Screening of Anti-hyperuricemia Peptides from Oat Protein Based on High-throughput Transcriptome Sequencing and Network Pharmacology
-
摘要: 从组学出发为挖掘和筛选抗高尿酸血症燕麦活性肽,并研究燕麦活性肽在抗高尿酸血症上的作用机制。本研究以燕麦籽粒为原料提取RNA,用于高通量转录组测序,通过与参考基因组比对和蛋白编码基因表达量定量以获取燕麦籽粒蛋白序列,利用高通量虚拟酶解、Peptide Ranker和ADME/T筛选燕麦活性肽成分,借助网络药理学技术挖掘燕麦蛋白源抗高尿酸血症活性多肽。结果表明,‘坝莜1号’和‘白燕7号’燕麦籽粒在籽粒形成期和灌浆期所表达重复性低于90%的蛋白序列数分别为6310、3157和5804、5107条。其中最优肽文库为在灌浆期裸燕麦‘坝莜1号’的蛋白序列经蛋白酶K模拟酶解产生的肽文库,在该条件获得的肽文库中预测筛选出42条具有潜在活性和良好成药性的燕麦活性肽。初步筛选主要抗高尿酸血症燕麦活性肽序列为PPF、PPPL、MPF、MPL和PPPF,可能通过靶向ALB、IL1B、SRC、CASP3和STAT3等基因,作用于癌症、脂质与动脉粥样硬化和化学致癌-受体激活等信号通路干预高尿酸血症。分子对接验证显示结合能小于-5 kJ/mol占整体82.86%,表示燕麦多肽主要活性成分与大部分靶点结合活性较好。此外,最优燕麦合成多肽PPF表现出良好的黄嘌呤氧化酶抑制效果(IC50=6.132 mmol/L)。裸燕麦蛋白可作为酶解释放抗高尿酸血症活性肽的良好前体,同时为燕麦蛋白酶解生产生物活性肽和利用燕麦活性肽开发抗高尿酸血症功能性食品提供理论参考。Abstract: Initiating from omics, the research aimed to discover and filter oat active peptides effective against hyperuricemia, and to study the operational mechanism of these oat active peptides in treating hyperuricemia. In the present study, RNA was extracted from oat grains for high-throughput transcriptomic sequencing, and oat grain protein sequences were acquired by comparing with a reference genome and quantifying the expression of protein-coding genes. Active components of oat peptides were selected by employing high-throughput enzymolysis in silico, Peptide Ranker, and ADME/T. Network pharmacology were utilized to discover active peptides from oat proteins that were effective against hyperuricemia. The findings indicated that for 'Bayou No.1' and 'Baiyan No.7' oat grains, the counts of protein sequences expressed with under 90% repeatability during the grain formation and grain-filling phases were respectively 6310, 3157, and 5804, 5107. The optimal peptide library was from the protein sequences of 'Bayou No.1' naked oat in the grain-filling stage, processed through simulated enzymatic digestion in silico with proteinase K, yielding a library with 42 oat active peptides predicted to have potential activity and favorable pharmacological properties. The initial screening revealed key oat active peptides sequences against hyperuricemia to be PPF, PPPL, MPF, MPL, and PPPF, potentially targeting genes like ALB, IL1B, SRC, CASP3, and STAT3, influencing pathways in cancer, lipid and atherosclerosis, and chemically induced carcinogenesis-receptor activation to mitigate hyperuricemia. Molecular docking showed that binding energy <-5 kJ/mol accounted for 82.86%, indicating that the main active components of oat peptides had good binding activity with most of the targets. The optimal oat synthetic peptide PPF showed good xanthine oxidase inhibition (IC50=6.132 mmol/L). Naked oat protein can act as a promising precursor for the enzymatic release of active peptides effective against hyperuricemia, and also offers theoretical guidance for producing bioactive peptides through oat protein enzymolysis and developing functional foods using oat active peptides to combat hyperuricemia.
-
高尿酸血症(Hyperuricemia,HUA)是一种体内尿酸产生过多或肾排泄受阻导致的代谢性疾病,临床表现为血清尿酸水平升高[1]。嘌呤代谢紊乱引起的高尿酸血症已成为继糖尿病、高血压、高血脂后的第四高,从2018~2019年中国慢性病及危险因素监测数据[2]表明,我国居民成人高尿酸血症患病率达到14.0%,患病人群约1.78亿,其中男性高达24.5%,女性3.6%,并有着显著年轻化的趋势。高尿酸血症可能会诱发痛风并伴随有多种如肾结石、糖尿病、高血脂症、高血压、动脉粥样硬化等代谢综合征的发生[1,3]。当前广泛应用于治疗高尿酸血症的药物,如别嘌呤醇和非布司他等,被研究发现存在过敏反应、皮疹、肾病等较大的毒副作用[4]。大量文献表明天然活性物质治疗高尿酸血症疗效确切,来源多样且副作用小,如天然提取物、从植物中提取的单体化合物、天然蛋白酶水解产物、多肽和益生菌[5]。食物蛋白源降尿酸活性肽是指以食源性动、植物蛋白为原料制得的具有降低生物体内血尿酸水平功效的生物活性肽。从稻米的水解产物中鉴定出一种大米衍生肽AAAAMAGPK(785.97 Da)有效减轻高尿酸血症小鼠的尿酸水平和肾脏损伤[6]。核桃水解产物可以有效降低高尿酸血症大鼠体内的血清尿酸水平从而保护肾脏功能[7]。金枪鱼寡肽能够减轻高尿酸血症和肾脏炎症,改变尿酸代谢途径,经金枪鱼寡肽处理的小鼠粪菌也具有抗高尿酸的作用[8]。研究发现海洋生物肽(如金枪鱼[8]、刺参[9]、太平洋白虾和梭子蟹[10]、鲣鱼[11]等)和植物肽(如大米[6]、核桃[7]、平菇[12]等)在降低尿酸方面具有良好的效果,但主要集中在合成尿酸的黄嘌呤氧化酶(Xanthine oxidase,XOD)关键酶活性的抑制及其对相关表型的影响上[5]。因此,从天然食品原料中开发安全有效的抗高尿酸血症活性成分并阐明其相关作用机制具有重要意义。
燕麦(Avena sativa)作为一种富含蛋白质、植物化学物质和膳食纤维的植物性食品,被认为是最健康的谷物之一[13]。而燕麦蛋白因其高含量、高质量和独特的氨基酸组成而备受关注。与其他谷物(包括大米7%~10%,小麦11%~15%和小米7%~11%)相比,燕麦籽粒的蛋白质含量达12%~20%,其中球蛋白占70%~80%[14]。燕麦蛋白含有相对较高的必需氨基酸含量,其氨基酸组成符合粮食及农业组织推荐的成年人的营养需求[14]。源自燕麦蛋白释放的活性肽表现出各种生物活性,如抗氧化、抗高血压、抗高血糖、抗菌和免疫调节活性等[14]。然而,燕麦蛋白源活性肽在抗高尿酸血症和痛风功效的研究较少,这也为燕麦活性肽潜在的应用领域挖掘与扩展提供新思路。
由于大多数非模式生物基因组研究数据不完备,转录组学研究能够很好地诠释该物种特定基因在基因组中的功能和结构,以及能获得足够遗传学信息满足蛋白多肽类成分挖掘[15]。李安[16]通过建立青环海蛇多组学数据库和毒素组学数据库,高通量精准系统地挖掘青环海蛇来源的新型生物活性肽。燕麦的完整基因组信息中包含燕麦整体蛋白和多肽的编码基因序列,包括表达丰度很低甚至没有表达的蛋白和多肽,通过结合基因组学和转录组学的序列信息,对燕麦蛋白序列中具有生物活性的多肽分子进行高通量挖掘[16−17]。近年来从天然蛋白质中筛选活性肽的最常规方法是使用水解蛋白酶进行酶解,并结合大量实验过程来纯化鉴定验证[18]。与传统酶解相比,模拟酶解可以显著缩短筛选潜在活性肽所需的时间和减少实验成本支出,并有望发现已知活性肽新的功效[19]。Bleakley等[20]从普通栽培燕麦(Avena sativa)的八种主要贮藏蛋白筛选了新型血管紧张素I转换酶抑制(ACE-I)、肾素和二肽基肽酶IV(DPP-IV)抑制肽,也证实了计算机模拟酶解技术在生物活性肽的鉴定和筛选上的可用性。网络药理学从系统层次和生物网络的整体角度出发,解析药物与治疗对象之间的分子关联,揭示药物的系统性药理机制,从而指导新药研发和临床诊疗[21−22]。为进一步了解燕麦活性肽抗高尿酸血症的作用机制,基于网络药理学筛选和分析燕麦活性肽改善高尿酸血症的主要活性成分、潜在靶点和作用途径进行系统研究[22],揭示燕麦肽潜在的活性作用机制。本研究构建了两种代表性燕麦品种完整蛋白序列,并挖掘燕麦蛋白源抗高尿酸血症活性多肽序列,为综合利用燕麦资源,开发抗高尿酸血症功效的功能性食品提供一定的科学参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
裸燕麦‘坝莜1号’、皮燕麦‘白燕7号’燕麦籽粒(籽粒形成期采收于2023年4月20日;灌浆期采收于2023年5月09日) 均来自于中国农业科学院深圳农业基因组研究所试验基地;RNAprep Pure多糖多酚植物总RNA提取试剂盒(Cat.DP441) 天根生化科技(北京)有限公司;Fast RNA-seq Lib Prep Kit V2(Cat.RK20306) 武汉爱博泰克生物科技有限公司;AMPure XP核酸纯化试剂盒(Cat.A63880) 美国Beckman Coulter公司;1×PBS缓冲液(pH7.2~7.4)(Cat.P1020) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;黄嘌呤氧化酶(Cat.X1875-5UN)、别嘌呤醇99%(Cat.A8003-2.5) 美国Sigma-Aldrich公司;黄嘌呤溶液(Cat.X104265) 美国Aladdin公司;合成目标多肽PPF、PPPL、MPF、MPL、PPPF(纯度≥98%) 生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司。
ST16R低速离心机 美国Thermo公司;5400高通量NGS核酸片段分析仪(AATI) 美国Agilent公司;Micro Drop超微量分光光度计 上海宝予德科学仪器有限公司;Qubit3.0荧光定量仪 美国Invitrogen公司;T100-PCR扩增仪、CFX96实时定量PCR仪 美国BioRad公司;Biomek-i7自动化实验系统 美国Beckman Coulter公司;LE220R-plus超声打断仪 美国Covaris公司;Nova PE150 Novaseq 6000测序系统 美国Illumina公司;Synergy™ H1酶标仪 美国BioTek公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 燕麦籽粒转录组数据的获取
