Plasma Activated Water Assisted Ultrasonic Extraction of Polysaccharides from Yellow Cauliflower and Its Hypoglycemic Activity
-
摘要: 为提高黄花菜多糖提取率,优化黄花菜多糖的提取工艺并探究其体外降血糖活性。本研究采用等离子体活化水(Plasma activated water,PAW)辅助超声工艺,并利用单因素实验和响应面试验优化PAW辅助超声法对黄花菜多糖的提取工艺。使用Sephadex G-100葡聚糖凝胶层析柱对提取的粗多糖进行纯化,得到黄花菜纯多糖(polysaccharides from Hemerocallis citrina Baroni,HCP)。对HCP进行结构鉴定,并通过α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶抑制实验,考察HCP的降糖活性。结果表明:黄花菜多糖最佳提取工艺为液固比23 mL/g、超声提取时间60 min、等离子体活化水制备时间90 s,此时多糖的实际提取率为36.33%±0.04%,其总糖含量、蛋白质含量和糖醛酸含量分别为88.07%±2.25%、2.72%±0.04%和7.27%±0.44%。HCP由岩藻糖、鼠李糖、阿拉伯糖、半乳糖、葡萄糖、甘露糖和半乳糖醛酸组成,为吡喃型酸性杂多糖,分子量为8.056 kDa,扫描电镜结果显示HCP呈片状且表面粗糙;HCP具有良好的降糖活性且呈浓度依赖性,在1 mg/mL的浓度下,HCP的α-葡萄糖苷酶和α-淀粉酶抑制能力分别达到83.02%和78.65%。本实验表明HCP有潜力成为降糖的功能性制剂原料。Abstract: To optimize the polysaccharides extraction process from Hemerocallis citrina Baroni and investigate the hypoglycemic activity of polysaccharides in vitro, the plasma activated water (PAW) was employed in conjunction with ultrasound treatment to improve the polysaccharides extraction rate. The optimum extraction rate was determined by using a single-factor experiment and response surface design. Then, the polysaccharides were purified using Sephadex G-100 dextran gel chromatographic column to obtain the pure polysaccharides from Hemerocallis citrina Baroni (HCP). The structure of HCP was identified and its hypoglycemic activity was evaluated by the approval α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibition experiments. The results indicated that the optimal process parameters were liquid-solid ratio of 23 mL/g, extraction time of ultrasound 60 min, PAW preparation time of 90 s, in which the maximum extraction rate of Hemerocallis citrina Baroni polysaccharides was 36.33%±0.04%. The total sugar content, protein content, and uronic acid content of HCP were 88.07%±2.25%, 2.72%±0.04%, and 7.27%±0.44%, respectively. HCP was an acidic heteropolysaccharide with α-pyranose configuration, consisting of fucose, rhamnose, arabinose, galactose, glucose, mannose, and galacturonic acid. The molecular weight of HCP was 8.056 kDa. The SEM showed that HCP was sheet-like with a rough surface. Additionally, the HCP exhibited great hypoglycemic activity in vitro and the concentration-dependent. When the concentration was 1 mg/mL, the inhibition ability of α-glucosidase and α-amylase reached 83.02% and 78.65% respectively. This experiment indicated that HCP had the potential to become functional raw materials for hypoglycemic preparations.
