Optimization of Starch Saccharification Process and Structural Characterization of Starch Using Low Transglycosidation Activity Glucoamylase GluM3
-
摘要: 本文旨在优化糖化酶GluM3的玉米淀粉糖化工艺,探究其对淀粉颗粒结构的影响,进一步推动糖化酶GluM3在淀粉制糖工业的应用。首先通过单因素实验和响应面试验确定低转苷活性糖化酶GluM3的最佳糖化工艺,采用电子扫描电镜、X-射线衍射法和红外光谱等方法对淀粉颗粒进行结构表征。结果表明,最佳糖化工艺条件为液化液的葡萄糖当量(DE)值16%,温度66 ℃,pH3.7,时间3 h,糖化酶添加量450 U/g和普鲁兰酶添加量1.25 U/g,优化后获得玉米淀粉糖化液的葡萄糖含量(DX)达到92.68%。糖化反应后玉米淀粉从光滑完整颗粒变成残破的碎屑状态;在糖化过程中淀粉内部的晶体结构遭到了一定程度的破坏;糖化反应后玉米淀粉短程有序化程度降低;玉米淀粉经淀粉酶液化反应后生成多种麦芽低聚糖,而经糖化酶GluM3糖化反应后麦芽低聚糖进一步转化成葡萄糖,其占比高达99.34%。本文确定了低转糖苷活性GluM3对玉米淀粉的最佳糖化工艺,并研究了糖化反应过程中淀粉微观结构和物理特性的变化规律,为糖化酶GluM3的后续工业应用提供理论依据和应用基础。Abstract: This paper discussed the optimization of the corn starch saccharification process using the glucoamylase GluM3, and explored its impact on the structure of starch granules to further promote the industrial application of GluM3 in starch sugar production. The study first determined the optimal saccharification process for low transglycosylation activity glucoamylase GluM3 through single-factor experiments and response surface experiments. Structural characterization of starch granules was conducted using methods such as scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, and infrared spectroscopy. The results showed that the optimal saccharification conditions were a liquefaction DE value of 16%, temperature at 66 ℃, pH at 3.7, time at 3 h, enzyme dosage at 450 U/g with pullulanase dosage at 1.25 U/g. After optimization, the glucose content (DX value) in corn starch saccharification liquid reached 92.68%. After saccharification reaction, corn starch changed from smooth intact particles to fragmented debris state. There was a certain degree of damage to internal crystalline structure during saccharification. A decrease in short-range order degree after saccharification reaction was observed. Furthermore, various maltodextrins were produced after corn starch enzymatic hydrolysis reaction while maltodextrins were further converted into glucose by GluM3 with a proportion as high as 99.34%. This study establishes the optimal saccharification process for low transglycosylation activity GluM3 on corn starch and investigates changes in microstructure and physical properties during the saccharification process, providing theoretical basis for subsequent industrial applications of GluM3.
-
葡萄糖是以淀粉为原料,通过酸或酶的催化水解反应生成,是淀粉深加工的主要产品[1]。玉米淀粉制糖过程包括糊化、液化和糖化工艺,糖化酶是糖化过程中需要使用的非常重要的酶类[2]。糖化酶是葡萄糖淀粉酶(Glucoamylase,EC.3.2.1.3)的简称,又称为淀粉α-1,4葡萄糖苷酶。因其具有外切酶活性,能从淀粉、糖原和糊精等碳水化合物的非还原性末端依次水解α-1,4葡萄糖苷键,最终得到葡萄糖[3];也能水解α-1,3和α-1,6糖苷键,但相对水解速率较慢[4]。该酶是工业上水解淀粉产生葡萄糖的主要酶类,广泛应用于食品、发酵、饲料和医药等工业,是我国产量最大、应用范围最广的酶类,具有很高的商品价值[5]。
