Preparation and Component Analysis of Camellia nitidissima Chi Polyphenols and Their Antioxidant Activites in Vivo and in Vitro
-
摘要: 为了探究金花茶多酚最佳提取工艺条件及纯化后总多酚成分及体内外抗氧化活性分析。本研究以金花茶为原料,在单因素实验的基础上,设计响应面试验,筛选超声功率、提取温度、乙醇浓度和料液比最佳提取参数。采用Lx-8型大孔树脂对提取物进行纯化,并以高效液相色谱法对5种多酚单体化合物进行定性定量分析,随后对提取物进行体内外抗氧化实验。结果表明,最优工艺条件为超声功率290 W,提取温度35 ℃,乙醇浓度55%,料液比1:30 g/mL,在此条件下,金花茶多酚得率为3.53%,茶多酚纯度为63.73%。5种多酚单体化合物没食子酸、绿原酸、表儿茶素、芦丁、鞣花酸含量分别为0.47、11.18、59.03、18.34、16.41 mg/g。体外抗氧化实验结果表明,金花茶花多酚能够有效清除DPPH自由基、ABTS+自由基和超氧阴离子自由基,其IC50值分别为0.38、0.16、0.39 mg/mL。此外,金花茶多酚还能够通过显著提高线虫体内SOD酶活力及降低MDA含量,有效增强秀丽隐杆线虫对氧化损伤的抵抗力。Abstract: This study aimed to investigate the optimal extraction process for polyphenols from Camellia nitidissima Chi and to analyze the total polyphenol composition and antioxidant activities both in vivo and in vitro post-purification. Camellia nitidissima Chi was the raw material and a response surface methodology based on single factor experiments was designed to screen the optimal extraction parameters including ultrasound power, extraction temperature, ethanol concentration and solid-liquid ratio. The extract was purified using Lx-8 macroporous resin, and five specific polyphenolic monomers were qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Subsequently, in vivo and in vitro antioxidant experiments were conducted on the extract. The results showed that the optimal conditions were an ultrasonic power of 290 W, an extraction temperature of 35 ℃, an ethanol concentration of 55%, and a material-liquid ratio of 1:30 g/mL. Under these conditions, the yield of polyphenols from Camellia nitidissima Chi was 3.53%, the purity was 63.73%. The content of five polyphenolic monomer compounds, namely gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, epicatechin, rutin, and ellagic acid was 0.47, 11.18, 59.03, 18.34, and 16.41 mg/g, respectively. In addition, the polyphenols extracted from Camellia nitidissima Chi demonstrated a significant ability to boost oxidative damage resistance in C. elegans. This was evidenced by a marked increase in SOD (superoxide dismutase) enzyme activity and a decrease in MDA (malondialdehyde) levels within the C. elegans specimens.
-
金花茶(Camellia nitidissima Chi)属于山茶科、山茶属植物,是一种常绿灌木或小乔木,是山茶家族中唯一开黄花的植物类群[1],是一种珍贵的药食同源植物。金花茶因其巨大药用价值和观赏价值被誉为“植物界大熊猫”和“茶族皇后”[2]。金花茶微苦,涩,平,民间主要用于治疗咽喉炎、尿道感染、高血压以及去腻减肥等症[3]。此外,现代研究表明金花茶具有降血糖[4]、降血脂[5]、抗肿瘤[6]、抗菌[7]、抗氧化[8]、抗衰老[9]等药理作用,其主要成分包括多酚、黄酮、皂苷、多糖等[10],其中金花茶多酚是金花茶中的主要潜在活性成分[11],具有缓解斑马鱼中性粒细胞炎症[12]、保护糖尿病大鼠的胰岛β细胞[13]和抑制巨噬细胞炎症[14]等多种药用活性,这些疾病的发生与氧化应激反应有关。
整体来看,药用(食用)作物种植和生产研究的主要目的是如何提高药用成分(特别是具有高药用价值的有效成分)的产量和质量。通过优化前处理方法提高活性成分的产量是实现上述目标的好方法。目前国内关于金花茶花部位有效成分提取工艺研究大多集中于黄酮[15]、多糖[16],且金花茶多酚提取工艺相关研究仅停留在金花茶叶片部位[17],金花茶多酚花部位有关文献报道较少。研究表明茶多酚的提取方法主要有溶剂提取法、超声波提取法、微波提取法、超临界萃取法等[18],微波和超临界流体萃取因设备要求高、价格贵导致目前应用难以普及,超声波辅助提取法因操作方便、设备简单等优点得到广泛应用,相较于其他传统提取方法而言,该方法避免了由于温度过高导致茶多酚成分遭到破坏,且具有工艺简单、回收率高、氧化耗能小且节能提取率高等优点[19]。
目前金花茶多酚抗氧化研究仍然只聚焦于体外实验[20],不能全面准确地反映物质的抗氧化活性,因此非常有必要结合体外和体内实验方法以便客观、准确地评价抗氧化效果。秀丽隐杆线虫(C.elegans)因其具有结构简单、生长周期短、饲养方便且其基因组成与人类高度一致等优势[21],近年来逐渐用作研究天然药物活性的可靠模型,尤其是在抗氧化、抗衰老和神经系统疾病等领域[22]。然而,以秀丽隐杆线虫为模型研究金花茶多酚抗氧化作用文章未见报道。
基于此,本研究在单因素实验的基础上结合响应面试验对金花茶花多酚的提取工艺进行优化,利用Lx-8型大孔树脂对其进行分离纯化,通过高效液相色谱法对金花茶花中主要多酚类成分进行定性及定量分析,以维生素C为对照,分析检测金花茶多酚体外氧化活性,并以秀丽隐杆线虫为模型进一步研究金花茶多酚的体内抗氧化活性,以期为金花茶多酚的开发应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