当同一株燕麦分别处于籽粒形成期和灌浆期时均采取10颗燕麦籽粒,液氮速冻后−80 ℃保存。委托北京诺禾致源科技股份有限公司进行样本RNA提取及二代转录组测序,共4组燕麦籽粒转录组数据。裸燕麦‘坝莜1号’(Avena sativa ssp. nuda)和皮燕麦‘白燕7号’(Avena sativa)的参考基因组、注释文件以及参考蛋白序列文件均来自OatBioDB(http://www.waooat.cn/)。
1.2.2 燕麦蛋白序列的获取
使用FastQC对原始测序数据(Raw reads)进行质量评估,采用Trimmomatic(v0.39)软件进行去除接头和低质量碱基质量预处理获取有效数据(Clean reads),设置Phred质量分数为33,ILLUMINACLIP参数指定包含测序接头序列的文件,其中最大错配数SeedMismatches为2、Palindrome clip threshold为30、Simple clip threshold为10、MinAdapterLength为1和KeepBothReads为true,其他参数设置LEADING为25和TRAILING为25,此处SLIDINGWINDOW设定4:20以执行滑动窗口质量控制,其中窗口大小为4,平均质量要求为20,最后MINLEN为40确保输出序列的最小长度为40个碱基。通过质量控制后的序列数据比对到相应的参考基因组上进行定量可以构建该组织或者细胞的所有基因的表达谱,当基因的表达水平越高,理论上匹配到该基因上的Reads数目就越多。导入裸燕麦(Avena sativa ssp. nuda)和皮燕麦(Avena sativa)的参考基因组[23−24]到Hisat2(v2.0.4)软件分别对两个参考基因组构建索引,以双端数据与质控后的有效数据默认参数进行比对分析,Samtools工具将Sam格式文件转换成Bam格式,并使用Samtools Sort工具对Bam文件排序。将有序的Bam文件和基因组注释文件导入Subread软件的Featurecounts工具进行定量分析,得到Gene、编码序列(Coding sequence,CDS)区域的Counts计数,再利用TPM标准化公式归一化,统计各基因表达TPM(Transcripts Per Kilobase Million),既每百万条Reads中来自于某转录本每千碱基长度的Reads数。设定TPM值≥10,根据得到不同样本的表达基因列表与参考蛋白序列文件匹配,输出表达基因的蛋白序列,储存为Fasta格式。使用CD-HIT程序对这些蛋白序列筛选去除重复性高于90%的序列[25]。TPM 的计算公式为:
TPM=R1×109L1×R(total) 式中,R1为目的基因Count值(比对到目的基因上的Reads数),L1为目的基因的长度,将比对到目的转录本的 Reads数/目的转录本长度以校正目的基因Count值;R(total)为所有基因的校正后count值总和。
1.2.3 高通量计算机虚拟酶解设计
从公开ExPASy Peptide Cutter数据库提供的蛋白水解酶中[26],选取11种具有代表性的蛋白酶和1种组合酶,参考其特定的酶切位点进行模拟酶解,分别为微生物源蛋白酶:碱性蛋白酶(Alcalase)、蛋白酶K(Proteinase K)和嗜热菌蛋白酶(Thermolysin);动物源蛋白酶:高特异性糜蛋白酶(Chymotrypsin-high)、低特异性糜蛋白酶(Chymotrypsin-low)、胃蛋白酶pH>2(Pepsin-pH>2)、胃蛋白酶pH>1.3(Pepsin-pH1.3)和胰蛋白酶(Trypsin);植物源蛋白酶:木瓜凝乳蛋白酶(Chymopapain)、木瓜蛋白酶(Papaya Proteinase)和菠萝蛋白酶(Stem Bromelain)和模拟胃肠道组合酶(低特异性糜蛋白酶+胃蛋白酶pH>2+胰蛋白酶)。
使用改良版的Refineing-PeptideCutter(R-PeptideCutter)并作简单修改以适用本研究的模拟酶解[27]。只需将含有母体蛋白序列的fasta格式文件,在R-PeptideCutter中设置酶或化学物质运行脚本,它将自动生成蛋白质序列中加密的所有可能的肽以及释放肽段的数量,最终获得由特定酶或多种酶组合产生的潜在生物活性肽文库[27]。
1.2.4 潜在生物活性预测
Peptide Ranker(http://distilldeep.ucd.ie/PeptideRanker/)是一个基于N-to-1神经网络进行五重交叉验证训练的生物活性肽预测服务器[28]。对来自于BIOPEP、PeptideDB、APD2和CAMP数据库涵盖的活性肽作为训练集,以帮助预测及筛选潜在生物活性肽。当多肽预测得分大于0.5时,认为其具有潜在生物活性[20]。
1.2.5 ADME/T预测
ToxinPred(http://crdd.osdd.net/raghava/toxinpred/index.html)是使用肽的各种特性来预测活性肽毒性的一个网站服务器[29]。使用Swiss ADME(http://www.swissadme.ch/)以输入SMILES式识别分子药物预测药物在体内的吸收、分布、代谢、排泄等影响药物疗效的关键性质[30−31]。筛选具有良好ADME性质的活性肽的标准为[32]:肠胃吸收(GI absorption)为“High”,表明成分具备良好口服生物利用度,可被胃肠道被动吸收;血脑屏障(BBB permeant)为“NO”,表明不通过血脑屏障;五类药性预测(Lipinski、Ghose、Veber、Egan、Muegge)结果中有2个及2个以上为“Yes”,表明药物相似性数据定性评估活性肽成为口服药物及其生物利用度的机会。
1.2.6 燕麦活性肽靶点筛选
将在ChemDraw 20.0构建的42种燕麦活性肽的空间构象分别上传到各种靶点预测网络服务器进行识别和预测,包括SwissTargetPrediction(http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/),PharmMapper(http://www.lilab-ecust.cn/pharmmapper/)。基于化学结构相似性预测目标的SwissTargetPrediction以“Homo Sapiens”模式检索目标,以Probability≥0进行筛选;利用基于药效团匹配法的PharmMapper,选择Normalized Fit Score≥0.9的靶点,输入Uniprot进行标准化和验证,物种限于“Homo Sapiens”。将所获取的靶点去除重复选项,建立燕麦活性肽靶点数据库。
1.2.7 高尿酸血症相关靶点筛选
以“Hyperuricemia”为关键词,搜索CTD(http://ctdbase.org/)、GeneCards(https://www. genecards. org)、DisGeNet(http://www. disgenet. org/home/)和OMIM库(http://www.omim.org)选择条件筛选大于中位数以获得高尿酸血症的潜在靶点[21]。CTD是一个公开可用的数据库,研究基于化学药品、基因、表型、疾病和环境之间的关联,促进人们对化学药物和人类健康的了解[33]。将所获取的靶点,删除重复值合并,建立高尿酸血症的潜在靶点数据库。
1.2.8 PPI网络构建
将燕麦活性肽与高尿酸血症的潜在靶点分别导入VENNY 2.1.0(https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/),获取燕麦活性肽干预高尿酸血症的交集靶点。将上述交集靶点提交至String(https://cn.string-db.org/),设置“Homo Sapiens”和0.4的置信度,下载数据导入Cytoscape 3.9.1软件,运用内置的Network Analyzer进行拓扑分析,设置各节点连接度、介度和紧密度大于中位数为最低阈值筛选和提取关键靶点。
1.2.9 GO功能富集和KEGG通路富集
Metascape(http://metascape.org/gp/index.html)拥有全面的注释功能并且每月更新基因注释的数据资料。将燕麦活性肽干预高尿酸血症的关键靶点录入Metascape,设置P<0.01,分析其主要的GO及KEGG代谢通路,选择排名前10的GO和排名前20的KEGG通路富集结果在微生信平台(http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/)进行数据可视化。
1.2.10 燕麦肽成分-靶点-通路网络图的构建
选取与高尿酸血症相关的KEGG富集分析排名前20的信号通路,建立参与相关通路的燕麦活性肽及交集靶点间的联系,利用CytoScape3.9.1内置的Network Analyzer分析有效成分及靶点的网络拓扑参数[34],构建“燕麦活性肽-靶点-通路”的相互关系网络图,判断核心靶点及干预高尿酸血症的燕麦活性肽主要活性成分。
1.2.11 分子对接验证
选择燕麦活性肽主要成分-高尿酸血症靶点网络图中连接度值排名前5的靶点和人类黄嘌呤氧化酶XOD进行分子对接验证。通过ChemDraw 20.0软件构建二维化学结构后,导入到Chem3D 20.0使用MMFF94力场对所构建的燕麦活性肽进行能量最小化,转化为pdb格式后导入AutoDock Tools-1.5.6软件并添加原子电荷、分配原子类型,将所有柔性键默认可旋转,保存为pdbqt文件。蛋白的晶体结构从蛋白质RCSB数据库(https://www.rcsb.org/)中获得,采用Pymol2.6软件删除无关小分子和水分子,转化为pdb格式后导入AutoDock Tools-1.5.6软件删除水分子、添加氢原子以及设置原子类型,保存为pdbqt文件。
使用Autodock vina对蛋白与多肽进行分子对接操作,XOD(PDB ID:2E1Q)使用pymol构建突变体,将缬氨酸(Val 803)恢复至原始谷氨酸(Glu 803),抽取其中的配体创建结合口袋,(i)center_x:y:z=30:11:189;(ii)center_x:y:z=35:14:152。蛋白ALB(PDB ID:1N5U)center_x:y:z=31.82:7.54:32.66;IL1B(PDB ID:1HIB)center_x:y:z=20.97:3.31:73.73;SRC(PDB ID:1KSW)center_x:y:z=-0.38:50.27:2.00;CASPS(PDB ID:1NMS)center_x:y:z=-9.1:-4.0:24.2;STATS(PDB ID:6NJS)center_x:y:z=13:56.64:0.25,口袋大小均为size_x:y:z=22.5:22.5:22.5。以结合能Binging energy(kJ/mol)来判断结合活性,当Binging energy<0 kJ/mol时,可以在自然状态下对接,具有结合活性;当Binging energy<-5 kJ/mol时,认为对接状态良好,结合活性较佳。
1.2.12 体外XOD抑制活性评价
参照Li等[35]和Owen等[36]描述的方法并根据实际实验情况作合理的调整。分别加入25 μL溶于PBS缓冲溶液(0.01 mol/L,pH7.2~7.4)的待测样品和25 μL XOD(终浓度为0.05 U/mL),37 ℃孵育30 min后,加入50 μL黄嘌呤溶液(终浓度为0.2 mmol/L)引发反应,37 ℃记录3 min内每30 s反应体系在290 nm下吸光值的动力学变化。以常见的XOD抑制药物别嘌呤醇(终浓度为40 μmol/L)作为阳性对照,PBS缓冲溶液作为阴性对照,涉及所需溶剂均现配现用。通过确定酶催化反应中尿酸的生成速率(吸光值的变化/时间)来量化XOD抑制活性,XOD的抑制率可表示为:
XOD抑制率(%)=VBlank−VSampleVBlank×100 式中,VBlank为没添加样品的初始反应速率;VSample为添加样品的反应速率;XOD的抑制活性采用IC50值表示。
1.3 数据处理
采用EXCEL 2019软件进行统计数据分析;部分数据使用Graph Prism 9.0软件进行多组间的方差分析(单因素ANOVA检验)和绘图,其中P<0.05时表示差异显著有统计学意义。测试样品进行3次重复分析,数据以均值±标准差表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 燕麦蛋白序列的获取
