Preparation and Characteristics of Acid-soluble Soybean Protein Hydrolysates
-
摘要: 本文采用不同pH对大豆蛋白酶解产物进行酸处理,分析比较产物在理化特性、呈味特性和体外抗氧化活性方面的差异,同时,基于肽组学解析产物多肽组成的变化,以探究酸溶性大豆蛋白酶解产物的制备特性。结果表明:酸处理虽造成产物氮回收率和游离氨基酸总量的下降,但对整体抗氧化活性和肽分子量分布影响较小。在pH5下对酶解产物进行酸处理,可使苦味疏水性氨基酸含量降低从而减弱产物的苦味。多肽组学分析发现,大豆蛋白酶解产物主要以二~五肽为主,在酸处理pH为5时,多肽长度分布变化较小,但在酸处理pH为3时,产物中五肽与八肽相对占比略微升高。与强酸(pH3)处理相比,在弱酸(pH5)条件下制备酸溶性大豆蛋白酶解产物,可有利于保留更高的氮回收率(约54.50%)、更强的体外抗氧化活性以及更多的潜在抗氧化肽数量(368条),并获得与中性条件下较为一致的多肽长度分布和更低的苦味,有助于酸溶性大豆蛋白酶解产物的工业化应用。Abstract: In this work, the enzymatic hydrolysates of soybean protein were treated with acid at different pH values, and the differences in physicochemical properties, taste characteristics and in vitro antioxidant activities of the products were analyzed. Meanwhile, changes in peptide composition were also analyzed based on the peptidomics analysis to investigate the preparation characteristics of acid-soluble soy protein hydrolysates. The results showed an evident decrease in nitrogen recovery rate and total free amino acid contents after the acid treatment process. Nevertheless, only slight changes were observed in the antioxidant activity and peptide molecular weight distribution of the products.When the hydrolysates were acid-treated at pH5, the content of bitter hydrophobic amino acids was reduced, thereby the bitterness decreased. Additionally, the peptides identified from the enzymatic hydrolysates of soybean protein were primarily presented with the length values ranging from 2 to 5. For products treated at pH3, more pentapeptides and octapeptides were observed through the peptidomic analysis, while minor changes were observed for those treated at pH5. Moreover, compared with the product treated at pH3, the bitter taste of the hydrolysates could be evidently reduced after the acid treatment at pH5. Therefore, the acid treatment at pH5 was recommended for preparation of the acid-soluble soybean protein hydrolysates, which could help to achieve higher product yield (about 54.50%), better antioxidant activity and more potential antioxidant peptides (368), as well as a consistent peptide distribution and lower bitter taste.
-
