Preparation of Composite Films Based on Methyl Cellulose/Polyvinyl Alcohol-loaded Nanosilver (AgNPs@PVA/MC) and Its Effect on Storage Quality of Ougan
-
摘要: 以甲基纤维素(MC)和聚乙烯醇(PVA)为复合膜基材,纳米银(AgNPs)为抑菌剂,甘油为增塑剂,制备具有抑菌作用的AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜。通过考察不同质量分数(0%、0.05%、0.1%、0.2%、0.3%)AgNPs对复合膜的性能影响并对其外观、机械性能、微观结构及抑菌性等性能进行表征,为开发瓯柑贮藏保鲜材料提供理论支撑。结果表明,随着AgNPs含量增加,复合膜对桔青霉生长的抑制作用越显著(P<0.05)。其中,0.1% AgNPs含量的复合膜综合性能最为优异,其抗拉强度达到12.45 MPa、断裂伸长率为6.47%、水蒸气透过率为21.03×10−6 g·mm/(m2·s·Pa)、氧气透过率为2.31×10−6 cm3/(cm2·s·Pa),扫描电子显微镜显示其横截面具有规则、紧密及分布均匀的AgNPs颗粒,红外光谱及热重分析表明其具有良好的结合性和热稳定性。0.1%AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜可有效减小瓯柑贮藏期间失重率,降低可溶性固形物、可滴定酸及VC的消耗速率,延缓瓯柑的成熟并显著抑制致腐菌桔青霉的生长,能较好地保持瓯柑贮藏期品质,为瓯柑产业的可持续发展提供支撑。Abstract: The antibacterial AgNPs@PVA/MC composite films were prepared by using methyl cellulose (MC) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as composite substrate, nanosilver (AgNPs) as antibacterial agent, and glycerin as plasticizer. The effects of different mass fractions (0%, 0.05%, 0.1%, 0.2%, 0.3%) of AgNPs on the properties of the composite films were investigated, and its appearance, mechanical properties, microstructure and antibacterial properties were characterized, in order to provide theoretical support for the development of preservation materials for storing Ougan. The results showed that as the content of AgNPs increased, the inhibitory effect of the composite film on the growth of Penicillium citrinum became more significant (P<0.05). Among them, the composite film with 0.1% AgNPs content had the best comprehensive performance, its tensile strength reached 12.45 MPa, elongation at break was 6.47%, water vapor permeability was 21.03×10−6 g·mm/(m2·s·Pa), and oxygen permeability was 2.31×10−6 cm3/(cm2·s·Pa). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that composite film with 0.1% AgNPs content was regular, compact and evenly distributed in cross section. Infrared spectroscopy and thermogravimetric analysis showed that composite film with 0.1% AgNPs content had good bonding and thermal stability. 0.1%AgNPs@PVA/MC composite film could effectively reduce the weight loss rate of Ougan during storage, and reduce the consumption rate of soluble solid, titratable acid and VC, delay the maturation of Ougan and significantly inhibit the growth of Penicillium citrinum, which could better maintain the quality of Ougan during the storage period, this study provided support for the sustainable development of Ougan industry.
-
Keywords:
- Ougan (Citrus reticulata cv. Suavissima) /
- composite film /
- nanosilver /
- methyl cellulose /
- polyvinyl alcohol /
- storage /
- quality
-
瓯柑(Citrus reticulata cv. Suavissima)是浙江南部地区优良的柑橘类品种,芸香科柑橘属,属于非呼吸跃变型果实,具有良好的贮藏性[1],作为中国国家地理标志的宽皮柑橘,至今已有上千年的栽培历史。瓯柑果皮鲜艳油亮,果肉多汁酸甜,富含P、K、Ca、Fe、VC等成分以及具有抗氧化、抗衰老的过氧化氢氧化酶和歧化酶[2];除了丰富的营养功能和优良的耐贮性,它还具有祛火生津、清凉解毒以及化痰止咳的药用价值和作用[3]。因此,在温州民间素有“端午瓯柑赛羚羊”一说[4]。然而,瓯柑在贮藏过程中容易出现由桔青霉(Penicillium citrinum)引起的腐败现象,这不仅影响了瓯柑的品质和食用价值,还因腐败造成了大量的食品浪费。因此,开发一种有效的抗菌包装材料,对保持瓯柑贮藏品质及减少瓯柑因腐败而造成的浪费具有重要意义。
纳米银(AgNPs)是指在1~100 nm尺度内的微观银粒子。由于银粒子的颗粒直径缩小至纳米级别时,其会呈现出独特的物理和化学性质,如比表面积迅速增大、表面原子比例增加以及因缺少配位原子而具有更高的催化活性[5]。独特的性质导致其与细胞结合作用强,可通过刺激微生物的凝聚、影响基因表达或抑制蛋白合成等途径,表现出较强的抑菌能力[6],同时通过抑制细胞呼吸、减少水分蒸发等生理作用保持水果的新鲜[7]。张朝涛等[8]将AgNPs和壳聚糖(CTS)制备成复合涂膜用于樱桃番茄的保鲜中,能够显著抑制交链孢霉菌的生长并降低腐烂率和失重率。Lin等[9]通过AgNPs和1-MCP制备抗菌保鲜复合纸并探究了其对樱桃的保鲜效果,研究表明该复合物能够有效抑制大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌,改善了樱桃的贮藏品质并使贮藏时间由4 d延长至12 d。因此,本研究通过复合膜负载AgNPs,旨在抑制瓯柑中的桔青霉,开发有效的抗菌包装材料。然而,AgNPs在常规条件下不稳定,需要通过基材负载形成稳定的纳米复合材料[10]。
