Process Optimization and Antioxidant Activity of Pine Needle Essential Oil Extracted by Microwave-assisted Extraction
-
摘要: 目的:优化油松松针精油的最佳萃取工艺,并对油松松针精油进行成分分析、抗氧化研究。方法:以响应面法优化微波辅助萃取(Microwave-assisted extraction,MAE)提取油松松针精油的工艺,利用气相色谱-质谱联用仪(Gaschromatography-mass spectrometry,GC-MS)对萃取的松针精油进行成分检测,并以DPPH、ABTS+自由基清除能力为指标探究其抗氧化活性。结果:最佳萃取工艺为:萃取时间55 min、微波功率550 W、液料比10:1 mL/g,得率预测值0.245%,优化工艺验证结果为0.238%。从精油中得到的候选化合物共104种,其主要成分有桑贝醇(3.938%)、[1R-(1R*, 3E,7E,11R*,12R*)]-4,8,12,15,15-五甲基[9.3.1]十五碳-3,7-二烯-12-醇(3.597%)等。抗氧化实验中以L-抗坏血酸为对照,测定其DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除能力,其半抑制浓度(Half maximal inhibitory concentration,IC50)分别为101.74和12.39 mg/mL。松针精油浓度为128.00 mg/mL时,DPPH自由基清除率可达64.92%,ABTS+自由基清除率可达84.11%。结论:通过优化微波辅助萃取油松松针精油的工艺,并测定该方法获得的松针精油的主要挥发性成分,证实其抗氧化活性,为开发松针精油绿色高效提取方法及进一步利用松针精油资源提供了理论支持。Abstract: Objective: To optimize the best process for the extraction of pine needle essential oil from Pinus tabuliformis, and to conduct its compositional analysis and antioxidant capacity. Methods: Response surface methodology was used to optimize the process of extracting the pine needle essential oil from Pinus tabuliformis by microwave-assisted extraction (MAE), the components of essential oil were identified by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and the antioxidant activity was verified by DPPH and ABTS+ free radicals scavenging ability as indicators. Results: The optimal extraction processes were as follows: extraction time 55 min, microwave power 550 W, liquid-to-solid ratio 10:1 mL/g, the predicted yield was 0.245%, and the validation result of the optimized process was 0.238%. A total of 104 candidate components were obtained from the essential oil, with major components including thunbergol (3.938%), and verticillol (3.597%), and so on. In the antioxidant experiment, L-ascorbic acid was used as a control to determine the DPPH and ABTS+ free radicals scavenging ability, and the half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was 101.74 and 12.39 mg/mL, respectively. Meanwhile, at the concentration of essential oil of 128.00 mg/mL, the DPPH free radical scavenging rate could reach 64.92% and the ABTS+ free radical scavenging rate could reach 84.11%. Conclusion: By optimizing the microwave-assisted extraction process of pine needle essential oil from Pinus tabuliformis, and measuring the main volatile components of pine needle essential oil obtained by this method, its antioxidant activity was confirmed, which would provide theoretical support for the development of green and efficient extraction methods of pine needle essential oil and further utilization of pine needle essential oil resources.
