. International journal of food engineering,2017,13(2):20160206. doi: 10.1515/ijfe-2016-0206
[22] LI J, PANG J H, DENG C, et al. Kinetics on the leaching of polysaccharide from Arctium lappal root[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2012,531:334−337. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.531.334
[23] 刘恋. 条斑紫菜中多糖的溶出动力学、模拟消化及生物活性[D]. 镇江:江苏大学, 2017. [LIU L. Dissolution kinetic models of polysaccharides from Porphyra yezoensis and their stimulated digestion in vitro and biological activitity research[D]. Zhenjiang:Jiangsu University, 2017.] LIU L. Dissolution kinetic models of polysaccharides from Porphyra yezoensis and their stimulated digestion in vitro and biological activitity research[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2017.
[24] SU C H, LAI M N, NG L T. Effects of different extraction temperatures on the physicochemical properties of bioactive polysaccharides from Grifola frondosa[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,220:400−405. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.09.181
[25] 瞿琳, 艾连中, 赖凤羲, 等. 豌豆种皮水溶性多糖的提取优化、动力学与分子特征[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(21):81−89. [QU L, AI L Z, LAI Phoency, et al. The optimization of the extract condition, kinetics, and molecular characteristics of water-soluble polysaccharides from Pisum sativum L. seed pericarp[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(21):81−89.] QU L, AI L Z, LAI Phoency, et al. The optimization of the extract condition, kinetics, and molecular characteristics of water-soluble polysaccharides from Pisum sativum L. seed pericarp[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(21): 81−89.
[26] DUBOIS M, GILLES H A, HAMILTON J K, et al. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances[J]. Analytical Chemistry,1956,28(3):22−25.
[27] SAQIB A A N, WHITNEY P J. Differential behaviour of the dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) reagent towards mono- and di-saccharide sugars[J]. Biomass & Bioenergy,2011,35(11):4748−4750.
[28] STAPLEY A G F. Modelling the kinetics of tea and coffee infusion[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2002,82(14):1661−1671. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.1250
[29] 龙慧, 李祎, 朱叶力, 等. 银耳多糖与大豆分离蛋白的相互作用及流变性能[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(16):160−168. [LONG H, LI Y, ZHU Y L, et al. Interaction between Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide and soybean protein isolate:Rheological properties of their mixtures[J]. Food Science,2022,43(16):160−168.] LONG H, LI Y, ZHU Y L, et al. Interaction between Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide and soybean protein isolate: Rheological properties of their mixtures[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(16): 160−168.
[30] 赵凯, 牛会平, 侯建平, 等. 香菇多糖提取动力学模型研究[J]. 河北师范大学学报(自然科学版),2019,43(1):52−59. [ZHAO K, NIU H P, HOU J P, et al. Study on kinetic model for extraction of lentinan[J]. Journal of Hebei Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2019,43(1):52−59.] ZHAO K, NIU H P, HOU J P, et al. Study on kinetic model for extraction of lentinan[J]. Journal of Hebei Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 43(1): 52−59.
[31] 刘晓霞, 苏平, 吴秋敏. 响应面分析法优化黄秋葵花中果胶的提取工艺研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(16):270−273. [LIU X X, SU P, WU Q M. Optimization of pectin extraction from Okra flowers by response surface method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(16):270−273.] LIU X X, SU P, WU Q M. Optimization of pectin extraction from Okra flowers by response surface method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2014, 35(16): 270−273.
[32] PEZOA-CONTE R, LEYTON A, BACCINI A, et al. Aqueous Extraction of the sulfated polysaccharide ulvan from the green Alga Ulva rigida—kinetics and modeling[J]. BioEnergy Research,2017,10(3):915−928. doi: 10.1007/s12155-017-9853-4
[33] 张琴, 李美东, 张子木, 等. 壶瓶碎米荠多糖提取动力学模型研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(14):31−37. [ZHANG Q, LI M D, ZHANG Z M, et al. Establishment of polysaccharide extraction process model and kinetic analysis of Cardamine hupingshanensis[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(14):31−37.] ZHANG Q, LI M D, ZHANG Z M, et al. Establishment of polysaccharide extraction process model and kinetic analysis of Cardamine hupingshanensis[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(14): 31−37.
[34] 周雅琳, 谭红军, 杨勇. 不同处理方式对银耳粗多糖提取效果及化学成分的影响[J]. 食品科技,2015,40(5):215−220. [ZHOU Y L, TAN H J, YANG Y. Effect of extraction rate and chemical composition of crude polysaccharides in Tremella fuciformis Berk by different extraction methods[J]. Food Science and Technology,2015,40(5):215−220.] ZHOU Y L, TAN H J, YANG Y. Effect of extraction rate and chemical composition of crude polysaccharides in Tremella fuciformis Berk by different extraction methods[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2015, 40(5): 215−220.
[35] ZHANG W N, ZHANG H L, LU C Q, et al. A new kinetic model of ultrasound-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Chinese chive[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,212:274−281. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.05.144
[36] XU K, GUO M M, DU J H. Molecular characteristics and rheological properties of water-extractable polysaccharides derived from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.)[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2017,20(sup1):S899−S909. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2017.1315594
[37] 郑良. 银耳多糖提取条件及提取液黏度特性的研究[D]. 成都:四川大学, 2003. [ZHENG L. Effect of extraction rate and chemical composition of crude polysaccharides in Tremella fuciformis Berk by different extraction methods[D]. Chengdu:Sichuan University, 2003.] ZHENG L. Effect of extraction rate and chemical composition of crude polysaccharides in Tremella fuciformis Berk by different extraction methods[D]. Chengdu: Sichuan University, 2003.
