Effects and Mechanisms of Low-temperature Plasma Pretreatment on the Ultrasound-assisted Extraction Process of Total Flavonoids from Ginger Powder
-
摘要: 目的:探究低温等离子体预处理对超声辅助提取姜粉总黄酮的提取效果,并对其可能机制进行初步探讨,为姜粉总黄酮的提取提供一种新方法。方法:以姜粉中总黄酮得率为考察指标,以低温等离子体放电电源功率、处理时间、进气量为考察因素,进行单因素实验和三因素三水平响应面优化试验。并应用高效液相色谱法测定低温等离子体处理前后姜粉中21种多酚类化合物的含量,通过扫描电镜(scan electronic microscope,SEM)和傅里叶变换红外光谱(Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy,FTIR)对低温等离子体处理前后姜粉的结构进行分析。结果:姜粉中总黄酮的最佳提取条件为:真空度小于100 Pa,放电电源功率295 W、处理时间60 s,进气量150 cm3/min,总黄酮得率为26.9 mg/g。色谱结果表明21种多酚类化合物得到较好的分离,且精密度高(relative standard deviation,RSD≤3.75%)、稳定性好(RSD≤4.25%)、重复性好(RSD≤4.75%)、加标回收结果准确可靠(平均回收率84.11%~100.86%)。低温等离子体处理后姜粉总黄酮的含量增加,酚酸的含量下降;低温等离子体处理增加了姜粉中淀粉颗粒以及细胞壁碎片的表面粗糙度,并且导致木质素的分解,加大了提取溶剂与姜粉的接触面积,因此有利于溶剂的渗透。结论:超声法辅助低温等离子体处理是提取姜粉总黄酮的一种有效方法。Abstract: Objective: Effects of low-temperature plasma pretreatment assisted by ultrasound on the extraction of total flavonoids from ginger powder were studied, and its mechanism was preliminary discussed, and provided a new method for the extraction of total flavonoids from ginger powder. Methods: The single-factor tests and three-factor three-level response surface optimization tests were carried out with the yield of total flavonoids in ginger powder as the index and discharge power, treatment time and air intake volume of low-temperature plasma as factors. Meanwhile, the contents of 21 kinds of polyphenols in ginger powder were determined by HPLC before and after low-temperature plasma treatment, and the structure of ginger powder were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Results: The optimum extraction conditions for total flavonoids from ginger powder were as follows: Vacuum degree less than 100 Pa, discharge power of 295 W, treatment time of 60 s, air intake volume of 150 cm3/min, and the yield of total flavonoids was 26.9 mg/g. Chromatographic results showed that 21 kinds of polyphenols were separated with high precision (relative standard deviation, RSD≤3.75%), good stability (RSD≤4.25%), good repeatability (RSD≤4.75%) and accurate and reliable recovery rate (average recovery rate of 84.11%~100.86%). After low-temperature plasma treatment, total flavonoids content in ginger was increased, and phenolic acids content was decreased. Etching effect of low-temperature plasma increased the surface roughness of starch particles and cell wall fragments in ginger powder and led to the decomposition of lignin, which increased the contact area between solvent and ginger powder, and it was conducive to solvent penetration. Conclusion: Ultrasound-assisted low-temperature plasma treatment is an effective method to extract total flavonoids from ginger powder.
-
Keywords:
- low-temperature plasma /
