Effect of Ultrasonic Treatment on the in Vitro Digestibility Properties of Black Bean Protein
-
摘要: 探究超声处理对黑豆蛋白消化特性的影响规律。采用不同功率(150、200、250、300、350 W)和不同持续时间(6、12、18、24 min)在低频(20 kHz)处理条件对黑豆蛋白进行超声处理。先探究超声处理对蛋白质消化率的影响,再通过扫描电镜、红外光谱、荧光光谱等分析超声处理对黑豆蛋白结构性质的影响,并通过粒度分布、乳化性、溶解度、Zeta电位等分析明确黑豆蛋白在超声处理过程中理化性质的变化。结果表明,300 W、6 min的超声处理后,减小了黑豆蛋白的粒径(由56 μm减小到32 μm);改变了黑豆蛋白的二级和三级结构,提高了溶解度、乳化性和Zeta电位绝对值,最终改善了黑豆蛋白的消化性,体外消化率从66.50%增加到90.9%。然而,不当的超声处理可能适得其反。在300 W下,12、18、24 min的超声处理会诱导聚集体的形成,从而降低溶解度和消化性。本研究结果可为超声处理在提高黑豆蛋白消化特性中的应用提供参考。Abstract: For exploring the effect of ultrasonic treatment on the digestive characteristics, the black bean protein was treated by ultrasonication at different power (150, 200, 250, 300, 350 W) and duration (6, 12, 18, 24 min) in low frequency (20 kHz). The effect of ultrasonication on protein digestibility was investigated. Furthermore, the effect of ultrasonication on the black bean protein structural properties was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy, infrared spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy. The particle size distribution, emulsifying properties, solubility and Zeta potential were performed to analyse the physicochemical properties variations of black bean protein during ultrasonic treatment. The particle size was decreased from 56 μm to 32 μm and the variation of secondary and tertiary structure of black bean protein was changed after the ultrasonic treatment at 300 W for 6 min. The solubility, emulsification, absolute value of Zeta potential of black bean protein were promoted. Finally, the digestibility of black bean protein was improved, the in vitro digestibility of black bean protein increased from 66.50% to 90.9%. However, improper sonication might be counterproductive. The black bean protein aggregation was formed during the sonication at 300 W for 12, 18, and 24 min with the decreasing solubility and digestibility. The results can provide a reference for improving the black bean protein digestibility by ultrasonic technology.