燕麦作为全世界种植最广泛的作物之一,也是最优质的谷物代表,成为生物活性肽制备的优良备选。燕麦属(Avena L.)目前发现有30个物种,包括25个野生种,5个栽培种。中国现在有27个燕麦物种[37],根据种型不同分为栽培种和野生种,根据染色体倍性水平不同分为二倍体、四倍体和六倍体,根据皮裸性不同分为裸燕麦和皮燕麦[38]。裸燕麦有二倍体和六倍体,建议二倍体裸燕麦保留Avena nuda L.的林奈名,六倍体裸燕麦作为六倍体普通栽培燕麦的一个亚种,命名为Avena sativa var. nuda[39]。从4个燕麦籽粒组织样本中测序产出Raw data共30.51 G,过滤后的Clean data共29.67 G的有效数据,过滤率分布在93%~95%,总比对率在94%~97%之间,成对唯一比对率在66%~75%之间,表明4组样本的测序文库数据质量较好及四组样本与对应参考基因组的比对结果良好。将4组样本的clean reads通过质量控制后的序列数据,对应品种分别比对到Avena sativa ssp. nuda和Avena sativa的参考基因组上,经转录本表达量定量后,裸燕麦‘坝莜1号’在籽粒形成期和灌浆期分别产出11920和6269条蛋白序列,皮燕麦‘白燕7号’在籽粒形成期和灌浆期分别产出9689和8595条蛋白序列(表1)。为了避免序列重复性导致的反复识别和酶解而浪费资源,剔除了数据集中序列相似性超过90%以上的大片重复蛋白序列进行模拟酶解分析。
表 1 燕麦基因组转录组测序数据及蛋白序列数据产出统计Table 1. Transcriptome sequencing and protein sequence data statistics of oat genome物种 样本 过滤率(%) 总比对率(%) 唯一比对率(%) 燕麦蛋白 燕麦蛋白(重复性低于90%) Avena sativa ssp. nuda 坝莜1号-籽粒形成期 94.96 96.06 75.27 11920 6310 Avena sativa ssp. nuda 坝莜1号-灌浆期 94.38 94.83 69.01 6269 3157 Avena sativa 白燕7号-籽粒形成期 95.1 94.84 66.67 9689 5804 Avena sativa 白燕7号-灌浆期 93.89 96.63 69.19 8595 5107 目前较多的研究主要是通过运用现有的蛋白数据库,选用部分蛋白序列进行低通量挖掘活性肽成分,其局限性在忽略当中可能具有独特的药理活性但表达丰度很低甚至没有表达的蛋白和多肽。Bleakley等[20]选用普通栽培燕麦(Avena sativa)八种主要贮藏蛋白预测筛选新型ACE-I、肾素和DPP-IV抑制肽,用于调节高血压和2型糖尿病。在本项研究中选用中国栽培种皮燕麦‘白燕7号’(Avena sativa,ACD)和裸燕麦‘坝莜1号’(Avena sativa ssp. nuda,ACD)在籽粒形成期和灌浆期的燕麦籽粒作为研究对象。通过对有参考基因组的转录组数据分析得到不同品种不同时期燕麦的蛋白序列信息[23−24],以实现对燕麦整体蛋白进行高通量挖掘。
2.2 燕麦活性肽的筛选
2.2.1 高通量虚拟酶解筛选
对生物活性肽的传统研究多采用水解蛋白酶对从食物中提取的蛋白质进行酶解粗提,进一步通过电泳技术,层析技术,膜分离技术,探针分离等多种方式分离纯化出多肽,再经过进一步质谱鉴定得到多肽组成序列,经一定的实验确定所具有的生理功能[40]。传统的实验方法存在的问题在于蛋白酶的选择或发酵的菌种均需要反复试错,活性多肽分离纯化、功能发现和评价过程复杂,不确定性大且成本较高。结合现有的大数据辅助虚拟酶解(如在线服务器BIOPEP和Peptide Cutter),利用生物信息学进行预测,两种方法有机结合起来,选择最优解,能够较大程度地降低原料的损耗,提高活性肽的筛选效率。这种计算机辅助蛋白酶酶解方法已成功应用于预测ACE-I、DPP-IV和XOD等抑制活性[20,41−42]。Du等[27]基于ExPASy Peptide Cutter程序,考虑水解顺序,构建一种注释良好且高通量模拟蛋白质水解工具改良版Refineing-PeptideCutter,可以生成任何长度的所有可能的肽,使用该蛋白质切割工具辅助筛选高粱蛋白中的高抗氧化二肽。许多生物活性肽已经通过计算机技术被筛选出,如藜麦蛋白水解物中鉴定出α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制肽PGGAR[43],12S燕麦球蛋白中鉴定出α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制肽GDVVALPA和DVVALPAG[44]。Zhao等[45]选用澳洲坚果较为丰富的三种蛋白序列进行虚拟酶解挖掘新型XOD抑制肽以预防和治疗高尿酸血症。
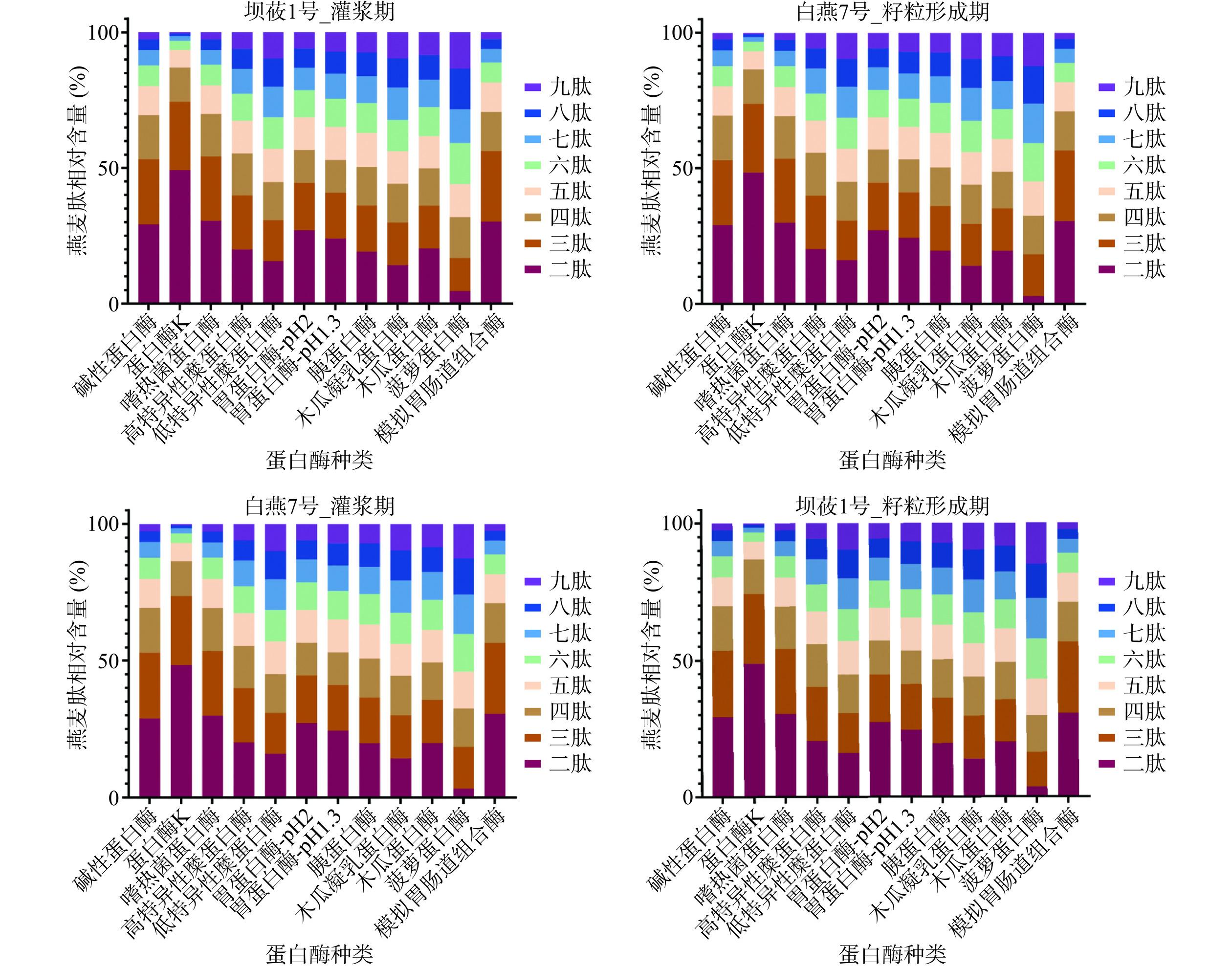
使用酶水解制备生物活性肽是基于蛋白酶具有切割位点特异性的事实[19]。不同的酶进行模拟酶解都能针对对应样本蛋白预测产生游离氨基酸和肽段,收集肽段形成独特的燕麦肽文库,统计数据见表2。肠腔中蛋白质消化的产物主要以游离氨基酸和小肽的形式出现[46],二/三肽主要由肠道表达的肽转运蛋白(PepT1)识别和转运以完整形式被吸收进入循环系统,而较长的寡肽(>四肽长度)通过细胞旁紧密连接扩散在体内以完整形式吸收[47−48]。使用12组蛋白酶水解燕麦蛋白,发现在肽文库里以小肽如二肽-六肽序列为主,并且微生物源水解蛋白酶酶解能释放更多的小肽,见图1。
表 2 高通量虚拟酶解后氨基酸和肽段数量产出统计Table 2. Production statistics of of amino acids and peptides in silico水解蛋白酶 坝莜1号-籽粒形成期 坝莜1号-灌浆期 白燕7号-籽粒形成期 白燕7号-灌浆期 氨基酸 肽段 氨基酸 肽段 氨基酸 肽段 氨基酸 肽段 碱性蛋白酶 238707 561972 99832 236477 249482 598197 207204 502321 蛋白酶K 682914 681962 291003 287698 723022 732716 605937 617901 嗜热菌蛋白酶 331396 552532 142180 234251 348087 590820 290238 497313 高特异性糜蛋白酶 83437 369198 34047 154017 87689 392963 72243 328195 低特异性糜蛋白酶 13079 142546 5921 58752 13441 154788 11328 129076 胃蛋白酶-pH2 306523 342476 125172 143382 320788 365171 265169 305373 胃蛋白酶-pH1.3 228652 281335 92799 116731 238810 298919 197108 249279 胰蛋白酶 40766 257293 17604 110503 45515 279664 39788 239514 木瓜凝乳蛋白酶 15961 137706 6621 57546 17201 147582 14136 122773 木瓜蛋白酶 21406 188694 10274 82363 23111 201295 20387 170610 菠萝蛋白酶 1727 18324 671 7983 2286 20387 1954 17267 模拟胃肠道组合酶 504718 519745 208049 219464 538438 559252 449286 472226 2.2.2 潜在活性的评价
蛋白酶K(Proteinase K)是一种切割活性较广的丝氨酸蛋白酶,可切割脂肪族氨基酸和芳香族氨基酸的羧基端肽键[49]。结果发现,四组样本经蛋白酶K酶解后产生的氨基酸和相关肽段在肽段数量和小肽相对含量相较于其他单酶和组合酶最高,后续选取经蛋白酶K酶解产生的四组肽文库进行活性预测评分。基于Peptide Ranker对燕麦肽进行潜在活性评价,选择score≥0.9中相对含量最高的一组,针对“坝莜1号-灌浆期”score≥0.9肽文库中1532条具有较好活性的燕麦肽进行毒性分析,获得1446个燕麦活性肽为无细胞毒性(见表3)。ToxinPred[29]是基于机器学习技术和定量矩阵的模型评估对肽段进行毒性预测,无毒性且具有良好物理化学性质的活性肽在功能性食品和药物开发至关重要。
表 3 Peptide Ranker预测具有潜在活性肽文库数据统计(蛋白酶K模拟酶解后)Table 3. Peptide Ranker predicts potentially active peptide library data (after Proteinase K in silico)评分 坝莜1号-籽粒形成期 坝莜1号-灌浆期 白燕7号-籽粒形成期 白燕7号-灌浆期 肽数 相对含量(%) 肽数 相对含量(%) 肽数 相对含量(%) 肽数 相对含量(%) 唯一项 85888 / 42793 / 89795 / 80149 / ≥0.5 24182 28.16 12448 29.09 25779 28.71 23062 28.77 ≥0.9 2664 3.10 1532 3.58 2842 3.16 2554 3.19 2.2.3 计算机辅助药物分析
药物的ADME/T性质,即药物在体内的吸收(Absorption)、分布(Distribution)、代谢(Metabolism)、排泄(Excretion)、毒性(Toxicity),是影响药物疗效的关键因素。基于SwissADME对上续经蛋白酶K模拟酶解后的“坝莜1号-灌浆期”的肽文库中Peptide Ranker评分≥0.9且无毒性的1446个燕麦活性肽,以输入SMILES式进行ADME预测筛选肠胃吸收为“High”,血脑屏障为“NO”,五类药性预测中有2个及2个以上为“Yes”,以评估活性肽成为口服药物及其生物利用度的机会。最终获取42条被胃肠道吸收、不通过血脑屏障且具有良好的类药性的燕麦活性肽,数据见表4。
表 4 ToxinPred和Swiss ADME筛选的燕麦活性肽Table 4. Oat active peptides screened by ToxinPred and Swiss ADME肽序列 活性评分 毒性 分子量(Da) 水溶性(ESOL) 肠道吸收 血脑屏障 P-糖蛋白 细胞色素P450 抑制性* 生物利用度 MF 0.9966 Non-Toxin 296.39 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 CF 0.9964 Non-Toxin 268.33 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 MW 0.9953 Non-Toxin 335.42 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 GF 0.9947 Non-Toxin 222.24 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 PF 0.9934 Non-Toxin 262.3 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 GW 0.9932 Non-Toxin 261.28 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 PW 0.9929 Non-Toxin 301.34 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 MPF 0.9927 Non-Toxin 393.5 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PMF 0.9924 Non-Toxin 393.5 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PPW 0.9894 Non-Toxin 398.46 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 GPF 0.9893 Non-Toxin 319.36 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 GPW 0.9888 Non-Toxin 358.39 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 PPPF 0.9887 Non-Toxin 456.53 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 PPF 0.9886 Non-Toxin 359.42 