Research Progress on Components, Biological Activities, Preservation and Processing of Akebia trifoliate (Thunb.) koidz. Fruit
-
摘要: 三叶木通是一种具有较高营养、药用和经济价值的植物,可全株入药,藤茎是中药材木通的主要来源,近成熟干燥果实是中药材“预知子”,果肉味道清香甘甜,口感爽滑细嫩,果实含有水分、碳水化合物、蛋白质、脂肪、矿物质、维生素等营养成分和黄酮类、多酚类、三萜及其皂苷、木脂素类、多糖、有机酸等活性成分,具有抗肿瘤、抗菌、抗炎、抗氧化、降血糖等生理功能。为此,本文对三叶木通果实营养及活性成分、生物活性及保鲜加工现状进行了综述,并对三叶木通果实未来的研究方向和应用前景进行了展望,以期为三叶木通果实的综合开发利用及功效成分的精准加工提供理论依据。Abstract: Akebia trifoliate (Thunb.) koidz. is a significant nutritional, medicinal, and economically valuable fruit. The whole plant of Akebia trifoliate (Thunb.) koidz. has medicinal activity. The vines of Akebia trifoliate (Thunb.) koidz. are the main source of the traditional Chinese medicine of Akebiae caulis. The mature dried fruits of Akebia trifoliate (Thunb.) koidz. is the traditional Chinese medicine named as “Yuzhiz”. The flesh fruit tastes sweet, smooth and fine-tender with delicate fragrance. The fruits contain nutrients (water, carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals, vitamins, etc.), functional components (flavonoids, polyphenols, triterpenes and their saponins, lignans, polysaccharides, organic acids, etc.), and have physiological activities (anti-tumor, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, hypoglycemic, etc.). In this paper, the nutritional components, bioactive components, biological activities, preservation, processing of Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) koidz. are reviewed with its research and application prospect. This review will provide theoretical basis for the comprehensive development and precise processing of functional ingredients in Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) koidz.
-
三叶木通[Akebia trifoliate (Thunb.) koidz.]是天然的药食两用木通科木通属的落叶木质藤本植物,是我国传统的中草药,其根、藤茎、叶、花、果肉、果皮和果籽中含有多种生物活性成分如黄酮类、多酚类、三萜及其皂苷、木脂素类、多糖、有机酸等[1−2]。三叶木通广泛分布于东亚地区,如中国、朝鲜和日本,在我国广泛分布于长江、黄河流域及秦岭地区,主要分布在湖南、贵州、云南、河南。野生三叶木通的人工栽培技术已经取得突破,在我国四川、湖南、湖北、陕西、河南等省份已开始规模化的种植;湖南的常德、浏阳、怀化等地已经有集中成片驯化种植基地[3−4]。三叶木通的果实又叫八月炸(扎)、八月瓜、合欢果、木通子、牛腰子果、野香蕉等,其近成熟果实干燥后作为常用中药“预知子”。三叶木通果实由果皮、果肉和果籽组成,农历8月到9月瓜成熟开口,其果实营养丰富、味道甜美。三叶木通果实具有抗氧化、抗菌、抗炎、抗癌等生物活性。作为药食两用的水果植物,果实可以生食、入药,或者加工成果酒、果茶、果脯、果酱、食用油等[2,5]。本文综述了三叶木通果实的营养成分、活性成分、生物活性、保鲜及加工的现状,提出了今后的研究方向和应用前景,为三叶木通果实的高效开发利用提供理论支持和参考。
1. 三叶木通果实的成分
1.1 营养成分
三叶木通果实具有很高的营养价值,果肉、果皮和果籽均含有水分、碳水化合物、蛋白质和氨基酸、脂肪和脂肪酸、矿物质和维生素等营养成分。由于种质资源、品种、生长环境和采集时间等因素的影响,三叶木通果实各营养成分含量不一,其营养成分含量见表1。三叶木通果皮中富含果胶(20.08%±0.20%),主要组成成分是酸性半乳糖醛酸基,其半乳糖醛酸(GalA)含量相当高,可达83.17%,溶解度大于80% [8−9]。蛋白质中的氨基酸组成有所差异,果肉中检测出17种氨基酸,其中8种为必需氨基酸,果皮中检测出15种氨基酸,其中7种为必需氨基酸,果籽中检测出17种氨基酸,8种为必需氨基酸,它们的氨基酸组成见表2。果籽中含有丰富的油脂,相关研究结果表明三叶木通果籽的营养价值因为产地的不同存在一定差异[12,14-16]。SU等[16]对中国14个省份共25个代表性分布区的三叶木通的果籽油脂含量和脂肪酸组成进行分析,发现三叶木通果籽富含油脂(30.2%~53.6%),脂肪酸种类有11种,主要以油酸(155.9~261.5 mg/g,36.6%~45.2%)、亚油酸(113.8~156.4 mg/g,23.5%~30.8%)、棕榈酸(101.8~149.1 mg/g,20.3%~25.7%)为主。三叶木通果肉、果皮和果籽中含有数种矿物质,它们中矿物质的含量和种类有所不同,均含有钙、镁、磷、钾、铜、铁、锰,在果肉中还检测出锌和钠,果籽中还检测出锌和硒[2−7]。三叶木通果皮中VE的含量为0.52 mg/100 g,VC的含量为28.02±0.85 mg/100 g,果肉中的VC的含量为0.72~108 mg/100 g、VE的含量为0.133 mg/100 g、VB1的含量为15.4 μg/100 g、VB2的含量为15.4 μg/100 g、VB6的含量为49.5 μg/100 g[7−8,17]。
成分 果肉(%) 果皮(%) 果籽(%) 脂肪 0.13~4.3 2.45±0.21 30.2~53.6 蛋白质 1.0~4.02 8.16±0.11 15.57~29.9 灰分 0.1 5.83±0.03 3.28 水分 68.77~85.74 8.65±0.02 7.35 粗纤维 − 16.00±0.03 17.45 总糖 6.42~15.78 32.61±0.18 2.92 还原糖 5.79~13.64 19.31±0.21 − 可溶性糖 1.94~17.68 − − 淀粉 − − 2.33 果胶 − 20.08±0.20 − 总酸 0.059~0.082 − 1.64 注:−表示未检测。 氨基酸种类 果肉(g/100 g) 果皮(g/100 g) 果籽(%) 天冬氨酸(Asp) 0.035~0.075 0.037 4.623 苏氨酸*(Thr) 0.005~0.022 0.017 1.331 丝氨酸(Ser) 0.005~0.04 0.016 2.484 谷氨酸(Glu) 0.035~0.08 0.029 7.783 甘氨酸(Gly) 0.015~0.04 0.017 1.753 蛋氨酸*(Met) 0~0.02 / 0.698 丙氨酸(Ala) 0.01~0.025 0.018 1.882 缬氨酸*(Val) 0.01~0.035 0.018 2.1854 异亮氨酸*(Ile) 0.005~0.03 0.02 1.611 亮氨酸*(Leu) 0.02~0.05 0.027 3.172 酪氨酸*(Tyr) 0~0.02 0.018 2.301 苯丙氨酸*(Phe) 0.015~0.025 0.018 2.2054 赖氨酸*(Lys) 0.01~0.04 0.023 2.8253 组氨酸(His) 0.010~0.04 0.010 2.1797 精氨酸(Arg) 0~0.04 0.025 2.18 脯氨酸(Pro) 0~0.46 0.020 2.18 半胱氨酸(Cys) 0.03 / 1.289 注:带*的表示必需氨基酸,/表示未检出。 1.2 活性成分
