Screening of α-Glucosidase Inhibitors in Cyclocarya paliurus Extracts Based on Affinity Ultrafiltration-Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Combined with Correlation Analysis
-
摘要: 目的:为快速筛选青钱柳提取物中的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂,采用亲和超滤-液质联用技术结合相关性分析探究其有效成分与酶抑制活性间的关系。方法:运用大孔吸附树脂,建立青钱柳不同浓度乙醇洗脱液中相同化学成分量变化矩阵(X矩阵);分析各乙醇洗脱部位体外α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制作用,构建效应矩阵(Y矩阵);通过偏最小二乘回归法(Partial least squares regression,PLS)预测潜在的活性成分与亲和超滤法(Affinity ultrafiltration,AUF)所筛选的化合物进行比对并通过分子对接进行验证。结果:青钱柳50%乙醇总提取物IC50值为14.8 μg/mL,经大孔树脂吸附后的10%~80%浓度乙醇洗脱液IC50为5.4~204.1 μg/mL。通过AUF法与相关性分析在正、负离子模式下共鉴定出10种青钱柳潜在的活性成分,其中鉴定出8种三萜类化合物、2种黄酮类化合物。进一步的分子对接结果表明,上述10种活性成分与α-葡萄糖苷酶对接的结合能小于−7.0 kcal·mol−1,其中熊果酸内酯的结合能最低(−10.0 kcal·mol−1)。结论:AUF与相关性分析相结合能快速筛选出青钱柳提取物中潜在的α-葡萄苷酶抑制剂,本研究结果可为进一步明确青钱柳活性成分奠定基础,为其活性成分质量控制研究、功能性食品开发的深入研究提供依据。
-
关键词:
- 青钱柳 /
- 亲和超滤 /
- 超高效液相色谱-四级杆飞行时间串联质谱法(UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS) /
- 偏最小二乘回归法(PLS) /
- 分子对接
Abstract: Objective: To rapidly screen α-glucosidase inhibitors in the extract of Cyclocarya paliurus, the affinity ultrafiltration-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry technique combined with correlation analysis were used to explore the relationship between the active components and enzyme inhibitory activities. Methods: The change matrix (X matrix) of the same chemical component in ethanol elutes of different concentrations of Cyclocarya paliurus was established by using macroporous adsorption resin. The inhibitory effects of α-glucosidase at each ethanol elution site in vitro were analyzed and the effect matrix (Y matrix) was constructed. Potential active ingredients were predicted by partial least squares regression (PLS) to be compared with compounds screened by affinity ultrafiltration (AUF) and validated by molecular docking. Results: The IC50 value of 50% ethanol extract of Cyclocarya paliurus was 14.8 μg/mL, while the IC50 values of the ethanol elution of concentrations ranging from 10% to 80% after adsorption on microporous resin ranged from 5.4 μg/mL to 204.1 μg/mL. Through AUF combined with correlation analysis, a total of 10 potential active components of Cyclocarya paliurus were identified in both positive and negative ion modes. Among them, 8 triterpenoids and 2 flavonoids were identified. Further molecular docking results showed that the binding energy of the 10 active ingredients to α-glucosidase was less than −7.0 kcal·mol−1, and the binding energy of ursolic acid lactone was the lowest (−10.0 kcal·mol−1). Conclusion: The combination of AUF with correlation analysis can quickly and effectively screen potential α-glucosidase inhibitors from Cyclocarya paliurus extracts. The results of this study can lay a foundation for further identifying the active ingredients of Cyclocarya paliurus and provide a basis for further research on the quality control of active ingredients and the development of functional food. -
青钱柳(Cyclocarya paliurus),又名甜茶树、金钱树、金钱柳、青钱李等,是中国南方特有的单种属植物。具有清热解毒、生津止渴、抗炎杀虫、祛风止痒等多种传统功效,是国家近年批准的新食品原料,为药食两用植物[1]。现代研究表明青钱柳叶具有抗炎[2]、降血脂[3]、降血糖[4]和抗氧化[5]等功效,广泛应用于治疗代谢性疾病,包括高脂血症、糖尿病和高血压,作用机制包括增强对葡萄糖耐受力、改善胰岛素抵抗[6]、抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性[7]等。其主要含有黄酮、三萜、多糖以及有机酸类等多种化学成分[8]。青钱柳成分复杂,且药效物质基础尚不明确,多以黄酮类成分或有机酸类作为青钱柳的活性成分[9],不利于相关产品的深入开发与利用,需要进一步用现代科学方法对其活性成分进行分析研究。
