Quality Characteristics of Fermented Chili Peppers Using Different Inoculated and Natural Fermentation Approaches
-
摘要: 为探究不同泡菜水和发酵方式对小米辣品质特性的影响,本研究对小米辣进行新泡菜水自然发酵、新泡菜水混菌(植物乳杆菌Lactiplantibacillus plantarum KUST-D1303:盔形毕赤酵母Pichia manshurica KUST-F1705=1:1)接种发酵、老泡菜水自然发酵和老泡菜水混菌接种发酵4种方式发酵,并对发酵小米辣的品质特性进行比较分析。结果表明,与其他发酵方式相比,老泡菜水混菌接种发酵显著(P<0.05)增加了发酵小米辣中乳酸菌数量、有机酸含量以及挥发性风味物质,特别是醇类、萜烯类和含硫化合物的种类和含量,降低了亚硝酸盐含量。此外,老泡菜水混菌接种发酵小米辣的pH下降迅速并保持稳定,可延缓小米辣在发酵过程中变黄、变软。综上,老泡菜水混合接种发酵可提高发酵小米辣的安全性、风味组分以及改善产品的滋味,是发酵小米辣的优选工艺。Abstract: To investigate the effects of different brine and fermentation methods on the quality characteristics of fermented chili peppers, this study employed four different fermentation methods: Natural fermentation with sterile water, co-inoculation fermentation (Lactiplantibacillus plantarum KUST-D1303:Pichia manshurica KUST-F1705=1:1) with sterile water, natural fermentation with aged brine and co-inoculation fermentation with aged brine. The quality characteristics of the fermented chili peppers were compared and analyzed. Results showed that compared to other fermentation methods, co-inoculation fermentation with aged brine significantly (P<0.05) increased the number of lactic acid bacteria, organic acid content, and the variety and concentration of volatile flavor compounds, especially alcohols, terpenes, and sulfur-containing compounds, while reducing nitrite content. Additionally, the pH of fermented chili peppers by co-inoculation with aged brine decreased rapidly and remained stable, which helped delay the yellowing and softening of chili peppers during fermentation. In conclusion, co-inoculation fermentation with aged brine can enhance the safety, flavor profile, and taste of fermented chili peppers, making it the optimal process for fermented chili peppers.
-
小米辣(Capsicum frutescens L.)作为我国唯一的野生辣椒资源,辣味浓郁,在云南的种植面积和产量均占全国的90%以上[1−2]。目前这些小米辣加工主要以发酵为主[2]。在传统发酵工艺中,发酵小米辣是将新鲜小米辣置于密闭泡菜坛或开放式泡菜池的卤水中自然发酵得到的泡菜产品,具有酸辣可口、风味鲜香、营养丰富和刺激食欲的特点,兼具改善肠道环境、健胃消食、预防风湿性关节炎等作用,深受广大消费者喜爱[3]。泡菜水是启动蔬菜发酵最具代表性的工艺[4]。老泡菜水从新泡菜水通过倒流的方式不断繁殖成熟,在此过程中使用时间较长。甚至有的老品牌长达一个世纪的陈年泡菜水(老泡菜水:至少重复使用一次的泡菜水)中含有稳定的微生物,这些微生物是在重复使用中重新选择出来的[4−6]。
自然发酵过程参与的菌株种类复杂多样,发酵过程难以控制,导致各批次的发酵产品质量与风味不同,很难获得稳定的品质[7]。微生物接种发酵是提高发酵蔬菜制品品质的一种有效手段[8],通过直投或其他方式加入单一发酵剂或复合发酵剂进行发酵[9],其中复合发酵剂是将两种或两种以上的菌株混合制成,具有更加优异的发酵效果[10]。王英等[10]利用复合菌种协同发酵提高豇豆发酵产品的风味组分和改善产品的滋味。Sun等[11]利用复合菌剂发酵香肠,发现复合菌剂能够提高产品的营养价值、改善产品的风味品质。陈凤等[12]对比了不同发酵方式对泡豇豆品质影响,研究结果表明,自然发酵、母水发酵及直投式发酵对豇豆品质的影响不同,其中直投式发酵剂发酵豇豆的品质较好。
传统自然发酵制品是微生物发酵菌种如乳酸菌、葡萄球菌、酵母菌等的主要来源[8],其中乳酸菌和酵母菌对发酵蔬菜品质提升有重要影响。植物乳杆菌因其具备良好的发酵耐受性,含有可修饰产品风味的众多酶类物质,是混合发酵领域研究的热点菌种[13]。罗丽蓉等[7]从四川农家自制泡椒老卤水中分离筛选出具有良好的发酵性能和一定益生性能的优势发酵菌株,并制备成直投式发酵剂。然而,目前对不同发酵环境下自然发酵和接种发酵小米辣产品品质特性的对比研究仍鲜有报道。因此,本研究基于前期微生物对风味物质的调控作用的基础上,进一步探究新泡菜水与老泡菜水、自然发酵与混菌(植物乳杆菌Lactiplantibacillus plantarum和盔形毕赤酵母Pichia manshurica)接种发酵小米辣的品质差异,以期为高品质泡椒的加工提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
新鲜小米辣 蒙自市滇安水果种植农民专业合作社;植物乳杆菌(Lactiplantibacillus plantarum)KUST-D1303、盔形毕赤酵母(Pichia manshurica)KUST-F1705 云南特色食品现代制造创新平台;氯化钠 食品级,云南省盐业有限公司;冰乙酸 食品级,广州康本生物科技有限公司;氯化钙 食品级,河南万邦化工科技有限公司;其余制备泡菜水配料 上海华联超市;MRS肉汤 广东环凯微生物科技有限公司;酵母粉、蛋白胨、葡萄糖 分析级,上海麦克林公司;甲醇 色谱级,Sigma-Aldrich;标准品(草酸、酒石酸、奎宁酸、苹果酸、乳酸、冰乙酸、柠檬酸、琥珀酸、富马酸、3-辛醇) 上海阿拉丁(中国);正构烷烃(C5~C10、C10~C25) 上海Anpel(中国);其余试剂均为分析纯。
BIOBASE BBS-SDC医用洁净工作台 济南鑫贝西生物技术有限公司;HPX-9162MBE电热恒温培养箱 上海博迅医疗生物仪器股份有限公司;FE28型pH计 上海梅特勒-托利多仪器有限公司;HunterLab Agera色差仪 美国Hunter Associates Laboratory有限公司;TA-XT. Plus质构仪 英国Stable Micro Systems公司;1200高效液相色谱仪 美国Agilent公司;cNose电子鼻 上海保圣实业发展有限公司;QP 2010气相色谱-质谱联用仪 日本岛津公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 泡菜水制作
按表1所示配方配制新泡菜水后加入液体体积数五分之三的小米辣,每天监测泡菜水pH变化,稳定(15 d,数据未显示)后即为老泡菜水。
表 1 泡菜水配方Table 1. Formulation of brine配料 比例(%) 配料 比例(%) 配料 比例(%) 去离子水 64.17 大蒜 3.33 小茴香 0.50 生姜 6.67 苹果 3.00 香叶 0.40 红皮萝卜 5.00 冰糖 1.20 丁香 0.24 白皮萝卜 5.00 白酒 1.00 冰醋酸 0.20 无碘盐 4.00 味精 1.00 氯化钙 0.10 洋葱 3.33 青花椒 0.80 八角 0.06 1.2.2 发酵剂制备
将分离自自然发酵小米辣中的植物乳杆菌KUST-D1303和盔形毕赤酵母KUST-F1705分别在MRS和YPD肉汤(1 L YPD肉汤由10 g酵母粉、20 g蛋白胨和20 g葡萄糖和水配制而成,灭菌后使用)中30 ℃培养48 h进行2次活化,菌悬液在4 ℃离心(4000×g)5 min,然后用生理盐水洗涤2次。
1.2.3 泡椒制备
挑选完整、新鲜、粗细长短相对一致的小米辣,清水漂洗后沥干水分、装坛。所有处理组中小米辣与水的比例均为3:5。其中,新泡菜水自然发酵处理组(SW-NF)注入含盐量6.6%的新泡菜水;新泡菜水混菌接种发酵(SW-LP)注入含盐量6.6%的新泡菜水后按泡菜水的2%加入植物乳杆菌和盔形毕赤酵母(1:1,v/v)至坛内;老泡菜水自然发酵(AB-NF)则注入含盐量6.6%的老泡菜水;老泡菜水混菌接种发酵(AB-LP)注入含盐量6.6%的老泡菜水后按泡菜水的2%加入植物乳杆菌和盔形毕赤酵母(1:1,v/v)至坛内。密封并在30 ℃条件下进行发酵,分别于0、1、3、5、7 d取样测定泡椒的各项品质指标,以上实验重复两次。
1.2.4 微生物计数
按照GB 4789.35-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 乳酸菌检验》和GB 4789.15-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 霉菌和酵母计数》测定泡椒发酵过程中乳酸菌和酵母菌的数量,结果以CFU/g表示。