-
蛋白质在全世界的需求越来越大,这为寻找营养价值高且可持续获得蛋白质来源带来了巨大机遇[1]。植物蛋白作为一种人类饮食中蛋白的主要来源,近年来引起了人们的广泛关注[2]。其中黑豆的蛋白含量较高,已被公认为优质蛋白质的最佳来源,并且具有许多潜在的生物学效益[3]。然而,到目前为止,黑豆蛋白的使用却未达到期望。但黑豆含硫氨基酸含量低,其中非蛋白质成分可以和膳食纤维相互作用,再与蛋白质形成不可逆的复合物,从而影响黑豆蛋白溶解度[4]。此外,与动物蛋白相比,抗生理蛋白(蛋白酶抑制剂、凝集素)的存在及其紧凑的结构使植物蛋白更不容易在体内被消化[5]。因此,尽管黑豆蛋白具有良好的营养潜力,但较低的蛋白质消化率限制了其营养价值和应用。
超声作为一种新兴的、有发展前景的技术,常常被用于生物大分子的结构修饰和功能优化。原因是超声具有绿色高效的特性,特别是对于蛋白质来讲[6],它可以通过空化、机械和热效应有效地改变蛋白质的物理化学(包括消化性)和结构性质[7]。超声处理过程中产生的自由基和超氧化物可导致蛋白质分子交联[8],可以破坏非共价键,从而具有改变二级以上蛋白质结构的能力[9]。目前,超声处理已广泛应用于动物和植物蛋白的修饰,如有研究报道超声波处理改变了鹰嘴豆蛋白的分子结构,提高了其消化性[10]。也有研究发现超声处理大大改善了南极磷虾蛋白质结构和功能特性,最终改善了南极磷虾蛋白质的消化性[11]。然而,不当的超声处理可能适得其反。超声空化不可避免地会产生活性自由基,这些自由基引起蛋白质的高氧化和严重的共价反应,导致蛋白质的溶解度和消化率下降[7]。并且超声处理的时间和功率的变化对蛋白质有显著的影响[12]。因此,适度的超声处理就显得尤为重要。
目前对于黑豆蛋白的体外消化相关研究较少,并且对于超声处理改善黑豆蛋白消化性与结构、理化性质变化的关系尚不清楚[13]。因此,本研究采用超声技术对黑豆蛋白进行处理,探究溶解度、乳化性和Zeta电位等理化性质和体外消化率的关系。并分别通过激光粒度分布仪、傅里叶变换红外光谱(Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometer,FTIR)、荧光光谱、扫描电镜,分析探讨超声处理下黑豆蛋白的结构变化和体外蛋白消化率的关系。研究结果将深入了解超声处理下黑豆蛋白的结构改变、功能特性与消化性之间的关系,为进一步提高黑豆蛋白的消化性提供借鉴。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
黑豆蛋白 实验室自制,蛋白含量为82.6%,灰分为4.8%,水分为7.1%,脂肪为3.8%;胃蛋白酶(1:3000 U) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;胰蛋白酶(1500 U/g) 上海西格玛奥德里奇贸易有限公司;无水乙醇、光谱纯级溴化钾(KBr) 天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;氢氧化钠(分析纯) 辽宁泉瑞试剂有限公司;牛血清白蛋白(BR) 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;磷酸盐缓冲液 上海阿拉丁生物科技股份有限公司;所有试剂均为国产分析纯。
Y99-IIDN超声波细胞粉碎机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;H2050R-1型离心机、H2100R型冻干机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司;Thermo Nicolet iS5傅里叶变换红外光谱 德国赛默飞世尔科技公司;S-4800扫描电子显微镜 日本日立公司;Bettersize 2000激光粒度分析仪 丹东百特仪器有限公司;RF-5301PC荧光分光光度计 岛津仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品制备
采用碱溶酸沉法[14]提取黑豆蛋白并作修改。加入10倍体积的水,轻轻搅拌混合。而后将黑豆蛋白溶液混匀,使用配备0.636 cm直径钛探头的超声处理器对60 mL黑豆蛋白进行超声处理。如表1所示,采用不同功率(150、200、250、300和350 W)下6 min和300 W下不同持续时间(6、12、18和24 min)的低频(20 kHz)超声处理方式(脉冲持续时间:开启时间,2 s;关闭时间,2 s)。其中,为了防止超声产生的热效应对黑豆蛋白的影响,将装有黑豆蛋白的烧杯置于冰水浴中。之后冻干超声处理后的样品,并将其储存在密封袋中直至分析。
