Optimization of the Process for Defatting Sea Cucumber Powder by Supercritical CO2 Extraction and Its Effect on Volatile Flavor Compounds
-
摘要: 本实验以海参粉为原料,以脱脂率为指标,采用单因素与正交试验优化了超临界 CO2萃取分离条件,通过气相色谱法检测萃取前后海参粉和萃取物中脂肪酸的组成变化,以顶空-气相色谱-离子迁移谱(HS-GC-IMS)考察超临界 CO2 萃取对挥发性风味物质的影响。结果表明:采用单因素与正交试验优化后得出超临界 CO2萃取的最佳条件为:萃取温度 60 ℃、萃取压力 40 MPa、萃取时间 2 h,在此条件下脱脂率为 57.6%±3.89%;海参粉、萃取后海参粉和萃取物中共检测出 25 种脂肪酸,其中萃取物中单不饱和脂肪酸含量占比明显较高,而花生四烯酸(ARA)、二十碳五烯酸(EPA)和二十二碳六烯酸(DHA)等多不饱和脂肪酸含量在萃取后海参粉中占比更高;HS-GC-IMS 定性检测到 70 种挥发性成分,萃取后海参粉中呈腥味或刺激性气味物质如二甲基硫醚、丁醛、反-2-丁烯醛、戊醛、庚醛、苯甲醛、戊醇、2-丁酮、2-己酮、3-己酮等物质含量比原料中含量明显减少,整体风味得到很大改善。因此,超临界 CO2萃取能够有效萃取分离出海参粉中脂类物质,同时去除大量腥味等挥发性成分。Abstract: In this study, supercritical CO2 extraction conditions for sea cucumber powder were optimized using single factor and orthogonal experimental design, with defatting rate as an indicator. The fatty acid composition of the sea cucumber powder before and after extraction as well as that in the supercritical CO2 extract were detected using gas chromatography, and supercritical CO2 extraction of volatile flavor substances was investigated using headspace-gas chromatography-ion migration spectroscopy (HS-GC-IMS). The results showed that the optimal conditions for supercritical CO2 extraction was optimized using single factor and orthogonal experiment, with an extraction temperature of 60 ℃, extraction pressure of 40 MPa, extraction time of 2 h, and a degreasing rate of 57.6%±3.89%. A total of 25 fatty acids were detected in the sea cucumber powder, extracted sea cucumber powder, and supercritical CO2 extract, with a higher proportion of monounsaturated fatty acids in the supercritical CO2 extract. In contrast, the proportions of polyunsaturated fatty acids such as arachidonic acid (ARA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) were higher in the extracted sea cucumber powder. HS-GC-IMS led to the identification of 70 volatile components. Notably, substances with fishy or pungent odors such as dimethyl sulfide, butanal, E-2-butenal, pentanal, heptanal, benzaldehyde, pentanol, 2-butanone, 2-hexanone, 3-hexanone and other substances were significantly reduced in the extracted sea cucumber powder, substantially improving the overall flavor. Therefore, supercritical CO2 extraction can effectively separate lipids from sea cucumber powder, while removing a large amount of volatile components with fishy odors.
-