本研究采用大孔吸附树脂与超高效液相色谱-四级杆飞行时间串联质谱法(Ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry,UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS),对青钱柳不同乙醇浓度洗脱液中相同化学组分峰面积进行统计,构建量变化矩阵(X矩阵)并通过体外α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制模型构建效应矩阵(Y矩阵),采用偏最小二乘回归法(Partial least squares regression,PLS)进行量-效(X-Y)矩阵相关性分析,将PLS分析结果与亲和超滤法(Affinity ultrafiltration,AUF)进行交集验证,初步确定青钱柳提取物中抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶的主要活性成分,进一步为青钱柳叶的药效成分筛选、青钱柳叶功能食品领域的开发等奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
青钱柳干燥叶(批号20210618) 江西省修水县,经江西中医大学舒任庚教授鉴定为胡桃科青钱柳属植物青钱柳的干燥叶;α-葡萄糖苷酶冻干粉(33 units/mg)、阿卡波糖 分析纯,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;甲醇、乙腈 色谱级,德国Merck公司;95%乙醇 食品级,阿普斯戴尔生物科技有限公司;HPD 100大孔吸附树脂 药用级,郑州和成新材料科技有限公司;其他试剂均为分析纯。
R-220 SE型大型旋转蒸发仪 瑞士Rotavapor公司;SL 8R型台式高速冷冻离心机、SPD131DDA-P1-230型离心浓缩系统 赛默飞世尔科技有限公司;SpectraMax Plus 384酶标仪 美谷分子仪器有限公司;ZDX型振荡培养箱 金坛市万华实验仪器厂;Milli-Q Advantage A10型超纯水仪 美国Millipore公司;Infinity 1290型超高效液相色谱仪、G6538型四级杆-飞行时间串联质谱仪 美国 Agilent 公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 青钱柳不同浓度乙醇洗脱液的制备
取青钱柳约500 g按料液比1:20(g:mL)加入10 L 50%乙醇加热回流提取1 h,再按料液比1:10提取2次,每次1 h,无菌纱布过滤,合并滤液浓缩至1 L即得质量浓度为0.5 g/mL的青钱柳50%乙醇总提取物。基于参考文献[10−12],预处理HPD 100大孔树脂(即向烧杯中加入720 g HPD 100大孔树脂,用95%乙醇浸渍不少于6 h,加入的乙醇量高于树脂层10 cm以上),装柱,量取100 mL青钱柳醇提物浓缩液用纯水稀释至2 L,上样完全吸附后,以5 BV(1 BV≈1.2 L)纯水过柱,去除多糖等杂质,将8个浓度乙醇(10%、20%、30%、40%、50%、60%、70%、80%)依次以3 BV进行洗脱。将收集的50%~80%浓度乙醇洗脱液分别加水稀释至40%左右,再将各洗脱液分别旋转蒸发至100 mL,于4 ℃储存备用。
1.2.2 青钱柳提取物效矩阵的建立
根据参考文献[13−14],以对硝基苯基-α-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷(4-Nitrophenyl-β-D-glucopyranoside,PNPG)为底物将实验分为空白组、样品组、样品背景组,样品组分别加入60 µL磷酸盐缓冲液(Phosphate Buffer,PB,0.1 mol/L,pH6.8)、青钱柳50%乙醇总提取物或不同浓度乙醇洗脱液20 μL和15 mmol/L PNPG 20 µL,37 ℃下孵育10 min,加入0.20 U/mL α-葡萄糖苷酶溶液20 µL混匀后,于37 ℃培养箱反应20 min,最后加入80 µL 0.20 mol/L的碳酸钠终止反应,在波长405 nm处测定吸光度值A。样品背景组与空白组用等体积的PB代替α-葡萄糖苷酶溶液与待测样品。按公式(1)计算青钱柳样品对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制率。平行实验3次,取平均值。
(1) 式中,AY:样品组吸光值;AD:样品背景组吸光值;AC:空白组吸光值。
1.2.3 青钱柳提取物量矩阵的建立
青钱柳中化学成分随乙醇浓度变化的量矩阵(X矩阵的建立)采用UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS技术统计青钱柳不同浓度乙醇洗脱部位中共有化合物峰面积的变化。
1.2.4 液相条件与质谱条件
1.2.4.1 液相条件
参考文献[15]采用安捷伦Poroshell 120 EC-C18色谱柱(3.0 mm×100 mm,2.7 μm),柱温为35 ℃,进样量3 μL,流速为0.3 mL/min,流动相为0.10%甲酸水溶液(A)-乙腈(B),正离子模式下洗脱条件(0~5 min,5%~30%B;5~8 min,30%~60%B;8~17 min,60%~65%B;17~25 min,65%~95%B;25~26 min,95%~5%B;26~27 min,5%B),负离子模式下洗脱条件(0~8 min,5%~41%B;8~10 min,41%~77%B;10~15 min,77%~95%B;15~16 min,95%~5%B;16~17 min,5%B)。
1.2.4.2 质谱条件
采用双喷雾大气压电喷雾离子源(Dual ESI),负离子模式下的毛细管电压3.5 kV,干燥气温度350 ℃,干燥气流量10 L/min,雾化气压力35 psi,毛细管出口电压120 V,锥孔电压60 V,扫描范围质荷比(m/z)50~1100,碰撞能量为10、20、40 V;正离子模式采集的毛细管电压4 kV,其他条件与负离子模式一致。
1.2.5 相关性分析
以各洗脱部位共有化合物的色谱峰面积为自变量(X),各洗脱部位对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制率为因变量(Y)[16],建立X-Y矩阵数据表,导入SIMCA.14.1软件进行PLS分析。
1.2.6 亲和超滤技术筛选α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂
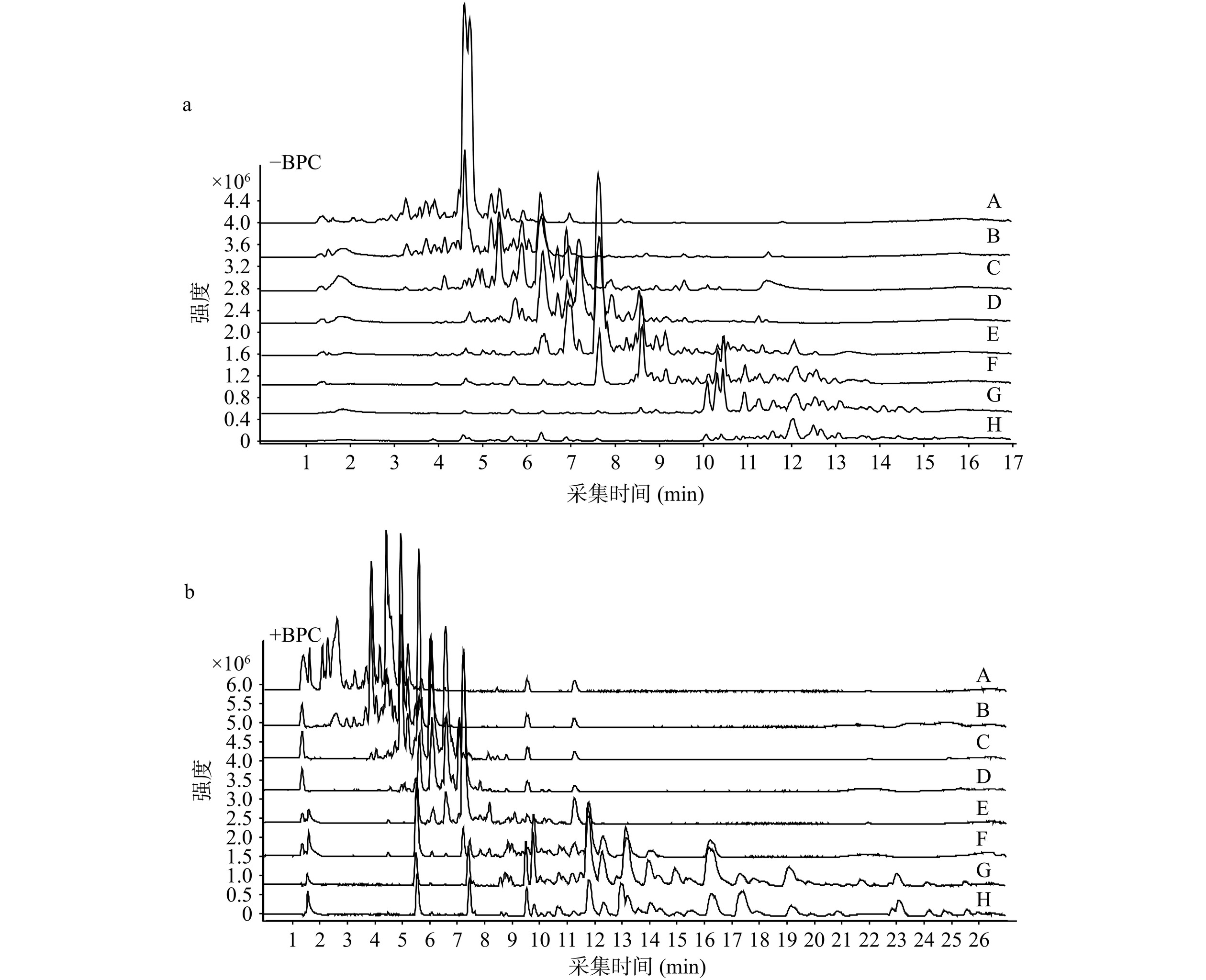
基于参考文献[17−18],设置空白组、对照组和实验组,其中实验组:量取青钱柳50%乙醇总提取物(330 µg/mL,200 μL)、α-葡萄糖苷酶溶液(0.2 U/mL,40 μL)、PB(0.1 mol/L,60 μL)混匀,于37 ℃孵育30 min,反应液移至10 K超滤离心管,于4 °C以10000 r/min离心15 min,再向滤膜中加入100 μL PB,离心清洗3次。加入200 μL甲醇4 ℃孵育10 min,以10000 r/min于4 ℃条件离心10 min,重复3次,收集下清液合并,用于UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS分析,色谱条件与质谱条件同“1.2.4”,其中空白组以PB溶液替代α-葡萄糖苷酶溶液,对照组仅加入灭活的α-葡萄糖苷酶(100 ℃,10 min)替代活性α-葡萄糖苷酶,以结合率(Bio-affinity degree,BD)评估青钱柳醇提物与α-葡萄糖苷酶的相互作用能力,计算公式如式(2)。
(2) 式中,A1为空白组的峰面积值;A2为实验组的峰面积值;A3为对照组峰面积值。
1.2.7 分子对接
从PubChem数据库(https://www.pubchem.org/)下载配体化合物的SDF格式文件,通过PyMOL转换为PDB格式文件,利用Autodock tools软件保存为PDBQT格式。在RSCB PDB数据库(https://www. rcsb. org/)下载α-葡萄糖苷酶(PDB ID:2QMJ)PDF结构文件,利用Autodock tools对蛋白结构删除水分子加氢加电荷后保存为PDBQT格式[19]。
1.3 数据处理