1.2.5 pH和亚硝酸盐含量的测定
将样品均质后称重,测定不同发酵小米辣样品的pH和亚硝酸盐含量。将10 g样品匀浆与90 mL去离子水混匀,过滤后采用pH计测定滤液的pH。亚硝酸盐含量按GB 5009.33-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中亚硝酸盐与硝酸盐的测定》测定。所有测量均进行了3次。
1.2.6 色泽的测定
采用色差仪测定发酵小米辣样品的表面颜色[14]。为尽量避免测定误差,每个辣椒样品检测2次,每种发酵辣椒随机选择10个样品进行测定。亮度L*、红绿度a*和黄蓝度b*被用来描述样品的颜色,并按照公式(1)计算色差(ΔE*)。
ΔE∗=√(L∗x−L∗0)2+(a∗x−a∗0)2+(b∗x−b∗0)2 (1) 式中:“0”和“x”分别代表新鲜样品和发酵样品。
1.2.7 质构的测定
采用配有P1/s探头的TA-XT. Plus质构仪进行2次压缩测定发酵小米辣的硬度和咀嚼度[3]。选择尺寸相近的发酵小米辣样品的中部位置进行质构测定。试验参数为:测前速度2.0 mm/s;测试速度2.0 mm/s;测后速度2.0 mm/s;形变75%;时间5.0 s;触发力5.0 g。所有测量均进行了15次。
1.2.8 有机酸含量的测定
根据Ye等[15]的方法提取和测定发酵小米辣样品中的有机酸。使用配备Prevail有机酸柱(250 mm×4.6 mm,5 µm)和紫外检测器(210 nm)的高效液相色谱分析提取物。流动相为25 mmol/L磷酸二氢钾缓冲液,pH为2.5,流速为0.8 mL/min。进样量为30 µL。有机酸标准溶液被用作鉴定和定量有机酸的外部标准,包括草酸、酒石酸、奎宁酸、苹果酸、乳酸、乙酸、柠檬酸、琥珀酸和富马酸。每个样品均进行三次平行实验。
1.2.9 挥发性风味物质的测定
1.2.9.1 电子鼻测定
将根据吴梓仟等[16]的实验方法略作修改,3 g发酵小米辣匀浆装入顶空瓶中,30 ℃水浴30 min后进行测试。测试条件如下:采样时间120 s,气体流速1 mL/min。每次测试后,用过滤空气清洗传感器系统120 s,以便在下一次样品注入前重新建立仪器基线。每个样本重复分析6次,取最大值的平均值进行后续统计分析。
1.2.9.2 顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱联用测定
采用顶空固相微萃取方法提取发酵小米辣中的挥发性成分[17]。将3 g发酵小米辣匀浆和3 mL饱和氯化钠溶液混合在样品瓶中,40 ℃,500 r/min平衡15 min后,将50/30 µm DVB/CAR/PDMS萃取探针插入样品瓶顶空部分,于相同条件下提取挥发性化合物40 min。萃取完成后将探针插入GC进样口,250 ℃解吸5 min。
采用气相色谱-质谱联用仪分离检测挥发性风味物质。仪器参数如下:色谱柱DB-5 MS(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 µm)。初始温度45 ℃保持5 min,然后以5 ℃/min升到250 ℃,保持2 min。载气为氦气,流速为2.0 mL/min。质谱条件:质量扫描范围m/z 35~500,电子能量70 eV,离子源温度230 ℃,传输管线温度280 ℃。每个样品均进行三次平行实验。
基于NIST 2014数据库与质谱数据进行匹配,匹配相似度≥90%,初步确定挥发物种类,并在相同的操作条件下,使用正构烷烃混合物(C5~C10和C10~C25)计算保留指数(RI),进一步确定挥发性风味物质。采用内标3-辛醇进行定量。
1.3 数据处理
数据以平均值±标准差表示。使用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)和Origin软件(2021版,Origin Lab Corporation)对结果进行分析。使用软件IBM SPSS 26.0进行Tukey检验,P<0.05表示具有显著性差异。
采用TBtools(1.098版)绘制有机酸数据的聚类热图。采用Origin(2021版,Origin Lab Corporation)根据一阶分数转化模型式(2)对四种发酵小米辣的硬度和咀嚼度随发酵时间的变化进行动力学建模。
C=C∞+(C0−C∞)exp(kt) (2) 式中,C为发酵时间的硬度和咀嚼度;C0为发酵第0 d的初始值;C∞为体系稳定后的数值;k为反应速率常数;t为发酵时间。
2. 结果与分析
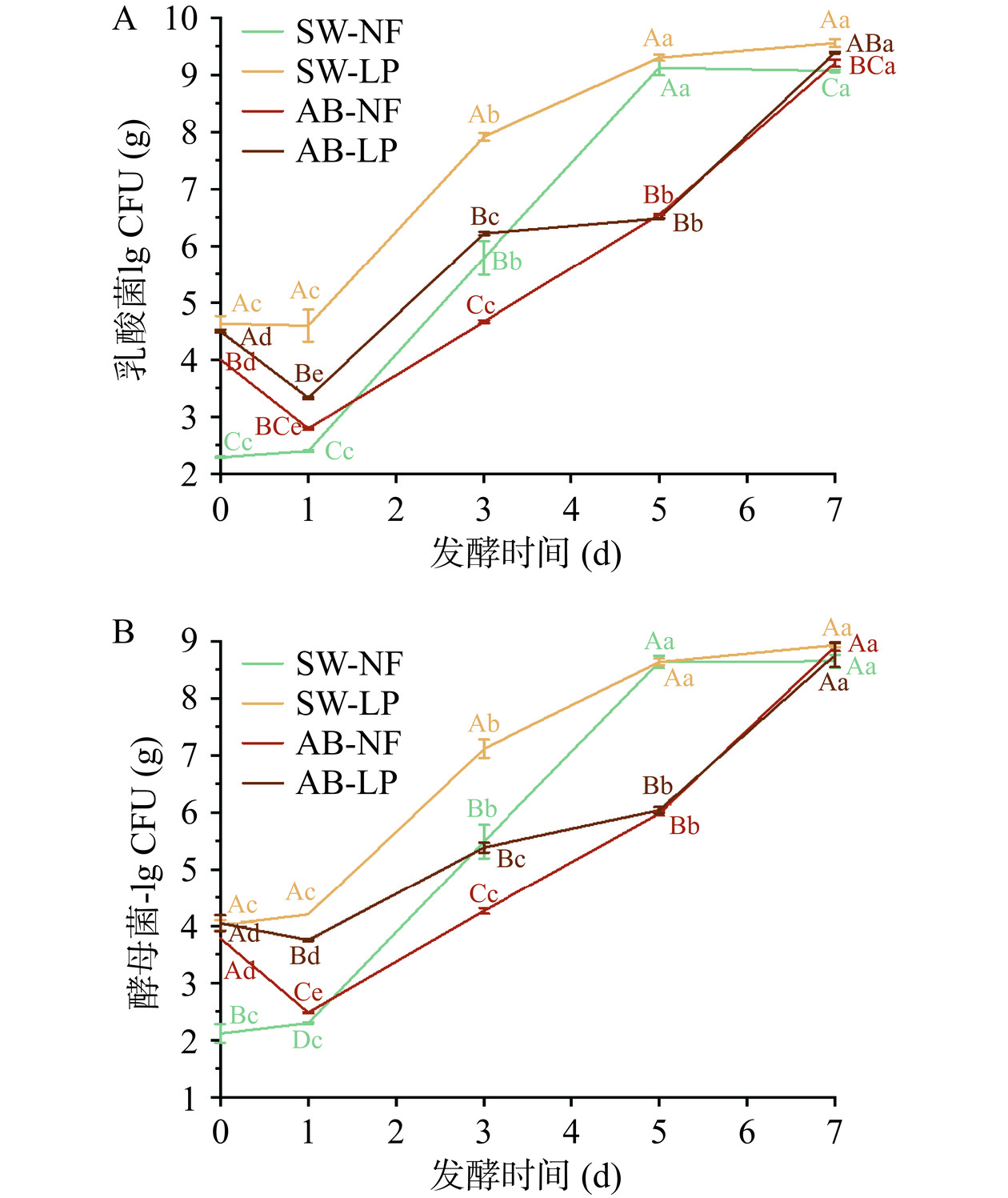
2.1 微生物数量的变化
在发酵过程中测定小米辣中的乳酸菌和酵母菌数量(图1)。发酵0 d时,新泡菜水混菌接种小米辣和老泡菜水混菌接种小米辣样品的乳酸菌和酵母菌数量无显著差异(P>0.05)。虽然在发酵初期接种样品与未接种样品之间的乳酸菌和酵母菌数量差异较大,但在发酵结束时二者数量差距减小,这可能是由于发酵结束时微生物的生长进入了平台期[11]。随着发酵时间的延长,各样品中乳酸菌和酵母菌含量逐渐升高(P<0.05)。比较相同泡菜水发酵样品,自然发酵组乳酸菌和酵母菌数量的增加率(第0~7 d)明显高于接种组,这可能是因为发酵剂的生长可能产生一些抗菌代谢物(如细菌素),可以抑制一些杂菌的生长[11]。相同泡菜水发酵样品间比较,在发酵前期(第0 d),乳酸菌和酵母菌在接种发酵小米辣样品中数量显著高于自然发酵小米辣样品(P<0.05);而在发酵末期(第7 d),酵母菌无显著差异(P>0.05),新泡菜水发酵样品间比较,接种发酵小米辣样品中乳酸菌数量高于自然发酵小米辣(P<0.05),而老泡菜水发酵样品间乳酸菌数量无显著差异(P>0.05)。上述结果表明,接种发酵剂是旺盛发酵的必要条件。
2.2 pH和亚硝酸盐含量变化
pH是蔬菜发酵过程中最重要的影响因素之一,它通过影响不同微生物的相对生长速率和代谢产物的积累速率,从而改变发酵蔬菜的安全性和风味[18]。由表2可知,相同泡菜水间比较发现自然发酵或接种发酵小米辣的pH无显著差异(P>0.05)。整个发酵过程中,相同发酵方式(自然/混菌接种发酵)间比较,老泡菜水发酵小米辣pH显著(P<0.05)低于新泡菜水发酵小米辣pH。这可能是因为老泡菜水中的微生物已经成为发酵过程中促进碳水化合物降解产生有机酸的优势菌株,降低了小米辣的pH。相同泡菜水中发酵小米辣,接种发酵小米辣pH更早达到稳定,这和Hu等[19]的研究结果一致。这可能是因为混合发酵剂具有较好的产酸特性,特别是乳酸菌在小米辣发酵过程中能够快速利用碳水化合物分解产生有机酸,从而促进pH下降[20],而接种发酵小米辣中乳酸菌含量更高,因此pH更低。通过微生物发酵降低pH可以抑制病原及腐败菌的生长,形成浓郁的酸香风味[21]。
表 2 不同发酵环境自然和接种发酵小米辣pH、亚硝酸盐含量和颜色的变化Table 2. Changes of pH, nitrite content, and color of natural and inoculated fermented chili peppers under different fermentation environments发酵时间(d) pH 亚硝酸盐
含量(mg/kg)颜色 L* a* b* ∆E* SW-NF 0 5.85±0.14Aa 2.92±0.64Ad 50.69±2.05Aa −5.64±0.21Bd 32.03±1.29Ba − 1 5.80±0.20Aa 0.29±0.45Ad 44.82±1.56Ab −3.97±0.76Bc 29.05±1.60Ab 7.16±2.20Ab 3 5.50±0.06Aab 26.38±2.30Aa 42.20±3.45Abc 1.11±0.68Ab 29.21±1.49Ab 11.57±3.27Aa 5 5.11±0.11Ab 9.51±2.07ABc 41.06±1.18Ac 1.76±0.42ABab 30.43±0.96Aab 12.38±1.71ABa 7 4.71±0.20Ac 13.62±1.86Bb 39.54±1.99Ac 1.92±0.72ABa 28.74±1.94Ab 14.05±2.30Aa SW-LP 0 5.82±0.16Aa 2.30±1.44Ad 49.50±1.63ABa −5.25±0.32ABd 31.80±1.06Ba − 1 5.82±0.21Aa 3.95±1.51Acd 43.90±1.24ABb −4.33±0.66Bc 28.19±1.59Ab 7.17±1.00Ab 3 5.20±0.15Bb 12.59±9.78Bbc 40.41±1.64Ac 1.72±0.39Ab 28.08±1.56Ab 12.19±1.95Aa 5 4.99±0.10Ab 16.71±5.26Aab 39.42±0.88Bc 1.93±0.25Aab 28.80±1.06Ab 12.80±1.54Aa 7 4.81±0.17Ab 23.70±5.16Aa 39.52±1.50Ac 2.51±0.58Aa 29.75±1.26Ab 13.03±1.74ABa AB-NF 0 5.57±0.14Aa 0.64±0.83Ab 50.26±1.29Aa −5.64±0.59Bc 33.61±1.24Aa − 1 5.19±0.11Bb 3.46±3.83Ab 43.12±0.85Bb −2.91±0.66Ab 28.87±1.55Ab 9.11±1.79Ab 3 4.65±0.08Cc 4.25±5.17Bb 40.44±0.91Ac 1.46±0.65Aa 28.52±2.81Ab 13.50±1.34Aa 5 4.46±0.07Bcd 0.25±0.39Cb 39.43±1.24Bcd 1.45±0.31BCa 30.25±1.28Ab 13.51±1.77Aa 7 4.33±0.06Bd 11.17±5.79Ba 38.96±0.77Ad 1.66±0.56Ba 29.01±1.33Ab 14.35±2.04Aa AB-LP 0 5.66±0.13Aa 6.83±10.31Aa 48.05±1.80Ba −5.12±0.29Ac 31.61±1.38Ba − 1 5.14±0.07Bb 4.54±6.32Aa 42.70±0.88Bb −2.83±0.67Ab 28.17±1.24Ab 7.22±2.05Ab 3 4.71±0.05Cc 6.17±6.97Ba 41.10±2.06Abc 1.28±0.66Aa 27.06±1.73Ab 10.74±2.46Aa 5 4.30±0.03Bd 5.92±8.59BCa 41.00±1.65Abc 1.34±0.38Ca 28.95±2.01Ab 10.31±2.24Ba 7 4.31±0.09Bd 5.25±8.13Ba 39.84±1.39Ac 1.35±0.32Ba 27.85±1.81Ab 11.37±1.66Ba 注:不同小写字母表示同一样品不同发酵时间Tukey's检验具有显著性差异(P<0.05);不同大写字母表示不同样品同一发酵时间Tukey's检验具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 亚硝酸盐含量是评价发酵蔬菜安全性的重要指标[22]。