海参是我国传统的营养滋补佳品,研究表明,海参体壁含有丰富的蛋白质、氨基酸、多糖、海参肽、脂质和皂苷等多种活性成分[1−2],具有抗氧化、抗炎、提高免疫力、抗癌、抗高血压、抗糖尿病以及抗菌等多种药理作用[3−4],是开发营养品、保健品和功能制品的优质原料。然而海参粉和海参肽粉等海参产品中腥味较严重,成为制约产品开发的重要因素[5]。近年来,有研究人员发现,海参脱腥的关键在于去除其体内的挥发性硫化物以及低分子质量醛、醇、酮类物质,这些化合物是导致海参腥味的主要原因[6]。通过在一定的酸碱条件下浸泡海参,可以显著降低其腥味,但存在试剂残留问题。利用吸附、掩盖、包埋等物理方法能够达到削弱或者掩盖海参中异味物质的目的,但无法从根本上去除海参的腥味[7−8]。利用微生物发酵改善产品风味也是一种热门方法,能够减少腥味物质,还能产生风味良好的物质,但整体风味会更复杂[9−10]。因此亟需一种更加绿色安全有效的脱腥技术促进海参产品的开发和改进。
超临界CO2萃取技术以CO2作为溶剂,可以很好地溶解碳原子数在20以内的脂肪烃、卤代烃、醛酮酯等分子质量较小的非极性和低极性物质,具有温度低、选择性强、易于分离、不破坏被萃取物的生理活性等优点[11],在不使用夹带剂的情况下萃取产物中无任何残留溶剂,符合消费者对于健康安全食品的追求。目前该技术已在食品工业中用于提取分离各种化合物,如脂质[12]、维生素[13]和色素[14]等。同时,因其独特优点还被广泛用于水产品脱腥及脂质的分离提取,如丁忠福等[15]采用超临界CO2萃取技术对林蛙卵油进行脱腥和脂质提取,利用碳链较长的重质组分(如EPA、DHA)与短链轻质组分(小于C12的能引起腥臭异味的小分子酮、醛、醇等物质)在超临界CO2中分配系数的差异而得到有效分离。李斌等[16]用超临界CO2萃取技术对罗非鱼鱼皮进行脱腥处理,结果发现超临界CO2萃取法相较于其他方法,不仅处理时间短、脱腥效果明显,还有能回收脂类物质、避免蛋白质损失等优势。Ali-Nehari等[17]不用夹带剂,直接利用超临界CO2萃取南极磷虾油,南极磷虾中的中性脂大部分可以被提取出来,利用此方法得到了质量更高、热稳定性更好的功能蛋白质。
而关于超临界CO2萃取技术在海参脱脂脱腥中的应用研究还鲜有报道。海参脂质是海参的主要化合物成分之一,其含有的多种脂肪酸在生物体代谢活动中起着关键作用[18]。有研究表明海参脂质含量占干基的3%~4%左右,由磷脂、糖脂、中性脂、胆固醇和游离脂肪酸等组成,磷脂的含量较高,占总脂的1/3左右,胆固醇的含量较低,仅占总脂的1%左右,是一种低胆固醇的海洋水产原料[19],海参中不饱和脂肪酸的占比普遍较高,具有低脂肪、高不饱和脂肪酸的特性[20−21]。超临界CO2萃取技术一方面可以脱除海参粉中腥味或刺激性风味成分,另一方面能够分离回收海参中的脂质成分,因此该技术在高品质海参粉及功能性脂质分离制备中具有较大的应用潜力。
基于此,本研究以海参粉为原料,采用单因素与正交试验优化超临界CO2萃取分离条件,通过气相色谱法检测原料、萃取后海参粉和萃取物中脂肪酸的组成变化,进一步以顶空-气相色谱-离子迁移谱(headspace-gas chromatography-ion migration spectroscopy,HS-GC-IMS)考察超临界CO2萃取对海参粉挥发性风味物质的影响。研究结果可为高品质海参粉的绿色制备提供技术支撑和理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
盐渍海参 烟台万事如意食品有限公司,原料来自烟台海域;甲醇(色谱纯)、正己烷(色谱纯) 美国Thermo公司;37种标准脂肪酸甲酯 美国Supelco公司;石油醚、盐酸 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;其他试剂均为国产分析纯。
HA220-50-06-C超临界CO2萃取装置 海安县石油科研仪器有限公司;GC2010气相色谱仪 配有氢火焰离子检测器(FID),日本岛津公司;SP-2560气相毛细管柱 美国Supelco公司;FlavourSpec®气相离子迁移谱(GC-IMS)联用仪 德国G.A.S公司;PL202电子天平 瑞士梅特勒-托利多公司;B-491恒温水浴锅 瑞士步琦有限公司;FXB101-1电热鼓风干燥箱 上海树立仪器仪表有限公司;Alpha1-4LDPlus真空冷冻干燥机 德国Christ公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 海参粉的制备
以盐渍海参为原料,参考陈子豪[22]的方法进行脱盐和干燥,在4 ℃冷藏中纯净水浸泡24 h,100 ℃蒸20 min后,纯净水浸泡一夜,再次蒸20 min,纯净水浸泡一夜后,利用真空冷冻干燥脱水,控制样品加热温度在50 ℃以内,最后粉碎过60目筛制得海参粉。
1.2.2 超临界CO2萃取实验
参考徐志利等[23]方法结合前期预实验结果,设定超临界CO2萃取海参粉基础条件:原料粒度60目,加样量100 g,CO2流量15 L/h,萃取压力40 MPa,萃取温度50 ℃,萃取时间1.5 h,选择对结果影响较大的萃取温度、萃取压力和萃取时间进一步考察和优化。每次萃取实验结束后,从出料口收集萃取物并采用索氏抽提法测定脂质质量[24],按照下列公式计算脱脂率,每组实验重复3次,取平均值。
脱脂率(%)=海参粉的脂质质量−萃取后海参粉的脂质质量海参粉的脂质质量×100 1.2.3 单因素实验
1.2.3.1 萃取温度对脱脂率的影响
设定萃取时间1.5 h,萃取压力40 MPa,考察不同萃取温度(30、40、50、60、70 ℃)对海参粉脱脂率的影响。
1.2.3.2 萃取压力对脱脂率的影响
设定萃取时间1.5 h,萃取温度50 ℃,考察不同萃取压力(30、35、40、45、50 MPa)对海参粉脱脂率的影响。
1.2.3.3 萃取时间对脱脂率的影响
设定萃取压力40 MPa,萃取温度50 ℃,考察不同萃取时间(0.5、1、1.5、2、2.5 h)对海参粉脱脂率的影响。
1.2.4 正交试验优化
在单因素实验的基础上,对萃取时间、萃取压力和萃取温度3个因素,利用正交试验表L9(34)进行正交试验,对每种因素的最佳萃取工艺条件进行优化(表1)。
