Effects of Different Lights on Seed Germination, Total Flavonoids Synthesis, and Related Enzyme Activities of Toona sinensis Seedlings
-
摘要: 为探索不同光照对香椿幼苗生长、总黄酮合成及相关酶活性的影响,以‘红油椿’为试验材料,采用LED光源,对萌发种子及幼苗进行白光(CK)、蓝光(B)、红蓝复合光2:1(R2B1)、红蓝复合光1:1(R1B1)、红蓝复合光1:2(R1B2)、红光(R)处理,在不同光照处理15 d后对种子发芽指标、幼苗总黄酮合成以及相关酶活性进行了测定。结果表明,与对照组CK相比,红光为主的光质处理(R、R1B1、R2B1)促进了香椿种子萌发,其中R2B1处理全株干质量与鲜质量最高,与CK相比分别提高了55.06%、82.86%。与CK和R相比,其他光照处理均显著(P<0.05)提高了香椿幼苗中总黄酮的含量,其中B处理显著高于其他处理组,同时B处理显著(P<0.05)提高了苯丙氨酸解氨酶(PAL)、查尔酮合成酶(CHS)、查尔酮异构酶(CHI)的活性,与香椿叶片中总黄酮含量的变化呈显著正相关。因此,采用R2B1处理香椿种子能促进其萌发,采用B处理香椿幼苗能有效促进PAL、CHS、CHI酶活性以显著提高总黄酮的合成。Abstract: In order to explore the effects of different lights on seed germination, total flavonoids synthesis, and related enzyme activities of Toona sinensis seedlings, LED were applied to the seeds and seedlings of Toona sinensis. The experimental materials were ‘Hongyou Toona sinensis’. White light (CK), blue light (B), red and blue light 2:1 (R2B1), red and blue light 1:1 (R1B1), red and blue light 1:2 (R1B2), red light (R) were used for 15 days respectively, and the seed germination, total flavonoid synthesis and related enzyme activities in seedlings were measured. The results showed that compared to the control group (CK), the red light dominated illumination (R, R1B1, R2B1) promoted the seeds germination, and the dry and fresh weight of the whole plant treated with light (R2B1) increased by 55.06% and 82.86% respectively, which were the highest among all the treatments. Compared with CK and R, other light treatments significantly increased the total flavonoid content in Toona sinensis seedlings (P<0.05). Treatment B was significantly higher than other groups, and the activities of phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL), chalcone synthase (CHS), and chalcone isomerase (CHI) were also significantly increased (P<0.05), which showed a significant positive correlation with the changes in total flavonoid. Therefore, the germination of Toona sinensis seeds can be facilitated by the treatment of R2B1, and a significant enhancement in total flavonoid synthesis can be achieved by the treatment of B for Toona sinensis seedlings, effectively promoting the activities of PAL, CHS, and CHI enzymes.
-
Keywords:
- Toona sinensis /
- light quality /