- ginger powder /
- total flavonoids content /
- polyphenol compounds /
- HPLC
-
生姜(Zingiber officinale Rosc.)是姜科姜属多年生草本植物,主要分布于中国、印度、尼日利亚等一些热带、亚热带地区和国家[1−2],而我国是世界上生姜种植面积最大、产量最多的国家[3]。生姜也是我国最常用的药食同源食材,生姜与干姜的功效不同;生姜具有止呕驱寒、止咳化痰、解鱼蟹毒的功效,干姜有治疗脾胃虚寒、回阳通脉、温肺化饮的功效[4−5]。目前已发现的生姜化学成分有一百多种,主要包括多酚类化合物、萜类、多糖、脂质、有机酸和粗纤维等,其中多酚和黄酮类化合物对改善健康状况、降低患某些疾病如心血管疾病和神经退行性疾病等的风险有一定的作用[6−7]。因此,近年来对姜中黄酮类化合物的提取和研究较多,传统的提取方法如浸渍、索氏提取等,存在提取时间长,提取率低的问题。现代提取方法有了较大进展,如超声波辅助提取、微波辅助提取、高压提取和超临界流体萃取等技术,使功能成分的提取率和纯度得到有效提高,并对缩短提取时间、减少溶剂消耗等问题有一定的改进[8]。
“等离子体”是1928年美国化学家、物理学家欧文·朗缪尔提出,定义物质的第四种状态,即部分或全部电离的气体状态[9],包括自由基、紫外线、光子和辐射热,以及不同组分如带电粒子(电子和离子)和中性物质(原子和分子)的复杂混合物[10]。根据带电粒子温度的高低,等离子体分为高温和低温等离子体[11]。电子温度(T电子)和离子温度(T离子)的关系跟等离子体电离程度有关,当T离子<T电子时,等离子体为轻度电离,总体温度无明显变化,称为“低温等离子体”[12]。近年来,低温等离子体作为一种新型的非热加工技术[13−15],因具有处理温度低、安全无害等优点,在食品加工领域成为研究热点。
近年来,一些学者应用等离子体处理果蔬,并探讨了等离子体处理对果蔬多酚和黄酮类化合物的影响。如Matan等[16]和Charoux等[17]用介质阻挡放电(dielectric barrier discharge system,DBD)等离子体处理果蔬,发现多酚含量增加;Lacombe等[18]用大气冷等离子体处理蓝莓,发现其多酚含量随着处理时间的延长而降低,认为长期暴露于自由基会导致酚类化合物的降解,而Bao等[19]发现使用高压等离子体处理葡萄渣5 min和15 min时,多酚的含量比对照组显著增加,而10 min时无显著性差异,可能与酚类化合物的存在形式有关。Kashfi等[20]应用不同功率等离子体处理干薄荷时,发现在20、50 W时总酚的含量显著增加,60 W时与对照组无显著性差异。Li等[14]、Keshavarzi等[15]研究表明使用低温等离子体处理鲜切草莓、绿茶叶,分别可以促进草莓中总酚类和总黄酮的积累,显著提高绿茶叶中多酚类化合物的提取率。所以,不同类型和参数的等离子体设备在不同果蔬中的应用效果不同。目前低温等离子体在姜粉总黄酮提取方面的应用研究未见报道。
超声波是一种机械波,频率超过人类听觉的极限,即频率在20 kHz及以上的声波。其主要作用原理是通过机械效应、剪切效应和空化效应使细胞破裂,孔隙率增加,细胞内容物溶出,易与溶剂发生相互作用,增加提取得率。而且超声辅助提取法所需仪器设备简单易得、试验过程易操作、用时较短,提取效率较高。因此,本文应用低温等离子体预处理,然后应用超声辅助溶剂处理姜粉,研究对姜粉总黄酮得率的影响,并初步探讨其机制,为姜多酚和总黄酮类化合物的深加工提供指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
生姜 山东潍坊昌邑,真空冷冻干燥制姜粉,过80目筛备用;溴化钾 光谱纯,上海市试剂一厂;芦丁标准品、没食子酸、焦性没食子酸、绿原酸、(+)-儿茶素、对羟基苯甲酸、香草酸、咖啡酸、丁香酸、表儿茶素、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯、香兰素、阿魏酸、对香豆酸、表儿茶素没食子酸酯、漆黄素、桑色素、木犀草素、槲皮素、芹菜素、山奈酚 HPLC≥98%,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;甲醇、乙腈 HPLC≥98%,美国Fisher公司。
SJIA-10N-50A冷冻干燥机 宁波双嘉仪器有限公司;1260 Infinity II 液相色谱 美国安捷伦科技公司;Synergy HT多功能微孔板检测仪 美国BioTek公司;KQ-400KDE型超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;XL 30 ESEM FEG型扫描电子显微镜 荷兰FEI公司;IRPRESTIGE-21 傅里叶红外光谱仪 日本岛津公司;SY-DT02S低温等离子体处理仪 苏州市奥普斯等离子体科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 姜粉总黄酮提取液的制备工艺流程
称取一定量的姜粉,放入称量皿中平铺,然后置于低温等离子体处理腔,设置等离子体放电功率和时间。取出后加入一定量75%乙醇混合,料液比为1:2(mg/mL),再进行超声处理,设置超声功率400 W和超声时间40 min。取出在4000 r/min下离心10 min,制备得到姜粉总黄酮的提取液。
1.2.2 单因素实验设计
准确称取姜粉0.2500 g,平铺在称量皿(规格50 mm×30 mm)的底部,如图1所示。置于真空室处理腔内,腔体规格为260 mm(W)×260 mm(D)×260 mm(H),然后打开真空泵,当真空度降至100 Pa以下时,开启放电电源和设置程序,进行低温等离子体处理。根据预实验,探究低温等离子体的放电电源功率、处理时间以及进气量对姜粉总黄酮得率的影响。固定放电电源功率为350 W、处理时间为40 s、空气进气量为100 cm3/min,分别设置放电电源功率为:50、200、350、500、650 W,处理时间为10、40、70、100、130 s,空气进气量为10、50、100、150、200 cm3/min进行单因素实验。
1.2.3 响应面优化试验设计
根据单因素实验结果,应用Box-Benhnken设计,以放电电源功率(A)、处理时间(B)、进气量(C)三个因素为自变量,姜粉中总黄酮得率(Y)为响应值,优化试验的因素水平及编码见表1。