我国年消费大豆约1.1亿吨,其中经油脂加工后产生的副产物(豆粕)约达6500万吨[1]。大豆蛋白作为豆粕的主要营养成分(含量高达40%以上),其加工方式与资源利用途径一直是国内外科研学者关注的焦点[2]。从豆粕中提取大豆蛋白,并将其进行生物酶解制成抗氧化肽是当前大豆蛋白资源利用的重要途径之一[3],但受相关产品实际应用局限性,大豆蛋白资源利用状况仍有待改善[4]。对大豆蛋白酶解产物进行酸处理,增强产品在酸性饮料中的溶解性和稳定性,从而借助庞大的饮料消费市场拓展和提升大豆蛋白资源利用率[5],对于充分挖掘大豆蛋白资源的营养价值和经济价值具有重要意义[6]。然而,关于酸处理对大豆蛋白酶解产物制备特性的影响尚未见有相关报道。
目前,相关研究主要聚焦于大豆蛋白酶解产物的制备纯化、多肽结构鉴定、构效分析等领域,而对其酸处理特性研究较少。胡晓倩等[7]通过探究不同条件对大豆蛋白酶解效果及抗氧化活性的影响,确认了其较优制备工艺为:加酶量2500 U/g、料液比1:50、温度51 ℃、酶解时间2 h、pH10.4。Zhang等[8]采用UPLC-MS/MS从大豆蛋白酶解产物中鉴定了4条抗氧化肽(VVFVDRL、VIYVVDLR、IYVVDLR和IYVFVR),发现缬氨酸残基对多肽抗氧化活性具有重要贡献。进一步的构效研究表明,亮氨酸残基对大豆多肽的抗氧化活性亦具有突出作用[9]。而大豆蛋白富含亮氨酸,是制备抗氧化肽的重要物质基础[10]。这些研究为大豆蛋白酶解产物的工业应用提供了良好的理论依据,极大地促进了早期相关产业的快速发展[11−13]。然而,由于酸处理下大豆蛋白酶解产物的制备特性研究缺乏,酶解产物酸溶性较差,限制了产品在酸性饮料、运动饮料等大宗消费品中的应用,以致当前相关产业发展缓慢[14]。
为此,本文采用不同pH对大豆蛋白酶解产物进行酸处理,分析比较产物在滋味、理化和体外抗氧化活性等方面的差异,再结合多肽组学技术明确产物的多肽组成及其变化情况,研究酸溶性大豆蛋白酶解产物的制备及其特性,以期为酸溶性多肽的工业制备与应用提供理论依据与技术指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
碱性蛋白酶(1000000 U/g) 丹麦诺维信有限公司;大豆分离蛋白 山东省临沂山松生物制品有限公司;多肽分子量标准品Gly-Gly-Gly(189 Da)、Gly-Gly-Tyr-Arg(451 Da)、胰岛素(5808 Da)、杆菌肽(1450 Da)、细胞色素C(12384 Da) 美国Sigma公司;甲酸、乙腈(LC-MS级) 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-苦肼基自由基(DPPH)、2,2’-联氮双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二胺盐(ABTS) 默克化工技术(上海)有限公司;过硫酸钾、氯化亚铁、氢氧化钠、盐酸、三氯乙酸等试剂 均为分析纯,上海迈瑞尔生化科技有限公司。
BSA223S 万位分析天平 赛多利斯科学仪器有限公司;K9840半自动凯式定氮仪 海能仪器股份有限公司;Multiskan SkyHigh 全波长酶标仪 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;Sciex X500R LC-ESI-Q-TOF高分辨液相色谱-质谱联用仪 美国AB SCIEX公司;ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3色谱柱(1.8 µm,2.1 mm×100 mm) 美国Waters公司;PB-10台式pH计 梅勒特-托利多仪器有限公司;SHA-B 双功能水浴恒温振荡器 常州市金坛友联实验仪器厂;TDL-5000BR冷冻离心机 上海安亭科学仪器厂;Milli-Q IX 7005超纯水系统 美国Millipore公司;SA402B型电子舌分析系统 日本Insent公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 蛋白的酶解与酸处理
配制大豆分离蛋白溶液(料水比1:10),调pH至8.0,加入碱性蛋白酶(1%,w/w,以干基计),在50 ℃下恒温振荡酶解24 h,酶解结束后,取出灭酶(95 ℃,15 min),待冷却至室温,在4000 r/min、4 ℃下离心20 min,弃去沉淀,取上清液,调pH,分别在pH7.0、5.0和3.0下静置30 min,离心取上清液,再次调pH7.0,冷冻干燥备用。
1.2.2 氮含量的测定
参考国标GB 5009.5-2016测定不同pH下酸处理后所得大豆肽的氮含量并以此计算回收率。
1.2.3 相对分子量分布分析
参考GB/T 22492-2008的方法,对水解产物的分子量进行测定。采用Thermo UltiMate 3000 HPLC系统,色谱条件:TSK gel G2000 SWXL凝胶色谱柱(7.8 mm×300 mm);流动相为V(乙腈):V(水)=40:60等度洗脱,三氟乙酸添加量0.1%;时间40 min;流速1 mL/min;进样量10 μL;检测波长214 nm。以多肽分子量的对数(lgMw)对保留时间(Rt)作图作线性回归方程(lgMw=−0.245Rt+6.977,R2=0.989)。
1.2.4 游离氨基酸含量的测定