采用安捷伦MassHunter工作站定性软件Qualitative Analysis B.06.00对所采集的数据进行分子特征峰提取并积分;GraphPad-Prism 8.0.2软件计算半数抑制浓度(IC50值);根据变量重要性投影(Variable importance for projection,VIP)>1和BD>10%,筛选出青钱柳提取物中潜在的活性成分,根据MassHunter工作站获取MS和MS/MS中的分子量、保留时间(tR)、特征离子碎片信息等,结合文献、相关数据库进行成分分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 青钱柳50%乙醇总提取物的α-葡萄糖苷酶活性抑制实验结果
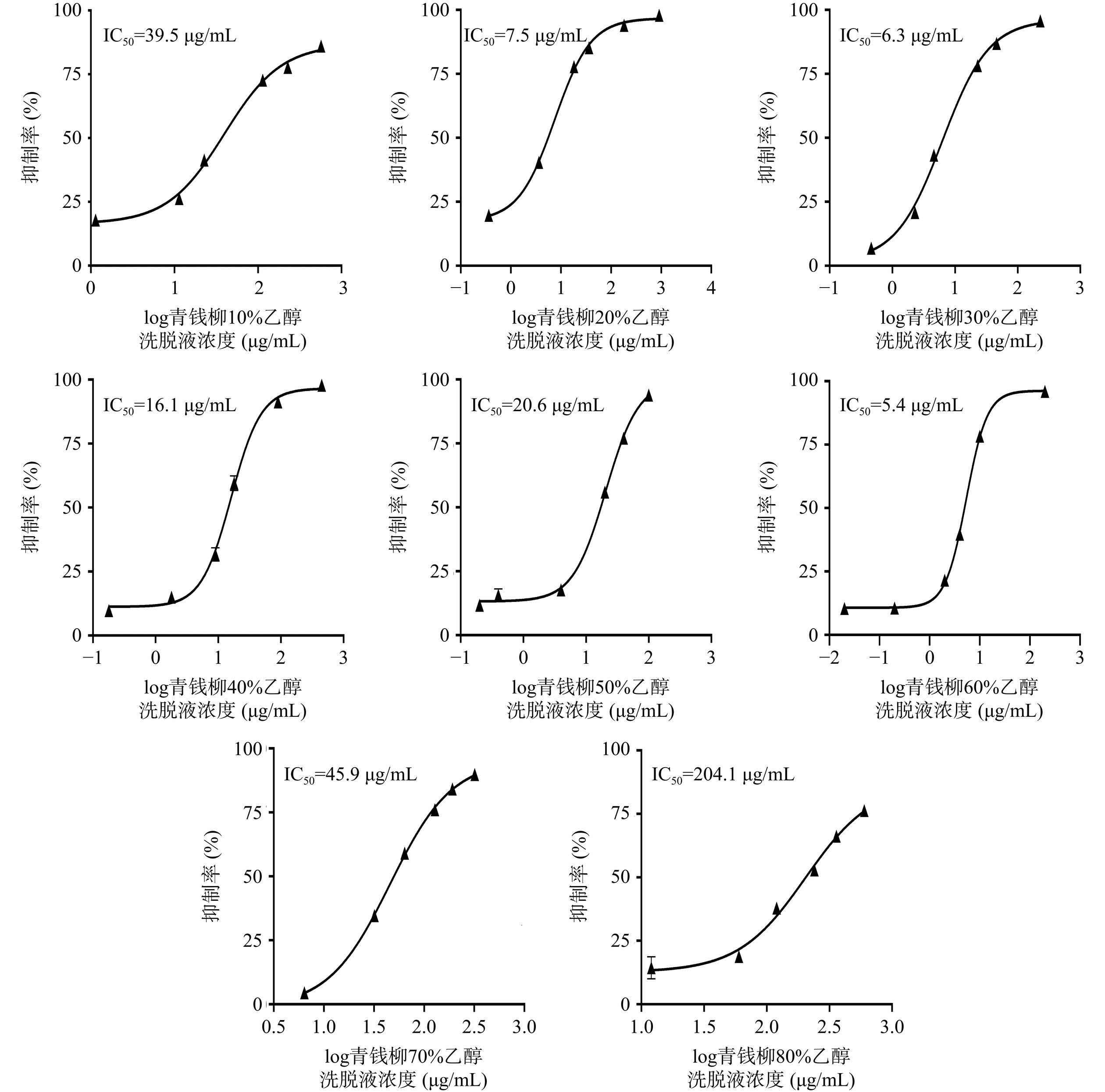
如表1所示,质量浓度为330 μg/mL的阿卡波糖对0.20 U/mL α-葡萄糖苷酶活性抑制率可达100.0%,IC50值为0.03 μg/mL;相同浓度下,青钱柳50%乙醇总提取物对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性抑制率为94.0%,IC50值为14.80 μg/mL,表明青钱柳50%乙醇总提取物具有良好的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性,可用于筛选α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂的研究。
表 1 不同质量浓度的青钱柳50%乙醇总提取物对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用Table 1. Inhibitory effect of Cyclocarya paliurus 50% ethanol extract at different mass concentrations on α-glucosidase浓度(μg/mL) 青钱柳50%乙醇总
提取物抑制率(%,n=3)阿卡波糖抑制率
(%,n=3)0.1 12.1±1.9 71.2±0.5 0.3 17.4±3.0 87.5±1.0 1.0 18.0±3.7 95.5±0.3 3.0 26.3±2.4 98.2±0.1 10.0 48.9±1.5 99.3±0.3 33.0 70.0±1.0 99.2±0.2 100.0 84.9±0.3 99.9±0.1 330.0 94.0±0.9 100.0±0.4 2.2 青钱柳提取物不同浓度乙醇洗脱部位量-效矩阵的建立
2.2.1 不同浓度乙醇洗脱部位的抑制作用(Y矩阵的建立)
由图1可知,不同乙醇浓度洗脱部位对α-葡萄糖苷酶具有较好抑制作用,10%~80%浓度乙醇洗脱液IC50值为5.4~204.1 μg/mL,其中抑制效果最佳的为60%乙醇浓度洗脱部位(IC50值为5.4 μg/mL)。
2.2.2 X矩阵的建立
由图2可知,可以通过峰面积侧面反映洗脱液中化学成分的含量变化。在正、负离子模式下,建立青钱柳提取物不同乙醇浓度洗脱液随浓度变化峰面积的量矩阵。建立量矩阵过程中发现,m/z值对应的峰面积在不同浓度乙醇洗脱液中有所不同,部分含量过低导致输出的峰面积为空值。为了不影响最终PLS模型的分析,对于空值的处理本实验基于大孔树脂分离的成分含量变化趋势线进行填充,填充数值均为负值<0表达其含量。
2.3 青钱柳不同浓度乙醇洗脱部位量-效矩阵相关性分析(X-Y矩阵相关性分析)
2.3.1 评估和分析PLS模型结果
PLS回归分析以拟合指数R2和模型的预测指数Q2评估模型[20],正离子模式下PLS模型的R2和Q2结果为R2X=0.646、R2Y=0.983、Q2=0.970,表示该模型中64.6%的变量为因变量,98.3%的样本符合模型回归,预测能力为97.0%;同理,负离子模式下PLS模型结果为R2X=0.577、R2Y=0.995、Q2=0.969,两种离子模式下的PLS模型预测数据集能力均良好。
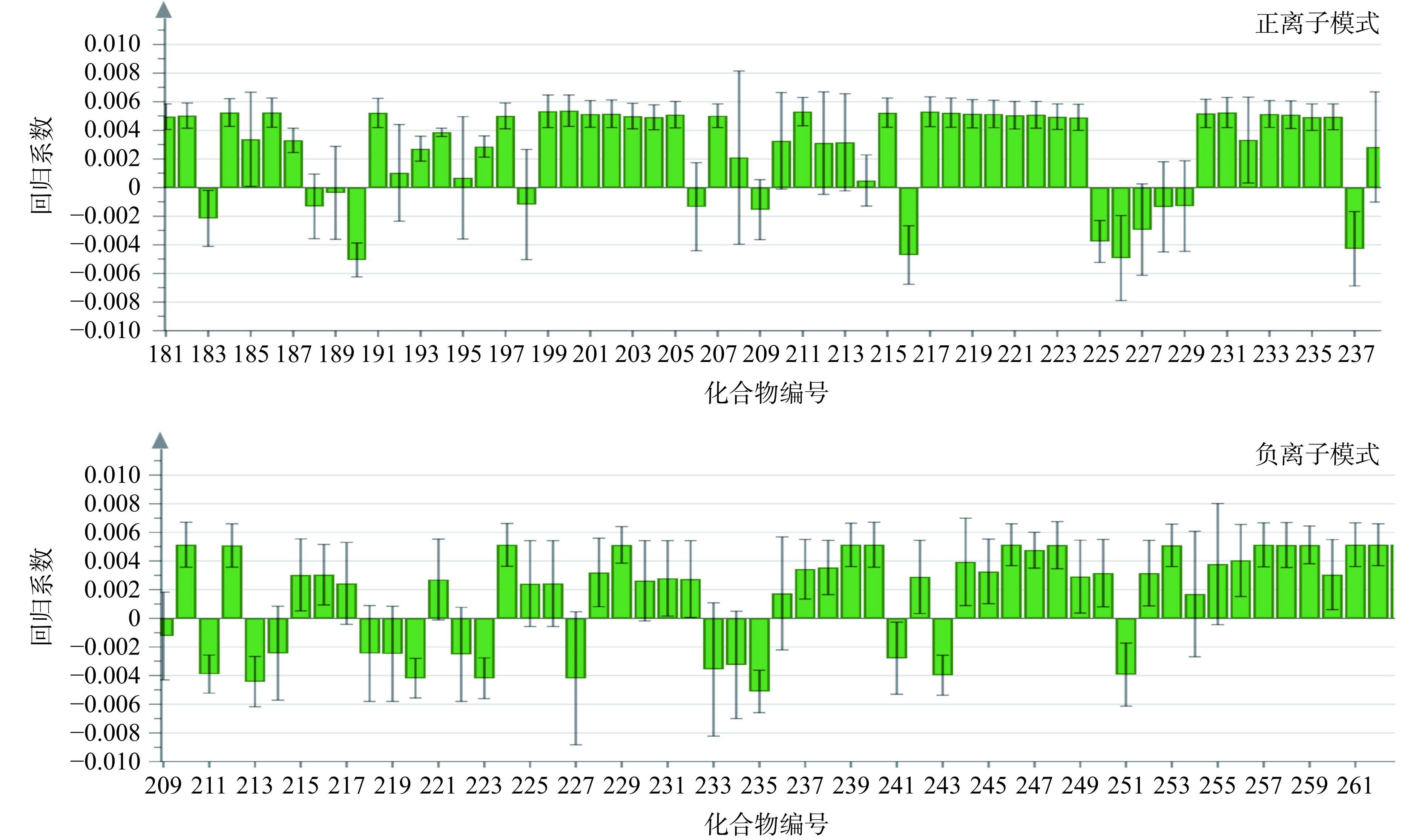
通过PLS模型的系数图,表示Y矩阵与每个X变量的相关性强弱,由于数据庞大,选取部分结果进行分析,如图3所示,图中系数的大小表示当X变量从0到1变化时Y变量的变化,因变量Y受多个自变量的共同影响[21],表明青钱柳提取物抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶的作用不是由某一化合物对其造成的影响。
2.3.2 PLS模型预测青钱柳中与α-葡萄糖苷酶相关的化合物结果
在PLS分析中,VIP反映自变量X对因变量Y的解释能力大小,VIP值越大,自变量X的解释能力越强[22]。基于PLS模型,筛选VIP>1的化合物,于正、负离子模式下分别预测出190个和231个化合物。
2.4 筛选亲和α-葡萄糖苷酶潜在活性成分的结果分析
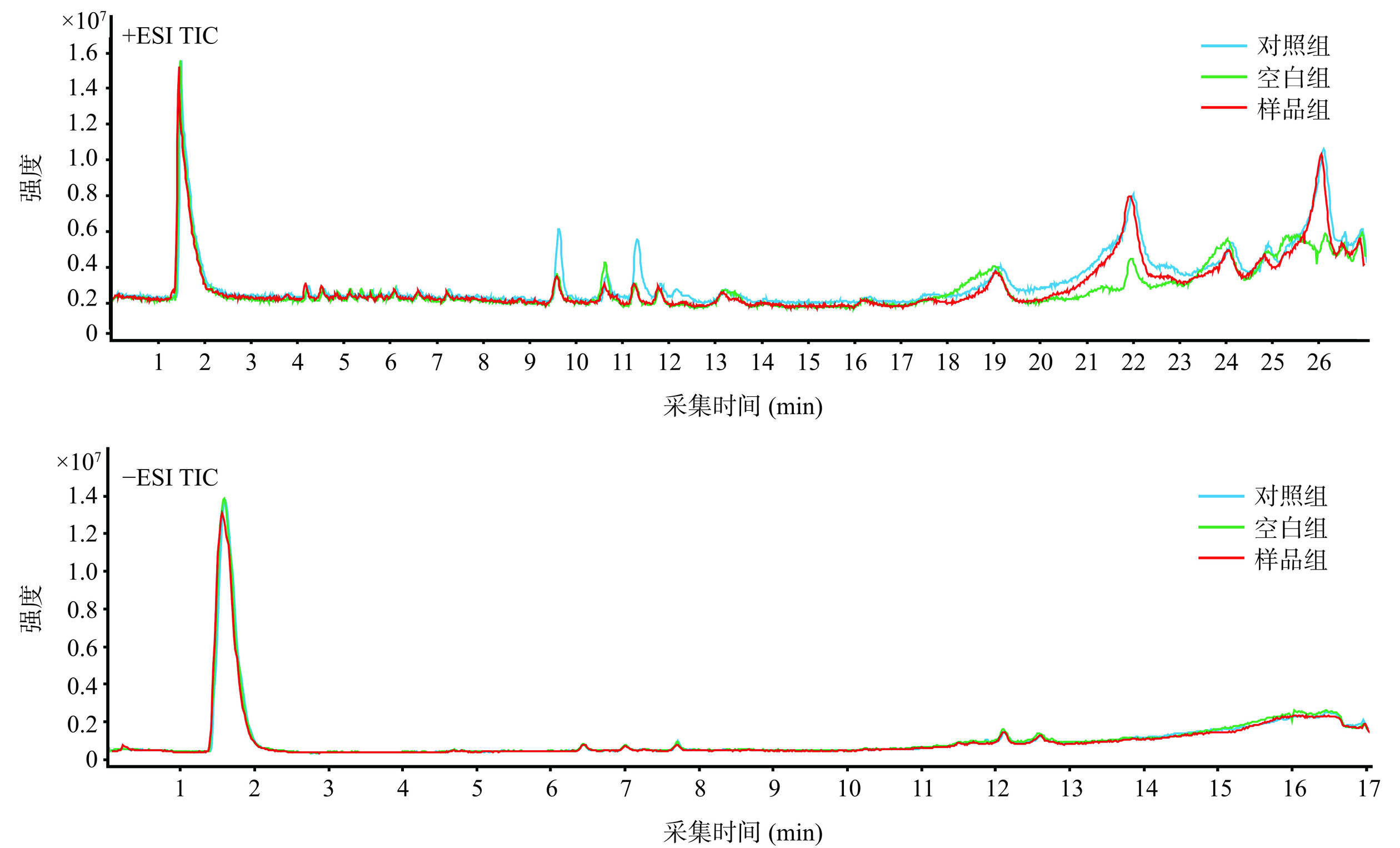
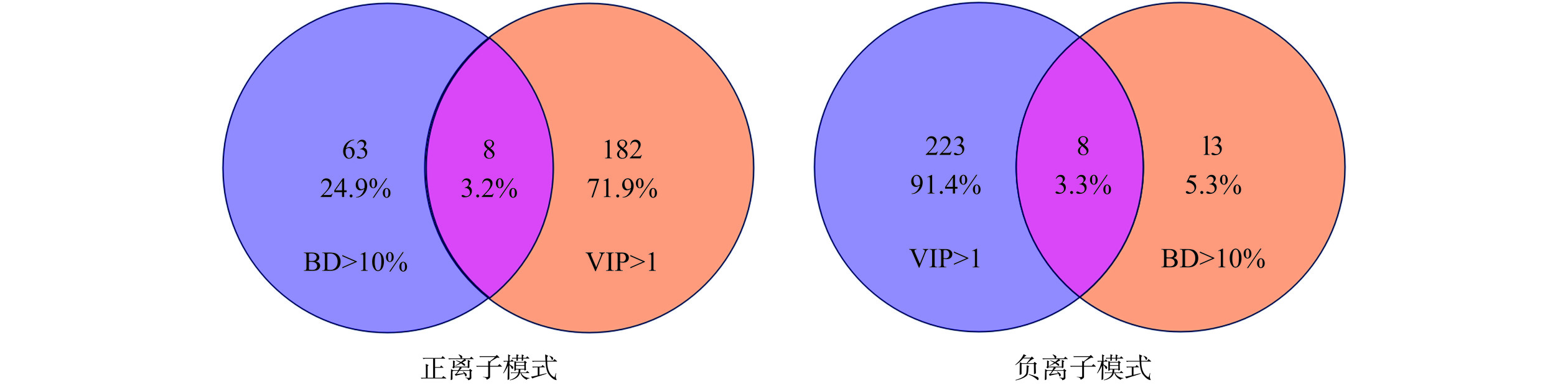
采用AUF-UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS从青钱柳50%乙醇总提取物中筛选具有亲和α-葡萄糖苷酶的化合物。正、负离子模式总离子流图(TIC)如图4所示,根据各组超滤液TIC提取的峰面积,计算出各m/z值与α-葡萄糖苷酶的BD[23],将BD>10%的潜在成分进行归纳整理,正离子模式下,BD>10%的m/z值有71个;负离子模式下,BD>10%的m/z值有21个。
2.5 青钱柳提取物中α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂的快速筛选
通过韦恩图(VIP>1和BD>10%)将PLS模型预测结果与AUF-UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS筛选的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂进行互相验证。如图5所示,在正、负离子模式下,共筛选出16种化合物。结合质谱数据库HMDB[24]、Pubchem[25]、相关文献[26−28]和自建青钱柳成分数据库(Cyclocarya paliurus.cdb)、安捷伦中药对照品成分数据库(Agilent TCM library-V20-04-17.cdb)推测可能化合物,最终鉴定出10种活性成分,其保留时间(tR)、分子式与碎片离子信息等见表2。
表 2 青钱柳提取物中α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂的鉴定结果Table 2. Identification results of α-glucosidase inhibitors in Cyclocarya paliurus extracts序号 m/z tR BD VIP 加和形式 分子式 MS2 推测化合物 1 814.5317 11.794 13.77 1.14 [M+H]+ C43H74O14 761.4934,655.4328,441.3628 未知化合物 2 814.53251 16.321 23.30 1.03 [M+NH4-H2O]+ C43H74O14 814.5082,778.9469,732.3811 青钱柳苷Z10-Li [Dammarane-(20S,24R,25)-penthydroxyl-11-O-β-D-quinovopyranosyl-3-O-(5'-O-acetyl)-α-L-arabinofuranoside] 3 645.3974 11.880 35.88 1.35 [M+Na]+ C35H58O9 645.4010,497.3537,452.3721,545.3826 Pterocaryoside B 4 355.2642 11.888 27.92 1.29 [M+H]+ C16H18O9 135.0436,145.0289,163.0397 未知化合物 5 373.2749 11.398 24.13 1.30 [M+H]+ C24H36O3 312.3216,270.3054 