因此,本研究以瓯柑为对象,探究甲基纤维素/聚乙烯醇负载纳米银(AgNPs@PVA/MC)复合膜对瓯柑贮藏品质的影响。具体来说,本文先以聚乙烯醇(PVA)和甲基纤维素(MC)共混复合物为基材,负载AgNPs制备成复合保鲜膜;然后,对其进行性能表征并设置市售PE保鲜膜和不作包膜对照组,以探究AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜对瓯柑贮藏过程中的品质影响。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
瓯柑 温州泽雅南山瓯柑基地提供;桔青霉 浙江省农业科学院食品科学研究所食品物流保鲜与营养品质调控团队从采后瓯柑中分离提取;纳米银 广州佳伲斯防霉抗菌科技有限公司;聚乙烯醇(粘度54~66 MPa·s) 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;甲基纤维素(粘度350~550 MPa·s) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;PE保鲜膜 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司。
DF-101S集热式恒温加热磁力搅拌器 杭州旌斐仪器科技有限公司;DK-S28电热恒温水浴锅 上海精宏实验设备有限公司;DGC-9070A电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海森信实验仪器有限公司;UV-9000紫外可见分光光度计 上海元析仪器有限公司;XLW型智能电子拉力试验机 济南兰光机电技术有限公司;CR-400色差仪 柯盛行(杭州)仪器有限公司;MRC-250B恒温恒湿气候箱 上海百典仪器设备有限公司;STA4493 F3 Jupiter热重分析仪 德国NETZSCH公司;FENSORII红外光谱仪 德国布鲁克有限公司;SBC-12小型离子溅射仪 北京中科科仪股份有限公司;TM3000扫描电子显微镜 日本日立(HITACHI)公司;C106H气体渗透测试仪 山东济南兰光机电技术有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜的制备
本实验以MC和PVA为基材,甘油为增塑剂,AgNPs为抑菌剂,采用溶液浇铸法制备了AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜[9]。首先,将0.8 g的MC加入到80~90 ℃的100 mL水中,然后在室温下持续搅拌4 h配制成MC溶液;在80~90 ℃的100 mL水中加入0.2 g的PVA,搅拌2 h,制得PVA溶液。为了制备出非交联混合物,将两种溶液混合后在室温下搅拌3 h,并加入0.125%(v/v)甘油作为增塑剂;按照上述步骤,分别加入0、0.05、0.1、0.2、0.3 g的AgNPs颗粒,设置不添加AgNPs为空白对照组,分别搅拌5 h得到AgNPs@PVA/MC复合溶液[11]。对上述制备的混合溶液加压及超声以去除气泡,然后将制备均匀且无气泡的混合溶液倒在有机玻璃模具上(15 cm×15 cm),让上述溶液在室温环境条件下(30 ℃)干燥3 d,然后从模具中剥离出复合膜,用于后续的性能表征和贮藏实验。
1.2.2 薄膜的性能表征
1.2.2.1 膜的外观和颜色特征
膜的外观由外观图和色差进行综合表征,外观图由照相机在固定的摄影棚中完成,并用图像处理软件Image viewer选取部分实物图作为外观图。
膜的颜色通常由色差仪测定,以标准调色板作为基准,参考Zong等[12]方法。根据CIE L*a*b*颜色系统,L*表示明亮值,通常越大代表越亮白;a*和b*分别代表红绿色和黄蓝色,是色度的两个分量,其中a*>0表示红色强度,反之表示绿色强度,b*>0表示黄色强度,反之表示蓝色强度。总色差值ΔE按照下列公式计算。
ΔE=√(ΔL*)2+(Δa*)2+(Δb*)2 式中:ΔL*=L−L0,Δa*=a−a0,Δb*=b−b0;其中,L、a、b值为实际待测值,L0、a0、b0为标准调色板的标准值。
1.2.2.2 膜厚及机械性能的测定
膜的厚度由数显电子游标卡尺测定,将膜裁切成60 mm×20 mm的长方形,选取复合膜的前、中、后三个位置并测量其厚度,取其平均值作为膜的厚度,单位为mm。
根据GB/T 1040.1-2018《塑料 拉伸性能的测定》[13],用XLW型智能电子拉力试验机测试复合膜的拉伸强度(tensile strength,TS)和断裂伸长率(elongation at break,EB)。将60 mm×20 mm的长方形待测样品放入测试台,设置初始夹距为50 mm,拉伸速度为0.5 mm/s,膜初始宽度B为20 mm,膜初始长度L为60 mm。每组样品测定3个平行。
1.2.2.3 膜的水蒸气透过性测定
根据GB/T 1037-2021《塑料薄膜和薄片水蒸气透过性能测定 杯式增重与减重法》[14],测定膜的水蒸气透过性(water vapor permeability,WVP)。首先称取10 g的无水氯化钙,将其粉碎放入小烧杯中,并在180 ℃的鼓风干燥箱中干燥2 h以保证烧杯内的相对湿度为0,然后将平整、均一、无孔洞的待测样品包裹住烧杯口,用透明胶带密封并称重,总质量记为m(g);然后将其放置在25 ℃和相对湿度为75%的恒温恒湿箱中,每隔4 h测定一次重量记为M,连续测定6次。膜的水蒸气透过性(WVP,g·mm/(m2·s·Pa))可用下式计算:
WVP=Δm×TΔP×ΔT×A 式中:∆m=M−m,为烧杯质量的变化,g;T为待测样品的平均厚度,mm;∆P为25 ℃、75%相对湿度下薄膜两侧水蒸气分压差值,即1753.55 Pa;∆T是时间间隔,s;A是待测样品的面积,㎡。
1.2.2.4 膜的氧气透过率测定
根据GB/T1038.1-2022《塑料制品薄膜和薄片气体透过性试验方法第1部分:差压法》[15],参考谢斌[16]的方法并做调整。通过C106H气体透过率测试仪,测试样品有效面积为5 cm2,设置温度为23 ℃,湿度为51%,试验气体为99.99%浓度的氧气,载气为99.99%浓度的氮气,取三次测试数据的平均值。
1.2.2.5 膜的热重测定
参考韩婉毓等[17]的方法,首先称取4 mg的AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜放入氧化铝坩埚中,然后将其放置在热重分析仪中的样品台上,以10 ℃/min的升温速率,在30~600 ℃的氮气(N2)氛围下进行复合膜的热特性扫描和分析[18]。
1.2.2.6 膜的傅里叶变换红外光谱
将待测样品在50 ℃条件下放置于鼓风干燥箱中烘干至恒重,使用FENSORII红外光谱仪扫描待测样品测得其吸收光谱,扫描范围为500~4000 cm−1[19]。
1.2.2.7 膜的扫描电镜
将待测样品在45 ℃条件下放置于鼓风干燥箱中烘干至恒重,然后将膜撕裂成2 mm×2 mm的方形待测样品,利用扫描电子显微镜在合适的观测视野中采集相应的横截断裂面微观结构,采用溅射喷金处理,加速电压为15 kV[10]。
1.2.2.8 膜的抑菌性能