表 1 超声处理黑豆蛋白参数Table 1. Parameters of ultrasonic treatment of black bean protein超声条件 A B C D E F G H I 超声功率(W) 0 150 200 250 300 350 300 300 300 超声时间(min) 0 6 6 6 6 6 12 18 24 1.2.2 黑豆蛋白体外消化率的测定
参考Zhou等[15]的方法并稍作修改。超声后黑豆蛋白溶液取10 mL,用1 mol/L HCl调节pH至1.6,然后添加胃蛋白酶(4% w/w,以蛋白质为基础)。37 ℃孵育在190 r/min下恒温振荡2 h,加入1 mol/L NaOH调节溶液pH至7.5,加入胰蛋白酶(4% w/w,以蛋白质为基础)。37 ℃连续在190 r/min下恒温振荡孵育悬液2 h,然后在沸水浴中浸泡10 min以停止消化。离心(11000×g,15 min,4 ℃)获得胃肠道消化产物,收集上清,用双缩脲法测定蛋白含量。根据式(1)计算黑豆蛋白质体外消化率。
蛋白质体外消化率(%)=消化后上清液中的蛋白含量总蛋白含量×100 (1) 1.2.3 溶解度测定
参考Gulsah等[16]描述方法并稍作修改。超声处理黑豆蛋白溶液样品20 ℃下以12000×g离心20 min。以牛血清白蛋白为标准,使用双缩脲方法测定上清液中的粗蛋白含量。溶解度的计算公式见式(2)。
溶解度(%)=上清液的蛋白含量总蛋白含量×100 (2) 1.2.4 粒径分析
参考Li等[17]的方法并稍作修改。从超声处理黑豆蛋白溶液中移取1 mL样品。使用激光粒度分析仪在室温下,折射率在12%的条件下,根据多模态光散射法预测黑豆蛋白粒度分布。
1.2.5 Zeta电位(ζ)测定
使用Zeta电位分析仪测定蛋白质的ζ电位。取黑豆蛋白冻干粉用0.1 mol/L磷酸缓冲液(pH6.8)稀释至2 mg/mL。五次测定的平均值为ζ电位。
1.2.6 乳化性(EAL)和乳化稳定性(ESL)分析
用磷酸盐缓冲液(0.2 mol/L,pH7.0)稀释黑豆蛋白样品为2 mg/mL,制成黑豆蛋白溶液。而后将大豆油和黑豆蛋白溶液(1:3,v/v)在10000 r/min下均质2 min形成乳状液。在均质后0和10 min,分别从烧杯底部取50 μL乳状液,用0.1% SDS溶液按1:100稀释后在500 nm处测定吸光度[18]。EAI和ESI计算公式见式(3)和(4)。
EAI(m2/g)=2×T×A0×N1000×θ×L×C (3) ESI(min)=A0A0−A10×(T10−T0) (4) 式中,T=2.303;N为稀释系数(100);θ为油相的比例(0.25);L为比色皿池长(1 cm);C为黑豆蛋白的浓度(g/mL);A0为0 min的吸光度;A10为10 min吸光度;T10为10 min。
1.2.7 扫描电子显微镜(SEM)
将样品稍微研磨,并喷金至15 nm的厚度,在5 kV下测试冻干黑豆蛋白样品的形态。
1.2.8 荧光光谱测定
在0.01 mol/L磷酸盐缓冲液(pH7.6)中制备蛋白质分散体2 mg/mL。激发波长为295 nm,发射光谱在300至400 nm范围内,采用5 nm狭缝进行激发和发射,每次扫描执行5次[10]。
1.2.9 红外光谱测定
参考Kang等[19]的方法并稍作修改。样品的结构信息采集使用IRTracer-10 FT-IR光谱仪在20 ℃记录。将黑豆蛋白样品(5 mg)与溴化钾(295 mg)混合并压缩。FT-IR光谱记录范围为4000~500 cm−1,扫描次数为64次,分辨率为4 cm−1。二级结构分析使用“Peakfit version 4.12”软件,并使用高斯峰值拟合算法。
1.3 数据处理
结果以平均数±标准差表示。采用SPSS 23进行单因素方差分析。采用Origin 2021进行绘图。采用邓肯多元极差检验分析,文中所有实验均比较三个重复样本的显著性(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 超声处理对黑豆蛋白消化率的影响
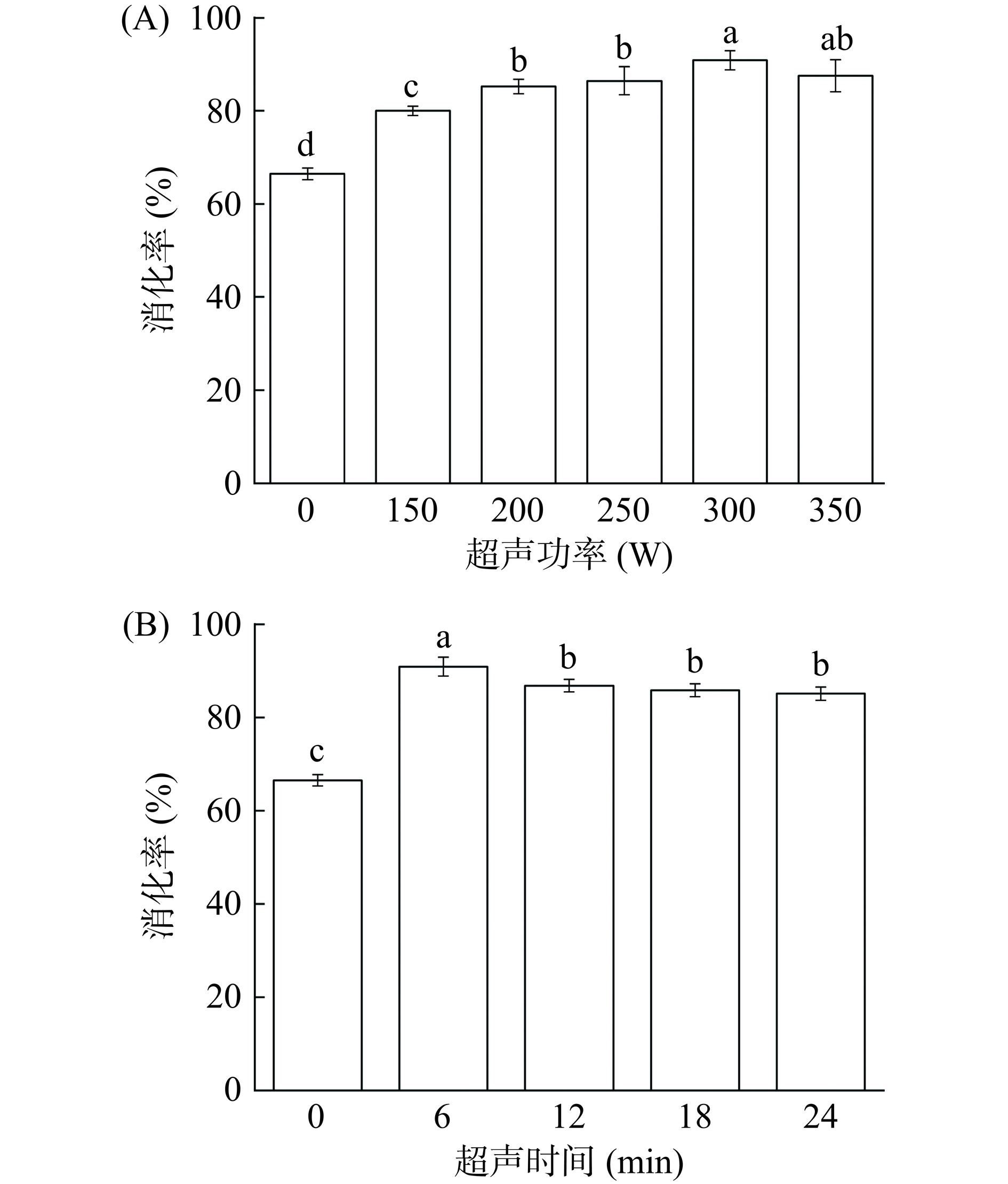
超声处理方式按照表1进行处理。如图1A所示,与未处理组(0 W,0 min)相比,经过超声处理后黑豆蛋白的消化率有显著改善(P<0.05)。当超声功率在0~300 W时,黑豆蛋白的体外消化率随超声功率的增加而增加,从66.50%增加到90.9%。但随着超声处理时间的增加,黑豆蛋白的消化率呈现降低的趋势。如图1B所示,蛋白消化率由90.9%降低到85.15%。可能是300 W下处理时间增加到12 min后,蛋白的二级结构发生变化,可溶性蛋白被重新包裹其中,导致消化率降低。在300 W,6 min条件下改性的黑豆蛋白样品的消化率最高为90.9%。这可能是由于合适的超声处理条件改变了蛋白质的构象,使蛋白质的裂解位点暴露在消化酶面前[20]。结果表明,适当的超声处理有利于提高黑豆蛋白的消化率。