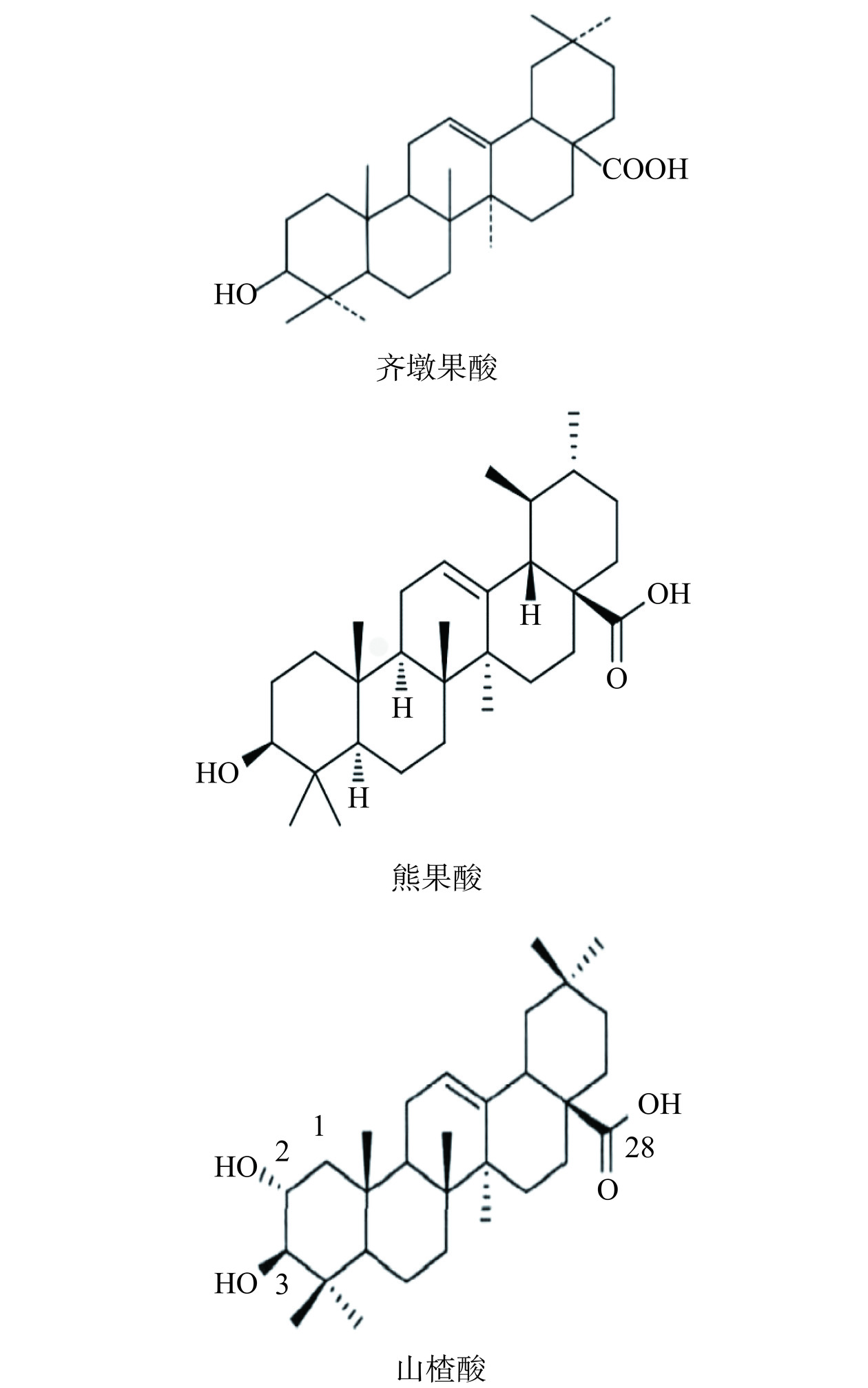
有关三叶木通果实活性成分的研究较多,发现其活性成分的种类和成分复杂。三叶木通果皮、果籽和果肉中含有多糖、多酚、黄酮、三萜及其皂苷等活性物质[17−22]。最新的研究通过超高液相色谱飞行时间高分辨串联质谱(UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS)构建了三叶木通提取物的代谢组学图谱,在果皮、果肉和果籽提取物中分别鉴定了352、342和447种次级代谢产物,因此果籽的次生代谢产物最丰富,其次是果皮和果肉。次级代谢产物主要有生物碱、木脂素和新木脂素、脂质和类脂分子、苯丙烷类和聚酮类[23]。而其中的生物碱、三萜类和黄酮类化合物及其衍生物可能是提供关键生物活性的主要次生代谢产物[24]。三叶木通的植物化学特征表明,三萜类化合物是其最重要的生物活性化合物,在此研究中,在果肉、果皮和果籽中共鉴定出45种三萜类化合物。齐墩果酸(OA)、熊果酸(UA)和山楂酸(MA)是植物中常见的三萜类化合物,三叶木通果籽和果皮中均有上述成分,果肉中仅检出OA,OA在果皮中的含量比果籽中的高,但UA和MA在果籽中的含量比在果皮中的高[23−24],它们的化学结构式见图1。三叶木通果肉、果皮和果籽中的活性成分及代谢产物见表3[17−24]。
表 3 三叶木通果肉、果皮和果籽中的活性成分及代谢产物Table 3. Active ingredients and metabolites in the flesh, pericarp, and seed of Akebia trifoliata活性成分 果肉 果皮 果籽 多糖总酚 3.51±0.03
mg/g0.18%~0.36%
2.56~74.03 mg/g
122.4±2.15 mg/g总黄酮 0.01%~0.2% 4.43~52.26 mg/g 85.2±3.12 mg/g 总皂苷 − 33.16~59.03 mg/g 90.9±7.2 mg/g 齐墩果酸 − 0.13%~0.24% 0.57%±0.14% α-常春藤皂苷 − 0.42%~3.81% − 常春藤皂苷元 − 0.69%±0.06% 0.57%±0.14% 木通苯乙醇苷B − 0.03%~0.19% − 通过UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS测定的代谢产物比例 生物碱和衍生物 1.66% 1.53% 1.71% 木脂素、新木脂素
及其相关化合物8.14% 9.86% 9.54% 苯型烃 1.66% 2.58% 2.2% 脂质和类脂分子 31.22% 35.05% 33.99% 核苷、核苷酸和类似物 4.07% 1.21% 3.18% 有机酸及其衍生物 10.26% 8.5% 8.18% 有机氮化合物 3.02% 2.43% 1.83% 有机氧化合物 11.92% 12.14% 10.64% 有机杂环化合物 9.8% 10.77% 10.64% 苯丙烷和聚酮类 18.25% 15.93% 18.09% 注:−表示未检测。 2. 三叶木通果实的生物活性
2.1 抗肿瘤作用
三叶木通果实、果籽和果皮提取物均具有抗肿瘤作用,通过对三叶木通果实不同部位提取物的抗肿瘤作用研究(表4)梳理后发现,果实提取物主要通过抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖和促进凋亡发挥抗肿瘤作用,果皮提取物主要通过抑制肿瘤细胞的生长发挥抗肿瘤作用,而果籽提取物可抑制肿瘤细胞增殖、转移和侵袭及促进肿瘤细胞凋亡,而且完全成熟的果籽比未成熟的果籽效果更好,可为临床炮制药材提供指导,但具体的机理还有待研究探讨。三叶木通果实提取物的抗肿瘤临床应用比较多,也取得了一定的进展,但是有关其抗肿瘤的主要活性成分及分子作用机理还有待深入研究,如何挖掘有效成分开发天然抗肿瘤药物还有待探索。
表 4 三叶木通果实不同部位提取物抗肿瘤活性Table 4. Anti-tumor effects of different parts of Akebia trifoliata fruit部位 体内/体外 癌种 作用对象 功效 机制 参考文献 果实水提物 体内 肝癌 H22荷瘤鼠 抑制肿瘤细胞生长
和增殖、诱导凋亡提高荷瘤鼠血清TNF-α和IL-2水平;阻止突变型(m)P53蛋白的生成,下调Bcl-2的表达,阻止PCNA蛋白的表达 [25−26] 果实提取物(乙醇、正丁醇等提取) 体内 肝癌 H22荷瘤鼠、
BEL-7404裸鼠抑制肿瘤的生长 未知 [27] 果实乙醇提取物 体内 肝癌 H22荷瘤小鼠 抑制肿瘤细胞增殖、
促进细胞凋亡抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路(与肿瘤疾病密切相关的通路)的活化 [28] 果籽乙醇提取物 体外 肝癌 SMMC-7721、
HepG2、Huh7抑制肝癌细胞的恶性
增殖、侵袭和转移诱导内质网应激,显著改变内质网功能相关的基因表达水平;促进或抑制MMP-9的分泌,降低或者促进
p-FAK的表达[29−31] 果籽乙醇提取物 体外 肝癌 HepG2 抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖
和黏附促进E-cadherin蛋白的表达;
调节Mdm2-p53信号通路[32−33] 果籽乙醇提取物 体外 肝癌 SMMC-7721 抑制肝癌细胞的增殖,影响细胞周期,轻微促进凋亡和坏死,诱导肿瘤细胞出现衰老特征 诱导内质网应激成分的富集,通过内
质网应激相关基因和副凋亡相关基因
表达的调节,诱导细胞空泡化与内质
网应激和副凋亡[34−35] 果皮果胶 体外 肺癌、血癌 人肺癌A549、人髓系慢性白血病K562-2 抑制肿瘤细胞生长 未知 [36] 2.2 抗菌作用
WANG等[23]从三叶木通果皮中提取分离得到13种三萜类化合物,通过测试它们对5种细菌(金黄色葡萄球菌、苏云金芽孢杆菌、大肠杆菌、肠炎沙门氏菌和痢疾志贺菌)的抗菌活性,发现MA、OA和2a,3b-二羟基油酸-13(18)-烯-28酸对上述的5种试验细菌有很强的抗菌活性,最低抑菌浓度(MIC)为0.9~15.6 μg/mL。CHEN等[24]对三叶木通活性成分的抑菌活性和抑菌机理进行了研究,发现生物碱、三萜类化合物和黄酮类化合物是三叶木通果皮、果肉和果籽中提供关键生物活性的主要次级代谢产物,它们在抗菌活性中起着至关重要的作用。研究结果发现三叶木通果皮乙醇提取物(EEPA)对所测试的革兰氏阳性细菌(金黄色葡萄球菌、枯草芽孢杆菌)和革兰氏阴性细菌(大肠杆菌、铜绿假单胞菌)均表现出抑菌和杀菌作用,革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌对EEPA的敏感性没有观察到显著差异。主要的抗菌机制是EEPA可增加细菌细胞的内容物泄漏,改变细胞形态,破坏细胞内部结构,最终导致细菌代谢功能障碍。三叶木通中最重要的次级代谢产物三萜类化合物MA、UA和OA对金黄色葡萄球菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、大肠杆菌和铜绿假单胞菌均表现出不同程度的抗菌活性,它们在抗菌活性方面没有显示出对革兰氏阳性菌或革兰氏阴性菌的特异性。MA对四种细菌均表现出最好的抑菌活性。MA、UA和OA对金黄色葡萄球菌抗菌效果最佳,对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌效果为MA>UA>OA。通过比较三种物质的结构发现,羟基和甲基的存在对其抗菌活性很重要。
李伟业[37]的研究结果表明不同处理方式(未处理、干热处理、压榨处理和精制处理)的三叶木通果籽油均能抑制金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌和铜绿假单胞菌的生长,且具有一定的杀菌效果。压榨处理的果籽油抑菌和杀菌效果最佳,精制的果籽油抑菌和杀菌效果较差,这主要与油脂精制过程中活性成分损失有关。果籽油对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制效果要优于大肠杆菌和铜绿假单胞菌,其中果籽油对金黄色葡萄球菌的对数期、稳定期影响最大,延长对数期最久、持续时间增长最为明显,且具有非常明显的剂量依赖性。