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 PPPW 0.9882 Non-Toxin 495.57 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 PGW 0.9879 Non-Toxin 358.39 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 PGF 0.9874 Non-Toxin 319.36 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 GGF 0.9873 Non-Toxin 279.29 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 PPGF 0.9862 Non-Toxin 416.47 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PGPF 0.9861 Non-Toxin 416.47 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 MP 0.9601 Non-Toxin 246.33 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 GM 0.9532 Non-Toxin 206.26 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 HW 0.9529 Non-Toxin 341.36 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 PM 0.9519 Non-Toxin 246.33 Highly soluble High No Yes No 0.55 HF 0.9510 Non-Toxin 302.33 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 SF 0.9488 Non-Toxin 252.27 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 QF 0.9461 Non-Toxin 293.32 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 MG 0.9440 Non-Toxin 206.26 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 CP 0.9433 Non-Toxin 218.27 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 DF 0.9424 Non-Toxin 280.28 Highly soluble High No No No 0.56 PPPL 0.9410 Non-Toxin 422.52 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PHF 0.9380 Non-Toxin 399.44 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 SW 0.9339 Non-Toxin 291.3 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 KPF 0.9224 Non-Toxin 390.48 Highly soluble High No Yes No 0.55 MPL 0.9224 Non-Toxin 359.48 Highly soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PML 0.9213 Non-Toxin 359.48 Highly soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PSF 0.9204 Non-Toxin 349.38 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 PGPL 0.9151 Non-Toxin 382.45 Highly soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PPGL 0.9128 Non-Toxin 382.45 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PPG 0.9113 Non-Toxin 269.3 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 KF 0.9068 Non-Toxin 293.36 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 GP 0.9055 Non-Toxin 172.18 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 *注:细胞色素P450抑制性包含CYP1A2 、CYP2C19 、CYP2C9、CYP2D6和CYP3A4 抑制酶的评估。 2.3 抗高尿酸血症燕麦活性肽的筛选
2.3.1 燕麦活性肽-高尿酸血症靶点获取
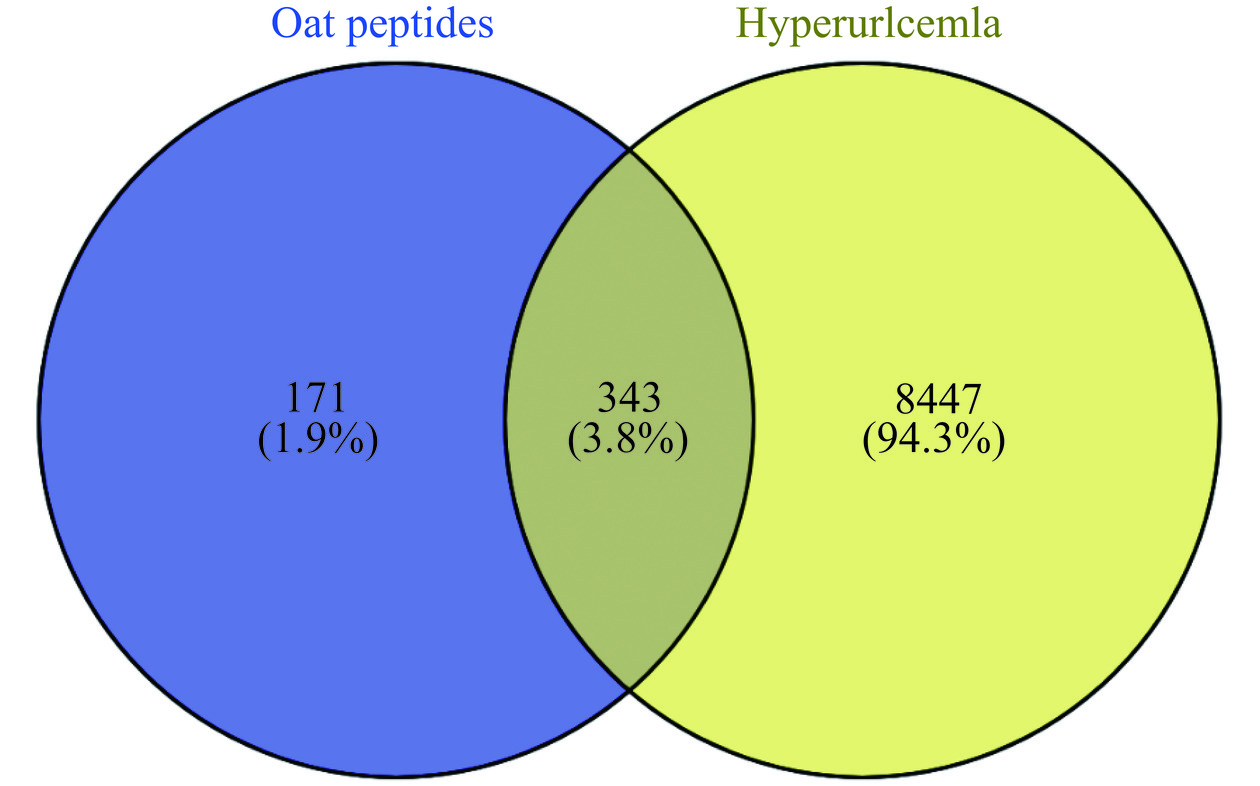
经SwissTarget Prediction和PharmMapper数据库预测以上筛选的42条燕麦活性肽靶点,去除重复后获得514个燕麦活性肽靶点。CTD结合Gene cards、DisGeNet和OMIM数据库筛选获得8790个高尿酸血症潜在靶点。将514个燕麦活性肽成分靶点与8790个高尿酸血症潜在靶点取交集,获得343个燕麦活性肽干预高尿酸血症的作用靶点(图2)。
2.3.2 PPI网络拓扑分析及核心靶点的筛选
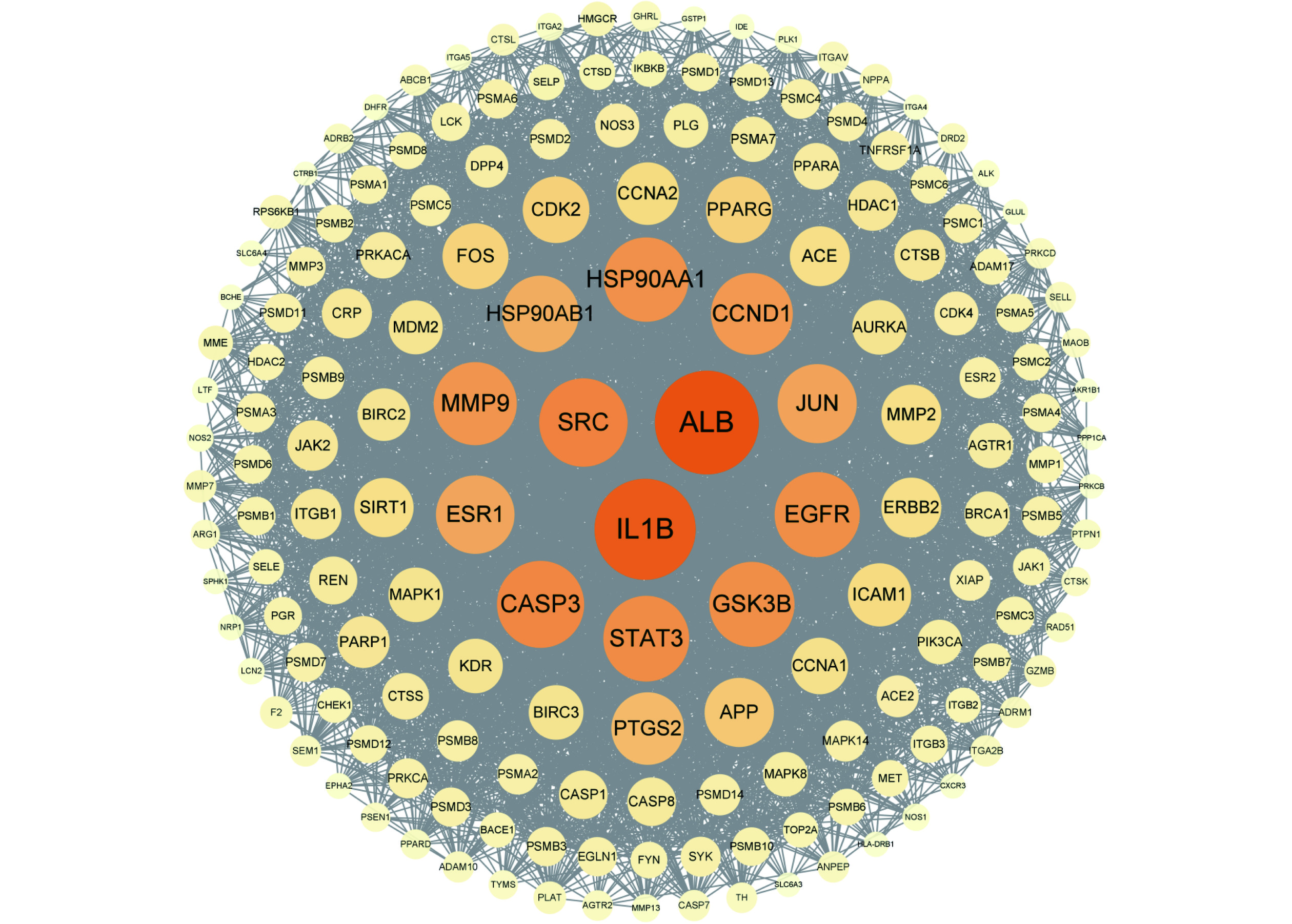
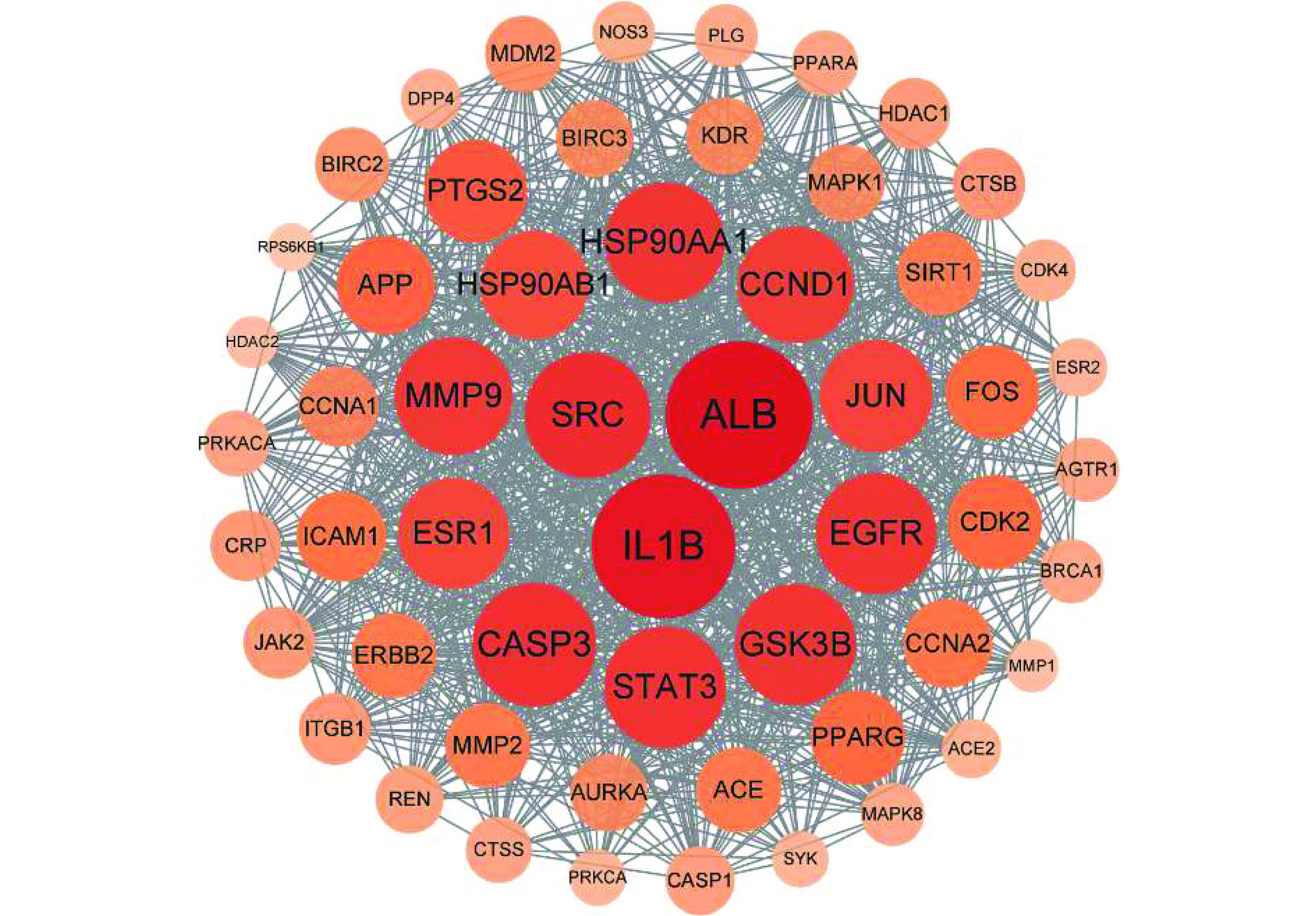
PPI网络图分析,提取连接度>中位数(22)PPI网络A,共168个节点,3619条边(图3),提取PPI网络A的介度>中位数(0.0031)和紧密度>中位数(0.4839)的PPI网络B,共55个节点,925条边(图4)。设置各节点连接度、介度和紧密度均大于中位数为最低阈值筛选并提取关键靶点,网络中关键节点靶点主要是ALB、IL1B、SRC、CASP3和STAT3(表5)。
表 5 燕麦活性肽干预高尿酸血症核心靶点网络节点特征参数Table 5. Node parameters of core target network of oat active peptides against hyperuricemia靶点 连接度 介度 紧密度 ALB 143 0.057 0.620 IL1B 139 0.050 0.620 SRC 120 0.054 0.591 CASP3 118 0.028 0.593 STAT3 116 0.027 0.591 本研究结果表明,燕麦活性肽调治高尿酸血症占据中心位置的关键靶点为ALB、IL1B、SRC、CASP3和STAT3,与高尿酸血症介导的肝肾损伤的机制有关。血清白蛋白(ALB)由肝脏合成,是反映肝脏合成功能的重要指标。ALB水平与新发高尿酸血症风险、尿酸水平的变化均呈显著负相关[50]。该研究结果提示,在临床实践中,常规白蛋白检测可能是识别高尿酸血症高危成人的一种简单可行的策略[50]。白细胞介素-1B(IL-1B)编码的蛋白是白细胞介素1细胞因子家族的一员。IL-1B是一种强效的促炎细胞因子,也是由单核和巨噬细胞产生的免疫反应的重要介质[51]。研究发现IL-1B被抑制表达能够抑制炎性介质释放,减轻氧化应激反应,减轻肾功能障碍[52−53]。核受体辅激活蛋白(SRC)家族是由原癌基因编码的非受体型酪氨酸蛋白激酶[54],SRC家族成员参与生殖,能量代谢和增殖分化,这类靶点关键性调节人体生理和疾病中重要的信号转导[55]。SRC参与调节Yes-associated蛋白(YAP)磷酸化和肾纤维化中的核定位,抑制SRC活性可防止肾纤维化和慢性肾脏疾病[56−57]。半胱氨酸蛋白酶3(CASP3)是细胞凋亡的重要信号分子,与免疫异常相关的肾脏疾病存在和发展有密切关系[58]。信号转导和转录激活因子(STAT3)参与生物体内复杂多样的生命活动,STAT3被抑制可改善肾功能障碍,降低血清尿酸水平,并延缓肾纤维化的进展[59]。
2.3.3 GO功能富集和KEGG通路富集
研究核心靶点投射于GO功能和KEGG通路富集与高尿酸血症之间的相关关系,明确燕麦活性肽潜在的药理机制和在体内的生物过程。对燕麦活性肽干预高尿酸血症的55个核心靶点的生物信息富集分析结果如图5、图6所示。其中如图5展示基因功能信息生物过程(BP)富集958个GO功能,主要参与激素反应(response to hormone)、氮化合物反应(cellular response to nitrogen compound)、有机氮化合物反应(cellular response to organonitrogen compound)、激素刺激反应(cellular response to hormone stimulus)、多肽反应(response to peptide)等生物过程。细胞组成(CC)富集89个GO功能,主要集中于脂筏(membrane raft)、膜微区(membrane microdomain)、等离子膜筏(plasma membrane raft)、小凹胞吐(caveola)、转录调节复合物(transcription regulator complex)等。分子功能(MF)富集94个GO功能,主要参与激酶结合(kinase binding)、蛋白激酶结合(protein kinase binding)、蛋白质结构域特异性结合(protein domain specific binding)、蛋白激酶活性(protein kinase activity)等。通过KEGG富集分析,共得到作用核心靶点参与的通路163条,图6中显示燕麦活性肽干预高尿酸血症排名前20的信号通路,关键通路包括癌症(Pathways in cancer)、脂质和动脉粥样硬化(Lipid and atherosclerosis)、化学致癌-受体激活(Chemical carcinogenesis-receptor activation)等。
燕麦活性肽调治高尿酸血症的通路在KEGG 富集分析中,癌症信号通路是富集基因最多的信号通路,因此推测癌症通路可能是燕麦活性肽干预高尿酸血症的关键通路。近年来流行病学资料表明高尿酸血症与恶性肿瘤的发生、发展和预后相关。高尿酸血症促进恶性肿瘤发生发展机制与血尿酸相关的慢性炎症环境有关[60]。Xie等[61]通过Meta分析与剂量反应分析,阐明血清中的尿酸水平(SUA)每增加1 mg,对总体癌症发病率影响不大,但高尿酸血症增加了癌症总死亡率,SUA水平与总癌症发病率(非线性P=0.238)和总癌症死亡率(非线性P=0.263)之间存在一定的线性关系。Meng等[62]首次提出高尿酸血症通过CXCL-13途径诱导脂质代谢紊乱。尿酸通过干扰脂质代谢,减少内皮细胞中的一氧化氮合成,促进血管平滑肌细胞的增殖并控制炎症反应来维持动脉粥样硬化过程[63]。
2.3.4 燕麦活性肽-作用靶点-潜在通路网络的构建
燕麦活性肽-作用靶点-潜在通路网络由117个节点和969条边构成(图7)。预测PPF、PPPL、MPF、MPL和PPPF为燕麦活性肽干预高尿酸血症的主要肽序列(表6)。预测SRC为燕麦活性肽干预高尿酸血症的核心靶点,PTGS2、MAPK1、ACE和MMP2亦为相对重要的靶点(表7)。网络分析中,每种活性成分对应多个靶点,每个靶点连接多种成分,通路间是通过共有靶点连接而非独立分开,体现燕麦活性肽内含的不同序列的肽序列,通过多靶点多通路之间发挥协同作用干预高尿酸血症。
