Colorimetric Biosensor Based on Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8 for the Detection of Total Antioxidant Capacity in Beverages
-
摘要: 食品的总抗氧化能力是评价其功效的关键指标之一,建立快速灵敏的分析方法用于食品总抗氧化能力检测具有十分重要的意义。本文首次设计合成了一种具有类过氧化物酶活性的金属-有机框架复合物纳米酶(Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8),并对其形貌、结构及催化活性进行了详细表征。结果表明,Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8是一种具有二维超薄片层结构的纳米酶,计算得到Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8纳米酶对H2O2的Km和Vmax分别为0.67 mmol/L和3.55×10−8 mol/L·s−1。进一步以抗坏血酸(Ascorbic acid,AA)作为典型抗氧化剂,基于其对纳米酶催化显色反应的抑制作用,构建了一种高效的可视化传感器方法。系统验证表明,该可视化传感器检测限低(1.67 μmol/L),线性范围宽(5.0~3000.0 μmol/L),准确度高(回收率为98.62%~103.13%)。利用此传感器对不同饮料的总抗氧化能力进行检测,结果与样品标示值基本一致。因此,本研究为食品总抗氧化能力的评价提供了一种简单、快捷、有效的可视化新方法。Abstract: Total antioxidant capacity of food is one of the critical parameters to evaluate its efficacy. Establishment of a fast and sensitive analytical method for the detection of total antioxidant capacity of food has great significance. In this paper, a metal-organic framework complex nanozyme (Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8) with peroxidase-like activity was firstly designed and successfully synthesized. Then, the morphology, structure and catalytic activity were characterized in detail. The results showed that Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8 possessed a two-dimensional ultra-thin layer structure while its Km and Vmax values towards H2O2 were 0.67 mmol/L and 3.55×10−8 mol/L·s−1, respectively. Ascorbic acid (AA) as a typical antioxidant, an efficient colorimetric biosensor was constructed based on its inhibitory effect on chromogenic reaction catalyzed by nanozyme. Comprehensive validation showed that the colorimetric biosensor had low limit of detection (1.67 μmol/L), wide linear range (5.0~3000.0 μmol/L) and high accuracy (recovery rate of 98.62%~103.13%). By using this colorimetric method, total antioxidant capacity of different beverages was detected and the obtained results were basically consistent with labeled values. Therefore, this study provided a simple, fast and effective colorimetric method for the evaluation of the total antioxidant capacity of food.
-
近年来,功能性食品的开发如火如荼,其中抗氧化是市场最重要的功能性诉求之一,因此食品的总抗氧化能力是评价其功效的关键指标之一。总抗氧化能力(Total antioxidant capacity,TAC)是指体系中各种抗氧化物质和抗氧化酶等构成的总抗氧化水平,如抗氧化物酶、维生素C、维生素E和胡萝卜素等。TAC是一种抗氧化剂估算模型,可以作为评估实际样品中抗氧化剂含量的综合参数[1−2],也是评估抗氧化食品质量的重要指标。抗坏血酸(Ascorbic acid,AA)可作为一种典型的抗氧化剂,通常作为代表可用于评价多种食品的TAC,特别是饮料样品。AA是一种水溶性维生素,存在于多种果蔬中,它是维持人类健康的必需营养素,摄取足够的AA对保持人体健康至关重要[3]。因此,开发一种简便灵敏的AA检测方法对于评价食品的TAC具有十分重要的意义。