金花茶 购自广西防城港市,经天津中医药大学中药学鉴定教研室鉴定为广西防城普通金花茶的干燥花朵;没食子酸标准品、绿原酸标准品、表儿茶素标准品、芦丁标准品、鞣花酸标准品(含量均>98%) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;1,1二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)、2,2-联氮-二(3-乙基苯并噻唑-6-磺酸)二铵盐(ABTS)、磷酸盐缓冲液(pH=7.4)、维生素C 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;野生型秀丽应杆线虫(N2)、大肠杆菌OP50 Caenorhabditis Genetics Center;无水乙醇、酒石酸钾钠、硫酸亚铁、磷酸、磷酸氢二钠、磷酸二氢钾、磷酸氢二钾、次氯酸钠、氢氧化钠、氯化钠、甲醇(色谱纯)、磷酸(色谱纯) 天津市大茂化学试剂厂;BCA试剂盒、MDA试剂盒、SOD试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;Lx-8型大孔树脂 郑州和成新材料科技有限公司;其他试剂均为分析纯。
MS2050U型十万分之一天平、ME403/02型千分之一天平 梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司;UV759型紫外可见分光光度计 上海佑科仪器仪表有限公司;11191614型超声波萃取仪 宁波新芝生物科技有限公司;SLK-R3000-S型恒温摇床 美国塞洛捷克有限公司;GZB-GF101-3-BS-II/H型电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海跃进医疗器械有限公司;1000gA多功能高速粉碎机 拓郝机电科技有限公司;RV10 digital V型旋转蒸发仪 广州艾卡仪器设备有限公司;1260高效液相色谱仪 美国Agilent公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 金花茶多酚的提取
50~60 ℃下干燥金花茶至恒重,粉碎过40目筛后,取1 g金花茶粉末,按实验所需料液比加入一定浓度乙醇溶液,采用超声辅助提取法在一定超声温度及超声功率下超声提取一定时间,进行金花茶多酚提取,并通过单因素实验及响应面试验对提取工艺参数进行优化。
1.2.2 单因素实验
1.2.2.1 提取时间对多酚得率的影响
固定乙醇浓度、料液比、超声温度及超声功率分别为55%、1:25、40 ℃、288 W,提取时间分别为15、25、35、45、55及65 min。考察不同提取时间对金花茶多酚得率的影响。
1.2.2.2 料液比对得率的影响
固定乙醇浓度、超声温度及超功率分别为55%、40 ℃、288 W,料液比分别为1:15、1:25、1:35、1:45和1:55 g/mL。考察不同料液比对金花茶多酚得率的影响。
1.2.2.3 超声功率对得率的影响
固定乙醇浓度、料液比及超声温度分别为55%、1:25 g/mL、40 ℃,超声功率分别为72、144、216、288和360 W。考察超声功率对金花茶多酚的影响。
1.2.2.4 乙醇浓度对得率的影响
固定料液比、超声温度及超声功率分别为1:25、40 ℃、288 W,乙醇浓度分别为25%、35%、45%、55%、和65%。考察不同乙醇浓度对金花茶多酚得率的影响。
1.2.2.5 超声温度对得率的影响
固定乙醇浓度、料液比及超声功率分别为55%、1:25 g/mL、288 W,超声温度分别为20、40、60和80 ℃。考察超声温度对得率的影响。
1.2.3 响应面试验
在单因素实验的基础上,选取料液比(g/mL)、乙醇浓度(%)、超声温度(℃)、超声功率(W)为响应面实验自变量,以多酚得率为实验的响应值,优化提取工艺参数(表1)。
表 1 响应面试验因素及水平设计Table 1. Factors and levels of response surface experiment水平 因素 A乙醇浓度
(%)B料液比
(g/mL)C超声功率
(W)D超声温度
(℃)−1 45 1:15 216 25 0 55 1:25 288 40 1 65 1:35 360 55 1.2.4 金花茶多酚的分离纯化
按照1.2.3项下的最优工艺制得金花茶多酚提取液,减压浓缩至2 mg/mL的金花茶多酚浓缩液,备用。参考课题组前期实验结果及Li等[23]的茶多酚纯化工艺,采用Lx-8型大孔吸附树脂纯化,湿法装柱(层析柱内径2.5 cm,高20 cm),上样浓度2.0 mg/mL(3 BV),水洗除杂(1 BV),后用60%乙醇(2 BV)洗脱,洗脱流速为2 mL/min。减压浓缩后,冷冻干燥。
1.2.5 金花茶多酚含量测定
采用酒石酸亚铁比色法进行金花茶多酚提含量的测定[24]。以没食子酸标准液浓度为横坐标,OD539 nm为纵坐标,绘制没食子酸的标准曲线:Y=0.584X+0.0092(0.2~1.2 mg/mL),R2=0.9997,根据标准曲线计算以没食子酸为当量的茶多酚质量浓度,并按照下列公式计算金花茶多酚含量:
金花茶多酚含量(%)=C×V×Nm×100 式中:C为回归方程计算出的多酚质量浓度(mg/mL);m为金花茶样品质量(mg);V为测定时反应体系总体积(mL);N为稀释倍数。
1.2.6 金花茶多酚HPLC分析
采用HPLC法对金花茶提取物中的没食子酸、绿原酸和表儿茶素等五个多酚类化合物进行定性定量分析。
1.2.6.1 样品前处理
精密称取适量的没食子酸、绿原酸、表儿茶素、芦丁、鞣花酸对照品适量置于10 mL容量瓶,加入甲醇溶液定容,过0.45 μm滤膜得待测混标溶液;按照精密称定5 mg金花茶多酚冻干粉末并溶解,加入甲醇溶液定容至10 mL,过0.45 μm滤膜后,得到待测样品的溶液。
1.2.6.2 色谱条件
Hypersil ODS 色谱柱(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm);流动相(A)为0.5%磷酸水溶液,流动相(B)为乙腈;梯度洗脱(0~10 min,7.0%~8.5% B;10~15 min,8.5%~14.5% B;15~35 min,14.5%~16.5% B;35~40 min,16.5%~17.6% B,40~45 min,17.6%~26.0% B;45~55 min,26.0%~30.0% B);检测波长为270 nm;流速为0.6 mL/min;柱温为25 ℃;运行时间为55 min。
1.2.6.3 标准曲线的绘制
将适量的没食子酸、绿原酸、表儿茶素、芦丁、鞣花酸储备液分别精密吸取至5 mL容量瓶中,以甲醇溶液依次稀释并定容,制得混合进样溶液。按照色谱条件测定。以进样浓度为横坐标,对应峰面积为纵坐标,记录待测成分峰面积,绘制标准曲线,得到线性回归方程。
1.2.7 金花茶多酚类物质的抗氧化能力分析
配制浓度为0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0、1.2 mg/mL的金花茶多酚溶液,以同等浓度的维生素C为对照,进行体外抗氧化试验。测定金花茶多酚样品对DPPH自由基[25]、ABTS阳离子自由基[26]及超氧阴离子自由基[27]清除能力,并计算其半数抑制浓度(IC50)。
1.2.8 秀丽隐杆线虫培养
线虫的培养参考李金泽[28]方法略作修改,线虫在固体培养基(Nematode Growth Medium,NGM)上培养,将OP50涂布在NGM培养基上作为线虫食物。线虫同期化采用次氯酸钠法进行,同期化的线虫培养至L4期,转移至含有50、100和200 μg/mL的金花茶多酚培养基中培养。
1.2.9 秀丽隐杆线虫的氧化应激实验
1.2.9.1 线虫热应激实验
将同期化后培养至L4期的线虫分别转移至含有50、100、200 μg/mL金花茶多酚培养基上,给药干预48 h。用M9缓冲液洗涤,转移至含1%五氟尿嘧啶的NGM培养基中,将培养箱温度调至35 ℃,此时设为0 h,每隔30 min观察记录线虫的存活情况,直至线虫死亡。
1.2.9.2 线虫氧化应激实验
培养方法同热应激实验,L4期线虫给药干预48 h后,转移至3 mmol/L H2O2平板上。转移后每30 min记录线虫存活情况,直至线虫死亡。
1.2.9.3 秀丽隐杆线虫体内抗氧化酶活力和丙二醛含量测定
根据Yu等[29]的方法略作修改。同期化后培养至L4期的两组N2线虫,在用金花茶多酚处理48 h后,一组转移到35 ℃下6 h以诱导氧化损伤,一组继续在20 ℃下培养。用生理盐水洗涤,待线虫沉淀后,加入200 μL线虫并在冰上匀浆,然后以2500 r/min离心10 min。根据试剂盒的说明测定上清液中SOD的活性以及MDA的含量。
1.3 数据处理
