Effects of Steam Explosion on Structural and Properties of Soluble Dietary Fiber in Rice Bran from Different Varieties
-
摘要: 以稻花香、长粒香、赣晚籼40号3种稻谷米糠为原料,探究蒸汽爆破对不同品种稻谷米糠可溶性膳食纤维的影响。应用傅里叶变换红外光谱、X射线衍射和扫描电镜探究蒸汽爆破对米糠SDF结构的影响;以持水力、持油力、吸附胆固醇能力、吸附葡萄糖能力、α-淀粉酶活性抑制能力及抗氧化能力为评价指标,研究蒸汽爆破对米糠SDF功能特性的影响。结果表明,蒸汽爆破使米糠SDF红外光谱中部分吸收峰的吸收强度增加、结晶度降低、结构疏松多孔;稻花香、长粒香、赣晚籼40号稻谷米糠经汽爆后其SDF的含量较其对照分别增加了87.22%、94.72%、70.31%;3种蒸汽爆破米糠SDF的持水性、持油性、在人体胃液环境下吸附胆固醇能力、吸附葡萄糖能力以及对ABTS+·、·OH清除率和总抗氧化能力较其对照均显著增加(P<0.05);蒸汽爆破长粒香和赣晚籼40号米糠SDF对α-淀粉酶活性的抑制能力较其对照分别增加了7.60%和21.72%。蒸汽爆破稻花香米糠SDF的持水力、吸附胆固醇的能力较强(pH2)以及对DPPH·的清除率最高,分别达到1.06 g/g、43.93 μmol/g和14.25%,而蒸汽爆破长粒香米糠SDF的持油力、对α-淀粉酶活性抑制能力和总抗氧化能力最高,分别达到4.02 g/g、86.53%和3.82 μmol/g;蒸汽爆破赣晚籼40号米糠SDF吸附葡萄糖的能力和对ABTS+·、·OH清除率较强,分别达到625.16 mg/g、98.26%和27.85%。综上,蒸汽爆破使3种米糠SDF的含量增加,功能特性较其对照得到改善,但3个蒸汽爆破品种米糠SDF的功能特性存在明显差异。Abstract: Rice bran from 3 rice varieties, namely Daohuaxiang, Changlixiang and Ganwanxian No.40 were used as raw materials to investigate the effect of steam explosion on structural and properties of soluble dietary fiber in rice bran of different varieties. The structure alteration of SDF in rice bran treated by steam explosion was observed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. The impact of steam explosion on SDF functional properties of rice bran was studied by a series of evaluation indicators, such as water holding, oil holding, cholesterol adsorption, glucose adsorption, α-amylase inhibition and antioxidant capacity. The results showed that steam explosion could increase some absorption peaks intensity in the infrared spectrum of SDF, decrease crystallinity and form loose and porous structure of rice bran SDF from 3 rice varieties. The SDF contents in Daohuaxiang, Changlixiang and Ganwanxian No.40 rice bran by steam explosion were increased by 87.22%, 94.72% and 70.31%, respectively. Notably, the functional properties of steam-exploded rice bran from 3 rice varieties, such as water retention, oil retention, cholesterol adsorption capacity under human gastric fluid environment, glucose adsorption