-
黄花菜(Hemerocallis citrina Baroni),属百合目阿福花科萱草属植物,又名金针菜、忘忧草,学名萱草,是我国特产蔬菜。研究表明,黄花菜多糖是黄花菜的重要活性成分之一,具有降血糖、抗肿瘤、抗病毒、抗氧化、抑菌等作用[1−2]。黄花菜多糖常见提取技术包括酶提取法、溶剂浸提法(水提取、酸碱提取或有机溶剂提取)、超声、微波等物理提取法[3−5]。其中,超声波技术由于绿色、提取时间短、不破坏多糖结构的特点,广泛应用于工业提取植物多糖,其机理是通过空化效应的高频率机械波破坏细胞壁[6],从而实现多糖溶出。
但单一超声法提取黄花菜多糖的得率在8%~17%之间[1],得率较低,这与黄花菜细胞壁结构和组成成分连接的紧密性有关,传统的处理手段难以有效地打开黄花菜细胞壁结构,不利于工业大规模提取黄花菜多糖。利用溶剂浸提技术辅助超声处理促进黄花菜细胞壁溶胀吸水与破裂是提高超声效率的有效方法之一。刘艺珠等[7]使用pH1.8的硝酸溶液处理黄花菜3.5 h,最终多糖提取率为0.72%,含量为34.91%。该结果表明,硝酸溶液能有效软化黄花菜细胞壁,促使其吸水破裂,更有利于多糖从细胞中游离出来。但是,较长时间的硝酸处理可能导致多糖降解,进而降低其功能活性。因此,利用含硝酸根的温和溶液与超声的复合提取法有望提高超声处理效率,在本研究中选取富含高能量活性粒子的等离子体活化水作为提取溶剂参与黄花菜多糖的提取。
等离子体是继固、液、气之后的第四态,富含超氧化物、羟基自由基、单线态氧和一氧化氮自由基,在水溶液中,这些不稳定物质会迅速转化为过氧化氢、亚硝酸盐、硝酸盐等中间物质[8],其中,亚硝酸根离子与过氧化氢反应进而生成硝酸根离子和氢离子,降低溶液pH。由于等离子体活化水具有大量活性粒子及较低的pH,因此,有利于活性物质穿透细胞壁。已有研究表明等离子体活化水可提高甘蔗渣废弃物和海藻废弃物中多糖提取率[9−10]。此外,等离子体活化水处理具有操作便捷、反应时间短、提取效率高、能耗低、对环境污染小的加工优点。
本研究使用射流放电等离子体活化水代替硝酸溶液提供酸性环境,辅助超声处理从黄花菜中提取多糖,通过单因素和响应面试验优化提取工艺,并对黄花菜多糖进行分离纯化、结构鉴定和降糖活性分析,为工业化开发高纯度具有降糖活性的黄花菜多糖资源提供技术支持和参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
干燥黄花菜 品种大乌嘴,产自宁夏吴忠太阳山农业合作社;石油醚、甲醇、无水乙醇 分析纯,天津市津东天正精细化学试剂厂;蒽酮、三氟乙酸 分析纯,上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司;浓硫酸 分析纯,天津市化学试剂供销公司;溴化钾 优级纯,天津博迪化工股份有限公司;单糖标准品 分析纯,北京索莱宝科技有限公司;α-葡萄糖苷酶(100 U)、α-淀粉酶(35 U/mg)、Sephadex G-100葡聚糖凝胶层析柱、阿卡波糖、可溶性淀粉 分析纯,天津索罗门生物科技有限公司。
CTP-2000K射流等离子体处理仪 南京苏曼等离子科技有限公司;JP-040ST超声波发生器 深圳市洁萌清洗设备有限公司;IS50傅里叶红外光谱分析仪 美国尼高利公司;Agilent1260高效液相色谱仪 美国安捷伦公司;ICS-5000+离子色谱仪 美国戴安公司;SU1510扫描电子显微镜 日本株式会社立高新技术那珂事业所;FlexA-200全波长酶联免疫分析仪 杭州奥盛仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 等离子体活化水(PAW)的制备
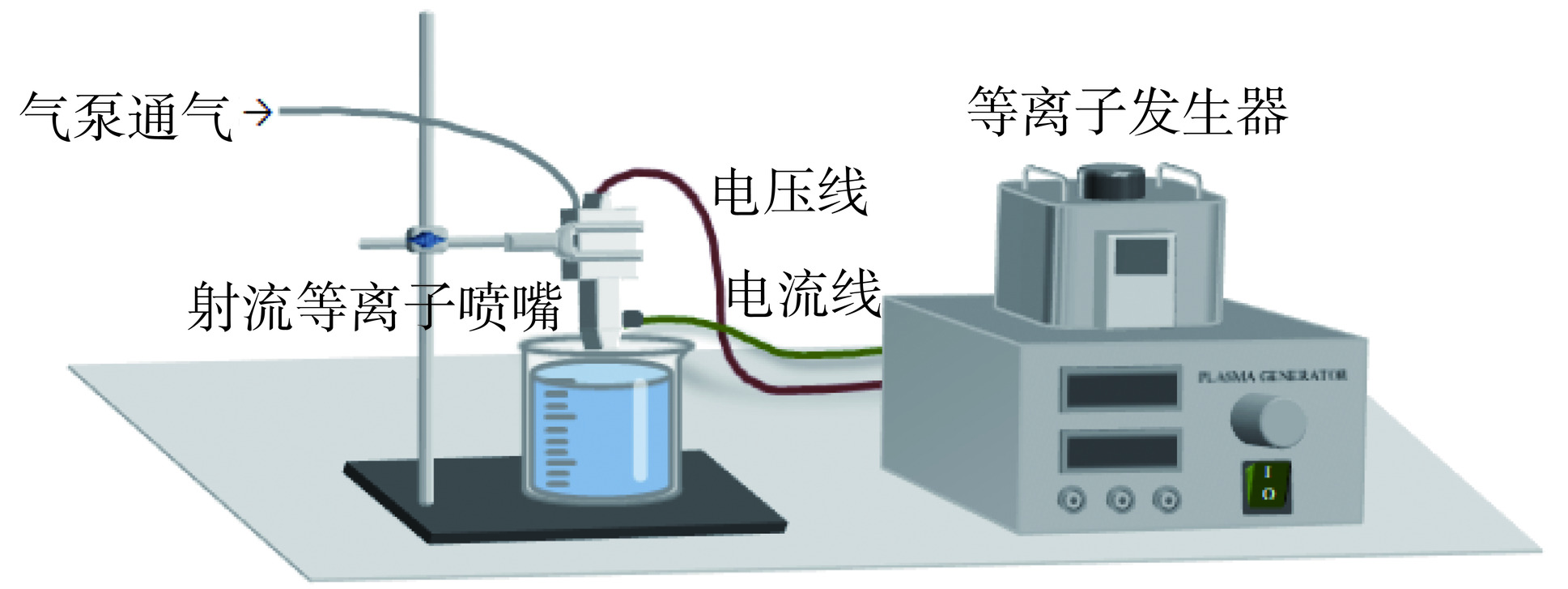
如图1所示,依次打开气泵、等离子体发生器的开关,调整等离子体发生器的电压为200 V、电流为0.5 A后,取400 mL蒸馏水于烧杯中,放置在射流等离子体喷嘴下,喷嘴没入水中0.5 cm,计时60 s,完成PAW的制备。
1.2.2 黄花菜预处理
取干燥黄花菜(水分含量15%)适量放置于打粉机中打碎,过60目筛。使用石油醚利用索式提取器进行脂质的脱除[11],实验结束后,加入80%的乙醇回流过夜,去除单糖寡糖类小分子有机物,干燥至恒重,得到预处理后的原料,放置于干燥器备用。
1.2.3 单因素实验
使用等离子体发生器制备PAW,称量1 g干燥的黄花菜粉末,选定液固比,分散于PAW中,充分摇匀后置于180 W超声发生器中,设定超声提取时间,常温下提取。提取完成后,使用高速离心机在8000 r/min下离心15 min,分离出上清液,将上清液浓缩至原体积的1/3,然后加入四倍体积无水乙醇至溶液中乙醇终浓度为80%,放置于4 ℃醇沉24 h,5000 r/min离心,收集沉淀复溶后冻干,得到黄花菜粗多糖。
固定超声提取时间30 min,PAW制备时间60 s,考察液固比(10:1、20:1、30:1、40:1、50:1 mL/g)对黄花菜多糖提取率的影响;固定液固比为20:1 mL/g,PAW制备时间60 s,考察超声提取时间(15、30、45、60、75 min)对黄花菜多糖提取率的影响;固定液固比为20:1 mL/g,超声提取时间为60 min,考察PAW制备时间(30、60、90、120、150 s)对黄花菜多糖提取率的影响。
1.2.4 响应面试验