目前工业生产上主要应用来源于黑曲霉和埃默森篮状菌的糖化酶,但这些糖化酶面临一个缺点:它们具有一定的转糖苷活性,在产物浓度较高时会将生成的葡萄糖继续转化形成如异麦芽糖、潘糖等低聚糖[6]。这些低聚糖副产物不仅影响葡萄糖的结晶效率,而且直接降低葡萄糖最终产品的纯度,所以人们一直致力于降低糖化酶的转糖苷酶活力的研究。实验室前期通过基因工程改造的方式成功获得了一株催化活力提升且转糖苷活性降低的糖化酶突变体GluM3。与野生型相比,突变体GluM3的催化效率提升至野生型的185%,而其转糖苷酶活力基本丧失,仅为野生型的0.04%[7]。与现有糖化酶相比,GluM3可以显著提升终产物葡萄糖的产率。为了更好地挖掘GluM3的应用潜力,本研究以玉米淀粉为原料,通过单因素实验与响应面法优化糖化酶GluM3糖化工艺中的相关工艺参数,确定玉米淀粉的最佳糖化工艺条件;同时解析糖化过程中淀粉微观结构和物理特性的变化规律,旨在为糖化酶突变体GluM3在淀粉制糖工业化生产中的应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
玉米淀粉(分析纯) 黑龙江龙凤玉米开发有限公司;耐高温α-淀粉酶(200000 U/mL)、普鲁兰酶(1000 U/mL) 白银赛诺生物科技有限公司;葡萄糖试剂盒 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;葡萄糖、麦芽低聚糖 标准品,西格玛奥德里奇(上海)贸易有限公司。
SpectraMax 190酶标仪 美谷分子仪器有限公司;DK-8D电热恒温水槽 上海一恒科技有限公司;A630全自动阿贝折光仪 山东海能未来技术集团有限公司;SU1510扫描电子显微镜 日本捷欧路公司;1200高效液相色谱仪 美国安捷伦科技公司;TENSOR 27傅里叶变换红外光谱仪、Discover D8 X-射线衍射仪 德国布鲁克公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 玉米淀粉液化方法及葡萄糖当量的测定
将玉米淀粉进行80 ℃烘干至恒重,称取一定量的玉米淀粉加水搅拌均匀,配制质量分数为10%(w/v)的玉米淀粉浆,用1 mol/L的Na2CO3调节pH至6.0,缓缓搅拌并加热至95 ℃,持续搅拌1 h,玉米淀粉液成浆糊状,随后加0.4 U/L耐高温α-淀粉酶,缓慢搅拌反应30~60 min进行液化。
用全自动阿贝折光仪测定液化液的干物质含量(质量分数,%)。取1 mL液化液加入1.5 mL 3,5-二硝基水杨酸(DNS),沸水浴5 min,冷却至室温,在540 nm测定吸光度,计算得到还原糖含量[8]。根据下面公式计算得到液化液的葡萄糖当量(DE),用于评价玉米淀粉的液化程度[9]。
DE(%)=还原糖含量干物质含量×100 1.2.2 糖化酶GluM3的制备
本文使用实验室前期获得转糖苷活性降低的糖化酶GluM3,通过对GluM3表达菌株X33-pJ912-M1-N22C/A29C/A32P/D259E进行诱导表达和蛋白纯化,获得重组的糖化酶酶液[7]。将GluM3表达菌株接种于1 L BMD1培养基(0.2 mol/L磷酸钾,13.4 g/L YNB,0.4 mg/L生物素,1.1%(w/w)葡萄糖)中,在28 ℃条件下培养48~60 h;然后加入1 L BMM2(0.2 mol/L磷酸钾,13.4 g/L YNB,0.4 mg/L生物素,1%(w/v)甲醇),每隔24 h补充加入1%(w/v)甲醇进行蛋白诱导,直至振荡培养72 h;然后在12000 r/min条件下离心10 min后收集上清;利用DNS法测定糖化酶的酶活力[8],取100 μL酶液加入到900 μL玉米淀粉浆溶液中,在65℃下反应10 min,反应结束加入1.5 mL DNS溶液,沸水浴5 min,冷却至室温,在540 nm测定吸光度,确定糖化酶GluM3的酶活性[10]。
1.2.3 玉米淀粉糖化及液化液葡萄糖含量的测定
将制备好的液化液降至60 ℃,用0.05 mol/L醋酸钠缓冲液调节pH至3.5,加入相应酶活力的糖化酶GluM3和普鲁兰酶,在恒温水浴摇床反应不同时间,测定糖化液的葡萄糖含量(DX)。取不同时间点的糖化液检测DX值。用全自动阿贝折光仪测定液化液的干物质含量(质量分数,%),用葡萄糖试剂盒测定葡萄糖含量(质量分数,%),计算得到DX,用于评价糖化液的糖化程度,其计算公式为:
DX(%)=葡萄糖含量干物质含量×100 1.2.4 糖化工艺单因素实验
为了优化玉米淀粉糖化工艺,将糖化温度、pH、糖化酶添加量、普鲁兰酶添加量、液化液DE值和糖化时间为主要工艺参数,利用单因素实验分析其对糖化液DX值的影响。
糖化温度对糖化液DX值的影响:将液化液(DE值15%)用醋酸钠缓冲液调节pH到3.5,在设定的各温度下预热10 min,加入200 U/g的糖化酶和1.25 U/g普鲁兰酶,糖化时间2 h,比较不同糖化温度50、55、60、65和70 ℃对糖化液DX值的影响,以确定最佳糖化反应温度。
pH对糖化液DX值的影响:用醋酸钠缓冲液将液化液调整至不同的pH(3.0、3.5、4.0、4.5、5.0)[11],设置糖化温度60 ℃,将液化液(DE值15%)进行预热10 min,加入200 U/g的糖化酶和1.25 U/g普鲁兰酶,糖化时间为2 h,比较不同pH的糖化液DX值,以确定最优糖化反应的pH。
糖化酶添加量对糖化液DX值的影响[12]:在液化液DE值15%、糖化温度为60 ℃、pH3.5、糖化时间2 h和1.25 U/g普鲁兰酶条件下,比较不同的糖化酶添加量(50、100、200、400、600 U/g)对糖化液DX值的影响,以确定糖化反应的糖化酶添加量。
普鲁兰酶添加量对糖化液DX值的影响[13]:在液化液DE值15%、糖化温度为60 ℃、pH3.5、糖化时间2 h和糖化酶添加量为200 U/g的实验条件下,考察普鲁兰酶添加量1.25、2.5、5、10 U/g对糖化液DX值的影响。
液化液DE值对糖化液DX值的影响:在糖化温度为60 ℃、糖化时间2 h、pH3.5、糖化酶添加量为200 U/g、普鲁兰酶添加量1.25 U/g的实验条件下,考察液化液不同DE值(9%、14%、16%、22%和27%)对糖化液DX值的影响。
糖化时间对糖化液DX值的影响[14]:糖化温度为60 ℃、pH3.5、液化液DE值15%、糖化酶添加量为200 U/g、普鲁兰酶添加量1.25 U/g的实验条件下,考察不同糖化反应时间(0.5、1、2、4、6、8、10 h)对糖化液DX值的影响。
1.2.5 响应面法优化玉米淀粉糖化工艺
为了优化淀粉糖化工艺,在上述单因素实验基础上,利用Design Expert软件的Box-Behnken模型[15],固定液化液的DE值为15%和普鲁兰酶添加量1.25 U/g,对糖化反应温度、pH、糖化酶添加量和时间进行4因素3水平的响应面试验设计(表1),以糖化液DX值为考察指标,确定4个因素之间的相互作用,获得糖化酶水解玉米淀粉的最优工艺条件。
