Extraction of Antioxidant Peptides and Activity Evaluation of Frog (Rana nigromaculata) Skin by Ultra-high Pressure Assisted Enzyme Hydrolysis
-
摘要: 为提高黑斑蛙加工副产物蛙皮的综合利用价值,对黑斑蛙蛙皮抗氧化肽的提取工艺及性能进行研究。采用超滤方法对黑斑蛙蛙皮的蛋白酶解液进行分离,得到不同分子量范围的小分子肽,通过体外抗氧化试验和秀丽隐杆线虫模型,评价不同分子量范围蛙皮小分子肽的抗氧化性能;以高活性小分子肽得率为目标,采用响应面方法对酶添加量、超高压压力、超高压时间、液料比四个参数优化,确定小分子肽最佳提取工艺。结果表明,1~2000 Da小分子肽具有最强的抗氧化能力,DPPH自由基、ABTS+自由基清除率分别达到了76.93%、59.23%,并显著提高了秀丽隐杆线虫的抗氧化能力;在中性蛋白酶水解的基础上,二次酶解最佳工艺参数为碱性蛋白酶用量10210 U/g,超高压压力315 MPa,压力作用时间9.3 min,液料比16倍,1~2000 Da小分子肽得率为25.26%。超高压辅助双酶水解显著提高了黑斑蛙蛙皮小分子肽的得率,为黑斑蛙副产物的高值化利用提供了参考。Abstract: In order to improve the comprehensive utilization value of the skin of the frog (Rana nigromaculata), the extraction process of antioxidant peptides of the skin of the frog (Rana nigromaculata) was studied in this experiment and its activity was evaluated. Ultrafiltration was used to separate the protease hydrolysis solution of the skin of the frog (Rana nigromaculata) to obtain small molecule peptides with different molecular weight. The antioxidant properties of frog (Rana nigromaculata) skin small molecule peptides were evaluated in Caenorhabditis elegans model as well as in vitro. Taking the yield of highly active small molecule peptides as the index, the response surface method was utilized to optimize the four parameters containing enzyme addition, ultra-high pressure, the action time, and liquid-to-material ratio to determine the best extraction process for small molecule peptides. Results showed that 1~2000 Da small molecule peptides possessed the optimal antioxidant effect compared to other peptides in the same molecular weight range, the scavenging capacity of DPPH free radicals and ABTS+ free radicals reached 76.93% and 59.23%, respectively. The antioxidant capacity of Caenorhabditis elegans was significantly improved. Besides, on the basis of neutral protease hydrolysis, the optimum technology parameters for secondary enzymatic hydrolysis were alkaline protease dosage 10210 U/g, ultra-high pressure pressure 315 MPa, pressure action time 9.3 min, liquid-material ratio 16 times, and the yield of small molecule peptides with 1~2000 Da was 25.26% under above condition. Ultra-high pressure assisted two-enzyme hydrolysis significantly increased the yield of small-molecule peptides from the skin of the frog (Rana nigromaculata). The results of this research provide a reference for the high-value utilization of by-products of the frog (Rana nigromaculata).
-