capacity, ABTS+ and OH free radical scavenging rate and total antioxidant capacity were significantly increased compared with control group (P<0.05). The α-amylase inhibition activity of SDF in steam-exploded Changlixiang rice bran and Ganwanxian No.40 rice bran increased by 7.60% and 21.72%, respectively. The SDF in steam-exploded Daohuaxiang No.40 rice bran showed stronger water retention, cholesterol adsorption ability (pH2) and higher clearance rate of DPPH·, which reached 1.06 g/g, 43.93 μmol/g and 14.25%, respectively. In contrast, the SDF from Changlixiang rice bran by steam explosion exhibited higher oil retention, α-amylase activity inhibition ability and total antioxidant capacity, which reached 4.02 g/g, 86.53% and 3.82 μmol/g, respectively. The SDF in Ganwanxian No.40 rice brans showed stronger ability to adsorb glucose, and the radical scavenging ability for ABTS+· and ·OH was 625.16 mg/g, 98.26% and 27.85%, respectively. In summary, the SDF content in bran of 3 rice varieties by steam explosion was increased and their functional properties were improved compared with the control group, the SDF treated by steam explosion from 3 rice varieties showed different functional properties.
-
Keywords:
- steam explosion /
- rice bran /
- soluble dietary fiber /
- structure /
- adsorb ability /
- antioxidant activity
-
稻谷是世界上重要的粮食作物之一,主要分布在亚洲、非洲、美洲。我国是稻谷种植大国,据国家统计局统计,2023年我国稻谷产量约2.066×108 t,约占谷物总产量的32.2%[1]。米糠是稻谷加工的副产物,其约占稻谷质量的10%[2],主要由种皮、果皮、胚芽、糊粉层和少量胚乳等组成,约含有14.5%的蛋白质、20.5%的脂肪、29.0%的膳食纤维[2],以及酚类化合物、植物甾醇等活性物质[3−4]。米糠因口感粗糙、适口性差、脂肪易氧化变质,绝大部分被用作饲料或废弃,造成膳食纤维的资源浪费。根据在水中溶解度的不同,膳食纤维可分为可溶性膳食纤维(soluble dietary fiber,SDF)和不溶性膳食纤维(insoluble dietary fiber,IDF)。SDF具有降低血糖、降低血清胆固醇以及预防心血管疾病和提高机体免疫力等生理功能[5],SDF对人体健康作用与其含量、结构和特性等相关[6]。米糠中SDF含量较低[7],其生理功能作用相对较弱。因此,寻求适当的改性处理方法以提高米糠SDF的含量,改变其结构,进而提升其功能特性,对于提高米糠膳食纤维的健康功能具有重要价值。
蒸汽爆破(steam explosion,SE)即汽爆,被认为是最有前景的膳食纤维处理方法[8],通过汽爆处理可使纤维的紧密结构松散,一些与纤维结合的材料解聚,高分子量多糖被部分降解,SDF含量增加及特性发生改变[9]。付晓康等[10]的实验表明汽爆处理使米糠SDF的提取率高达6.987%,SDF的膨胀力、持油力和葡萄糖吸附力显著增加;何晓琴等[8]对苦荞麸皮进行汽爆处理,使SDF的含量提高了54.11%,SDF的持水性、α-淀粉酶活性抑制能力及葡萄糖吸附能力均得到提升;MA等[11]的研究结果也表明汽爆处理降低了荞麦麸皮SDF的结晶度,提高了SDF的热稳定性、抗氧化性和抗菌性能。稻谷品种繁多,不同品种稻谷米糠膳食纤维的总量、细胞壁组成与结构存在差异性。然而,汽爆处理对不同品种米糠膳食纤维结构变化与功能特性变化的差异性影响尚不明确。
