Construction and Application of a New Type of Foam Separation Equipment with the Hollow Octagonal Prismoid with Sieve Tray Inner Component
-
摘要: 目的:本研究设计了一种新型的含筛孔八棱锥内构件,用以强化泡沫排液,提高泡沫分离效率。方法:以重组β-葡萄糖苷酶(Glu-linker-ELP50-GB,GLEGB)发酵液为模型,考察内构件的结构参数(个数、间距、筛孔直径)和泡沫分离实验参数(温度、初始蛋白浓度、气体流速、装液量)对GLEGB富集比和回收率的影响。此外,基于弹性蛋白样多肽(elastin-like polypeptides,ELPs)的温敏性,对重组β-葡萄糖苷酶泡沫液进一步纯化,并通过圆二色光谱仪(CD)、紫外-可见分光光度计(UV-vis)和傅里叶-红外光谱仪(FT-IR)对纯化后GLEGB的结构进行分析。结果:在内构件数量为5、间距为78 mm、筛孔直径为2 mm、蛋白质初始浓度为0.3 mg/mL、温度为45 ℃、气体流速为200 mL/min、装液量为100 mL的最佳条件下,GLEGB的蛋白富集比为2.46±0.10是对照柱的1.33倍,对重组β-葡萄糖苷酶泡沫液进一步纯化后GLEGB的纯化倍数为37.25±0.60,此外,结果证明纯化过程不会影响GLEGB的结构。结论:本研究设计的含筛孔八棱锥内构件可以有效地提高从发酵液中分离GLEGB的富集比,为泡沫分离设备的设计、研究及工艺优化提供了新的研究思路。Abstract: Objective: In this study, a novel type of the hollow octagonal prismoid with sieve tray inner component was designed to enhance liquid drainage from foam and improve the efficiency of foam separation. Methods: The model used in this work was a fermentation broth containing recombinant β-glucosidase (Glu-linker-ELP50-GB, GLEGB). The effects of structural parameters of the internal component (number, spacing, and pore diameter) and operational parameters of the foam separation experiment (temperature, initial protein concentration, gas flow rate, and liquid loading volume) on the enrichment ratio and recovery rate of GLEGB were investigated. In addition, based on the temperature sensitivity of elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs), the recombinant β-glucosidase foam solution was further purified. The structure of purified GLEGB was analyzed by circular dichroism spectrometer (CD), ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-vis) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). Results: Under the optimal conditions of 5 internal components, 78 mm spacing, 2 mm pore diameter, 0.3 mg/mL initial protein concentration, 45 ℃ temperature, 200 mL/min gas flow rate and 100 mL liquid loading volume, the protein enrichment ratio of GLEGB was 2.46±0.10, 1.33 times that of the control column. After further purification of recombinant β-glucosidase foam solution, the purification ratio of GLEGB was 37.25±0.60. In addition, the results showed that the purification process did not affect the structure of GLEGB. Conclusion: The hollow octagonal prismoid with sieve tray inner component can effectively improve the enrichment ratio of GLEGB separation from fermentation liquid, which provides a new research idea for the design, research and process optimization of foam separation equipment.