表 1 响应面因素水平设计Table 1. Response surface factor level design因素 编码 水平编码值 −1 0 1 温度(℃) A 60 65 70 pH B 3.0 3.5 4.0 糖化酶添加量(U/g) C 100 350 600 时间(h) D 2 3 4 1.2.6 扫描电子显微镜观察淀粉颗粒的表面形态变化
使用无菌水将玉米淀粉、液化产物和糖化产物进行三次洗涤,然后进行冷冻干燥。将具有导电的双面胶剪成小长方形,贴在圆形的样品台上,用棉签沾取少部分样品,将其分散地涂在导电胶上[16]。把涂有淀粉粉末的圆形样品台放入镀金装置中,约20 min后将其取出,样品台的高度经校准后放入扫描仪器中观察,拍下电镜图,观察淀粉颗粒的形态变化。
1.2.7 X-射线衍射分析玉米淀粉颗粒的结晶结构
将干燥的样品进行超微粉碎处理,过200目筛。测试时称取0.5 g样品放入测试池中,用载玻片将样品表面压平,厚度均匀。淀粉试样放入X-射线衍射仪中,采用连续扫描方式,广角衍射,特征射线为CuKα,扫描速率为2°/min,扫描区域为5°~50°,步长为0.02°。测定条件为管压40 kV,管流40 mA[17]。
1.2.8 红外光谱分析淀粉短程有序化结构变化
称取溴化钾粉末200 mg置于105 ℃烘箱中至恒质量,称取1 mg样品与100 mg溴化钾粉末,充分混合均匀,用玛瑙研钵研磨混合物后收集,将混合物置于压力7 MPa的条件下,压制成直径为13 mm的薄片,扫描波数范围为500~4000 cm−1,对试样进行红外光谱测定[18]。
1.2.9 液化液和糖化液的组成成分分析
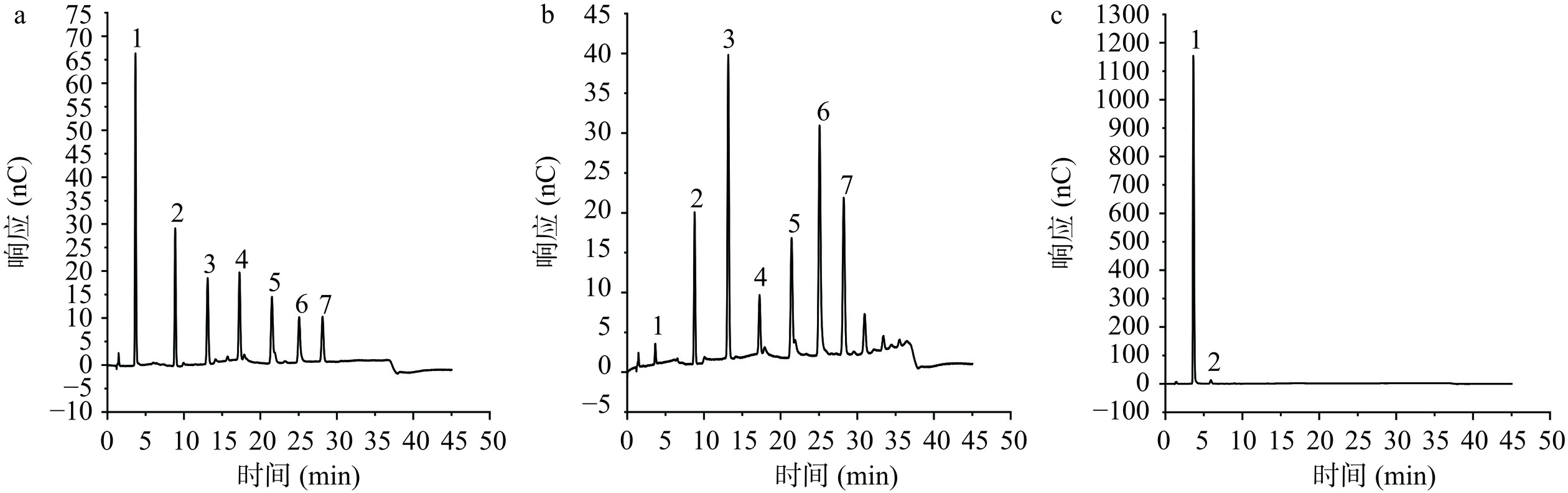
采用安捷伦高效阴离子交换色谱仪,使用CarboPac PA1保护柱(4 mm×50 mm)、CarboPac PA1分析柱(4 mm×250 mm)进行分析;设定柱温30 ℃,流速1.0 mL/min,进样量10 μL,使用脉冲安培检测器作为检测器;洗脱液A为超纯水,洗脱液B为氢氧化钠溶液(200 mmol/L),洗脱液C为氢氧化钠(150 mmol/L)和乙酸钠(500 mmol/L)混合溶液,具体洗脱程序见表2[19]。分别吸取2、5、10、20 μL的100 mg/mL标准品溶液(葡萄糖、麦芽糖、麦芽三糖、麦芽四糖、麦芽五糖、麦芽六糖和麦芽七糖等样品的标准曲线见表3)。然后取5 μL液化液和糖化液样品溶液,按上述色谱条件进样分析,根据保留时间定性分析糖化液和液化液的产物成分。依据各标准曲线计算得到液化液和糖化液中各组分的含量,以所有葡萄糖和麦芽低聚糖的和为总量,计算得到各成分的占比。
表 2 梯度洗脱程序Table 2. Program of gradient elution时间(min) A(%) B(%) C(%) 2 90 10 0 25 80 20 0 28 70 30 0 30 0 100 0 40 0 100 0 45 0 0 100 表 3 葡萄糖和麦芽低聚糖的定量标准曲线Table 3. Standard curves of glucose and maltoligosaccharides名称 标准曲线 葡萄糖 y=21.897x−0.7212,R2=1 麦芽糖 y=11.039x−0.3312,R2=0.9999 麦芽三糖 y=9.1944x−0.2753,R2=0.9999 麦芽四糖 y=9.3136x−0.2624,R2=1 麦芽五糖 y=10.324x−0.4551,R2=1 麦芽六糖 y=6.8517x−0.3147,R2=1 麦芽七糖 y=6.232x−0.2519,R2=1 1.3 数据处理
所有单因素及响应面试验进行3组重复并取平均值,使用Origin Lab进行数据分析,响应面设计和数据处理采用Design Expert12.0分析,使用GraphPad Prism8进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 糖化工艺单因素实验结果
2.1.1 糖化温度对糖化工艺的影响
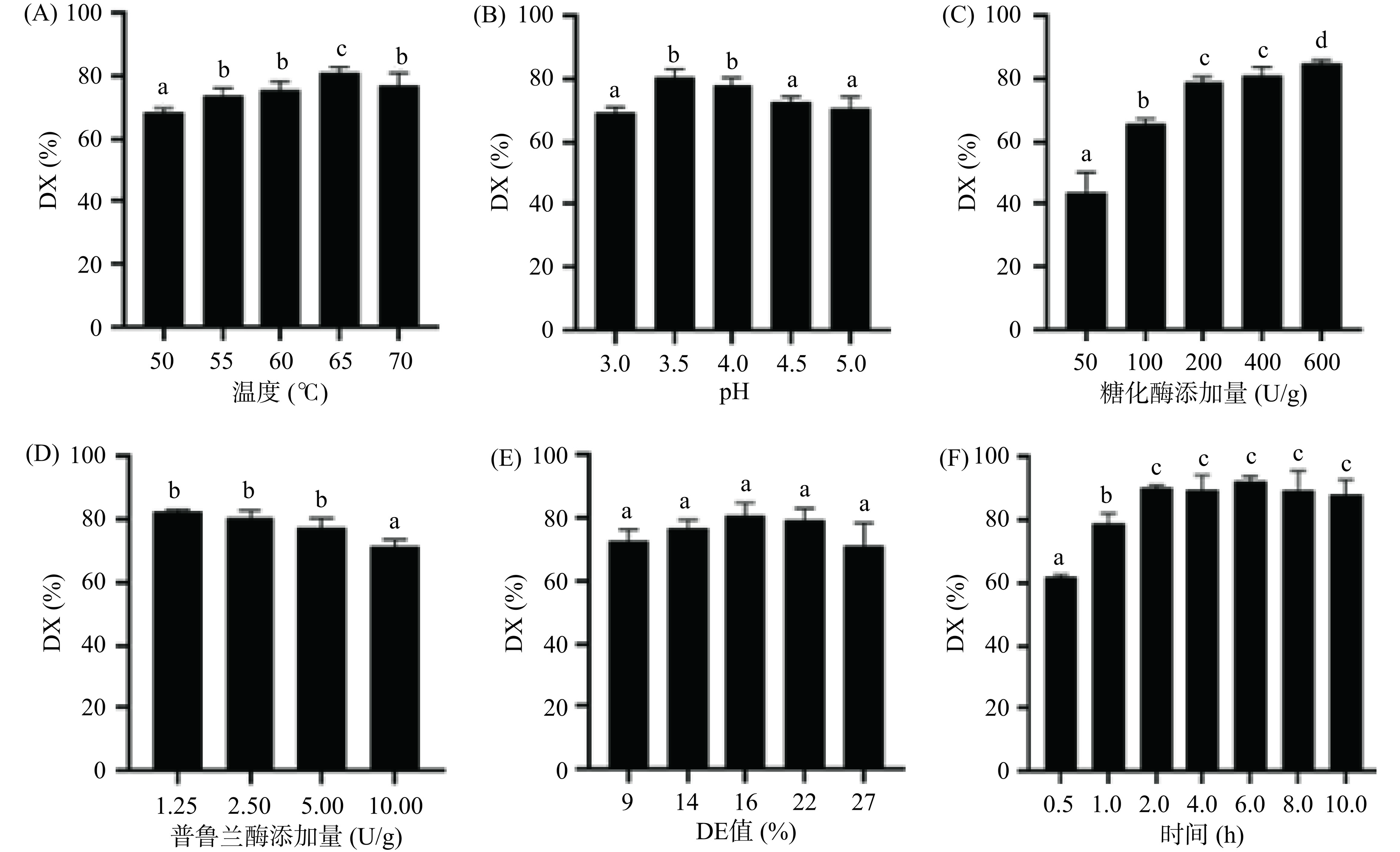
在玉米淀粉制备葡萄糖的反应过程中,糖化酶作为玉米淀粉水解反应的催化剂,温度对糖化酶的活性有显著的影响。由图1A可知,糖化液DX值随着糖化反应温度的不断升高呈现出先升高再下降的趋势。当温度处于65 ℃时,糖化液DX值达到最高(P<0.05),说明65 ℃是糖化酶突变体GluM3的最佳糖化反应温度。这可能是因为随着糖化液温度升高,高温促使淀粉吸水膨胀,酶更加容易进入淀粉内部发挥催化作用。但是当反应温度过高则会破坏酶自身蛋白结构,导致酶活性降低;而且导致淀粉发生糊化现象。因此,选择60~70 ℃作为后续响应面的水平。
2.1.2 pH对糖化工艺的影响
环境pH能改变酶活性部位有关基团的解离状态,从而显著影响酶的催化活性[20−21]。由图1B可知,玉米淀粉糖化液DX值随pH升高也呈现先升高再降低的趋势。在pH3.5时达到最高(P<0.05),说明该糖化酶的最适反应pH为3.5~4.0。所以在玉米淀粉制备葡萄糖的反应过程中,需要先调整液化液再进行糖化反应,以更好促进糖化酶发挥作用。因此选取pH3.0~4.0作为后续响应面优化条件。
2.1.3 糖化酶添加量对糖化工艺的影响
与温度和pH的变化趋势相比,糖化酶添加量对糖化液DX值的影响呈现了不同的趋势[22]。随着糖化酶添加量的增多,DX值呈显著增长趋势(P<0.05)。当糖化酶添加量较少时,糖化液DX值较低;随着糖化酶添加量的增加,糖化液DX值快速上升;但当糖化酶添加量超过200 U/g后,DX值的变化趋势则趋于平缓,在添加600 U/g糖化酶时,DX值达到最高(图1C)。所以选择100~600 U/g作为进一步响应面试验优化的水平。
2.1.4 普鲁兰酶添加量对糖化工艺的影响
淀粉是葡萄糖单体通过糖苷键连接而成的聚合物,线性连接的为直链淀粉,分支连接的为支链淀粉[20]。由于糖化酶属于一种外切酶,其分解支链α-1,6葡萄糖苷键时效率比较低,因此添加一定量的特异分解支链α-1,6葡萄糖苷键的普鲁兰酶可以更有效地促进糖化反应[20]。由图1D可知,在添加1.25、2.5和5 U/g时,糖化液的DX值基本一致;当普鲁兰酶添加量达到10 U/g时,DX值则呈现下降趋势。由此可见普鲁兰酶的用量并不是越多越好,其具体原因需进一步探究[23]。