参照Klikarova等[15]方法并略作修改,取样品200 μL,加入0.1 mol/L三乙胺乙腈溶液100 μL和0.2 mol/L异硫氰酸苯酯乙腈溶液100 μL涡旋混匀,室温静置1 h,加入600 μL正己烷涡旋混匀去除过量衍生试剂,静置10 min,吸取下层溶液并用0.05 mol/L的乙酸钠水溶液进行稀释,采用Thermo UltiMate 3000 HPLC系统上机分析,色谱柱为Elite-AAP氨基酸专用柱(250 mm×4.6 mm),进样量10 μL,流速1 mL/min,波长254 nm。
1.2.5 电子舌分析
化学传感器有C00(苦味)、AE1(涩味)、CA0(酸味)、CT0(咸味)、AAE(鲜味)共5个,经活化、校正后测样。为保证实验结果,整个测试过程在25 ℃的环境中进行,取30 mmol/L氯化钾、0.3 mmol/L酒石酸作唾液参比液,取70 mL样品稀释液,测试时间30 s,每个样品重复测试4次,取后三次平均值作为测试结果。
1.2.6 体外抗氧化活性
1.2.6.1 DPPH自由基清除率的测定
参照Qi等[16]的方法略作修改,配制0.1 mol/L DPPH乙醇溶液与样品等体积混合,室温避光反应30 min,无水乙醇、蒸馏水分别作空白和对照组,测定反应液在517 nm的吸光值,并计算样品的DPPH自由基清除率。
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=(1−As−AbA0)×100 式中:As为样品加DPPH自由基517 nm的吸光值;A0为蒸馏水加DPPH自由基517 nm的吸光值;Ab为样品加无水乙醇517 nm的吸光值。
1.2.6.2 ABTS+自由基清除率的测定
参照Patrycja等[17]的方法,将7 mmol/L ABTS溶液和2.45 mmol/L过硫酸钾溶液等量混合,避光静置16 h,无水乙醇稀释至734 nm吸光值为0.7±0.02的工作溶液。10 μL样品与200 μL工作液混合,室温避光反应6 min,于734 nm测定吸光值,蒸馏水作空白,根据下列公式计算样品的ABTS+自由基清除率:
ABTS+自由基清除率(%)=A0−AsA0×100 式中:As为样品加ABTS+自由基734 nm的吸光值;A0为水加ABTS+自由基734 nm的吸光值。
1.2.6.3 铁离子还原力的测定
参照Chen等[18]的方法略作修改,取1 mL样品与0.2 mol/L pH6.6磷酸盐缓冲溶液、1%铁氰化钾溶液各2 mL混合,以蒸馏水作空白,50 ℃水浴20 min,再加入10%三氯乙酸溶液2 mL,4000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液加入2 mL蒸馏水和0.1%三氯化铁溶液2 mL,混合后测定样品700 nm下吸光值,减去空白后的吸光值即为样品还原力。
1.2.7 多肽组学分析
参照课题组前期实验方法[19],将样品稀释至蛋白浓度为2 mg/mL,过0.22 μm水系膜,上机分析。采用Sciex X500R LC-ESI-Q-TOF高分辨液相色谱-质谱联用仪对样品质谱数据进行采集。色谱条件:流动相 A为0.1%甲酸-水溶液,B为乙腈,梯度洗脱:0~4 min 5.0%B,4~6 min 5.0%~10.0%B,6~30 min 10.0%~40.0%B,30~34 min 40.0%~90.0%B,34~40 min 90%B,40~42 min 90.0%~5.0%B,42~52 min 5.0%B,流速0.05 mL/min,进样量1 μL,柱温40 ℃。质谱条件:扫描周期0.642 s,ESI离子源温度500 ℃,正离子模式,喷雾电压5500 V,TOF一级扫描范围100~1200 Da,二级扫描范围50~1200 Da,工作模式IDA,最大候选离子数4,开启动态排除,其余参数为默认优化值。对采集到的质谱数据使用ProteoWizard 3.0进行格式转换,从Uniport下载大豆蛋白数据库(关键词:soybean),采用实验室自研肽组学分析软件PepOS 2.0.3[19](五邑大学,广东江门)进行多肽鉴定,并就不同样品中谱图鉴定数量、多肽鉴定数量-长度分布、相对峰面积占比-长度分布及潜在抗氧化肽数量(序列中含有已知抗氧化肽片段的多肽)进行统计分析。参数设置:使用Exhaust和Search双引擎解谱,多肽鉴定长度设置2~25,一级离子偏差0.005 Da,二级离子偏差0.02 Da,并行核心数量12,子离子簇匹配类型a、b和y,贝叶斯评分阈值为60,保留其他存在完整子离子簇匹配的解谱结果。
1.3 数据处理
实验重复三次,结果取平均值±标准差,采用Excel 2016对实验数据进行整理,利用SPSS 2.0进行单因素方差分析和显著性分析,Orgin 2018进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同pH酸处理对大豆蛋白酶解产物氮回收率和肽分子量分布的影响
氮回收率可用于表征蛋白、多肽、氨基酸类物质在经过相应处理后的资源回收利用情况。对大豆蛋白酶解产物离心所得上清液进行不同pH酸处理,最终产物的氮回收率和肽分子量分布如表1所示。由表1可知,未经酸处理时(pH7),产物的氮回收率达72%,表明大豆蛋白酶促水解效果和终产物蛋白资源回收利用效果较好。然而,样品在pH分别为5和3时的氮回收率均有所下降,在pH3时最低,氮回收率仅约38%。这说明酶解产物中较大部分多肽的等电点接近3或5[20]。由于等电点附近多肽分子间静电斥力减小,易产生聚集和沉淀,从而导致终产物氮回收率降低。这在一定程度上亦反映了通过酸处理去除酸不可溶性多肽成分的有效性。