以上研究说明三叶木通果皮和果籽中均含有抑菌活性成分,但有关果籽的抑菌活性成分及抑菌机理还有待进一步深入研究。
2.3 抗氧化作用
抗氧化活性评价的方法有体外实验和体内实验,体外实验方法主要有自由基清除能力法、还原能力法、金属离子螯合能力法与细胞模型法,体内实验以大、小鼠模型、人体模型和其他模型(如果蝇模型、秀丽隐杆线虫模型)等为主。
表5列出了三叶木通不同部位提取物的体外抗氧化活性。由表5可知,许多学者的研究认为三叶木通提取物的抗氧化活性与其黄酮、多酚类和多糖物质的含量相关,而多酚和黄酮是提取物呈现抗氧化能力的主要活性成分,且产地及提取物制备的方法不同也会造成抗氧化能力有所差异[13,39−41]。
表 5 三叶木通果实不同部位提取物体外抗氧化活性Table 5. In vitro antioxidant activity of the different parts of Akebia trifoliata fruit提取方法 提取部位 活性成分 抗氧化活性 结论 参考文献 超声波法和
回流提取法果皮、果籽、
果肉多酚、黄酮 DPPH自由基清除能力(DPPH)、ABTS+自由基清除能力(ABTS)、铁离子还原能力(FRAP)不同部位抗氧化活性有所差异 多酚、黄酮的含量和抗氧化活性呈强相关
[19]索氏提取法 果籽(来自湖南、湖北和云南) 湖南产三叶木通籽油黄酮
含量最高,多酚和类胡萝卜素以云南产的高于湖南和湖北产的DPPH抗氧化活性最高的为湖南产三叶木通籽油,ABTS和FRAP抗氧化活性以云南产的三叶木通籽油最高 抗氧化能力与活性成分含量和种类相关 [13] 甲醇溶液超声
波辅助提取果皮、果肉 果皮和果肉中的酚类物质主要成分为没食子酸、儿茶素、绿原酸、阿魏酸、鞣花酸、芦丁和槲皮素,果皮的表儿茶素、绿原酸和总黄酮含量相对较高,果肉的各成分含量低 儿茶素、阿魏酸、总酚和总黄酮对总还原力(TRAP)值贡献极强,阿魏酸、总酚和总黄酮对FRAP值贡献极强,儿茶素、阿魏酸和总酚对ABTS+自由基清除能力贡献极强 各部位的抗氧化能力与黄酮类、VC、多酚和相应酚类成分含量呈强相关的关系 [17] 石油醚脱脂后
甲醇抽提果皮、果籽 富含多酚、黄酮和皂苷,果籽中的含量高于果皮中的 果籽和果皮的提取物均具有较强的DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除能力 具有显著的剂量效应 [21] 乙醇粗提,不同溶剂萃取(石油醚、氯仿、乙酸乙酯、正丁醇) 果肉 多酚和黄酮是样品呈现抗氧化能力的主要活性成分 石油醚相萃取物的DPPH自由基清除能力最强,氯仿相的ABTS+自由基清除能力和氧化自由基吸收能力最强,乙醇粗提物的FRAP能力最强 与多酚、黄酮含量较高相关 [38] 乙醇提取 果皮 总黄酮、总酚、总皂苷 具有较强的清除DPPH自由基、ABTS+自由基能力 总黄酮、总酚、总皂苷的含量与抗氧化活性均呈正相关 [8] 酸提醇沉法 果皮(河南南阳、贵州凯里) 果胶(高酯) 能清除·OH及DPPH自由基,在高浓度时河南南阳三叶木通果胶的抗氧化活性更强 主要与半乳糖醛酸含量及酯化度有关 [36] 三叶木通果实提取物在体内实验中也具有很好的抗氧化作用。WANG等[42]发现三叶木通果皮提取物(APE)可降低右旋糖酐硫酸钠(DSS)诱导的小鼠结肠炎氧化应激。DSS诱导小鼠结肠炎后其肠组织中丙二醛(MDA)水平显著增加,而过氧化氢酶(CAT)和超氧化物岐化酶(SOD)活性及总抗氧化能力(T-AOC)水平下降,而APE可降低结肠炎小鼠肠组织MDA含量,提高CAT、SOD活性和T-AOC水平,且作用效果呈剂量依赖性。由于氧化应激在炎症发展中起至关重要的作用,可诱导细胞损伤,炎症和氧化应激相互促进,从而使炎症持续并扩散[43]。活性氧(ROS)是生物体中的一种氧化剂,可在病理条件下产生,如缺氧或炎症,对脂质、蛋白质和核酸产生各种氧化损伤,造成细胞信号转导过程的细微调节或生物分子的损伤和细胞死亡。ROS超氧化物阴离子(O2-)可被SOD转化为过氧化氢(H2O2),之后CAT或谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)将H2O2转变成水被清除[44]。清除ROS的能力与生物体的抗氧化能力密切相关,因此,APE可通过提高机体抗氧化能力减少氧化应激和炎症造成的损害。ZHANG等[45]用双水相系统提取三叶木通果实中的多糖(ATFP),通过纤维素-52和葡聚糖凝胶G-200 纯化得到ATFP-3,含有93.24%的多糖,多糖主要由葡萄糖(47.55%)和半乳糖(20.39%)组成。ATFP-3在体外有较强的抗羟基自由基活性,可显著提高秀丽隐杆线虫在热应激或氧化应激下的存活率,提高老龄秀丽隐杆线虫抗氧化酶的活性,减少体内脂褐素的积累和MDA含量。因此,ATFP-3可通过提高抗氧化能力减轻老龄化过程中生物膜系统的氧化损伤。CHEN等[46]研究发现具有低分子量和高糖醛酸含量的多糖具有优异的羟基自由基清除能力,而ATFP-3优异的羟基自由基还原能力也证实了CHEN的观点。
综上所述,三叶木通果实提取物在体内外均具有较好的抗氧化作用,主要与其活性成分多酚、黄酮和多糖有关,但其各活性成分的抗氧化活性机制还有待深入研究。
2.4 抗炎作用
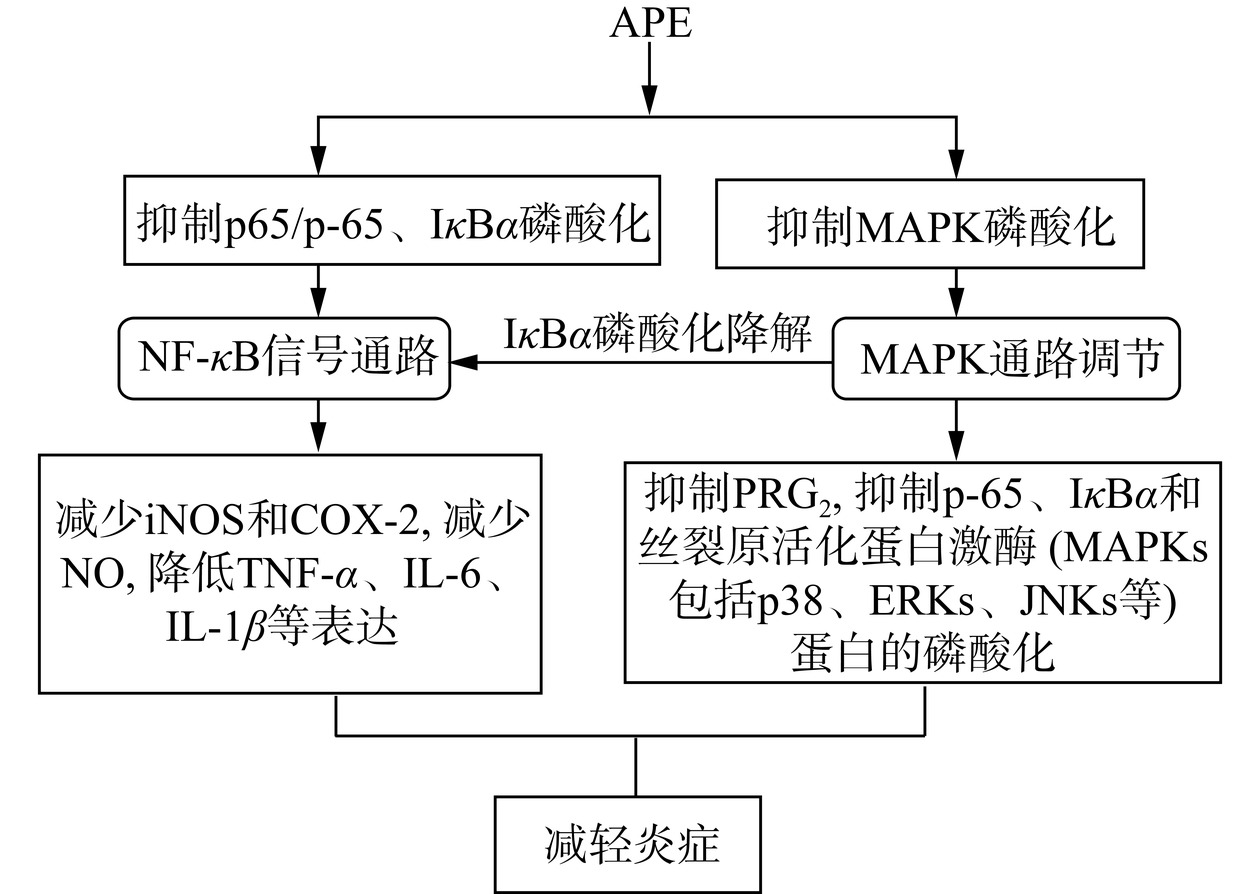
炎症是机体对微生物感染、物理损伤和化学刺激等作出的一种生理反应,若控制不好会引起全身炎症,造成器官功能障碍[47]。WANG等[42]发现APE可降低右旋糖酐硫酸钠(DSS)诱导的小鼠结肠炎,改善上皮屏障破坏,减少一氧化氮(NO)和前列腺素E2(PGE2)的分泌,抑制一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)和环氧合酶-2(COX-2)的表达,通过分析认为APE三萜类化合物及其代谢产物是抗炎活性的主要贡献者。之后,WANG等[48]研究了APE的生物活性和抗炎机制,结果发现酚酸类和萜类化合物是APE中的主要生物活性成分,在体外和体内均能通过阻断小鼠单核巨噬细胞白血病细胞(RAW264.7)中诱导型 iNOS和COX-2的表达,抑制NO和PGE2的生成,降低α-肿瘤坏死因子(TNF-α)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)和白细胞介素-1β(IL-1β)的表达,抑制核转录因子p-65(p-65)、核转录因子κB抑制蛋白α(IκBα)和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPKs)包括[p38激酶(p38)、细胞外信号调节激酶(ERKs)、应激激活蛋白激酶(JNKs等)]蛋白的磷酸化。脂多糖(LPS)常在试验中用来诱导炎症的发生,巨噬细胞在诱导炎症反应中发挥重要作用,LPS 诱导巨噬细胞产生iNOS与炎症密切相关,可诱导NO产生,而过量NO会促进炎症发展,产生能活化自身的COX,其中COX-2是引起炎症反应的关键酶[49]。LPS还可诱导巨噬细胞启动NF-κB/MAPK信号通路,造成炎症因子TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β等以及炎症介质NO、PGE2的过量表达和分泌。核因子κB(NF-κB)是炎症反应中的关键转录因子,NF-κB被抑制后可下调炎症因子水平,减少炎症反应。NF-κB由不同的二聚体组成,如p65、核转录因子p50(p50),而IκBα是NF-κB的抑制蛋白。当细胞受到LPS刺激后IκBα会发生磷酸化降解,激活NF-κB。MAPKs信号通路对炎症因子的释放起着重要的调节作用,由p38、ERKs和JNKs 3条信号通路组成[50]。由上所知,APE可通过NF-κB/MAPK信号通路抑制细胞因子的产生减轻炎症,表明APE是一种防治机体炎症的天然物质。APE的炎症调节机制见图2。
2.5 降血糖