参照Zhao等[20]的方法并做适当修改,采用细胞计数法研究AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜对桔青霉的抑菌性能。具体操作步骤如下:桔青霉活化并传代2~3次,然后用无菌生理盐水稀释制备成106 CFU/mL的菌悬液;然后制备PDB液体培养基并将100 μL菌悬液添加到100 mL液体培养基中,在摇床中以28 ℃、160 r/min培养24 h;最后,将上述干燥灭菌(先用烘箱在30 ℃条件下干燥2 h,然后在通风橱中用紫外灯照射30 min进行灭菌)后的复合膜置于含菌培养基中,继续培养6 h,采用平板计数法用显微镜观察并记录孢子数,生长抑制率按照如下公式计算:
生长抑制率(%)=A−BA×100 式中:A代表未经AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜处理的孢子数(个);B代表经过AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜处理的孢子数(个)。
1.2.3 复合膜在瓯柑贮藏中的应用
实验设置1个对照组和2个处理组。其中,对照组不做任何处理,处理1组用上述制备的0.1%AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜将其封膜处理,处理2组用市售PE保鲜膜将其封膜处理。将无机械损伤、成熟度和大小均一的瓯柑放置在温度为(4±1)℃,湿度为90%~95%的低温环境下贮藏。分别在第0、30、60、90、120 d进行取样测定。取样完成相应基础指标测定后,将其用液氮速冻后置于−80 ℃超低温冰箱保存。
1.2.3.1 失重率(WLR)测定
采用称量法测定瓯柑的失重率[21],计算公式如下:
WLR(%)=Wi−WsWi×100 式中:Wi表示贮藏前的质量,Ws表示取样时的质量,单位为g。
1.2.3.2 可溶性固形物(TSS)含量测定
TSS含量的测定参照房祥军等[22]的方法。不同处理组和对照组分别取样,利用压榨法获取果汁;然后用蒸馏水将手持式阿贝折光仪调零,用折光仪测定TSS含量。
1.2.3.3 可滴定酸(TA)含量测定
根据Taha等[23]的方法并做出改进,在酚酞存在的情况下,通过滴定0.1 mol/L NaOH来测定TA含量,计算结果为每100 mL果汁中可滴定酸的克数。
1.2.3.4 抗坏血酸(VC)含量测定
VC含量的测定参考蔡继业等[24]的方法,通过2,6二氯酚-吲酚染料滴定法测定VC含量,以每100 mL果汁中的毫克数表示。
1.2.3.5 乙醇含量测定
乙醇含量的测定参照徐思朦等[25]基于气相色谱的方法。用液氮将称取的20 g果肉充分研磨成粉末,取3 g粉末加入含有4 mL饱和NaCl的离心管中,使其混合均匀;然后吸取3 mL匀浆至顶空萃取瓶,经过1 h的60 ℃水浴加热后进行静态顶空气相色谱检测。色谱柱:HP-INNOWAX(30 m×0.25 mm,0.25 µm);升温程序:60 ℃保持1 min,以20 ℃/min升至160 ℃,保持4 min;载气(N2)流速1 mL/min,压力2.4 kPa,进样量3 mL;分流比1:24。
1.2.3.6 乙醛含量测定
乙醛含量的测定参照上述1.2.3.5乙醇含量的测定方法。
1.3 数据处理
文中所有指标测定均重复3次,最终结果以平均值±标准差表示。本文实验采用IBM SPSS Statistics 26对数据进行统计、处理;采用Origin2021、Graphpad prism8软件对其进行作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 AgNPs含量对复合膜性能影响的表征分析
2.1.1 外观和颜色特征分析
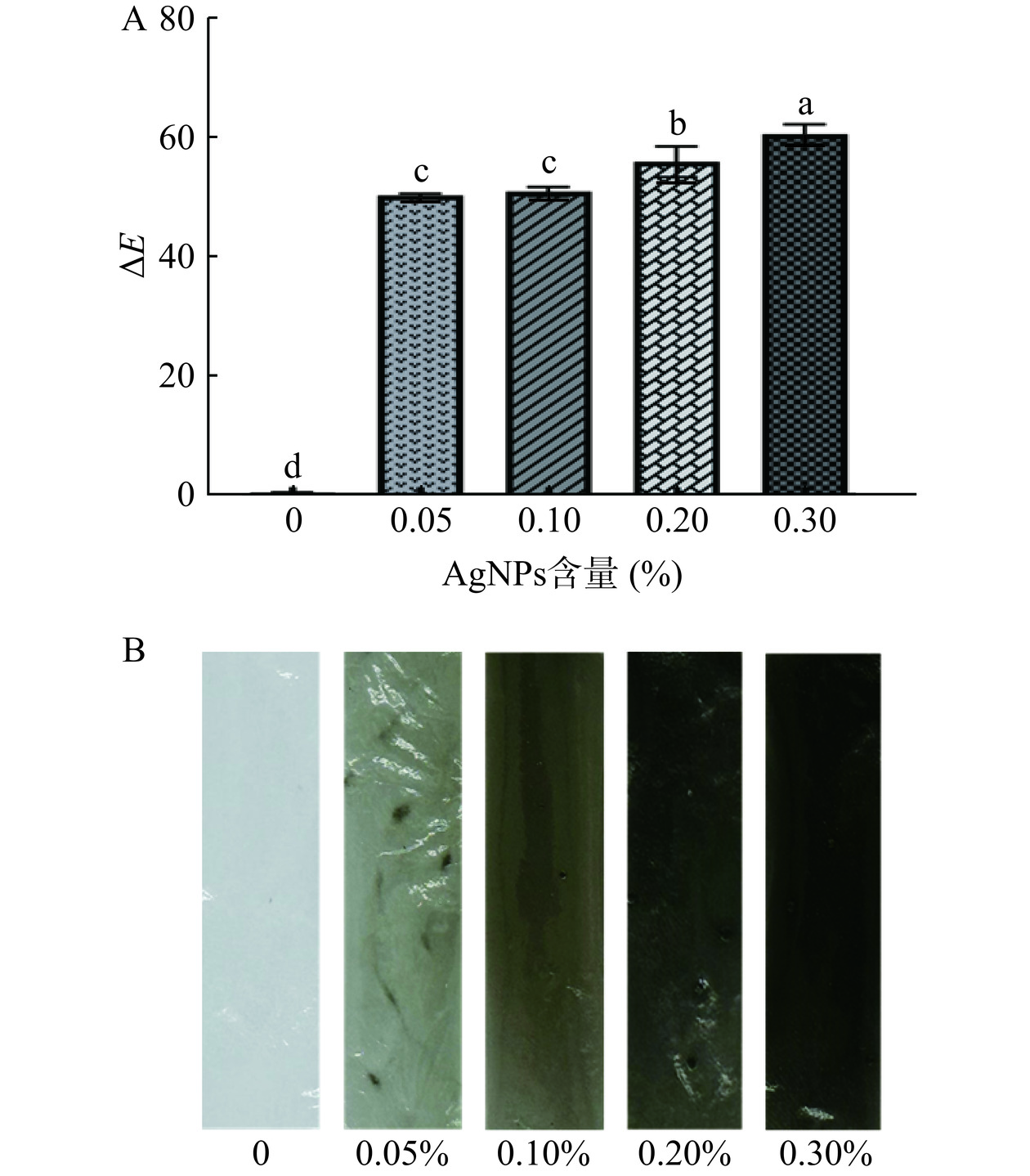
图1A可知,随着AgNPs含量的不断增加,总色差值ΔE也随之增大,表明含有AgNPs的复合膜L*、a*、b*均大于零且红、黄强度大于绿、蓝强度,即呈现出黑色,与表1数据及图1B复合膜实物图一致,具有较好的阻光性能。研究表明,水果在可见光长时间的暴露下,会加速食品成分的降解和氧化,加剧水果的成熟腐烂[26],选择阻光性较好的包装膜对水果贮藏具有重要意义。由图1B可知,随着AgNPs含量的增加,复合膜的黑色程度加深且出现黑色点状现象;分析表明,AgNPs颗粒通常呈现黑色,由于AgNPs在堆积状态下,发生了团聚现象,导致其出现黑色点状或絮状现象,这与梅洁等[27]的研究结论一致,在不同AgNPs添加比例下,有不同程度的团聚现象。
![]() 图 1 不同AgNPs含量对复合膜色差和外观的影响注:不同字母表示不同处理组的数据之间差异显著,P<0.05;图5同。Figure 1. Effects of different AgNPs contents on color difference and appearance of composite films表 1 不同AgNPs含量复合膜的颜色参数Table 1. Color parameters of composite films with different AgNPs contents
图 1 不同AgNPs含量对复合膜色差和外观的影响注:不同字母表示不同处理组的数据之间差异显著,P<0.05;图5同。Figure 1. Effects of different AgNPs contents on color difference and appearance of composite films表 1 不同AgNPs含量复合膜的颜色参数Table 1. Color parameters of composite films with different AgNPs contentsAgNPs含量(%) ΔE L* a* b* 0 0.49±0.03d 95.78±0.03a −0.18±0.01c 2.59±0.06c 0.05 50.21±0.37c 46.05±0.36b 0.44±0.02a 4.59±0.13a 0.1 50.83±0.67c 45.40±0.67b 0.36±0.01b 3.73±0.05b 0.2 56.09±2.01b 40.13±2.01c 0.43±0.07a 2.65±0.70c 0.3 60.49±1.41a 35.74±1.41d 0.36±0.03b 4.07±0.36ab 注:同列不同字母表示不同处理组的数据之间差异显著,P<0.05,表2、表3同。 2.1.2 膜厚及机械性能分析
复合膜良好的机械性能有助于果蔬运输和贮藏过程中的保存。由表2可知,未添加AgNPs薄膜和不同AgNPs含量复合膜的厚度无显著差异(P>0.05),这与相关结论一致,说明AgNPs含量对厚度的影响较小[6,28],其抗拉强度和断裂伸长率随着AgNPs含量的增加而降低。初步分析表明,可能是采用非交联的制备方式,AgNPs颗粒及其负载基材未发生化学结合[11],随着AgNPs含量增加,易发生聚集现象[29],降低了复合膜的机械强度,使得实验组的抗拉强度和断裂伸长率急剧下降。
表 2 不同AgNPs含量对复合膜机械性能的影响Table 2. Effects of different AgNPs contents on mechanical properties of composite filmsAgNPs含量(%) 厚度(mm) 抗拉强度(MPa) 断裂伸长率(%) 0 0.04±0.01ab 33.91±6.05a 19.83±0.76a 0.05 0.04±0.01b 17.92±0.89b 7.33±1.03b 0.1 0.05±0.01ab 12.45±0.55bc 6.47±0.48b 0.2 0.05±0.01a 11.52±1.12bc 3.55±0.55c 0.3 0.05±0.01ab 10.91±0.67c 2.94±0.66c 2.1.3 膜的水蒸气透过性分析
