Quality Evaluation of Fresh Cayenne Pepper for Chili Sauce from Different Origins
-
摘要: 目的:卡宴辣椒是国外辣椒酱加工生产常用品种,但在国内少有研究和应用。同时,辣椒酱加工行业品种选择缺乏科学规范和指导。亟需探明酱用卡宴辣椒原料品质特征,挖掘不同产地卡宴辣椒品质差异,为酱用辣椒品种选择提供科学数据支撑。方法:针对甘肃酒泉和内蒙古巴彦淖尔两产地卡宴辣椒,采用靶向检测结合非靶向代谢组学技术,测定原料水分、糖、酸、蛋白质、辣椒碱、类胡萝卜素、挥发性及非挥发性化合物等20余项指标。结果:甘肃和内蒙两产地卡宴辣椒水分含量分别为86.1%和87.9%,总还原糖含量分别为5.28 g/100 g和4.67 g/100 g,总酸含量分别为4.44 g/kg和5.09 g/kg,辣度分别为1386.26 SHU和1116.41 SHU;其中甘肃产地卡宴辣椒糖含量更高、辣度更高、挥发性香气化合物更加丰富,包括水杨酸甲酯、3-甲基丁酸乙酯、芳樟醇等;内蒙产地卡宴辣椒酸度更高,抗氧化能力更强,非挥发性代谢物更为丰富,包括7-羟基香豆素、槲皮素、植物鞘氨醇等。结论:卡宴辣椒具有糖含量高、辣度低、籽肉比低、富含香气和滋味物质等特点,满足辣椒制酱加工需求。不同地区种植的卡宴辣椒在品质方面略有差异,因此在选择制酱用辣椒前对不同产地原料评价至关重要。本研究将为国内酱用辣椒品种的选育和加工企业品种的选择提供科学指导。Abstract: Objective: Cayenne pepper is a common variety used in the production of chili sauce abroad. However, it is rarely studied and applied in China. Meanwhile, variety selection for chili pepper processing industry is lack of scientific guidance. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct the quality evaluation of fresh cayenne pepper, and summary the quality characteristics of sauce using peppers, in order to provide a scientific basis for variety selection. Methods: Targeted detection combined with non-targeted metabolomics technology were employed to conduct the quality evaluation on cayenne pepper from Jiuquan City, Gansu Province and Bayannur City, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. More than 20 indicators such as moisture, sugar, acid, protein, capsaicinoids, carotenoids, volatile and non-volatile compounds were analyzed. Results: The moisture content of cayenne pepper from Gansu and Inner Mongolia was 86.1% and 87.9%, the total reducing sugar content was 5.28 g/100 g and 4.67 g/100 g, the total acid content was 4.44 g/kg and 5.09 g/kg, and the spiciness level was 1386.26 SHU and 1116.41 SHU, respectively. Cayenne pepper from Gansu showed a higher sugar and capsaicinoids content, and a more abundant profile of volatile aromatic compounds, including methyl salicylate, ethyl 3-methylbutyrate, linalool and so on. On the other hand, cayenne pepper from Inner Mongolia exhibited higher acid content and antioxidant capacity, and a more abundant profile of non-volatile compounds, including umbelliferone, quercetin, phytosphingosine and so on. Conclusion: Cayenne pepper, characterized by its high sugar content, mild spiciness, low seed-to-flesh ratio, and richness of aromatic and flavorful substances, meets the requirements for chili sauce processing. The peppers from different regions exhibit slight variations in quality, which make it necessary to evaluate the raw materials before sauce using species selection. This study will provide scientific guidance for the breeding and the selection of chili pepper varieties for sauce processing.
-
Keywords:
- cayenne pepper /
- origin /
- chili sauce processing /
- fresh chili pepper /
- quality evaluation
-
辣椒(Capsicum annuum L.)起源于南美洲,最早作为观赏植物于16世纪传入中国[1]。而近年来,由于辣椒具有独特的辛辣口感,并且含有丰富的辣椒碱、类黄酮、酚酸、类胡萝卜素和抗坏血酸等物质,因而表现出抗炎、抗癌、抗肥胖等功能活性,逐渐成为深受人们喜爱的食物[2]。我国辣椒种植规模巨大。据联合国粮农组织(FAO)统计数据显示[3],2000至2022年我国辣椒种植面积和年产量渐提高,2022年我国辣椒种植面积为80.55万公顷,占世界总种植面积的21.97%,年产量为1712.86万吨,占世界总年产量的40.90%,均位居世界首位。
新鲜辣椒初加工方式可分为鲜制和干制等,鲜制中制酱是主要加工手段,制品包括鲜椒酱或发酵辣椒酱等;而干制除生产辣椒干外,还可加工为辣椒粉、辣椒丝、辣椒圈等。多种多样的加工方式对辣椒原料提出不同的要求,而辣椒品种的选择直接影响到产品品质。比如,制酱要求辣椒原料具有果肉含量高、肉质肥厚、糖含量高的特点,而干制则要求辣椒籽含量高、粗纤维含量高等[4−5]。卡宴辣椒(Cayenne Pepper)形似螺丝椒、椒形硕大、肉厚、水分含量高、辣度低,适宜制酱用。目前,国外市场普遍选用卡宴辣椒制酱,如世界闻名的Tabasco辣椒酱产品便将卡宴辣椒作为原料之一使用。而国内仅有出口企业依据客户需求将其引种,应用于辣椒酱加工生产,为全球最大的香辛料供应商之一—美国味好美公司(McCormick & Company,Incorporated)提供辣椒酱底料,此外未见其他大规模种植。因此,分析卡宴辣椒原料品质有助于明晰该品种辣椒品质特征,提炼制酱用辣椒特点,提供酱用辣椒品种新选择,对国内选育制酱品种、加工企业选择加工品种具有指导意义。
近年来,由于气候适宜、土地资源充沛、种植技术成熟,我国西北地区辣椒种植规模逐年扩大。甘肃省酒泉市和内蒙古自治区巴彦淖尔市是国内卡宴椒的两个主产地,均属于温带大陆性气候,酒泉位于北纬38°09′~42°48′、东经92°20′~100°20′之间,而巴彦淖尔位于北纬40°13′~42°28′,东经105°12′~109°53′之间,因此巴彦淖尔降水量相对丰沛,而酒泉地区相对干燥。此外,两地均具有日照时间长、昼夜温差大、可播种土地面积广阔的特点,在有助于辣椒干物质和糖分积累的同时,也适合开展机械化种植[6−7]。因此,探究不同产地间同一辣椒品种的品质差异,能够为育种推广和加工选种提供参考。此外,现阶段辣椒酱加工产业仍然存在着品种选择依赖经验判断、缺乏科学规范和指导的问题。而在加工适宜性评价方面,已有针对干制用辣椒品种品质评价的研究基础,但针对酱用辣椒品种的研究较为缺乏;同时国内卡宴辣椒并非主栽品种,缺乏数据信息。
基于此,本研究创新地借助靶向技术结合非靶向研究手段,针对上述两产地卡宴鲜椒开展系统、全面的品质评价和分析比较,旨在深入剖析酱用卡宴辣椒的品质特征和物质组成,探究产地对卡宴辣椒品质的影响,旨在扩充国内酱用辣椒品种信息数据库,为国内制酱品种选育、加工企业品种选择提供科学指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
卡宴辣椒原料 河北乾亿食品有限公司,辣椒形态如图1所示,样品分别来自甘肃省酒泉市和内蒙古自治区巴彦淖尔市,于2022年9月采收,两产地辣椒总产量超过100吨,从中分批次、有代表性地均匀采取足量辣椒样品以供后续实验开展,文中分别以“甘肃产地卡宴辣椒”和“内蒙产地卡宴辣椒”指代;甲醇、丙酮、乙腈 质谱纯及色谱纯,美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;果糖、葡萄糖、蔗糖分析标准品 色谱纯,上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;麦芽糖、抗坏血酸、乳酸、苹果酸、琥珀酸、柠檬酸、莽草酸、奎宁酸、乌头酸、咖啡酸、绿原酸、香草酸、辣椒碱、二氢辣椒碱、玉米黄质、叶黄素、β-隐黄质、没食子酸、Trolox、芦丁分析标准品 色谱纯,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;β-胡萝卜素分析标准品 色谱纯,北京曼哈格生物科技有限公司;辣椒红素、2-甲基-3-庚酮分析标准品 色谱纯,德国默克集团Sigma-Aldrich®;其他所有提取用有机溶剂均为分析纯。
Waters e2695高效液相色谱、Waters Acquity I Class超高效液相色谱、Waters Xevo TQ-S三重四级杆质谱、ACQUITY UPLC® HSS T3色谱柱、ACQUITY UPLC® BEH C18色谱柱 美国沃特世科技有限公司;Agilent 7890A-5975C气相色谱质谱联用仪、Agilent 1290 Infinity LC超高效液相色谱、Agilent 6560四级杆飞行时间质谱、Agilent J&W DB-5ms色谱柱 美国安捷伦科技有限公司;Innoval NH2色谱柱、Venusil XBP C18色谱柱 天津博纳艾杰尔科技有限公司;SPARK 10M酶标仪 瑞士帝肯贸易有限公司;CF16RXII高速冷冻离心机 日本日立有限公司;ColorQuest XE全自动色差仪 中美合资上海信联创作电子有限公司;DR-A1数字阿贝折光仪 上海精密科学仪器有限公司;Orion 868 pH计 美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;DHG-9053A电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海精宏试验设备有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 结构特征值
均匀采选取多根新鲜整椒,观察椒形,测定纵径(从果顶至基部的距离)、横径(果实最宽横断面处的宽度),籽肉分离后分别称重,籽肉比以籽、肉分别占总重量的百分比表示。
1.2.2 原料处理
将鲜椒去梗去蒂去籽,果肉于破壁机中充分破碎,于−80 ℃保存。
1.2.3 水分含量
参照GB 5009.3-2016第一法[8],称取5.000 g试样,于105 ℃干燥箱烘干至恒重,根据公式计算水分含量。
X(g/100g)=m1−m2m1−m3×100 (1) 式中:X表示试样中的水分含量,g/100 g;m1表示称量皿和新鲜试样的总质量,g;m2表示称量皿和干燥试样的总质量,g;m3表示称量皿的质量,g。
1.2.4 粗纤维
参照GB/T 5009.10-2003[9],称取20.0 g试样,先后经1.25%硫酸和1.25%氢氧化钾处理,充分洗涤后烘干称重,重复至恒重,根据公式计算粗纤维含量。
X(%)=Gm×100 (2) 式中:X表示试样中的粗纤维含量,%;G表示残余物质量,g;m表示试样质量,g。
1.2.5 可溶性固形物
参考NY/T 2637-2014[10],采用折光仪法测量可溶性固形物,吸取2滴辣椒浆于棱镜上,调节旋钮,读取折光率。
1.2.6 总还原糖
参考GB 5009.7-2016第一法[11]略作修改,称取5.0 g试样,加入50 mL水、5.0 mL乙酸锌溶液和5.0 mL亚铁氰化钾溶液,定容至100 mL,混匀后静置30 min,过滤,滤液稀释2倍用于滴定;以1 mg/mL葡萄糖标定碱性酒石酸铜甲乙液;于锥形瓶中加入碱性酒石酸铜甲乙液各5.0 mL,加入10 mL水,放入5粒小钢珠,以试样稀释液滴定至沸腾状态下蓝色刚好褪去,根据公式计算还原糖含量。
X(g/100g)=m1m×F×V/100×1000×100 (3) 式中:X表示试样中的还原糖含量(以葡萄糖计),g/100 g;m1表示碱性酒石酸铜溶液(甲乙液各半)相当于葡萄糖的含量,mg;m表示试样质量,g;F表示系数,为0.5;V表示滴定时消耗的稀释液体积,mL。
1.2.7 单糖
参照GB 5009.8-2016第一法[12]略作修改,称取5.0 g左右试样,加入50 mL水、5.0 mL乙酸锌溶液和5.0 mL亚铁氰化钾溶液,定容至100 mL,混匀后静置30 min,过滤,滤液过0.22 μm滤膜备用;选用高效液相色谱(HPLC),配合NH2色谱柱(5 µm,4.6×250 mm)和示差折光检测器使用,以80%乙腈为流动相等度洗脱,流速0.5 mL/min,柱温40 ℃,流通池温度40 ℃,进样量10.0 μL;配制0.50、0.83、1.0、2.0、2.5 mg/mL果糖、葡萄糖、蔗糖及麦芽糖标准溶液,分别绘制标准曲线如下:y=119838x−7048.7,R2=0.9970;y=81767x−3654.3,R2=0.9956;y=130633x−10844,R2=0.9951;y=75418x−12939,R2=0.9953。