-
Keywords:
- foam separation /
- enrichment ratio /
- recombinant β-glucosidase /
- internal components
-
泡沫分离技术主要是基于表面吸附原理,利用液体中产生的气泡作为介质,对液相中的溶质进行富集或分离,利用目标物质与溶液中其他组分的表面活性差异,优先富集吸附在气泡表面的目标物质[1]。该技术具有设备简单、操作温和、能耗低、效率高、处理能力大等优点,已广泛应用于冶金工业[2]、环保工业[3−4]、食品工业[5−6]、生物分离[7−9]。
近年来,该技术已被广泛用于蛋白质分离[10−12]。影响泡沫分离效率的两个关键因素是表面吸附和泡沫排液[13]。强化泡沫排液被认为是提高富集比的有效方法[14−15]。通过调节溶液的体系性质(如温度、pH等)可以提高目标物质的吸附能力[16],在小范围内促进排水。但是,由于不同目标物质的耐受程度不同,调节范围有限[17]。通过改变传统泡沫分离设备结构(如添加内构件或改变分离柱形状)来提高泡沫分离效果已成为泡沫分离的研究重点[18−19]。与改变泡沫柱的形状相比[20],添加内件可以直接作用于泡沫本身[15],影响气泡的形状和分布,以及目标物质在气泡上的吸附都发生了一定的变化,延长了目标物质在气泡表面吸附的时间[21],加强了目标物质在气液界面上的吸附,促进泡沫的排水,从而提高了富集比[22−24]。
本研究设计了一种新型的含筛孔八棱锥内构件的泡沫分离设备,用于强化泡沫排液提高泡沫分离效率。基于本团队前期研究[25],本文以重组β-葡萄糖苷酶(Glu-linker-ELP50-GB,GLEGB)发酵液为液体体系研究含筛孔八棱柱内构件的泡沫分离设备的泡沫分离性能。首先,以富集比和回收率为评价指标对内构件的结构参数(种类、数量、间距、筛孔直径)和泡沫分离的实验参数(温度、初始蛋白浓度、气体流速、装液量)进行分离条件优化。最后,基于类弹性蛋白(elastin-like polypeptides,ELPs)的温敏性,进一步纯化GLEGB的泡沫溶液。此外,利用CD、UV-vis和FT-IR对纯化后的GLEGB的二级结构进行测定。本研究旨在改进泡沫分离设备以提高泡沫分离的效果,为泡沫分离蛋白技术提供新的研究思路。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
胰蛋白胨、酵母提取物、琼脂粉 英国OXID公司;乙二胺四乙酸二钠、丙烯酰胺、甘油、β-巯基乙醇、冰醋酸、异丙醇、过硫酸铵 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;硫酸卡那霉素、氢氧化钠、无毒型核酸染料-4S、异丙基β-D-硫代半乳糖苷、三羟甲基氨基甲烷、考马斯亮蓝R250、十二烷基硫酸钠、苯甲基磺酰氟 生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司;N,N-亚甲基二丙烯酰胺 阿拉丁试剂(上海)有限公司;四甲基乙二胺 美国西格玛公司;氯化钠、无水乙酸钠、碳酸钠 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;对硝基苯-β-d-吡喃葡萄糖苷(p-NPG)、对硝基苯酚 郑州阿尔法化工有限公司;BCA蛋白检测试剂盒 美国Thermo Scientific公司;商品化β-葡萄糖苷酶 合肥博美生物科技有限责任公司。
B-013204乌式粘度计 镇江华东器化玻有限公司;J-815圆二色光谱仪 日本分光JASCO;Nicolet Nexus 470傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 美国尼高力仪器公司;UV-2450紫外-可见分光光度计 日本岛津公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 发酵液制备
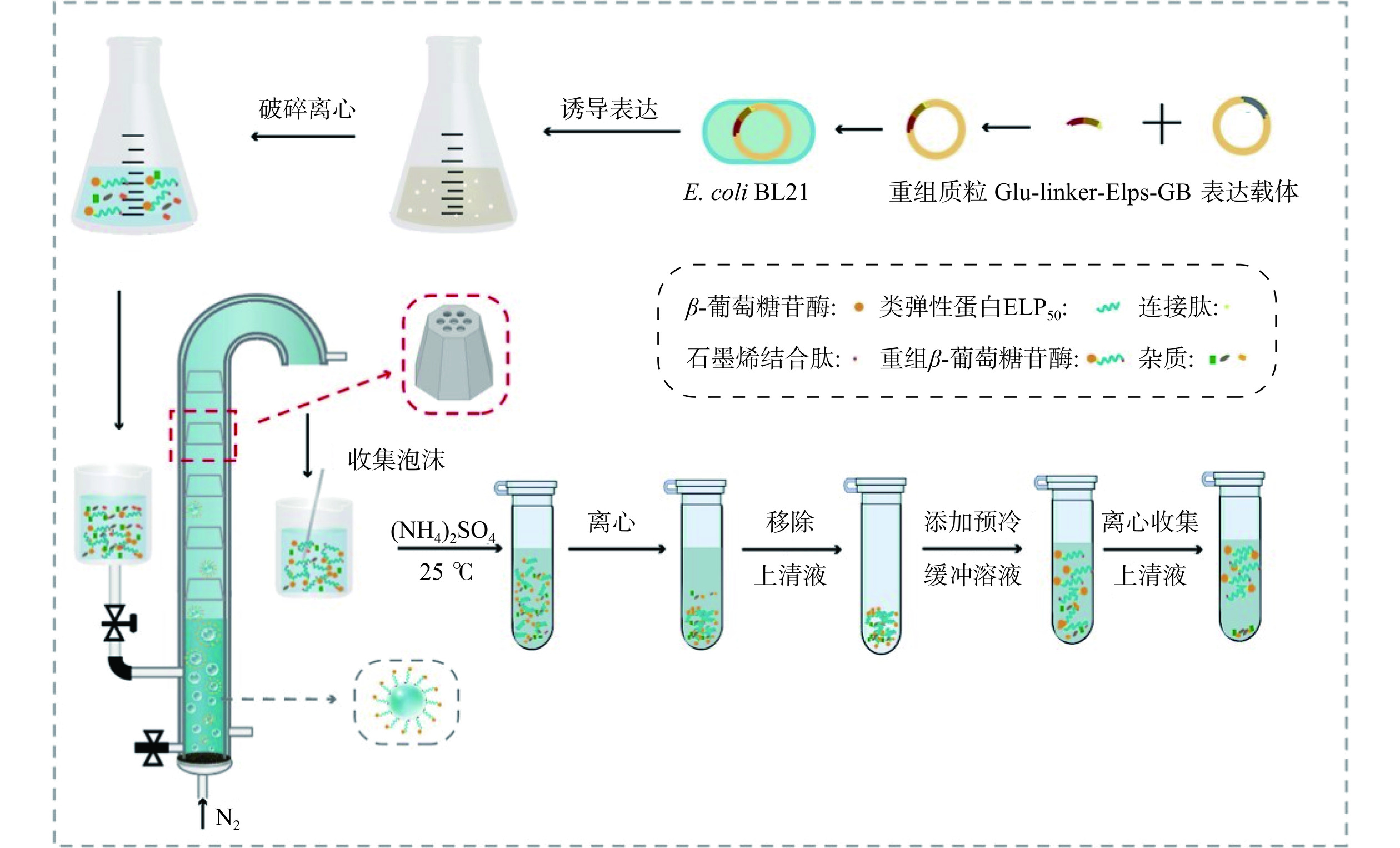
本研究首先将ELPs(VPGVG)50和GB(HNWYHWWPH)与β-葡萄糖苷酶基因融合,然后与空质粒(pET-28a+)重组,构建重组质粒(pET-Glu-linker-ELP50-GB)。最后,通过热激法将重组质粒转化到大肠杆菌BL21中诱导表达重组β-葡萄糖苷酶。蛋白表达的具体步骤参考本团队之前的研究[26],细胞破碎后收集的上清液即为GLEGB发酵液。