表 1 响应面试验因素水平及编码Table 1. Response surface test factor level and coding因素 水平 −1 0 1 A(W) 200 350 500 B(s) 10 40 70 C(cm3/min) 50 100 150 1.2.4 总黄酮含量的测定
1.2.4.1 芦丁标准曲线的制备
参考文献[21]报道方法,进行适当修改。准确称取芦丁标准品5 mg,无水乙醇溶解、于10 mL容量瓶定容,即0.5 mg/mL芦丁标准液。准确移取芦丁标准溶液0.2、0.36、0.52、0.68、0.84、1 mL,分别置于2 mL离心管中,各加5% NaNO2溶液60 μL,摇匀,静置7 min,加10% Al(NO)3溶液60 μL,摇匀,静置6 min,最后加0.8 mL 4% NaOH溶液,用蒸馏水定容,静置15 min后,于510 nm处用酶标仪测其吸光度。以芦丁的质量浓度为横坐标,吸光值为纵坐标,绘制芦丁标准曲线。其回归方程为:y=0.0034x+0.0371(R2=0.9929)。芦丁标准溶液在50~250 μg/mL 范围内呈线性关系。
1.2.4.2 样品总黄酮含量的测定
取0.8 mL 1.2.1制备的样品溶液置于2 mL离心管中,按照1.2.4.1方法进行测定,同时用75%乙醇作空白。由标准曲线查出相应的质量浓度,再按照公式(1)计算样品中总黄酮得率,单位为mg/g。
Y=C×V×NM (1) 式中:Y为样品中总黄酮的得率,mg/g;C为样液中总黄酮的浓度,mg/mL;V为样液体积,mL;N为稀释倍数;M为样品的质量,g。
1.2.5 高效液相色谱法分析姜粉中多酚类化合物的含量
1.2.5.1 标准品及样品溶液的制备
准确称取21种多酚类单体标准品5.000 mg,用甲醇溶解后定容于10 mL棕色容量瓶中,作为标准品母液。用甲醇将各标准品母液稀释成系列梯度浓度的标准品溶液,备用。
将1.2.1得到的样品提取液,在50 ℃下旋转蒸发,去除乙醇,然后冻干。准确称取冻干样粉末0.1000 g,用甲醇定容至10 mL棕色容量瓶中。经0.22 µm微孔滤膜过滤,作为HPLC待测液。
1.2.5.2 色谱条件
色谱柱Poroshell120 EC-C18柱(4.6 mm×150 mm,4 µm),流动相0.1%磷酸(A)和乙腈(B),检测波长230 nm,柱温30℃,进样量10 μL,流速0.8 mL/min,梯度洗脱程序见表2。
表 2 梯度洗脱程序Table 2. Gradient elution procedure时间(min) 流动相A(%) 流动相B(%) 0 93 7 7 93 7 14 83 17 20 75 25 30 50 50 1.2.5.3 方法学考察
标准曲线的绘制:将多酚标准品母液分别稀释至5、10、15、20、25、30 µg/mL,在1.2.5.2色谱条件下进样测定,计算峰面积。横坐标为标准品的质量浓度(X,µg/mL),纵坐标为峰面积(Y)绘制标准曲线。参考徐艳阳等[22]的方法进行精密度试验、稳定性试验、重复性试验、回收率试验。
1.2.6 姜粉的扫描电镜(SEM)观察
应用SEM观察等离子处理前后姜粉表面形貌的变化,用导电胶将姜粉固定于载物片上,喷金后在扫描电镜下观察,加速电压为10 kV。
1.2.7 姜粉的傅里叶变换红外光谱扫描(FTIR)
准确称取2 mg经等离子体处理后的姜粉和200 mg溴化钾,混合研磨后压片,在红外灯下干燥30 min,以不含姜粉的色谱纯溴化钾为空白,然后进行红外光谱扫描,扫描40次,扫描范围为4000~500 cm−1,并与未处理的姜粉对比。
1.3 数据处理
每组实验重复三次,实验结果用平均值±标准差的形式表示,应用SPSS 21进行单因素方差分析;应用Design-Expert 10进行响应面优化试验设计及分析;应用Origin 2021软件作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
2.1.1 放电电源功率对姜粉总黄酮得率的影响
由图2可知,总黄酮得率随着放电电源功率的增大而逐渐提高,这可能是由于一些结合型黄酮类物质以共价键形式连接到细胞壁多糖上,在施加更高的能量时被释放出来。低温等离子体产生的反应性气体携带了足够的能量,可以引发化学反应来破坏共价键,从而释放出结合的黄酮类物质[23]。当放电电源功率超过350 W后,总黄酮得率趋于稳定,无显著性差异(P>0.05)。因此,放电电源功率选取350 W作为进一步优化试验的零水平。
2.1.2 低温等离子体处理时间对姜粉总黄酮得率的影响
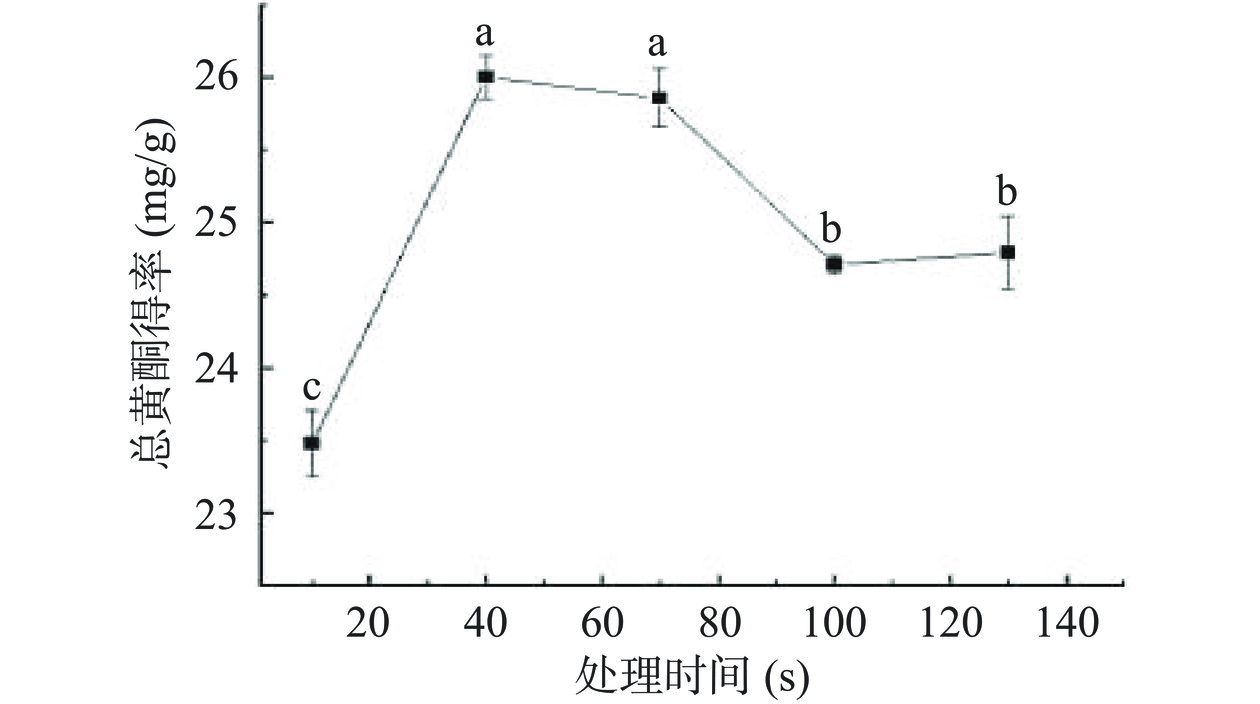
如图3所示,在10~40 s范围,随着低温等离子体处理时间的增加,总黄酮得率逐渐提高,这与赵玉娟[24]使用低温等离子体提取人参叶总黄酮的研究结果一致。当处理时间为40 s时,总黄酮得率达到最大值26 mg/g。当处理时间超过70 s时,总黄酮得率逐渐降低,这可能是由于被等离子体活性物质如羟自由基、原子氧或单线态氧氧化[25]。因此,低温等离子体处理时间选取40 s作为进一步优化试验的零水平。
2.1.3 低温等离子体进气量对姜粉总黄酮得率的影响
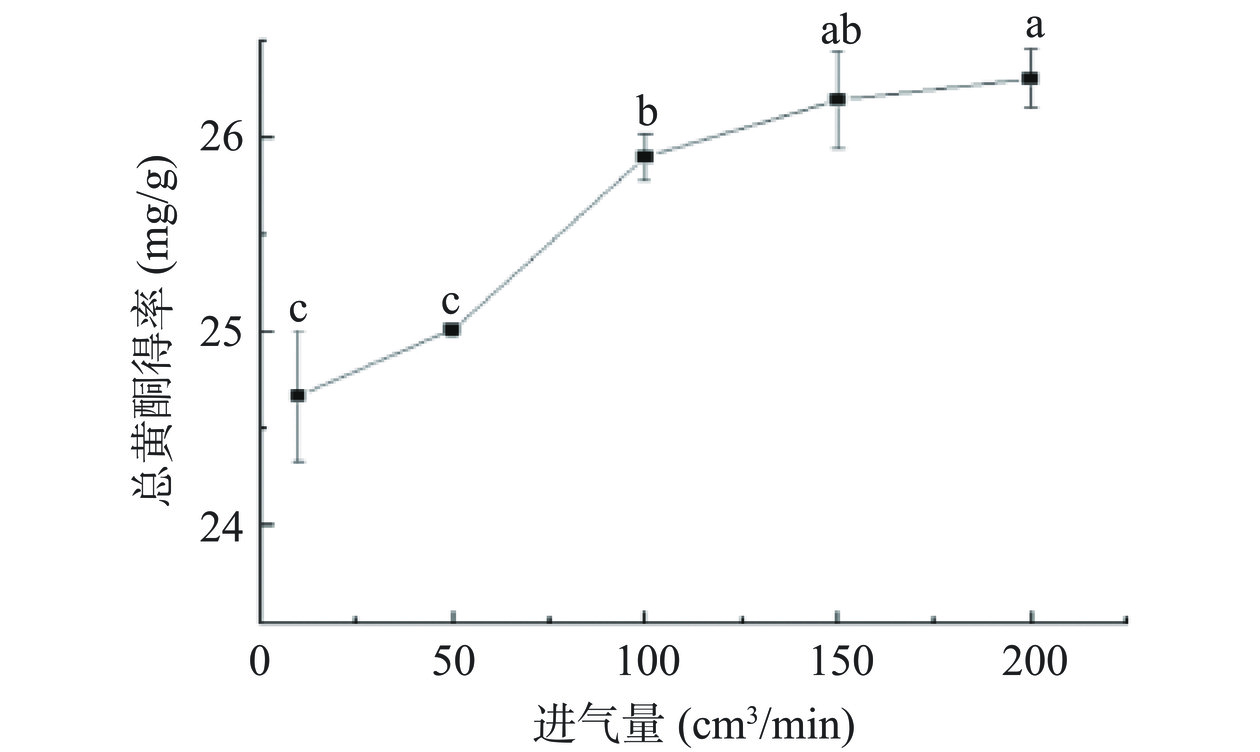
由图4可知,气体流速在10~200 cm3/min范围,前期总黄酮得率增加较大,后期较小。气体流速从10到100 cm3/min时,总黄酮得率由24.66 mg/g提高到25.89 mg/g(P<0.05);气体流速在100~200 cm3/min,总黄酮得率的变化不显著(P>0.05)。气体流速为10时,真空度过高,处理腔内气体少,产生的等离子体含量少,导致等离子处理不充分;气体流速在100~200 cm3/min,产生的等离子体含量充足,姜粉与等离子体接触充分,总黄酮得率高,由此选用100 cm3/min为进一步响应面优化试验的零水平。
2.2 响应面法优化试验结果与分析
2.2.1 响应面法优化试验结果
根据单因素实验结果,以放电电源功率(A)、处理时间(B)、进气量(C)为自变量,总黄酮得率(Y)为响应值进行提取条件的优化设计,试验结果见表3。
