Protective Effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum Saponins on Liver Injury in Guinea Pigs of Hyperlipemia Based on Oxidative Stress
-
摘要: 目的:从氧化应激角度探讨绞股蓝皂苷(Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins,GPs)对高脂血症模型豚鼠肝脏损伤的保护作用。方法:将32只豚鼠随机分为模型组、GPs低剂量组(85 mg/kg)、GPs高剂量组(170 mg/kg)和辛伐他汀组(1.5 mg/kg),每组8只。采用高脂饲料喂养5周,构建高脂血症模型。同时将8只豚鼠设立为正常组,给予普通饲料。从第6周开始,造模同时灌胃给药,正常组和模型组给予等量生理盐水,每日给药1次,连续4周。每周测量各组豚鼠的体质量、体长,并计算Lee's 指数。实验结束时,测定豚鼠血清中脂质(TC、TG、HDL和LDL)水平;豚鼠肝质量、肝体比与空腹血糖;肝脏中氧化应激(SOD、MDA、CAT和GSH-px)水平;采用HE和油红O染色观察豚鼠肝脏组织的形态;采用免疫荧光方法观察豚鼠肝脏Nrf2和HO-1的蛋白表达。结果:实验结束时,与模型组比较,GPs高、低剂量组豚鼠的体质量均极显著降低(P<0.01)。GPs低剂量组Lee's指数显著降低(P<0.05);GPs高剂量组Lee's指数极显著降低(P<0.01)。GPs低剂量组血清中TG和LDL水平均显著降低(P<0.05,P<0.01);GPs高剂量组血清中TC、TG和LDL水平均显著降低(P<0.05,P<0.01)。GPs低剂量组肝组织中MDA水平显著下降(P<0.05);GPs高剂量组肝组织中SOD水平显著上升(P<0.05),MDA水平极显著下降(P<0.01)。病理观察发现,GPs高剂量组可缓解肝脏的脂肪变性,减少脂滴聚集。GPs高、低剂量组Nrf2和HO-1蛋白的荧光表达均极显著增强(P<0.01)。结论:GPs可通过激活肝脏的Nrf2/HO-1信号通路改善高脂血症豚鼠肝脏的氧化应激水平,从而改善高脂血症导致的豚鼠肝脏损伤。Abstract: Objective: To observe the protective effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins (GPs) on liver injury in guinea pigs of hyperlipemia based on oxidative stress. Methods: A total of 32 guinea pigs were randomly divided into a model group, a low dose GPs group (85 mg/kg), a high dose GPs group (170 mg/kg), and a simvastatin group (1.5 mg/kg), with 8 animals in each group. All animals were fed with high-fat diet for 5 weeks to prepare a hyperlipemia model. At the same time, 8 guinea pigs were set up as a normal group and given regular feed. From the 6 th week onwards, hyperlipemia model guinea pigs were fed with high-fat diet go on, and were given intragastric administration at the same time, once a day for 4 consecutive weeks. The normal group and model group were given equal amount of normal saline. The body mass, body length, and Lee's index of each group of guinea pigs were measured weekly. After the experiment, the levels of total TC, TG, HDL and LDL of guinea pigs were measured. The liver mass, liver to body ratio, and fasting blood glucose of guinea pigs were measured. The levels of SOD, MDA, CAT and GSH-px in the liver were detected. HE and oil red staining were used to observe the pathological and morphological changes of guinea pig liver tissue. Immunofluorescence method was used to observe the protein expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 in the liver of guinea pigs. Results: At the end of the experiment, compared with the model group, the high dose and low dose group of GPs significantly decreased the level of the body mass (P<0.01) in hyperlipidemic guinea pigs. The low dose group of GPs significantly decreased the Lee's index (P<0.05). The high dose group of GPs significantly decreased