1.2.2 含筛孔八棱锥内构件结构参数优化
1.2.2.1 含筛孔八棱锥内构件泡沫装置的构建
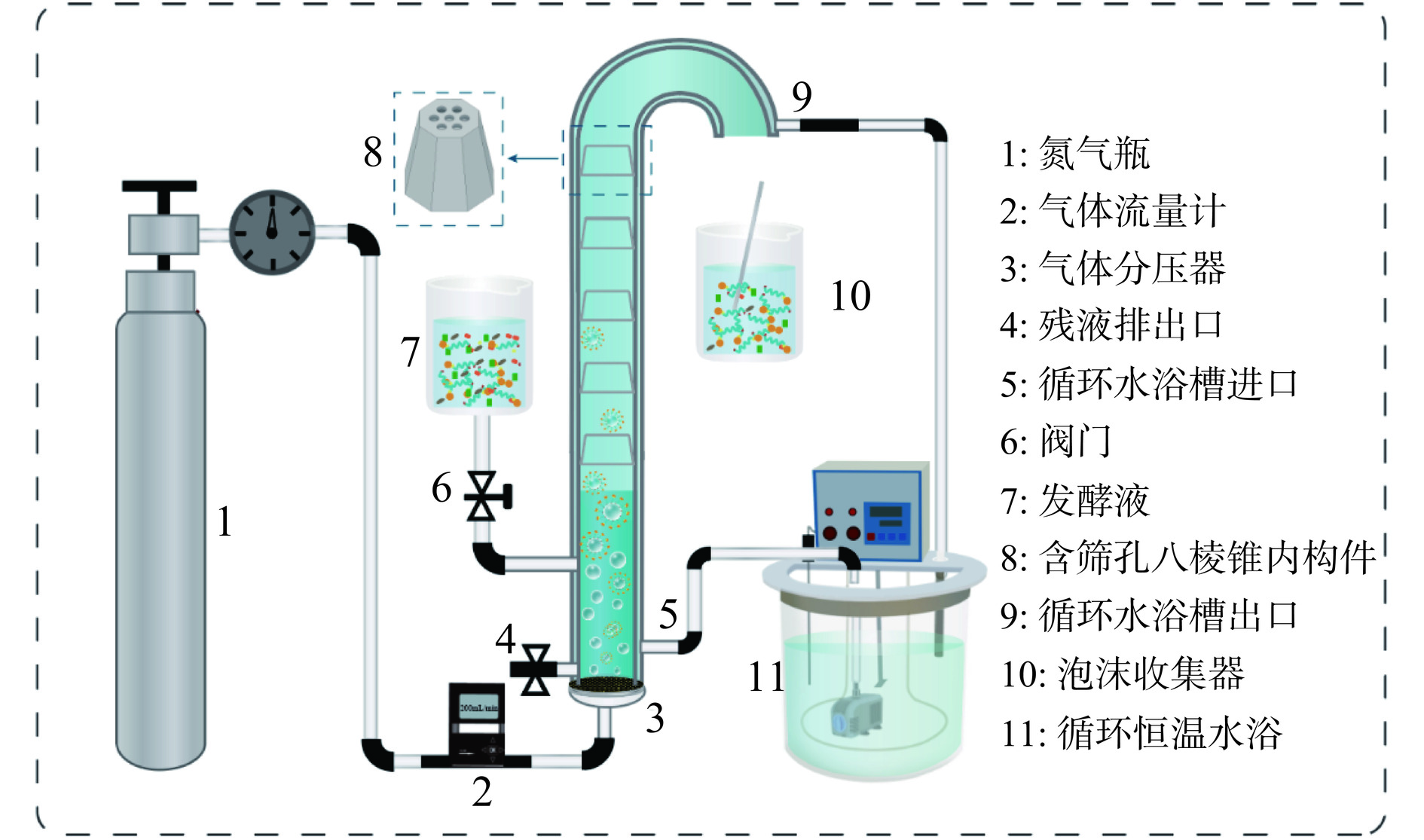
含筛孔八棱锥内构件泡沫分离设备如图1所示,泡沫分离柱由高度600 mm、内径30 mm的透明有机玻璃制成。选择平均直径为200 μm的烧结玻璃作为气体分布器,安装在塔的底部。首先,将不同数量不同筛孔直径的含筛孔八棱锥内构件均匀地排列在分离柱中,向泡沫分离柱中加入一定量的GLEGB发酵液和少量消泡剂,通过循环水浴控制GLEGB发泡液的温度,设置不同的气体流速。收集泡沫,直到不再产生泡沫时停止收集,然后通过机械搅拌破碎泡沫。
1.2.2.2 内构件个数的选择
在内构件筛孔直径为2 mm,内构件间距为78 mm,初始蛋白浓度为0.3 mg/mL,温度45 ℃,气体流速200 mL/min,装液量为100 mL时,探究含筛孔八棱锥内构件数量对泡沫排液和GLEGB泡沫分离效果的影响,分别在泡沫分离柱中添加0、1、2、3、4、5个内构件,以富集比为主要评价指标确定内构件的最佳数量。
1.2.2.3 内构件间距的选择
在内构件筛孔直径为2 mm,内构件数量为5,初始蛋白浓度为0.3 mg/mL,温度45 ℃,气体流速200 mL/min,装液量为100 mL时,探究含筛孔八棱锥内构件间距对泡沫排液和GLEGB泡沫分离效果的影响,分别将内构件以48、78、108 mm的间距均匀地排列在泡沫分离柱内,以富集比为主要评价指标确定最佳间距。
1.2.2.4 内构件筛孔直径的选择
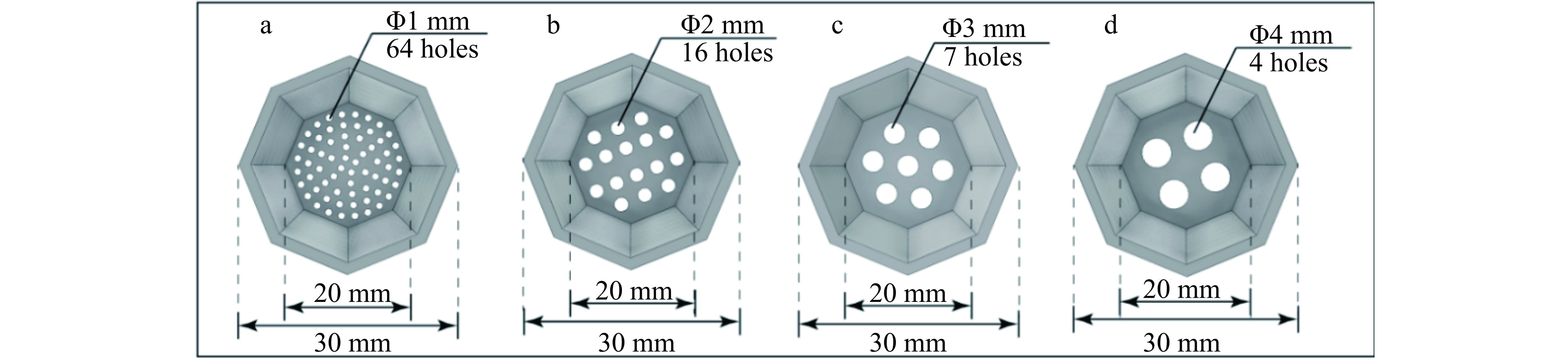
在内构件间距为78 mm,内构件数量为5,初始蛋白浓度为0.3 mg/mL,温度45 ℃,气体流速200 mL/min,装液量为100 mL时,探究含筛孔八棱锥内构件的筛孔直径对泡沫排液和GLEGB泡沫分离效果的影响。如图2所示,本研究设计了筛孔直径为1、2、3、4 mm的内构件,分别将不同筛孔直径的内构件添加到泡沫分离柱内,以富集比为主要评价指标确定最佳筛孔直径。
1.2.3 泡沫分离GLEGB的条件优化及纯化
1.2.3.1 分离纯化过程
采用泡沫分离和基于ELPs温敏性进一步纯化GLEGB泡沫液的流程如图3所示。首先,向泡沫分离柱中加入100 mL 0.3 mg/mL的GLEGB发酵液和少量消泡剂(110 μL),通过循环水浴控制GLEGB发酵液的温度为45 ℃,设置气体流速为200 mL/min。收集泡沫,直到不再产生泡沫时停止收集,然后通过机械搅拌破碎泡沫。其次,利用ELPs的温敏性对第一步收集的GLEGB泡沫溶液进一步纯化。在泡沫溶液中加入不同质量的(NH4)2SO4使其终浓度为(0.3、0.5、0.7、1 mol/L),在25 ℃条件下孵育20 min,25 ℃(10000 r/min)离心10 min,弃去上清液。取适量预冷Tris-HCl缓冲液(50 mmol/L,pH8.0)重悬沉淀,悬浮液在冰水中静置50 min,4 ℃离心10 min,收集上清液。采用PierceTM BCA蛋白检测试剂盒检测纯化前后各溶液的蛋白浓度[27]。
1.2.3.2 温度对泡沫分离效果的影响
在向加入数量为5个、筛孔直径为2 mm、间距为78 mm的内构件的泡沫柱中添加100 mL 0.3 mg/mL的GLEGB发酵液,在气体流速为200 mL/min的条件下从发酵液中分离GLEGB,探究温度对泡沫分离GLEGB的影响,分别在25、35、45、55、65 ℃条件下进行泡沫分离实验,以富集比和回收率为评价指标,确定最佳实验温度。
1.2.3.3 初始蛋白浓度对泡沫分离效果的影响
向内构件的数量为5个、筛孔直径为2 mm、间距为78 mm的泡沫柱中添加100 mL GLEGB发酵液,在温度为45 ℃、气体流速为200 mL/min的条件下,配制初始蛋白浓度为0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5、0.6 mg/mL的GLEGB泡沫发酵液加入到泡沫分离柱中,以富集比和回收率为评价指标,确定泡沫分离GLEGB的最适蛋白浓度。
1.2.3.4 气体流速对泡沫分离效果的影响
向内构件的数量为5个、筛孔直径为2 mm、间距为78 mm的泡沫柱中添加100 mL 0.3 mg/mL的GLEGB发酵液,在45 ℃的条件下,研究气体流速对泡沫分离GLEGB效果的影响,本实验以不同的气体流速(100、150、200、250、300 mL/min)进行泡沫分离实验,以富集比和回收率为评价指标,确定最佳气体流速。
1.2.3.5 装液量对泡沫分离效果的影响
分别向内构件的数量为5个、筛孔直径为2 mm、间距为78 mm的泡沫柱中加入体积为75、100、125、150、175 mL的0.3 mg/mL GLEGB发酵液,在温度为45 ℃、气体流速为200 mL/min的条件下,探究不同装液量对GLEGB泡沫分离效果的影响,以富集比和回收率为评价指标,确定泡沫分离GLEGB的最佳装液量。
1.2.4 分离纯化效果评价指标测定