测定结果均以平均值±标准差(n=3)表示,组间进行单因素方差分析比较。P<0.05表示差异性具有统计学意义。通过Origin 2022和Design-Expert 11.1.0软件进行作图和分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
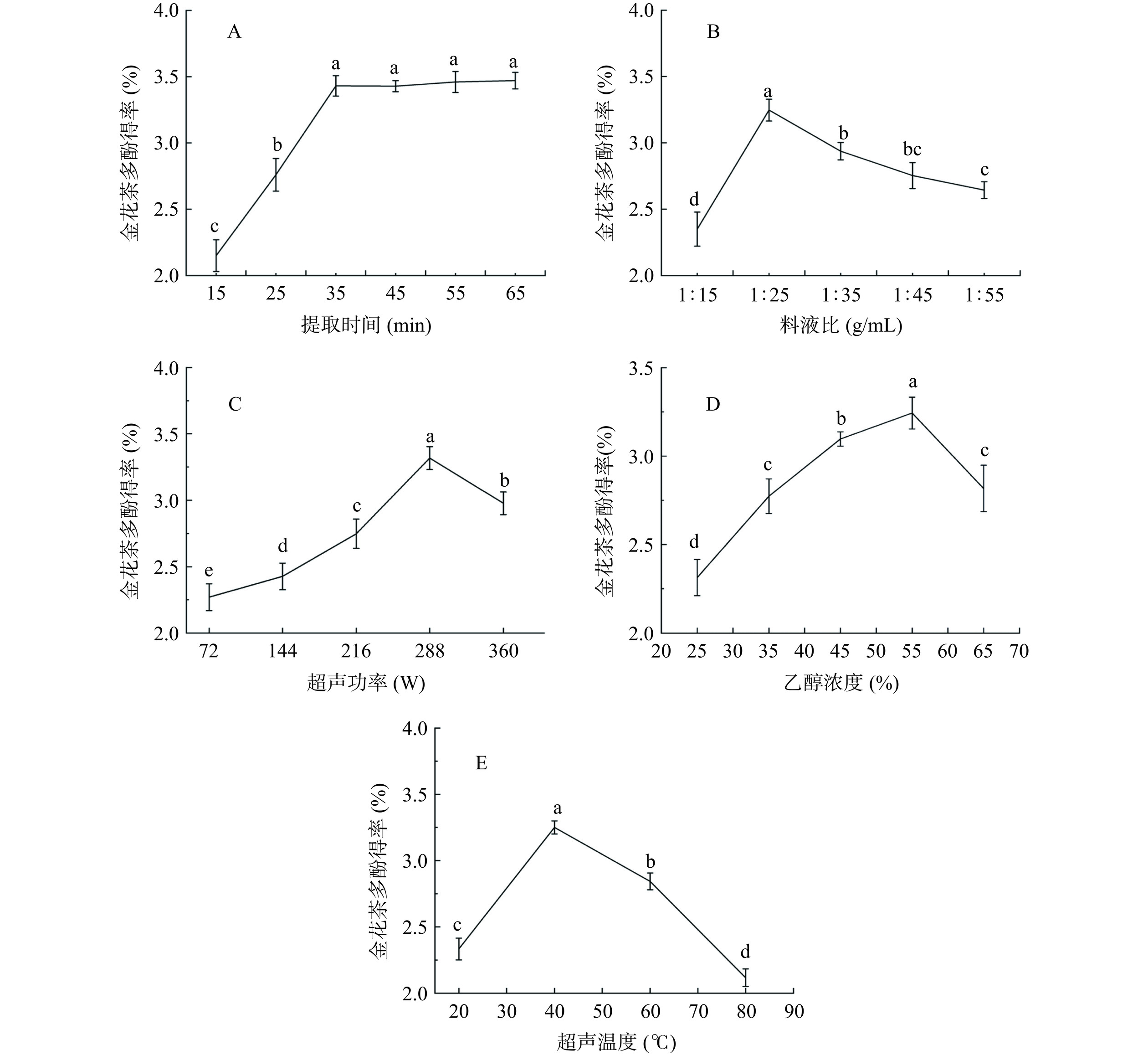
2.1.1 提取时间对金花茶多酚得率的影响
如图1A所示,随着提取时间的增加,金花茶多酚得率呈现先上升至35 min左右后无显著变化趋势,金花茶多酚得率不再增加且趋于平稳,因此后续单因素实验及响应面试验选择35 min为金花茶多酚的提取时间,由于增加提取时间会造成能源资源浪费,降低时间成本,且避免超声时间过长可能会增加其他杂质成分[28]。
2.1.2 料液比对金花茶多酚得率的影响
如图1B所示,随溶剂的增加金花茶多酚得率呈现先上升后下降的趋势,料液比为1:25 g/mL时金花茶多酚得率最大为3.15%±0.08%。当溶剂量较低时细胞中金花茶多酚扩散和溶出缓慢,随着溶剂量的增加,金花茶多酚的溶出速率增加,一定程度时金花茶多酚溶出到达顶峰[30]。故选取料液比1:15、1:25、1:35 g/mL进行响应面优化试验。
2.1.3 超声功率对金花茶多酚得率的影响
如图1C所示,随超声功率的增加,金花茶多酚得率呈现先增加后下降的趋势,超声功率为288 W时,金花茶多酚得率最大为3.25%±0.08%。当超声功率增大可加剧空化效应,进而破坏细胞壁和细胞膜加快金花茶多酚物质溶出,而功率进一步增大也会导致提取的温度过高,破坏多酚的结构[31]。故选取超声功率216、288、360 W进行响应面优化试验。
2.1.4 乙醇浓度对金花茶多酚得率的影响
如图1D所示,随乙醇浓度的增加,金花茶多酚得率呈现先增加后下降的趋势,乙醇浓度为55%时金花茶多酚得率最大为3.24%±0.09%。当乙醇浓度较小时,无法将氢键和疏水键之间的复合物打断。而乙醇浓度过高时,其他脂溶性物质更易溶解浸出,导致多酚得率降低[32]。故选取乙醇浓度为45%、55%、65%进行响应面优化试验。
2.1.5 超声温度对金花茶多酚得率的影响
如图1E所示,随超声温度的增加,金花茶多酚得率呈现先增加后下降的趋势,超声温度为40 ℃时金花茶多酚得率最大为3.26%±0.049%。当超声温度较低时,各种物质的溶解度降低,且多酚与糖类及蛋白质之间形成的复合物较稳定,导致金花茶多酚得率较低,而过高的温度会导致多酚物质结构易被破坏或与其他物质发生不可逆的反应,因此提取温度过高不利于多酚的提取[33]。
2.2 响应面试验结果
2.2.1 响应面试验结果与分析
采用Design-Expert 11.0.1软件对响应面实验的结果进行分析,响应面试验结果见表2所示,得到金花茶总多酚提取液的拟合回归方程为:Y=3.51−0.015A+0.32B+0.05C−0.17D+0.02AB+0.052AC−0.052AD+0.11BC+0.037BD− 0.05CD−0.45A2−0.43B2−0.43C2−0.30D2。
表 2 响应面试验设计及结果Table 2. Design and results of Box-Behnken experiment实验号 A B C D 茶多酚得率(%) 1 −1 −1 0 0 2.71±0.43 2 1 −1 0 0 2.31±0.32 3 −1 1 0 0 3.29±0.28 4 1 1 0 0 3.04±0.47 5 0 0 −1 −1 2.74±0.34 6 0 0 1 −1 2.86±0.52 7 0 0 −1 1 2.43±0.08 8 0 0 1 1 2.76±0.59 9 −1 0 0 −1 2.62±0.36 10 1 0 0 −1 2.5±0.33 11 −1 0 0 1 2.9±0.62 12 1 0 0 1 2.57±0.73 13 0 −1 −1 0 2.29±0.23 14 0 1 −1 0 2.74±0.32 15 0 −1 1 0 2.13±0.07 16 0 1 1 0 3.01±0.45 17 −1 0 −1 0 2.98±0.17 18 1 0 −1 0 2.63±0.29 19 −1 0 1 0 3.1±0.25 20 1 0 1 0 2.55±0.44 21 0 −1 0 −1 2.41±0.67 22 0 1 0 −1 2.98±0.39 23 0 −1 0 1 2.31±0.72 24 0 1 0 1 2.96±0.60 25 0 0 0 0 3.38±0.21 26 0 0 0 0 3.43±0.13 27 0 0 0 0 3.53±0.09 28 0 0 0 0 3.67±0.20 29 0 0 0 0 3.52±0.24 2.2.2 二次多项回归方程拟合与方差分析
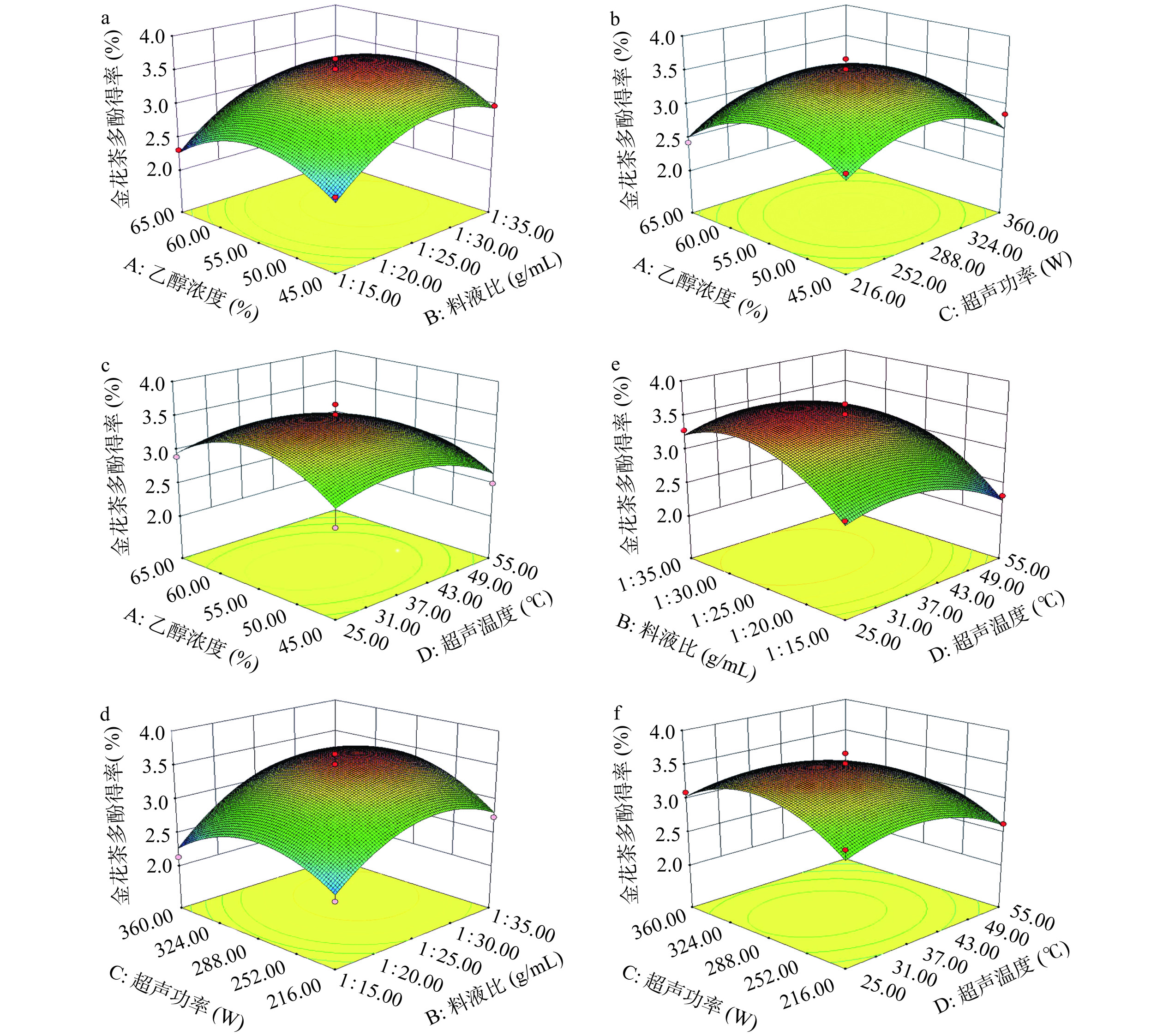
由表3可知,回归模型的P<0.01,表明二次方程模型极显著,具有统计学意义;各因素对多酚得率的影响大小依次为料液比(B)>超声温度(D)>超声功率(C)>乙醇浓度(A);B、A2、B2、C2、D2对多酚得率的影响均为极显著(P<0.01);失拟项不显著(P>0.05),表明回归方程拟合效果较好;回归方程的决定系数R2=0.9350,表明金花茶多酚提取工艺中93.50%的变异分布均包含在所研究的4个因素中[34]。因此,利用该回归方程确定最佳提取工艺条件是可行的。
表 3 回归方程各项的方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance of the regression equation方差来源 平方和 自由度 方差 F值 P值 回归模型 4.48 14 0.32 14.39 <0.0001 A 2.7×10−3 1 2.7×10−3 0.12 0.7328 B 1.24 1 1.24 55.81 <0.0001 C 0.030 1 0.030 1.35 0.2650 D 0.33 1 0.33 14.98 0.0017 AB 1.6×10−3 1 1.6×10−3 0.072 0.7925 AC 0.011 1 0.011 0.50 0.4930 AD 0.011 1 0.011 0.50 0.4930 BC 0.046 1 0.046 2.08 0.1715 BD 5.625×10−3 1 5.625×10−3 0.25 0.6229 CD 0.010 1 0.010 0.45 0.5135 A2 1.31 1 1.31 58.73 <0.0001 B2 1.21 1 1.21 54.24 <0.0001 C2 1.18 1 1.18 52.99 <0.0001 D2 0.60 1 0.60 26.99 0.0001 残差 0.31 14 0.022 2.13>0.05 失拟项 0.26 10 0.026 纯误差 0.049 4 0.012 合计 4.79 28 R2=0.9350,R2adj=0.8700,R2pred=0.6689 注:P<0.05表示差异显著;P<0.01表示差异极显著。 2.2.3 响应面分析及最佳工艺条件确定
根据数据模拟结果的三维响应面图,确定最佳优化工艺,并判定各因素对金花茶多酚得率的影响。如图2所示,坡度的陡峭程度反应了不同因素对响应面的影响程度。同时通过Design Expert 11.1.0软件对回归方程的模型进行拟合分析,确定金花茶多酚的最佳提取工艺条件为:乙醇浓度55.14 ℃、料液比1:28.78 g/mL、超声功率296.77 W、超声温度36.07%,总金花茶多酚得率测定值为3.59%。考虑试验的可操作性,调整为乙醇浓度55%,料液比1:30 g/mL,超声功率290 W,提取温度35 ℃,进行三次重复试验。结果显示,金花茶多酚得率为3.53%±0.098%,与模型预测结果相对误差为1.70%,接近预测值,可用于金花茶总多酚的提取工艺。
2.3 金花茶多酚分离纯化
通过1.2.5项下方法测定金花茶多酚冻干粉末中多酚纯度为63.73%±2.43%,较粗提取(3.53%)纯度增大18.05倍左右。
2.4 金花茶多酚HPLC分析
2.4.1 标准曲线的绘制
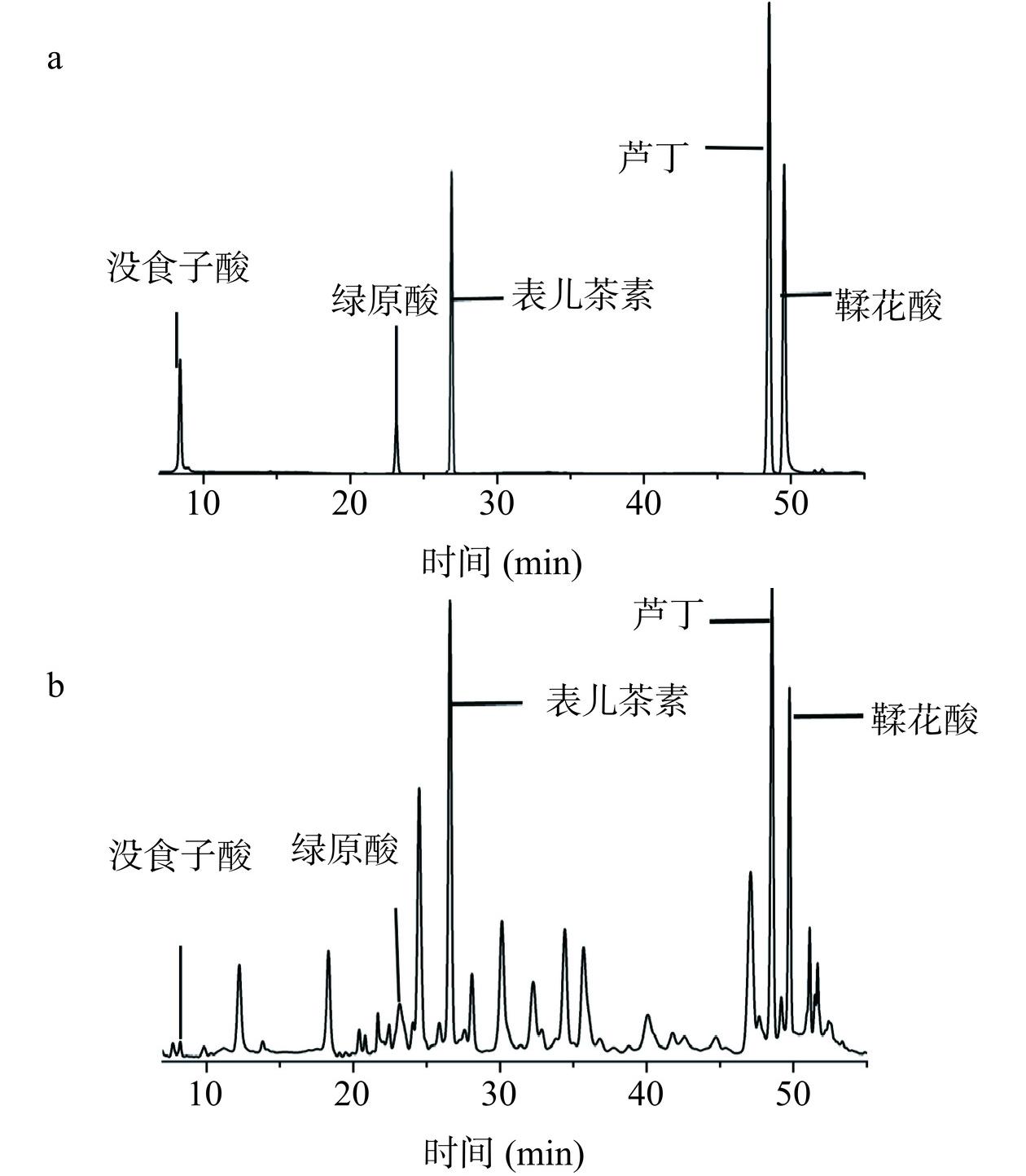