目前已报道的AA检测方法包括电化学法[4]、液相色谱法[5]、荧光法[6]和可视化传感法等[7]。其中,可视化传感法因其灵敏度高、成本低、操作简单而受到越来越多的关注,引入功能多样化的新型纳米材料构建高灵敏的可视化传感器已经成为食品分析领域的研究热点。纳米酶作为一种代表性纳米材料,它是具有类似于天然酶活性的纳米材料,因其具有活性高、成本低、稳定性好、制备方便、易于修饰等无可比拟的优点而备受关注[8]。依据类酶活性进行分类,纳米酶包括:过氧化物酶类似物、氧化酶类似物、过氧化氢酶类似物、超氧化物歧化酶类似物等[9]。其中,多种具有类酶活性的纳米材料已用于食品TAC的测定,如:具有增强过氧化物酶活性的分层多孔S/N共掺杂碳纳米酶以AA为典型模型用于测定商业饮料的总抗氧化能力[10];高效碳负载Co-Ir过氧化物酶测定水果的总抗氧化能力[11];铁锰双金属氧化酶类纳米酶测定果蔬食品中的总抗氧化能力[12]。金属有机骨架(Metal organic frameworks,MOFs)基纳米酶以其良好的类酶特性和材料本身可控孔径大小和表面化学性质、超高表面积和空隙率、以及结构多样性等优势在纳米酶研究领域内大放异彩,但这类材料易受结块和分散性差的影响,对其模拟酶活性有所限制[13]。因此,如何提高MOFs基纳米酶的类酶活性是当前纳米酶研究的难点之一。
本研究通过合成沸石咪唑骨架-8(Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8,ZIF-8)分散的二维铁-2,3,6,7,10,11-六羟基三亚苯基纳米酶(Iron-2,3,6,7,10,11-hexahydroxytriphenylene,Fe-HHTP)的方法来制备MOFs基纳米酶复合物Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8,实现其模拟过氧化物酶活性的提高,进一步结合Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8出色的催化能力和AA对显色体系的抑制作用,设计一种新型比色传感方法,快速、准确地测定食品中AA含量,并评价其抗氧化能力,为食品中AA的检测及抗氧化能力评价提供一种新方法。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
六水氯化铁(FeCl3∙6H2O,99%) 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;2,3,6,7,10,11-六羟基三亚苯(HHTP,97%) 上海笛柏生物科技有限公司;过氧化氢溶液(AR,30% w/w) 天津天力化学试剂有限公司;二甲基亚砜(DMSO,AR,99.5%)、甲醇(AR,99.7%)、无水乙酸钠(AR,99%)、无水乙醇(AR,99.7%)、冰醋酸(AR,99.5%)、盐酸(GR,36%~38%)、氯化钠(AR,99.8%)、氯化钾(AR,99.8%)、氯化钙(AR,96%)、六水硝酸锌(AR,99%)、氯化镁(AR,98%)、葡萄糖(AR)、蔗糖(AR)、抗坏血酸(AA,AR,99.7%) 上海国药集团化学试剂有限公司;三羟甲基氨基甲烷(Tris,99.5%) 北京兰杰柯科技有限公司;2-甲基咪唑(98%)、邻苯二胺(OPD,99%)、2,2'-联氮双-3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸(ABTS,98%) 上海阿拉丁化学有限公司;3,3',5,5'-四甲基联苯胺(TMB,BR,99%)、苹果酸(BR,99%)、甘氨酸(AR,99%)、L-亮氨酸(BR,98%)、L-赖氨酸(BR,99%) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;四种市售饮料(果粒橙、怡泉+C汽水、C维他命水、水溶C100) 湖北省武汉市永旺超市。
ThermoStat C恒温孵育仪 德国Eppendorf公司;HS-10磁力加热搅拌台 德国IKA工业设备集团;FiveEasy Plus pH计 美国Mettler Toledo集团;TGL-16高速台式冷冻离心机 长沙英泰仪器有限公司;JEM-2100F透射电子显微镜 日本JEOL公司;D8 Advanced X-射线粉末衍射仪 德国Bruker公司;SCIENTIFIC E SCALAB 250Xi X-射线光电子能谱仪、Evolution 220紫外分光光度计 美国赛默飞公司;DZF-6050真空干燥箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 Fe-HHTP@ ZIF-8的合成
Fe-HHTP的合成:根据前人文献[14]制备并进行少量修改。首先将202.73 mg六水氯化铁(FeCl3·6H2O,10.0 mmol/L)溶解于75.0 mL去离子水中,81.08 mg 2,3,6,7,10,11-六羟基三亚苯(HHTP,10.0 mmol/L)溶解于25.0 mL二甲基亚砜(DMSO)中。然后,将HHTP溶液加入到铁溶液中,得到的混合溶液搅拌(800 r/min)10 min。随后,用Tris-HCl缓冲液(20 mmol/L,pH8.0)将上述混合溶液的pH调整到7.4,室温下搅拌(800 r/min)1 h,然后离心(8000 r/min,10 min),用甲醇和水分别洗涤3次,最后真空干燥8 h,得到Fe-HHTP。
ZIF-8的合成:根据文献[15],将1.78 g六水合硝酸锌(Zn(NO3)2·6H2O,6.0 mmol/L)和2.96 g 2-甲基咪唑(36.0 mmol/L)分别溶解于120.0 mL甲醇中。将锌溶液加入到2-甲基咪唑溶液中,得到的混合溶液在室温下搅拌(800 r/min)3 h,8000 r/min离心5 min,甲醇洗涤3次,并在70 ℃干燥5 h,得到ZIF-8纳米颗粒。
Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8的合成:根据文献[13]制备并进行少量修改。将40.0 mL 2.175 mg/mL的ZIF-8分散液加入到40.0 mL 2.0 mg/mL的Fe-HHTP分散液中,30 ℃水浴搅拌12 h,然后离心(8000 r/min,10 min),用去离子水:甲醇为1:1的混合溶液洗涤3次,真空干燥即可。
Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8的表征:使用多种仪器对Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8的形貌和结构进行全面表征。利用透射电镜(TEM,JEM-2100 F)对Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8的整体形貌进行表征;利用EDS元素图(JEM-2100 F TEM)对五种元素(C、O、N、Zn、Fe)进行可视化分析;利用X射线粉末衍射(XRD,D8 Advanced)对晶体结构进行表征;利用X射线光电子能谱(XPS,Thermo SCIENTIFIC E SCALAB 250Xi)鉴定合成材料的化学成分和价电子态;利用紫外可见光谱(Evolution 220)测定Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8的过氧化物酶活性。