水蒸气透过性是衡量食品包装材料水分交换能力的重要指标,在食品包装材料中应当使水蒸气透过性尽可能小以减少食品的水分交换,从而更有利于食品的保存和贮藏[30]。由表3可知,随着AgNPs含量的增加,复合膜的水蒸气透过性逐渐增加,但是不含AgNPs薄膜的水蒸气透过性最大,显著高于含AgNPs复合膜(P<0.05)。分析表明,随着AgNPs含量的增加,加剧了AgNPs颗粒的团聚现象,使得AgNPs颗粒周围的复合膜空隙逐渐增大,从而导致水蒸气透过性随AgNPs含量的增加而增大。
表 3 不同复合膜的水蒸气透过性和氧气透过率Table 3. Water vapor permeability and oxygen permeability of different composite films膜的类别及AgNPs含量
(%)水蒸气透过性×10−6
(g·mm·m−2·s−1·Pa−1)氧气透过率×10−6
(cm3·cm−2·s−1·Pa−1)PE 347.10±0.20a 29.02±0.20a 0 25.43±0.43b 1.46±0.01e 0.05 19.40±0.61e 2.19±0.23d 0.1 21.03±0.30d 2.31±0.11d 0.2 21.56±0.69cd 3.46±0.13c 0.3 22.69±0.42c 5.57±0.24b 2.1.4 膜的氧气透过率分析
膜的氧气透过率是一项重要的性能指标,通常用来评估材料的气体交换能力[31]。通常,较小氧气透过率的包装材料有利于减弱果蔬的呼吸作用,从而延长果蔬的贮藏时间,但要防止氧气透过率过低使果蔬发生无氧呼吸进而加剧腐烂变质。如表3所示,PE组的氧气透过率显著大于AgNPs复合膜组(P<0.05);对于复合膜组,随着AgNPs含量的增加,膜的氧气透过率呈现显著增加的趋势(P<0.05)。结合上述分析,复合膜组的氧气透过率增加是由于AgNPs颗粒导致复合膜空隙增大,减小了复合膜的致密性,从而提高材料对气体的透过性能[32]。综合膜的水蒸气透过性及氧气透过率分析,0.05% AgNPs含量的复合膜性能较好,0.1% AgNPs含量的复合膜次之。
2.1.5 膜的热重分析
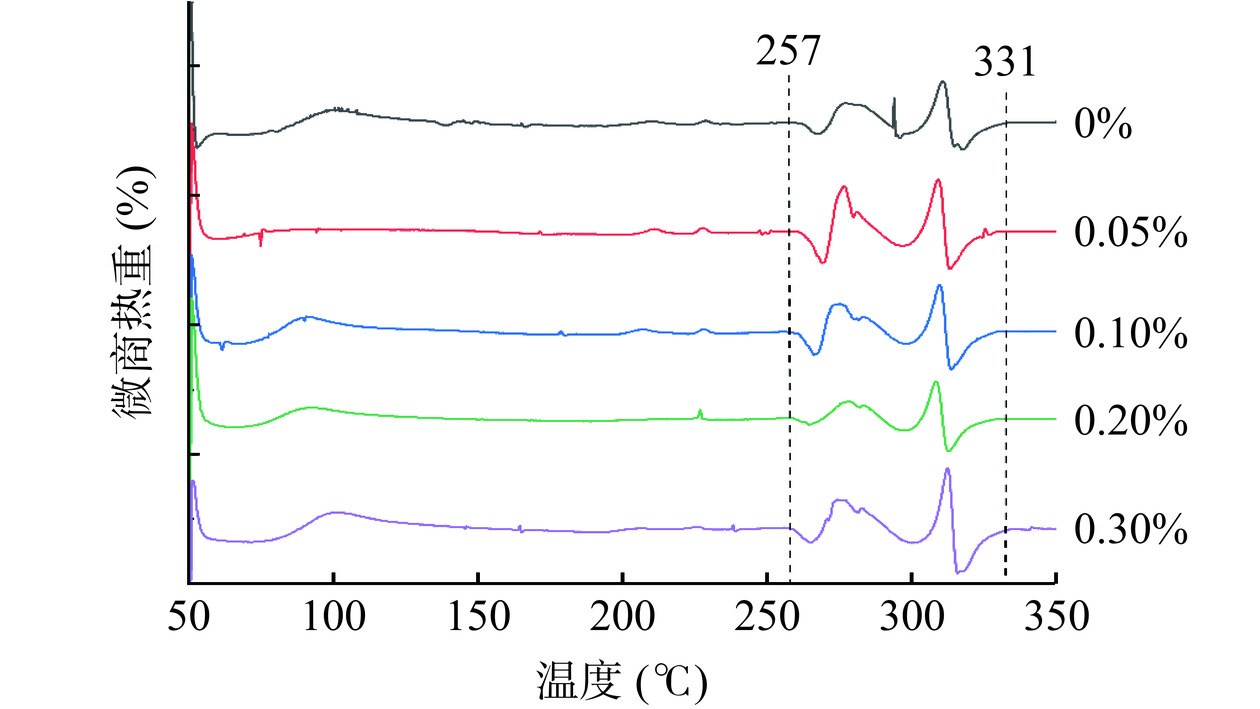
热重分析是衡量样品在相应温度范围内的热稳定性,阐明样品重量随温度变化的有效方法[11]。由图2可知,在50~257 ℃之间,所有的复合膜热重表现稳定,无明显重量损失;在257~331 ℃之间,复合膜的质量波动较大且出现峰值;当大于331 ℃时,复合膜的质量趋于稳定。分析表明,当温度高于257 ℃时,可能是由于甲基纤维素的系水力导致游离和结合的水分被蒸发;257~331 ℃之间的质量波动可能与非交联混合物的分解和分离以及水分的蒸发有关;当温度高于331 ℃后,由于AgNPs的存在使复合膜的热稳定性保持不变。
2.1.6 膜的傅里叶变换红外光谱分析
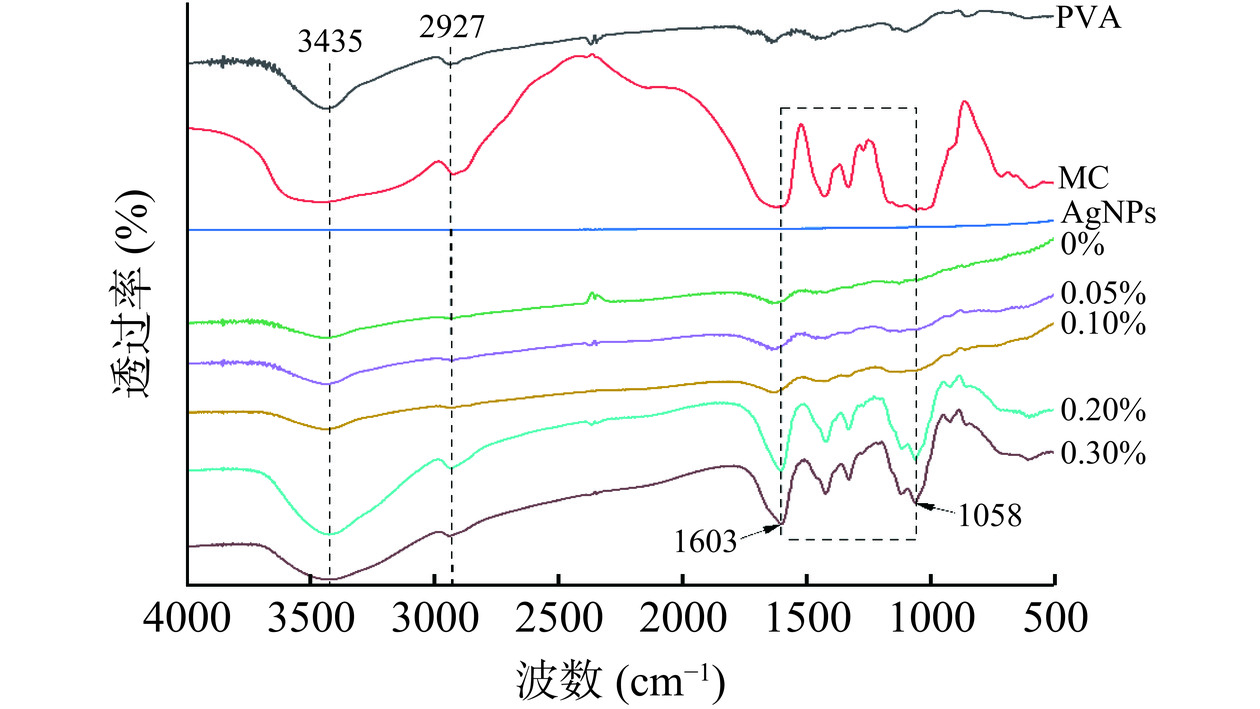
图3所示,分别为单体和不同AgNPs含量复合膜的红外光谱图。由图可知,在3435 cm−1处对应PVA的特征透过峰,为-OH伸缩振动峰,在2927 cm−1处对应MC的特征透过峰,为-CH2伸缩振动峰[33],5种不同复合膜中均包含此两种特征透过峰,说明复合膜中含有上述两种物质。由图所示,由于AgNPs颗粒单体的透过峰几乎为0,所以含有AgNPs的复合膜在1058~1603 cm−1处对应透过峰均被削弱,而随着AgNPs含量的增加导致其发生团聚现象,进而导致其透过峰削弱能力的下降,呈现与MC特征峰一致的现象。结果表明,由于采用非交联制备方式,复合膜没有出现新的透过峰和显著的波数偏移现象,即复合膜未发生化学组分的改变,复合膜内的组分主要通过分子间作用力进行物理结合。
2.1.7 膜的扫描电镜分析
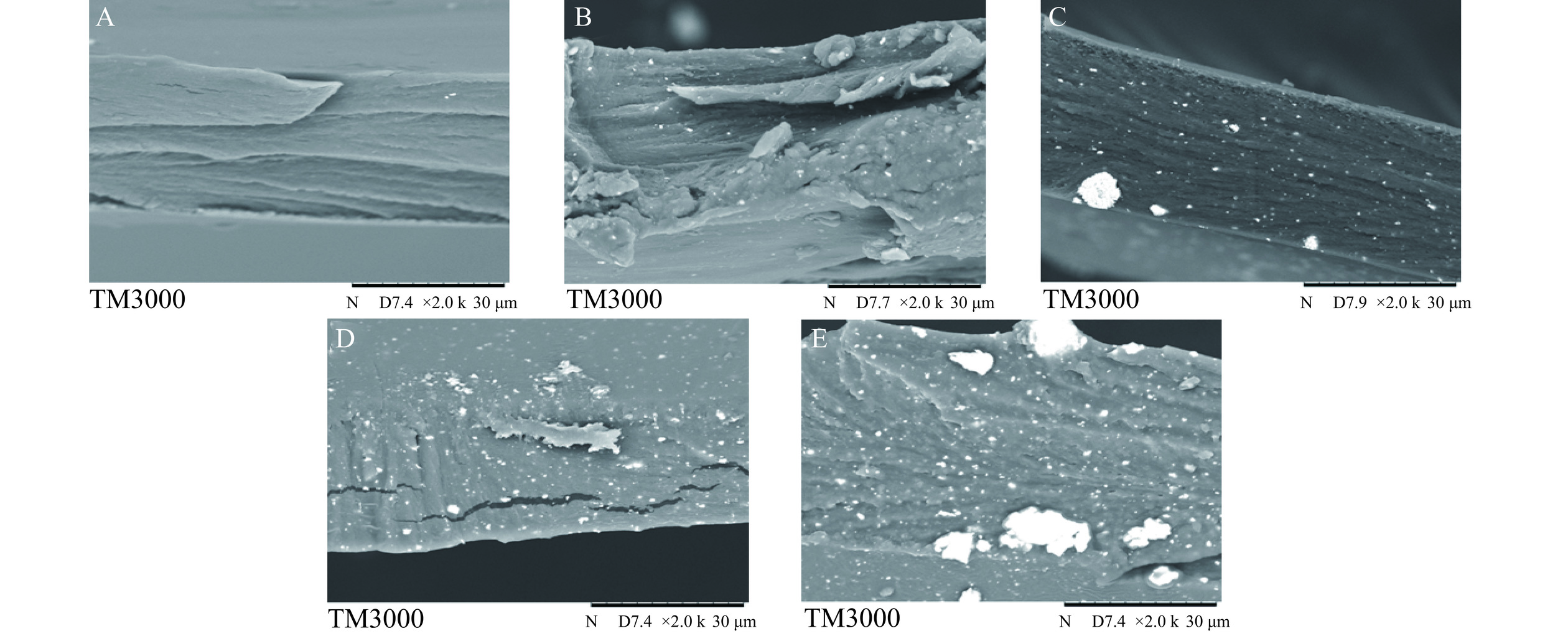
通过电子扫描显微镜可以直观地观察到复合膜表面、横截面等不同角度的结构、尺寸和形态信息[34]。如图4A~4E所示,分别是不同AgNPs含量复合膜横截面的扫描电镜图。由图4A可知,未见明显的白色颗粒状物质,说明其中不含有AgNPs颗粒;图4B~4E中随着AgNPs含量的递增,白色颗粒状物质逐渐增多并呈现团聚现象,AgNPs颗粒的团聚会降低复合膜的机械性能,增加复合膜的空隙从而提高水蒸气透过率及氧气透过率,这与上述的机械性能、水蒸气透过性、氧气透过率分析均有一致性。此外,AgNPs在复合膜不同层级的分布和聚集,特别是在表面的团聚现象,有助于增加复合膜的抑菌作用。
2.1.8 膜的抑菌活性分析
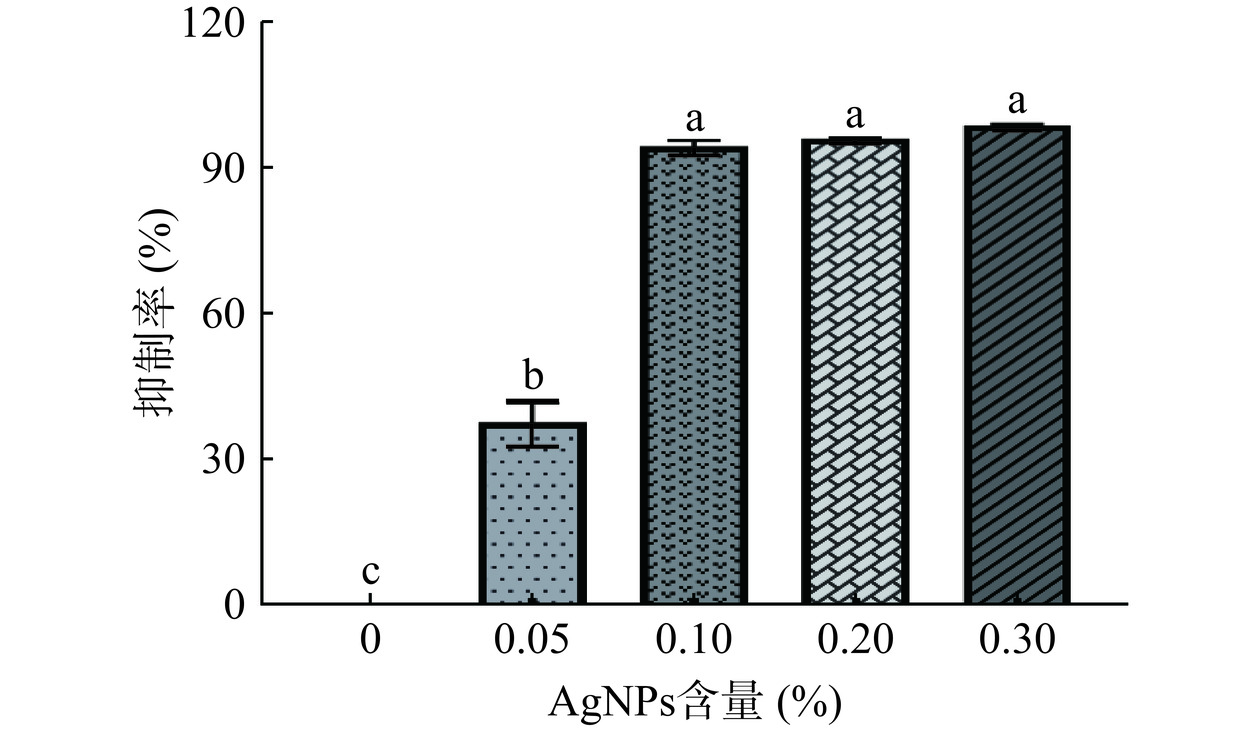
如图5所示,采用细胞计数法检测不同AgNPs含量的AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜对桔青霉的抑菌活性影响。随着AgNPs含量的增加,桔青霉的菌落数量减少,AgNPs复合膜对桔青霉的抑制率明显提高。在AgNPs含量为0.05%时,抑制率为38.08%;当AgNPs含量为0.1%时,抑制率骤升为94.57%;随着AgNPs含量的继续增加,复合膜对桔青霉的抑制率增长速率较慢,表明当AgNPs含量为0.1%时,该复合膜对桔青霉具有显著的抑制效果。结合扫描电镜分析表明,该现象可能是AgNPs含量增加导致复合膜形成不同程度的颗粒团聚现象,AgNPs对桔青霉产生抑制作用并形成不同的显著性抑制效果,最终趋于峰值;当AgNPs含量达到0.1%并继续增加,其抑制率增加缓慢。
2.2 AgNPs@PVA/MC(0.1% AgNPs)复合膜对瓯柑贮藏品质的影响
根据前文薄膜性能表征(机械性能、水蒸气透过性、氧气透过性等)、微观结构分析,0.05% AgNPs含量的薄膜上述性能最好,0.1% AgNPs含量的薄膜性能次之;但结合抑菌率分析,0.05% AgNPs含量的薄膜不及0.1% AgNPs含量的薄膜的二分之一,0.1% AgNPs含量的薄膜抑菌作用差异显著;综合薄膜的整体性能,选择0.1% AgNPs含量的薄膜进行接下来的实验。
2.2.1 AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜对瓯柑低温贮藏下失重率(WLR)的影响
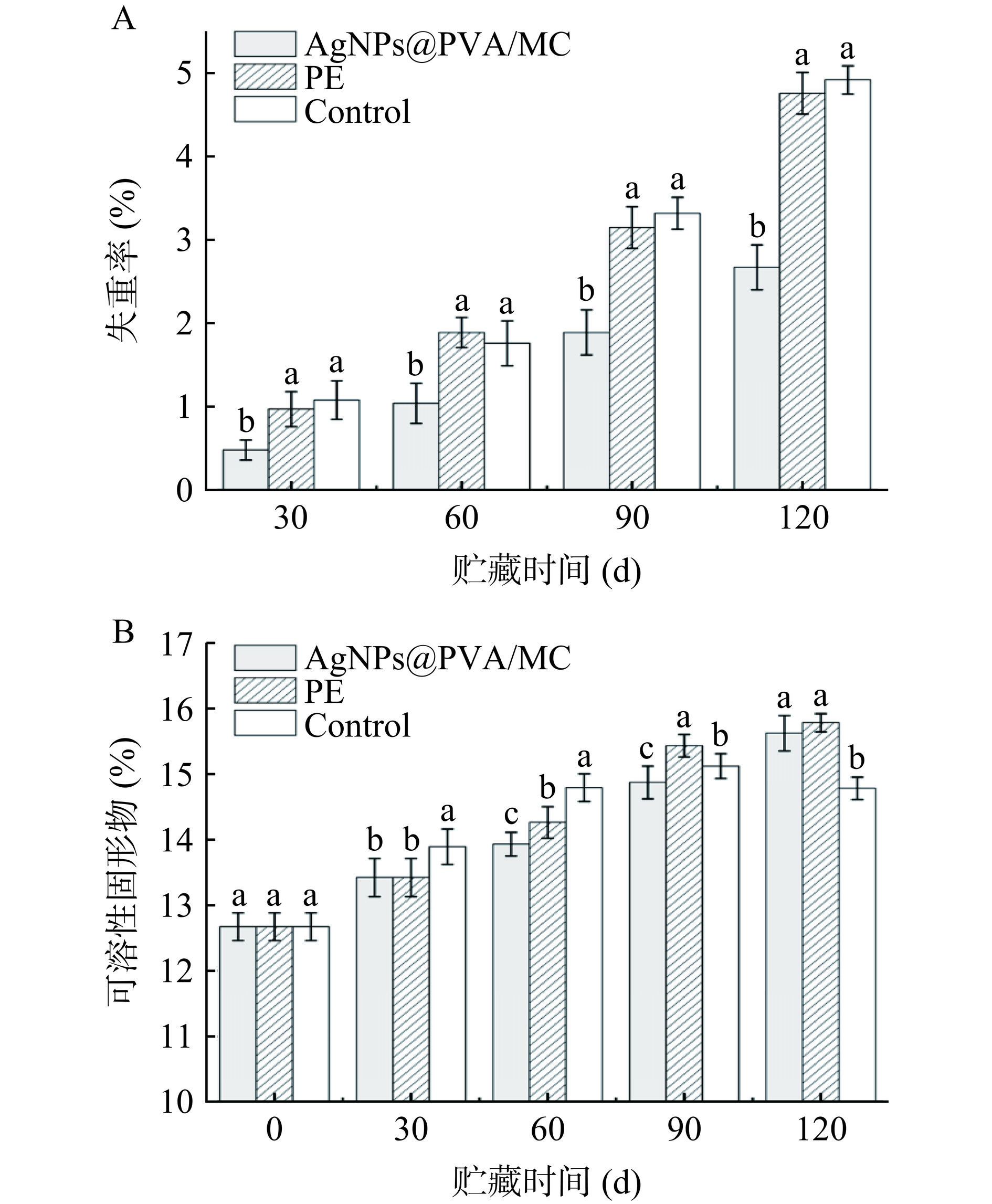
由于果实采后仍然进行着呼吸作用和蒸腾作用,随着贮藏时间的延长,果实的重量会逐渐减轻[35]。如图6A所示,各组瓯柑的失重率随着贮藏时间的延长呈现不断上升的趋势;同一贮藏时间下,对照组和PE组的失重率显著大于AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜组(P<0.05),且在第120 d时均未出现峰值。分析表明,相对于PE组和对照组,由于复合膜具备较低的水蒸气透过性,使得瓯柑和外界减少了水分交换,降低了瓯柑的失重率,进而可有效延长瓯柑的贮藏期。
2.2.2 AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜对瓯柑低温贮藏下可溶性固形物(TSS)的影响
如图6B所示,复合膜组和PE组的可溶性固形物随着贮藏时间的延长呈现上升趋势,而对照组则随贮藏时间呈现先上升后下降的趋势。研究表明,由于瓯柑为非呼吸跃变型果实,采后随着成熟度增加而导致TSS含量逐渐上升;随着贮藏时间进一步延长,呼吸作用的消耗使TSS含量逐渐降低[36]。对于同一贮藏时间下的TSS变化,第90 d前均是对照组>PE组>复合膜组;第90 d时,对照组的TSS含量达到峰值,复合膜组和PE组的TSS含量继续增加;第90 d后,复合膜组的TSS含量继续上升,PE组的增速减慢,而对照组逐渐降低。结果表明,由于覆膜处理,减缓了瓯柑的成熟,导致复合膜组和PE组瓯柑在120 d未达到TSS最大值;相较于PE组,复合膜组的阻隔作用较强,抑制了瓯柑的呼吸作用,即表现为TSS增速小于PE组;相较于复合膜组和PE组,由于对照组无隔绝能力,导致瓯柑呼吸作用最强,瓯柑中的糖分被快速合成后又消耗分解,使得TSS变化较快。综上,复合膜的阻隔能力较强,减弱了瓯柑的呼吸作用,延缓了瓯柑的成熟[37],使其有效延长贮藏期。