the Lee's index (P<0.01). The low dose group of GPs significantly decreased the levels of TG and LDL in serum (P<0.05, P<0.01). The high dose group of GPs significantly decreased the levels of TC, TG, and LDL in serum (P<0.05, P<0.01). The low dose group of GPs significantly decreased the level of MDA in the liver tissue (P<0.05). The high dose group of GPs significantly increased the level of SOD (P<0.05), and decreased the level of MDA (P<0.01) in the liver tissue. Pathology showed that the high dose group of GPs reduced the fatty degeneration and lipid droplet accumulation in the hepatocytes of hyperlipidemic guinea pigs. The fluorescence expression of Nrf2 and HO-1 proteins in both the high and low dose groups of GPs significantly increased (P<0.01). Conclusion: GPs would have a good hepatic protective effect through significantly improve oxidative stress levels by activate the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in guinea pigs of hyperlipemia.
-
Keywords:
- Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins /
- hyperlipidemia /
- guinea pigs /
- liver /
- oxidative stress
-
高脂血症是由于人体脂质代谢紊乱,导致血脂浓度超过正常水平而出现的一种代谢性疾病。由于遗传、饮食、营养、药物等因素的影响,近年来高脂血症的发病率显著升高,已成为人类最常见的疾病之一[1]。高脂血症被认为是导致心脑血管疾病,特别是动脉粥样硬化(atherosclerosis,AS)的一个非常危险的因素[2]。
肝脏是脂肪酸代谢的中心器官,在正常情况下,肝脏只储存少量的以甘油三酯作为代表的脂肪酸,在营养过剩和肥胖的情况下,肝脏的脂肪酸代谢发生改变,肝细胞内甘油三酯的积累导致脂肪性肝脏疾病[3]。高脂血症会进一步诱导肝脏损伤[4]。氧化应激在代谢紊乱的发展中起着重要作用。减少活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)的产生可以逆转代谢紊乱,进而改善高脂血症或肝脏脂肪变性[5]。因此,改善氧化应激,控制高脂血症的发生发展,对于保护肝脏的正常功能具有重要意义。
绞股蓝(Gynostemma pentaphyllum)为葫芦科植物,因味道怡人,具有减肥功效而作为茶食用。2002年,绞股蓝被中国卫生部列入功能性食品名录。作为食药同源植物,绞股蓝具有调脂作用、神经保护、护肝和降血糖等药理作用[6]。目前已经从绞股蓝中分离出210多种化合物,包括180多种绞股蓝皂苷,以及黄酮类化合物和多糖[7]。因此,绞股蓝皂苷(Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins,GPs)是绞股蓝的主要有效成分。有研究发现,GPs可以通过调节ApcMin/+小鼠的肠道微生物而发挥抗结直肠癌活性[8]。GPs通过抑制应激小鼠海马中的小胶质细胞的激活和NF-κB信号通路的活化而发挥抗抑郁作用[9]。在治疗糖尿病方面,GPs可以降低糖尿病大鼠的血糖,提高糖尿病大鼠的肝肾组织中超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathion peroxidase,GSH-px)活性而改善其抗氧化能力[10]。除了上述的抗癌、抗抑郁、降血糖等药理作用,GPs还具有抗痴呆[6]和抗帕金森病[11]的作用。由于GPs有着众多的药理作用,若将其开发成高端保健产品,会具有良好市场前景。
由于GPs有着突出的调节血脂异常的功能,现代药理在此方面的研究越来越多。Weng等[12]发现GPs可以抑制HepG2细胞中前蛋白转换酶枯草溶菌素9(proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9,PCSK9)的表达而发挥降脂作用。在改善高脂引起肝脏损伤方面,赵卓等[13]研究发现GPs可缓解高脂饮食所致AS小鼠血脂紊乱和肝脏病理改变。滕菲等[14]也发现GPs可以改善高脂血症大鼠肝细胞脂肪变性,降低血清中脂质水平。GPs能改善高脂引起肝脏损伤,但是深入研究其作用机制的报道较少,特别是GPs是否能通过改善肝脏氧化应激,控制高脂血症的发生发展,从而改善肝脏损伤目前尚无报道。
小鼠和大鼠是常用于建立高脂血症模型的动物,但是小鼠和大鼠在基因表达和胆固醇代谢方面与人有着极大的差异[15]。豚鼠的肝脏对胆固醇的合成、运输、分解的方式上都与人类的具有高度的相似性,故而豚鼠是极好的研究模型[16]。因此,本研究制备了高脂血症豚鼠模型,观察GPs对豚鼠形体、体质量、体长、血脂水平和肝脏病理的影响,同时观察GPs对豚鼠肝组织中的氧化应激指标的影响,从而探讨GPs对高脂血症豚鼠肝脏损伤的保护作用,为进一步研发Gps作为功能性食品提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