- germination /
- total flavonoids /
- enzyme activity
-
香椿(Toona sinensis)为楝科香椿属植物,其嫩叶可食,芳香馥郁,是一种深受消费者喜爱的绿色保健食品,素有“树上蔬菜”之称[1]。研究发现香椿中含有黄酮、生物碱、皂苷等多种活性成分,其中黄酮类化合物是主要药效成分,具有显著的药理作用[2],如抗氧化、抗炎[3]、抗肿瘤[4]等。因此,香椿具有较高的食用和药用价值[5]。光是影响植物生长发育的主要环境因素之一,研究表明,不同光的照射会直接或间接影响植物的发育和物质代谢,对幼苗形态和有机物合成具有调节作用[6]。叶片作为植物光合作用的主要器官,受光质影响较为明显[7]。石勇志[8]在对甘草的研究中发现,红蓝组合光对叶面积的生长有明显的促进作用。樊小雪等[9]研究表明,蓝光处理下的小白菜叶片更厚,发育更好。杨俊伟等[10]报道,红蓝组合光处理对番茄幼苗叶片生物量积累的效果更加显著。
黄酮类化合物受光照调控的结果较为明显,研究表明,光照会影响苯丙烷类代谢途径中相关酶的活性从而影响黄酮的合成。Guo等[11]在对水母雪莲的叶片研究中发现蓝光可以促进黄酮的合成,章雷[12]对银杏叶的研究中证实了发光二极管(Light-emitting diode,LED)对植物中黄酮含量的积累具有显著的生物学调控作用。黄酮类化合物作为植物的次级代谢产物,是相关代谢酶通过复杂的协同调控产生的。黄酮类物质生物合成中受多种催化酶影响[13]。其中苯丙氨酸脱氨酶(Phenylaanine ammon-ialyase,PA)作为关键限速酶,可以进一步转化类黄酮等物质[14];查尔酮合成酶(Chalcone synthase,CHS)作为苯丙烷类代谢转向类黄酮合成过程中的第一个关键酶[15],能够催化香豆酰辅酶A(Coumaroyl-CoA)与丙二酰辅酶A(malonyl-CoA)结合生成黄酮的前体;查尔酮异构酶(Chalcone isomerose,CHI)作为黄酮合成途径中的第二个关键性酶,可催化柚皮素查尔酮分子内环化反应生成生松素等类黄酮母核,进一步修饰为不同类的黄酮结构[16]。关于LED光调控在不同品种植物上的应用已有相关研究,Hogewoning等[17]在辐照对黄瓜叶片的影响中发现蓝光能有效诱导PAL活性升高;赵德修等[18]在光质对水母雪莲黄酮生成物的影响中发现白光对植物体内PAL活性促进作用最好;Thwe等[19]在荞麦芽植株光照射试验中发现蓝光处理对CHS酶活性有明显的促进作用;徐琳煜[20]研究发现红光对三叶青CHS酶活性的促进效果最好。
香椿属喜光植物,可以通过光质调节改善香椿生长状况,提高香椿营养价值[21]。除此之外,可以通过光调控的方式实现香椿的反季节栽培,替代传统的香椿种植方式,实现周年供应。LED作为可以人为控制操作的电光源,其优势在于质量轻、体积小、更节能,有巨大的市场应用潜力[22]。目前国内有关光质对香椿幼苗中黄酮及相关酶活性影响的研究较少,本文旨在探究光质对香椿幼苗中总黄酮积累与相关酶活性影响的关系,通过不同光质配比处理,优化香椿培育条件,为香椿产业化生产及光照管理提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
香椿(品种‘红油椿’,太和香椿种子) 安徽省阜阳市太和县;植物查尔酮合成酶(CHS)酶联免疫分析试剂盒、植物查尔酮异构酶(CHI)酶联免疫分析试剂盒 江苏晶美生物科技有限公司;苯丙氨酸解氨酶(PAL)试剂盒、芦丁(纯度>98%) 南京建成生物工程研究所。
730紫外分光光度计 上海奥析科学仪器有限公司;AR224CN电子天平 奥豪斯仪器(上海)有限公司;台式高速冷冻离心机、MuitiskanGO全波长酶标仪 赛默飞世尔科技有限公司;KHLG-260B-3LED智能光照培养箱 杭州绿博仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 香椿种子萌发试验
选取大小一致、籽粒饱满且无损伤的香椿种子。将种子用1% NaClO溶液浸泡0.5 h,后用无菌水冲洗3~5次,消毒后的种子置25 ℃温水浸泡12 h完成浸种。将浸种后的香椿种子分为6组,每个培养皿内均匀放置55粒种子,置于25 ℃的LED培养箱中,在蓝光(B)、红光:蓝光=2:1(R2B1)、红光:蓝光=1:1(R1B1)、红光:蓝光=1:2(R1B2)、红光(R)处理下进行种子发芽试验,以白光(CK)作为对照。
1.2.2 香椿幼苗生长试验
分别从培养皿中选取长势一致的幼苗30株,将其置于25 ℃的LED培养箱中。在生长过程中,分别用蓝光(B)、红光:蓝光=2:1(R2B1)、红光:蓝光=1:1(R1B1)、红光:蓝光=1:2(R1B2)、红光(R)5种不同光质不间断处理15 d,培养期间每隔24 h浇一次水。
1.2.3 香椿种子萌发及幼苗阶段各指标测定
在香椿种子培养第3 d统计种子发芽数,计算种子发芽势。在种子培养第7 d计算种子发芽率。参照刘珂等[23]的方法,统计第15 d的发芽数,并计算发芽指数、活力指数。在育苗第15 d,随机选取15株长势一致的幼苗进行鲜重、株高及干重测定。使用游标卡尺测量幼苗的株高,1/10000天平测量幼苗的鲜重和干重。其中干重先在烘干箱105 ℃下杀青30 min,然后在55 ℃下烘至恒质量后称重。计算公式如下:
发芽势GE(%)=发芽3d种子发芽数种子总数×100 发芽率GR(%)=香椿萌发种子总数供试种子总数×100 发芽指数GI=Σ(Gt/Dt) 活力指数=GI×S 式中:GI为发芽指数;Gt为在时间为t日的萌发数;Dt为相对应的萌发日数;S为幼苗长度。
1.2.4 香椿幼苗黄酮类化合物提取及含量测定
在参考陈丛瑾等[24]方法的基础上加以改进。精确称取0.2 g香椿叶片,置研钵内充分研磨成浆。用2.5 mL、75%乙醇溶液于55 ℃,80 W下超声振荡提取80 min,将提取液于10000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液于4 ℃下保存备用。以芦丁为标准品绘制标准曲线,在510 nm下测定吸光度[25],得到吸光值y与芦丁浓度x (mg/mL)关系曲线的回归方程:y=0.7207x+0.0025,R2=0.9993,将吸光值带入回归方程曲线中计算黄酮含量并分析数据。
1.2.5 香椿幼苗总黄酮类化合物合成相关酶活性测定
采用苯丙氨酸解氨酶测定试剂盒进行香椿样品中的PAL酶活性测定。采用植物查尔酮异构酶酶联免疫分析试剂盒进行CHI活性测定。采用查尔酮合酶酶联免疫试剂盒进行CHS酶活性测定。
1.3 数据处理
用Excel 2003对数据进行处理与作图;采用SPSS 26.0进行分析,以平均值±标准差表示,并对不同处理间的数据用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)进行差异显著性检验,P<0.05表示显著差异;采用Origin 9.0软件进行柱状图绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同光质对香椿幼苗生长的影响
2.1.1 发芽指标分析
由表1数据可知,R处理下香椿发芽势、活力指数高于CK处理,与CK相比分别增加了21.25%、19.23%。其中R1B1的发芽势、发芽指数均为最高,与CK相比分别提高了44.34%、14.08%。不同比例的红蓝光复合处理下,香椿幼苗的各发芽指标随红光比例的增加呈上升趋势,而蓝光则呈相反趋势。综上说明红光以及红蓝复合光的处理可以促进香椿种子萌发,且复合光处理效果优于单源红光处理,与Yang等[26]研究结果一致。
表 1 不同光质下香椿种子发芽指标Table 1. Germination indicators of Toona sinensis seedlings under different light quality处理 发芽势(%) 发芽率(%) 发芽指数 活力指数 CK 43.3±1.94b 86.72±4.39a 28.27±0.66b 393.20±26.77b B 31.7±3.69c 75.01±3.41c 24.34±1.06c 86.30±12.19e R2B1 60.0±2.06a 85.84±4.23a 31.86±0.91a 461.71±33.32a R1B1 62.5±5.34a 84.43±5.72ab 32.25±0.74a 307.70±22.94c R1B2 48.3±3.78b 81.74±5.19b 29.25±0.55b 173.85±21.00d R 52.5±2.45ab 79.10±3.78bc 29.57±2.78b 468.80±25.76a 注:同列不同小写字母表示在0.05水平上具有差异显著性;表2同。 2.1.2 基础表观指标分析
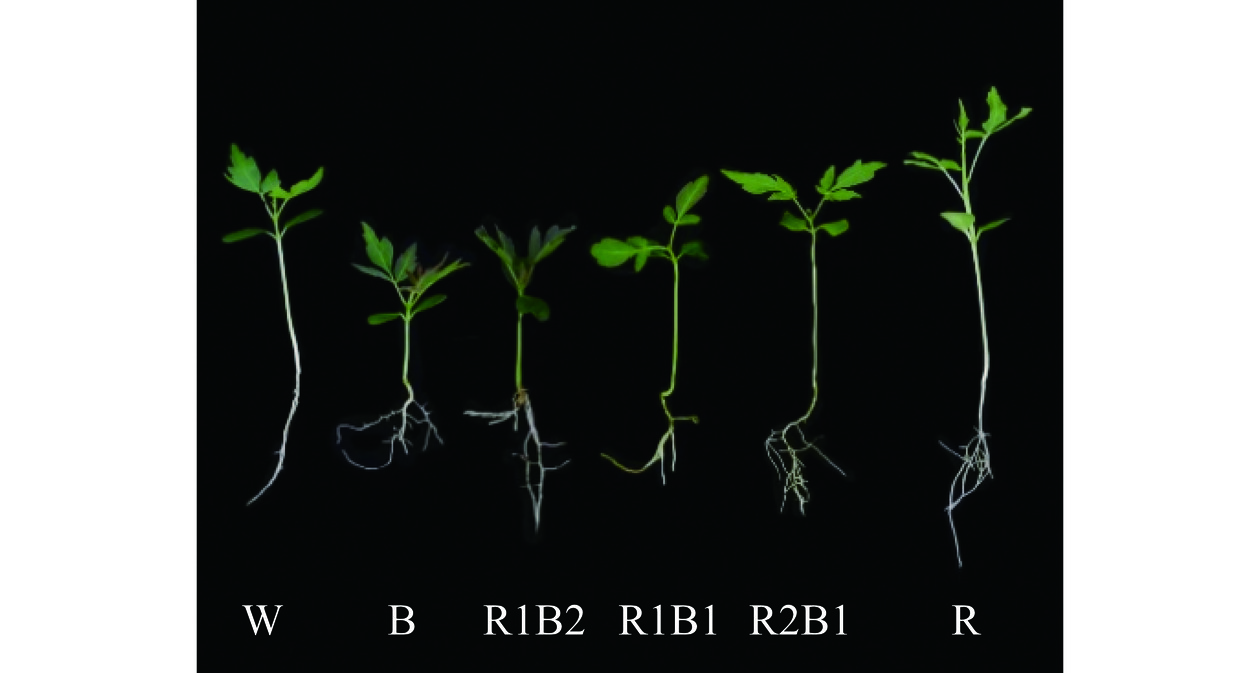
从表2可知,随着红光比例的增加,香椿幼苗株高也随之增加。R处理香椿幼苗株高显著高于其他处理(P<0.05),与CK相比提高了13.25%;R2B1幼苗的鲜质量、干质量均为最大,分别比CK增加了55.06%、82.86%;B处理对香椿幼苗的株高、鲜质量具有显著的抑制作用(P<0.05),且比例越高抑制作用越明显。此外,对培育第15 d的香椿幼苗进行观察,由图1可知,随着蓝光比例的增加,幼苗叶片绿色加深,这表明蓝光与香椿幼苗叶片的色素积累方面可能存在着一定关系。红光可以促进香椿幼苗的茎长伸长以及干、鲜质量的积累,这与红光可以提高菊花的株高、干鲜重和氮代谢[27],蓝光可使菊花植株变矮[28]的结果一致。
表 2 不同光质下香椿幼苗基础指标Table 2. Basic indexes of Toona sinensis seedlings under different light quality处理 株高(cm) 全株鲜质量(g) 全株干质量(g) CK 13.96±0.89c 0.0721±0.0011b 0.0070±0.0005c B 3.53±0.29f 0.0446±0.0025c 0.0062±0.0003c R2B1 14.54±1.03b 0.1118±0.094a 0.0128±0.0003a R1B1 9.52±0.72d 0.0903±0.0017bc 0.0106±0.0006b R1B2 5.96±0.72e 0.0563±0.0078bc 0.0064±0.0005c R 15.81±0.92a 0.1055±0.0035a 0.0099±0.0007b 2.2 不同光质对香椿幼苗总黄酮含量的影响