1.2.8 pH
使用校正后的pH计测定试样pH。
1.2.9 总酸
参照GB 5009.235-2016第二法[13],称取2.5 g试样,用25 mL 80 ℃蒸馏水分次洗入烧杯,冷却后转入容量瓶中定容至50 mL,过滤;取10 mL滤液,加60 mL蒸馏水,用0.05009 mol/L的氢氧化钠溶液滴定至pH8.2,根据公式计算总酸含量。
X(g/kg)=c×(V1−V0)×k×Fm×1000 (4) 式中:X表示试样中的总酸含量(以乳酸计),g/kg;c表示氢氧化钠标准滴定溶液的浓度,mol/L;V1表示滴定试样消耗的氢氧化钠体积,mL;V0表示滴定空白消耗的氢氧化钠体积,mL;k表示乳酸的换算系数,为0.090;F表示试样的稀释倍数;m表示试样的质量,g。
1.2.10 有机酸
参照Wen等[14]的方法略作修改,称取5.0 g左右试样加入15 mL 70%甲醇溶液(v/v)混匀,超声10 min,在4300×g、4 ℃下离心10 min,收集上清液,重复三次,合并后定容至50 mL,过0.22 μm滤膜备用;采用Waters超高效液相色谱-三重四级杆-质谱联用仪(UPLC-QQQ-MS)分离检测,选用HSS T3色谱柱(1.8 µm,2.1×150 mm)进行分离,柱温30 ℃,流速0.2 mL/min,进样量1 μL,流动相A为0.1%甲酸水溶液(v/v),流动相B为纯甲醇,梯度洗脱条件如下:0~0.5 min,2% B;0.5~4 min,2%~35% B;4~8 min,35%~50% B;8~12 min,50%~2% B;12~16 min,2% B;配制0.1、0.5、1、2.5、7.5、10、15、50、75 μg/mL浓度抗坏血酸、乳酸、苹果酸、琥珀酸、柠檬酸、莽草酸、奎宁酸、乌头酸、咖啡酸、绿原酸、香草酸标准溶液(根据样品实际选择范围);选择电喷雾电离源(electron spray ionization,ESI)正离子模式监测和多反应监测(multiple reaction monitoring,MRM)模式扫描,使用标准品进行条件优化,质谱参数为脱溶剂气温度500 ℃,脱溶剂气流量1000 L/h,毛细管电压2 kV;标准曲线如表1。
表 1 有机酸标准曲线Table 1. Standard curves of organic acids名称 标准曲线 R2 抗坏血酸 y=156205x+8879.1 0.9965 乳酸 y=754.85x−134.52 0.9981 苹果酸 y=19950x+280815 0.9910 琥珀酸 y=3988.8x+335.1 0.9944 柠檬酸 y=241539x−110852 0.9966 莽草酸 y=48828x+30834 0.9898 奎宁酸 y=127965x−4764.7 0.9951 乌头酸 y=114011x+14385 0.9971 咖啡酸 y=914091x+144891 0.9985 绿原酸 y=1000000x+132020 0.9977 香草酸 y=79081x+14851 0.9976 1.2.11 蛋白质
参照GB 5009.5-2016第一法[15],称取5.0 g试样,加入0.4 g硫酸铜、6 g硫酸钾、20 mL硫酸充分消化,使用自动凯式定氮仪加液、蒸馏和滴定,根据公式计算蛋白质含量。
X(%)=c×(V1−V2)×0.0140m×F×100 (5) 式中:X表示试样中的蛋白质含量,%;c表示盐酸标准滴定溶液的浓度,mol/L;V1表示滴定试样消耗的盐酸体积,mL;V2表示滴定空白消耗的盐酸体积,mL;0.0140表示与1.00 mL盐酸溶液(1.000 mol/L)相当的氮的质量,g;m表示试样的质量,g;F表示蛋白质折算系数,为6.25。
1.2.12 氨基酸态氮
参照GB 5009.235-2016第二法[13],前处理方法同1.2.9,pH8.2时加入10.0 mL甲醛溶液,继续用氢氧化钠溶液滴定至pH9.2,根据公式计算氨基酸态氮含量。
X(g/100g)=c×(V3−V2)×nm×V4/V5×100 (6) 式中:X表示试样中的氨基酸态氮含量,g/100 g;c表示氢氧化钠标准滴定溶液的浓度,mol/L;V3表示滴定试样消耗的氢氧化钠体积,mL;V2表示滴定空白消耗的氢氧化钠体积,mL;n表示与1.00 mL氢氧化钠溶液(1.000 mol/L)相当的氮的质量,为0.014,g;m表示试样的质量,g;V4表示试样稀释液取用量,mL;V5表示试样稀释液定容体积,mL。
1.2.13 色差
使用全自动色差仪配合Hunter Lab系统,在大孔反射模式下测定L*、a*、b*值,其中L*是亮度指数,a*表示红绿色,b*表示黄蓝色。根据公式计算总色差△E[16]。
ΔE=√ΔL*2+Δa*2+Δb*2 (7) 式中:△E表示总色差,△L*、△a*、△b*分别表示样品间L*、a*、b*差值。
1.2.14 类胡萝卜素
参考Xu等[17]的方法略作修改,称取试样2.0 g,加入15 mL丙酮和15 mL无水乙醚,在40 ℃、50 W条件下超声20 min,10000 r/min、4 ℃条件下离心5 min,收集上清液,重复提取两次并合并上清液,加入50 mL 20% KOH甲醇溶液(w/v),室温下避光放置1~2 h充分皂化,皂化液转入分液漏斗中,水洗至中性,收集上层萃取液,使用旋转蒸发仪在35 ℃下蒸干,得到色素提取物,用丙酮溶解并定容至10 mL,过0.22 µm滤膜备用;采用HPLC,配合C18色谱柱(5 µm,4.6×250 mm)和光电二极管阵列检测器使用,检测波长为450 nm,流动相A为丙酮、流动相B为超纯水,梯度洗脱条件:0~5 min,75% A;5~10 min,75%~95% A;10~17 min,95% A;17~22 min,95%~100% A;22~27 min,100%~75% A,进样量10 μL,流速1.0 mL/min,柱温30 ℃;配制2、5、10、20、50 μg/mL浓度的辣椒红素、玉米黄质、叶黄素、β-隐黄质、β-胡萝卜素标准溶液,分别绘制标准曲线如下:y=100675x+123706,R2=0.9977;y=77676x+70332,R2=0.9988;y=107694x+75553,R2=0.9991;y=100549x+151362,R2=0.9975;y=106719x+126630,R2=0.9984。
1.2.15 总酚
参考张新悦等[18]的方法略作修改,称取试样1.0 g,加入3 mL甲醇,室温下超声提取30 min,在4 ℃、12000 r/min条件下离心10 min,收集上清液,重复提取两次并合并,得到提取液;配制10、20、40、60、80、100 μg/mL浓度的没食子酸标准溶液;取400 μL提取液或没食子酸标准溶液,以甲醇作对照,加入2 mL 10%福林酚水溶液(v/v),混匀后加入1.8 mL 7.5%的Na2CO3溶液(w/v),室温下反应1 h,于酶标仪中测定765 nm下的吸光度;绘制标准曲线为y=0.0059x+0.0251,R2=0.9941;结果用每克样品所含没食子酸的当量来表示,单位为mg GAE/g。
1.2.16 总黄酮
参考马燕[19]的方法略作修改,称取1.0 g试样,加入70%甲醇水溶液(v/v)3 mL,室温下超声提取20 min,在4 ℃、12000 r/min条件下离心10 min,收集上清液,重复提取两次并合并得到提取液;配制2、4、6、8、10 μg/mL浓度的芦丁标准溶液;取1 mL提取液或标准溶液,以甲醇水溶液作对照,加入0.2 mL 5% NaNO2溶液,常温下反应6 min,加入0.2 mL 10% Al(NO3)3溶液,常温下反应6 min,加入4% NaOH溶液2 mL,常温下反应15 min,蒸馏水定容至5 mL,于酶标仪中测定510 nm下的吸光度;绘制芦丁标准曲线为y=0.0031x−0.0033,R2=0.9996;结果用每克样品所含芦丁的当量表示,单位为mg RE/g。
1.2.17 抗氧化能力
1.2.17.1 DPPH(1,1-diphenyl-2-picryl-hydrazyl radical,1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼)自由基清除能力测定
配制浓度为0.1、0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0 mmol/L Trolox标准溶液;提取方法同1.2.15,取200 μL提取液或标准溶液,以甲醇作对照,加入4 mL 0.14 mmol/L DPPH溶液,室温下避光反应30 min,于酶标仪中测定517 nm下的吸光度;绘制Trolox标准曲线为y=−0.5066x+0.7084,R2=0.9963;结果用每克样品所含Trolox当量表示,单位为mg Trolox/g。
1.2.17.2 铁离子还原能力(ferric ion reducing antioxidant power,FRAP)测定
提取及标准溶液配制方法同1.2.17.1,取100 μL提取液或标准溶液,以甲醇作对照,加入4 mL TPTZ工作液(按照10:1:1的体积比,将pH3.6的醋酸缓冲液、10 mmol/L的TPTZ溶液、20 mmol/L的FeCl3溶液混合),在37 ℃下水浴加热10 min,于酶标仪中测定593 nm下的吸光度;绘制Trolox标准曲线为y=0.5095x+0.0184,R2=0.9977;结果用每克样品所含Trolox当量表示,单位为mg Trolox/g。
1.2.18 辣椒碱
参考GB/T 40348-2021[20]略作修改,称取5.0 g试样,加5.0 g无水亚硫酸钠,15 mL甲醇,混匀后在60 ℃下超声15 min,8000×g离心5 min,收集上清液,重复提取3次,合并上清液定容至50 mL;用甲醇进行20倍稀释,过0.22 μm滤膜;配制15、30、50、100、150、300、500、1000 μg/mL浓度的辣椒碱、二氢辣椒碱标准溶液;采用UPLC-QQQ-MS分离检测,选用C18色谱柱(1.8 µm,2.1×100 mm)进行分离,柱温室温,流速0.2 mL/min,进样量2 μL,流动相A为0.1%甲酸水溶液(v/v),流动相B为纯甲醇,梯度洗脱条件如下:0~3 min,60% B;3~8 min,60%~70% B;8~12 min,70% B;12~14 min,70%~99% B;14~19 min,99% B;19~19.1 min,99%~60% B;19.1~23 min,60% B;质谱方法为采用ESI正离子模式监测和MRM模式扫描,使用标准品进行条件优化,质谱参数为脱溶剂气温度500 ℃,脱溶剂气流量1000 L/h,毛细管电压2 kV;分别绘制标准曲线为y=15422x+173984,R2=0.9992;y=44840x+661289,R2=0.9965。参考GB/T 21266-2007[21]中的公式计算辣椒碱类化合物总含量、斯科维尔指数和辣度。
W=(W1+W2)/0.9 (8) X(SHU)=W×0.9×(16.1×103)+W×0.1×(9.3×103) (9) 式中:W表示辣椒碱类化合物总含量,g/kg;W1、W2分别表示辣椒碱、二氢辣椒碱含量,g/kg;X表示斯科维尔指数,SHU;150 SHU=1度。
1.2.19 挥发性化合物
参考Peng等[22]的方法略作修改,准确称取4.0 g样品,加入5 μL稀释10000倍的2-甲基-3-庚酮作为内标物质;采用顶空固相微萃取(HS-SPME)-气相色谱质谱联用仪(GC-MS)富集和检测挥发性化合物:样品在60 ℃下振荡平衡20 min,60 ℃下恒温萃取40 min,250 ℃下解析5 min;采用非极性DB-5ms毛细管色谱柱(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm)分离化合物,以氦气为载气,流速为1 mL/min,进样口温度250 ℃,不分流模式,色谱柱升温程序为初始3 min保持40 ℃,以5 ℃/min升温至150 ℃,以10 ℃/min升温至250 ℃,保持10 min;质谱选用电子轰击离子源(EI),离子源温度230 ℃,四级杆温度150 ℃,电子轰击电压70 eV,全扫描模式(Scan)下扫描范围为30~500 m/z,扫描间隔1 s;定性方法为:将化合物与NIST14标准质谱库比对,保留匹配率高于60%的物质;定量方法为:根据内标浓度和峰面积计算挥发性化合物含量,根据挥发性化合物含量和阈值计算香气活性值(odor activity value,OAV),计算公式如下。
Xn(μg/g)=ρi×Vim×AnAi (10) OAVn=Xn/OTn (11) 式中:Xn表示某挥发性化合物含量,μg/g;ρi表示标准品稀释液中2-甲基-3-庚酮的浓度,0.0816 μg/μL;Vi表示添加标准品稀释液的体积,5 μL;m表示称取辣椒样品的质量,g;An表示该化合物的峰面积;Ai表示标准品的峰面积;OAVn表示该化合物的OAV值;OTn表示该化合物在空气中的香气阈值,mg/m3。
1.2.20 非挥发性化合物
参考Wang等[23]的方法略作修改,准确称取3.0 g样品,加入15 mL 4 ℃的70%甲醇水溶液(v/v),冰浴下破碎匀浆,静置12 h,4 ℃下10000×g离心10 min,收集上清液,过0.22 μm滤膜备用;采用Agilent超高效液相色谱-四级杆飞行时间质谱(UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS)分离和检测:选用C18色谱柱(1.8 µm,2.1×100 mm)进行分离,柱温40 ℃,流速0.3 mL/min,进样量2 μL,流动相A为0.1%甲酸水溶液(v/v),流动相B为0.1%甲酸乙腈溶液(v/v),梯度洗脱条件如下:0~2.00 min,2% B;2.01~2.50 min,2%~18% B;2.51~6.00 min,18%~30% B;6.01~9.50 min,30%~54% B;9.51~14.00 min,54%~82% B;14.01~15.00 min,82%~99% B;15.01~15.10 min,99%~2% B;15.11~18.00 min,2% B;质谱部分正离子模式气体温度325 ℃,干燥器流速7 L/min,喷雾气压35 psi,鞘气温度350 ℃,鞘气流速11 L/min,毛细管电压为3500 V,喷嘴电压0 V,碎裂电压380 V;负离子模式毛细管电压为3000 V,喷嘴电压为1500 V,其他参数同上;采用MS模式采集一级母离子,质量范围50~1200 m/z,采集速率为2 spectra/s;采用Targeted MSMS模式采集二级产物离子,范围50~1200 m/z,采集速率为2 spectra/s,MS/MS采集范围30~1200 m/z,采集速率为4 spectra/s,碰撞能量分别为10、20和40 eV;保留时间窗口0.3 min,其余同一级母离子质谱条件;定性方法为:化合物与METLIN数据库比对,保留出现频率高于33%的物质。