表 1 不同pH酸处理所得产物的氮回收率与多肽分子量分布Table 1. Nitrogen recovery rate and peptide molecular weight distribution of the products after acid treatments at different pHpH 氮回收率(%) 分子量范围及分布百分比(%) >10 kDa 5~10 kDa 3~5 kDa 1~3 kDa <1 kDa 7 72.68±1.08a 0.43±0.03a 1.53±0.03a 2.65±0.14a 13.84±0.27a 81.55±0.47c 5 54.50±0.47b 0.39±0.01ab 1.43±0.03b 2.34±0.02b 10.37±0.06c 85.40±0.04a 3 37.82±1.48c 0.33±0.01b 1.33±0.03c 2.29±0.01b 11.63±0.47b 84.34±0.32b 注:同列数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 此外,由表1可知,各产物的肽分子量分布均主要集中于1 kDa以下[21],反映大豆蛋白酶解效果较好,产物中主要以短链多肽为主。同时,与原酶解产物(pH7)的肽分子量分布结果相比,不同pH酸处理对产物肽分子量分布影响较小,主要表现为3 kDa以下组分的小幅变化。其中,经pH5酸处理所得产物1 kDa以下组分占比较高,而未经酸处理时(pH7)产物<1 kDa多肽组分分布占比最低。这说明适度的酸处理在一定程度上有利于去除部分大分子肽段成分。考虑不同pH下酸处理所得产物肽分子量分布相近,而产物整体氮回收率明显下降,推测产物中被酸处理沉淀去除的多肽组分拥有与原酶解产物相似的分子量分布特性。
2.2 不同pH酸处理对大豆蛋白酶解产物游离氨基酸组成的影响
不同pH酸处理后所得产物的游离氨基酸组成如表2所示。由表2可知,经不同pH酸处理后必需氨基酸含量、疏水性氨基酸含量、鲜味氨基酸含量及游离氨基酸总量均呈现下降趋势,且酸处理pH越低,下降幅度越高,其中尤以疏水性氨基酸含量的下降幅度最大,由此推测酸处理可能将对大豆蛋白酶解产物的苦味及抗氧化活性产生较为明显的影响。此外,当pH由7下降为5时,必需氨基酸含量、疏水性氨基酸含量与游离氨基酸总量降幅远超pH由5下降为3时的降幅,分析原因主要与大多数氨基酸的等电点为5~6有关。产物中游离脯氨酸较为丰富,反映碱性蛋白酶可能对大豆蛋白中的脯氨酸残基具有酶切倾向[22]。同时,经酸处理后,产物中游离氨基酸的总量明显下降,间接说明多肽的相对组成占比有所升高,这可为酸溶性多肽的制备提供良好的物质基础。
表 2 不同pH酸处理所得产物的游离氨基酸组成(mg/g)Table 2. Free amino acid composition of the products after acid treatments at different pH (mg/g)游离氨基酸名称 pH3 pH5 pH7 天冬氨酸(Asp) 2.15±0.25c 4.47±0.04b 6.59±0.44a 谷氨酸(Glu) 8.18±0.18b 11.40±0.13a 11.47±0.00a 丝氨酸(Ser) 3.13±0.01a 0.88±0.59c 1.18±0.05b 甘氨酸(Gly) 2.05±0.12c 4.26±0.15b 7.02±0.02a 组氨酸(His) 9.62±0.00a 7.60±0.10b 7.54±0.02b 精氨酸(Arg) 2.32±0.29b 1.53±0.41c 9.48±1.20a 苏氨酸(Thr) 5.77±0.43c 8.63±0.03b 10.85±0.84a 丙氨酸(Ala) 2.99±0.02c 9.46±0.08a 6.47±0.00b 脯氨酸(Pro) 82.61±0.01b 79.73±0.00c 171.68±0.00a 酪氨酸(Tyr) 4.05±0.02c 8.85±0.01b 18.99±0.00a 缬氨酸(Val) 5.65±0.03b 4.06±0.03c 6.70±0.01a 蛋氨酸(Met) 11.76±0.02c 14.71±0.02b 16.85±0.02a 半胱氨酸(Cys) 10.65±0.01b 10.50±0.03b 14.67±0.17a 异亮氨酸(Ile) 8.74±0.05a 7.79±0.01b 4.90±0.07c 亮氨酸(Leu) 5.72±0.03c 16.40±0.00b 31.20±0.00a 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 10.73±0.03c 15.43±0.02b 26.52±0.07a 赖氨酸(Lys) 5.99±0.02c 12.28±0.00b 17.72±0.00a EAA 63.98±0.61c 86.90±0.21b 122.28±1.03a HAA 132.25±0.21c 156.43±0.17b 283.31±0.17a UAA 10.33±0.43c 15.87±0.17b 18.06±0.44a TAA 182.11±0.02c 217.98±0.01b 369.83±0.01a 注:同行数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);EAA(Essential amino acids)表必需氨基酸总量;HAA(Hydrophobic amino acids)表疏水性氨基酸总量;UAA(Umami amino acids)表鲜味氨基酸总量;TAA(Total amino acids)表游离氨基酸总量。 2.3 不同pH酸处理所得产物的电子舌滋味评价