-
松科是裸子植物中最大的一科,包括松属、雪松属、落叶松属、金钱松属、银杉属、云杉属、黄杉属、油杉属、铁杉属和冷杉属,共有10属230种[1],我国松科植物资源丰富,拥有松科植物所有的属。松针是松科(Pinaceae)松属(Pinus)植物的叶,因其形状似针,故名松针。松针是松树的主要副产物之一,而且其再生速度快、可一年四季采收。作为松属植物重要的林产品之一,松针精油近年来受到广泛关注和研究。已有研究表明松针精油其组分及含量可因地域、树种、生长环境、采收季节和提取方法的不同而有一定差异[2],其挥发油中主要含有α-蒎烯、β-蒎烯等萜烯类成分[3−4],具有明显的镇咳和祛痰作用,并有抗氧化[5]、抗真菌[6−7]、细菌和抗肿瘤活性[8]。植物精油具有分子结构小且渗透性强的特点,已发现具有延缓衰老、美白、杀菌消炎等多种护肤功效,近些年开发成天然护肤品受到人们关注[9−10]。
目前,从天然植物提炼萃取精油的方法有水蒸气蒸馏法[11]、有机溶剂萃取法[12]、压榨法等传统提取方法,以及超临界CO2流体萃取法[13−14]、分子蒸馏法、亚临界水萃取法等新型提取方法。传统提取植物精油常用压榨法,该方法原理简单,易操作,所得精油的品质不受影响,但压榨法得率低,更适用于精油含量高的植物组织且小规模生产[15]。有机溶剂萃取法提取精油具有得率高的优点,但该方法所得到的精油产物有溶剂残留,存在溶剂损耗大、萃取时间长、生产成本低等诸多弊端[16−17]。传统水蒸气蒸馏法工艺流程简单,设备低廉是较为常用的方法,但存在油水分离效果差、提取率较其他方法低,且生产周期长,仅适用于挥发性强、不与水反应、难溶或不溶于水的精油提取[18]。超临界CO2流体萃取法效率更高,收率更高,避免了传统溶剂萃取过程中有机溶剂残留和高温对产品的不利影响,但该方法对设备要求高,适用面窄[19]。王勋等[20]以杜香叶片为原料,考察了原料的含水率、微波辐照时间以及微波辐照功率对精油得率的影响,得到的最佳提取条件为含水率75%,微波辐照时间30 min,微波辐照功率540 W。刘欢等[21]研究微波辅助水蒸气蒸馏法提取金盏花精油,其最佳最佳工艺条件为:NaCl浓度3%、料液比1:30 g/mL、微波功率240 W,在此条件下精油得率为0.156%。Haro-González等[22]研究表明,使用微波辅助萃取工艺提取丁香挥发油具有能耗低、加热时间短,且设备简单维护成本低等诸多优点。Rezvankhah等[23]研究微波辅助提取对大麻籽油产量、氧化稳定性和抗氧化活性的影响,结果表明响应面方法优化最佳点为450 W和7.19 min,此时,提取得率可达33.91%(w/w),且提取物质中γ-生育酚占主导地位,表明具有较好的抗氧化作用。通过近几年的发展,微波辅助萃取法逐步成为一种用于提取植物精油的新型技术,综合水蒸气蒸馏法和微波萃取法的优点,具有快速、简便、无需溶剂、环保节能等优点,越来越受到重视[24−25]。
目前关于微波辅助萃取油松松针精油还未见报道,基于现有的精油提取方法具有生产周期长、生产效率低,投资门槛高,溶剂损耗大等诸多弊端,本研究以微波辅助萃取油松松针精油,探究萃取时间、微波功率、液料比对油松松针精油得率的影响,并通过响应面法优化工艺条件,旨在提高油松松针精油的得率,结合GC-MS技术分析松针精油的成分,测定其抗氧化性,为油松松针精油的提取和开发利用提供理论依据和试验基础,为进一步开发利用松针资源提供理论支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
油松(Pinus tabuliformis Carr.)松针粉 18~30目(4 ℃条件下储存备用),辽宁朝阳松海生物科技有限公司提供;无水乙醇、正己烷(分析纯) 天津市富宇精细化工有限公司;磷酸缓冲盐溶液(PBS) 翌圣生物科技(上海)有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)、2,2-联氮-二(3-乙基-苯并噻唑-6-磺酸)二铵盐(ABTS)、L-抗坏血酸 上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司;过硫酸钾(分析纯) 北京化工厂。
8890-7250 GC/Q-TOF气相色谱-高分辨四极杆飞行时间质谱仪 美国Agilent公司;GL224I-1SCN万分之一电子天平 赛多利斯科学仪器(北京)有限公司;将家用格兰仕微波炉WD750 顺德市格兰仕电器实业有限公司,改造为微波辅助萃取装置。旋钮式分档,低火、解冻、中低火、中火、中高火和高火对应的微波辐照功率分别为100、200、300、400、550和700 W。微波炉改造由山东师范大学天然产物研究中心完成。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 微波辅助萃取松针精油