黑斑蛙(Rana nigromaculata)属于蛙科(Ranidae)两栖类动物,俗称青蛙、田鸡,由于其营养丰富、肉质鲜美,深受消费者的欢迎,是国内特色水产品之一,目前人工养殖已经具有一定的规模[1]。由于黑斑蛙养殖业和加工业的快速发展,产生了大量的副产物,如何对这些副产物综合利用成为了行业亟需解决的技术和环保难题[2]。黑斑蛙副产物主要为蛙头、蛙皮、内脏等,其中蛙皮粗蛋白含量高达77.8%[3],相关研究也表明蛙类皮肤是提取蛋白及制备活性多肽的优质原料[4]。通常把分子量<5000 Da的肽称为小分子肽,很多研究证实小分子肽可以抑制自由基的产生,加速蛋白质合成,改善矿物质的吸收和利用,增强机体免疫力[5−7]。由于小分子肽易于消化,具有更高的生物利用度[8],因此从蛙皮中提取小分子肽作为功能食品成分,具有很高的应用价值。酶法水解是动物加工副产品中回收蛋白质的有效方法之一,具有高效、无污染的特点,本课题组前期试验发现,碱性蛋白酶和中性蛋白酶均能有效降解黑斑蛙皮蛋白。双酶水解与单酶水解相比,双酶法可以协同区分不同的酶切割位点,双酶二步水解是目前抗氧化肽提取较多的酶解方式,能够显著提高水解效率,降低多肽链的长度,提升水解产物的生物活性[9]。
黑斑蛙皮中的胶原蛋白含有较高的脯氨酸,据报道脯氨酸含量与蛋白质水解难度成正比,其稳固的结构阻碍了生物活性肽的释放[10]。采用物理方法适度解聚并暴露埋藏的疏水基团,可以促进活性更高的疏水基团裂解成短肽[11]。超高压处理是采用水作为传压介质,在高压容器中对物料施加100 MPa以上的压力[12]。由于超高压能够使蛋白质的非共价键断裂,破坏蛋白质的空间螺旋结构,有利于酶和蛋白质水解位点的接触,提高水解效率[11],因此超高压预处理在蛙皮抗氧化肽的提取方面具有应用潜力。THORESEN等[13]对鸡肉残渣酶解之前进行了超高压预处理,发现200 MPa的高压处理可以显著提高蛋白质的得率和水解产物的抗氧化性能,王艳茹等[14]采用超高压辅助酶解制备牛皮胶原肽,其抗氧化性能相比对照组提高了约1.3倍。超高压辅助酶法制备小分子肽具有理论基础和应用前景,目前,超高压辅助双酶水解提取蛙皮中的生物活性肽还未见报道。
本研究从黑斑蛙皮中提取粗蛋白,经过超高压预处理,然后采用碱性蛋白酶和中性蛋白酶双酶水解提取小分子肽,以秀丽隐杆线虫为模型,对制备的小分子肽抗氧化性能进行分析,确定小分子肽抗氧化性能最佳的分子量范围,并使用响应面软件对提取工艺进行优化,确定最佳的蛙皮小分子肽提取工艺,以期为黑斑蛙蛙皮的高值化利用提供思路,提高我国黑斑蛙产业经济效益。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
黑斑蛙皮 湖北君坤农业科技有限公司提供;碱性蛋白酶(12000 U/g)、中性蛋白酶(50000 U/g) 南京杜莱生物技术有限公司;ABTS、DPPH 试剂、乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)、冰乙酸、NaOH、Tris-HCl、HCl 北京博奥拓达科技有限公司;BCA 蛋白浓度测定试剂盒 南京建成生物科技有限公司;秀丽隐杆线虫 荆楚理工学院农业生物技术研究所;其余试剂均为分析纯 武汉华易丰生物科技有限公司。
L2-700/1超高压实验设备 天津华泰森淼超高压装备工程技术有限公司;BONA-GM-18超滤实验设备 山东济南博纳有限公司;WFL-D1倒置式荧光显微镜 微特视界科技(深圳)有限公司;5427R高速冷冻离心机 德国 Eppendorf有限公司;LGJ-12真空冷冻冻干机 北京松源华兴科技发展有限公司;TU-190紫外分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 黑斑蛙皮脱脂处理
黑斑蛙蛙皮首先冷冻干燥,然后切成0.2×0.2 cm 小片,加入50倍的异丙醇脱脂,搅拌1 h后静置12 h,过滤后在4 ℃下低温干燥。
1.2.2 不同方法制备蛙皮小分子肽
1.2.2.1 中性蛋白酶处理
脱脂后的蛙皮与蒸馏水1:10的质量比混合,然后加入中性蛋白酶(10000 U/g),用0.1 mol/L NaOH将pH调节至6.0,45℃下静置4 h;然后离心取上清液,得到蛙皮肽提取液,部分冷冻干燥,其余通过超滤设备,分别通过1、2、3、5 kDa滤膜,得到分子量分别为<1、1~2、2~3、3~5、>5000 Da的肽段[15]。
1.2.2.2 碱性蛋白酶处理
脱脂后的蛙皮与蒸馏水1:10的质量比混合,碱性蛋白酶添加量为10000 U/g,调整pH为7.5,在45 ℃下酶解3 h,离心取上清液,部分冷冻干燥,部分如前述通过超滤设备分离不同分子量肽段[15]。
1.2.2.3 双酶处理
将脱脂后的蛙皮先用中性蛋白酶处理,酶解物冻干后再用碱性蛋白酶进行二次酶解,酶解的条件分别和1.2.2.1与1.2.2.2保持一致,通过超滤设备分离不同分子量肽段。
1.2.2.4 超高压-双酶处理
将冻干的中性蛋白酶提取物与蒸馏水1:10混合,然后在200 MP压力下作用10 min,取出后用碱性蛋白酶进行二次酶解,酶解条件保持一致,酶解物通过超滤设备分离不同分子量肽段。
1.2.3 不同分子量的小分子肽体外抗氧化性能测定
1.2.3.1 DPPH 自由基清除能力测定
参照BOUGATEF等[16]的方法并稍作修改,将不同分子量的小分子肽溶于磷酸盐缓冲液(0.1 mol/L,pH7.0),配制成5 mg/mL的浓度,DPPH试剂溶解于95%乙醇中(0.2 mmol/L),将 2 mL DPPH溶液添加到 2 mL样品溶液中,使用涡旋振荡器混合,并在室温下避光反应 30 min。使用紫外可见分光光度法在517 nm波长处测定吸光度。自由基清除率计算公式如下:
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (1) 式中:A0为2 mL DPPH 与 2 mL 乙醇混合溶液的吸光度,A1为2 mL 样品与2 mL DPPH 溶液的吸光度,A2为 2 mL样品与 2 mL乙醇混合溶液的吸光度。
1.2.3.2 ABTS+自由基清除能力测定
参考He等[17]的方法测定蛙皮小分子肽ABTS+自由基清除能力。ABTS工作液现配现用,其在734 nm波长处的吸光度值(记为 A1 )。将5 mg/mL的小分子肽 2 mL加入试管中,再加 2 mL ABTS 工作液,振荡混匀 10 s 后避光反应 10 min。使用空白溶剂作为参考,以抗坏血酸作为阳性对照,在 405 nm 波长处测定。
ABTS+自由基清除率(%)=(1−A1A2)×100 (2) 式中:A1为2 mL样品溶液+2 mL ABTS工作液的吸光度;A2为2 mL空白溶剂+2 mL ABTS 工作液的吸光度。
1.2.4 不同分子量的小分子肽对秀丽隐杆线虫抗氧化性能测定