表 6 燕麦活性肽网络节点特征参数Table 6. Node parameters of main oat active peptides network肽序列 连接度 介度 紧密度 PPF 27 0.020 0.498 PPPL 26 0.022 0.494 MPF 26 0.025 0.494 MPL 25 0.032 0.489 PPPF 25 0.015 0.489 表 7 燕麦活性肽靶点网络节点特征参数Table 7. Node parameters of main target network of oat active peptides靶点 连接度 介度 紧密度 SRC 42 0.059 0.552 PTGS2 42 0.051 0.552 MAPK1 41 0.069 0.547 ACE 40 0.041 0.542 MMP2 36 0.036 0.513 本研究通过网络药理学方法初步预测筛选出燕麦活性肽调治高尿酸血症的主要活性成分肽序列为PPF、PPPL、MPF、MPL和PPPF等。氨基酸种类、数目是影响降尿酸活性肽的重要因素。He等[64]研究发现含苯丙氨酸(F)的二/三肽可能是针对高尿酸血症的有效XOD抑制剂,苯丙氨酸-组氨酸(FH)具有最强的XOD抑制活性(IC50=25.7 mmol)。Huang等[65]收集已报道的33种降尿酸肽(共117氨基酸),其中氨基酸数目均在2~9个范围内,而在降尿酸肽中大多数含有芳香族氨基酸(W、F、Y)和疏水性氨基酸(P、L、A),在33种降尿酸肽中,脯氨酸(P)占比8.5%,苯丙氨酸(F)占比6.8%,亮氨酸(L)占比6%。一些研究表明,肽中氨基酸的疏水性与降尿酸活性存在一定的关联。疏水性肽与XOD的氨基酸残基之间主要涉及疏水相互作用,疏水性肽比亲水性肽更容易进入XOD的活性位点,与XOD形成催化底物竞争的机制,疏水氨基酸与活性位点残基具有更强的相互作用,故含疏水性氨基酸的降尿酸活性肽具有更强的XOD抑制活性[35,65−66]。
研究结果表明燕麦活性肽的同一肽序列可调控不同靶点,而同一靶点可干预不同的生物学过程及信号通路,体现了燕麦活性肽多通路、多靶点联合作用的特点,为临床运用燕麦活性肽调治高尿酸血症提供科学依据,也为发掘燕麦活性肽的潜在作用机制提供新的方向。
2.4 功能验证
2.4.1 分子对接验证
从燕麦多肽中筛选前5的主要活性成分与5个核心靶点和1个人类XOD(2个口袋)进行分子对接,最终获得35组受体-配体对接结果,见图8。其中Binging energy<0 kJ/mol有32组,91.43%的受体-配体在自然状态下具有结合活性;Binging energy<-5 kJ/mol有29组,82.86%的受体-配体对接状态良好且结合活性较佳。发现燕麦多肽中主要活性成分为PPF、PPPL、MPF、MPL和PPPF与主要靶点(ALB、SRC、CASP3)和人类XOD的结合能相对较高,提示具有较强的结合活性。
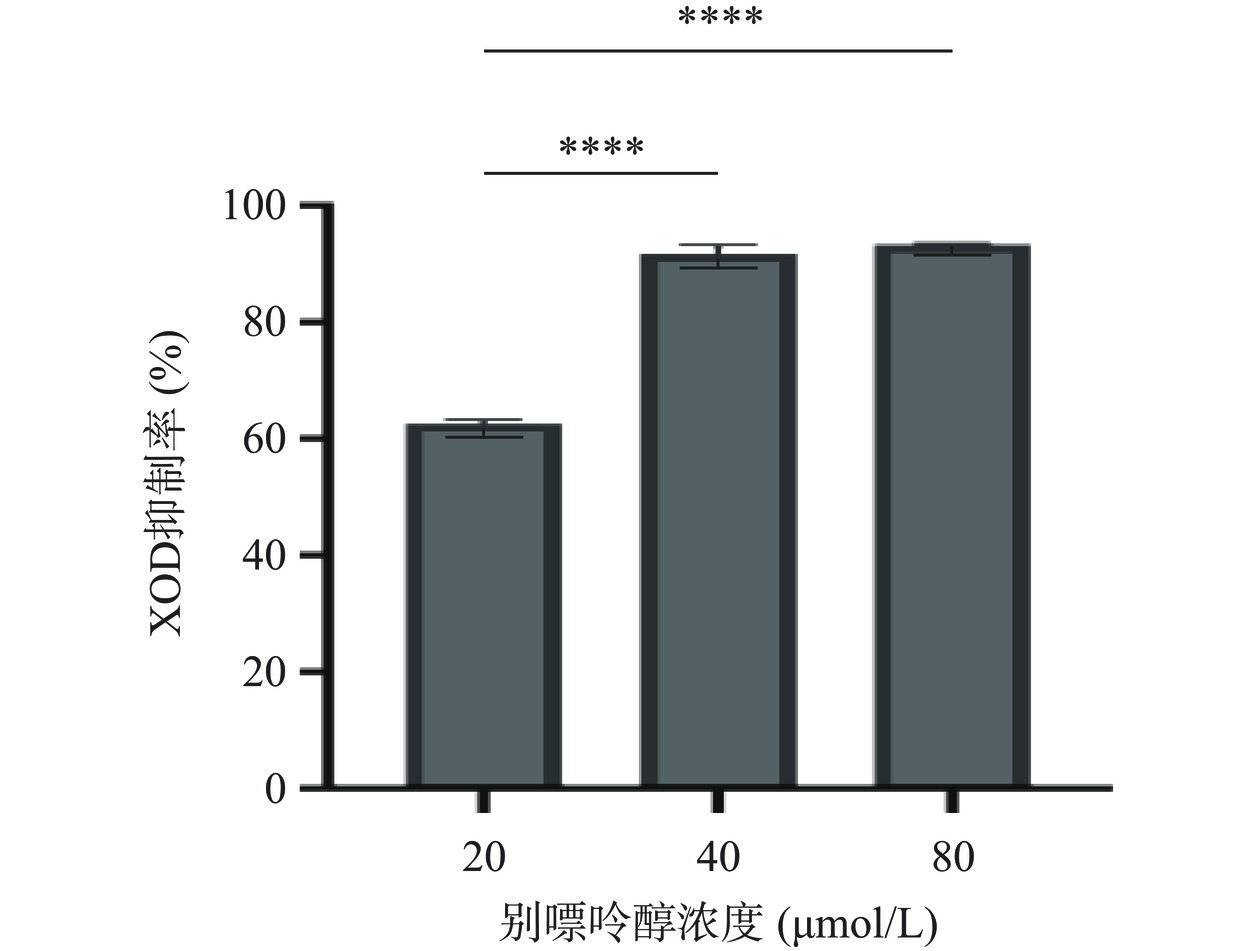
2.4.2 体外XOD抑制活性验证
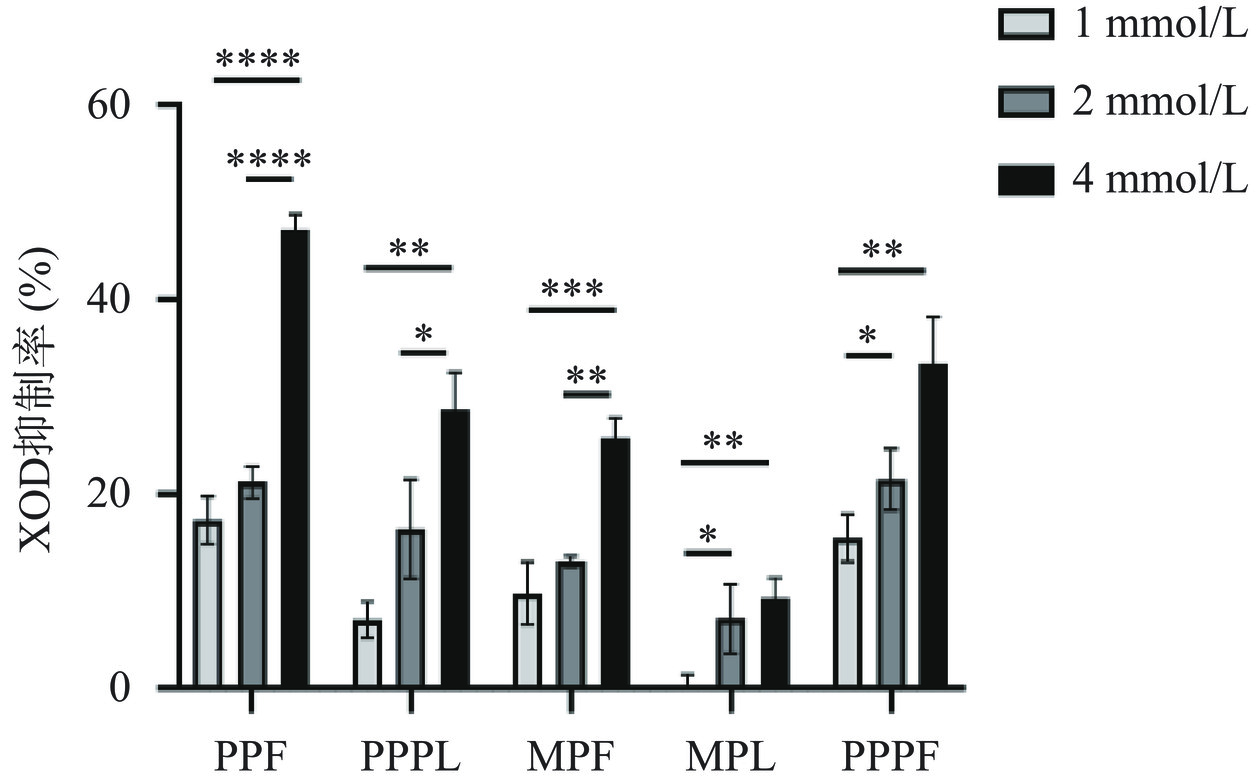
XOD可将黄嘌呤转化成尿酸,当抑制该酶的活性,在一定程度上能降低尿酸产生。如图9所示,以别嘌呤醇为阳性对照,40 μmol/L的阳性药物体外XOD抑制率为91.69%±1.54%,表明高尿酸血症体外化学法模型建立成功。随着多肽溶液浓度的增加,其XOD抑制活性随剂量递增,如图10所示,PPF和PPPF相较于PPPL、MPF、MPL具有较强的XOD抑制活性。合成多肽PPF、PPPL、MPF、MPL和PPPF的IC50值分别为6.132、27.811、143.983、1156.481和15.360 mmol/L。
3. 结论
本研究探讨完整裸燕麦蛋白作为生物活性肽前体的潜力和裸燕麦蛋白源抗高尿酸血症活性肽的主要活性成分、潜在靶点和作用机制。通过构建一套从燕麦籽粒转录组测序数据经参考基因组比对,转录本表达量定量分析以获取燕麦完整蛋白序列的方法,改良高通量虚拟酶解技术,优化选择裸燕麦‘坝莜1号’在灌浆期的蛋白序列经蛋白酶K水解产生的肽文库,经生物活性预测和计算机辅助药物分析(ADME/T)流程筛选具有潜在活性和良好成药性的肽段。基于网络药理学筛选和分析裸燕麦活性肽改善高尿酸血症潜在靶点为ALB、IL1B、SRC、CASP3和STAT3等基因,作用于癌症、脂质与动脉粥样硬化和化学致癌-受体激活等信号通路,干预高尿酸血症和发挥主要活性成分为PPF、PPPL、MPF、MPL和PPPF。然而虚拟酶解和网络药理学方法仍存在一些局限性,如虚拟酶解在一些预测肽段上没有考虑CDS区域内的重叠序列而忽略肽段在整体数量上的定量,网络药理学是海量数据进行网络建模,尚未考虑在酶解时发生化学反应的复杂性而存在一定的假阳性率和假阴性率[32]。后续将在此基础上结合细胞或动物实验验证,进而明晰燕麦活性肽的主要活性成分、调控靶点和作用机制。
-
表 1 燕麦基因组转录组测序数据及蛋白序列数据产出统计
Table 1 Transcriptome sequencing and protein sequence data statistics of oat genome
物种 样本 过滤率(%) 总比对率(%) 唯一比对率(%) 燕麦蛋白 燕麦蛋白(重复性低于90%) Avena sativa ssp. nuda 坝莜1号-籽粒形成期 94.96 96.06 75.27 11920 6310 Avena sativa ssp. nuda 坝莜1号-灌浆期 94.38 94.83 69.01 6269 3157 Avena sativa 白燕7号-籽粒形成期 95.1 94.84 66.67 9689 5804 Avena sativa 白燕7号-灌浆期 93.89 96.63 69.19 8595 5107 表 2 高通量虚拟酶解后氨基酸和肽段数量产出统计
Table 2 Production statistics of of amino acids and peptides in silico
水解蛋白酶 坝莜1号-籽粒形成期 坝莜1号-灌浆期 白燕7号-籽粒形成期 白燕7号-灌浆期 氨基酸 肽段 氨基酸 肽段 氨基酸 肽段 氨基酸 肽段 碱性蛋白酶 238707 561972 99832 236477 249482 598197 207204 502321 蛋白酶K 682914 681962 291003 287698 723022 732716 605937 617901 嗜热菌蛋白酶 331396 552532 142180 234251 348087 590820 290238 497313 高特异性糜蛋白酶 83437 369198 34047 154017 87689 392963 72243 328195 低特异性糜蛋白酶 13079 142546 5921 58752 13441 154788 11328 129076 胃蛋白酶-pH2 306523 342476 125172 143382 320788 365171 265169 305373 胃蛋白酶-pH1.3 228652 281335 92799 116731 238810 298919 197108 249279 胰蛋白酶 40766 257293 17604 110503 45515 279664 39788 239514 木瓜凝乳蛋白酶 15961 137706 6621 57546 17201 147582 14136 122773 木瓜蛋白酶 21406 188694 10274 82363 23111 201295 20387 170610 菠萝蛋白酶 1727 18324 671 7983 2286 20387 1954 17267 模拟胃肠道组合酶 504718 519745 208049 219464 538438 559252 449286 472226 表 3 Peptide Ranker预测具有潜在活性肽文库数据统计(蛋白酶K模拟酶解后)
Table 3 Peptide Ranker predicts potentially active peptide library data (after Proteinase K in silico)
评分 坝莜1号-籽粒形成期 坝莜1号-灌浆期 白燕7号-籽粒形成期 白燕7号-灌浆期 肽数 相对含量(%) 肽数 相对含量(%) 肽数 相对含量(%) 肽数 相对含量(%) 唯一项 85888 / 42793 / 89795 / 80149 / ≥0.5 24182 28.16 12448 29.09 25779 28.71 23062 28.77 ≥0.9 2664 3.10 1532 3.58 2842 3.16 2554 3.19 表 4 ToxinPred和Swiss ADME筛选的燕麦活性肽
Table 4 Oat active peptides screened by ToxinPred and Swiss ADME
肽序列 活性评分 毒性 分子量(Da) 水溶性(ESOL) 肠道吸收 血脑屏障 P-糖蛋白 细胞色素P450 抑制性* 生物利用度 MF 0.9966 Non-Toxin 296.39 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 CF 0.9964 Non-Toxin 268.33 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 MW 0.9953 Non-Toxin 335.42 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 GF 0.9947 Non-Toxin 222.24 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 PF 0.9934 Non-Toxin 262.3 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 GW 0.9932 Non-Toxin 261.28 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 PW 0.9929 Non-Toxin 301.34 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 MPF 0.9927 Non-Toxin 393.5 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PMF 0.9924 Non-Toxin 393.5 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PPW 0.9894 Non-Toxin 398.46 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 GPF 0.9893 Non-Toxin 319.36 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 GPW 0.9888 Non-Toxin 358.39 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 PPPF 0.9887 Non-Toxin 456.53 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 PPF 0.9886 Non-Toxin 359.42 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 PPPW 0.9882 Non-Toxin 495.57 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 PGW 0.9879 Non-Toxin 358.39 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 PGF 0.9874 Non-Toxin 319.36 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 GGF 0.9873 Non-Toxin 279.29 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 PPGF 0.9862 Non-Toxin 416.47 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PGPF 0.9861 Non-Toxin 416.47 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 MP 0.9601 Non-Toxin 246.33 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 GM 0.9532 Non-Toxin 206.26 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 HW 0.9529 Non-Toxin 341.36 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 PM 0.9519 Non-Toxin 246.33 Highly soluble High No