由表2可知,新泡菜水接种发酵小米在发酵过程中亚硝酸盐含量持续升高,新泡菜水自然发酵小米辣的亚硝酸盐含量先升高后降低,在第3 d出现亚硝酸盐峰,而老泡菜水自然发酵小米辣在发酵前5 d亚硝酸盐含量无明显变化,5~7 d含量陡增,老泡菜水接种发酵小米辣在发酵过程中亚硝酸盐的含量无显著变化。发酵末期,老泡菜水接种发酵小米辣的亚硝酸盐含量显著低于其他处理(P<0.05)。Wu等[23]发现乳酸菌和酵母菌混合接种发酵的酸菜中亚硝酸盐含量与自然发酵相比显著降低,这与本研究结果一致。乳酸菌是蔬菜发酵的主要菌群,能通过酶解、酸降解及抑制硝酸还原菌与腐败菌生长等机制显著降低发酵蔬菜中亚硝酸盐含量,乳酸及细菌素等乳酸菌代谢产物能通过抑制大肠杆菌、肺炎克雷伯氏杆菌、荧光假单胞菌等硝酸还原菌生长的机制降低发酵蔬菜中亚硝酸盐的生成与积累[24]。此外,参考我国亚硝酸盐在腌渍蔬菜中的国家食品安全标准GB 2762-2017《食品安全国家标准 食品中污染物限量》,发酵小米辣中除新泡菜水接种发酵外的亚硝酸盐含量均低于其限量指标20 mg/kg,本研究中另外三组发酵小米辣中的亚硝酸盐含量符合国家食品安全标准,均属于安全范围内。
2.3 色泽变化
色泽是发酵小米辣重要的品质特性之一,直接影响消费者的购买欲望[1]。四种小米辣发酵过程中颜色指标的变化如表2所示。发酵过程中,亮度值(L*)显著降低(P<0.05),红绿度(a*)显著增高(P<0.05),黄蓝度(b*)显著降低(P<0.05),这说明成熟发酵小米辣颜色变深(P<0.05)。与无菌水发酵相比,老泡菜水发酵小米辣的a*值更低,说明老泡菜水可以延缓发酵小米辣变黄。小米辣果实中含有丰富的叶绿素,叶绿素的种类及其含量使辣椒呈现独特的绿色,同时也提供了一定的抗氧化活性[1]。发酵过程中pH降低导致叶绿素降解,酸性条件下,叶绿素分子卟啉环中的镁离子被取代形成脱镁叶绿素,脱镁叶绿素的形成伴随着从亮绿色到橄榄棕色的颜色变化,从而降低了辣椒的亮度和绿度[1]。发酵前后总色差(ΔE*)值较高(>10),说明发酵显著改变了小米辣的颜色(P<0.05)[1]。而混菌接种发酵小米辣的总色差最小,说明混菌接种发酵有利于小米辣颜色的保持。
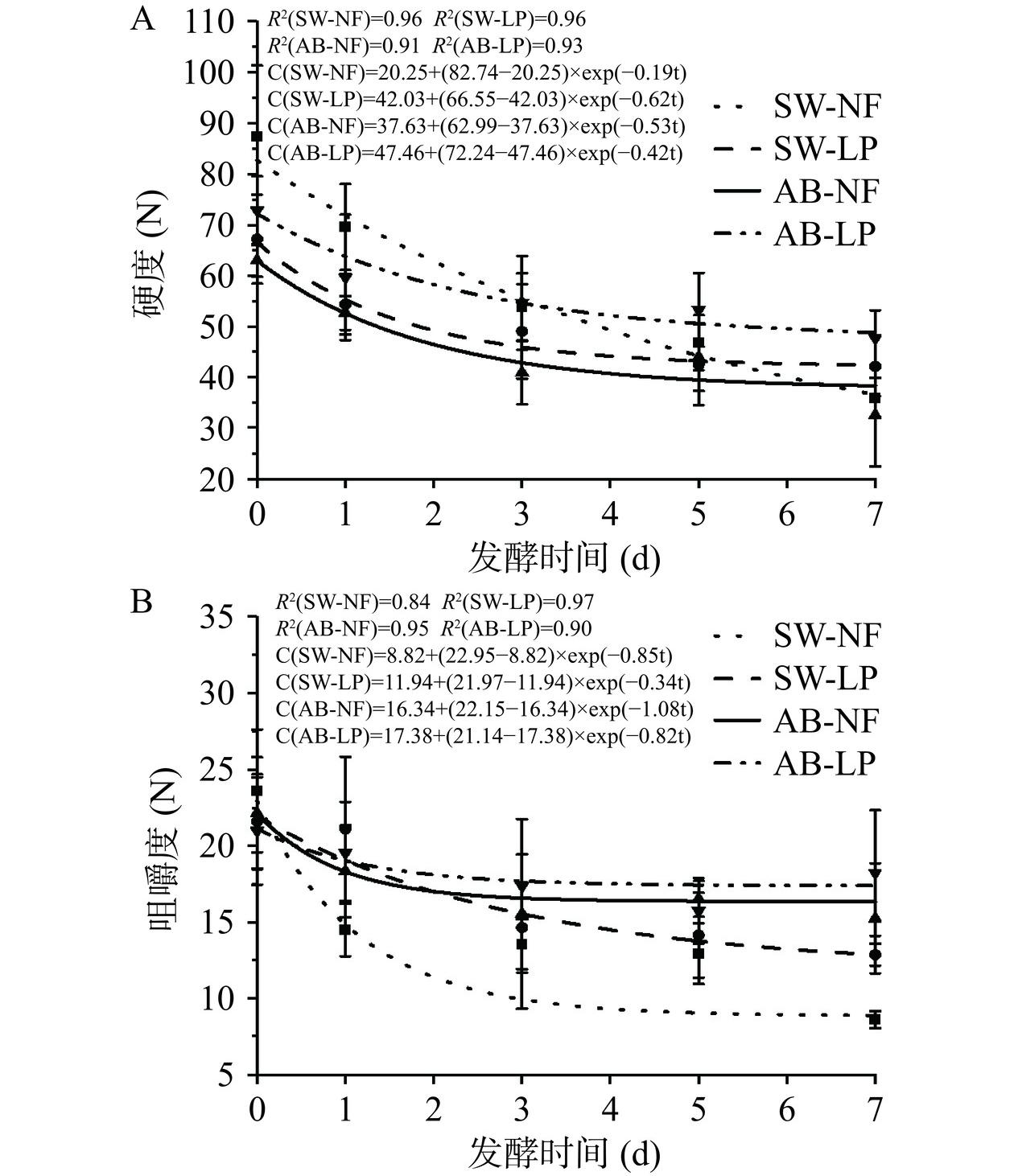
2.4 质构特性的变化
质构是决定发酵蔬菜口感和影响消费者接受度的主要因素之一[3]。图2显示了四种小米辣发酵过程中的硬度和咀嚼度的变化。一阶分数转化模型(R2>0.80)较好地模拟了硬度和咀嚼度的下降趋势。在发酵过程中,4种发酵样品的硬度和咀嚼度显著降低(P<0.05)。在发酵佛手瓜的研究中也观察到发酵导致质构软化的类似结果[17]。发酵过程中的微生物可以通过代谢过程改变体系环境而影响组织细胞壁状态,还可以通过产生果胶降解酶系来降解植物细胞壁成分,从而降低辣椒的硬度和咀嚼度[1]。在相同泡菜水发酵小米辣中,接种发酵小米辣的硬度和咀嚼度均高于自然发酵小米辣(P<0.05)。比较硬度变化率(k值)发现,新泡菜水接种发酵小米辣的k值最大(0.62),其次是老泡菜水自然发酵(0.53)、老泡菜水接种发酵(0.42)和新泡菜水自然发酵(0.19)。而对于咀嚼度变化来说,自然发酵小米辣(SW-NF:0.85;AB-NF:1.08)的咀嚼度变化率高于混菌接种发酵(SW-LP:0.34;AB-LP:0.82),老泡菜水的变化率高于新泡菜水。发酵7 d后,老泡菜水接种发酵小米辣的硬度和咀嚼度最高(P<0.05)。该结果和陈宇昱等[25]的研究结果类似,接种发酵剁辣椒的硬度和咀嚼度显著高于自然发酵。
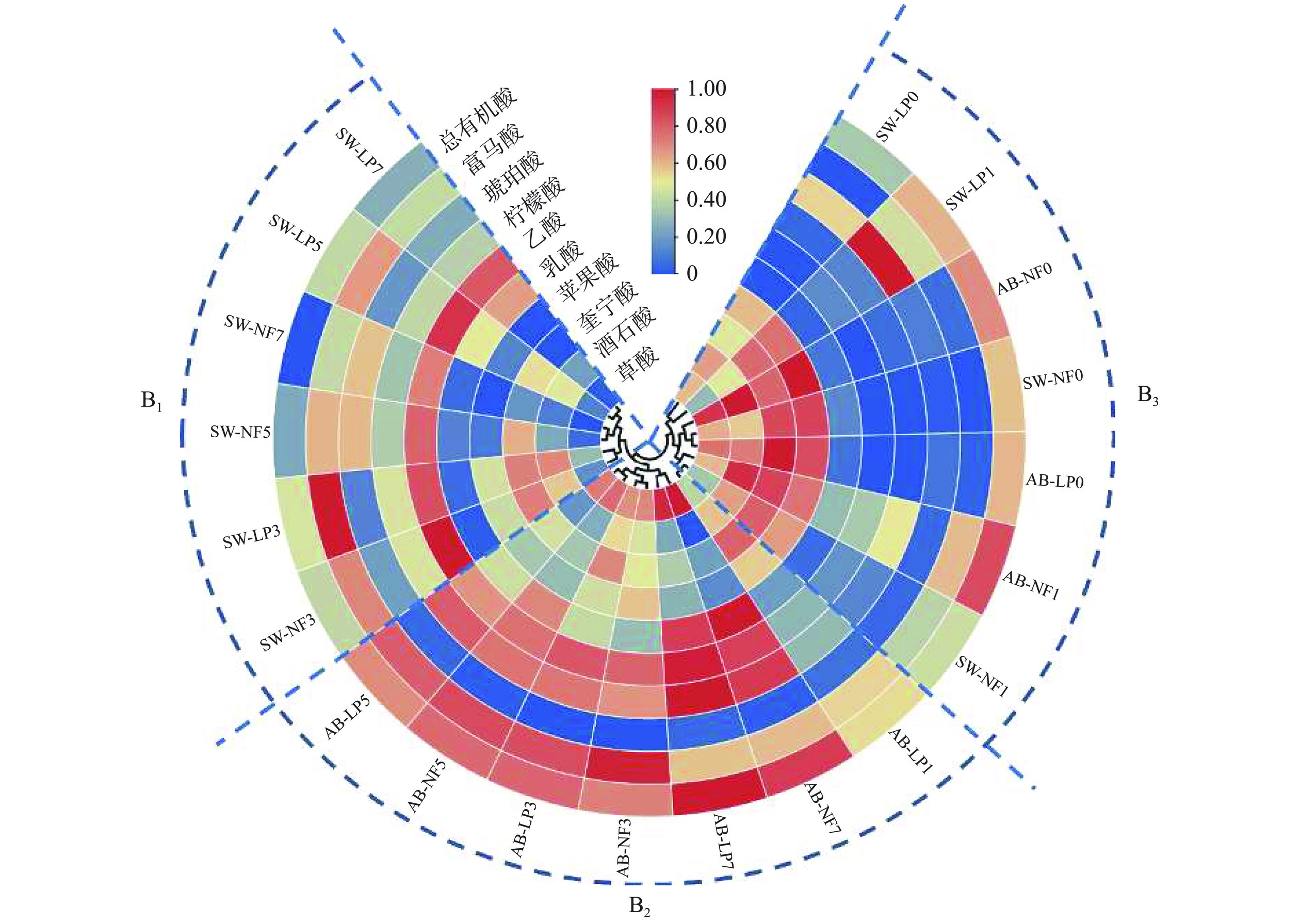
2.5 有机酸含量的变化
有机酸可改善食物的风味和感官特性,并可通过抑制有害细菌的生长提高食品的安全性[20]。图3显示了四种发酵小米辣样品中有机酸含量的变化,包括草酸、酒石酸、奎宁酸、苹果酸、乳酸、乙酸、柠檬酸、琥珀酸和富马酸九种有机酸及这些酸组成的总有机酸。由图3可知,所有样品的有机酸聚类可分为三类。B1包括发酵3~7 d的新泡菜水组,B2包括发酵3~7 d的老泡菜水组,B3包括发酵0~1 d的所有发酵小米辣样品。结果表明,泡菜水对有机酸分布的影响比自然/接种发酵更大。这与嵇晨等[26]的研究结果相似,不同卤水在发酵过程中微生物的代谢活动和功能具有显著差异,从而导致最终代谢产物不同。此外,发酵3 d前后的小米辣有机酸分布存在较大差异。发酵末期,老泡菜水发酵小米辣中总有机酸含量显著高于新泡菜水发酵小米辣(P<0.05),且老泡菜水接种发酵小米辣总有机酸含量最高,新泡菜水自然发酵小米辣的总有机酸含量最低。这是因为新泡菜水发酵是利用小米辣表面的乳酸菌进行发酵,带有大量杂菌,且耐酸能力较差,因此发酵初期产酸较慢,而发酵后其总有机酸的大量生成,又抑制了乳酸菌的生理活动[12];老泡菜水发酵时采用经过较长时期发酵的泡菜水,含有较多的具有一定耐酸能力的乳酸菌[12],且接种的植物乳杆菌是具有较强耐酸能力的乳酸菌。因此,老泡菜水发酵特别是老泡菜水混菌接种发酵较新泡菜水发酵产酸多。在相同泡菜水发酵小米辣中,接种发酵小米辣的总有机酸含量高于自然发酵小米辣,说明混菌接种发酵有利于有机酸的生成。
2.6 挥发性风味物质的变化
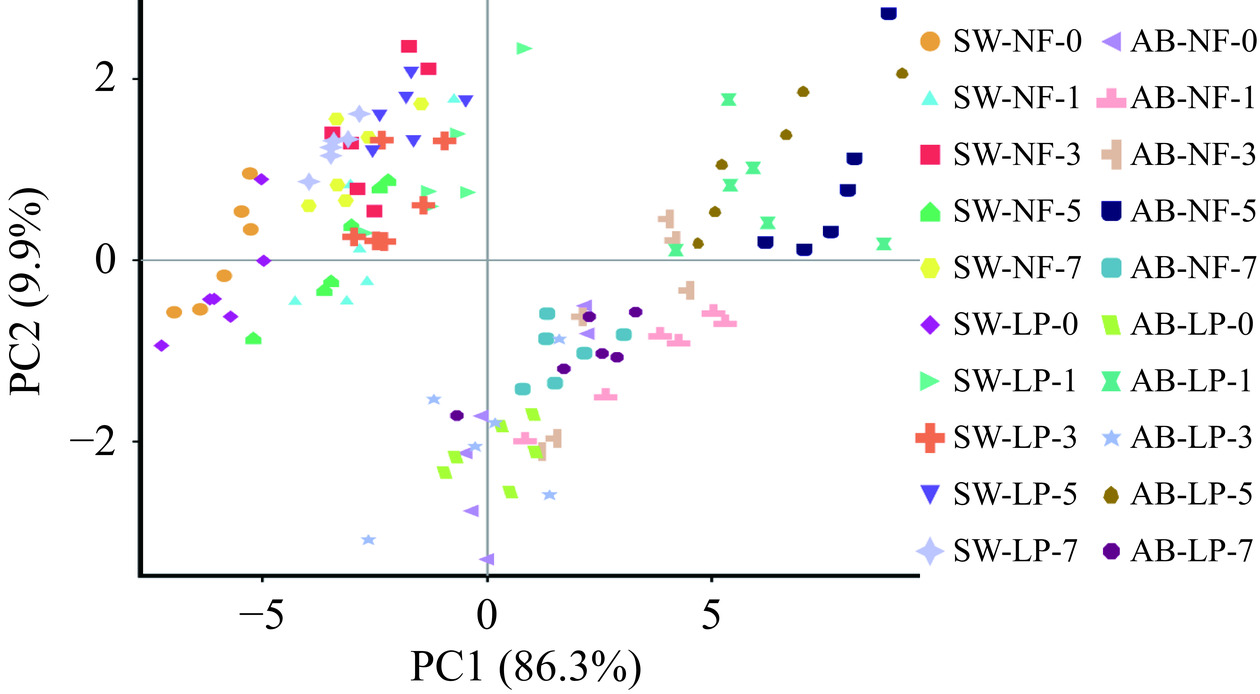
通过PCA模型分析四种发酵小米辣样品中挥发性风味物质的差异。前两个PCs解释了96.2%的方差(图4),能够较好地代表原始数据所反映的信息,即发酵方式对风味物质有影响。由图4可知,PC1方差贡献率大于PC2,说明4种发酵小米辣的风味在PC1成分上反映明显。PC1主成分中4种发酵方式分成2组,新泡菜水发酵和老泡菜水发酵可以完全区分开,说明泡菜水引起的挥发性风味物质差异大于自然/混菌接种发酵,这和鲜双等[27]研究结果一致。此外,随着发酵的进行,挥发性风味物质出现显著性变化(图4)。
为进一步分析发酵方式对发酵小米辣挥发性风味物质的影响,将发酵末期(第7 d)的挥发性风味物质种类和相对含量进行统计分析,结果见表3。从数量上看,老泡菜水接种发酵小米辣有63个挥发性风味物质,其次是老泡菜水自然发酵小米辣(61个)、新泡菜水自然发酵小米辣(54个)和新泡菜水接种发酵小米辣(49个)。从含量上看,新泡菜水自然发酵小米辣、新泡菜水接种发酵小米辣、老泡菜水自然发酵小米辣和老泡菜水接种发酵小米辣中总物质含量分别为18.33、16.42、38.83和43.69 μg/g。挥发性风味物质在老泡菜水混合接种微生物发酵小米辣中含量更高,可能是新泡菜水发酵小米辣发酵速度慢,而老泡菜水发酵和接种发酵小米辣发酵速度快,微生物代谢活动旺盛,风味物质可更快产生[28]。因此,老泡菜水混合接种微生物发酵有助于增加小米辣挥发性风味物质的种类和含量,丰富发酵小米辣的风味,这些丰富的代谢产物与发酵微生物群落相互作用紧密相关[2]。
表 3 不同发酵环境自然和接种发酵小米辣挥发性风味物质的变化Table 3. Changes of volatile compounds of natural and inoculated fermented chili peppers under different fermentation environments序号 物质 CAS RT RI RI 含量(μg/g) 气味描述 WJS-NF WJS-LP AB-NF AB-LP 醇类 1 乙醇 64-17-5 2.252 0.09±0.09b 0.05±0.01b 0.35±0.01a 0.48±0.07a 强烈、酒精 2 3-甲基-2-丁醇 598-75-4 3.961 0.07±0.00b 0.08±0.00a − − 水果味 3 异戊醇 123-51-3 5.124 737 737 0.28±0.01ab 0.33±0.02a 0.23±0.03b 0.23±0.04b 油、酒精、水果味 4 2-甲基丁醇 137-32-6 5.247 741 736 0.04±0.00c 0.06±0.01bc 0.08±0.01ab 0.08±0.01a 油、酒精、皮革味 5 正戊醇 71-41-0 6.088 769 768 − 0.07±0.00 − − 油、甜味、香脂味 6 4-甲基-1-戊醇 626-89-1 8.651 843 837 2.91±0.07b 3.36±0.12a 1.93±0.20c 1.71±0.20c 坚果味 7 反式-3-己烯-1-醇 928-97-2 9.379 862 861 0.13±0.03a 0.18±0.03a − − 草、花香、油、泥土味 8 正己醇 111-27-3 9.848 873 872 0.50±0.03ab 0.58±0.02a 0.46±0.05b 0.43±0.05b 油、水果、酒味、甜味 9 2-庚醇 543-49-7 11.124 901 903 0.08±0.01b 0.06±0.00b 0.17±0.01a − 青草、草药、甜味、花香 10 桉叶油醇 470-82-6 16.233 1037 1037 0.16±0.03b 0.12±0.02b 2.37±0.14a 2.58±0.09a 桉树、草药、樟脑味 11 顺-α,α-5-三甲基-5-乙烯基
