Effect of Exogenous Melatonin Treatment on Quality and Antioxidant Capacity of Fresh-cut Purple Cabbage
-
摘要: 为探究褪黑素(Melatonin,MT)对鲜切紫甘蓝的保鲜效果,以紫甘蓝为实验材料,在4 ℃,85% RH条件下贮藏12 d。采用0、0.01、0.1、0.5、1 mmol/L褪黑素处理鲜切紫甘蓝,通过颜色、失重率、硬度和总需氧菌数量的变化筛选出合适的褪黑素浓度,进一步评估最佳浓度褪黑素处理对鲜切紫甘蓝营养品质和抗氧化能力的影响。结果表明,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理能显著减少鲜切紫甘蓝明度和红度降低以及黄度增加、失重增加、硬度降低和总需氧菌数量增加(P<0.05)。此外,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理能显著促进花青素积累(P<0.05),显著抑制总硫代葡萄糖苷降解(P<0.05),延缓黑芥子酶活性、萝卜硫素和吲哚-3-甲醇含量降低,并通过提高DPPH、ABTS+自由基清除能力和超氧化物歧化酶活性、延缓过氧化氢酶和过氧化物酶活性降低提高抗氧化活性。总之,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理能有效保持鲜切紫甘蓝的营养品质和抗氧化能力,为褪黑素在鲜切蔬菜中的应用提供理论依据。Abstract: To investigate the effect of melatonin treatment on maintaining the freshness of fresh-cut purple cabbage, purple cabbage was used as the subject and stored it under conditions of 4 ℃ and 85% RH for 12 d. Melatonin was used to treat fresh-cut purple cabbage at concentrations of 0, 0.01, 0.1, 0.5, and 1 mmol/L. Subsequently, the most effective concentration of melatonin was identified based on changes in color, weight loss, firmness, and the total number of aerobic bacteria. Furthermore, the effect of optimal melatonin concentration on the nutritional quality and antioxidant capacity of the fresh-cut purple cabbage was further evaluated. Results showed that 0.5 mmol/L melatonin treatment effectively reduced the decrease in lightness and redness, as well as the increase in yellowness, weight loss, softening, and the total number of aerobic bacteria in the fresh-cut purple cabbage (P<0.05). Additionally, fresh-cut purple cabbage treated with 0.5 mmol/L melatonin significantly enhanced the accumulation of anthocyanins (P<0.05), markedly inhibited the degradation in total glucosinolate content (P<0.05), and slowed the decrease of myrosinase activity, as well as the contents of sulforaphane and indole-3-carbinol. It also improved antioxidant activity by increasing DPPH and ABTS+ radical scavenging capacities, enhancing superoxide dismutase activity, and delaying the decrease in both catalase and peroxidase activities. In conclusion, 0.5 mmol/L melatonin treatment effectively maintained the nutritional quality and antioxidant capacity of fresh-cut purple cabbage, thereby providing a theoretical basis for the application of melatonin in fresh-cut vegetables.
-
Keywords:
- fresh-cut /
- purple cabbage /
- melatonin /
- nutritional quality /
- antioxidant capacity
-
紫甘蓝(Brassica oleraceal L.)是一种富含多种维生素、矿物质、花青素、硫代葡萄糖苷等物质的十字花科类蔬菜,具有抗癌、抗炎、抗氧化、预防心血管疾病等功效[1−2]。鲜切果蔬具有方便、快捷、营养等优点,然而,鲜切产生的机械损伤造成紫甘蓝组织细胞破裂,同时增加了与空气的接触面积,导致呼吸作用增强、内容物流失、酶促褐变增加、极易受到微生物污染等问题,从而引起感官、营养品质的降低和贮藏期的缩短[3−4]。已有研究报道,聚偏二氯乙烯保鲜膜[3]、1-甲基环丙烯与生物保鲜剂(木瓜蛋白酶+菠萝蛋白酶+ε-聚赖氨酸)复合处理[4]、气调包装[5]等处理方法可以延缓鲜切甘蓝感官品质和营养品质降低。然而,考虑到保鲜膜的生物可降解性、气调保鲜成本较高等原因,迫切需要天然、安全、无毒、具有良好生物相容性和抗菌活性的保鲜剂,对鲜切紫甘蓝进行简单有效的保鲜处理,从而减少其品质损失。