Yes No 0.55 HF 0.9510 Non-Toxin 302.33 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 SF 0.9488 Non-Toxin 252.27 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 QF 0.9461 Non-Toxin 293.32 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 MG 0.9440 Non-Toxin 206.26 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 CP 0.9433 Non-Toxin 218.27 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 DF 0.9424 Non-Toxin 280.28 Highly soluble High No No No 0.56 PPPL 0.9410 Non-Toxin 422.52 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PHF 0.9380 Non-Toxin 399.44 Very soluble High No No No 0.55 SW 0.9339 Non-Toxin 291.3 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 KPF 0.9224 Non-Toxin 390.48 Highly soluble High No Yes No 0.55 MPL 0.9224 Non-Toxin 359.48 Highly soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PML 0.9213 Non-Toxin 359.48 Highly soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PSF 0.9204 Non-Toxin 349.38 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 PGPL 0.9151 Non-Toxin 382.45 Highly soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PPGL 0.9128 Non-Toxin 382.45 Very soluble High No Yes No 0.55 PPG 0.9113 Non-Toxin 269.3 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 KF 0.9068 Non-Toxin 293.36 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 GP 0.9055 Non-Toxin 172.18 Highly soluble High No No No 0.55 *注:细胞色素P450抑制性包含CYP1A2 、CYP2C19 、CYP2C9、CYP2D6和CYP3A4 抑制酶的评估。 表 5 燕麦活性肽干预高尿酸血症核心靶点网络节点特征参数
Table 5 Node parameters of core target network of oat active peptides against hyperuricemia
靶点 连接度 介度 紧密度 ALB 143 0.057 0.620 IL1B 139 0.050 0.620 SRC 120 0.054 0.591 CASP3 118 0.028 0.593 STAT3 116 0.027 0.591 表 6 燕麦活性肽网络节点特征参数
Table 6 Node parameters of main oat active peptides network
肽序列 连接度 介度 紧密度 PPF 27 0.020 0.498 PPPL 26 0.022 0.494 MPF 26 0.025 0.494 MPL 25 0.032 0.489 PPPF 25 0.015 0.489 表 7 燕麦活性肽靶点网络节点特征参数
Table 7 Node parameters of main target network of oat active peptides
靶点 连接度 介度 紧密度 SRC 42 0.059 0.552 PTGS2 42 0.051 0.552 MAPK1 41 0.069 0.547 ACE 40 0.041 0.542 MMP2 36 0.036 0.513 -
[1] LIU N, XU H, SUN Q, et al. The role of oxidative stress in hyperuricemia and xanthine oxidoreductase (XOR) inhibitors[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2021,2021:1470380.
[2] ZHANG M, ZHU X, WU J, et al. Prevalence of hyperuricemia among Chinese adults:Findings from two nationally representative cross-sectional surveys in 2015-16 and 2018-19[J]. Frontiers in Immunology,2021,12:791983.
[3] YI B, SUN J, LIU Y, et al. Virtual screening and multi-targets investigation of novel diazine derivatives as potential xanthine oxidase inhibitors based on QSAR, molecular docking, ADMET properties, dynamics simulation and network pharmacology[J]. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2023,19(7):704−716. doi: 10.2174/1573406419666230209092231
[4] DALBETH N, GOSLING A L, GAFFO A, et al. Gout[J]. Lancet,2021,397(10287):1843−1855. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00569-9
[5] ZHANG X, CUI J, HOU J, et al. Research progress of natural active substances with uric-acid-reducing activity[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2022,70(50):15647−15664. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06554
[6] LIU N, WANG Y, ZENG L, et al. RDP3, a novel antigout peptide derived from water extract of rice[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(27):7143−7151. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c02535
[7] LI Q, KANG X, SHI C, et al. Moderation of hyperuricemia in rats via consuming walnut protein hydrolysate diet and identification of new antihyperuricemic peptides[J]. Food & Function,2018,9(1):107−116.
[8] HAN J, WANG X, TANG S, et al. Protective effects of tuna meat oligopeptides (TMOP) supplementation on hyperuricemia and associated renal inflammation mediated by gut microbiota[J]. FASEB Journal,2020,34(4):5061−5076. doi: 10.1096/fj.201902597RR
[9] FAN S, HUANG Y, LU G, et al. Novel anti-hyperuricemic hexapeptides derived from apostichopus japonicus hydrolysate and their modulation effects on the gut microbiota and host microrna profile[J]. Food & Function,2022,13(7):3865−3878.
[10] MAO Z, JIANG H, MAO X. Identification and anti-hyperuricemic activity of xanthine oxidase inhibitory peptides from pacific white shrimp and swimming crab based on molecular docking screening[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2023,71(3):1620−1627. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c07881
[11] KEILIN J. The biological significance of uric acid and guanine excretion[J]. Biological Reviews,1959,34:265−296.
[12] JANG I T, HYUN S H, SHIN J W, et al. Characterization of an anti-gout xanthine oxidase inhibitor from pleurotus ostreatus[J]. Mycobiology,2014,42(3):296−300. doi: 10.5941/MYCO.2014.42.3.296
[13] LI X, ZHOU L, YU Y, et al. The potential functions and mechanisms of oat on cancer prevention:A review[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2022,70(46):14588−14599. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06518
[14] RAFIQUE H, DONG R, WANG X, et al. Dietary-nutraceutical properties of oat protein and peptides[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2022,9:950400. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.950400
[15] 黄小清. 基于组学的动物药快速鉴定及活性肽筛选研究[D]. 武汉:武汉大学, 2020. [HUANG Xiaoqing. Rapid species identification and active peptide screening in Chinese medicinal animals based on omics technologies[D]. Wuhan:Wuhan University, 2020.] HUANG Xiaoqing. Rapid species identification and active peptide screening in Chinese medicinal animals based on omics technologies[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2020.