2.1.5 液化液DE值对糖化工艺的影响
在玉米淀粉的液化过程中,淀粉的长链发生断裂,形成分子量小的短链多糖和糊精,一般用液化液DE值来衡量淀粉的液化程度[6]。液化液DE值对糖化质量的影响较大,液化液DE值过高或过低都会影响糖化质量,降低葡萄糖的生成量,液化液的DE值一般选择15%~20%[6]。本实验研究了9%~27%液化液DE值对糖化液DX值的影响。由图1E可知,在9%~27%液化液DE值条件下,糖化液DX值的差异不显著(P>0.05),说明本实验设置液化液DE值范围没有显著影响后续的糖化工艺。
2.1.6 糖化时间对糖化工艺的影响
由图1F可知,在糖化反应初期2 h内,糖化液的DX值随糖化反应时间的延长显著提高(P<0.05),在糖化反应2 h时DX值达到最大;但随着糖化反应时间的延长,糖化酶DX值基本保持不变。说明在糖化反应初期2 h内,随着糖化反应的进行,淀粉结构开始松散,糖化酶结合淀粉的速度变快;到达一定时间(2 h)之后糖化过程基本完成,DX值不再显著升高;说明选取合理的糖化时间对产物纯度、设备利用率和时间成本至关重要。因此选择2~4 h作为后续响应面优化的条件。
基于以上单因素实验结果,明确了反应温度等6个因素对糖化液DX值的影响及作用范围。考虑到本文主要围绕糖化酶进行研究,糖化酶添加量、酶解温度、pH和糖化时间与糖化酶活力的关系更为密切,且DE值和普鲁兰酶添加量对DX值的影响相对较小,所以后续选取糖化酶添加量、酶解温度、pH和糖化时间这四个因素开展后续响应面试验。
2.2 响应面法优化糖化工艺结果
通过DesignExpert软件[14]对29组试验的响应值进行回归分析,结果见表4,并进行回归方程拟合,得到各试验因子对响应值影响的多元二次回归方程:
表 4 响应面分析试验设计与结果Table 4. Experimental design and results of response surface analysis试验号 A温度
(℃)B pH C糖化酶添加量
(U/g)D时间
(h)DX(%) 1 60 3.0 350 3 71.51±0.01 2 70 3.0 350 3 52.02±0.02 3 60 4.0 350 3 70.12±0.07 4 70 4.0 350 3 80.30±0.01 5 65 3.5 100 2 72.79±0.00 6 65 3.5 600 2 85.00±0.02 7 65 3.5 100 4 77.91±0.04 8 65 3.5 600 4 89.62±0.02 9 60 3.5 350 2 76.94±0.03 10 70 3.5 350 2 76.77±0.04 11 60 3.5 350 4 73.59±0.01 12 70 3.5 350 4 82.40±0.00 13 65 3.0 100 3 64.76±0.05 14 65 4.0 100 3 78.71±0.01 15 65 3.0 600 3 78.29±0.04 16 65 4.0 600 3 86.46±0.03 17 60 3.5 100 3 57.72±0.03 18 70 3.5 100 3 71.59±0.04 19 60 3.5 600 3 75.59±0.01 20 70 3.5 600 3 79.85±0.02 21 65 3.0 350 2 62.88±0.05 22 65 4.0 350 2 82.99±0.02 23 65 3.0 350 4 72.96±0.01 24 65 4.0 350 4 86.05±0.04 25 65 3.5 350 3 88.58±0.02 26 65 3.5 350 3 89.05±0.03 27 65 3.5 350 3 88.81±0.01 28 65 3.5 350 3 90.55±0.02 29 65 3.5 350 3 84.11±0.01 DX=88.22+0.79×A+6.18×B+4.86×C+2.01×D+6.17×AB+0.097×AC+3.00×AD−0.70×BC-0.75×BD−0.12×CD−9.72×A2−8.14×B2−4.36×C2−2.41×D2
回归方程的方差分析结果见表5,其中,F值反映各试验因子对响应值影响的显著性,变量的显著性越高其F值越大。当模型中P<0.05时,证明该模型具有统计学意义[24]。P值越小越显著,该模型的P<0.0001,说明回归模型效果极显著[24]。其中5组条件完全相同决定了模型失拟项的P值,该模型失拟项P值为0.1427>0.05,说明失拟项不显著,说明模型比较稳定,拟合良好,误差小。一次项B、C、二次项A2、B2、C2、交互项AB对结果影响极显著(P<0.01)。根据F值可以看出影响糖化液DX值的因素顺序为:pH>糖化酶添加量>时间>温度。
表 5 回归方程的方差分析Table 5. ANOVA results of the regression equation来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 2422.63 14 173.05 11.75 <0.0001 ** A 25.40 1 25.40 1.73 0.2101 B 563.21 1 563.21 38.25 <0.0001 ** C 424.00 1 424.00 28.80 <0.0001 ** D 52.75 1 52.75 3.58 0.0792 AB 220.08 1 220.08 14.95 0.0017 ** AC 23.09 1 23.09 1.57 0.2310 AD 20.16 1 20.16 1.37 0.2615 BC 8.35 1 8.35 0.57 0.4638 BD 12.32 1 12.32 0.84 0.3758 CD 0.063 1 0.063 4.245E-003 0.9490 A2 762.78 1 762.78 51.81 <0.0001 ** B2 470.07 1 470.07 31.93 <0.0001 ** C2 137.73 1 137.73 9.35 0.0085 ** D2 23.58 1 23.58 1.60 0.2263 残差项 206.12 14 14.72 失拟项 182.63 10 18.26 3.11 0.1427 误差 23.49 4 5.87 总和 2628.75 28 注:**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。 通过Design Expert软件得到温度与pH交互作用的响应曲面及等高线图,曲面图越陡表示交互作用越强,曲面图越平表示交互作用越弱[25]。结果表明,温度和pH交互作用对糖化液DX值的交互影响显著(图2),与上述方差分析结果一致。