1.2.4.1 线虫氧化应激抗性
将同步化完成后的线虫,置于96 孔平板培养中,每孔放置约15条线虫,参考吴梦思等[18]的方法进行培养,将不同分子量的小分子肽稀释为100 μg/mL,每孔吸取10 µL小分子肽溶液与90 µL S-complete 培养基混合,以蒸馏水作为对照组。培养一周后,用挑针随机挑取线虫至96孔平板,每个试验组至少50条线虫,暴露于过氧化氢溶液中,试验温度37 ℃,过氧化氢浓度1 mmol/L,观察并记录线虫的死亡情况,间隔时间1 h,直至全部死亡。
1.2.4.2 线虫热应激抗性
线虫培养与氧化应激试验一致,将培养完成的线虫转移到烘箱中,设置温度37 ℃,1 h后降温至20 ℃,观察并计算线虫的死亡率。
线虫热应激死亡率(%)=L1L0×100 (3) 式中:L1为死亡的线虫数目,L0为每个试验组初始的线虫数目。
1.2.4.3 线虫抗氧化蛋白荧光定量
以携带荧光蛋白标记基因的线虫CF1553和LD1171系列为对象,首先对线虫进行同步化,然后置于不同分子量肽段的培养液中,培养2 d后采用NaN3溶液对线虫麻醉,倒置荧光显微镜观察并采集图像,每个试验组约50条线虫。荧光强度参考王析瑞等[19]的方法,利用 Image J(版本1.8.0)软件处理图像,分析不同试验组的荧光强度。
1.2.5 不同方法处理高活性小分子肽得率
通过抗氧化实验确定活性最高的分子量范围肽段,首先将蛙皮蛋白酶解后的粗产物冷冻干燥并称重,然后将通过超滤膜的分子量<2000 Da小分子肽冷冻干燥并称重,计算不同方法试验组高活性小分子肽得率,即得率为分子量<2000 Da小分子肽占粗产物的比例,计算公式如下:
Y(%)=X1X×100 (4) 式中:Y表示高活性小分子肽得率,X1表示通过超滤膜的抗氧化活性最高的分子量范围(<2000 Da)肽段质量,X表示酶解粗产物的总质量。
1.2.6 响应面优化蛙皮小分子肽提取工艺
1.2.6.1 单因素实验
由于不同酶处理结果显示碱性蛋白酶的二次酶解对小分子肽得率影响较大,因此单因素选定碱性蛋白酶添加量、超高压压力、超高压时间和料液比。设定加酶量10000 U/g,压力200 MPa,保压时间5min,液料比10:1,固定其中3个因素,分别考察加酶量6000、8000、10000、12000、14000 U/g对得率的影响,压力0、10、200、3000、400 MPa对得率的影响,高压时间0、5、10、15、20 min对得率的影响,液料比5倍、10倍、15倍、20倍、25倍对分子量<2000 Da小分子肽得率的影响。
1.2.6.2 响应面试验设计
以单因素实验结果为依据,采用四因素三水平,设计了29组试验,包括7次重复,采用Box-Behnken方法建立响应面模型,以高活性小分子肽得率为指标,确定最优化提取工艺并验证。 响应面试验因素与水平见表1。
表 1 响应面试验因素与水平设计Table 1. Test factors and levels design of response surface水平 因素 A加酶量
(U/g)B超高压压力
(MPa)C超高压时间
(min)D液料比 −1 8000 200 5 10 0 10000 300 10 15 1 12000 400 15 20 1.3 数据处理
所有样品取样随机重复3次,试验除注明外均重复3次,结果以平均值加减标准差表示。采用SPSS软件单因素方差分析(ANOVA)对所有数据统计分析,P<0.05被认为具有显著差异。采用Origin 2018软件绘图,使用Design Expert 8.0.6.1软件进行响应面分析,Image J 1.8.0软件用于荧光强度分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同分子量的小分子肽体外抗氧化性能分析
2.1.1 不同分子量小分子肽DPPH 自由基清除能力分析
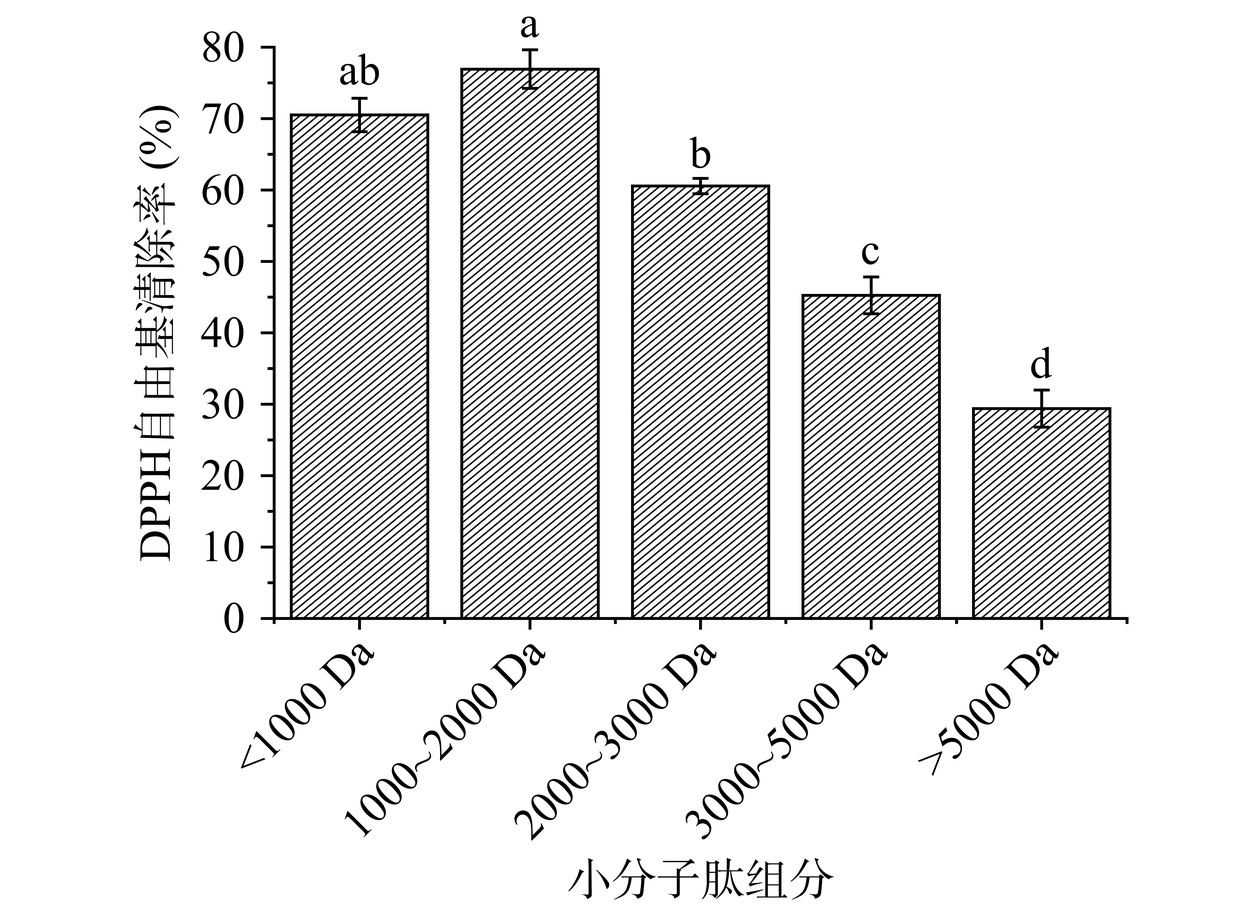
如图1所示,黑斑蛙皮不同分子量的小分子肽都具有一定的DPPH 自由基清除能力,并且整体上看分子量越小,DPPH自由基清除能力越强,分子量范围>5000 Da的组分抗氧化性最弱,分子量<3000 Da的小分子肽则表现出较强的抗氧化能力。有关研究证实小分子肽的抗氧化性能和分子量与氨基酸组成相关,LEE等[20]发现从牛肉中提取的生物活性肽分子量<3000 Da的组分也展现出了较强的DPPH自由基清除能力。
分子量较大的肽组分疏水氨基酸含量较低,并且抗氧化的基团被遮蔽,这可能是导致抗氧化性能相比小分子肽较低的原因[15],但是从图1可以看到分子量在1000~2000 Da的肽段DPPH自由基清除能力则超过了分子量<1000 Da的肽段,虽然很多研究都表示肽的分子量和抗氧化性能呈现负相关,但是BASHIR等[21]从鲭鱼分离的抗氧化肽中发现1049 Da的组分具有较高的抗氧化性,WU等[22]的研究也揭示鲭鱼水解物中分子量约为1400 Da的肽比900和200 Da的肽具有更强的体外抗氧化活性,这说明抗氧化肽的性能除了和分子量相关,还受到特定的氨基酸序列的影响。
2.1.2 不同分子量小分子肽ABTS+自由基清除能力分析
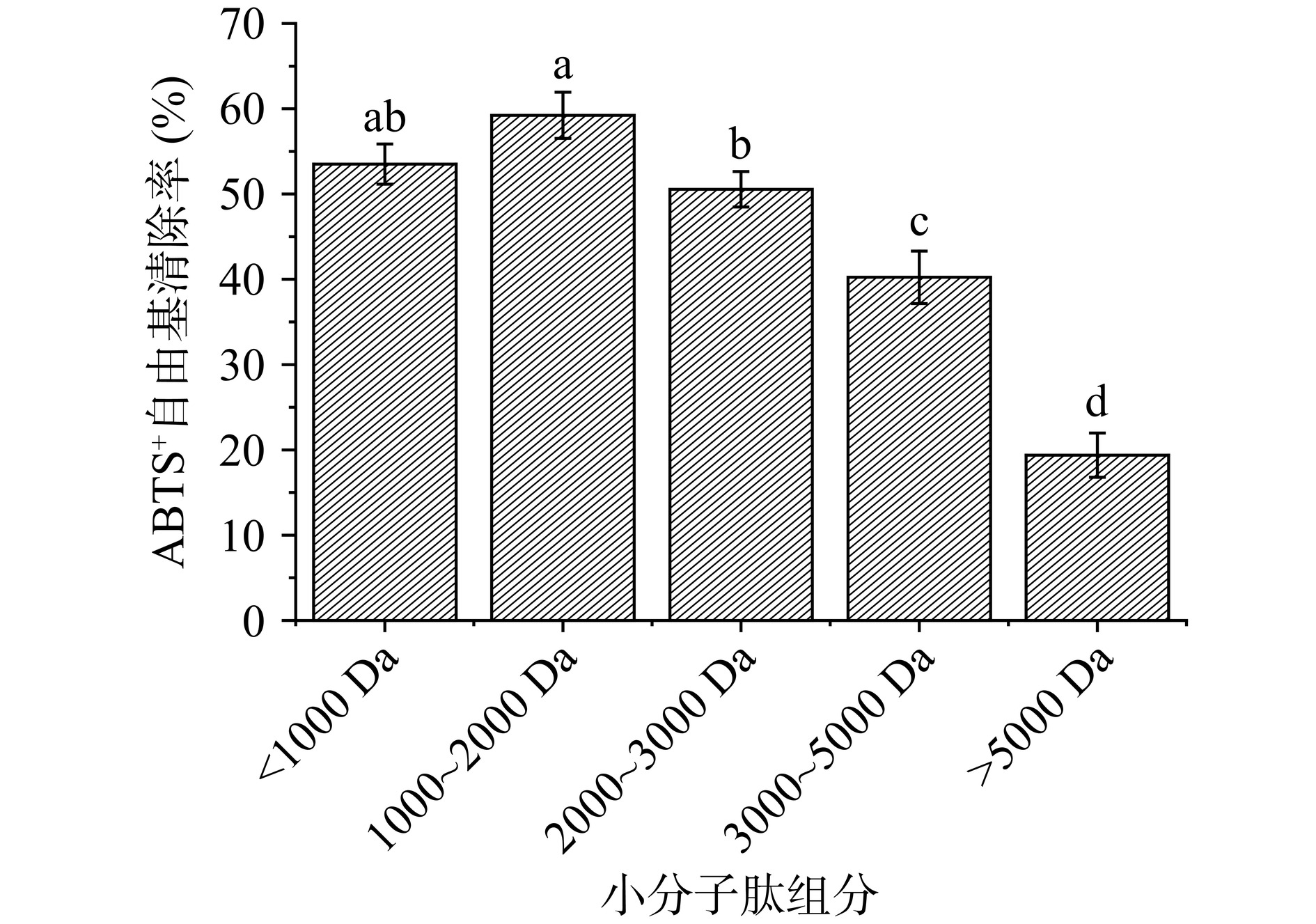
图2展示了不同分子量的黑斑蛙皮小分子肽对ABTS+自由基的清除能力。<5000 Da的小分子肽都具有一定的ABTS+自由基清除能力,与DPPH 自由基清除能力类似,1000~2000 Da的ABTS+自由基清除能力最强,其次为<1000 Da的肽段。LI等[23]在对鱼鳔抗氧化肽分离中发现,在不同分子量范围内,分子量范围为5000~100000 Da的肽组分ABTS+自由基清除率高于3000 Da肽组分,说明不同来源的抗氧化肽ABTS+自由基清除能力与分子量的关系存在差异,另外也证实了并不是分子量越小的小分子肽抗氧化能力就越强。
2.2 不同分子量的小分子肽对秀丽隐杆线虫抗氧化性能的影响分析
2.2.1 线虫氧化应激抗性分析
当机体受到氧化因素的刺激,会激发抗氧化反应,但是抗氧化能力不足的时候,体内就会积累自由基等过氧化物,损害细胞线粒体的结构和功能,从而导致细胞程序性死亡,引发机体衰老[24]。不同分子量的蛙皮小分子肽喂食秀丽隐杆线虫,对其氧化应激抗性的影响如表2所示。