2.2 超声处理对黑豆蛋白溶解度的影响
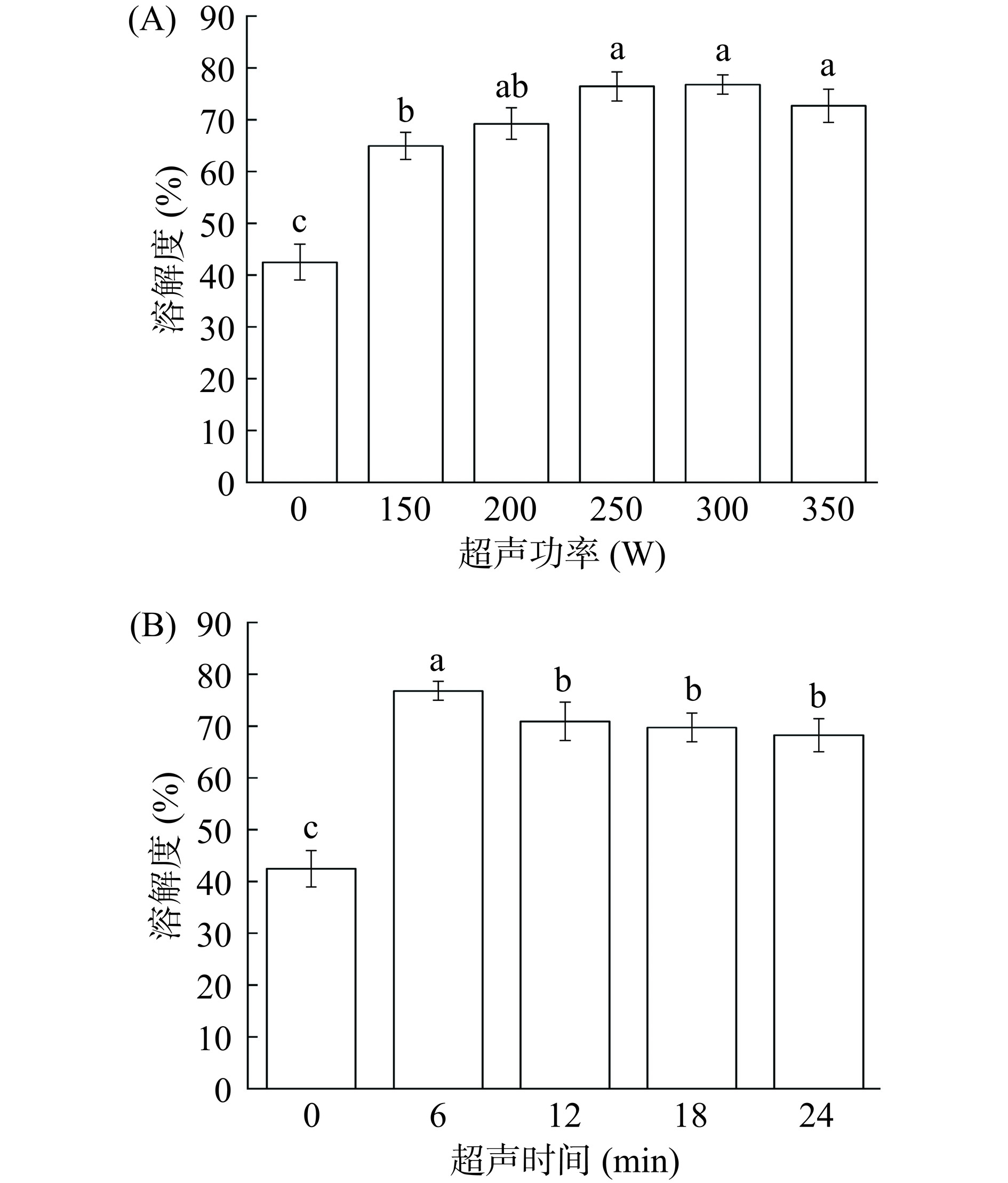
溶解度不仅影响蛋白质的功能特性,决定蛋白质的应用。而且溶解度也是蛋白质消化性能的先决条件,与蛋白质变性和聚集直接相关[21]。从图2可以看出,与未处理组相比,经过超声处理的黑豆蛋白样品的溶解度都有显著提高(P<0.05)。并且在不同功率下,随着超声功率的增加,除350 W组外溶解度均增加。有研究超声对分离羽扇豆和黑豆分离物溶解度的影响,得到了类似的结果[22]。溶解度由未处理的42.45%增加到300 W,6 min的76.75%。并且超声处理300 W,6 min的样品的溶解度高于其他样品。溶解度的增加一种可能是由于蛋白质聚集体的粒径减小和蛋白质颗粒与水的接触面积增加,导致蛋白质的亲水性相互作用增加[23]。此外,另有文献表明,溶解度的增加也可能由于超声产生的机械力诱导蛋白质分解和极性氨基酸(亲水性氨基酸残基)暴露于水[24]。这与超声波处理可使大豆分离蛋白分散体部分展开,改善其溶解度和流体特性的研究发现相似[8]。黑豆蛋白质溶解度增加,从而导致消化性增加,所以可以通过控制超声参数获得较高的溶解度,来提高黑豆蛋白的消化性。然而,如图2B所示,当超声时间增加到12 min时,继续增加超声时间溶解度未发生显著变化(P>0.05)。即超声处理时间对蛋白质溶解度的影响存在上限[25]。溶解度随处理时间的增加而降低。由300 W,6 min的76.75%降低到300 W,18 min的68.23%。发生这种现象的原因是超声的空化作用和剪切力使蛋白质分子部分展开,这增加了蛋白质和水分子之间的相互作用。黑豆蛋白分子膨胀,疏水性基团暴露,分子内巯基埋藏。蛋白质分子通过非共价相互作用重组大分子聚集体,导致溶解度降低[16]。
2.3 超声处理对黑豆蛋白粒径影响
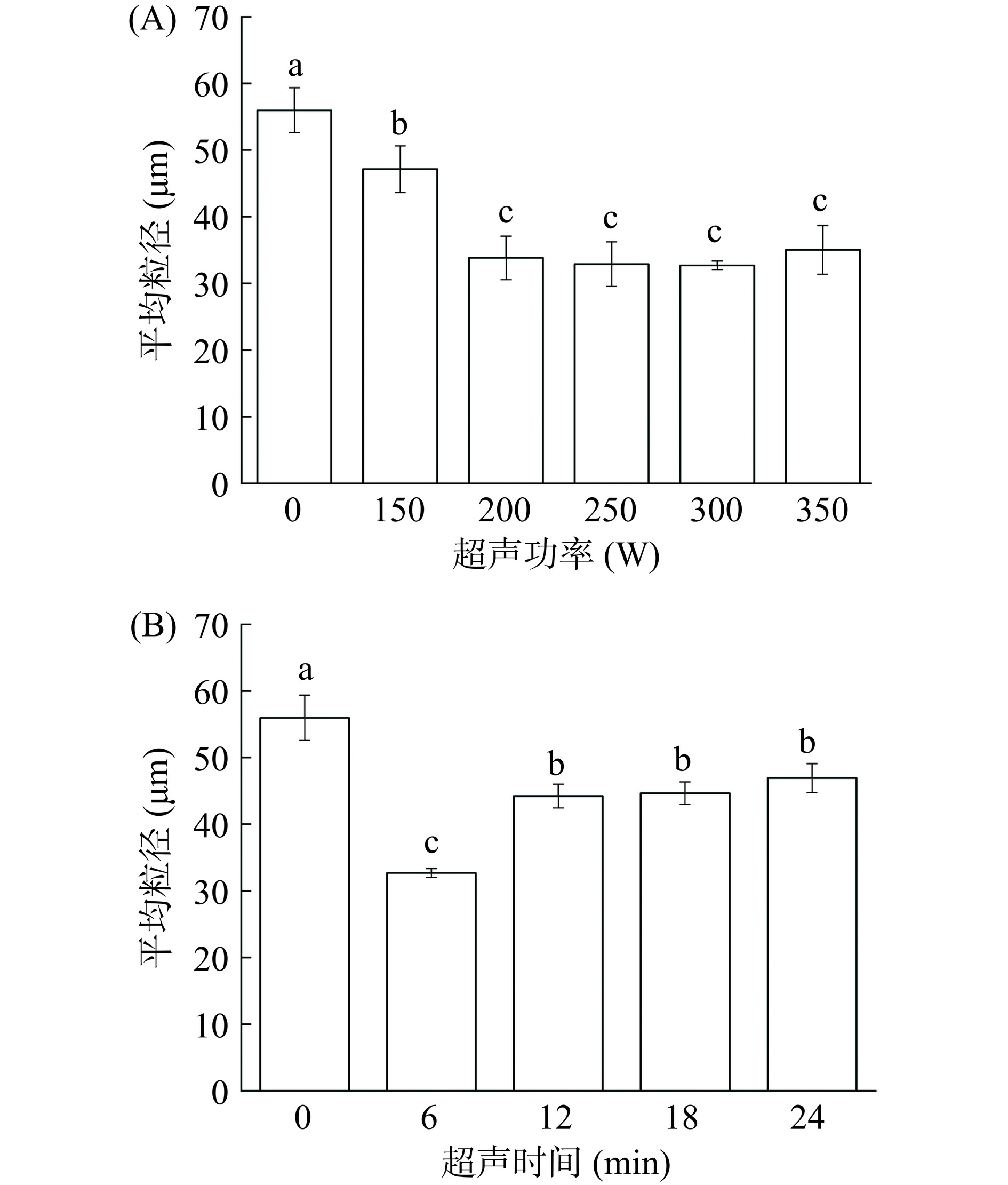
图3显示了不同超声功率和不同超声时间对黑豆蛋白粒径分布的影响。与未处理组相比,经超声处理的样品的平均粒径明显减小。如图3A所示,黑豆蛋白平均粒径由未处理组的56 μm减小到300 W组的32 μm。随着超声功率的增加,黑豆蛋白粒径进一步减小,表明超声具有良好的破坏较大植物蛋白聚集体的能力。通过空化效应产生的湍流和剪切力破坏颗粒分子间的非共价键,打开了颗粒内部紧密堆积的结构,导致蛋白质聚集体解离,使黑豆蛋白的粒径显著减小[26]。在此超声参数下,消化性提升,可能是超声通过空化作用和微射流减小黑豆蛋白分子大小,使其更易于消化吸收。如图3B所示,随着超声处理时间的增加,粒径呈现增加的状态,平均粒径由6 min的32.7 μm增加到24 min的46.9 μm。说明超声处理时间的增加反而增加了粒径较大的聚集体的数量。这可能是由于超声导致蛋白质分子运动更快,增加了蛋白质分子之间碰撞的机会,导致蛋白质分子重新团聚形成更大的颗粒[17]。在此超声参数下消化性下降,可能是黑豆蛋白分子粒径的增大,不利于消化性的提升。
2.4 超声处理对黑豆蛋白Zeta电位影响
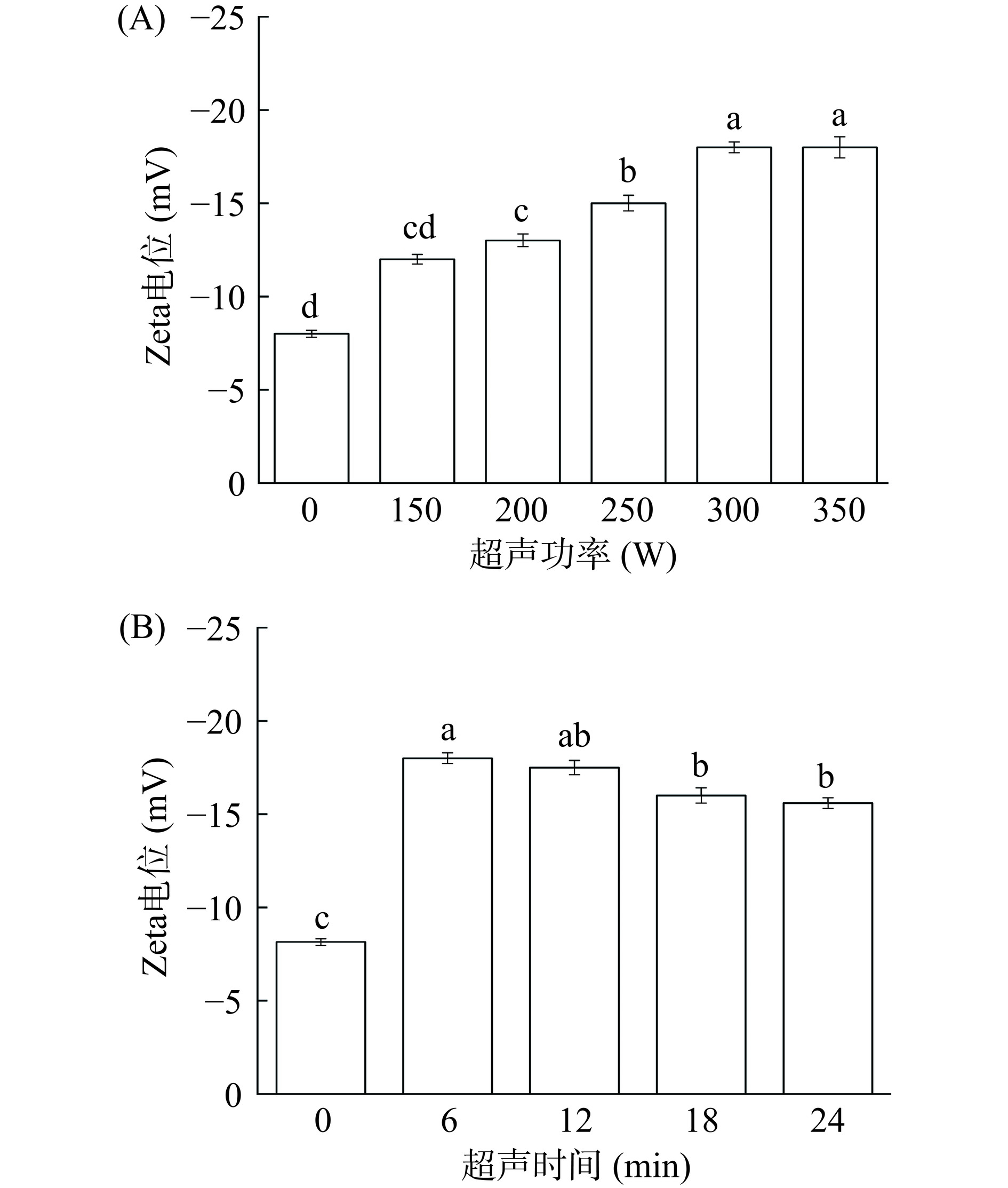
Zeta电位被广泛用于测定粒子的表面电荷性质,电位的绝对值越高,系统的稳定性越好。黑豆蛋白经不同超声处理后的电位分布如图4所示。通常,如果带正电的氨基酸多于带负电的氨基酸,则蛋白质溶液的Zeta电位为正[27]。所有样品的Zeta电位均为负(图4),这表明黑豆蛋白溶液中含有的带负电的氨基酸多于带正电的氨基酸。并且,超声处理后样品的电位绝对值增大,从未超声处理乳液的电位绝对值8.15 mV(0 W)增加到18 mV(300 W)。Zeta电位绝对值增加的原因可能是黑豆蛋白大聚集体被解离和暴露更多阴离子基团导致颗粒尺寸减小。暴露的阴离子基团会增加静电斥力,提高蛋白质的分散性,从而提高黑豆蛋白的稳定性[25]。但随着时间的延长,该电位绝对值又略有下降。如图4B所示,样品经过300 W超声处理12、18、24 min后,由6 min的18 mV降低到24 min的15.6 mV。可能是由于超声处理引起的非共价相互作用的影响,使其中暴露的阴离子基团被重新封闭在新形成的蛋白质聚集体中[28]。形成聚集体后,其Zeta电位的绝对值降低。因为粒子的有效表面电荷主要决定它们的分散和聚集[29]。因此,低、中(150~300 W)短时间(6 min)超声处理可以增加蛋白质表面的负电荷,增强粒子间的静电斥力。静电斥力的增加会破坏现有的蛋白质聚集,并且抑制蛋白质进一步聚集,提高蛋白质分散体的稳定性,从而提升黑豆蛋白消化性和溶解性。