SPF级豚鼠 雄性,40 只,体质量250~320 g,购自成都达硕实验动物有限公司 [生产许可证号:SCXK(川) 2020-030];GPs 纯度≥95%(UV),上海源叶生物科技有限公司;辛伐他汀片 规格20 mg/片,广州香山堂药业有限公司;胆固醇 成都市科隆化学品有限公司;GA-3型血糖试纸 三诺生物传感股份有限公司;普通豚鼠饲料 成都达硕实验动物有限公司;总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)测定试剂盒、甘油三酯(triglyceride,TG)测定试剂盒、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(high density liptein cholesterol,HDL)测定试剂盒、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low-density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL)测定试剂盒、SOD试剂盒、丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)试剂盒、GSH-px试剂盒、过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;HE染色试剂盒、油红O染色试剂盒 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;浓缩型DyLight488-SABC(兔IgG)试剂盒 武汉博士德生物工程有限公司;核因子 E2 相关因子 2(nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2,Nrf2)抗体、血红素氧合酶-1(heme oxygenase-1,HO-1)抗体 武汉三鹰生物技术有限公司。
Thermo Varioskan Flash酶标仪 美国Thermo公司;F8型匀浆机 上海弗鲁克流体机械制造有限公司;BX63正置荧光显微镜 日本Olympus公司;Leica CM 1950冷冻切片机 美国feica公司;Leica RM 2016超薄切片机 美国feica公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 高脂血症豚鼠模型的建立
将40只豚鼠饲养于成都医学院科研实验中心,单位使用许可证编号:SYXK(川) 2020-196。所有动物实验严格按照成都医学院伦理委员会的伦理准则和使用指南执行(2023-032号)。饲养期间所有豚鼠可随意饮水。
豚鼠适应性喂养1周后,随机分为正常组和造模组,正常组8只,饲喂普通豚鼠饲料,其余豚鼠喂养高脂饲料(0.1%胆固醇、10%猪油和89.9%普通豚鼠饲料[17])5周建立高脂血症模型。第5周后通过测量豚鼠体质量、Lee's 指数以及血脂水平,以明显高于正常豚鼠判定高脂血症模型建立成功[18]。
1.2.2 豚鼠的分组和给药
第6周,将建立了高脂血症模型的豚鼠随机分为模型组、GPs低剂量组、GPs高剂量组和辛伐他汀组,每组8只。参考大鼠、小鼠在灌胃GPs治疗高脂血症、糖尿病和动脉粥样硬化等疾病时设置的剂量,通过不同动物之间体表面积等效剂量比值计算出豚鼠对应的等效剂量[19−21]。GPs低、高剂量组分别灌胃85、170 mg/kg GPs(以0.5%羧甲基纤维素钠作为溶媒配制成的混悬液),辛伐他汀组灌胃1.5 mg/kg辛伐他汀。正常组和模型组灌胃等体积生理盐水,每日给药1次,连续4周。在给药期间,正常组喂养普通饲料,其余各组豚鼠继续给予高脂饲料。
1.2.3 豚鼠体质量、Lee's 指数的测定
每周测量各组豚鼠的空腹体质量;测量体长,即鼻到肛门的距离,计算Lee's 指数=体质量(g)∧(1/3)÷体长(cm)×103,Lee's 指数≥300表明肥胖[22]。
1.2.4 豚鼠血脂水平的测定
第9周末,豚鼠禁食12 h后,眼眶取血2 mL,取血清后测定豚鼠TC、TG、HDL、LDL水平。
1.2.5 豚鼠肝质量、肝体比与空腹血糖的测定
末次给药后,测量各组豚鼠空腹血糖值,然后颈椎脱臼处死豚鼠,取肝脏,测定肝脏重量,计算肝体比(肝质量/体质量×100)。
1.2.6 豚鼠肝组织氧化应激水平的测定
取部分肝脏,匀浆后按照试剂盒的方法测定豚鼠肝组织中SOD、MDA、CAT与GSH-px水平。
1.2.7 豚鼠肝脏病理组织形态的改变
取部分肝脏,石蜡包埋后,4 μm厚度切片,进行HE染色。另取部分肝脏,OCT包埋,冰冻切片10 μm厚度,然后进行油红O染色。显微镜下观察豚鼠肝脏病理组织形态的改变。
1.2.8 免疫荧光检测豚鼠肝脏中Nrf2和HO-1的表达
取部分肝脏,冰冻切片,滴加山羊血清封闭,然后分别滴加Nrf2 (1:100)、HO-1 (1:150)抗体,4 ℃孵育过夜,二抗37 ℃孵育30 min后,滴加稀释的SABC-DyLight 488,37 ℃孵育30 min,然后滴加DAPI染色3 min。封片后用BX63正置荧光显微镜拍照。用Image J 软件对平均荧光强度进行定量分析。
1.3 数据处理
所有数据均以平均值±标准差(x±s)表示。采用SPSS 21.0软件对实验数据进行统计分析,多组间差异的比较采用One-Way ANOVA分析,两两比较采用LSD-t 检验。以P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
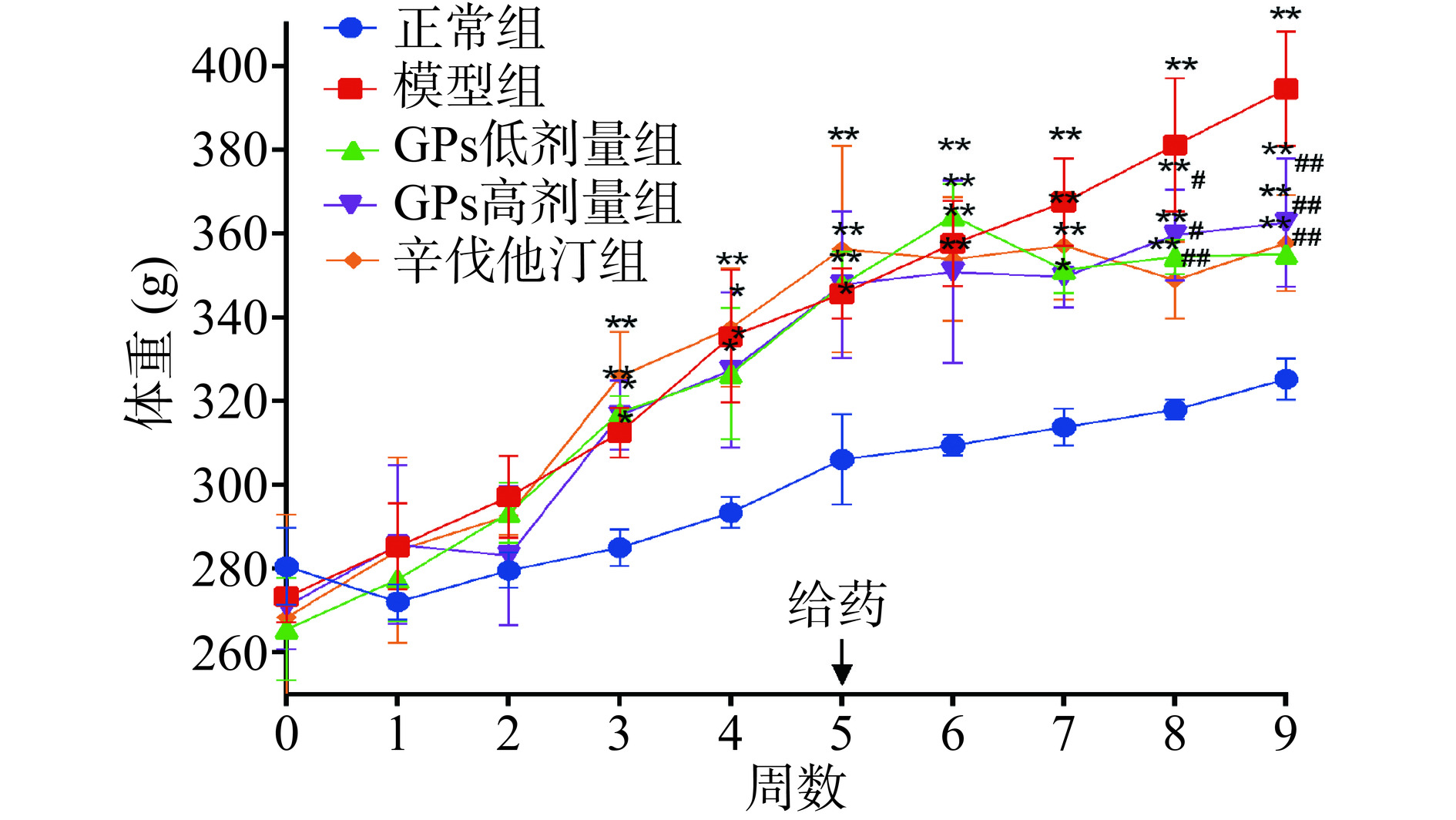
2.1 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠体质量的影响
由图1可见,与正常组相比,从第3~9周,制造了高脂血症模型的各组豚鼠体质量均显著增加(P<0.05,P<0.01),说明饲喂高脂饲料的方法能够增加豚鼠的体质量。给药3周以后,即第8~9周,与模型组相比,GPs高、低剂量组和辛伐他汀组的豚鼠体质量均显著下降(P<0.05,P<0.01),说明GPs能降低高脂血症模型豚鼠的体质量。体质量是肥胖的指标之一,体质量增加与高脂血症之间呈因果关系[23]。Shu等[24] 采用高脂饮食喂养建立肥胖模型小鼠后,发现GPs能降低小鼠体质量,降低脂肪质量/体重比,抑制脂肪细胞肥大而预防肥胖发展,也印证了本研究结果。因此,GPs可降低高脂血症模型豚鼠的体质量。