四氢化呋喃-2-甲醇5989-33-3 17.636 1075 1071 − − 0.11±0.00b 0.12±0.01a 泥土、花香、甜、木头味 12 反式芳樟醇氧化物 34995-77-2 18.182 1089 1086 0.04±0.00a 0.04±0.00a − − 花香 13 芳樟醇 78-70-6 18.648 1101 1101 2.44±0.07c 1.48±0.02d 10.33±0.42b 11.46±0.45a 柑橘、花香、甜、蓝莓 14 苯乙醇 60-12-8 19.129 1116 1112 − − 0.05±0.00b 0.08±0.00a 花香、玫瑰花味 15 葑醇 1632-73-1 19.435 1126 1123 − − 0.03±0.00a 0.03±0.00a 樟脑、木头味、甜、柠檬 16 2-茨醇 507-70-0 21.215 1179 1173 − − 0.05±0.00b 0.11±0.01a 木头味、樟脑味、香脂味 17 4-萜烯醇 562-74-3 21.441 1185 1186 0.20±0.00c 0.05±0.00c 3.75±0.17b 4.19±0.26a 胡椒、木头、泥土、甜味 18 橙花醇 106-25-2 22.781 1227 1225 − − 0.30±0.01b 0.37±0.03a 甜味、成华、柑橘、玉兰 19 香叶醇 106-24-1 23.527 1252 1253 0.03±0.00b 0.02±0.00b 0.28±0.02a 0.29±0.02a 甜味、花香、水果、蜡味 酸类 20 乙酸 64-19-7 2.945 0.07±001b 0.15±0.02a − − 浓烈、刺鼻、醋酸 21 正壬酸 112-05-0 22.921 1232 1237 − − 0.09±0.01a 0.11±0.01a 蜡味、奶酪、发酵乳制品 醛类 22 异戊醛 590-86-3 3.555 0.07±0.01a 0.05±0.00b − − 巧克力味、桃味 23 正戊醛 110-62-3 4.225 700 704 0.06±0.01 − − − 发酵、水果味、坚果味 24 正己醛 66-25-1 7.207 801 801 0.08±0.02a 0.04±0.00b 0.04±0.00b − 脂肪、青草、水果味 25 2-已烯醛 6728-26-3 9.210 858 857 0.01±0.02 − − − 香蕉、脂肪、奶酪味 26 2-庚烯醛 57266-86-1 13.306 961 963 0.03±0.01b − 0.12±0.00a 0.11±0.04a 27 苯甲醛 100-52-7 13.516 966 964 − − 0.04±0.00 − 强烈、甜、苦、杏仁、樱桃 28 苯乙醛 122-78-1 16.613 1047 1046 0.06±0.01ab 0.05±0.00bc 0.06±0.01a 0.04±0.01c 甜、花香、蜂蜜、可可味 酮类 29 2-庚酮 110-43-0 10.630 891 893 0.04±0.01b 0.06±0.00ab 0.04±0.00b 0.05±0.00b 水果味、辛辣、甜、草药、
椰子、木头味30 2-甲基-3-辛酮 923-28-4 14.398 987 985 − − − 0.09±0.01 31 (-)-α-侧柏酮 546-80-5 19.358 1123 1117 − − 0.07±0.00b 0.09±0.01a 雪松叶味 32 2-莰酮 76-22-2 20.392 1155 1153 − − − 0.09±.0.01 樟脑味 33 香芹酮 99-49-0 23.452 1249 1249 − − 0.04±0.00a 0.03±0.00a 薄荷、甘草味 34 2-十一酮 112-12-9 24.853 1293 1296 − 0.03±0.00 − − 蜡味、水果、奶油、花香 酯类 35 乙酸乙酯 141-78-6 3.042 − − − 0.16±0.07 水果味、甜味 36 2-甲基丁酸乙酯 7452-79-1 9.086 855 850 − − − 0.11±0.00 强烈、甜味、水果味 37 异戊酸乙酯 108-64-5 9.271 859 856 − − − 0.23±0.03 甜味、水果味 38 己酸乙酯 123-66-0 13.650 969 959 0.14±0.03c 0.16±0.01c 0.47±0.04b 0.80±0.03a 甜味、水果味、蜡味 39 异戊酸异戊酯 659-70-1 18.826 1107 1105 0.19±0.02b 0.22±0.02b 0.30±0.00a 0.35±0.04a 甜味、水果味、果酱味 40 水杨酸甲酯 119-36-8 21.797 1194 1191 0.71±0.02b 0.83±0.02a 0.72±0.04b 0.69±0.03b 鹿蹄草、薄荷味 41 异戊酸叶醇酯 35154-45-1 23.003 1235 1235 − − − 0.06±0.01 新鲜、绿色、水果味 42 异戊酸己酯 10032-15-2 23.078 1237 1237 0.35±0.02b 0.32±0.05b 0.57±0.01a 0.60±0.09a 绿色、蜡味、水果味 43 庚酸丁酯 5454-28-4 28.244 1410 0.10±0.02b 0.10±0.02b 0.15±0.01ab 0.18±0.04a 水果、甘草、青草、油味 44 二氯乙酸壬酯 83004-99-3 28.489 1419 0.09±0.02b 0.08±.02b 0.17±0.01a 0.19±0.05a 45 8-甲基壬-6-烯酸异戊酯 1215128-16-7 32.986 1589 0.03±0.01a − 0.03±0.00a 0.02±0.01a 46 壬酸己酯 6561-39-3 33.441 1607 0.04±0.01a − 0.04±0.01a 0.04±0.01a 白兰地、蔬菜、水果味 47 4-甲基戊基-8-甲基壬-6-烯酸酯 1215128-18-9 35.412 1688 0.15±0.03a 0.11±0.02a 0.16±0.01a 0.12±0.03a 48 8-甲基壬酸-4-甲基戊酯 1215127-97-1 35.845 1706 0.09±0.02a 0.06±0.01a 0.08±0.01a 0.07±0.02a 49 棕榈酸乙酯 628-97-7 42.140 1992 1991 − − 0.06±0.01a 0.06±0.00a 蜡味、水果、奶油、奶香 萜烯类化合物 50 苯乙烯 100-42-5 10.714 892 895 0.19±0.04a 0.23±0.01a 0.10±0.01b − 甜、香脂味、花香、塑料 51 α-蒎烯 80-56-8 12.425 938 937 − − 0.07±0.01a 0.06±0.01a 樟脑、甜、松树、泥土味 52 月桂烯 123-35-3 14.580 991 992 0.07±0.00b 0.03±0.00b 0.63±0.05a 0.68±0.04a 胡椒、辛辣、香脂、塑料 53 水芹烯 99-83-2 15.253 1008 1010 − − 0.08±0.01b 0.10±0.01a 柑橘、草药、木头、胡椒 54 α-松油烯 99-86-5 15.655 1020 1022 − − 0.11±0.01b 0.14±0.01a 木头、柠檬、草药、柑橘 55 邻伞花烃 527-84-4 15.942 1029 1028 − − 0.17±0.01a 0.17±0.01a 56 柠檬烯 138-86-3 16.101 1033 1034 0.11±0.02b 0.09±0.01b 1.39±0.09a 1.52±0.13a 柑橘、草药、樟脑味 57 (Z)-3,7-二甲基-1,3,6-十八烷三烯 3338-55-4 16.700 1050 1047 0.05±0.02b 0.03±0.00b 0.25±0.02a 0.27±0.03a 花香、草药、甜味 58 γ-松油烯 99-85-4 17.172 1063 1062 − − 0.33±0.02b 0.39±0.03a 油、木头、柠檬、草药味 59 萜品油烯 586-63-0 18.165 1089 1081 − − 0.28±0.02b 0.31±0.02a 60 (+)-α-长叶蒎烯 5989-08-2 26.774 1360 1356 0.23±0.04 − − − 61 (−)-α-蒎烯 3856-25-5 27.498 1384 1381 − 0.13±0.01b 0.16±0.02ab 0.21±0.03a 木头味、辛辣味、蜂蜜味 62 β-石竹烯 87-44-5 28.790 1431 1430 − − 0.02±0.00b 0.03±0.00a 甜味、木头、香料、丁香 63 反式-β-金合欢烯 18794-84-8 29.542 1458 1456 0.46±0.71 − − − 木头、柑橘、草药、甜味 64 十五烯 13360-61-7 30.207 1482 1488 0.08±0.02 − − − 65 花柏烯 18431-82-8 30.414 1490 1488 0.93±0.14b 1.16±0.13ab 1.37±0.10ab 1.62±0.29a 66 雪松烯 1461-03-6 30.963 1510 1516 0.22±0.06a 0.15±0.03a 0.16±0.02a 0.15±0.03a 烷烃 67 1,1,3-三甲基环己烷 3073-66-3 14.669 993 0.04±0.00b 0.04±0.00a − − 绿色、甜味 68 1,4-桉叶素 470-67-7 15.577 1018 − − 0.03±0.00b 0.04±0.00a 松树、薄荷、樟脑味 69 顺式-1,1,3,5-四甲基