没食子酸、绿原酸、表儿茶素、芦丁和鞣花酸均为金花茶中多酚类化合物[35],且以上茶多酚单体成分均具有良好的药用价值[36−37]。因此,本研究选择以上标品进行成分分析。峰面积作为纵坐标、分别以没食子酸、绿原酸、表儿茶素、芦丁、鞣花酸质量浓度为横坐标得线性方程及线性范围如表4所示。
表 4 金花茶标品的线性方程及线性范围Table 4. Linear equation and linear range of Camellia nitidissima Chi standard roduct标准品 线性方程 线性范围(μg/mL) 没食子酸 y=19411x−17.69(r=0.9994) 8~40 绿原酸 y=4959.9x−52.128(r=0.999) 24~120 表儿茶素 y=3863.5x−11.994(r=0.9993) 64~320 芦丁 y=11997x−62.186(r=0.999) 64~320 鞣花酸 y=21544x−1399.4(r=0.993) 64~320 2.4.2 方法学考察
参照叶梦倩等[38]研究方法,测得没食子酸、表儿茶素、绿原酸、芦丁、鞣花酸的精密度实验、重复性实验、24 h稳定性实验及加样回收率实验的RSD值分别在0.23%~2.29%、0.68%~2.86%、0.42%~3.0%、0.80%~2.91%,RSD值均小于5%,表明实验方法及仪器符合要求。
2.4.3 样品测定
图3为金花茶花多酚样品溶液和混标溶液的HPLC图。根据图中各组分的保留时间可知,样品中均含以上五种多酚类化合物。经定量分析,金花茶花多酚冻干粉末中没食子酸、绿原酸、表儿茶素、芦丁、鞣花酸含量分别为0.47、11.18、59.03、18.34、16.41 mg/g。
2.5 金花茶多酚的体外抗氧化活性
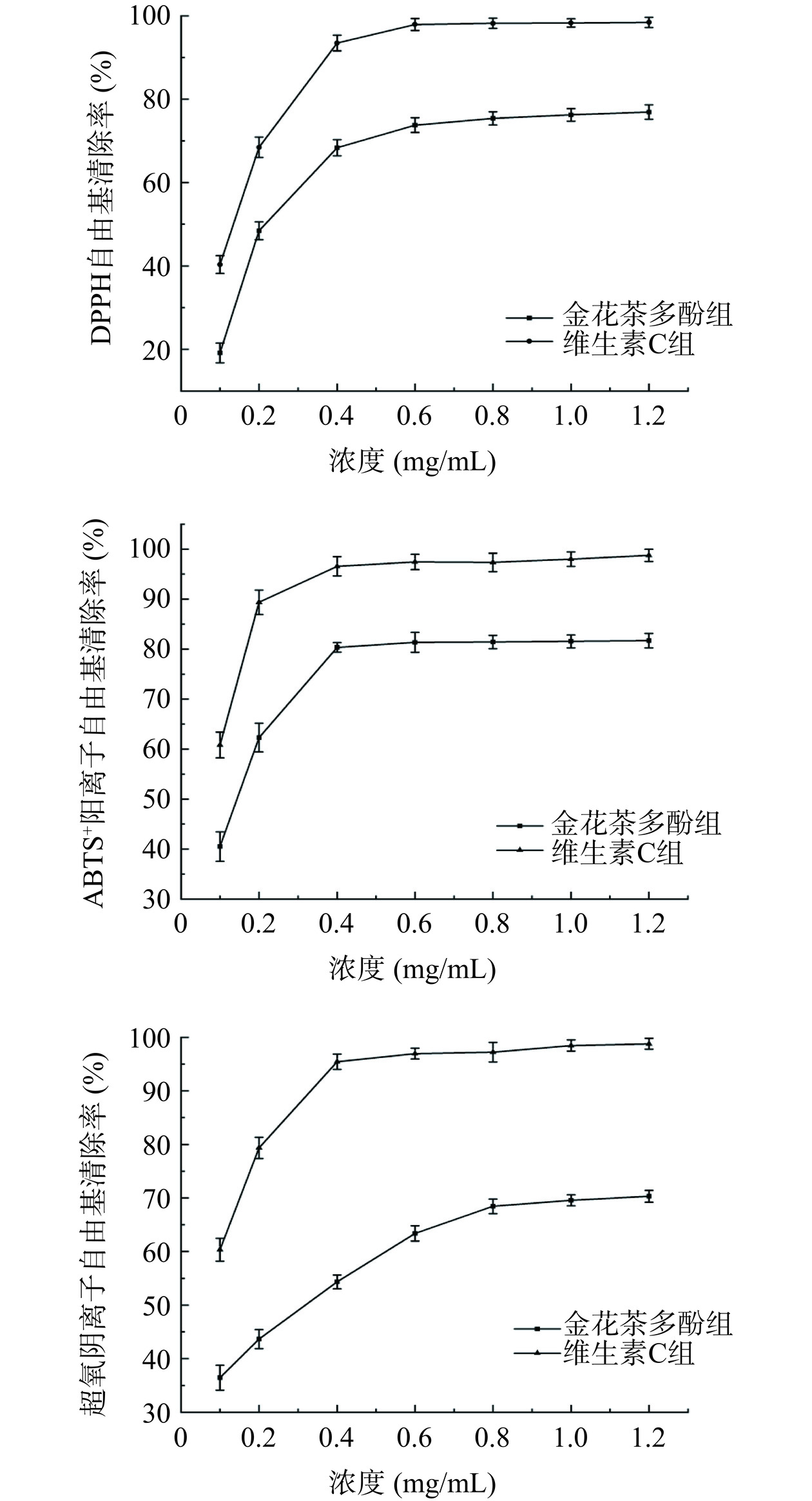
由图4可知,样品的质量浓度在0.4~1.2 mg/mL范围内,随着金花茶多酚浓度升高DPPH自由基、ABTS+自由基、超氧阴离子自由基清除率均呈上升趋势,并且随质量浓度增加,清除率增大,金花茶多酚清除DPPH、ABTS+、超氧阴离子自由基的IC50值分别为0.38、0.16、0.39 mg/mL。金花茶多酚在质量浓度为1.2 mg/mL时清除率依次为76.91%、81.69%、70.32%(此时维生素C的清除率依次为98.74%、98.42%、98.78%)。相对颜栋美等[20]对于金花茶多酚抗氧化活性研究,本研究金花茶多酚的还原能力较强,表现出良好的体外自由基清除能力。
2.6 金花茶多酚对秀丽隐杆线虫氧化损伤的影响
2.6.1 金花茶多酚增强秀丽隐杆线虫热应激抗性
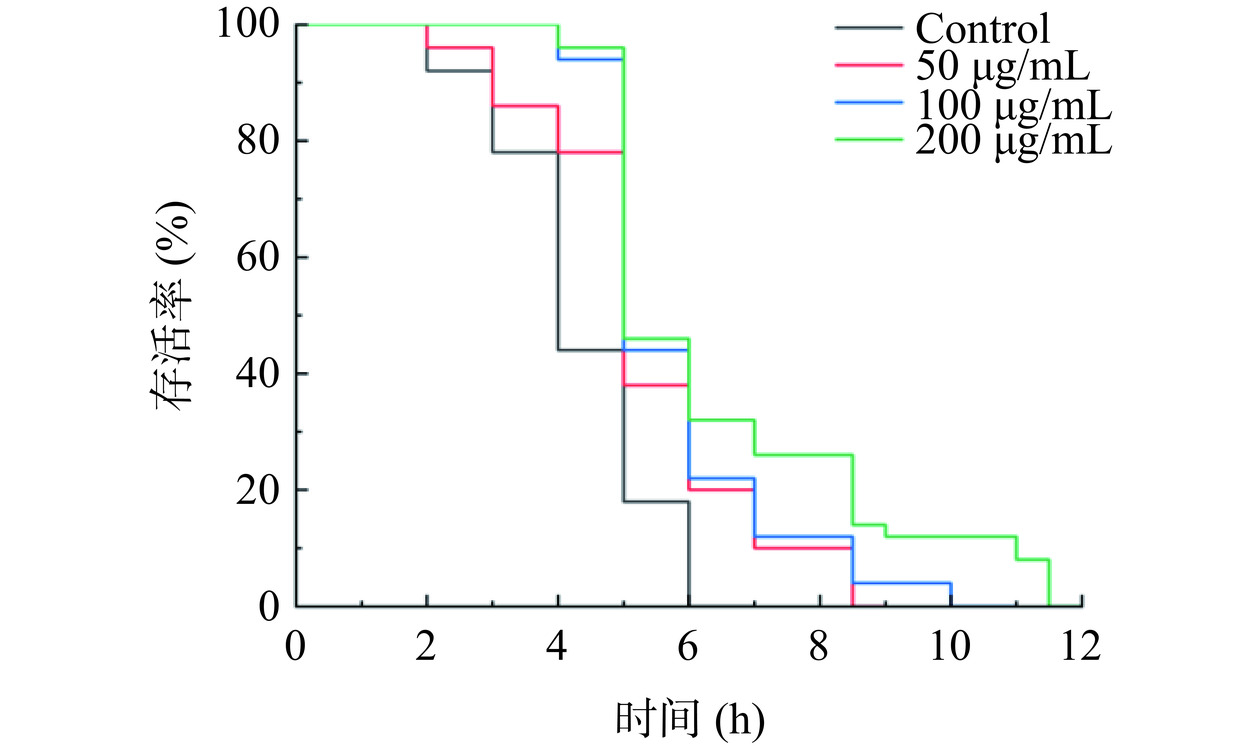
大量研究表明,热环境会将线虫体内的热平衡破坏,对体内的氧化系统造成影响[39]。将野生型秀丽隐杆线虫从20 ℃转移至35 ℃培养,35 ℃条件会引起线虫体内产生大量活性氧。延长热应激条件下线虫的寿命是评价样品给药干预下发挥抗氧化活性的重要指标[40−41]。如图5所示,金花茶多酚能增强秀丽隐杆线虫的生存能力,延长线虫寿命。数据统计结果如表5显示,与对照组相比,50、100及200 μg/mL金花茶多酚延长线虫平均生存时间为6.96%、28.70%及37.99%。对延长线虫生存时间有剂量依赖性,统计学结果显示与对照组相比,给药组具有显著差异(P<0.05)。说明金花茶多酚可显著提高线虫对热应激的抵抗能力。
表 5 金花茶多酚对秀丽隐杆线虫热应激损伤的影响Table 5. Effects of polyphenols from Camellia nitidissima Chi on the heat stress injury of C.elegans组别 质量浓度
(μg/mL)平均寿命
(h)平均寿命
延长率(%)最高寿命
(h)最高寿命
延长率(%)对照组 0 4.29±0.24a − 6.00±1.00a − 给药组 50 5.25±0.21b 6.96 8.50±1.32b 33.33 100 5.70±0.27c 28.70 9.67±1.53c 66.67 200 5.92±0.14c 37.99 11.17±0.76c 91.67 注:同列不同字母表示同列数据具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 2.6.2 金花茶多酚增强秀丽隐杆线虫氧化应激抗性
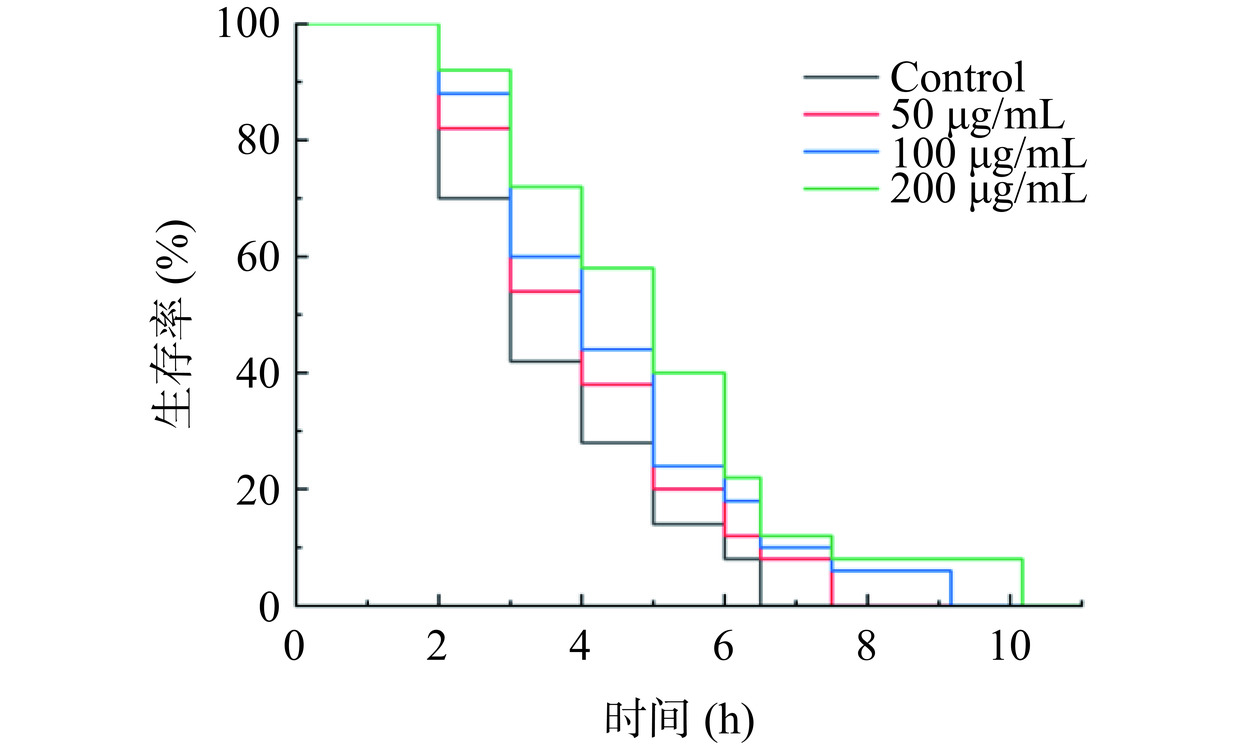
H2O2是机体内最常见的一种活性氧,能触发细胞脂质进而发生过氧化反应产生自由基,进而造成线虫急性氧化损伤[42]。本研究通过H2O2造模干预秀丽隐杆线虫,使其发生氧化损伤,通过比较给药组和对照组生存时间进一步来验证金花茶多酚抗氧化活性。如图6所示,与对照组相比,金花茶多酚可延长H2O2氧化损伤条件下线虫存活时间,数据统计结果如表6所示,其中50、100和200 μg/mL的金花茶多酚分别延长秀丽隐杆线虫平均生存时间21.57%、39.49%、45.10%,同样对延长氧化损伤线虫生存时间具有剂量依赖性。统计学结果显示与对照组相比,给药组具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。金花茶多酚能显著增强线虫对氧化应激的抵抗能力。
表 6 金花茶多酚对秀丽隐杆线虫氧化应激损伤的影响Table 6. Effects of polyphenols from Camellia nitidissima Chi on the oxidative stress injury of C.elegans质量浓度
(μg/mL)平均寿命
(h)平均寿命
延长率(%)最高寿命 最高寿命
延长率(%)对照组 0 3.57±0.35a − 6.50±0,50a − 给药组 50 4.34±0.24b 21.57 7.50±0.50a 15.38% 100 4.98±0.11c 39.49 9.17±0.76b 41.08% 200 5.18±0.14c 45.10 10.17±0.76b 56.46% 注:不同字母表示同列数据具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 2.6.3 金花茶多酚对线虫体内抗氧化酶及丙二醛含量的影响
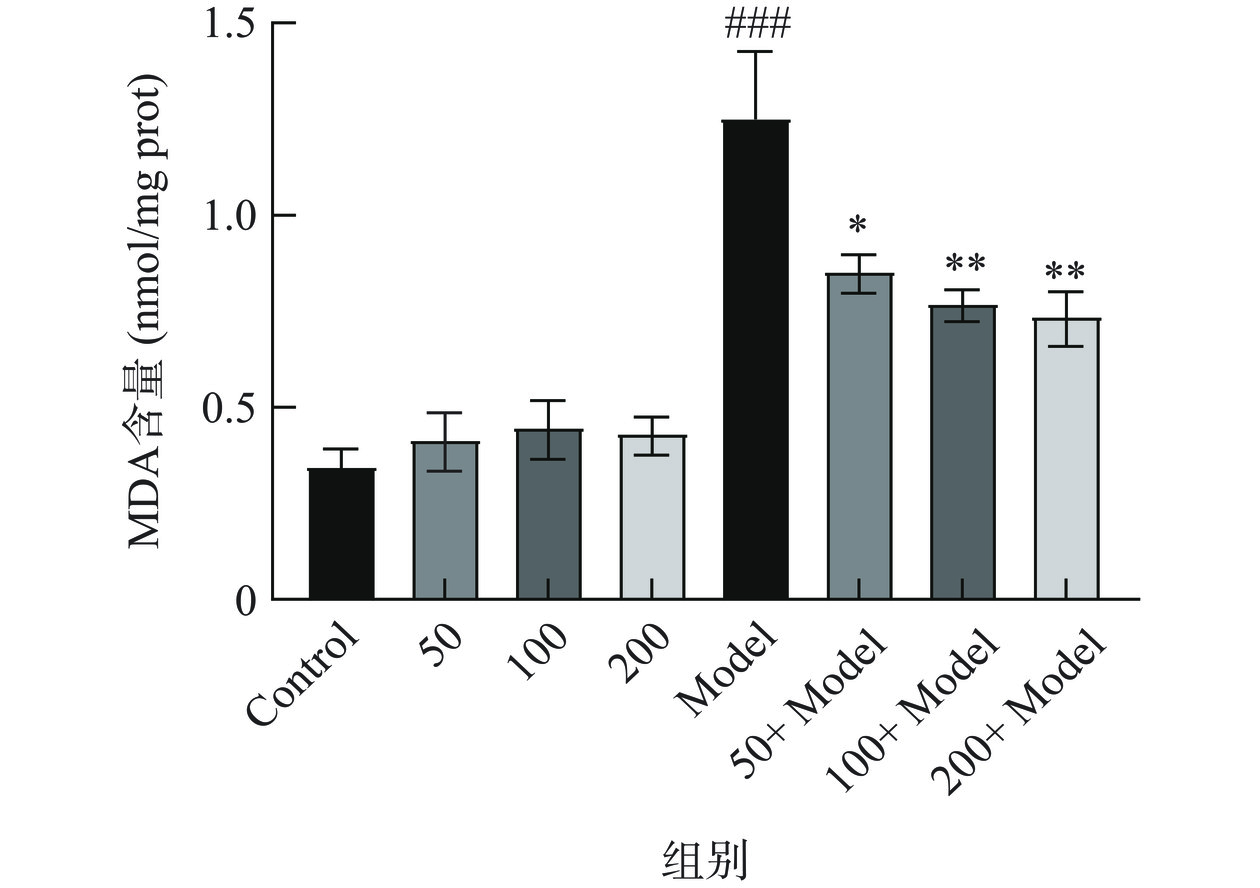
MDA是生物体内脂质过氧化的最终产物,被广泛应用为生物体氧化损伤的指标[43]。如图7所示,在正常情况下,金花茶多酚给药组相较于对照组无显著性差异,说明金花茶多酚对于秀丽隐杆线虫无毒副作用。而在热应激诱发线虫发生氧化应激条件下,金花茶多酚可以显著降低(P<0.05)线虫体内的MDA含量,进一步说明金花茶多酚可以在一定程度上抑制脂质发生过氧化反应,且抑制程度与金花茶多酚给药量呈剂量依赖性。
![]() 图 7 金花茶多酚对线虫MDA含量的影响注:#表示与Control组比较,*表示与Model组相比,#或*表示P<0.05差异显著,##或**表示P<0.01差异极显著,###或***表示P<0.001差异高度显著;图8同。Figure 7. Effects of Camellia nitidissima Chi polyphenols on the MDA contents of C.elegans
图 7 金花茶多酚对线虫MDA含量的影响注:#表示与Control组比较,*表示与Model组相比,#或*表示P<0.05差异显著,##或**表示P<0.01差异极显著,###或***表示P<0.001差异高度显著;图8同。Figure 7. Effects of Camellia nitidissima Chi polyphenols on the MDA contents of C.elegans2.6.4 金花茶多酚对线虫体内抗氧化酶活力的影响
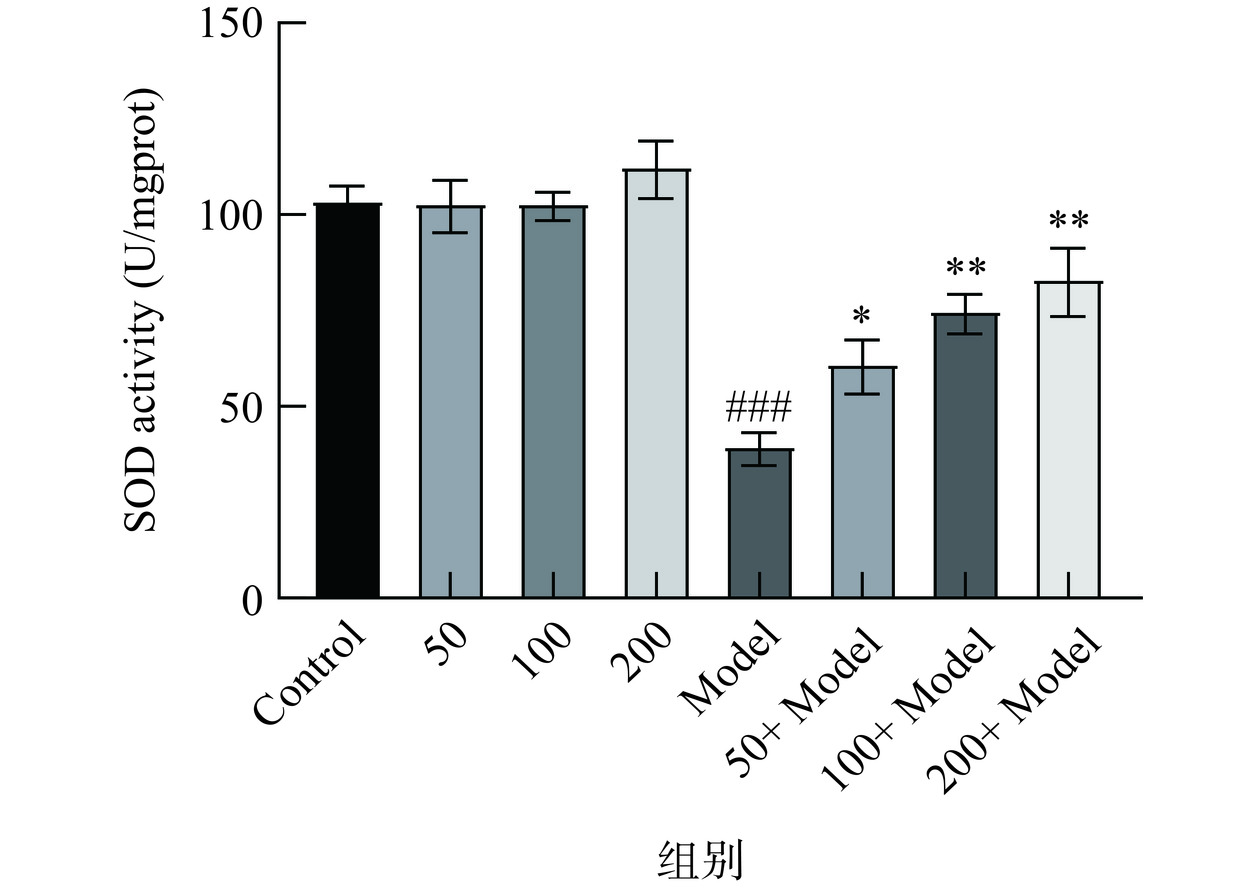
SOD是线虫体内主要的抗氧化酶,在机体的氧化和抗氧化平衡中发挥重要作用。当机体受到氧化应激作用时会导致体内氧化酶活性降低,从而导致氧自由基过度积累,从而引发氧化应激,因此测定SOD酶活力可作为生物体氧化损伤的指标[44]。如图8所示,在正常情况下,金花茶多酚给药组对于对照组无显著性差异,说明金花茶多酚对于秀丽隐杆线虫无毒副作用。而在热应激造模诱发线虫氧化应激条件下,金花茶多酚可以显著提高(P<0.05)秀丽隐杆线虫体内抗氧化酶SOD的活性,说明金花茶多酚可以在一定程度上抑制脂质发生氧化反应,且SOD酶活力与金花茶多酚给药量呈剂量依赖性。