[16] 李安. 青环海蛇抗炎活性肽Hydrostatin-SN10的靶点拮抗机制及基于三代测序的青环海蛇多组学研究[D]. 上海:中国人民解放军海军军医大学, 2022. [LI An. Study on the target-antagonizing mechanism of the sea snake anti-inflammatory peptide Hydrostatin-SN10 and the multi-omics of Hydrophis cyanocinctus based on third-generation sequencing[D]. Shanghai:Naval Medical University, 2022.] LI An. Study on the target-antagonizing mechanism of the sea snake anti-inflammatory peptide Hydrostatin-SN10 and the multi-omics of Hydrophis cyanocinctus based on third-generation sequencing[D]. Shanghai: Naval Medical University, 2022.
[17] LI A, WANG J, SUN K, et al. Two reference-quality sea snake genomes reveal their divergent evolution of adaptive traits and venom systems[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution,2021,38(11):4867−4883. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab212
[18] JIA L, WANG L, LIU C, et al. Bioactive peptides from foods:Production, function, and application[J]. Food & Function,2021,12(16):7108−7125.
[19] LIN K, ZHANG L W, HAN X, et al. Yak milk casein as potential precursor of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides based on in silico proteolysis[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,254:340−347. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.02.051
[20] BLEAKLEY S, HAYES M, N O S, et al. Predicted release and analysis of novel ACE-I, renin, and DPP-IV inhibitory peptides from common oat (Avena sativa) protein hydrolysates using in silico analysis[J]. Foods (Basel, Switzerland),2017,6(12):108.
[21] LUO J J, CHEN X H, LIANG P Y, et al. Mechanism of anti-hyperuricemia of isobavachin based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine,2023,155:106637. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106637
[22] YUAN Z, PAN Y, LENG T, et al. Progress and prospects of research ideas and methods in the network pharmacology of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences,2022,25:218−226.
[23] GUTIERREZ-GONZALEZ J J, TU Z J, GARVIN D F. Analysis and annotation of the hexaploid oat seed transcriptome[J]. BMC Genomics,2013,14:471. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-471
[24] PENG Y, YAN H, GUO L, et al. Reference genome assemblies reveal the origin and evolution of allohexaploid oat[J]. Nature Genetics,2022,54(8):1248−1258. doi: 10.1038/s41588-022-01127-7
[25] LI W, GODZIK A. CD-Hit:A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences[J]. Bioinformatics,2006,22(13):1658−1659. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl158
[26] WILKINS M R, GASTEIGER E, BAIROCH A, et al. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology,1999,112:531−552.
[27] DU Z, LI Y. Computer-aided approaches for screening antioxidative dipeptides and application to sorghum proteins[J]. ACS Food Science & Technology,2022,2(11):1781−1788.
[28] MOONEY C, HASLAM N J, POLLASTRI G, et al. Towards the improved discovery and design of functional peptides:Common features of diverse classes permit generalized prediction of bioactivity[J]. PLoS One,2012,7(10):e45012. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045012
[29] GUPTA S, KAPOOR P, CHAUDHARY K, et al. In silico approach for predicting toxicity of peptides and proteins[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(9):e73957. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073957
[30] DAINA A, MICHIELIN O, ZOETE V. SwissADME:A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7:42717. doi: 10.1038/srep42717
[31] 胡百淳, 田金鑫, 张逸腾, 等. 化合物成药性的在线预测[J]. 中国药物化学杂志,2022,32(2):90−101. [HU Baichun, TIAN Jinxin, ZHANG Yiteng, et al. Online prediction of compound's druggability[J]. Chinese Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2022,32(2):90−101.] HU Baichun, TIAN Jinxin, ZHANG Yiteng, et al. Online prediction of compound's druggability[J]. Chinese Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2022, 32(2): 90−101.
[32] 但文超, 刘红旭, 何庆勇, 等. 基于网络药理学与分子对接方法探讨黄山药干预冠心病的作用机制研究[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2021,23(6):1829−1843. [DAN Wenchao, LIU Hongxu, HE Qingyong, et al. Based on the network pharmacology and molecular docking method to explore the mechanism of Dioscorea panthaica rhizoma in the intervention of coronary heart disease[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology,2021,23(6):1829−1843.] DAN Wenchao, LIU Hongxu, HE Qingyong, et al. Based on the network pharmacology and molecular docking method to explore the mechanism of Dioscorea panthaica rhizoma in the intervention of coronary heart disease[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology, 2021, 23(6): 1829−1843.
[33] DAVIS A P, GRONDIN C J, JOHNSON R J, et al. Comparative toxicogenomics database (CTD):Update 2021[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2021,49(D1):D1138−d1143. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa891
[34] 但文超, 何庆勇, 曲艺, 等. 基于网络药理学的枳术丸调治血脂异常的分子机制研究[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2019,21(11):2396−2405. [DAN Wenchao, HE Qingyong, QU Yi, et al. Molecular mechanism of ZHIZHU pill in treatment of dyslipidemia based on network pharmacology[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology,2019,21(11):2396−2405.] DAN Wenchao, HE Qingyong, QU Yi, et al. Molecular mechanism of ZHIZHU pill in treatment of dyslipidemia based on network pharmacology[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology, 2019, 21(11): 2396−2405.