1.3 数据处理
所有样品开展三重复两平行试验,使用WPS Office Excel 2019记录和处理数据,使用Origin 2018软件作图,使用IBM SPSS Statistics 26进行差异性分析,使用MetaboAnalyst 6.0进行差异分析和作图,显著性水平α=0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同产地卡宴辣椒基本结构信息
表2所示为不同产地辣椒果实纵径、横径、籽肉比、水分含量、粗纤维含量的基本信息。两产地卡宴辣椒椒形态无明显差异,纵径长19.0~19.5 cm、横径均为3 cm,而张庆银等[24]列举了一些国内常见品种,最大纵径为14.20 cm,最大横径为2.28 cm,相比之下卡宴椒椒形更为硕大,接近于螺丝椒形态[25];同样,甘肃和内蒙卡宴辣椒籽肉比分别为7.87%和7.69%,更接近适宜制作剁辣椒的籽肉比(4.09%~5.97%)的线椒辣丰33号[26],远远低于适宜干制的籽肉比为18%~33%的羊角椒红龙23号[18],且因此后续研究围绕辣椒果肉开展;两产地卡宴辣椒果肉含水量均高于86%,独立样本t检验结果表明,内蒙卡宴辣椒水分含量显著高于甘肃卡宴辣椒(P<0.05),韩金朝等[27]的研究结果表明灌溉用水会影响辣椒果实的水分含量和可溶性糖、辣椒碱、可溶性蛋白质、维生素C等干物质的含量,因此这一差异可能是由于地区降水量不同所致;而两产地卡宴辣椒粗纤维含量分别为1.80%和1.97%,差异不显著(P>0.05),说明除水分含量外,卡宴辣椒其他基本结构特征不受产地差异影响。
2.2 不同产地卡宴辣椒可溶性固形物、还原糖及单糖含量
辣椒中的糖类化合物主要产生自光合作用,它们既是细胞的重要物质组成部分,又起到信号调节、为生长发育提供基础能源等作用[28]。表3所示为不同产地卡宴辣椒的可溶性固形物、还原糖(葡萄糖、果糖、麦芽糖)和非还原糖(蔗糖)的含量。可溶性固形物是指样品中所有溶于水的化合物的总称,包括可溶性糖、酸、矿物质和维生素等,而对于果蔬而言,糖类是可溶性固形物的主要组成部分[29]。甘肃和内蒙两产地卡宴辣椒可溶性固形物含量分别为11.35%和9.75%,相较于与之水分含量相当的线椒辣丰33号,其可溶性固形物为4.67%~10.23%,卡宴椒表现出较高的可溶性固形物含量,说明在其生长过程中糖类积累充足[26]。根据独立样本t检验结果,甘肃产地辣椒可溶性固形物显著高于内蒙产地(P<0.05),这种差异可能是由于甘肃产地干旱的气候特征导致,Bozkurt等[30]的研究表明适当的土壤水分亏缺有助于辣椒可溶性固形物的积累。
表 3 不同产地卡宴辣椒可溶性固形物、还原糖及单糖含量Table 3. Contents of total soluble solids, reducing sugars and monosaccharides of cayenne pepper from different regions产地 可溶性固形物含量(%) 葡萄糖含量
(g/100 g)果糖含量
(g/100 g)麦芽糖含量
(g/100 g)蔗糖含量
(g/100 g)总还原糖含量
(g/100 g,滴定法,以葡萄糖计)总还原糖含量
(g/100 g,液相色谱法)甘肃 11.35±0.19b 2.59±0.05Ab 2.97±0.14Bb ND ND 5.28±0.11b 5.56±0.15b 内蒙 9.75±0.32a 2.09±0.15Aa 2.67±0.16Ba ND ND 4.67±0.27a 4.76±0.30a 注:同行不同大写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),ND表示未检出。 利用液相色谱法和滴定法检测得到的总还原糖含量相当,均显示为4~6 g/100 g,且蔗糖未检出,因此总糖含量与美国农业部2019年统计数据所示[31]红甜椒4.2 g/100 g的总糖含量相近,说明两产地卡宴辣椒具有较高的含糖量。与可溶性固形物含量相同,甘肃产地卡宴辣椒总还原糖、葡萄糖和果糖单糖含量均显著高于内蒙产地(P<0.05),即综合上述结果均反映出甘肃产地卡宴辣椒生长发育过程中积累了更高水平的糖类化合物。在两产地卡宴辣椒果肉中,果糖含量均显著高于葡萄糖含量(P<0.05),这一点同样与美国农业部红甜椒的果糖(2.26 g/100 g)高于葡萄糖含量(1.94 g/100 g)的数据一致[31]。麦芽糖和蔗糖在辣椒果肉中均未检出,同样在张新悦等[18]所研究的红龙23羊角椒中也未检出,原因可能是果实成熟过程中,双糖在转化酶的作用下水解,产生更多的葡萄糖和果糖,以此维持细胞渗透压的平衡,因此最终成熟果实中积累的糖类化合物以葡萄糖和果糖为主[28]。充足的糖类化合物可以增添辣椒酱产品的口感,也可以充当发酵辣椒酱中发酵微生物代谢活动的底物[32],因此卡宴椒用于制酱较为适宜。
2.3 不同产地卡宴辣椒pH、总酸及有机酸含量
酸类化合物除了影响果肉风味品质,其中部分也是辣椒中重要的营养物质,或是细胞代谢通路中的关键物质。表4展示了两产地卡宴辣椒的pH和总酸含量,甘肃和内蒙两产地卡宴辣椒pH为4.83和4.85,无显著差异(P>0.05),且和江雪梅等[16]发酵所用辣椒原料pH为4.90~5.38的研究结果接近;但卡宴辣椒总酸低于其12%~20%的总酸含量,可能由于有机酸组成和含量不同,导致氢离子解离程度存在差异[33];且内蒙产地卡宴辣椒总酸含量显著高于甘肃产地(P<0.05),而如前所述甘肃产地具有更高的糖含量,这种含量差异可能与辣椒果实生长发育程度、贮藏期间细胞代谢活动等有关[34]。
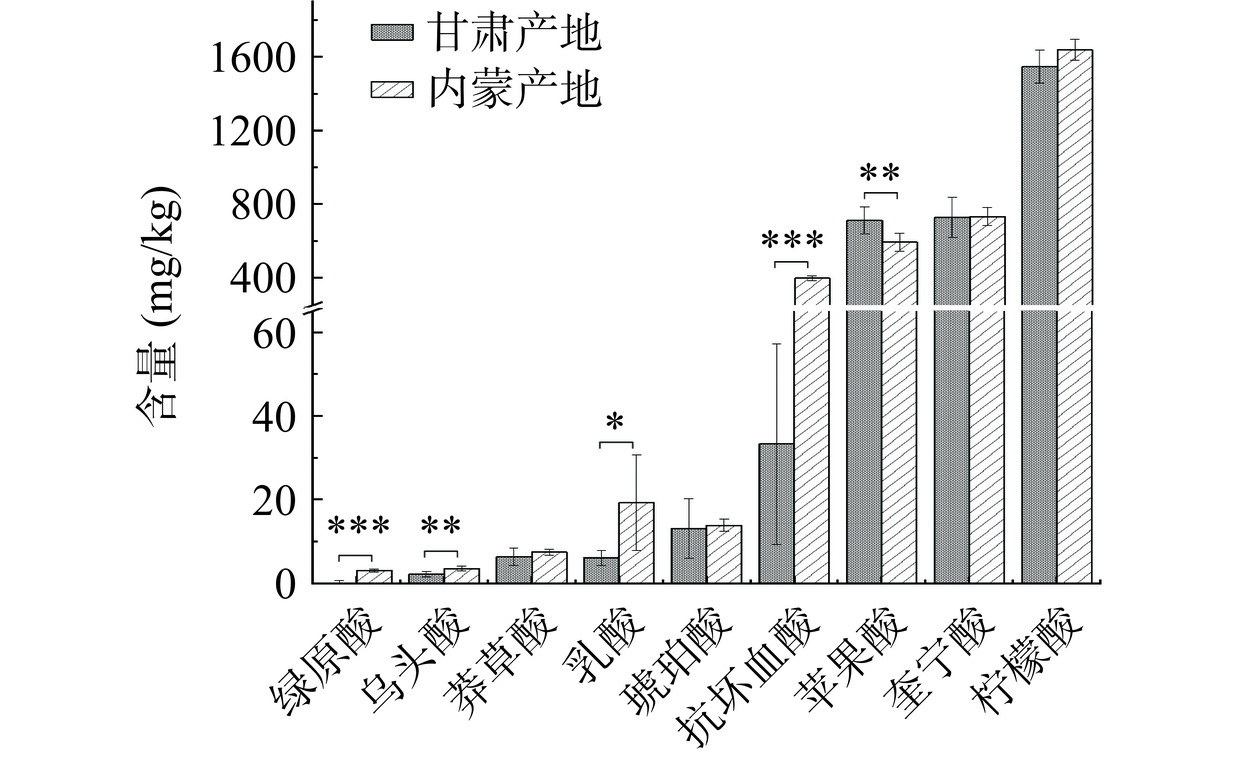
表 4 不同产地卡宴辣椒pH和总酸含量Table 4. pH and contents of total acid of cayenne pepper from different regions产地 pH 总酸含量(g/kg) 甘肃 4.83±0.01a 4.44±0.26a 内蒙 4.85±0.03a 5.09±0.57b 图2展示了在UPLC-QQQ-MS检测方法下各类常见有机酸类化合物的定量结果。其中,柠檬酸既是三羧酸循环中的关键代谢中间体[35],也能为食物增添柑橘类的风味[36],两产地卡宴辣椒果肉中柠檬酸含量最高,且远远高于其他种类有机酸,平均占总酸含量的33.4%,为辣椒酸味的呈现作出较大贡献;平均占总酸含量13.7%的苹果酸同属于三羧酸循环中的代谢中间体,在果实中占据较高含量,但含量过高会导致果实携有酸涩味和苦味[37];琥珀酸、乳酸、莽草酸、乌头酸分别与细胞三羧酸循环和乙醛酸循环、乳酸菌发酵和莽草酸代谢途径密切相关[38−41],而本身在辣椒果实中少量存在。辣椒中多酚种类丰富,为其抗氧化特性作出贡献,卡宴椒中的酚酸以奎宁酸为主,平均含量高达总酸含量的15.3%,绿原酸由咖啡酸和奎宁酸缩合而成[42],但结果显示卡宴椒中其含量较低,而咖啡酸未检出;香草酸同样未检出。抗坏血酸是一种水溶性维生素,是重要的抗氧化剂和酶的辅助因子,卡宴辣椒抗坏血酸含量低于Olatunji等[43]所提到的成熟辣椒果实43~247 mg/100 g的抗坏血酸含量,可能是受到成熟程度、生长环境条件和遗传因素的影响。
![]() 图 2 不同产地卡宴辣椒有机酸含量注:显著性差异分别用*(P<0.05)、**(P<0.01)、***(P<0.001)表示,图3同。Figure 2. Contents of organic acids of cayenne pepper from different regions
图 2 不同产地卡宴辣椒有机酸含量注:显著性差异分别用*(P<0.05)、**(P<0.01)、***(P<0.001)表示,图3同。Figure 2. Contents of organic acids of cayenne pepper from different regions从各种有机酸总含量来看,内蒙产地卡宴辣椒高于甘肃产地,与总酸含量检测结果一致;其中内蒙卡宴辣椒绿原酸、乌头酸、乳酸、抗坏血酸含量显著高于甘肃产地(P<0.05),尤其抗坏血酸是甘肃产地的12倍,可能是由于葡萄糖作为前体物质影响着抗坏血酸合成[43],因此也与内蒙产地较低的葡萄糖水平相对应,而甘肃卡宴辣椒苹果酸含量极显著高于内蒙产地(P<0.01)。这些有机酸含量的差异共同影响着两产地卡宴辣椒的感官品质。
2.4 不同产地卡宴辣椒蛋白质和氨基酸态氮含量
表5所示为两产地卡宴辣椒蛋白质和氨基酸态氮含量。含水量86.1%和87.9%的卡宴辣椒果肉的蛋白质含量分别为1.59%和1.44%,换算后接近含水量9.80%~16.50%的不同品种干辣椒10.10%~14.20%的蛋白质含量[44]。蛋白质可在微生物和酶的作用下被分解成肽和氨基酸,因此常用氨基酸态氮来反映蛋白质的水解程度和鲜味。在蛋白质含量较高的酱油、豆瓣酱等原料蛋白质含量丰富的发酵制品中,氨基酸态氮可高达1 g/100 g左右[45−46];但由于辣椒果肉蛋白质含量较低,且新鲜原料未经微生物发酵,氨基酸态氮也远远低于上述发酵制品,而经过发酵的辣椒酱氨基酸态氮可达0.25~0.34 g/100 g[47]。
表 5 不同产地卡宴辣椒蛋白质和氨基酸态氮含量Table 5. Contents of protein and amino acid nitrogen of cayenne pepper from different regions产地 蛋白质含量(%) 氨基酸态氮含量(g/100 g) 甘肃 1.59±0.07a 0.14±0.01a 内蒙 1.44±0.08a 0.13±0.01a 2.5 不同产地卡宴辣椒色差及类胡萝卜素含量
表6所示为不同产地卡宴辣椒色差,结果用L*、a*、b*表示。两产地卡宴辣椒L*为39.32左右,与江雪梅等[16]的研究一致,其结果表明辣椒原料L*值在37.10~47.21之间。a*、b*均为正值,说明样品呈红色和黄色。经独立样本t检验,两样本L*值和b*值无显著差异(P>0.05),即不同产地辣椒样品亮度及黄蓝色相近;甘肃产地卡宴辣椒a*值显著低于内蒙产地(P<0.05),即内蒙产地卡宴辣椒红色更深。计算发现△E值<2,说明两产地辣椒颜色视觉差异较小,无法用肉眼分辨。
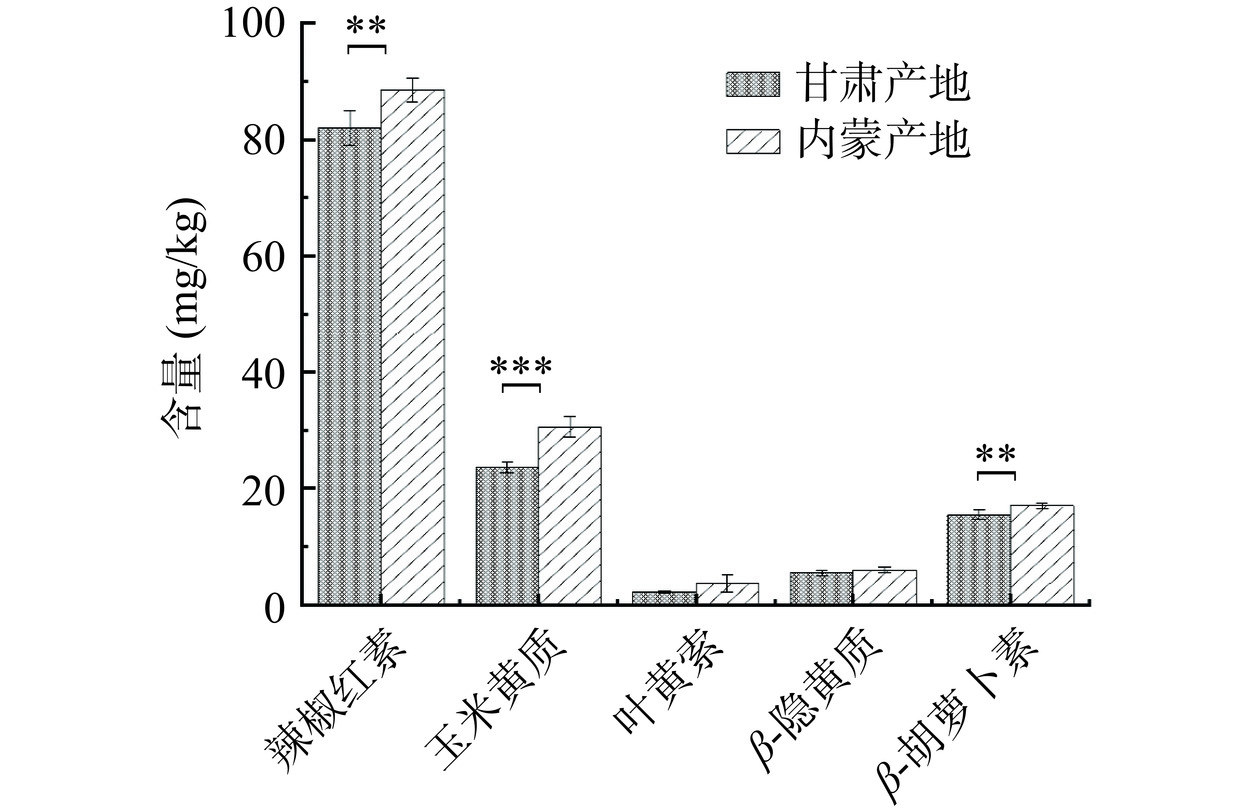
表 6 不同产地卡宴辣椒L*、a*、b*和△E值Table 6. L*, a*, b* and △E value of cayenne pepper from different regions产地 L* a* b* △E 甘肃 39.32±0.15a 32.23±0.23a 21.20±0.23a 1.04 内蒙 39.33±0.03a 33.23±0.08b 21.30±0.09a 辣椒中的类胡萝卜素主要包括辣椒红素、玉米黄质、叶黄素、β-隐黄质、β-胡萝卜素等,一方面赋予辣椒颜色,另一方面又充当着重要的活性物质[17]。尤其辣椒红素是含量最高的红色色素,目前被提取为天然着色剂广泛使用,其抗氧化、抗癌、调节免疫等生物活性也已得到证实[48]。图3展示了卡宴辣椒五种主要类胡萝卜素的含量,从高到低依次为辣椒红素>玉米黄质>β-胡萝卜素>β-隐黄质>叶黄素,这一点与Xu等[17]的研究结果一致;卡宴辣椒中辣椒红素平均占五种类胡萝卜素总量的62.1%,接近长椒类鲜椒辣椒红素占总类胡萝卜素65%~70%的比例[48]。从总含量上来看,内蒙产地高于甘肃产地;其中内蒙卡宴辣椒辣椒红素、玉米黄质、β-胡萝卜素极显著高于甘肃产地(P<0.01),对内蒙卡宴辣椒更高的a*值做出贡献。
2.6 不同产地卡宴辣椒总酚、总黄酮含量及抗氧化能力评价
辣椒中的酚酸、类黄酮、维生素C等植物化学物质综合作用,赋予其较强的抗氧化能力[49],表7所示为不同产地卡宴辣椒总酚、总黄酮含量、DPPH自由基清除能力和FRAP铁离子还原能力。甘肃和内蒙卡宴辣椒总酚含量相对较低,分别为0.52和0.62 mg GAE/g,比如同样以没食子酸作为标准对照,肖何等[26]测得辣丰33品种辣椒成熟期总酚含量为1.60~1.75 mg GAE/g;以儿茶素作为标准对照,Sricharoen等[49]测得不同品种辣椒总酚含量换算为鲜重约0.83~1.57 mg CE/g,而两产地卡宴辣椒总黄酮含量接近辣丰33号成熟期0.23 mg RE/g的含量[26],可见卡宴椒中黄酮类化合物占多酚类化合物总量的比例更高。同样,换算标准对照品及干鲜重,发现卡宴辣椒DPPH自由基清除能力与FRAP铁离子还原能力表现相当,且接近肖何等[26]、Sricharoen等[49]的研究结果。经比较发现,内蒙产地卡宴椒总酚含量和总黄酮含量均显著高于甘肃产地(P<0.05);且在抗氧化能力上,表现出更高的DPPH自由基清除能力与FRAP铁离子还原能力,分别是甘肃产地的1.63和1.60倍。
表 7 不同产地卡宴辣椒总酚、总黄酮含量及抗氧化能力Table 7. Contents of total phenols, total flavonoids and antioxidant capacity of cayenne pepper from different regions产地 总酚含量(mg GAE/g) 总黄酮含量(mg RE/g) DPPH自由基清除能力(mg Trolox/g) FRAP铁离子还原能力(mg Trolox/g) 甘肃 0.52±0.03a 0.15±0.01a 0.87±0.04a 0.84±0.04a 内蒙 0.62±0.03b 0.23±0.02b 1.42±0.04b 1.34±0.07b 2.7 不同产地卡宴辣椒辣椒碱类物质含量及辣度评价
辣椒碱类物质是辣椒独特辛辣味的贡献者,主要包括辣椒碱、二氢辣椒碱、降二氢辣椒碱、高辣椒碱、高二氢辣椒碱等,但辣椒碱含量最多,二氢辣椒碱次之,二者占辣椒碱类物质的约90%[50]。因此检测了两产地卡宴辣椒辣椒碱和二氢辣椒碱的含量,并由此计算辣椒碱类物质的总含量、斯科维尔指数及辣度情况。如表8所示,卡宴辣椒辣椒碱、二氢辣椒碱含量远低于常见品种,总含量不足100 mg/kg,斯科维尔指数不足1400 SHU;而如王楠艺等[51]检测的30个品种辣椒辣椒碱含量为110~5790 mg/kg,二氢辣椒碱含量为170~2920 mg/kg;再如Sricharoen等[49]检测的辣椒品种斯科维尔指数最低为38271 SHU,可见卡宴辣椒辣度较低;根据Sricharoen等[49]指出的辣度等级,卡宴辣椒斯科维尔指数介于700~3000 SHU,属于轻微辣度辣椒,适宜制酱。经独立样本t检验,甘肃产地卡宴辣椒辣椒碱含量显著高于内蒙产地(P<0.05),二氢辣椒碱含量无显著差异(P>0.05),即甘肃产地辣椒具有更高的辣度。