糖尿病是一种以高血糖为特征的慢性内分泌代谢疾病。α-葡萄糖苷酶是造成餐后血糖升高的主要酶之一,通过抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶的活性,能减缓餐后血糖的升高,缓和糖尿病和并发症的发生[51−53]。罗宗洪等[21]研究发现三叶木通果皮提取物和果籽提取物均可抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶的活性,且提取物对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制呈现剂量效应,果籽提取物效果优于果皮提取物,通过分析发现三叶木通果籽中的总酚、总黄酮和总皂苷的含量均高于果皮,且果籽总酚含量显著高于果皮中的。丁林玲等[38]通过用不同的试剂提取果肉中的活性成分,发现各萃取物均对α-葡萄糖苷酶具有抑制能力,其中氯仿相和乙酸乙酯相中的活性最强,这与其中的多酚类物质有关。以上研究可为三叶木通果实提取物作为α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制剂天然来源和降血糖功能食品的开发提供科学依据,但其具体的作用成分和机制有待进一步深入研究。
2.6 其他作用
三叶木通果实除了上述的功能作用外,还发现果籽油具有很好的创伤修复作用[36,54]、三叶木通果实正丁醇提取物和水提取物具有对CCl4致小鼠肝脏损伤的保护作用[55],三叶木通果肉多糖可延长秀丽隐杆线虫的寿命,具有抗衰老作用[45]。三叶木通果肉不同溶剂萃取物均具有一定的体外抑制乙酰胆碱酯酶能力[38],三叶木桶果皮提取物可改善炎症小鼠的肠道菌群结构[48]。
3. 三叶木通果实的保鲜及加工
三叶木通果实富含对人体有益的营养成分和功能活性成分。通过果实保鲜,果籽功能油脂提取,果肉加工成果汁、果酒、果酱,果皮加工成果茶、果脯和提取果胶等可实现三叶木通果实的全面开发利用。
3.1 三叶木通果实保鲜
三叶木通鲜果属于呼吸跃变型,容易腐烂变质,不利于长途运输和长期贮藏,采收成熟度的确定和保质保鲜的研究非常重要,因为这最终将决定水果品质和贮藏潜力。由于三叶木通果实在完全成熟时纵向开裂,应在果实开裂前收获以确保质量。JIANG等[56]通过试验发现用0.15%蒙脱土、0.15%三叶木通果皮提取物和1.5%壳聚糖制备的涂膜剂涂膜三叶木通果实,于5 ℃贮藏可延迟果实开裂和成熟35 d,保鲜效果良好。ZOU等[57]的研究发现在三叶木通开花后148 d采摘三叶木通果实是长途运输的理想收获成熟期,并且在果实开裂之前消费者接受度更高。蔡芳丽等[6]对4个采收时间(9月3日和17日、10月1日和7日)的三叶木通果实的物理参数和营养成分进行测定和比较,发现果实在10月1日达到了生理成熟,果实硬度急剧下降后无明显变化,可溶性糖含量显著升高,此时果实未开裂,果实硬度稍高,有利于长途运输和贮藏,因此,建议在生理成熟期采收。对三叶木通果实的保鲜研究具有重要的现实意义,通过探索合适的成熟期进行科学的保鲜贮藏,可满足市场对优质水果的需求。
3.2 三叶木通果实的加工
3.2.1 果酒和果汁饮料的加工
李朝阁[11]用三叶木通果实和葡萄为原料,发酵制备的三叶木通-葡萄复合果酒呈深红色,透明澄清、酸度适宜、口感柔滑,兼有八月瓜和葡萄的香味,饮后回味无穷。研究发现三叶木通果酒成品酒清亮澄清,酒色淡黄,酒香浓郁,回味悠长,氨基酸种类较齐全且含量高,有机酸含量丰富,含有酚类物质并具有一定的抗氧化性[58−59]。用三叶木通果肉(冻储果)与百香果复合制作的果汁口感细腻、酸甜适中,色泽、滋味与气味等各个方面均优于三叶木通纯果肉(冻储果)制作的果汁[60]。因此,可将三叶木通果肉开发为营养价值高的果酒和果汁饮料,以解决果实采收高峰期不耐贮藏和运输等问题,同时也能满足消费者对三叶木通产品多样化的需求。
3.2.2 果酱、果粉、果脯的加工
用三叶木通果肉或者果皮和果肉可制作营养健康美味的果酱。张婧等[61]用三叶木通果皮和果肉为主要原料,采用单因素和正交试验进行优化制作的果酱色泽均匀、口感细腻、酸甜适中,涂抹性较好,富含多酚、黄酮和氨基酸,具备健康、绿色、营养的优点。果皮加工成果粉能较好地保持水果原有的品质,有利于保存,二次加工方便,用途广泛,是一种优良的水果深加工方式。肖彦达等[62]用麦芽糊精为助干剂,采用喷雾干燥法制备的三叶木通果粉具有较好的溶解性且具有三叶木通天然的香味。
此外,雷颂等[63]研究了三叶木通果皮制作果脯加工工艺。通过单因素和正交试验优化了烫漂、护色、去苦、糖制和干燥工艺,确定了果脯的最佳加工工艺,其成品色泽金黄、酸甜可口、饱满度好。果皮除了通过适宜的加工工艺制作可口的果脯,还可通过提取果胶在食品、医药、化妆品和印染等领域使用,使果皮副产物得到有效利用。
3.2.3 果茶加工
三叶木通果肉和果皮都可以通过合适的加工工艺制作成果茶。用亚硫酸钠进行护色处理可以增强三叶木通果茶水浸出物的抗氧化性,增加浸出物总量,提升三叶木通果茶的品质[64]。孙晓东等[65]对三叶木通果皮预处理后与麦冬、玄参和蜂蜜进行复配加工得到的三叶木通果皮茶,果胶含量和低聚糖含量较高,对茶叶品质有提高作用。邓爱华等[66]用三叶木通的果浆、栀子果粉、蜂蜜、柠檬酸、白糖为原料,通过单因素和正交试验研发的三叶木通果茶具有三叶木通的特有风味、酸甜可口、口感细腻且有一定的保健功能。
3.2.4 果籽加工
三叶木通果籽富含油脂,饱和:单不饱和:多不饱和脂肪酸比例为1:1.5:1,符合世界卫生组织的建议[67]。蔡雪梅等[68]对三叶木通籽油挥发性风味成分进行鉴定发现有195种,包括醇类(30种)、醛类(20种)、酮类(16种)、酯类(29种)、酸类( 19种)、吡嗪类(13种)、烃类(48种)、呋喃(3种)以及其他物质(16种),其中醛类物质是三叶木通籽油中最主要的风味物质。此外,三叶木通果籽中的蛋白质含量较高,氨基酸含量丰富,含有8种人体必需氨基酸和7种药用氨基酸,氨基酸组成和比例优于花生和玉米[15]。微波辅助酶法提取果籽蛋白质可得到较高的蛋白质产量,其蛋白质持水性、发泡能力和泡沫稳定性较好[69],三叶木通果籽油还具有抗氧化和修复创伤等作用[13,36]。因此,富含油脂的三叶木通果籽可用于生产食用油和生物燃料[70],榨油后的油饼可用作食品原料或生产谷蛋白[71],果籽也可以作为很好的膳食纤维原料的来源[72]。
4. 结论与展望
三叶木通是一种药食两用的植物资源,其果实中的果肉、果籽和果皮均含有多种营养成分和生物活性物质,具有抗菌、抗氧化、抗炎、抗肿瘤、降血糖等生物活性作用,因此对人体具有很好的营养和生理调节功能。目前,三叶木通虽然在育种、栽培、资源分布调查方面取得了进展,但是还缺乏优良品种和大规模栽培种植,功效成分的开发利用和精深加工还没有形成产业化,因此今后除加强对三叶木通药用价值和功能作用机理的研究之外,还应加强对三叶木通资源的开发、新品种的选育、种苗繁育、高效栽培技术、贮藏保鲜、精深加工及新产品研发等方面的研究;加强对三叶木通果实中的生物活性成分进行分离鉴定及构效关系的研究,充分挖掘三叶木通的潜在食用和医用价值,为三叶木通的综合开发利用和高效开发提供理论支撑。
-
成分 果肉(%) 果皮(%) 果籽(%) 脂肪 0.13~4.3 2.45±0.21 30.2~53.6 蛋白质 1.0~4.02 8.16±0.11 15.57~29.9 灰分 0.1 5.83±0.03 3.28 水分 68.77~85.74 8.65±0.02 7.35 粗纤维 − 16.00±0.03 17.45 总糖 6.42~15.78 32.61±0.18 2.92 还原糖 5.79~13.64 19.31±0.21 − 可溶性糖 1.94~17.68 − − 淀粉 − − 2.33 果胶 − 20.08±0.20 − 总酸 0.059~0.082 − 1.64 注:−表示未检测。 氨基酸种类 果肉(g/100 g) 果皮(g/100 g) 果籽(%) 天冬氨酸(Asp) 0.035~0.075 0.037 4.623 苏氨酸*(Thr) 0.005~0.022 0.017 1.331 丝氨酸(Ser) 0.005~0.04 0.016 2.484 谷氨酸(Glu) 0.035~0.08 0.029 7.783 甘氨酸(Gly) 0.015~0.04 0.017 1.753 蛋氨酸*(Met) 0~0.02 / 0.698 丙氨酸(Ala) 0.01~0.025 0.018 1.882 缬氨酸*(Val) 0.01~0.035 0.018 2.1854 异亮氨酸*(Ile) 0.005~0.03 0.02 1.611 亮氨酸*(Leu) 0.02~0.05 0.027 3.172 酪氨酸*(Tyr) 0~0.02 0.018 2.301 苯丙氨酸*(Phe) 0.015~0.025 0.018 2.2054 赖氨酸*(Lys) 0.01~0.04 0.023 2.8253 组氨酸(His) 0.010~0.04 0.010 2.1797 精氨酸(Arg) 0~0.04 0.025 2.18 脯氨酸(Pro) 0~0.46 0.020 2.18 半胱氨酸(Cys) 0.03 / 1.289 注:带*的表示必需氨基酸,/表示未检出。 表 3 三叶木通果肉、果皮和果籽中的活性成分及代谢产物