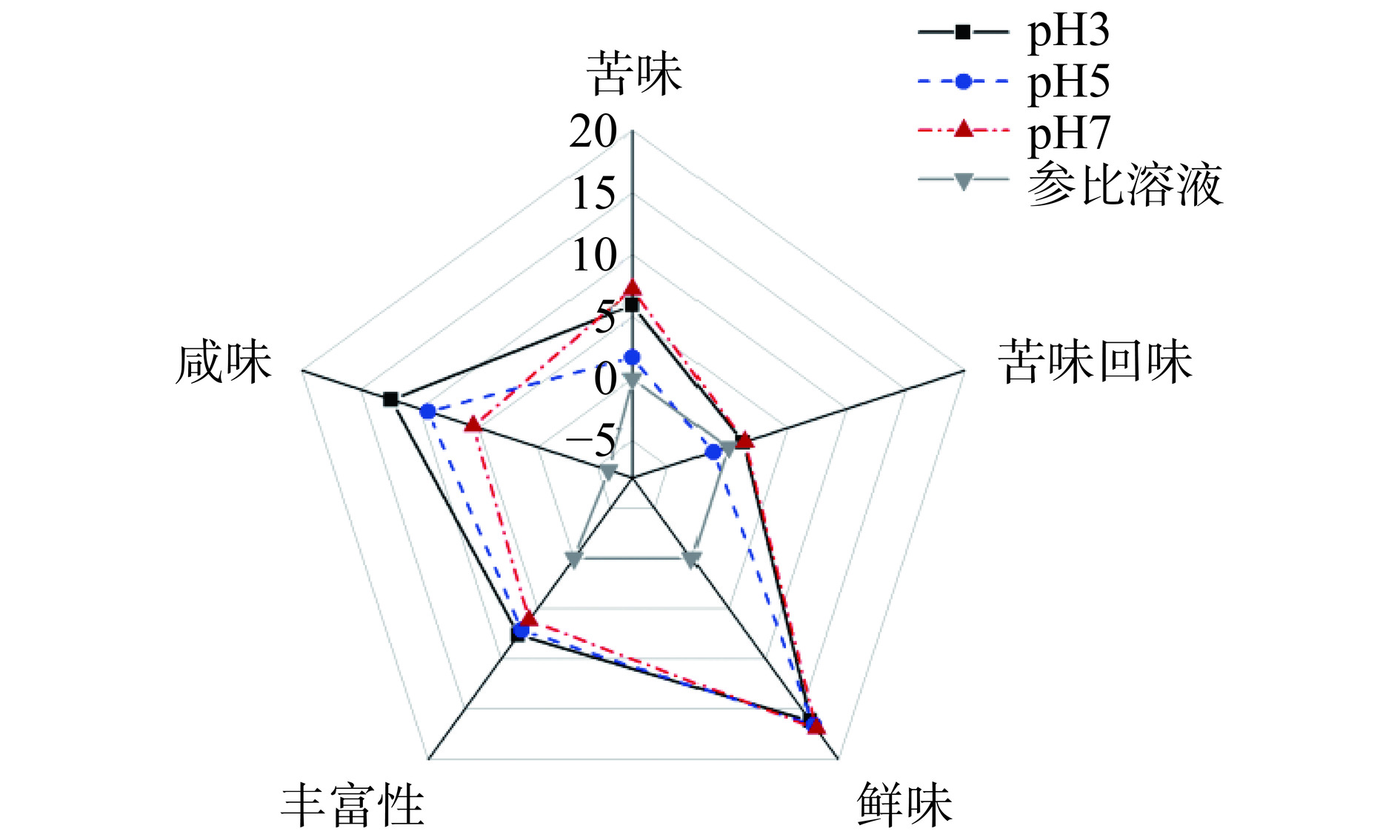
良好的滋味是食品原料在工业应用和推广中的重要因素之一[23]。使用电子舌对不同pH下酸处理所得产物进行滋味评价,结果如图1所示。由图1可知,随着酸处理pH的下降,样品咸味逐渐增加,推测可能原因之一是酸处理pH越低,在回调pH时加入的碱量越大,造成产物咸度增大;另一方面,酸处理亦可能导致了咸味肽的相对含量增加,从而使得产物咸度增大[24]。此外,经不同pH酸处理后,各产物鲜味得分差异不大,这与上文中表2所述鲜味氨基酸含量差异变化较小的结果相一致。经酸处理后,产物苦味出现明显降低,在pH5条件下酸处理时,所得产物苦味最低,分析原因,可能与产物中苦味疏水性氨基酸(如Arg、Tyr和Phe等)含量的降低有关(见表2),同时,考虑表2中酸处理pH5时,对应疏水性氨基酸含量并非最低,据此推测产物苦味的降低还可能与疏水性寡肽减少有关[25]。这一实验结果确证了通过酸处理去除酶解产物中苦味物质的可行性,为酶解产物的脱苦提供了新思路。这也为弱酸性条件下大豆蛋白酶解产物的工业应用提供了良好的滋味基础。
2.4 不同pH酸处理所得产物的体外抗氧化活性评价
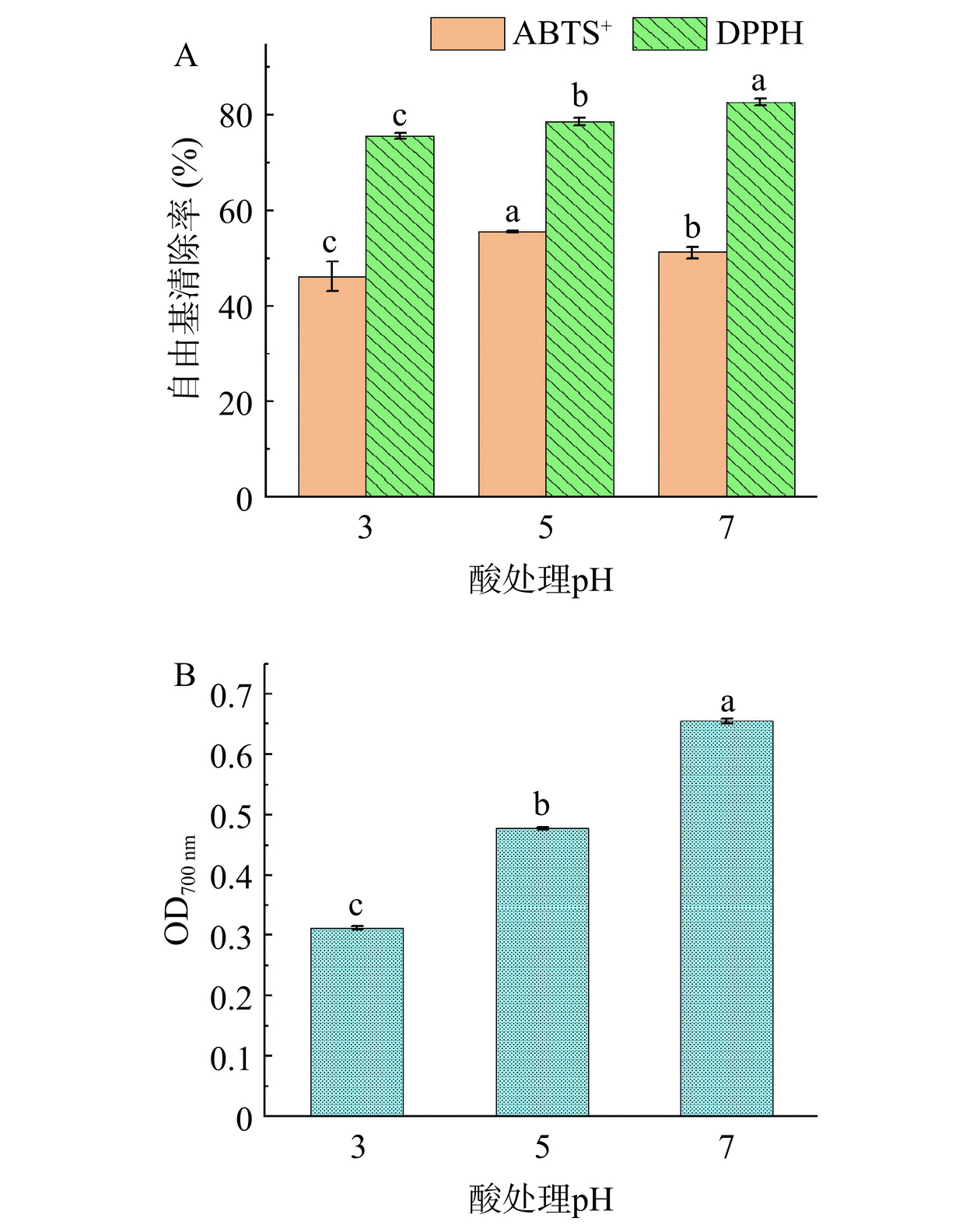
对不同pH酸处理后所得产物分别测定其ABTS+、DPPH自由基清除率和铁离子还原力,结果如图2所示。由图2A可知,原酶解产物(未经酸处理,pH7)的DPPH自由基清除率最高,而经pH5酸处理后酶解产物的ABTS+自由基清除率最高。相反地,在pH3下酸处理所得产物对两种自由基的清除能力均较弱。铁离子还原力的变化趋势(图2B)与图2A中DPPH自由基清除率的变化趋势一致,但变化趋势更为明显,分析原因可能与产物中疏水性氨基酸及抗氧化多肽的变化有关。结合表2可知,经pH5酸处理后产物中疏水性氨基酸的含量明显高于pH3下对应产物,而疏水性氨基酸被多次报道具有较强的抗氧化活性[26]。这一实验结果表明,过强的酸处理可能导致大豆蛋白酶解产物中更多的抗氧化成分被沉淀去除,这与Verfaillie等[27]的研究一致。尽管经酸处理后产物的体外抗氧化活性存在一定减弱,但pH5下酸处理所得产物其整体ABTS+、DPPH自由基清除率仍保持相对较高水平[28],为酸溶性大豆蛋白酶解产物的制备奠定了良好基础。
2.5 不同pH酸处理所得产物的多肽组学分析
2.5.1 总离子流热度分析
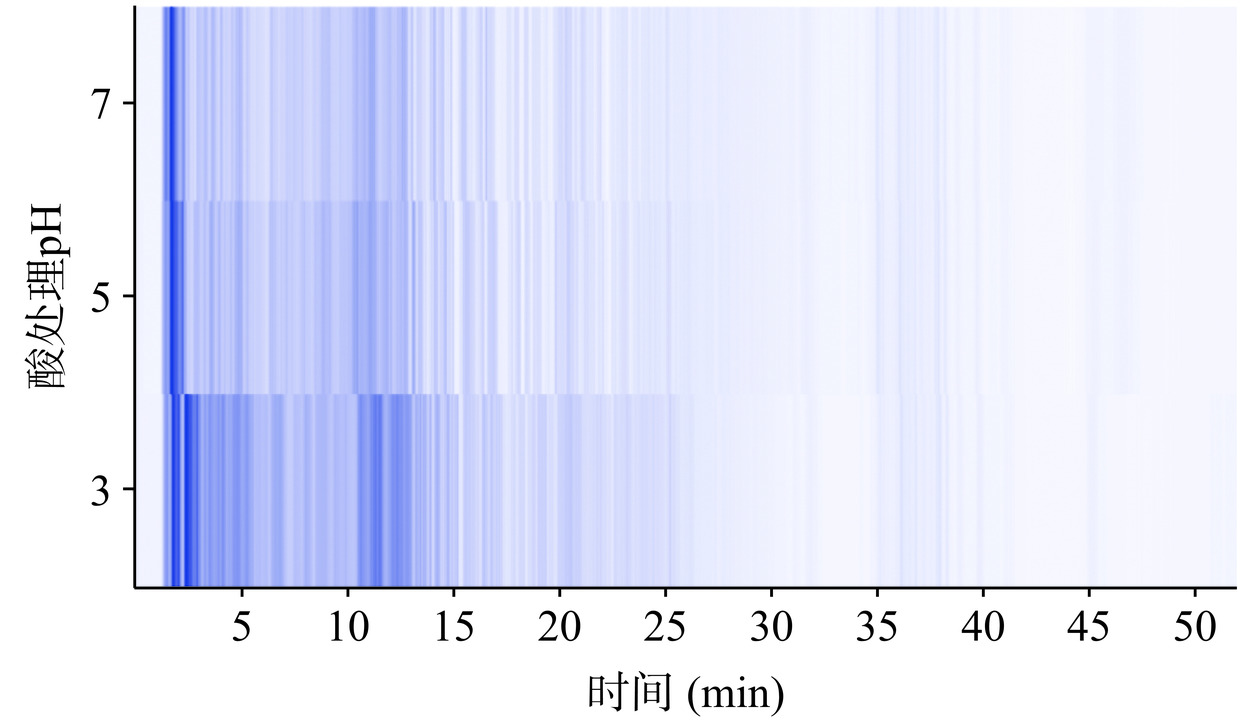
总离子流(TIC)热度图可反映样品在质谱检测过程中离子响应随洗脱时间的变化情况[29]。依据反相色谱洗脱规律,洗脱时间越长,相应物质或成分疏水性越强,反之亲水性愈强[30]。由图3可知,样品离子响应丰度集中于1~25 min,表明大量物质主要在该时间段内被洗脱和检测出来,对应物质亲水性较强而疏水性相对较弱;此外,不同样品间TIC分布整体具有一定的相似性,说明酸处理对酶解产物疏水性分布的影响较小[31]。pH3时,产物在保留时间1~2.5 min处部分组分呈现强响应,且与另外两个样品存在明显差异,这可能与酸处理造成了部分强亲水性组分沉淀有关,具体差异成分有待后续研究进一步分析和确认。
2.5.2 多肽组学鉴定分析
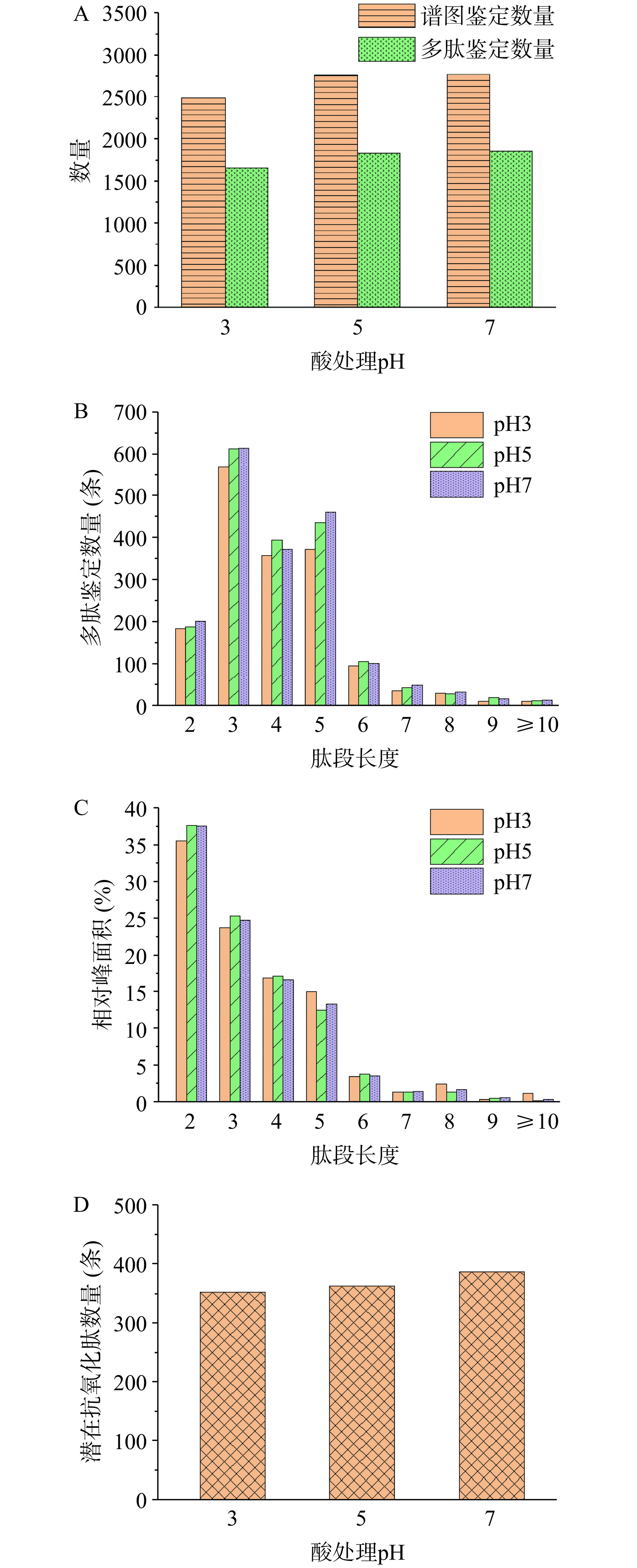
对不同pH酸处理所得产物中多肽进行鉴定与统计分析,结果如下图4所示。由图4A可知,各样品谱图鉴定数量(Peptide-Spectrum Matches,PSMs)均超过2000,多肽鉴定数量(NumPeptides)均超过1500,说明本次分析取得了较好的多肽组学分析性能与效果,为解析酶解产物在酸处理前后的多肽组成变化提供了良好的数据支撑。图4B反映了酸处理后,多肽的鉴定数量-长度分布变化情况。由图可知,各产物多肽组学鉴定所得多肽大部分长度为3~5,这与“食源性蛋白质酶解产物常使用非特异性酶处理故短肽居多[32]”的预期推测一致,亦与表1中分子量分布结果相符。前期相关文献报道中,食源性蛋白质酶解产物多肽大多被鉴定为6以上的长肽[33],与图中结果存在明显差异,推测这一差异的原因主要是前期相关科学研究缺乏合适的全肽组学分析工具[34]。课题组自主研发的PepOSX全肽组学分析技术采用无穷枚举与序列搜库两种方式对多肽进行鉴定,解析结果较为全面,且无长度歧视,在非特异多肽鉴定中具有较好的适应性[19]。