[35] LI Y, KANG X, LI Q, et al. Anti-hyperuricemic peptides derived from bonito hydrolysates based on in vivo hyperuricemic model and in vitro xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity[J]. Peptides,2018,107:45−53. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2018.08.001
[36] OWEN P L, JOHNS T. Xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of northeastern north American plant remedies used for gout[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,1999,64(2):149−160. doi: 10.1016/S0378-8741(98)00119-6
[37] 潘莹, 程时锋. 燕麦基因组学研究进展[J]. 植物遗传资源学报,2021,22(2):304−308. [PAN Ying, CHENG Shifeng. Research progress on oat genomics study[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources,2021,22(2):304−308.] PAN Ying, CHENG Shifeng. Research progress on oat genomics study[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2021, 22(2): 304−308.
[38] 张曼, 张美莉, 郭军, 等. 中国燕麦分布、生产及营养价值与生理功能概述[J]. 内蒙古农业科技,2014(2):116−118,126. [ZHANG Man, ZHANG Meili, GUO Jun, et al. Summary of distribution, production, nutritional and physiological value of Avena sativa L. in China[J]. Journal of Northern Agriculture,2014(2):116−118,126.] ZHANG Man, ZHANG Meili, GUO Jun, et al. Summary of distribution, production, nutritional and physiological value of Avena sativa L. in China[J]. Journal of Northern Agriculture, 2014(2): 116−118,126.
[39] LOSKUTOV I G, GNUTIKOV A A, BLINOVA E V, et al. The origin and resource potential of wild and cultivated species of the genus of oats (Avena L.)[J]. Russian Journal of Genetics,2021,57(6):642−661. doi: 10.1134/S1022795421060065
[40] 郭明荣. 计算机辅助的蛋白质虚拟酶解和降血压肽构效机理研究及筛选[D]. 上海:华东理工大学, 2015. [GUO Mingrong. Computer-aided protein virtual enzymatic hydrolysis and study on the mechanism of ACE inhibitory peptides and their screening[D]. Shanghai:East China University of Science and Technology, 2015.] GUO Mingrong. Computer-aided protein virtual enzymatic hydrolysis and study on the mechanism of ACE inhibitory peptides and their screening[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2015.
[41] FITZGERALD R J, CERME O M, KHALESI M, et al. Application of in silico approaches for the generation of milk protein-derived bioactive peptides[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,64:103636. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103636
[42] YU Z, CAO Y, KAN R, et al. Identification of egg protein-derived peptides as xanthine oxidase inhibitors:Virtual hydrolysis, molecular docking, and in vitro activity evaluation[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2022,11(6):1591−1597. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.06.017
[43] MUDGIL P, KILARI B P, KAMAL H, et al. Multifunctional bioactive peptides derived from quinoa protein hydrolysates:Inhibition of α-glucosidase, dipeptidyl peptidase-IV and angiotensin I converting enzymes[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2020,96:103130. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2020.103130
[44] FUENTES L R, RICHARD C, CHEN L. Sequential alcalase and flavourzyme treatment for preparation of α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)-IV inhibitory peptides from oat protein[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2021,87:104829. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104829
[45] ZHAO L, AI X, PAN F, et al. Novel peptides with xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity identified from macadamia nuts:Integrated in silico and in vitro analysis[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2022,248(8):2031−2042. doi: 10.1007/s00217-022-04028-5
[46] WOITISKI C B, NEUFELD R J, RIBEIRO A J, et al. Colloidal carrier integrating biomaterials for oral insulin delivery:Influence of component formulation on physicochemical and biological parameters[J]. Acta Biomaterialia,2009,5(7):2475−2484. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2009.03.007
[47] HONG S-M, TANAKA M, KOYANAGI R, et al. Structural design of oligopeptides for intestinal transport model[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2016,64(10):2072−2079. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00279
[48] SHEN W, MATSUI T. Current knowledge of intestinal absorption of bioactive peptides[J]. Food & Function,2017,8(12):4306−4314.
[49] SWEENEY P J, WALKER J M. Proteinase K (EC 3.4. 21.14)[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology,1993,16:305−311.
[50] ZHOU C, LI R, ZHANG S, et al. Association between serum albumin and new-onset hyperuricemia among participants with hypertension[J]. Precision Nutrition,2023,2(1):e00027.
[51] WENJING F, TINGTING T, QIAN Z, et al. The role of IL-1β in aortic aneurysm[J]. Clinica Chimica Acta,2020,504:7−14. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.01.007
[52] 曹文琼, 黄新梅, 高红梅, 等. 抑制NLRP3/IL-1β信号通路对高尿酸血症CKD大鼠肾功能的影响[J]. 西部医学,2023,35(6):830−836. [CAO Wenqiong, HUANG Xinmei, GAO Hongmei, et al. Effects of inhibition of NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway on renal function in hyperuricemic CKD rats[J]. Medical Journal of West China,2023,35(6):830−836.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2023.06.009 CAO Wenqiong, HUANG Xinmei, GAO Hongmei, et al. Effects of inhibition of NLRP3/IL-1β signaling pathway on renal function in hyperuricemic CKD rats[J]. Medical Journal of West China, 2023, 35(6): 830−836. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2023.06.009
[53] KRISHNAN S M, LING Y H, HUUSKES B M, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome reduces blood pressure, renal damage, and dysfunction in salt-sensitive hypertension[J]. Cardiovascular Research,2019,115(4):776−787. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy252
[54] LEO C, CHEN J D. The SRC family of nuclear receptor coactivators[J]. Gene,2000,245(1):1−11. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00024-X
[55] DASGUPTA S, LONARD D M, O'MALLEY B W. Nuclear receptor coactivators:Master regulators of human health and disease[J]. Annual Review of Medicine,2014,65:279−292. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-051812-145316
[56] KIM D H, CHOI H I, PARK J S, et al. Src-mediated crosstalk between FXR and YAP protects against renal fibrosis[J]. FASEB Journal,2019,33(10):11109−11122. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900325R
[57] YAN Y, MA L, ZHOU X, et al. Src inhibition blocks renal interstitial fibroblast activation and ameliorates renal fibrosis[J]. Kidney International,2016,89(1):68−81. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.293
[58] SUZUKI T, ICHII O, NAKAMURA T, et al. Immune-associated renal disease found in caspase 3-deficient mice[J]. Cell and Tissue Research,2020,379(2):323−335. doi: 10.1007/s00441-019-03084-w
[59] PAN J, SHI M, GUO F, et al. Pharmacologic inhibiting STAT3 delays the progression of kidney fibrosis in hyperuricemia-induced chronic kidney disease[J]. Life Sciences,2021,285:119946. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119946
[60] 吴冕, 陈海冰. 高尿酸血症与癌症[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志,2016,32(5):429−432. [WU Mian, CHEN Haibing. Hyperuricemia and cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism,2016,32(5):429−432.] doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2016.05.018 WU Mian, CHEN Haibing. Hyperuricemia and cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, 2016, 32(5): 429−432. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2016.05.018
[61] XIE Y, XU P, LIU K, et al. Hyperuricemia and gout are associated with cancer incidence and mortality:A meta-analysis based on cohort studies[J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology,2019,234(8):14364−14376. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28138
[62] MENG J, LÜ Q, SUI A, et al. Hyperuricemia induces lipid disturbances by upregulating the CXCL-13 pathway[J]. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2022,322(2):G256−g267. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00285.2021
[63] JAYACHANDRAN M, QU S. Harnessing hyperuricemia to atherosclerosis and understanding its mechanistic dependence[J]. Medicinal Research Reviews,2021,41(1):616−629. doi: 10.1002/med.21742
[64] HE W, SU G, SUN-WATERHOUSE D, et al. In vivo anti-hyperuricemic and xanthine oxidase inhibitory properties of tuna protein hydrolysates and its isolated fractions[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,272:453−461. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.057
[65] HUANG X N, ZHANG Y M, WEN Y, et al. Protease-catalyzed rational synthesis of uric acid-lowering peptides in non-aqueous medium[J]. International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics,2022,28(2):61. doi: 10.1007/s10989-022-10367-4
[66] 胡晓, 周雅, 杨贤庆, 等. 食物蛋白源降尿酸活性肽的研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(4):287−293. [HU Xiao, ZHOU Ya, YANG Xianqing, et al. Research progress on anti-hyperuricemic peptides obtained from food proteins[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(4):287−293.] HU Xiao, ZHOU Ya, YANG Xianqing, et al. Research progress on anti-hyperuricemic peptides obtained from food proteins[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(4): 287−293.
-
期刊类型引用(17)
1. 李柏阳,李国巍,姬妍茹,董艳,魏连会,杨庆丽,张正海,石杰. 基于SPME-GC-MS技术分析黑海棠果加工前后挥发性香气成分. 中国食品添加剂. 2025(01): 136-143 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘洋,迟明,张艳珍,王菲,白家瑞. 牦牛肉膨化薯片配方工艺优化及其食用品质分析. 高原农业. 2025(01): 112-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 潘国杨,王亚琦,邓丽,童星,晏春悦,安飞宇,姜锦惠,乌日娜,武俊瑞. 嗜盐四联球菌源鲜味肽的呈味特性及其稳定性. 食品科学. 2025(05): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王岸娜,李胜强,吴立根. 杂粮粉对面团特性及烤饼品质的影响. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(01): 90-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 罗东辉,陈淇,董浩. 潮州咸菜发酵工艺优化及其品质研究. 中国调味品. 2024(05): 142-147 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 孟德梅,贾子怡,李书红. 食品工程专业学位硕士研究生案例教学模式探讨——以“食品感官评价”课程为例. 农产品加工. 2024(10): 121-124 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 田师一,姜国新,毛岳忠,秦玉梅,石双妮,曹艳芸,秦子涵,韩剑众,程时文. 食品智能感知技术的发展与前沿探索. 中国食品学报. 2024(06): 1-11 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 胡紫倩,王嘉,谭欣,何文佩,时小东. 基于智能感官评价技术的苦荞米饭差异分析. 食品科技. 2024(07): 163-170 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 柳泽洋,张钊,王才立,张兆兴,李翠芳,史晓斐. 蛋白棒的研发及配方优化. 食品工业. 2024(08): 13-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 丁亚欣,陆冰怡,刘宝林,魏紫莹,刘志东. 贮藏温度和时间对麻辣蛤蜊罐制品贮藏期间品质的影响. 包装工程. 2024(19): 215-222 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 何洪,王蓓蓓,胡敢,王金秋,耿放. 新形势下食品感官评价的教学改革与实践. 中国食品工业. 2024(18): 138-140 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 项雅科,张瑶,钟葵,赵镭,云振宇,陈剑,汪厚银,胡馨予,邱志平,王晶岩,史波林. 基于适合项评级法和多元统计分析五常大米的优势食味品质. 食品科学. 2024(22): 2201-2207 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 李欣怡,孙翔宇,张文慧,张敏,彭雯,张春玲,马婷婷. 家庭贮藏条件下‘翠香’猕猴桃果实品质演变规律解析. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(22): 19-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 龙门,于士军,周頔,詹歌. OBE理念下学生课程成绩考核体系评价与改进. 保山学院学报. 2024(05): 86-92 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 周海伦,曾月,周浩,黄祖波,王超,黄勤挽. 一种基于安神药方的功能性饼干的制备工艺优化. 保鲜与加工. 2024(10): 67-73 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 王睿,彭郁,单子明,李茉,温馨,倪元颖. 植物基肉制品的减钠策略研究进展. 食品科学. 2024(24): 367-376 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 顾嘉慧,曹园,邵娟娟. 响应面结合模糊数学感官评价法探究泥鳅血管紧张素转化酶抑制肽脱苦工艺. 食品科技. 2024(11): 182-191 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(8)





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