表 8 不同产地卡宴辣椒辣椒碱类物质含量及辣度Table 8. Contents of capsaicinoids and pungency degrees of cayenne pepper from different regions产地 辣椒碱含量(mg/kg) 二氢辣椒碱含量(mg/kg) 总含量(mg/kg) 斯科维尔指数(SHU) 辣度 甘肃 69.30±7.94b 11.61±2.93a 89.90±9.02b 1386.26±139.09b 9.24±0.93b 内蒙 55.98±3.48a 9.18±6.62a 72.40±8.29a 1116.41±127.87a 7.44±0.85a 2.8 不同产地卡宴辣椒挥发性化合物
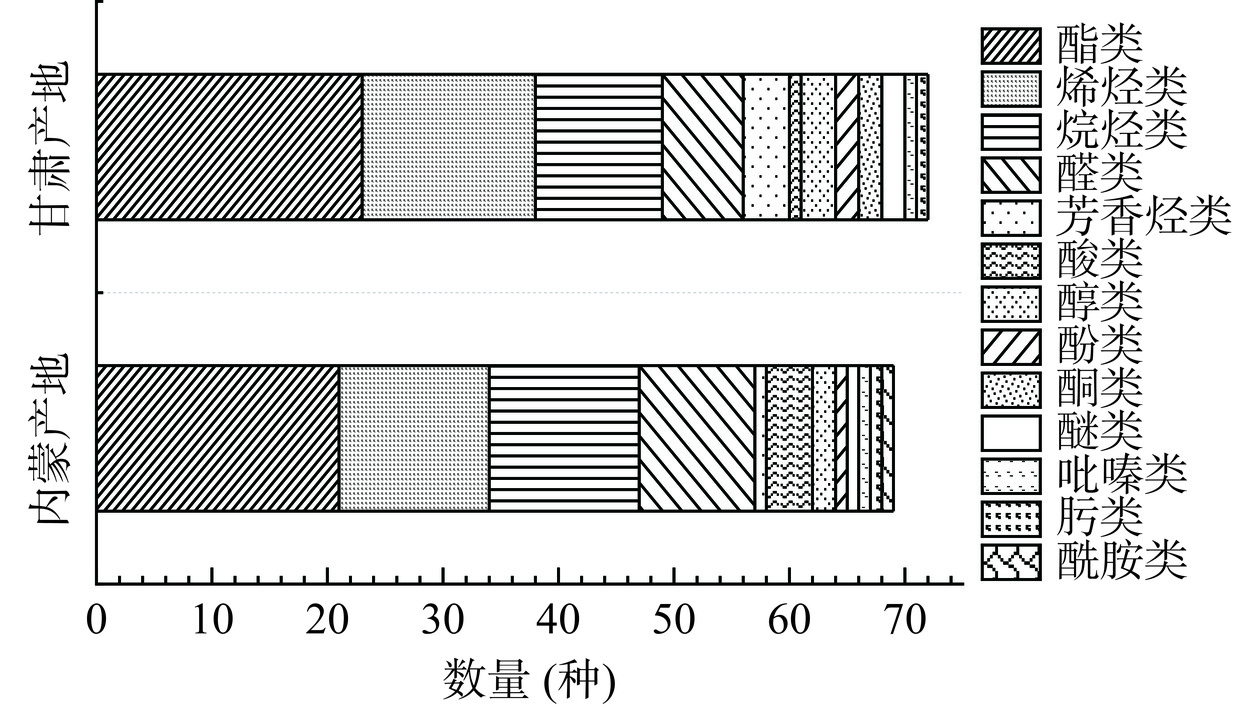
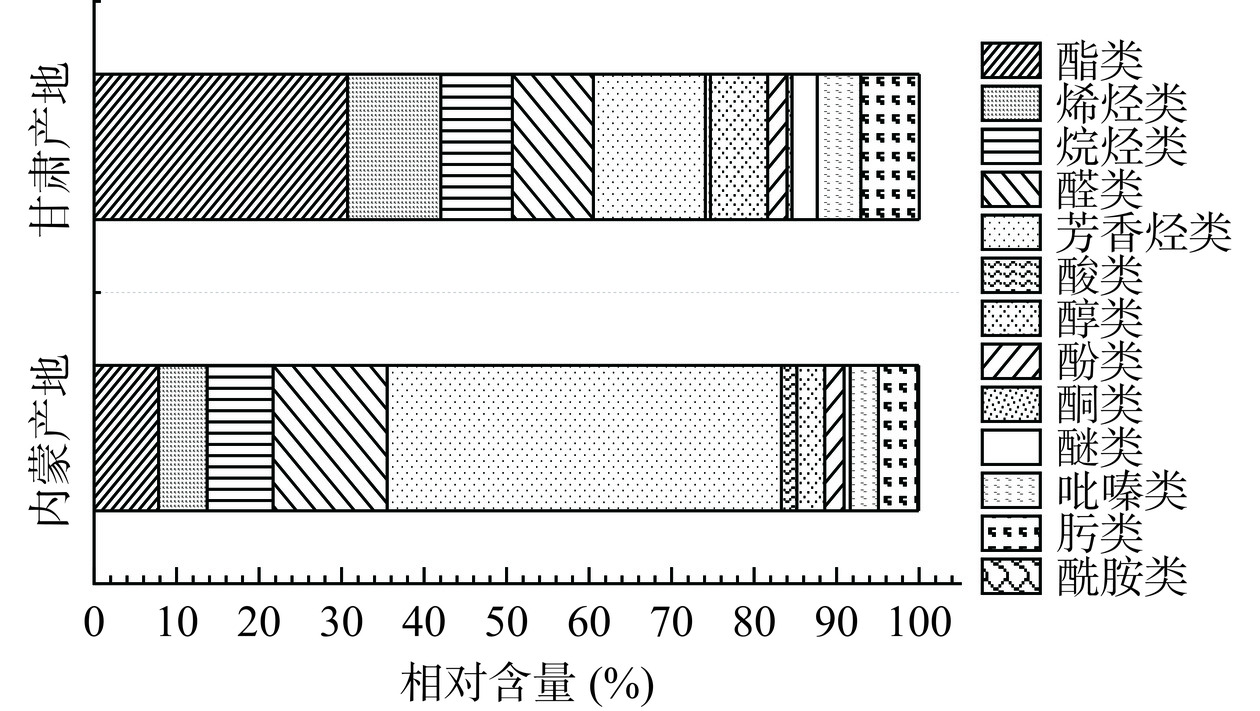
两产地卡宴辣椒共检出挥发性化合物99种,其中种类数量最多的是常对香气作出较大贡献的酯类化合物共31种,另有20种烯烃类化合物,17种烷烃类化合物,10种醛类化合物等。图4~图5所示分别为不同产地卡宴辣椒挥发性化合物种类分布和各类化合物相对含量占比。不同产地种类分布略有不同,其中甘肃产地挥发性化合物种类更丰富。尽管种类分布相近,各类化合物相对含量在两产地卡宴辣椒中的表现不同。23种酯类化合物总含量占甘肃产地辣椒挥发性化合物总量的30.78%,其中含量最高的是水杨酸甲酯(11.03%),其次为3-甲基丁酸乙酯(3.36%);而内蒙产地的21种酯类化合物仅占7.80%,含量最高的同样是水杨酸甲酯(2.02%)。甘肃产地15种烯烃类化合物占其总挥发性化合物含量的11.34%,内蒙产地13种烯烃仅占其5.86%。此外,甘肃产地卡宴辣椒挥发性烷烃类和醇类等化合物含量高于内蒙产地,包括芳樟醇、苯乙醇等。内蒙产地卡宴辣椒具有更高含量的醛类化合物(13.85%)和芳香烃类化合物(47.59%),而上述两类分别占甘肃产地的9.82%和13.61%。醛类化合物中,内蒙卡宴辣椒含有较高含量的苯甲醛,占总挥发性化合物的4.74%,其次为反式-2-己烯醛,而甘肃卡宴辣椒以反式-2-壬烯醛、苯乙醛、壬醛为主;甘肃卡宴辣椒中芳香烃类化合物有4种,但内蒙卡宴辣椒中仅有一种为1,2,4,5-四乙基苯,含量高达47.59%,但未见其对香气的贡献作用。
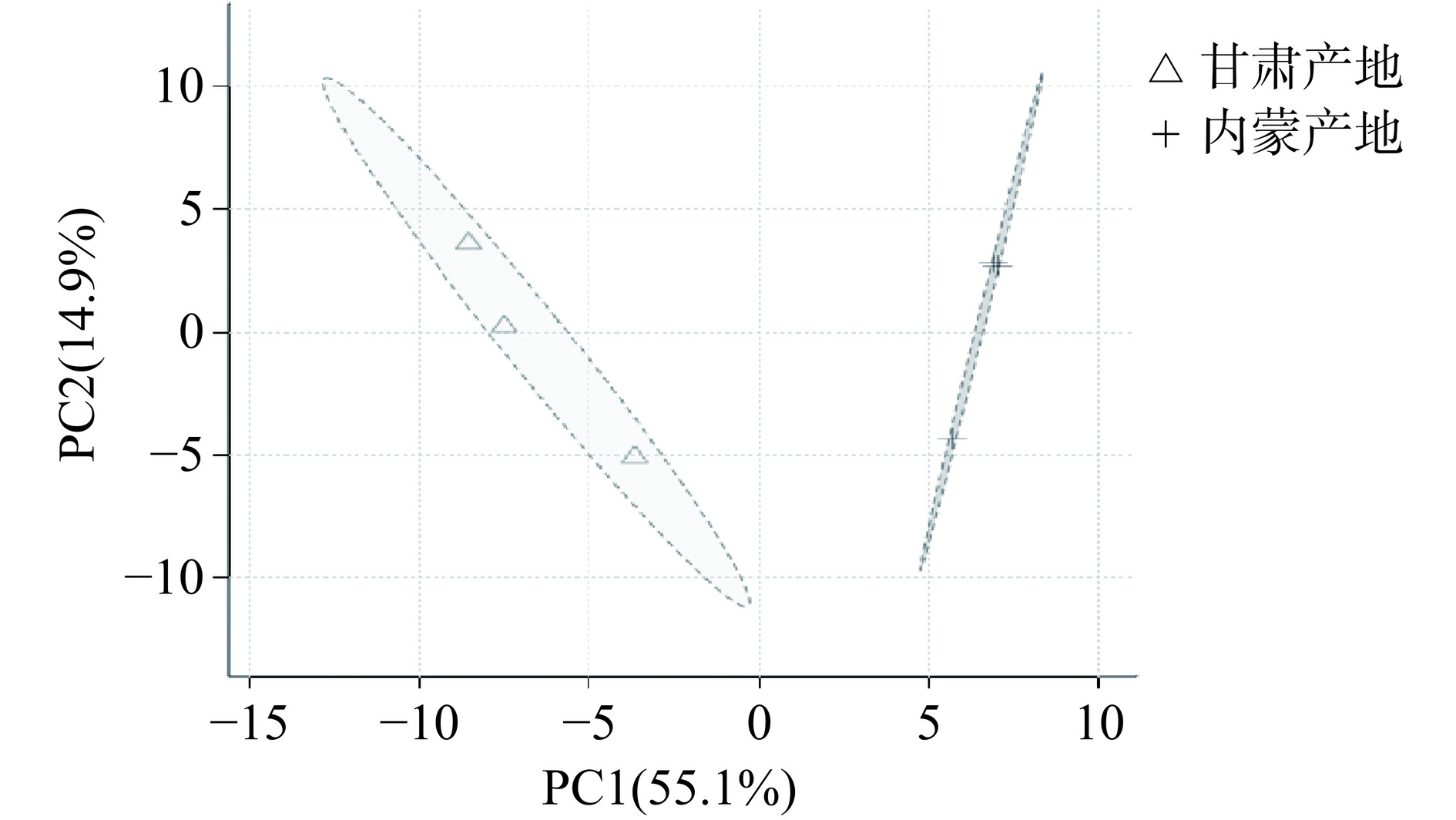
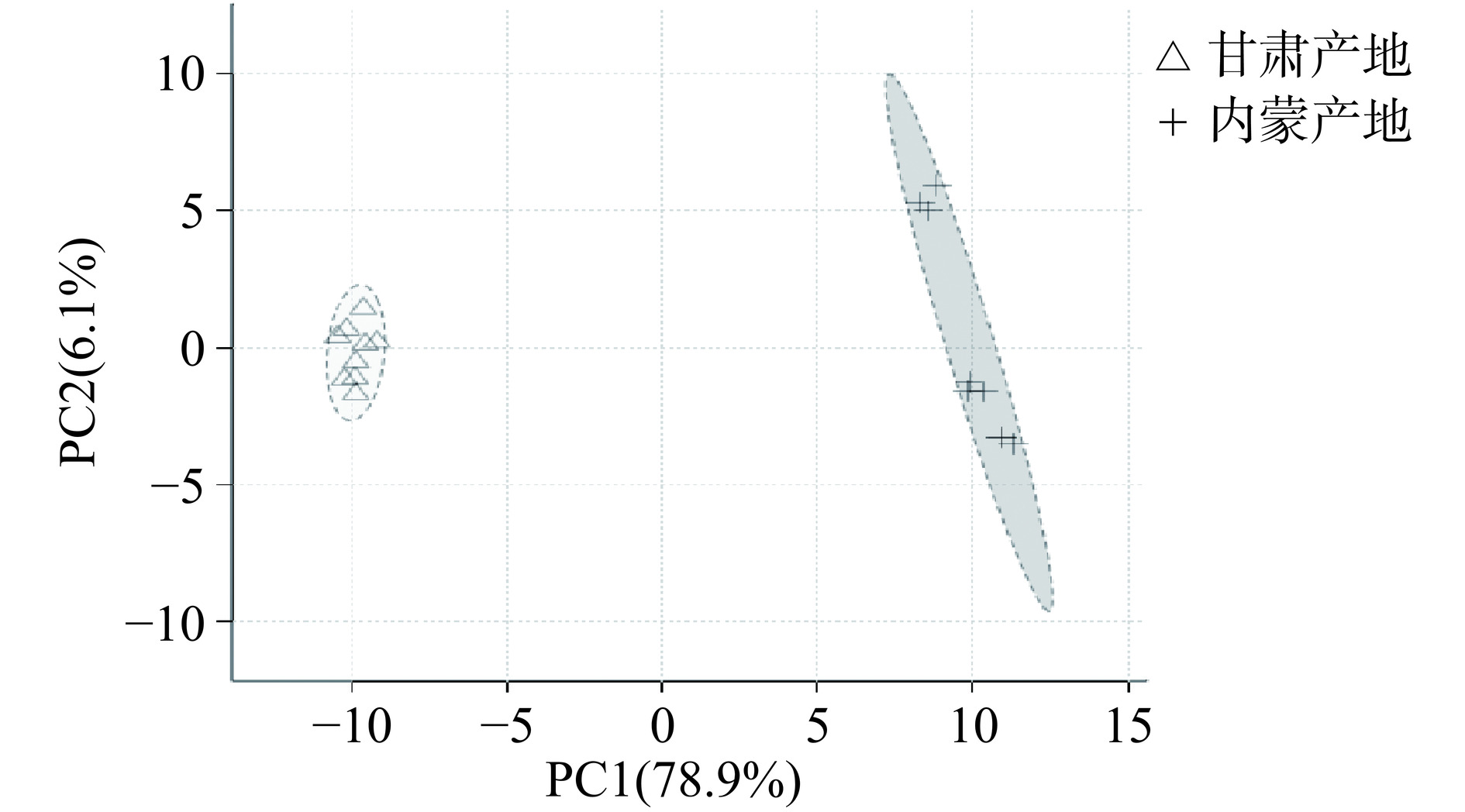
对99种挥发性化合物进行无监督的主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA),如图6所示,发现两产地卡宴辣椒挥发性化合物明显分离,产地对挥发性组分影响显著。进一步针对两组挥发性化合物进行有监督的正交偏最小二乘法分析(orthogonal projections to latent structures discriminant analysis,OPLS-DA),该方法结合了正交信号过滤技术和PLS-DA来筛选差异变量,能够产生更好的分离效果,最大化凸显组间差异。如图7所示,两样本聚类分离明显,组间差异显著,说明两产地辣椒挥发性化合物组分具有较大差异。对OPLS-DA模型进行置换检验,以判别是否发生过度拟合。经100次循环迭代后的置换检验结果显示模型的Q2值和R2值分别为0.944和0.999,其中Q2表示所建模型的预测能力,R2代表对Y变量的解释率。Q2、R2两者均大于0.5且差值小于0.3说明模型可靠性较好,Q2大于0.9说明模型可靠性非常好,说明无过度拟合现象,结果可用于不同产地卡宴辣椒挥发性化合物的组间对比。
通过筛选差异倍数(fold change,FC)大于2或小于0.5,且满足t检验结果P<0.05,同时满足OPLS-DA分析VIP>1的挥发性化合物,最终筛得27种差异化合物,如表9所示,包括9种酯类化合物、5种烯烃类化合物、6种烷烃类化合物、4种醛类化合物、1种醇类化合物、1种醚类化合物和1种芳香烃类化合物。甘肃卡宴辣椒中酯类含量更为丰富,为鲜椒的风味做出贡献,其中水杨酸甲酯含量为0.0652 μg/g,明显高于内蒙产地;3-甲基丁酸-4-甲苯酯和2-甲基丁酸-4-甲苯酯同样在甘肃卡宴辣椒中含量更高。烯烃类化合物中,巴伦西亚橘烯和β-榄香烯更多存在于甘肃卡宴辣椒中,含量分别高达0.0082 μg/g和0.0091 μg/g;而4-甲基-1,5-庚二烯和喜马偕-2,4-二烯仅在内蒙卡宴辣椒中检出。醛类化合物中,内蒙卡宴辣椒中具有更高浓度的苯甲醛和反式-2-己烯醛,含量分别高达0.0236 μg/g和0.0126 μg/g,甘肃卡宴辣椒中壬醛含量略高于内蒙卡宴辣椒,含量为0.0134 μg/g。此外,甘肃和内蒙产地卡宴辣椒中均含有较高含量的芳樟醇,分别为0.0284 μg/g和0.0114 μg/g。其中,水杨酸甲酯、3-甲基丁酸-4-甲苯酯和2-甲基丁酸-4-甲苯酯,为辣椒贡献香甜气味和果香[52−53]。巴伦西亚橘烯能够为甘肃卡宴辣椒增添柑橘香气[54];内蒙卡宴辣椒中的4-甲基-1,5-庚二烯、喜马偕-2,4-二烯已被证实为茶树花中的主要香气成分[55]。内蒙卡宴辣椒中高浓度的苯甲醛具有果香和甜香,也是桑葚等水果中的典型香气化合物[56],而反式-2-己烯醛具有苹果清香气味[57];甘肃卡宴辣椒中高含量的壬醛则具有脂肪香气、柑橘清新香气[57]。芳樟醇具有辣椒和柑橘香气,已有研究证实芳樟醇是辣椒制品中的关键香气物质[58]。
表 9 不同产地卡宴辣椒差异挥发性化合物及含量Table 9. Differential volatile compounds and contents of cayenne pepper from different regions类别 挥发性化合物 含量(μg/g) log2 FC P值 VIP值 甘肃产地 内蒙产地 酯类 水杨酸甲酯 0.0652±0.0180 0.0101±0.0014 2.70 0.0061 2.20 3-甲基丁酸-4-甲苯酯 0.0199±0.0076 0.0018±0.0016 3.40 0.0162 1.80 2-甲基丁酸-4-甲苯酯 0.0176±0.0046 − 2.80 0.0049 2.30 3-甲基丁酸乙酯 0.0308±0.0091 − 2.80 0.0074 2.10 异戊酸异丁酯 0.0047±0.0017 − 3.00 0.0129 1.90 邻苯二甲酸二异丁酯 0.0005±0.0001 − 2.50 0.0008 3.10 亚油酸甲酯 0.0039±0.0011 0.0008±0.0009 2.30 0.0187 1.70 顺式-3-己烯基异戊酸酯 0.0019±0.0008 3.30 0.0238 1.60 亚麻酸甲酯 0.0008±0.0013 0.0011±0.0005 −3.30 0.0253 1.60 烯烃类 巴伦西亚橘烯 0.0082±0.0026 − 2.70 0.0097 2.00 4-氰基-1-环己烯 0.0007±0.0006 0.0019±0.0002 −1.30 0.0208 1.70 喜马偕-2,4-二烯 − 0.0001±0.0000 −2.60 0.0021 2.70 4-甲基-1,5-庚二烯 − 0.0029±0.0003 −2.50 0.0002 3.70 β-榄香烯 0.0091±0.0032 0.0014±0.0002 2.70 0.0142 1.80 烷烃类 十五烷 0.0064±0.0013 − 2.60 0.0019 2.70 十八烷 0.0007±0.0002 − 3.00 0.0102 2.00 环十四烷 0.0008±0.0003 − 2.80 0.0158 1.80 4-乙基癸烷 0.0008±0.0003 − 2.70 0.0163 1.80 十二烷 − 0.0100±0.0008 −2.50 0.0000 4.30 壬基环戊烷 − 0.0006±0.0002 −2.60 0.0071 2.10 醛类 苯甲醛 0.0038±0.0010 0.0236±0.0065 −2.60 0.0064 2.20 壬醛 0.0134±0.0013 0.0058±0.0012 1.20 0.0018 2.70 2,6,6-三甲基-1-环己烯-1-甲醛 0.0012±0.0002 0.0005±0.0001 1.20 0.0031 2.50 反式-2-己烯醛 − 0.0126±0.0012 −2.50 0.0001 4.00 醇类 芳樟醇 0.0284±0.0034 0.0114±0.0009 1.30 0.0011 3.00 醚类 莳萝醚 0.0176±0.0035 0.0037±0.0034 2.15 0.0065 1.28 芳香烃类 2-异丙烯基-4α,8-二甲基-1,2,3,4,4A,5,6,7-八氢萘 0.0034±0.0015 0.0002±0.0004 3.10 0.0244 1.60 采用OAV分析法从甘肃和内蒙产地卡宴辣椒中筛选得到关键香气活性成分10种(表10)。其中OAV值最高的是3-异丁基-2-甲氧基吡嗪(3-isobutyl-2-methoxypyrazine,IBMP),具有典型的甜椒香气,也是甜椒芳香活性化合物3-烷基-2-甲氧基吡嗪类化合物中含量最高的一种[59],在两产地卡宴辣椒中OAV值分别高达10426.32和5660.98。此外,醛类化合物反式2-壬烯醛、壬醛、苯乙醛同属于两产地卡宴辣椒中的关键香气成分,为二者贡献了脂肪香气、果香、甜香和生青气味等。β-紫罗兰酮和苯甲酸甲酯也同时为两产地辣椒贡献了花香、果香、草药香气等。甘肃卡宴辣椒中,另有酯类化合物对香气呈现做出关键贡献,包括3-甲基丁酸乙酯(446.48)、水杨酸甲酯、十一酸乙酯。内蒙卡宴辣椒中,另有反式-2-己烯醛为其增添生青味和叶子香气。
表 10 不同产地卡宴辣椒关键香气活性成分与气味描述Table 10. Key aroma active compounds and odor description in cayenne pepper from different regions挥发性化合物名称 含量(μg/g) 阈值(mg/m3)a OAV值b 香气描述c 甘肃产地 内蒙产地 甘肃产地 内蒙产地 3-异丁基-2-甲氧基吡嗪 0.0313±0.0053 0.0170±0.0049 0.000003 10426.32 5660.98 土壤,香料,青椒香气 3-甲基丁酸乙酯 0.0308±0.0091 − 0.000069 446.48 − 果香 反式-2-壬烯醛 0.0117±0.0103 0.0088±0.0037 0.00009 130.17 97.50 脂肪,黄瓜香气,生青味 β-紫罗兰酮 0.0016±0.0015 0.0005±0.0008 0.00012 13.27 3.84 海藻,紫罗兰,覆盆子香气,花香 壬醛 0.0134±0.0013 0.0058±0.0012 0.0031 4.33 1.87 脂肪,柑橘香气,生青味 水杨酸甲酯 0.0652±0.0180 0.0101±0.0014 0.016 4.07 − 胡椒薄荷香气 反式-2-已烯醛 − 0.0126±0.0012 0.0031 − 4.07 生青味,叶子香气 苯甲酸甲酯 0.0044±0.0012 0.0024±0.0001 0.0015 2.92 1.60 西梅,生菜,草药香气,甜香 苯乙醛 0.0151±0.0046 0.0102±0.0024 0.0063 2.40 1.62 山楂,蜂蜜香气,甜香 十一酸乙酯 0.0005±0.0005 0.0001±0.0001 0.0003 1.75 − 干邑白兰地、椰子香气 注:a:表中各物质香气阈值通过查阅Gemert的书籍[60]得到;b:表中仅展示OAV≥1的物质及相应OAV值;c:表中各物质香气描述通过查阅www.flavornet.org/得到。 2.9 不同产地卡宴辣椒非挥发性化合物
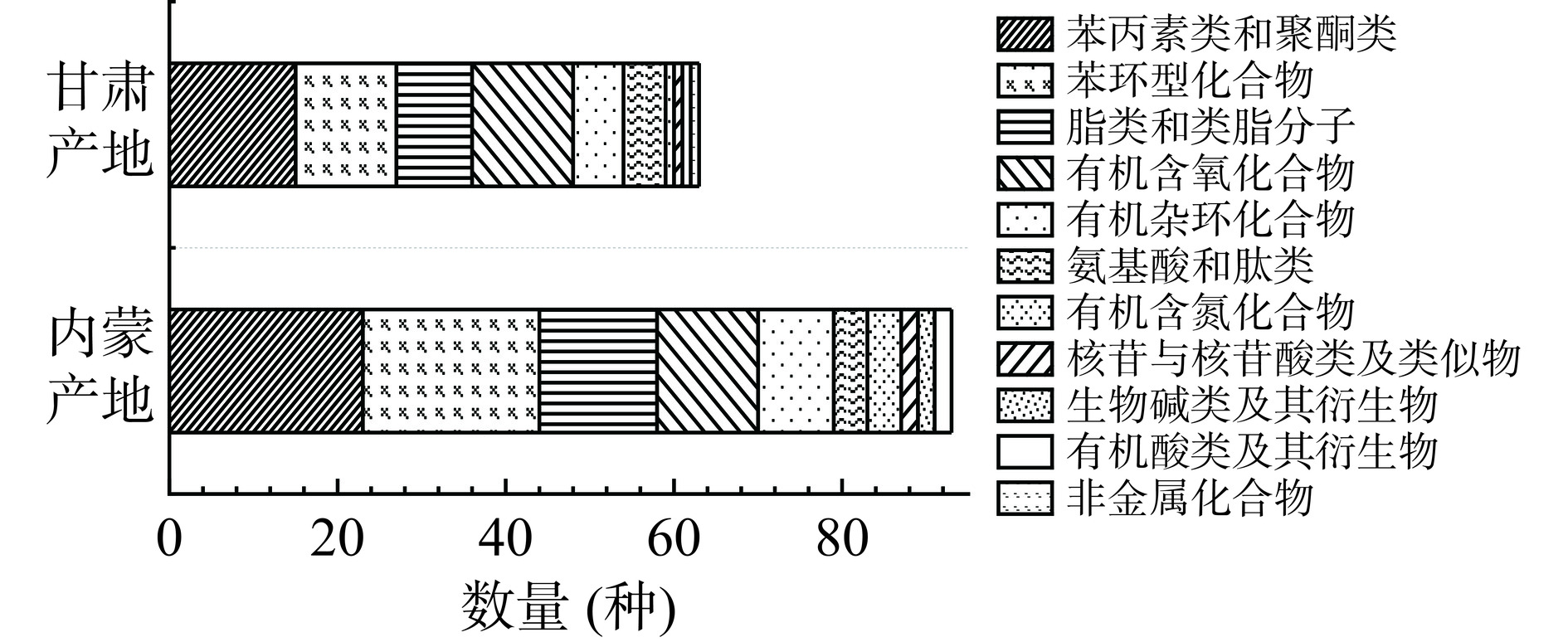
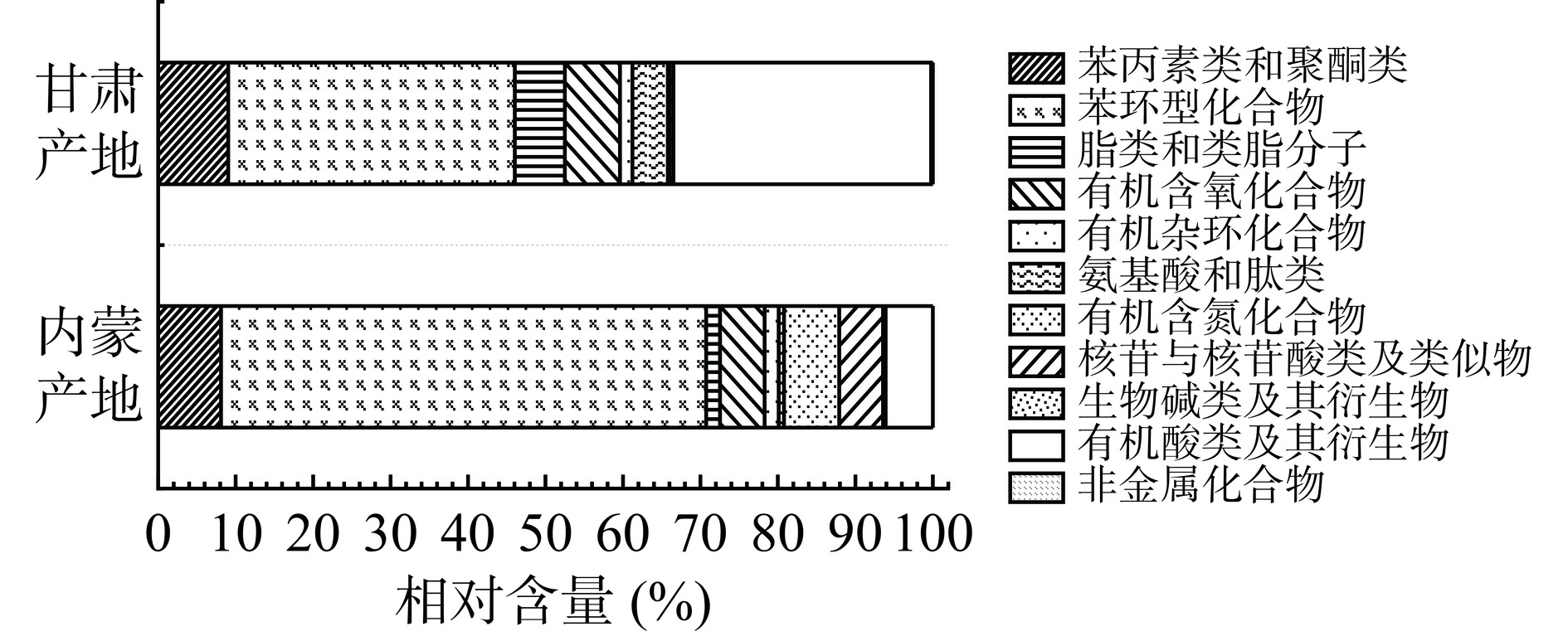
两产地卡宴辣椒共检出非挥发性化合物132种,包括苯丙素类和聚酮类化合物32种,苯环型化合物29种,脂类和类脂分子19种,有机含氧化合物17种,有机杂环化合物14种,氨基酸和肽类8种,有机含氮化合物5种,核苷类与核苷酸类及类似物3种,生物碱类及其衍生物2种,有机酸类及其衍生物2种,非金属化合物1种。图8~图9所示为不同产地卡宴辣椒非挥发性化合物种类分布及各类化合物相对含量占比。从非挥发性化合物种类数量来看,内蒙产地卡宴辣椒化合物种类更加丰富。从相对含量来看,两产地卡宴辣椒中含量最高的均为苯环型化合物,分别占甘肃卡宴辣椒总非挥发性化合物和内蒙卡宴辣椒总非挥发性化合物的37.00%和62.64%,且苯环型化合物中含量最高的均为辣椒中的特征性成分辣椒碱,分别占总非挥发性化合物的19.0%和30.3%,其次为二氢辣椒碱、1-萘胺、2,6-二甲基苯胺等。此外,两产地卡宴辣椒中均含有丰富的苯丙素类和聚酮类化合物、有机含氧化合物,占各自总非挥发性化合物的5.75%~9.04%。甘肃产地卡宴辣椒比内蒙产地含有更丰富的有机酸类及其衍生物、脂类和类脂分子、氨基酸和肽类,其中甘肃产地有机酸类含量最高的是TCA循环中的关键中间代谢物柠檬酸,占比高达33.27%。而内蒙产地具有更丰富的有机含氮化合物、核苷类与核苷酸类及类似物。
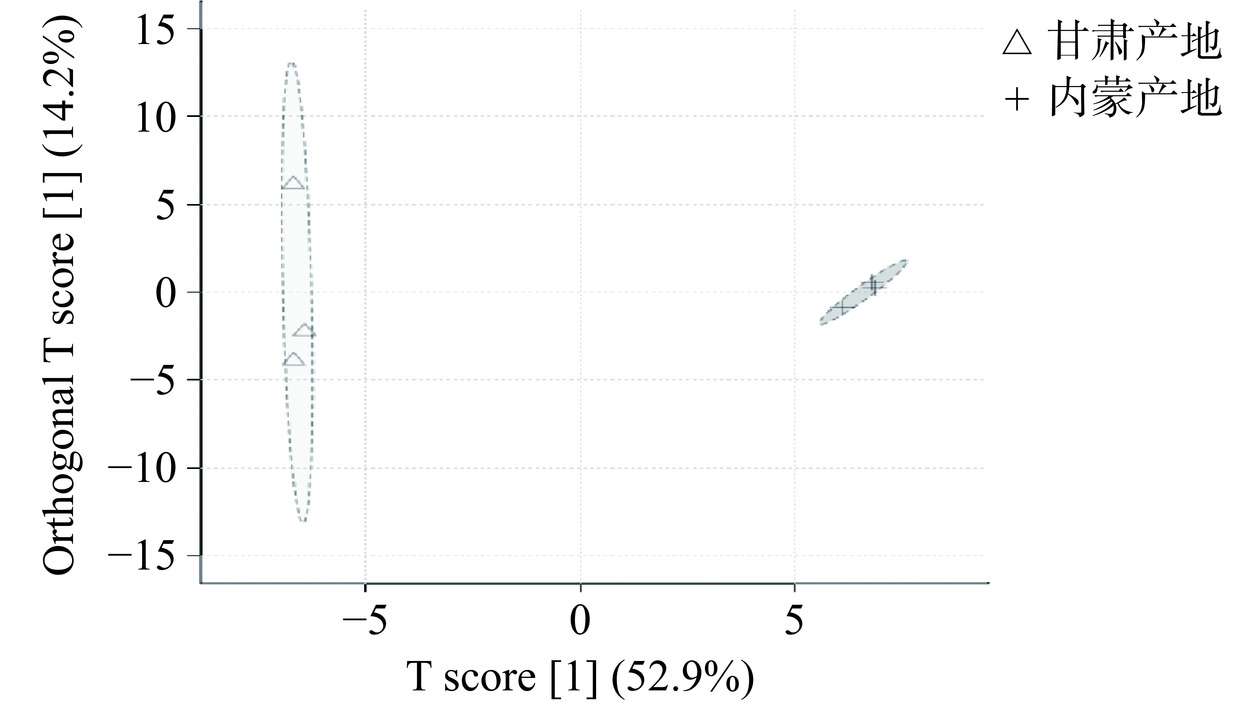
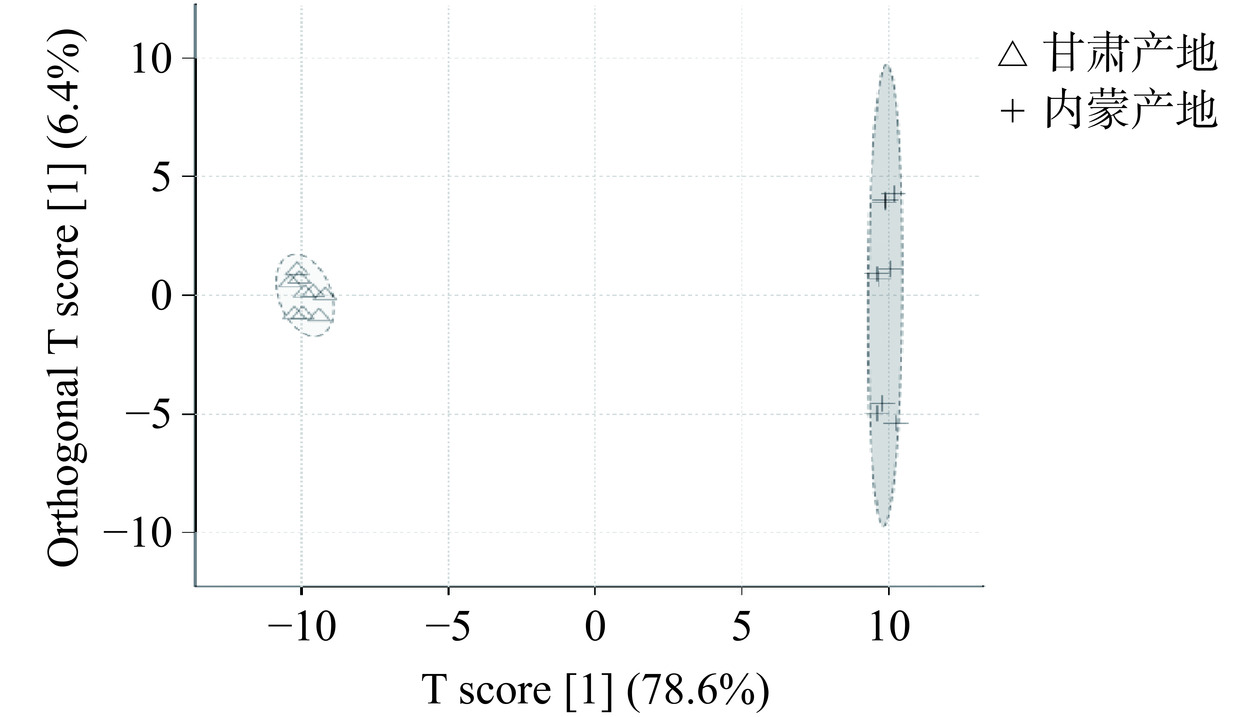
对132种非挥发性化合物进行无监督的PCA分析,如图10所示,发现两产地卡宴辣椒非挥发性化合物明显分离,产地对非挥发性代谢物影响显著。进一步针对两组非挥发性化合物进行有监督的OPLS-DA分析,如图11所示,两样本聚类分离明显,组间差异显著,说明两产地辣椒非挥发性化合物具有显著差异。对该OPLS-DA模型进行置换检验,经100次循环迭代后的置换检验结果显示模型的Q2值和R2值分别为0.998和0.999。Q2、R2两者均大于0.5且差值小于0.3,说明模型可靠性较好;Q2大于0.9,说明模型可靠性非常好。由此说明模型无过度拟合现象,结果可用于不同产地卡宴辣椒非挥发性化合物的组间对比。