未知化合物 6 455.3527 13.268 90.46 1.30 [M+H]+ C30H46O3 123.1126,437.3324 青钱柳酸A(Cyclocaric acid A) 7 455.3527 16.254 23.46 1.30 [M+H]+ C30H46O3 83.0823,189.1584,287.1906 熊果酸内酯(Ursolic acid lactone) 8 228.1972 9.724 14.13 1.02 [M+H]+ C13H25NO2 177.8817,153.0161,91.0524 未知化合物 9 635.4158 12.548 20.15 1.29 [M-H]− C36H60O9 472.3584,426.4435 青钱柳苷III(Cyclocarioside III) 10 827.4795 11.637 17.81 1.26 [M-H]− C43H72O15 809.7563,131.0381 Vinaginsenoside R2 11 461.0705 6.964 16.29 1.22 [M-H]− C32H14O4 353.0958,285.0478,175.0295 未知化合物 12 663.4088 12.724 19.67 1.19 [M-H]− C37H60O10 635.425,191.3179 青钱柳苷P-Qin[(24R)-12β,20,24-trihydroxy-3,4-seco-dammara-4(28),25-diene-3-oic acid 20-O-(5-O-acetyl)-α-L-arabinofuranoside] 13 651.4094 11.651 16.87 1.18 [M-H]− C36H60O10 427.1057,607.4158,328.7585 青钱柳苷Z11-Sun[(12R, 20S, 24S)-20,24-dihydroxy-12-O-b-D-glucopyranosyl-3,4-secodammara-4(28),25(26)-dien-3-oic acid] 14* 301.0350 6.407 14.70 1.12 [M-H]− C15H10O7 151.0041,187.0441,117.0379 槲皮素(Quercetin) 15 477.0682 6.404 14.31 1.09 [M-H]− C32H14O5 301.0415,151.0084,113.0300 未知化合物 16* 285.0408 6.969 10.05 1.02 [M-H]− C15H10O6 285.0484,229.0563,196.0547 山柰酚(Kaempferol) 注:*经安捷伦中药对照品成分数据库(Agilent TCM library-V20-04-17.cdb)质谱比对。 2.6 分子对接结果
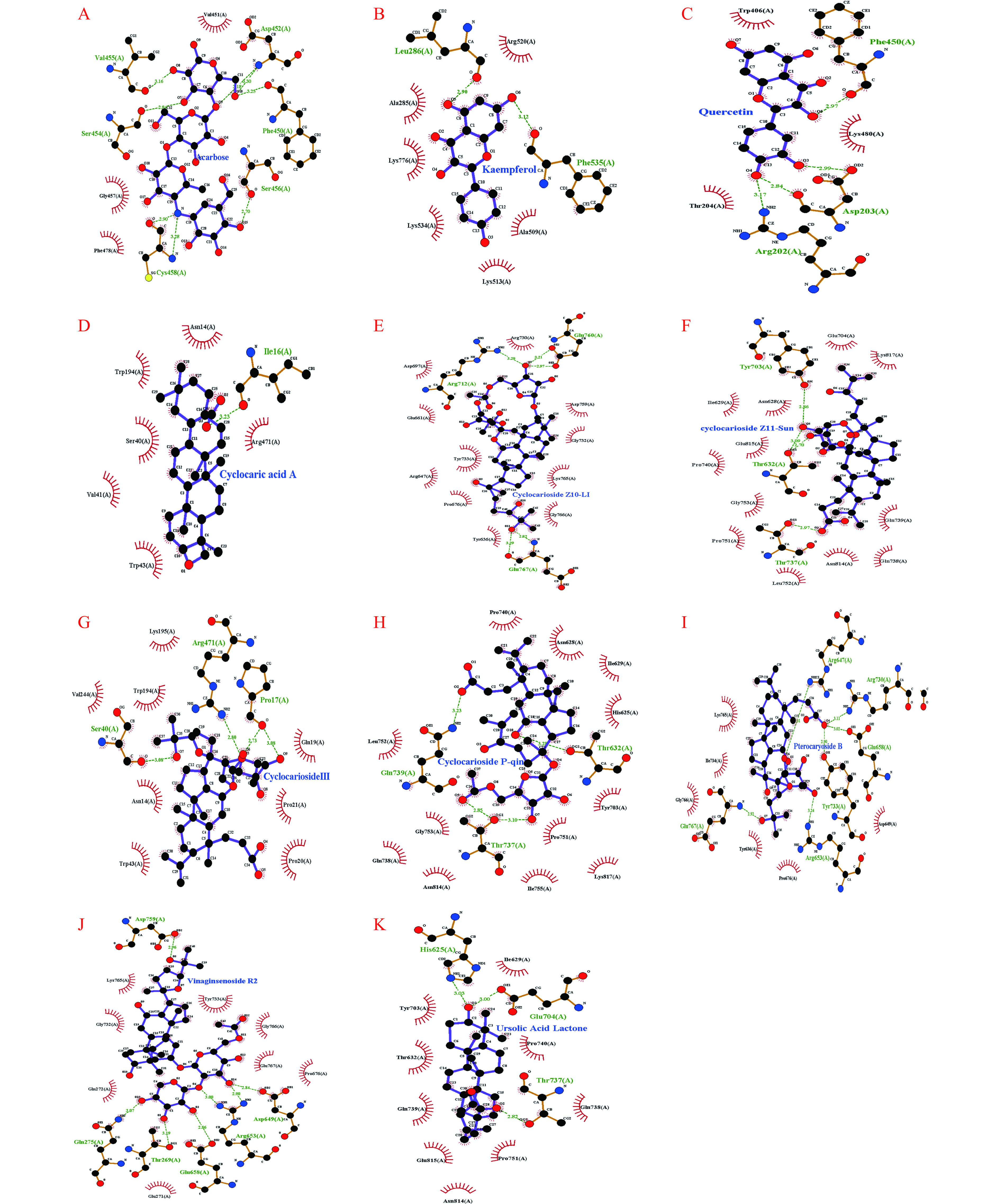
由表3可知,活性成分在氢键和疏水作用力的共同作用下与α-葡萄糖苷酶相互作用。一般认为活性成分与靶蛋白的结合能小于−5 kcal·mol−1表明结合能力良好,而小于−7 kcal·mol−1视作有较强的结合作用[29],其中山柰酚、槲皮素、青钱柳酸A、青钱柳苷Z10-Li、青钱柳苷Z11-Sun、青钱柳苷III、青钱柳苷P-Qin、Pterocaryoside B、Vinaginsenoside R2、熊果酸内酯与α-葡萄糖苷酶结合能均小于−7.0 kcal·mol−1,说明对α-葡萄糖苷酶具有较强的亲和力,是潜在的活性成分。用LigPlus软件进行配体与蛋白之间相互作用力分析,结果如图6所示。以熊果酸内脂为例,能够顺利与α-葡萄糖苷酶蛋白活性口袋结合,熊果酸内酯可通过Glu704、Thr737、His625氨基酸残基形成氢键,与Pro751、Gln738等氨基酸残基形成疏水作用来维持配体与蛋白活性口袋的稳定,与表3结果一致。
表 3 青钱柳关键成分与α-葡萄糖苷酶对接结果Table 3. Docking results of key components of Cyclocarya paliurus with α-glucosidase化合物 结合能
(kcal·mol−1)相互作用 疏水作用力 氢键 阿卡波糖 −5.2 Val451、Gly457、Phe478 Val455、Ser454、Cys458、Ser456、Phe450、Asp452 山柰酚 −7.7 Ala258、Lys776、Lys534、Lys513、Ala509、Arg520 Leu286、Phe535 槲皮素 −8.1 Trp406、Thr204、Lys480 Arg202、Asp203、Phe450 青钱柳酸A −8.4 Asn14、Trp194、Ser40、Val41、Trp43、Arg471 He16 青钱柳苷Z10-Li −8.3 Ayp697、Glu561、Tyr733、Arg647、Pre676、Tyr636、Gly766、Lys765、Cay732、Asp759 Arg712、Glu760、Glu767 青钱柳苷Z11-Sun −7.7 Glu704、Lya817、Ilr629、Asn628、Glu815、、Pru740、Gly753、Pru751、Leu752、Asn814、Gln738、Gln739 Tyr703、Tlu632、Tlu737 青钱柳苷III −8.3 Lys195、Trp194、Val244、Asn14、Trp43、Pro20、Pro21、Gln19 Arg471、Ser40、Pro17 青钱柳苷P-Qin −7.1 Pro740、Asn628、He629、His625、Tyr703、Pro751、Lys817、He755、Asn814、Gln738、Gly753、Leu752 Gln739、Thr737、Thr632 Pterocaryoside B −8.3 Lyr765、Be734、Gly66、Tyr636、Pro676、Asp649 Arg647、Arg730、Glu658、Tyr733、Glu767、Arg653 Vinaginsenoside R2 −8.4 Lyr765、Gly732、Gln272、Glu271、Pro656、Glu767、
Yyr733、Gly755Asp759、Gln275、Thr269、Glu658、Arg653、Asp649 熊果酸内酯 −10.0 He629、Tyr703、Thr632、Gln739、Glu815、Asn814、
Pro751、Gln738、Pro740His625、Glu704、Thr737 3. 讨论与结论
通过前期体外酶抑制实验发现,青钱柳50%乙醇总提取物与不同乙醇浓度青钱柳洗脱液对α-葡萄糖苷酶具有较好的抑制作用,但存在较大差异。大孔吸附树脂分离和纯化后,提取物的活性成分浓度上升,有助于增强其抑制效果。此外,多种化合物共同竞争α-葡萄糖苷酶的活性中心,可能产生协同作用,进一步增强抑制效果。这些因素可能导致IC50的最大值与最小值之间存在较大差异[30]。
为了进一步探讨药效差异与活性成分之间的关系,本研究采用PLS分析研究不同乙醇浓度青钱柳洗脱液与α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率之间的量-效关系,可较大程度反映成分对药效的贡献作用。同时以AUF-UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS技术得到单体化合物与α-葡萄糖苷酶的结合率[31]。通过对两种实验方法进行互相验证,鉴定出与α-葡萄糖苷酶结合率较高、对抑制率影响较大的10种活性成分,然而仍有6种未知化合物需要进一步研究。前期构建量矩阵时发现,10种成分于60%乙醇洗脱液的含量较高,且60%乙醇浓度液在体外酶抑制实验中效果最佳(IC50值为5.4 µg/mL),说明青钱柳的酶抑制能力是多种活性成分共同作用的结果。