2.2.3 AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜对瓯柑低温贮藏下可滴定酸(TA)的影响
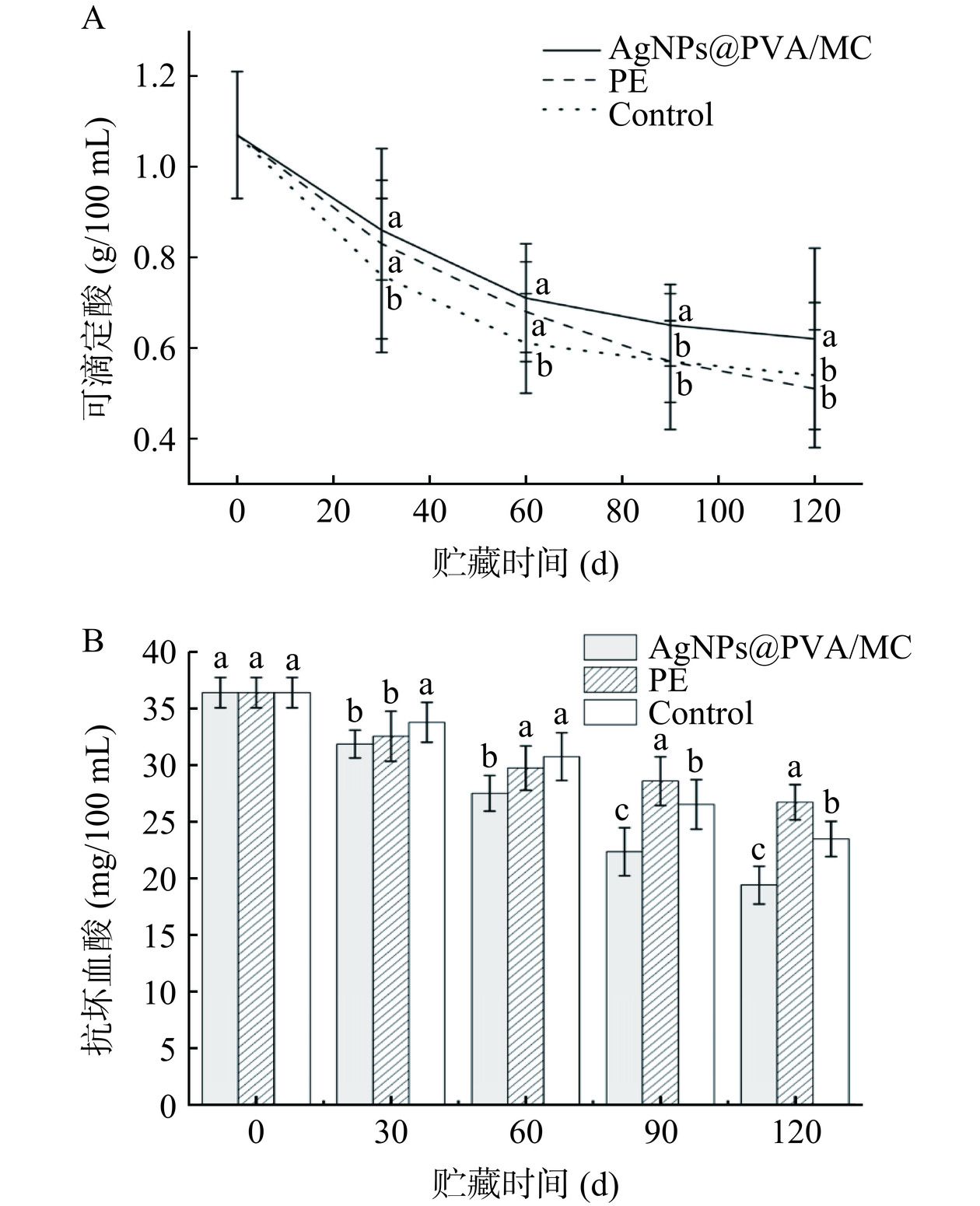
如图7A所示,不同包装膜下的瓯柑TA含量随着贮藏时间的延长而逐渐降低;同一贮藏时间下的瓯柑可滴定酸含量,复合膜组下降速率显著小于PE组和对照组(P<0.05)。结果表明,经过复合膜包装的瓯柑在贮藏期间的生理活动受到了抑制,使其可滴定酸的含量消耗速度显著弱于PE组和对照组,进而可有效延长瓯柑的贮藏期。
2.2.4 AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜对瓯柑低温贮藏下抗坏血酸(VC)的影响
VC是柑橘类水果中最为丰富的营养素之一,水果的抗衰老和抗逆性能力与VC的强抗氧化性有密切关系[8]。由图7B可知,随着贮藏时间延长,不同包装的瓯柑VC含量均呈现下降趋势,复合膜组的VC降解速率显著强于PE组和对照组(P<0.05),且PE组的降解速率最慢。结果表明,由于复合膜抑制瓯柑的呼吸强度,PE组和对照组的呼吸强度较强,使得PE组和对照组的分解糖速率变快;同时,酸作为呼吸底物被分解受到抑制,PE组和对照组VC在贮藏期间随时间推移,降解速率随之降低,呈现PE组和对照组的VC降解速率弱于复合膜组的现象[38]。
2.2.5 AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜对瓯柑低温贮藏下乙醇的影响
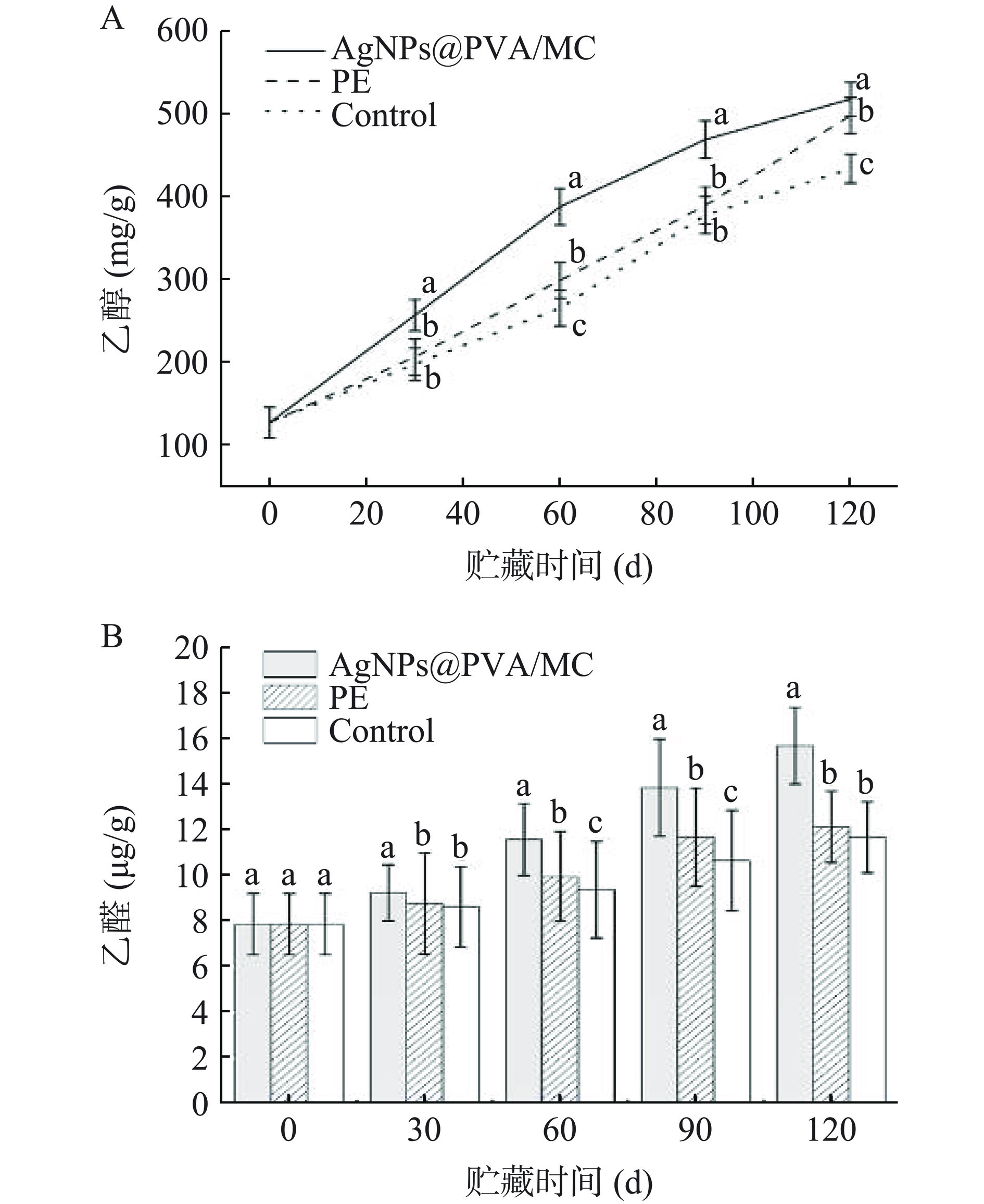
采后瓯柑的呼吸作用会伴随着乙醇和乙醛的积累,其含量变化衡量着果实的衰老情况[39]。由图8A可知,不同包装的瓯柑乙醇含量随贮藏时间增加而上升,且复合膜组的增长速率最快。结果表明,复合膜阻碍了瓯柑和外界的空气交换,加剧了瓯柑的无氧呼吸而产生较多乙醇,使其乙醇含量显著增加(P<0.05),而PE组相较于对照组亦是如此,由此呈现出复合膜组的乙醇含量增长最快的趋势。
2.2.6 AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜对瓯柑低温贮藏下乙醛的影响
在水果长期贮藏过程中,由于呼吸作用以及自身代谢的进行,组织内部会进行无氧呼吸而产生乙醇和乙醛,进而导致异味产生、衰败加剧[40]。由图8B可知,不同包装的瓯柑乙醛含量随贮藏时间增加而上升;在同一贮藏时间下,复合膜组的乙醛含量显著高于PE膜组(P<0.05),对照组最低。结果表明,由于复合膜对瓯柑和外界的阻绝能力较强,导致其空气交换能力降低,随着贮藏时间的增加,复合膜组相较于PE组和对照组的无氧呼吸作用较强,表现为同一贮藏条件下的乙醛含量较高;而PE组的隔绝能力较弱,其乙醛的增加量显著低于复合膜组。
2.2.7 AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜对瓯柑低温贮藏下抑菌效果的影响
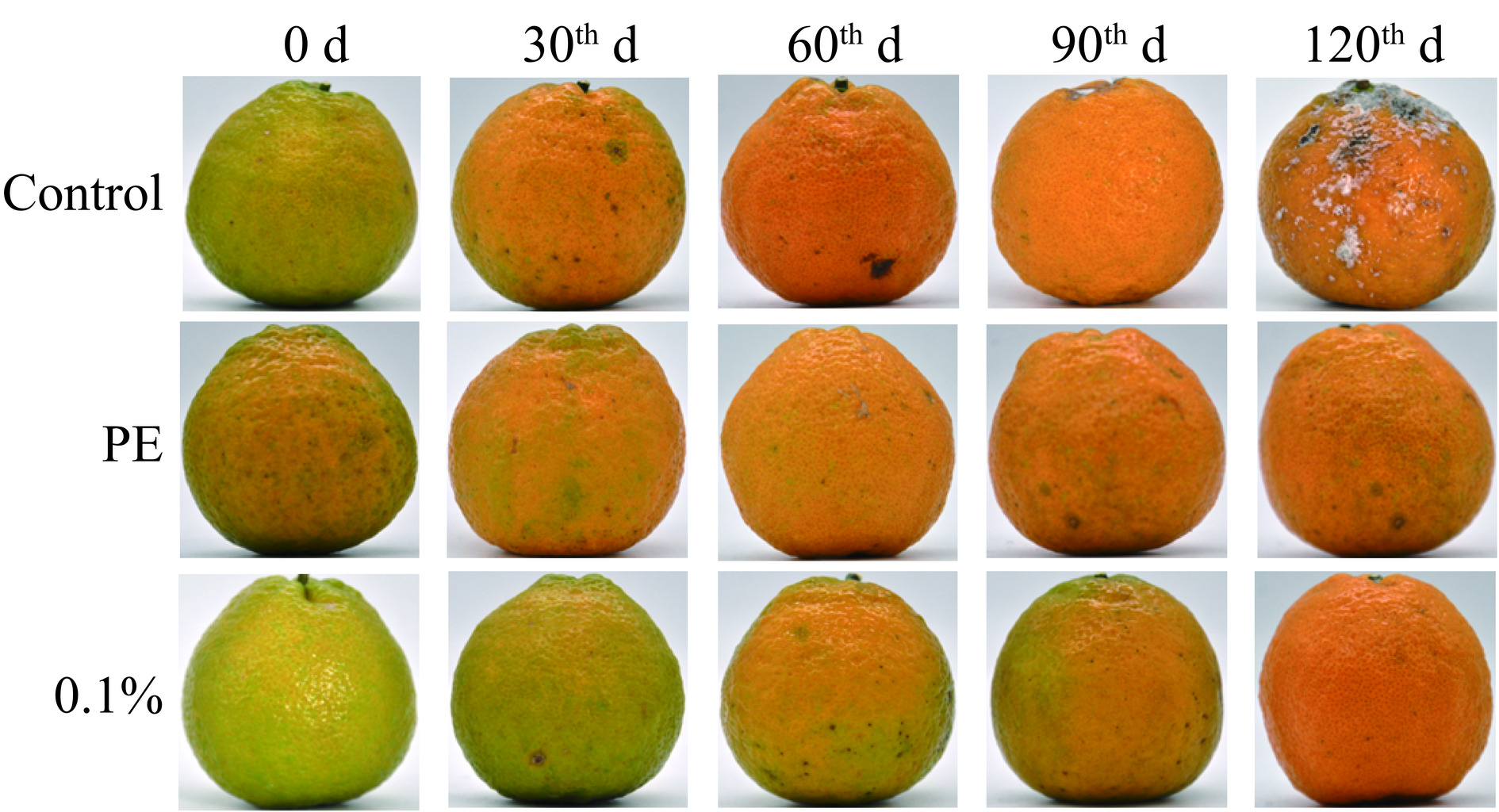
抑菌包装能够有效抑制微生物的生长,从而延长食品的保质期[41]。上述分析表明,AgNPs含量为0.1%时的抑菌性能最为优良,因此本研究选择0.1%的AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜和市售PE保鲜膜为实验组,设置不覆盖保鲜膜为对照组进行瓯柑的抑菌实验。由图9可知,随着贮藏期的延长,所有瓯柑表皮色泽由青绿色逐渐变黄并产生黑色斑点;在第120 d时,对照组和PE组的瓯柑果蒂出开始出现桔青霉,且对照组的菌落显著多于PE组,而经过0.1%AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜包裹的瓯柑贮藏情况良好,无明显菌落的产生。分析表明,随着贮藏时间的增加,由于AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜中AgNPs的存在,PVA/MC基材中包裹的AgNPs被溶出,银离子和菌落中的蛋白质、核酸等物质作用或结合,进而通过抑制其代谢或生理活性,实现抑菌作用。结果表明,0.1%AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜对瓯柑具有良好的抑菌效果。
3. 结论
本研究以甲基纤维素和聚乙烯醇为复合膜基材,负载不同含量的AgNPs颗粒为抑菌剂,通过对复合膜的外观、机械性能、微观结构及抗菌性等性能进行表征,筛选出性能优良的复合膜,旨在研究AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜对瓯柑低温贮藏品质的影响。结果表明,当AgNPs含量为0.05%和0.1%时,复合膜的机械性能和水蒸气透过性较好;而当AgNPs含量为0.1%时,复合膜横断截面的纳米银团聚现象更有利于AgNPs颗粒的溶出,导致其抑菌性最好;此外,含量为0.1% AgNPs的复合膜热稳定性较好。综上,0.1%含量的AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜综合性能最为优异。最后,将0.1%AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜、PE保鲜膜和对照组进行瓯柑的贮藏应用。本研究表明,0.1%AgNPs@PVA/MC复合膜抑制瓯柑致腐菌桔青霉的生长作用显著,有效减弱了瓯柑贮藏品质的衰变现象,保持瓯柑在低温贮藏期间的品质。本研究为开发抑菌包装材料及其在瓯柑采后贮藏保鲜中的应用提供了方法和理论依据。
-
图 1 不同AgNPs含量对复合膜色差和外观的影响
注:不同字母表示不同处理组的数据之间差异显著,P<0.05;图5同。
Figure 1. Effects of different AgNPs contents on color difference and appearance of composite films
表 1 不同AgNPs含量复合膜的颜色参数
Table 1 Color parameters of composite films with different AgNPs contents
AgNPs含量(%) ΔE L* a* b* 0 0.49±0.03d 95.78±0.03a −0.18±0.01c 2.59±0.06c 0.05 50.21±0.37c 46.05±0.36b 0.44±0.02a 4.59±0.13a 0.1 50.83±0.67c 45.40±0.67b 0.36±0.01b 3.73±0.05b 0.2 56.09±2.01b 40.13±2.01c 0.43±0.07a 2.65±0.70c 0.3 60.49±1.41a 35.74±1.41d 0.36±0.03b 4.07±0.36ab 注:同列不同字母表示不同处理组的数据之间差异显著,P<0.05,表2、表3同。 表 2 不同AgNPs含量对复合膜机械性能的影响
Table 2 Effects of different AgNPs contents on mechanical properties of composite films
AgNPs含量(%) 厚度(mm) 抗拉强度(MPa) 断裂伸长率(%) 0 0.04±0.01ab 33.91±6.05a 19.83±0.76a 0.05 0.04±0.01b 17.92±0.89b 7.33±1.03b 0.1 0.05±0.01ab 12.45±0.55bc 6.47±0.48b 0.2 0.05±0.01a 11.52±1.12bc 3.55±0.55c 0.3 0.05±0.01ab 10.91±0.67c 2.94±0.66c 表 3 不同复合膜的水蒸气透过性和氧气透过率