1.2.4.1 泡沫持液率和出口液体流速的测定
泡沫分离时每隔60 s收集一次泡沫,称重并记录泡沫液体积。泡沫的持液率(ε)和出口液体流速(jfout, mm/s)的计算公式如下:
ε(%)=VoutVout+Vg×100 (1) jfout(mm/s)=1ρfAcdGdt (2) 式中,Vout为每60 s收集泡沫液的体积,mL;Vg为每60 s进入塔内的气体体积,mL;G是泡沫的重量,g;ρf是泡沫的密度,kg/m3;Ac为泡沫分离柱的截面积,mm2;t为时间,s。
1.2.4.2 酶活性测定
通过测定p-NPG产物p-NP的吸光度值来评价β-葡萄糖苷酶的水解活性。取40 μL p-NPG加入到450 μL NaAc-HAc缓冲液(50 mmol/L,pH5.5)中40 ℃ 预热10 min,然后加入10 μL酶溶液,40 ℃反应10 min。加入500 μL Na2CO3(1 mol/L)溶液终止反应。用紫外分光光度计测定反应液在410 nm处的吸光度。代入标准曲线计算产物p-NP的浓度。酶的比活度A(U/mg)是指每毫克酶在一分钟内催化底物反应生成的产物量,计算公式如式(3)所示。
A(U/mg)=Cp-NP×Vreactiontreaction×m (3) 式中,Cp-NP为p-NP的浓度,μmol/L;Vreaction为反应体系的总体积,mL;treaction为酶与底物的反应时间,min;m为添加酶的质量,mg。
1.2.4.3 泡沫分离效果评价
以蛋白质回收率(Rp)[12]、蛋白质富集比(Ep)[18]、酶活回收率(Re)[26]、酶活富集比(Ee)[15]、纯化倍数(Pf)[26]评价泡沫分离性能,计算公式如下:
Rp(%)=Vf×CfVi×Ci×100 (4) Ep=CfCi (5) Re(%)=Af×Vf×CfAi×Vi×Ci×100 (6) Ee=Af×CfAi×Ci (7) Pf=AfAi (8) 式中,Ci、Cf分别为纯化前后的GLEGB发酵液蛋白浓度,mg/mL;Vi和Vf分别表示纯化前后的GLEGB蛋白体积,mL;Ai和Af分别表示纯化前后的GLEGB的比酶活性,U/mg。
1.2.5 SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳
根据蛋白分子量的大小(70~80 kDa),本研究选择使用12%的分离胶和5%的浓缩胶浓度,采用两步法进行电泳检测:第一步电压85 V,电流85 mA,功率50 W,时间30 min;第二步电压160 V,电流160 mA,功率50 W,时间1 h。电泳结束后,将凝胶置于染色盒中加入适量的考马斯亮蓝R-250染色液并加热至轻微沸腾,将其置于摇床染色1 h。冲洗颜色盒中残留的染色液,加入适量的脱色液,并置于微波炉加热至轻微沸腾,再次放到摇床脱色,每20 min更换一次脱色液,直至看到清晰的条带。
1.2.6 蛋白质结构表征
1.2.6.1 纯化后GLEGB的圆二色谱分析
配制蛋白浓度为0.1 mg/mL的商品化酶(Glu)和纯化后的GLEGB,在室温条件下,使用圆二色光谱仪和光程长度为0.1 mm的石英皿在190~250 nm内进行CD光谱的测定,以去离子水作为空白对照。
1.2.6.2 纯化后GLEGB的紫外色谱分析
配制蛋白浓度为0.5 mg/mL的商品化酶(Glu)和纯化后的GLEGB,在室温条件下,向石英皿中加入1 mL蛋白溶液,使用紫外可见分光光度计进行紫外吸收光谱检测,扫描波长范围为200~800 nm。
1.2.6.3 纯化后GLEGB的红外光谱分析
配制蛋白浓度为0.1 mg/mL的商品化酶(Glu)和纯化后的GLEGB,在室温条件下,取100 μL蛋白溶液滴加在FT-IR光谱仪的液体池中检测其在4000~500 cm−1范围内的红外光谱。
1.3 数据处理
每组实验均重复三次,数据的方差和显著性分析分别采用Microsoft Excel进行,P<0.05时进行t检验。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 含筛孔八棱锥内构件的结构参数对泡沫排液和分离效果的影响
2.1.1 含筛孔八棱锥内构件的数量对泡沫排液及分离效果的影响
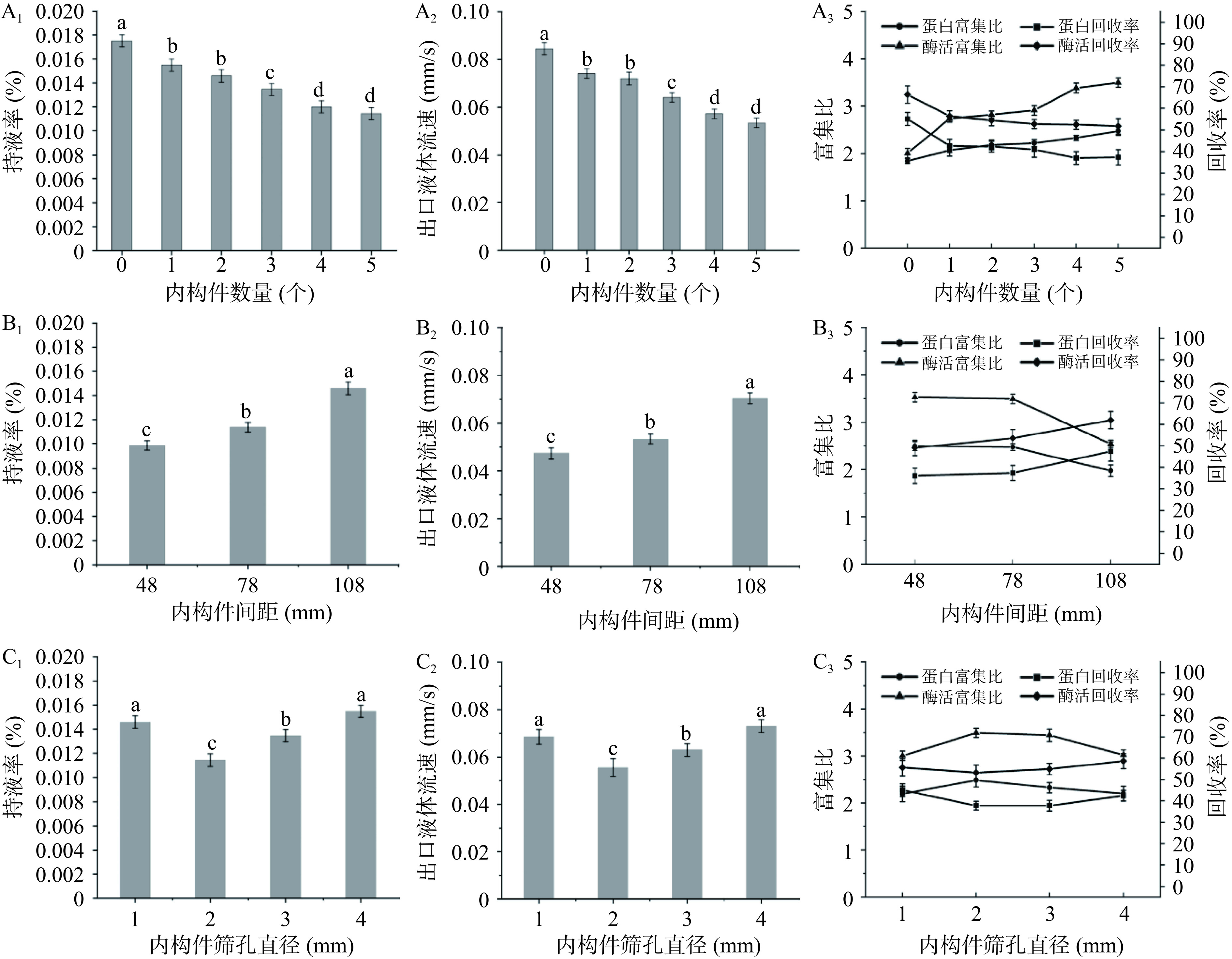
由于柱高度的限制,并考虑到内构件数量过多引起的装置复杂和回收率低,本文仅讨论0~5个内构件对泡沫分离效果的影响。由图4A可知,当内构件的数量逐渐增加时,GLEGB泡沫分离的持液率、出口液体流速、蛋白回收率和酶活性回收率逐渐降低,而蛋白富集比和酶活富集比缓慢增加。这是由于内构件主要作用是通过优化液体流动模式,促进泡沫液中的液体有效排出,增加内构件的数量,可以更有效地促进泡沫液中的液体排出。随着内构件数量的增加,泡沫上升的阻碍能力较强,增强了GLEGB与气泡表面的有效接触和吸附,从而大幅度提高泡沫液中GLEGB的浓度,即提高了富集比。然而,由于内构件产生的流体阻力,导致部分已经携带了GLEGB的泡沫无法完全被回收,而是随着尾流被排出系统之外,这就导致总体上GLEGB的回收率出现一定程度的下降。结果表明,泡沫通过的内构件越多,泡沫的持液率下降越明显,泡沫稳定性越差,泡沫聚合效果越明显,强化了泡沫排液,提高了蛋白质的富集率。以富集比为主要评价指标,选取5个含筛孔八棱锥内构件对GLEGB进行后续泡沫分离实验。