α-葡萄糖苷酶是临床上用于降血糖的关键靶点[32],将筛选得到的活性成分与α-葡萄糖苷酶进行分子对接模拟,其结合能小于−7.0 kcal·mol−1,进一步说明这些成分与α-葡萄糖苷酶结合具有较强的亲和力,为潜在的活性成分。Ning等[33]发现青钱柳中黄酮类化合物如槲皮素、山柰酚等在体外模型中对α-葡萄糖苷酶有较好的抑制作用,并在动物实验中验证了其具有降低血糖的作用。且山柰酚还具有抗氧化、抗炎、等药理作用,对2型糖尿病大鼠的慢性并发症起到保护作用[34]。Li等[35]对青钱柳叶中所分离出的20种三萜类化合物进行了生物活性测定,发现青钱柳苷Z10-Li对α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制效果最佳并能显著下调LPS介导的RAW264.7细胞中iNOS、COX-2、IL-1β、NF-κB、IL-6和TNF-α的mRNA表达,并显著抑制iNOS、NF-NF-κB/p65和COX-2的蛋白表达。何付琴[36]在抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性最强组分中鉴定出pterocaryoside B,该化合物可能是抑制该酶的活性成分。由于青钱柳苷III、Pterocaryoside B等三萜类成分市面上缺少对照品,将在后续深入研究中,通过色谱分离等相关技术获得较高浓度的化合物,进一步验证其活性。
本文利用相关性分析方法与亲和超滤-液质联用技术,并通过MS/MS质谱信息成功鉴定出山柰酚、槲皮素、青钱柳酸A、青钱柳苷P-Qin等10种活性成分,可为青钱柳新药理活性研究、活性成分质量控制研究、青钱柳功能性食品开发的深入研究提供依据。
-
表 1 不同质量浓度的青钱柳50%乙醇总提取物对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用
Table 1 Inhibitory effect of Cyclocarya paliurus 50% ethanol extract at different mass concentrations on α-glucosidase
浓度(μg/mL) 青钱柳50%乙醇总
提取物抑制率(%,n=3)阿卡波糖抑制率
(%,n=3)0.1 12.1±1.9 71.2±0.5 0.3 17.4±3.0 87.5±1.0 1.0 18.0±3.7 95.5±0.3 3.0 26.3±2.4 98.2±0.1 10.0 48.9±1.5 99.3±0.3 33.0 70.0±1.0 99.2±0.2 100.0 84.9±0.3 99.9±0.1 330.0 94.0±0.9 100.0±0.4 表 2 青钱柳提取物中α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂的鉴定结果
Table 2 Identification results of α-glucosidase inhibitors in Cyclocarya paliurus extracts
序号 m/z tR BD VIP 加和形式 分子式 MS2 推测化合物 1 814.5317 11.794 13.77 1.14 [M+H]+ C43H74O14 761.4934,655.4328,441.3628 未知化合物 2 814.53251 16.321 23.30 1.03 [M+NH4-H2O]+ C43H74O14 814.5082,778.9469,732.3811 青钱柳苷Z10-Li [Dammarane-(20S,24R,25)-penthydroxyl-11-O-β-D-quinovopyranosyl-3-O-(5'-O-acetyl)-α-L-arabinofuranoside] 3 645.3974 11.880 35.88 1.35 [M+Na]+ C35H58O9 645.4010,497.3537,452.3721,545.3826 Pterocaryoside B 4 355.2642 11.888 27.92 1.29 [M+H]+ C16H18O9 135.0436,145.0289,163.0397 未知化合物 5 373.2749 11.398 24.13 1.30 [M+H]+ C24H36O3 312.3216,270.3054 未知化合物 6 455.3527 13.268 90.46 1.30 [M+H]+ C30H46O3 123.1126,437.3324 青钱柳酸A(Cyclocaric acid A) 7 455.3527 16.254 23.46 1.30 [M+H]+ C30H46O3 83.0823,189.1584,287.1906 熊果酸内酯(Ursolic acid lactone) 8 228.1972 9.724 14.13 1.02 [M+H]+ C13H25NO2 177.8817,153.0161,91.0524 未知化合物 9 635.4158 12.548 20.15 1.29 [M-H]− C36H60O9 472.3584,426.4435 青钱柳苷III(Cyclocarioside III) 10 827.4795 11.637 17.81 1.26 [M-H]− C43H72O15 809.7563,131.0381 Vinaginsenoside R2 11 461.0705 6.964 16.29 1.22 [M-H]− C32H14O4 353.0958,285.0478,175.0295 未知化合物 12 663.4088 12.724 19.67 1.19 [M-H]− C37H60O10 635.425,191.3179 青钱柳苷P-Qin[(24R)-12β,20,24-trihydroxy-3,4-seco-dammara-4(28),25-diene-3-oic acid 20-O-(5-O-acetyl)-α-L-arabinofuranoside] 13 651.4094 11.651 16.87 1.18 [M-H]− C36H60O10 427.1057,607.4158,328.7585 青钱柳苷Z11-Sun[(12R, 20S, 24S)-20,24-dihydroxy-12-O-b-D-glucopyranosyl-3,4-secodammara-4(28),25(26)-dien-3-oic acid] 14* 301.0350 6.407 14.70 1.12 [M-H]− C15H10O7 151.0041,187.0441,117.0379 槲皮素(Quercetin) 15 477.0682 6.404 14.31 1.09 [M-H]− C32H14O5 301.0415,151.0084,113.0300 未知化合物 16* 285.0408 6.969 10.05 1.02 [M-H]− C15H10O6 285.0484,229.0563,196.0547 山柰酚(Kaempferol) 注:*经安捷伦中药对照品成分数据库(Agilent TCM library-V20-04-17.cdb)质谱比对。 表 3 青钱柳关键成分与α-葡萄糖苷酶对接结果
Table 3 Docking results of key components of Cyclocarya paliurus with α-glucosidase
化合物 结合能
(kcal·mol−1)相互作用 疏水作用力 氢键 阿卡波糖 −5.2 Val451、Gly457、Phe478 Val455、Ser454、Cys458、Ser456、Phe450、Asp452 山柰酚 −7.7 Ala258、Lys776、Lys534、Lys513、Ala509、Arg520 Leu286、Phe535 槲皮素 −8.1 Trp406、Thr204、Lys480 Arg202、Asp203、Phe450 青钱柳酸A −8.4 Asn14、Trp194、Ser40、Val41、Trp43、Arg471 He16 青钱柳苷Z10-Li −8.3 Ayp697、Glu561、Tyr733、Arg647、Pre676、Tyr636、Gly766、Lys765、Cay732、Asp759 Arg712、Glu760、Glu767 青钱柳苷Z11-Sun −7.7 Glu704、Lya817、Ilr629、Asn628、Glu815、、Pru740、Gly753、Pru751、Leu752、Asn814、Gln738、Gln739 Tyr703、Tlu632、Tlu737 青钱柳苷III −8.3 Lys195、Trp194、Val244、Asn14、Trp43、Pro20、Pro21、Gln19 Arg471、Ser40、Pro17 青钱柳苷P-Qin −7.1 Pro740、Asn628、He629、His625、Tyr703、Pro751、Lys817、He755、Asn814、Gln738、Gly753、Leu752 Gln739、Thr737、Thr632 Pterocaryoside B −8.3 Lyr765、Be734、Gly66、Tyr636、Pro676、Asp649 Arg647、Arg730、Glu658、Tyr733、Glu767、Arg653 Vinaginsenoside R2 −8.4 Lyr765、Gly732、Gln272、Glu271、Pro656、Glu767、