1.2.2 Fe-HHTP@ ZIF-8纳米酶的过氧化物酶活性
为了探究Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8纳米酶的过氧化物酶样活性,以H2O2和TMB为底物,充分考察了pH、温度和孵育时间对该纳米酶催化活性的影响。将50.0 μL Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8(1.0 mg/mL)、40.0 μL TMB(5.0 mg/mL)和40.0 μL H2O2(1.0 mmol/L)混合在870.0 μL不同pH(2.6、3.0、3.6、4.0、4.6、5.0、5.6、6.0、6.6)的乙酸缓冲液(0.2 mol/L)中,并在37 ℃条件下孵育8 min。同样,为了探究温度的影响,固定乙酸缓冲液的pH为3.6和孵育时间为8 min不变,改变混合物在不同温度(20、25、30、37、45、55、60、70 ℃)下反应。此外,固定乙酸缓冲液的pH为3.6和反应温度为37 ℃不变,将Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8、TMB、H2O2和乙酸缓冲液的混合物孵育不同时间(1~13 min),探讨时间的影响。反应后,用紫外-可见光谱法测定不同溶液在652 nm处的吸光度。在最佳条件下,比较ZIF-8、Fe-HHTP和Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8的过氧化物酶模拟物活性。此外,以OPD和ABTS为底物测试Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8的过氧化物酶活性,利用40.0 μL OPD(5.0 mg/mL)或利用40.0 μL ABTS(20.0 mg/mL)代替40.0 μL TMB(5.0 mg/mL),测定反应液在300~600 nm范围内的紫外吸收信号。
在最佳pH和温度条件下,通过改变H2O2浓度和TMB浓度,评估了稳态动力学参数,包括Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8纳米酶的Michaelis-Menten常数(Km)和最大反应速度(Vmax)。改变TMB溶液或H2O2溶液的浓度,具体而言,进行两个系列实验,分别将40.0 μL H2O2溶液(1.0 mmol/L)和40.0 μL不同浓度TMB溶液(0.0~10.0 mmol/L)加入到870.0 μL乙酸缓冲液(0.2 mol/L,pH3.6)中混合,或将40.0 μL TMB溶液(5.0 mg/mL)和40.0 μL不同浓度H2O2溶液(0~1.0 mmol/L)加入到870.0 μL乙酸缓冲液(0.2 mol/L,pH3.6)中混合,再加入50.0 μL Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8(1.0 mg/mL),37 ℃孵育8 min,在652 nm处用紫外分光光度计测定溶液吸光度。
根据Michaelis-Menten方程和Lineweaver-Burk倒数方程确定各底物的两个酶学参数(Km和Vmax):
1v=KmVmax×1[S]+1Vmax 式中,Km和Vmax分别为Michaelis常数和最大反应速率;[S]为底物浓度;v为反应速率。
1.2.3 可视化传感器测定AA
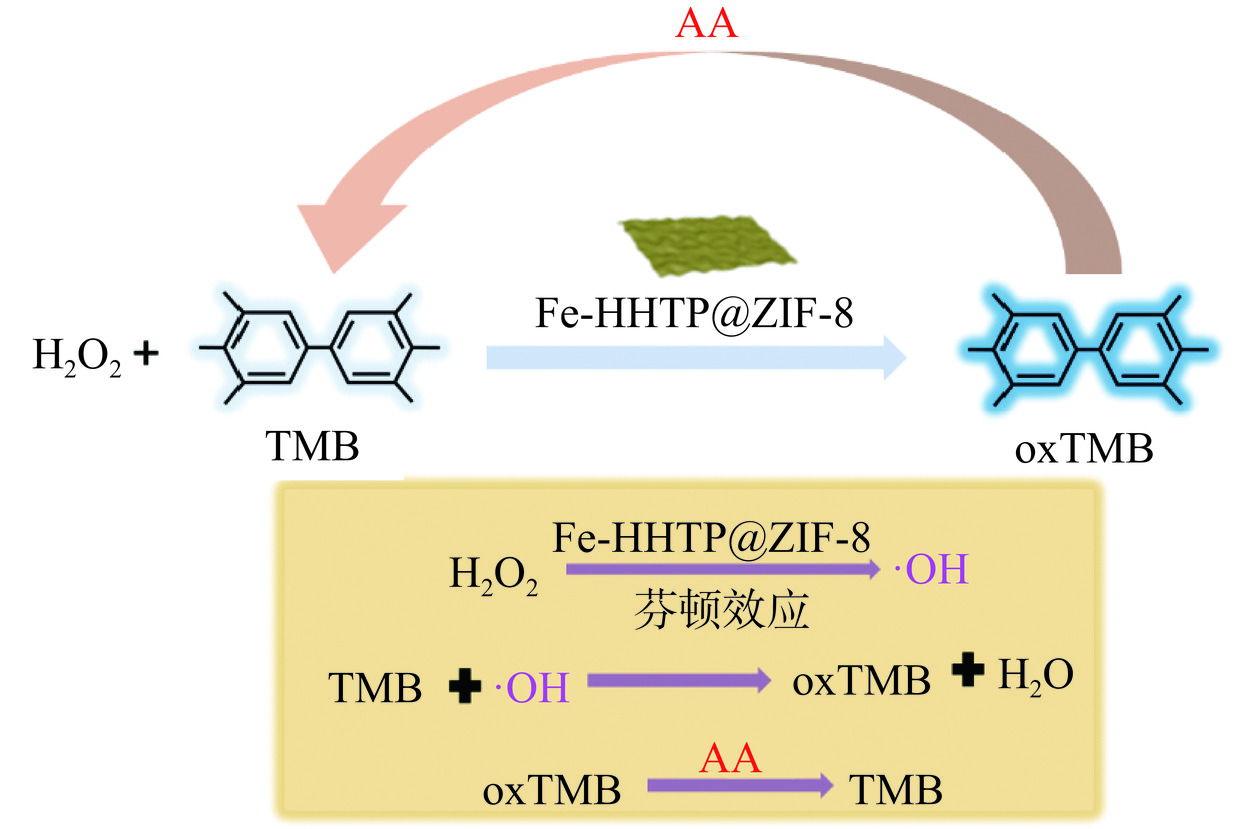
如图1所示,Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8具有过氧化物酶活性,无色TMB在过氧化物酶催化的过氧化氢反应中可被氧化成相应的氧化物oxTMB,产物oxTMB 呈蓝色,利用AA的还原作用,使蓝色物质被还原为无色,构建了一种可视化检测AA的方法[16]。具体步骤如下:在最佳反应条件下,50 μL Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8纳米酶(1.0 mg/mL)加入到820 μL的乙酸缓冲溶液(pH3.6,0.2 mol/L)中,然后依次加入40 μL H2O2溶液(1.0 mmol/L),40 μL TMB溶液(5.0 mg/mL)和50 μL不同浓度的AA溶液(5.0~3000.0 μmol/L),37 ℃孵育8 min,反应结束后,用手机记录不同溶液的颜色,在652 nm的波长下使用紫外分光光度计测定其吸光度,处理获得的数据以计算AA的标准曲线和检测限(LOD)。
此外,对三种不同浓度的AA溶液标准样品(40、100、400 μmol/L)进行3次测定,将测得的结果与标准曲线的计算结果进行准确性分析以获得回收率并评价准确性。对AA标准样品(40.0 μmol/L)进行6次重复分析,以验证重现性。为了验证选择性,通过该比色生物传感器测量了一些可能的干扰化合物(配制浓度为500.0 μmol/L)。
1.2.4 饮料中AA的检测
实际样品包括四种饮料(果粒橙、怡泉+C汽水、C维他命水和水溶C100),均购自当地超市,在通过该可视化传感器法准确测定实际饮料样品中的AA之前,根据先前的文献[17]对购买的饮料进行预处理。因为饮料属于人工合成的产物,所含成分种类不多,这四种饮品(果粒橙、怡泉+C汽水、C维他命水和水溶C100)均采用超纯水稀释10倍后即可放置备用。
1.3 数据处理
本研究实验重复次数为6次,所有实验数据采用Excel 2019 软件进行整理,使用Origin 2018进行分析作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 Fe-HHTP@ ZIF-8的合成与表征
本研究将ZIF-8用于分散Fe-HHTP的良好载体,通过简单搅拌的一步合成法制得Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8,该方法具有操作简单、安全性高、能耗低等优点。
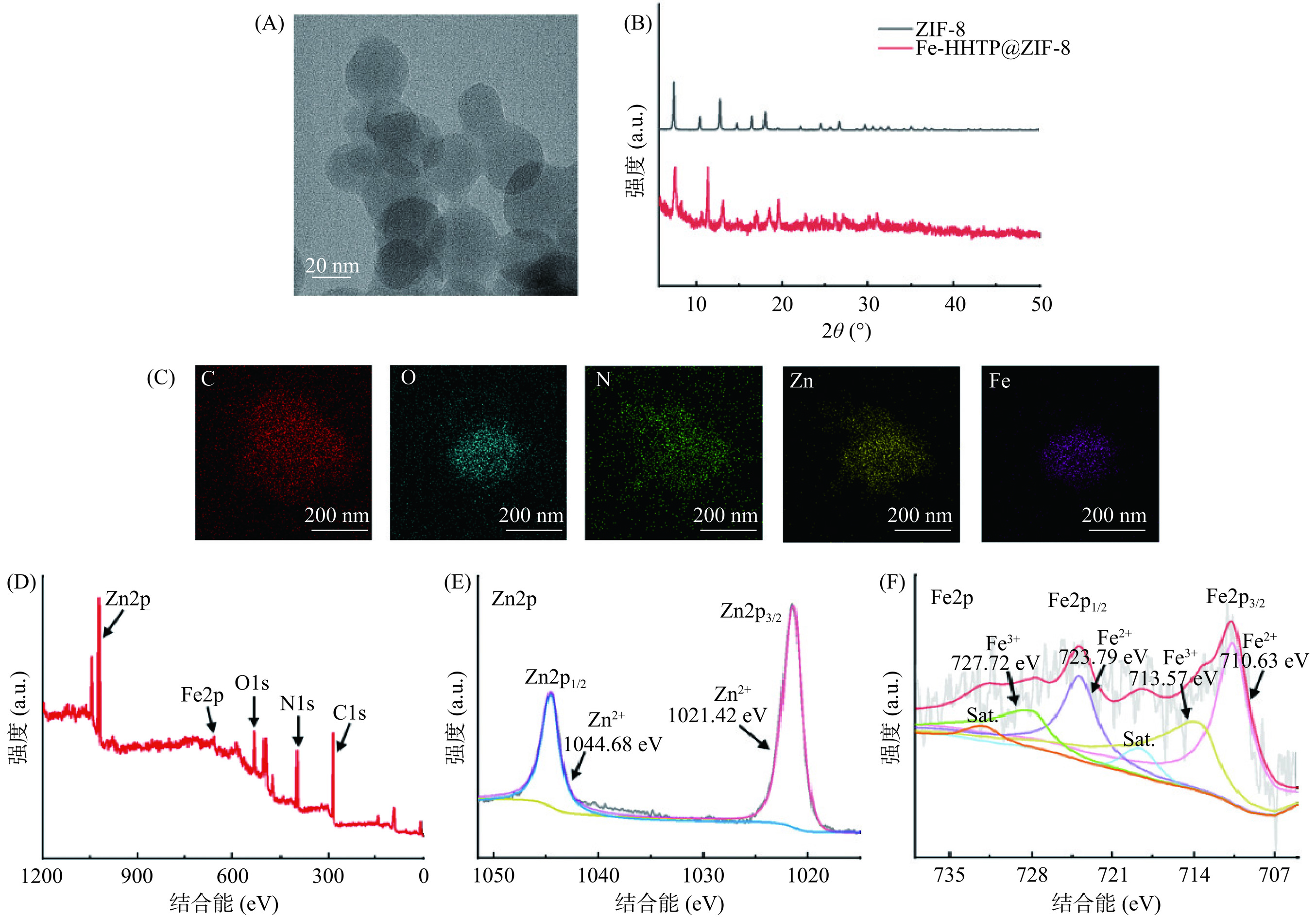