在单因素实验的基础上,以黄花菜多糖提取率为响应值进行响应面优化试验,试验设计见表1。
表 1 响应面优化试验设计Table 1. Response surface optimization experimental design水平 因素 A液固比(mL/g) B超声提取时间(min) C PAW制备时间(s) −1 10:1 45 60 0 20:1 60 90 1 30:1 75 120 1.2.5 黄花菜粗多糖提取率计算
1.2.5.1 葡萄糖标准曲线的绘制
将葡萄糖干燥至恒重后准确称取0.100 g,用蒸馏水定容至1000 mL,制得浓度为0.1 mg/mL的葡萄糖溶液,分别移取0、0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0 mL该葡萄糖溶液于试管中,用蒸馏水补足至1 mL,各试管分别加入5%现配的蒽酮-硫酸溶液4 mL混匀,沸水浴加热15 min,之后迅速放入冰水浴冷却至室温,测定625 nm波长下的吸光度值[12−13]。
1.2.5.2 粗多糖提取率的计算
将黄花菜粗多糖水溶液稀释一定倍数。取稀释后的多糖水溶液1 mL,后续测定方法同1.2.5.1。根据标准曲线方程计算多糖浓度,按照公式计算粗多糖提取率:
Y=C×V×XM×100 式中:Y为粗多糖提取率,%;C为标准曲线中吸光度值对应葡萄糖浓度,mg/mL;V为多糖水溶液体积,mL;X为稀释倍数;M为黄花菜原料质量,mg。
1.2.6 黄花菜多糖的分离纯化
使用Sephadex G-100葡聚糖凝胶层析柱分离纯化黄花菜粗多糖(柱尺寸为1.6 cm×50 cm),上样纯度为1 mg/mL,上样量为1 mL,洗脱液为蒸馏水,洗脱流速15 mL/h,洗脱液每管收集5 min。使用蒽酮硫酸法测定每管多糖含量,建立洗脱曲线,收取洗脱曲线峰值处多糖含量高的洗脱液,得到纯化多糖组分[14],命名为HCP。冻干备用,以进行纯化多糖的高效液相色谱分析及后续实验。
1.2.7 分子量测定
采用高效液相色谱(HPLC)测定黄花菜多糖的分子量。用超纯水配制1 mg/mL不同分子量葡聚糖标准品溶液和黄花菜纯化多糖样品溶液,过0.22 μm水系滤膜后装入液相瓶中待测。选用示差检测器,温度设置为35 ℃;凝胶色谱柱型号为TSKgel GMPWXL(7.8 mm×300 mm),柱温设置为30 ℃;以超纯水作为流动相,流速为0.6 mL/min,样品进样量为20 μL,检测时间25 min[15]。
根据葡聚糖标准品的相对分子量(T2000、T150、T60、T40和T20)和保留时间建立lgMw-Rt标准曲线,计算黄花菜多糖的分子量。
1.2.8 基本成分测定
对于分离纯化得到的黄花菜纯化多糖进行化学组分分析。采用蒽酮-硫酸法测定总糖含量;采用3,5-二硝基水杨酸法测定还原糖的含量[16];采用硫酸-咔唑法测定糖醛酸含量[5];采用BCA试剂盒测定蛋白质含量。
1.2.9 单糖组成分析
称取1.5 mg HCP置于安瓿瓶中,加入2 mol/L的三氟乙酸1.5 mL,封口后在120 ℃油浴中水解3 h,准确吸取酸水解液转移至管中氮气吹干,再加入0.5~2 mL的无水甲醇,之后氮气吹干,重复5次以除去残留的三氟乙酸,最后将产物完全溶解于1.5 mL去离子水中,混匀,4 ℃保存,取上清液进行离子色谱(IC)分析。
离子色谱检测条件:采用戴安ICS-5000+离子色谱仪[3];分析柱型号为:Dionex CarboPacTM PA20(3 mm×150 mm);柱温:30 ℃;流动相A:超纯水;流动相B:200 mmol/L NaOH;流动相C:100 mmol/L NaAC;流速:0.35 mL/min;进样量:1 mL。
以鼠李糖(Rha)、岩藻糖(Fuc)、阿拉伯糖(Ara)、半乳糖(Gal)、葡萄糖(Glc)、甘露糖(Man)、核糖(Rib)、葡萄糖醛酸(GlcA)和半乳糖醛酸(GalA)作为标准品对照。
1.2.10 红外光谱分析
对黄花菜多糖进行红外光谱分析,称取冻干后的黄花菜纯化多糖样品1 mg,加入溴化钾150 mg,混合充分研磨至粉末状,取粉末置于模具上进行压片处理,之后将压缩片放入红外光谱仪中,采集黄花菜多糖在4000~400 cm−1区域内的红外光谱[6],扫描次数:32次。以空白背景校正光谱,绘制多糖红外吸收光谱图。
1.2.11 扫描电子显微镜
使用导电胶将经过冷冻干燥的HCP粘于圆形载物台上,使用离子溅射仪喷金镀膜后,于加速电压10 kV下进行观察[17]。
1.2.12 降糖活性测定
1.2.12.1 α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制能力测定
参照赵寒青[18]的方法稍作改动。配制1 mg/mL的HCP溶液,梯度稀释至0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8 mg/mL。于96孔板中,依次加入浓度为0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0 mg/mL的纯化多糖样品40 μL、0.4 U/mL α-葡萄糖苷酶溶液80 μL,混合均匀后,将96孔板置于37 ℃孵育5 min。随后加入2 mmol/L P-NPG 40 μL,37 ℃反应30 min,最后加入40 μL Na2CO3(0.2 mol/L)溶液以终止反应,于405 nm处测定吸光度。阳性对照以阿卡波糖来代替多糖样品,每组三个平行,α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制率计算公式如下:
α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率(%)=(1−A1−A2A3−A4)×100 式中:A1表示黄花菜多糖样品吸光度值;A2表示将α-葡萄糖苷酶溶液换为PBS测得吸光度值;A3表示将多糖溶液换为PBS测得吸光度值;A4表示以PBS代替α-葡萄糖苷酶溶液和多糖得到的吸光度值。
1.2.12.2 α-淀粉酶抑制能力测定
采用李成华等[4]的方法并略作修改。分别量取浓度为0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0 mg/mL的样品50 μL置于离心管中,后加入50 μL α-淀粉酶溶液(0.5 g/mL),充分混匀,于37 ℃水浴锅中水浴反应15 min,然后加入50 μL可溶性淀粉溶液,混匀后置于37 ℃水浴锅中反应15 min。反应结束后加入50 μL DNS置于沸水浴中15 min终止反应。于660 nm处测定吸光度,阳性对照以阿卡波糖来代替多糖样品,每组三个平行,α-淀粉酶抑制率的计算公式如下:
α-淀粉酶抑制率(%)=(1−A1−A2A3−A4)×100 式中:A1表示黄花菜多糖样品吸光度值;A2表示将α-淀粉酶溶液换为PBS测得吸光度值;A3表示将多糖溶液换为PBS测得吸光度值;A4表示以PBS代替α-淀粉酶溶液和多糖得到的吸光度值。
1.3 数据处理
本实验中的实验数据均使用SPSS 22.0软件进行分析,平均值和标准偏差均通过3次重复实验计算得到。显著性分析使用Tukey模型,显著水平为0.05。图像绘制均使用OriginPro 2016软件。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
2.1.1 液固比对黄花菜多糖提取率的影响
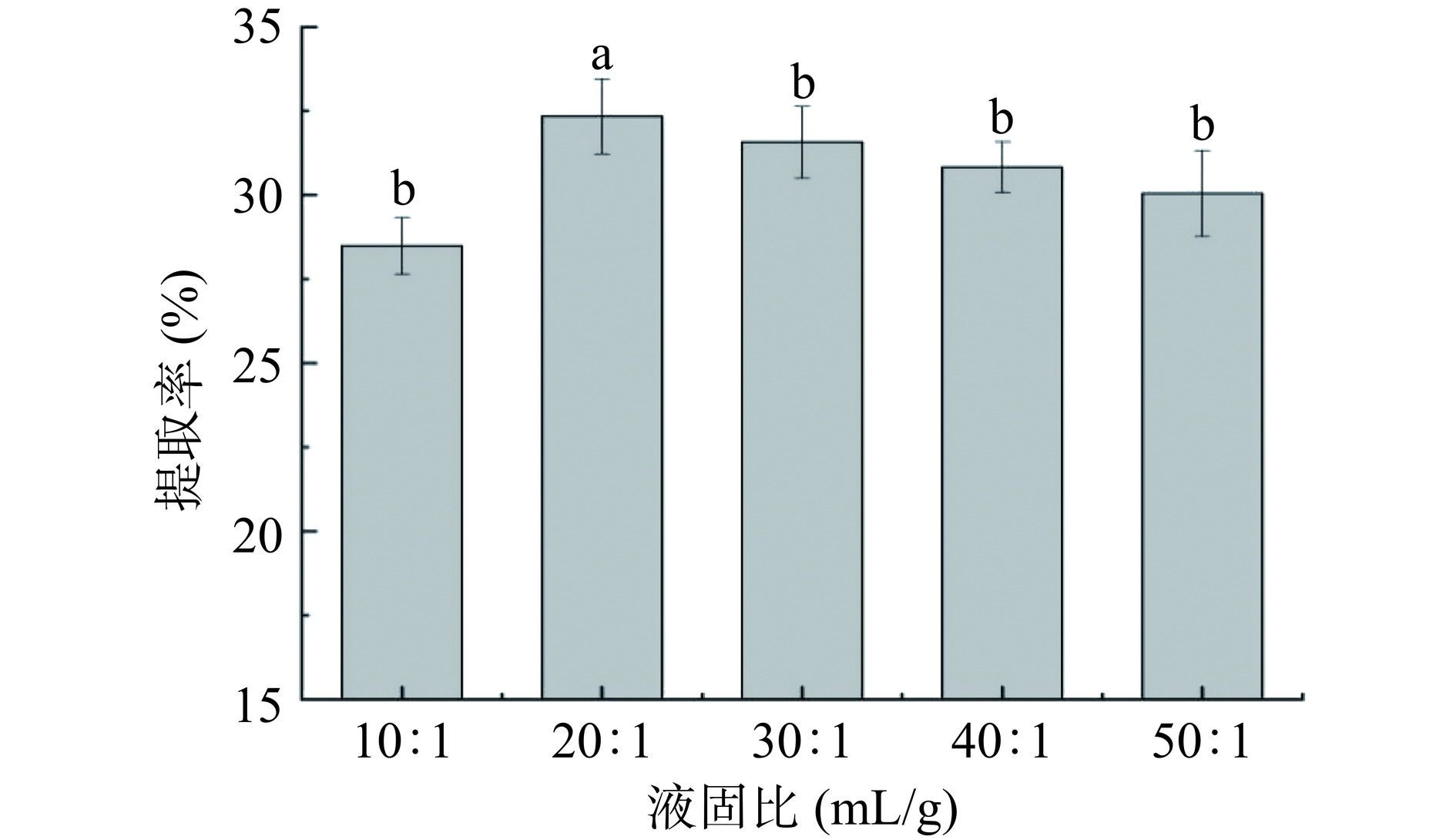
由图2可知,黄花菜多糖提取率随着液固比的增大呈现先上升后下降的趋势,其中20:1 mL/g与其他液固比有显著性差异(P<0.05),黄花菜多糖提取率达到最高值为32.34%。这与Li等[19]研究发现的黄花菜多糖提取率随液固比变化的趋势相同。这种现象是因为当蒸馏水比例过低时,受液固接触面积及植物细胞内部与溶剂之间浓度差的限制,多糖无法全部溶出,溶剂比例越大,浓度差异越明显,多糖分子扩散得越快。但液固比过大时,会延长分子从组织内部扩散的距离并导致杂质溶出的增多而抑制多糖的溶出[20−21]。因此选择液固比10:1、20:1、30:1 mL/g进行后续响应面试验。
2.1.2 超声提取时间对黄花菜多糖提取率的影响
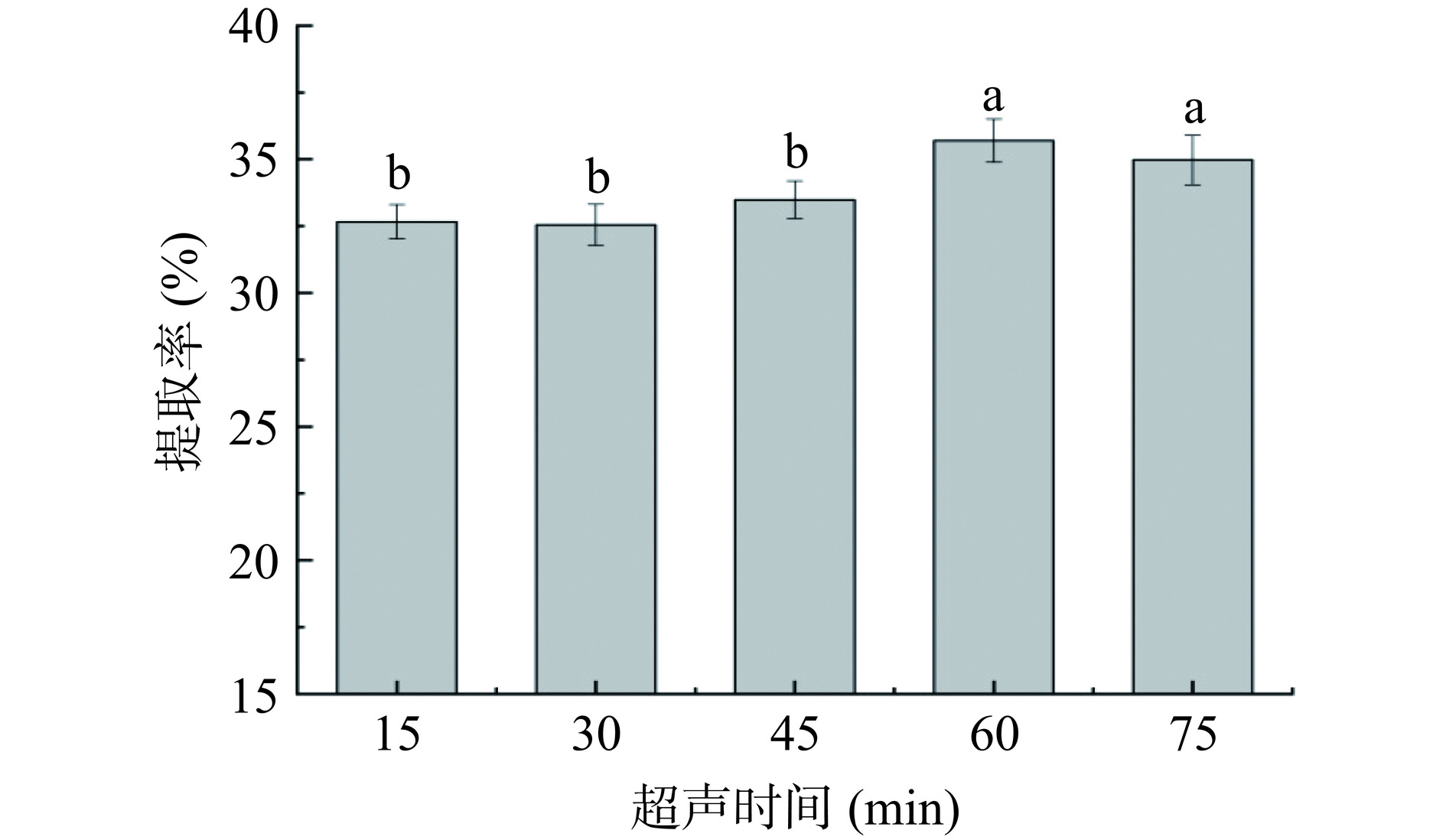
超声波辅助提取过程中,不同提取时间对黄花菜多糖提取率的影响如图3所示,提取时间为60 min时,提取率显著提高(P<0.05)。当提取时间从15 min延长至60 min时,黄花菜的提取率随之增加,这可能是由于超声过程中产生的空化泡,破坏了黄花菜颗粒表层细胞壁,促进了物质的溶出[22],提取率从32.66%增至35.7%。继续延长提取时间,黄花菜的提取率呈现下降趋势,这是由于提取时间过长的情况下,空化效应和超声传播过程产生的机械振动造成多糖降解而导致的[3]。因此选择超声提取时间45、60、75 min进行后续响应面试验。
2.1.3 PAW制备时间对黄花菜多糖提取率的影响
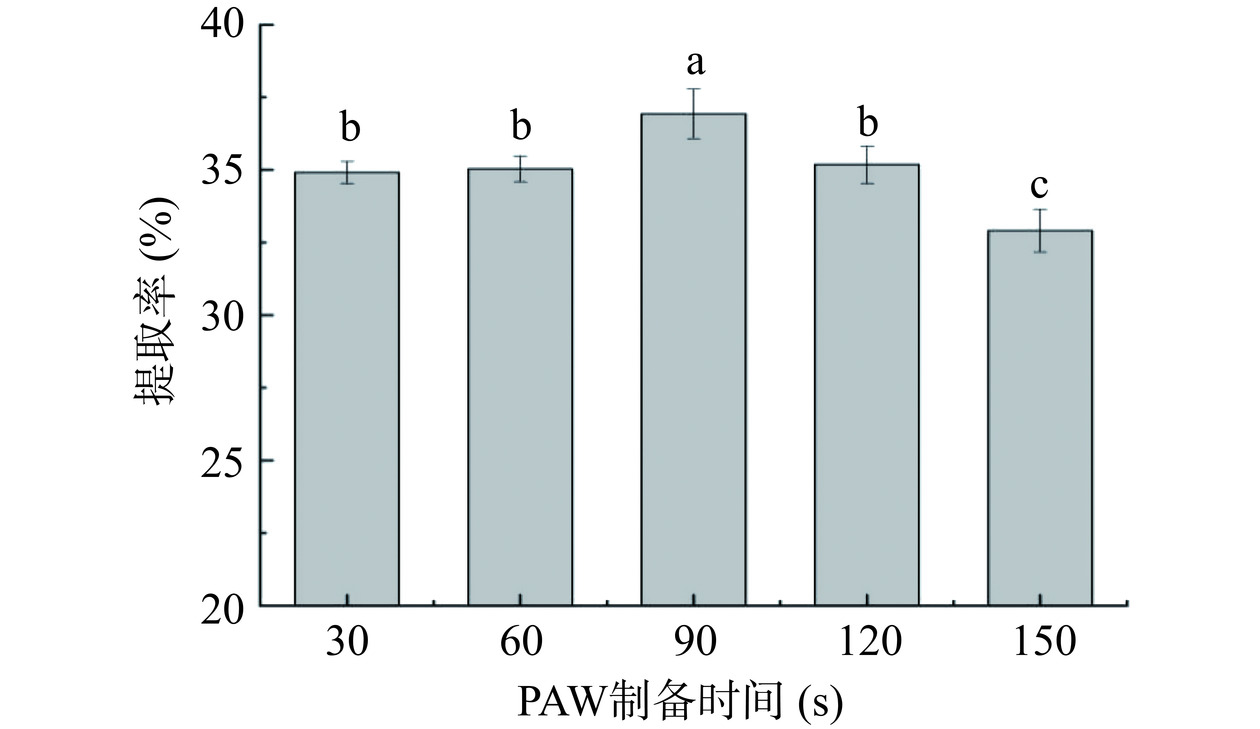
如图4所示,随着射流等离子体处理时间的延长,黄花菜多糖提取率有所提高,当等离子体处理时间为90 s时,提取率达到最大值并具有显著性(P<0.05),后呈下降趋势。PAW制备时间延长的情况下,浸提液过酸会破坏黄花菜多糖的立体结构及稳定性[23],导致多糖被酸解为半乳糖醛酸流失[24]。张星启等[25]研究称pH为多糖提取的极显著因素。与此同时,等离子体水制备的过程中,随着等离子体作用时间延长,电导率过高,会影响黄花菜颗粒中溶出的离子扩散到溶液中。因此选择PAW制备时间60、90、120 s进行后续响应面试验。
2.2 响应面结果分析
2.2.1 响应面试验设计
通过对单因素实验结果进行分析,确定了液固比:10:1、20:1、30:1 mL/g,超声提取时间:45、60、75 min,PAW制备时间:60、90、120 s,作为响应面试验各因素取值。以黄花菜多糖提取率为响应值,利用Design Expert 8.0.6软件设计3因素3水平的响应面试验,试验方案共17组,结果见表2。
表 2 响应面试验设计与结果Table 2. Response surface experimental design and results试验号 A液固比 B超声提取时间 C PAW制备时间 提取率(%) 1 0 1 1 29.71 2 1 −1 0 29.47 3 −1 1 0 28.00 4 0 0 0 36.08 5 1 0 1 34.11 6 0 0 0 36.48 7 0 1 −1 31.16 8 0 0 0 37.47 9 0 −1 −1 31.24 10 1 1 0 29.64 11 −1 0 1 26.15 12 0 0 0 35.49 13 0 0 −1 31.81 14 0 0 0 36.15 15 0 −1 1 30.60 16 −1 −1 0 27.56 17 −0 0 −1 29.54 2.2.2 方差分析和二次多项回归方程拟合