通过筛选差异倍数FC大于2或小于0.5,且满足t检验结果P<0.05,同时满足OPLS-DA分析VIP>1的非挥发性化合物,最终筛得86种差异化合物。表11列举了部分相对含量较高的差异化合物相关信息。例如,苯丙素类和聚酮类化合物中的一些糖苷类化合物,例如矢车菊素-3-O-桑布双糖苷和山奈酚-3-O-槐角苷更多存在于甘肃卡宴辣椒中;多酚类化合物7-羟基香豆素和槲皮素更多存在于内蒙卡宴辣椒中。苯环型化合物中,除辣椒中的特征化合物辣椒碱,另有4-羟基苯甲酰胆碱在甘肃卡宴辣椒中检出。有机含氧化合物中的芦荟苦素在内蒙卡宴辣椒中被检出。氨基酸和肽类化合物中,甘肃卡宴辣椒中更多检出L-色氨酸、L-焦谷氨酸等氨基酸,而内蒙卡宴辣椒中则检出甘氨酸-亮氨酸等二肽。此外,内蒙卡宴辣椒中检出一种含量较高的有机含氮化合物为植物鞘氨醇,以及含量较高的核苷类化合物腺苷。甘肃和内蒙卡宴辣椒中丰富的差异代谢物赋予鲜椒不同的生理活性。例如甘肃卡宴辣椒中更多存在的花青素衍生物矢车菊素-3-O-桑布双糖苷曾在石榴种皮中检出[61];山奈酚-3-O-槐角苷曾在山参叶、藏红花等中被分离出来,且被证实具有抗炎、抗抑郁等作用[62−63];4-羟基苯甲酰胆碱则曾作为传统中药白芥菜籽的活性成分被分离鉴定[64]。内蒙卡宴辣椒中更多存在的7-羟基香豆素,其抗氧化应激、抗炎等功效已得到充分证实[65];槲皮素则具有抗氧化、抗肿瘤、降血压等功能,是辣椒中重要的黄酮类化合物之一,且槲皮素与辣椒素具有协同降血糖、抗氧化的功效[66−67];芦荟苦素是芦荟中的重要活性成分,具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗肿瘤等功效[68];植物鞘氨醇具有抗炎、抗菌、刺激表皮分化等生物活性[69];腺苷作为重要的中间体起到参与提供能量、传递信号、调节代谢等生理作用[70]。此外,甘肃和内蒙卡宴辣椒中分别含有较为丰富的能够贡献果实的风味和生物活性的氨基酸和肽类物质[71]。
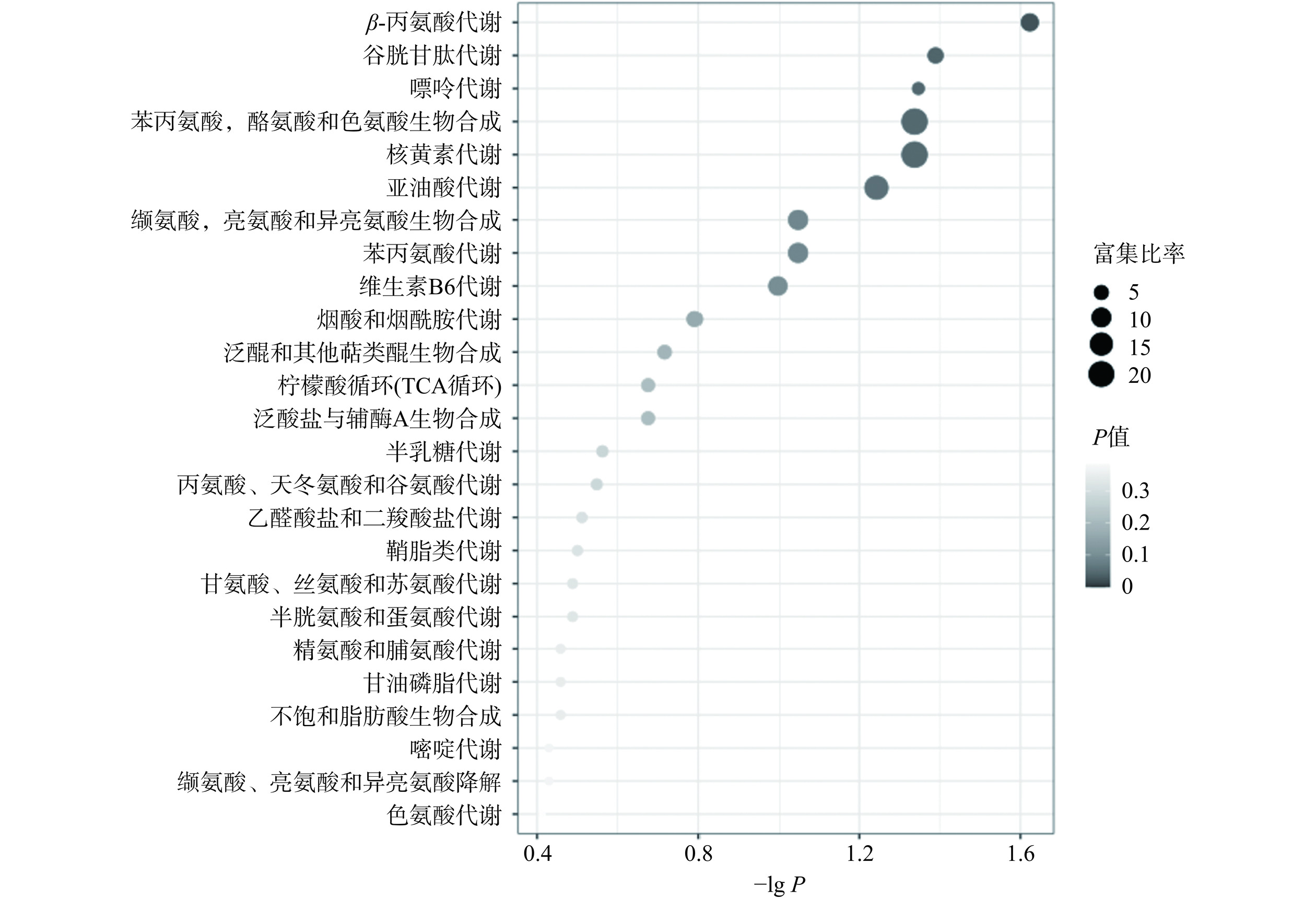
表 11 不同产地卡宴辣椒部分差异非挥发性化合物信息Table 11. Partial differential non-volatile compounds information of cayenne pepper from different regions类别 非挥发性化合物名称 分子式 保留时间(min) 质荷比 离子模式 log2 FC lg P VIP值 苯丙素类和聚酮类化合物 矢车菊素-3-O-桑布双糖苷 C26H29O15 4.796 581.1512 [M]+ 2.90 7.44 1.05 山奈酚-3-O-槐角苷 C27H30O16 3.907 609.1466 [M-H]− 2.60 11.75 1.11 7-羟基香豆素 C9H6O3 8.132 163.0393 [M+H]+ −2.48 13.50 1.11 槲皮素 C15H10O7 5.378 303.0503 [M+H]+ −2.52 13.81 1.12 5,7-二羟基-2-[4-羟基-3-[(2S,3R,4S,5R)-3,4,5-三羟基氧杂环己烷基]氧基苯基]-3-甲氧基苯并吡喃-4-酮 C21H20O11 5.367 447.0934 [M-H]− −2.64 10.51 1.09 苯环型化合物 4-羟基苯甲酰胆碱 C12H18NO3 3.671 224.1292 [M+H]+ 2.70 10.63 1.09 8-氮杂双环[3.2.1]辛烷基-4-羟基-3-甲氧基苯甲酸酯 C15H19NO4 3.851 278.1396 [M+H]+ 2.68 10.68 1.09 辣椒碱 C18H27NO3 8.029 306.2067 [M+H]+、[M+Na]+ −8.31 9.11 1.08 2-苯乙酰胺 C8H9NO 1.338 136.0756 [M+H]+ −2.70 9.59 1.08 1-萘胺 C10H9N 4.025 144.0817 [M+H]+ −2.41 19.99 1.13 4-癸烷基苯磺酸 C16H26O3S 13.764 297.1534 [M-H]− −2.42 19.74 1.13 4-十一烷基苯磺酸 C17H28O3S 14.678 311.1690 [M-H]− −2.45 15.25 1.12 有机含氧化合物 (3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-(6-羟基-2,6-二甲基-2,7-二烯氧基)-6-(羟甲基)氧杂环-3,4,5-三醇 C16H28O7 5.975 355.1735 [M+Na]+ −1.38 15.61 1.12 芦荟苦素 C19H22O9 8.456 393.1232 [M-H]− −2.62 9.14 1.08 有机杂环化合物 L-色氨酸 C11H12N2O2 3.856 205.0974 [M+H]+ −3.13 6.50 1.02 氨基酸和肽类 L-焦谷氨酸 C5H7NO3 1.301 130.0496 [M+H]+ 2.70 9.88 1.09 有机含氮化合物 植物鞘氨醇 C18H39NO3 11.382 318.3012 [M+H]+ −2.89 8.24 1.06 核苷类与核苷酸类及类似物 腺苷 C10H13N5O4 1.343 268.1049 [M+H]+ −2.41 20.57 1.13 进一步将差异化合物富集到KEGG代谢通路,如图12所示,筛选条件−lg P≥1且命中该通路的代谢物数≥2,筛得8条相对显著的代谢通路,分别为β-丙氨酸代谢、谷胱甘肽代谢、嘌呤代谢、苯丙氨酸,酪氨酸和色氨酸生物合成、核黄素代谢、亚油酸代谢、缬氨酸,亮氨酸和异亮氨酸生物合成、苯丙氨酸代谢。8条代谢通路中有5条与氨基酸合成与代谢有关,而氨基酸代谢可产生挥发性香气物质,如缬氨酸、异亮氨酸、苯丙氨酸在酶的作用下代谢产生挥发性有机酸类或酯类化合物,进而影响果实风味品质[72]。
3. 结论
研究发现,卡宴辣椒具有椒形硕大、籽肉比低的特点;甘肃和内蒙产地卡宴辣椒果肉水分含量高达86.1%和87.9%,总还原糖含量分别高达5.28 g/100 g和4.67 g/100 g,说明糖类化合物积累丰富;总酸含量低,蛋白质和氨基酸含量低;辣度均低于1400 SHU,属于轻微辣度辣椒;总体而言,满足辣椒酱制品的口感要求和加工需求,是制作鲜椒酱或发酵辣椒酱的优选品种。对比来看,受到产地环境因素影响,甘肃产地卡宴辣椒具有高糖低酸、辣度更高、挥发性香气化合物种类丰富的特点;而内蒙产地卡宴辣椒水分含量高,红色强度及类胡萝卜素含量更高,抗氧化物质含量及能力更强,非挥发性化合物种类丰富。因此,甘肃卡宴辣椒更适用于对甜度、辣度和香气要求较高的鲜椒酱和需要为微生物提供充足代谢底物的发酵辣椒酱生产,而内蒙卡宴辣椒更适合生产对水分、酸度、色泽、滋味和功能活性提出更高要求的辣椒酱产品。本研究揭示了卡宴辣椒的品种特征和不同产地辣椒品质差异信息,填充国内酱用辣椒原料品质研究数据库,为国内制酱品种选育、加工企业品种选择提供科学指导,从根本上提高辣椒酱制品品质,助力辣椒加工行业发展。
-
图 2 不同产地卡宴辣椒有机酸含量
注:显著性差异分别用*(P<0.05)、**(P<0.01)、***(P<0.001)表示,图3同。
Figure 2. Contents of organic acids of cayenne pepper from different regions
表 1 有机酸标准曲线
Table 1 Standard curves of organic acids
名称 标准曲线 R2 抗坏血酸 y=156205x+8879.1 0.9965 乳酸 y=754.85x−134.52 0.9981 苹果酸 y=19950x+280815 0.9910 琥珀酸 y=3988.8x+335.1 0.9944 柠檬酸 y=241539x−110852 0.9966 莽草酸 y=48828x+30834 0.9898 奎宁酸 y=127965x−4764.7 0.9951 乌头酸 y=114011x+14385 0.9971 咖啡酸 y=914091x+144891 0.9985 绿原酸 y=1000000x+132020 0.9977 香草酸 y=79081x+14851 0.9976 表 2 不同产地卡宴辣椒基本结构信息
Table 2 Basic structure information of cayenne pepper from different regions
表 3 不同产地卡宴辣椒可溶性固形物、还原糖及单糖含量
Table 3 Contents of total soluble solids, reducing sugars and monosaccharides of cayenne pepper from different regions
产地 可溶性固形物含量(%) 葡萄糖含量
(g/100 g)果糖含量
(g/100 g)麦芽糖含量
(g/100 g)蔗糖含量
(g/100 g)总还原糖含量
(g/100 g,滴定法,以葡萄糖计)总还原糖含量
(g/100 g,液相色谱法)甘肃 11.35±0.19b 2.59±0.05Ab 2.97±0.14Bb ND ND 5.28±0.11b 5.56±0.15b 内蒙 9.75±0.32a 2.09±0.15Aa 2.67±0.16Ba ND ND 4.67±0.27a 4.76±0.30a 注:同行不同大写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),ND表示未检出。 表 4 不同产地卡宴辣椒pH和总酸含量
Table 4 pH and contents of total acid of cayenne pepper from different regions
产地 pH 总酸含量(g/kg) 甘肃 4.83±0.01a 4.44±0.26a 内蒙 4.85±0.03a 5.09±0.57b 表 5 不同产地卡宴辣椒蛋白质和氨基酸态氮含量
Table 5 Contents of protein and amino acid nitrogen of cayenne pepper from different regions
产地 蛋白质含量(%) 氨基酸态氮含量(g/100 g) 甘肃 1.59±0.07a 0.14±0.01a 内蒙 1.44±0.08a 0.13±0.01a 表 6 不同产地卡宴辣椒L*、a*、b*和△E值
Table 6 L*, a*, b* and △E value of cayenne pepper from different regions
产地 L* a* b* △E 甘肃 39.32±0.15a 32.23±0.23a 21.20±0.23a 1.04 内蒙 39.33±0.03a 33.23±0.08b 21.30±0.09a 表 7 不同产地卡宴辣椒总酚、总黄酮含量及抗氧化能力
Table 7 Contents of total phenols, total flavonoids and antioxidant capacity of cayenne pepper from different regions
产地 总酚含量(mg GAE/g) 总黄酮含量(mg RE/g) DPPH自由基清除能力(mg Trolox/g) FRAP铁离子还原能力(mg Trolox/g) 甘肃 0.52±0.03a 0.15±0.01a 0.87±0.04a 0.84±0.04a 内蒙 0.62±0.03b 0.23±0.02b 1.42±0.04b 1.34±0.07b 表 8 不同产地卡宴辣椒辣椒碱类物质含量及辣度
Table 8 Contents of capsaicinoids and pungency degrees of cayenne pepper from different regions
产地 辣椒碱含量(mg/kg) 二氢辣椒碱含量(mg/kg) 总含量(mg/kg) 斯科维尔指数(SHU) 辣度 甘肃 69.30±7.94b 11.61±2.93a 89.90±9.02b 1386.26±139.09b 9.24±0.93b 内蒙 55.98±3.48a 9.18±6.62a 72.40±8.29a 1116.41±127.87a 7.44±0.85a 表 9 不同产地卡宴辣椒差异挥发性化合物及含量
Table 9 Differential volatile compounds and contents of cayenne pepper from different regions
类别 挥发性化合物 含量(μg/g) log2 FC P值 VIP值 甘肃产地 内蒙产地 酯类 水杨酸甲酯 0.0652±0.0180 0.0101±0.0014 2.70 0.0061 2.20 3-甲基丁酸-4-甲苯酯 0.0199±0.0076 0.0018±0.0016 3.40 0.0162 1.80 2-甲基丁酸-4-甲苯酯 0.0176±0.0046 − 2.80 0.0049 2.30 3-甲基丁酸乙酯 0.0308±0.0091 − 2.80 0.0074 2.10 异戊酸异丁酯 0.0047±0.0017 − 3.00 0.0129 1.90 邻苯二甲酸二异丁酯 0.0005±0.0001 − 2.50 0.0008 3.10 亚油酸甲酯 0.0039±0.0011 0.0008±0.0009 2.30 0.0187 1.70 顺式-3-己烯基异戊酸酯 0.0019±0.0008 3.30 0.0238 1.60 亚麻酸甲酯 0.0008±0.0013 0.0011±0.0005 −3.30 0.0253 1.60 烯烃类 巴伦西亚橘烯 0.0082±0.0026 − 2.70 0.0097 2.00 4-氰基-1-环己烯 0.0007±0.0006 0.0019±0.0002 −1.30 0.0208 1.70 喜马偕-2,4-二烯 − 0.0001±0.0000 −2.60 0.0021 2.70 4-甲基-1,5-庚二烯 − 0.0029±0.0003 −2.50 0.0002 3.70 β-榄香烯 0.0091±0.0032 0.0014±0.0002 2.70 0.0142 1.80 烷烃类 十五烷 0.0064±0.0013 − 2.60 0.0019 2.70 十八烷 0.0007±0.0002 − 3.00 0.0102 2.00 环十四烷 0.0008±0.0003 − 2.80 0.0158 1.80 4-乙基癸烷 0.0008±0.0003 − 2.70 0.0163 1.80 十二烷 − 0.0100±0.0008 −2.50 0.0000 4.30 壬基环戊烷 − 0.0006±0.0002 −2.60 0.0071 2.10 醛类 苯甲醛 0.0038±0.0010 0.0236±0.0065 −2.60 0.0064 2.20 壬醛 0.0134±0.0013 0.0058±0.0012 1.20 0.0018 2.70 2,6,6-三甲基-1-环己烯-1-甲醛 0.0012±0.0002 0.0005±0.0001 1.20 0.0031 2.50 反式-2-己烯醛 − 0.0126±0.0012 −2.50 0.0001 4.00 醇类 芳樟醇 0.0284±0.0034 0.0114±0.0009 1.30 0.0011 3.00 醚类 莳萝醚 0.0176±0.0035 0.0037±0.0034 2.15 0.0065 1.28 芳香烃类 2-异丙烯基-4α,8-二甲基-1,2,3,4,4A,5,6,7-八氢萘 0.0034±0.0015 0.0002±0.0004 3.10 0.0244 1.60 表 10 不同产地卡宴辣椒关键香气活性成分与气味描述