Yyr733、Gly755Asp759、Gln275、Thr269、Glu658、Arg653、Asp649 熊果酸内酯 −10.0 He629、Tyr703、Thr632、Gln739、Glu815、Asn814、
Pro751、Gln738、Pro740His625、Glu704、Thr737 -
[1] 李俊, 梁晓琴, 常燕玲, 等. 青钱柳的化学成分及药理活性研究进展[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版),2022,40(5):227−252. [LI J, LIANG X Q, CHANG Y L, et al. Review on the constituents and pharmacological activities of Cyclocarya paliurus[J]. Journal of Guangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2022,40(5):227−252.] LI J, LIANG X Q, CHANG Y L, et al. Review on the constituents and pharmacological activities of Cyclocarya paliurus[J]. Journal of Guangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 40(5): 227−252.
[2] 李燕, 蔡儒安, 潘如梨, 等. 青钱柳水提物降血糖及抗发炎功效研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(9):102−109. [LI Y, CAI R A, PAN R L, et al. Studies on hypoglycemic and anti-inflammatory effects of Cyclocarya paliurus extract[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(9):102−109.] LI Y, CAI R A, PAN R L, et al. Studies on hypoglycemic and anti-inflammatory effects of Cyclocarya paliurus extract[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2021, 21(9): 102−109.
[3] JIANG C, WANG Q, WEI Y J, et al. Cholesterol-lowering effects and potential mechanisms of different polar extracts from Cyclocarya paliurus leave in hyperlipidemic mice[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2015,176:17−26. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.10.006
[4] WANG H, TANG C, GAO Z, et al. Potential role of natural plant medicine Cyclocarya paliurus in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Journal of Diabetes Research,2021,2021(1):1655336.
[5] LIU W, DENG S, ZHOU D, et al. 3,4-seco-Dammarane triterpenoid saponins with anti-inflammatory activity isolated from the leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(7):2041−2053. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b06898
[6] 袁中文, 许婳婳, 钟柳婷, 等. 青钱柳黄酮干预肥胖大鼠胰岛素抵抗的作用研究[J]. 中药药理与临床,2019,35(3):50−55. [YUAN Z W, XU H H, ZHONG L T, et al. Effect of sinomenine on the proliferation of human fibroblast-like synoviocyte induced by lipopolysaccharide[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica,2019,35(3):50−55.] YUAN Z W, XU H H, ZHONG L T, et al. Effect of sinomenine on the proliferation of human fibroblast-like synoviocyte induced by lipopolysaccharide[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 2019, 35(3): 50−55.
[7] 刘杰, 向燕茹, 丁嘉瑜, 等. 青钱柳抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶有效成分筛选及其对Ⅱ型糖尿病小鼠血糖的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(14):363−369. [LIU J, XIANG Y R, DING J Y, et al. Screening the active fraction from Cyclocaryapaliurus (Batal.) Ijinskaja which inhibits α-glucosidase and study its effects on hyperglycemia in mice with type II diabetes mellitus[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(14):363−369.] LIU J, XIANG Y R, DING J Y, et al. Screening the active fraction from Cyclocaryapaliurus (Batal.) Ijinskaja which inhibits α-glucosidase and study its effects on hyperglycemia in mice with type II diabetes mellitus[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2015, 36(14): 363−369.