![]() 图 4 含筛孔八棱锥内构件的结构参数对泡沫排液和分离效果的影响注:A内构件数量;B内构件间距;C内构件筛孔直径;图中不同小写字母表示差异显著P<0.05,图7同。Figure 4. Effect of structural parameters on foam drainage and separation of the hollow octagonal prismoid with sieve tray inner component
图 4 含筛孔八棱锥内构件的结构参数对泡沫排液和分离效果的影响注:A内构件数量;B内构件间距;C内构件筛孔直径;图中不同小写字母表示差异显著P<0.05,图7同。Figure 4. Effect of structural parameters on foam drainage and separation of the hollow octagonal prismoid with sieve tray inner component2.1.2 含筛孔八棱锥内构件的间距对泡沫排液及分离效果的影响
结果如图4B所示,随着内构件间距的增大,泡沫持液率和出口液体流速逐渐增加,含筛孔八棱锥内构件对泡沫的排水作用越弱,当内构件间距从48 mm增加到108 mm时,蛋白质富集比和酶活性富集比分别从2.50、3.53下降到1.97、2.54,而蛋白质回收率和酶活性回收率分别从35.98%、49.82%上升到47.33%、62.54%。这是因为随着内构件间距的增大,内构件的位置逐渐下降,下层泡沫比较稳定,泡沫通过内构件时不容易发生湍流引起气泡的聚并,从而降低了富集比,提高了回收率[28]。综合考虑富集比和回收率,选择内构件的间距为78 mm进行后续实验研究。
2.1.3 含筛孔八棱锥内构件的筛孔直径对泡沫排液及分离效果的影响
由图4C1和图4C2可知,随着含筛孔八棱锥内构件筛孔直径的增大,泡沫持液率和出口液体流速先减小后增大,在直径为2 mm时最小,这说明筛孔直径为2 mm时,该内构件促进泡沫排液的能力最强。从图4C3中可以看出,随着筛孔直径从1 mm增大到4 mm,GLEGB的富集比先增大后减小,回收率先减小后增大,这是因为随着筛孔直径的增大气泡之间自上而下流动的液体更容易通过筛孔流出,不利于气泡与间隙液体的相对运动,导致持液率逐渐增大[28]。然而,当筛孔的直径从2 mm减少到1 mm时,泡沫很难通过筛孔上升,只能通过内构件和分离柱之间的间隙上升,内构件周边间隙对泡沫湍流的促进作用不及筛孔,使得泡沫相通过筛孔直径为1 mm的内构件时气泡并没有显著的聚集,导致当筛孔直径为1 mm时GLEGB的富集比较低、回收率较高。以富集比为主要评价指标,选择直径为2 mm的含筛孔八棱锥内构件进行GLEGB泡沫分离的后续实验。
2.2 泡沫分离GLEGB的条件优化
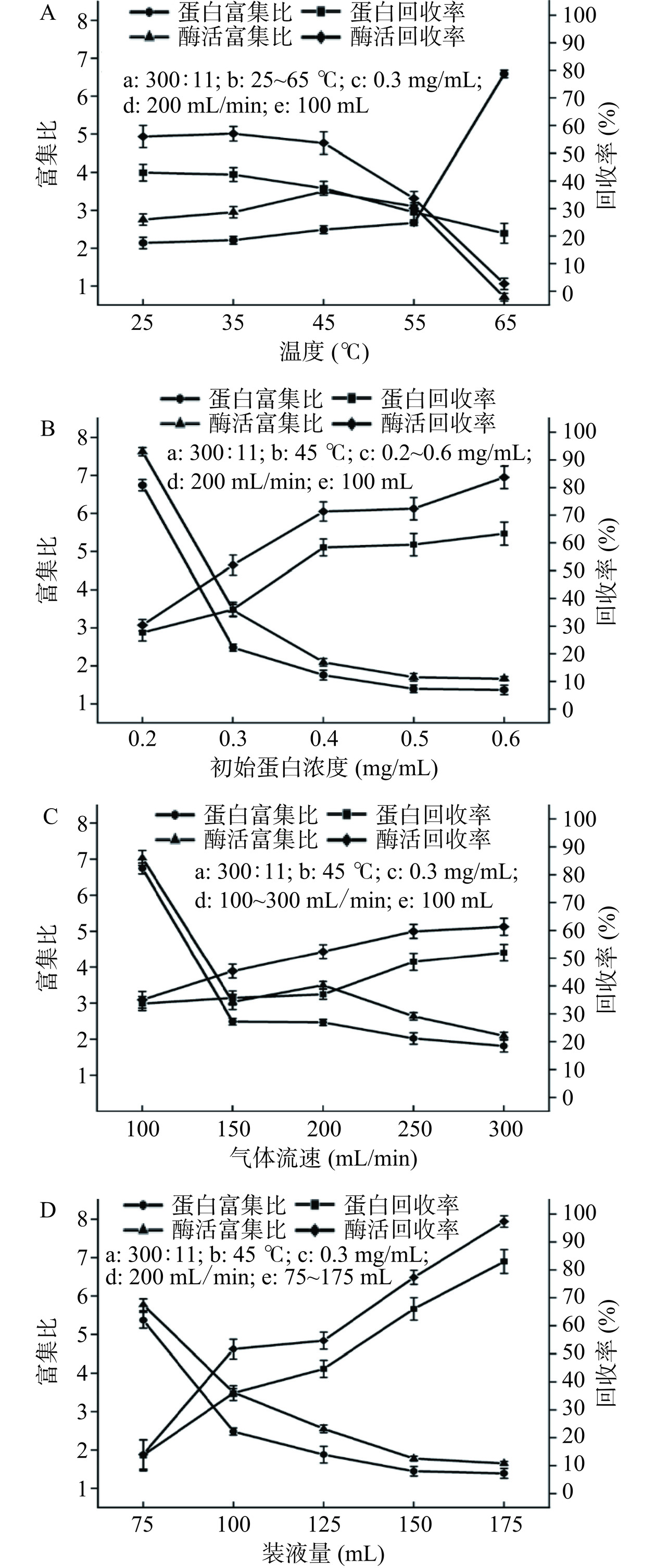
2.2.1 温度对GLEGB回收率和富集比的影响
由图5A可知,随着温度从25 ℃升高到65 ℃,蛋白质富集比从2.11增加到6.56,酶活性回收率先从56.1%增加到57.36%,然后下降到2.67%。当温度较低时,液体黏度较高造成液体中GLEGB之间的吸引力较大,导致流动性差。上升泡沫中夹带的液体难以回流到发酵液中,导致泡沫排液速度减慢。温度的升高会加剧分子运动,降低GLEGB发酵液的黏度,减少表面活性物质吸附到气泡表面的阻力,同时随着温度的升高形成的泡沫稳定性变差促进泡沫排液,提高了GLEGB的蛋白质富集比。当温度高于45 ℃时,Glu的比酶活显著降低[29],导致GLEGB的酶活富集比和回收率迅速下降,为了获得较高的蛋白质富集比和酶活回收率,本研究选择45 ℃作为最佳实验温度。
2.2.2 初始蛋白浓度对GLEGB回收率和富集比的影响
初始蛋白浓度不仅会影响GLEGB在泡沫表面的吸附,还会影响泡沫的稳定性,因此选择最佳初始蛋白浓度以获得高纯度的GLEGB。由图5B所示,随着初始蛋白浓度的增加,蛋白富集比从6.73下降到1.35,酶活富集比从7.67下降到1.81,蛋白回收率从27.08%上升到62.69%,酶活回收率从30.87%上升到83.25%。蛋白质浓度低时,发酵液中表面活性物质减少,降低了发酵液的黏度,形成的泡沫数量少且不稳定,强化了泡沫排液,导致富集比高,回收率低。随着初始蛋白浓度的增加,发酵液的溶液黏度和泡沫的稳定性增加,不利于泡沫排液,增加了泡沫液中液体含量,降低了GLEGB的富集比,提高了回收率。综合考虑富集比和回收率,本研究选择初始蛋白浓度为0.3 mg/mL的GLEGB发酵液进行后续实验研究。
2.2.3 气体流速对GLEGB回收率和富集比的影响