表 3 响应面试验设计及结果Table 3. Response surface test design and results试验号 A(W) B(s) C(cm3/min) Y(mg/g) 1 200 10 100 25.16 2 350 10 150 25.27 3 350 40 100 26.44 4 200 40 50 25.00 5 500 40 150 25.98 6 350 70 150 26.30 7 350 40 100 26.31 8 350 40 100 26.00 9 500 10 100 25.96 10 500 40 50 25.12 11 350 70 50 24.81 12 350 40 100 26.30 13 200 40 150 25.8 14 350 10 50 25.93 15 350 40 100 26.35 16 200 70 100 25.77 17 500 70 100 24.40 利用Design-Expert 10软件对表3数据进行分析,总黄酮得率(Y)与低温等离子体处理功率(A)、处理时间(B)、进气量(C)之间的二次多项回归方程为:
Y=26.28−0.033A−0.13B+0.31C−0.54AB+0.016AC+0.54BC−0.53A2−0.43B2−0.27C2
方程的决定系数R2为0.9374,说明此方程拟合性较好。模型的校正系数RAdj2为0.8570,表明85.70%以上的试验数据可用该模型解释。由表4可知,该模型极显著(P<0.01),失拟项(P=0.1336>0.05)不显著,说明在整个回归区域的拟合情况良好,可用该模型对试验结果进行分析。一次项进气量(C)对总黄酮得率(Y)的影响极显著(P<0.01)。平方项放电电源功率和处理时间(A2、B2)的影响极显著(P<0.01),进气量(C)的平方项对总黄酮得率(Y)的影响显著(P<0.05);交互项放电电源功率和处理时间(AB)、交互项处理时间和进气量(BC)对总黄酮得率(Y)的影响极显著(P<0.01),表明各因素对姜粉总黄酮得率的影响不是简单的线性关系。
表 4 回归模型的方差分析Table 4. Analysis of variance of regression model方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F 值 P 值 模型 5.77 9 0.64 11.65 0.0019** A放电电源功率 8.63 1 8.63 0.16 0.7038 B处理时间 0.14 1 0.14 2.50 0.1578 C进气量 0.78 1 0.78 14.16 0.0070** AB 1.18 1 1.18 21.53 0.0024** AC 9.84 1 9.84 0.018 0.8974 BC 1.15 1 1.15 20.95 0.0026** A2 1.17 1 1.17 21.28 0.0024** B2 0.77 1 0.77 14.07 0.0072** C2 0.32 1 0.32 5.78 0.0472* 残差 0.39 7 0.055 失拟项 0.28 3 0.092 3.41 0.1336 净误差 0.11 4 0.027 总和 6.15 16 R2=0.9374;RAdj2=0.8570;CV=0.91% 注:*表示影响显著(P<0.05),**表示影响极显著(P<0.01)。 2.2.2 响应面交互作用分析
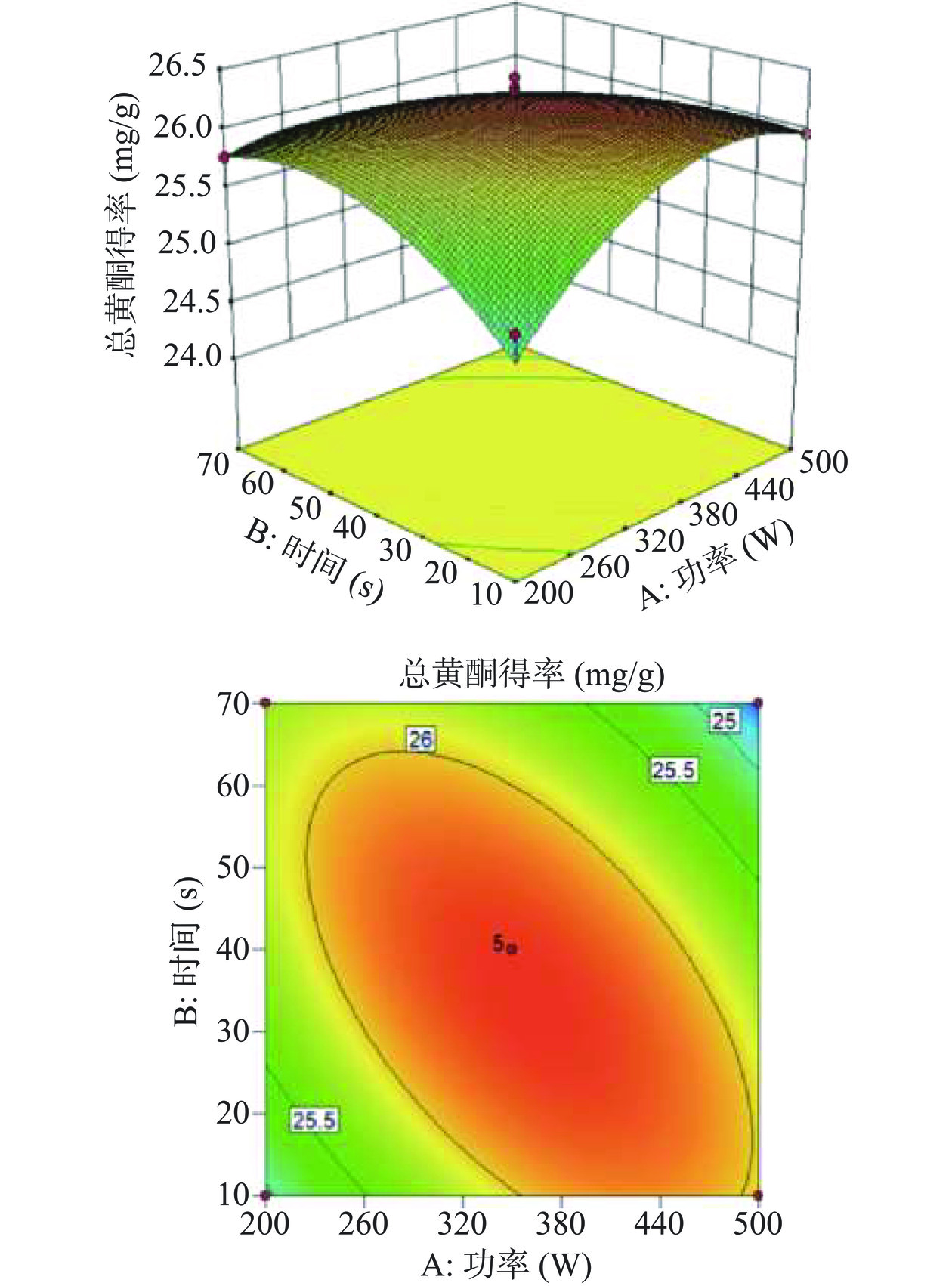
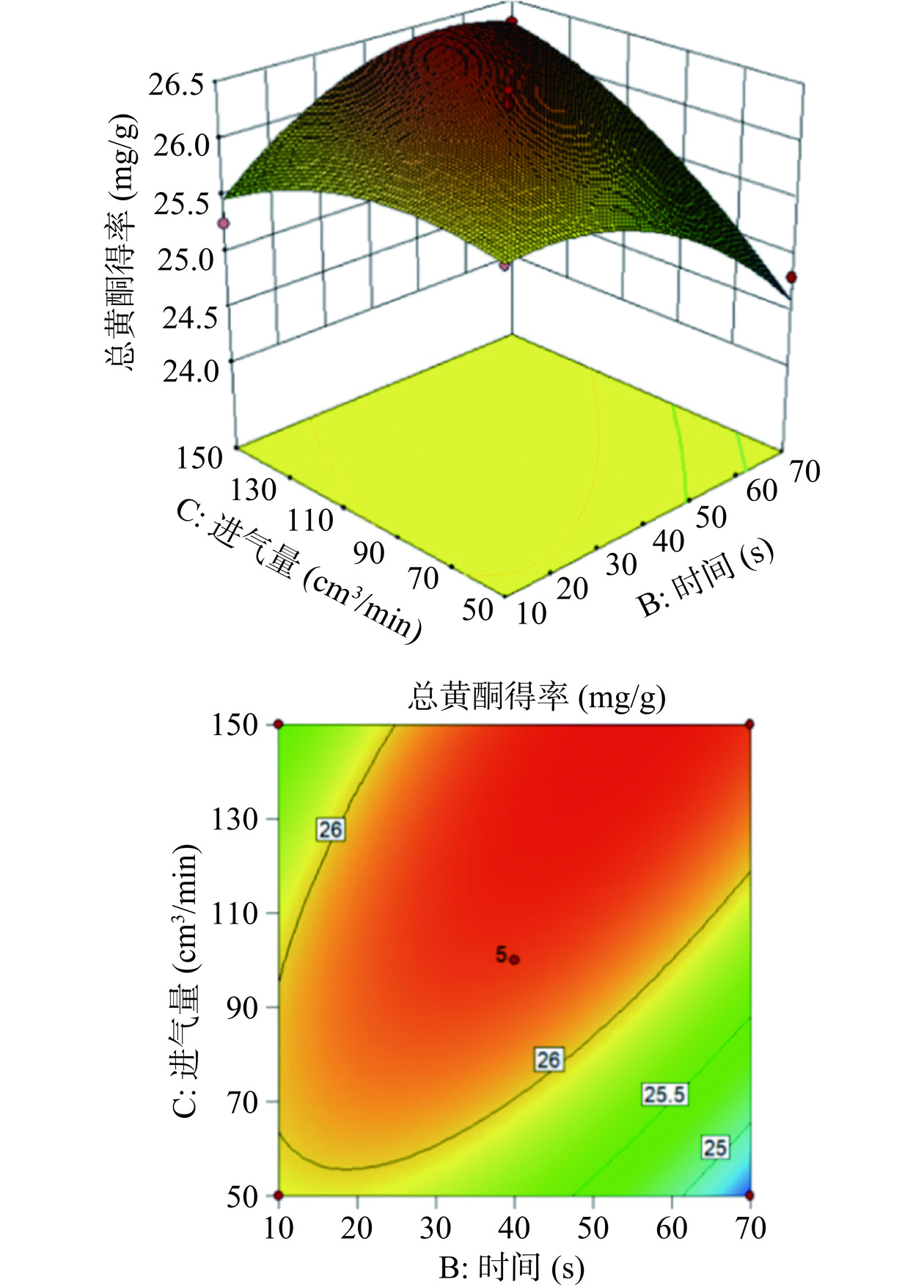
图5表明进气量为100 cm3/min时,放电电源功率和处理时间两个因素的协同作用明显。图6表明放电电源功率为350 W时,处理时间和进气量两个因素的协同作用明显。
2.2.3 验证实验
响应面预测条件为:放电电源功率294.6 W、处理时间60.1 s,进气量149.7 cm3/min。预测值为24.2 mg/g。根据实际条件分析得到最佳提取条件为:放电电源功率295 W、处理时间60 s,进气量150 cm3/min。响应面法得到的最佳等离子体处理条件下,提取总黄酮的得率为26.9 mg/g,理论预测值与实际测定值之间的相对误差为0.11%,表明利用响应面法优化得到的低温等离子体辅助超声法提取姜粉总黄酮的工艺具有可行性。与单纯超声提取姜粉总黄酮得率(16.5 mg/g)相比,经过低温等离子体预处理后姜粉总黄酮的得率提高了63%。因此,低温等离子体预处理显著提高了姜粉总黄酮的提取效率。
2.3 姜粉中多酚类化合物的HPLC分析
2.3.1 方法学验证
2.3.1.1 多酚类化合物标准品的液相色谱图和标准曲线
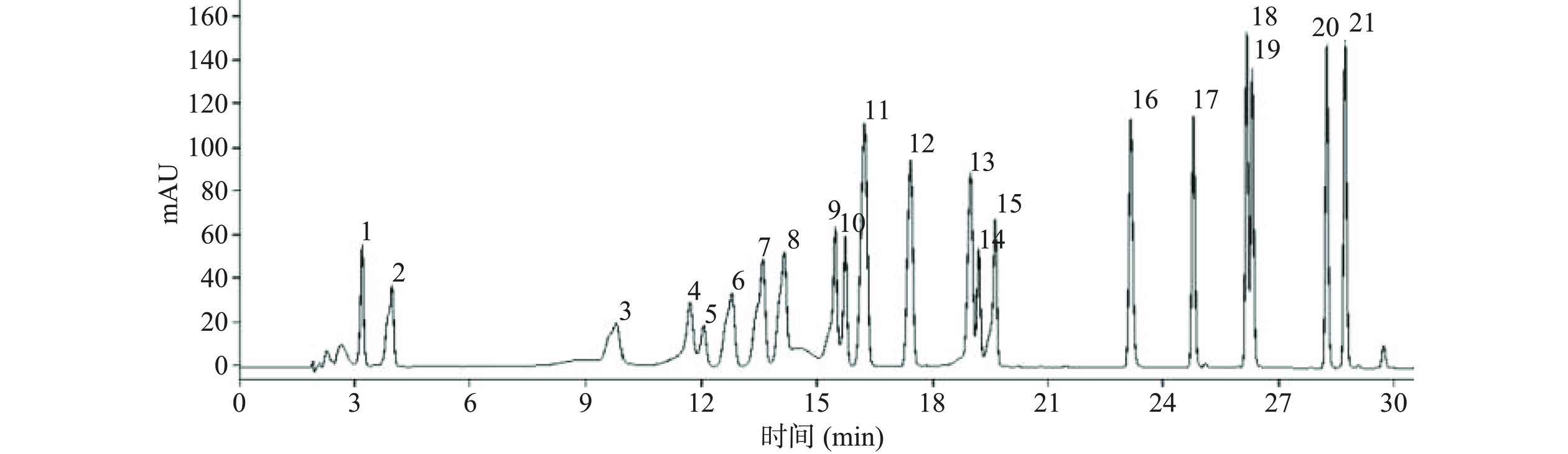
21种多酚类化合物标准品的液相色谱如图7所示。
21种多酚标准品的回归方程如表5所示。由回归系数(R2>0.9909)可知,21种多酚的质量浓度在5.0~30.0 μg/mL范围内线性关系良好。
表 5 21种多酚标准品的回归方程、回归系数、检测范围Table 5. Regression equation, regression coefficient and detection range of 21 polyphenol standards标品名称 回归方程 R2 线性范围(µg/mL) 检出限(µg/mL) 定量限(µg/mL) 没食子酸 Y=34.60X+20.80 0.9926 5.0~30.0 0.215 0.716 焦性没食子酸 Y=17.18X+73.57 0.9992 5.0~30.0 0.318 1.059 绿原酸 Y=18.06X+29.44 0.9999 5.0~30.0 0.587 1.958 儿茶素 Y=37.63X+14.30 0.9999 5.0~30.0 0.394 1.313 对羟基苯甲酸 Y=13.88X+74.24 0.9912 5.0~30.0 0.573 1.908 香草酸 Y=35.86X+133.02 0.9959 5.0~30.0 0.372 1.241 咖啡酸 Y=75.46X−75.64 0.9985 5.0~30.0 0.262 0.874 丁香酸 Y=42.45X+61.24 0.9950 5.0~30.0 0.280 0.933 表儿茶素 Y=45.53X−14.60 0.9960 5.0~30.0 