表 1 正交因素水平Table 1. Orthogonal factors and levels因素 水平 1 2 3 A 萃取温度(℃) 40 50 60 B 萃取压力(MPa) 45 40 35 C 萃取时间(h) 2 1 1.5 1.2.5 脂肪酸成分测定
按照正交试验的最优工艺条件进行样品制备,分别对海参粉原料、萃取后海参粉和萃取物进行脂肪酸组成分析,参考马长兴等[25]方法并作适当修改。
1.2.5.1 样品前处理
称取0.1 g的样品于带螺帽的15 mL玻璃试管中,加入1 mL正己烷和2 mL甲醇盐酸,混匀后70 ℃恒温水浴2 h,冷却,加入5 mL 6% K2CO3和2 mL正己烷,混匀,在8000 r/min、室温下离心10 min后取上清液,采用气相色谱仪进行测定。
1.2.5.2 GC条件
色谱柱:SP-2560气相毛细管柱(100 m×0.25 mm,0.2 μm),进样器温度250 ℃;检测器为氢火焰离子检测器(FID),温度250 ℃;载气纯度为高纯N2,柱流速1.8 mL/min;进样体积1 μL,分流比90:1;程序升温:起始温度140 ℃,保持5 min,以4 ℃/min升至240℃,保持40 min。采用面积归一法计算脂肪酸相对含量。
1.2.6 HS-GC-IMS检测分析
HS-GC-IMS检测分析参考Li等[26]的方法并作适当修改。
1.2.6.1 自动进样条件
准确称取2.0 g海参粉和萃取后海参粉置于20 mL顶空瓶中,加盖密封后置于500 r/min振荡器60 ℃孵化15 min,顶空进样针温度为85 ℃,进样量为500 μL。
1.2.6.2 GC 条件
气相色谱柱为WAX-5色谱柱(L:15 m,ID:0.53 mm,膜厚1 μm),柱温为60 ℃,运行时间30 min,载气为高纯N2。
1.2.6.3 IMS 条件
离子迁移谱漂移管温度为45 ℃,漂移气为高纯N2,流速为150 mL/min保持不变。
应用软件内置的NIST数据库和IMS数据库对挥发性风味物质进行定性分析,采用Reporter和Gallery Plot构建有机物的差异谱图和指纹图谱,采用Dynamic PCA进行动态主成分分析。
1.3 数据处理
数据均是3次重复实验取平均值,结果以平均值±标准差表示,采用SPSS Statistics 26.0软件对数据进行ANOVA差异显著性分析,P<0.05表示具有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验
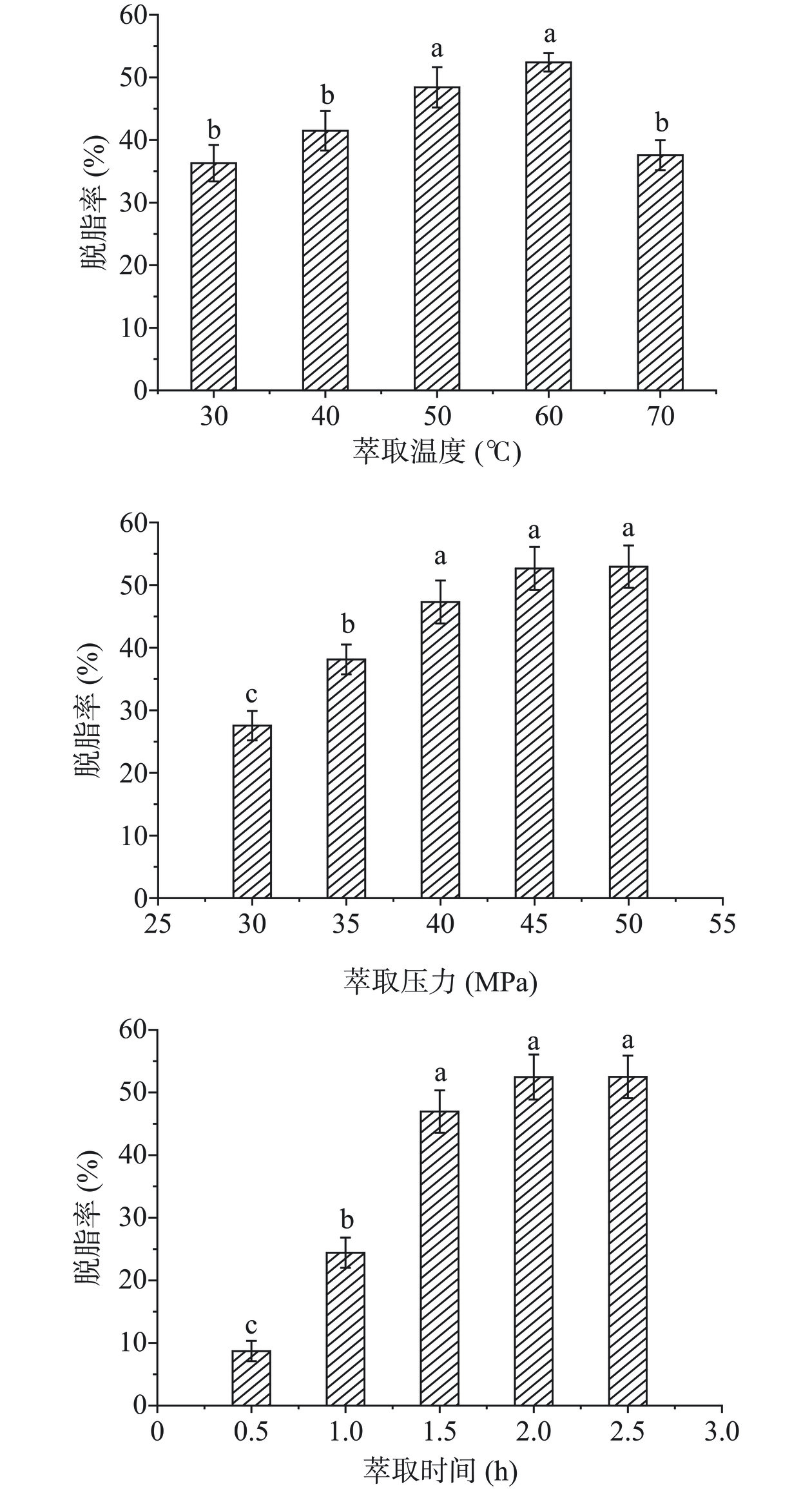
由图1所示,萃取温度对海参粉脱脂率的影响呈现先升高再下降趋势,当萃取温度从40 ℃升高到50 ℃时,脱脂率显著性升高(P<0.05),随着温度增加到60 ℃时,脱脂率达到最高点,这可能是因为萃取温度的升高,蒸汽压增大,加剧了分子间热运动,提高了海参粉脂质在CO2中的溶解度,从而提高了萃取速率。继续升高温度到70 ℃,脱脂率反而出现显著性下降情况(P<0.05),这是因为温度继续升高会导致CO2流体的密度降低,从而降低了海参粉脂质溶解度[27],同时过高温度会使油脂氧化并造成一些挥发性成分的散失,导致脱脂率的下降[23]。因此,将40、50、60 ℃这三个萃取温度值作为正交试验考察水平。
萃取压力对海参粉脱脂率的影响呈现逐步升高趋势,当萃取压力从30 MPa增加到40 MPa时,脱脂率显著性升高(P<0.05),在萃取压力继续升高到50 MPa时,脱脂率无显著性变化(P>0.05)。这可能是因为在低压区段时,由于超临界流体的高度可压缩性,在分子间的吸引作用下,CO2分子聚集,密度增大,从而提升了对溶质溶解性能,而在高压力区段时,超临界流体可压缩性较小,密度增加过低,以致溶解性能的增速减弱或达到平衡[28]。考虑到在实际生产过程中,萃取压力过大会增加企业的投资和经营成本。因此,将35、40、45 MPa这三个萃取压力值作为正交试验考察水平。
萃取时间对海参粉脱脂率的影响较大,当萃取时间在0.5~1.5 h之间时,脱脂率随着萃取时间增加而显著性升高(P<0.05),在萃取时间继续增加到2.5 h时,脱脂率无显著性变化(P>0.05)。这是由于萃取刚开始时,超临界流体未完全渗入到海参粉内部,脂质与超临界流体未能充分接触和渗透,导致萃取率较低,当萃取一段时间后,海参粉脂质与超临界流体之间接触比表面积增加,萃取效率达到最大值,传质也趋于饱和[29],继续增加萃取时间还会导致能耗增大。因此,将1、1.5、2 h这三个萃取时间作为正交试验考察水平。
2.2 正交试验
在单因素实验结果基础上,采用L9(34)正交表,考察萃取温度、萃取压力和萃取时间3个因素对海参粉脱脂率的影响,正交试验结果及方差分析如表2~表3所示。
表 2 正交试验结果Table 2. Orthogonal test results试验号 因素 脱脂率(%) A萃取温度 B萃取压力 C萃取时间 空列 1 1 1 1 1 42.8 2 1 2 2 2 20.2 3 1 3 3 3 36.7 4 2 1 2 3 34.1 5 2 2 3 1 47.4 6 2 3 1 2 48.3 7 3 1 3 2 54.2 8 3 2 1 3 57.6 9 3 3 2 1 34.5 k1 33.233 43.700 49.567 41.567 k2 43.267 41.733 29.600 40.900 k3 48.767 39.833 46.100 42.800 R 15.534 3.867 19.967 1.900 表 3 正交试验结果方差分析Table 3. Variance analysis for the results of orthogonal test因素 偏差平方和 自由度 F比 F临界值 P值 显著性 A 373.202 2 66.751 19.000 0.015 * B 22.429 2 4.022 19.000 0.199 C 682.936 2 122.478 19.000 0.008 * 误差 5.58 注:*为差异性显著,置信水平为0.95。 