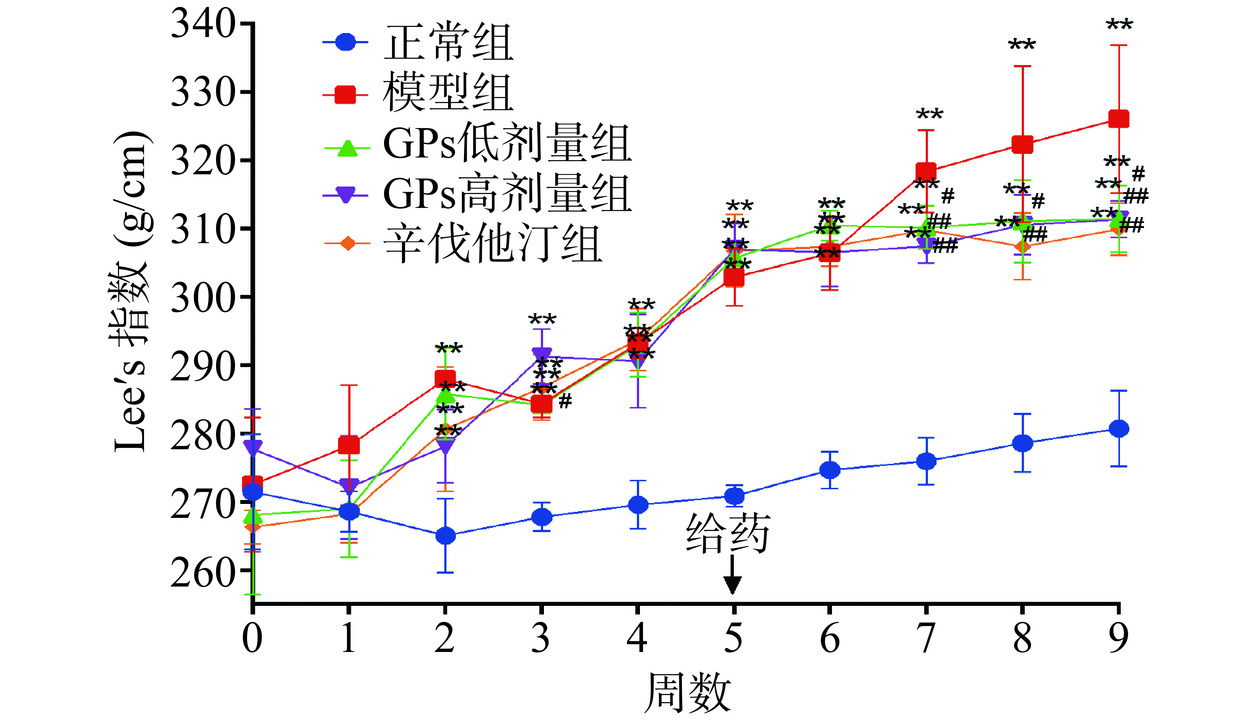
2.2 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠不同时间点Lee's 指数的影响
由图2可见,在第2~9周,各组豚鼠的Lee's指数均缓慢增加。与正常组相比,从第2周到第9周,制造了高脂血症模型的各组豚鼠Lee's 指数均极显著增加(P<0.01)。与模型组相比,第7周和第9周,GPs低剂量组豚鼠的Lee's 指数均显著降低(P<0.05);第7~9周,GPs高剂量组豚鼠的Lee's 指数均显著降低(P<0.05,P<0.01);第7~9周,辛伐他汀组豚鼠的Lee's 指数均极显著降低(P<0.01),说明GPs能降低高脂血症模型豚鼠的Lee's 指数。Lee's 指数也可以反映肥胖程度[25]。高脂膳食会导致小鼠肥胖从而使Lee's指数升高[26]。本研究发现,高脂血症模型豚鼠的Lee's 指数会升高,印证了文献观点,而GPs可降低高脂血症模型豚鼠的Lee's 指数,降低豚鼠的肥胖程度。
2.3 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠血脂水平的影响
由表1可见,与正常组相比,模型组豚鼠血清中TC、TG和LDL水平均极显著上升(P<0.01),HDL水平极显著下降(P<0.01)。与模型组相比,GPs低剂量组血清中TG和LDL水平均显著降低(P<0.05,P<0.01);GPs高剂量组血清中TC、TG和LDL水平均显著降低(P<0.05,P<0.01);辛伐他汀组血清中TC、TG和LDL水平均极显著降低(P<0.01),说明GPs能降低高脂血症模型豚鼠的血脂水平。血清中TC和TG水平是反映机体血脂代谢水平最常用的2个生化指标,LDL和HDL分别是运输胆固醇到肝外组织和将胆固醇从肝外组织转运到肝脏进行代谢的主要运载工具[27]。高脂血症以血清中TG、TC、LDL含量高于正常值,HDL含量过低作为诊断标准。滕菲等[14]采用高脂饮食喂养6周建立高脂血症大鼠模型后,发现绞股蓝地下部分总皂苷能降低大鼠血清中TG、TC和LDL水平,升高HDL水平。本研究也发现,GPs可以降低高脂血症豚鼠血清中TG、TC和LDL水平,但并不能升高豚鼠血清中HDL水平。
表 1 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠血脂水平的影响(mmol/L,n=8)Table 1. Effects of GPs on blood lipid levels of hyperlipidemic guinea pigs (mmol/L, n=8)组别 TC TG HDL LDL 正常组 0.74±0.17 0.98±0.14 1.15±0.25 0.30±0.07 模型组 2.51±0.09** 2.27±0.19** 0.43±0.20** 1.87±0.31** GPs低剂量组 2.24±0.04** 1.36±0.09*## 0.62±0.07** 1.37±0.27**# GPs高剂量组 1.87±0.18**## 1.46±0.19**## 0.58±0.27** 1.39±0.23**# 辛伐他汀组 1.55±0.40**## 1.33±0.17**## 0.69±0.27** 0.96±0.56**## 注:与正常组相比,*P<0.05,**P<0.01;与模型组相比,#P<0.05,##P<0.01,表2~表3同。 2.4 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠肝质量、肝体比与血糖水平的影响
由表2可见,与正常组相比,制造了高脂血症模型的各组豚鼠肝脏重量均极显著升高(P<0.01),验证了高脂饮食会增加动物的肝脏重量[28]。而制造了高脂血症模型的各组豚鼠各组之间肝脏重量无统计学差异,说明GPs不能减轻高脂血症造成的肝质量增加。
表 2 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠肝质量、肝体比与血糖水平的影响(n=8)Table 2. Effects of GPs on liver weight, liver to body ratio, and blood glucose levels of hyperlipidemic guinea pigs (n=8)组别 肝质量(g) 肝体比(%) 血糖(mmol/L) 正常组 9.76±0.63 3.00±0.21 4.03±1.19 模型组 11.58±0.54** 2.94±0.22 4.29±1.63 GPs低剂量组 12.08±0.82** 3.40±0.23*# 3.46±1.35 GPs高剂量组 11.38±0.68** 3.14±0.20 4.32±0.43 辛伐他汀组 12.05±0.91** 3.37±0.18*# 3.71±1.19 正常状态下,动物的脏器指数较稳定,一旦组织受到损伤,脏器指数也会随之变化[29]。GPs低剂量组和辛伐他汀组的肝体比较模型组均显著升高(P<0.05),甚至超过了正常组的肝体比值(P<0.05),其原因是由于GPs低剂量组和辛伐他汀组降低了豚鼠的体质量,但并没有减轻高脂血症造成的肝质量增加,导致肝体比较模型组和正常组均更高。
同时,本研究发现,制造了高脂血症模型的豚鼠与正常组之间的血糖值没有统计学差异,说明此种造模方法并不能升高豚鼠的血糖值。
2.5 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠肝组织氧化应激水平的影响
由表3可知,与正常组相比,模型组豚鼠肝组织中MDA水平极显著上升(P<0.01),SOD和CAT水平均极显著下降(P<0.01)。与模型组相比,GPs低剂量组肝组织中MDA水平显著下降(P<0.05);GPs高剂量组肝组织中SOD水平显著上升(P<0.05),MDA水平极显著下降(P<0.01);辛伐他汀组肝组织中SOD和CAT水平均显著上升(P<0.05),MDA水平显著下降(P<0.05)。而与正常组、GPs高、低剂量和辛伐他汀组相比,模型组豚鼠肝组织中GSH-px虽有下降趋势,但各组之间均无统计学差异。以上结果说明GPs可以通过升高豚鼠肝脏中SOD水平,降低MDA水平而缓解高脂血症造成的肝脏氧化应激。在脂肪性肝脏疾病中,高脂导致肝脏发生氧化应激和脂质过氧化,最终导致肝脏损伤[30]。钟方为等[31]发现GPs可以显著降低高脂饮食诱导的非酒精性脂肪肝病大鼠肝脏中MDA水平,升高CAT和SOD的水平,印证了本研究结果。因此可知,高脂血症会造成的肝脏氧化应激,GPs可以缓解高脂血症豚鼠肝脏的氧化应激水平而减轻肝脏损伤。