褪黑素是一种内源性植物生长调节剂,在调节植物生长发育和代谢等方面发挥着重要作用[6]。近年来,褪黑素在鲜切果蔬保鲜上展现出巨大的应用潜力,是一种天然、高效、安全的化学保鲜剂[7]。研究表明,外源褪黑素处理可抑制鲜切西兰花叶绿素降解导致的小花黄化,提高抗氧化能力,并减少硫苷类物质含量的降低[8]。刘帅民等[9]研究发现褪黑素处理可有效延缓鲜切芒果褐变和硬度降低,减少活性氧生成,并提高了DPPH自由基清除能力。此外,褪黑素处理能延缓鲜切梨中抗坏血酸含量降低,提高总酚含量和抗氧化能力,抑制微生物生长,降低酶促褐变相关基因表达,从而保持良好的贮藏品质[10]。师聪等[11]研究表明褪黑素处理可有效减缓鲜切莴苣颜色变化、硬度降低和失重增加,提高DPPH自由基清除能力以及抗氧化酶活性,有效维持鲜切莴苣贮藏品质。综上所述,褪黑素不仅可以延缓鲜切果蔬衰老,防止抗氧化酶钝化,抑制微生物生长,还可以降低果蔬中营养物质损耗,延长货架期。然而,目前尚缺乏褪黑素处理对鲜切紫甘蓝品质影响的研究。因此,本研究以紫甘蓝为实验材料,探究褪黑素对鲜切紫甘蓝品质及抗氧化能力的影响,以期为褪黑素在鲜切果蔬保鲜方面的应用提供理论依据,并为鲜切紫甘蓝的贮藏保鲜提供新思路。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
紫甘蓝(品种:紫甘1号) 采购于安徽省合肥徽商城农贸产品批发市场,挑选叶片完整、无机械损伤、无虫害、无萎蔫、大小一致(直径为15~18 cm)的同一批紫甘蓝作为实验材料;褪黑素(纯度98%)、抗坏血酸 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;萝卜硫素(Sulforaphane,SFN)、吲哚-3-甲醇(Indole-3-carbinol,I3C)、2,2-联苯基-1-苦基肼基(2,2-diphenyl-1-picryhydrazyl,DPPH)、2,2'-联氨-双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二胺盐(2,2'-Azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt,ABTS) 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;聚乙烯保鲜自封袋 上海橙至包装材料有限公司;葡萄糖测定试剂盒 南京建成生物科技有限公司;超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)试剂盒、过氧化氢酶(CAT)试剂盒、过氧化物酶(POD)试剂盒 北京索莱宝科技有限公司。
ZE7700电色差仪 上海首放电子科技有限公司;TA.XT-Plus C物性仪 英国Stable Micro System公司;1510全波长酶标仪、G10S UV-Vis分光光度计 赛默飞世尔科技有限公司;Agilent 1260高效液相色谱仪(配有可变波长紫外检测器) 安捷伦科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品处理
将新鲜紫甘蓝除去松散叶片,超纯水清洗叶片沥干。用灭菌刀片将叶片切成1×10 cm的条状,充分混合后,选择纹理相近的样品准确称量250 g,每组3个平行。空白组用超纯水浸泡5 min,处理组分别用0.01、0.1、0.5、1 mmol/L的褪黑素溶液浸泡5 min后取出,自然沥干装入聚乙烯袋。同时,每组准备3袋40 g/袋的鲜切甘蓝用于失重率的测量。将样品放置在4 ℃,85% RH条件下贮藏12 d,分别在第0、1、4、8、12 d进行取样,测量鲜切紫甘蓝的色泽、失重率、硬度和总需氧菌数量。每组样品用液氮冷冻粉碎,保存于−80 ℃。
1.2.2 测定指标和方法
1.2.2.1 颜色
采用色差仪测量L*、a*和b*,计算色差ΔE。每组随机抽取6个样品,分别在叶片上中下位置,选择平整部位测量3次。
ΔE=√(L∗−L∗0)2+(a∗−a∗0)2+(b∗−b∗0)2 式中:L∗0、a∗0、b∗0为第0 d鲜切紫甘蓝色度值;L*、a*、b*为贮藏期鲜切紫甘蓝色度值。
1.2.2.2 失重率
采用称重法分别在第0、1、4、8、12 d对样品进行称重,计算其重量变化。
失重率(%)=m1−m2m1×100 式中:m1和m2分别为贮藏前和贮藏不同时间后鲜切紫甘蓝的重量,g。
1.2.2.3 硬度
参考王冉冉等[12]方法稍作修改,采用平底柱形探头P/6,测试前、中、后速度分别为 1、1、3 mm/s,压缩30%,触发力5 g,间隔时间2 s,结果以g表示。每组随机抽取6个样品,分别在叶片上中下位置,选择平整部位测量3次。
1.2.2.4 总需氧菌数量
参考GB 4789.2-2022《食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定》[13]方法测定,称取紫甘蓝25 g,加入225 mL无菌生理盐水,匀浆后用无菌生理盐水将原液进行浓度梯度稀释,取200 μL匀浆液接种在平板计数琼脂培养基上平板涂布,每个梯度3个平行,结果以lg(CFU/g)表示。
1.2.2.5 抗坏血酸(AsA)含量
采用钼蓝比色法[14]测定,取0.5 g样品加45 g/L偏磷酸溶液混匀离心,取1 mL上清液依次加入45 g/L偏磷酸溶液、5%硫酸溶液、5%钼酸铵溶液,用蒸馏水定容至50 mL,避光反应15 min,测定705 nm处吸光度值。以抗坏血酸浓度为横坐标,吸光度值为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线,得到线性回归方程为y=0.2066x+0.035(R2=0.9992),样品中AsA含量以mg/g表示。
1.2.2.6 花青素含量
采用王颖等[15]方法稍作修改,取1 g样品加入含2%甲酸的甲醇溶液,冰浴超声30 min制备样液,取两份0.5 mL样液分别加2 mL pH1.0(50 mmol/L氯化钾+150 mmol/L盐酸)溶液和pH4.5(400 mmol/L乙酸钠+240 mmol/L盐酸)溶液,静置90 min后测定两份溶液分别在510 nm和700 nm处吸光度值。通过下列公式计算样品中花青素含量,结果以mg Cy/g表示。