通过TEM、XRD、元素映射图谱和XPS对Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8的形貌和结构进行了表征。如图2A的TEM图像所示,可以观察到Fe-HHTP@ ZIF-8为圆形颗粒,灰色透明层代表的是二维超薄片层结构。图2B中的XRD图像显示Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8保持与ZIF-8对应的高分辨率衍射峰,但由于Fe-HHTP无定形物的影响,导致其他的峰出现[18]。图2C中的TEM元素图谱分析了Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8中五种元素(C、O、N、Zn和Fe)的均匀分布。此外,利用XPS鉴定了合成材料的化学组成,如图2D所示,Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8纳米片的XPS呈现五个峰,分别对应于Zn2p、Fe2p、O1s、N1s和C1s的特征峰。如图2E所示,Zn元素在1021.42和1044.68 eV出现双峰,对应于Zn2p3/2峰和Zn2p1/2峰。如图2F所示,在高分辨率Fe2p光谱中,710.63、713.57、723.79和727.72 eV处出现的四个峰,分别属于FeII2p3/2、FeIII2p3/2、FeII2p1/2和FeIII2p1/2峰,此外,还有两个小卫星峰,可能属于Fe3+[19],这些峰表明Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8中的Fe元素以Fe2+和Fe3+的形式存在。
2.2 Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8模拟过氧化物酶活性
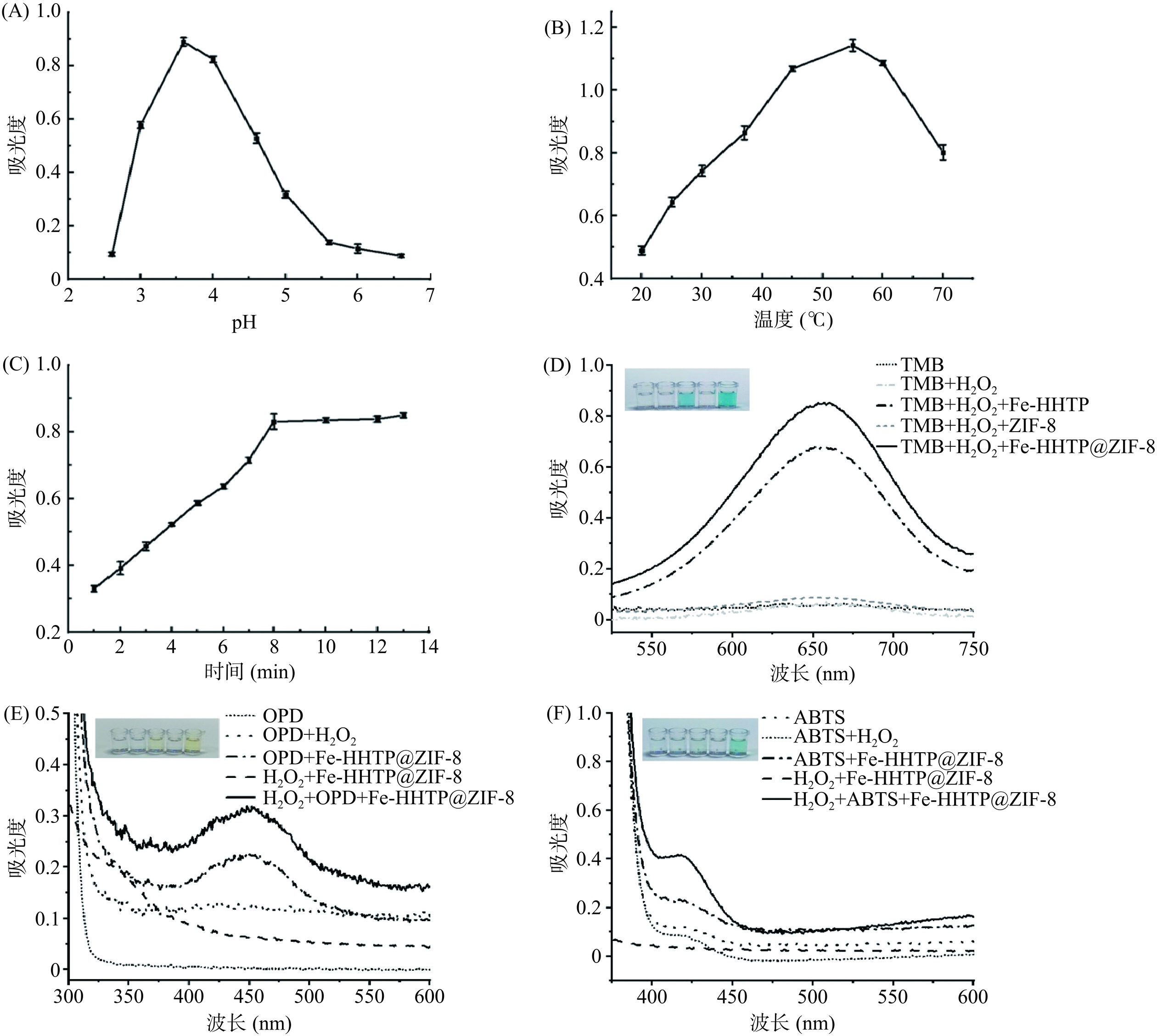
以TMB和H2O2为底物,综合考察了Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8的模拟过氧化物酶活性,探讨了pH(2.6~6.6)、反应温度(20~70 ℃)和孵育时间(1~13 min)对Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8纳米酶催化活性的影响。如图3A所示,在pH3.6时Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8表现出最佳的催化活性,而在强酸或接近中性条件下的催化活性下降。这一结果与本课题组合成的其他类过氧化物酶材料基本一致[20−22]。这种变化可以通过pH对材料表面电荷的影响以及Fe2+与H2O2之间的Fenton反应来解释[23−24]。
从图3B所示反应温度的影响来看,在20~55 ℃范围内,Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8表现出的催化活性逐渐上升,55 ℃时催化活性最高,之后活性逐渐下降。55 ℃前的升高趋势可能与分子热运动加剧有关,高于55 ℃时的下降趋势可能与H2O2的分解有关。考虑到实验的温和性和与其他纳米酶催化活性的可比性,因此,本研究选择37 ℃作为最佳反应温度。图3C显示了孵育时间对Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8过氧化物酶活性的影响。紫外吸光度在1~8 min有明显的上升趋势,在8~13 min基本维持稳定。考虑到实验的便捷性和温和性,最后选择pH3.6、37 ℃和孵育时间8 min作为显色反应的最佳优化条件。图3D比较了最佳条件下Fe-HHTP,ZIF-8和Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8的过氧化物酶活性,Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8较Fe-HHTP和ZIF-8而言,活性显著提升,说明用ZIF-8作为Fe-HHTP的分散剂,使得Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8在溶剂中的分散性更好,更多的活性位点暴露出来,这可以显著提高Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8的过氧化物酶活性[13,25−26]。根据图3E~F,以OPD和ABTS为底物进一步验证了Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8具有优异的过氧化物酶活性[27]。
在优选条件下,通过单独改变H2O2或TMB的浓度来研究稳态动力学(图4A~B),旨在评价Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8的催化性能。根据Michaelis-Menten方程,计算得到Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8纳米酶对H2O2的Km和Vmax分别为0.67 mmol/L和3.55×10−8 mol/L·s−1,该Km值远低于辣根过氧化物酶(Horseradish peroxidase,HRP)和其他纳米酶的Km值[28−31],说明Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8与H2O2之间具有良好的亲和力;根据Michaelis-Menten方程,计算得到Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8纳米酶对TMB的Km和Vmax分别为20.75 mmol/L和8.92×10−8 mol/L·s−1,该Km值远高于HRP和其他纳米酶的Km值[28−31],说明Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8与TMB之间的亲和力较弱。根据表1比较可知,Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8具有优异的过氧化物酶催化性能。Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8催化性能的优越性可能归因于两个原因:一是ZIF-8的加入提高了Fe-HHTP在溶剂的分散性;二是二维纳米片结构赋予了该材料具有更大的表面积和更多的表面活性位点暴露量[32−33]。