1.2.1.1 松针精油的提取
将松针粉置于1000 mL圆底烧瓶,按10:1液料比加入超纯水,进行微波萃取并收集精油部分,于4 ℃保存。
1.2.1.2 松针精油得率计算
称量所得松针提取物,按公式(1)计算松针精油得率。
(1) 式中:Y表示精油得率,%;MO表示精油质量,g;MP表示松针质量,g。
1.2.1.3 单因素实验
分别考察萃取时间(15、30、45、60、75 min)、萃取功率(150、300、400、550、700 W)、液料比(6:1、8:1、10:1、12:1、14:1 mL/g)对松针精油得率的影响。每组实验重复3次。
1.2.1.4 Box-Behnken试验设计(BBD)
根据单因素实验结果,采用响应面分析的BBD试验设计方法,以油松松针精油的得率为指标,选取萃取时间(A)、萃取功率(B)、液料比(C)三个因素,采用三因素三水平进行响应面分析(Response surface methodology,RSM)。经多元回归拟合得到油松松针精油得率与各因素变量的二次多项式回归方程的预测模型。根据单因素实验结果,选择相关参数作为最小、最佳和最大水平(−1、0、1),并对每个变量进行编码,如表1所示。
表 1 响应面设计因素及水平Table 1. Response surface design factors and levels因素水平 A 萃取时间(min) B 萃取功率(W) C 液料比(mL/g) −1 30 400 8:1 0 45 550 10:1 1 60 700 12:1 1.2.2 松针精油GC-MS测定
1.2.2.1 GC-MS条件
气相条件:色谱柱:Agilent HP-5MS (30.0 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm);程序柱温:初始温度60 ℃保持1 min,8 ℃/min的速率升温到140 ℃保持2 min,再以2 ℃/min的速率升温到240 ℃保持2 min,再以8 ℃/min的速率升温到280 ℃,保持5 min;载气:氦气(≥99.999%),速率1.0 mL/min;进样口温度:260 ℃;进样方式:分流进样,分流比10:1;进样量:1.0 μL;
质谱条件:HES源,电离方式:EI,电压70 eV;离子源温度:280 ℃,传输线温度:280 ℃;测定方式:全扫描模式(SCAN);碰撞气:氮气(≥99.999%);溶剂延迟:3 min。
1.2.2.2 松针精油成分分析及相对峰面积计算
利用NIST数据库进行检索,结合现有文献数据信息,保留相似度≥80%的成分。采用峰面积归一化法计算各化合物的相对峰面积。
1.2.3 松针精油抗氧化能力测定
1.2.3.1 对DPPH自由基清除能力测定
参考李嘉欣等[26]研究进行DPPH自由基清除实验。无水乙醇配制4 mg/mL的DPPH溶液。在96孔板中加入100 μL浓度分别为1、2、4、8、16、32、64、128 mg/mL的松针精油,再分别向各孔中加入100 μL的DPPH溶液,避光反应30 min,在517 nm处检测吸光度值。以抗坏血酸作为阳性对照,对各浓度松针精油分别进行DPPH自由基清除能力测定,平行操作重复3次。DPPH自由基清除率按公式(2)计算。
(2) 式中:S表示DPPH自由基清除率,%;AC表示等体积的乙醇吸光度值;AO表示松针精油吸光度值。
1.2.3.2 ABTS+自由基的清除能力测定
ABTS+自由基的清除试验参照文献[26−27]进行,并稍作修改。以PBS缓冲溶液(pH7.4)作为溶剂配制终浓度为7 mmol/L的ABTS水溶液和2.45 mmol/L过硫酸钾(K2S2O8)水溶液,等体积混合,室温避光条件下静置过夜得到ABTS+自由基储存液,将储存液稀释至合适浓度备用。
取100 μL浓度分别为1、2、4、8、16、32、64、128 mg/mL松针精油样品溶液于96孔板中,再加入100 μL稀释过的ABTS+自由基储存液,在室温下反应10 min,在734 nm处记录吸光度值。ABTS+自由基清除率按公式(3)计算。
(3) 式中:S表示ABTS+自由基清除率,%;Ac表示100 μL的无水乙醇加100 μL的ABTS+储存液吸光度值;AO表示100 μL的松针精油加100 μL的ABTS+储存液吸光度值。
1.3 数据处理
实验均重复3次,结果表示为平均值±标准偏差,采用Design Expert.10和GraphPad Prism 9.0.0对实验数据进行做图分析,数据采用单因素方差分析,P<0.05表示差异显著,P<0.01表示差异极显著。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 油松松针精油微波辅助萃取单因素实验
2.1.1 萃取时间、萃取功率、液料比对精油得率的影响
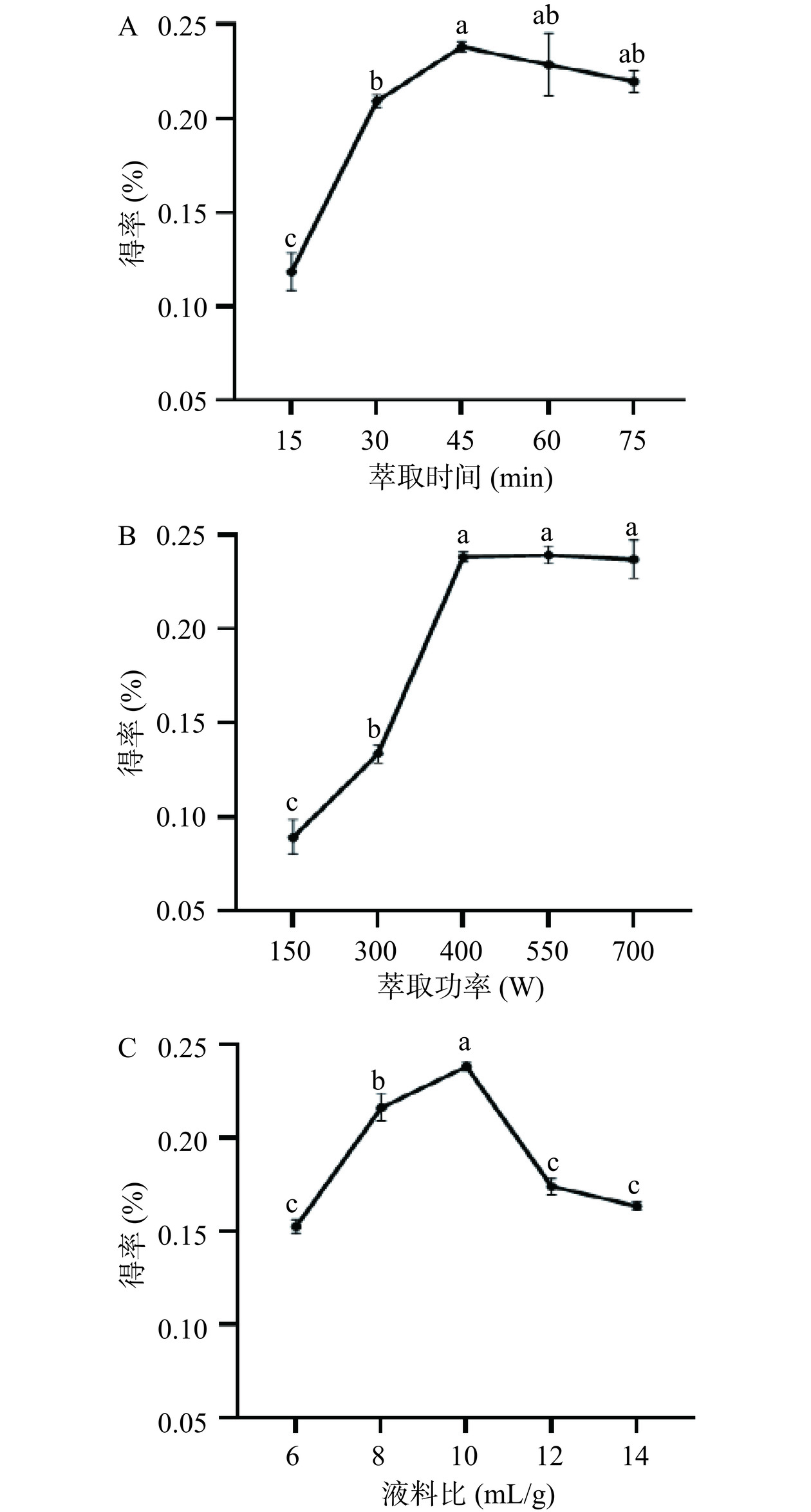
在萃取功率400 W、液料比10:1的条件下,随着萃取时间的增加,松针精油得率呈现先上升后下降的趋势,最高得率的萃取时间是45 min(图1A)。微波功率的影响见图1B。在萃取时间45 min、液料比10:1的条件下,萃取功率高于400 W时,松针精油得率一直维持在较高水平,在550 W时获得最高得率,微波功率继续提高对得率影响不大,取最佳萃取功率为550 W。液料比的影响见图1C,在萃取时间45 min、微波功率400 W条件下,改变液料比,所获得最佳液料比10:1。