3. 结论
在单因素实验的基础上,通过响应面试验设计优化金花茶多酚的提取工艺,最佳多酚提取工艺条件为料液比1:30 g/mL,乙醇浓度为55%,超声温度为35 ℃,超声功率为290 W,金花茶多酚的得率为3.53%±0.098%。该工艺技术操作简易,成本低,且能提高金花茶多酚提取得率,是一种金花茶多酚提取的高效方法,适合用于工业化生产。
采用Lx-8型大孔树脂进行纯化,金花茶多酚的纯度为63.73%。另外,通过采用高效液相色谱法对金花茶花中的主要多酚类成分进行定性及定量分析,其中没食子酸、绿原酸、表儿茶素、芦丁和鞣花酸的含量分别为0.47、11.18、59.03、18.34和16.41 mg/g,说明金花茶多酚冻干粉末中含有较多具有良好药用价值的多酚单体成分。
通过体外抗氧化实验,研究发现金花茶花多酚对DPPH自由基、ABTS+自由基、超氧阴离子自由基的IC50分别为0.38、0.16和0.39 mg/mL。进一步的体内实验显示金花茶多酚可显著缓解秀丽隐杆线虫氧化损伤,且提高线虫体内抗氧化酶活力,同时降低MDA含量,表明金花茶多酚具有优良的抗氧化活性,可作为一种安全的天然抗氧化剂。本研究为金花茶多酚的深入研究及开发利用提供理论依据。
-
图 7 金花茶多酚对线虫MDA含量的影响
注:#表示与Control组比较,*表示与Model组相比,#或*表示P<0.05差异显著,##或**表示P<0.01差异极显著,###或***表示P<0.001差异高度显著;图8同。
Figure 7. Effects of Camellia nitidissima Chi polyphenols on the MDA contents of C.elegans
表 1 响应面试验因素及水平设计
Table 1 Factors and levels of response surface experiment
水平 因素 A乙醇浓度
(%)B料液比
(g/mL)C超声功率
(W)D超声温度
(℃)−1 45 1:15 216 25 0 55 1:25 288 40 1 65 1:35 360 55 表 2 响应面试验设计及结果
Table 2 Design and results of Box-Behnken experiment
实验号 A B C D 茶多酚得率(%) 1 −1 −1 0 0 2.71±0.43 2 1 −1 0 0 2.31±0.32 3 −1 1 0 0 3.29±0.28 4 1 1 0 0 3.04±0.47 5 0 0 −1 −1 2.74±0.34 6 0 0 1 −1 2.86±0.52 7 0 0 −1 1 2.43±0.08 8 0 0 1 1 2.76±0.59 9 −1 0 0 −1 2.62±0.36 10 1 0 0 −1 2.5±0.33 11 −1 0 0 1 2.9±0.62 12 1 0 0 1 2.57±0.73 13 0 −1 −1 0 2.29±0.23 14 0 1 −1 0 2.74±0.32 15 0 −1 1 0 2.13±0.07 16 0 1 1 0 3.01±0.45 17 −1 0 −1 0 2.98±0.17 18 1 0 −1 0 2.63±0.29 19 −1 0 1 0 3.1±0.25 20 1 0 1 0 2.55±0.44 21 0 −1 0 −1 2.41±0.67 22 0 1 0 −1 2.98±0.39 23 0 −1 0 1 2.31±0.72 24 0 1 0 1 2.96±0.60 25 0 0 0 0 3.38±0.21 26 0 0 0 0 3.43±0.13 27 0 0 0 0 3.53±0.09 28 0 0 0 0 3.67±0.20 29 0 0 0 0 3.52±0.24 表 3 回归方程各项的方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of the regression equation
方差来源 平方和 自由度 方差 F值 P值 回归模型 4.48 14 0.32 14.39 <0.0001 A 2.7×10−3 1 2.7×10−3 0.12 0.7328 B 1.24 1 1.24 55.81 <0.0001 C 0.030 1 0.030 1.35 0.2650 D 0.33 1 0.33 14.98 0.0017 AB 1.6×10−3 1 1.6×10−3 0.072 0.7925 AC 0.011 1 0.011 0.50 0.4930 AD 0.011 1 0.011 0.50 0.4930 BC 0.046 1 0.046 2.08 0.1715 BD 5.625×10−3 1 5.625×10−3 0.25 0.6229 CD 0.010 1 0.010 0.45 0.5135 A2 1.31 1 1.31 58.73 <0.0001 B2 1.21 1 1.21 54.24 <0.0001 C2 1.18 1 1.18 52.99 <0.0001 D2 0.60 1 0.60 26.99 0.0001 残差 0.31 14 0.022 2.13>0.05 失拟项 0.26 10 0.026 纯误差 0.049 4 0.012 合计 4.79 28 R2=0.9350,R2adj=0.8700,R2pred=0.6689 注:P<0.05表示差异显著;P<0.01表示差异极显著。 表 4 金花茶标品的线性方程及线性范围
Table 4 Linear equation and linear range of Camellia nitidissima Chi standard roduct
标准品 线性方程 线性范围(μg/mL) 没食子酸 y=19411x−17.69(r=0.9994) 8~40 绿原酸 y=4959.9x−52.128(r=0.999) 24~120 表儿茶素 y=3863.5x−11.994(r=0.9993) 64~320 芦丁 y=11997x−62.186(r=0.999) 64~320 鞣花酸 y=21544x−1399.4(r=0.993) 64~320 表 5 金花茶多酚对秀丽隐杆线虫热应激损伤的影响
Table 5 Effects of polyphenols from Camellia nitidissima Chi on the heat stress injury of C.elegans
组别 质量浓度
(μg/mL)平均寿命
(h)平均寿命
延长率(%)最高寿命
(h)最高寿命
延长率(%)对照组 0 4.29±0.24a − 6.00±1.00a − 给药组 50 5.25±0.21b 6.96 8.50±1.32b 33.33 100 5.70±0.27c 28.70 9.67±1.53c 66.67 200 5.92±0.14c 37.99 11.17±0.76c 91.67 注:同列不同字母表示同列数据具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 表 6 金花茶多酚对秀丽隐杆线虫氧化应激损伤的影响
Table 6 Effects of polyphenols from Camellia nitidissima Chi on the oxidative stress injury of C.elegans
质量浓度
(μg/mL)平均寿命
(h)平均寿命
延长率(%)最高寿命 最高寿命
延长率(%)对照组 0 3.57±0.35a − 6.50±0,50a − 给药组 50 4.34±0.24b 21.57 7.50±0.50a 15.38% 100 4.98±0.11c 39.49 9.17±0.76b 41.08% 200 5.18±0.14c 45.10 10.17±0.76b 56.46% 注:不同字母表示同列数据具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] MENGTING W, GUILIANG Z, PEIYAO X, et al. In vitro propagation of Camellia fascicularis:A plant species with extremely small populations[J]. Journal of Canadian Journal of Plant Science,2019,100(2):202−208.