表 2 不同分子量的肽段对线虫氧化应激抗性的影响Table 2. Effects of peptides with different molecular weights on oxidative stress resistance of Caenorhabditis elegans试验组 平均寿命(h) 存活时间提高率(%) 对照组 8.36±0.23d − <1000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 10.26±0.29ab 21.34 1000~2000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 10.91±0.15a 30.50 2000~3000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 10.03±0.18b 19.98 3000~5000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 9.54±0.24c 14.11 >5000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 9.17±0.31c 9.68 注:不同字母表示试验组之间存在显著性差异(P<0.05),表3同。 在过氧化氢溶液的刺激下,喂食蒸馏水的线虫平均寿命为8.36 h,<2000 Da小分子肽给药试验组线虫寿命达到了10.26 h,系比对照组提高了约30%,在所有试验组中存活寿命最高。其次是<1000 Da肽段给药组,>5000 Da肽段给药组则对线虫的寿命影响不明显,和对照组相比差异不显著。数据表明从黑斑蛙皮中提取1~2000 Da小分子肽具有较高的抗氧化性能,这与体外抗氧化试验结果一致。线虫氧化应激抗性试验意味着从黑斑蛙皮中分离小分子肽,特别是分子量<2000 Da的肽段,可以作为抗氧化剂用于功能食品开发,具有一定的市场应用潜力。
2.2.2 线虫热应激抗性分析
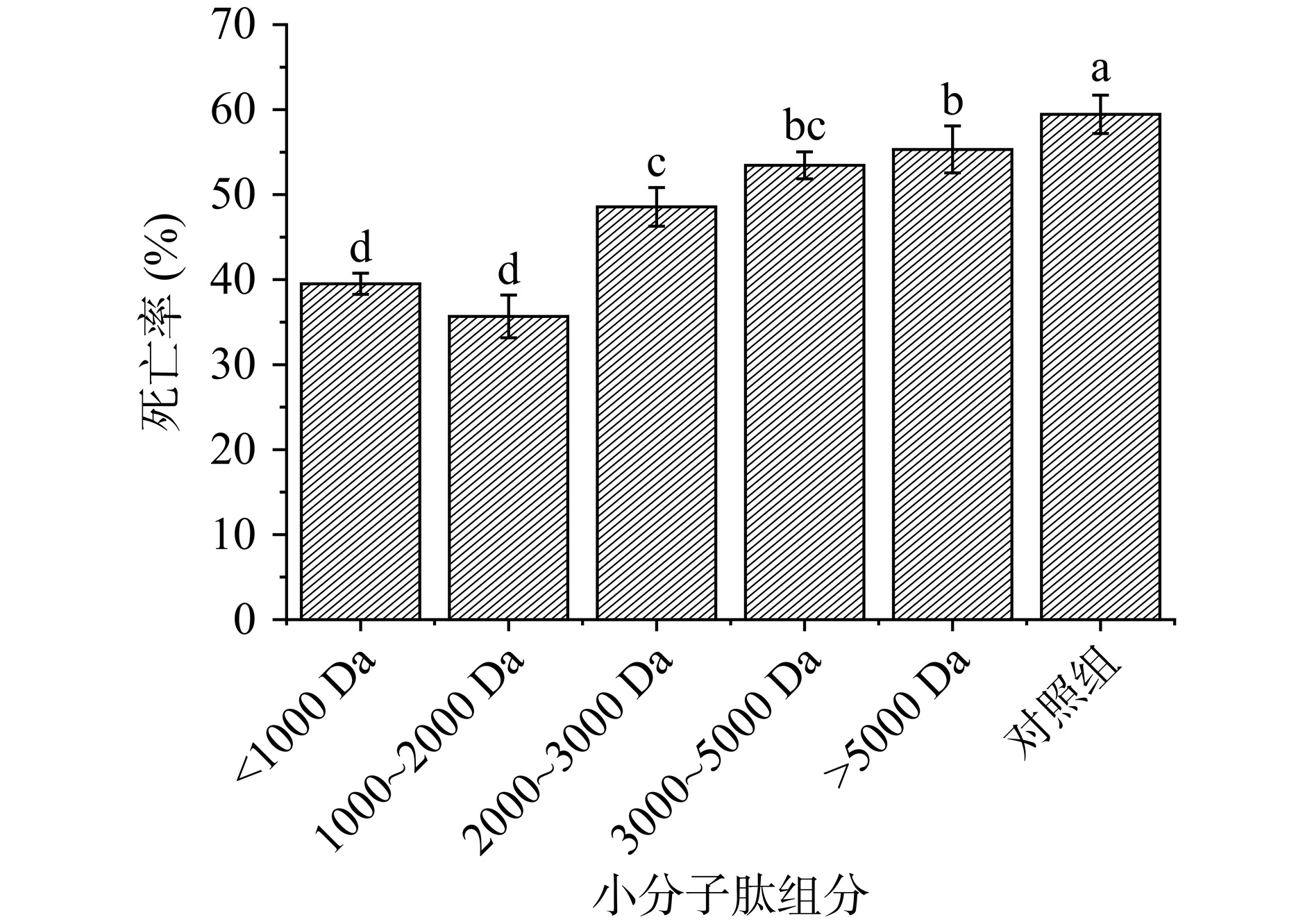
热应激被认为是刺激活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)产生并引起氧化应激的环境因素,过量的ROS会刺激自由基介导的链式反应以及对脂质、DNA和其他物质的无差别靶向攻击[25]。
图3的结果表明,分子量<2000 Da的肽段可以显著(P<0.05)抑制热应激反应。烘箱内高温1 h后对照组死亡率达到了约60%,而1000~2000 Da小分子肽给药组死亡率则只有约35%,由此可见黑斑蛙皮小分子肽可以提高线虫机体的抵抗力。
2.2.3 线虫氧荧光表达量分析
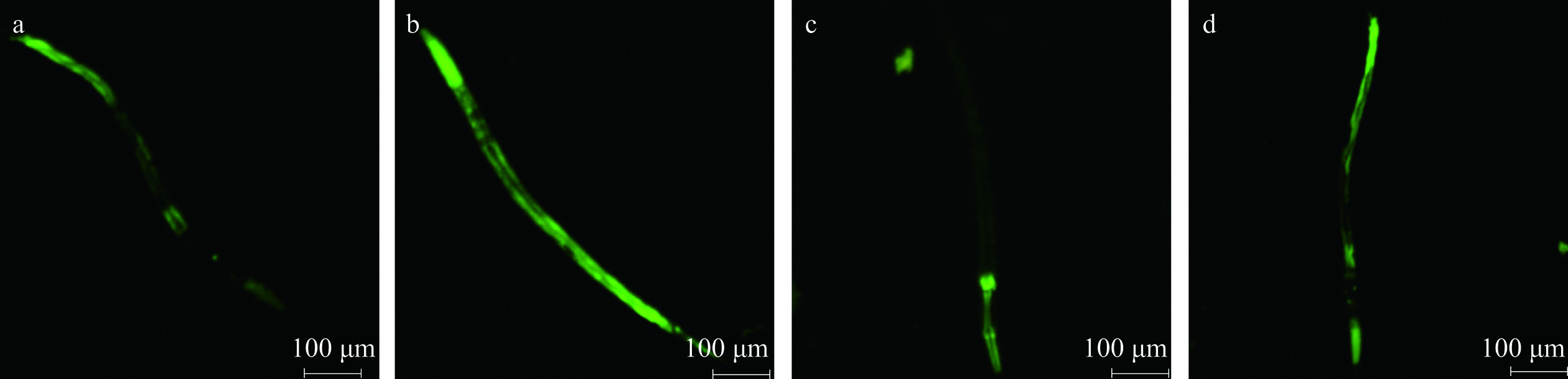
荧光强度可以表征超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、谷氨酸半胱氨酸合成酶(glutamate-cysteine synthesase,GCS)的表达量。CF1553 线虫荧光强度反应SOD-3 蛋白的表达,LD1171 线虫荧光强度则反应GCS-1 蛋白的表达。线虫体内具有抗氧化的活性物质会刺激SOD-3和GCS-1等抗氧化蛋白的表达,在蓝光照射下会影响荧光的强度,表达量与荧光强度之间存在正相关[26−27],荧光显微镜下可以明显看到绿色荧光差异,图4为喂食1000~2000 Da小分子肽试验组与空白组的对比。
不同分子量的蛙皮小分子肽喂食转基因秀丽隐杆线虫,对其荧光表达量的影响如表3所示。CF1533线虫和LD1171线虫在喂食黑斑蛙皮小分子肽后,荧光强度相比对照组都有所增强,特别是1000~2000 Da肽段试验组提高的幅度最大,说明小分子肽可以提高线虫抗氧化蛋白的表达,其原因可能是与DAF-16 转录因子有关,推测小分子肽可以提高该转录因子的转录活性[28]。
表 3 不同分子量的肽段对线虫荧光表达量的影响Table 3. Effects of peptides with different molecular weights on fluorescence expression of Caenorhabditis elegans试验组 CF1553荧光表达量 LD1171荧光表达量 对照组 92.25±3.21e 82.41±2.09d <1000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 116.46±2.78b 102.34±1.69b 1000~2000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 120.06±3.05a 109.42±3.60a 2000~3000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 105.47±3.62c 101.52±3.11b 3000~5000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 96.71±1.56d 89.43±2.15c >5000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 94.34±2.66de 85.06±1.79cd 2.3 不同提取方式高活性小分子肽得率分析
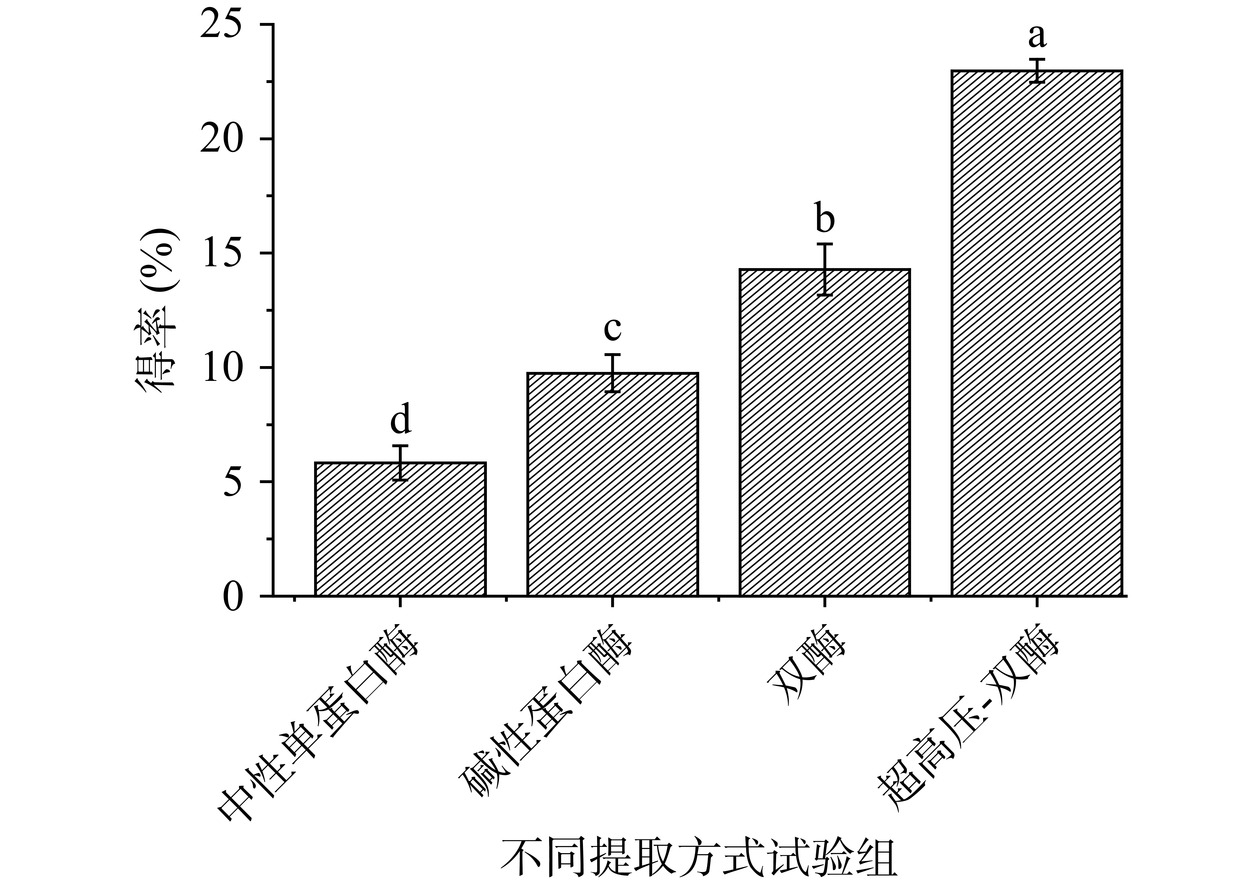
由图5可知,中性蛋白酶处理的小分子肽得率最低,1000~2000 Da肽段的得率只有5.82%,碱性蛋白酶效果要好一些,但是得率依然不到10%,双酶处理可以显著提升得率,而效果最好的超高压-双酶试验组得率达到了22.97%。试验结果说明碱性蛋白酶二次水解和超高压处理是提高活性小分子肽的有效手段,其他研究也有类似结论,刘子毅等[29]的研究也发现超高压处理联合碱性蛋白酶可以提高玉米黄粉ACE抑制肽的得率。为了进一步提高高活性小分子肽的得率,后续对试验条件进行响应面优化。
2.4 响应面试验结果分析
2.4.1 单因素实验结果分析