图4C为不同样品间多肽相对峰面积占比-长度分布的变化情况。由图可知,与图4B不同的是,尽管多肽鉴定结果中三~五肽的数量更多,但其相对峰面积占比呈现短链集中趋势,即多肽链长越短,相应色谱峰面积占比越高。这说明产物中多肽主要以二~五肽为主。此外,结合图4A和B可知,不同 pH酸处理后,样品的多肽鉴定数量、多肽数量-长度分布以及多肽相对面积占比-长度分布呈现一定差异,主要表现为:pH3时,样品多肽鉴定数量和三~五肽鉴定数量减少,二~三肽相对峰面积占比减小,而五肽及八肽峰面积占比升高。推测原因可能与二~三肽在酸性条件下被沉淀有关。此外,强酸条件亦可使多肽的氢键发生断裂,并与游离的氨基或羧基形成盐[34],从而导致多肽鉴定数量的减少。但整体而言,不同pH酸处理下,各产物中多肽长度分布整体保持一致,这与表1 中所述肽分子量分布结果相一致。图4D为各产物中潜在抗氧化活性肽(包含已知抗氧化活性肽段的多肽序列)的统计情况。由图可知,原酶解产物经不同pH酸处理后,潜在抗氧化肽数量出现减少,这可能是图2中所示产物抗氧化活性减弱的主要原因。
3. 结论
本文通过研究不同pH酸处理对大豆蛋白酶解产物理化特性、滋味特性、抗氧化活性和多肽组成的影响,探讨了酸溶性大豆蛋白酶解产物的制备特性。结果表明,酸处理可造成酶解产物氮回收率和游离氨基酸含量在一定程度上的下降,但对产物的抗氧化活性和肽分子量分布影响较小。大豆蛋白酶解产物主要以二~五肽为主,且包含潜在抗氧化肽近400条,可能是其抗氧化活性的重要来源。在pH5下对酶解产物进行酸处理,可使苦味疏水性氨基酸含量减少从而减弱产物的苦味,且产物多肽长度分布变化较小,但pH为3.0时,产物中五肽和八肽相对占比略有升高,同时苦味仍旧较重。综合考虑,以弱酸(pH5.0)条件制备酸溶性大豆蛋白酶解产物,可有利于获得更高的产物得率并保持较好的抗氧化活性,同时所得产物苦味更低,有利于其工业应用。本研究将可为酸溶性多肽的制备与应用提供理论依据与技术指导。
-
表 1 不同pH酸处理所得产物的氮回收率与多肽分子量分布
Table 1 Nitrogen recovery rate and peptide molecular weight distribution of the products after acid treatments at different pH
pH 氮回收率(%) 分子量范围及分布百分比(%) >10 kDa 5~10 kDa 3~5 kDa 1~3 kDa <1 kDa 7 72.68±1.08a 0.43±0.03a 1.53±0.03a 2.65±0.14a 13.84±0.27a 81.55±0.47c 5 54.50±0.47b 0.39±0.01ab 1.43±0.03b 2.34±0.02b 10.37±0.06c 85.40±0.04a 3 37.82±1.48c 0.33±0.01b 1.33±0.03c 2.29±0.01b 11.63±0.47b 84.34±0.32b 注:同列数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 2 不同pH酸处理所得产物的游离氨基酸组成(mg/g)
Table 2 Free amino acid composition of the products after acid treatments at different pH (mg/g)
游离氨基酸名称 pH3 pH5 pH7 天冬氨酸(Asp) 2.15±0.25c 4.47±0.04b 6.59±0.44a 谷氨酸(Glu) 8.18±0.18b 11.40±0.13a 11.47±0.00a 丝氨酸(Ser) 3.13±0.01a 0.88±0.59c 1.18±0.05b 甘氨酸(Gly) 2.05±0.12c 4.26±0.15b 7.02±0.02a 组氨酸(His) 9.62±0.00a 7.60±0.10b 7.54±0.02b 精氨酸(Arg) 2.32±0.29b 1.53±0.41c 9.48±1.20a 苏氨酸(Thr) 5.77±0.43c 8.63±0.03b 10.85±0.84a 丙氨酸(Ala) 2.99±0.02c 9.46±0.08a 6.47±0.00b 脯氨酸(Pro) 82.61±0.01b 79.73±0.00c 171.68±0.00a 酪氨酸(Tyr) 4.05±0.02c 8.85±0.01b 18.99±0.00a 缬氨酸(Val) 5.65±0.03b 4.06±0.03c 6.70±0.01a 蛋氨酸(Met) 11.76±0.02c 14.71±0.02b 16.85±0.02a 半胱氨酸(Cys) 10.65±0.01b 10.50±0.03b 14.67±0.17a 异亮氨酸(Ile) 8.74±0.05a 7.79±0.01b 4.90±0.07c 亮氨酸(Leu) 5.72±0.03c 16.40±0.00b 31.20±0.00a 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 10.73±0.03c 15.43±0.02b 26.52±0.07a 赖氨酸(Lys) 5.99±0.02c 12.28±0.00b 17.72±0.00a EAA 63.98±0.61c 86.90±0.21b 122.28±1.03a HAA 132.25±0.21c 156.43±0.17b 283.31±0.17a UAA 10.33±0.43c 15.87±0.17b 18.06±0.44a TAA 182.11±0.02c 217.98±0.01b 369.83±0.01a 注:同行数据后不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);EAA(Essential amino acids)表必需氨基酸总量;HAA(Hydrophobic amino acids)表疏水性氨基酸总量;UAA(Umami amino acids)表鲜味氨基酸总量;TAA(Total amino acids)表游离氨基酸总量。 -