ΔA=(A510−A700)pH1.0−(A510−A700)pH4.5 花青素含量(mgCy/g)=ΔA×M×V×Fε×L×m 式中:ε为矢车菊-3-葡萄糖苷的摩尔消光系数,26900 L/(mol·cm);M:矢车菊-3-葡萄糖苷相对分子质量,449.2 g/mol;V:最后定容体积,mL;F:样品稀释倍数;m:样品质量,g;L:比色皿的宽度,cm。
1.2.2.7 总硫代葡萄糖苷含量
参考罗淑芬等[16]方法稍作修改,取两份0.2 g样品分别加入40%的酸化甲醇(pH4.0)和蒸馏水,浸提20 min后加入40%酸化甲醇终止反应。取上清液依次加入蒸馏水、21.9%乙酸、10.6%亚铁氰化钾溶液,蒸馏水定容至50 mL,混匀静止30 min,上清液用葡萄糖测定试剂盒检测水解产生葡萄糖含量,总硫代葡萄糖苷含量为两份样品葡萄糖浓度的差值,结果以mmol/kg表示。
1.2.2.8 黑芥子酶活性
采用魏黎阳[17]的方法测定,取0.2 g样品与0.1 mol/L磷酸盐缓冲液(pH6.5)混匀,于4 ℃、10000×g离心10 min,取400 μL上清与等体积2 mmol/L黑芥子酶酸钾溶液混匀,37 ℃孵育15 min,转移至沸水加热5 min。用葡萄糖测定试剂盒检测溶液中葡萄糖含量,结果以U/g表示。
1.2.2.9 萝卜硫素(SFN)和吲哚-3-甲醇(I3C)含量
采用魏黎阳[17]的方法提取SFN和I3C。使用Hypersil GOLD-C18色谱柱(5 μm,250 mm×4.6 mm)和Agilent 1260高效液相色谱仪进行测定,流速为1 mL/min,进样量20 μL。SFN采用等梯度洗脱:10%乙腈和90%的超纯水,洗脱时间为40 min,柱温30 ℃,检测波长为201 nm。I3C的洗脱条件参考Anderton等[18]的方法稍作修改,采用梯度洗脱:0~2 min,15%~20%乙腈;2~3 min,20%乙腈;3~5 min,20%~30%乙腈;5~7 min,30%~45%乙腈;7~9 min,45%乙腈;9~11 min,45%~55%乙腈;11~14 min,55%乙腈;14~16 min,55%~65%乙腈;16~22 min,65%乙腈;22~24 min,65%~15%乙腈;24~30 min,15%乙腈;洗脱时间为30 min,柱温25 ℃,检测波长为280 nm。采用外标法分别进行SFN和I3C定量,SFN标准曲线为y=43.096x+368.65(R2=0.9993),I3C标准曲线为y=25.613x−49.895(R2=0.9991),样品中SFN和I3C含量以μg/g表示。
1.2.2.10 DPPH自由基清除率和ABTS+自由基清除率
采用郝文茁[19]的方法进行测定。取1.0 g样品与70%乙醇(含1%盐酸)溶液混匀,避光超声提取60 min,在4 ℃、5000×g条件下离心10 min取上清液,将沉淀重复提取1次,合并上清液保存于−80 ℃待测。
DPPH自由基清除率:向96孔板中加入40 μL样液和200 μL 6×10−5 mol/L DPPH甲醇溶液混匀,室温避光反应30 min,测定517 nm处吸光度值,以70%乙醇溶液为空白对照。DPPH自由基清除率按照以下公式计算:
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=A2−A1A2×100 式中:A1:样品的吸光度值,A2:空白对照的吸光度值。
ABTS+自由基清除率:取0.1 mL样品上清液加入2.9 mL ABTS工作液混匀,室温避光反应6 min,测定734 nm处吸光度值,以70%乙醇溶液为空白对照,计算公式同DPPH自由基清除率。
1.2.2.11 抗氧化酶活性
取0.2 g样品加入1.8 mL预冷的磷酸盐缓冲液(100 mmol/L,pH7.8)涡旋混匀,于4 ℃、8000×g离心10 min,取上清液置于冰上待测。将上清液稀释2倍后,采用试剂盒分别测定其SOD、CAT和POD活性,单位为U/g FW。
1.3 数据处理
实验数据均为3次重复实验的平均值±标准差。采用Excel 2021和SPSS 26进行数据处理,用SPSS 26进行显著性分析(P<0.05代表差异显著),使用GraphPad Prism 9软件绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 褪黑素处理鲜切紫甘蓝最佳浓度的筛选
2.1.1 褪黑素对鲜切紫甘蓝颜色的影响
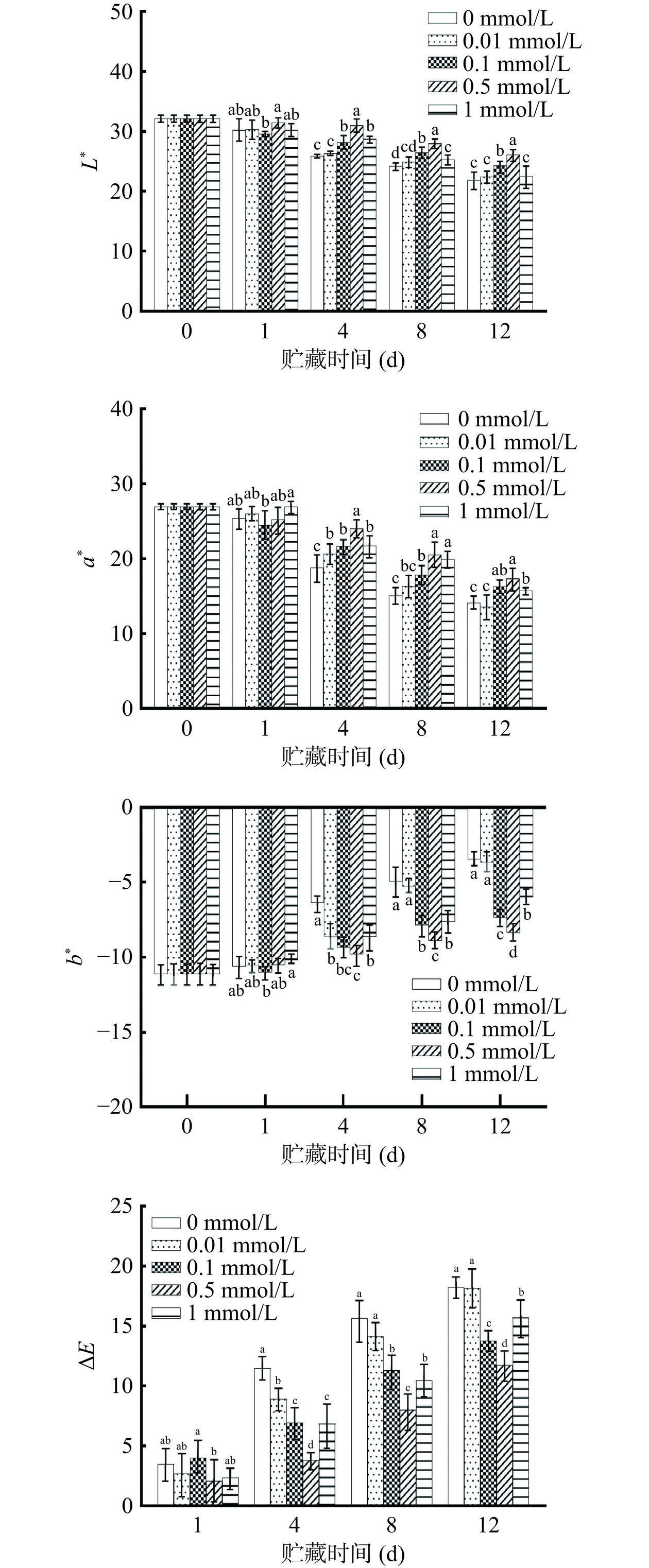
如图1所示,贮藏期内鲜切紫甘蓝L*值随着贮藏时间增加而降低,a*值呈下降趋势,b*值呈现上升趋势,ΔE随着贮藏时间的增加而增加,表明紫甘蓝的颜色逐渐由亮变暗、由红变绿和由蓝变黄,紫甘蓝颜色变化可能与贮藏过程中水分流失、细胞色素损失以及愈伤诱导细胞呼吸速率加快有关[9,20]。在第4~12 d,与对照组相比,0.1、0.5和1 mmol/L褪黑素处理可以不同程度的延缓紫甘蓝明度和红度降低以及黄度增加,而0.01 mmol/L褪黑素处理对颜色变化影响较小,可能是褪黑素浓度较低达不到作用效果。在第4~12 d,与0.1和1 mmol/L褪黑素处理组相比,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组L*值和a*值更大,b*值和ΔE更小。贮藏结束时,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组ΔE分别是0.01、0.1和1 mmol/L褪黑素处理组的0.64、0.84和0.74倍,表明0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理对延缓鲜切紫甘蓝明度和红度降低以及黄度增加最为有效。
![]() 图 1 褪黑素对鲜切紫甘蓝颜色的影响注:图中不同小写字母代表同一贮藏时间不同组间差异显著(P<0.05),图2同。Figure 1. Effects of melatonin on color of fresh-cut purple cabbage
图 1 褪黑素对鲜切紫甘蓝颜色的影响注:图中不同小写字母代表同一贮藏时间不同组间差异显著(P<0.05),图2同。Figure 1. Effects of melatonin on color of fresh-cut purple cabbage2.1.2 褪黑素对鲜切紫甘蓝失重率的影响
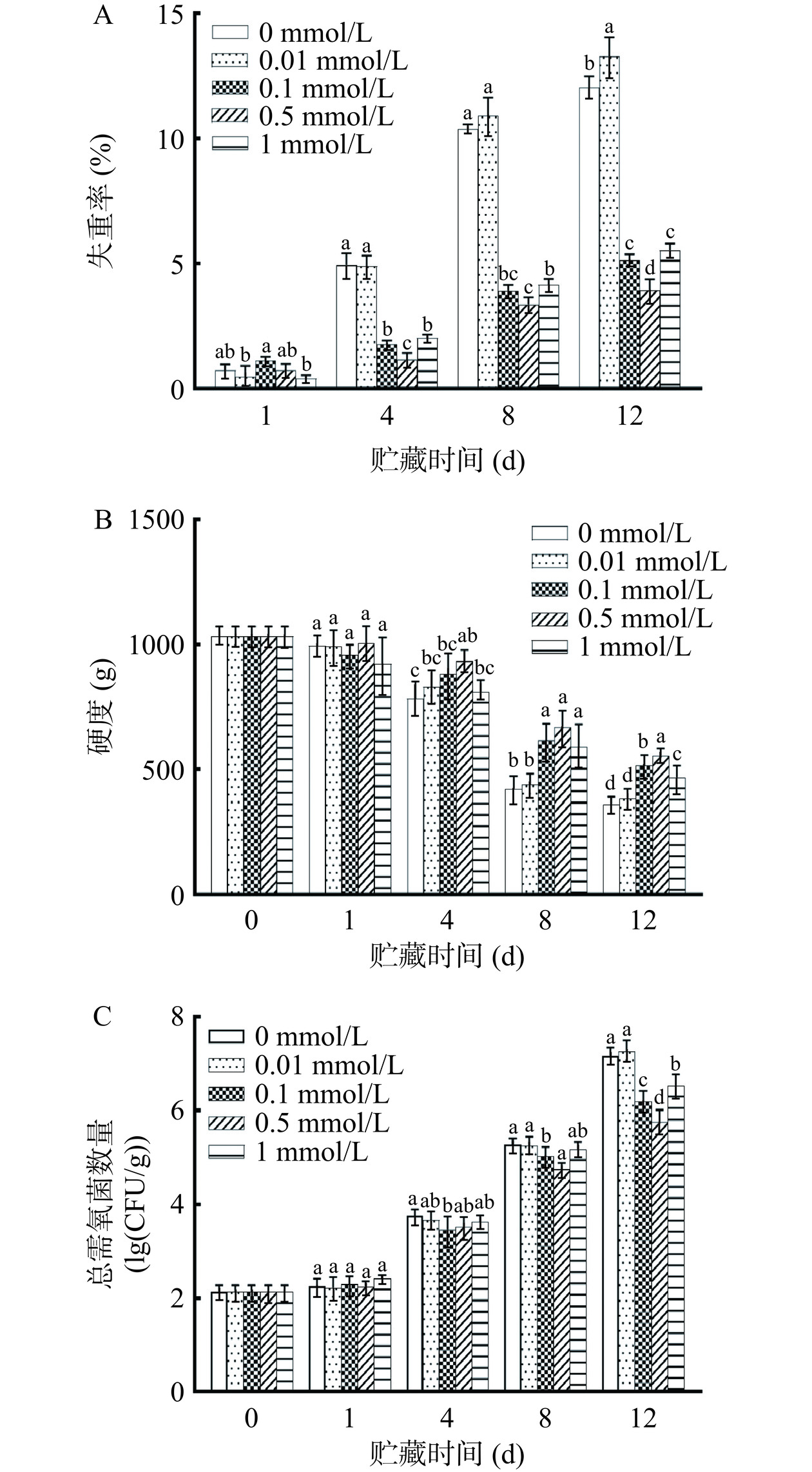