2.2 响应面优化油松松针精油提取工艺试验设计与结果
2.2.1 Box-Behnken试验设计方案及结果
以油松松针精油得率为响应值,选用中心符合模型,做三因素三水平共17个实验点(5个中心点,12个析因点)响应面分析试验,设计组合及结果见表2。
表 2 响应面设计方案及结果Table 2. Response surface design scheme and results试验号 萃取时间(min) 萃取功率(W) 液料比(mL/g) 得率(%) 1 60 400 10:1 0.229 2 30 550 12:1 0.209 3 45 400 12:1 0.174 4 60 550 12:1 0.208 5 45 700 12:1 0.204 6 30 700 10:1 0.199 7 60 700 10:1 0.234 8 30 400 10:1 0.191 9 60 550 8:1 0.219 10 45 550 10:1 0.234 11 45 550 10:1 0.233 12 45 550 10:1 0.247 13 45 400 8:1 0.216 14 45 700 8:1 0.205 15 45 550 10:1 0.242 16 30 550 8:1 0.195 17 45 550 10:1 0.242 2.2.2 回归模型的建立
根据响应面分析试验,采用Design Expert 10.0软件对所得数据进行分析,结果如表2所示,各因素经回归拟合后,得到油松松针精油得率Y与A、B、C的二次多项回归方程为:Y=0.2396+0.0120A+0.0040B−0.0050C−0.0007AB−0.0063AC+0.0103BC−0.0092A2−0.0172B2−0.0227C2。由表3中F值的大小可知,3个实验因素对松针精油得率的影响大小排序是A(萃取时间)>C(液料比)>B(萃取功率)。
表 3 模型回归系数与显著性检验Table 3. Model regression coefficients and significance tests方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 模型 0.0062 9 0.0007 6.67 0.0102 A-萃取时间 0.0012 1 0.0012 11.16 0.0124 B-萃取功率 0.0001 1 0.0001 1.24 0.3023 C-液料比 0.0002 1 0.0002 1.94 0.2066 AB 2.25E-06 1 2.25E-06 0.02 0.8868 AC 0.0002 1 0.0002 1.51 0.2584 BC 0.0004 1 0.0004 4.07 0.0834 A2 0.0004 1 0.0004 3.43 0.1063 B2 0.0012 1 0.0012 12.03 0.0104 C2 0.0022 1 0.0022 20.97 0.0025 残差 0.0007 7 0.0001 失拟项 0.0006 3 0.0002 5.49 0.0667 纯误差 0.0001 4 0 总误差 0.0069 16 由表3可知,回归模型P值为0.0102,P<0.05,表明模型具有显著性,失拟项P值=0.0667>0.05不显著,表示回归模型与预测值之间拟合度较好,可用于响应值预测。AB、AC、BC、A2对响应值的影响不显著,B2对响应值的影响显著(P<0.05),C2对响应值的影响极显著(P<0.01)。响应面数据结果显示,模型响应值得率的决定系数R2为0.8956,校正后R2为0.7613,表明模型拟合度高;模型的变异系数为4.69%小于10%,说明模型对响应值的置信度良好,模型精密度为7.5837说明模型建立合理,该模型可以较好地反映真实的试验结果。综上所述,该回归模型对响应值的拟合程度较高,方程能够较好地反映响应值与自变量的关系。
2.2.3 等高线和响应面分析
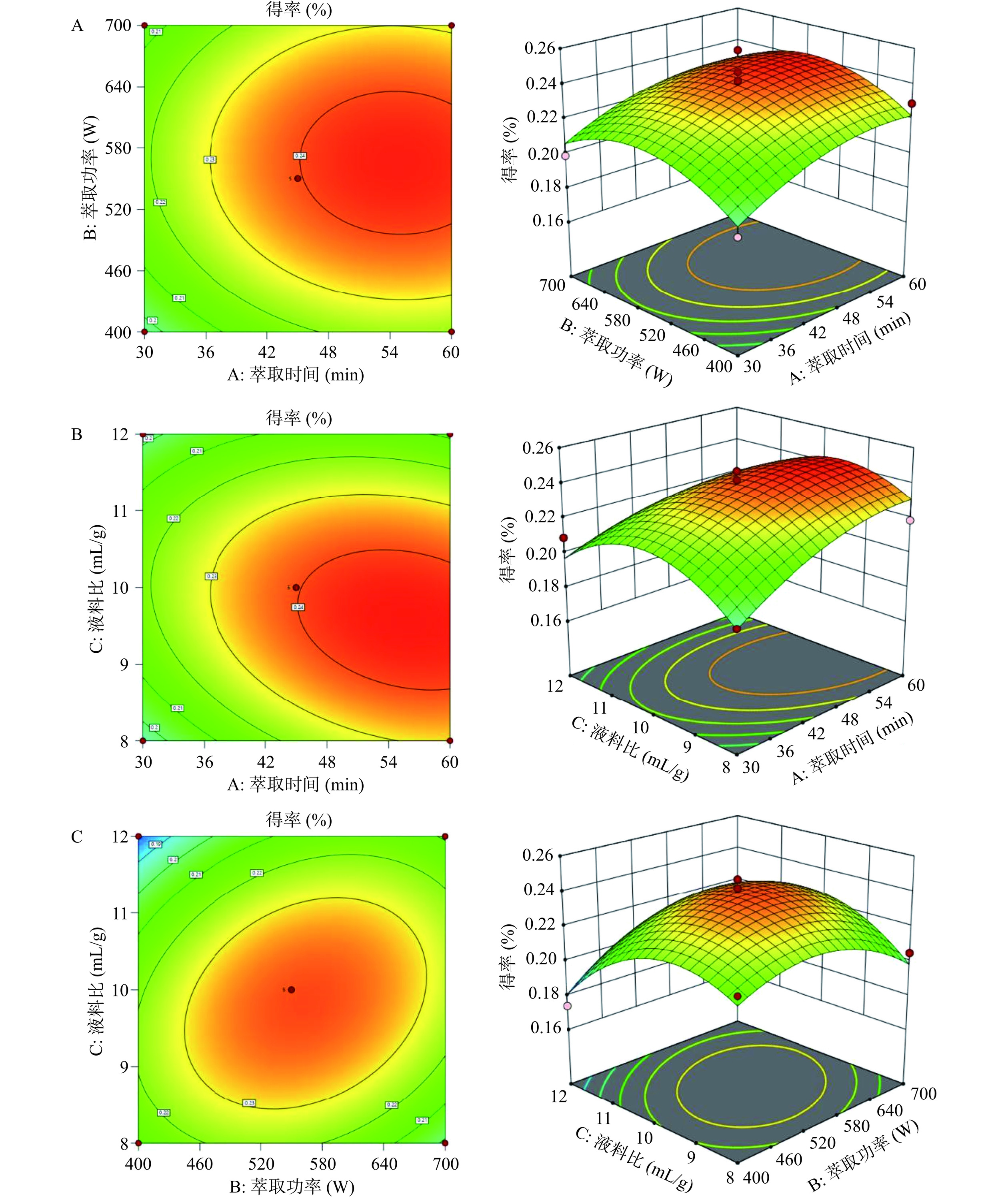
萃取时间与萃取功率、萃取时间与液料比、萃取功率与液料比这3组交互作用获得的等高线图和响应曲面图见图2。
由图2可知,等高线排列稀疏,3张响应面图坡度平缓,说明两因素的交互作用对响应值无显著性影响,此与方差分析结果一致。
2.2.4 最佳工艺条件试验验证
通过单因素分析与响应面模型优化松针精油的提取工艺,得到松针精油的最优工艺为萃取时间55.82 min、萃取功率556.20 W、液料比9.60:1。在此优化工艺下的松针精油理论得率为0.245%。根据操作试验的可行性,将工艺条件调整为萃取时间55 min、萃取功率550 W、液料比10:1,并进行3次重复试验,松针精油平均得率为0.238%±0.008%,与响应面预测结果相近。已有研究表明使用乙醇为溶剂微波辅助法提取长白山高山松针挥发油得率为0.138%[28],油松松针精油得率提高了72.46%。但与乙醇溶剂相比,松针中极性成分短暂时间不能充分溶解,所需萃取时间较长。本实验与常规水蒸气蒸馏法提取马尾松松针挥发油相比,提取时间减少2 h,提取效率提高3倍[29]。表明了微波辅助萃取油松松针精油更节能高效且适用面较广,为油松松针精油的提取提供了更加绿色环保的方法。
2.3 微波辅助提取松针精油GC-MS分析
微波辅助提取松针精油所得总离子流图如图3所示,其成分和相对峰面积汇总表见附表 1(详见本刊官网 http://www.spgykj.com/文章的网络版)。