表 1 不同纳米酶及辣根过氧化物酶的催化活性比较Table 1. Comparison of catalytic activities of different nanozymes and horseradish peroxidase2.3 AA的比色测定及总抗氧化能力评价
基于纳米酶Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8具有优异的类过氧化物酶活性,本研究建立了一种用于AA检测的比色方法,用于评价市售饮料的总抗氧化能力。如图1机理图所示,无色TMB在Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8催化的H2O2反应中可被氧化成相应的氧化物oxTMB,产物oxTMB呈蓝色,利用AA的还原作用,使蓝色物质被还原为无色[34−35]。基于上述显色反应的变化,通过测定紫外信号的变化值,实现AA的高灵敏检测。
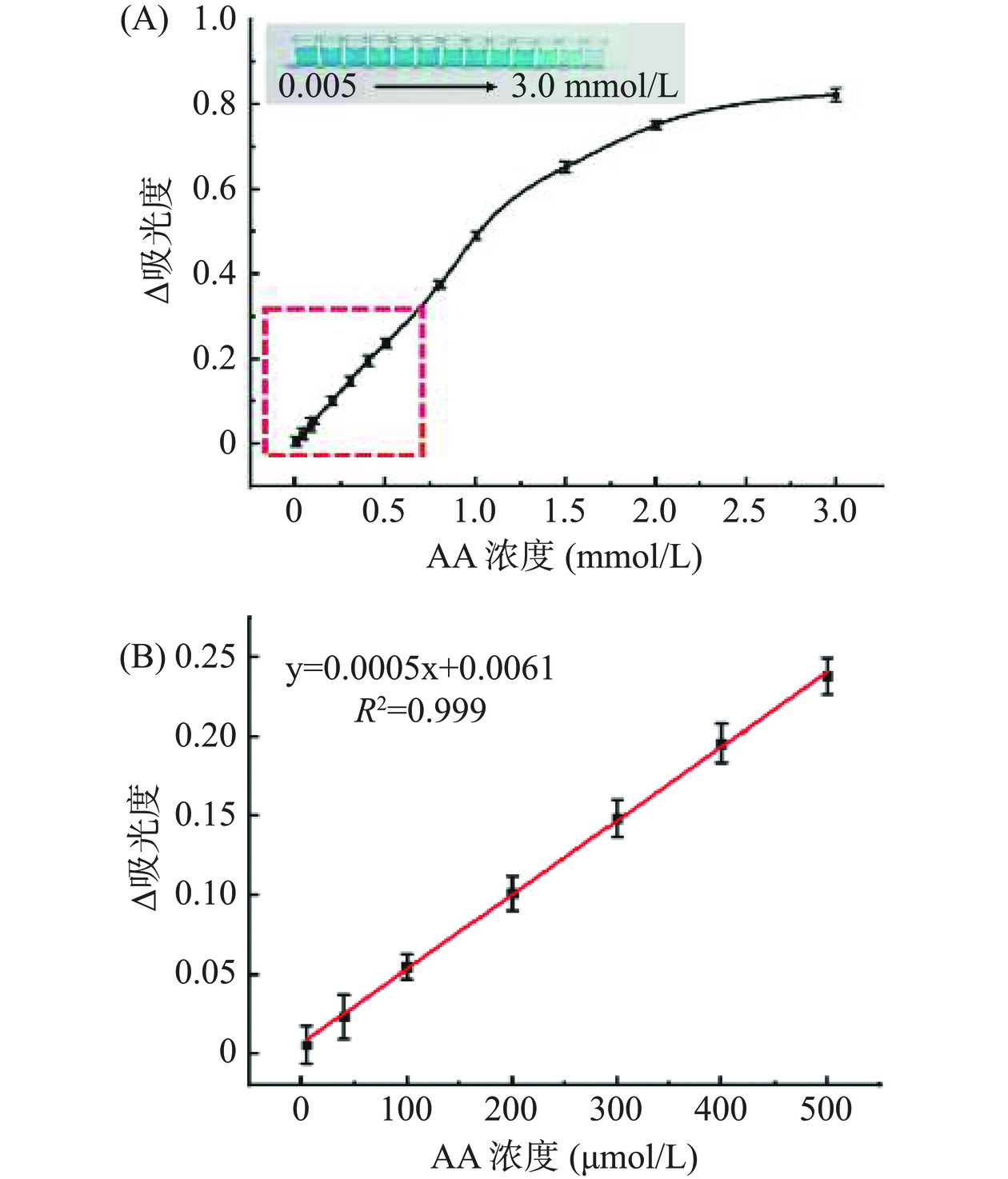
如图5A所示,在5.0~3000.0 μmol/L范围内,随着AA浓度的增加,Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8介导的反应溶液颜色逐渐变为浅蓝色甚至无色,紫外吸光度明显降低。
通过计算紫外吸光度与AA浓度之间的线性关系,证实所得比色体系在5.0~500.0 μmol/L的线性范围内表现出良好的线性响应。如图5B所示,校准曲线方程为ΔA=0.0005C+0.0061(R2=0.999),其中AA浓度(C)为自变量,紫外吸光度(ΔA=A−A0,A和A0分别为标准样品和空白样品在652 nm处的紫外吸光度)为因变量。根据S/N=3计算检测限(LOD)为1.67 μmol/L,由表2可知,本研究所提出的传感系统与其他已报道的AA传感检测方法相比较具有一定的优势。
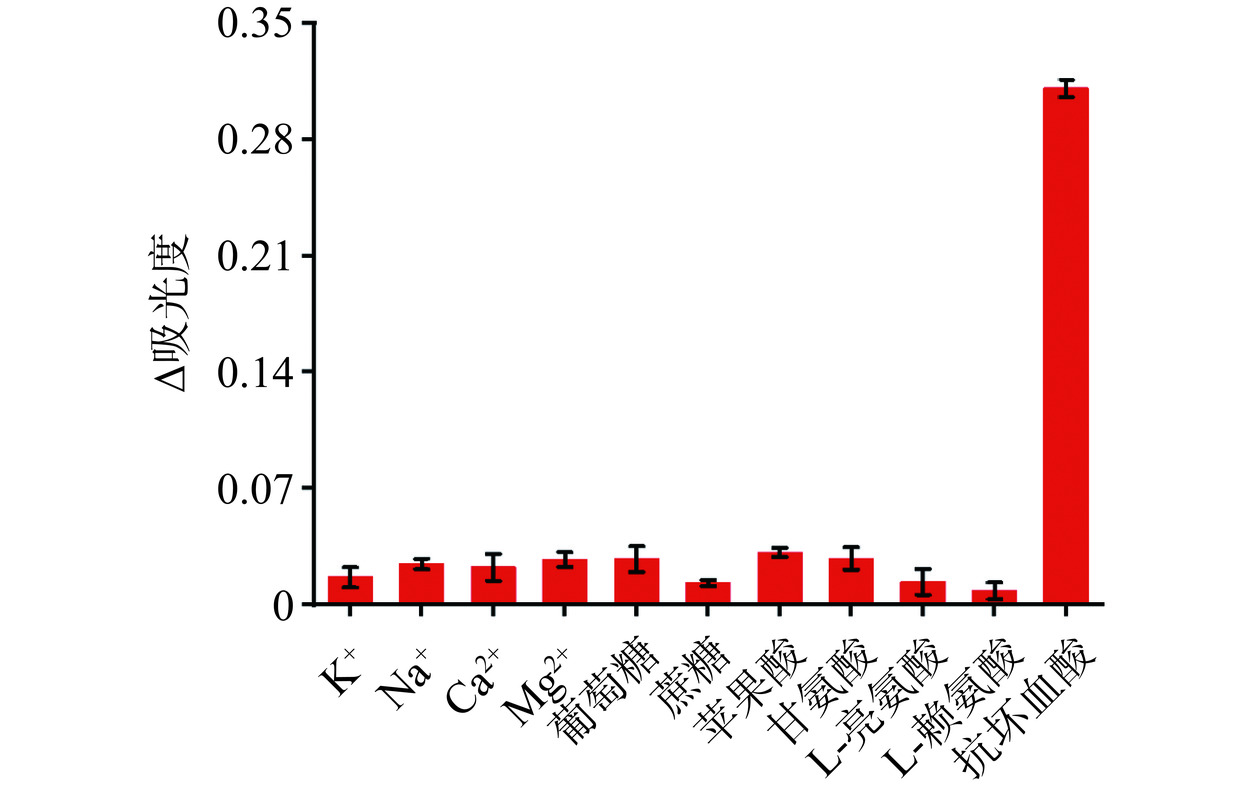
此外,进一步对AA可视化传感器的重现性、准确性和选择性进行了验证。对40.0 μmol/L AA标准样品进行6次重复分析,相对标准偏差(RSD)为2.9%,重现性良好。分析了3种不同浓度的AA标准物(40.0、100.0、400.0 μmol/L),回收率在98.62%~103.13%范围内(表3),表明该比色生物传感器具有良好的准确性。同时,还研究了该生物传感器的选择性。以市售饮料中与抗坏血酸共存的几种组分为干扰物,包括氯化钾(K+)、氯化钠(Na+)、氯化钙(Ca2+)、氯化镁(Mg2+)、葡萄糖、蔗糖、苹果酸、甘氨酸、L-亮氨酸和L-赖氨酸。干扰物质检测浓度设定为500.0 μmol/L,为AA检测线性范围内的上限值。图6显示了在相同条件下,只有AA的吸光度产生显著的变化,而其他干扰物质产生的变化很小,显示了该比色生物传感器对AA检测的高选择性。
表 3 AA检测方法的准确性研究Table 3. Accuracy study of AA determination method样品 加标浓度(μmol/L) 实测浓度(μmol/L) 回收率(%) RSD(%,n=3) 1 40.0 39.80 99.50 1.56 2 100.0 103.13 103.13 1.65 3 400.0 394.47 98.62 2.43 2.4 市售饮料中总抗氧化能力的评价
根据所构建的比色传感体系对实际样品中AA含量进行分析,如图7和表4所示,通过对四种含有AA的饮品进行检测,结果如下:饮料1中AA浓度为45.80±0.01 μmol/L,饮料2中AA浓度为41.13±0.02 μmol/L,饮料3中AA浓度为110.47±0.01 μmol/L,饮料4中AA浓度为135.80±0.01 μmol/L,AA可作为一种抗氧化剂模型,说明饮料4的总抗氧化能力最高,饮料3的总抗氧化能力次之,饮料1和饮料2的总抗氧化能力相对较弱,检测结果与饮料的标示值高度一致,可见该方法对于检测食品中的AA具有良好的应用价值,因此本方法可用于评价实际样品的TAC。
表 4 四种不同品牌饮料样品中AA含量测定Table 4. Determination of AA content in beverage samples of four different brands样品名称 吸光度
(A−A0)标示浓度
(mmol/L)检测浓度
(mmol/L)RSD
(%,n=3)果粒橙 0.029±0.006 42.58 45.80±0.01 1.35 怡泉+C汽水 0.027±0.011 42.58 41.13±0.02 2.46 C维他命水 0.061±0.008 113.56 110.47±0.01 1.84 水溶C100 0.074±0.007 127.59 135.80±0.01 1.07 3. 结论
本研究利用ZIF-8分散Fe-HHTP纳米片,通过简单搅拌的一步合成法制得复合MOF基纳米酶(Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8),并详细表征了其形貌、结构及催化活性,结果表明Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8是一种具有二维超薄片层结构的纳米酶,通过优化选择pH3.6、37 ℃和孵育时间8 min作为其显色反应的最佳条件。与辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)和其他纳米酶相比,Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8纳米酶具有更小的Km,表明Fe-HHTP@ZIF-8纳米酶具有较高的过氧化物酶活性和更好的底物亲和力,基于其良好的催化活性并以AA为典型抗氧化模型,构建了一种检测AA的比色方法,用于市售饮料中AA的定量比色检测和总抗氧化能力评估,回收率在98.62%~103.13%,且与饮料中AA的标示值基本一致。这项研究为食品样品TAC的测定提供了可靠方法和有效手段,为高效纳米酶材料的开发提供了新的思路。
-
表 1 不同纳米酶及辣根过氧化物酶的催化活性比较
Table 1 Comparison of catalytic activities of different nanozymes and horseradish peroxidase