如图5C所示,随着气体流速从100 mL/min增加到300 mL/min,蛋白富集比从6.73下降到1.73,酶活富集比从7.09下降到2.08,蛋白回收率从33.64%上升到51.89%,酶活回收率从35.48%上升到62.39%。在低气体流速时,泡沫在塔内停留时间较长,使泡沫在塔柱内上升时重力引起的排水效果较充分,且泡沫相对干燥,因此收集的泡沫液体积较小,蛋白质浓度较大,蛋白质富集比较高。较高的气体流速可以在单位时间和体积内产生更多的气泡,增加发酵液中GLEGB的传输量,为GLEGB的捕获提供更大的接触面,使更多的GLEGB吸附在气泡表面,因此回收率随气体流速的增加而增加。然而,气体流速的增加缩短了气泡在液相中的停留时间,阻碍了间隙液回流,不利于泡沫排液[30],导致收集的泡沫液中GLEGB浓度较低。综合考虑GLEGB的富集比和回收率,适宜的气体流速为200 mL/min。
2.2.4 装液量对GLEGB回收率和富集比的影响
如图5D所示,随着装液量从75 mL增加到175 mL,蛋白富集比从5.31降低到1.42,酶活富集比从5.81降低到1.64,蛋白回收率从10.61%增加到86.48%,酶活回收率从11.63%增加到97.75%。在泡沫分离过程中,当气体流速和泡沫分离柱高度固定时,塔内装液量的增加,意味着柱内液相高度增加,泡沫相高度相对降低,即气泡在液相中的停留时间增加,有利于GLEGB在气泡表面吸附。但是,气泡在泡沫相的停留时间较短,导致泡沫排液时间较短,不利于泡沫聚并,增大了泡沫的持液能力,导致泡沫液中目标蛋白浓度降低,富集比降低[10]。综合考虑GLEGB的富集比和回收率,后续实验选择装液量为100 mL。
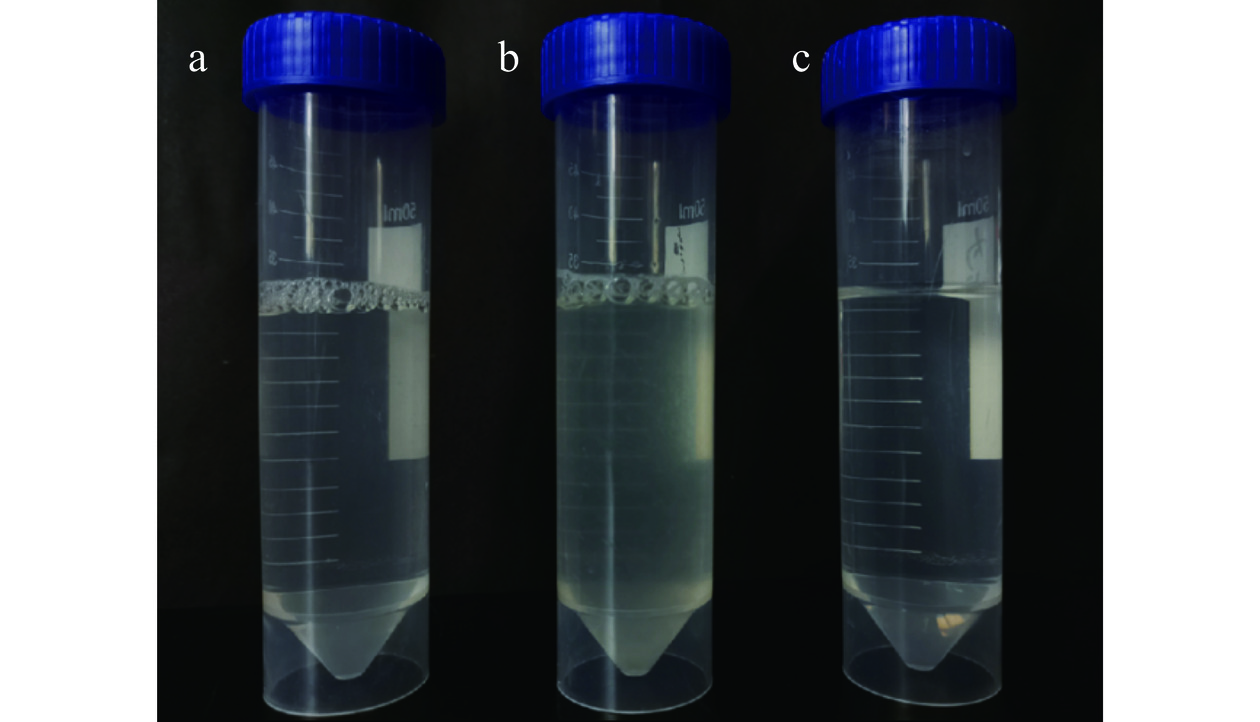
为了获得较高的富集比和回收率,确定了从发酵液中分离GLEGB的最佳条件。由图6可以明显看出,与进料液和残液相比,泡沫液颜色最深,蛋白质浓度最高,说明泡沫分离效果显著。在初始蛋白浓度0.3 mg/mL、温度45 ℃、气体流速200 mL/min、装液量100 mL的适宜条件下,蛋白富集比为2.46±0.10,蛋白回收率为36.88%±1.10%,酶活富集比为3.50±0.11,酶活回收率为52.49%±2.50%。相比于传统的泡沫分离或萃取技术,通常其目标物的富集比相对较低,例如Qin等[31]利用泡沫分离技术从毕赤酵母上清发酵液分离β-葡萄糖苷酶,在最佳条件下β-葡萄糖苷酶的富集比为0.56。本研究取得的富集比明显提高了目标蛋白的分离效率,表明内构件的引入对优化气液接触、增强目标蛋白吸附以及提高泡沫稳定性等方面起到了积极作用。此外,许多学者致力于通过优化工艺参数或采用新型表面活性剂来提高目标物的富集比。例如Shao等[9]以十二烷基硫酸钠(sodium dodecyl sulfate,SDS)为表面活性剂,利用泡沫分离技术分离念珠菌南极洲脂肪酶B(Candida antarctica Lipase B,CALB),并对实验条件进行优化。在最佳条件下,CALB的富集比为0.95。尽管这个数值相较于传统方法有所改进,但仍低于本文所提到的富集比。相比之下,本文通过添加内构件的方式成功地将泡沫分离的蛋白富集比提高到了2.46±0.10,显示出该技术在提高分离效率方面的优势。
2.3 GLEGB泡沫液的纯化
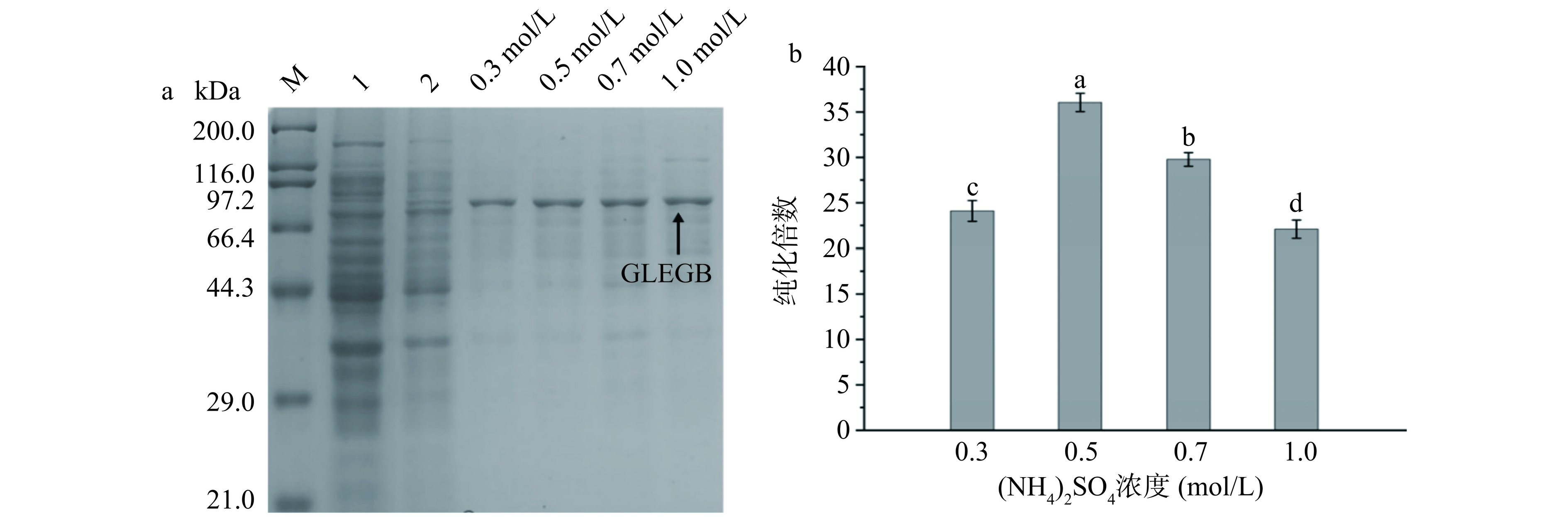
鉴于本团队前期基于ELPs的温度敏感性特性对GLEGB的分离纯化进行的研究,本实验选择(NH4)2SO4作为还原浊点盐[26]。如图7a所示,在80 kDa附近有一个与GLEGB理论分子量相一致的条带,当(NH4)2SO4浓度为0.5 mol/L时,GLEGB的最大纯化倍数为37.25±0.60。由图7b所示,随着(NH4)2SO4浓度的进一步增加,GLEGB的纯化倍数逐渐降低,这可能是由于高浓度(NH4)2SO4引起的强盐析作用,导致杂质蛋白共沉淀[32]。
2.4 结构分析
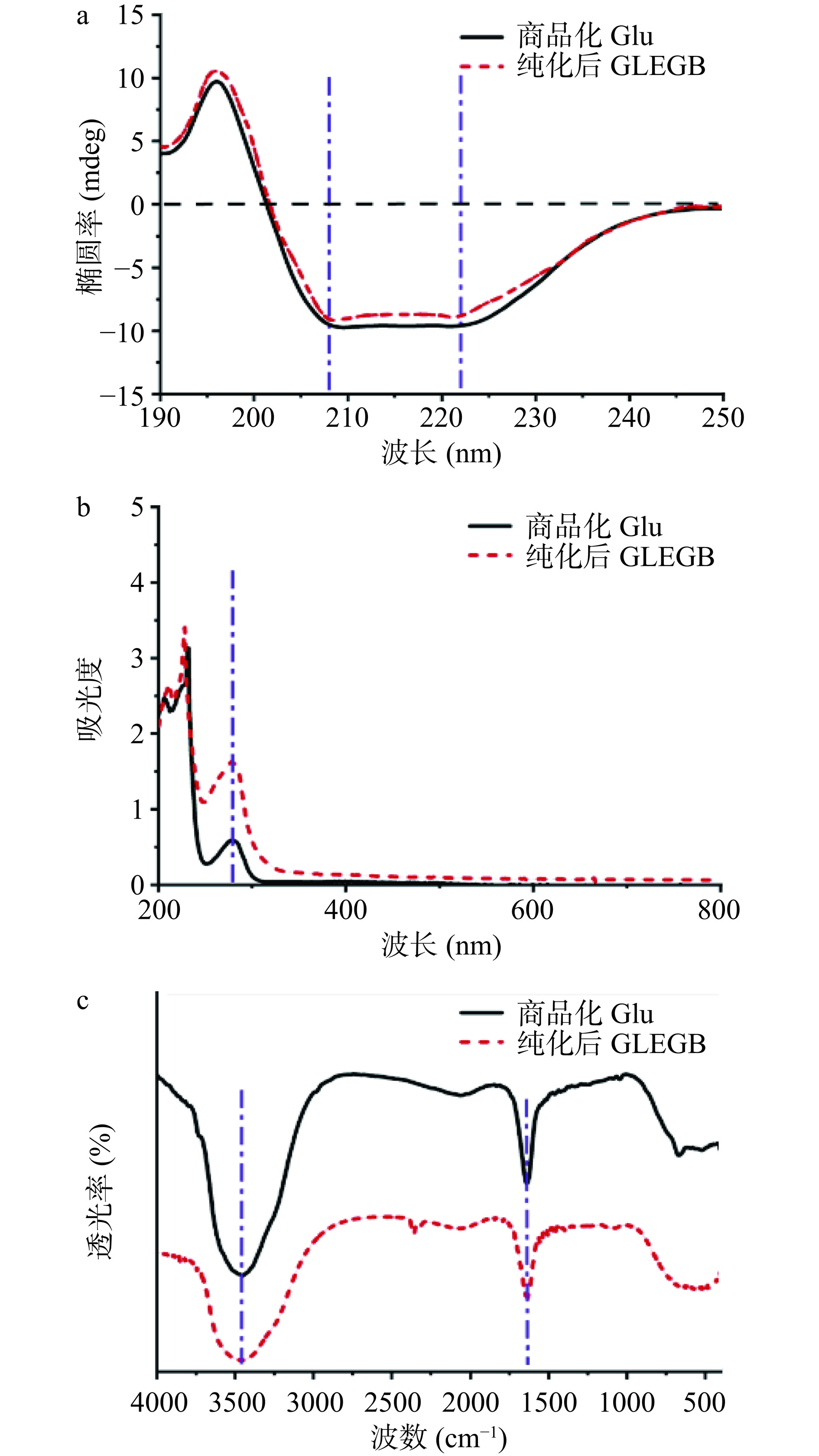
为了验证泡沫分离过程是否会引起Glu的二级结构发生改变,分别使用圆二色光谱仪、UV-vis分光光度计和FT-IR光谱仪对商品化的Glu和纯化后的GLEGB进行结构分析。如图8a所示,GLEGB和Glu在196 nm处有一个正峰,在208 nm和222 nm处有两个负峰,表明GLEGB具有Glu的典型α-螺旋结构[33]。同样,UV-vis检测结果图8b显示,经过两步纯化后的GLEGB在278 nm处有一个与Glu相似的峰。此外,由图8c的FT-IR分析可知,在1500~1750 cm−1和3250~3500 cm−1处,Glu和GLEGB的峰均无显著性差异[34]。上述结果表明,泡沫分离过程不会改变GLEGB的结构。
3. 结论
本研究设计了一种新型含筛孔八棱锥内构件,用以从发酵液中分离GLEGB,该内构件的加入有效地提高了GLEGB的富集比。实验结果显示,在内构件数量为5、间距为78 mm、筛孔直径为2 mm、蛋白质初始浓度为0.3 mg/mL、温度为45 ℃、气体流速为200 mL/min、装液量为100 mL的最佳操作条件下,通过这种内构件的辅助作用,GLEGB的富集比提高至2.46±0.10为对照柱的1.33倍,虽然酶活回收率有小幅度下降,降至52.49%±2.50%,但仍体现出良好的分离效果。此外,本研究还利用ELPs的温敏特性对GLEGB泡沫溶液进行了进一步纯化处理,GLEGB的纯化倍数为37.25±0.60。最后,对纯化后的GLEGB的结构进行表征,结果证明纯化过程并未对GLEGB的结构造成明显改变,保证了其活性与功能的完整性。