Table 10 Key aroma active compounds and odor description in cayenne pepper from different regions
挥发性化合物名称 含量(μg/g) 阈值(mg/m3)a OAV值b 香气描述c 甘肃产地 内蒙产地 甘肃产地 内蒙产地 3-异丁基-2-甲氧基吡嗪 0.0313±0.0053 0.0170±0.0049 0.000003 10426.32 5660.98 土壤,香料,青椒香气 3-甲基丁酸乙酯 0.0308±0.0091 − 0.000069 446.48 − 果香 反式-2-壬烯醛 0.0117±0.0103 0.0088±0.0037 0.00009 130.17 97.50 脂肪,黄瓜香气,生青味 β-紫罗兰酮 0.0016±0.0015 0.0005±0.0008 0.00012 13.27 3.84 海藻,紫罗兰,覆盆子香气,花香 壬醛 0.0134±0.0013 0.0058±0.0012 0.0031 4.33 1.87 脂肪,柑橘香气,生青味 水杨酸甲酯 0.0652±0.0180 0.0101±0.0014 0.016 4.07 − 胡椒薄荷香气 反式-2-已烯醛 − 0.0126±0.0012 0.0031 − 4.07 生青味,叶子香气 苯甲酸甲酯 0.0044±0.0012 0.0024±0.0001 0.0015 2.92 1.60 西梅,生菜,草药香气,甜香 苯乙醛 0.0151±0.0046 0.0102±0.0024 0.0063 2.40 1.62 山楂,蜂蜜香气,甜香 十一酸乙酯 0.0005±0.0005 0.0001±0.0001 0.0003 1.75 − 干邑白兰地、椰子香气 注:a:表中各物质香气阈值通过查阅Gemert的书籍[60]得到;b:表中仅展示OAV≥1的物质及相应OAV值;c:表中各物质香气描述通过查阅www.flavornet.org/得到。 表 11 不同产地卡宴辣椒部分差异非挥发性化合物信息
Table 11 Partial differential non-volatile compounds information of cayenne pepper from different regions
类别 非挥发性化合物名称 分子式 保留时间(min) 质荷比 离子模式 log2 FC lg P VIP值 苯丙素类和聚酮类化合物 矢车菊素-3-O-桑布双糖苷 C26H29O15 4.796 581.1512 [M]+ 2.90 7.44 1.05 山奈酚-3-O-槐角苷 C27H30O16 3.907 609.1466 [M-H]− 2.60 11.75 1.11 7-羟基香豆素 C9H6O3 8.132 163.0393 [M+H]+ −2.48 13.50 1.11 槲皮素 C15H10O7 5.378 303.0503 [M+H]+ −2.52 13.81 1.12 5,7-二羟基-2-[4-羟基-3-[(2S,3R,4S,5R)-3,4,5-三羟基氧杂环己烷基]氧基苯基]-3-甲氧基苯并吡喃-4-酮 C21H20O11 5.367 447.0934 [M-H]− −2.64 10.51 1.09 苯环型化合物 4-羟基苯甲酰胆碱 C12H18NO3 3.671 224.1292 [M+H]+ 2.70 10.63 1.09 8-氮杂双环[3.2.1]辛烷基-4-羟基-3-甲氧基苯甲酸酯 C15H19NO4 3.851 278.1396 [M+H]+ 2.68 10.68 1.09 辣椒碱 C18H27NO3 8.029 306.2067 [M+H]+、[M+Na]+ −8.31 9.11 1.08 2-苯乙酰胺 C8H9NO 1.338 136.0756 [M+H]+ −2.70 9.59 1.08 1-萘胺 C10H9N 4.025 144.0817 [M+H]+ −2.41 19.99 1.13 4-癸烷基苯磺酸 C16H26O3S 13.764 297.1534 [M-H]− −2.42 19.74 1.13 4-十一烷基苯磺酸 C17H28O3S 14.678 311.1690 [M-H]− −2.45 15.25 1.12 有机含氧化合物 (3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-(6-羟基-2,6-二甲基-2,7-二烯氧基)-6-(羟甲基)氧杂环-3,4,5-三醇 C16H28O7 5.975 355.1735 [M+Na]+ −1.38 15.61 1.12 芦荟苦素 C19H22O9 8.456 393.1232 [M-H]− −2.62 9.14 1.08 有机杂环化合物 L-色氨酸 C11H12N2O2 3.856 205.0974 [M+H]+ −3.13 6.50 1.02 氨基酸和肽类 L-焦谷氨酸 C5H7NO3 1.301 130.0496 [M+H]+ 2.70 9.88 1.09 有机含氮化合物 植物鞘氨醇 C18H39NO3 11.382 318.3012 [M+H]+ −2.89 8.24 1.06 核苷类与核苷酸类及类似物 腺苷 C10H13N5O4 1.343 268.1049 [M+H]+ −2.41 20.57 1.13 -
[1] 李国琛, 徐昊, 刘周斌, 等. 辣椒在世界的传播[J]. 热带作物学报,2023,44(7):1307−1316. [LI G C, XU H, LIU Z B, et al. The global dissemination of Capsicum[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2023,44(7):1307−1316.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2023.07.001 LI G C, XU H, LIU Z B, et al. The global dissemination of Capsicum[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2023, 44(7): 1307−1316. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2023.07.001
[2] AZLAN A, SULTANA S, HUEI C S, et al. Antioxidant, anti-obesity, nutritional and other beneficial effects of different chili pepper:A review[J]. Molecules,2022,27(3):898. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030898
[3] FAO. Food and agriculture data[EB/OL]. (2023-12-27) [2024-01-31]. http://www.fao.org/faostat/en.
[4] 年国芳, 郭超男, 徐建宗, 等. 新疆制干辣椒品质综合评价及加工适宜性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(4):317−325. [NIAN G F, GUO C N, XU J Z, et al. Comprehensive quality evaluation and processing suitability analysis of Xinjiang dried pepper[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(4):317−325.] NIAN G F, GUO C N, XU J Z, et al. Comprehensive quality evaluation and processing suitability analysis of Xinjiang dried pepper[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(4): 317−325.
[5] 王兴波, 饶雷, 王永涛, 等. 9个品种干辣椒的品质分析及评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(18):300−310. [WANG X B, RAO L, WANG Y T, et al. Quality analysis and evaluation of nine varieties of dried peppers[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(18):300−310.] WANG X B, RAO L, WANG Y T, et al. Quality analysis and evaluation of nine varieties of dried peppers[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(18): 300−310.
[6] 王兰兰. 甘肃辣椒育种工作现状及发展建议[J]. 甘肃农业科技,2021,52(3):74−79. [WANG L L. Current situation and development suggestion of chili pepper breeding in Gansu Province[J]. Gansu Agriculture Science and Technology,2021,52(3):74−79.] WANG L L. Current situation and development suggestion of chili pepper breeding in Gansu Province[J]. Gansu Agriculture Science and Technology, 2021, 52(3): 74−79.
[7] 杨志刚, 常海文, 胡栓红, 等. 内蒙古辣椒产业发展现状、存在问题及建议[J]. 中国蔬菜,2023(12):14−19. [YANG Z G, CHANG H W, HU S H, et al. Development status, existing problems and suggestions of chili industry in Inner Mongolia[J]. China Vegetables,2023(12):14−19.] YANG Z G, CHANG H W, HU S H, et al. Development status, existing problems and suggestions of chili industry in Inner Mongolia[J]. China Vegetables, 2023(12): 14−19.
[8] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.3-2016 食品中水分的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.3- 2016 Determination of moisture in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.3- 2016 Determination of moisture in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[9] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB/T 5009.10-2003 植物类食品中粗纤维的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2003. [National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 5009.10-2003 Determination of crude fiber in vegetable foods[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2003.] National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB/T 5009.10-2003 Determination of crude fiber in vegetable foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2003.
[10] 中华人民共和国农业部. NY/T 2637-2014 水果和蔬菜可溶性固形物的测定 折射仪法[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2014. [Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China. NY/T 2637-2014 Refractometric method for determination of total soluble solids in fruits and vegetables[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2014.] Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China. NY/T 2637-2014 Refractometric method for determination of total soluble solids in fruits and vegetables[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2014.