利用Design-Expert 8.0软件对试验数据进行多元回归拟合,得到二次回归方程为,提取率(%)=36.33+1.72A−0.045B−0.3975C−0.0675AB+1.42AC−0.2025BC−3.97A2−3.7B2−1.96C2。表3为响应面模型方差分析结果。
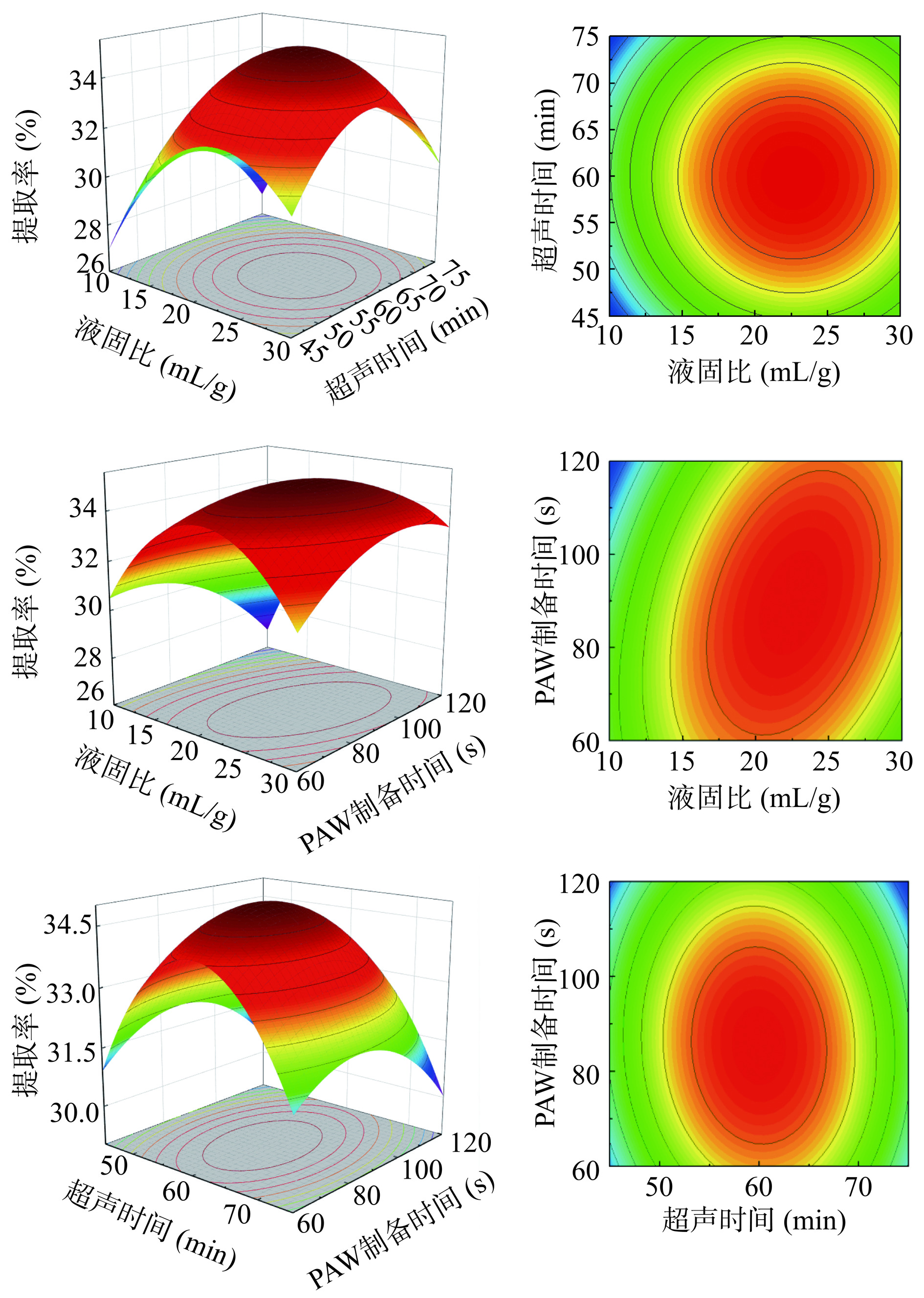
表 3 响应面模型方差分析结果Table 3. Response surface model analysis of variance results方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 188.18 9 20.91 17.99 0.0005 *** A液固比 23.74 1 23.74 20.42 0.0027 ** B超声提取时间 0.0162 1 0.0162 0.0139 0.9093 C PAW制备时间 1.26 1 1.26 1.09 0.3317 AB 0.0182 1 0.0182 0.0157 0.9039 AC 8.09 1 8.09 6.96 0.0335 * BC 0.164 1 0.164 0.1411 0.7183 A2 66.39 1 66.39 57.11 0.0001 *** B2 57.51 1 57.51 49.47 0.0002 *** C2 16.19 1 16.19 13.92 0.0073 ** 残差 8.14 7 1.16 失拟误差 6.01 3 2.00 3.78 0.1159 不显著 纯误差 2.12 4 0.5306 总和 196.32 16 注:*显著性水平P<0.05;**显著性水平P<0.01;***显著性水平P<0.001。 由表3可知,模型P<0.001极显著,说明该模型与实际拟合较好,能够良好地拟合出黄花菜最高提取率时的最优工艺条件。失拟项误差P>0.05,不显著,表明此模型拟合度良好,非试验因素对试验结果影响不大。3个因素影响黄花菜多糖提取率的程度为A(液固比)>C(PAW制备时间)>B(超声提取时间)。
2.2.3 响应面试验结果分析
3个因素的两两交互作用对提取率的影响见图5。等高线若为圆形或曲线稀疏则表明两因素间的相互作用对提取率的影响很小,若是椭圆形且曲线密集则说明影响很大[11]。由图5可知,对黄花菜多糖提取率影响最大的交互作用是液固比和PAW制备时间,结果显著,而液固比和超声提取时间的影响最小。
拟合出黄花菜多糖提取的最佳条件为:液固比22.57 mL/g,超声提取时间59.67 min,PAW制备时间88.62 s。此条件下,二次多项式回归方程拟合模型预测黄花菜多糖提取率为36.77%。出于实际考虑,选取液固比23 mL/g,超声提取时间60 min,PAW制备时间90 s,进行验证实验,实际黄花菜多糖提取率为36.33%±0.04%。表明该回归模型可用作黄花菜多糖提取的工艺优化。PAW辅助超声提取法与周纪东等[26]使用超声提取法所得多糖得率(28.23%)相比提高8.1%,这可能是因为在PAW辅助超声提取中,PAW酸性环境有利于植物细胞在溶液中的吸水溶胀作用,导致细胞破裂,并释放出多糖,促进多糖溶解提高多糖提取率。
2.3 黄花菜多糖的分离纯化实验分析
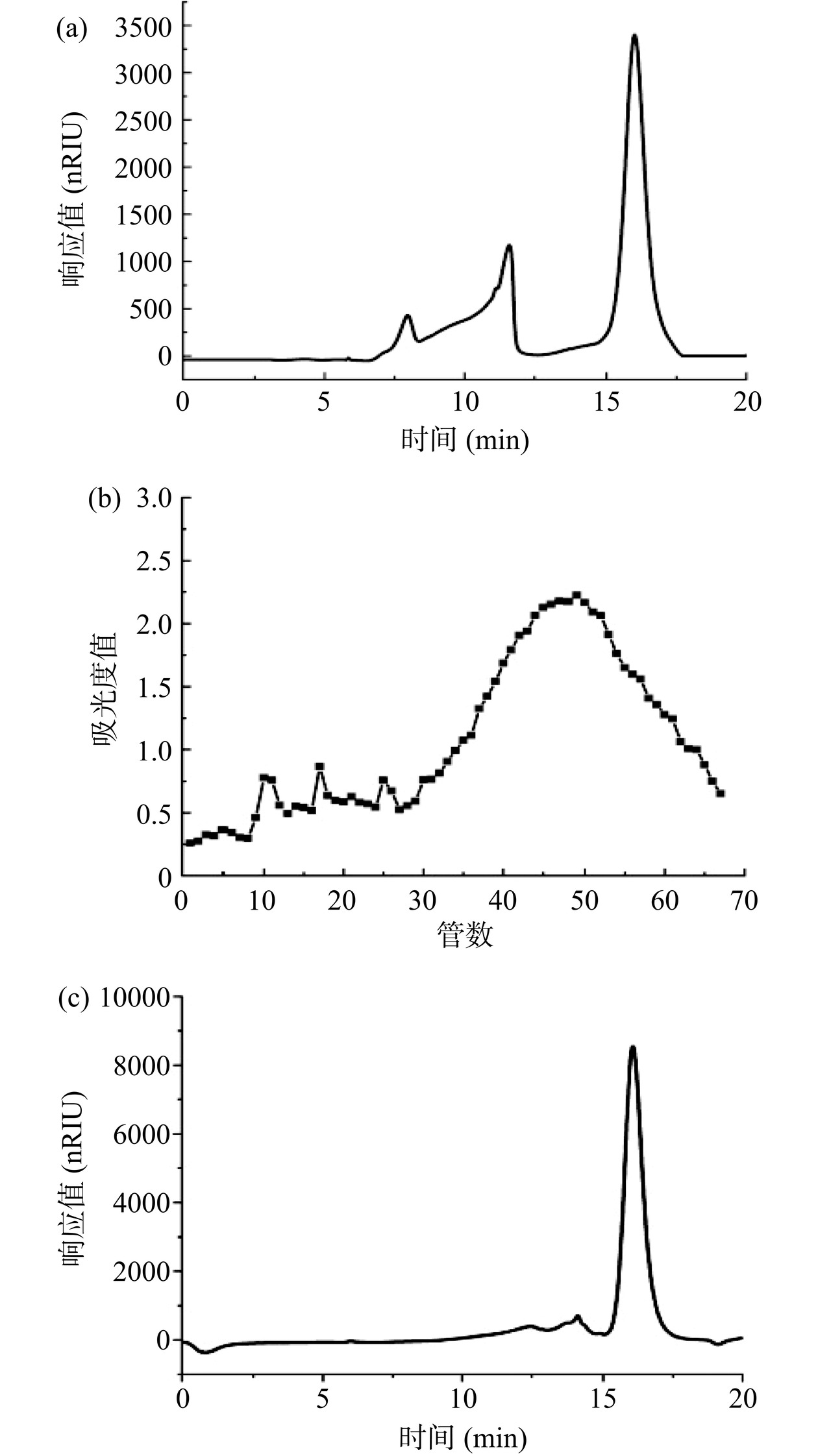
黄花菜粗多糖的高效液相色谱图如图6(a)所示,将黄花菜粗多糖用Sephadex G-100层析柱纯化,以超纯水作为洗脱液进行洗脱,测定每管多糖含量。得到洗脱曲线如图6(b)所示,收集洗脱曲线最高处第47~51管,透析并冻干后得到单一组分黄花菜多糖HCP。由图6(c)可知,谱图在16.082 min出现单一对称峰,表明HCP是一种均质多糖,经洗脱纯化纯度从54.81%升至93.53%。
2.4 分子量测定分析
根据标准曲线回归方程y=−0.3284x+9.1874(R2=0.9979),得到HCP分子量约为8.056 kDa(Rt=16.082 min)。李毅花[23]使用大同黄花菜提取多糖,后纯化得到的3种黄花菜多糖组分,分子量分别为4.217、9.3468、16.2167 kDa,可以看出与本实验所得黄花菜多糖分子量差异较大,这是由于黄花菜品种差异导致。
2.5 基本成分测定结果
经测定,HCP中的总糖含量为88.07%±4.25%,还原糖含量为4.38%±0.11%,蛋白质含量为2.72%±0.04%,糖醛酸含量为7.27%±0.44%。HCP含有糖醛酸,为酸性多糖,且蛋白质杂质含量较少,这可能是因为PAW较低的pH提取环境会抑制提取物中蛋白质、淀粉、脂溶性色素等大分子的溶出,得到较为纯净的多糖提取物[27]。
2.6 单糖组成分析
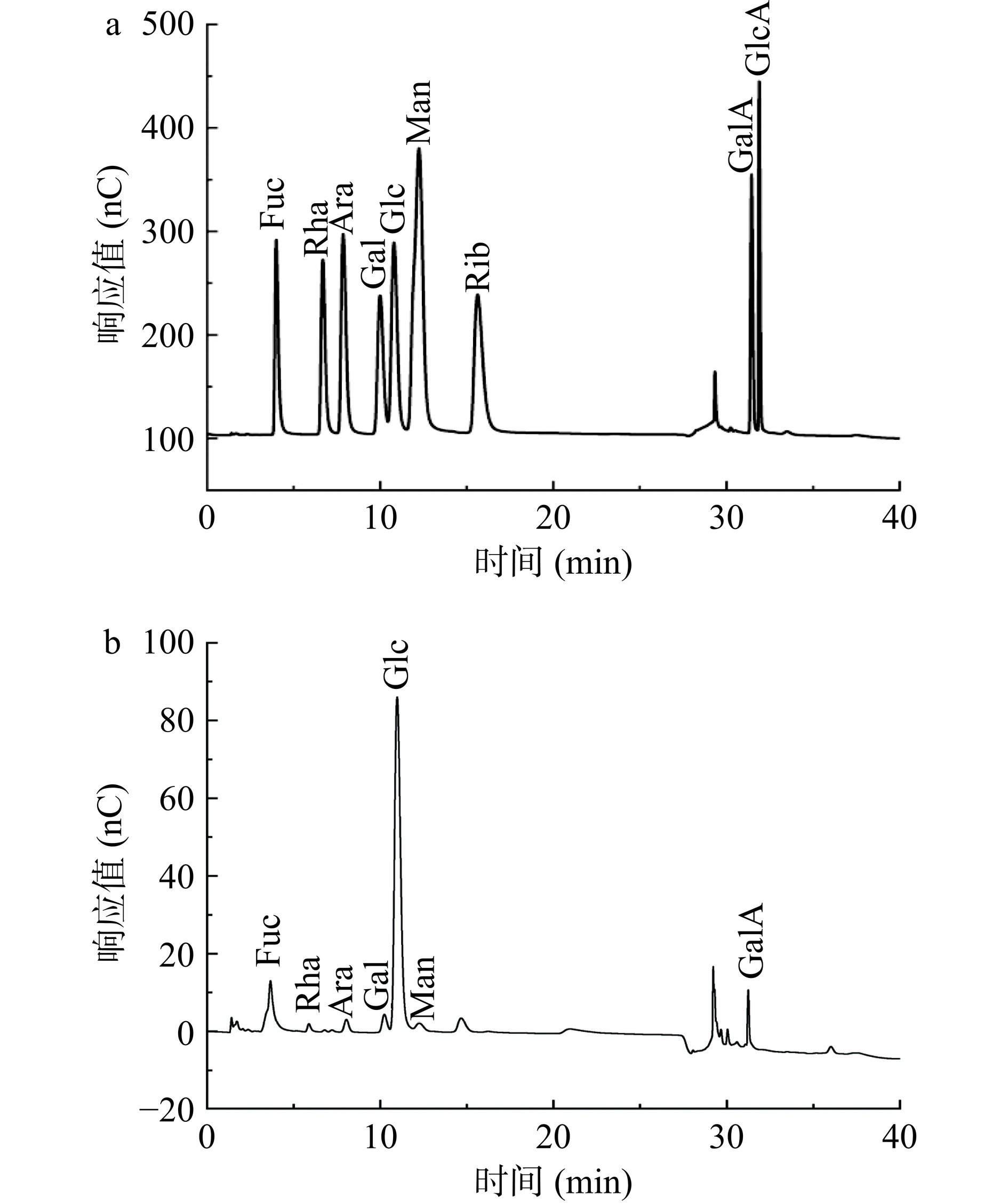
单糖标准品离子色谱图见图7(a),HCP离子色谱图见图7(b)。由图可知,HCP由岩藻糖(Fuc)、鼠李糖(Rha)、阿拉伯糖(Ara)、半乳糖(Gal)、葡萄糖(Glc)、甘露糖(Man)、半乳糖醛酸(GalA)组成,是一种酸性杂多糖,且葡萄糖占比最大。其中,单糖组成的摩尔比是:Fuc:Rha:Ara:Gal:Glc:Man:GalA=12.03:1.04:2.19:3.3:75.15:2.59:3.7。
2.7 傅里叶红外光谱分析
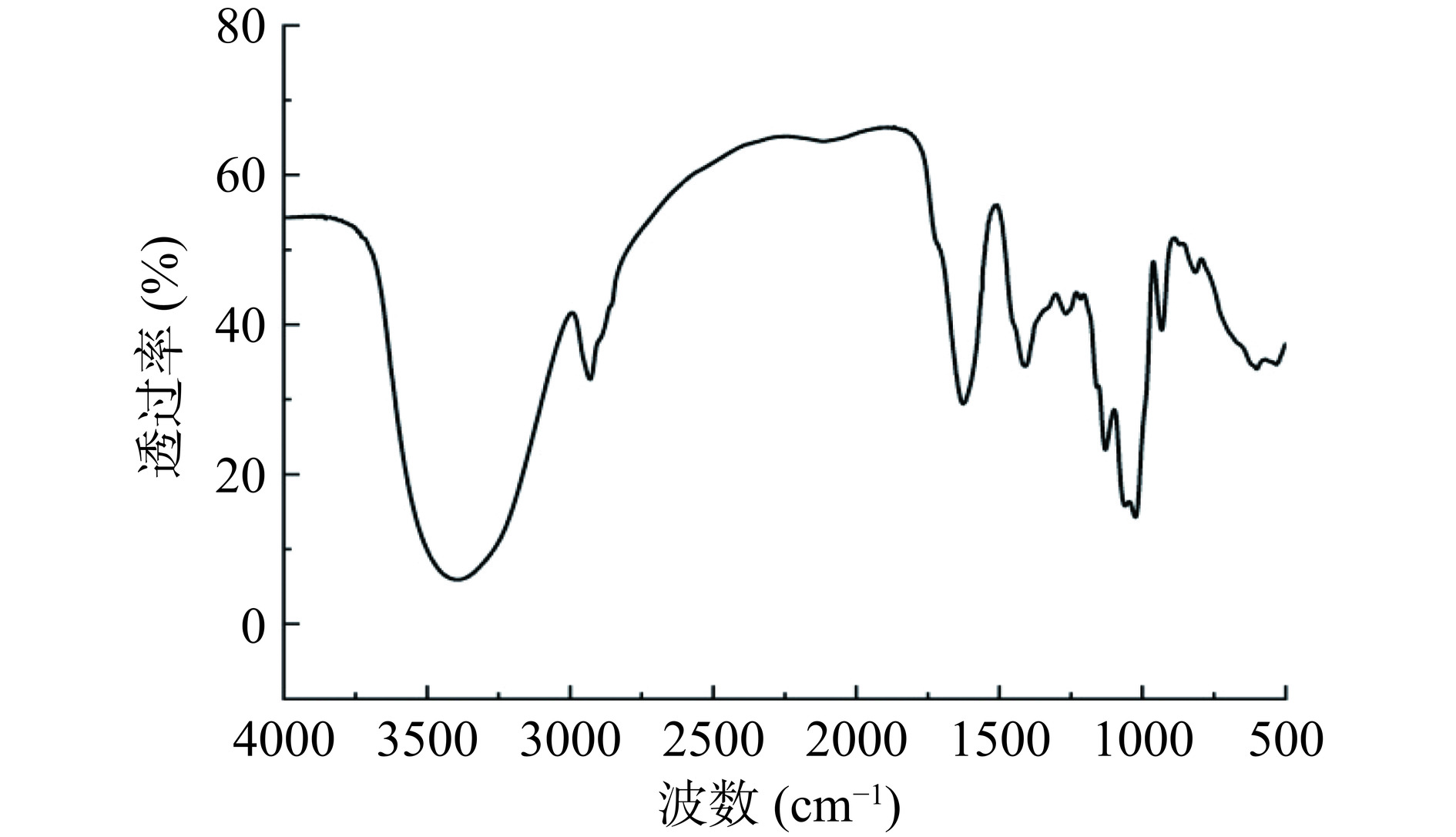