[8] 王凯平, 李文蕊, 宋梦姿, 等. 青钱柳的化学成分、药理作用及产品开发研究进展[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2023,43(18):2100−2104. [WANG K P, LI W R, SONG M Z, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents, biological activities and product development of Cyclocarya paliurus[J]. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy,2023,43(18):2100−2104.] WANG K P, LI W R, SONG M Z, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents, biological activities and product development of Cyclocarya paliurus[J]. Chinese Journal of Hospital Pharmacy, 2023, 43(18): 2100−2104.
[9] 杨玉莹, 张丹丹, 罗心遥, 等. 指纹图谱及多成分定量结合化学模式识别法评价不同产地青钱柳质量[J]. 中草药,2020,51(4):1082−1088. [YANG Y Y, ZHANG D D, LUO X Y, et al. Quality evaluation of Cyclocarya paliurus from different habitats by fingerprint and multicomponent quantification combined with chemical pattern recognition[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2020,51(4):1082−1088.] doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.04.036 YANG Y Y, ZHANG D D, LUO X Y, et al. Quality evaluation of Cyclocarya paliurus from different habitats by fingerprint and multicomponent quantification combined with chemical pattern recognition[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2020, 51(4): 1082−1088. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.04.036
[10] 吴彩娥, 方升佐, 徐琳, 等. 青钱柳叶三萜大孔吸附树脂纯化工艺[J]. 农业机械学报,2010,41(9):143−147. [WU C E, FANG S Z, XU L, et al. Purification of triterpenes in Cyclocarya paliurus leaves by macroporous resins[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2010,41(9):143−147.] WU C E, FANG S Z, XU L, et al. Purification of triterpenes in Cyclocarya paliurus leaves by macroporous resins[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2010, 41(9): 143−147.
[11] 徐国良, 肖兵华, 邹胡斌, 等. 大孔吸附树脂分离肿节风中总黄酮的研究[J]. 中草药,2006(7):1014−1017. [XU G L, XIAO B H, ZOU H B, et al. Separation of total flavone in Sarcandra glabra by macroporous adsorption resins[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2006(7):1014−1017.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2670.2006.07.021 XU G L, XIAO B H, ZOU H B, et al. Separation of total flavone in Sarcandra glabra by macroporous adsorption resins[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2006(7): 1014−1017. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2670.2006.07.021
[12] WANG Z, PENG S, PENG M, et al. Adsorption and desorption characteristics of polyphenols from Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. leaves with macroporous resin and its inhibitory effect on α-amylase and α-glucosidase[J]. Annals of Translational Medicine,2020,8(16):1004. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-5468
[13] IHMAID S. Exploring the dual inhibitory activity of novel anthranilic acid derivatives towards α-glucosidase and glycogen phosphorylase antidiabetic targets:Design, in vitro enzyme assay, and docking studies[J]. Molecules,2018,23(6):1304. doi: 10.3390/molecules23061304
[14] 郑丽婷. 黄柏碱对α-葡萄糖苷酶和胰岛素抵抗糖脂代谢的影响及机制[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学, 2020. [ZHENG L T. The effect and mechanism of phellodendrine on α-glucosidase and insul in resistance glucolipid metabolism[D]. Guangzhou:Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2020.] ZHENG L T. The effect and mechanism of phellodendrine on α-glucosidase and insul in resistance glucolipid metabolism[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2020.