表 3 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠肝组织氧化应激水平的影响(n=8)Table 3. Effects of GPs on oxidative stress levels in liver tissue of hyperlipidemic guinea pigs (n=8)组别 SOD
(U/mg protein)MDA
(nmol/g
protein)CAT
(U/mg protein)GSH-px
(U/mg protein)正常组 216.42±38.95 1.49±0.18 35.68±1.55 23.17±5.48 模型组 156.51±18.94** 2.27±0.36** 29.58±2.82** 16.74±5.82 GPs低剂量组 174.61±39.97 1.51±0.60# 29.91±3.58** 23.66±7.00 GPs高剂量组 208.62±45.89# 1.30±0.31## 32.82±6.50 22.11±2.02 辛伐他汀组 204.34±21.07# 1.64±0.42# 34.81±3.75# 22.57±7.20 2.6 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠肝脏HE染色的影响
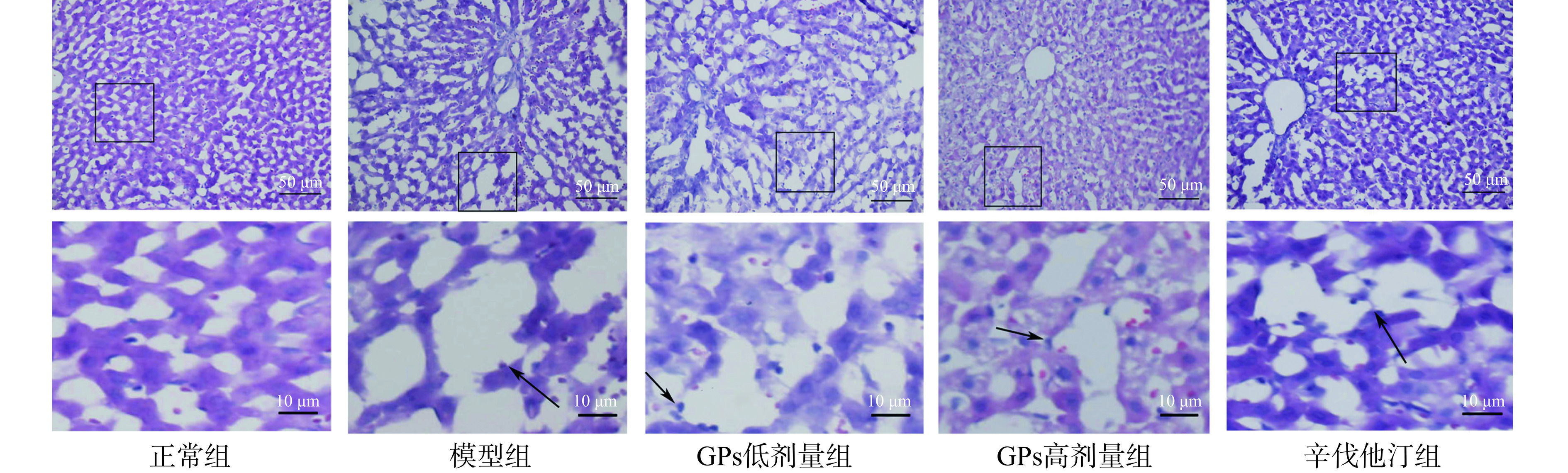
在200倍光镜下可见,正常组豚鼠肝脏结构完整,肝细胞以中央静脉为中心呈放射状排列,无肿胀和脂肪变性。模型组豚鼠肝细胞索排列紊乱,大小不一的脂滴空泡将细胞核挤于一侧。与模型组相比,GPs高剂量组和辛伐他汀组的肝细胞索排列有序,脂肪变性程度均减轻(图3)。表明GPs能缓解高脂血症豚鼠肝细胞的脂肪变性,缓解肝脏的病理改变。
2.7 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠肝脏油红O染色的影响
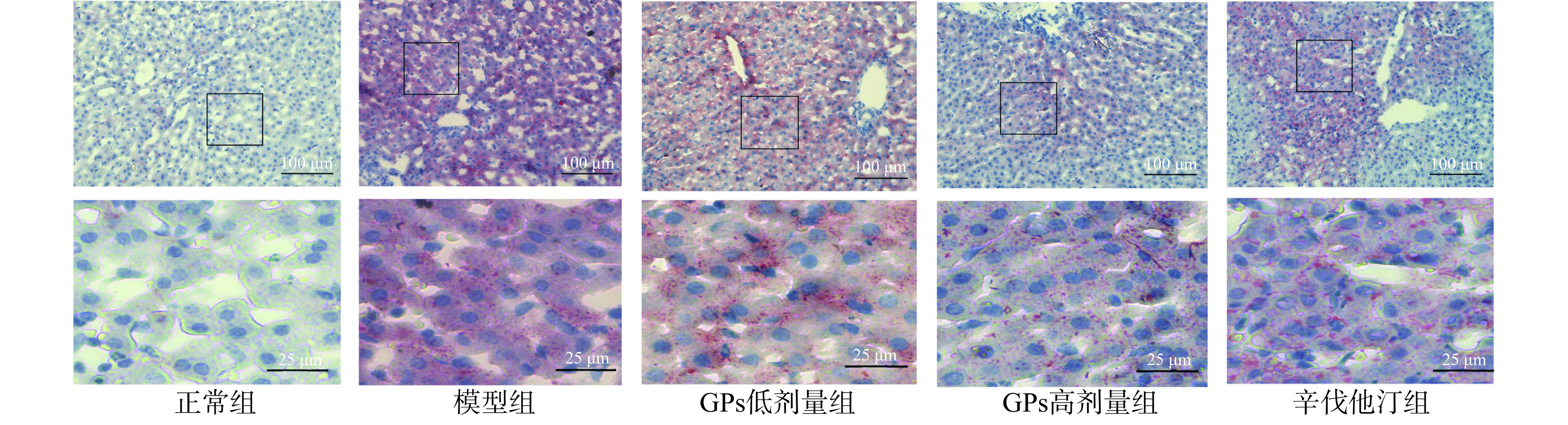
在200倍光镜下可见,正常组肝细胞内未出现红色脂滴。模型组豚鼠肝细胞内脂滴明显,占据了大部分的细胞质。GPs高剂量组和辛伐他汀组脂滴主要聚集在中央静脉周围,远离中央静脉的肝细胞内脂滴聚集明显减少,且GPs高、低剂量组和辛伐他汀组肝细胞内脂滴均较模型组明显减少(图4)。以上结果表明GPs能缓解高脂血症豚鼠肝细胞的脂滴聚集,缓解肝脏损伤。
2.8 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠肝脏Nrf2和HO-1蛋白荧光表达的影响
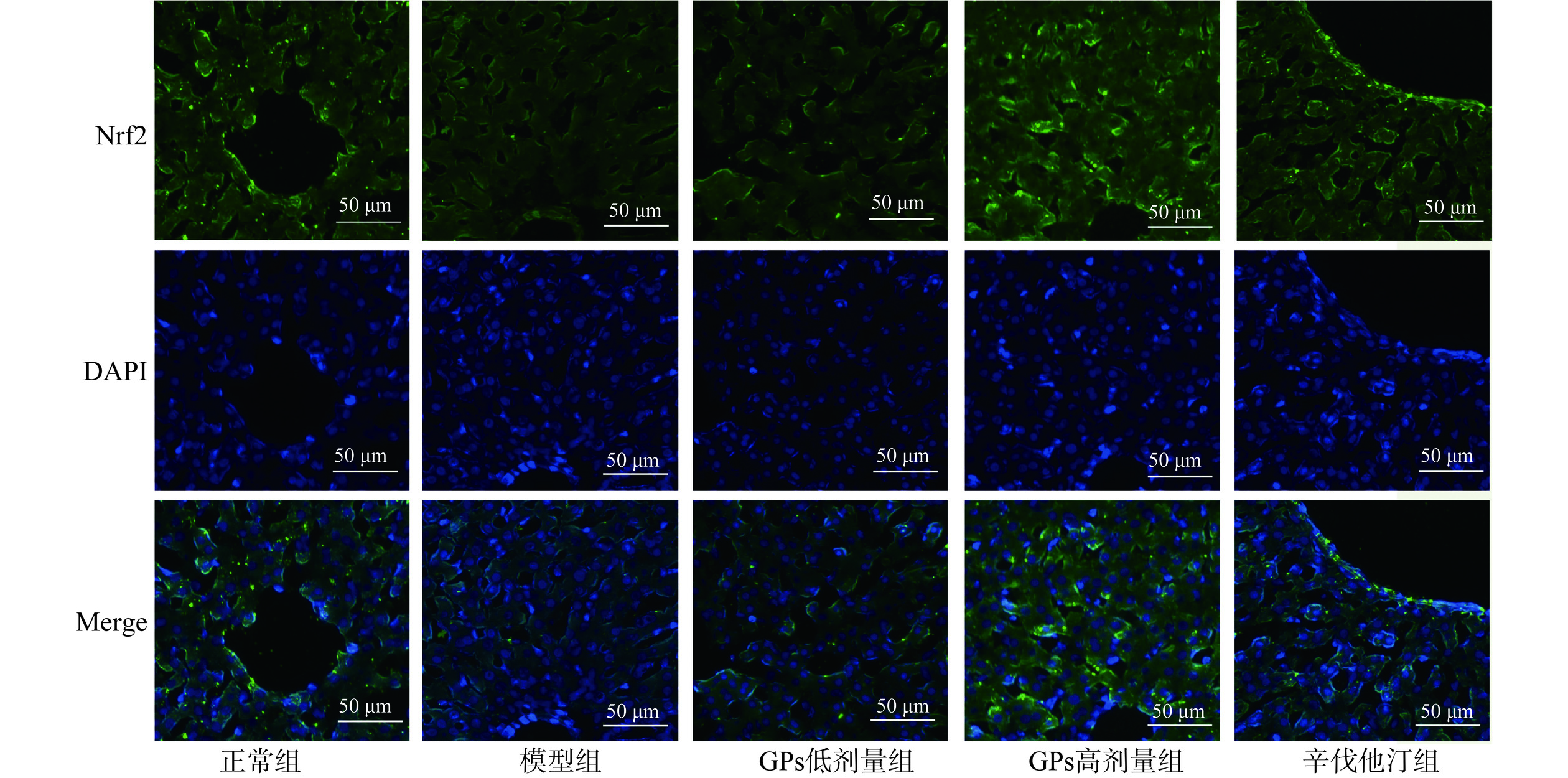
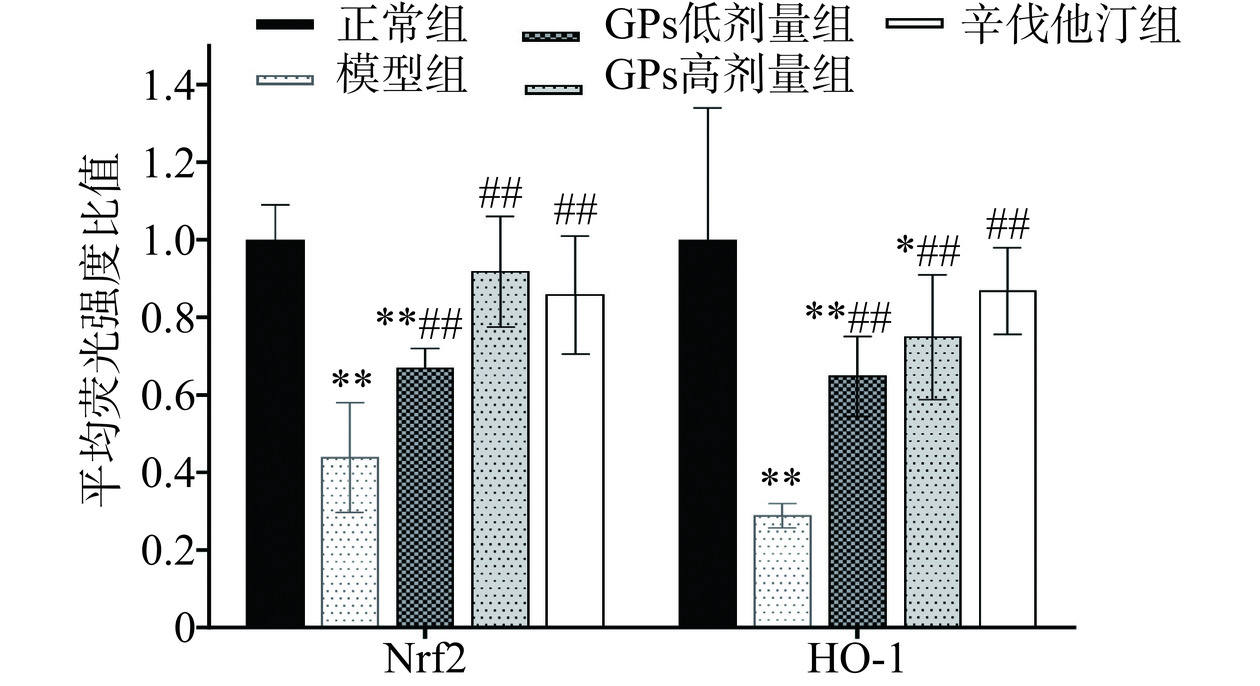
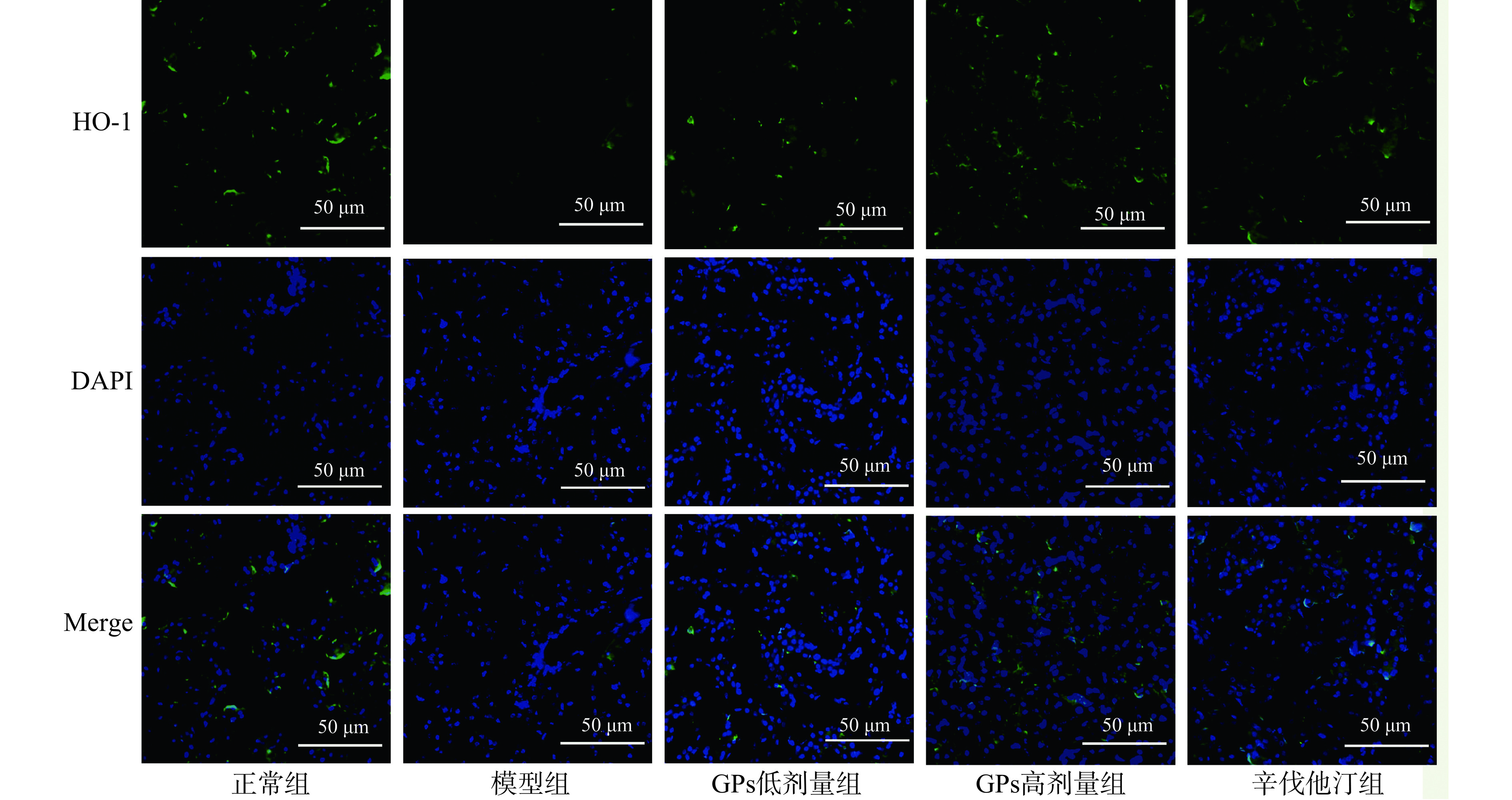
在荧光显微镜下观察发现,与正常组比较,模型组豚鼠肝脏的Nrf2和HO-1蛋白的荧光强度均极显著降低(P<0.01)。与模型组相比,GPs高、低剂量组和辛伐他汀组的Nrf2和HO-1蛋白的荧光强度均极显著升高(P<0.01)(图5~图7)。说明GPs能增强高脂血症豚鼠肝脏Nrf2和HO-1蛋白的荧光表达。
![]() 图 5 各组豚鼠肝脏Nrf2蛋白荧光表达情况注:免疫荧光,200×,标尺=50 μm,图6同。Figure 5. Fluorescence expression of Nrf2 protein in the liver of guinea pigs in each group
图 5 各组豚鼠肝脏Nrf2蛋白荧光表达情况注:免疫荧光,200×,标尺=50 μm,图6同。Figure 5. Fluorescence expression of Nrf2 protein in the liver of guinea pigs in each group3. 讨论与结论
近年来,高脂血症发病率逐年上升。2002年、2010年、2011年及2012年,≥18岁的中国人血脂异常发生率分别为8.6%、34.0%、39.91%和40.4%,呈现出快速增长的趋势[32]。高脂血症是心血管疾病的主要危险因素,严重影响着患者的身心健康。高脂血症患者多表现为TC、TG、LDL的升高和HDL的降低,并伴随肝功能损伤和肝脏的脂质沉积,因此,临床常通过检测TC、TG、LDL和HDL的含量来评价血脂水平[33]。在高脂饮食诱导形成高脂血症的过程中,血脂代谢紊乱会导致内脏脂肪沉积[27]。当肝脏的脂滴过度聚集,会导致肝脏损伤[28]。本研究结果显示,高脂血症豚鼠模型组血脂TC、TG和LDL水平升高,HDL水平降低,肝脏出现明显的脂滴聚集,与小鼠、大鼠高脂血症模型表现一致[34−35]。与模型组相比,GPs给药组能有效降低高脂血症豚鼠血清中TC、TG和LDL水平,降低体质量和Lee's指数。HE和油红O的病理研究发现,GPs能有效改善高脂饮食导致的豚鼠肝脏脂滴聚集,且大部分指标都呈剂量依赖性。综合上述结果,表明GPs可以通过改善高脂导致的豚鼠脂质代谢紊乱,减少肝脏脂类物质的蓄积,从而改善肝脏损伤,达到保护肝脏的目的。