由图8可知,3390 cm−1处是羟基的O-H伸缩振动引起的;2930 cm−1处的吸收峰是碳氢键C-H伸缩振动引起的;O-H和C-H都是多糖类物质的特征基团,证明HCP是多糖类物质[22]。1623 cm−1 附近吸收峰可能是由多糖中的羧酸基团的伸缩振动引起的,这证实了HCP中存在糖醛酸[28],这与单糖组成分析结果一致;1408 cm−1附近是由于C-H键的变角振动;1130 cm−1附近是吡喃糖环C-O的吸收峰;1060 cm−1和1020 cm−1附近是由C-O-H和糖环的醚键C-O-C中的两种C-O伸缩振动引起的,证明HCP为吡喃糖[29];840 cm−1处出现的峰代表多糖的α-糖苷键[30];可知HCP为α-吡喃型多糖[31]。
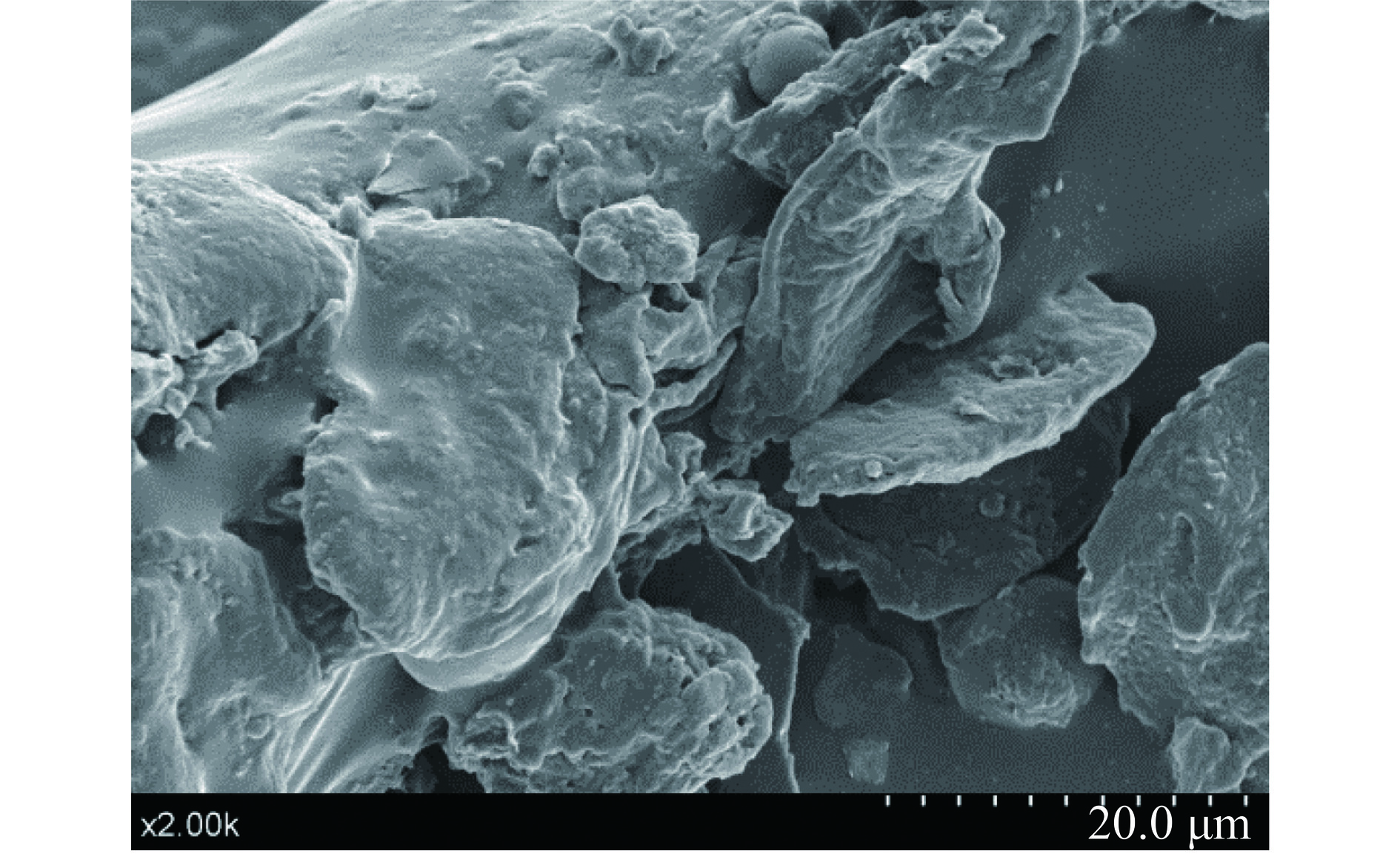
2.8 扫描电子显微镜分析
图9为HCP扫描电子显微镜图。由图9可知,多糖样品大多数呈片状,且多糖碎片结构不规则,边缘不完整。多糖分子整体结构较为疏松,可明显看到表面凹凸不平且有小空洞状凹陷,总体较为粗糙。
2.9 黄花菜多糖的降糖活性分析
2.9.1 HCP对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性的影响
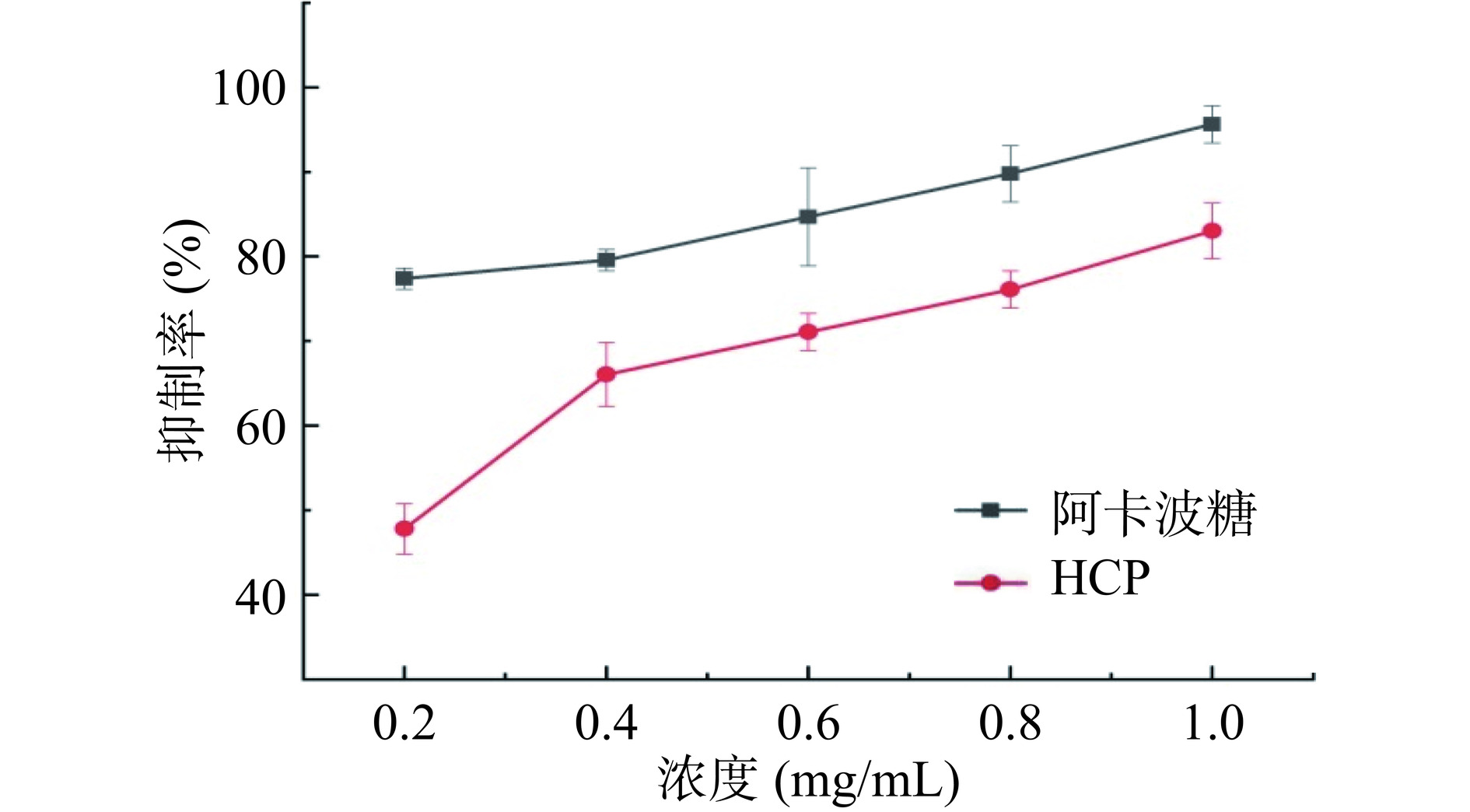
由图10可知,HCP对α-淀粉酶有一定的抑制作用,且随着浓度的增加,HCP对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制率呈现上升趋势,从47.8%上升到83.02%。当浓度为1 mg/mL时,HCP对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制率可达到阳性对照阿卡波糖的86.82%,表明HCP具有良好的降糖活性。
2.9.2 HCP对α-淀粉酶活性的影响
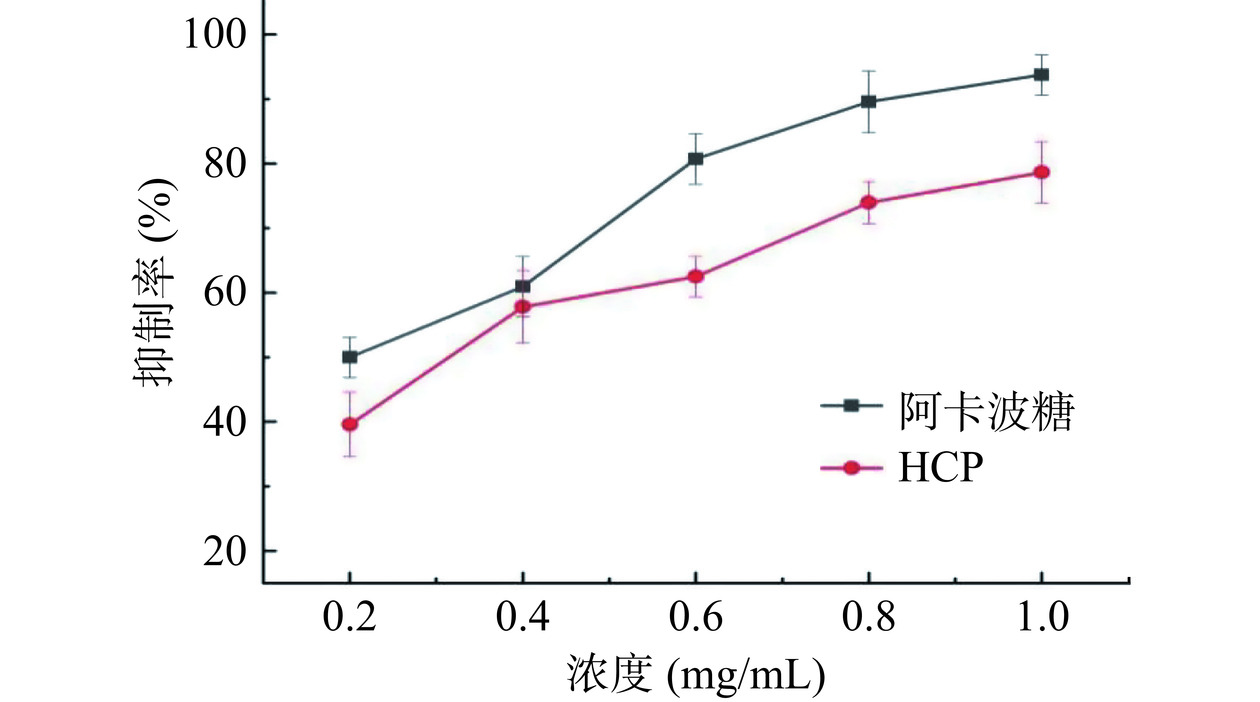
由图11可知,α-淀粉酶的抑制率随着HCP浓度的增加而增加,且两者之间存在一定的量效关系。当HCP的浓度为1 mg/mL时,α-淀粉酶的抑制率为78.65%,可达到阳性对照阿卡波糖的83.9%,这是因为HCP具有较低的分子量和α-糖苷键[32],并且具有粗糙的片层结构,有助于其与受体结合充分发挥其活性[30]。研究表明多糖的生物活性很大程度上取决于其分子量,且多糖通常与受体或蛋白质结合,充分发挥其生物活性[33]。
3. 结论
本实验对黄花菜多糖进行提取、分离与纯化。采用PAW辅助超声提取法优化多糖提取工艺,通过单因素和响应面试验得到当液固比为23 mL/g、超声提取时间60 min、PAW制备时间90 s时,黄花菜多糖提取率最佳为36.33%。HCP中总糖含量为88.07%,糖醛酸含量为7.27%,红外光谱和离子色谱结果显示HCP是由岩藻糖、鼠李糖、阿拉伯糖、半乳糖、葡萄糖、甘露糖和半乳糖醛酸组成的α-吡喃型酸性杂多糖,分子量为8.056 kDa,具有粗糙的片状结构。通过体外降糖实验研究HCP的降糖活性,结果发现HCP具有良好的α-葡萄糖苷酶与α-淀粉酶的抑制能力。本研究使黄花菜多糖的研究得到进一步扩展,也为黄花菜的综合开发和功能因子的应用提供参考。
-
表 1 响应面优化试验设计
Table 1 Response surface optimization experimental design
水平 因素 A液固比(mL/g) B超声提取时间(min) C PAW制备时间(s) −1 10:1 45 60 0 20:1 60 90 1 30:1 75 120 表 2 响应面试验设计与结果
Table 2 Response surface experimental design and results
试验号 A液固比 B超声提取时间 C PAW制备时间 提取率(%) 1 0 1 1 29.71 2 1 −1 0 29.47 3 −1 1 0 28.00 4 0 0 0 36.08 5 1 0 1 34.11 6 0 0 0 36.48 7 0 1 −1 31.16 8 0 0 0 37.47 9 0 −1 −1 31.24 10 1 1 0 29.64 11 −1 0 1 26.15 12 0 0 0 35.49 13 0 0 −1 31.81 14 0 0 0 36.15 15 0 −1 1 30.60 16 −1 −1 0 27.56 17 −0 0 −1 29.54 表 3 响应面模型方差分析结果
Table 3 Response surface model analysis of variance results
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 188.18 9 20.91 17.99 0.0005 *** A液固比 23.74 1 23.74 20.42 0.0027 ** B超声提取时间 0.0162 1 0.0162 0.0139 0.9093 C PAW制备时间 1.26 1 1.26 1.09 0.3317 AB 0.0182 1 0.0182 0.0157 0.9039 AC 8.09 1 8.09 6.96 0.0335 * BC 0.164 1 0.164 0.1411 0.7183 A2 66.39 1 66.39 57.11 0.0001 *** B2 57.51 1 57.51 49.47 0.0002 *** C2 16.19 1 16.19 13.92 0.0073 ** 残差 8.14 7 1.16 失拟误差 6.01 3 2.00 3.78 0.1159 不显著 纯误差 2.12 4 0.5306 总和 196.32 16 注:*显著性水平P<0.05;**显著性水平P<0.01;***显著性水平P<0.001。 -