环己烷50876-32-9 15.751 1023 0.04±0.01b 0.05±0.00a 0.04±0.00b 0.04±0.00b 70 正十四烷 629-59-4 27.976 1400 0.08±0.02a 0.05±0.02a − − 蜡味 71 1α-丁基-2β-丙基环戊烷 62199-50-2 29.228 1447 1.49±0.22a 1.24±0.27a 1.10±0.15a 1.28±0.42a 72 正十五烷 629-62-9 29.738 1.54±0.23a 1.32±0.26a 1.27±0.15a 1.43±0.43a 蜡味 73 1,5-二甲基环辛烷 21328-57-4 31.885 1547 0.15±0.03a 0.14±0.04a 0.09±0.01a 0.15±0.06a 74 正十六烷 544-76-3 33.277 1600 0.60±0.13a 0.39±0.10a 0.43±0.06a 0.58±0.20a 75 1-戊基-2-丙基环戊烷 62199-51-3 34.362 1646 0.18±0.04a 0.11±0.03a 0.11±0.01a 0.16±0.05a 76 正十七烷 629-78-7 35.707 1700 0.35±0.07a 0.20±0.05a 0.30±0.03a 0.30±0.10a 酚类 77 愈创木酚 90-05-1 18.083 1087 1086 0.12±0.00b 0.18±0.01a − − 烟味、香料、香草、木头味 78 4-乙基苯酚 123-07-9 20.783 1166 1163 0.53±0.01a 0.48±0.02b − − 海狸香、烟味、愈创木酚 79 2-甲氧基-4-甲基苯酚 93-51-6 21.620 1190 1191 0.60±0.00b 1.11±0.05a − − 辛辣、香草、皮革、烟熏 80 4-乙基-2-甲氧基苯酚 2785-89-9 24.303 1276 1268 0.75±0.01a 0.51±0.02b − − 辛辣、烟熏、培根、丁香 81 丁香酚 97-53-0 26.657 1356 1356 0.20±0.00b − 4.45±0.23a 4.64±0.47a 甜味、辛辣、丁香、木头 吡嗪类化合物 82 2-甲氧基-3-异丁基
吡嗪24683-00-9 21.182 1178 1179 0.04±0.00a 0.04±0.00a − − 绿色、豌豆、白松香 含硫化合物 83 二烯丙基硫醚 592-88-1 9.438 867 − − 0.33±0.06a 0.36±0.04a 硫磺、葱、蒜、金属味 84 烯丙基甲基二硫 2179-58-0 11.713 918 919 − − 0.34±0.04b 0.59±0.01a 葱味、蒜味 85 二烯丙基二硫醚 2179-57-9 17.962 1083 1080 − − 1.24±0.08b 1.63±0.08a 葱味、蒜味、金属味 86 甲基烯丙基三硫醚 34135-85-8 20.054 1145 1135 − − 0.19±0.01b 0.30±0.02a 葱味、蒜味、奶油味 87 二烯丙基三硫醚 2050-87-5 25.291 1308 1300 − − 0.05±0.00b 0.09±0.01a 蒜味、葱味、金属味 注:RT为保留时间;RI为计算保留指数;RI为参考保留指数,来源于文献数据(https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/cas-ser/);气味描述来源于文献数据(http://www.thegoodscentscompany.com);−表示未检出;同一行中不同小写字母表示Tukey's检验具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 醇类、酯类和萜烯类化合物是小米辣的主要挥发性风味物质成分,但不同发酵方式下小米辣挥发性风味物质组成和占比存在着差异。醇类物质是发酵小米辣中占比最大的风味物质,老泡菜水发酵小米辣中醇类占全部风味物质的50%左右,而新泡菜水发酵小米辣约为40%,这与云琳等[28]研究结果相似,卤水泡菜中醇类物质种类和含量高于无菌水发酵泡菜。乙醇、异戊醇、2-甲基丁醇、4-甲基-1-戊醇、正己醇、桉叶油醇、芳樟醇、4-萜烯醇和香叶醇是四种发酵小米辣的共有醇类物质,这些物质具有酒精味、花香味、坚果味等特征。尽管醇类物质阈值一般较高,对风味贡献较小,但不饱和醇类阈值较低,对小米辣整体风味贡献较大[8],如4-甲基-1-戊醇具有坚果味;芳樟醇具有柑橘味、花香、木香等特征风味[8],其在自然发酵和接种发酵小米辣中均被检出,但在老泡菜水混菌接种发酵样品中含量最高(P<0.05)。
萜烯类物质是发酵小米辣中第二大类风味物质,该类物质阈值较低,具有花香和果香,对总体风味的贡献较大[2]。老泡菜水发酵小米辣中萜烯类物质(老泡菜水自然发酵小米辣:13.19%;老泡菜水接种发酵小米辣:12.93%)含量比例高于新泡菜水发酵小米辣(新泡菜水自然发酵小米辣:12.77%;新泡菜水接种发酵小米辣:11.08%),且在相同泡菜水发酵小米辣中,自然发酵小米辣中萜烯类化合物含量占比高于混菌接种发酵小米辣。月桂烯、柠檬烯、(Z)-3,7-二甲基-1,3,6-十八烷三烯、花柏烯和雪松烯是四种发酵小米辣的共有萜烯类物质,为发酵小米辣提供胡椒、辛辣、柑橘、草药和花香等气味。此外,老泡菜水发酵小米辣中检测出独有的萜烯类化合物较多,如α-蒎烯、水芹烯、α-松油烯、邻伞花烃、γ-松油烯、萜品油烯和β-石竹烯,且接种发酵小米辣中上述物质含量显著高于自然发酵(P<0.05)。
酯类物质是发酵小米辣中第三大类风味物质,为样品提供水果味和甜味。新泡菜水发酵小米辣(新泡菜水自然发酵小米辣:10.31%;新泡菜水接种发酵小米辣:11.45%)中酯类物质含量占比高于老泡菜水发酵小米辣(老泡菜水自然发酵小米辣:7.08%;老泡菜水接种发酵小米辣:8.42%),且在相同泡菜水发酵小米辣中,与自然发酵小米辣相比,混菌接种发酵小米辣的酯类物质含量占比更高,这是由于植物乳杆菌中的酯酶活性能促进酯类物质的形成[29]。此外,乳酸菌也能将部分酸类物质通过酯化反应生成相应的乙酯类化合物[29],其含量的积累对发酵小米辣的花果类香气具有较大的贡献[2]。在所有检测的酯类物质中,己酸乙酯在混菌接种发酵小米辣中含量最高(P<0.05),异戊酸叶醇酯是老泡菜水混菌接种发酵小米辣独有的挥发性风味物质。
除醇类、酯类和萜烯类物质外,发酵小米辣中的挥发性风味成分还有酸类、醛类、酮类、烷烃、酚类、吡嗪类和含硫化合物,但相对含量较低。在这些物质里,所有样品中均检出苯乙醛、2-庚酮、顺式-1,1,3,5-四甲基环己烷、1α-丁基-2β-丙基环戊烷、正十五烷、1,5-二甲基环辛烷、正十六烷、1-戊基-2-丙基环戊烷和正十七烷。苯乙醛在老泡菜水接种发酵小米辣中含量最低(P<0.05),其他物质均无显著性差异(P>0.05)。4种发酵小米辣中酸类物质含量较低(<0.15 μg/g),新泡菜水发酵小米辣中仅检测出乙酸,接种发酵样品中乙酸含量显著高于自然发酵(P<0.05);而老泡菜水发酵中仅检出壬酸,且自然发酵和接种发酵样品间壬酸含量无显著性差异(P>0.05)。相同泡菜水发酵样品间比较,接种发酵小米辣中检测到的醛类物质种类低于自然发酵小米辣;相同发酵方式间比较,自然发酵小米辣中醛类物质种类高于接种发酵小米辣。老泡菜水混菌接种发酵小米辣中酮类物质种类较多,为5种,其余发酵方式则小于3种,酮类物质主要是脂质氧化和氨基酸降解的产物,感官阈值较醛类高,但具有独特的清香和果香[8],如2-庚酮,在自然发酵和接种发酵小米辣中均有检出,具有果香味和药香味的风味特征[30]。四种发酵小米辣间烷烃种类和含量均无显著性差异(P>0.05)。本研究中,老泡菜水发酵小米辣中检测到5种含硫化合物,而新泡菜水发酵样品中未检出,这可能是在新泡菜水发酵小米辣中含量过低而未能检出。已有研究表明,乳酸菌参与的发酵过程能显著促进含硫风味化合物前体物质的合成,进而促进酵母菌产香水平的提升[29],这与本实验结果一致,老泡菜水混菌接种发酵小米辣中含硫化合物含量显著高于老泡菜水自然发酵小米辣(P<0.05)。发酵小米辣的挥发性风味物质种类含量的差异与微生物区系有关。新泡菜水自然发酵小米辣依赖原料、器皿表面的微生物进行发酵,微生物种类复杂;经过长期的筛选作用,老泡菜水发酵小米辣菌群相对稳定;接种发酵小米辣中两种微生物迅速成为优势菌群,抑制杂菌生长。大量研究表明,泡菜水中的优势微生物与发酵蔬菜产品品质密切相关。Yang等[5]通过高通量测序技术研究陈年老卤水发酵萝卜的微生物群落与品质相关的理化特性之间的相关性发现,植物乳杆菌、耐酸乳杆菌、食窦魏斯氏菌和假肠膜明串珠菌与pH、质构、有机酸等大部分理化指标均呈显著相关,强相关性表明这些细菌对重庆泡萝卜的成功发酵有重要作用以及酵母有助于在发酵蔬菜产品中形成理想的风味特征。Ye等[15]研究发现优势真菌Colletotrichum simmondsii和Cladosporium tenuissimum,与己酸庚酯、抗坏血酸和咀嚼性呈正相关。因此本文泡菜水中微生物组成的差异造成对风味化合物前体物质的代谢能力不同,使得四种发酵小米辣中挥发性风味物质种类和含量各不相同[28]。
3. 结论
本研究对比了自然发酵和混菌接种发酵在不同发酵环境下(新泡菜水/老泡菜水)对小米辣品质的影响。结果表明,老泡菜水对小米辣品质具有影响显著,且接种发酵可显著(P<0.05)加快发酵速度,提高产品品质。其中老泡菜水接种发酵显著(P<0.05)增加了发酵小米辣中乳酸菌的数量,且亚硝酸盐含量最低(仅为5.25 mg/kg),发酵过程pH下降速度快并率先进入平台期,对小米辣后期变黄和变软具有显著的延缓效果,同时对有机酸和香气物质形成具有积极的作用。与其他发酵组相比,老泡菜水接种发酵的小米辣挥发性风味物质种类多、含量高,尤其是醇类、萜烯类和含硫化合物等特征香气物质。综上所述,老泡菜水混菌接种发酵可以提高发酵小米辣的品质和安全性。基于此,课题组将进一步通过组学技术分析老泡菜水中的微生物群落组成及其代谢通路,解析老泡菜水混菌接种发酵品质形成机制,为接种发酵小米的产业化应用和特定直投菌剂的挖掘开发提供有力的理论支撑。
-
表 1 泡菜水配方
Table 1 Formulation of brine
配料 比例(%) 配料 比例(%) 配料 比例(%) 去离子水 64.17 大蒜 3.33 小茴香 0.50 生姜 6.67 苹果 3.00 香叶 0.40 红皮萝卜 5.00 冰糖 1.20 丁香 0.24 白皮萝卜 5.00 白酒 1.00 冰醋酸 0.20 无碘盐 4.00 味精 1.00 氯化钙 0.10 洋葱 3.33 青花椒 0.80 八角 0.06 表 2 不同发酵环境自然和接种发酵小米辣pH、亚硝酸盐含量和颜色的变化
Table 2 Changes of pH, nitrite content, and color of natural and inoculated fermented chili peppers under different fermentation environments
发酵时间(d) pH 亚硝酸盐