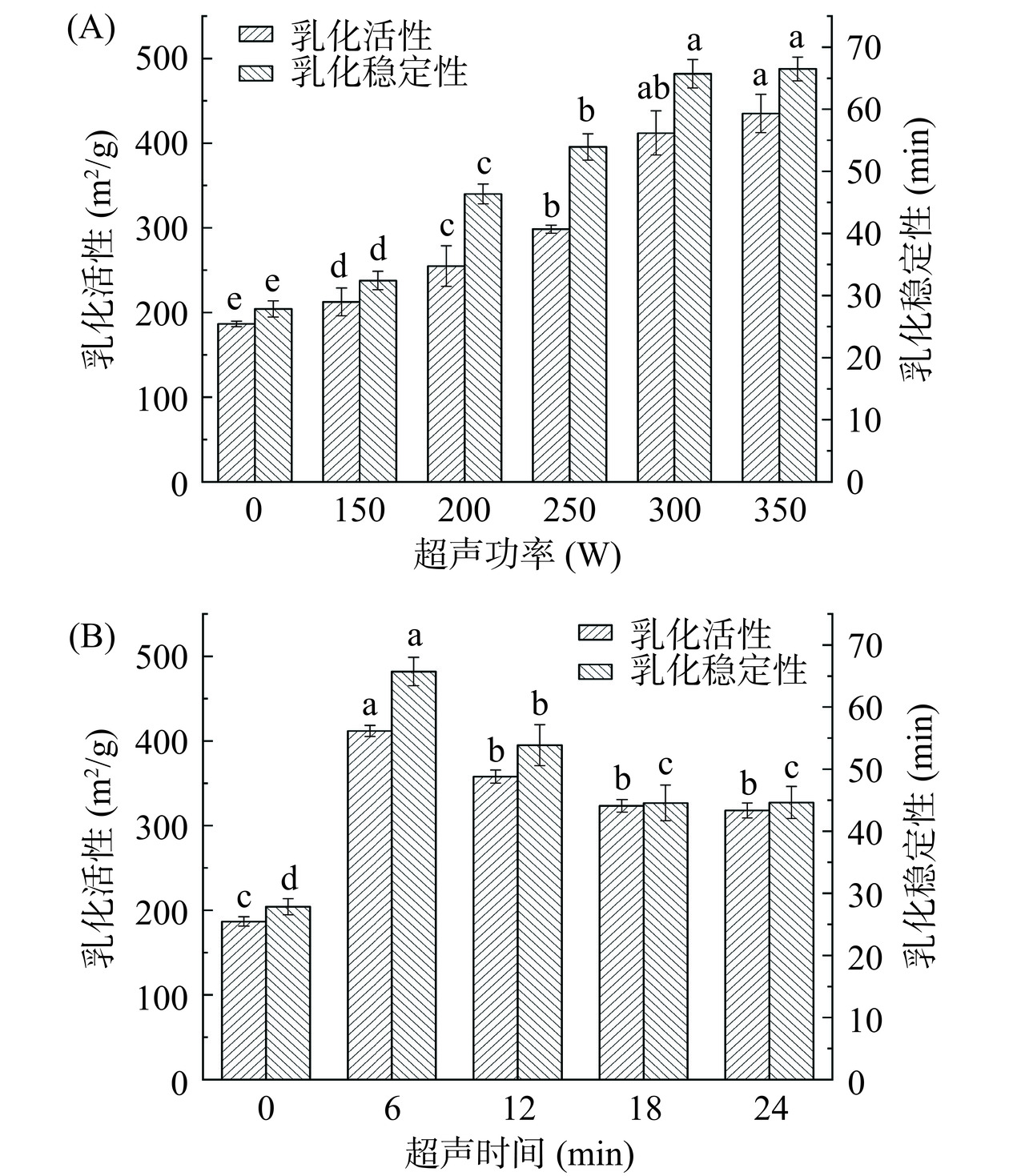
2.5 超声处理对黑豆蛋白乳化活性(EAI)和乳化稳定性(ESI)影响
乳化液的乳化性能可以通过乳化活性和乳化稳定性来评价。EAI表示每单位质量蛋白质稳定的界面面积,ESI则是在特定时间内对乳液抵抗外界不稳定因素的表征。如图5所示,超声处理后乳剂的EAI和ESI显著提高(P<0.05)。如图5A所示,随着超声功率的增加,黑豆蛋白的EAI在低、中功率(150~300 W)短时间(6 min)下呈现升高的趋势,这是由于短时间、低功率的超声使蛋白质分子部分展开,埋在分子内部的亲水性基团暴露出来,使黑豆蛋白溶解度提高,从而增强了黑豆蛋白的乳化能力[10]。且经300 W超声处理6 min的乳化液乳化能力最高,EAI达到了411.78 m2/g,ESI达到了65.71 min。与未处理样品相比,300 W,6 min的超声处理有效提高了黑豆蛋白乳液的EAI和ESI,分别是未处理样品的2.21倍和2.36倍。350 W,6 min的样品虽然经历了最高的超声功率处理,但其EAI 434.88 m2/g和ESI 66.49 min相比300 W,6 min差异并不显著(P>0.05)。与Zhang等[30]趋势相一致,即超声功率超过300 W时,乳化活性没有显著差异(P>0.05)。并且超声时间大于6 min时,乳化性能逐渐降低。用300 W超声功率处理12、18、24 min样品的EAI和ESI低于300 W,6 min超声处理的样品。可能是随着超声时间的增加,蛋白质变性程度增加,导致分子聚集,使不溶性蛋白质含量增加,表面疏水性降低,使其乳化能力减弱[31]。
2.6 超声处理对黑豆蛋白扫描电镜影响
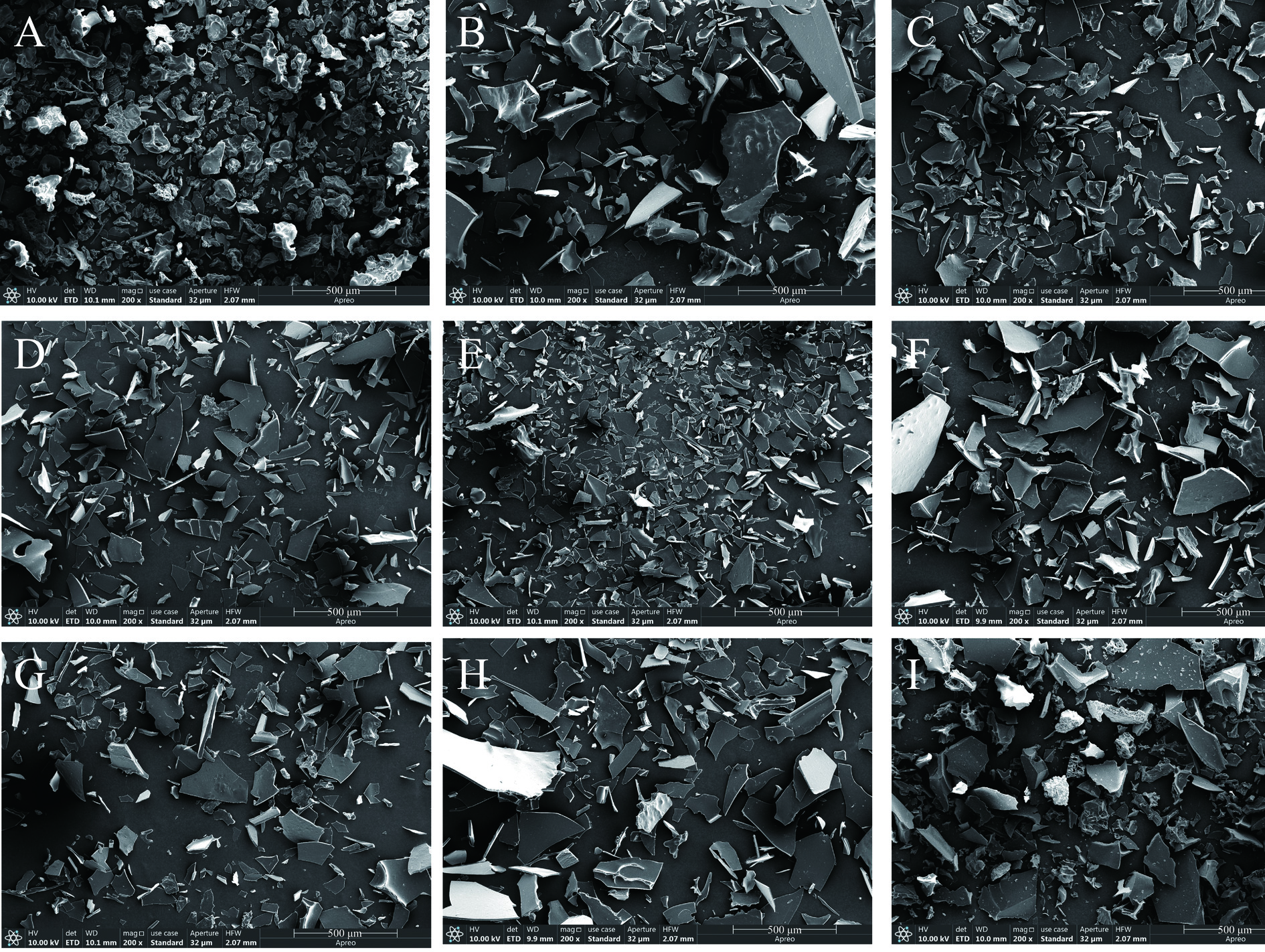
为了了解不同超声处理对黑豆蛋白微观结构的影响,对超声处理前后黑豆蛋白的SEM显微图进行了采集。图6显示了不同超声处理黑豆蛋白,在放大500倍下获得扫描电镜图像。与A样品(未处理)相比,超声处理样品经过不同功率和不同时间的处理和冻干后,由大颗粒块状变成平面状,呈现出更多的无序结构和不规则碎片。并且随着功率的增加,碎片更小、更规则,说明超声强度越高,分散体越小。这些可能是由于超声波处理过程中探头施加的空化力以及微流和湍流力而产生的[32]。样品E和F比其他样品更均匀,表明中等超声功率300 W,6 min和350 W,6 min可以产生基本均匀的结构。这可能是由超声诱导蛋白质展开和黑豆蛋白分子表面疏水性基团增加引起的。然而,H~I样品经过长时间超声处理后,黑豆蛋白样品却呈现SEM显微图增大的趋势。这可能是超声导致黑豆蛋白质的部分展开,功能基团暴露,产生相互作用,导致蛋白质聚集和网络形成,使黑豆蛋白分子增大。通常,分散体中的聚集体越小,其溶解度和消化性就越高。上文的粒径分析和溶解度分析也印证了这一现象。因此,通过适当的超声处理控制聚集体大小在一定范围,将有利于消化性提升。
2.7 超声处理对黑豆蛋白荧光光谱影响
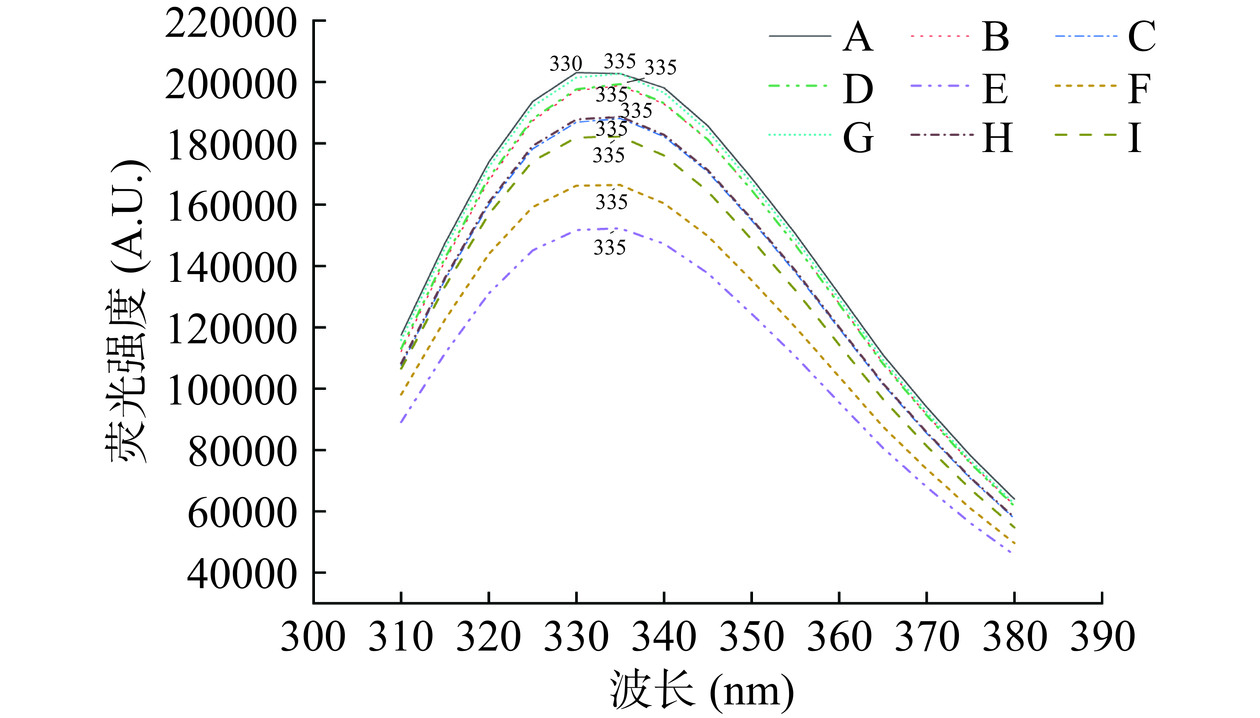
获得未经处理(A)和超声处理的黑豆蛋白样品(B~I)的荧光光谱(图7)。蛋白质的内源性荧光光谱可以进一步揭示蛋白质结构的变化[33]。在蛋白质中,氨酸残基对溶剂的极性非常敏感。色氨酸和苯丙氨酸残基的荧光量子产率可用于表征酪氨酸、色氨酸和苯丙氨酸残基对溶剂极性的敏感性。因此,色氨酸的荧光量子产率可用于表征蛋白质三级结构的变化。超声作用对黑豆蛋白荧光光谱形状几乎没有影响。通过与样品A进行比较,将样品暴露于不同的超声波处理会导致其向更长的波长(深慢性位移)的显著变化,这表明色氨酸侧链移动到蛋白质分子的外部,从而导致其微环境的极性增加[34]。样品最大发射波长的色移表明,在超声过程中,黑豆蛋白样品的构象发生了变化。这是因为超声波诱导黑豆蛋白分子展开,从而破坏了蛋白质分子的疏水相互作用[35]。与其他样品相比,E(300 W,6 min)的荧光强度最低,这可能是黑豆蛋白结构变化最剧烈导致其消化率最高的原因。
2.8 超声处理对黑豆蛋白红外光谱(FT-IR)影响