由表2可知,各因素对海参粉脱脂率的影响主次顺序为萃取时间>萃取温度>萃取压力(C>A>B),萃取时间和萃取温度R值较大,是重要因素,而萃取压力的R值较小,为不重要因素。由表3可知,萃取时间(C)和萃取温度(A)对超临界CO2萃取海参粉脂质均具有显著性影响(P<0.05),萃取压力(B)无显著性影响。极差分析结果表明,最优组合为A3B1C1,通过验证实验,重复操作3次,脱脂率为59.0%±3.58%,而在正交试验列表中出现的最优组合为A3B2C1,通过验证实验,重复操作3次,脱脂率为57.6%±3.89%,与A3B1C1组合的脱脂率相比并无显著性差异(P>0.05),考虑到萃取压力较大会对设备要求变高和增加生产成本,因此经综合分析,选择海参粉超临界CO2萃取脱脂的最优条件为:A3B2C1,即萃取温度60 ℃、萃取压力40 MPa,萃取时间2 h。
2.3 超临界CO2萃取前后脂肪酸成分测定
海参粉、萃取后海参粉以及萃取物中脂肪酸组成检测结果如表4所示,共检测出25种脂肪酸,其中饱和脂肪酸9种,在三个样品中饱和脂肪酸占比分别为25.56%±1.43%、24.65%±1.64%和26.95%±1.19%,在萃取物中比例略高,但三者之间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。检测到单不饱和脂肪酸7种,在三个样品中单不饱和脂肪酸占比分别为34.26%±1.93%、31.46%±1.52%和43.15%±1.59%,在萃取物中占比显著性高于其他两个样品(P<0.05),结合超过50%的脱脂率,说明经过超临界萃取,较高比例的单不饱和脂肪酸被萃取分离出来,这与超临界CO2萃取秋刀鱼内脏油脂的分析结果类似[30],其中棕榈油酸(21.64%±0.63%)在萃取物中含量是最高的。单不饱和脂肪酸(MUFA)是脂肪酸的一种,其碳链上只有一个双键,有研究表明富含MUFA(棕榈油酸、油酸)的饮食与降低心血管疾病、糖尿病的风险以及与许多物种寿命相关[31]。
表 4 超临界CO2萃取对脂肪酸组成的影响(%)Table 4. Effect of supercritical CO2 extraction on fatty acid composition (%)脂肪酸 海参粉 萃取后海参粉 萃取物 肉豆蔻酸 C14:0 2.09±0.10b 1.78±0.18b 3.71±0.14a 十四碳一烯酸 C14:1 1.39±0.28b 1.22±0.21b 2.59±0.23a 十五烷酸 C15:0 0.15±0.02a 0.13±0.10a 0.27±0.07a 软脂酸 C16:0 9.41±0.27b 6.79±0.17c 11.39±0.14a 棕榈油酸 C16:1 13.79±0.52b 11.67±0.36c 21.64±0.63a 珠光脂酸 C17:0 0.85±0.03a 0.80±0.21a 0.70±0.10a 硬脂酸 C18:0 8.02±0.44a 8.36±0.29a 7.83±0.37a 油酸 C18:1n-9c 5.72±0.11b 4.72±0.04c 7.64±0.04a 反式油酸 C18:1n-7 6.39±0.10b 6.64±0.06a 6.19±0.12b 亚油酸 C18:2n-6c 3.02±0.24b 2.71±0.12b 7.85±0.62a 花生酸 C20:0 1.70±0.16a 2.03±0.31a 1.00±0.25b γ-亚麻酸 C18:3n-6 3.88±0.24b 5.69±0.24a 1.86±0.30c 二十碳一烯酸 C20:1 3.05±0.45a 2.80±0.13a 3.33±0.40a α-亚麻酸 C18:3n-3 1.34±0.10a 1.25±0.04a 1.61±0.08a 二十一烷酸 C21:0 0.80±0.11b 1.14±0.15a 0.45±0.07c 二十碳二烯酸 C20:2 1.21±0.19a 1.22±0.24a 1.13±0.51a 山嵛酸 C22:0 0.90±0.09a 1.13±0.21a 0.56±0.03b 芥子酸 C22:1n-9 0.43±0.12a 0.49±0.22a 0.05±0.04b 二十碳三烯酸 C20:3n-3 1.03±0.04a 1.14±0.18a 0.86±0.20a 二十三烷酸 C23:0 1.64±0.20b 2.49±0.02a 1.04±0.02c 花生四烯酸(ARA) C20:4n-6 8.26±0.79a 8.46±0.38a 3.68±0.56b 二十二碳二烯酸 C22:2 3.41±0.85a 4.34±0.09a 1.36±0.15b 二十碳五烯酸(EPA) C20:5n-3 13.97±0.26a 14.64±0.40a 8.52±0.92b 鲨油酸 C24:1 3.50±0.35a 3.93±0.49a 1.72±0.14b 二十二碳六烯酸(DHA) C22:6n-3 4.06±0.22a 4.44±0.18a 3.02±0.24b 饱和脂肪酸 25.56±1.43a 24.65±1.64a 26.95±1.19a 单不饱和脂肪酸 34.26±1.93b 31.46±1.52b 43.15±1.59a 多不饱和脂肪酸 40.19±2.93a 43.89±1.89a 29.90±3.58b 注:同行不同小写字母表示各样品之间具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 检测到多不饱和脂肪酸9种,在三个样品中多不饱和脂肪酸占比分别为40.19%±2.93%、43.89%±1.89%和29.90%±3.58%,在萃取物中占比最低,萃取后海参粉中花生四烯酸(ARA)、二十碳五烯酸(EPA)和二十二碳六烯酸(DHA)等多不饱和脂肪酸占比均显著性高于萃取物(P<0.05),与海参粉原料相比无显著性差异(P>0.05),有研究表明海参中多不饱和脂肪酸(PUFA)含量最高的是极性脂质,其次是总脂质和中性脂质[32],本研究采用超临界CO2萃取海参粉,中性脂质和低极性脂质被萃取出来,结合实验检测结果,说明经过超临界CO2萃取多不饱和脂肪酸分离较少,在萃取后海参粉中占比仍较高。海参中富含的EPA和DHA,可预防心脑血管疾病,延缓大脑衰老,抑制肿瘤细胞生长等功能,治疗高脂血症,缓解脂肪肝等疾病,促进人体正常发育[33−34]。ARA也能够促进组织修复、伤口愈合、骨骼肌生长和早期神经发育[35−36]。利用超临界CO2萃取技术实现了海参粉脂质的有效分离,在开发海参功能脂质和脂肪酸产品方面具有较大的应用潜力。