如图2A所示,贮藏期间鲜切紫甘蓝失重率持续增加,可能是鲜切造成植物组织呼吸速率增加和营养物质损耗导致失重增加[21]。在第4、8和12 d,0.1、0.5、1 mmol/L褪黑素处理均可降低鲜切紫甘蓝失重率增加,并且0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组失重率最低,显著低于1 mmol/L褪黑素处理组(P<0.05),可能是高浓度褪黑素处理促进乙烯产生,增强水通道蛋白基因表达,从而导致水分流失增加[22]。在第12 d,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组失重率比对照组低3.05倍(P<0.05),可见0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理能显著降低鲜切紫甘蓝重量损失。
2.1.3 褪黑素对鲜切紫甘蓝硬度的影响
如图2B所示,整个贮藏期内鲜切紫甘蓝随着贮藏时间的增加而逐渐软化,可能是鲜切产生的细胞机械损伤导致细胞壁果胶多糖的酶解和非酶促降解增加[12]。在第4和第12 d,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组的硬度显著高于0.1和1 mmol/L褪黑素处理组(P<0.05),这与褪黑素处理草莓果实[23]所获结果相似。贮藏结束时,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组硬度分别比0.1和1 mmol/L褪黑素处理组高7.3%和18.7%,可见0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理能有效延缓鲜切紫甘蓝的软化。
2.1.4 褪黑素对鲜切紫甘蓝总需氧菌数量的影响
如图2C所示,鲜切紫甘蓝总需氧菌数量随贮藏时间增加而增加。在第4和第8 d,0.1和1 mmol/L褪黑素处理组总需氧菌数量不存在显著区别(P>0.05),1 mmol/L褪黑素处理组总需氧菌数量增加可能是高浓度褪黑素处理加速果蔬衰老,产生过量的ROS,抑制植物防御相关酶的活性,从而导致微生物数量增加[24]。在第8 d,与0.1和1 mmol/L褪黑素处理组相比,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理显著抑制总需氧菌数量增加(P<0.05)。在第12 d,0.1、0.5和1 mmol/L褪黑素处理组总需氧菌数量分别比对照组减少了13.54%、19.59%和9.04%。综上所述,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理可有效抑制鲜切紫甘蓝颜色变化、失重增加、硬度降低和总需氧菌数量增加,故选择0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理的鲜切紫甘蓝做后续指标测定。
2.2 褪黑素对鲜切紫甘蓝AsA和花青素含量的影响
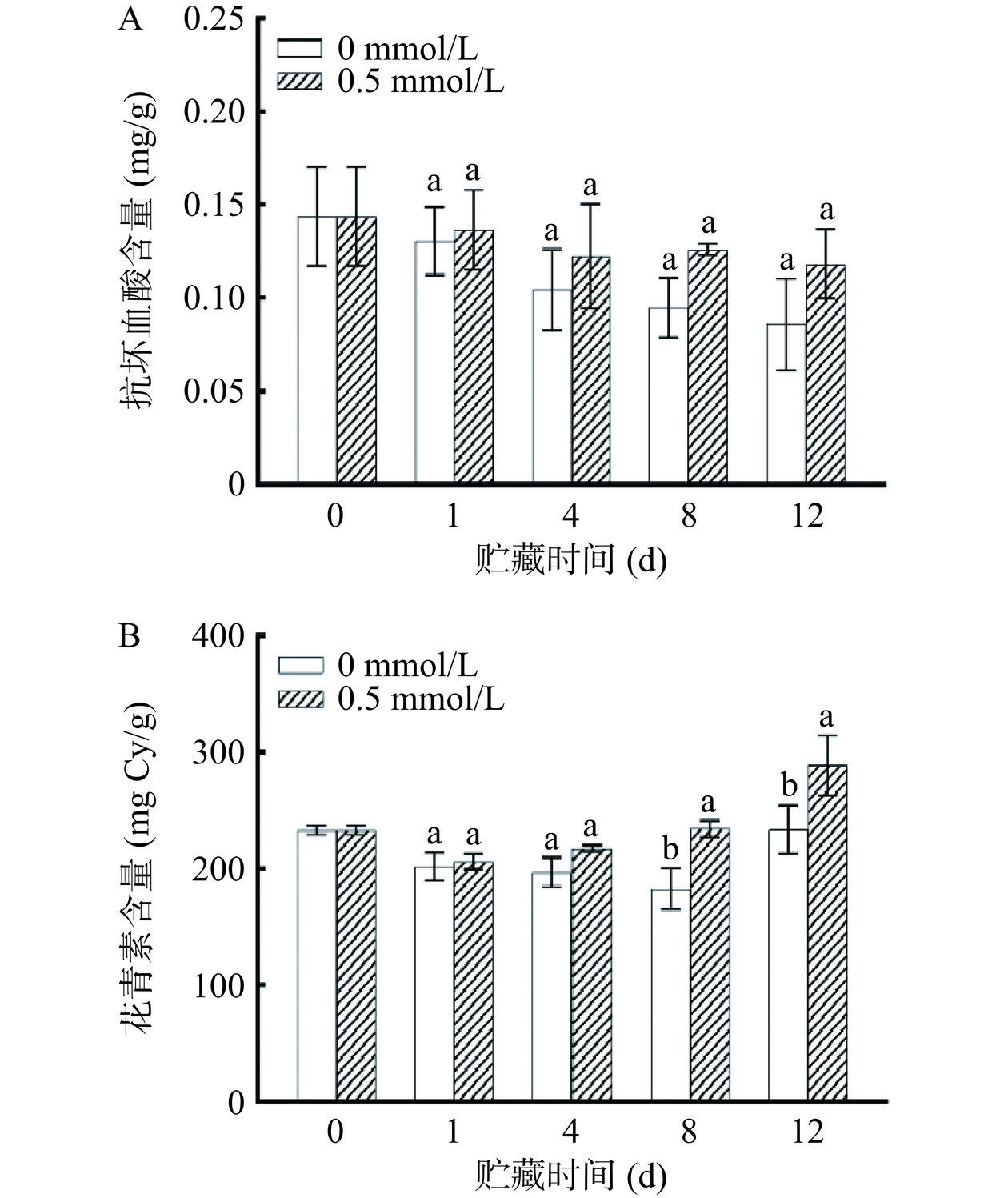
AsA是一种非酶抗氧化剂,在保护植物免受非生物胁迫等方面发挥重要作用,并且与果蔬的抗氧化能力密切相关[25]。如图3A所示,同一贮藏时间对照组和0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组AsA含量无显著差异(P>0.05)。在贮藏期内鲜切紫甘蓝中AsA的含量呈现逐渐减少的趋势,可能是由于植物细胞的破裂,AsA作为抗氧化剂与氧气接触增加,从而导致AsA含量的降低[10]。
花青素是紫甘蓝重要的生物活性物质,由于花青素非常不稳定,各种因素如温度、光、氧、pH、酶和抗坏血酸均可导致花青素的褪色[1]。如图3B所示,在贮藏期内对照组和0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组花青素含量呈现先降低后增加的趋势。在第8和第12 d,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理能显著促进鲜切紫甘蓝花青素的积累(P<0.05)。贮藏结束时,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组花青素含量是对照组的1.24倍,且两组花青素含量均有增加,这与王丹等[20]研究发现鲜切紫甘蓝经过9 d贮藏后,花青素含量增加的结果相似。Sun等[26]研究发现褪黑素处理通过上调花青素生物合成关键基因和转录因子(AN2和ANT1)的翻译水平促进采后番茄果实贮藏期间花青素的积累。故鲜切紫甘蓝中花青素含量增加可能是褪黑素处理与花青素自然积累共同作用的结果。
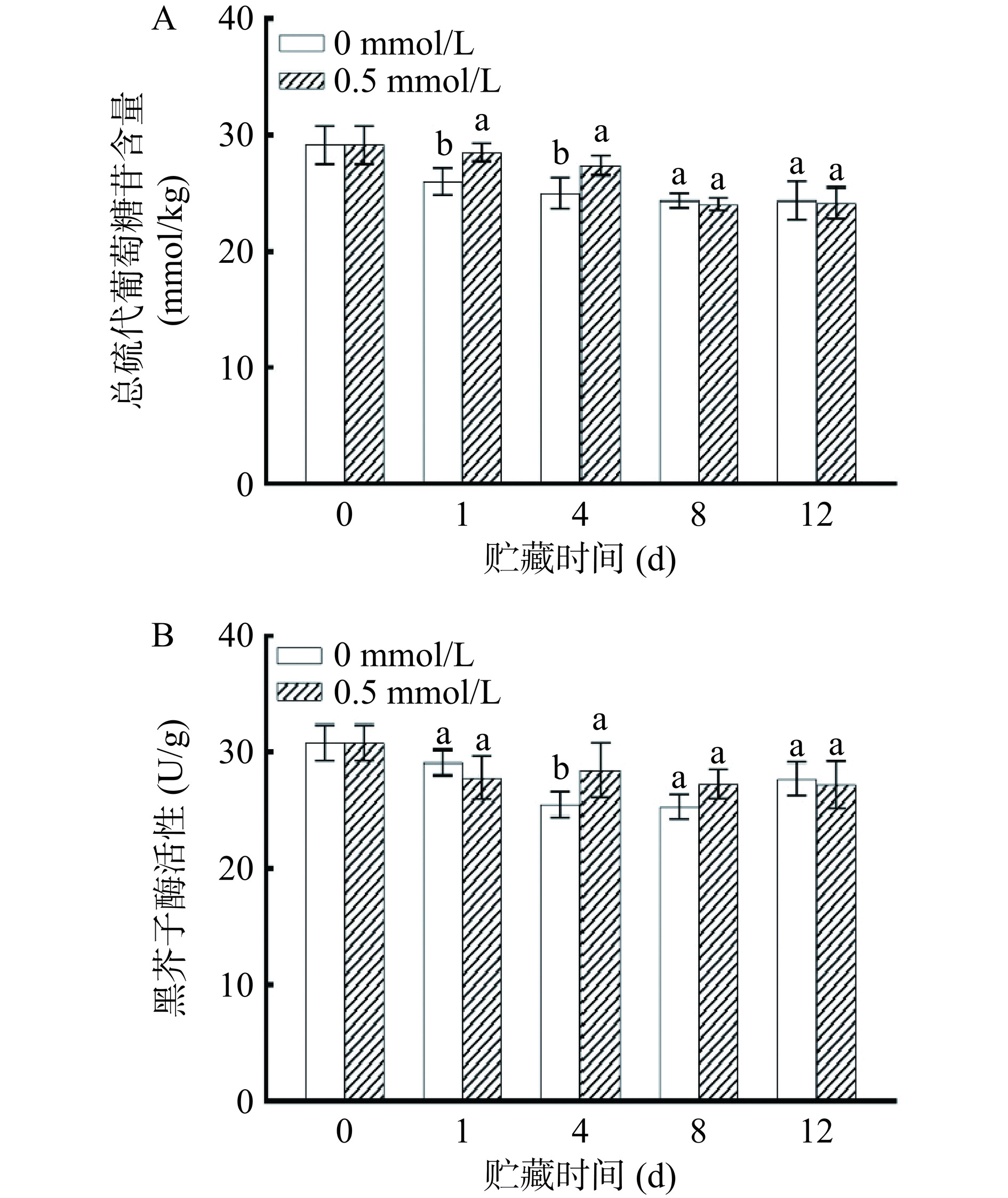
2.3 褪黑素对鲜切紫甘蓝总硫代葡萄糖苷含量和黑芥子酶活性的影响
硫代葡萄糖苷是一类植物次生代谢产物,在十字花科蔬菜中含量较高,多集中在叶球和茎中,它们是抗氧化和抗癌活性物质的前体物质[2]。如图4A所示,总硫代葡萄糖苷含量随着贮藏时间的增加而减少。在贮藏的第1 d和第4 d,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组中总硫代葡萄糖苷含量显著高于对照组(P<0.05),但是延缓总硫代葡萄糖苷含量降低的作用随着贮藏时间的增加而减弱。这与Miao等[8]研究结果一致,其原因可能是随着时间的推移,鲜切后组织发生失水,细胞完整性被破坏,黑芥子酶与硫代葡萄糖苷接触增加,进而导致总硫代葡萄糖苷水解。然而,褪黑素可以维持组织硬度,有效避免黑芥子酶和总硫代葡萄糖苷之间的接触,从而延缓总硫代葡萄糖苷水解[8]。
总硫代葡萄糖苷在黑芥子酶的催化下进行水解,形成具有生物活性功能的产物如异硫氰酸酯、硫氰酸盐、吲哚等,黑芥子酶活性会影响水解产物的含量[27]。如图4B所示,贮藏期内黑芥子酶活性呈现先减少后稳定的趋势,可能是切割导致损伤程度增加,加速了黑芥子酶的降解,从而引起酶活的降低[28]。在第4 d,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组黑芥子酶活性显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。因此,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理可在短期内有效抑制鲜切紫甘蓝中总硫代葡萄糖苷含量和黑芥子酶活性降低。