通过Design Expert软件分析得到最佳糖化工艺条件为糖化工艺温度66.09 ℃、pH3.68、糖化酶添加量431.84 U/g、时间2.98 h,DX值理论预测值为91.04%。结合实验实际情况和操作便利性,最终选择温度66 ℃、pH3.7、糖化酶添加量450 U/g、时间3 h。为了验证模型的准确性,采取优化后的糖化条件做验证实验,3次平行,DX值实际平均值为92.68%,与理论预测值基本一致,表明此回归方程用于预测糖化酶的糖化工艺条件是可行的。此外,本实验优化产物的DX值高于目前工业化制糖产品的平均DX值(90%)[14],说明本实验糖化条件优化效果良好,具有良好的实际应用价值。
2.3 扫描电镜观察酶解后淀粉颗粒表面变化
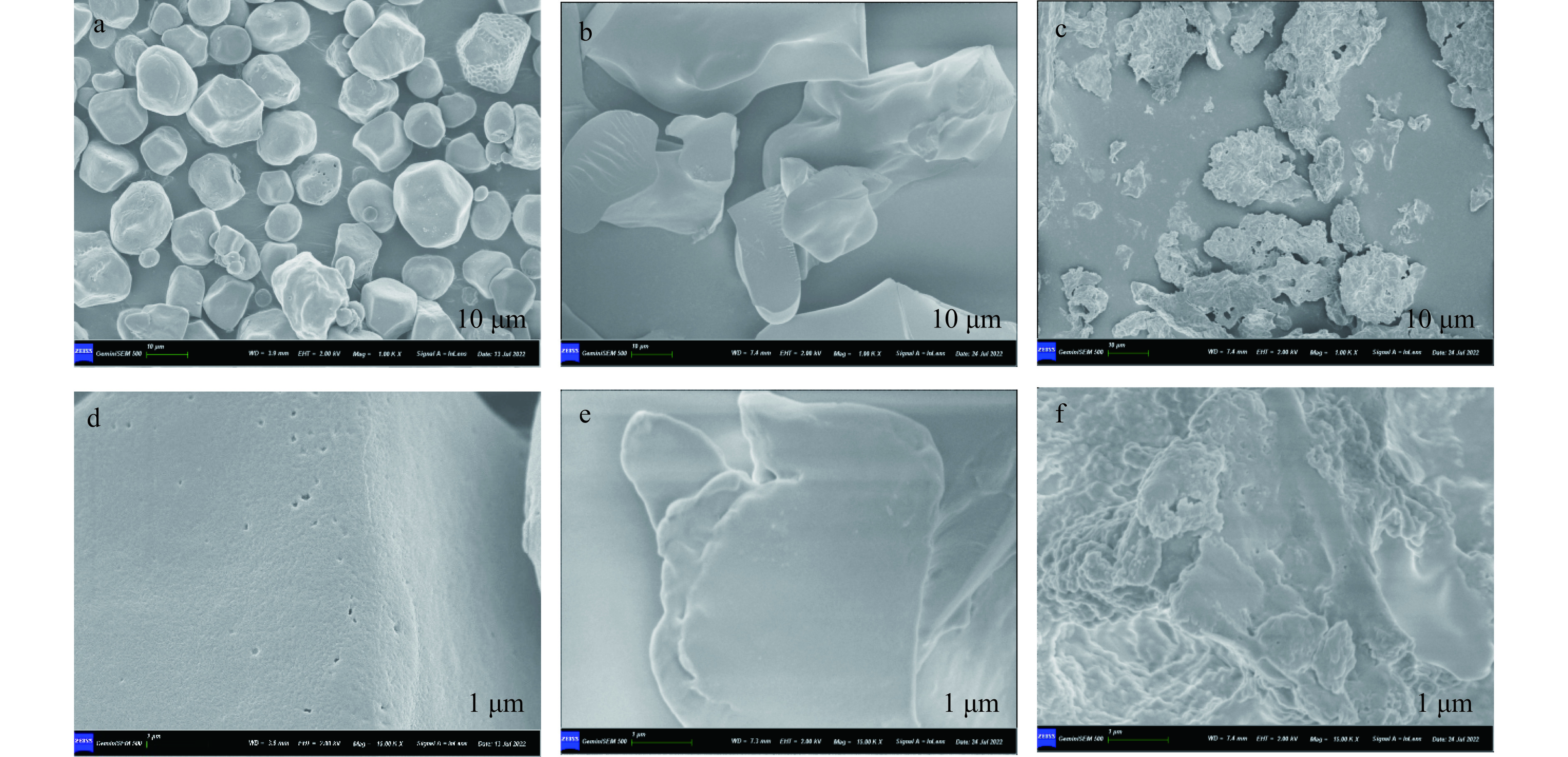
通过扫描电镜图像(图3)可以直接观察到玉米淀粉在液化和糖化过程中的表面形态,在淀粉酶酶解前的玉米淀粉颗粒呈现完整颗粒形态,形状近似椭球形、少数呈无规则多角形,表面光滑且带有微孔(图3a、3d),与蒲华寅等[26]、王郡瑶等[27]观察到淀粉呈完整的颗粒状一致 ,玉米淀粉是非常完整的颗粒,且分布比较稀松;液化后淀粉表面形态发生显著变化,淀粉颗粒表面被侵蚀,出现裂痕和凹坑(图3b、3e);而糖化后淀粉的侵蚀现象更加明显,玉米淀粉形成无规则形状,表面变得非常粗糙,出现了不规则的凹陷(图3c、3f)。玉米淀粉从光滑完整颗粒酶解成支离破碎不规则碎屑,说明玉米淀粉在淀粉酶、糖化酶和普鲁兰酶的作用下被逐步水解。
2.4 X-射线衍射观察玉米淀粉结晶结构变化
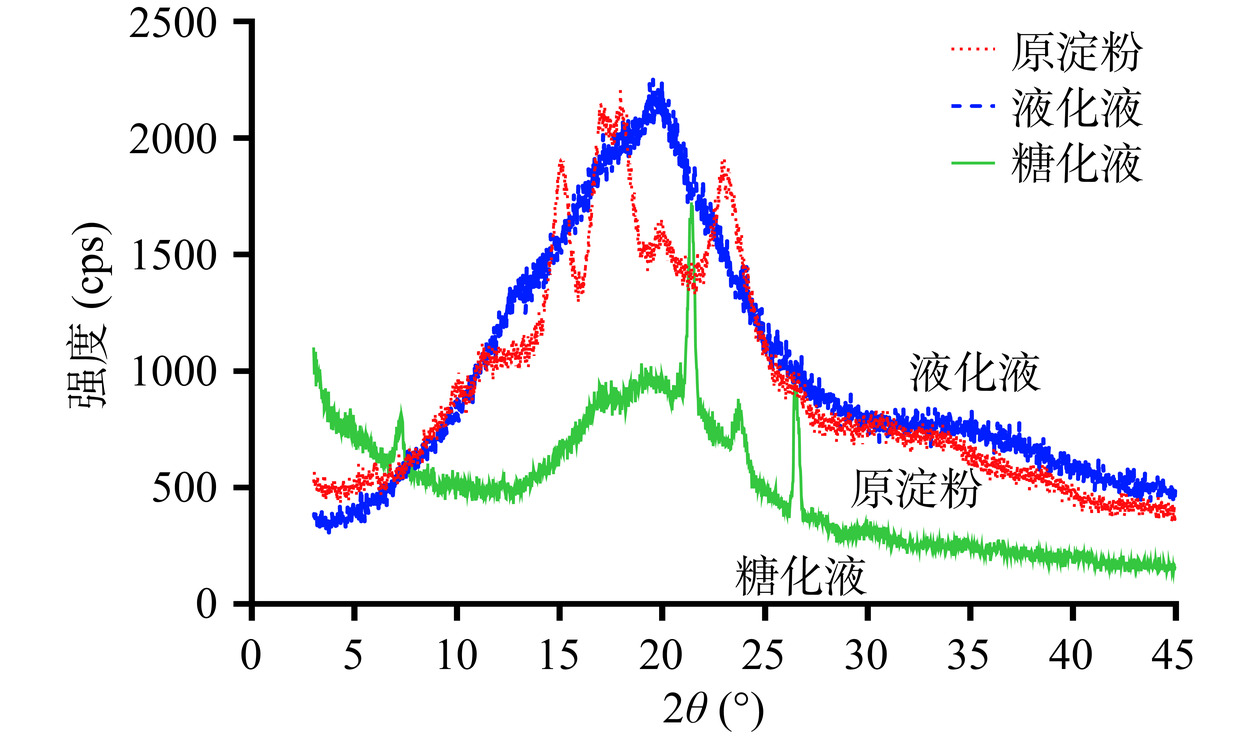
淀粉颗粒是半结晶的,具有各种结晶结构和结晶度,对淀粉的物化功能有重要影响。通常使用X射线衍射(X-ray diffraction)方法来分析淀粉颗粒结晶区和非结晶区的差异[28]。不同来源的淀粉在X-射线衍射下显示出各自的特征衍射峰,例如玉米和小麦等谷物类淀粉在15°、17°、18°和23°处有强峰,属于A型晶型结构;马铃薯和红薯等根茎类淀粉在5.6°、17°、22°和24°有较强的衍射峰,属于B型晶型结构[29]。如图4所示,玉米淀粉在15°、17°、18°和23°处呈现出明显的衍射峰,呈现出A型结构,与前人报道的一致[28];在液化产物的X-射线衍射峰图中,A型的特征峰基本消失,只在20°呈现出单一峰;而糖化产物的X-射线衍射峰图进一步发生改变,在7°、22°、24°和27°处呈现较强的衍射峰。X-射线衍射峰型的剧烈变化表明,液化和糖化过程使玉米淀粉内部的晶体结构遭到了一定程度的破坏。
2.5 红外光谱分析淀粉短程有序化结构变化
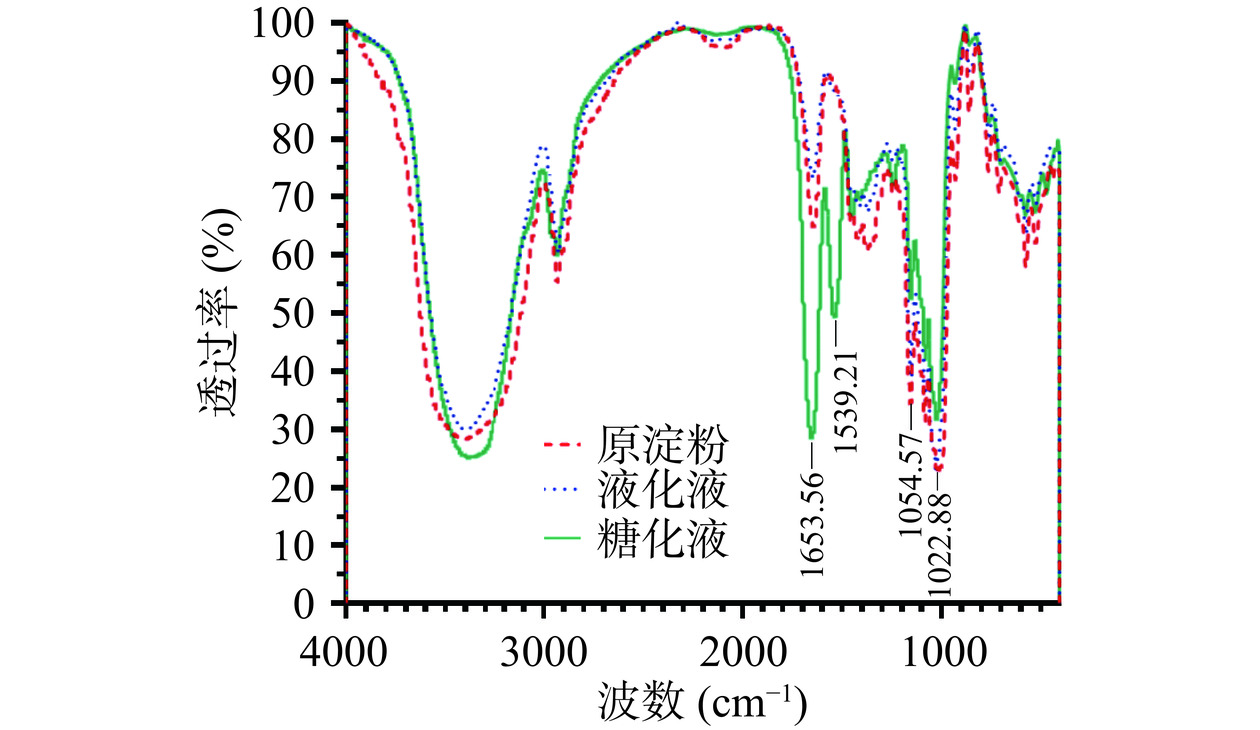
如图5所示,未处理玉米淀粉、液化液和糖化液的特征吸收峰振动基本保持一致,没有产生明显新的峰和新的基团,说明糖化和液化过程并没有引起淀粉基本化学键的变化。与液化液相比,糖化液的特征吸收峰未发生剧烈变化,但是糖化液在1539 cm−1和1653 cm−1处出现了双峰,且透过率增加,这可能是由糖化后淀粉颗粒内部破碎严重导致的,淀粉颗粒变得疏松可结合更多的H2O分子,造成H-O-H键弯曲振动导致的吸收峰增加。此外,1047和1022 cm−1的红外吸收峰分别代表了淀粉的有序化和无定形区域,其比值(R1047/1022)可作为量化淀粉短程有序化程度的指标[30]。未处理淀粉R1047/1022比值为1.16,而糖化液的R1047/1022比值降低为1.11,表明糖化后玉米淀粉短程有序化程度降低[31]。
2.6 液化液和糖化液的糖组分分析
高效阴离子交换色谱安培检测法凭借灵敏度高、短时高效、操作简单以及重复性好等优点,可用于分析几乎所有的单糖和大部分低聚糖[27]。本实验以样品浓度为横坐标,峰面积为纵坐标,并根据各标准曲线计算获得葡萄糖和各低聚糖在液化液和糖化液中的含量。结果发现,在液化液中可以检测到多种麦芽低聚糖,包括72.12 mg/mL麦芽糖、193.61 mg/mL麦芽三糖、44.86 mg/mL麦芽四糖、108.22 mg/mL麦芽五糖、268.30 mg/mL麦芽六糖、103.14 mg/mL麦芽七糖,也有少量葡萄糖(1.27%)存在;在糖化过程完成后,糖化液以葡萄糖为主,达到1597.88 mg/mL(占99.34%)(图6c),可见液化液中多糖在糖化过程中被有效转化为葡萄糖,说明糖化酶和普鲁兰酶在糖化过程中发挥了重要作用。
3. 结论
本文研究了低转糖苷活力糖化酶突变体对玉米淀粉的糖化工艺,并确定在最佳工艺条件(液化DE值16%,糖化反应pH3.7,糖化酶450 U/g,普鲁兰酶1.25 U/g,温度66 ℃,反应3 h),糖化液DX值可达到92.68%;进一步分析糖化过程中淀粉微观结构的变化规律,利用电子扫描电镜可以观察到玉米淀粉从光滑完整颗粒酶解成残破的碎屑;利用X-射线衍射法发现淀粉内部的晶体结构遭到了一定程度的破坏;红外光谱分析发现糖化后玉米淀粉短程有序化程度降低;利用高效液相色谱法分析发现液化液以麦芽六糖等多糖为主,经糖化酶和普鲁兰酶共同作用下,多糖基本完全生成葡萄糖。该研究为低转糖苷活力糖化酶突变体后续糖化应用提供了依据和理论基础。
-
表 1 响应面因素水平设计
Table 1 Response surface factor level design
因素 编码 水平编码值 −1 0 1 温度(℃) A 60 65 70 pH B 3.0 3.5 4.0 糖化酶添加量(U/g) C 100 350 600 时间(h) D 2 3 4 表 2 梯度洗脱程序
Table 2 Program of gradient elution
时间(min) A(%) B(%) C(%) 2 90 10 0 25 80 20 0 28 70 30 0 30 0 100 0 40 0 100 0 45 0 0 100 表 3 葡萄糖和麦芽低聚糖的定量标准曲线
Table 3 Standard curves of glucose and maltoligosaccharides