Table 3 Active ingredients and metabolites in the flesh, pericarp, and seed of Akebia trifoliata
活性成分 果肉 果皮 果籽 多糖总酚 3.51±0.03
mg/g0.18%~0.36%
2.56~74.03 mg/g
122.4±2.15 mg/g总黄酮 0.01%~0.2% 4.43~52.26 mg/g 85.2±3.12 mg/g 总皂苷 − 33.16~59.03 mg/g 90.9±7.2 mg/g 齐墩果酸 − 0.13%~0.24% 0.57%±0.14% α-常春藤皂苷 − 0.42%~3.81% − 常春藤皂苷元 − 0.69%±0.06% 0.57%±0.14% 木通苯乙醇苷B − 0.03%~0.19% − 通过UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS测定的代谢产物比例 生物碱和衍生物 1.66% 1.53% 1.71% 木脂素、新木脂素
及其相关化合物8.14% 9.86% 9.54% 苯型烃 1.66% 2.58% 2.2% 脂质和类脂分子 31.22% 35.05% 33.99% 核苷、核苷酸和类似物 4.07% 1.21% 3.18% 有机酸及其衍生物 10.26% 8.5% 8.18% 有机氮化合物 3.02% 2.43% 1.83% 有机氧化合物 11.92% 12.14% 10.64% 有机杂环化合物 9.8% 10.77% 10.64% 苯丙烷和聚酮类 18.25% 15.93% 18.09% 注:−表示未检测。 表 4 三叶木通果实不同部位提取物抗肿瘤活性
Table 4 Anti-tumor effects of different parts of Akebia trifoliata fruit
部位 体内/体外 癌种 作用对象 功效 机制 参考文献 果实水提物 体内 肝癌 H22荷瘤鼠 抑制肿瘤细胞生长
和增殖、诱导凋亡提高荷瘤鼠血清TNF-α和IL-2水平;阻止突变型(m)P53蛋白的生成,下调Bcl-2的表达,阻止PCNA蛋白的表达 [25−26] 果实提取物(乙醇、正丁醇等提取) 体内 肝癌 H22荷瘤鼠、
BEL-7404裸鼠抑制肿瘤的生长 未知 [27] 果实乙醇提取物 体内 肝癌 H22荷瘤小鼠 抑制肿瘤细胞增殖、
促进细胞凋亡抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路(与肿瘤疾病密切相关的通路)的活化 [28] 果籽乙醇提取物 体外 肝癌 SMMC-7721、
HepG2、Huh7抑制肝癌细胞的恶性
增殖、侵袭和转移诱导内质网应激,显著改变内质网功能相关的基因表达水平;促进或抑制MMP-9的分泌,降低或者促进
p-FAK的表达[29−31] 果籽乙醇提取物 体外 肝癌 HepG2 抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖
和黏附促进E-cadherin蛋白的表达;
调节Mdm2-p53信号通路[32−33] 果籽乙醇提取物 体外 肝癌 SMMC-7721 抑制肝癌细胞的增殖,影响细胞周期,轻微促进凋亡和坏死,诱导肿瘤细胞出现衰老特征 诱导内质网应激成分的富集,通过内
质网应激相关基因和副凋亡相关基因
表达的调节,诱导细胞空泡化与内质
网应激和副凋亡[34−35] 果皮果胶 体外 肺癌、血癌 人肺癌A549、人髓系慢性白血病K562-2 抑制肿瘤细胞生长 未知 [36] 表 5 三叶木通果实不同部位提取物体外抗氧化活性
Table 5 In vitro antioxidant activity of the different parts of Akebia trifoliata fruit
提取方法 提取部位 活性成分 抗氧化活性 结论 参考文献 超声波法和
回流提取法果皮、果籽、
果肉多酚、黄酮 DPPH自由基清除能力(DPPH)、ABTS+自由基清除能力(ABTS)、铁离子还原能力(FRAP)不同部位抗氧化活性有所差异 多酚、黄酮的含量和抗氧化活性呈强相关
[19]索氏提取法 果籽(来自湖南、湖北和云南) 湖南产三叶木通籽油黄酮
含量最高,多酚和类胡萝卜素以云南产的高于湖南和湖北产的DPPH抗氧化活性最高的为湖南产三叶木通籽油,ABTS和FRAP抗氧化活性以云南产的三叶木通籽油最高 抗氧化能力与活性成分含量和种类相关 [13] 甲醇溶液超声
波辅助提取果皮、果肉 果皮和果肉中的酚类物质主要成分为没食子酸、儿茶素、绿原酸、阿魏酸、鞣花酸、芦丁和槲皮素,果皮的表儿茶素、绿原酸和总黄酮含量相对较高,果肉的各成分含量低 儿茶素、阿魏酸、总酚和总黄酮对总还原力(TRAP)值贡献极强,阿魏酸、总酚和总黄酮对FRAP值贡献极强,儿茶素、阿魏酸和总酚对ABTS+自由基清除能力贡献极强 各部位的抗氧化能力与黄酮类、VC、多酚和相应酚类成分含量呈强相关的关系 [17] 石油醚脱脂后
甲醇抽提果皮、果籽 富含多酚、黄酮和皂苷,果籽中的含量高于果皮中的 果籽和果皮的提取物均具有较强的DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除能力 具有显著的剂量效应 [21] 乙醇粗提,不同溶剂萃取(石油醚、氯仿、乙酸乙酯、正丁醇) 果肉 多酚和黄酮是样品呈现抗氧化能力的主要活性成分 石油醚相萃取物的DPPH自由基清除能力最强,氯仿相的ABTS+自由基清除能力和氧化自由基吸收能力最强,乙醇粗提物的FRAP能力最强 与多酚、黄酮含量较高相关 [38] 乙醇提取 果皮 总黄酮、总酚、总皂苷 具有较强的清除DPPH自由基、ABTS+自由基能力 总黄酮、总酚、总皂苷的含量与抗氧化活性均呈正相关 [8] 酸提醇沉法 果皮(河南南阳、贵州凯里) 果胶(高酯) 能清除·OH及DPPH自由基,在高浓度时河南南阳三叶木通果胶的抗氧化活性更强 主要与半乳糖醛酸含量及酯化度有关 [36] -
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典2015年版一部[S]. 北京:中国医药科技出版社, 2015: 63−64. [National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China, Volume I, 2015 edition[S]. Beijing:China Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Press, 2015: 63−64.] National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China, Volume I, 2015 edition[S]. Beijing: China Pharmaceutical Science and Technology Press, 2015: 63−64.
[2] WANG M, GUO X C, SONG J Y. Analysis of the shape characteristics and nutritional components of Akebia trifoliata in Qinba Mountains[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2022,13:1−18.
[3] 杨西萌, 李桂香, 潘玉芳, 等. 三叶木通种质资源形态学标记的遗传多样性分析[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版),2022,44(9):32−40. [YANG X M, LI G X, PAN Y F, et al. Genetic diversity of morphological traits of Akebia trifoliate germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition),2022,44(9):32−40.] YANG X M, LI G X, PAN Y F, et al. Genetic diversity of morphological traits of Akebia trifoliate germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 44(9): 32−40.