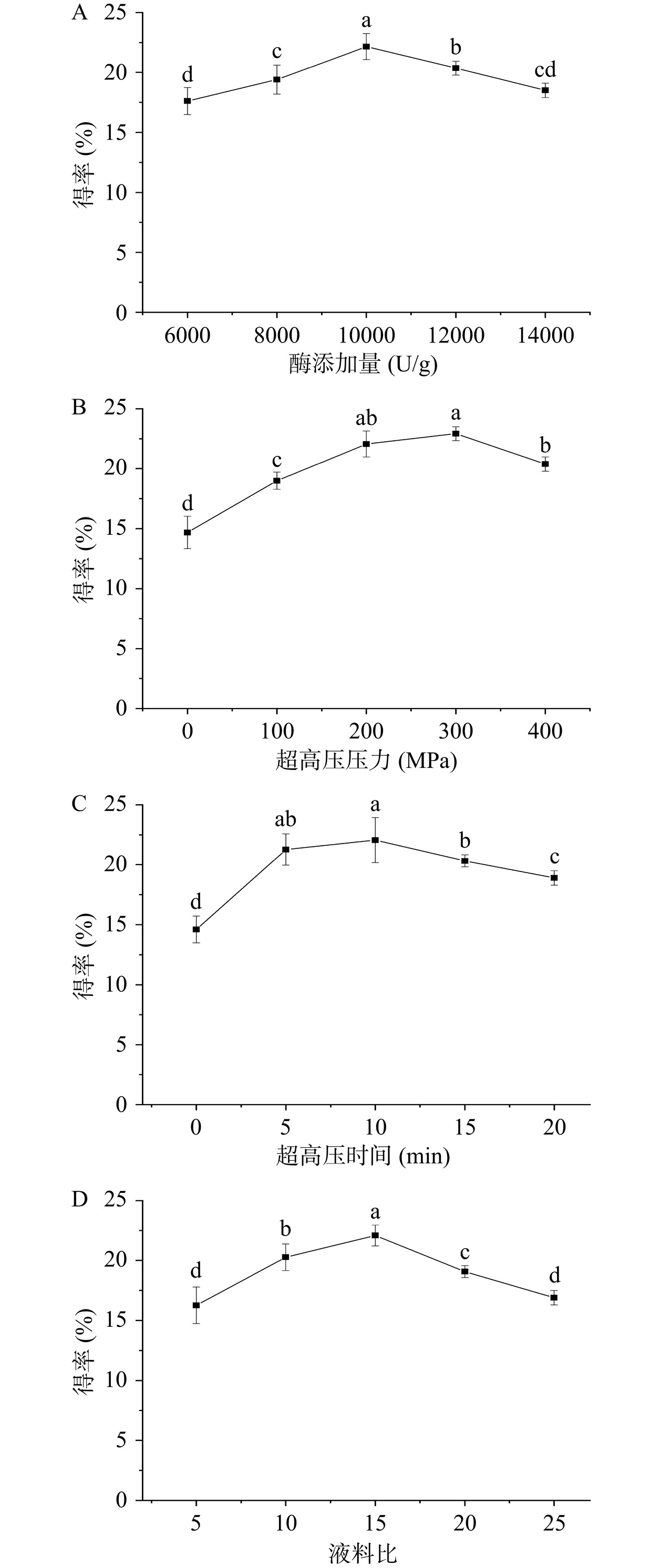
单因素实验结果如图6所示。由图6A可知,小分子肽得率随着酶添加量的增加逐渐增大,在10000 U/g时得率达到最高为22.16%,酶添加量进一步加大,得率呈现下降的趋势,QIAN等[30]在用碱蛋白酶从大眼金枪鱼暗肌中提取ACE抑制肽的研究也得到类似的结论,原因可能是酶浓度过高会与底物形成复合物阻碍水解,酶浓度过高还会导致酶活下降,另外推测酶浓度过高也可能会导致目标分子量肽段解离为更小的肽段而降低得率。有可能合适的酶添加量是提高得率的关键因素。图6B显示超高压适度的处理有利于提高小分子肽得率,在300 MPa时达到最高,此后随着压力的增大而下降,超高压时间对得率的影响也有类似的趋势(图6C),在10 min时达到最高,可能是过高的压力和过长的保压时间会引起蛋白质的过度聚集,不利于蛋白酶和底物的接触,另外压力作用下蛋白质被压实,也不利于蛋白酶的作用[31]。图6D表明液料比为15倍时得率最高,超高压是通过液体传递压力,所以适当的水分可以起到溶解和传递压力的作用,液料比过低导致黏度过高,但是过高的液料比会降低底物浓度,都不利于酶的水解进行[32]。
2.4.2 响应面优化试验结果分析
根据单因素实验结果,选择加酶量8000~12000 U/g,超高压压力200~400 MPa,超高压时间 5~15 min,液料比10~20倍进行响应面试验。响应面试验结果如表4所示,方差分析如表5所示。
表 4 响应面优化试验设计及结果Table 4. Experimental design and results of response surface optimization试验号 A加酶量
(U/g)B超高压压力
(MPa)C超高压时间
(min)D液料比 得率
(%)1 8000 300 10 10 20.82 2 10000 300 10 15 24.64 3 12000 300 10 20 22.72 4 10000 300 5 20 22.41 5 12000 400 10 15 21.82 6 8000 300 5 15 21.48 7 10000 400 10 20 23.52 8 10000 200 5 15 21.1 9 10000 400 10 10 21.83 10 12000 200 10 15 21.75 11 10000 200 15 15 21.61 12 10000 400 5 15 21.98 13 10000 400 15 15 21.01 14 8000 300 15 15 21.08 15 10000 300 15 10 21.55 16 10000 300 10 15 24.44 17 10000 200 10 10 22.46 18 8000 400 10 15 21.85 19 10000 300 10 15 24.56 20 8000 200 10 15 19.98 21 12000 300 15 15 21.1 22 10000 300 10 15 24.21 23 10000 200 10 20 21.44 24 8000 300 10 20 21.93 25 12000 300 5 15 22.52 26 12000 300 10 10 21.89 27 10000 300 10 15 24.09 28 10000 300 15 20 22.1 29 10000 300 5 10 22.92 表 5 小分子肽提取试验方差分析Table 5. Analysis of variance for small molecule peptide extraction experiments来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 39.74 14 2.84 22.39 <0.0001 *** A 1.81 1 1.81 14.25 0.002 ** B 1.13 1 1.13 8.92 0.0098 ** C 1.31 1 1.31 10.36 0.0062 ** D 0.59 1 0.59 4.62 0.0496 * AB 0.81 1 0.81 6.42 0.0239 * AC 0.26 1 0.26 2.07 0.1724 AD 0.02 1 0.02 0.15 0.7041 BC 0.55 1 0.55 4.34 0.0500 BD 1.84 1 1.84 14.51 0.0019 ** CD 0.28 1 0.28 2.24 0.1566 A2 16.88 1 16.88 133.17 <0.0001 *** B2 13.39 1 13.39 105.63 <0.0001 *** C2 12.20 1 12.20 96.25 <0.0001 *** D2 3.97 1 3.97 31.29 <0.0001 *** 残差 1.77 14 0.13 失拟项 1.56 10 0.16 2.88 0.1597 不显著 误差项 0.22 4 0.05 总误差 41.51 28 R2=0.9572 R2Adj=0.9145 注:*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001。 利用方差分析得到响应面模型的二次多项式回归方程,可表示为:
Y=24.39+0.39A+0.31B−0.33C+0.22D−0.45AB−0.26AC−0.069AD−0.37BC+0.68BD+0.27CD−1.61A2−1.44B2−1.37C2−0.78D2
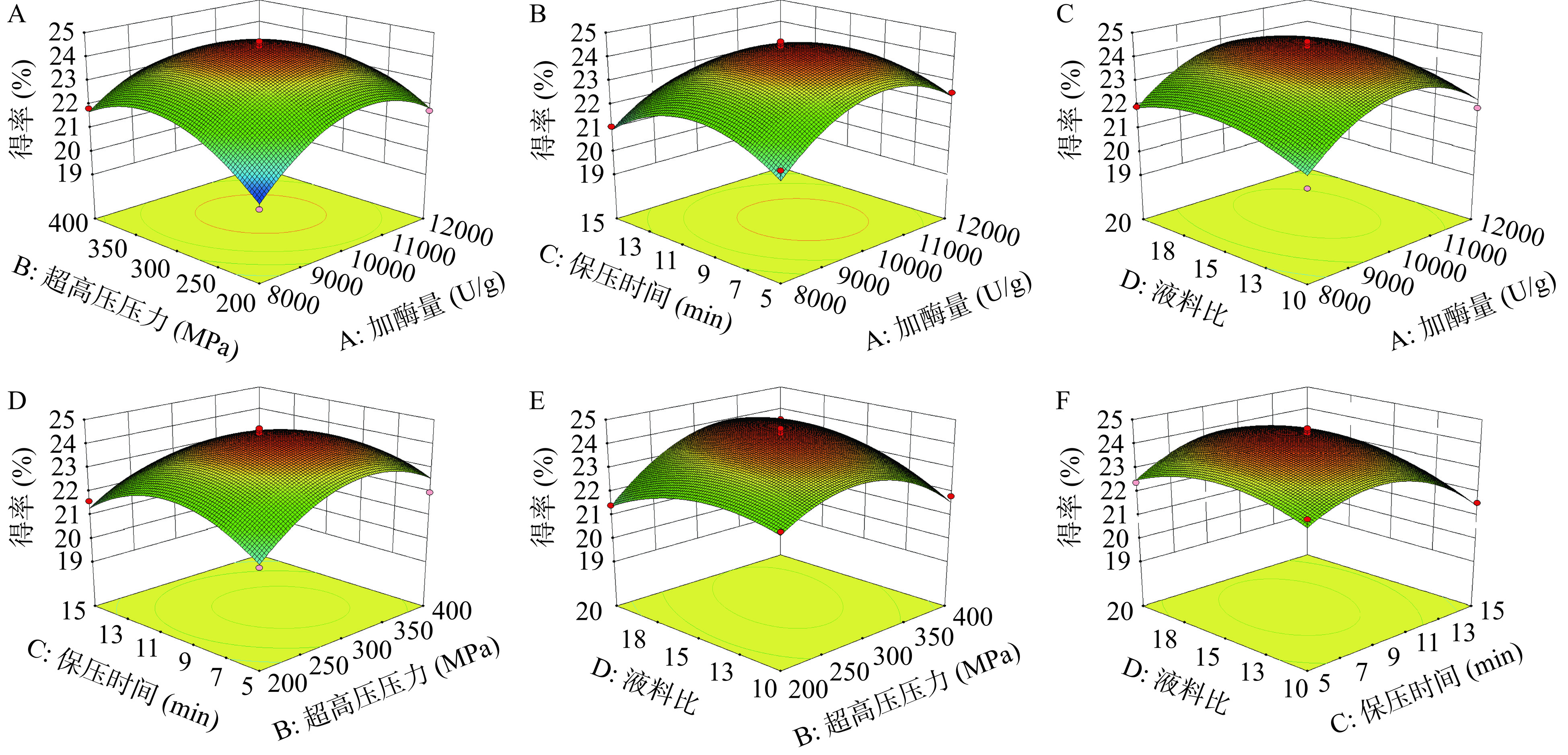
表5的结果显示R2和R2Adj均>0.9,回归模型的P值<0.0001为极显著,而失拟项不显著,这表明了该模型的结果准确可靠,此外C.V.%为1.60,表明各模型方差系数的数据具有较低的离散度,进一步证明了模型的良好拟合性[33]。由表5可知,加酶量、超高压压力、超高压时间对得率的影响非常显著,液料比影响显著,对得率的影响顺序A>C>B>D。通过对图7的曲面陡峭程度以及等高线密度分析,可知加酶量与超高压压力、超高压压力与液料比之间均存在较强的交互作用,红色代表试验的极值范围,其中红色中心是最佳值,使用单向分析得到了类似的结果,响应值从中心点向外明显减小,表明其受试验因素波动的影响较大。