[2] 何秋梅, 高慧, 白燕远, 等. 越南金花茶化学成分差异及基于表型性状的亲缘关系分析[J]. 中草药,2022,53(2):557−568. [HE Q M, GAO H, BAI Y Y, et al. Analysis of difference in chemical composition and phenotypic characteristicsrelated genetic relationships of Camellia insularis samples[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2022,53(2):557−568.] HE Q M, GAO H, BAI Y Y, et al. Analysis of difference in chemical composition and phenotypic characteristicsrelated genetic relationships of Camellia insularis samples[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2022, 53(2): 557−568.
[3] 杜鸿志, 汤文敏, 刘青, 等. 金花茶本草考证何物种鉴定的研究进展[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2020,22(9):3136−3141. [DU H Z, TANG W M, LIU Q, et al. The herbalogical study and the research progress of species identification about Camellia nitidissima Chi[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Materia-World Science and Technology,2020,22(9):3136−3141.] DU H Z, TANG W M, LIU Q, et al. The herbalogical study and the research progress of species identification about Camellia nitidissima Chi[J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Materia-World Science and Technology, 2020, 22(9): 3136−3141.
[4] XING X, CHUAN S P, LIN H, et al. Effect of Camellia nitidissima extract on pancreatic function in diabetes mice[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,2013,24(12):2863−2865.
[5] ZHANG H L , WU Q X , QIN X M . Camellia nitidissima Chi flower extract alleviates obesity and related complications and modulates gut microbiota composition in rats with high-fat-diet-induced obesity[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2020, 100(12):4378-4389.
[6] DAI L, LI J, LIANG X Q , et al. Flowers of Camellia nitidissima cause growth inhibition, cell-cycle dysregulation and apoptosis in a human esopha geal squamous cell carcinoma cell line[J]. Molecular Medicine Reports, 2016, 14(2):117−122.
[7] GUPTA D, KUMAR M. Evaluation of in vitro antimicrobial potential and GC-MS analysis of Camellia sinensis and Terminalia arjuna[J]. Biotechnology Reports (Amsterdam, Netherlands),2017,13:19−25. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2016.11.002
[8] SONG L X, WANG X S, ZHENG X Q, et al. Polyphenolic antioxidant profiles of yellow Camellia[J]. Food Chemistry,2011,129(2):351−357. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.04.083
[9] WANG W X, LIU H Y, WANG Z N, et al. Phytochemicals from Camellia nitidissima Chi inhibited the formation of advanced glycation end-products by scavenging methylglyoxal[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,20(5):204−211.
[10] 陈瑶, 龚苏晓, 徐旭, 等. 金花茶化学成分和药理作用研究进展[J]. 药物评价研究,2022,45(3):575−582. [CHEN Y, GONG S X, XU X et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological studies of Camellianitidiss sima[J]. Drug Evaluation Research,2022,45(3):575−582.] CHEN Y, GONG S X, XU X et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological studies of Camellianitidiss sima[J]. Drug Evaluation Research, 2022, 45(3): 575−582.
[11] 姜丽娜, 李纪元, 范正琪, 等. 金花茶组植物花朵内多酚组分含量分析[J]. 林业科学研究,2020,33(4):117−126. [JIANG L N, LI J Y, FAN Z Q, et al. Content analysis of polyphenols in flowers of yellow Camellia[J]. Forest Research,2020,33(4):117−126.] JIANG L N, LI J Y, FAN Z Q, et al. Content analysis of polyphenols in flowers of yellow Camellia[J]. Forest Research, 2020, 33(4): 117−126.