[1] 张磊, 王佳玮, 费鹏, 等. 黄花菜多糖的提取方法及药理活性研究进展[J]. 现代食品,2023,29(17):60−64. [ZHANG Lei, WANG Jiawei, FEI Peng, et al. Research progress on extraction methods and pharmacological activities of Hemerocallis citrina polysaccharide[J]. Modern Food,2023,29(17):60−64.] ZHANG Lei, WANG Jiawei, FEI Peng, et al. Research progress on extraction methods and pharmacological activities of Hemerocallis citrina polysaccharide[J]. Modern Food, 2023, 29(17): 60−64.
[2] 何莉, 张天伦. 黄花菜的生物学特性及应用价值分析[J]. 农业科技通讯,2012(3):176−178. [HE Li, ZHANG Tianlun. Analysis of biological characteristics and application value of yellow flower vegetable[J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology,2012(3):176−178.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6400.2012.03.076 HE Li, ZHANG Tianlun. Analysis of biological characteristics and application value of yellow flower vegetable[J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2012(3): 176−178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6400.2012.03.076
[3] 郭佳. 超声波辅助提取对枸杞细胞壁多糖解聚规律的研究[D]. 银川:宁夏大学, 2022. [GUO Jia. Depolymerization of Lycium barbarum cell wall polysaccharides by ultrasonic assisted extraction[D]. Yinchuan:Ningxia University, 2022.] GUO Jia. Depolymerization of Lycium barbarum cell wall polysaccharides by ultrasonic assisted extraction[D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2022.
[4] 李成华, 秦汝兰, 关颖丽, 等. 超声-微波辅助提取酸浆宿萼多糖及其体外降糖活性[J]. 食品研究与开发,2023,44(14):93−98. [LI Chenghua, QIN Ruhua, GUAN Yingli, et al. Ultrasonic-microwave assisted extraction of polysaccharide from calyx of Physali alkekengi L. and its hypoglycemic activity[J]. Food Research and Development,2023,44(14):93−98.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2023.14.014 LI Chenghua, QIN Ruhua, GUAN Yingli, et al. Ultrasonic-microwave assisted extraction of polysaccharide from calyx of Physali alkekengi L. and its hypoglycemic activity[J]. Food Research and Development, 2023, 44(14): 93−98. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2023.14.014
[5] 于双. 提取方法对海参煮液多糖的组成、结构及性质的影响[D]. 大连:大连海洋大学, 2022. [YU Shuang. Effects of extraction methods on the composition, structure and properties of polysaccharides from sea cucumber cooking liquid[D]. Dalian:Dalian Ocean University, 2022.] YU Shuang. Effects of extraction methods on the composition, structure and properties of polysaccharides from sea cucumber cooking liquid[D]. Dalian: Dalian Ocean University, 2022.