名称 标准曲线 葡萄糖 y=21.897x−0.7212,R2=1 麦芽糖 y=11.039x−0.3312,R2=0.9999 麦芽三糖 y=9.1944x−0.2753,R2=0.9999 麦芽四糖 y=9.3136x−0.2624,R2=1 麦芽五糖 y=10.324x−0.4551,R2=1 麦芽六糖 y=6.8517x−0.3147,R2=1 麦芽七糖 y=6.232x−0.2519,R2=1 表 4 响应面分析试验设计与结果
Table 4 Experimental design and results of response surface analysis
试验号 A温度
(℃)B pH C糖化酶添加量
(U/g)D时间
(h)DX(%) 1 60 3.0 350 3 71.51±0.01 2 70 3.0 350 3 52.02±0.02 3 60 4.0 350 3 70.12±0.07 4 70 4.0 350 3 80.30±0.01 5 65 3.5 100 2 72.79±0.00 6 65 3.5 600 2 85.00±0.02 7 65 3.5 100 4 77.91±0.04 8 65 3.5 600 4 89.62±0.02 9 60 3.5 350 2 76.94±0.03 10 70 3.5 350 2 76.77±0.04 11 60 3.5 350 4 73.59±0.01 12 70 3.5 350 4 82.40±0.00 13 65 3.0 100 3 64.76±0.05 14 65 4.0 100 3 78.71±0.01 15 65 3.0 600 3 78.29±0.04 16 65 4.0 600 3 86.46±0.03 17 60 3.5 100 3 57.72±0.03 18 70 3.5 100 3 71.59±0.04 19 60 3.5 600 3 75.59±0.01 20 70 3.5 600 3 79.85±0.02 21 65 3.0 350 2 62.88±0.05 22 65 4.0 350 2 82.99±0.02 23 65 3.0 350 4 72.96±0.01 24 65 4.0 350 4 86.05±0.04 25 65 3.5 350 3 88.58±0.02 26 65 3.5 350 3 89.05±0.03 27 65 3.5 350 3 88.81±0.01 28 65 3.5 350 3 90.55±0.02 29 65 3.5 350 3 84.11±0.01 表 5 回归方程的方差分析
Table 5 ANOVA results of the regression equation
来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 2422.63 14 173.05 11.75 <0.0001 ** A 25.40 1 25.40 1.73 0.2101 B 563.21 1 563.21 38.25 <0.0001 ** C 424.00 1 424.00 28.80 <0.0001 ** D 52.75 1 52.75 3.58 0.0792 AB 220.08 1 220.08 14.95 0.0017 ** AC 23.09 1 23.09 1.57 0.2310 AD 20.16 1 20.16 1.37 0.2615 BC 8.35 1 8.35 0.57 0.4638 BD 12.32 1 12.32 0.84 0.3758 CD 0.063 1 0.063 4.245E-003 0.9490 A2 762.78 1 762.78 51.81 <0.0001 ** B2 470.07 1 470.07 31.93 <0.0001 ** C2 137.73 1 137.73 9.35 0.0085 ** D2 23.58 1 23.58 1.60 0.2263 残差项 206.12 14 14.72 失拟项 182.63 10 18.26 3.11 0.1427 误差 23.49 4 5.87 总和 2628.75 28 注:**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] WANG B, DONG Y, FANG Y, et al. Effects of different moisture contents on the structure and properties of corn starch during extrusion[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,368:130804. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130804
[2] PARASHAR D T, SATYANARAYANA. An insight into ameliorating production, catalytic efficiency, thermostability and starch saccharification of acid-stable α-amylases from acidopHiles[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology,2018,6:125. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2018.00125
[3] GANDRA J R, OLIVEIRA E R, TAKIYA C S, et al. Amylolytic activity and chemical composition of rehydrated ground maize ensiled with α-amylase or glucoamylase[J]. The Journal of Agricultural Science,2019,157(5):449−455. doi: 10.1017/S0021859619000698
[4] ALMEIDA P Z, MESSIAS J M, PEREIRA M G, et al. Mixture design of starchy substrates hydrolysis by an immobilized glucoamylase from Aspergillus brasiliensis[J]. Biocatalysis and Biotransformation,2017,36(5):389−395.