[38] BEELDERS, THERESA, DE, et al. Modeling of thermal degradation kinetics of the C-glucosyl xanthone mangiferin in an aqueous model solution as a function of pH and temperature and protective effect of honeybush extract matrix[J]. Food Research International,2018,103:103−109.
[39] WANG Y G, ZHANG X, MA X Q, et al. Study on the kinetic model, thermodynamic and physicochemical properties of Glycyrrhiza polysaccharide by ultrasonic assisted extraction[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2019,51:249−257. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.10.012
[40] 王文骏. 柑橘皮果胶超声辅助提取的作用机制研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2018. [WANG W J. The research on the mechanism of ultrasound-assisted extraction of pectin from citrus peel[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2018.] WANG W J. The research on the mechanism of ultrasound-assisted extraction of pectin from citrus peel[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018.
[41] 徐柔. 秋葵多糖基本结构和流变学特征及高压均质对其结构的影响[D]. 南昌:南昌大学, 2019. [XU R. Basic structural and rheological characteristics of polysaccharide from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) and the effect of high pressure homogenization on its structure[D]. Nanchang:Nanchang University, 2019.] XU R. Basic structural and rheological characteristics of polysaccharide from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) and the effect of high pressure homogenization on its structure[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2019.
[42] 贾丰, 刘冬, 郭玉蓉, 等. 发酵对苹果渣多糖流变性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(14):106−111. [JIA F, LIU D, GUO Y R, et al. Effect of fermentation on rheology of apple pomace polysaccharides[J]. Food Science,2017,38(14):106−111.] JIA F, LIU D, GUO Y R, et al. Effect of fermentation on rheology of apple pomace polysaccharides[J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(14): 106−111.
[43] PAN X, ZHAO W T, WANG Y X, et al. Physicochemical and structural properties of three pectin fractions from muskmelon (Cucumis melo) and their correlation with juice cloud stability[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,124:107313. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107313
[44] SMITH I H, LAWSON C J, HARDING S E, et al. Viscosity development during aqueous dispersion and dissolution:A comparison of PGX® with other dietary supplements and individual polysaccharides[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2014,38:152−162. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.12.004
[45] 田文静, 周瑫, 黄群惠, 等. 超声处理对肉苁蓉多糖流变学性质的影响[J]. 生物学通报,2021,56(2):48−53. [TIAN W J, ZHOU T, HUANG Q H, et al. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on rheological properties of cistanche polysaccharide[J]. Bulletin of Biology,2021,56(2):48−53.] TIAN W J, ZHOU T, HUANG Q H, et al. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on rheological properties of cistanche polysaccharide[J]. Bulletin of Biology, 2021, 56(2): 48−53.
[46] 夏强. 超声波降解对大粒车前子多糖流变性质、溶液构象及生物活性的影响[D]. 南昌:南昌大学, 2016. [XIA Q. Effects of ultrasonic depolymerization on the rheological property, solution conformation and bioactivities of polysaccharides isolated from the seeds of Plantago Asiatica L D]. Nanchang:Nanchang University, 2016.
[47] 杨诗沅, 邹宇晓, 黎尔纳, 等. 桑枝多糖与桑枝低聚糖的流变学特性[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(8):1−6. [YANG S Y, ZOU Y X, LI E N, et al. Rheological properties of ramulus mori polysaccharides and Ramulus mori oligosaccharides[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(8):1−6.] YANG S Y, ZOU Y X, LI E N, et al. Rheological properties of ramulus mori polysaccharides and Ramulus mori oligosaccharides[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(8): 1−6.
[48] GONZALEZ-CENTENO R, MARIA, FEMENIA, et al. Effect of different drying procedures on the bioactive polysaccharide acemannan from Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller)[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers:Scientific and Technological Aspects of Industrially Important Polysaccharides,2017,168:327−336.
[49] 李梦钰, 刘会平, 贾琦, 等. 天冬多糖理化性质和流变学特性研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(5):48−56. [LI M Y, LIU H P, JIA Q, et al. Physicochemical properties and rheological properties of asparagi radix polysaccharide[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(5):48−56.] LI M Y, LIU H P, JIA Q, et al. Physicochemical properties and rheological properties of asparagi radix polysaccharide[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(5): 48−56.
[50] WANG H L, KE L J, DING Y N, et al. Effect of calcium ions on rheological properties and structure of Lycium barbarum L. polysaccharide and its gelation mechanism[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,122:107079. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107079
[51] 杨嘉丹, 刘婷婷, 张闪闪, 等. 微波辅助提取银耳多糖工艺优化及其流变、凝胶特性[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(14):289−295. [YANG J D, LIU T T, ZHANG S S, et al. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction and rheological and gelling properties of polysaccharide from Tremella fuciformis[J]. Food Science,2019,40(14):289−295.] YANG J D, LIU T T, ZHANG S S, et al. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction and rheological and gelling properties of polysaccharide from Tremella fuciformis[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(14): 289−295.
[52] 李秀秀, 尚静, 杨曦, 等. 多糖的增稠、胶凝及乳化特性研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(15):300−308. [LI X X, SHANG J, YANG X, et al. A review on thickening, gelling and mulsifying properties of polysaccharides[J]. Food Science,2021,42(15):300−308.] LI X X, SHANG J, YANG X, et al. A review on thickening, gelling and mulsifying properties of polysaccharides[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(15): 300−308.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