氧化应激是高脂血症发病机制中的一个关键因素[36]。长期、大量的高脂或高热量食物摄入体内,机体会产生大量ROS,这些ROS可引起肝细胞氧化损伤和肝内脂质过氧化,影响肝细胞正常脂质代谢功能,最终造成肝内脂肪酸、胆固醇沉积和肝细胞脂肪变[37−38]。Nrf2是一种转录因子,能维持细胞的正常功能,同时也是启动细胞防御机制而对抗氧化应激的关键调节因子[39]。HO-1是一种诱导型酶,催化血红素氧化降解为胆绿素。当细胞发生氧化应激时,Nrf2被激活并介导HO-1在转录水平表达,发挥抗炎、抗氧化及调控细胞凋亡的作用[40]。正常和病理条件下,Nrf2维持着体内平衡,避免肝脏中反应性物质的过度产生而导致的氧化还原失衡,从而避免氧化损伤和器官稳态受损[41]。氧化应激时,ROS水平的增加激活了Nrf2信号传导,Nrf2启动下游的如HO-1、CAT、GSH-px和SOD等抗氧化酶的表达增加,对抗氧化应激所产生的细胞毒性,促进肝细胞修复氧化损伤[42]。因此促进肝脏Nrf2的激活是治疗高脂血症的一种新的临床治疗策略。例如使用Nrf2活化剂富马酸二甲酯会显著改善高脂诱导小鼠肝脏的氧化应激和炎症[43]。而敲除或抑制Nrf2会导致线粒体功能障碍和细胞凋亡,阻碍对肝细胞的保护作用[44−45]。本研究发现,GPs干预后,高脂血症豚鼠肝脏中SOD水平明显升高,MDA水平明显降低,Nrf2和HO-1蛋白的荧光表达明显增强。由此可知,GPs可能通过改善高脂血症豚鼠肝脏的氧化应激水平,激活Nrf2/HO-1信号通路而改善氧化应激,从而减轻肝脏损伤。
综上所述,GPs有改善血脂代谢紊乱,减少肝脏脂滴聚集,激活肝脏的Nrf2/HO-1信号通路而改善氧化应激水平,从而减轻高脂血症导致的肝脏损伤,起到肝脏保护的功效,这些结果为GPs作为一种能够改善高脂血症导致的肝脏损伤的天然产物提供了实验基础。因此GPs作为天然植物绞股蓝的提取物,具有广泛的发展前景。且本实验建立的是高脂血症豚鼠模型,豚鼠已被证实可作为研究高脂肪饮食诱导的代谢性疾病的模型,因为它们的抗氧化代谢和脂质特征与人类相似,并且易患动脉粥样硬化和血管内皮疾病[46],因此,本研究结果更具有可靠性。虽然本研究对GPs的降血脂和减轻肝脏损伤进行了验证,确定GPs通过激活Nrf2/HO-1信号通路而改善氧化应激,但未用westerning blot方法对肝脏中Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达的整体水平进一步验证,是本文的不足之处。GPs是否参与调控了Nrf2/HO-1信号通路的所有分子,以及GPs是否能调节更多的基因而调控高脂血症豚鼠的脂质代谢和氧化应激,尚需要进一步研究。
-
图 5 各组豚鼠肝脏Nrf2蛋白荧光表达情况
注:免疫荧光,200×,标尺=50 μm,图6同。
Figure 5. Fluorescence expression of Nrf2 protein in the liver of guinea pigs in each group
表 1 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠血脂水平的影响(mmol/L,n=8)
Table 1 Effects of GPs on blood lipid levels of hyperlipidemic guinea pigs (mmol/L, n=8)
组别 TC TG HDL LDL 正常组 0.74±0.17 0.98±0.14 1.15±0.25 0.30±0.07 模型组 2.51±0.09** 2.27±0.19** 0.43±0.20** 1.87±0.31** GPs低剂量组 2.24±0.04** 1.36±0.09*## 0.62±0.07** 1.37±0.27**# GPs高剂量组 1.87±0.18**## 1.46±0.19**## 0.58±0.27** 1.39±0.23**# 辛伐他汀组 1.55±0.40**## 1.33±0.17**## 0.69±0.27** 0.96±0.56**## 注:与正常组相比,*P<0.05,**P<0.01;与模型组相比,#P<0.05,##P<0.01,表2~表3同。 表 2 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠肝质量、肝体比与血糖水平的影响(n=8)
Table 2 Effects of GPs on liver weight, liver to body ratio, and blood glucose levels of hyperlipidemic guinea pigs (n=8)
组别 肝质量(g) 肝体比(%) 血糖(mmol/L) 正常组 9.76±0.63 3.00±0.21 4.03±1.19 模型组 11.58±0.54** 2.94±0.22 4.29±1.63 GPs低剂量组 12.08±0.82** 3.40±0.23*# 3.46±1.35 GPs高剂量组 11.38±0.68** 3.14±0.20 4.32±0.43 辛伐他汀组 12.05±0.91** 3.37±0.18*# 3.71±1.19 表 3 GPs对高脂血症豚鼠肝组织氧化应激水平的影响(n=8)
Table 3 Effects of GPs on oxidative stress levels in liver tissue of hyperlipidemic guinea pigs (n=8)
组别 SOD
(U/mg protein)MDA
(nmol/g
protein)CAT
(U/mg protein)GSH-px
(U/mg protein)正常组 216.42±38.95 1.49±0.18 35.68±1.55 23.17±5.48 模型组 156.51±18.94** 2.27±0.36** 29.58±2.82** 16.74±5.82 GPs低剂量组 174.61±39.97 1.51±0.60# 29.91±3.58** 23.66±7.00 GPs高剂量组 208.62±45.89# 1.30±0.31## 32.82±6.50 22.11±2.02 辛伐他汀组 204.34±21.07# 1.64±0.42# 34.81±3.75# 22.57±7.20 -
[1] 龚韧. Caspase-1介导高脂血症弱化心肌梗死后内皮祖细胞血管修复研究[D]. 南昌:南昌大学, 2022. [GONG R. Caspase-1 mediates hyperlipidemia-weakened endothelial progenitor cell vessel repair[D]. Nanchang:Nanchang University, 2022.] GONG R. Caspase-1 mediates hyperlipidemia-weakened endothelial progenitor cell vessel repair[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2022.