本实验以我国3个重要的稻谷品种(稻花香、长粒香和赣晚籼40号)为实验材料,在前期实验(已分别筛选出3种米糠SDF含量高的最佳汽爆条件)的基础上,以最佳汽爆条件对3种米糠进行汽爆处理,探究汽爆前后3种米糠SDF的含量、结构和功能特性的差异性,为阐明米糠SDF的营养健康功效提供理论参考,以提高米糠SDF在食品中的利用率。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
稻花香稻谷米糠、长粒香稻谷米糠 黑龙江省哈尔滨市五常金禾米业有限公司;赣晚籼40号稻谷米糠 江西省抚州市永庆米业有限公司;糖化酶(100 U/mg)、α-淀粉酶(10 U/mg)、碱性蛋白酶(100 U/mg) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;总胆固醇含量检测试剂盒、ABTS自由基检测试剂盒、DPPH自由基检测试剂盒、OH自由基检测试剂盒、总抗氧化能力试剂盒 北京市索莱宝科技有限公司;D-葡萄糖 北京奥博星生物技术有限责任公司;溴化钾(光谱纯)、正己烷 国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
QBS-80蒸汽爆破工艺实验台 河南正道环启宝有限公司;TGL-16M台式高速冷冻离心机 上海卢湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;S-3000N扫描电子显微镜 日本HITACHI公司;D8 ADVANCE X-射线衍射仪 德国BRUKER公司;Nicolet iN10-iZ10傅里叶变换显微红外光谱仪 赛默飞世尔科技公司;UV5 Bio紫外可见分光光度计 上海梅特勒托利多仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 脱脂米糠的制备
3种米糠分别与正己烷以1:5的质量比于具塞锥形瓶中混合均匀,25 ℃下静置8 h,抽滤,重复上述操作,直到上清液澄清为止;将滤渣置于通风橱内自然风干,干燥脱脂的米糠粉碎后过60目筛,装袋密封于-18 ℃储存。
1.2.2 蒸汽爆破米糠的制备
称取过60目筛的脱脂稻花香米糠(daohuaxiang rice bran,DRB)、长粒香米糠(changlixiang rice bran,CRB)、赣晚籼40号米糠(ganwanxian NO.40 rice bran,GRB)各200 g,分别于1.2、0.4、1.2 MPa的蒸汽压力及100、200、300 s的维压时间条件下制备汽爆米糠,经45 ℃烘干(水分含量5.0%)、粉碎、过100目筛,得到汽爆稻花香米糠(steam explosion daohuaxiang rice bran,SEDRB)、汽爆长粒香米糠(steam explosion changlixiang rice bran,SECRB)、汽爆赣晚籼40号米糠(steam explosion ganwanxian No.40 rice bran,SEGRB),装袋密封,4 ℃下贮存备用。3种汽爆米糠分别以其未汽爆脱脂米糠为对照。
1.2.3 米糠膳食纤维含量的测定及水溶性膳食纤维的提取
参考GB 5009.88-2014《食品中膳食纤维的测定》的方法进行SDF的测定。参考付晓康等[10]的方法提取米糠膳食纤维。将一定质量(M2)的脱脂米糠粉与蒸馏水以质量比1:10的比例于烧杯中混合,在50 ℃下水浴搅拌100 min后再于95 ℃下保持15 min,待温度降至60 ℃后,加入米糠质量0.3%的α-淀粉酶,60 ℃下反应45 min后调节pH至10.5,加入米糠质量0.6%的碱性蛋白酶,45 ℃下反应30 min后调节pH至4.1,59 ℃水浴下加入米糠质量0.3%的糖化酶,反应30 min(取1 mL溶液并加入1滴碘液,不显示蓝色表明已糖化完全)后于95 ℃下水浴15 min灭酶,冷却后离心(4000 r/min、30 min),将上清液中加入4倍体积无水乙醇沉淀过夜,离心(4000 r/min、15 min),将沉淀物于45 ℃烘干至水分含量为5.0%,称重(M1)、粉碎过100目筛即得SDF待测样品。依照公式(1)计算SDF的提取率。
SDF提取率(%)=M1M2×100 (1) 式中:M1表示干沉淀物的质量,g;M2表示脱脂米糠粉的质量,g。