红外光谱在分子水平上与结构性质的变化(如:构象、溶解性、消化性)相关[36]。如图8所示,超声处理后光谱的峰位置没有改变,而处理后峰的强度降低。表明超声处理未改变黑豆蛋白的总体结构,但影响了其二级结构。FT-IR通常用于评价蛋白质的二级结构。蛋白质的酰胺I波段(1700~1600 cm−1)主要基于酰胺基团(约80%)的C=O伸缩振动,可用于分析蛋白质二级结构[37]。如图8所示,经过超声处理后黑豆蛋白的酰胺I带发生了明显的红移,说明黑豆蛋白的二级结构可能发生了变化。因此,所有超声处理样品的酰胺I波段的光谱用peakfit version 4.0分析。1650~1660 cm−1范围的谱带归属为α-螺旋,1600~1640 cm−1和1670~1690 cm−1范围的谱带归属为β-折叠,1660~1670 cm−1和1690~1700 cm−1范围的谱带归属为β-转角,1640~1650 cm−1范围的谱带为无规卷曲[38]。
未处理和超声处理黑豆蛋白的二级结构如表2所示。β-折叠占比较大,表明β-折叠是黑豆蛋白主要的二级结构。与天然黑豆蛋白相比,超声处理后黑豆蛋白α-螺旋和无规则卷曲含量降低,β-结构(β-折叠和β-转角)含量显著升高(P<0.05)。可能是超声产生的空化和机械作用破坏了多肽链上稳定α-螺旋结构的羰基和氨基之间的氢键,造成氨基酸序列的拉伸振动和蛋白质分子不同部分之间的分子间相互作用的破坏。从而导致蛋白质构象的变化和无序的分子排列,最终使α-螺旋含量减少、β-结构含量增加[39]。表明一定功率内的超声处理可以促进蛋白质链的扩展,这可能有助于分子间相互作用的发生。然而,在增大超声功率和超声时间后,无规则卷曲转化为β-结构,表明长时间超声可促进蛋白质交联。高功率超声较长的处理时间显著增加了处理后黑豆蛋白中α-螺旋和β-转角结构的含量,同时降低了无规则卷曲结构的含量(P<0.05)。处理后的黑豆蛋白中β-折叠结构的增加可能与聚集体的形成有关[40],因为分子间的β-折叠结构通常存在于聚集的蛋白质中[41]。超声产生的空化效应和机械力可能加速了蛋白质分子的运动,增加了分子碰撞的可能性,导致聚集体的形成。粒径的增加、消化性和溶解性的减少也印证了这一点。因此,超声处理是修饰蛋白质二级结构,改善黑豆蛋白消化率的有效方法。
表 2 超声处理对黑豆蛋白二级结构的影响Table 2. Effect of ultrasonic treatment on secondary structure of black bean protein样品 α-螺旋(%) β-折叠(%) β-转角(%) 无规则卷曲(%) A 17.2±0.2b 38.7±0.2f 27±0.1g 17.1±0.2a B 16.9±0.2c 40.6±0.1e 27.3±0.2f 15.2±0.1b C 16.6±0.2d 41.5±0.2cd 27.8±0.1e 14.1±0.1c D 16.7±0.1cd 42.4±0.1c 28.3±0.2de 12.6±0.2d E 16.4±0.2e 43.1±0.2b 28.9±0.2d 11.6±0.1e F 16.9±0.1c 42.9±0.2bc 30±0.2a 10.2±0.2f G 17.1±0.2b 43.2±0.2b 29.6±0.1b 10.1±0.1f H 17.5±0.2a 43.3±0.1b 29.3±0.2bc 9.9±0.2fg I 17.6±0.1a 43.5±0.2a 28.9±0.1c 10±0.1f 注:同列不同字母代表同一指标差异显著(P<0.05)。 3. 结论
在本研究中,超声处理对黑豆蛋白体外消化率的影响,不仅伴随着黑豆蛋白二级和三级结构的变化,还伴随着理化性质,如溶解度、分子大小、乳化性、Zeta电位等的变化。在低、中功率(150~300 W)短时间(6 min)处理条件下,随着超声功率的增加黑豆蛋白消化性提高。并且300 W,6 min的超声处理的黑豆蛋白消化性最高。然而,在超声功率300 W,超声时间12 min后,随着超声时间的增加,黑豆蛋白各项性能的改善不再增加并有下降趋势。通过对超声处理对黑豆蛋白消化特性的研究发现,消化性的改善与其结构和其他功能性质变化有相同趋势。黑豆蛋白消化性的提升往往伴随着粒径的减小,α-螺旋和无规则卷曲含量的降低,β-结构(β-折叠和β-转角)含量的增加,Zeta电位绝对值的增加,乳化活性和乳化稳定性的增加。研究结果可为超声处理下黑豆蛋白的结构改变、功能特性与消化性之间关系的探讨和提高黑豆蛋白消化率提供借鉴。
-
表 1 超声处理黑豆蛋白参数
Table 1 Parameters of ultrasonic treatment of black bean protein
超声条件 A B C D E F G H I 超声功率(W) 0 150 200 250 300 350 300 300 300 超声时间(min) 0 6 6 6 6 6 12 18 24 表 2 超声处理对黑豆蛋白二级结构的影响