含量(mg/kg)颜色 L* a* b* ∆E* SW-NF 0 5.85±0.14Aa 2.92±0.64Ad 50.69±2.05Aa −5.64±0.21Bd 32.03±1.29Ba − 1 5.80±0.20Aa 0.29±0.45Ad 44.82±1.56Ab −3.97±0.76Bc 29.05±1.60Ab 7.16±2.20Ab 3 5.50±0.06Aab 26.38±2.30Aa 42.20±3.45Abc 1.11±0.68Ab 29.21±1.49Ab 11.57±3.27Aa 5 5.11±0.11Ab 9.51±2.07ABc 41.06±1.18Ac 1.76±0.42ABab 30.43±0.96Aab 12.38±1.71ABa 7 4.71±0.20Ac 13.62±1.86Bb 39.54±1.99Ac 1.92±0.72ABa 28.74±1.94Ab 14.05±2.30Aa SW-LP 0 5.82±0.16Aa 2.30±1.44Ad 49.50±1.63ABa −5.25±0.32ABd 31.80±1.06Ba − 1 5.82±0.21Aa 3.95±1.51Acd 43.90±1.24ABb −4.33±0.66Bc 28.19±1.59Ab 7.17±1.00Ab 3 5.20±0.15Bb 12.59±9.78Bbc 40.41±1.64Ac 1.72±0.39Ab 28.08±1.56Ab 12.19±1.95Aa 5 4.99±0.10Ab 16.71±5.26Aab 39.42±0.88Bc 1.93±0.25Aab 28.80±1.06Ab 12.80±1.54Aa 7 4.81±0.17Ab 23.70±5.16Aa 39.52±1.50Ac 2.51±0.58Aa 29.75±1.26Ab 13.03±1.74ABa AB-NF 0 5.57±0.14Aa 0.64±0.83Ab 50.26±1.29Aa −5.64±0.59Bc 33.61±1.24Aa − 1 5.19±0.11Bb 3.46±3.83Ab 43.12±0.85Bb −2.91±0.66Ab 28.87±1.55Ab 9.11±1.79Ab 3 4.65±0.08Cc 4.25±5.17Bb 40.44±0.91Ac 1.46±0.65Aa 28.52±2.81Ab 13.50±1.34Aa 5 4.46±0.07Bcd 0.25±0.39Cb 39.43±1.24Bcd 1.45±0.31BCa 30.25±1.28Ab 13.51±1.77Aa 7 4.33±0.06Bd 11.17±5.79Ba 38.96±0.77Ad 1.66±0.56Ba 29.01±1.33Ab 14.35±2.04Aa AB-LP 0 5.66±0.13Aa 6.83±10.31Aa 48.05±1.80Ba −5.12±0.29Ac 31.61±1.38Ba − 1 5.14±0.07Bb 4.54±6.32Aa 42.70±0.88Bb −2.83±0.67Ab 28.17±1.24Ab 7.22±2.05Ab 3 4.71±0.05Cc 6.17±6.97Ba 41.10±2.06Abc 1.28±0.66Aa 27.06±1.73Ab 10.74±2.46Aa 5 4.30±0.03Bd 5.92±8.59BCa 41.00±1.65Abc 1.34±0.38Ca 28.95±2.01Ab 10.31±2.24Ba 7 4.31±0.09Bd 5.25±8.13Ba 39.84±1.39Ac 1.35±0.32Ba 27.85±1.81Ab 11.37±1.66Ba 注:不同小写字母表示同一样品不同发酵时间Tukey's检验具有显著性差异(P<0.05);不同大写字母表示不同样品同一发酵时间Tukey's检验具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 表 3 不同发酵环境自然和接种发酵小米辣挥发性风味物质的变化
Table 3 Changes of volatile compounds of natural and inoculated fermented chili peppers under different fermentation environments
序号 物质 CAS RT RI RI 含量(μg/g) 气味描述 WJS-NF WJS-LP AB-NF AB-LP 醇类 1 乙醇 64-17-5 2.252 0.09±0.09b 0.05±0.01b 0.35±0.01a 0.48±0.07a 强烈、酒精 2 3-甲基-2-丁醇 598-75-4 3.961 0.07±0.00b 0.08±0.00a − − 水果味 3 异戊醇 123-51-3 5.124 737 737 0.28±0.01ab 0.33±0.02a 0.23±0.03b 0.23±0.04b 油、酒精、水果味 4 2-甲基丁醇 137-32-6 5.247 741 736 0.04±0.00c 0.06±0.01bc 0.08±0.01ab 0.08±0.01a 油、酒精、皮革味 5 正戊醇 71-41-0 6.088 769 768 − 0.07±0.00 − − 油、甜味、香脂味 6 4-甲基-1-戊醇 626-89-1 8.651 843 837 2.91±0.07b 3.36±0.12a 1.93±0.20c 1.71±0.20c 坚果味 7 反式-3-己烯-1-醇 928-97-2 9.379 862 861 0.13±0.03a 0.18±0.03a − − 草、花香、油、泥土味 8 正己醇 111-27-3 9.848 873 872 0.50±0.03ab 0.58±0.02a 0.46±0.05b 0.43±0.05b 油、水果、酒味、甜味 9 2-庚醇 543-49-7 11.124 901 903 0.08±0.01b 0.06±0.00b 0.17±0.01a − 青草、草药、甜味、花香 10 桉叶油醇 470-82-6 16.233 1037 1037 0.16±0.03b 0.12±0.02b 2.37±0.14a 2.58±0.09a 桉树、草药、樟脑味 11 顺-α,α-5-三甲基-5-乙烯基
四氢化呋喃-2-甲醇5989-33-3 17.636 1075 1071 − − 0.11±0.00b 0.12±0.01a 泥土、花香、甜、木头味 12 反式芳樟醇氧化物 34995-77-2 18.182 1089 1086 0.04±0.00a 0.04±0.00a − − 花香 13 芳樟醇 78-70-6 18.648 1101 1101 2.44±0.07c 1.48±0.02d 10.33±0.42b 11.46±0.45a 柑橘、花香、甜、蓝莓 14 苯乙醇 60-12-8 19.129 1116 1112 − − 0.05±0.00b 0.08±0.00a 花香、玫瑰花味 15 葑醇 1632-73-1 19.435 1126 1123 − − 0.03±0.00a 0.03±0.00a 樟脑、木头味、甜、柠檬 16 2-茨醇 507-70-0 21.215 1179 1173 − − 0.05±0.00b 0.11±0.01a 木头味、樟脑味、香脂味 17 4-萜烯醇 562-74-3 21.441 1185 1186 0.20±0.00c 0.05±0.00c 3.75±0.17b 4.19±0.26a 胡椒、木头、泥土、甜味 18 橙花醇 106-25-2 22.781 1227 1225 − − 0.30±0.01b 0.37±0.03a 甜味、成华、柑橘、玉兰 19 香叶醇 106-24-1 23.527 1252 1253 0.03±0.00b 0.02±0.00b 0.28±0.02a 0.29±0.02a 甜味、花香、水果、蜡味 酸类 20 乙酸 64-19-7 2.945 0.07±001b 0.15±0.02a − − 浓烈、刺鼻、醋酸 21 正壬酸 112-05-0 22.921 1232 1237 − − 0.09±0.01a 0.11±0.01a 蜡味、奶酪、发酵乳制品 醛类 22 异戊醛 590-86-3 3.555 0.07±0.01a 0.05±0.00b − − 巧克力味、桃味 23 正戊醛 110-62-3 4.225 700 704 0.06±0.01 − − − 发酵、水果味、坚果味 24 正己醛 66-25-1 7.207 801 801 0.08±0.02a 0.04±0.00b 0.04±0.00b − 脂肪、青草、水果味 25 2-已烯醛 6728-26-3 9.210 858 857 0.01±0.02 − − − 香蕉、脂肪、奶酪味 26 2-庚烯醛 57266-86-1 13.306 961 963 0.03±0.01b − 0.12±0.00a 0.11±0.04a 27 苯甲醛 100-52-7 13.516 966 964 − − 0.04±0.00 − 强烈、甜、苦、杏仁、樱桃 28 苯乙醛 122-78-1 16.613 1047 1046 0.06±0.01ab 0.05±0.00bc 0.06±0.01a 0.04±0.01c 甜、花香、蜂蜜、可可味 酮类 29 2-庚酮 110-43-0 10.630 891 893 0.04±0.01b 0.06±0.00ab 0.04±0.00b 0.05±0.00b 水果味、辛辣、甜、草药、