[11] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.7-2016 食品中还原糖的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.7-2016 Determination of reducing sugar in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.7-2016 Determination of reducing sugar in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[12] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.8-2016 食品中果糖、葡萄糖、蔗糖、麦芽糖、乳糖的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.8-2016 Determination of fructose, glucose, sucrose, maltose and lactose in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.8-2016 Determination of fructose, glucose, sucrose, maltose and lactose in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[13] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.235-2016 食品中氨基酸态氮的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.235-2016 Determination of amino acid nitrogen in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.235-2016 Determination of amino acid nitrogen in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[14] WEN M C, ZHOU F, ZHU M T, et al. Monitoring of pickled tea during processing:From LC-MS based metabolomics analysis to inhibitory activities on α-amylase and α-glycosidase[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2023(117):105108.
[15] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.5-2016 食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.5-2016 Determination of protein in food[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2016.] National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. GB 5009.5-2016 Determination of protein in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
[16] 江雪梅, 王锋, 周书栋, 等. 不同辣椒品种对发酵剁辣椒品质及风味的影响[J]. 中国调味品,2023,48(4):1−6,19. [JIANG X M, WANG F, ZHOU S D, et al. Effects of different chili varieties on the quality and flavor of fermented minced chili[J]. China Condiment,2023,48(4):1−6,19.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2023.04.001 JIANG X M, WANG F, ZHOU S D, et al. Effects of different chili varieties on the quality and flavor of fermented minced chili[J]. China Condiment, 2023, 48(4): 1−6,19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2023.04.001
[17] XU J Y, LIN J L, PENG S J, et al. Development of an HPLC-PDA method for the determination of capsanthin, zeaxanthin, lutein, β-cryptoxanthin and β-carotene simultaneously in chili peppers and products[J]. Molecules,2023,28(5):2362. doi: 10.3390/molecules28052362
[18] 张新悦, 连畅, 宋文胜, 等. 新疆地区辣椒自然干制的关键节点品质分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(12):90−101. [ZHANG X Y, LIAN C, SONG W S, et al. Quality analysis of key nodes of natural drying chilis in Xinjiang region[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(12):90−101.] ZHANG X Y, LIAN C, SONG W S, et al. Quality analysis of key nodes of natural drying chilis in Xinjiang region[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(12): 90−101.
[19] 马燕. 辣椒籽油、膳食纤维和分离蛋白的超高压提取工艺优化及其特性研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学, 2019. [MA Y. The extraction optimization and characterization of pepper seed oil, dietary fiber and isolated protein by high pressure processing[D]. Beijing:China Agriculture University, 2019.] MA Y. The extraction optimization and characterization of pepper seed oil, dietary fiber and isolated protein by high pressure processing[D]. Beijing: China Agriculture University, 2019.
[20] 中华人民共和国国家市场监督管理总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 40348-2021 植物源产品中辣椒素类物质的测定 液相色谱-质谱/质谱法[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2021. [State Administration for Market Regulation of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 403480-2021 Determination of capsaiciniod in plant derived products liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2021.] State Administration for Market Regulation of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 403480-2021 Determination of capsaiciniod in plant derived products liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2021.
[21] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 21266-2007 辣椒及辣椒制品中辣椒素类物质测定及辣度表示方法[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2007. [General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 21266-2007 Determination of total capsaiciniod content and representation of pungency degree in Capsium and its products[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2007.] General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 21266-2007 Determination of total capsaiciniod content and representation of pungency degree in Capsium and its products[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2007.
[22] PENG S J, XU J Y, XU J G, et al. Microbial community and volatile metabolites related to the fermentation degree of salted fermented chili peppers[J]. LWT,2023,181:114752. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2023.114752
[23] WANG Y, LI C, LI L, et al. Application of UHPLC-Q/TOF-MS-based metabolomics in the evaluation of metabolites and taste quality of Chinese fish sauce (Yu-lu) during fermentation[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,296:132−141. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.05.043
[24] 张庆银, 王子凡, 王丹丹, 等. 基于主成分分析法的加工辣椒品种筛选与品质指标分析[J]. 蔬菜,2022,7:17−21. [ZHANG Q Y, WANG Z F, WANG D D, et al. Cultivar selection and quality index analysis of processing pepper based on principal component analysis[J]. Vegetables,2022,7:17−21.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8336.2022.7.sc202207003 ZHANG Q Y, WANG Z F, WANG D D, et al. Cultivar selection and quality index analysis of processing pepper based on principal component analysis[J]. Vegetables, 2022, 7: 17−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8336.2022.7.sc202207003
[25] 孔德男, 刘伟. “螺丝椒”类型辣椒的栽培现状和主要品种介绍[J]. 中国蔬菜,2012,17:34−37. [KONG D N, LIU W. The introduction of cultivation status and main varieties of ‘screw pepper’ type[J]. China Vegetables,2012,17:34−37.] KONG D N, LIU W. The introduction of cultivation status and main varieties of ‘screw pepper’ type[J]. China Vegetables, 2012, 17: 34−37.
[26] 肖何, 刘洋, 王馨瑶, 等. 不同产地辣椒生长过程品质变化分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(13):316−324. [XIAO H, LIU Y, WANG X Y, et al. Analysis of quality change of Capsicum annuum in growing process from different producing areas[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(13):316−324.] XIAO H, LIU Y, WANG X Y, et al. Analysis of quality change of Capsicum annuum in growing process from different producing areas[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(13): 316−324.