响应面回归优化小分子肽提取最佳提取参数为:加酶量10211.7 U/g,超高压压力315 MPa,压力作用时间9.33 min,液料比16倍,预测此条件下小分子肽得率为25.47%。结合实际操作的便利性,确定最佳最佳工艺参数为加酶量10210 U/g,超高压压力315 MPa,压力作用时间9.3 min,液料比16倍,按照此进行试验验证,三次试验的平均值为25.26%,与预测值25.47%接近,表明响应面优化超高压辅助双酶提取黑斑蛙皮小分子肽结果可靠,具有应用价值和参考意义。
3. 结论
本研究利用不同提取方式从黑斑蛙皮中提取小分子肽,并研究了不同分子量小分子肽的抗氧化性能,体外抗氧化和线虫试验结果表明,1~2000 Da小分子肽相比较其他分子量组分,抗氧化能力最强。通过响应面优化,1~2000 Da小分子肽最佳提取工艺确定为:首先中性蛋白酶处理,料液比1:10混合,用量10000 U/g,pH调节至5.5~6.0,时间4 h,所得的产物加16倍蒸馏水然后超高压处理,超高压压力315 MPa,压力作用时间9.3 min,最后加入碱性蛋白酶(加酶量10210 U/g)二次酶解,pH为7.5,酶解时间为3 h,最终1~2000 Da小分子肽得率为25.26%。综上,黑斑蛙皮中1~2000 Da小分子肽具有作为天然抗氧化剂的潜力,超高压辅助双酶水解法能显著提高1~2000 Da小分子肽的得率,为黑斑蛙皮的高值化利用提供了理论依据和技术支持。
-
表 1 响应面试验因素与水平设计
Table 1 Test factors and levels design of response surface
水平 因素 A加酶量
(U/g)B超高压压力
(MPa)C超高压时间
(min)D液料比 −1 8000 200 5 10 0 10000 300 10 15 1 12000 400 15 20 表 2 不同分子量的肽段对线虫氧化应激抗性的影响
Table 2 Effects of peptides with different molecular weights on oxidative stress resistance of Caenorhabditis elegans
试验组 平均寿命(h) 存活时间提高率(%) 对照组 8.36±0.23d − <1000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 10.26±0.29ab 21.34 1000~2000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 10.91±0.15a 30.50 2000~3000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 10.03±0.18b 19.98 3000~5000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 9.54±0.24c 14.11 >5000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 9.17±0.31c 9.68 注:不同字母表示试验组之间存在显著性差异(P<0.05),表3同。 表 3 不同分子量的肽段对线虫荧光表达量的影响
Table 3 Effects of peptides with different molecular weights on fluorescence expression of Caenorhabditis elegans
试验组 CF1553荧光表达量 LD1171荧光表达量 对照组 92.25±3.21e 82.41±2.09d <1000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 116.46±2.78b 102.34±1.69b 1000~2000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 120.06±3.05a 109.42±3.60a 2000~3000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 105.47±3.62c 101.52±3.11b 3000~5000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 96.71±1.56d 89.43±2.15c >5000 Da组分(100 μg/mL) 94.34±2.66de 85.06±1.79cd 表 4 响应面优化试验设计及结果
Table 4 Experimental design and results of response surface optimization
试验号 A加酶量
(U/g)B超高压压力
(MPa)C超高压时间
(min)D液料比 得率
(%)1 8000 300 10 10 20.82 2 10000 300 10 15 24.64 3 12000 300 10 20 22.72 4 10000 300 5 20 22.41 5 12000 400 10 15 21.82 6 8000 300 5 15 21.48 7 10000 400 10 20 23.52 8 10000 200 5 15 21.1 9 10000 400 10 10 21.83 10 12000 200 10 15 21.75 11 10000 200 15 15 21.61 12 10000 400 5 15 21.98 13 10000 400 15 15 21.01 14 8000 300 15 15 21.08 15 10000 300 15 10 21.55 16 10000 300 10 15 24.44 17 10000 200 10 10 22.46 18 8000 400 10 15 21.85 19 10000 300 10 15 24.56 20 8000 200 10 15 19.98 21 12000 300 15 15 21.1 22 10000 300 10 15 24.21 23 10000 200 10 20 21.44 24 8000 300 10 20 21.93 25 12000 300 5 15 22.52 26 12000 300 10 10 21.89 27 10000 300 10 15 24.09 28 10000 300 15 20 22.1 29 10000 300 5 10 22.92 表 5 小分子肽提取试验方差分析