2.4 褪黑素对鲜切紫甘蓝SFN和I3C含量的影响
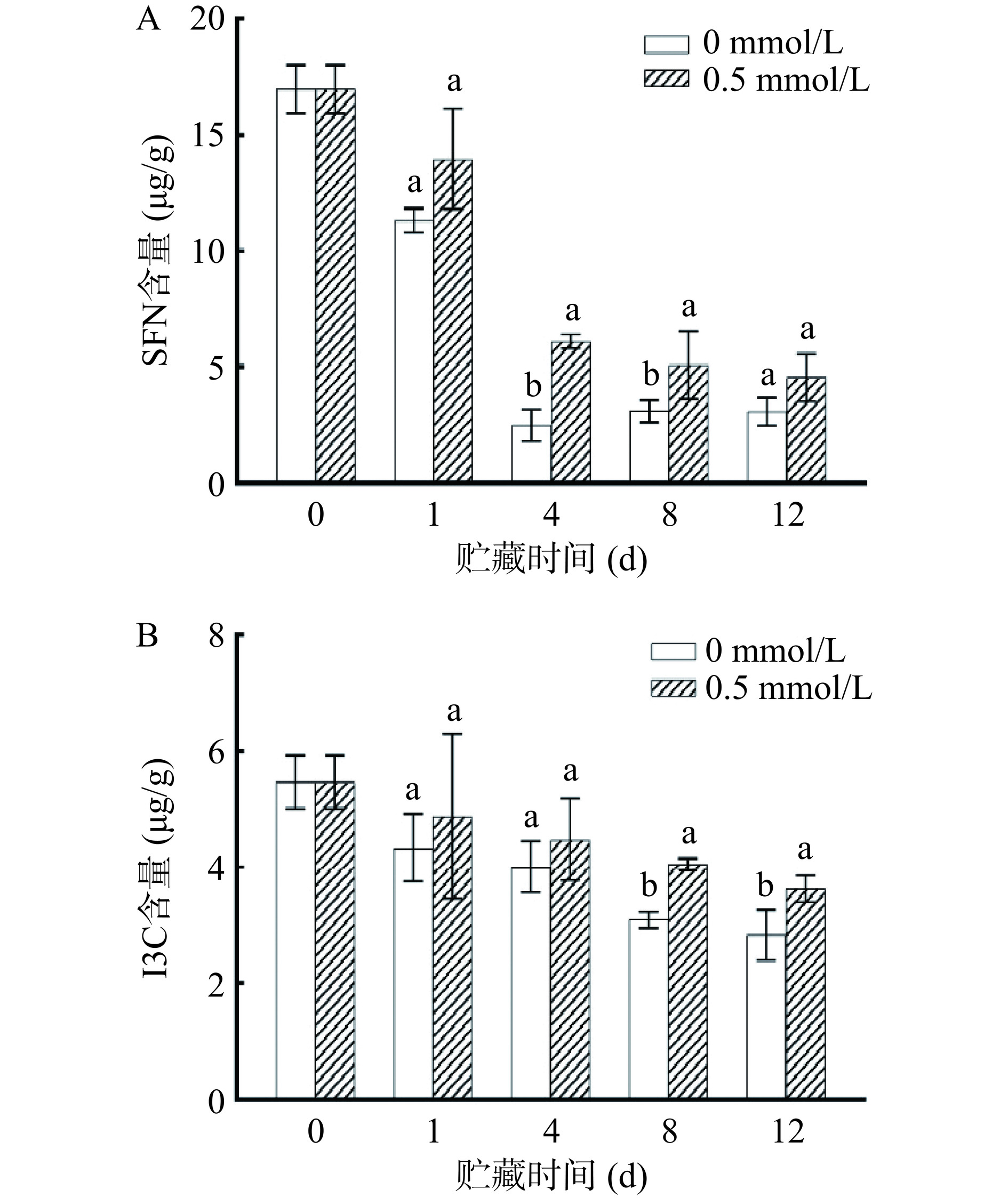
总硫代葡萄糖苷中萝卜硫苷和芸薹葡糖硫苷经过黑芥子酶水解后分别产生SFN和I3C,具有抗炎、抗癌等生物活性功能[29−30]。如图5A所示,随着贮藏时间的增加SFN含量逐渐减少,且在1~4 d内变化最为明显。第4 d与第0 d相比,对照组SFN含量减少了85.24%,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组SFN含量减少63.75%。此外,在第4和第8 d,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组SFN含量显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。如图5B所示,I3C含量在整个贮藏期内与SFN呈现相同的趋势,随着贮藏时间的增加而减少。在第8和第12 d,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组中I3C含量显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。结果表明,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理能有效延缓SFN和I3C含量降低。
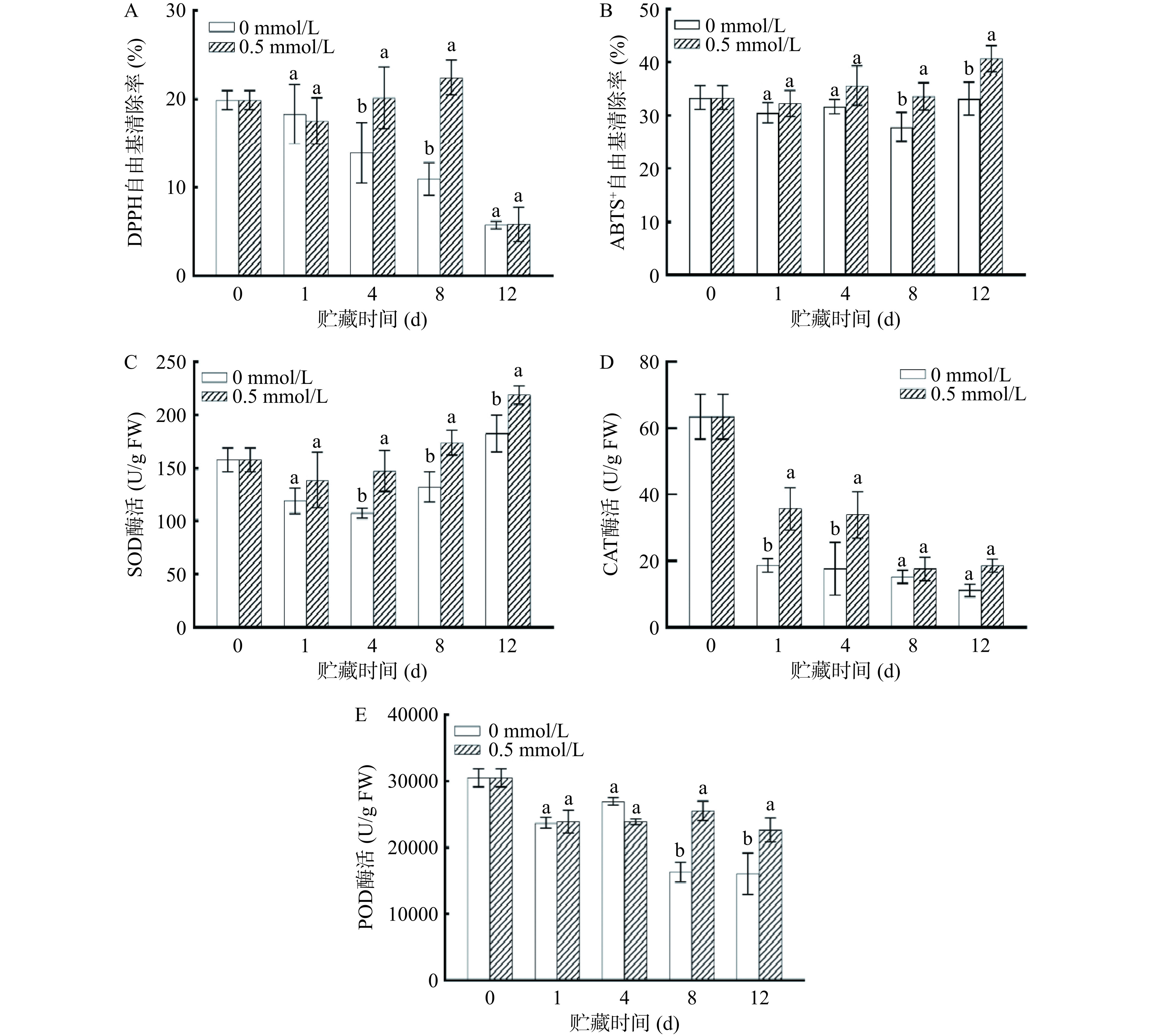
2.5 褪黑素对鲜切紫甘蓝DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除率的影响
果蔬采后病害或衰老产生大量活性氧导致脂质过氧化和腐烂变质[31]。DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除率能反应出鲜切紫甘蓝的自由基清除能力。如图6A所示,对照组DPPH自由基清除率随贮藏时间延长而降低,而0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组呈现先增加后降低的趋势,可能是贮藏前期褪黑素处理增强了DPPH自由基清除能力,随着贮藏时间增加紫甘蓝中自由基产生增加,DPPH自由基清除能力降低,这与Aghdam等[32]用褪黑素处理草莓的结果相似。在第4和第8 d,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组DPPH自由基清除率显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。如图6B所示,鲜切紫甘蓝ABTS+自由基清除率随贮藏时间增加先降低后增加。在第8和第12 d,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组ABTS+自由基清除率显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。可能与褪黑素对植物组织中酶促与非酶促防御系统的促进作用有关,褪黑素对二者的促进作用提高了植物组织的抗氧化能力,使得DPPH和ABTS+清除自由基的能力均显著提升[23]。
2.6 褪黑素对鲜切紫甘蓝抗氧化酶活性的影响
SOD、CAT、POD是清除ROS关键抗氧化酶,可以保护植物免受氧化损伤,使其在各种环境压力下维持正常生理功能[3,33]。如图6C所示,在贮藏期内,鲜切紫甘蓝中SOD酶活在贮藏期间呈现先降低后增加的趋势。在第4、8和12 d,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组SOD酶活显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。这可能与褪黑素通过增加抗氧化酶、非酶抗氧化剂和与氧化蛋白修复相关酶的含量来清除采后果蔬中多余活性氧,提升了抗氧化能力,延缓果蔬衰老有关[34−35]。
如图6D所示,鲜切紫甘蓝中CAT酶活随贮藏时间的增加而降低。经过1 d贮藏,两组CAT酶活均出现显著降低,对照组CAT酶活降低了70.63%,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组降低了43.77%。在第1和第4 d,与对照组相比,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组能显著抑制CAT酶活降低(P<0.05)。在第8和12 d,对照组和褪黑素处理组CAT酶活无显著差异,可能是鲜切处理造成组织细胞完整性降低,随着贮藏时间增加鲜切紫甘蓝中丙二醛含量增加,并产生过量ROS,从而引起CAT酶活降低[36]。
如图6E所示,鲜切紫甘蓝中POD酶活在贮藏期内呈现下降趋势。在第8和第12 d,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理组POD酶活显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。POD酶活的降低可能是由于鲜切紫甘蓝呼吸强度增加、营养物质流失和氧化胁迫增加,导致抗氧化能力的降低[4]。结果表明0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理能提高鲜切紫甘蓝中SOD酶活,延缓CAT和POD酶活降低。
3. 结论
综上所述,0.5 mmol/L褪黑素处理可显著减少鲜切紫甘蓝在贮藏期内明度和红度降低以及黄度增加、失重增加、硬度降低和总需氧菌数量增加(P<0.05)。褪黑素处理有效提高了花青素积累及黑芥子酶活,并延缓了总硫代葡萄糖苷、SFN和I3C含量的降低,从而维持了鲜切紫甘蓝良好的营养品质。此外,褪黑素处理通过提高鲜切紫甘蓝的DPPH、ABTS+自由基清除率,并维持较高的SOD、CAT和POD活性,进而有效保持鲜切紫甘蓝的抗氧化能力。总之,褪黑素在维持鲜切紫甘蓝贮藏品质方面展现出了优良的性能。本研究为褪黑素在鲜切蔬菜贮藏保鲜过程中的应用提供了理论依据,但关于贮藏过程中硫代葡萄糖苷具体成分含量变化,以及代谢相关基因的转录和翻译水平变化有待进一步研究。
-
图 1 褪黑素对鲜切紫甘蓝颜色的影响
注:图中不同小写字母代表同一贮藏时间不同组间差异显著(P<0.05),图2同。