1.2.4 米糠SDF的红外光谱测试
参考LIU等[12]的方法测试膳食纤维的傅里叶变换红外光谱(fourier transform infrared spectroscopy,FT-IR)。称取可溶性膳食纤维2 mg,分别与100 mg干燥的KBr粉末于研钵中混合并研磨均匀,压片后进行扫描,扫描次数:32,分辨率:4 cm−1,波数扫描范围:400~4000 cm−1,应用OMNIC 8.2软件进行光谱数据处理。
1.2.5 米糠SDF的X-射线衍射和结晶度的测定
参考MA等[13]的方法,使用X-射线衍射仪测定样品的衍射图谱,应用MDI Jade 5.0软件处理数据,采用面积比法计算纤维的结晶度。参数设置:铜靶管压管流40 kv/40 mA,步长0.02°,衍射角2θ,扫描速度2°/min,扫描范围3.5°~60°。
1.2.6 米糠SDF超微结构的观察
取少量SDF样品均匀粘在导电胶上,用离子溅射镀膜法进行表面喷金,置于扫描电镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM)下观察样品并拍照。
1.2.7 米糠SDF持水力、持油力及胆固醇吸附能力、葡萄糖吸附能力的测定
参考ZHANG等[14]的方法测定SDF的持水力和持油力。参考QIAO等[15]方法测定SDF吸附胆固醇能力,取0.2 g米糠SDF与15 mL蛋黄稀释液混匀,分别调节溶液pH为7.0和2.0,以模拟小肠和胃环境条件,测定胆固醇的吸附能力。依照公式(2)计算SDF吸附胆固醇能力(cholesterol adsorption capacity,CAC)。
吸附胆固醇能力(µmol/g)=D2−D1M×V (2) 式中:D1表示上清液中胆固醇的含量,µmol/L;D2表示蛋黄溶液中胆固醇含量,µmol/L;V表示蛋黄溶液的体积,L;M表示SDF的质量,g。
参考LI等[16]的方法测定SDF吸附葡萄糖能力,略有修改。将0.1 g SDF(mol/L)和50 mL(V)葡萄糖溶液(2 mg/mL)置于离心管中混合均匀,在37 ℃的条件下水浴振荡6 h,待吸附达到平衡后,离心(2500 r/min、30 min),在可见分光光度计505 nm下测定上清液中葡萄糖的浓度。依照公式(3)计算吸附葡萄糖能力(glucose adsorption capacity,GAC)。
吸附葡萄糖能力(mg/g)=C1−C2M×V (3) 式中:C1表示葡萄糖溶液的浓度,mg/mL;C2表示上清液中葡萄糖的浓度,mg/mL;V表示葡萄糖溶液的体积,mL;M表示SDF的质量,g。
1.2.8 米糠SDF对α-淀粉酶活性抑制能力的测定
参考何晓琴等[8]的方法测定SDF对α-淀粉酶活性的抑制能力(α-amylase activity inhibition ratio,α-AAIR)。取0.1 g米糠SDF与25 mL马铃薯淀粉溶液(浓度40 g/L、pH6.5)混合,加入0.1 g的α-淀粉酶,37 ℃下水浴振荡2 h后,离心(3000 r/min,15 min),利用可见分光光度计测定上清液中的葡萄糖浓度和对照组葡萄糖浓度,依照公式(4)计算α-淀粉酶活性的抑制能力。
α-淀粉酶活性抑制能力(%)=C2−C1C1×100 (4) 式中:C1表示SDF组上清液中葡萄糖浓度,mg/mL;C2表示对照组上清液中葡萄糖浓度,mg/mL。
1.2.9 米糠SDF抗氧化能力的测定
由于单一方法不能代表复杂体系中的抗氧化活性,因此通过ABTS+·、DPPH·、·OH清除率和总抗氧化能力来测定SDF的抗氧化活性。测定方法按照试剂盒说明书进行操作。
称取0.05 g的SDF与1 mL提取液混合,水浴(40 ℃)浸提30 min,25 ℃下离心(10000 r/min、10 min),取25 μL上清液、975 μL的工作液混匀,25 ℃避光静置30 min,测定515 nm处的吸光度,以无水乙醇作为空白对照,按照公式(5)计算DPPH·的清除率。
DPPH⋅清除率(%)=1−Am−AcAb×100 (5) 式中:Am为样液与工作液的吸光值;Ac为样液与无水乙醇的吸光值;Ab为无水乙醇与工作液的吸光值。
取50 μL上清液(测定DPPH·清除率时已制备)、850 μL的工作液和100 μL缓冲液涡旋混匀,25 ℃避光静置6 min,测定405 nm处的吸光度,以蒸馏水作为空白对照,参考公式(5)计算ABTS+·的清除率。
称取约0.1 g的SDF,加入1 mL提取液冰浴匀浆,4 ℃下离心(10000 r/min、10 min),混合液于37 ℃下反应60 min,20 ℃下离心(10000 r/min、10 min),取上清液测定536 nm处的吸光度,以蒸馏水作为空白对照,按照公式(6)计算·OH的清除率。