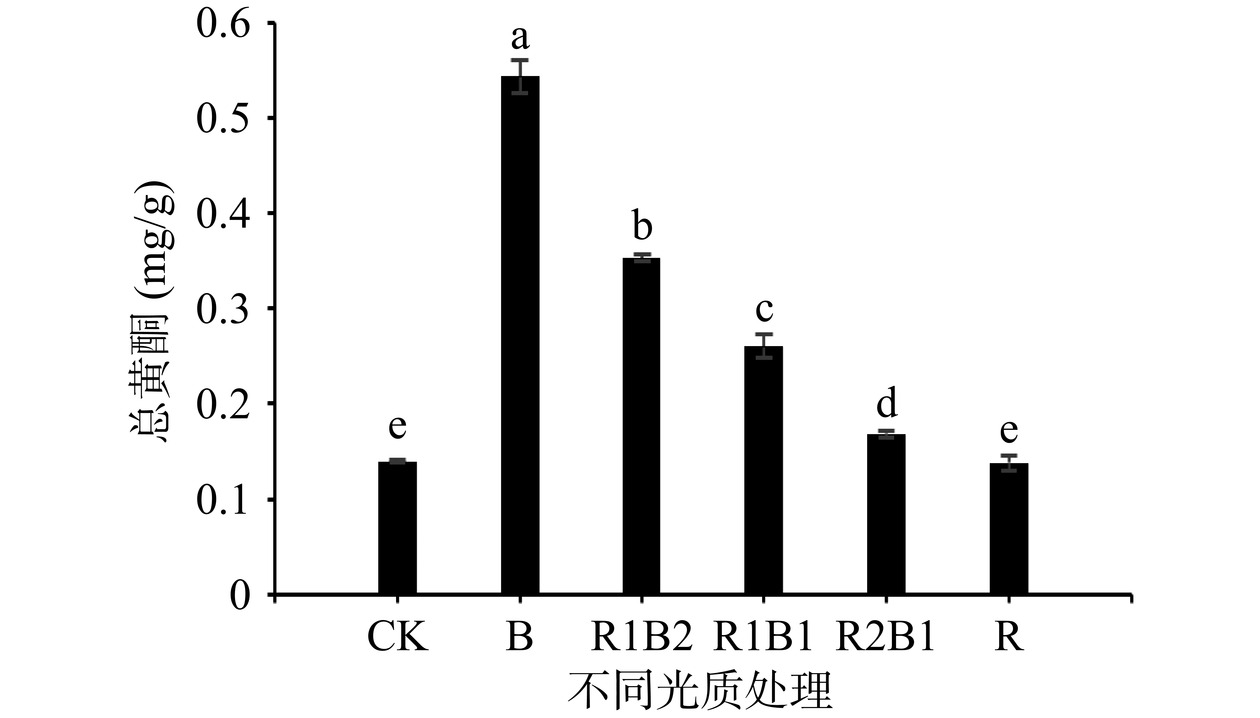
总黄酮具有多种生物活性和药理作用,其含量的高低是衡量香椿营养价值的重要指标之一[29]。由图2可知,香椿叶片中总黄酮含量随蓝光比例增加而增加,其中B处理黄酮含量最高,R1B2次之,CK最低,而R与CK差异不显著(P>0.05),其他处理均显著高于CK(P<0.05)。B与R1B2中黄酮含量分别为0.5227、0.3490 mg/g。说明黄酮类化合物的合成与积累受蓝光的影响十分显著,与崔琳琳等[30]研究结果一致。
2.3 不同光质对香椿黄酮类化合物相关酶活性的影响
2.3.1 PAL活性分析
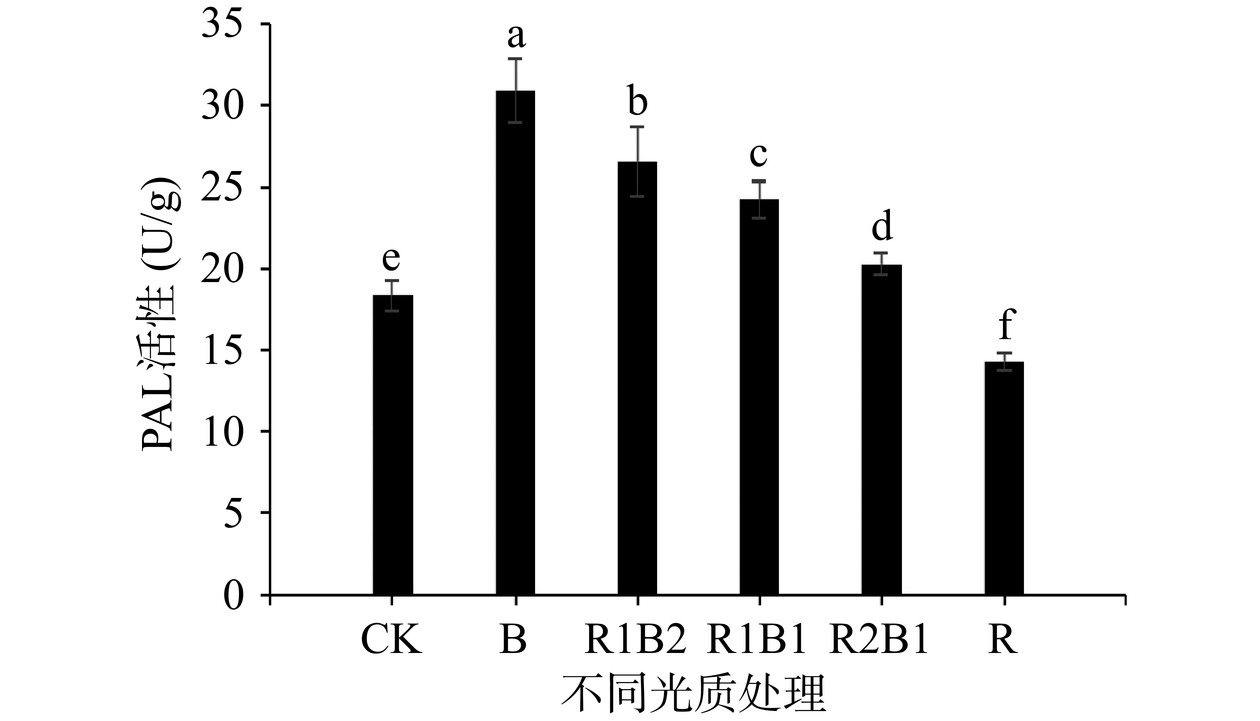
PAL是苯丙烷途径的关键酶,与黄酮类物质合成密切相关[31],对外界环境因子较为敏感。由图3可知,R处理下PAL酶活性最低,香椿幼苗中PAL酶活性随蓝光比例的增高而逐渐上升,B处理下PAL酶活性最高,B、R1B2、R1B1、R2B1显著高于CK,R处理显著低于CK组(P<0.05)。结果表明蓝光和红蓝复合光在一定程度上能提高香椿幼苗中PAL酶活性,而单源红光处理对其有抑制作用。
2.3.2 CHS活性分析
由图4可知,与CK相比,B、R1B2、R1B1处理下香椿叶片的CHS酶活性有显著差异(P<0.05)。B处理下CHS酶活性最高,R1B2次之,具体表现为B>R1B2>R1B1>R2B1>CK>R。B与CK相比提高了53.35%,三种不同配比的红蓝复合光(R1B2、R1B1、R2B1)处理对于CHS酶活性均起促进作用,与CK相比分别提高了23.21%、17.33%、7.01%,这与Thwe等[19]研究结果一致。
2.3.3 CHI活性分析
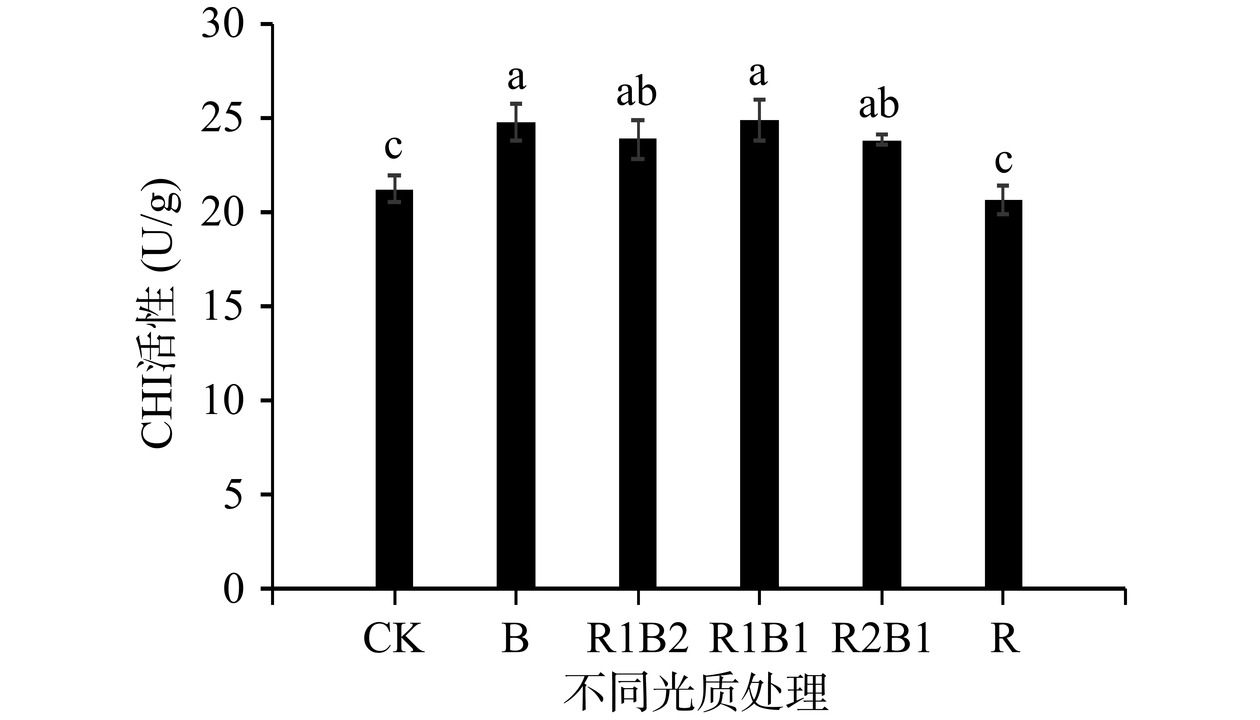
由图5可知,红蓝复合光处理均显著提高了香椿幼苗中CHI酶的活性,B处理CHI酶的活性达到最高值,显著高于CK与R(P<0.05),但与其他处理差异不显著(P>0.05)。说明蓝光和红蓝复合光处理均可以提高香椿幼苗中CHI酶的活性,而单源红光处理对其则有抑制作用。
2.3.4 相关性分析
总黄酮是香椿中重要成分之一[32],其合成主要依赖于苯丙烷代谢途径,PAL是连接初生代谢和次生代谢途径的枢纽,而CHS和CHI是总黄酮合成途径早期阶段的关键酶和限速酶,对于总黄酮的合成起着重要作用[33]。由表3可知总黄酮含量与PAL、CHS酶活性均呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与CHS活性相关系数最高,达0.953,其次是PAL,达0.936。由此可知,光处理提高香椿幼苗中总黄酮的含量是通过提高相关酶活性实现的。
表 3 总黄酮含量与PAL、CHS、CHI酶活性的相关性分析Table 3. Correlation analysis of total flavonoid content with PAL, CHS and CHI enzyme activities项目 总黄酮含量 PAL CHS CHI 总黄酮含量 − PAL 0.936** − CHS 0.953** 0.982** − CHI 0.700 0.829* 0.794 − 注:*表示显著相关(P<0.05);**表示极显著相关(P<0.01)。 3. 讨论
3.1 不同光质对香椿幼苗生长的影响
本试验研究结果表明,红光有利于香椿种子发芽,对香椿幼苗生长有促进作用,而蓝光则起到抑制作用,该结果与Yang等[26]结果一致。与CK相比,红蓝复合光显著提高了香椿幼苗中有机物的积累(P<0.05),其中R2B1处理全株鲜质量与干质量最高。与R相比,复合光处理香椿种子的发芽率、发芽势较高,这可能与单色光导致植物光和系统可见光的能量分布不均衡有关[34],王丽伟[35]在番茄幼苗植株的研究发现,复合光处理番茄幼苗植株干重质量、根系活力等比单源光处理幼苗生长更健壮,壮苗指数更大;邵明杰等[36]在紫叶生菜连续光照处理的试验中也观察到红蓝光照射处理效果更好,类似的现象也在金鱼草[37]、金钗石斛[38]等研究中被发现。
3.2 不同光质对香椿幼苗中总黄酮含量的影响
不同光质处理下,香椿幼苗中总黄酮含量随蓝光比例的升高而上升,B处理总黄酮含量最高,R处理则受到抑制。说明光的波段长短会影响植物体内的黄酮积累,与Gyu等[39]研究一致。因此,可采用R1B2复合光处理香椿幼苗,从而有效调控光环境促进黄酮合成。
3.3 不同光质对香椿黄酮类化合物相关酶活性的影响
试验结果表明,PAL酶活性受到光质的影响差异显著,而蓝光对其有促进作用,与潘俊倩等[40]的研究结果一致。同时,在光谱中,蓝光所占比例降低,致使影响香椿幼苗中蓝光受体的光信号减少,据此可以认为蓝光信号通量减少时,PAL酶的活性降低。CHS作为黄酮代谢上游的关键酶,本试验研究结果表明CHS酶活性变化与PAL酶活性有类似的趋势。CHI作为第二个关键性酶,可将查尔酮异构后的物质进一步修饰为不同类的黄酮结构[41]。从总体上看,蓝光对CHI酶活性有显著的促进作用,红光处理下CHI酶活性与CK组无显著差异。相关性分析结果表明,香椿幼苗中黄酮含量的变化与各酶活性变化趋势呈正相关。总黄酮作为香椿幼苗重要的次生代谢产物,其合成主要依赖于苯丙烷代谢途径[42],分析认为,蓝光提高了代谢途径中黄酮合成相关酶的活性,促进了黄酮合成中前体物质的转化,进而促进了黄酮含量的积累。大量的研究证明了这一观点,如刘守赞等[43]对三叶青的黄酮含量及酶活性之间的相关性进行了分析,结果表明黄酮与PAL、CHS酶活性有较强的相关性;李娜[44]对蓝光照射下的大豆芽苗菜进行了分析,发现PAL酶活性增加,可促进其黄酮合成;在西兰花[45]的研究中亦有类似发现。而试验中CHI酶的活性与总黄酮含量相关性不显著可能是由于香椿中次级代谢具有一定的复杂性,还需要进一步的研究来揭示其潜在机制。