[4] 杨玉宁, 刘红昌, 高尔刚, 等. 木通属种质资源物候期、产量和品质差异分析[J]. 南方农业学报,2022,53(1):134−145. [YANG Y N, LIU H C, GAO E G, et al. Phenological investigation and variation analysis of yield and quality of Akebia Decne. germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture,2022,53(1):134−145.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2022.01.015 YANG Y N, LIU H C, GAO E G, et al. Phenological investigation and variation analysis of yield and quality of Akebia Decne. germplasm resources[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2022, 53(1): 134−145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1191.2022.01.015
[5] 唐成林, 杨斌, 陶光灿, 等. 八月瓜果实营养成分分析和评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(3):299−303. [TANG C L, YANG B, TAO G C, et al. Analysis and evaluation of nutritional components in Akebia trifoliate fruit[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(3):299−303.] TANG C L, YANG B, TAO G C, et al. Analysis and evaluation of nutritional components in Akebia trifoliate fruit[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(3): 299−303.
[6] 蔡芳丽, 邹帅宇, 高浦新, 等. 不同采收时间三叶木通果实品质变化分析[J]. 植物资源与环境学报,2022,31(1):83−85. [CAI F L, ZOU S Y, CAO P X, et al. Analysis on quality variations of Akebia trifoliata fruit at different harvesting times[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment,2022,31(1):83−85.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2022.01.10 CAI F L, ZOU S Y, CAO P X, et al. Analysis on quality variations of Akebia trifoliata fruit at different harvesting times[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2022, 31(1): 83−85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2022.01.10
[7] 杨月欣. 中国食物成分表[M]. 北京:北京大学医学出版社, 2020. [YANG Y X. Chinese food composition table[M]. Beijing:Peking University Medical Press, 2020.] YANG Y X. Chinese food composition table[M]. Beijing: Peking University Medical Press, 2020.
[8] 张孟琴, 徐路, 张俊波, 等. 三叶木通果皮主要营养成分、活性成分含量测定及果皮提取物抗氧化活性评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(10):388−394. [ZHANG M Q, XU L, ZHANG J B, et al. Determination of contents of the main nutritional components, functional components of Akebia trifoliata pericarp and the antioxidant activity of its extracts[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(10):388−394.] ZHANG M Q, XU L, ZHANG J B, et al. Determination of contents of the main nutritional components, functional components of Akebia trifoliata pericarp and the antioxidant activity of its extracts[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(10): 388−394.
[9] 李加兴, 吴萍, 吴越, 等. 八月瓜果皮果胶提取工艺优化及其理化特性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(1):275−277,283. [LI J X, WU P, WU Y, et al. Optimization of extraction conditions and analysis of physicochemical property of pectin from Akebia trifoliata peel[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(1):275−277,283.] LI J X, WU P, WU Y, et al. Optimization of extraction conditions and analysis of physicochemical property of pectin from Akebia trifoliata peel[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2016, 37(1): 275−277,283.
[10] 欧阳玉祝, 张晓旭, 唐顼婉, 等. 八月瓜果籽油功能成分与抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国油脂,2015,40(8):85−88. [OUYANG Y Z, ZHANG X X, TANG X W, et al. Functional components and antioxidant activity of Akebia trifoliate seed oil[J]. China Oils Fats,2015,40(8):85−88.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2015.08.021 OUYANG Y Z, ZHANG X X, TANG X W, et al. Functional components and antioxidant activity of Akebia trifoliate seed oil[J]. China Oils Fats, 2015, 40(8): 85−88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2015.08.021
[11] 李朝阁. 八月瓜酒酿造及籽油、多酚提取和抗氧化性研究[D]. 西安:陕西科技大学, 2016. [LI C G. Akebia trifoliate wine brewing, extraction of seed oil, polyphenols and its antioxidant activity research[D]. Xi'an:Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2016.] LI C G. Akebia trifoliate wine brewing, extraction of seed oil, polyphenols and its antioxidant activity research[D]. Xi'an: Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2016.
[12] 仲伟敏, 马玉华. 三叶木通种子的营养成分分析与评价[J]. 西南农业学报,2016,29(1):169−173. [ZHONG W M, MA Y H. Analysis and evaluation of nutritional components in Akebia trifoliate seeds[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2016,29(1):169−173.] ZHONG W M, MA Y H. Analysis and evaluation of nutritional components in Akebia trifoliate seeds[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 29(1): 169−173.
[13] 周娜娜. 三叶木通籽油提取及生物活性研究[D]. 长沙:中南林业科技大学, 2018. [ZHOU N N. Research on extraction and bioactivity of Akebia trifoliate seed oil[D]. Changsha:Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2018.] ZHOU N N. Research on extraction and bioactivity of Akebia trifoliate seed oil[D]. Changsha: Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2018.
[14] 周瑜, 梁良, 石向群, 等. 不同种源预知子籽的油脂含量及其油脂脂肪酸组成分析[J]. 中国油脂,2018,43(3):83−86,89. [ZHOU Y, LIANG L, SHI X Q, et al. Oil content of Akebiae Fructus deed from different provenances and its oil fatty acid composition[J]. China Oils and Fats,2018,43(3):83−86,89.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2018.03.019 ZHOU Y, LIANG L, SHI X Q, et al. Oil content of Akebiae Fructus deed from different provenances and its oil fatty acid composition[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2018, 43(3): 83−86,89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2018.03.019
[15] ZHONG Y C, ZHANG Z Q, CHEN J, et al. Physicochemical properties, content, composition and partial least squares models of A. trifoliata seeds oil[J]. Food Chemistry:X,2021,12:100131.
[16] SU S, WU J, PENG X Y, et al. Genetic and agro-climatic variability in seed fatty acid profiles of Akebia trifoliata (Lardizabalaceae) in China[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2021,102:104064. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2021.104064
[17] 刘永玲, 谢国芳, 王威, 等. 八月瓜叶、果皮和果肉中酚类、VC含量及其抗氧化能力分析[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(15):66−72. [LIU Y L, XIE G F, WANG W, et al. Analysis of phenolic and VC contents and antioxidant activity of leaves, peels and pulp of Akebia trifoliate[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(15):66−72.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.15.011 LIU Y L, XIE G F, WANG W, et al. Analysis of phenolic and VC contents and antioxidant activity of leaves, peels and pulp of Akebia trifoliate[J]. Food Research and Development, 2019, 40(15): 66−72. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.15.011
[18] 石兵艳, 李祥, 刘毅, 等. 八月瓜果皮中常春藤皂苷元水解工艺优化及图谱分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(2):239−245. [SHI B Y, LI Y, LIU Y, et al. Optimization of hydrolysis process and structure map analysis of hederagenin in Akebia trifoliata pericarp[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(2):239−245.] SHI B Y, LI Y, LIU Y, et al. Optimization of hydrolysis process and structure map analysis of hederagenin in Akebia trifoliata pericarp[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(2): 239−245.
[19] 陆俊, 罗丹, 张佳琦, 等. 三叶木通不同部位多酚、黄酮含量及抗氧化活性比较[J]. 食品与机械,2016,32(8):132−135,223. [LU J, LUO D, ZHANG J Q, et al. Comparative study on polyphenol, flavonoid and antioxidant activities from different part of Akebia trifoliate[J]. Food & Machinery,2016,32(8):132−135,223.] LU J, LUO D, ZHANG J Q, et al. Comparative study on polyphenol, flavonoid and antioxidant activities from different part of Akebia trifoliate[J]. Food & Machinery, 2016, 32(8): 132−135,223.
[20] 金洪光, 李玉全, 李同建, 等. 三叶木通果皮中绿原酸提取工艺的正交试验优选[J]. 时珍国医国药,2017,28(6):1306−1307. [JIN H G, LI Y Q, LI T J, et al. Optimization of the extraction technology of chlorogenic acid from Akebia trifoliate peels by orthogonal test[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,2017,28(6):1306−1307.] JIN H G, LI Y Q, LI T J, et al. Optimization of the extraction technology of chlorogenic acid from Akebia trifoliate peels by orthogonal test[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2017, 28(6): 1306−1307.
[21] 罗宗洪, 蔡圣宝, 易俊洁. 八月瓜的化学组成、抗氧化性及α-葡萄糖苷酶活性抑制研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(1):130−135. [LUO Z H, CAI S B, YI J J. Phytochemical composition, antioxidant activity and α-glucosidase inhibitory ability of Akebia trifoliate[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(1):130−135.] LUO Z H, CAI S B, YI J J. Phytochemical composition, antioxidant activity and α-glucosidase inhibitory ability of Akebia trifoliate[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(1): 130−135.
[22] LUO M, ZHOU D D, SHANG A, et al. Influences of microwave-assisted extraction parameters on antioxidant activity of the extract from Akebia trifoliata peels[J]. Foods,2021,10(6):1432. doi: 10.3390/foods10061432
[23] WANG J, REN H, XU Q L, et al. Antibacterial oleanane-type triterpenoids from pericarps of Akebia trifoliata[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,168:623−629. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.105
[24] CHEN J, SUN Z M, CHEN J H, et al. Metabolomic profile and antibacterial bioactivity of Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz pericarp extract[J]. Processes,2022,10(7):1394. doi: 10.3390/pr10071394
[25] 白雪, 关宝生, 孙艳男, 等. 八月札水提物对H22肝癌荷瘤鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2015,35(7):1946−1948. [BAI X, GUAN B S, SUN Y N, et al. Effect of the water extract of Akebia Fructus on the immune function of in H22 hepatoma bearing mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology,2015,35(7):1946−1948.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2015.07.096 BAI X, GUAN B S, SUN Y N, et al. Effect of the water extract of Akebia Fructus on the immune function of in H22 hepatoma bearing mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 2015, 35(7): 1946−1948. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2015.07.096
[26] 白雪, 崔文超, 王丽敏, 等. 八月札水提物对H22荷瘤小鼠突变型P53、Bcl-2和增殖细胞核抗原表达的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2020,40(2):374−379. [BAI X, CUI W C, WANG L M, et al. Effect of Akebia Fructus on the expression of mP53, Bcl-2 and PCNA in H22 tumor-bearing mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology,2020,40(2):374−379.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2020.02.046 BAI X, CUI W C, WANG L M, et al. Effect of Akebia Fructus on the expression of mP53, Bcl-2 and PCNA in H22 tumor-bearing mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 2020, 40(2): 374−379. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2020.02.046
[27] 王春玲, 郑作文. 八月札抗肝癌活性部位的筛选[J]. 中国现代应用药学,2021,38(7):784−789. [WANG C L, ZHEN Z W. Screening of anti-hepatocarcinoma active fractions from Akebiae Fructus[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy,2021,38(7):784−789.] WANG C L, ZHEN Z W. Screening of anti-hepatocarcinoma active fractions from Akebiae Fructus[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Applied Pharmacy, 2021, 38(7): 784−789.