-
图 4 含筛孔八棱锥内构件的结构参数对泡沫排液和分离效果的影响
注:A内构件数量;B内构件间距;C内构件筛孔直径;图中不同小写字母表示差异显著P<0.05,图7同。
Figure 4. Effect of structural parameters on foam drainage and separation of the hollow octagonal prismoid with sieve tray inner component
-
[1] STEVENSON P, LI X, EVANS G M. A mechanism for internal reflux in foam fractionation[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal,2008,39(3):590−593. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2007.11.022
[2] LIU C, ZHANG W, SONG S, et al. Study on the activation mechanism of lead ions in wolframite flotation using benzyl hydroxamic acid as the collector[J]. Minerals Engineering,2019,141:105859. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2019.105859
[3] MATSUOKA K, YAMAGUCHI N. Removal of period 4 transition metals by foam separation[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids,2021,325:115185. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2020.115185
[4] 孙宇格, 陈林, 姚楠, 等. 紫苏籽蛋白协助泡沫分离去除亚甲基蓝[J]. 当代化工研究,2023(4):163−166. [SUN Yuge, CHEN Lin, YAO Nan, et al. Perilla seed protein assists the bubble separation to remove the armor blue[J]. Contemporary Chemical Research,2023(4):163−166.] SUN Yuge, CHEN Lin, YAO Nan, et al. Perilla seed protein assists the bubble separation to remove the armor blue[J]. Contemporary Chemical Research, 2023(4): 163−166.
[5] ROBEY N M, DA SILVA B F, ANNABLE M D, et al. Concentrating per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in municipal solid waste landfill leachate using foam separation[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2020,54(19):12550−12559.
[6] 刘丹宇, 张怡, 刘伟, 等. 超声波辅助泡沫分离回收溶液中牛血清白蛋白的性质研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(6):67−72. [LIU Danyu, ZHANG Yi, LIU Wei, et al. Study on the properties of bovine serum albumin in ultrasonic assisted foam separation recovery solution[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(6):67−72.] LIU Danyu, ZHANG Yi, LIU Wei, et al. Study on the properties of bovine serum albumin in ultrasonic assisted foam separation recovery solution[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(6): 67−72.