4. 结论
综上所述,光调节能够刺激香椿种子萌发,尤其是R为主的光质处理(R、R1B1、R2B1),其中R2B1全株鲜质量与干质量最大,与CK相比分别提高了55.06%、82.86%。不同配比的红蓝光处理对香椿幼苗中PAL、CHS酶活性有促进作用,其中B处理显著高于其他处理,与总黄酮含量的变化呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),同时B处理下黄酮含量最高为0.5227 mg/g,推测蓝光刺激幼苗中黄酮的合成是因为提高了相关酶的活性。生产上可以采用R2B1处理萌发期的香椿种子,B处理生长中的芽苗菜及香椿嫩芽,以此提高香椿芽苗菜及嫩叶品质。
-
表 1 不同光质下香椿种子发芽指标
Table 1 Germination indicators of Toona sinensis seedlings under different light quality
处理 发芽势(%) 发芽率(%) 发芽指数 活力指数 CK 43.3±1.94b 86.72±4.39a 28.27±0.66b 393.20±26.77b B 31.7±3.69c 75.01±3.41c 24.34±1.06c 86.30±12.19e R2B1 60.0±2.06a 85.84±4.23a 31.86±0.91a 461.71±33.32a R1B1 62.5±5.34a 84.43±5.72ab 32.25±0.74a 307.70±22.94c R1B2 48.3±3.78b 81.74±5.19b 29.25±0.55b 173.85±21.00d R 52.5±2.45ab 79.10±3.78bc 29.57±2.78b 468.80±25.76a 注:同列不同小写字母表示在0.05水平上具有差异显著性;表2同。 表 2 不同光质下香椿幼苗基础指标
Table 2 Basic indexes of Toona sinensis seedlings under different light quality
处理 株高(cm) 全株鲜质量(g) 全株干质量(g) CK 13.96±0.89c 0.0721±0.0011b 0.0070±0.0005c B 3.53±0.29f 0.0446±0.0025c 0.0062±0.0003c R2B1 14.54±1.03b 0.1118±0.094a 0.0128±0.0003a R1B1 9.52±0.72d 0.0903±0.0017bc 0.0106±0.0006b R1B2 5.96±0.72e 0.0563±0.0078bc 0.0064±0.0005c R 15.81±0.92a 0.1055±0.0035a 0.0099±0.0007b 表 3 总黄酮含量与PAL、CHS、CHI酶活性的相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of total flavonoid content with PAL, CHS and CHI enzyme activities
项目 总黄酮含量 PAL CHS CHI 总黄酮含量 − PAL 0.936** − CHS 0.953** 0.982** − CHI 0.700 0.829* 0.794 − 注:*表示显著相关(P<0.05);**表示极显著相关(P<0.01)。 -
[1] 史冠莹, 王晓敏, 赵守涣, 等. 不同产地香椿嫩芽主要营养成分、活性物质及挥发性成分分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(3):207−215,22. [SHI G Y, WANG X M, ZHAO S H, et al. Analysis of main nutrients, active ingredients and volatile components of Toona sinensis buds from different regions[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(3):207−215,22.] SHI G Y, WANG X M, ZHAO S H, et al. Analysis of main nutrients, active ingredients and volatile components of Toona sinensis buds from different regions[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(3): 207−215,22.