[5] 高振鹏, 岳田利, 袁亚宏, 等. 超声波对糖化酶酶解作用的影响[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(10):138−142. [GAO Z P, YUE T L, YUAN Y H, et al. The effect of ultrasound on enzymatic hydrolysis of saccharifying enzymes[J]. Journal of Agricultural Machinery,2012,43(10):138−142.] doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2012.10.025 GAO Z P, YUE T L, YUAN Y H, et al. The effect of ultrasound on enzymatic hydrolysis of saccharifying enzymes[J]. Journal of Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(10): 138−142. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2012.10.025
[6] 王志. 异源表达α-葡萄糖苷酶高效合成低聚异麦芽糖[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2023. [WANG Z. Efficient synthesis of oligomeric isomaltose using heterologous expression of α-glucosidase[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2023.] WANG Z. Efficient synthesis of oligomeric isomaltose using heterologous expression of α-glucosidase[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2023.
[7] 黎明, 路福平. 糖化%酶突变体及其应用:中国, CN202210619541.7[P]. 2023-07-07. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=F5NaIWgMQ1CXjGelDt3AgZdn1_Gkca5g_aio6TBM5ejUQXMkhrx4k4G715gWEBtmpG7M5c0RME2RzKaZ46VjTKKWEKKj0-PRRTNbKOmfFAXue5KrKR4GmOLqThOjooL9&uniplatform=NZKPT&flag=copy. [LI M, LU F P. Glycase mutant and its application:China, CN202210619541.7[P]. 2023-07-07. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=F5NaIWgMQ1CXjGelDt3AgZdn1_Gkca5g_aio6TBM5ejUQXMkhrx4k4G715gWEBtmpG7M5c0RME2RzKaZ46VjTKKWEKKj0-PRRTNbKOmfFAXue5KrKR4GmOLqThOjooL9&uniplatform=NZKPT&flag=copy.] LI M, LU F P. Glycase mutant and its application: China, CN202210619541.7[P]. 2023-07-07. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=F5NaIWgMQ1CXjGelDt3AgZdn1_Gkca5g_aio6TBM5ejUQXMkhrx4k4G715gWEBtmpG7M5c0RME2RzKaZ46VjTKKWEKKj0-PRRTNbKOmfFAXue5KrKR4GmOLqThOjooL9&uniplatform=NZKPT&flag=copy.
[8] 赵凯, 许鹏举, 谷广烨. 3, 5-二硝基水杨酸比色法测定还原糖含量的研究[J]. 食品科学,2008(8):534−536. [ZHAO K, XU P J, GU G Y. Study on the colorimetric determination of reducing sugar content using 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid[J]. Food Science,2008(8):534−536.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2008.08.127 ZHAO K, XU P J, GU G Y. Study on the colorimetric determination of reducing sugar content using 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid[J]. Food Science, 2008(8): 534−536. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2008.08.127
[9] 孙铭泽, 宋遥遥, 卢晓霆. 玉米粉液化及糖化工艺条件优化[J]. 中国酿造,2021,40(3):186−190. [SUN M Z, SONG Y Y, LU X T. Optimization of corn flour liquefaction and saccharification process conditions[J]. China Brewing,2021,40(3):186−190.] doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2021.03.035 SUN M Z, SONG Y Y, LU X T. Optimization of corn flour liquefaction and saccharification process conditions[J]. China Brewing, 2021, 40(3): 186−190. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2021.03.035
[10] 于朝. 低转糖苷酶活力糖化酶的基因挖掘及淀粉糖化工艺研究[D]. 天津:天津科技大学, 2023. [YU Z. Gene mining and starch saccharification process of low transglycosidase activity glycase[D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2023.] YU Z. Gene mining and starch saccharification process of low transglycosidase activity glycase[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2023.
[11] 雷英杰, 于孝民, 任元元, 等. 玉米淀粉糖化反应影响因素研究[J]. 粮油食品科技,2023,31(3):48−54. [LEI Y J, YU X M, REN Y Y, et al. Study on the influencing factors of corn starch saccharification reaction[J]. Grain and Oil Food Technology,2023,31(3):48−54.] LEI Y J, YU X M, REN Y Y, et al. Study on the influencing factors of corn starch saccharification reaction[J]. Grain and Oil Food Technology, 2023, 31(3): 48−54.
[12] 刘露露, 王若兰, 吴远, 等. 小麦淀粉加工废液制备葡萄糖浆的糖化工艺优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(9):131−135,227. [LIU L L, WANG R L, WU Y, et al. Optimization of saccharification process for preparing glucose syrup from wheat starch processing waste liquid[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(9):131−135,227.] LIU L L, WANG R L, WU Y, et al. Optimization of saccharification process for preparing glucose syrup from wheat starch processing waste liquid[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2018, 39(9): 131−135,227.
[13] 于远洋. 玉米淀粉糖生产关键酶系的优化[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2017. [YU Y Y. Optimization of key enzyme systems for corn starch sugar production[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2017.] YU Y Y. Optimization of key enzyme systems for corn starch sugar production[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017.
[14] 孟悦, 王英哲, 田志刚, 等. 玉米粉制备葡萄糖的糖化工艺优化[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(18):97−101. [MENG Y, WANG Y Z, TIAN Z G, et al. Optimization of saccharification process for preparing glucose from corn flour[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(18):97−101.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.18.016 MENG Y, WANG Y Z, TIAN Z G, et al. Optimization of saccharification process for preparing glucose from corn flour[J]. Food Research and Development, 2019, 40(18): 97−101. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.18.016
[15] 李金婷, 钱心燚, 雍一丹, 等. 蝉花多糖酶法辅助双水相提取工艺优化及其抗氧化、降血糖和降血脂活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2024,45(12):179−188. [LI J T, QIAN X Y, YONG Y D, et al. Optimization of cicada flower polysaccharide enzymatic assisted two phase extraction process and analysis of its antioxidant, hypoglycemic, and hypolipidemic activities[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2024,45(12):179−188.] LI J T, QIAN X Y, YONG Y D, et al. Optimization of cicada flower polysaccharide enzymatic assisted two phase extraction process and analysis of its antioxidant, hypoglycemic, and hypolipidemic activities[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2024, 45(12): 179−188.