0.206 0.687 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 Y=39.66X−62.76 0.9956 5.0~30.0 0.220 0.732 香兰素 Y=146.90X−190.41 0.9990 5.0~30.0 0.117 0.388 阿魏酸 Y=30.55X+201.08 0.9998 5.0~30.0 0.138 0.460 对香豆酸 Y=66.73X+194.38 0.9990 5.0~30.0 0.140 0.468 芦丁 Y=25.56X+17.32 0.9992 5.0~30.0 0.207 0.688 表儿茶素没食子酸酯 Y=47.62X−78.75 0.9946 5.0~30.0 0.190 0.635 漆黄素 Y=68.53X−11.77 0.9923 5.0~30.0 0.087 0.291 桑色素 Y=83.59X−296.10 0.9909 5.0~30.0 0.097 0.325 木犀草素 Y=70.01X−142.30 0.9909 5.0~30.0 0.074 0.248 槲皮素 Y=44.64X+39.58 0.9969 5.0~30.0 0.085 0.283 芹菜素 Y=56.08X−74.28 0.9979 5.0~30.0 0.080 0.267 山奈酚 Y=52.21X+3.60 0.9980 5.0~30.0 0.078 0.261 2.3.1.2 精密度、稳定性、重复性、回收率试验结果
如表6所示,对21种多酚类化合物进行精密度试验,RSD均小于3.75%,表明本方法的精密度良好。稳定性试验的RSD均小于4.25%,本方法在测定时间内稳定性良好。重复性试验结果的RSD均小于4.75%,说明本方法的重复性良好。21种多酚类化合物的加标回收率在84.11%~100.86%之间,证明本方法对目标物的损失和污染较小,回收率良好,与李玄[26]利用高效液相色谱检测黄酮多酚化合物的结果一致。
表 6 21种多酚类化合物的精密度、稳定性、重复性及加标回收率试验结果Table 6. Results of precision, stability, repeatability and spiked recovery rate of 21 polyphenols名称 精密度RSD(%) 稳定性RSD(%) 重复性RSD(%) 加标回收率(%) 没食子酸 1.77 2.52 4.49 89.47 焦性没食子酸 0.46 1.24 2.12 100.64 绿原酸 1.77 2.96 4.01 95.21 儿茶素 2.27 0.90 3.9 86.94 对羟基苯甲酸 1.74 0.87 3.13 99.15 香草酸 0.27 1.67 4.75 93.54 咖啡酸 1.04 1.17 3.67 96.28 丁香酸 2.06 3.44 3.51 97.09 表儿茶素 1.06 1.71 4.31 89.54 表没食子儿茶素没
食子酸酯3.75 4.25 1.00 100.29 香兰素 2.66 0.91 2.32 94.86 阿魏酸 0.22 0.27 4.02 95.61 对香豆酸 1.26 1.50 1.16 100.41 芦丁 2.15 1.67 2.77 89.94 表儿茶素没食子酸酯 3.49 2.24 3.86 100.86 漆黄素 0.25 0.19 1.60 95.33 桑色素 0.25 1.51 1.96 84.11 木犀草素 0.26 0.66 3.13 87.19 槲皮素 0.28 0.42 3.25 100.74 芹菜素 0.20 0.49 3.74 98.69 山奈酚 0.40 0.63 3.22 98.14 2.3.2 低温等离子体处理前后姜粉中21种多酚类化合物含量的测定
等离子体处理前后姜粉中21种多酚类化合物的含量见表7。等离子体处理后姜粉中黄酮类化合物总体呈现增加的趋势,酚酸类化合物总体呈现下降的趋势,原因可能是等离子体处理破坏细胞壁结构和通过刻蚀作用增加了细胞壁表面粗糙度,从而使黄酮类化合物溶出增加;酚酸类化合物与等离子体中活性氧物质(ROS如羟基自由基、原子氧和单线态氧氧化)发生反应导致酚酸类化合物的降解。
表 7 低温等离子体处理前后姜粉中21种多酚类化合物含量(n=5)Table 7. Contents of 21 polyphenols in ginger powder before and after low-temperature plasma treatment (n=5)分类 名称 等离子体处理前(μg/g) 等离子体处理后(μg/g) 酚酸 没食子酸 166.44±3.23a 145.22±2.99b 焦性没食子酸 / / 绿原酸 112.39±3.12a 112.22±3.06a 对羟基苯甲酸 110.27±2.86a 99.27±2.74b 香草酸 60.70±2.88a 56.10±2.83a 咖啡酸 146.96±3.24a 152.84±3.17a 丁香酸 49.61±2.68 / 香兰素 / / 阿魏酸 / / 对香豆酸 / / 儿茶素 / / 表儿茶素 / / 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 / / 黄酮 表儿茶素没食子酸酯 214.72±3.31b 248.32±3.05a 芦丁 / / 漆黄素 56.57±2.98b 106.92±2.87a 桑色素 158.40±3.24b 203.79±3.29a 木犀草素 / 30.10±3.22 槲皮素 / / 芹菜素 / / 山奈酚 / / 注:同一行不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);/表示未检出。 2.4 姜粉的SEM分析
应用低温等离子体处理,使植物组织中黄酮类化合物含量变化的原因,多数学者认为其作用机制主要有四个方面[19,27−28]:首先,等离子体处理破坏了植物细胞壁的结构,使内容物流出,从而促进黄酮类化合物的释放。其次,等离子体中活性氧和氮,可以增加材料表面的氧/碳和氮/碳比,从而导致亲水性的增加。再次,等离子体处理通过刻蚀作用增加材料的表面能和粗糙度,从而降低其疏水性。最后,等离子体产生的反应性气体携带了足够的能量,可以引发化学反应,破坏共价键,从而释放出结合型黄酮类物质。