⋅OH清除率(%)=Ac−AdAk−Ad×100 (6) 式中:Ac为样液与工作液的吸光值;Ad为样液与蒸馏水的吸光值;Ak为蒸馏水与工作液的吸光值。
总抗氧化能力的测定应用铁离子还原抗氧化能力测定法。以不同浓度的FeSO4溶液绘制出标准曲线,取30 μL上清液(测定·OH清除率时已制备)、90 μL蒸馏水和900 μL混合液混合均匀,20 ℃反应10 min后,测定593 nm处的吸光度,按照公式(7)计算总抗氧化能力。
总抗氧化能力(µmol/g)=34×X×VW (7) 式中:X为根据线性回归方程求得的样品浓度值,μmol/mL;V为提取液体积,mL;W为样品的质量,g。
1.3 数据处理
除1.2.4、1.2.5和1.2.6步骤外,各实验重复测定3次,结果以平均值±标准差表示;分别使用SPSS 22和Origin 2015软件对数据进行分析和作图处理。
2. 结果与分析
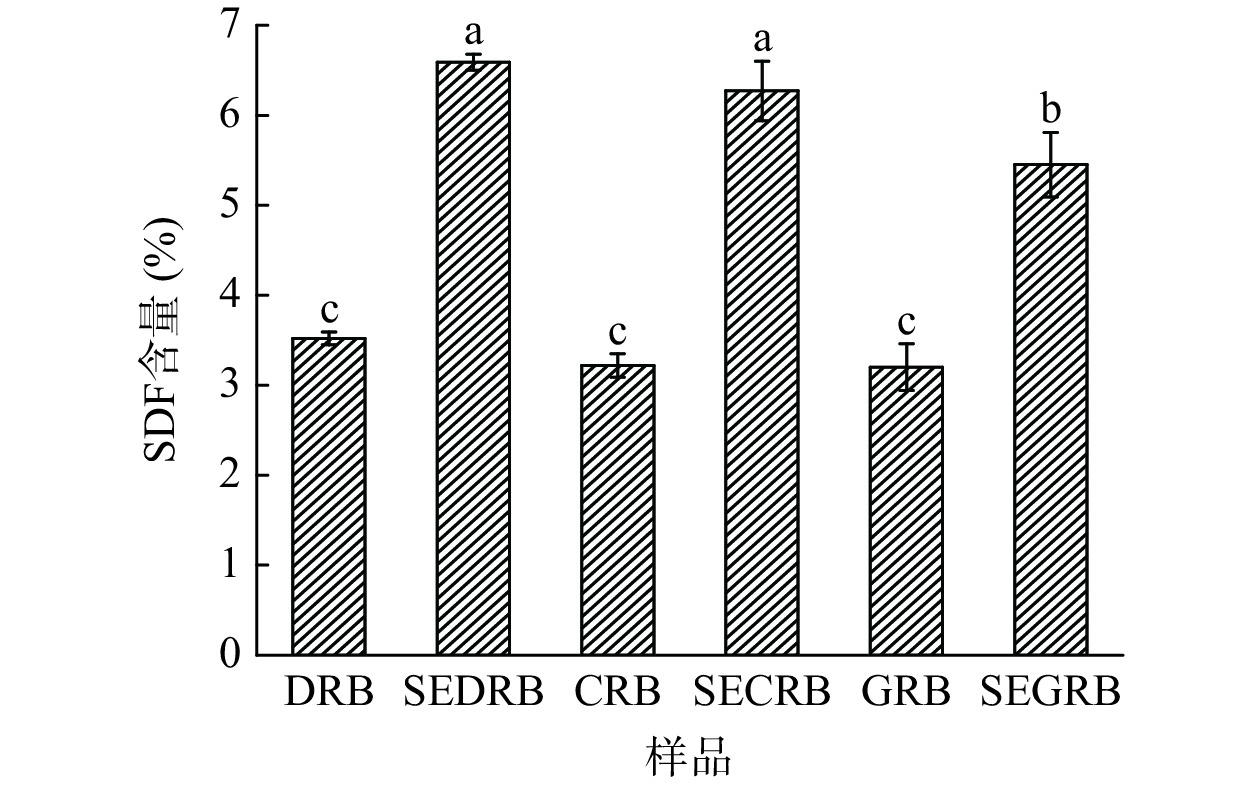
2.1 蒸汽爆破对米糠SDF含量的影响
图1为汽爆前后米糠SDF含量的变化情况。由图1可知,稻花香、长粒香及赣晚籼40号脱脂米糠的SDF含量分别为3.52%、3.22%和3.20%,经汽爆处理后其分别增加到6.59%、6.27%和5.45%。推测汽爆处理过程中,在热降解、氢键破坏、结构重排等的共同作用下,米糠纤维内部的组织结构被破坏[8],与纤维素结合的部分物质发生了解聚[17],不溶性半纤维素和纤维素水解为低聚糖、单糖等可溶性成分,因而导致SDF含量增多[18]。
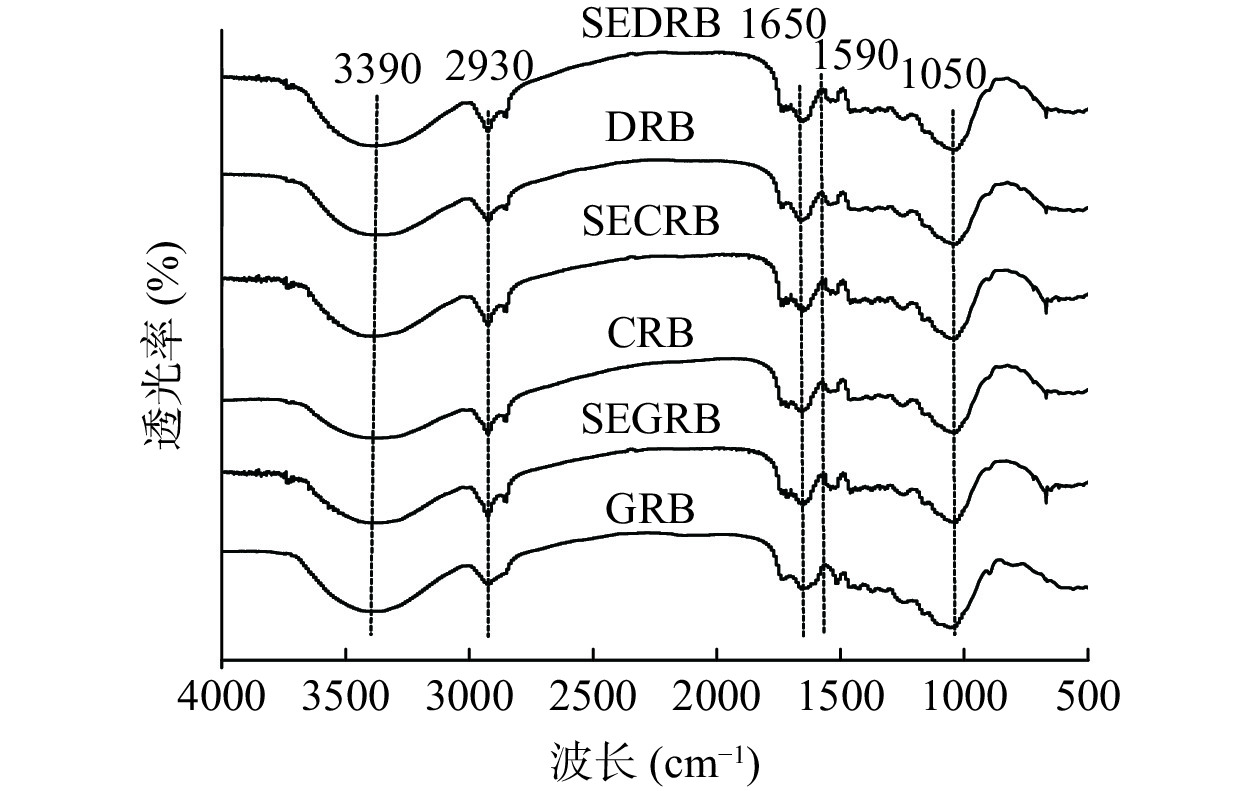
2.2 蒸汽爆破前后米糠SDF的红外光谱分析
图2为汽爆前后米糠SDF的FT-IR图谱。由图2可知,3种米糠的SDF在汽爆前后的特征吸收峰相似,汽爆前后SDF特征吸收峰的峰型、位置、数量均未发生显著变化,表明汽爆未改变米糠SDF的化学成分。图2中,在3390 cm−1附近的强宽峰是纤维素和半纤维素中O-H的伸缩振动引起的,汽爆处理导致3种米糠SDF的吸收峰峰形变窄,吸收强度较其对照均有不同程度的显著增加,表明汽爆处理破坏了纤维素之间的氢键,使更多的羟基基团暴露[8],从而改变其吸收峰强度;2930 cm−1附近的特征峰是纤维素和半纤维素中C-H的伸缩振动引起的[19];1050 cm–1附近的峰是半纤维素糖环中C-O-C的C=O基团的特征峰[20];以上这几种峰为多糖的特征吸收峰,表明米糠SDF的主要成分是糖类物质[8]。1650 cm−1附近的尖峰与木质素中芳香环的C–C拉伸振动有关[21],3种汽爆米糠SDF在1650 cm−1附近的吸收峰较其对照略有减弱;1590 cm−1处吸收峰的出现是由于C=O键的存在,表明SDF汽爆过程中产生了糖醛酸[22]。
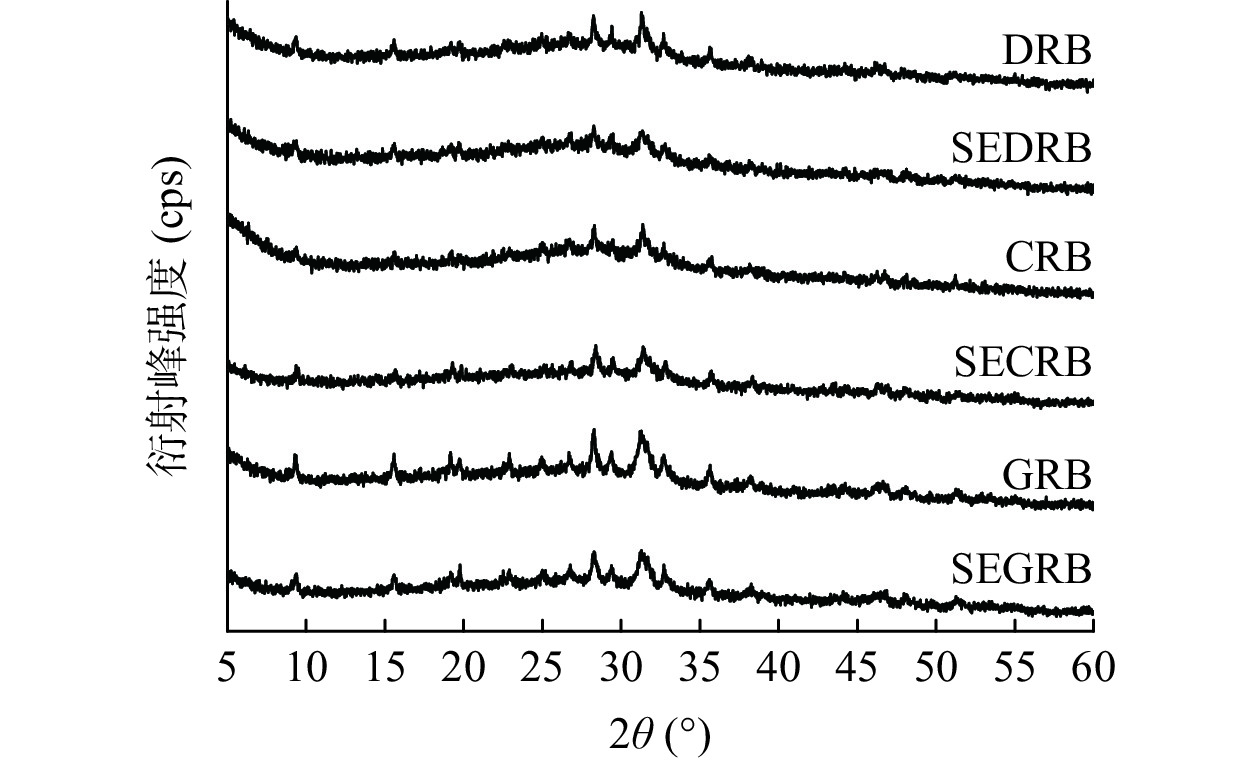
2.3 蒸汽爆破前后米糠SDF的晶体结构分析
米糠SDF的X射线衍射图谱如图3所示。由图3可知,汽爆处理前后3种米糠SDF的衍射峰位置无显著差异,表明汽爆处理没有改变米糠SDF的晶型,其均为纤维素I型结晶结构,是结晶区与非结晶区共存的状态[23]。稻花香米糠、长粒香米糠、赣晚籼40号米糠的相对结晶度分别由汽爆前的11.42%、7.41%、9.35%降至汽爆后的4.91%、3.34%和7.56%,这可能是由于汽爆处理使纤维素适度降解和半纤维素部分溶解,结晶区聚合度下降,结构变得疏松多孔所导致[24]。汽爆米糠SDF结晶度的下降表明其分子间的作用力有所减弱,结构疏松,有利于其持水力、持油力的改善[25]。
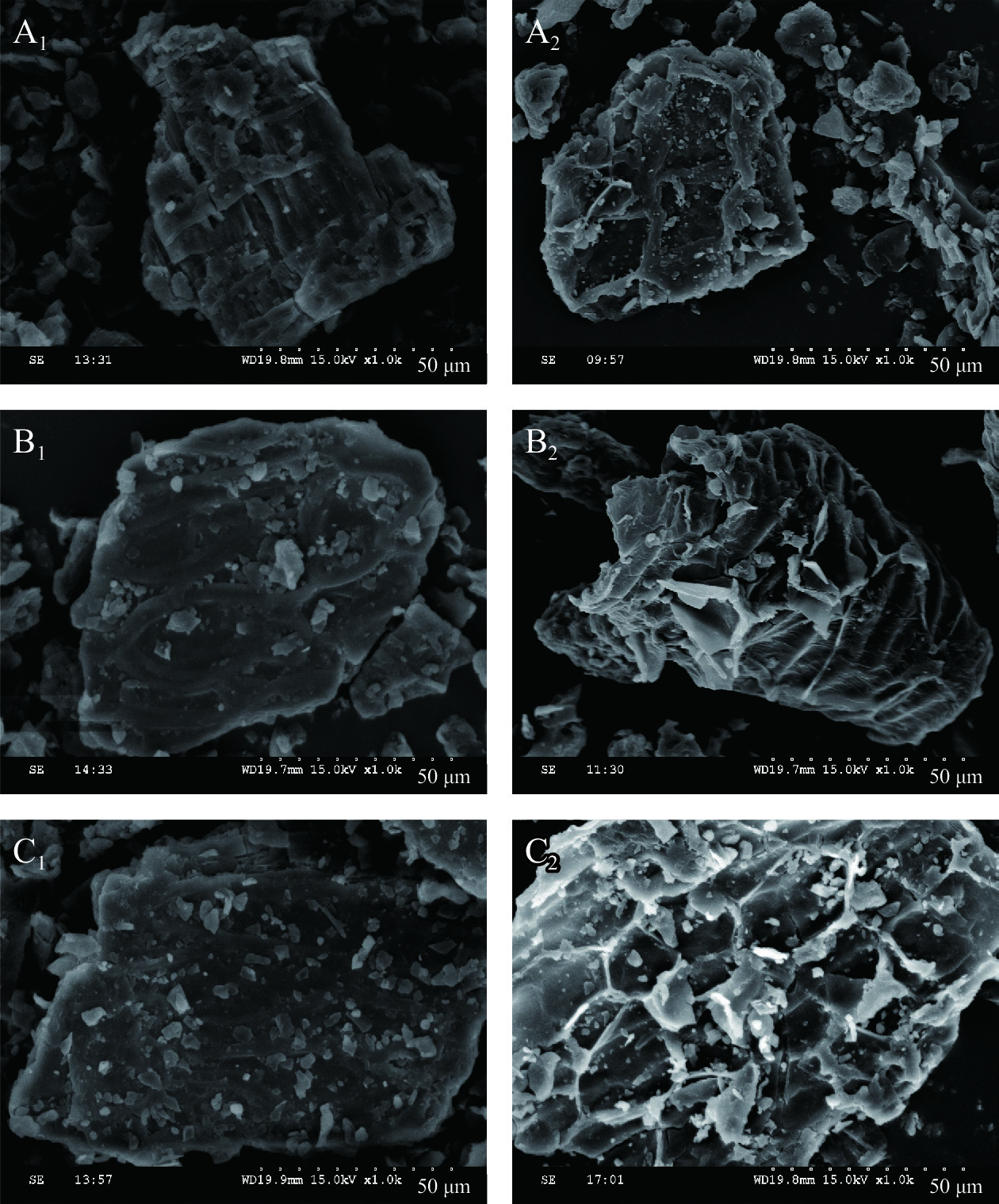
2.4 蒸汽爆破前后米糠膳食纤维结构的变化
米糠SDF的电镜扫描结果如图4所示。由图4可知,未汽爆处理米糠SDF呈较大的团块状、细胞壁较厚、表面较光滑、结构致密完整(图4A1、图4B1、图4C1);汽爆处理后米糠SDF呈现小碎片或不规则片状结构、细胞壁明显变薄、完整致密的表面变得松散破裂,纤维的有序性被破坏(图4A2、图4B2、图4C2),这可能是由于汽爆过程中瞬时强大的压力差导致米糠膳食纤维中的半纤维素和木质素被软化和水解,聚合度减小。何晓琴等[8]发现汽爆改性处理使得苦荞麸皮SDF呈现疏松多层的蓬松结构,内部比表面积和孔隙率明显增大,这与本文的实验结果一致。米糠SDF的多孔疏松结构使其吸附位点增加,因而能够结合更多的水分子、葡萄糖、α-淀粉酶等分子,从而改变米糠SDF的理化性质及降血糖能力[26],有利于其在食品工业中的应用。
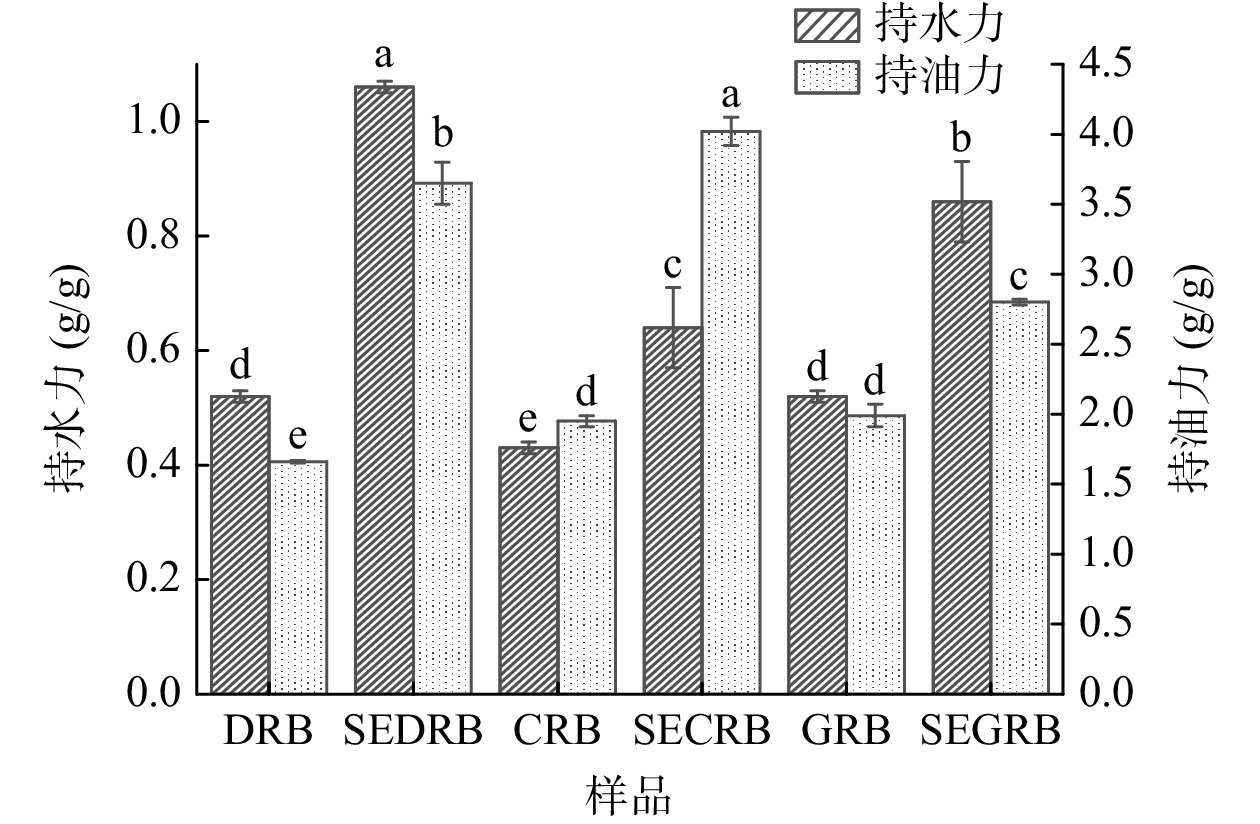
2.5 蒸汽爆破对米糠SDF持水力和持油力的影响