[2] HE N N, YE H H. Exercise and hyperlipidemia[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol,2020,1228(1):79−90.
[3] ALVES-BEZERRA M, COHEN D E. Triglyceride metabolism in the liver[J]. Compr Physiol,2017,8(1):1−8.
[4] WANG F, YAO W, YU D X, et al. Protective role of thymoquinone in hyperlipidemia-induced liver injury in LDL-R−/− mice[J]. BMC Gastroenterol,2023,23(1):276−285. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02895-0
[5] LE L S, SIMARD G, MARTINEZ M C, et al. Oxidative stress and metabolic pathologies:from an adipocentric point of view[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev,2014,20(7):908539−908558.
[6] SU C, LI N, REN R R, et al. Progress in the medicinal value, bioactive compounds, and pharmacological activities of Gynostemma pentaphyllum[J]. Molecules,2021,26(20):6249−6284. doi: 10.3390/molecules26206249
[7] CHEN P Y, CHANG C C, HUANG H C, et al. New dammarane-type saponins from Gynostemma pentaphyllum[J]. Molecules,2019,24(7):1375−1388. doi: 10.3390/molecules24071375
[8] LIAO W L, KHAN I, HUANG G X, et al. Bifidobacterium animalis:the missing link for the cancer-preventive effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum[J]. Gut Microbes,2021,13(1):1847629−1847643. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1847629
[9] DONG S Q, ZHANG Q P, ZHU J X, et al. Gypenosides reverses depressive behavior via inhibiting hippocampal neuroinflammation[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2018,106(10):1153−1160.
[10] GAO D W, ZHAO M, QI X M, et al. Hypoglycemic effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins by enhancing the nrf2 signaling pathway in stz-inducing diabetic rats[J]. Arch Pharm Res,2016,39(2):221−230. doi: 10.1007/s12272-014-0441-2
[11] ZHAO T T, KIM K S, SHIN K S, et al. Gypenosides ameliorate memory deficits in mptp-lesioned mouse model of parkinson's disease treated with l-dopa[J]. BMC Complement Altern Med,2017,17(1):449−456. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1959-x
[12] WENG X, LOU Y Y, WANG Y S, et al. New dammarane-type glycosides from Gynostemma pentaphyllum and their lipid-lowering activity[J]. Bioorg Chem,2021,111(6):104843−104854.
[13] 赵卓, 高浩, 杨莹, 等. 绞股蓝皂苷抑制Bcl2L12凋亡通路改善ApoE−/-动脉粥样硬化小鼠肝脏脂质沉积[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志,2023,43(10):1221−1227. [ZHAO Z, GAO H, YANG Y, et al. Gypenosides improve liver lipid deposition in apoE−/− as mice by inhibiting the Bcl2L12 apoptosis pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine,2023,43(10):1221−1227.] doi: 10.7661/j.cjim.20230317.007 ZHAO Z, GAO H, YANG Y, et al. Gypenosides improve liver lipid deposition in apoE−/− as mice by inhibiting the Bcl2L12 apoptosis pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, 2023, 43(10): 1221−1227. doi: 10.7661/j.cjim.20230317.007
[14] 滕菲, 李祥溦, 李敏, 等. 绞股蓝地下部位总皂苷化学成分分析及降脂作用研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2022,47(18):5022−5031. [TENG F, LI X W, LI M, et al. Components and lipid-lowering effect of total saponins from underground part of Gynostemma pentaphyllum[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2022,47(18):5022−5031.] TENG F, LI X W, LI M, et al. Components and lipid-lowering effect of total saponins from underground part of Gynostemma pentaphyllum[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2022, 47(18): 5022−5031.
[15] ZHAO Y H, QU H, WANG Y H, et al. Small rodent models of atherosclerosis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2020,129(9):110426−110439.
[16] TVEDEN-NYBORG P, BIRCK M M, IPSEN D H, et al. Diet-induced dyslipidemia leads to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and oxidative stress in guinea pigs[J]. Transl Res,2016,168(2):146−160.
[17] 李金莲, 高南南, 杨润梅. 豚鼠高脂血症模型的建立及机制探讨[J]. 中国实验动物学报,2009,17(2):115−119. [LI J L, GAO N N, YANG R M. Establishment and mechanisms of a guinea pig model of hyperlipidemia and comparison with the rat model[J]. Acta Laboratorium Animalis Scientia Sinica,2009,17(2):115−119.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2009.02.008 LI J L, GAO N N, YANG R M. Establishment and mechanisms of a guinea pig model of hyperlipidemia and comparison with the rat model[J]. Acta Laboratorium Animalis Scientia Sinica, 2009, 17(2): 115−119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2009.02.008
[18] 张斐, 黄成宝, 张晓芳, 等. 二陈汤对高脂血症模型大鼠脂肪酸代谢的影响[J]. 中医杂志,2020,61(3):241−245. [ZHANG F, HUANG C B, ZHANG X F, et al. Effects of erchen decoction on fatty acid metabolism in rat model of hyperlipemia with phlegm syndrome[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2020,61(3):241−245.] ZHANG F, HUANG C B, ZHANG X F, et al. Effects of erchen decoction on fatty acid metabolism in rat model of hyperlipemia with phlegm syndrome[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 61(3): 241−245.
[19] 马菲菲. 绞股蓝总皂苷治疗小鼠高脂血症过程中对肝脏免疫相关基因转录水平的调控研究[D]. 遵义:遵义医科大学, 2019. [MA F F. Regulation of hepatic immune-related genes in hyperlipidemia mice treated with gypenosides[D]. Zunyi:Zunyi Medical University, 2019.] MA F F. Regulation of hepatic immune-related genes in hyperlipidemia mice treated with gypenosides[D]. Zunyi: Zunyi Medical University, 2019.
[20] 杨佳鑫, 马粉花, 张吉涛, 等. 绞股蓝总皂苷抑制大鼠动脉粥样硬化炎症反应并影响TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路表达[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2022,41(1):193−202. [YANG J X, MA F H, ZHANG J T, et al. Gypenosides suppress the inflammatory response to atherosclerosis in rats and interfere the expression of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology,2022,41(1):193−202.] YANG J X, MA F H, ZHANG J T, et al. Gypenosides suppress the inflammatory response to atherosclerosis in rats and interfere the expression of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2022, 41(1): 193−202.
[21] 诸夔妞, 田莎莎, 王辉, 等. 绞股蓝总皂苷调节NF-κB信号通路改善糖尿病大鼠胰岛素敏感性的实验研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2021,46(17):4488−4496. [ZHU K N, TIAN S S, WANG H, et al. Study on effect of gypenosides on insulin sensitivity of rats with diabetesmellitus via regulating NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2021,46(17):4488−4496.] ZHU K N, TIAN S S, WANG H, et al. Study on effect of gypenosides on insulin sensitivity of rats with diabetesmellitus via regulating NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2021, 46(17): 4488−4496.
[22] 杨雪, 孙晓菲, 范慧洁, 等. 肥胖对糖尿病模型大鼠血清胰高血糖样肽-1表达的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2017,37(11):2659−2660. [YANG X, SUN X F, FAN H J, et al. Effect of obesity on the expression of serum glucagon like peptide-1 in diabetes model rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology,2017,37(11):2659−2660.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2017.11.025 YANG X, SUN X F, FAN H J, et al. Effect of obesity on the expression of serum glucagon like peptide-1 in diabetes model rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 2017, 37(11): 2659−2660. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2017.11.025
[23] LAI S W, NG K C, LIN H F, et al. Association between obesity and hyperlipidemia among children[J]. Yale J Biol Med,2001,74(4):205−10.