贾茹羽[29]、An等[30]发现鲜切姜经冷冻干燥,由于脱水作用导致薄壁组织的细胞壁破裂,表面油细胞消失,干燥后的淀粉颗粒分散在整个组织上,鲜切姜片经冷冻干燥后,又经过粉碎,进一步导致细胞壁的破碎,细胞的内容物泄出。由于本文姜粉经冷冻干燥、粉碎过80目筛后,其细胞壁结构已经完全破裂,由此认为姜粉中总黄酮含量增加的原因不是等离子体对其细胞壁结构的破坏。由本文图8A、B比较可知,等离子体的刻蚀作用增加了姜粉中淀粉颗粒及破碎的细胞壁表面粗糙度,因此与溶剂的接触面积增大,从而增加了总黄酮的提取得率。
2.5 姜粉的FTIR分析
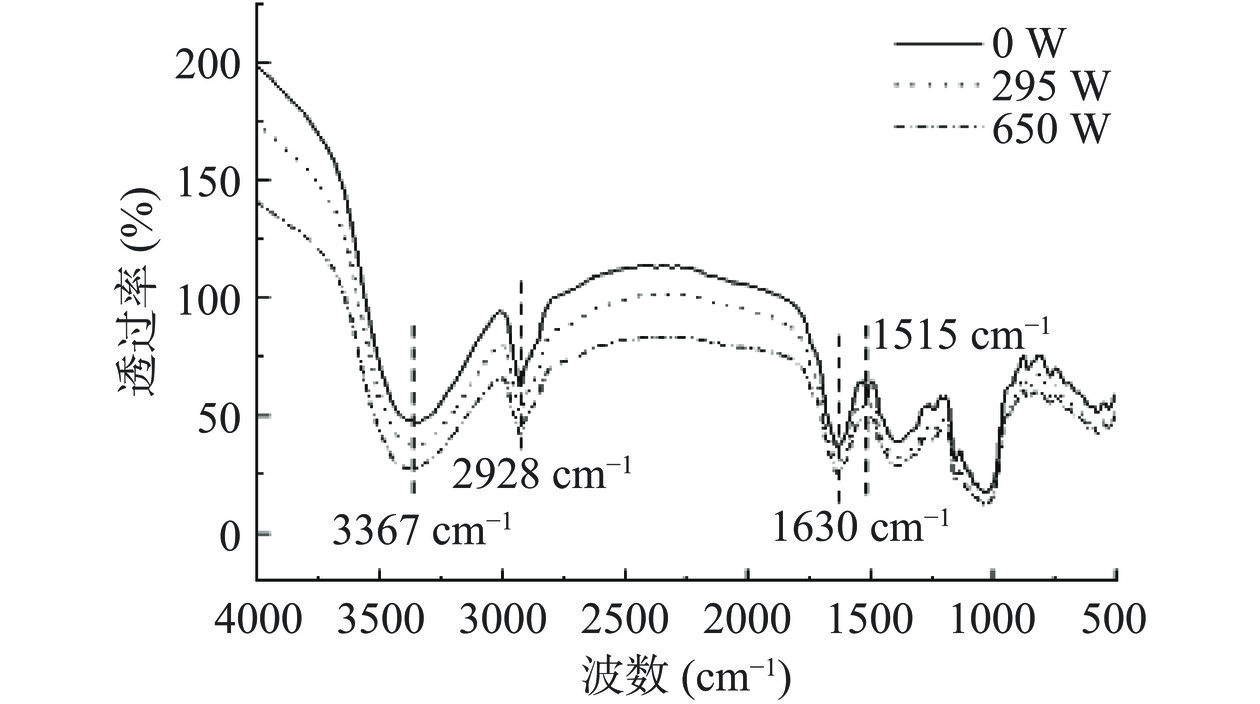
为了研究等离子体处理对姜粉化学成分的影响,比较了低温等离子体处理前后姜粉的FTIR光谱。结果表明:低温等离子体处理后姜粉中未产生新的化学基团带。然而,随着低温等离子体功率的增大,一些特征谱带的吸光度发生了变化,吸收峰强度发生变化,说明分子结构遭到了一定程度的破坏[31]。姜粉在3367 cm−1处有一条宽带,这是由于姜粉纤维结构中的O-H羟基伸缩振动所致,说明姜粉中可能含有较多的羟基以及结合水[32]。在2928 cm−1处出现一个吸收峰,此为C-H的伸缩振动。其中在1630 cm−1处是蛋白质的酰胺Ⅰ带吸收峰,主要是C=O的伸缩振动[33]。由图9可知,低温等离子体处理后姜粉的FTIR谱带峰值强度下降,表明等离子体是有效的[34]。未经低温等离子体处理的姜粉在1515 cm−1处的条带峰值强度小于处理的,该处为木质素中芳香环上C=C键的伸缩振动,说明低温等离子体处理过程中木质素的分解明显[35],这种部分降解有利于溶剂的渗透。
3. 结论
本文采用低温等离子体辅助超声法提取姜粉总黄酮,并通过单因素实验和响应面试验进行优化,对低温等离子体处理后姜粉的21种多酚类化合物含量、微观结构和FTIR光谱分析,初步探讨了低温等离子体处理对提取姜粉总黄酮的机理。结果表明:低温等离子体辅助超声法提取姜粉中总黄酮的最佳提取条件为:放电电源功率295 W、处理时间60 s、进气量150 cm³/min。在此条件下总黄酮得率为26.9 mg/g,理论值与实际值的相对误差为0.11%,验证实验与模型拟合良好,利用响应面法优化得到的低温等离子体辅助超声法提取姜粉中总黄酮的工艺具有可行性。
本文建立了姜粉中多酚类化合物含量测定的液相色谱条件,并对低温等离子体处理前后姜粉中21种多酚类化合物进行了定量检测。低温等离子体处理后,姜粉总黄酮含量总体上呈现增加的趋势,酚酸类化合物的含量总体上呈现下降的趋势。通过扫描电镜观察结果表明:低温等离子体的刻蚀作用增加了姜粉中淀粉颗粒以及细胞壁碎片的表面粗糙度,进一步增大了溶剂与其接触的面积,因此,经低温等离子体处理后姜粉中总黄酮的得率提高。通过红外FTIR光谱分析表明低温等离子体处理使姜粉中木质素发生部分降解,这有利于溶剂的渗透。
-
表 1 响应面试验因素水平及编码
Table 1 Response surface test factor level and coding
因素 水平 −1 0 1 A(W) 200 350 500 B(s) 10 40 70 C(cm3/min) 50 100 150 表 2 梯度洗脱程序
Table 2 Gradient elution procedure
时间(min) 流动相A(%) 流动相B(%) 0 93 7 7 93 7 14 83 17 20 75 25 30 50 50 表 3 响应面试验设计及结果
Table 3 Response surface test design and results
试验号 A(W) B(s) C(cm3/min) Y(mg/g) 1 200 10 100 25.16 2 350 10 150 25.27 3 350 40 100 26.44 4 200 40 50 25.00 5 500 40 150 25.98 6 350 70 150 26.30 7 350 40 100 26.31 8 350 40 100 26.00 9 500 10 100 25.96 10 500 40 50 25.12 11 350 70 50 24.81 12 350 40 100 26.30 13 200 40 150 25.8 14 350 10 50 25.93 15 350 40 100 26.35 16 200 70 100 25.77 17 500 70 100 24.40 表 4 回归模型的方差分析
Table 4 Analysis of variance of regression model
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F 值 P 值 模型 5.77 9 0.64 11.65 0.0019** A放电电源功率 8.63 1 8.63 0.16 0.7038 B处理时间 0.14 1 0.14 2.50 0.1578 C进气量 0.78 1 0.78 14.16 0.0070** AB 1.18 1 1.18 21.53 0.0024** AC 9.84 1 9.84 0.018 0.8974 BC 1.15 1 1.15 20.95 0.0026** A2 1.17 1 1.17 21.28 0.0024** B2 0.77 1 0.77 14.07 0.0072** C2 0.32 1 0.32 5.78 0.0472* 残差 0.39 7 0.055 失拟项 0.28 3 0.092 3.41 0.1336 净误差 0.11 4 0.027 总和 6.15 16 R2=0.9374;RAdj2=0.8570;CV=0.91% 注:*表示影响显著(P<0.05),**表示影响极显著(P<0.01)。 表 5 21种多酚标准品的回归方程、回归系数、检测范围
Table 5 Regression equation, regression coefficient and detection range of 21 polyphenol standards