[1] FENG L, WANG H, MA X, et al. Modeling the current land suitability and future dynamics of global soybean cultivation under climate change scenarios[J]. Field Crops Research,2021,263:378−429.
[2] GUZELER N, YILDIRIM C. The utilization and processing of soybean and soybean products[J]. Journal of Agricultural Faculty of Uludağ University,2016,30:546−553.
[3] TKACZEWSKA J, ZAJĄC M, JAMRÓZ E, et al. Utilising waste from soybean processing as raw materials for the production of preparations with antioxidant properties, serving as natural food preservatives-A pilot study[J]. LWT,2022,160:113−282.
[4] CAI J S, FENG J Y, NI Z J, et al. An update on the nutritional, functional, sensory characteristics of soy products, and applications of new processing strategies[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,112:676−689.
[5] 刘静波, 王子秦, 于一丁, 等. 响应面法优化豆粕肽制备工艺[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(8):216−223. [LIU J B, WANG Z Q, YU Y D, et al. Response surface method was used to optimize the preparation of soybean meal peptide[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(8):216−223.] LIU J B, WANG Z Q, YU Y D, et al. Response surface method was used to optimize the preparation of soybean meal peptide[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2021, 21(8): 216−223.
[6] KEREZSI A D, JACQUET N, BLECKER C. Advances on physical treatments for soy allergens reduction-A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2022,122:24−39.
[7] 胡晓倩, 桂子康, 邓军伟, 等. 大豆发酵食品毛豆腐中活性肽的制备及功效评价[J]. 中国食品学报,2023,23(3):217−228. [HU X Q, GUI Z K, DENG J W, et al. Preparation and function evaluation of bioactive peptides in hairy tofu of fermented soybean curd[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2023,23(3):217−228.] HU X Q, GUI Z K, DENG J W, et al. Preparation and function evaluation of bioactive peptides in hairy tofu of fermented soybean curd[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 23(3): 217−228.