[27] 韩金朝, 冯俊杰, 翟国亮, 等. 生育期连续水分亏缺对秋冬茬辣椒生长特性和品质的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报,2024,43(3):11−18. [[HAN J Z, FENG J J, ZHAI G L, et al. Effects of water deficit in continuous growth period on growth characteristics and quality of pepper in autumn and winter[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage,2024,43(3):11−18.] [HAN J Z, FENG J J, ZHAI G L, et al. Effects of water deficit in continuous growth period on growth characteristics and quality of pepper in autumn and winter[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2024, 43(3): 11−18.
[28] 魏华伟. 辣椒蔗糖合酶(SUS)全基因组鉴定及表达分析[D]. 合肥:安徽农业大学, 2021. [WEI H W. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of the sucrose synthase (SUS) in Capsicum[D]. Hefei:Anhui Agricultural University, 2021.] WEI H W. Genome-wide identification and expression profiling of the sucrose synthase (SUS) in Capsicum[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2021.
[29] 董晓林, 吴龙, 徐庆, 等. 胡萝卜、辣椒干燥过程中的介电特性与其理化品质的关系研究[J]. 包装与食品机械,2020,38(2):1−7. [DONG X L, WU L, XU Q, et al. Study on the relationship between dielectric properties and physiochemical properties of carrot and pepper during drying[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery,2020,38(2):1−7.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1295.2020.02.001 DONG X L, WU L, XU Q, et al. Study on the relationship between dielectric properties and physiochemical properties of carrot and pepper during drying[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery, 2020, 38(2): 1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1295.2020.02.001
[30] BOZKURT ÇOLAK Y, YAZAR A, YILDIZ M, et al. Assessment of crop water stress index and net benefit for surface- and subsurface-drip irrigated bell pepper to various deficit irrigation strategies[J]. The Journal of Agricultural Science,2023,161(2):254−271. doi: 10.1017/S0021859623000205
[31] FoodData Central. U. S. Department of Agriculture. FoodData Central Search Results[EB/OL]. (2019-04-01) [2024-01-31]. https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/fdc-app.html#/food-details/170108/nutrients.
[32] XIONG T, LI X, GUAN Q, et al. Starter culture fermentation of Chinese sauerkraut:Growth, acidification and metabolic analyses[J]. Food Control,2014,41:122−127. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.12.033
[33] 刘炎, 赵鹏涛, 赵擎豪, 等. 有机酸对果酒品质的影响及调控技术研究进展[J]. 江苏农业学报,2023,39(3):904−912. [LIU Y, ZHAO P T, ZHAO Q H, et al. Research progress on the effect of organic acids on fruit wine quality and regulation technology[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Science,2023,39(3):904−912.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2023.03.032 LIU Y, ZHAO P T, ZHAO Q H, et al. Research progress on the effect of organic acids on fruit wine quality and regulation technology[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Science, 2023, 39(3): 904−912. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2023.03.032
[34] 黄丽, 王亮, 赵迎丽, 等. 3种梨贮藏期间果实品质、可溶性糖和有机酸含量变化[J]. 食品研究与开发,2023,44(10):46−52. [HUANG L, WANG L, ZHAO Y L, et al. Changes in fruit quality, soluble sugar and organic acid content of three pear species during storage[J]. Food Research and Development,2023,44(10):46−52.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2023.10.007 HUANG L, WANG L, ZHAO Y L, et al. Changes in fruit quality, soluble sugar and organic acid content of three pear species during storage[J]. Food Research and Development, 2023, 44(10): 46−52. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2023.10.007
[35] KIRIMURA K, HONDA Y, HATTORI T. Comprehensive biotechnology[M]. 2nd ed. Salt Lake:Academic Press, 2011:135−142.
[36] SØLTOFT-JENSEN J, HANSEN F. Emerging technologies for food processing[M]. Salt Lake:Academic Press, 2005:387−416.
[37] 周清丽, 周绍琴, 周艳. 自然发酵猕猴桃果酒中降苹果酸酵母的筛选与鉴定[J]. 中国酿造,2023,42(12):76−80. [ZHOU Q L, ZHOU S Q, ZHOU Y. Screening and identification of malic acid-reducing yeast in naturally fermented kiwifruit wine[J]. China Brewing,2023,42(12):76−80.] ZHOU Q L, ZHOU S Q, ZHOU Y. Screening and identification of malic acid-reducing yeast in naturally fermented kiwifruit wine[J]. China Brewing, 2023, 42(12): 76−80.
[38] GOLDBERG I, ROKEM J S. Encyclopedia of microbiology[M]. 3rd ed. Salt Lake:Academic Press, 2009:421−442.
[39] 叶陵, 王晶晶, 王蓉蓉, 等. 剁辣椒发酵过程中菌群与有机酸变化规律分析[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(6):116−121. [YE L, WANG J J, WANG R R, et al. Changes in microflora and organic acid contents during the fermentation of chopped pepper[J]. Food Science,2018,39(6):116−121.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201806019 YE L, WANG J J, WANG R R, et al. Changes in microflora and organic acid contents during the fermentation of chopped pepper[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(6): 116−121. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201806019
[40] SINGH P, GUPTA E, MISHRA N, et al. Phytochemicals as lead compounds for new drug discovery[M]. Amsterdam:Elsevier, 2020:245-256.
[41] KUMARI A. Sweet biochemistry[M]. Salt Lake:Academic Press, 2018:7-11.
[42] 陈治民, 李翠, 韦继天, 等. 绿原酸生物合成调控及其应用研究进展[J]. 生物技术通报,2024,40(1):57−71. [CHEN Z M, LI C, WEI J T, et al. Research progress in the regulation of chlorogenic acid biosynthesis and its application[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin,2024,40(1):57−71.] CHEN Z M, LI C, WEI J T, et al. Research progress in the regulation of chlorogenic acid biosynthesis and its application[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2024, 40(1): 57−71.
[43] OLATUNJI T L, AFOLAYAN A J. The suitability of chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) for alleviating human micronutrient dietary deficiencies:A review[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2018,6(8):2239−2251.
[44] 屠大伟, 翁盈秋, 李青青, 等. 火锅常用干辣椒品质及挥发性成分研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(16):358−366. [TU D W, WENG Y Q, LI Q Q, et al. Quality and volatile components of dried peppers commonly used in hot pot[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(16):358−366.] TU D W, WENG Y Q, LI Q Q, et al. Quality and volatile components of dried peppers commonly used in hot pot[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(16): 358−366.
[45] 牛丽丽, 崔艳, 闫志华, 等. 不同酿造工艺对黑豆酱油理化特性和感官品质的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2023,44(18):88−93. [NIU L L, CUI Y, YAN Z H, et al. Effects of different brewing techniques on physicochemical properties and sensory quality of black bean soy sauce[J]. Food Research and Development,2023,44(18):88−93.] NIU L L, CUI Y, YAN Z H, et al. Effects of different brewing techniques on physicochemical properties and sensory quality of black bean soy sauce[J]. Food Research and Development, 2023, 44(18): 88−93.
[46] 周晓, 李跑, 吴梓仟, 等. 不同黄曲霉菌株强化发酵对浏阳豆豉鲜味形成的影响[J]. 食品科学,2024,45(4):4116−4124. [ZHOU X, LI P, WU Z Q, et al. Study on the effect of enhanced fermentation with different Aspergillus on the umami taste in liuyang douchi[J]. Food Science,2024,45(4):4116−4124.] ZHOU X, LI P, WU Z Q, et al. Study on the effect of enhanced fermentation with different Aspergillus on the umami taste in liuyang douchi[J]. Food Science, 2024, 45(4): 4116−4124.
[47] 陈蓉, 胡继贵, 李静, 等. 新型发酵辣椒酱中有害物质及其品质分析[J]. 农产品加工,2023(19):61−64. [CHEN R, HU J G, LI J, et al. Analysis of harmful substances and quality in new fermented chili sauce[J]. Farm Products Processing,2023(19):61−64.] CHEN R, HU J G, LI J, et al. Analysis of harmful substances and quality in new fermented chili sauce[J]. Farm Products Processing, 2023(19): 61−64.
[48] 林佳璐. 辣椒及制品中5种类胡萝卜素HPLC测定方法的建立和应用[D]. 北京:中国农业大学, 2021. [LIN J L. Establishment and application of a HPLC method for determination of 5 kinds of carotene in pepper and pepper product[D]. Beijing:China Agriculture University, 2021.] LIN J L. Establishment and application of a HPLC method for determination of 5 kinds of carotene in pepper and pepper product[D]. Beijing: China Agriculture University, 2021.
[49] SRICHAROEN P, LAMAIPHAN N, PATTHAWARO P, et al. Phytochemicals in Capsicum oleoresin from different varieties of hot chilli peppers with their antidiabetic and antioxidant activities due to some phenolic compounds[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2017,38:629−639. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.08.018
[50] 王海帆, 郭梦嫣, 王玉洁, 等. 辣椒、花椒等辛辣香辛料对肉制品风味影响的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(15):389−395. [WANG H F, GUO M Y, WANG Y J, et al. A review on the effects of pungent spices including chili and prickly ash on the flavor of meat products[J]. Food Science,2022,43(15):389−395.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210606-079 WANG H F, GUO M Y, WANG Y J, et al. A review on the effects of pungent spices including chili and prickly ash on the flavor of meat products[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(15): 389−395. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210606-079
[51] 王楠艺, 付文婷, 周鹏, 等. 基于PCA分析的30个辣椒品种果实品质综合评价[J]. 中国瓜菜,2024,37(4):46−55. [WANG N Y, FU W T, ZHOU P, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of fruit quality of 30 pepper varieties based on PCA analysis[J]. China Cucurbits and Vegetables,2024,37(4):46−55.] WANG N Y, FU W T, ZHOU P, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of fruit quality of 30 pepper varieties based on PCA analysis[J]. China Cucurbits and Vegetables, 2024, 37(4): 46−55.
[52] CARLIN S, MASUERO D, GUELLA G, et al. Methyl salicylate glycosides in some italian varietal wines[J]. Molecules,2019,24(18):3260. doi: 10.3390/molecules24183260
[53] YU J, ZHANG Y, WANG Q, et al. Capsaicinoids and volatile flavor compounds profile of Sichuan hotpot as affected by cultivar of chili peppers during processing[J]. Food Research International,2023,165:112476. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112476
[54] 周琦, 谈安群, 欧阳祝, 等. 橙汁与宽皮橘汁关键香气的比较及其在各自主体风味呈现中的作用[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(21):259−267. [ZHOU Q, TAN A Q, OUYANG Z, et al. Comparison of key aromas between sweet orange and mandarin juices and their roles in the presentation of main flavors of the two juices[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(21):259−267.] ZHOU Q, TAN A Q, OUYANG Z, et al. Comparison of key aromas between sweet orange and mandarin juices and their roles in the presentation of main flavors of the two juices[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(21): 259−267.
[55] 吴颖瑞, 龙启发, 蒋小华, 等. SPME-GC/MS联用分析六堡茶茶花香气成分[J]. 广西植物,2016,36(11):1389−1395. [WU Y R, LONG Q F, JIANG X H, et al. SPME-GC/MS analysis of the aroma components from flower buds of Liubao tea plant[J]. Guihaia,2016,36(11):1389−1395.] WU Y R, LONG Q F, JIANG X H, et al. SPME-GC/MS analysis of the aroma components from flower buds of Liubao tea plant[J]. Guihaia, 2016, 36(11): 1389−1395.
[56] ZHU J, WANG L, XIAO Z, et al. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in mulberry fruits by application of gas chromatography-olfactometry (GC-O), odor activity value (OAV), gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and flame photometric detection (FPD)[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,245:775−785. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.11.112
[57] 陈鹏, 庄永亮, 耿树香, 等. 两种压榨条件下深纹核桃油挥发性物质成分研究[J/OL]. 中国油脂:1−13[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.19902/j.cnki.zgyz.1003-7969.230387. [CHEN P, ZHUANG Y L, GENG S X, et al. Study on volatile matters of walnut oil from Juglans Sigillata under two pressing conditions[J/OL]. China Oils and Fats: 1−13[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.19902/j.cnki.zgyz.1003-7969.230387.] CHEN P, ZHUANG Y L, GENG S X, et al. Study on volatile matters of walnut oil from Juglans Sigillata under two pressing conditions[J/OL]. China Oils and Fats: 1−13[2024-02-12]. https://doi.org/10.19902/j.cnki.zgyz.1003-7969.230387.
[58] XU X, WU B, ZHAO W, et al. Shifts in autochthonous microbial diversity and volatile metabolites during the fermentation of chili pepper (Capsicum frutescens L.)[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,335:127512. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127512
[59] ZAMOLO F, WÜST M. Investigation of biosynthetic precursors of 3-isobutyl-2-methoxypyrazine using stable isotope labeling studies in bell pepper fruits (Capsicum annuum L.)[J]. J Agric Food Chem,2022,70(22):6719−6725. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c01747
[60] GEMERT L J VAN. Odour thresholds:Compilations of odour threshold values in air, water and other media[M]. Second enlarged and revised edition. The Netherlands:Oliemans Punter & Partners BV, 2011.
[61] 王森. 超声波对石榴果实品质的影响及基于代谢组解析褐变机理[D]. 郑州:河南农业大学, 2023. [WANG S. Effect of ultrasound on pomegranate fruit quality and analyzing browning mechanism based on metabolome[D]. Zhengzhou:Henan Agricultural University, 2023.] WANG S. Effect of ultrasound on pomegranate fruit quality and analyzing browning mechanism based on metabolome[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2023.
[62] KIM T H, KU S K, LEE I C, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of kaempferol-3-O-sophoroside in human endothelial cells[J]. Inflammation Research,2012,61(3):217−24. doi: 10.1007/s00011-011-0403-9
[63] WANG R, HU X, LIU S, et al. Kaempferol-3-O-sophoroside (PCS-1) contributes to modulation of depressive-like behaviour in C57BL/6J mice by activating AMPK[J]. British Journal of Pharmacology,2024,181(8):1182−1202. doi: 10.1111/bph.16283
[64] LIU L, LIU T, LI G, et al. Isolation and determination of p-hydroxybenzoylcholine in traditional Chinese medicine Semen sinapis Albae[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2003,376(6):854−858. doi: 10.1007/s00216-003-1964-4
[65] LIN Z, CHENG X, ZHENG H. Umbelliferon:A review of its pharmacology, toxicity and pharmacokinetics[J]. Inflammopharmacology,2023,31(4):1731−1750. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01256-3
[66] 张向楠. 辣椒素与槲皮素协同降糖活性研究及产品创制[D]. 保定:河北农业大学, 2022. [ZHANG X N. Study on synergistic hypoglycemic activity of capsaicin and quercetin and development of new products[D]. Baoding:Hebei Agricultural University, 2022.] ZHANG X N. Study on synergistic hypoglycemic activity of capsaicin and quercetin and development of new products[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2022.
[67] 段方娥, 何强. 辣椒素与槲皮素、芦丁协同抗氧化作用研究[J]. 食品科技,2019,44(10):294−299. [DUAN F E, HE Q. Synergistic antioxidant effect of capsaicin with quercetin or rutin[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,44(10):294−299.] DUAN F E, HE Q. Synergistic antioxidant effect of capsaicin with quercetin or rutin[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2019, 44(10): 294−299.
[68] SÁNCHEZ M, GONZÁLEZ-BURGOS E, IGLESIAS I, et al. Pharmacological update properties of aloe vera and its major active constituents[J]. Molecules,2020,25(6):1324. doi: 10.3390/molecules25061324
[69] CHOI H K, CHO Y H, LEE E O, et al. Phytosphingosine enhances moisture level in human skin barrier through stimulation of the filaggrin biosynthesis and degradation leading to NMF formation[J]. Archives of Dermatological Research,2017,309(10):795−803. doi: 10.1007/s00403-017-1782-8
[70] 朱佐银, 郭文博, 赵含珂, 等. 超高效液相色谱-三重四极杆质谱法测定心脏组织中腺苷含量[J]. 色谱,2024,42(4):345−351. [ZHU Z Y, GUO W B, ZHAO H K, et al. Determination of adenosine in cardiac tissue by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry[J]. China Journal of Chromatography,2024,42(4):345−351.] doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2023.09016 ZHU Z Y, GUO W B, ZHAO H K, et al. Determination of adenosine in cardiac tissue by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry[J]. China Journal of Chromatography, 2024, 42(4): 345−351. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2023.09016
[71] LU Y, BAO T, MO J, et al. Research advances in bioactive components and health benefits of jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) fruit[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University Science B,2021,22(6):431−449. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2000594
[72] 顾晔, 周宇, 张爽, 等. 阳山水蜜桃非靶标代谢组学特征[J]. 食品科学,2024,45(15):237−244. [GU Y, ZHOU Y, ZHANG S, et al. Non-target metabolomics profiles of Yangshan honey peach[J]. Food Science,2024,45(15):237−244.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20231121-164 GU Y, ZHOU Y, ZHANG S, et al. Non-target metabolomics profiles of Yangshan honey peach[J]. Food Science, 2024, 45(15): 237−244. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20231121-164
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(4)






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