[24] SHU X, CHEN R, YANG M L, et al. Gynostemma pentaphyllum and gypenoside-IV ameliorate metabolic disorder and gut microbiota in diet-induced-obese mice[J]. Plant Foods Hum Nutr,2022,77(3):367−372. doi: 10.1007/s11130-022-00982-3
[25] LIU J Y, HUA J X, CHEN S X, et al. The potential mechanisms of bergamot-derived dietary fiber alleviating high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia and obesity in rats[J]. Food Funct,2022,13(15):8228−8242. doi: 10.1039/D2FO00747A
[26] 李淑珍, 杨巍巍, 康爱娟, 等. 柑橘多甲氧基黄酮饼干对高血脂症小鼠的降脂效应[J]. 中国实验动物学报,2021,29(1):63−70. [LI S Z, YANG W W, KANG A J, et al. Lipid-lowering effect of citrus polymethoxyflavonoid cookies on hyperlipidemia mice[J]. Acta Lab Anim Sci Sin,2021,29(1):63−70.] LI S Z, YANG W W, KANG A J, et al. Lipid-lowering effect of citrus polymethoxyflavonoid cookies on hyperlipidemia mice[J]. Acta Lab Anim Sci Sin, 2021, 29(1): 63−70.
[27] 刘嘉平, 王博, 张晓伟, 等. 绞股蓝皂苷饮食干预小鼠肥胖及肠道菌群研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(7):88−96. [LIU J P, WANG B, ZHANG X W, et al. Effect of gypenosides diet intervention on obesity controland gut microbiota regulation in mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(7):88−96.] LIU J P, WANG B, ZHANG X W, et al. Effect of gypenosides diet intervention on obesity controland gut microbiota regulation in mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22(7): 88−96.
[28] LI J L, WU H S, LIU Y T, et al. High fat diet induced obesity model using four strainsof mice:Kunming, C57BL/6, BALB/c and ICR[J]. Exp Anim,2020,69(3):326−335. doi: 10.1538/expanim.19-0148
[29] 孙宏莱, 刘悦, 刘德江, 等. 毛水苏多糖对糖尿病小鼠肾脏的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(17):373−380. [SUN H L, LIU Y, LIU D J, et al. Protective effect of polysaccharides from Stachys baicalensis on kidneys of diabeticdisease mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(17):373−380.] SUN H L, LIU Y, LIU D J, et al. Protective effect of polysaccharides from Stachys baicalensis on kidneys of diabeticdisease mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(17): 373−380.
[30] JORGAČEVIĆ B, VUČEVIĆ D, SAMARDŽIĆ J, et al. The effect of CB1 Antagonism on hepatic oxidative/nitrosative stress and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Curr Med Chem,2021,28(1):169−180.
[31] 钟方为, 李庚喜, 曾立. 基于肠道菌群和短链脂肪酸代谢探讨绞股蓝总皂苷改善大鼠非酒精性脂肪肝病的实验研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2022,47(9):2500−2508. [ZHONG F W, LI G X, ZENG L. Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease inrats by regulating intestinal flora and short-chain fatty acid metabolism[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2022,47(9):2500−2508.] ZHONG F W, LI G X, ZENG L. Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins alleviate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease inrats by regulating intestinal flora and short-chain fatty acid metabolism[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2022, 47(9): 2500−2508.
[32] 国家心血管病中心. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2019[M]. 北京:科学出版社, 2020. [National Cardiovascular Disease Center. Annual Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China (2019)[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 2020.] National Cardiovascular Disease Center. Annual Report on Cardiovascular Health and Diseases in China (2019)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020.
[33] 张誉方, 陈健, 张一昕, 等. 基于PPARγ/LXRα/ABCG1信号通路探讨黄芪总皂苷-荷叶总生物碱防治高脂血症的机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(13):37−44. [ZHANG Y F, CHEN J, ZHANG Y X, et al. Exploring mechanism of total saponin of astragalus and total alkaloids of Nelumbinis folium against hyperlipidemia based on PPARγ/LXRα/ABCG1 signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2024,30(13):37−44.] ZHANG Y F, CHEN J, ZHANG Y X, et al. Exploring mechanism of total saponin of astragalus and total alkaloids of Nelumbinis folium against hyperlipidemia based on PPARγ/LXRα/ABCG1 signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2024, 30(13): 37−44.
[34] JIANG X F, TANG N N, LIU Y Y, et al. Integrating network analysis and pharmacokinetics to investigate the mechanisms of Danzhi Tiaozhi decoction in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)[J]. J Ethnopharmacol,2024,318(10):117008−117021.
[35] LÜ W J, HUANG J Y, LIN J, et al. Phytosterols alleviate hyperlipidemia by regulating gut microbiota and cholesterol metabolism in mice[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev,2023,26(8):6409385−6409398.
[36] ZHAO X J, YU H W, YANG Y Z, et al. Polydatin prevents fructose-induced liver inflammation and lipid deposition through increasing miR-200a to regulate Keap1/Nrf2 pathway[J]. Redox Biol,2018,18(9):124−137.
[37] 张明, 林道斌, 卓书江. 黎药鹧鸪茶对高脂血症的影响及作用机制研究[J]. 中药药理与临床,2021,37(4):106−110. [ZHANG M, LIN D B, ZHUO S J. Effect and mechanism of li medicine partridge tea on hyperlipidemia[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica,2021,37(4):106−110.] ZHANG M, LIN D B, ZHUO S J. Effect and mechanism of li medicine partridge tea on hyperlipidemia[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 2021, 37(4): 106−110.
[38] 王语晴, 郭婉琴, 刘欣欣, 等. 丹参注射液对高脂血症模型小鼠脂质代谢的影响[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报,2022,42(6):911−916. [WANG Y Q, GUO W Q, LIU X X, et al. Effect of Danshen Injection on lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemia model mice[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine,2022,42(6):911−916.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2022.06.007 WANG Y Q, GUO W Q, LIU X X, et al. Effect of Danshen Injection on lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemia model mice[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(6): 911−916. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2022.06.007
[39] TONELLI C, CHIO IIC, TUVESON D A. Transcriptional regulation by Nrf2[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal,2018,29(17):1727−1745. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7342
[40] 平烨, 张珮雯, 袁馨梦, 等. 运动调节Nrf2/HO-1通路改善HFFC膳食诱导肝细胞氧化应激的作用研究[J]. 中国实验动物学报,2024,32(5):566−575. [PING Y, ZHANG P W, YUAN X M, et al. Effects of exercise regulated the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway on improving HFFC dietinduced oxidative stress in hepatocytes[J]. Acta Laboratorium Animalis Scientia Sinica,2024,32(5):566−575.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2024.05.003 PING Y, ZHANG P W, YUAN X M, et al. Effects of exercise regulated the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway on improving HFFC dietinduced oxidative stress in hepatocytes[J]. Acta Laboratorium Animalis Scientia Sinica, 2024, 32(5): 566−575. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2024.05.003
[41] BELLANTI F, VENDEMIALE G. The aging liver:redox biology and liver regeneration[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal,2021,35(10):832−847. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0048
[42] G BARDALLO R, PANISELLO-ROSELLÓ A, SANCHEZ-NUNO S, et al. Nrf2 and oxidative stress in liver ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. FEBS J,2022,289(18):5463−5479. doi: 10.1111/febs.16336
[43] VANANI A R, KALANTARI H, MAHDAVINIA M, et al. Dimethyl fumarate reduces oxidative stress, inflammation and fat deposition by modulation of Nrf2, SREBP-1c and NF-κB signaling in HFD fed mice[J]. Life Sci,2021,283(10):119852−119862.
[44] LI L Z, ZHAO Z M, ZHANG L, et al. Atorvastatin induces mitochondrial dysfunction and cell apoptosis in HepG2 cells via inhibition of the Nrf2 pathway[J]. J Appl Toxicol,2019,39(10):1394−1404. doi: 10.1002/jat.3825
[45] WANG W, CHEN Z X, ZHENG T S, et al. Xanthohumol alleviates T2DM-induced liver steatosis and fibrosis by mediating the NRF2/RAGE/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Future Med Chem,2021,13(23):2069−2081. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2021-0241
[46] MULLER C R, WILLIAMS A T, EAKER A M, et al. High fat high sucrose diet-induced dyslipidemia in guinea pigs[J]. J Appl Physiol (1985),2021,130(4):1226−1234. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00013.2021
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 李亚俐,王雪莉,石柳,吴文锦,陈胜,陈朗,郭晓嘉,熊光权,汪兰,孙智达. 壳聚糖-绿原酸复合保鲜剂对冷藏鮰鱼片食用品质的影响. 肉类研究. 2025(01): 42-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 武玫怡,焦文娟,赵甜甜,刘俊,周芳,刘伟峰,张业辉,南海军,陈晓瑛,黄利华. 高静水压与水煮处理对热带海参品质的影响. 肉类研究. 2025(01): 25-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 崔燕,刘韩欣,朱麟,尚海涛,林旭东,陈曙颖,宣晓婷. 超高压杀菌对大黄鱼理化性质及滋味、风味的影响. 食品工业科技. 2025(05): 44-55 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