[6] AKBAL A, ŞAHIN S, GÜROY B. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from ulva rigida and evaluation of their antioxidant activity[J]. Algal Research,2024,77:103356. doi: 10.1016/j.algal.2023.103356
[7] 刘艺珠, 刘佩冶, 赵玉梅, 等. 黄花菜多糖的表征与抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(12):54−61. [LIU Yizhu, LIU Peiye, ZHAO Yumei, et al. Characterization and antioxidant activity analysis of daylily polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(12):54−61.] LIU Yizhu, LIU Peiye, ZHAO Yumei, et al. Characterization and antioxidant activity analysis of daylily polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(12): 54−61.
[8] LUKES P, DOLEZALOVA E, SISROVA I, et al. Aqueous-phase chemistry and bactericidal effects from an air discharge plasma in contact with water:Evidence for the formation of peroxynitrite through a pseudo-second-order post-discharge reaction of H2O2 and HNO2[J]. Plasma Sources Science Technology,2014,23(1):015019. doi: 10.1088/0963-0252/23/1/015019
[9] 董思琦. 液相脉冲放电法处理甘蔗渣废弃物及提取多糖的研究[D]. 大连:大连海事大学, 2023. [DONG Siqi. Study on the treatment of bagasse waste and polysaccharide extraction by liquid phase pulse disch[D]. Dalian:Dalian Maritime University, 2023.] DONG Siqi. Study on the treatment of bagasse waste and polysaccharide extraction by liquid phase pulse disch[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2023.
[10] 刘静鸿, 桂琴, 欧阳健明. 海藻多糖中硫酸基含量对抑制草酸钙晶体形成和修复受损伤肾小管上皮细胞的影响[J]. 无机化学学报,2023,39(3):465−474. [LIU Jinghong, GUI Qin, OUYANG Jianming. Effect of seaweed polysaccharides with different sulfate group contents on crystal growth of calcium oxalate and on the repair of damaged renal epithelial cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry,2023,39(3):465−474.] LIU Jinghong, GUI Qin, OUYANG Jianming. Effect of seaweed polysaccharides with different sulfate group contents on crystal growth of calcium oxalate and on the repair of damaged renal epithelial cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2023, 39(3): 465−474.
[11] 张强, 韦婉珍, 罗小莉, 等. 响应面优化南酸枣叶多糖的提取工艺及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(22):150−156. [ZHANG Qiang, WEI Wanzhen, LUO Xiaoli, et al. Response surface method-assisted extraction and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Choerospondias axillaris leaves[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(22):150−156.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.22.023 ZHANG Qiang, WEI Wanzhen, LUO Xiaoli, et al. Response surface method-assisted extraction and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Choerospondias axillaris leaves[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(22): 150−156. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.22.023
[12] 惠秋沙. 蒽酮—硫酸法测定桑葚乌发粥中粗多糖的含量[J]. 农产品加工(学刊),2011(10):105−107. [HUI Qiusha. Content determination of total polysaccharides in Sangshen Wufa gruel by anthrone-sulfuric acid method[J]. Academic Periodical of Farm Products Processing,2011(10):105−107.] HUI Qiusha. Content determination of total polysaccharides in Sangshen Wufa gruel by anthrone-sulfuric acid method[J]. Academic Periodical of Farm Products Processing, 2011(10): 105−107.
[13] 孙晓玲. 蒽酮-硫酸法测定秋葵多糖条件的优化[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2019,30(9):154−158. [SUN Xiaoling. Optimization of polysaccharide determination in okra by anthrone-sulfuric acid method[J]. China Food Additives,2019,30(9):154−158.] SUN Xiaoling. Optimization of polysaccharide determination in okra by anthrone-sulfuric acid method[J]. China Food Additives, 2019, 30(9): 154−158.
[14] 柳红. 南瓜多糖的修饰、结构分析及抗氧化活性的研究[D]. 西安:陕西师范大学, 2008. [LIU Hong. Study on chemical modification, structure and antioxidant activity of pumpkin polysaccharides[D]. Xi’an:Shaanxi Normal University, 2008.] LIU Hong. Study on chemical modification, structure and antioxidant activity of pumpkin polysaccharides[D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2008.
[15] 徐勇. 姬松茸碱提水溶性多糖提取、结构鉴定及抗氧化活性研究[D]. 杭州:浙江工业大学, 2019. [XU Yong. Extraction, structural elucidation and antioxidant activity of water-soluble polysaccharides alkali extracted from Agaricus blazei Murill[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University of Technology, 2019.] XU Yong. Extraction, structural elucidation and antioxidant activity of water-soluble polysaccharides alkali extracted from Agaricus blazei Murill[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2019.
[16] 何业通. 柠檬桉树脂多糖的提取纯化及其生物活性的研究[D]. 南宁:广西大学, 2022. [HE Yetong. Extraction, purification and bioactivity of eucalyptus citri resin polysaccharides[D]. Nanning:Guangxi University, 2022.] HE Yetong. Extraction, purification and bioactivity of eucalyptus citri resin polysaccharides[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2022.
[17] CHEN X, JIN J, TANG J, et al. Extraction, purification, characterization and hypoglycemic activity of a polysaccharide isolated from the root of Ophiopogon japonicus[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2011,83(2):749−754. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.08.050
[18] 赵寒青. 玉米须复合袋泡茶的研制及其抗氧化、降血糖活性研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2021. [ZHAO Hanqing. Research and development of corn silk bagged tea and its antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2021.] ZHAO Hanqing. Research and development of corn silk bagged tea and its antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021.
[19] LI W, SHAO C, HUANG P, et al. Optimization, characterization of Astragalus polysaccharides, and evaluation of anti-inflammation effect in primary cultured astrocytes via HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB/NLRP3 signal pathway[J]. Industrial Crops Products,2023,197:116594. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2023.116594
[20] CAO Z, DING Y, LIU Z, et al. Extraction condition optimization and prebiotic potential of dandelion (Taraxacum mongolicum Hand. Mazz.) polysaccharides[J]. Industrial Crops Products,2023,194:116318.
[21] 杜佳, 金桂勇, 陈芝飞, 等. 蓝莓果渣多糖提取工艺的响应面优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 山东农业科学,2022,54(10):135−142. [DU Jia, JIN Guiyong, CHEN Zhifei, et al. Response surface optimization of extraction process and antioxidant activity of blueberry pomace polysaccharide[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences,2022,54(10):135−142.] DU Jia, JIN Guiyong, CHEN Zhifei, et al. Response surface optimization of extraction process and antioxidant activity of blueberry pomace polysaccharide[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 54(10): 135−142.
[22] TAN J, CUI P, GE S, et al. Ultrasound assisted aqueous two-phase extraction of polysaccharides from Cornus officinalis fruit:Modeling, optimization, purification, and characterization[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2022,84:105966. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.105966
[23] 李毅花. 超声协同高压静电场提取黄花菜多糖的机理研究及其结构表征[D]. 南宁:广西大学, 2018. [LI Yihua. The mechanism of ultrasound-synergized electrostatic field extraction of polysaccharide from Hemerocallis citrina Baroni and structure characterization[D]. Nanning:Guangxi University, 2018.] LI Yihua. The mechanism of ultrasound-synergized electrostatic field extraction of polysaccharide from Hemerocallis citrina Baroni and structure characterization[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2018.
[24] 宋贤良, 张星启, 蔡纯, 等. 菠萝蜜皮果胶酸提醇沉工艺优化及其结构分析[J]. 南方农业学报,2015,46(4):664−668. [SONG Xianliang, ZHANG Xingqi, CAI Chun, et al. Optimization of process of pectin by acid extraction and alcohol precipitation from jackfruit peel and structure analysis[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture,2015,46(4):664−668.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2015.4.664 SONG Xianliang, ZHANG Xingqi, CAI Chun, et al. Optimization of process of pectin by acid extraction and alcohol precipitation from jackfruit peel and structure analysis[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2015, 46(4): 664−668. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2015.4.664
[25] 张星启, 宋贤良, 陈颖森, 等. 响应面优化菠萝蜜果皮果胶的酶法提取工艺[J]. 广东农业科学,2015,42(3):89−93,98. [ZHANG Xingqi, SONG Xianliang, CHEN Yingsen, et al. Optimization of enzymatic extraction process for pectin from jackfruit peel by response surface methodology[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2015,42(3):89−93,98.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2015.03.020 ZHANG Xingqi, SONG Xianliang, CHEN Yingsen, et al. Optimization of enzymatic extraction process for pectin from jackfruit peel by response surface methodology[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 42(3): 89−93,98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2015.03.020
[26] 周纪东, 李余动. 黄花菜多糖超声波提取技术的研究[J]. 岳阳职业技术学院学报,2014,29(5):86−89. [ZHOU Jidong, LI Yudong. Study on the extraction of polysaccharides from daylily by ultrasonic technique[J]. Yueyang Vocational Technical College,2014,29(5):86−89.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-738X.2014.05.024 ZHOU Jidong, LI Yudong. Study on the extraction of polysaccharides from daylily by ultrasonic technique[J]. Yueyang Vocational Technical College, 2014, 29(5): 86−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-738X.2014.05.024
[27] HU X, XU F, LI J, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from coix seeds:Optimization, purification, and in vitro digestibility[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,374:131636. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131636
[28] NIE C, ZHU P, MA S, et al. Purification, characterization and immunomodulatory activity of polysaccharides from stem lettuce[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,188:236−242. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.02.009
[29] MA J S, LIU H, HAN C R, et al. Extraction, characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Pouteria campechiana seed[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,229:115409. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115409
[30] 汪梦雯. 灵芝、香菇和茯茶多糖的提取、结构表征及降糖活性研究[D]. 西安:陕西科技大学, 2021. [WANG Mengwen. Optimization of extration technology and biological activity of Polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum, Lentinus edodes and Fu brick tea[D]. Xi’an:Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2021.] WANG Mengwen. Optimization of extration technology and biological activity of Polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum, Lentinus edodes and Fu brick tea[D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2021.
[31] CHEN H, ZENG J, WANG B, et al. Structural characterization and antioxidant activities of Bletilla striata polysaccharide extracted by different methods[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,266:118149. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118149
[32] ZHAO B, WANG X, LIU H, et al. Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of oligosaccharides from Panax ginseng CA Meyer[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,150:737−745. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.016
[33] DONG X D, LIU Y N, ZHAO Y, et al. Structural characterization of a water-soluble polysaccharide from Angelica dahurica and its antitumor activity in H22 tumor-bearing mice[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,193:219−227. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.110





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