微波辅助萃取方法所得松针精油通过GC-MS检测,共测得332种物质,将匹配度超过80%的峰为候选化合物,采用NIST谱库进行检索后进行比对定性,鉴定所得到的化学化合物数量为104种,占总成分的47.29%,利用面积归一化计算得出松针精油中各成分相对百分含量,具体结果见附表 1(详见本刊官网 http://www.spgykj.com/文章的网络版)。占比前十位的主要成分见图4,分别为桑贝醇(Thunbergol,3.938%)、[1R-(1R*,3E,7E,11R*,12R*)]-4,8,12,15,15-五甲基[9.3.1]十五碳-3,7-二烯-12-醇(Verticillol,3.597%)、三十一烷(Hentriacontane,2.189%)、α-乙酸松油酯(α-Terpinyl acetate,1.901%)、脱氢枞酸甲酯(Methyl dehydroabietate,1.842%)、α-香叶烯(α-Cadinene,1.534%)、8(14),15-异海松二烯-19-甲酯(Isopimara-8(14),15-dien-19-saeure-methylester,1.517%)、新植二烯(Neophytadiene,1.306%)、(4aR,8aS)-7-异丙基亚甲基-4a-甲基-1-亚甲基十氢萘(γ-Selinene,瑟琳烯,1.196%)、西松烯(Cembrene,1.139%)。主要是酯类、醇类、烯烃化合物的衍生物及其他化合物。已有研究表明精油的抗氧化活性与含氧萜类化合物的含量相关并且与多种活性物质协同作用,这提示松针精油具有一定的抗氧化能力[27]。
2.4 松针精油抗氧化能力
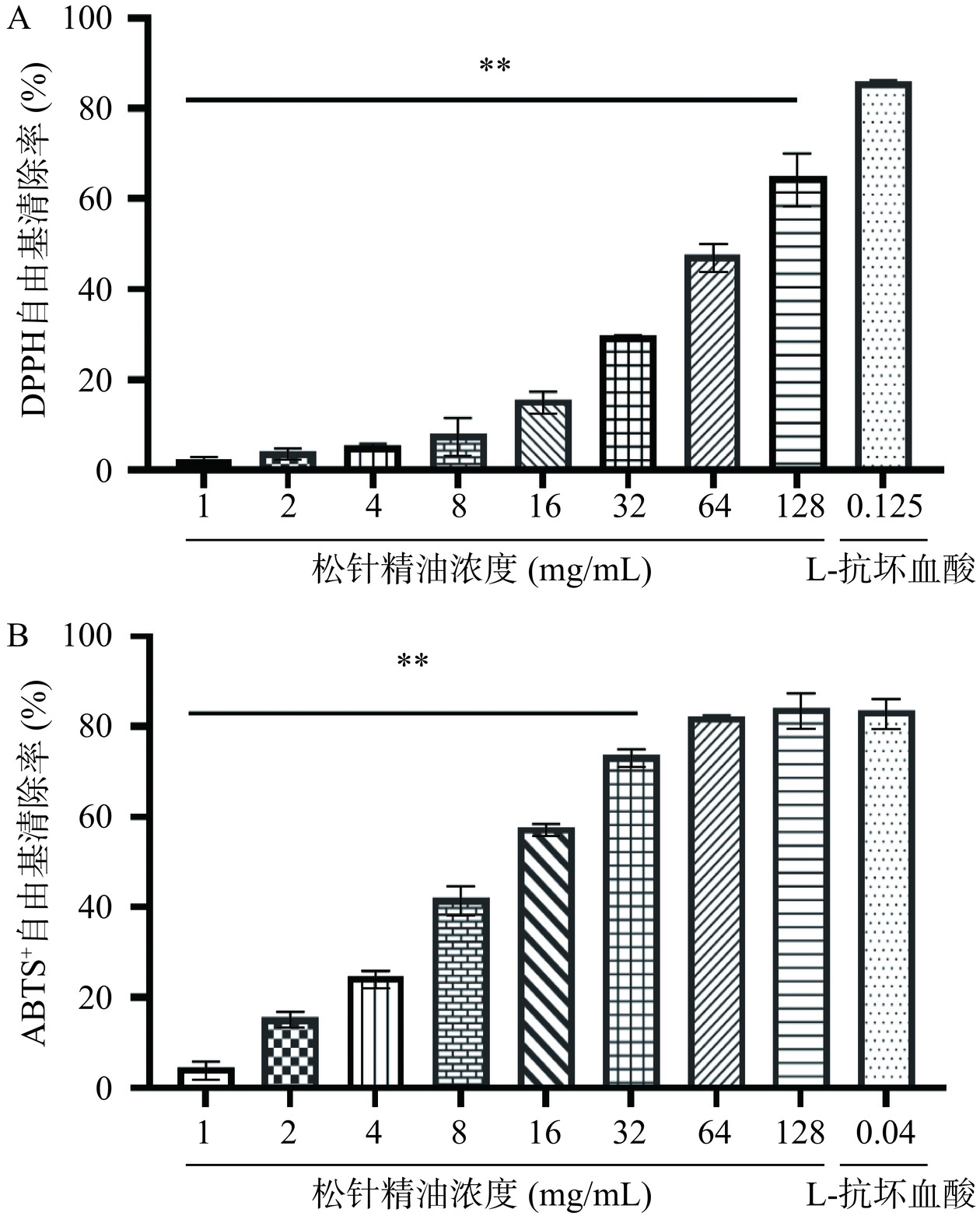
微波辅助提取松针精油对DPPH、ABTS+自由基清除能力比较结果如图5所示。结果表明精油的DPPH自由基清除能力呈浓度依赖性,在128 mg/mL松针精油浓度下DPPH自由基清除率达64.92%,同等浓度条件下ABTS+自由基清除率可达84.11%,表明松针精油具有一定的抗氧化能力,但与抗坏血酸相比仍有一定的差距。已有研究表明松针萃取物和挥发油具有一定的抗氧化能力[30−32],以云南松针为原料,采用共水法提取松针精油其主要化学成分为单萜和倍半萜类化合物,其中α-蒎烯(64.23%)、β-蒎烯(10.66%)、α-水芹烯(7.61%)占比较高,对ABTS+、DPPH自由基半数清除率IC50值分别为4.03、47.29 mg/mL[31]。黄檗果实精油具备一定的抗氧化活性,除β-蒎烯(51.92%)为主要成分外还含有西松烯(3.17%)[33]。本研究体外抗氧化结果表明油松松针精油具有一定的抗氧化能力,对DPPH、ABTS+自由基半抑制浓度分别为101.74和12.39 mg/mL,考虑与精油成分中的萜烯类物质相关。松针精油中的主要成分西松烯(1.139%)可能在抗氧化方面也发挥作用。
3. 结论
油松松针精油中醇类、萜烯类、烃类等物质具有多种生理活性,开发绿色高效的油松松针精油提取技术在提高得率并探究其功能方面具有较高的研究价值。本研究采用微波辅助萃取技术提取油松松针精油,在单因素实验的基础上,进行响应面优化,得出油松松针精油的优化提取工艺:萃取时间55 min、萃取功率550 W、液料比为10:1 mL/g,在此条件下验证试验得率为0.238%。说明采用响应面优化得到的油松松针精油提取工艺条件可靠,提高了油松松针精油得率,可为油松松针精油的提取方法提供参考依据。GC-MS结果表明,鉴定了油松松针精油104种化学组分,其主要成分是桑贝醇(3.938%)、[1R-(1R*,3E,7E,11R*,12R*)]- 4,8,12,15,15-五甲基[9.3.1]十五碳-3,7-二烯-12-醇(3.597%)、三十一烷(2.189%)、α-乙酸松油酯(1.901%)等。抗氧化结果表明油松松针精油对DPPH、ABTS+自由基具备一定的清除能力,且随着精油浓度的增加,其抗氧化能力不断提升。通过对已有研究结果进行分析,精油的抗氧化能力与含氧萜类化合物相关,后续研究工作将对油松松针精油中主要成分的抗氧化能力进行探究。
目前对于油松松针精油的研究还处于初级阶段,理化性质及其生理活性还有待于进一步开发。本研究为优化油松松针精油的提取及进一步探究松针精油抗氧化能力提供了数据支持,有望开发潜在的天然抗氧化产品,以期为油松松针精油在食品领域的开发利用提供理论依据。
-
表 1 响应面设计因素及水平
Table 1 Response surface design factors and levels
因素水平 A 萃取时间(min) B 萃取功率(W) C 液料比(mL/g) −1 30 400 8:1 0 45 550 10:1 1 60 700 12:1 表 2 响应面设计方案及结果
Table 2 Response surface design scheme and results
试验号 萃取时间(min) 萃取功率(W) 液料比(mL/g) 得率(%) 1 60 400 10:1 0.229 2 30 550 12:1 0.209 3 45 400 12:1 0.174 4 60 550 12:1 0.208 5 45 700 12:1 0.204 6 30 700 10:1 0.199 7 60 700 10:1 0.234 8 30 400 10:1 0.191 9 60 550 8:1 0.219 10 45 550 10:1 0.234 11 45 550 10:1 0.233 12 45 550 10:1 0.247 13 45 400 8:1 0.216 14 45 700 8:1 0.205 15 45 550 10:1 0.242 16 30 550 8:1 0.195 17 45 550 10:1 0.242 表 3 模型回归系数与显著性检验