SDF良好的持水力有利于其在肠道内吸水膨胀,促进肠道蠕动[27],防止食品水分流失,减少食品干耗[7];良好的持油力可通过阻止食物中多余胆固醇的吸收从而起到降血脂的作用[28],防止食品加工中的脂质损失[7]。图5为汽爆处理对米糠SDF持水力和持油力变化的影响。由图5可知,与对照相比,汽爆米糠SDF的持水力和持油力显著增加(P<0.05)。SEDRB、SECRB、SEGRB的持水力较其对照分别提高了103.8%、48.8%和65.34%,持油力分别提高了119.88%、106.15%和40.70%。这是由于汽爆过程中巨大压差作用使纤维素、半纤维素大分子物质被截断,形成各种小分子片段,导致膳食纤维的一些亲水性、亲油性活性位点暴露出来,更有利于颗粒与水或油接触,且分散性增强[29]。何晓琴等[8]的实验也表明汽爆处理增加了米糠的持水力和持油力。不同品种汽爆米糠间SDF持水力和持油力的差异可能与其SDF的结构特性、表面暴露的化学基团的种类与数量等有关[7]。
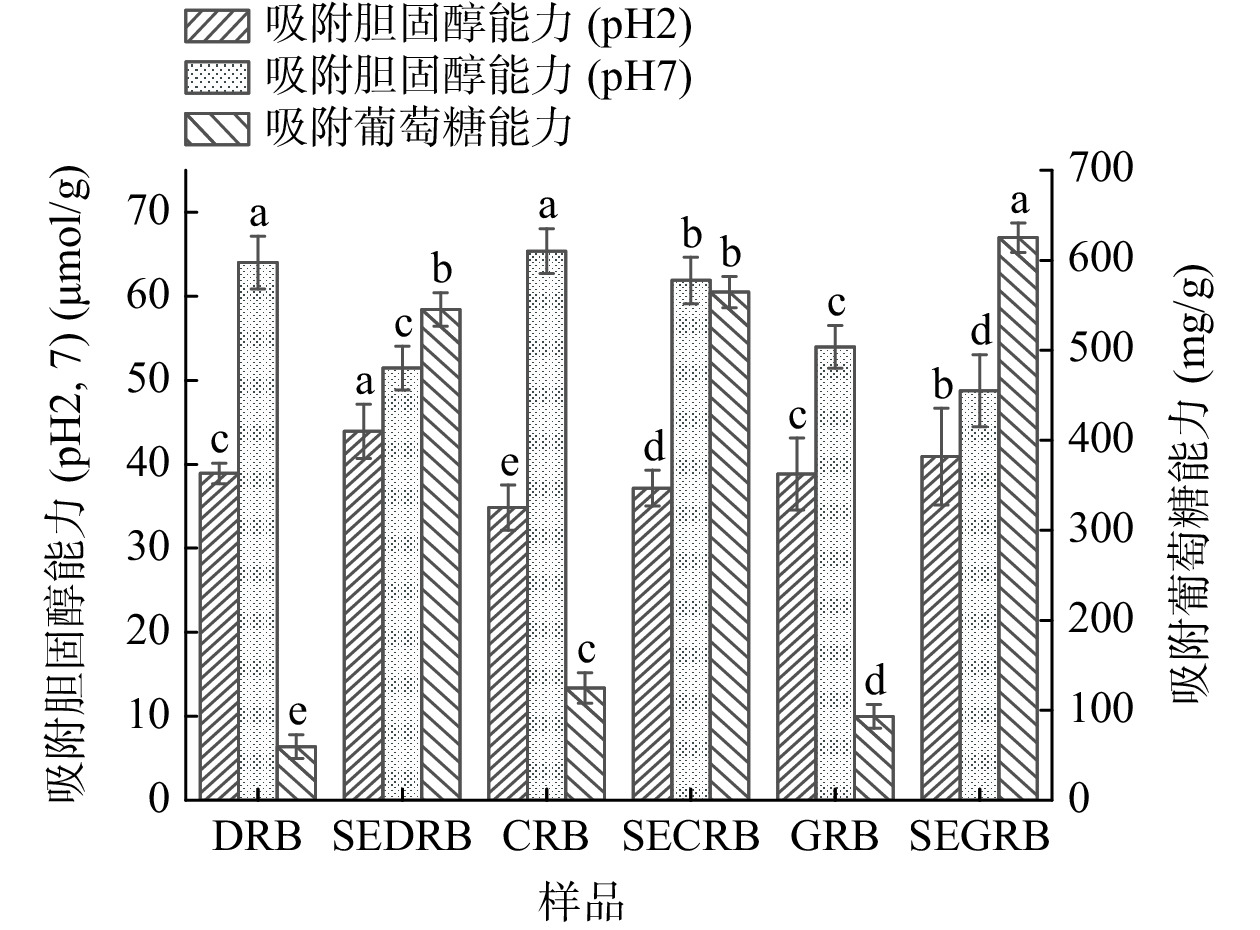
2.6 蒸汽爆破米糠SDF对胆固醇和葡萄糖吸附能力的影响
汽爆米糠SDF对胆固醇和葡萄糖吸附能力的影响如图6所示。由图6可知,汽爆前后米糠SDF在人体小肠环境下对胆固醇的吸附量均高于胃液环境下,这是由于酸性环境中的H+与SDF和胆固醇携带的正电荷之间相互排斥,随着pH的升高,SDF中羧基发生解离,与胆固醇结合更加紧密,从而表现出更强的胆固醇结合能力[30];pH2时,3种汽爆米糠SDF的胆固醇吸附能力较其对照均显著(P<0.05)提高,这是由于汽爆米糠SDF内部的无序结构被破坏,暴露出更多的极性基团,有利于吸附胆固醇,其中,SEDRB的SDF吸附胆固醇的能力最强,可能是其结构更加疏松多孔;而pH7时,3种汽爆米糠SDF的胆固醇吸附能力较其对照均有一定程度的下降,可能是SDF对胆固醇的吸附已达到饱和状态,或者是汽爆处理的高强度破坏了SDF的多孔结构,不利于胆固醇的吸附。
3种汽爆米糠SDF的GAC显著(P<0.05)高于其对照,SEDRB、SECRB、SEGRB的SDF的GAC较处理前分别增加了8.81、3.53倍和5.71倍,而SEGRB的GAC最强。汽爆处理使SDF的内部结构变得疏松,比表面积增大,孔隙数量增加,从而增强了GAC;而片层状结构的形成使更多的功能基团暴露,进一步增强了SDF与葡萄糖分子之间的相互作用[31],这与付晓康等[10]、何晓琴等[8]的实验结果相一致。
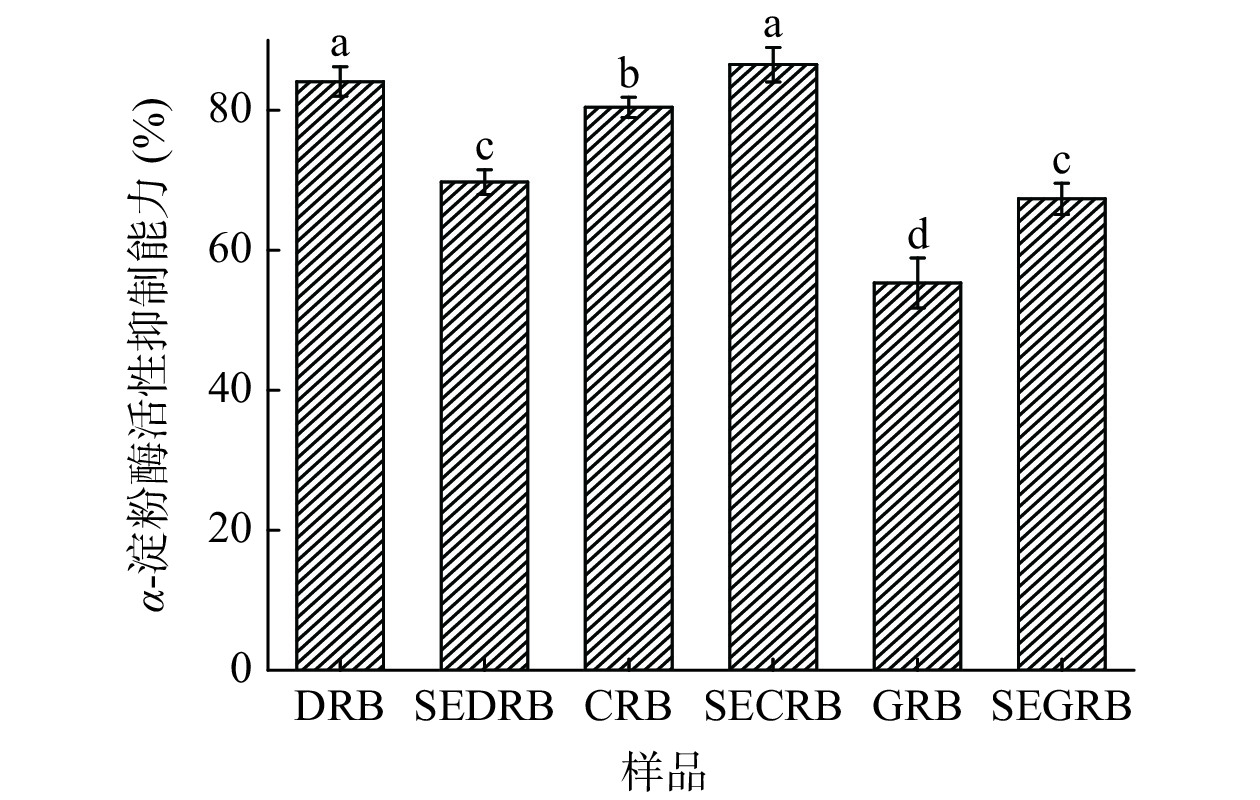
2.7 蒸汽爆破米糠SDF对α-淀粉酶活性抑制能力的影响
汽爆处理破坏了SDF的网状结构,纤维网络多孔性增加,更多的α-淀粉酶的极性基团与纤维表面相互作用产生界面诱导的酶失活,从而降低α-淀粉酶的活性[32]。汽爆米糠SDF对α-AAIR的影响如图7所示。由图7可知,SECRB、SEGRB较其对照分别增加了7.60%和21.72%,而SEDRB中的SDF对α-淀粉酶抑制能力较对照反而降低了17.09%。汽爆处理对3种米糠SDF网状结构的破坏程度不同,导致其对α-淀粉酶活性的抑制能力产生差异;另外,米糠中的酚类化合物对α-淀粉酶的活性具有一定的抑制作用[33],3种米糠不同的汽爆条件对米糠酚类物质的破坏程度不同[34],或者不同稻谷品种麸皮中游离和结合形式的酚类成分和含量存在差异性[33],这些因素导致3种汽爆米糠SDF对α-淀粉酶活性抑制能力的不同。
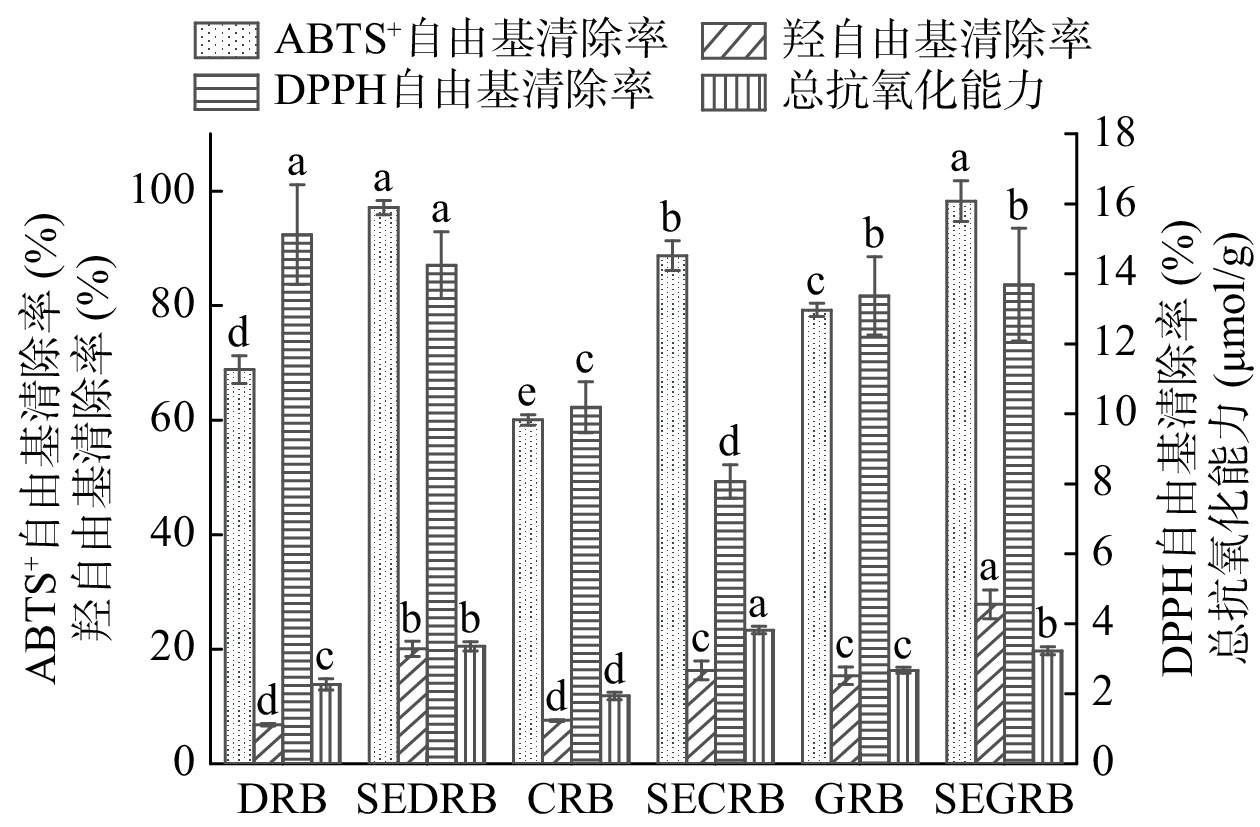
2.8 蒸汽爆破米糠SDF的抗氧化能力分析
汽爆米糠SDF对ABTS+·、DPPH·、·OH清除率和总抗氧化能力的影响如图8所示。由图8可知,3种汽爆米糠SDF对ABTS+·、·OH清除率和总抗氧化能力较其对照均显著提高,这可能是汽爆处理使物料细胞壁被破坏,一些酚类化合物释放或暴露,清除自由基的能力得到增强[35],或者是汽爆处理改变了酚类物质与纤维素、半纤维素的结合形式,促进了结合态酚类物质向游离态转变,使抗氧化活性增强[35];SEDRB、SECRB中SDF对DPPH·的清除能力较其对照则不同程度降低,而SEGRB的SDF对DPPH·的清除能力较其对照略有增加,但差异不显著,这可能是不同汽爆处理条件使DRB、CRB和GRB米糠中具有抗氧化能力的物质如多酚、黄酮等流失或分解有关[34,36]。郑佳欣[36]的实验表明汽爆处理使刺梨渣SDF对DPPH·的清除能力略有下降,这与本实验SEDRB、SECRB中SDF对DPPH·的清除能力的结果相符。3种汽爆米糠中,SEDRB中SDF对ABTS+·和DPPH·的清除率最强,而SECRB中SDF的总抗氧化能力最高,SEGRB中SDF对ABTS+·、·OH清除率较强。
3. 结论