表 2 本研究传感器与其他AA检测方法的比较
Table 2 Comparison of the sensor in this study with other methods for AA detection
表 3 AA检测方法的准确性研究
Table 3 Accuracy study of AA determination method
样品 加标浓度(μmol/L) 实测浓度(μmol/L) 回收率(%) RSD(%,n=3) 1 40.0 39.80 99.50 1.56 2 100.0 103.13 103.13 1.65 3 400.0 394.47 98.62 2.43 表 4 四种不同品牌饮料样品中AA含量测定
Table 4 Determination of AA content in beverage samples of four different brands
样品名称 吸光度
(A−A0)标示浓度
(mmol/L)检测浓度
(mmol/L)RSD
(%,n=3)果粒橙 0.029±0.006 42.58 45.80±0.01 1.35 怡泉+C汽水 0.027±0.011 42.58 41.13±0.02 2.46 C维他命水 0.061±0.008 113.56 110.47±0.01 1.84 水溶C100 0.074±0.007 127.59 135.80±0.01 1.07 -
[1] HONG C, CHEN L, HUANG J, et al. Gold nanoparticle-decorated MoSe2 nanosheets as highly effective peroxidase-like nanozymes for total antioxidant capacity assay[J]. Nano Research,2023,16(5):7180−7186. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-5328-9
[2] WANG X, WEI G, LIU W, et al. Platinum-nickel nanoparticles with enhanced oxidase-like activity for total antioxidant capacity bioassay[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2023,95(14):5937−5945. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c05425
[3] PENG L J, ZHANG C Y, ZHANG W Y, et al. The peroxidase-like catalytic activity of in situ prepared cobalt carbonate and its applications in colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide, glucose and ascorbic acid[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2022,651:129744.
[4] 朱碧宁. 高效液相色谱电化学发光法检测抗坏血酸的效果研究[J]. 山西化工,2019,39(3):50−51,58. [ZHU B N. Study on the determination of ascorbic acid by high performance liquid chromatography electrochemiluminescence[J]. Shanxi Chemical Industry,2019,39(3):50−51,58.] ZHU B N. Study on the determination of ascorbic acid by high performance liquid chromatography electrochemiluminescence[J]. Shanxi Chemical Industry, 2019, 39(3): 50−51,58.
[5] 沈海波, 张连钢, 周鑫魁, 等. 基于高灵敏度荧光衍生剂的痕量维生素C液相检测方法建立[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(23):272−276,283. [SHEN H B, ZHANG L G, ZHOU X K, et al. A HPLC method for the determination of trace vitamin C based on high sensitivity fluorescent derivatives was established[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(23):272−276,283.] SHEN H B, ZHANG L G, ZHOU X K, et al. A HPLC method for the determination of trace vitamin C based on high sensitivity fluorescent derivatives was established[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(23): 272−276,283.
[6] 贾宝珠, 蔡美玲, 邱芷靖, 等. 基于CoOOH纳米片氧化酶活性的比率荧光传感器检测抗坏血酸[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(8):273−280. [JIA B Z, CAI M L, QIU Z J, et al. A ratio fluorescence sensor based on oxidase activity of CoOOH nanosheets for the detection of ascorbic acid[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(8):273−280.] JIA B Z, CAI M L, QIU Z J, et al. A ratio fluorescence sensor based on oxidase activity of CoOOH nanosheets for the detection of ascorbic acid[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(8): 273−280.