[28] 王春玲, 张瑜, 文晓东, 等. 八月札乙醇提取物通过PI3K/Akt通路抑制H22细胞增殖并诱导其凋亡[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2022,40(9):73−77,267-268. [WANG C L, ZHANG Y, WEN X D, et al. Ethanol extract of Bayuezha [Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz.] inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of H22 liver cancer mice cell via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2022,40(9):73−77,267-268.] WANG C L, ZHANG Y, WEN X D, et al. Ethanol extract of Bayuezha [Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz.] inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of H22 liver cancer mice cell via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 40(9): 73−77,267-268.
[29] LU W L, REN H Y, LIANG C, et al. Akebia trifoliate (Thunb.) Koidz seed extract inhibits the proliferation of human pepatocellular carcinoma cell lines via inducing rndoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine:eCAM,2014,2014:192749. doi: 10.1155/2014/192749
[30] 任红艳, 方肇勤, 梁超, 等. 预知子籽对多种肝癌细胞恶性增殖的抑制作用研究[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2015,42(3):459−461,1-2. [REN H Y, FANG Z Q, LIANG C, et al. Inhibitory effect of Akebia trifoliate seed on malignant proliferation of various hepatoma cells[J]. Liaoning Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2015,42(3):459−461,1-2.] REN H Y, FANG Z Q, LIANG C, et al. Inhibitory effect of Akebia trifoliate seed on malignant proliferation of various hepatoma cells[J]. Liaoning Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 42(3): 459−461,1-2.
[31] LU W L, YANG T, SONG Q J, et al. Akebia trifoliate (Thunb.) Koidz seed extract inhibits humanhepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion in vitro[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2019,234:204−215.
[32] 宋秋佳, 卢文丽, 方肇勤, 等. 预知子种子提取物抑制HepG2肝癌细胞的增殖及黏附作用及相关机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2018,24(24):146−151. [SONG Q J, LU W L, FANG Z Q, et al. Inhibitory effect of Akebia trifoliate seed extract on proliferation and adhesion of HepG2 cells and corresponding mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2018,24(24):146−151.] SONG Q J, LU W L, FANG Z Q, et al. Inhibitory effect of Akebia trifoliate seed extract on proliferation and adhesion of HepG2 cells and corresponding mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2018, 24(24): 146−151.
[33] 王枭宇, 卢涛, 梁超, 等. 预知子种子提取物对核糖体蛋白抑制HepG2肝癌细胞增殖调控作用研究[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志,2019,26(16):1156−1162. [WANG X Y, LU T, LIANG C, et al. Regulation effect of Akebiae trifoliate seed extract on inhibiting malignant proliferation in HepG2 hepatoma cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Cancer Prevention and Treatment,2019,26(16):1156−1162.] WANG X Y, LU T, LIANG C, et al. Regulation effect of Akebiae trifoliate seed extract on inhibiting malignant proliferation in HepG2 hepatoma cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Cancer Prevention and Treatment, 2019, 26(16): 1156−1162.
[34] 卢涛, 许群瑶, 郝尧, 等. 不同成熟度预知子种子对人肝癌细胞恶性增殖的影响实验[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2018,36(1):193−196. [LU T, XU Q Y, HAO Y, et al. Research of Akebia fruit seeds of different maturity levels inhibiting hepatoma carcinoma cells malignant proliferation[J]. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2018,36(1):193−196.] LU T, XU Q Y, HAO Y, et al. Research of Akebia fruit seeds of different maturity levels inhibiting hepatoma carcinoma cells malignant proliferation[J]. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 36(1): 193−196.
[35] 卢涛. 预知子种子提取物抑制肝癌细胞增殖和诱导其胞质空泡机制的研究[D]. 上海:上海中医药大学, 2019. [LU T. A study of Akebiae fructus seeds ethanol extract inhibits proliferation of hepatoma cells and induces cytoplasmic vacuoles[D]. Shanghai:Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019.] LU T. A study of Akebiae fructus seeds ethanol extract inhibits proliferation of hepatoma cells and induces cytoplasmic vacuoles[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019.
[36] 张孟琴, 欧根友, 徐路, 等. 不同产地三叶木通果胶的理化性质、抗氧化活性及对癌细胞A549和K562-2生长的抑制作用[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(22):128−133. [ZHANG M Q, OU G Y, XU L, et al. Physicochemical properties, antioxidant activities, and inhibitory capabilities of pectins in the pericarps of Akebia trifoliata from different regions on cancer cells A549 and K562-2[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(22):128−133.] ZHANG M Q, OU G Y, XU L, et al. Physicochemical properties, antioxidant activities, and inhibitory capabilities of pectins in the pericarps of Akebia trifoliata from different regions on cancer cells A549 and K562-2[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(22): 128−133.
[37] 李伟业. 三叶木通籽油制备及创伤修复研究[D]. 吉首:吉首大学, 2021. [LI W Y. The preparation of Akebia trifoliate seed oil and its effect on wound healing[D]. Jishou:Jishou University, 2021.] LI W Y. The preparation of Akebia trifoliate seed oil and its effect on wound healing[D]. Jishou: Jishou University, 2021.
[38] 丁林玲, 谢颖欣, 高伟, 等. 三叶木通果肉提取物的体外抗氧化及抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶和乙酰胆碱酯酶能力[J]. 南方农业学报,2021,52(4):1058−1065. [DING L L, XIE Y X, GAO W, et al. In vitro antioxidant activities, α-glucosidase and acetylcholinesterase inhibition ability of Akebia trifoliata pulp extracts[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture,2021,52(4):1058−1065.] DING L L, XIE Y X, GAO W, et al. In vitro antioxidant activities, α-glucosidase and acetylcholinesterase inhibition ability of Akebia trifoliata pulp extracts[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2021, 52(4): 1058−1065.
[39] 苗永美, 简兴, 汪雁, 等. 广东石豆兰不同溶剂提取物抗氧化及与总黄酮、总酚含量的关系[J]. 核农学报,2020,34(5):1038−1046. [MIAO Y M, JIAN X, WANG Y, et al. Antioxidant activities and their relationship with contents of total flavonoids and total phenols of various solvent extracts from Bublophyllum kwangtungense[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2020,34(5):1038−1046.] doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.05.1038 MIAO Y M, JIAN X, WANG Y, et al. Antioxidant activities and their relationship with contents of total flavonoids and total phenols of various solvent extracts from Bublophyllum kwangtungense[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 34(5): 1038−1046. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.05.1038
[40] 郭刚军, 胡小静, 付镓榕, 等. 澳洲坚果青皮不同极性溶剂分步提取物功能成分与抗氧化活性及其相关性分析[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(7):74−82. [GUO G J, HU X J, FU J R, et al. Analysis and correlations of functional components and antioxidant activity of different polar solvent separate-step extracts from macadamia green husk[J]. Food Science,2021,42(7):74−82.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200310-154 GUO G J, HU X J, FU J R, et al. Analysis and correlations of functional components and antioxidant activity of different polar solvent separate-step extracts from macadamia green husk[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(7): 74−82. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200310-154
[41] 杨玉宁, 陈松树, 高尔刚, 等. 3种木通属植物21份种质果实的果皮品质评价[J]. 中药材,2021,44(5):1091−1098. [YANG Y N, CHEN S S, GAO E G, et al. Quality evaluation of pericarp and fruits of twenty-one germplasms in three Akebia plants[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2021,44(5):1091−1098.] YANG Y N, CHEN S S, GAO E G, et al. Quality evaluation of pericarp and fruits of twenty-one germplasms in three Akebia plants[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2021, 44(5): 1091−1098.
[42] WANG X Y, YU N X, PENG H L, et al. The profiling of bioactives in Akebia trifoliata pericarp and metabolites, bioavailability and in vivo antiinflammatory activities in DSS-induced colitis mice[J]. Food & Function,2019,10:3977−3991.
[43] LUGRIN J, ROSENBLATT-VELIN N, PARAPANOV R, et al. The role of oxidative stress during inflammatory processes[J]. Biological Chemistry,2014,395(2):203−230. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2013-0241
[44] SASOT G, MARTINEZ-HUELAMO M, VALLVERDU-QUERALT A, et al. Identification of phenolic metabolites in human urine after the intake of a functional food made from grape extract by a high resolution LTQ-Orbitrap-MS approach[J]. Food Research International,2017,100:435−444. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.01.020
[45] ZHANG Z H, GAO T, YAN N N, et al. Characterization and anti-aging activity of polysaccharides from Akebia trifoliata fruit separated by an aqueous two-phase system[J]. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition (Dordrecht, Netherlands),2023,78(1):154−159. doi: 10.1007/s11130-022-01031-9
[46] CHEN G J, LI C F, WANG S S, et al. Characterization of physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from shoot residues of bamboo (Chimonobambusa quadrangularis):Effect of drying procedures[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,292:281−293. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.04.060
[47] PERIASAMY S, LIN C H, NAGARAJAN B, et al. Mucoadhesive role of tamarind xyloglucan on inflammation attenuates ulcerative colitis[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2018,47:1−10. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.05.035
[48] WANG X Y, YU N X, WANG Z L, et al. Akebia trifoliata pericarp extract ameliorates inflammation through NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathways and modifies gut microbiota[J]. Food & Function,2020,11(5):4682−4696.