汽爆处理使稻花香、长粒香、赣晚籼40号稻谷米糠中SDF的含量显著增加(P<0.05),分别达到6.59%、6.27%和5.45%。汽爆处理使SDF红外光谱波长吸收峰的吸收强度增加,表明纤维素之间的氢键受到了破坏。稻花香、长粒香、赣晚籼40号稻谷米糠SDF的相对结晶度由汽爆前的11.42%、7.41%、9.35%分别降至汽爆后的4.91%、3.34%和7.56%。汽爆处理导致稻谷米糠的完整致密结构变得松散破裂,纤维的有序性被破坏,3种汽爆米糠SDF的含量、持水性、持油性、在人体胃液环境下吸附胆固醇能力、吸附葡萄糖能力以及对ABTS+·、·OH清除率和总抗氧化能力较其对照均显著增加(P<0.05),但其SDF表现出的这些功能特性也具有一定的差异性。汽爆米糠SDF具有的α-淀粉酶活性抑制能力、胆固醇吸附能力和抗氧化能力,为开发具有降血糖、降血脂、抗氧化等营养健康食品提供了新思路。汽爆处理米糠SDF功能特性变化的机制,及其在米线、面包、饼干等食品中的应用有待进一步探究。
-
-
[1] 国家统计局. 国家统计局关于2023年粮食产量数据的公告[EB/OL]. 2023-12-11[2023-12-28]. [State Statistics Bureau. Announcement of the national bureau of statistics on the grain production data in 2023[EB/OL]. 2023-12-11[2023-12-28].] State Statistics Bureau. Announcement of the national bureau of statistics on the grain production data in 2023[EB/OL]. 2023-12-11[2023-12-28].
[2] 徐浩. 米糠资源硏究与应用[D]. 合肥:安徽农业大学, 2015. [XU H. The research and application of rice bran[D]. Hefei:Anhui Agricultural University, 2015.] XU H. The research and application of rice bran[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2015.
[3] DEMIRCI T, AKTAS K, SÖZERI D, et al. Rice bran improve probiotic viability in yoghurt and provide added antioxidative benefits[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2017,36:396−403. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.07.019
[4] 熊本海, 罗清尧, 郑姗姗, 等. 中国饲料成分及营养价值表[J]. 中国饲料,2020,21:88−97. [XONG B H, LUO Q Y, ZHENG S S, et al. Chinese feed composition and nutritive value table[J]. China Feed,2020,21:88−97.] XONG B H, LUO Q Y, ZHENG S S, et al. Chinese feed composition and nutritive value table[J]. China Feed, 2020, 21: 88−97.
[5] QADIR N , WANI I A. Physicochemical and functional characterization of dietary fibres from four Indian temperate rice cultivars[J]. Bioactive Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre, 2022, 28:100336.
[6] GIDLEY M J, YAKUBOV, G E. Functional categorisation of dietary fibre in foods:Functional categorisation of dietary fibre in foods:Beyond ‘soluble’ vs ‘insoluble’[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2019,86:563−568.