2.4 超临界CO2萃取前后海参粉HS-GC-IMS检测分析
2.4.1 HS-GC-IMS谱图对比分析
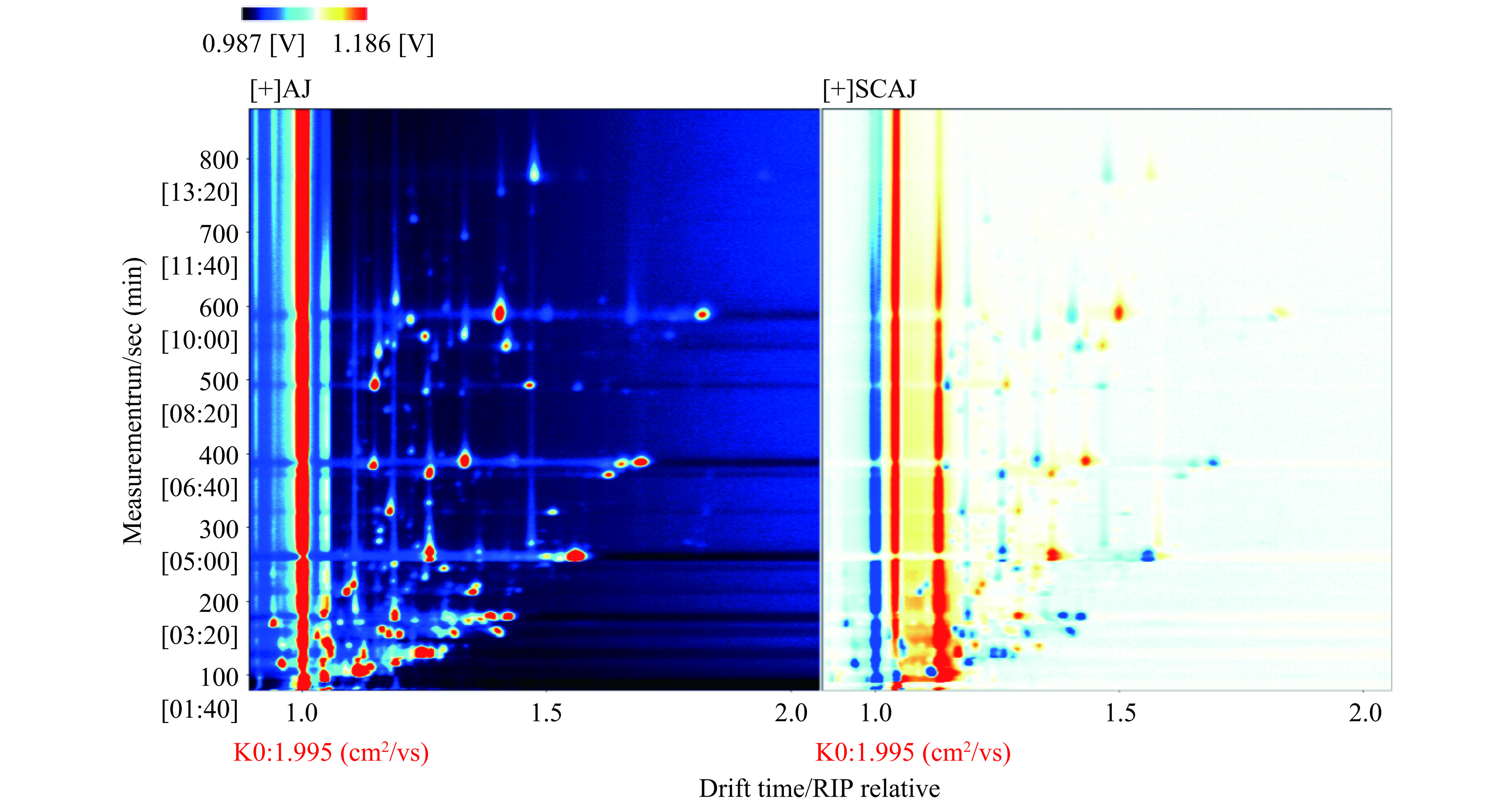
HS-GC-IMS谱图可以对样品之间的挥发性物质组成进行直观比较和初步的判断。图2为海参粉超临界萃取前后HS-GC-IMS检测的挥发性物质成分对比差异化谱图,以海参粉样品为参照,对比显示超临界萃取后样品中所有挥发性物质在不同样品中的差异情况,红色代表该物质在该样品中浓度高于参照样品,而蓝色则代表低于参照样品。由图2可见,海参粉超临界萃取前后样品中的挥发性有机物通过HS-GC-IMS得到了较好的分离,且可直观比较处理前后样品挥发性风味成分间的差异。
2.4.2 挥发性风味物质定性分析
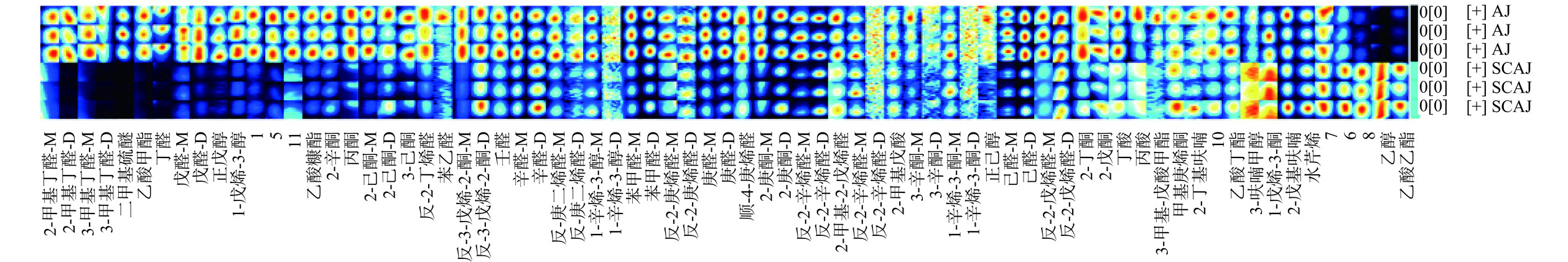
通过绘制挥发性物质的指纹谱图,可直观且定量地比较超临界萃取前后海参粉的挥发性风味物质变化。结果如图3所示,图中每个亮点代表一种挥发性化合物,每一行代表一个样品中选取的全部信号峰,每一列代表同一挥发性有机物在不同样品中的含量/信号强度,颜色越深表明物质含量越高[37],两种样品均是平行测定3次。两组样品中共检测出85种挥发性成分,定性后得到70种挥发性风味物质,由图3可以看出AJ和SCAJ的挥发性风味物质组成存在明显差异,大部分挥发性风味物质,如二甲基硫醚、丁醛、反-2-丁烯醛、戊醛、庚醛、苯甲醛、戊醇、1-戊烯-3-醇、丙酮、2-丁酮、2-己酮、3-己酮等在超临界萃取后含量明显降低。少部分化合物如乙醇、乙酸乙酯等物质含量在SCAJ中增加,这可能与高压CO2存在下发生了乙醇/乙酸醋化反应有关[38−39]。
醛类是海参主要挥发性化合物,由于醛类气味阈值相对较低,使其对风味贡献较大[40],且低分子量的醛类具有不同程度的腥味或刺激性气味,如庚醛具有鱼腥味,经过超临界萃取后,SCAJ中丁醛、反-2-丁烯醛、戊醛、庚醛等含量明显减少,使海参粉风味得到很大改善。另外,SCAJ中二甲基硫醚和酮类化合物被有效分离从而含量降低,这与Shimoda等[41]对鱼露进行超临界CO2萃取除臭观察到含硫化合物和2-丁酮等酮类化合物显著减少结果一致。可见,超临界CO2萃取降低了样品中腥味和刺激性气味的化合物含量,表明超临界CO2萃取对海参粉脱腥作用效果较好。
2.4.3 HS-GC-IMS主成分分析
选取的GC-IMS特征峰作为特征变量,运用主成分分析的方法对结果进行进一步分析。图4中横坐标轴PC1和纵坐标轴PC2分别表示PCA分析后各主成分的贡献率。其中第一主成分(PC1)的贡献率为79%,第二主成分(PC2)的贡献率为14%,前两个主成分的累计贡献率为93%,说明进行特征压缩后,依然保留了较完整的信息,能较好地表征海参样品的绝大部分特征差异。从图4中可以看出,AJ和SCAJ样品间在主成分1上有明显的分离,样本组内距离较近,平行性良好;样本间距离较远,且相互之间没有明显的重叠区域,具有明显的特征差异。因此,超临界CO2萃取后和萃取前海参粉中挥发性风味成分之间存在明显的差异,尤其腥味和刺激性成分被脱除,表明超临界CO2萃取技术是改善海参粉品质的一个有效技术方法。
3. 结论
本文利用单因素与正交试验优化得出海参粉超临界CO2萃取脱脂脱腥的最佳条件为:萃取温度60 ℃、萃取压力40 MPa,萃取时间2 h,在此条件下脱脂率为57.6%±3.89%;通过检测分析海参粉、萃取后海参粉和萃取物中的脂肪酸组成,发现萃取物中单不饱和脂肪酸含量占比明显较高,而萃取后海参粉中多不饱和脂肪酸含量占比更高;HS-GC-IMS检测证明超临界CO2萃取前后海参粉的挥发性风味成分差异明显,超临界CO2萃取能脱离出醛类、酮类和含硫化合物等腥味挥发性物质。综上所述,超临界CO2萃取是改善海参产品不良风味的有效手段之一,通过提升产品感官品质,进而提高海参粉相关产品的市场接受度。这为高品质海参产品的高效绿色制备提供新的思路和技术支撑。后期计划进一步探索超临界CO2萃取对功能性脂质成分的影响,以及该技术在海参脱腥中的操作条件优化、产物品质提升、成本效益分析等方面展开更深入的研究。
-
表 1 正交因素水平
Table 1 Orthogonal factors and levels
因素 水平 1 2 3 A 萃取温度(℃) 40 50 60 B 萃取压力(MPa) 45 40 35 C 萃取时间(h) 2 1 1.5 表 2 正交试验结果
Table 2 Orthogonal test results
试验号 因素 脱脂率(%) A萃取温度 B萃取压力 C萃取时间 空列 1 1 1 1 1 42.8 2 1 2 2 2 20.2 3 1 3 3 3 36.7 4 2 1 2 3 34.1 5 2 2 3 1 47.4 6 2 3 1 2 48.3 7 3 1 3 2 54.2 8 3 2 1 3 57.6 9 3 3 2 1 34.5 k1 33.233 43.700 49.567 41.567 k2 43.267 41.733 29.600 40.900 k3 48.767 39.833 46.100 42.800 R 15.534 3.867 19.967 1.900 表 3 正交试验结果方差分析