[8] ZHANG Q, TONG X, LI Y, et al. Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptides from alcalase-hydrolyzed soybean (Glycine max L.) hydrolysate and their cytoprotective effects in human intestinal Caco-2 cells[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019,67(20):5772−5781.
[9] 郑淋. 抗氧化肽的构效关系及定向制备的研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2015. [ZHENG L. Structure-activity relationship and directional preparation of antioxidant peptide[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2015.] ZHENG L. Structure-activity relationship and directional preparation of antioxidant peptide[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2015.
[10] 杨涵. 大豆抗氧化肽的制备及其应用[D]. 重庆:重庆大学, 2022. [YANG H. Preparation and application of soybean antioxidant peptides[D]. Chongqing:Chongqing University, 2022.] YANG H. Preparation and application of soybean antioxidant peptides[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2022.
[11] TAN E S, NGOH Y Y, GAN C Y. A comparative study of physicochemical characteristics and functionalities of pinto bean protein isolate (PBPI) against the soybean protein isolate (SPI) after the extraction optimisation[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,152:447−455. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.12.008
[12] ABU-SALEM F M, MAHMOUD M H, EL-KALYOUB M, et al. Characterization of antioxidant peptides of soybean protein hydrolysate[J]. World Acad Sci Eng Technol,2013,79:249−253.
[13] YOO S H, CHANG Y H. Volatile compound, physicochemical, and antioxidant properties of beany flavor-removed soy protein isolate hydrolyzates obtained from combined high temperature pre-treatment and enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Preventive Nutrition and Food Science,2016,21(4):338−347. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2016.21.4.338
[14] 梁雪荣, 路振康, 毛晓英, 等. 发芽鹰嘴豆多肽/沙棘复合饮料配方优化[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(24):166−174. [LIANG X R, LU Z K, MAO X Y, et al. Optimization of germinated Cicer arietinum L. polypeptide/sea-buckthorn compound beverage[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(24):166−174.] LIANG X R, LU Z K, MAO X Y, et al. Optimization of germinated Cicer arietinum L. polypeptide/sea-buckthorn compound beverage[J]. Food Research and Development, 2022, 43(24): 166−174.
[15] KLIKAROVA J, CESLOVA L, FISCHER J. Rapid analysis of phenyl isothiocyanate derivatives of amino acids present in Czech meads[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2021,1644:21−34.
[16] QI Q, ZHANG G, WANG W, et al. Preparation and antioxidant properties of germinated soybean protein hydrolysates[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2022,9:166−239.
[17] PUCHALSKA P, MARINA M L, GARCIA M C. Isolation and identification of antioxidant peptides from commercial soybean-based infant formulas[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,148:147−154. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.10.030
[18] CHEN C, SUN-WATERHOUSE D, ZHANG Y, et al. The chemistry behind the antioxidant actions of soy protein isolate hydrolysates in a liposomal system:Their performance in aqueous solutions and liposomes[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,323:67−89.
[19] LIU W, ZHAO M, GAN L, et al. PeposX-Exhaust:A lightweight and efficient tool for identification of short peptides[J]. Food Chemistry X,2024,22:101−249.
[20] MALIK M A, SAINI C S. Heat treatment of sunflower protein isolates near isoelectric point:Effect on rheological and structural properties[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,276:554−561. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.10.060
[21] XU Y, YANG Y, MA C M, et al. Characterization of the structure, antioxidant activity and hypoglycemic activity of soy (Glycine max L.) protein hydrolysates[J]. Food Research International, 2023, 173:113473.
[22] YIN H, ZHANG X, HUANG J. Study on enzymatic hydrolysis of soybean β-conglycinin using alkaline protease from Bacillus subtilis ACCC 01746 and antigenicity of its hydrolysates[J]. Grain & Oil Science and Technology,2021,4(1):18−25.
[23] JIANG S, WANG X, YU M, et al. Bitter peptides in fermented soybean foods-A Review[J]. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition,2023,78(2):261−269. doi: 10.1007/s11130-023-01077-3
[24] CAI Y, HUANG L, TAO X, et al. Adjustment of the structural and functional properties of okara protein by acid precipitation[J]. Food Bioscience,2020,37:100−677.
[25] HOU H, LI B, ZHAO X, et al. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of Alaska pollock frame for preparing protein hydrolysates with low-bitterness[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2011,44(2):421−428. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2010.09.009
[26] FANG J, LU J, ZHANG Y, et al. Structural properties, antioxidant and immune activities of low molecular weight peptides from soybean dregs (okara)[J]. Food Chemistry:X,2021,12:100−175.
[27] VERFAILLIE D, JANSSEN F, VAN ROYEN G, et al. A systematic study of the impact of the isoelectric precipitation process on the physical properties and protein composition of soy protein isolates[J]. Food Research International,2023,163:112−177.
[28] OLIVEIRA C, COLETTO D, CORREA A, et al. Antioxidant activity and inhibition of meat lipid oxidation by soy protein hydrolysates obtained with a microbial protease[J]. International Food Research Journal,2014,21(2):775−781.
[29] FIELD J K, EUERBY M R, LAU J, et al. Investigation into reversed phase chromatography peptide separation systems part I:Development of a protocol for column characterisation[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2019,1603:113−129. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2019.05.038
[30] TRUFELLI H, PALMA P, FAMIGLINI G, et al. An overview of matrix effects in liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Mass Spectrometry Reviews,2011,30(3):491−509. doi: 10.1002/mas.20298
[31] TANIGUCHI M, NODA Y, AIDA R, et al. Cationic peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of soybean proteins exhibit LPS-neutralizing and angiogenic activities[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering,2019,127(2):176−182. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2018.07.013
[32] 范丽琪, 郁晓艺, 刘磊, 等. 肽组学分析技术及其在食品研究中的应用进展[J]. 现代食品科技,2023,39(8):352−359. [FAN L Q, YU X Y, LIU L, et al. Progress on peptidomic analysis technologies and their applications in food research[J]. Modern Food Science & Technology,2023,39(8):352−359.] FAN L Q, YU X Y, LIU L, et al. Progress on peptidomic analysis technologies and their applications in food research[J]. Modern Food Science & Technology, 2023, 39(8): 352−359.
[33] TSIATSIANI L, HECK A J. Proteomics beyond trypsin[J]. The FEBS journal,2015,282(14):2612−2626. doi: 10.1111/febs.13287
[34] DAMODARAN S. Amino acids, peptides and proteins[J]. Fennema’s Food Chemistry,2008,4:425−439.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