Table 3 Model regression coefficients and significance tests
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 模型 0.0062 9 0.0007 6.67 0.0102 A-萃取时间 0.0012 1 0.0012 11.16 0.0124 B-萃取功率 0.0001 1 0.0001 1.24 0.3023 C-液料比 0.0002 1 0.0002 1.94 0.2066 AB 2.25E-06 1 2.25E-06 0.02 0.8868 AC 0.0002 1 0.0002 1.51 0.2584 BC 0.0004 1 0.0004 4.07 0.0834 A2 0.0004 1 0.0004 3.43 0.1063 B2 0.0012 1 0.0012 12.03 0.0104 C2 0.0022 1 0.0022 20.97 0.0025 残差 0.0007 7 0.0001 失拟项 0.0006 3 0.0002 5.49 0.0667 纯误差 0.0001 4 0 总误差 0.0069 16 -
[1] 郝金伟, 张国锋, 容井容, 等. 松针精油的提取及开发利用的研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2018,9(23):6118−6123. [HAO J W, ZHANG G F, RONG J R, et al. Research progress on extraction and exploitation of pine needle oil[J]. Food Safety & Quality,2018,9(23):6118−6123.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2018.23.008 HAO J W, ZHANG G F, RONG J R, et al. Research progress on extraction and exploitation of pine needle oil[J]. Food Safety & Quality, 2018, 9(23): 6118−6123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2018.23.008
[2] 高治平, 刘刚, 赵绿英, 等. 水蒸气蒸馏提取马尾松松针挥发油工艺研究[J]. 应用化工,2010,39(10):1502−1503,1506. [GAO Z P, LIU G, ZHAO L Y, et al. Extracting technology of volatile oil from the pine needle of Pinus massoniana by steam distillation[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2010,39(10):1502−1503,1506.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2010.10.017 GAO Z P, LIU G, ZHAO L Y, et al. Extracting technology of volatile oil from the pine needle of Pinus massoniana by steam distillation[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2010, 39(10): 1502−1503,1506. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2010.10.017
[3] 李梓. 拉雅松和细叶云南松挥发性成分的提取及生物活性研究[D]. 柳州:广西工学院, 2012. [LI Z. Extraction technology and bioactivity research of volatile components from Pinus crassicorticea and Pinus yunnanensis Franch. var tenuifolia[D]. Liuzhou:Guangxi University of Science and Technology, 2012.] LI Z. Extraction technology and bioactivity research of volatile components from Pinus crassicorticea and Pinus yunnanensis Franch. var tenuifolia[D]. Liuzhou: Guangxi University of Science and Technology, 2012.