[49] LI F Y, FU Y H, LIU B, et al. Stevioside suppressed inflammatory cytokine secretion by down regulation of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells[J]. Inflammation,2012,35(5):1669−1675. doi: 10.1007/s10753-012-9483-0
[50] 王雪, 刘燕, 史玉柱. 基于NF-κB/MAPK信号通路探讨天山堇菜七叶内酯对脂多糖诱导RAW 264.7细胞的保护作用及机制[J]. 中国药理学通报,2022,38(9):1340−1349. [WANG X, LIU Y, SHI Y Z. The anti-inflammation effects of aesculetin from Viola tianshanica Maxim via NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 cells stimulated by LPS and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin,2022,38(9):1340−1349.] doi: 10.12360/CPB202111021 WANG X, LIU Y, SHI Y Z. The anti-inflammation effects of aesculetin from Viola tianshanica Maxim via NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 cells stimulated by LPS and its mechanism[J]. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin, 2022, 38(9): 1340−1349. doi: 10.12360/CPB202111021
[51] DI STEFANO E, OLIVIERO T, UDENIGWE C C. Functional significance and structure-activity relationship of food-derived α-glucosidase inhibitors[J]. Current Opinion in Food Science,2018,20:7−12. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2018.02.008
[52] TU W J, XUE Y M, NIE D. The prevalence and treatment of diabetes in China from 2013 to 2018[J]. The Journal of the American Medical Association,2021,327(17):1706−1706.
[53] 彭川, 胡学芳, 陈正涛, 等. 中药皂苷类成分的降糖作用及机制研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(11):266−275. [PENG C, HU X F, CHEN Z T, et al. Research progress on hypoglycemic effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine saponins[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2023,29(11):266−275.] PENG C, HU X F, CHEN Z T, et al. Research progress on hypoglycemic effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine saponins[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2023, 29(11): 266−275.
[54] YU N X, WANG X Y, NING F J, et al. Development of antibacterial pectin from Akebia trifoliata var. australis waste for accelerated wound healing[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,217:58−68. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.03.071
[55] 张亚平, 周瑜, 金洪光, 等. 八月瓜提取物对四氯化碳诱导小鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(3):301−304. [ZHANG Y P, ZHOU Y, JIN H G, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of Fructus Akebiae extract on liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(3):301−304.] ZHANG Y P, ZHOU Y, JIN H G, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of Fructus Akebiae extract on liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2018, 39(3): 301−304.
[56] JIANG Y L, YIN H, ZHOU X F, et al. Antimicrobial, antioxidant and physical properties of chitosan film containing Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz. peel extract/montmorillonite and its application[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,361:130111−130111. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130111
[57] ZOU S, GAO P, JIA T, et al. Physicochemical characteristics and nutritional composition during fruit ripening of Akebia trifoliata (Lardizabalaceae)[J]. Horticulturae,2022,8:326. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae8040326
[58] 贺江, 李博恩, 段亚丽, 等. 三叶木通果酒抗氧化活性及有机酸组成研究[J]. 食品工业,2019,40(2):181−184. [HE J, LI B E, DUAN Y L, et al. Research on the antioxidant activity and organic acid profile of Akebia trifoliate wine[J]. Food Industry,2019,40(2):181−184.] HE J, LI B E, DUAN Y L, et al. Research on the antioxidant activity and organic acid profile of Akebia trifoliate wine[J]. Food Industry, 2019, 40(2): 181−184.
[59] 王殿东, 潘丽梅, 侯学俊, 等. 一种发酵型八月瓜果酒及其制备方法:CN106635698B[P]. 2016-10-31 [2020-07-21]. [WANG D D, PAN L M, HOU X J, et al. A fermented Akebia trifoliate wine and its preparation method:CN106635698B[P]. 2016-10-31 [2020-07-21].] WANG D D, PAN L M, HOU X J, et al. A fermented Akebia trifoliate wine and its preparation method: CN106635698B[P]. 2016-10-31 [2020-07-21].
[60] 李秀彤, 胡海军, 刘冬雪. 八月瓜鲜果营养成分及果汁感官品质分析[J]. 南方农业,2020,14(25):11−14. [LI X T, HU H J, LIU D X. Analysis of nutritional composition and sensory quality of fresh fruit of Akebia trifoliate[J]. South China Agriculture,2020,14(25):11−14.] LI X T, HU H J, LIU D X. Analysis of nutritional composition and sensory quality of fresh fruit of Akebia trifoliate[J]. South China Agriculture, 2020, 14(25): 11−14.
[61] 张婧, 乐洋, 程莉媛, 等. 八月瓜果酱加工工艺研究[J]. 农产品加工,2021,539(21):37−41,44. [ZHANG J, YUE Y, CHENG L Y, et al. Optimum process of Akebia trifoliate jam[J]. Farm Products Processing,2021,539(21):37−41,44.] ZHANG J, YUE Y, CHENG L Y, et al. Optimum process of Akebia trifoliate jam[J]. Farm Products Processing, 2021, 539(21): 37−41,44.
[62] 肖彦达, 李加兴, 肖秀凤, 等. 八月瓜果粉喷雾干燥工艺优化及溶解特性研究[J]. 食品与机械,2015,31(5):246−249. [XIAO Y D, LI J X, XIAO X F, et al. Optimization of spray drying technology and analysis of dissolution characteristics on fruit powder from Akebia trifoliate[J]. Food & Machinery,2015,31(5):246−249.] XIAO Y D, LI J X, XIAO X F, et al. Optimization of spray drying technology and analysis of dissolution characteristics on fruit powder from Akebia trifoliate[J]. Food & Machinery, 2015, 31(5): 246−249.
[63] 雷颂, 涂庆会, 张利, 等. 三叶木通果皮制作果脯加工工艺[J]. 食品研究与开发,2016,37(19):100−104. [LEI S, TU Q H, ZHANG L, et al. Study on preserved Akebia trifoliate Kiodz peel processing technology[J]. Food Research and Development,2016,37(19):100−104.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.19.024 LEI S, TU Q H, ZHANG L, et al. Study on preserved Akebia trifoliate Kiodz peel processing technology[J]. Food Research and Development, 2016, 37(19): 100−104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.19.024
[64] 何松榆, 战英策, 刘冰舟, 等. 不同护色工艺处理对八月瓜茶品质的影响[J]. 黑龙江农业科学,2016,270(12):94−96. [HE S Y, ZHAN Y C, LIU B Z, et al. Effects of different color-protection processes on the quality of Akebia trifoliate tea[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,2016,270(12):94−96.] HE S Y, ZHAN Y C, LIU B Z, et al. Effects of different color-protection processes on the quality of Akebia trifoliate tea[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 270(12): 94−96.
[65] 孙晓东, 张心伟, 谭书明. 三叶木通果皮茶工艺优化[J]. 贵州农业科学,2018,46(11):134−137,141. [SUN X D, ZHANG X W, TAN S M. Processing technology optimization of Akebia trifoliate peel tea[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2018,46(11):134−137,141.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2018.11.033 SUN X D, ZHANG X W, TAN S M. Processing technology optimization of Akebia trifoliate peel tea[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(11): 134−137,141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2018.11.033
[66] 邓爱华, 李红勇, 王云, 等. 三叶木通果茶加工工艺研究[J]. 广州化工,2018,46(1):120−123. [DENG A H, LI H Y, WANG Y, et al. Study on fabrication of Akebia trifoliata fruit tea[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry,2018,46(1):120−123.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2018.01.043 DENG A H, LI H Y, WANG Y, et al. Study on fabrication of Akebia trifoliata fruit tea[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2018, 46(1): 120−123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2018.01.043
[67] World Health Organization (WHO), 2008. Interim summary of conclusions and dietary recommendations on total fat and fatty acids. The Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Fats and Fatty Acids in Human Nutrition. Geneva.
[68] 蔡雪梅, 陈巍, 李晓, 等. 炒籽时间对八月瓜籽油挥发性风味成分的影响[J]. 中国油脂,2021,46(11):14−20. [CAI X M, CHEN W, LI X, et al. Impact of roasting time on volatile flavor compounds of Akebia trifoliate seed oil[J]. China Oils and Fats,2021,46(11):14−20.] CAI X M, CHEN W, LI X, et al. Impact of roasting time on volatile flavor compounds of Akebia trifoliate seed oil[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2021, 46(11): 14−20.
[69] JIANG Y L, ZHOU X F, ZHENG Y R, et al. Impact of ultrasonication/shear emulsifying/microwave-assisted enzymatic extraction on rheological, structural, and functional properties of Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz. seed protein isolates[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,112:106355. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106355
[70] 刘灿, 江慎华, 徐玲玲, 等. 氢化裂解三叶木通油制备生物柴油的研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2015,30(1):76−80. [LIU C, JIANG S H, XU L L. Biodiesel prepared by hydrocracking Akebia trifoliata oil[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2015,30(1):76−80.] LIU C, JIANG S H, XU L L. Biodiesel prepared by hydrocracking Akebia trifoliata oil[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2015, 30(1): 76−80.
[71] LEI L, ZHAO Q, SELOMULYA C, et al. The effect of deamidation on the structural, functional, and rheological properties of glutelin prepared from Akebia trifoliata var. australis seed[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,178:96−105. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.01.081
[72] JIANG Y L, YIN H, ZHENG Y R, et al. Structure, physicochemical and bioactive properties of dietary fibers from Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz. seeds using ultrasonication/shear emulsifying/microwave-assisted enzymatic extraction[J]. Food Research International,2020,136:109348−109348. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109348





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