Table 5 Analysis of variance for small molecule peptide extraction experiments
来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 39.74 14 2.84 22.39 <0.0001 *** A 1.81 1 1.81 14.25 0.002 ** B 1.13 1 1.13 8.92 0.0098 ** C 1.31 1 1.31 10.36 0.0062 ** D 0.59 1 0.59 4.62 0.0496 * AB 0.81 1 0.81 6.42 0.0239 * AC 0.26 1 0.26 2.07 0.1724 AD 0.02 1 0.02 0.15 0.7041 BC 0.55 1 0.55 4.34 0.0500 BD 1.84 1 1.84 14.51 0.0019 ** CD 0.28 1 0.28 2.24 0.1566 A2 16.88 1 16.88 133.17 <0.0001 *** B2 13.39 1 13.39 105.63 <0.0001 *** C2 12.20 1 12.20 96.25 <0.0001 *** D2 3.97 1 3.97 31.29 <0.0001 *** 残差 1.77 14 0.13 失拟项 1.56 10 0.16 2.88 0.1597 不显著 误差项 0.22 4 0.05 总误差 41.51 28 R2=0.9572 R2Adj=0.9145 注:*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001。 -
[1] 何志刚, 伍远安, 徐永福, 等. 野生与养殖黑斑蛙肌肉营养品质的比较分析[J]. 水产科学,2019,38(4):506−513. [HE Z G, WU Y A, XU Y F, et al. Comparative analysis on nutritional quality of muscles between wild and cultured black-spotted frog rana nigromaculata[J]. Aquatic Science,2019,38(4):506−513.] HE Z G, WU Y A, XU Y F, et al. Comparative analysis on nutritional quality of muscles between wild and cultured black-spotted frog rana nigromaculata[J]. Aquatic Science, 2019, 38(4): 506−513.
[2] 李健, 曹原浩, 苏德锦, 等. 中国7种养殖食用蛙类副产品精深加工的研究进展[J]. 集美大学学报(自然科学版),2023,28(3):222−229. [LI J, CAO Y H, SU D J, et al. Research progress on deep processing of seven species of edible frog by-products in China[J]. Journal of Jimei University (Natural Science),2023,28(3):222−229.] LI J, CAO Y H, SU D J, et al. Research progress on deep processing of seven species of edible frog by-products in China[J]. Journal of Jimei University (Natural Science), 2023, 28(3): 222−229.
[3] 劳梦甜, 曾璐瑶, 王海滨, 等. 黑斑蛙副产物营养成分分析与综合利用评价[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(11):129−135. [LAO M T, ZENG L Y, WANG H B, et al. Nutrient composition analysis and comprehensive utilization evaluation of by-products of frog ( Rana Nigromaculata)[J]. Food Technology,2022,47(11):129−135.] LAO M T, ZENG L Y, WANG H B, et al. Nutrient composition analysis and comprehensive utilization evaluation of by-products of frog ( Rana Nigromaculata)[J]. Food Technology, 2022, 47(11): 129−135.
[4] HADDAD R L, ORTIGOZA V T, CAMPO S T M, et al. Evaluation of nutritional composition and technological functionality of whole American Bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus), its skin, and its legs as potential food ingredients[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,372:131232.1−131232.7.