标品名称 回归方程 R2 线性范围(µg/mL) 检出限(µg/mL) 定量限(µg/mL) 没食子酸 Y=34.60X+20.80 0.9926 5.0~30.0 0.215 0.716 焦性没食子酸 Y=17.18X+73.57 0.9992 5.0~30.0 0.318 1.059 绿原酸 Y=18.06X+29.44 0.9999 5.0~30.0 0.587 1.958 儿茶素 Y=37.63X+14.30 0.9999 5.0~30.0 0.394 1.313 对羟基苯甲酸 Y=13.88X+74.24 0.9912 5.0~30.0 0.573 1.908 香草酸 Y=35.86X+133.02 0.9959 5.0~30.0 0.372 1.241 咖啡酸 Y=75.46X−75.64 0.9985 5.0~30.0 0.262 0.874 丁香酸 Y=42.45X+61.24 0.9950 5.0~30.0 0.280 0.933 表儿茶素 Y=45.53X−14.60 0.9960 5.0~30.0 0.206 0.687 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 Y=39.66X−62.76 0.9956 5.0~30.0 0.220 0.732 香兰素 Y=146.90X−190.41 0.9990 5.0~30.0 0.117 0.388 阿魏酸 Y=30.55X+201.08 0.9998 5.0~30.0 0.138 0.460 对香豆酸 Y=66.73X+194.38 0.9990 5.0~30.0 0.140 0.468 芦丁 Y=25.56X+17.32 0.9992 5.0~30.0 0.207 0.688 表儿茶素没食子酸酯 Y=47.62X−78.75 0.9946 5.0~30.0 0.190 0.635 漆黄素 Y=68.53X−11.77 0.9923 5.0~30.0 0.087 0.291 桑色素 Y=83.59X−296.10 0.9909 5.0~30.0 0.097 0.325 木犀草素 Y=70.01X−142.30 0.9909 5.0~30.0 0.074 0.248 槲皮素 Y=44.64X+39.58 0.9969 5.0~30.0 0.085 0.283 芹菜素 Y=56.08X−74.28 0.9979 5.0~30.0 0.080 0.267 山奈酚 Y=52.21X+3.60 0.9980 5.0~30.0 0.078 0.261 表 6 21种多酚类化合物的精密度、稳定性、重复性及加标回收率试验结果
Table 6 Results of precision, stability, repeatability and spiked recovery rate of 21 polyphenols
名称 精密度RSD(%) 稳定性RSD(%) 重复性RSD(%) 加标回收率(%) 没食子酸 1.77 2.52 4.49 89.47 焦性没食子酸 0.46 1.24 2.12 100.64 绿原酸 1.77 2.96 4.01 95.21 儿茶素 2.27 0.90 3.9 86.94 对羟基苯甲酸 1.74 0.87 3.13 99.15 香草酸 0.27 1.67 4.75 93.54 咖啡酸 1.04 1.17 3.67 96.28 丁香酸 2.06 3.44 3.51 97.09 表儿茶素 1.06 1.71 4.31 89.54 表没食子儿茶素没
食子酸酯3.75 4.25 1.00 100.29 香兰素 2.66 0.91 2.32 94.86 阿魏酸 0.22 0.27 4.02 95.61 对香豆酸 1.26 1.50 1.16 100.41 芦丁 2.15 1.67 2.77 89.94 表儿茶素没食子酸酯 3.49 2.24 3.86 100.86 漆黄素 0.25 0.19 1.60 95.33 桑色素 0.25 1.51 1.96 84.11 木犀草素 0.26 0.66 3.13 87.19 槲皮素 0.28 0.42 3.25 100.74 芹菜素 0.20 0.49 3.74 98.69 山奈酚 0.40 0.63 3.22 98.14 表 7 低温等离子体处理前后姜粉中21种多酚类化合物含量(n=5)
Table 7 Contents of 21 polyphenols in ginger powder before and after low-temperature plasma treatment (n=5)
分类 名称 等离子体处理前(μg/g) 等离子体处理后(μg/g) 酚酸 没食子酸 166.44±3.23a 145.22±2.99b 焦性没食子酸 / / 绿原酸 112.39±3.12a 112.22±3.06a 对羟基苯甲酸 110.27±2.86a 99.27±2.74b 香草酸 60.70±2.88a 56.10±2.83a 咖啡酸 146.96±3.24a 152.84±3.17a 丁香酸 49.61±2.68 / 香兰素 / / 阿魏酸 / / 对香豆酸 / / 儿茶素 / / 表儿茶素 / / 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 / / 黄酮 表儿茶素没食子酸酯 214.72±3.31b 248.32±3.05a 芦丁 / / 漆黄素 56.57±2.98b 106.92±2.87a 桑色素 158.40±3.24b 203.79±3.29a 木犀草素 / 30.10±3.22 槲皮素 / / 芹菜素 / / 山奈酚 / / 注:同一行不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);/表示未检出。 -
[1] 吴曼, 赵帮宏, 宗义湘. 世界姜粉生产布局与贸易格局分析[J]. 北方园艺,2019,43(10):141−150. [WU M, ZHAO B H, ZONG Y X, et al. Analysis of world ginger powder production layout and trade pattern[J]. North Horticu,2019,43(10):141−150.] WU M, ZHAO B H, ZONG Y X, et al. Analysis of world ginger powder production layout and trade pattern[J]. North Horticu, 2019, 43(10): 141−150.