[7] PENG J, LING J, ZHANG X Q, et al. A rapid, sensitive and selective colorimetric method for detection of ascorbic acid[J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical,2015,221:708−716. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2015.07.002
[8] WEI H, WANG E. Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes):Next-generation artificial enzymes[J]. Chemical Society Reviews,2013,42(14):6060−6093. doi: 10.1039/c3cs35486e
[9] LIU B, LIU J. Surface modification of nanozymes[J]. Nano Research,2017,10:1125−1148. doi: 10.1007/s12274-017-1426-5
[10] CHEN Y, JIAO L, YAN H, et al. Hierarchically porous S/N codoped carbon nanozymes with enhanced peroxidase-like activity for total antioxidant capacity biosensing[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2020,92(19):13518−13524. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02982
[11] LI S, KEOINGTHONG P, XU J, et al. Highly efficient carbon supported Co-Ir nanozyme for the determination of total antioxidant capacity in foods[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2023,236:115416. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2023.115416
[12] HAN X, LIU L, GONG H, et al. Dextran-stabilized Fe-Mn bimetallic oxidase-like nanozyme for total antioxidant capacity assay of fruit and vegetable food[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,371:131115. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131115
[13] LIANG N, GE X, ZHAO Y, et al. Promoting sensitive colorimetric detection of hydroquinone and Hg2+ via ZIF-8 dispersion enhanced oxidase-mimicking activity of MnO2 nanozyme[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2023,454:131455. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131455
[14] LIU J, YUAN Y, CHENG Y, et al. Copper-based metal-organic framework overcomes cancer chemoresistance through systemically disrupting dynamically balanced cellular redox homeostasis[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2022,144(11):4799−4809. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c11856
[15] KEUM C, PARK S, LEE S Y. Cancer-cell imaging using copper-doped zeolite imidazole framework-8 nanocrystals exhibiting oxidative catalytic activity[J]. Chemistry-An Asian Journal,2018,13(18):2641−2648. doi: 10.1002/asia.201800749
[16] GUO D, LI C, LIU G, et al. Oxidase mimetic activity of a metalloporphyrin-containing porous organic polymer and its applications for colorimetric detection of both ascorbic acid and glutathione[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2021,9(15):5412−5421.