Figure 1. Effects of melatonin on color of fresh-cut purple cabbage
-
[1] TAN S, LAN X, CHEN S, et al. Physical character, total polyphenols, anthocyanin profile and antioxidant activity of red cabbage as affected by five processing methods[J]. Food Research International,2023,169:112929. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.112929
[2] MANCHALI S, CHIDAMBARA K N, PATIL B S. Crucial facts about health benefits of popular cruciferous vegetables[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2012,4(1):94−106. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2011.08.004
[3] GUAN Y G, JI Y R, YANG X Z, et al. Antioxidant activity and microbial safety of fresh-cut red cabbage stored in different packaging films[J]. LWT,2023,175:114478. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2023.114478
[4] 李金金, 杨钧翔, 赵楠, 等. 1-MCP结合生物保鲜剂对鲜切甘蓝保鲜效果的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2024,50(2):159−167. [LI J J, YANG J X, ZHAO N, et al. Effect of 1-MCP combined with biological antistaling agent on fresh-keeping of fresh-cut cabbage[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2024,50(2):159−167.] LI J J, YANG J X, ZHAO N, et al. Effect of 1-MCP combined with biological antistaling agent on fresh-keeping of fresh-cut cabbage[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024, 50(2): 159−167.
[5] LI H, LI X L, WANG R R, et al. Quality of fresh-cut purple cabbage stored at modified atmosphere packaging and cold-chain transportation[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2020,23(1):138−153.
[6] 郜栀萍, 田云芳, 姜淑宁, 等. 外源褪黑素在果蔬保鲜中的作用研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技,2022,14:171−174. [GAO Z P, TIAN Y F, JIANG S N, et al. Research progress on effect of exogenous melatonin in fruit and vegetable preservation[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2022,14:171−174.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2022.02.055 GAO Z P, TIAN Y F, JIANG S N, et al. Research progress on effect of exogenous melatonin in fruit and vegetable preservation[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 14: 171−174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2022.02.055
[7] WANG S Y, SHI X C, WANG R, et al. Melatonin in fruit production and postharvest preservation:A review[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,320:126642. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126642
[8] MIAO H Y, ZENG W, ZHAO M, et al. Effect of melatonin treatment on visual quality and health-promoting properties of broccoli florets under room temperature[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,319:126498. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126498