[2] 王晓敏, 杨慧, 张乐, 等. 香椿废弃组织中总黄酮提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(11):232−237. [WANG Xiaomin, YANG Hui, ZHANG Le, et al. Optimization of extraction process of total flavonoids from the abandoned branches of Toona sinensis and antioxidant activities evaluation[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(11):232−237.] WANG Xiaomin, YANG Hui, ZHANG Le, et al. Optimization of extraction process of total flavonoids from the abandoned branches of Toona sinensis and antioxidant activities evaluation[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2016, 37(11): 232−237.
[3] ZHAO K. Rhizoma drynariae total flavonoids inhibit the inflammatory response and matrix degeneration via MAPK pathway in a rat degenerative cervical intervertebral disc model[J]. Biomedicine& Pharmacotherapy,2021,138:111466.
[4] HOU M, HU W, XIU Z, et al. Efficient enrichment of total flavonoids from Pteris ensiformis Burm. extracts by macroporous adsorption resins and in vitro evaluation of antioxidant and antiproliferative activities[J]. Journal of Chromatography B,2020,1138:121960. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2019.121960
[5] 刘素慧, 张立伟. 红蓝光质对香椿芽苗菜营养品质的影响[J]. 中国农业气象,2015,36(3):306−312. [LIU S H, ZHANG L W. Effects of red and blue spectra on nutritional quality of Toona sinensis seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology,2015,36(3):306−312.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2015.03.008 LIU S H, ZHANG L W. Effects of red and blue spectra on nutritional quality of Toona sinensis seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 2015, 36(3): 306−312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6362.2015.03.008
[6] 王燕, 张亚见, 何茂盛, 等. 光质对植物形态结构和生长的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学,2018,46(19):22−25. [WANG Y, ZHANG Y J, HE M S, et al. Effects of light quality on plant morphological structure and growth[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2018,46(19):22−25.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2018.19.008 WANG Y, ZHANG Y J, HE M S, et al. Effects of light quality on plant morphological structure and growth[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 46(19): 22−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2018.19.008
[7] 王哲, 王宇航, 解山森, 等. 植物工厂LED光质调控对生菜幼苗生长的影响[J]. 现代农业科技,2023(3):76−81. [WANG Z, WANG Y H, XIE S S, et al. Effects of LED light quality regulation on the growth of lettuce seedlings in plant factories[J]. Modern Agricultural Technology,2023(3):76−81.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2023.03.019 WANG Z, WANG Y H, XIE S S, et al. Effects of LED light quality regulation on the growth of lettuce seedlings in plant factories[J]. Modern Agricultural Technology, 2023(3): 76−81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2023.03.019
[8] 石勇志. 不同光质及光周期对花椰菜幼苗生长的影响[D]. 泰安:山东农业大学, 2022. [SHI Y Z. Effects of different light quality and photoperiod on the growth of cauliflower seedlings[D]. Taian:Shandong Agricultural University, 2022.] SHI Y Z. Effects of different light quality and photoperiod on the growth of cauliflower seedlings[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2022.
[9] 樊小雪, 高文瑞, 孙艳军, 等. 不同光质对小白菜叶片发育和光合作用的影响[J]. 信阳师范学院学报(自然科学版),2018,31(4):562−567. [FAN X X, GAO W R, SUN Y J, et al. Effects of different light qualities on leaf development and photosynthesis of pakchoi[J]. Journal of Xinyang Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2018,31(4):562−567.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0972.2018.04.010 FAN X X, GAO W R, SUN Y J, et al. Effects of different light qualities on leaf development and photosynthesis of pakchoi[J]. Journal of Xinyang Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 31(4): 562−567. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0972.2018.04.010
[10] 杨俊伟, 鲍恩财, 张珂嘉, 等. 不同红蓝光比例对番茄幼苗叶片结构及光合特性的影响[J]. 西北农业学报,2018,27(5):716−726. [YANG J W, BAO E C, ZHANG K J, et al. Effects of different red-blue to blue ratios on leaf structure and photosynthetic characteristics of tomato seedlings[J]. Northwest Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2018,27(5):716−726.] doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1004-1389.2018.05.014 YANG J W, BAO E C, ZHANG K J, et al. Effects of different red-blue to blue ratios on leaf structure and photosynthetic characteristics of tomato seedlings[J]. Northwest Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 27(5): 716−726. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1004-1389.2018.05.014
[11] GUO B, LIU Y G, YAN Q, et al. Spectral composition of irradiation regulates the cell growth and flavonoids biosynthesis in callus cultures of Saussurea medusa Maxim[J]. Plant Growth Regulation,2007,52:259−263. doi: 10.1007/s10725-007-9192-0
[12] 章雷. 不同光质下银杏生长及黄酮醇积累规律探究[D]. 南京:南京林业大学, 2023. [ZHANG L. Study on the growth and accumulation of ginkgo biloba under different light qualities[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Forestry University, 2023.] ZHANG L. Study on the growth and accumulation of ginkgo biloba under different light qualities[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2023.
[13] 杨文博, 彭丹, 曹思邈, 等. 微生物合成黄酮类化合物研究进展[J]. 生命科学,2022,34(2):220−227. [YANG W B, PENG D, CAO S M, et al. Research progress on microbial synthesis of flavonoids[J]. Life Sciences,2022,34(2):220−227.] YANG W B, PENG D, CAO S M, et al. Research progress on microbial synthesis of flavonoids[J]. Life Sciences, 2022, 34(2): 220−227.