Table 3 Water vapor permeability and oxygen permeability of different composite films
膜的类别及AgNPs含量
(%)水蒸气透过性×10−6
(g·mm·m−2·s−1·Pa−1)氧气透过率×10−6
(cm3·cm−2·s−1·Pa−1)PE 347.10±0.20a 29.02±0.20a 0 25.43±0.43b 1.46±0.01e 0.05 19.40±0.61e 2.19±0.23d 0.1 21.03±0.30d 2.31±0.11d 0.2 21.56±0.69cd 3.46±0.13c 0.3 22.69±0.42c 5.57±0.24b -
[1] 宋洋, 郭秀珠, 黄品湖, 等. 钙肥对瓯柑品质及耐贮性的影响[J]. 农业科技通讯,2019(1):92−96. [SONG Y, GUO X Z, HUANG P H, et al. Effect of calcium fertilizer on the quality and storability of Citrus reticulata cv. Suavissima[J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology,2019(1):92−96.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6400.2019.01.030 SONG Y, GUO X Z, HUANG P H, et al. Effect of calcium fertilizer on the quality and storability of Citrus reticulata cv. Suavissima[J]. Bulletin of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2019(1): 92−96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6400.2019.01.030
[2] 朱峰. 青瓯柑果实成熟衰老延缓调控机制研究[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学, 2017. [ZHU F. The regulation mechanism of delayed ripening and senescence of green Ougan[D]. Wuhan:Hua Zhong Agricultural University, 2017.] ZHU F. The regulation mechanism of delayed ripening and senescence of green Ougan[D]. Wuhan: Hua Zhong Agricultural University, 2017.
[3] 吴宝玉, 徐建国, 郑小艳, 等. 采收期对瓯柑果实贮藏品质的影响[J]. 中国南方果树,2021,50(5):42−45,49. [WU B Y, XU J G, ZHENG X Y, et al. Effect of harvesting time on storage quality of Ougan fruit[J]. South China Fruits,2021,50(5):42−45,49.] WU B Y, XU J G, ZHENG X Y, et al. Effect of harvesting time on storage quality of Ougan fruit[J]. South China Fruits, 2021, 50(5): 42−45,49.
[4] 黄祥俊. 瓯海区瓯柑产业现状与出路[J]. 中国果业信息,2019,36(4):17−20. [HUAGN X J. Ougan industry status and prospects on Ouhai county[J]. China Fruit News,2019,36(4):17−20.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1514.2019.04.003 HUAGN X J. Ougan industry status and prospects on Ouhai county[J]. China Fruit News, 2019, 36(4): 17−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1514.2019.04.003
[5] GOPALAKRISHNAN K, CHANDEL M, GUPTA V, et al. Valorisation of fruit peel bioactive into green synthesized silver nanoparticles to modify cellulose wrapper for shelf-life extension of packaged bread[J]. Food Research International,2023,164:112321. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112321
[6] MACIEJA S, ŚRODA B, ZIELIŃSKA B, et al. Bioactive carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)-based films modified with melanin and silver nanoparticles (AgNPs)-the effect of the degree of cmc substitution on the in situ synthesis of AgNPs and films’ functional properties[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2022,23(24):15560. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415560
[7] DAS NEVES M D S, SCANDORIEIRO S, PEREIRA G N, et al. Antibacterial activity of biodegradable films incorporated with biologically-synthesized silver nanoparticles and the evaluation of their migration to chicken meat[J]. Antibiotics,2023,12(1):178. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010178