[12] 高妙姿, 唐军荣, 邓佳, 等. 基于斑马鱼模型及网络药理学研究云南金花茶多酚的抗炎作用[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(11):134−142. [GAO M Z, TANG J R, DENG J, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of Camellia fascicularis polyphenols based on zebrafish model and network pharmacology[J]. Food Science,2023,44(11):134−142.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220525-318 GAO M Z, TANG J R, DENG J, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of Camellia fascicularis polyphenols based on zebrafish model and network pharmacology[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(11): 134−142. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220525-318
[13] 文治瑞, 王佳菜, 刘丽明, 等. 超声波辅助提取金花茶中黄酮类物质工艺及体外抗氧化研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(13):4364−4370. [WEN Z R, WANG J C, LIU L M, et al. Study on the ultrasonic assisted extraction of flavonoids from Camellia chrysantha and the antioxidant in vitro[J]. Food Safety & Quality,2020,11(13):4364−4370.] WEN Z R, WANG J C, LIU L M, et al. Study on the ultrasonic assisted extraction of flavonoids from Camellia chrysantha and the antioxidant in vitro[J]. Food Safety & Quality, 2020, 11(13): 4364−4370.
[14] GAO M Z, PENG X W, TANG J R, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Camellia fascicularis polyphenols via attenuation of NF-κB and MAPK pathways in LPS-Induced THP-1 macrophages[J]. Journal of Inflammation Reseach,2022,15:851−864. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S349981
[15] 徐嘉鸿, 刘美美, 戚滇杰, 等. 金花茶花总黄酮双水相提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(3):155−161. [XU J H, LIU M M, QI D J, et al. Optimization of aqueous two-phase extraction technology of total flavonoids from the flowers of camellia chrysantha and analysis of its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(3):155−161.] XU J H, LIU M M, QI D J, et al. Optimization of aqueous two-phase extraction technology of total flavonoids from the flowers of camellia chrysantha and analysis of its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(3): 155−161.
[16] 刘茜, 许子竞, 胡旭飞. 响应面微波辅助提取金花茶花多糖工艺研究[J]. 湖南师范大学自然科学学报,2016,39(3):40−45. [LIU Q, XU Z J, HU X F. Study on the microwave-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Camellia chrysantha(hu) tuyama flowers by response surface analysis[J]. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University,2016,39(3):40−45.] doi: 10.7612/j.issn.1000-2537.2016.03.008 LIU Q, XU Z J, HU X F. Study on the microwave-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Camellia chrysantha(hu) tuyama flowers by response surface analysis[J]. Journal of Natural Science of Hunan Normal University, 2016, 39(3): 40−45. doi: 10.7612/j.issn.1000-2537.2016.03.008
[17] 颜栋美, 李仁菊, 丘华, 等. 金花茶多酚提取工艺的研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2007(9):45−49. [YAN D M, LI R J, QIU H, et al. Extraction of Tea polyphenols in Camellia chryscath[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2007(9):45−49.] YAN D M, LI R J, QIU H, et al. Extraction of Tea polyphenols in Camellia chryscath[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2007(9): 45−49.
[18] 杨新, 陈莉, 卢红梅, 等. 茶多酚提取及纯化方法及其功能活性研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(5):322−328,332. [YANG X, CHEN L, LU H M, et al. Research progress on extraction and purification methods of tea polyphenols and its functional activities[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(5):322−328,332.] YANG X, CHEN L, LU H M, et al. Research progress on extraction and purification methods of tea polyphenols and its functional activities[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(5): 322−328,332.