[14] 申威. 苦荞苯丙氨酸解氨酶体外泛素化体系的建立[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2023. [SHEN W. Establishment of in vitro ubiquitination system of buckwheat phenylalanine ammonia-lyase[D]. Yangling:Northwest A&F University, 2023.] SHEN W. Establishment of in vitro ubiquitination system of buckwheat phenylalanine ammonia-lyase[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2023.
[15] WU J J, DU G C, CHEN J Z, et al. Enhancing flavonoid production by systematically tuning the central metabolic pathways based on a CRISPR interference system in Escherichia coli[J]. Scientific Reports,2015,5:13477. doi: 10.1038/srep13477
[16] 麻新妍, 南春利, 薛永常. 植物查尔酮异构酶的结构与功能研究概述[J]. 生物学教学,2022,47(1):2−4. [MA X Y, NAN C L, XUE Y C. Overview of the structure and function of plant chalcone isomerases[J]. Biology Teaching,2022,47(1):2−4.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7549.2022.01.001 MA X Y, NAN C L, XUE Y C. Overview of the structure and function of plant chalcone isomerases[J]. Biology Teaching, 2022, 47(1): 2−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7549.2022.01.001
[17] HOGEWONING S W, TROUWBORST G, MALJAARS H, et al. Blue light dose-responses of leaf photosynthesis, morphology, and chemical composition of Cucumis sativus grown under different combinations of red and blue light[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2010,61(11):3107−3117. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq132
[18] 赵德修, 李茂寅, 邢建民, 等. 光质光强和光期对水母雪莲愈伤组织生长和黄酮生物合成的影响[J]. 植物生理学报,1999(2):127−132. [ZHAO D X, LI M Y, XING J M, et al. Effects of light intensity and photoperiod on callus growth and flavonoid biosynthesis of jellyfish yaconia[J]. Plant Physiology Journal,1999(2):127−132.] doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-3877.1999.02.005 ZHAO D X, LI M Y, XING J M, et al. Effects of light intensity and photoperiod on callus growth and flavonoid biosynthesis of jellyfish yaconia[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 1999(2): 127−132. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-3877.1999.02.005
[19] THWE A A, KIM Y B, LI X, et al. Effects of light-emitting diodes on expression of phenylpropanoid biosynthetic genes and accumulation of phenylpropanoids in Fagopyrum tataricum sprouts[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2014,62(21):4839−4845. doi: 10.1021/jf501335q
[20] 徐琳煜. 光质对三叶青生长及黄酮类化合物合成的影响研究[D]. 杭州:浙江农林大学, 2018. [XU L Y. Effects of light quality on the growth of clover and the synthesis of flavonoids[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang A&F University, 2018.] XU L Y. Effects of light quality on the growth of clover and the synthesis of flavonoids[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A&F University, 2018.
[21] 燕娟娟. 香椿露地配套矮化密植栽培技术[J]. 绿色科技,2013(3):46−47. [YAN J J. Analysis of dwarfing dense planting technique of Chinese toon in open fields[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology,2013(3):46−47.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9944.2013.03.019 YAN J J. Analysis of dwarfing dense planting technique of Chinese toon in open fields[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology, 2013(3): 46−47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9944.2013.03.019
[22] 刘厚诚. LED植物照明产业的发展现状与趋势[J]. 照明工程学报,2018,29(4):8−9. [LIU H C. Development status and trend of LED horticultural lighting industry[J]. Journal of Lighting Engineering,2018,29(4):8−9.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-440X.2018.04.002 LIU H C. Development status and trend of LED horticultural lighting industry[J]. Journal of Lighting Engineering, 2018, 29(4): 8−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-440X.2018.04.002
[23] 刘珂, 张嘉欣, 杜清洁, 等. 外源褪黑素对盐胁迫下香椿种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 中国瓜菜,2020,33(5):53−58. [LIU K, ZHANG J X, DU Q J, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on seed germination and seeding growth of Toona sinensis under salt stress[J]. Chinese Melon Vegetables,2020,33(5):53−58.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2871.2020.05.010 LIU K, ZHANG J X, DU Q J, et al. Effects of exogenous melatonin on seed germination and seeding growth of Toona sinensis under salt stress[J]. Chinese Melon Vegetables, 2020, 33(5): 53−58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2871.2020.05.010
[24] 陈丛瑾, 黄克瀛, 张合玲. 香椿叶中总黄酮的提取工艺研究[J]. 应用化工,2006(8):606−609. [CHEN C J, HUANG K Y, ZHANG H L. Study on technique of extraction of total flavonoids from Toona sinensis leaves[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2006(8):606−609.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2006.08.014 CHEN C J, HUANG K Y, ZHANG H L. Study on technique of extraction of total flavonoids from Toona sinensis leaves[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2006(8): 606−609. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2006.08.014
[25] 王丽丽, 林清霞, 宋振硕, 等. 分光光度法测定茶叶中总黄酮含量[J]. 茶叶学报,2021,62(1):1−6. [WANG L L, LIN Q X, SONG Z S, et al. Spectrophotometric determination of total flavonoid content in tea[J]. Journal of Tea,2021,62(1):1−6.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4872.2021.01.002 WANG L L, LIN Q X, SONG Z S, et al. Spectrophotometric determination of total flavonoid content in tea[J]. Journal of Tea, 2021, 62(1): 1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4872.2021.01.002
[26] YANG L, SONG L, YU W. Light quality modifies camptothecin production and gene expression of biosynthesis in Camptotheca acuminata Decne seedlings[J]. Industrial Crops& Products,2015,66:137−143.
[27] CUI J, MA Z, XU Z. Effects of supplemental lighting with different light qualities on growth and physiological characteristics of cucumber, pepper and tomato seedlings[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2009:663-670.
[28] 刘涛, 程培蕾, 赵坤坤, 等. 蓝光处理对夏菊优香组培苗生长发育的影响及其分子机制[J]. 江苏农业科学,2022,50(12):150−156. [LIU T, CHENG P L, ZHAO K K, et al. Effect and molecular mechanism of blue light treatment on growth and development of fine fragrance tissue culture seedlings of summer chrysanthemum[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2022,50(12):150−156.] LIU T, CHENG P L, ZHAO K K, et al. Effect and molecular mechanism of blue light treatment on growth and development of fine fragrance tissue culture seedlings of summer chrysanthemum[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(12): 150−156.
[29] TAGOUSOP C N, TAMOKOU J, EKOM S E, et al. Antimicrobial activities of flavonoid glycosides from Graptophyllum grandulosum and their mechanism of antibacterial action[J]. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2018,18(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2321-7
[30] 崔琳琳, 周一鸣, 季红斌, 等. 不同光质对苦荞萌发过程中的黄酮类化合物及其抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技, 2016, 37(6):104−108. [CUI L L, ZHOU Y M, JI H B, et al. Effects of different light qualities on flavonoids and their antioxidant activity during tartary buckwheat germination[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2016, 37(6):104−108.] CUI L L, ZHOU Y M, JI H B, et al. Effects of different light qualities on flavonoids and their antioxidant activity during tartary buckwheat germination[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2016, 37(6): 104−108.