[5] YANG L H, GUO Z L, WEI J Q, et al. Extraction of low molecular weight peptides from bovine bone using ultrasound-assisted double enzyme hydrolysis:Impact on the antioxidant activities of the extracted peptides[J]. LWT,2021,146:111470. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111470
[6] ELANGO J, ROBINSON J, ZHANG J Y, et al. Collagen peptide upregulates osteoblastogenesis from bone marrow mesenchymal Stem cells through MAPK- Runx2[J]. Cells,2019,8:446. doi: 10.3390/cells8050446
[7] YANG X L, JIA Q J, DUAN F H, et al. Multiwall carbon nanotubes loaded with MoS2 quantum dots and MXene quantum dots:Non–Pt bifunctional catalyst for the methanol oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions in alkaline solution[J]. Applied Surface Science,2019,464:78−87. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.09.069
[8] LI J Z, YANG L, LI G Y, et al. Low-molecular-weight oyster peptides ameliorate cyclophosphamide-chemotherapy side-effects in Lewis lung cancer mice by mitigating gut microbiota dysbiosis and immunosuppression[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2022,95:105196. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2022.105196
[9] ARIHARA K, YOKOYAMA I, OHATA M. Bioactivities generated from meat proteins by enzymatic hydrolysis and the Maillard reaction[J]. Meat Science,2021,180:108561. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2021.108561
[10] SUN S S, GAO Y H, CHEN J D, et al. Identification and release kinetics of peptides from tilapia skin collagen during alcalase hydrolysis[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,378:132089. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132089
[11] KARNJANAPRATUM S, BENJAKUL S. Asian bullfrog (Rana tigerina) skin gelatin extracted by ultrasound-assisted process:Characteristics and in vitro cytotoxicity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,148:391−400. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.01.150
[12] 胡爱军, 王威, 于作昌, 等. 超高压技术在果品加工中的应用研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2024,45(2):212−217. [HU A J, WANG W, YU Z C, et al. Research progress on application of ultra-high pressure technology in fruit processing[J]. Food Research and Development,2024,45(2):212−217.] HU A J, WANG W, YU Z C, et al. Research progress on application of ultra-high pressure technology in fruit processing[J]. Food Research and Development, 2024, 45(2): 212−217.
[13] THORESEN P P, ÁLVAREZ R G, VAKA M R, et al. Potential of innovative pre-treatment technologies for the revalorisation of residual materials from the chicken industry through enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2020,64:102377.
[14] 王艳茹, 王欣悦, 何龙, 等. 超高压辅助酶解制备胶原蛋白抗氧化肽及构效分析[J/OL]. 食品科学, 1−17[2024-02-23]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.TS.20231218.0844.004.html. [WANG Y R, WANG X Y, HE L, et al. Preparation of collagen antioxidant peptides by ultrahigh-pressure-assisted enzymatic digestion and constitutive analysis [J/OL]. Food Science, 1−17[2024-02-23]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.TS.20231218.0844.004.html.] WANG Y R, WANG X Y, HE L, et al. Preparation of collagen antioxidant peptides by ultrahigh-pressure-assisted enzymatic digestion and constitutive analysis [J/OL]. Food Science, 1−17[2024-02-23]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.TS.20231218.0844.004.html.
[15] 蔡路昀, 冷利萍, 李秀霞, 等. 草鱼鱼皮不同分子量肽段体外抗氧化性能的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(12):58−64. [CAI L Y, LENG L P, LI X X, et al. Evaluation of the in vitro antioxidant properties of different molecular weight peptide fractions from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) skin[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(12):58−64.] CAI L Y, LENG L P, LI X X, et al. Evaluation of the in vitro antioxidant properties of different molecular weight peptide fractions from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) skin[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2017, 38(12): 58−64.
[16] BOUGATEF A, NEDJAR A N, MANNI L, et al. Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) by-products proteins[J]. Food Chemistry,2010,118(3):559−565. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.05.021
[17] HE P, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Y Z, et al. Isolation, identification of antioxidant peptides from earthworm proteins and analysis of the structure–activity relationship of the peptides based on quantum chemical calculations[J]. Food Chemistry,2024,431:137137. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137137
[18] 吴梦思, 金建宇, 尚书游, 等. 卷丹百合黄酮提取物抗氧化活性研究[J/OL]. 食品与发酵工业, 1−9[2024-02-23]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.036421. [WU M S, JIN J Y, SHANG S Y. et al. Study on antioxidant activity of Lilium lancifolium Thunb flavonoid extract [J/OL]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 1−9[2024-02-23]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.036421.] WU M S, JIN J Y, SHANG S Y. et al. Study on antioxidant activity of Lilium lancifolium Thunb flavonoid extract [J/OL]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 1−9[2024-02-23]. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.036421.
[19] 王析瑞, 刘永建, 刘岑, 等. 邻甲氧基肉桂酸抗衰老活性及机制研究[J]. 中国现代中药,2022,24(8):1481−1486. [WANG X R, LIU Y J, LIU C, et al. Anti-aging activity and mechanism of o-methoxycinnamic acid[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine,2022,24(8):1481−1486.] WANG X R, LIU Y J, LIU C, et al. Anti-aging activity and mechanism of o-methoxycinnamic acid[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2022, 24(8): 1481−1486.
[20] LEE S Y, LEE D Y, HUR S J. Changes in the stability and antioxidant activities of different molecular weight bioactive peptide extracts obtained from beef during in vitro human digestion by gut microbiota[J]. Food Research International,2021,141:110116. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110116
[21] BASHIR K M I, SOHN J H, KIM J S, et al. Identification and characterization of novel antioxidant peptides from mackerel (Scomber japonicus) muscle protein hydrolysates[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,323:126809. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126809
[22] WU H C, CHEN H M, SHIAU C Y. Free amino acids and peptides as related to antioxidant properties in protein hydrolysates of mackerel (Scomber austriasicus)[J]. Food Research International,2003,36(9):949−957.
[23] LI S X, GU J H, ZHONG B L, et al. Isolation and purification of antioxidant peptides from swim bladder of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J/OL]. Aquaculture and Fisheries, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aaf.2023.12.009.
[24] FU W, DAI C, MA Z F, et al. Enhanced glutathione production protects against zearalenone-induced oxidative stress and ferroptosis in female reproductive system[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2024,185:114462. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2024.114462
[25] ZHANG S X, WANG D L, QI J J, et al. Chlorogenic acid ameliorates the heat stress-induced impairment of porcine Sertoli cells by suppressing oxidative stress and apoptosis[J]. Theriogenology,2024,214:148−156. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2023.10.018
[26] BALKRISHNA A, GOHEL V, PATHAK N, et al. Anti-oxidant response of lipidom modulates lipid metabolism in Caenorhabditis elegans and in OxLDL-induced human macrophages by tuning inflammatory mediators[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2023,160:114309.
[27] YANG Y Q, CHEN X, YE D Y, et al. Exploring the anti-aging effects of chlorogenic acid and the underlying mechanisms based on a Caenorhabditis elegans model[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medical Sciences,2023,10(2):208−217. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcms.2023.02.003
[28] AI L, LUO D, WANG H L, et al. Ameliorative effects of bifidobacterium longum peptide-1 on benzo(α)pyrene induced oxidative damages via daf-16 in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Cell Stress and Chaperones,2023,28(6):909−920. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01385-2
[29] 刘子毅, 顾丰颖, 王博伦, 等. 超高压协同碱性蛋白酶制备玉米黄粉ACE抑制肽[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(4):222−228. [LIU Z Y, GU F Y, WANG B L, et al. Preparation of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from corn gluten meal by ultra-high pressure-assisted alcalase hydrolysis[J]. Food science,2020,41(4):222−228.] LIU Z Y, GU F Y, WANG B L, et al. Preparation of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from corn gluten meal by ultra-high pressure-assisted alcalase hydrolysis[J]. Food science, 2020, 41(4): 222−228.
[30] QIAN Z J, JE J Y, SK K. Anti hypertensive effect of anglotensin I converting enzyme-inhibitory peptide from hydrolysates of bigeye tuna dark muscle, Thunnus obesus[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2007,55(21):8398−8403. doi: 10.1021/jf0710635
[31] ZHANG Y C, SUN Q X, LIU S C, et al. Extraction of fish oil from fish heads using ultra-high pressure pre-treatment prior to enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2021,70:102670.
[32] 吴玉娟, 陈壹刘, 张靖松, 等. 超高压辅助酶解豌豆蛋白工艺优化研究[J]. 粮食与油脂,2023,36(11):90−94. [WU Y J, CHEN Y L, ZHANG J S, et al. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of pea protein assisted by ultra-high pressure[J]. Cereals & Oils,2023,36(11):90−94.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2023.11.020 WU Y J, CHEN Y L, ZHANG J S, et al. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of pea protein assisted by ultra-high pressure[J]. Cereals & Oils, 2023, 36(11): 90−94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2023.11.020
[33] MAZAREI F, JOOYANDEH H, NOSHAD M, et al. Polysaccharide of caper (Capparis spinosa L.) Leaf:Extraction optimization, antioxidant potential and antimicrobial activity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2017, 95:224−231.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