Table 3 Variance analysis for the results of orthogonal test
因素 偏差平方和 自由度 F比 F临界值 P值 显著性 A 373.202 2 66.751 19.000 0.015 * B 22.429 2 4.022 19.000 0.199 C 682.936 2 122.478 19.000 0.008 * 误差 5.58 注:*为差异性显著,置信水平为0.95。 表 4 超临界CO2萃取对脂肪酸组成的影响(%)
Table 4 Effect of supercritical CO2 extraction on fatty acid composition (%)
脂肪酸 海参粉 萃取后海参粉 萃取物 肉豆蔻酸 C14:0 2.09±0.10b 1.78±0.18b 3.71±0.14a 十四碳一烯酸 C14:1 1.39±0.28b 1.22±0.21b 2.59±0.23a 十五烷酸 C15:0 0.15±0.02a 0.13±0.10a 0.27±0.07a 软脂酸 C16:0 9.41±0.27b 6.79±0.17c 11.39±0.14a 棕榈油酸 C16:1 13.79±0.52b 11.67±0.36c 21.64±0.63a 珠光脂酸 C17:0 0.85±0.03a 0.80±0.21a 0.70±0.10a 硬脂酸 C18:0 8.02±0.44a 8.36±0.29a 7.83±0.37a 油酸 C18:1n-9c 5.72±0.11b 4.72±0.04c 7.64±0.04a 反式油酸 C18:1n-7 6.39±0.10b 6.64±0.06a 6.19±0.12b 亚油酸 C18:2n-6c 3.02±0.24b 2.71±0.12b 7.85±0.62a 花生酸 C20:0 1.70±0.16a 2.03±0.31a 1.00±0.25b γ-亚麻酸 C18:3n-6 3.88±0.24b 5.69±0.24a 1.86±0.30c 二十碳一烯酸 C20:1 3.05±0.45a 2.80±0.13a 3.33±0.40a α-亚麻酸 C18:3n-3 1.34±0.10a 1.25±0.04a 1.61±0.08a 二十一烷酸 C21:0 0.80±0.11b 1.14±0.15a 0.45±0.07c 二十碳二烯酸 C20:2 1.21±0.19a 1.22±0.24a 1.13±0.51a 山嵛酸 C22:0 0.90±0.09a 1.13±0.21a 0.56±0.03b 芥子酸 C22:1n-9 0.43±0.12a 0.49±0.22a 0.05±0.04b 二十碳三烯酸 C20:3n-3 1.03±0.04a 1.14±0.18a 0.86±0.20a 二十三烷酸 C23:0 1.64±0.20b 2.49±0.02a 1.04±0.02c 花生四烯酸(ARA) C20:4n-6 8.26±0.79a 8.46±0.38a 3.68±0.56b 二十二碳二烯酸 C22:2 3.41±0.85a 4.34±0.09a 1.36±0.15b 二十碳五烯酸(EPA) C20:5n-3 13.97±0.26a 14.64±0.40a 8.52±0.92b 鲨油酸 C24:1 3.50±0.35a 3.93±0.49a 1.72±0.14b 二十二碳六烯酸(DHA) C22:6n-3 4.06±0.22a 4.44±0.18a 3.02±0.24b 饱和脂肪酸 25.56±1.43a 24.65±1.64a 26.95±1.19a 单不饱和脂肪酸 34.26±1.93b 31.46±1.52b 43.15±1.59a 多不饱和脂肪酸 40.19±2.93a 43.89±1.89a 29.90±3.58b 注:同行不同小写字母表示各样品之间具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] HOSSAIN A, DAVE D, SHAHIDI F. Sulfated polysaccharides in sea cucumbers and their biological properties:A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023:127329.
[2] XU C, ZHANG R, WEN Z. Bioactive compounds and biological functions of sea cucumbers as potential functional foods[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2018,49:73−84. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.08.009
[3] SIDDIQUI R, BOGHOSSIAN A, KHAN N A. Sea cucumber as a therapeutic aquatic resource for human health[J]. Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences,2022,25(5):251−263. doi: 10.47853/FAS.2022.e23
[4] ZHANG J, LIU S, LI L, et al. Effect of polysaccharide extract SPSS1 from Apostichopus japonicus spermary on HepG2 cells via iTRAQ-based proteome analysis[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2020,44(5):e13168.