[4] SATYAL P, PAUDE P, RAUT J, et al. Volatile constituents of Pinus roxburghii from Nepal[J]. Pharmacognosy Research,2013,5(1):43−48. doi: 10.4103/0974-8490.105650
[5] FERRENTINO G, MOROZOVA K, HOM C, et al. Extraction of essential oils from medicinal plants and their utilization as food antioxidants[J]. Current Pharmaceutical Design,2020,26(5):519−541. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200121092018
[6] KARPINSKI T M. Essential oils of lamiaceae family plants as antifungals[J]. Biomolecules,2020,10(1):103. doi: 10.3390/biom10010103
[7] CAI J, YAN R, SHI J, et al. Antifungal and mycotoxin detoxification ability of essential oils:A review[J]. Pharmacognosy Research,2022,36(1):62−72.
[8] 类程月, 周晓琴, 王琪, 等. 松树精油成分分析及其生理功能的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(11):398−405. [LEI C Y, ZHOU X Q, WANG Q, et al. Research progress on composition analysis and physiological function of essential oils of pines[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(11):398−405.] LEI C Y, ZHOU X Q, WANG Q, et al. Research progress on composition analysis and physiological function of essential oils of pines[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(11): 398−405.
[9] 唐寅, 王莹, 吕晓帆, 等. 植物精油的护肤应用研究进展[J]. 广州化工,2022,50(8):30−33. [TANG Y, WANG Y, LÜ X F, et al. Research progress on plant essential oil on skin care application[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2022,50(8):30−33.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2022.08.010 TANG Y, WANG Y, LÜ X F, et al. Research progress on plant essential oil on skin care application[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2022, 50(8): 30−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2022.08.010
[10] CUNHA C, RIBEIRO H M, RODRIGUES M, et al. Essential oils used in dermocosmetics:Review about its biological activities[J]. Cosmet Dermatol,2022,21(2):513−529. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14652
[11] EKATERINA J, ZHELJAZKOV V D, KACANIOVA M, et al. Sequential elution of essential oil constituents during steam distillation of hops (Humulus lupulus L.) and influence on oil yield and antimicrobial activity[J]. Oleo Science,2018,67(7):871−883. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess17216
[12] LIN S, MENG X, TAN C, et al. Composition and antioxidant activity of anthocyanins from Aronia melanocarpa extracted using an ultrasonic-microwave-assisted natural deep eutectic solvent extraction method[J]. Ultrason Sonochem,2022,89:106102. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2022.106102
[13] 张晓月, 杨晓芳, 肖培云, 等. 超临界CO2萃取不同产地云南松松针挥发油及其GC-MS分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2020,26(11):161−169. [ZHANG X Y, YANG X F, XIAO P Y, et al. Supercritical CO2 extraction of volatile oil in pine need of Pinus yunnanensis from different habitats and analysis by GC-MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formula,2020,26(11):161−169.] ZHANG X Y, YANG X F, XIAO P Y, et al. Supercritical CO2 extraction of volatile oil in pine need of Pinus yunnanensis from different habitats and analysis by GC-MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formula, 2020, 26(11): 161−169.
[14] 冯文池, 张维维. 浅谈超临界CO2萃取技术[J]. 山东化工,2022,51(10):80−82. [FENG W C, ZHANG W W. Discussion on supercritical CO2 extraction technology[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry,2022,51(10):80−82.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2022.10.025 FENG W C, ZHANG W W. Discussion on supercritical CO2 extraction technology[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2022, 51(10): 80−82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-021X.2022.10.025
[15] 白雨佳, 张丽荣, 黄佳琪, 等. 压榨法制备甜橙油的研究[J]. 食品工业,2015,36(7):87−90. [BAI Y J, ZHANG L R, HUANG J Q, et al. Compression method for essential oils extraction from Citrus sinensis[J]. The Food Industry,2015,36(7):87−90.] BAI Y J, ZHANG L R, HUANG J Q, et al. Compression method for essential oils extraction from Citrus sinensis[J]. The Food Industry, 2015, 36(7): 87−90.
[16] 王德靖, 唐湘湘, 罗海, 等. 植物精油提取技术研究进展综述[J]. 中阿科技论坛(中英文),2023(1):108−112. [WANG D J, TANG X X, LUO H, et al. Research on the progress of plant essential oil extraction technology[J]. China-Arab States Science and Technology Forum,2023(1):108−112.] WANG D J, TANG X X, LUO H, et al. Research on the progress of plant essential oil extraction technology[J]. China-Arab States Science and Technology Forum, 2023(1): 108−112.
[17] 毋敏. 溶剂法提取新疆伊犁地区薰衣草精油[J]. 生物化工,2021,7(2):30−32. [WU M. Solvent extraction of lavender essential oil[J]. Biological Chemical Engineering,2021,7(2):30−32.] WU M. Solvent extraction of lavender essential oil[J]. Biological Chemical Engineering, 2021, 7(2): 30−32.