[31] YU G B, CHEN F Q, WANG Y T, et al. Exogenous γ-aminobutyric acid strengthens phenylpropanoid and nitrogen metabolism to enhance the contents of flavonoids, amino acids, and the derivatives in edamame[J]. Food Chemistry:X,2022,16:100511.
[32] 管培燕, 刘美玲, 赵明玉. 香椿嫩叶及老叶中黄酮类物质的提取定量及抗氧化功能分析[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2020,31(11):50−54. [GUAN P Y, LIU M L, ZHAO M Y. Extraction and quantification of flavonoids from young and old leaves of Toona sinensis and analysis of antioxidant function[J]. China Food Additives,2020,31(11):50−54.] GUAN P Y, LIU M L, ZHAO M Y. Extraction and quantification of flavonoids from young and old leaves of Toona sinensis and analysis of antioxidant function[J]. China Food Additives, 2020, 31(11): 50−54.
[33] 周明, 朱晓娟, 尧梅香, 等. ‘修水化红’甜橙成熟过程中黄酮含量与相关酶活性及抗氧化能力的关系[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(4):60−67. [ZHOU M, ZHU X J, YAO M X, et al. Correlation between flavonoids content, related enzymes activity and antioxidant capacity during the maturation of 'Xiushui Huahong' sweet orange[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(4):60−67.] ZHOU M, ZHU X J, YAO M X, et al. Correlation between flavonoids content, related enzymes activity and antioxidant capacity during the maturation of 'Xiushui Huahong' sweet orange[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(4): 60−67.
[34] SHIN K S, MURTHY H N, HEO J W, et al. The effect of light quality on the growth and development of in vitro cultured Doritaenopsis plants[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum,2008,30(3):339−343. doi: 10.1007/s11738-007-0128-0
[35] 王丽伟. 红蓝光质对番茄碳氮代谢和果实品质的影响机制研究与应用[D]. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2017. [WANG L W. Study and application of the effect mechanism of red and blue light on carbon and nitrogen metabolism and fruit quality of tomato[D]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2017.] WANG L W. Study and application of the effect mechanism of red and blue light on carbon and nitrogen metabolism and fruit quality of tomato[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2017.
[36] 邵明杰, 陈艳琦, 刘文科. 连续光照条件下LED红蓝光供光模式对紫叶生菜生长和品质的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报,2023,25(4):77−85. [SHAO M J, CHEN Y Q, LIU W K. Effects of red-blue LED bight supply modes on growth and quality of purple leaf lettuce under continuous light[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology,2023,25(4):77−85.] SHAO M J, CHEN Y Q, LIU W K. Effects of red-blue LED bight supply modes on growth and quality of purple leaf lettuce under continuous light[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2023, 25(4): 77−85.
[37] NABIPOUR S R, HIR Y P, CHAMANI E, et al. LED lighting influences germination, growth, and biochemical indices of snapdragon[J]. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology,2023,70(6):121. doi: 10.1134/S1021443723601052
[38] GUO Y X, ZHONG Y F, MO L W, et al. Different combinations of red and blue LED light affect the growth, physiology metabolism and photosynthesis of in vitro-cultured Dendrobium nobile 'Zixia'[J]. Horticulture, Environment, and Biotechnology,2023,64(3):393−407. doi: 10.1007/s13580-022-00491-x
[39] GYU T N, DAE-OK K, HYUN S E. Effects of light sources on major flavonoids and antioxidant activity in common buckwheat sprouts[J]. Food Science and Biotechnology,2018,27(1):169−176. doi: 10.1007/s10068-017-0204-1
[40] 潘俊倩, 佟曦然, 郭宝林. 光对植物黄酮类化合物的影响研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志,2016,41(21):3897−3903. [PAN J Q, TONG X R, GUO B L. Research progress on the effect of light on plant flavonoids[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica,2016,41(21):3897−3903.] PAN J Q, TONG X R, GUO B L. Research progress on the effect of light on plant flavonoids[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica, 2016, 41(21): 3897−3903.
[41] 隋娟娟, 屈长青, 杨京霞, 等. 香椿查尔酮异构酶基因的克隆及在幼苗中的表达分析[J]. 分子植物育种,2021,19(14):4649−4656. [SUI J J, QU C Q, YANG J X, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of chalcone isomerase gene in Toona sinensis seedlings[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding,2021,19(14):4649−4656.] SUI J J, QU C Q, YANG J X, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of chalcone isomerase gene in Toona sinensis seedlings[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(14): 4649−4656.
[42] 卜红宇, 韩峰, 郝美玲, 等. 药用植物类黄酮生物合成调控的研究进展[J]. 北方药学,2021,18(7):192−196. [BU H Y, HAN F, HAO M L, et al. Research progress in regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis in medicinal plants[J]. Journal of North Pharmacy,2021,18(7):192−196.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8351.2021.07.093 BU H Y, HAN F, HAO M L, et al. Research progress in regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis in medicinal plants[J]. Journal of North Pharmacy, 2021, 18(7): 192−196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8351.2021.07.093
[43] 刘守赞, 蒋玲苔, 张韵, 等. 蓝、紫单色光处理对三叶青生理及总黄酮含量时空变化的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文),2023,31(6):885−894. [LIU S Z, JIANG L T, ZHANG Y, et al. Spatiotemporal changes in physiology and total flavonoids of Tetrastigma hems-leyanum in response to blue and purple monochromatic light[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture (Chinese and English),2023,31(6):885−894.] LIU S Z, JIANG L T, ZHANG Y, et al. Spatiotemporal changes in physiology and total flavonoids of Tetrastigma hems-leyanum in response to blue and purple monochromatic light[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture (Chinese and English), 2023, 31(6): 885−894.
[44] 李娜. 蓝光诱导大豆芽苗菜黄酮类化合物合成机理的初步研究[D]. 南京:南京农业大学, 2017. [LI N. A preliminary study on the mechanism of blue light induced synthesis of flavonoids in soybean sprouts[D]. Nanjing:Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017.] LI N. A preliminary study on the mechanism of blue light induced synthesis of flavonoids in soybean sprouts[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017.
[45] JARA R M A, GÓMEZ-LOBATO E M, CIVELLO M P. et al. Phenylalanine ammonia lyase is more relevant than chalcone synthase and chalcone isomerase in the biosynthesis of flavonoids during postharvest senescence of broccoli[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2022,46(2):e14054.





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