[19] LI H, GUO H, LUO Q, et al. Current extraction, purification, and identification techniques of tea polyphenols:An updated review[J]. Critical Review in Food Science and Nutrition,2023,63(19):3912−3930. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1995843
[20] 颜栋美, 姚艾东. 金花茶多酚抗氧化性能的研究[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版),2009,30(2):42−45. [YAN D M, YAO A D. Study on anti-oxidation of tea-polyphenols in Camellia chryscath[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2009,30(2):42−45.] YAN D M, YAO A D. Study on anti-oxidation of tea-polyphenols in Camellia chryscath[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2009, 30(2): 42−45.
[21] ZHU A, ZHENG F L, ZHANG W J, et al. Oxidation and antioxidation of natural products in the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Antioxidants,2022,11(4):705. doi: 10.3390/antiox11040705
[22] MA L, ZHAO D Y, CHEN C Y, et al. Caenorhabditis elegans as a model system for target identification and drug screening against neurodegenerative diseases[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,2018,819:169−180. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.11.051
[23] LI H, GUO H, LUO Q, et al. Current extraction, purification, and identification techniques of tea polyphenols: An updated review[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr,2023,63(19):3912−3930.
[24] 邓祥, 韩伟. 酒石酸亚铁-标准曲线法检测绿茶提取物中茶多酚含量[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 42(5):677−682. [DENG X, HAN W. Determination of tea polyphenols in green tea extracts by ferrous tartrate-standard curve method[J] Journal of Nanjing Tech University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 42(5):677−682.] DENG X, HAN W. Determination of tea polyphenols in green tea extracts by ferrous tartrate-standard curve method[J] Journal of Nanjing Tech University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 42(5): 677−682.
[25] 宋佳敏, 王鸿飞, 孙朦, 等. 响应面法优化金蝉花多糖提取工艺及抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(4):275−281. [SONG J M, WANG H F, SUN M, et al. Optimization of extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from cordycepscicadae by response surface methodology[J]. Food Science,2018,39(4):275−281.] SONG J M, WANG H F, SUN M, et al. Optimization of extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from cordycepscicadae by response surface methodology[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(4): 275−281.
[26] SUN Y, ZHANG Y Q, QI W Q, et al. Saponins extracted by ultrasound from Zizyphus jujuba Mil var. spinosa leaves exert resistance to oxidative damage in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2021,15(1):541−554.
[27] 施利奇, 张彦青, 戚务勤, 等. 酸枣水提物不同提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品与机械,2019,35(11):182−190. [SHI L Q, ZHANG Y Q, QI W Q, et al. Optimization of different extraction process of sour jujube juice and study on its antioxidant[J]. Food & Machinery,2019,35(11):182−190.] SHI L Q, ZHANG Y Q, QI W Q, et al. Optimization of different extraction process of sour jujube juice and study on its antioxidant[J]. Food & Machinery, 2019, 35(11): 182−190.
[28] 李金泽. 鞣花酸对秀丽隐杆线虫的抗衰老作用及其机制的研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2023. [LI J Z. Study on the anti-aging effect and mechanisms of ellagic acid in caenorhabditis elegans[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2023.] LI J Z. Study on the anti-aging effect and mechanisms of ellagic acid in caenorhabditis elegans[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023.
[29] YU X S, SU Q N, SHEN T Q, et al. Antioxidant peptides from sepia esculenta hydrolyzate attenuate oxidative stress and fat accumulation in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Marine Drugs,2020,18(10):490. doi: 10.3390/md18100490
[30] 谢佳函, 刘回民, 刘美宏, 等. 红豆皮多酚提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性分析[J]. 中国食品学报,2020,20(1):147−157. [XIE J H, LIU H M, LIU M H, et al. Extraction process optimization and ant ioxidant activity analysis of polyphenols from azuki bean coats(Vigna angularis)[J]. Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2020,20(1):147−157.] XIE J H, LIU H M, LIU M H, et al. Extraction process optimization and ant ioxidant activity analysis of polyphenols from azuki bean coats(Vigna angularis)[J]. Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2020, 20(1): 147−157.
[31] 田建华, 张春媛, 魏璐. 沙棘果渣总黄酮提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2021,33(1):65−72. [TIAN J H, ZHANG C Y, WEI L. Study on the extraction technology and antioxidant activity of total flavonoids from the pomace of sea buckthorn[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2021,33(1):65−72.] TIAN J H, ZHANG C Y, WEI L. Study on the extraction technology and antioxidant activity of total flavonoids from the pomace of sea buckthorn[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2021, 33(1): 65−72.
[32] 张华, 孟博, 王莉, 等. 桑叶多糖超声-微波协同提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 中成药,2020,42(8):1972−1977. [ZHANG H, MENG B, WANG L, et al. Ultrasonic-microwave synergistic extraction process optimization and anti-oxidant activity for polysaccharides from Mori Folium[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2020,42(8):1972−1977.] ZHANG H, MENG B, WANG L, et al. Ultrasonic-microwave synergistic extraction process optimization and anti-oxidant activity for polysaccharides from Mori Folium[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2020, 42(8): 1972−1977.
[33] JI H Y, YU J, JIAO J S, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction of Codonopsis pilosula glucofructan: Optimization, structure, and immunoregulatory activity[J]. Nutrients,2022,14(5):927.
[34] 只德贤, 李建颖, 欧燕芳, 等. 黑果腺肋花楸原花青素提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品研究与开发,2023,44(8):96−104. [ZHI D X, LI J Y, OU Y F, et al. Extraction of proanthocyanidins from aronia melanocarpa and its antioxidant activity[J]. Food Research and Development,2023,44(8):96−104.] doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2023.08.014 ZHI D X, LI J Y, OU Y F, et al. Extraction of proanthocyanidins from aronia melanocarpa and its antioxidant activity[J]. Food Research and Development, 2023, 44(8): 96−104. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2023.08.014
[35] YANG R, GUAN Y, WANG W X, et al. Antioxidant capacity of phenolics in Camellia nitidissima Chi flowers and their identification by HPLC triple TOF MS/MS[J]. PLoS One,2018,13(4):e0195508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195508
[36] 郑时旭, 陈丽, 丁雅容, 等. 没食子酸激活Nrf-2信号通路降低高糖诱导NIH-3T3细胞氧化应激与炎症反应[J]. 中药药理与临床,2024,40(2):78−84. [ZHENG S X, CHEN L, DING Y R, et al. Gallic acid activates Nrf-2 signaling pathway to alleviate high glucose-induced oxidative stress and inflammation of NIH-3T3 cells[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica,2024,40(2):78−84.] ZHENG S X, CHEN L, DING Y R, et al. Gallic acid activates Nrf-2 signaling pathway to alleviate high glucose-induced oxidative stress and inflammation of NIH-3T3 cells[J]. Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 2024, 40(2): 78−84.
[37] 余婷, 谢宇端, 刘晶, 等. 绿原酸通过cGAS-STING信号通路改善慢性肾小球肾炎大鼠的T淋巴细胞免疫[J]. 免疫学杂志,2023,39(9):737−745. [YU T, XIE Y D, LIU J, et al. Chlorogenic acid improves T lymphocyte immunity in rats with chronic glomerulonephritis through cGAS-STING signal pathway[J]. Immunological Journal,2023,39(9):737−745.] YU T, XIE Y D, LIU J, et al. Chlorogenic acid improves T lymphocyte immunity in rats with chronic glomerulonephritis through cGAS-STING signal pathway[J]. Immunological Journal, 2023, 39(9): 737−745.
[38] 叶梦倩, 吴孟华, 马志国, 等. 香薰HPLC指纹图谱及多指标成分定量分析[J]. 药物分析杂质,2023,43(2):236−244. [YE M Q, WU M H, MA Z G, et al. HPLC fingerprint and multi-components quantitative analysis of moslae herba[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis,2023,43(2):236−244.] YE M Q, WU M H, MA Z G, et al. HPLC fingerprint and multi-components quantitative analysis of moslae herba[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2023, 43(2): 236−244.
[39] BRUSKOV V I, MALAKHOVA L V, MASALIMOV Z K, et al. Heat-induced formation of reactive oxygen species and 8-oxoguanine, a biomarker of damage to DNA[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2002,20(6):1354−1363.
[40] OLIVEIRA B F, NOGUEIRA-MACHADO J A, CHAVES M M. The role of oxidative stress in the aging process[J]. The Scientific World Journal,2010,10:1121−1128. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2010.94
[41] CAÑELO A, GILBERT-LÓPEZ B, PACHECO-LIÑÁN P, et al. Tyrosol, a main phenol present in extra virgin olive oil, increases lifespan and stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development,2012,133(8):563−574. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2012.07.004
[42] VAN RAAMSDONK J M, HEKIMI S. Deletion of the mitochondrial superoxide dismutase SOD-2 extends lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. PLoS Gentics,2009,5(2):e1000361. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000361
[43] YAN Z M, ZHONG Y, DUAN Y, et al. Antioxidant mechanism of tea polyphenols and its impact on the health benefits[J]. Animal Nutrition,2020,6(2):115−123. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2020.01.001
[44] 何宛诗, 郑钦生, 陈小艳, 等. 雨生红球藻新型抗氧化肽的制备纯化、鉴定筛选及其对秀丽线虫抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(22):116−125. [HE W S, ZHENG Q S, CHEN X Y, et al. Isolation, identification and evaluation by Caenorhabditis elegans of Haematococcus pluvialis novel antioxidant peptide[J]. Food Science,2023,44(22):116−125.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230208-077 HE W S, ZHENG Q S, CHEN X Y, et al. Isolation, identification and evaluation by Caenorhabditis elegans of Haematococcus pluvialis novel antioxidant peptide[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(22): 116−125. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20230208-077
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 曲扬,刘振红. 复合凝聚法制备山奈酚微胶囊及对剧烈运动所致氧化应激损伤保护作用. 食品科技. 2025(01): 275-283 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赵雅玲,卞赢莹,房耀维,周文梅,韩舒婷,冯娟,刘姝. 嗜热链球菌FUA329发酵红茶工艺优化及贮藏品质变化. 中国食品添加剂. 2024(11): 178-186 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李国巍,石雨,张正海,姬妍茹,杨庆丽,董艳,高宝昌,李柏阳. 黑海棠果多酚提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性分析. 中国食品添加剂. 2024(12): 19-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 卢翠文,欧萍,叶有明,何晓燕,杨东美. 微波辅助酶法提取茶酒糟中可溶性膳食纤维及其抗氧化性能研究. 饲料研究. 2024(20): 75-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