[9] 刘帅民, 胡康琦, 刘港帅, 等. 外源褪黑素处理对鲜切芒果贮藏品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(21):160−166. [LIU S M, HU K Q, LIU G S, et al. Effect of exogenous melatonin treatment on storage quality of fresh-cut mango[J]. Food Science,2020,41(21):160−166.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191031-358 LIU S M, HU K Q, LIU G S, et al. Effect of exogenous melatonin treatment on storage quality of fresh-cut mango[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(21): 160−166. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191031-358
[10] ZHENG H H, LIU W, LIU S, et al. Effects of melatonin treatment on the enzymatic browning and nutritional quality of fresh-cut pear fruit[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,299:125116. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125116
[11] 师聪, 刘大豪, 沈苏婉, 等. 外源褪黑素处理对鲜切莴苣品质与活性氧代谢的影响[J]. 北方园艺,2023,19:84−91. [SHI C, LIU D H, SHEN S W, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin treatment on quality and reactive oxygen species metabolism in fresh-cut lettuce[J]. Northern Horticulture,2023,19:84−91.] doi: 10.11937/bfyy.20225295 SHI C, LIU D H, SHEN S W, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin treatment on quality and reactive oxygen species metabolism in fresh-cut lettuce[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2023, 19: 84−91. doi: 10.11937/bfyy.20225295
[12] 王冉冉, 蒋子敬, 李金姝, 等. 速冻联合低温贮藏处理对切块紫甘蓝保鲜的影响[J]. 食品科技,2017,42(7):38−43. [WANG R R, JIANG Z J, LI J S, et al. The effects of quick-frozen combined cryogenic storage treatment on fresh-keeping of purple cabbage slices[J]. Food Science and Technology,2017,42(7):38−43.] WANG R R, JIANG Z J, LI J S, et al. The effects of quick-frozen combined cryogenic storage treatment on fresh-keeping of purple cabbage slices[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2017, 42(7): 38−43.
[13] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB 4789.2-2022, 食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2022. [National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 4789.2-2022, National food safety standard - Microbiological examination of food - Determination of total bacterial count[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2022.] National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 4789.2-2022, National food safety standard - Microbiological examination of food - Determination of total bacterial count[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2022.
[14] 徐茂军, 马卫兴, 华士川. 钼蓝比色法测定食品中的还原型维生素C[J]. 食品与发酵工业,1993(5):38−41. [XU M J, MA W X, HUA S C. Determination of vitamin C in food by molybdenum blue spectrophotometry[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,1993(5):38−41.] XU M J, MA W X, HUA S C. Determination of vitamin C in food by molybdenum blue spectrophotometry[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 1993(5): 38−41.