椰子、木头味30 2-甲基-3-辛酮 923-28-4 14.398 987 985 − − − 0.09±0.01 31 (-)-α-侧柏酮 546-80-5 19.358 1123 1117 − − 0.07±0.00b 0.09±0.01a 雪松叶味 32 2-莰酮 76-22-2 20.392 1155 1153 − − − 0.09±.0.01 樟脑味 33 香芹酮 99-49-0 23.452 1249 1249 − − 0.04±0.00a 0.03±0.00a 薄荷、甘草味 34 2-十一酮 112-12-9 24.853 1293 1296 − 0.03±0.00 − − 蜡味、水果、奶油、花香 酯类 35 乙酸乙酯 141-78-6 3.042 − − − 0.16±0.07 水果味、甜味 36 2-甲基丁酸乙酯 7452-79-1 9.086 855 850 − − − 0.11±0.00 强烈、甜味、水果味 37 异戊酸乙酯 108-64-5 9.271 859 856 − − − 0.23±0.03 甜味、水果味 38 己酸乙酯 123-66-0 13.650 969 959 0.14±0.03c 0.16±0.01c 0.47±0.04b 0.80±0.03a 甜味、水果味、蜡味 39 异戊酸异戊酯 659-70-1 18.826 1107 1105 0.19±0.02b 0.22±0.02b 0.30±0.00a 0.35±0.04a 甜味、水果味、果酱味 40 水杨酸甲酯 119-36-8 21.797 1194 1191 0.71±0.02b 0.83±0.02a 0.72±0.04b 0.69±0.03b 鹿蹄草、薄荷味 41 异戊酸叶醇酯 35154-45-1 23.003 1235 1235 − − − 0.06±0.01 新鲜、绿色、水果味 42 异戊酸己酯 10032-15-2 23.078 1237 1237 0.35±0.02b 0.32±0.05b 0.57±0.01a 0.60±0.09a 绿色、蜡味、水果味 43 庚酸丁酯 5454-28-4 28.244 1410 0.10±0.02b 0.10±0.02b 0.15±0.01ab 0.18±0.04a 水果、甘草、青草、油味 44 二氯乙酸壬酯 83004-99-3 28.489 1419 0.09±0.02b 0.08±.02b 0.17±0.01a 0.19±0.05a 45 8-甲基壬-6-烯酸异戊酯 1215128-16-7 32.986 1589 0.03±0.01a − 0.03±0.00a 0.02±0.01a 46 壬酸己酯 6561-39-3 33.441 1607 0.04±0.01a − 0.04±0.01a 0.04±0.01a 白兰地、蔬菜、水果味 47 4-甲基戊基-8-甲基壬-6-烯酸酯 1215128-18-9 35.412 1688 0.15±0.03a 0.11±0.02a 0.16±0.01a 0.12±0.03a 48 8-甲基壬酸-4-甲基戊酯 1215127-97-1 35.845 1706 0.09±0.02a 0.06±0.01a 0.08±0.01a 0.07±0.02a 49 棕榈酸乙酯 628-97-7 42.140 1992 1991 − − 0.06±0.01a 0.06±0.00a 蜡味、水果、奶油、奶香 萜烯类化合物 50 苯乙烯 100-42-5 10.714 892 895 0.19±0.04a 0.23±0.01a 0.10±0.01b − 甜、香脂味、花香、塑料 51 α-蒎烯 80-56-8 12.425 938 937 − − 0.07±0.01a 0.06±0.01a 樟脑、甜、松树、泥土味 52 月桂烯 123-35-3 14.580 991 992 0.07±0.00b 0.03±0.00b 0.63±0.05a 0.68±0.04a 胡椒、辛辣、香脂、塑料 53 水芹烯 99-83-2 15.253 1008 1010 − − 0.08±0.01b 0.10±0.01a 柑橘、草药、木头、胡椒 54 α-松油烯 99-86-5 15.655 1020 1022 − − 0.11±0.01b 0.14±0.01a 木头、柠檬、草药、柑橘 55 邻伞花烃 527-84-4 15.942 1029 1028 − − 0.17±0.01a 0.17±0.01a 56 柠檬烯 138-86-3 16.101 1033 1034 0.11±0.02b 0.09±0.01b 1.39±0.09a 1.52±0.13a 柑橘、草药、樟脑味 57 (Z)-3,7-二甲基-1,3,6-十八烷三烯 3338-55-4 16.700 1050 1047 0.05±0.02b 0.03±0.00b 0.25±0.02a 0.27±0.03a 花香、草药、甜味 58 γ-松油烯 99-85-4 17.172 1063 1062 − − 0.33±0.02b 0.39±0.03a 油、木头、柠檬、草药味 59 萜品油烯 586-63-0 18.165 1089 1081 − − 0.28±0.02b 0.31±0.02a 60 (+)-α-长叶蒎烯 5989-08-2 26.774 1360 1356 0.23±0.04 − − − 61 (−)-α-蒎烯 3856-25-5 27.498 1384 1381 − 0.13±0.01b 0.16±0.02ab 0.21±0.03a 木头味、辛辣味、蜂蜜味 62 β-石竹烯 87-44-5 28.790 1431 1430 − − 0.02±0.00b 0.03±0.00a 甜味、木头、香料、丁香 63 反式-β-金合欢烯 18794-84-8 29.542 1458 1456 0.46±0.71 − − − 木头、柑橘、草药、甜味 64 十五烯 13360-61-7 30.207 1482 1488 0.08±0.02 − − − 65 花柏烯 18431-82-8 30.414 1490 1488 0.93±0.14b 1.16±0.13ab 1.37±0.10ab 1.62±0.29a 66 雪松烯 1461-03-6 30.963 1510 1516 0.22±0.06a 0.15±0.03a 0.16±0.02a 0.15±0.03a 烷烃 67 1,1,3-三甲基环己烷 3073-66-3 14.669 993 0.04±0.00b 0.04±0.00a − − 绿色、甜味 68 1,4-桉叶素 470-67-7 15.577 1018 − − 0.03±0.00b 0.04±0.00a 松树、薄荷、樟脑味 69 顺式-1,1,3,5-四甲基
环己烷50876-32-9 15.751 1023 0.04±0.01b 0.05±0.00a 0.04±0.00b 0.04±0.00b 70 正十四烷 629-59-4 27.976 1400 0.08±0.02a 0.05±0.02a − − 蜡味 71 1α-丁基-2β-丙基环戊烷 62199-50-2 29.228 1447 1.49±0.22a 1.24±0.27a 1.10±0.15a 1.28±0.42a 72 正十五烷 629-62-9 29.738 1.54±0.23a 1.32±0.26a 1.27±0.15a 1.43±0.43a 蜡味 73 1,5-二甲基环辛烷 21328-57-4 31.885 1547 0.15±0.03a 0.14±0.04a 0.09±0.01a 0.15±0.06a 74 正十六烷 544-76-3 33.277 1600 0.60±0.13a 0.39±0.10a 0.43±0.06a 0.58±0.20a 75 1-戊基-2-丙基环戊烷 62199-51-3 34.362 1646 0.18±0.04a 0.11±0.03a 0.11±0.01a 0.16±0.05a 76 正十七烷 629-78-7 35.707 1700 0.35±0.07a 0.20±0.05a 0.30±0.03a 0.30±0.10a 酚类 77 愈创木酚 90-05-1 18.083 1087 1086 0.12±0.00b 0.18±0.01a − − 烟味、香料、香草、木头味 78 4-乙基苯酚 123-07-9 20.783 1166 1163 0.53±0.01a 0.48±0.02b − − 海狸香、烟味、愈创木酚 79 2-甲氧基-4-甲基苯酚 93-51-6 21.620 1190 1191 0.60±0.00b 1.11±0.05a − − 辛辣、香草、皮革、烟熏 80 4-乙基-2-甲氧基苯酚 2785-89-9 24.303 1276 1268 0.75±0.01a 0.51±0.02b − − 辛辣、烟熏、培根、丁香 81 丁香酚 97-53-0 26.657 1356 1356 0.20±0.00b − 4.45±0.23a 4.64±0.47a 甜味、辛辣、丁香、木头 吡嗪类化合物 82 2-甲氧基-3-异丁基
吡嗪24683-00-9 21.182 1178 1179 0.04±0.00a 0.04±0.00a − − 绿色、豌豆、白松香 含硫化合物 83 二烯丙基硫醚 592-88-1 9.438 867 − − 0.33±0.06a 0.36±0.04a 硫磺、葱、蒜、金属味 84 烯丙基甲基二硫 2179-58-0 11.713 918 919 − − 0.34±0.04b 0.59±0.01a 葱味、蒜味 85 二烯丙基二硫醚 2179-57-9 17.962 1083 1080 − − 1.24±0.08b 1.63±0.08a 葱味、蒜味、金属味 86 甲基烯丙基三硫醚 34135-85-8 20.054 1145 1135 − − 0.19±0.01b 0.30±0.02a 葱味、蒜味、奶油味 87 二烯丙基三硫醚 2050-87-5 25.291 1308 1300 − − 0.05±0.00b 0.09±0.01a 蒜味、葱味、金属味 注:RT为保留时间;RI为计算保留指数;RI为参考保留指数,来源于文献数据(https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/cas-ser/);气味描述来源于文献数据(http://www.thegoodscentscompany.com);−表示未检出;同一行中不同小写字母表示Tukey's检验具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 叶子, 商智勋, 李美奇, 等. 不同品种发酵小米辣品质特性比较与综合分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(10):87−95. [YE Z, SHANG Z X, LI M Q, et al. Comparison and comprehensive analysis of quality characteristics of fermented Xiaomila in different cultivars[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(10):87−95.] YE Z, SHANG Z X, LI M Q, et al. Comparison and comprehensive analysis of quality characteristics of fermented Xiaomila in different cultivars[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(10): 87−95.