[18] 邱守昊, 张依倩, 赵俊赫, 等. 水蒸气蒸馏法提取中药挥发油的研究进展[J]. 天津药学,2023,35(4):63−68. [QIU S H, ZHANG Y Q, ZHAO J H, et al. Reserarch progress in the extraction of volatile oil from traditional Chinese medicine by steam distillation[J]. Tianjin Pharmacy,2023,35(4):63−68.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5687.2023.04.016 QIU S H, ZHANG Y Q, ZHAO J H, et al. Reserarch progress in the extraction of volatile oil from traditional Chinese medicine by steam distillation[J]. Tianjin Pharmacy, 2023, 35(4): 63−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5687.2023.04.016
[19] ZHANG H M, LI Q, QIAO G, et al. Optimizing the supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) leaves and UPLC-MS/MS analysis[J]. Anal Methods,2020,12(23):3004−3013.
[20] 王勋, 黄伊嘉, 杨磊, 等. 无溶剂微波蒸馏法提取杜香精油的工艺研究[J]. 四川林业科技,2021,42(5):73−76. [WANG X, HUANG Y J, YANG L, et al. Study on solvent-free microwave distillation technology of essential oil from Ledum palustre L doi: 10.12172/202103050002 J]. Sichuan Forestry Science and Technology,2021,42(5):73−76. doi: 10.12172/202103050002
[21] 刘欢, 赵巨堂, 何力, 等. 金盏花精油的微波辅助提取及其成分与抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(10):180−188. [LIU H, ZHAO J T, HE L, et al. Microwave-assisted extraction of essential oil from Calendula officinalis L. and its components and antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(10):180−188.] LIU H, ZHAO J T, HE L, et al. Microwave-assisted extraction of essential oil from Calendula officinalis L. and its components and antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(10): 180−188.
[22] HARO-GONZÁLEZ J N, CASTILLO-HERRERA G A, MARTINEZ-VELAZQUEZ M, et al. Clove essential oil (Syzygium aromaticum L. Myrtaceae):Extraction, chemical composition, food applications, and essential bioactivity for human health[J]. Molecules,2021,26(21):6387. doi: 10.3390/molecules26216387
[23] REZVANKHAH A, ZAHRA EMAM-DJOMEH, SAFARI M, et al. Microwave-assisted extraction of hempseed oil:Studying and comparing of fatty acid composition, antioxidant activity, physiochemical and thermal properties with Soxhlet extraction[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,56(9):4198−4210.
[24] BAGADE S B, PATIL M. Recent advances in microwave assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from complex herbal samples:A review[J]. Crit Rev Anal Chem,2021,51(2):138−149. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2019.1686966
[25] LUO M, ZHOU D D, SHANG A, et al. Influences of microwave-assisted extraction parameters on antioxidant activity of the extract from Akebia trifoliata peels[J]. Foods,2021,10(6):1432. doi: 10.3390/foods10061432
[26] 李嘉欣, 孟斌斌, 朱凯. 樟树叶精油组成分析及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 林产化学与工业,2020,40(1):84−90. [LI J X, MENG B B, ZHU K. Components and antioxidant activity of camphor leaves essential oil[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products,2020,40(1):84−90.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2020.01.012 LI J X, MENG B B, ZHU K. Components and antioxidant activity of camphor leaves essential oil[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products, 2020, 40(1): 84−90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2020.01.012
[27] LI M, ZHAO X, XU M. Chemical composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of essential oil from Allium tenuissimum L. flowers[J]. Foods,2022,11(23):3876. doi: 10.3390/foods11233876
[28] 李扬. 微波辅助法提取长白山高山松针挥发油及其抑菌效果研究[J]. 黑龙江农业科学,2013(12):105−108. [LI Y. Study on the extraction and antibacterial effect of alpine pine needle volatile oil of changbai mountain by microwave-assisted extraction[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,2013(12):105−108.] LI Y. Study on the extraction and antibacterial effect of alpine pine needle volatile oil of changbai mountain by microwave-assisted extraction[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2013(12): 105−108.
[29] 王委, 刘映良, 高尔刚, 等. 马尾松松针挥发油提取工艺研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2013,25(8):1120−1123. [WANG W, LIU Y L, GAO E G, et al. Extraction of volatile oil from the leaves of Pinus massoniana[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2013,25(8):1120−1123.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2013.08.024 WANG W, LIU Y L, GAO E G, et al. Extraction of volatile oil from the leaves of Pinus massoniana[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2013, 25(8): 1120−1123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2013.08.024
[30] 石晓峰, 沈薇, 宁红霞, 等. 雪松松针总多酚的纯化工艺和抗氧化活性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2016,28(8):1325−1331. [SHI X F, SHEN W, NING H X, et al. Purification and antioxidant activity of polyphenol from pine needles of Cedrus deodara[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2016,28(8):1325−1331.] SHI X F, SHEN W, NING H X, et al. Purification and antioxidant activity of polyphenol from pine needles of Cedrus deodara[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2016, 28(8): 1325−1331.
[31] 李晓娇, 李悦, 董锦, 等. 云南松针精油的提取及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2020,31(7):27−35. [LI X J, LI Y, DONG J, et al. Optimization of extraction process and antioxidant activity of essential oil from needles of Pinus yunnanensis[J]. China Food Additives,2020,31(7):27−35.] LI X J, LI Y, DONG J, et al. Optimization of extraction process and antioxidant activity of essential oil from needles of Pinus yunnanensis[J]. China Food Additives, 2020, 31(7): 27−35.
[32] 周思杰, 张智红, 段久芳, 等. 雪松松针多糖超声波酶法提取及其抗氧化性[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2019,31(2):284−291. [ZHOU S J, ZHANG Z H, DUAN J F, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Cedrus deodara pine needles[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2019,31(2):284−291.] ZHOU S J, ZHANG Z H, DUAN J F, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Cedrus deodara pine needles[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2019, 31(2): 284−291.
[33] 陈小强, 刘帅, 于雯, 等. 黄檗果实精油的化学成分、抗氧化及细胞毒活性[J]. 精细化工,2016,33(2):147−151. [CHEN X Q, LIU S, YU W, et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant and cytotoxic activity of the essential oil from Phellodendron amurense fruits[J]. Fine Chemicals,2016,33(2):147−151.] CHEN X Q, LIU S, YU W, et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant and cytotoxic activity of the essential oil from Phellodendron amurense fruits[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2016, 33(2): 147−151.





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