[7] WANG Z, ZHANG W, GAN W, et al. Preparation of dioscin from Trigonella foenum-graecum by foam separation-preparative high-performance liquid chromatography[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2022,248(2):477−483. doi: 10.1007/s00217-021-03893-w
[8] 黄磊磊, 刘佳怡, 王天怡, 等. 纤维素酶辅助超声提取丁香叶黄酮工艺优化及抗氧化性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,45(4):1−10. [HUANG Leilei, LIU Jiayi, WANG Tianyi, et al. Optimization of cellulase-assisted ultrasound extraction and antioxidant analysis of flavonoids from syringa oblata leaves[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,45(4):1−10.] HUANG Leilei, LIU Jiayi, WANG Tianyi, et al. Optimization of cellulase-assisted ultrasound extraction and antioxidant analysis of flavonoids from syringa oblata leaves[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 45(4): 1−10.
[9] SHAO W, LIN Y, LU Y. Study on the extraction technology of candida antarctica lipase b by foam separation[J]. Processes,2020,9(1):14. doi: 10.3390/pr9010014
[10] 张可可, 胡楠, 李会珍, 等. 植物蛋白泡沫分离技术研究现状[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(24):278−283. [ZHANG Keke, HU Nan, LI Huizhen, et al. Advances in foam fractionation technology of plant protein[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(24):278−283.] ZHANG Keke, HU Nan, LI Huizhen, et al. Advances in foam fractionation technology of plant protein[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(24): 278−283.
[11] HU N, WU Z, JIN L, et al. Nanoparticle as a novel foam controller for enhanced protein separation from sweet potato starch wastewater[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2019,209:392−400. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2018.07.064
[12] LI R, DING L, WU Z, et al. β-Cyclodextrin assisted two-stage foam fractionation of bromelain from the crude extract of pineapple peels[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2016,94:233−239. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.08.046
[13] LIU W, HE Z, YIN H, et al. Maillard reaction products for strengthening the recovery of trans-resveratrol from the muscat grape pomace by alkaline extraction and foam fractionation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2021,256:117754. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117754
[14] 姜建星, 李瑞, 刘桂敏, 等. 螺旋内构件强化排液的泡沫分离塔内上升泡沫的流体力学[J]. 河北工业大学学报,2015(2):75−80. [JIANG Jianxing, LI Rui, LIU Guimin, et al. Hydrodynamics of rising foam in foam fractionation column with spiral internal components[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Technology,2015(2):75−80.] JIANG Jianxing, LI Rui, LIU Guimin, et al. Hydrodynamics of rising foam in foam fractionation column with spiral internal components[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Technology, 2015(2): 75−80.
[15] XU N, WANG L, DOU N, et al. Foam fractionation for enhancing silica gel adsorption of urokinase from human urine[J]. Asia-Pacific Journal of Chemical Engineering,2019,14(4):e2334. doi: 10.1002/apj.2334
[16] 宋林, 张炜, 荆永康, 等. 裸藻蛋白泡沫分离的工艺优化及功能特性分析[J]. 精细化工,2023,46(6):1341−1349. [SONG Lin, ZHANG Wei, JING Yongkang, et al. Process optimization and functional characteristics analysis of Euglena protein foam separation[J]. Fine Chemicals,2023,46(6):1341−1349.] SONG Lin, ZHANG Wei, JING Yongkang, et al. Process optimization and functional characteristics analysis of Euglena protein foam separation[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2023, 46(6): 1341−1349.
[17] ZHANG Z, ZHANG Y, WU Z, et al. Intensification of the interfacial adsorption of whey soy protein in the liquid phase using a foam separation column with the vertical sieve tray internal[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2014,53:308−313. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.12.040
[18] HU N, SHU T, WU Z, et al. BS12-assisted flotation for the intensification of SNPs separation from CMP wastewater using a novel flotation column[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2018,344:788−796. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.028
[19] 史萌. 温度和构件共同强化排液的泡沫分离回收高浓度表面活性剂工艺[D]. 天津:河北工业大学, 2015:22−29. [SHI Meng. The process of foam separation and recovery of high concentration surfactant by temperature and component together strengthening drainage[D]. Tianjin:Hebei University of Technology, 2015:22−29.] SHI Meng. The process of foam separation and recovery of high concentration surfactant by temperature and component together strengthening drainage[D]. Tianjin: Hebei University of Technology, 2015: 22−29.
[20] 卢珂, 吴兆亮, 侯凯湖, 等. 泡沫相塔壁对泡沫分离牛血清蛋白分离性能的影响[J]. 化工学报,2012,63(6):1765−1772. [LU Ke, WU Zhaoliang, HOU Kaihu, et al. Effect of foam-based column wall on the separation performance of bovine serum protein[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering,2012,63(6):1765−1772.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2012.06.016 LU Ke, WU Zhaoliang, HOU Kaihu, et al. Effect of foam-based column wall on the separation performance of bovine serum protein[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2012, 63(6): 1765−1772. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0438-1157.2012.06.016
[21] LI R, WU Z L, WANG Y J, et al. Separation of total saponins from the pericarp of Sapindus mukorossi Gaerten. by foam fractionation[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2013,51:163−170. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.08.079
[22] LUO X, LIN Q, WEN S, et al. Effect of sodium dodecyl sulfonate on the foam stability and adsorption configuration of dodecylamine at the gas-liquid interface[J]. Langmuir,2021,37(3):1235−1246. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c03248
[23] YANG Q W, WU Z L, ZHAO Y L, et al. Enhancing foam drainage using foam fractionation column with spiral internal for separation of sodium dodecyl sulfate[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011,192(3):1900−1904. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.07.018
[24] LI Z, ZHENG H, WU Z. Separation of bovine serum albumin by foam fractionation with wire gauze structured packing column[J]. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology,2015,175:502−512. doi: 10.1007/s12010-014-1288-1
[25] FANG S, HUANG W, WU J, et al. Separation and purification of recombinant β-glucosidase with hydrophobicity and thermally responsive property from cell lysis solution by foam separation and further purification[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2023,71(7):3362−3372. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c07405
[26] RONG J, HAN J, ZHOU Y, et al. Process integration of production, purification, and immobilization of β-glucosidase by constructing Glu-linker-ELP-GB system[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2018,57(46):15620−15631.
[27] SOKOL C L, BARTON G M, FARR A G, et al. A mechanism for the initiation of allergen-induced T helper type 2 responses[J]. Nature Immunology,2008,9(3):310−318. doi: 10.1038/ni1558
[28] 李志强. 塔板和填料式泡沫分离塔的开发及其强化排液性能研究[D]. 天津:河北工业大学, 2015. [LI Zhiqiang. Development of tray and packing foam separation columns and their properties of enhancing foam drainage[D]. Tianjin:Hebei University of Technology, 2015.] LI Zhiqiang. Development of tray and packing foam separation columns and their properties of enhancing foam drainage[D]. Tianjin: Hebei University of Technology, 2015.
[29] PILON L, VISKANTA R. Minimum superficial gas velocity for onset of foaming[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing:Process Intensification,2004,43(2):149−160. doi: 10.1016/S0255-2701(03)00012-6
[30] ALNADARI F, XUE Y, ALSUBHI N H, et al. Reusability of immobilized β-glucosidase on sodium alginate-coated magnetic nanoparticles and high productivity applications[J]. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society,2022,26(5):101517. doi: 10.1016/j.jscs.2022.101517
[31] QIN Yuhang, CHEN Yuqing, PENG Yajuan, et al. Application of foam separation in production of β-glucanase in Pichia[J]. Polish Journal of Chemical Technology,2022,24(3):1−7. doi: 10.2478/pjct-2022-0015
[32] 张煜, 王建英, 王晶妍. 硫酸铵盐析法分级分离大豆酸沉蛋白[J]. 河南师范大学学报:自然科学版,2011,39(6):99−100. [ZHANG Yu, WANG Jianying, WANG Jingyan. Separation of soybean acid proteins by ammonium sulfate salt fraction[J]. Journal of Henan Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2011,39(6):99−100.] ZHANG Yu, WANG Jianying, WANG Jingyan. Separation of soybean acid proteins by ammonium sulfate salt fraction[J]. Journal of Henan Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(6): 99−100.
[33] FAN L, XIE P, WANG Y, et al. Biosurfactant-protein interaction:Influences of mannosylerythritol lipids-A on β-glucosidase [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(1):238−246. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04469
[34] COUTINHO T C, ROJAS M J, TARDIOLI P W, et al. Nanoimmobilization of β-glucosidase onto hydroxyapatite[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,119:1042−1051. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.08.042





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