[2] 叶子, 商智勋, 李美奇, 等. 基于HS-SPME-GC-MS非靶向分析不同发酵小米辣的风味差异[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(6):309−316. [YE Z, SHANG Z X, LI M Q, et al. Untargeted analysis on flavor differences of different fermented chili peppers (Xiaomila) based on the HS-SPME-GC-MS[J]. Food Science,2022,43(6):309−316.] YE Z, SHANG Z X, LI M Q, et al. Untargeted analysis on flavor differences of different fermented chili peppers (Xiaomila) based on the HS-SPME-GC-MS[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(6): 309−316.
[3] YE Z, SHANG Z X, LI M Q, et al. Evaluation of the physiochemical and aromatic qualities of pickled Chinese pepper (Paojiao) and their influence on consumer acceptability by using targeted and untargeted multivariate approaches[J]. Food Research International,2020,137:109535. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109535
[4] ZHAO N, YANG B, LU W W, et al. Divergent role of abiotic factors in shaping microbial community assembly of paocai brine during aging process[J]. Food Research International,2020,137:109559. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109559
[5] YANG Y L, FAN Y, LI T, et al. Microbial composition and correlation between microbiota and quality-related physiochemical characteristics in chongqing radish paocai[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,369:130897. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130897
[6] ZHAO N, LAI H M, WANG Y L, et al. Assessment of biogenic amine and nitrite production in low-salt Paocai during fermentation as affected by reused brine and fresh brine[J]. Food Bioscience,2021,41:100958. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.100958
[7] 罗丽蓉, 李宏洋, 吴拥军, 等. 泡椒老卤水中乳酸菌筛选及益生性能分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2023,49(20):159−165. [LUO L R, LI H Y, WU Y J, et al. Screening and probiotic performance analysis of lactic acid bacteria in pickled pepper sauces[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2023,49(20):159−165.] LUO L R, LI H Y, WU Y J, et al. Screening and probiotic performance analysis of lactic acid bacteria in pickled pepper sauces[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2023, 49(20): 159−165.
[8] 曾金秀, 尹红梅, 张权, 等. 霉鱼源清酒乳杆菌的分离筛选及其在霉鱼发酵中的应用[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2024,50(6):56−64. [ZENG J X, YIN H M, ZHANG Q, et al. Isolation, identification of Lactobacillus sakei of traditional fermented bighead carp and its application in inoculated fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2024,50(6):56−64.] ZENG J X, YIN H M, ZHANG Q, et al. Isolation, identification of Lactobacillus sakei of traditional fermented bighead carp and its application in inoculated fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2024, 50(6): 56−64.
[9] 何珍. 传统酸菜中优势菌群筛选及其共酵对风味品质的影响[D]. 大连:大连工业大学, 2021. [HE Z. Screening of dominant bacteria in traditional Suancai and its effect of co-fermentation on flavor quality[D]. Dalian:Dalian Polytechnic University, 2021.] HE Z. Screening of dominant bacteria in traditional Suancai and its effect of co-fermentation on flavor quality[D]. Dalian: Dalian Polytechnic University, 2021.
[10] 王英, 张会, 刘小莉, 等. 不同发酵剂对浅渍发酵豇豆风味成分和滋味的影响[J]. 中国酿造,2022,41(11):89−95. [WANG Y, ZHANG H, LIU X L, et al. Effect of different starters on the flavor components and taste of low-salt curing cowpea[J]. China Brewing,2022,41(11):89−95.] WANG Y, ZHANG H, LIU X L, et al. Effect of different starters on the flavor components and taste of low-salt curing cowpea[J]. China Brewing, 2022, 41(11): 89−95.
[11] SUN Q X, SUN F D, ZHENG D M, et al. Complex starter culture combined with vacuum packaging reduces biogenic amine formation and delays the quality deterioration of dry sausage during storage[J]. Food Control,2019,100:58−66. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.01.008
[12] 陈凤, 游玉明, 张冬梅, 等. 发酵方式对泡豇豆品质的影响[J]. 中国调味品,2018,43(12):44−49. [CHEN F, YOU Y M, ZHANG D M, et al. Effect of fermentation methods on the quality of pickled cowpea[J]. China Condiment,2018,43(12):44−49.] CHEN F, YOU Y M, ZHANG D M, et al. Effect of fermentation methods on the quality of pickled cowpea[J]. China Condiment, 2018, 43(12): 44−49.
[13] BRIZUELA N S, BRAVO-FERRADA B M, CURILÉN Y, et al. Advantages of using blend cultures of native L. plantarum and O. oeni strains to induce malolactic fermentation of patagonian Malbec wine[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2018,9:2109. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02109
[14] YE Z, SHANG Z X, LI M Q, et al. Effect of ripening and variety on the physiochemical quality and flavor of fermented Chinese chili pepper (Paojiao)[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,368:130797. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130797
[15] YE Z, SHANG Z X, ZHANG S Y, et al. Dynamic analysis of flavor properties and microbial communities in Chinese pickled chili pepper (Capsicum frutescens L.):A typical industrial-scale natural fermentation process[J]. Food Research International,2022,153:110952. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.110952
[16] 吴梓仟, 刘晶晶, 邓高文, 等. 曲霉强化发酵对浏阳豆豉风味品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(22):267−275. [WU Z Q, LIU J J, DENG G W, et al. Effect of enhanced fermentation with Aspergillus on the flavor quality of Liuyang Douchi[J]. Food Science,2023,44(22):267−275.] WU Z Q, LIU J J, DENG G W, et al. Effect of enhanced fermentation with Aspergillus on the flavor quality of Liuyang Douchi[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(22): 267−275.
[17] SHANG Z X, YE Z, LI M Q, et al. Dynamics of microbial communities, flavor, and physicochemical properties of pickled chayote during an industrial-scale natural fermentation:Correlation between microorganisms and metabolites[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,377:132004. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.132004
[18] WU R N, YU M L, LIU X Y, et al. Changes in flavour and microbial diversity during natural fermentation of suan-cai, a traditional food made in Northeast China[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2015,211:23−31. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2015.06.028
[19] HU W Z, YANG X Z, JI Y R, et al. Effect of starter cultures mixed with different autochthonous lactic acid bacteria on microbial, metabolome and sensory properties of Chinese northeast sauerkraut[J]. Food Research International,2021,148:110605. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110605
[20] LEE J J, CHOI Y J, LEE M J, et al. Effects of combining two lactic acid bacteria as a starter culture on model kimchi fermentation[J]. Food Research International,2020,136:109591. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109591
[21] 田旭艳, 高沛, 夏文水, 等. 接种戊糖乳杆菌和酿酒酵母菌对低盐发酵鳊鱼品质的影响[J]. 南方水产科学,2022,18(2):124−133. [TIAN X Y, GAO P, XIA W S, et al. Effects of inoculation of Lactiplantibacillus pentosus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on quality of low-salt fermented bream[J]. South China Fisheries Science,2022,18(2):124−133.] TIAN X Y, GAO P, XIA W S, et al. Effects of inoculation of Lactiplantibacillus pentosus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on quality of low-salt fermented bream[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2022, 18(2): 124−133.
[22] 胡丹丹, 吴祖芳, 孙志栋, 等. 腌制叶用芥菜发酵菌分离鉴定及应用研究[J]. 核农学报,2022,36(6):1174−1182. [HU D D, WU Z F, SUN Z D, et al. Study on isolation and identification of fermentation bacteria for pickled leaf mustard and optimization of fermentation echnology[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2022,36(6):1174−1182.] HU D D, WU Z F, SUN Z D, et al. Study on isolation and identification of fermentation bacteria for pickled leaf mustard and optimization of fermentation echnology[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 36(6): 1174−1182.
[23] WU C D, ZHENG J, HUANG J, et al. Reduced nitrite and biogenic amine concentrations and improved flavor components of Chinese sauerkraut via co-culture of Lactobacillus plantarum and Zygosaccharomyces rouxii[J]. Annals of Microbiology,2014,64:847−857. doi: 10.1007/s13213-013-0724-8
[24] 龚福明, 何彩梅, 吴桂容, 等. 乳酸菌降解发酵蔬菜中亚硝酸盐的研究现状[J]. 中国调味品,2022,47(10):201−205. [GONG F M, HE C M, WU G R, et al. Research status of nitrite degradation in fermented vegetables by lactic acid bacteria[J]. China Condiment,2022,47(10):201−205.] GONG F M, HE C M, WU G R, et al. Research status of nitrite degradation in fermented vegetables by lactic acid bacteria[J]. China Condiment, 2022, 47(10): 201−205.
[25] 陈宇昱. 剁辣椒发酵及贮藏过程中质构品质及果胶特性变化研究[D]. 长沙:湖南农业大学, 2021. [CHEN Y Y. Changes of texture qualities and pectin properties in fermentation minced pepper during fermentation and preservation[D]. Changsha:Hunan Agricultural University, 2021.] CHEN Y Y. Changes of texture qualities and pectin properties in fermentation minced pepper during fermentation and preservation[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2021.
[26] 嵇晨, 周溯, 韩晓华, 等. 臭豆腐发酵过程中丙酸形成的机制[J]. 中国食品学报,2023,23(5):352−361. [JI C, ZHOU S, HAN X H, et al. The mechanisms of propionic acid formation in the fermentation of stinky tofu[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2023,23(5):352−361.] JI C, ZHOU S, HAN X H, et al. The mechanisms of propionic acid formation in the fermentation of stinky tofu[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2023, 23(5): 352−361.
[27] 鲜双, 姜林君, 李艳兰, 等. 不同方式发酵的哈密瓜幼果泡菜理化特性和氨基酸含量分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(5):224−230. [XIAN S, JIANG L J, LI Y L, et al. Physicochemical properties and amino acid content of Hami melon fruitlet pickles fermented by different processes[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(5):224−230.] XIAN S, JIANG L J, LI Y L, et al. Physicochemical properties and amino acid content of Hami melon fruitlet pickles fermented by different processes[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(5): 224−230.
[28] 云琳, 毛丙永, 崔树茂, 等. 不同发酵方式对萝卜泡菜理化特性和风味的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(13):69−75. [YUN L, MAO B Y, CUI S M, et al. Effects of different fermentation methods on the physicochemical properties and flavor of pickles[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(13):69−75.] YUN L, MAO B Y, CUI S M, et al. Effects of different fermentation methods on the physicochemical properties and flavor of pickles[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(13): 69−75.
[29] 李斌斌, 李宇辉, 刘战霞, 等. 植物乳杆菌与酿酒酵母混合发酵对红枣酒挥发性风味物质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(8):170−179. [LI B B, LI Y H, LIU Z X, et al. Effects of mixed fermentation of Lactobacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on volatile flavor compounds of jujube wine[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(8):170−179.] LI B B, LI Y H, LIU Z X, et al. Effects of mixed fermentation of Lactobacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on volatile flavor compounds of jujube wine[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(8): 170−179.
[30] 周艳. 生物法制备稀奶油-乳清复合风味乳基的研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2018. [ZHOU Y. Study on the mixed milk base flavor of cream and whey prepared by biochemical methods[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018.] ZHOU Y. Study on the mixed milk base flavor of cream and whey prepared by biochemical methods[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