[7] LIU H C, AINIWAN D, LIU Y X, et al. Adsorption and controlled release performances of flavor compounds by rice bran insoluble dietary fiber improved through steam explosion method[J]. Current Research in Food Science,2023,7:100550. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2023.100550
[8] 何晓琴, 刘昕, 李苇舟, 等. 蒸汽爆破处理苦荞麸皮膳食纤维改性分析[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(9):46−54. [HE X Q, LIU X, LI W Z, et al. Modifification of dietary fiber from tartary buckwheat bran by steam explosion[J]. Food Science,2021,42(9):46−54.] HE X Q, LIU X, LI W Z, et al. Modifification of dietary fiber from tartary buckwheat bran by steam explosion[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(9): 46−54.
[9] LI B, YANG W, NIE Y Y, et al. Effect of steam explosion on dietary fiber, polysaccharide, protein and physicochemical properties of okara[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,94:48−56. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.02.042
[10] 付晓康, 苏玉, 黄亮, 等. 蒸汽爆破-超微粉碎对米糠膳食纤维结构和功能性质的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2020,35(4):142−150. [FU X K, SU Y, HUANG L, et al. Effect of steam explosion-superfine pulverization on structure and functional properties of rice bran dietary fiber[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2020,35(4):142−150.] FU X K, SU Y, HUANG L, et al. Effect of steam explosion-superfine pulverization on structure and functional properties of rice bran dietary fiber[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2020, 35(4): 142−150.
[11] MA Q W, YU Y , ZHOU Z K, et al. Effects of different treatments on composition, physicochemical and biological properties of soluble dietary fiber in buckwheat bran[J]. Food Bioscience, 2023, 53:102517.
[12] LIU H C, FAN H X, ZHANG J, et al. Isolation, purification, structural characteristic and antioxidative property of polysaccharides from A. cepa L. var. agrogatum Don[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2020,9(1):71−79. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2019.12.006
[13] MA M M, MU T H. Effects of extraction methods and particle size distribution on the structural, physicochemical, and functional properties of dietary fiber from deoiled cumin[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,194:237−246. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.095
[14] ZHANG S Y, ZHENG L L, ZHENG X Y, et al. Effect of steam explosion treatments on the functional properties and structure of camellia (Camellia oleifera Abel.) seed cake protein[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,93:189−197. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.02.017
[15] QIAO C C, ZENG F K, WU N N, et al. Functional, physicochemical and structural properties of soluble dietary fiber from rice bran with extrusion cooking treatment[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,121:107057. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107057
[16] LI L Y, LIU J F, ZHANG Y, et al. Qualitative and quantitative correlation of microstructural properties and in vitro glucose adsorption and diffusion behaviors of pea insoluble dietary fiber induced by ultrafine grinding[J]. Foods,2022,11(18):2814. doi: 10.3390/foods11182814
[17] 康芳芳, 聂远洋, 邓楚君, 等. 蒸汽爆破对豆渣膳食纤维的影响及在韧性饼干中的应用[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(2):188−191. [KANG F F, NIE Y Y, DENG C J, et al. Effect of steam explosion on dietary fiber of okara and its application in semi hard biscuit[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industy,2018,39(2):188−191.] KANG F F, NIE Y Y, DENG C J, et al. Effect of steam explosion on dietary fiber of okara and its application in semi hard biscuit[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industy, 2018, 39(2): 188−191.
[18] 刘蕊琪, 宋莲军, 沈玥, 等. 蒸汽爆破技术在食品大分子物质改性中的研究概述[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(15):292−297. [LIU R Q, SONG L J, SHEN Y, et al. Research progress of steam explosion technology in modification of food macromolecules[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(15):292−297.] LIU R Q, SONG L J, SHEN Y, et al. Research progress of steam explosion technology in modification of food macromolecules[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(15): 292−297.
[19] LI S, HU N N, ZHU J Y, et al. Influence of modification methods on physicochemical and structural properties of soluble dietary fiber from corn bran[J]. Food Chemistry: X,2022,14:100298. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100298
[20] DONG W J, WANG D D, HU R S, et al. Chemical composition, structural and functional properties of soluble dietary fiber obtained from coffee peel using different extraction methods[J]. Food Research International,2020,136:109497. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109497
[21] SUN X F, XU F, SUN R C, et al. Characteristics of degraded cellulose obtained from steam-exploded wheat straw[J]. Carbohydrate Research,2005,340(1):97−106. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2004.10.022
[22] HONGRATTANAVICHIT I, AHT-ONG D. Nanofibrillation and characterization of sugarcane bagasse agro-waste using water-based steam explosion and high-pressure homogenization[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,277:123471. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123471
[23] KHAWAS P, DEKA S C. Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanofibers from culinary banana peel using high-intensity ultrasonication combined with chemical treatment[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,137:608−616. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.020
[24] XI H H, WANG A X, QIN W Y, et al. The structural and functional properties of dietary fibre extracts obtained from highland barley bran through different steam explosion-assisted treatments[J]. Food Chemistry,2023,406:135025. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135025
[25] LIN Y, WANG H X, RAO W, et al. Structural characteristics of dietary fiber (Vigna radiata L. hull) and its inhibitory effect on phospholipid digestion as an additive in fish floss[J]. Food Control, 2019, 98:74-81.
[26] SUI W J, CHEN H Z. Effects of water states on steam explosion of lignocellulosic biomass[J]. Bioresource Technology,2016,199:155−163. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.09.001
[27] YALEGAMA L L W C, NEDRA KARUNARATNE D, SIVAKANESAN R, et al. Chemical and functional properties of fibre concentrates obtained from by-products of coconut kernel[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,141(1):124−130. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.02.118
[28] 马梦梅. 孜然膳食纤维改性及降血糖活性研究[D]. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2016. [MA M M. Study on modification and anti-Hyperglycemic activity of deoiled cumin dietary fiber[D]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences Dissertation, 2016.] MA M M. Study on modification and anti-Hyperglycemic activity of deoiled cumin dietary fiber[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences Dissertation, 2016.
[29] CHAU C F, HUANG Y L. Comparison of the chemical composition and physicochemical properties of different fibers prepared from the peel of Citrus sinensis L. Cv. Liucheng[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2003,51:2615−2618. doi: 10.1021/jf025919b
[30] SHEN M, GE Y F, KANG Z Y, et al. Yield and physicochemical properties of soluble dietary fiber extracted from untreated and steam explosion-treated black soybean hull[J]. Journal of Chemistry,2019,2019:9736479.
[31] ZHANG M Y, LIAO A M, THAKUR K, et al. Modification of wheat bran insoluble dietary fiber with carboxymethylation, complex enzymatic hydrolysis and ultrafine comminutione[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,297:124983. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.124983
[32] CHEN J L, GAO D X, YANG L T, et al. Effect of microfluidization process on the functional properties of insoluble dietary fiber[J]. Food Research International,2013,54(2):1821−1827. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2013.09.025
[33] WU N N, LI H H, TAN B, et al. Free and bound phenolic profiles of the bran from different rice varieties and their antioxidant activity and inhibitory effects on α-amylose and α-glucosidase[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2018,82:206−212. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2018.06.013
[34] CHEN G Z, CHEN H Z. Extraction and deglycosylation of flavonoids from sumac fruits using steam explosion[J]. Food Chemisty,2011,126(4):1934−1938. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.12.025
[35] ZHU K X, HUANG S, PENG W, et al. Effect of ultrafine grinding on hydration and antioxidant properties of wheat bran dietary fiber[J]. Food Research International,2010,43(4):943−948. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2010.01.005
[36] 郑佳欣. 刺梨渣膳食纤维蒸汽爆破改性及结构、功能性质研究[D]. 北京:北京林业大学, 2020. [ZHENG J X. Structural and functional properties of dietary fiber from chestnut rose residue modified by steam explosion[D]. Beijing:Beijing Forestry University, 2020.] ZHENG J X. Structural and functional properties of dietary fiber from chestnut rose residue modified by steam explosion[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2020.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 熊鑫龙,刘宇,孙迪,宋诗军,董芮娟,姜维. 甲基-β-环糊精高效脱除鱼油中胆固醇. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2025(01): 74-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 付尧,张东举,别海. 油莎豆油提取技术及其生物活性研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2025(06): 151-160 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘贵涛,权煜,饶欢,赵丹丹,赵霞,郝建雄,刘学强. 亚麻籽粕蛋白多肽的制备及其抗氧化性. 食品研究与开发. 2024(24): 84-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