Table 2 Effect of ultrasonic treatment on secondary structure of black bean protein
样品 α-螺旋(%) β-折叠(%) β-转角(%) 无规则卷曲(%) A 17.2±0.2b 38.7±0.2f 27±0.1g 17.1±0.2a B 16.9±0.2c 40.6±0.1e 27.3±0.2f 15.2±0.1b C 16.6±0.2d 41.5±0.2cd 27.8±0.1e 14.1±0.1c D 16.7±0.1cd 42.4±0.1c 28.3±0.2de 12.6±0.2d E 16.4±0.2e 43.1±0.2b 28.9±0.2d 11.6±0.1e F 16.9±0.1c 42.9±0.2bc 30±0.2a 10.2±0.2f G 17.1±0.2b 43.2±0.2b 29.6±0.1b 10.1±0.1f H 17.5±0.2a 43.3±0.1b 29.3±0.2bc 9.9±0.2fg I 17.6±0.1a 43.5±0.2a 28.9±0.1c 10±0.1f 注:同列不同字母代表同一指标差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
[1] MCCARTY M F, BARROSO-ARANDA J, CONTRERAS F. The low-methionine content of vegan diets may make methionine restriction feasible as a life extension strategy[J]. Medical Hypotheses,2009,72(2):125−128. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2008.07.044
[2] ZAHIR M, FOGLIANO V, CAPUANO E. Food matrix and processing modulatein vitroprotein digestibility in soybeans[J]. Food & Function,2018,9(12):6326−6336.
[3] JIANG L, WANG J, LI Y, et al. Effects of ultrasound on the structure and physical properties of black bean protein isolates[J]. Food Research International,2014,62(8):595−601.
[4] ZHANG C, SANDERS J P M, XIAO T T, et al. How does alkali aid protein extraction in green tea leaf residue:A basis for integrated biorefinery of leaves[J]. PLoS One,2015,10(7):1−10.
[5] WANG W, TAI F J, CHEN S H, et al. Optimizing protein extraction from plant tissues for enhanced proteomics analysis[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2008,31(3):2032−2039.
[6] FLPRES-JIMENEZ N T, ARMANDO ULLOA J, URIAS SILVAS J E, et al. Effect of high-intensity ultrasound on the compositional, physicochemical, biochemical, functional and structural properties of canola (Brassica napus L.) protein isolate[J]. Food Research International,2019,121(7):947−956.
[7] RAHMAN M M, BYANJU B, GREWELL D, et al. High-power sonication of soy proteins:Hydroxyl radicals and their effects on protein structure[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2020,64(6):105019.