[16] 郁映涛, 肖刘洋, 杨晓凡, 等. 超声波结合酶解对玉米淀粉多层级结构及其吸附性能的影响[J]. 食品科学,2024,45(5):174−183. [YU Y T, XIAO L Y, YANG X F, et al. The effect of ultrasound combined with enzymatic hydrolysis on the multilayer structure and adsorption performance of corn starch[J]. Food Science,2024,45(5):174−183.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230323-233 YU Y T, XIAO L Y, YANG X F, et al. The effect of ultrasound combined with enzymatic hydrolysis on the multilayer structure and adsorption performance of corn starch[J]. Food Science, 2024, 45(5): 174−183. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230323-233
[17] OSKAYBAŞ-EMLEK B, ÖZBEY A, AYDEMIR L Y, et al. Production of buckwheat starch-myristic acid complexes and effect of reaction conditions on the physicochemical properties, X-ray pattern and FT-IR spectra[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,207:978−989. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.03.189
[18] 秦智欣, 郑明珠, 林楠, 等. 复合酶法大黄米多孔淀粉的制备及其微观结构和理化性质[J]. 中国食品学报,2023,23(5):138−150. [QIN Z X, ZHENG M Z, LIN N, et al. Preparation, microstructure, and physicochemical properties of porous starch from rhubarb rice using composite enzyme method[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2023,23(5):138−150.] QIN Z X, ZHENG M Z, LIN N, et al. Preparation, microstructure, and physicochemical properties of porous starch from rhubarb rice using composite enzyme method[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science, 2023, 23(5): 138−150.
[19] 彭丽诗, 陈琼, 黄盼, 等. 离子色谱-脉冲安培法同时测定食品中9种糖和糖醇的含量[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(9):250−254,259. [PENG L S, CHEN Q, HUANG P, et al. Simultaneous determination of nine sugars and sugar alcohols in food by ion chromatography pulse amperometry[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(9):250−254,259.] PENG L S, CHEN Q, HUANG P, et al. Simultaneous determination of nine sugars and sugar alcohols in food by ion chromatography pulse amperometry[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(9): 250−254,259.
[20] 彭念, 陈婷婷, 王璐, 等. 纤维二糖磷酸化酶表达条件的优化及其酶学性质研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2024,50(16):125−131. [PENG N, CHEN T T, WANG L, et al. Optimization of expression conditions and study of enzymatic properties of cellulose disaccharide phosphorylase[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2024,50(16):125−131.] PENG N, CHEN T T, WANG L, et al. Optimization of expression conditions and study of enzymatic properties of cellulose disaccharide phosphorylase[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2024, 50(16): 125−131.
[21] 李保军. 糖化酶发酵工艺优化及糖化酶原液在酒精发酵中的应用[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2017. [LI B J. Optimization of saccharifying enzyme fermentation process and application of saccharifying enzyme stock in alcohol fermentation[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University, 2017.] LI B J. Optimization of saccharifying enzyme fermentation process and application of saccharifying enzyme stock in alcohol fermentation[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017.
[22] 陈乾睿, 赵锐环, 徐志强, 等. 双酶法优化禄丰香醋糖化工艺[J]. 中国调味品,2024,49(5):80−88. [CHEN Q R, ZHAO R H, XU Z Q, et al. The double enzymatic method optimized the saccharification process of Lufeng balsamic vinegar[J]. China Condiment,2024,49(5):80−88.] CHEN Q R, ZHAO R H, XU Z Q, et al. The double enzymatic method optimized the saccharification process of Lufeng balsamic vinegar[J]. China Condiment, 2024, 49(5): 80−88.
[23] 岳婉婷. 玉米淀粉酶法水解制糖及纯化过程的研究[J]. 科技与企业,2014(23):203. [YUE W T. Research on the hydrolysis and purification process of corn starch for sugar production[J]. Science and Technology and Enterprise,2014(23):203.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9207.2014.23.190 YUE W T. Research on the hydrolysis and purification process of corn starch for sugar production[J]. Science and Technology and Enterprise, 2014(23): 203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9207.2014.23.190
[24] 高熳熳, 刘腾云, 白俊岩, 等. 响应面法优化麦汁糖化工艺条件[J]. 中国酿造,2019,38(8):127−131. [GAO M M, LIU T Y, BAI J Y, et al. Optimization of wort saccharification process conditions using response surface methodology[J]. Chinese Brewing,2019,38(8):127−131.] doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2019.08.025 GAO M M, LIU T Y, BAI J Y, et al. Optimization of wort saccharification process conditions using response surface methodology[J]. Chinese Brewing, 2019, 38(8): 127−131. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2019.08.025
[25] ZHANG X, DU L, JIN W. Screening and optimization of conditions for the adsorption of Cd in serpentine by using response surface methodology[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2022,19(24):16848. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416848
[26] 蒲华寅, 陈旭艳, 郭思敏. 微波处理对不同链支比玉米淀粉结构及理化性质的影响[J]. 陕西科技大学学报,2022,40(2):39−45. [PU H Y, CHEN X Y, GUO S M. The effect of microwave treatment on the structure and physicochemical properties of corn starch with different chain to branch ratios[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science and Technology,2022,40(2):39−45.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5811.2022.02.007 PU H Y, CHEN X Y, GUO S M. The effect of microwave treatment on the structure and physicochemical properties of corn starch with different chain to branch ratios[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2022, 40(2): 39−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5811.2022.02.007
[27] 王郡瑶, 程显隆, 李明华, 等. 基于衍生化-HPLC测定酶解葡萄糖的方法评价六神曲中糖化酶活力[J]. 药物分析杂志,2022,42(1):121−126. [WANG J Y, CHENG X L, LI M H, et al. Evaluation of glycosylase activity in Liushenqu based on derivatization HPLC method for enzymatic hydrolysis of glucose[J]. Journal of Drug Analysis,2022,42(1):121−126.] WANG J Y, CHENG X L, LI M H, et al. Evaluation of glycosylase activity in Liushenqu based on derivatization HPLC method for enzymatic hydrolysis of glucose[J]. Journal of Drug Analysis, 2022, 42(1): 121−126.
[28] WANG J, GUO K, FAN X, et al. Physicochemical properties of C-type starch from root tuber of Apios fortunei in comparison with maize, potato, and pea starches[J]. Molecules,2018,23(9):2132. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092132
[29] 杨景峰, 罗志刚, 罗发兴. 淀粉晶体结构研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2007(7):240−243. [YANG J F, LUO Z G, LUO F X. Research progress on starch crystal structure[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2007(7):240−243.] YANG J F, LUO Z G, LUO F X. Research progress on starch crystal structure[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2007(7): 240−243.
[30] GARCIA-DIAZ S, HERNANDEZ-JAIMES C, ESCALONA-BUENDIA H B, et al. Effects of CaCO3 treatment on the morphology, crystallinity, rheology and hydrolysis of gelatinized maize starch dispersions[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,207:139−147. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.03.095
[31] 王宏伟, 余颜圃, 张菁, 等. 冻藏处理对糯玉米淀粉微观结构和理化特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(14):35−40. [WANG H W, YU Y P, ZHANG J, et al. The effect of frozen storage on the microstructure and physicochemical properties of glutinous corn starch[J]. Food Science,2022,43(14):35−40.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20211018-198 WANG H W, YU Y P, ZHANG J, et al. The effect of frozen storage on the microstructure and physicochemical properties of glutinous corn starch[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(14): 35−40. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20211018-198
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 付严昆,蔡语铮,冯志强,陈思如,王田林,宋莲军,李天歌. 核桃肽通过促进白色脂肪棕色化预防肥胖的作用. 食品工业科技. 2025(03): 376-385 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 张文凯,洪滔,郑梓泓,李雨露,徐佳玲,刘志勇. 肝纯片对实验性肥胖高脂血症大鼠生理生化指标的影响. 江西科学. 2024(04): 698-703 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