[15] 王颖, 潘哲超, 李先平, 等. 不同肉色马铃薯花色苷含量及总抗氧化能力的分析研究[J]. 中国食物与营养,2017,23(2):66−69. [WANG Y, PAN Z C, LI X P, et al. Differences in anthocyanin content and total antioxidant capacity of potato tubers with different flesh colour[J]. Food and Nutrition in China,2017,23(2):66−69.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2017.02.017 WANG Y, PAN Z C, LI X P, et al. Differences in anthocyanin content and total antioxidant capacity of potato tubers with different flesh colour[J]. Food and Nutrition in China, 2017, 23(2): 66−69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2017.02.017
[16] 罗淑芬, 郭峰, 孙莹, 等. 6-苄氨基嘌呤处理对鲜切西兰花硫代葡萄糖苷代谢的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(13):295−304. [LUO S F, GUO F, SUN Y, et al. Effects of 6-benzylaminopurine treatments on the glucosinolate metabolism[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2022,38(13):295−304.] doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.13.032 LUO S F, GUO F, SUN Y, et al. Effects of 6-benzylaminopurine treatments on the glucosinolate metabolism[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(13): 295−304. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.13.032
[17] 魏黎阳. 西兰花萝卜硫素的采后富集调控及肠保护性作用研究[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学, 2022. [WEI L Y. Research on the enrichment of sulforaphane in postharvest broccoli and its effect on chemotherapy-induced intestinal damage[D]. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology, 2022.] WEI L Y. Research on the enrichment of sulforaphane in postharvest broccoli and its effect on chemotherapy-induced intestinal damage[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2022.
[18] ANDERTON M J, MANSON M M, VERSCHOYLE R D, et al. Pharmacokinetics and tissue disposition of indole-3-carbinol and its acid condensation products after oral administration to mice[J]. Clinical Cancer Research,2004,10(15):5233−5241. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0163
[19] 郝文茁. 采后褪黑素处理对黄桃果实酚类物质、内源褪黑素和GABA合成的影响[D]. 合肥:合肥工业大学, 2023. [HAO W Z. Effect of melatonin treatment on biosynthesis of phenolic, endogenous melatonin and GABA in postharvest yellow-flesh peach[D]. Hefei:Hefei University of Technology, 2023.] HAO W Z. Effect of melatonin treatment on biosynthesis of phenolic, endogenous melatonin and GABA in postharvest yellow-flesh peach[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2023.
[20] 王丹, 鲁榕榕, 马越, 等. 切分方式对鲜切紫甘蓝营养品质和挥发性风味物质的影响[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2020,38(4):27−36,62. [WANG D, LU R R, MA Y, et al. Effect of cutting direction on nutritional quality and volatile flavor substances of fresh-cut purple cabbage[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2020,38(4):27−36,62.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2020.04.004 WANG D, LU R R, MA Y, et al. Effect of cutting direction on nutritional quality and volatile flavor substances of fresh-cut purple cabbage[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2020, 38(4): 27−36,62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2020.04.004
[21] 濮艳清, 卢立新, 潘嘹, 等. 预处理结合气调包装对混合鲜切果蔬品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(6):114−120. [PU Y Q, LU L X, PAN L, et al. Effect of pretreatment combined with modified atmosphere packaging on the quality of mixed fresh-cut fruits and vegetables[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(6):114−120.] PU Y Q, LU L X, PAN L, et al. Effect of pretreatment combined with modified atmosphere packaging on the quality of mixed fresh-cut fruits and vegetables[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(6): 114−120.
[22] SUN Q Q, ZHANG N, WANG J F, et al. Melatonin promotes ripening and improves quality of tomato fruit during postharvest life[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2015,66(3):657−668. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru332
[23] 黄鸿晖, 顾里娟, 李美琳, 等. 褪黑素处理对草莓品质与活性氧代谢的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(15):187−193. [HUANG H H, GU L J, LI M L, et al. Effect of postharvest melatonin treatment on quality and reactive oxygen species metabolism in strawberry[J]. Food Science,2021,42(15):187−193.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200819-254 HUANG H H, GU L J, LI M L, et al. Effect of postharvest melatonin treatment on quality and reactive oxygen species metabolism in strawberry[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(15): 187−193. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200819-254
[24] SHARAFI Y, JANNATIZADEH A, FARD J R, et al. Melatonin treatment delays senescence and improves antioxidant potential of sweet cherry fruits during cold storage[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2021,288:110304. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110304
[25] CHEN H, HAO H B, HAN C C, et al. Exogenous L-ascorbic acid regulates the antioxidant system to increase the regeneration of damaged mycelia and induce the development of fruiting bodies in Hypsizygus marmoreus[J]. Fungal Biology,2020,124(6):551−561. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2020.02.010
[26] SUN Q Q, ZHANG N, WANG J F, et al. A label-free differential proteomics analysis reveals the effect of melatonin on promoting fruit ripening and anthocyanin accumulation upon postharvest in tomato[J]. Journal of Pineal Research,2016,61(2):138−153. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12315
[27] MAHN A, PÉREZ C. Optimization of an incubation step to maximize sulforaphane content in pre-processed broccoli[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2016,53:4110−4115. doi: 10.1007/s13197-016-2386-6
[28] 黄晓欣. 不同切割方式处理青花菜贮藏过程中硫苷代谢及抗氧化活性研究[D]. 北京:北京中医药大学, 2022. [HUANG X X. Thioglycoside metabolism and antioxidant activity during storage of broccoli treated with different cutting methods[D]. Beijing:Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2022.] HUANG X X. Thioglycoside metabolism and antioxidant activity during storage of broccoli treated with different cutting methods[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2022.
[29] 张璇, 田明硕, 王健, 等. 萝卜硫素提取纯化及其抗癌功能研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(17):424−434. [ZHANG X, TIAN M S, WANG J, et al. Research progress in extraction, purification and anticancer function of sulforaphane[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(17):424−434.] ZHANG X, TIAN M S, WANG J, et al. Research progress in extraction, purification and anticancer function of sulforaphane[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(17): 424−434.
[30] 田艳, 邓放明, 卿志星, 等. 十字花科植物中硫代葡萄糖苷类物质的结构与功能研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(1):292−303. [TIAN Y, DENG F M, QING Z X, et al. Advances in understanding the structure and function of glucosinolates in brassicaceae[J]. Food Science,2020,41(1):292−303.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190328-354 TIAN Y, DENG F M, QING Z X, et al. Advances in understanding the structure and function of glucosinolates in brassicaceae[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(1): 292−303. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190328-354
[31] HUANG X Q, REN J, LI P H, et al. Potential of microbial endophytes to enhance the resistance to postharvest diseases of fruit and vegetables[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2021,101(5):1744−1757. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10829
[32] AGHDAM M S, FARD J R. Melatonin treatment attenuates postharvest decay and maintains nutritional quality of strawberry fruits (Fragaria×anannasa cv. Selva) by enhancing GABA shunt activity[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,221:1650−1657. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.10.123
[33] WANG M Y, XU J, DING Z Y, et al. Prolong the postharvest shelf life of spinach through the antioxidative ability of melatonin[J]. Food Chemistry:X,2023,19:100769.
[34] 王洁琼, 王军萍, 朱丽娟, 等. 褪黑素对低温贮藏期间荠菜衰老和抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(17):263−271. [WANG J Q, WANG J P, ZHU L J, et al. Effect of melatonin on the senescence and antioxidant capacity of capsella bursa-pastoris during low-temperature storage[J]. Food Science,2022,43(17):263−271.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210825-325 WANG J Q, WANG J P, ZHU L J, et al. Effect of melatonin on the senescence and antioxidant capacity of capsella bursa-pastoris during low-temperature storage[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(17): 263−271. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210825-325
[35] XU T, CHEN Y, KANG H. Melatonin is a potential target for improving post-harvest preservation of fruits and vegetables[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2019,10:1388. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01388
[36] CAI S Y, ZHANG Z Q, WANG J L, et al. Effect of exogenous melatonin on postharvest storage quality of passion fruit through antioxidant metabolism[J]. LWT,2024,194:115835. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2024.115835





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