[8] HU H, WU J H, LI-CHAN E C Y, et al. Effects of ultrasound on structural and physical properties of soy protein isolate (SPI) dispersions[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2013,30(2):647−655. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.08.001
[9] ZHAO C C, KIM P H, EUN J B. Influence of high-intensity ultrasound application on the physicochemical properties, isoflavone composition, and antioxidant activity of tofu whey[J]. LWT-Food Science & Technology,2020,117(1):108618.
[10] KANG S, ZHANG J, GUO X, et al. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on the structure, functional properties of chickpea protein isolate and its digestibility in vitro[J]. Foods,2022,11(6):1−13.
[11] LI Y, WANG J, ZHU X, et al. Basic electrolyzed water coupled with ultrasonic treatment improves the functional properties and digestibility of Antarctic krill proteins[J]. Food Research International,2022,162(10):112201.
[12] BI C H, CHI S Y, ZHPU T, et al. Effect of low-frequency high-intensity ultrasound (HIU) on the physicochemical properties of chickpea protein[J]. Food Research International,2022,159(9):111474.
[13] WANG K, GAO Y, ZHAO J, et al. Effects of in vitro digestion on protein degradation, phenolic compound release, and bioactivity of black bean tempeh[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2022,9(10):1−13.
[14] 吴桂玲, 刘立品, 李文浩, 等. 碱溶酸沉法提取青稞蛋白质的工艺研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2015,36(5):19−24. [WU G L, LIU L P, LI W H, et al. Process study of barley protein extraction by alkali solubilization and acid precipitation[J]. Food Research and Development,2015,36(5):19−24.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2015.05.006 WU G L, LIU L P, LI W H, et al. Process study of barley protein extraction by alkali solubilization and acid precipitation[J]. Food Research and Development, 2015, 36(5): 19−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2015.05.006
[15] ZHOU F B, ZHAO M M, CUI C, et al. Influence of linoleic acid-induced oxidative modifications on physicochemical changes and in vitro digestibility of porcine myofibrillar proteins[J]. LWT-Food Science & Technology,2015,61(2):414−421.
[16] GULSAH K, OKTAY Y. Modification of hemp seed protein isolate (Cannabis sativa L.) by high-intensity ultrasound treatment. Part 1:Functional properties[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,375(6):131084.
[17] LI T, WANG L, ZHANG X, et al. Assembly behavior, structural characterization and rheological properties of legume proteins based amyloid fibrils[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,111(2):1−34.
[18] SUI X, BI S, QI B, et al. Impact of ultrasonic treatment on an emulsion system stabilized with soybean protein isolate and lecithin:Its emulsifying property and emulsion stability[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,63(1):1−8.
[19] KANG D C, ZOU Y H, CHENG Y P, et al. Effects of power ultrasound on oxidation and structure of beef proteins during curing processing[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2016,33(5):47−53.
[20] WANG X, GAO W, ZHANG J, et al. Subunit, amino acid composition and in vitro digestibility of protein isolates from Chinese kabuli and desi chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars[J]. Food Research International,2010,43(2):567−572. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2009.07.018
[21] HIGUERA-BARRAZA O, DEL TORO-SANCHEZ C, RUIZ-CRUZ S, et al. Effects of high-energy ultrasound on the functional properties of proteins[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2016,31(4):558−562.
[22] LO B, KASAPIS S, FARAHNAKY A. Effect of low frequency ultrasound on the functional characteristics of isolated lupin protein[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,124(2):1−10.
[23] KHATKAR A B, KAUR A, KHATKAR S K, et al. Optimization of processing time, amplitude and concentration for ultrasound-assisted modification of whey protein using response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2018,55(2):2298−2309.
[24] XUE F, ZHU C, LIU F, et al. Effects of high-intensity ultrasound treatment on functional properties of plum (Pruni domesticae semen) seed protein isolate[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2018,98(15):5690−5699. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9116
[25] WANG H, YANG H, CHEN X, et al. Structural basis for high-intensity ultrasound treatment in the rheology of myofibrillar protein extracted from white croaker in relation to their solubility[J]. LWT-Food Science & Technology,2022,156(2):1−9.
[26] WANG Y, WANG Y, LI K, et al. Effect of high intensity ultrasound on physicochemical, interfacial and gel properties of chickpea protein isolate[J]. LWT-Food Science & Technology,2020,129(7):109563.
[27] BOUZID H, RABILLER-BAUDRY M, PAUGAM L, et al. Impact of zeta potential and size of caseins as precursors of fouling deposit on limiting and critical fluxes in spiral ultrafiltration of modified skim milks[J]. Journal of Membrane Science,2008,314(1−2):67−75. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2008.01.028
[28] LIANG Q F, REN X F, QU W J, et al. The impact of ultrasound duration on the structure of β-lactoglobulin[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2021,292(2):1−7.
[29] HU H, FAN X, ZHOU Z, et al. Acid-induced gelation behavior of soybean protein isolate with high intensity ultrasonic pre-treatments[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2013,20(1):187−195. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2012.07.011
[30] ZHANG Q T, TU Z C, XIAO H, et al. Influence of ultrasonic treatment on the structure and emulsifying properties of peanut protein isolate[J]. Food and Bioproducts Processing,2014,92(1):30−37. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2013.07.006
[31] O'SULLIVAN J. The effect of ultrasound treatment on the structural, physical and emulsifying properties of animal and vegetable proteins[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,53(2):141−154.
[32] XIONG T, XIONG W, GE M, et al. Effect of high intensity ultrasound on structure and foaming properties of pea protein isolate[J]. Food Research International,2018,109(7):260−267.
[33] 刘兴丽, 杨龙松, 赵双丽, 等. 马铃薯蛋白-黄原胶微凝胶的制备及其乳化特性研究[J]. 轻工学报,2021,36(1):1−8. [LIU X L, YANG L S, ZHAO S L, et al. Preparation of potato protein-xanthan gum microgel and its emulsification characteristics[J]. Journal of Light Industry,2021,36(1):1−8.] doi: 10.12187/2021.01.001 LIU X L, YANG L S, ZHAO S L, et al. Preparation of potato protein-xanthan gum microgel and its emulsification characteristics[J]. Journal of Light Industry, 2021, 36(1): 1−8. doi: 10.12187/2021.01.001
[34] MIRIANI M, KEERATI-U-RAI M, CORREDIG M, et al. Denaturation of soy proteins in solution and at the oil-water interface:A fluorescence study[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25(4):620−626. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.07.020
[35] SUBHEDAR P B, GOGATE P R. Enhancing the activity of cellulase enzyme using ultrasonic irradiations[J]. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B:Enzymatic,2014,101(2):108−114.
[36] CUI R, ZHU F. Effect of ultrasound on structural and physicochemical properties of sweetpotato and wheat flours[J]. Ultrason Sonochem,2020,66(5):1−35.
[37] LIU L, ZENG J, SUN B, et al. Ultrasound-assisted mild heating treatment improves the emulsifying properties of 11S globulins[J]. Molecules,2020,25(4):1−15.
[38] CAO Y, ZHANG M, DONG S, et al. Impact of potato pulp on the processing characteristics and gluten structures of wheat flour dough[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2020,44(6):1−8.
[39] ARZENI C, MARTINEZ K, ZEMA P, et al. Comparative study of high intensity ultrasound effects on food proteins functionality[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2012,108(3):463−472. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2011.08.018
[40] DUAN X, LI M, SHAO J, et al. Effect of oxidative modification on structural and foaming properties of egg white protein[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,75(1):223−228.
[41] LEE S H, LEFEVRE T, SUBIRADE M, et al. Changes and roles of secondary structures of whey protein for the formation of protein membrane at soy oil/water interface under high-pressure homogenization[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2007,55(26):10924−10931. doi: 10.1021/jf0726076





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