[15] 肖岩, 马博稷, 李冰涛, 等. 青钱柳醇提物中化学成分的UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(16):196−204. [XIAO Y, MA B J, LI B T, et al. Analysis of chemical constituents in ethanol extract of Cyclocarya paliurus dried leaves by UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2022,28(16):196−204.] XIAO Y, MA B J, LI B T, et al. Analysis of chemical constituents in ethanol extract of Cyclocarya paliurus dried leaves by UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2022, 28(16): 196−204.
[16] ZHU L X, ZHANG M M, XXIANG X F, et al. Aromatic characterization of traditional Chinese wine Msalais by partial least-square regression analysis based on sensory quantitative descriptive and odor active values, aroma extract dilution analysis, and aroma recombination and omission tests[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,361:129781. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129781
[17] WANG L, LIU Y, LUO Y, et al. Quickly screening for potential α-glucosidase inhibitors from guava leaves tea by bioaffinity ultrafiltration coupled with HPLC-ESI-TOF/MS method[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(6):1576−1582. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05280
[18] LI Y J, WAN G Z, XU F C, et al. Screening and identification of α-glucosidase inhibitors from Cyclocarya paliurus leaves by ultrafiltration coupled with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and molecular docking[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2022,1675:463160. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463160
[19] SAIKIA S, BORDOLOI M. Molecular docking:Challenges, advances and its use in drug discovery perspective[J]. Current Drug Targets,2019,20(5):501−521. doi: 10.2174/1389450119666181022153016
[20] 肖岩. 基于血清药物组的青钱柳降糖药效物质基础研究[D]. 南昌:江西中医药大学, 2022. [XIAO Y. Research on the material basis of hypoglycemic efficacy of Cyclocarya paliurus based on serum drug components[D]. Nanchang:Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, 2022.] XIAO Y. Research on the material basis of hypoglycemic efficacy of Cyclocarya paliurus based on serum drug components[D]. Nanchang: Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, 2022.
[21] 李会芳, 刘静婷, 郎霞, 等. 基于偏最小二乘法关联分析栀子不同炮制品化学成分与肝肾毒性[J]. 药物评价研究,2021,44(9):1890−1896. [LI H F, LIU J T, LANG X, et al. Partial least squares analysis of chemical constituents and hepatorenal toxicity in different processed products of Gardenia jasminoides[J]. Drug Evaluation Research,2021,44(9):1890−1896.] LI H F, LIU J T, LANG X, et al. Partial least squares analysis of chemical constituents and hepatorenal toxicity in different processed products of Gardenia jasminoides[J]. Drug Evaluation Research, 2021, 44(9): 1890−1896.
[22] 常星, 王露, 程江雪, 等. 基于偏最小二乘回归分析的逍遥软胶囊中柴胡-白芍药对抗抑郁作用谱-效关系研究[J]. 中草药,2023,54(8):2509−2515. [CHANG X, WANG L, CHENG J X, et al. Study on spectrum-effect relationship of Bupleuri Radix-Paeoniae Raidx Alba herb pair of Xiaoyao soft capsule for anti-depressant effect based on partial least squares-discriminant analysis[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2023,54(8):2509−2515.] CHANG X, WANG L, CHENG J X, et al. Study on spectrum-effect relationship of Bupleuri Radix-Paeoniae Raidx Alba herb pair of Xiaoyao soft capsule for anti-depressant effect based on partial least squares-discriminant analysis[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2023, 54(8): 2509−2515.
[23] 陈海君, 秦惠玉, 龙飞, 等. 超滤亲和结合液相色谱-质谱联用和分子对接技术筛选毛菊苣种子中高亲和性α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂[J]. 分析化学,2017,45(6):889−897. [CHEN H J, QIN H Y, LONG F, et al. Screening of high-affinity a-glucosidase inhibitors from Cichorium Glandulosum Boiss. et Hout seed based on ultrafiltration liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and molecular docking[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2017,45(6):889−897.] doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.170050 CHEN H J, QIN H Y, LONG F, et al. Screening of high-affinity a-glucosidase inhibitors from Cichorium Glandulosum Boiss. et Hout seed based on ultrafiltration liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and molecular docking[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 45(6): 889−897. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.170050
[24] WISHART D S, FEUNANG Y D, MARCU A, et al. HMDB 4.0:The human metabolome database for 2018[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2018,46(D1):D608−D617. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1089
[25] KIM S, THIESSEN P A, BOLTON E E, et al. PubChem substance and compound databases[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2016,44(D1):D1202−D1213. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv951
[26] 马博稷, 肖岩, 陈祖德, 等. UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS分析青钱柳嫩叶渗漉提取液化学成分[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(13):281−291. [MA B J, XIAO Y, CHEN Z D, et al. Analysis of chemical constituents in percolate the extract of Cyclocarya paliurus tender leaves by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(13):281−291.] MA B J, XIAO Y, CHEN Z D, et al. Analysis of chemical constituents in percolate the extract of Cyclocarya paliurus tender leaves by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(13): 281−291.
[27] 秦俊俊. 四种植物—黄花杠柳、戟叶牛皮消、青钱柳和独子藤的化学成分及生物活性研究[D]. 上海:中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海药物研究所), 2018. [QIN J J. Study on chemical constituents of Periploca chrysantha, Cynanchum bungei, Cyclocarya paliurus, and Celastrus monospermus and evaluation of their biological activities[D]. Shanghai:University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica. Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2018.] QIN J J. Study on chemical constituents of Periploca chrysantha, Cynanchum bungei, Cyclocarya paliurus, and Celastrus monospermus and evaluation of their biological activities[D]. Shanghai: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica. Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2018.
[28] SUN H H, LÜ W Y, TAN J, et al. Cytotoxic triterpenoid glycosides from leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus[J]. Natural Product Research,2021,35(21):4018−4024. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2020.1756801
[29] HUANG Z Z, DU X, MA C D, et al. Identification of antitumor active constituents in Polygonatum sibiricum flower by UPLC-Q-TOF-MSE and Network Pharmacology[J]. ACS Omega,2020,5(46):29755−29764. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03582
[30] 潘福璐, 冀艳华, 于国华, 等. 茶多酚与α-葡萄糖苷酶结合动力学特征研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2020,45(18):4472−4481. [PAN F L, JI Y H, YU G H, et al. Study on binding kinetics profiles of tea polyphenols-α-glucosidase interaction[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2020,45(18):4472−4481.] PAN F L, JI Y H, YU G H, et al. Study on binding kinetics profiles of tea polyphenols-α-glucosidase interaction[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2020, 45(18): 4472−4481.
[31] WANG L, TAN N, WANG H, et al. A systematic analysis of natural α-glucosidase inhibitors from flavonoids of Radix scutellariae using ultrafiltration UPLC-TripleTOF-MS/MS and network pharmacology[J]. BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies,2020,20:1−17. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2780-5
[32] XUE N, HE B, JIA Y, et al. The mechanism of binding with the α-glucosidase in vitro and the evaluation on hypoglycemic effect in vivo:Cocrystals involving synergism of gallic acid and conformer[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics,2020,156:64−74. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.08.024
[33] NING Z, ZHAI L, HUANG T, et al. Identification of α-glucosidase inhibitors from Cyclocarya paliurus tea leaves using UF-UPLC-Q/TOF-MS/MS and molecular docking[J]. Food & Function,2019,10(4):1893−1902.
[34] 吴巧敏, 金雅美, 倪海祥. 山柰酚对2型糖尿病大鼠慢性并发症相关因子的影响[J]. 中草药,2015,46(12):1806−1809. [WU Q M, JIN Y M, NI H X. Effect of kaempferol on correlation factors of chronic complications of type 2 diabetic rats[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2015,46(12):1806−1809.] doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2015.12.018 WU Q M, JIN Y M, NI H X. Effect of kaempferol on correlation factors of chronic complications of type 2 diabetic rats[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2015, 46(12): 1806−1809. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2015.12.018
[35] LI C, DDENG S, LIU W, et al. α-Glucosidase inhibitory and anti-inflammatory activities of dammarane triterpenoids from the leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus[J]. Bioorganic Chemistry,2021,111:104847. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104847
[36] 何付琴. 基于谱效关系的青钱柳叶、五味子活性物质基础研究[D]. 兰州:兰州大学, 2022. [HE F Q. Study on the active subsance of Cyclocarya paliurus leaves and Schisandra chinensis fruits based on spectrum-effect relationship[D]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University, 2022.] HE F Q. Study on the active subsance of Cyclocarya paliurus leaves and Schisandra chinensis fruits based on spectrum-effect relationship[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2022.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