[5] 汪韬, 温运启, 于娇, 等. 富含乳酸菌的脱腥海参肽粉的制备[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(18):187−191. [WANG Tao, WEN Yunqi, YU Jiao, et al. Preparation of deodorized sea cucumber peptide powder rich in lactic acid bacteria[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(18):187−191.] WANG Tao, WEN Yunqi, YU Jiao, et al. Preparation of deodorized sea cucumber peptide powder rich in lactic acid bacteria[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(18): 187−191.
[6] 石友盛, 谢文强, 陈贤功, 等. 3种海参脱腥方法的效果比较研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(20):79−85. [SHI Yousheng, XIE Wenqiang, CHEN Xiangong, et al. Comparative study on the effects of three deodorization methods on sea cucumber[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(20):79−85.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.20.012 SHI Yousheng, XIE Wenqiang, CHEN Xiangong, et al. Comparative study on the effects of three deodorization methods on sea cucumber[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(20): 79−85. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.20.012
[7] 郑金娃, 汪秋宽, 何云海, 等. 海参多肽脱色脱腥工艺的优化研究[J]. 大连海洋大学学报,2013,28(3):303−306. [ZHENG Jinwa, WANG Qiukuan, HE Yunhai, et al. Technique optimization of decolorization and deodorization for sea cucumber hydrolysates[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University,2013,28(3):303−306.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1388.2013.03.017 ZHENG Jinwa, WANG Qiukuan, HE Yunhai, et al. Technique optimization of decolorization and deodorization for sea cucumber hydrolysates[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University, 2013, 28(3): 303−306. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1388.2013.03.017
[8] 贾楠, 沙炫利, 吴琳蓉, 等. 海参胶的脱腥精制及体外消化特性研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测报,2023,14(8):138−147. [JIA Nan, SHA Xuanli, WU Linrong, et al. Investigation of the deodorization refinement and in vitro digestion properties of sea cucumber gelatin[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2023,14(8):138−147.] JIA Nan, SHA Xuanli, WU Linrong, et al. Investigation of the deodorization refinement and in vitro digestion properties of sea cucumber gelatin[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2023, 14(8): 138−147.
[9] 邹媛婷, 张健, 刘芳, 等. 菌酶联用处理对刺参体壁降解效果及风味特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(11):118−126. [ZOU Yuanting, ZHANG Jian, LIU Fang, et al. Effects of combined treatments of bacteria and enzyme on the degradation and flavor components of body wall of sea cucumber[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(11):118−126.] ZOU Yuanting, ZHANG Jian, LIU Fang, et al. Effects of combined treatments of bacteria and enzyme on the degradation and flavor components of body wall of sea cucumber[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(11): 118−126.
[10] 刘咏霖. 红曲海参和乳酸菌发酵红曲海参的制备及其挥发性成分分析[D]. 烟台:烟台大学, 2023. [LIU Yonglin. Preparation and volatile component analysis of red yeast sea cucumber and lactic acid bacteria fermented red yeast sea cucumber[D]. Yantai:Yantai University, 2023.] LIU Yonglin. Preparation and volatile component analysis of red yeast sea cucumber and lactic acid bacteria fermented red yeast sea cucumber[D]. Yantai: Yantai University, 2023.
[11] 龚舒哲, 张浩. 二氧化碳在“绿色化学”中的应用[J]. 中国科技信息,2005(15A):54,69. [GONG Shuzhe, ZHANG Hao. The application of carbon dioxide in “green chemistry”[J]. China Science and Technology Information,2005(15A):54,69.] GONG Shuzhe, ZHANG Hao. The application of carbon dioxide in “green chemistry”[J]. China Science and Technology Information, 2005(15A): 54,69.
[12] GETACHEW A T, JACOBSEN C, SØRENSEN A M. Supercritical CO2 for efficient extraction of high-quality starfish (Asterias rubens) oil[J]. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2024,206:106161. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2023.106161
[13] LIK NANG LAU H, CHOO Y M, MA A N, et al. Selective extraction of palm carotene and vitamin E from fresh palm-pressed mesocarp fiber (Elaeis guineensis) using supercritical CO2[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2008,84(2):289−296. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2007.05.018
[14] MOUAHID A, SEENGEON K, MARTINO M, et al. Selective extraction of neutral lipids and pigments from Nannochloropsis salina and Nannochloropsis maritima using supercritical CO2 extraction:Effects of process parameters and pre-treatment[J]. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2020,165:104934. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2020.104934
[15] 丁忠福, 金莉莉, 李强, 等. 超临界CO2萃取精馏技术在林蛙卵油脱腥中的应用研究[J]. 特产研究,2007(2):18−21. [DING Zhongfu, JIN Lili, LI Qiang, et al. The study of ovum oil of Rana chensinensis on deodorization with finestill technique of SC-CO2[J]. Special Wild Economic Animal and Plant Research,2007(2):18−21.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4721.2007.02.008 DING Zhongfu, JIN Lili, LI Qiang, et al. The study of ovum oil of Rana chensinensis on deodorization with finestill technique of SC-CO2[J]. Special Wild Economic Animal and Plant Research, 2007(2): 18−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4721.2007.02.008
[16] 李斌, 李长江, 杜志欣, 等. 罗非鱼皮制胶原蛋白脱腥技术的比较研究[J]. 淡水渔业,2013,43(6):82−85. [LI Bin, LI Changjiang, DU Zhixin, et al. Comparison on the techniques of deodorization of Tilapia skin collagen[J]. Freshwater Fisheries,2013,43(6):82−85.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2013.06.015 LI Bin, LI Changjiang, DU Zhixin, et al. Comparison on the techniques of deodorization of Tilapia skin collagen[J]. Freshwater Fisheries, 2013, 43(6): 82−85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6907.2013.06.015
[17] ALI-NEHARI A, CHUN B S. Characterization of purified phospholipids from krill (Euphausia superba) residues deoiled by supercritical carbon dioxide[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering,2012,29:918−924. doi: 10.1007/s11814-011-0273-4
[18] ANISUZZAMAN M, FENG Jin, KABERY K, et al. Lipid class and fatty acid compositions of dried sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus[J]. The Open Food Science Journal,2019,11(1):79−86. doi: 10.2174/1874256401911010079
[19] LI M, GAO Y, QI Y, et al. Assessment of the nutritional value of cultured sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus[J]. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology,2021,30(7):868−879. doi: 10.1080/10498850.2021.1949769
[20] ZHANG X, CHENG J, HAN D , et al. Regional differences in fatty acid composition of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) and scallop (Patinopecten yesoensis) in the coastal areas of China[J]. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 2019, 31(4):100782.
[21] XU Q, XU Q, ZHANG X, et al. Fatty acid component in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus from different tissues and habitats[J]. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom,2016,96(1):197−204. doi: 10.1017/S002531541500168X
[22] 陈子豪. 脱盐及干燥工艺对干制仿刺参品质的影响[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学, 2017. [CHEN Zihao. Effect of desalination and drying processes on the quality of dried Apostichopus japonicus[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University, 2017.] CHEN Zihao. Effect of desalination and drying processes on the quality of dried Apostichopus japonicus[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2017.