[17] 周晨雨, 房琦, 张玉, 等. 基于Au@Pt纳米粒子-双亲性气凝胶的模拟酶可视化检测抗坏血酸[J]. 分析化学,2021,49(6):982−991. [ZHOU C Y, FANG Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Visual detection of ascorbic acid by simulated enzyme based on Au@Pt nanoparticle parental aerogel[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2021,49(6):982−991.] ZHOU C Y, FANG Q, ZHANG Y, et al. Visual detection of ascorbic acid by simulated enzyme based on Au@Pt nanoparticle parental aerogel[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 49(6): 982−991.
[18] ZHU H, LIU B, WANG M, et al. Amorphous Fe-containing phosphotungstates featuring efficient peroxidase-like activity at neutral pH:Toward portable swabs for pesticide detection with tandem catalytic amplification[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2023,95(10):4776−4785. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.3c00008
[19] ZHANG D, LIU J, DU P, et al. Cross-linked surface engineering to improve iron porphyrin catalytic activity[J]. Small,2020,16(17):1905889. doi: 10.1002/smll.201905889
[20] ZHANG H Z, WU H Y, QIN X G, et al. Metalloporphyrin and gold nanoparticles modified hollow zeolite imidazole Framework-8 with excellent peroxidase like activity for quick colorimetric determination of choline in infant formula milk powder[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,384:132552. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132552
[21] YANG H Y, SUN Z P, QIN X G, et al. Ultrasmall Au nanoparticles modified 2D metalloporphyrinic metal-organic framework nanosheets with high peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric detection of organophosphorus pesticides[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,376:131906. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131906
[22] WU H Y, XU Z L, XIONG D N, et al. Two dimensional iron metal-organic framework nanosheet with peroxidase-mimicking activity for colorimetric detection of hypoxanthine related to shrimp freshness[J]. Talanta,2023:124833.
[23] RAINERI M, WINKLER E L, TORRES T E, et al. Effects of biological buffer solutions on the peroxidase-like catalytic activity of Fe3O4 nanoparticles[J]. Nanoscale,2019,11(39):18393−18406. doi: 10.1039/C9NR05799D
[24] YANG W, YANG X, ZHU L, et al. Nanozymes:Activity origin, catalytic mechanism, and biological application[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews,2021,448:214170. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2021.214170
[25] GUO L, LIANG M, WANG X, et al. The role of L-histidine as molecular tongs:A strategy of grasping Tb3+ using ZIF-8 to design sensors for monitoring an anthrax biomarker on-the-spot[J]. Chemical Science,2020,11(9):2407−2413. doi: 10.1039/D0SC00030B
[26] ZHANG Y, WANG F, LIU C, et al. Nanozyme decorated metal-organic frameworks for enhanced photodynamic therapy[J]. ACS Nano,2018,12(1):651−661. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b07746
[27] KONG J, ZHENG J, LI Z, et al. One-pot synthesis of AuAgPd trimetallic nanoparticles with peroxidase-like activity for colorimetric assays[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2021,413:5383−5393. doi: 10.1007/s00216-021-03514-1
[28] GAO L, ZHUANG J, NIE L, et al. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles[J]. Nature nanotechnology,2007,2(9):577−583. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2007.260
[29] WANG S, XU D, MA L, et al. Ultrathin ZIF-67 nanosheets as a colorimetric biosensing platform for peroxidase-like catalysis[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2018,410:7145−7152. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1317-y
[30] YU H, WU H, TIAN X, et al. A nano-sized Cu-MOF with high peroxidase-like activity and its potential application in colorimetric detection of H2O2 and glucose[J]. RSC Advances,2021,11(43):26963−26973. doi: 10.1039/D1RA04877E
[31] LÜ J, ZHANG C, WANG S, et al. MOF-derived porous ZnO-Co3O4 nanocages as peroxidase mimics for colorimetric detection of copper(ii) ions in serum[J]. Analyst,2021,146(2):605−611. doi: 10.1039/D0AN01383H
[32] GE K, SUN S, ZHAO Y, et al. Facile synthesis of two-dimensional iron/cobalt metal-organic framework for efficient oxygen evolution electrocatalysis[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2021,60(21):12097−12102. doi: 10.1002/anie.202102632
[33] WANG Y, ZHAO M, PING J, et al. Bioinspired design of ultrathin 2D bimetallic metal-organic-framework nanosheets used as biomimetic enzymes[J]. Advanced Materials,2016,28(21):4149−4155. doi: 10.1002/adma.201600108
[34] UZUNOGLU D, ÖZER A. Facile synthesis of magnetic iron-based nanoparticles from the leach solution of hyperaccumulator plant pinus brutia for the antibacterial activity and colorimetric detection of ascorbic acid[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials,2022,5(11):5465−5476. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.2c00782
[35] 王若男, 孟佩俊, 李淑荣, 等. 纳米二氧化铈/石墨烯传感器的构建及其对饮品中抗坏血酸的检测[J]. 现代化工,2023,43(8):236−240,245. [WANG R N, MENG P J, LI S R, et al. Construction of nano-cerium dioxide/graphene sensor and its detection of ascorbic acid in drinks[J]. Modern Chemical Industry,2023,43(8):236−240,245.] WANG R N, MENG P J, LI S R, et al. Construction of nano-cerium dioxide/graphene sensor and its detection of ascorbic acid in drinks[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2023, 43(8): 236−240,245.
[36] KEELEY G P, O'NEILL A, MCEVOY N, et al. Electrochemical ascorbic acid sensor based on DMF-exfoliated graphene[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry,2010,20(36):7864−7869. doi: 10.1039/c0jm01527j
[37] YANG L, LIU D, HUANG J, et al. Simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid at electrochemically reduced graphene oxide modified electrode[J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical,2014,193:166−172. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2013.11.104
[38] WANG C, DU J, WANG H, et al. A facile electrochemical sensor based on reduced graphene oxide and Au nanoplates modified glassy carbon electrode for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid[J]. Sensors and Actuators B:Chemical,2014,204:302−309. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2014.07.077
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 杜康,花扬扬,魏帅飞,王婷婷,曲冠男,赵猛,蔡红星. 基于内标法的低质量浓度葡萄糖溶液拉曼测定研究. 光学学报(网络版). 2024(05): 4-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 韩春然,岳振歌,遇世友,王鑫,张丝瑶. 检测葡萄糖的Ni基电化学传感器研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2023(14): 482-489 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