[8] 张朝涛, 王春慧, 高光晔, 等. 用于樱桃番茄保鲜的纳米银复合膜材料研究与应用[J]. 生物技术进展,2023,13(6):925−933. [ZHANG Z T, WANG C H, GAO G Y, et al. Research and application of silver nanocmposite film materials for cherry tomato preservation[J]. Current Biotechnology,2023,13(6):925−933.] ZHANG Z T, WANG C H, GAO G Y, et al. Research and application of silver nanocmposite film materials for cherry tomato preservation[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2023, 13(6): 925−933.
[9] LIN G, LI X, ZHAO C. Preparation and application of in-situ loaded silver nanoparticles antibacterial fresh-keeping composite paper[J]. Polymers,2022,14(18):3798. doi: 10.3390/polym14183798
[10] YANG J, ZHANG X, CHEN L, et al. Antibacterial aerogels with nano-silver reduced in situ by carboxymethyl cellulose for fresh meat preservation[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,213:621−630. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.05.145
[11] AMRUTHA N R, DHALE M A, JOB A, et al. Silver nanoparticles incorporated PVA-MC blends:A systematic approach to understand its properties for food packaging applications[J]. Chemistry Select (Weinheim),2023,8(27):e202205031. doi: 10.1002/slct.202205031
[12] ZONG Z H, LIU M, CHEN H Z, et al. Preparation and characterization of a novel intelligent starch/gelatin binary film containing purple sweet potato anthocyanins for flammulina velutipes mushroom freshness monitoring[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,405:134839. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134839
[13] 全国塑料标准化技术委员会通用方法和产品分会. GB/T 1040.1-2018 塑料 拉伸性能的测定 第1部分:总则[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2019. [Methods of Test and Material. GB/T 1040.1-2018 Plastics-Determination of tensile properties-Part 1:General principles[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2019.] Methods of Test and Material. GB/T 1040.1-2018 Plastics-Determination of tensile properties-Part 1: General principles[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2019.
[14] 全国塑料标准化技术委员会通用方法和产品分会. GB/T 1037-2021 塑料薄膜与薄片水蒸气透过性能测定 杯式增重与减重法[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2022. [Methods of Test and Material. GB/T 1037-2021 Test method for water vapor transmission of plastic film and sheet-Desiccant method and water method[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2022.] Methods of Test and Material. GB/T 1037-2021 Test method for water vapor transmission of plastic film and sheet-Desiccant method and water method[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2022.
[15] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 1038.1-2022 塑料制品 薄膜和薄片 气体透过性试验方法 第1部分:差压法[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2022. [State Administration for Market Regulation, National Standardization Administration. GB/T 1038.1-2022 Plastics-Film and sheeting-Determination of gas transmission rate-Part 1:Differential pressure methods[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China, 2022.] State Administration for Market Regulation, National Standardization Administration. GB/T 1038.1-2022 Plastics-Film and sheeting-Determination of gas transmission rate-Part 1: Differential pressure methods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2022.
[16] 谢斌. 基于聚乙烯醇/壳聚糖活性包装薄膜的制备与性能研究[D]. 株洲:湖南工业大学, 2022. [XIE B. Preparation and properties of active packaging films based on PVA/chitosan[D]. Zhuzhou:Hunan University of Technology, 2022.] XIE B. Preparation and properties of active packaging films based on PVA/chitosan[D]. Zhuzhou: Hunan University of Technology, 2022.