[23] 徐志利, 赵雄伟, 孙剑锋, 等. 超临界萃取海参脑苷脂及HPLC检测分析[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(2):46−50. [XU Zhili, ZHAO Xiongwei, SUN Jianfeng, et al. Supercritical fluid extraction and HPLC detection analysis of cerebroside from sea cucumber[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(2):46−50.] XU Zhili, ZHAO Xiongwei, SUN Jianfeng, et al. Supercritical fluid extraction and HPLC detection analysis of cerebroside from sea cucumber[J]. Food Research and Development, 2018, 39(2): 46−50.
[24] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.6-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中脂肪的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 5009.6-2016 National food safety standard Determination of fats in foods[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 5009.6-2016 National food safety standard Determination of fats in foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[25] 马长兴, 王际英, 李宝山, 等. n-3/n-6 HUFA对许氏平鲉幼鱼生长、体组成及组织脂肪酸组成的影响[J]. 水产学报,2019,43(10):2138−2153. [MA Changxing, WANG Jiying, LI Baoshan, et al. Effects of dietary n-3/n-6 HUFA on growth, body composition and fatty acid composition of tissue in juvenile rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli)[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China,2019,43(10):2138−2153.] MA Changxing, WANG Jiying, LI Baoshan, et al. Effects of dietary n-3/n-6 HUFA on growth, body composition and fatty acid composition of tissue in juvenile rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli)[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China, 2019, 43(10): 2138−2153.
[26] LI X, DONG Y, JIANG P, et al. Identification of changes in volatile compounds in sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus during seasonings soaking using HS-GC-IMS[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022,154:112695. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112695
[27] 潘迪, 马挺军. 超临界二氧化碳萃取黄榆籽油工艺及抗疲劳活性研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2021,36(1):105−111. [PAN Di, MA Tingjun. Supercritical CO2 extraction and anti-fatigue activity of Ulmus macrocarpa Hance seed oil[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2021,36(1):105−111.] PAN Di, MA Tingjun. Supercritical CO2 extraction and anti-fatigue activity of Ulmus macrocarpa Hance seed oil[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2021, 36(1): 105−111.
[28] 黄秋伟. 锯叶棕果油的超临界二氧化碳萃取及抗氧化活性研究[D]. 南宁:广西大学, 2019. [HUANG Qiuwei. Study on supercritical carbon dioxide extraction and anti-oxidation of oil from saw palmetto[D]. Nanning:Guangxi University, 2019.] HUANG Qiuwei. Study on supercritical carbon dioxide extraction and anti-oxidation of oil from saw palmetto[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2019.
[29] ZHAO S, ZHANG D. Supercritical CO2 extraction of Eucalyptus leaves oil and comparison with Soxhlet extraction and hydro-distillation methods[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2014,133:443−451. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2014.07.018
[30] 叶彬清. 超临界CO2萃取秋刀鱼内脏油脂及卵磷脂氧化特性研究[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学, 2015. [YE Binqing. Extraction and characterization of oil and lecithin extracted from pacific saury (Cololabis saira) viscera by supercritical carbon dioxide[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai Ocean University, 2015.] YE Binqing. Extraction and characterization of oil and lecithin extracted from pacific saury (Cololabis saira) viscera by supercritical carbon dioxide[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2015.
[31] PAPSDORF K, MIKLAS J W, HOSSEINI A, et al. Lipid droplets and peroxisomes are co-regulated to drive lifespan extension in response to mono-unsaturated fatty acids[J]. Nature Cell Biology,2023,25(5):672−684. doi: 10.1038/s41556-023-01136-6
[32] JIN F, MD A, JEONG U, et al. Comparison of fatty acid composition of wild and cultured sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus[J]. Korean Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences,2016,49(4):474−485. doi: 10.5657/KFAS.2016.0474
[33] O'ROURKE E J, KUBALLA P, XAVIER R, et al. ω-6 Polyunsaturated fatty acids extend life span through the activation of autophagy[J]. Genes and Development,2013,27(4):429−440. doi: 10.1101/gad.205294.112
[34] ZÁRATE R, EL JABER-VAZDEKIS N, TEJERA N, et al. Significance of long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in human health[J]. Clinical and Translational Medicine,2017,6(1):1−19. doi: 10.1186/s40169-016-0134-1
[35] TRAPPE T A, LIU S Z. Effects of prostaglandins and COX-inhibiting drugs on skeletal muscle adaptations to exercise[J]. Journal of Applied Physiology,2013,115(6):909−919. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00061.2013
[36] JAIS AMM, MCCULLOCH R, CROFT K. Fatty acid and amino acid composition in haruan as a potential role in wound healing[J]. Gen Pharmacol,1994,25(5):947−950. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(94)90101-5
[37] 邵悦春, 付晓婷, 许加超, 等. 基于气相离子迁移谱的发酵海带风味分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(12):300−306. [SHAO Yuechun, FU Xiaoting, XU Jiachao, et al. Flavor analysis of fermented Laminaria japonica based on gas chromatograph-ion mobility spectrometer (GC-IMS)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(12):300−306.] SHAO Yuechun, FU Xiaoting, XU Jiachao, et al. Flavor analysis of fermented Laminaria japonica based on gas chromatograph-ion mobility spectrometer (GC-IMS)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(12): 300−306.
[38] 胡拖平, 秦张峰, 王建国. 高压CO2存在下的乙醇/乙酸酯化反应[J]. 石油化工,2004,33(4):335−337. [HU Tuoping, QIN Zhangfeng, WANG Jianguo. Esterification of acetic acid and ethanol in the presence of carbon dioxide under high pressure[J]. Petrochemical Technology,2004,33(4):335−337.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8144.2004.04.009 HU Tuoping, QIN Zhangfeng, WANG Jianguo. Esterification of acetic acid and ethanol in the presence of carbon dioxide under high pressure[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2004, 33(4): 335−337. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-8144.2004.04.009
[39] BLANCHARD L A, BRENNECKE J F. Esterification of acetic acid with ethanol in carbon dioxide[J]. Green Chemistry,2001,3(1):17−19. doi: 10.1039/b007734h
[40] 井月欣, 张健, 王茂剑, 等. 盐渍海参在冻藏过程中的品质变化[J]. 食品科技,2022(3):149−154. [JING Yuexin, ZHANG Jian, WANG Maojian, et al. Changes in quality of salted sea cucumber during freezing storage[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022(3):149−154.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2022.3.spkj202203021 JING Yuexin, ZHANG Jian, WANG Maojian, et al. Changes in quality of salted sea cucumber during freezing storage[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2022(3): 149−154. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2022.3.spkj202203021
[41] SHIMODA M, YAMAMOTO Y, COCUNUBO-CASTELLANOS J. Deodorization of fish sauce by continuous-flow extraction with microbubbles of supercritical carbon dioxide[J]. Journal of Food Science,2000,65(8):1349−1351. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2000.tb10610.x





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