[17] 韩婉毓, 李会珍, 张志军, 等. 紫苏籽壳提取物纳米银颗粒的制备及性能表征[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(6):49−58. [HAN W Y, LI H Z, ZHANG Z J, et al. Preparation and performance characterization of silver nanoparticles of perilla seed shell extract[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(6):49−58.] HAN W Y, LI H Z, ZHANG Z J, et al. Preparation and performance characterization of silver nanoparticles of perilla seed shell extract[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(6): 49−58.
[18] YANG D, LIU Q, GAO Y, et al. Characterization of silver nanoparticles loaded chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol antibacterial films for food packaging[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2023,136:108305. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.108305
[19] DE MATTEIS V, CASCIONE M, COSTA D, et al. Aloe vera silver nanoparticles addition in chitosan films:Improvement of physicochemical properties for eco-friendly food packaging material[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2023,24:1015−1033. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.03.025
[20] ZHAO X, TIAN R, ZHOU J, et al. Multifunctional chitosan/grape seed extract/silver nanoparticle composite for food packaging application[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,207:152−160. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.02.180
[21] 舒小芳, 郜海燕, 韩延超, 等. CO2气调处理对鲜莲贮藏品质的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2023,23(2):243−253. [SHU X F, GAO H Y, HAN Y C, et al. Effects of CO2 controlled atmosphere treatments on the storage quality of fresh lotus[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2023,23(2):243−253.] SHU X F, GAO H Y, HAN Y C, et al. Effects of CO2 controlled atmosphere treatments on the storage quality of fresh lotus[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 23(2): 243−253.
[22] 房祥军, 吴伟杰, 穆宏磊, 等. 外源脱落酸处理对蓝莓采后低温胁迫下生理响应的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2023,23(2):232−242. [FANG X J, WU W J, MU H L, et al. Effect of exogenous abscisic acid on physiological response of blueberries to low temperature stress during postharvest[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2023,23(2):232−242.] FANG X J, WU W J, MU H L, et al. Effect of exogenous abscisic acid on physiological response of blueberries to low temperature stress during postharvest[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 23(2): 232−242.
[23] TAHA I M, ZAGHLOOL A, NASR A, et al. Impact of starch coating embedded with silver nanoparticles on strawberry storage time[J]. Polymers,2022,14(7):1439. doi: 10.3390/polym14071439
[24] 蔡继业, 房祥军, 韩延超, 等. 气调贮藏对东魁杨梅品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报,2022,34(2):352−359. [CAI J Y, FANG X J, HAN Y C, et al. Effect controlled atmosphere storage on postharvest preservation of Dongkui bayberry[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2022,34(2):352−359.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2022.02.17 CAI J Y, FANG X J, HAN Y C, et al. Effect controlled atmosphere storage on postharvest preservation of Dongkui bayberry[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2022, 34(2): 352−359. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2022.02.17
[25] 徐思朦, 艾少杰, 薛蕾, 等. 自发气调处理对桃果实采后冷害及风味品质的调控效应[J]. 果树学报,2023,40(9):1952−1965. [XU S M, AI S J, XUE L, et al. Effects of modified atmosphere treatments on chilling injury and flavor quality of peach fruit during storage[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2023,40(9):1952−1965.] XU S M, AI S J, XUE L, et al. Effects of modified atmosphere treatments on chilling injury and flavor quality of peach fruit during storage[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2023, 40(9): 1952−1965.
[26] 杨洁茹, 刘海波, 张雯雯, 等. 漂白紫胶/海藻酸钠复合膜的制备及其在冷鲜肉保鲜中的应用[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(18):407−414. [YANG J R, LIU H B, ZHANG W W, et al. Preparation of bleached shellac/sodium alginate composite film and its application in chilled fresh meat preservation[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(18):407−414.] YANG J R, LIU H B, ZHANG W W, et al. Preparation of bleached shellac/sodium alginate composite film and its application in chilled fresh meat preservation[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(18): 407−414.
[27] 梅洁, 李彬欣, 朱仁广, 等. 纳米银的制备及抑菌性能研究[J]. 化学研究与应用,2023,35(4):961−967. [MEI J, LI B X, ZHU R G, et al. Preparation and antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Research and Application,2023,35(4):961−967.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2023.04.032 MEI J, LI B X, ZHU R G, et al. Preparation and antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2023, 35(4): 961−967. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2023.04.032
[28] ALIZADEH SANI M, KHEZERLOU A, TAVASSOLI M, et al. Bionanocomposite active packaging material based on soy protein isolate/persian gum/silver nanoparticles; Fabrication and characteristics[J]. Colloids and Interfaces,2022,6(4):57. doi: 10.3390/colloids6040057
[29] 叶芷欣, 任蓝图, 许雨茵, 等. 纳米银-聚乙烯抗菌复合材料的研究进展[J]. 材料导报,2023,37(S2):557−561. [YE Z X, REN L T, XU Y Y, et al. Research progress of nano-silver-polyethylene antibacterial composites[J]. Materials Reports,2023,37(S2):557−561.] YE Z X, REN L T, XU Y Y, et al. Research progress of nano-silver-polyethylene antibacterial composites[J]. Materials Reports, 2023, 37(S2): 557−561.
[30] 杨欧, 张晓湘, 徐小涵, 等. 抗氧化型壳聚糖/大豆蛋白复合食用膜的制备与应用[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(6):210−218. [YANG O, ZHANG X X, XU X H, et al. Preparation and application of antioxidative chitosan/soybean protein isolate composite edible membrane[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(6):210−218.] YANG O, ZHANG X X, XU X H, et al. Preparation and application of antioxidative chitosan/soybean protein isolate composite edible membrane[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(6): 210−218.
[31] NIU B, SHAO P, CHEN H, et al. Structural and physiochemical characterization of novel hydrophobic packaging films based on pullulan derivatives for fruits preservation[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,208:276−284. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.12.070
[32] CHEN C, CHEN W, DAI F, et al. Development of packaging films with gas selective permeability based on poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/poly (butylene succinate) and its application in the storage of white mushroom (Agaricus bisporus)[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2022,15(6):1268−1283. doi: 10.1007/s11947-022-02794-4
[33] 李彦山, 汪树军, 刘红研, 等. 聚乙二醇/甲基纤维素定形相变材料的制备及其性能研究[J]. 石油化工,2013,42(9):1023−1027. [LI Y S, WANG S J, LIU H Y, et al. Preparation and characterization of polyethylene glycol/methyl cellulose form-stable phase change materials[J]. Petrochemical Technology,2013,42(9):1023−1027.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8144.2013.09.015 LI Y S, WANG S J, LIU H Y, et al. Preparation and characterization of polyethylene glycol/methyl cellulose form-stable phase change materials[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2013, 42(9): 1023−1027. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8144.2013.09.015
[34] 王哲, 钟成, 赵雪晴, 等. 微波辅助法制备细菌纤维素-纳米银(BC-AgNPs)复合材料及其表征[J]. 生物加工过程,2023,21(1):25−31. [WANG Z, ZHONG C, ZHAO X Q, et al. Preparation and characterization of bacterial cellulose-silver nanopariticles (BC-AgNPs) composites[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering,2023,21(1):25−31.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3678.2023.01.003 WANG Z, ZHONG C, ZHAO X Q, et al. Preparation and characterization of bacterial cellulose-silver nanopariticles (BC-AgNPs) composites[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2023, 21(1): 25−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3678.2023.01.003
[35] 黎星延, 黄丽金, 刘汉美, 等. 不同分子量壳聚糖涂膜对采后西番莲果实贮藏品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(22):319−326. [LI X Y, HUANG L J, LIU H M, et al. Effect of chitosan coating with different molecular weights on the storage quality of postharvest passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(22):319−326.] LI X Y, HUANG L J, LIU H M, et al. Effect of chitosan coating with different molecular weights on the storage quality of postharvest passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(22): 319−326.
[36] 李晓霞. 电生功能水热处理对柑橘冷害及贮藏效果的影响[D]. 晋中:山西农业大学, 2016. [LI X X. Study on effect of heated electrolyzed functional water treatment on chilling injury and storage of citrus[D]. Jinzhong:Shanxi Agricultural University, 2016.] LI X X. Study on effect of heated electrolyzed functional water treatment on chilling injury and storage of citrus[D]. Jinzhong: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2016.
[37] 李保祥. 壳聚糖/纳米纤维素复合涂膜对柑橘贮藏品质的影响[D]. 重庆:西南大学, 2021. [LI B X. Effects of chitosan/nanocrystal cellulose composite coating on storage quality of citrus[D]. Chongqing:Southwest University, 2021.] LI B X. Effects of chitosan/nanocrystal cellulose composite coating on storage quality of citrus[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2021.
[38] 徐舒曼, 温明霞. 瓯柑贮藏过程中果实品质的变化规律[J]. 浙江农业科学,2016,57(6):918−920. [XU S M, WEN M X. Changing law of fruit quality in the storage process of Ougan[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,2016,57(6):918−920.] XU S M, WEN M X. Changing law of fruit quality in the storage process of Ougan[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 57(6): 918−920.
[39] 曾顺德, 张超, 尹旭敏, 等. 生物保鲜剂对“白凤”桃和“巨峰”葡萄采后贮藏生理的影响[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(24):457−460. [ZENG S D, ZHANG C, YIN X M, et al. Effect of biological preservative on postharvest physiology of Baifeng peach and Jufeng grape[J]. Food Science,2010,31(24):457−460.] ZENG S D, ZHANG C, YIN X M, et al. Effect of biological preservative on postharvest physiology of Baifeng peach and Jufeng grape[J]. Food Science, 2010, 31(24): 457−460.
[40] 王呈阳. 不同物流温度对椪柑果实品质的影响[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2015. [WANG C Y. Effect of different logistics temperatures on the quality of Ponkan fruits[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2015.] WANG C Y. Effect of different logistics temperatures on the quality of Ponkan fruits[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2015.
[41] PANDIAN H, SENTHILKUMAR K, NAVEENKUMAR M, et al. Azadirachta indica leaf extract mediated silver nanoparticles impregnated nano composite film (AgNP/MCC/starch/whey protein) for food packaging applications[J]. Environmental Research,2023,216:114641. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.114641





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