[2] 张文焕. 姜粉质量安全标准比对分析及特征成分差异研究[D]. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2019. [ZHANG W H. Comparative analysis of quality and safety standard of ginger powder and study on difference of characteristic components[D]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2019.] ZHANG W H. Comparative analysis of quality and safety standard of ginger powder and study on difference of characteristic components[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2019.
[3] 周陆红, 李萌, 韩太利, 等. 姜粉加工产品应用研究现状与前景展望[J]. 蔬菜,2021(1):51−57. [ZHOU L H, LI M, HAN T L, et al. Application research status and prospect of ginger powder processing products[J]. Vegetables,2021(1):51−57.] ZHOU L H, LI M, HAN T L, et al. Application research status and prospect of ginger powder processing products[J]. Vegetables, 2021(1): 51−57.
[4] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典:2020年版一部[M]. 北京:中国医药科技出版社, 2020. [National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia:2020, I[M]. Beijing:China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020.] National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia: 2020, I[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020.
[5] 方文韬, 詹志来, 彭华胜, 等. 干姜、生姜、炮姜分化的历史沿革与变迁[J]. 中国中药杂志,2017,42(9):1641−1645. [FANG W T, ZHAN Z L, PENG H S, et al. Differentiation of ginger, ginger powder and ginger[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2017,42(9):1641−1645.] FANG W T, ZHAN Z L, PENG H S, et al. Differentiation of ginger, ginger powder and ginger[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2017, 42(9): 1641−1645.
[6] DAS A, MILLER R, LEE P, et al. A novel component from citrus, ginger, and mushroom family exhibits antitumor activity on human meningioma cells through suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Tumor Biology,2015,36(9):1−8.
[7] CONCETTA T M, MALFA G A, MARCO B, et al. LC-ESI-QTOF-MS profiling, protective effects on oxidative damage, and inhibitory activity of enzymes linked to type 2 diabetes and nitric oxide production of Vaccinium corymbosum L. (Ericaceae) extracts[J]. Journal of Berry Research,2020,10(4):603−622.
[8] AZMIR J, ZAIDUL I, RAHMAN M, et al. Techniques for extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials:A review[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2013,117(4):426−436. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.01.014
[9] THIRUMDAS R, SARANGAPANI C, ANNAPURE U S, et al. Cold plasma:A novel non-thermal technology for food processing[J]. Food Biophysics,2014,10(1):1−11.
[10] HERTWIG C, MENESES N, MATHYS A, et al. Cold atmospheric pressure plasma and low energy electron beam as alternative nonthermal decontamination technologies for dry food surfaces:A review[J]. Trends Food Science & Technology,2018,77:131−142. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgs.2018.05.011
[11] 张晔, 刘志伟, 谭兴和, 等. 冷等离子体食品杀菌应用研究进展[J]. 中国酿造,2019,38(1):20−24. [ZHANG Y, LIU Z W, TAN X H, et al. Research progress of cold plasma food sterilization application[J]. China Brewing,2019,38(1):20−24.] ZHANG Y, LIU Z W, TAN X H, et al. Research progress of cold plasma food sterilization application[J]. China Brewing, 2019, 38(1): 20−24.
[12] 王佳媚, 黄明明, 乔维维, 等. 冷源等离子体冷杀菌技术及其在食品中的应用研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报,2015,17(5):55−62. [WANG J M, HUANG M M, QIAO W W, et al. Research on cold source plasma cold sterilization technology and its application in food[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology,2015,17(5):55−62.] WANG J M, HUANG M M, QIAO W W, et al. Research on cold source plasma cold sterilization technology and its application in food[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2015, 17(5): 55−62.
[13] MUNEKATA P E S, DOMINGUEZ R, PATEIRO M, et al. Influence of plasma treatment on the polyphenols of food products-A review[J]. Foods,2020,9(7):929. doi: 10.3390/foods9070929
[14] LI M, LI X, HAN C, et al. Physiological and metabolomic analysis of cold plasma treated fresh-cut strawberries[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019,67(14):4043−4053. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00656
[15] KESHAVARZI M, NAJAFI G, GAVLIGHI H A, et al. Enhancement of polyphenolic content extraction rate with maximal antioxidant activity from green tea leaves by cold plasma[J]. Journal of Food Science,2020,85(10):3415−3422. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15448
[16] MATAN N, PUANGJINDA K, PHOTHISUWAN S, et al. Combined antibacterial activity of green tea extract with atmospheric radio-frequency plasma against pathogens on fresh-cut dragon fruit[J]. Food Control,2015,50:291−296. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.09.005
[17] CHAROUX C M G, FREE L, HINDS L M, et al. Effect of non-thermal plasma technology on microbial inactivation and total phenolic content of a model liquid food system and black pepper grains[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,118:108716. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108716
[18] LACOMBE A, NIEMIRA B A, GURTLER J B, et al. Atmospheric cold plasma inactivation of aerobic microorganisms on blueberries and effects on quality attributes[J]. Food Microbiology,2015,46:479−484. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2014.09.010
[19] BAO Y, REDDIVARI L, HUANG J Y, et al. Enhancement of phenolic compounds extraction from grape pomace by high voltage atmospheric cold plasma[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,133:109970. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109970
[20] KASHFI A S, RAMEZAN Y, KHANI M R, et al. Simultaneous study of the antioxidant activity, microbial decontamination and color of dried peppermint (Mentha piperita L.) using low pressure cold plasma[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,123:109121. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109121
[21] 张宁芸, 邓爱华, 王云油, 等. 茶叶黄酮超声辅助提取工艺优化[J]. 农产品加工,2023(16):33−36,40. [ZHANG N Y, DENG A H, WANG Y Y, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of tea flavonoids[J]. Processing of Agricultural Products,2023(16):33−36,40.] ZHANG N Y, DENG A H, WANG Y Y, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of tea flavonoids[J]. Processing of Agricultural Products, 2023(16): 33−36,40.
[22] 徐艳阳, 赵玉娟, 高峰, 等. 高效液相色谱法分析中国人参不同部位中多酚类化合物[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(4):240−246. [XU Y Y, ZHAO Y J, GAO F, et al. Analysis of polyphenols in different parts of Chinese ginseng by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Food Science,2021,42(4):240−246.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200214-140 XU Y Y, ZHAO Y J, GAO F, et al. Analysis of polyphenols in different parts of Chinese ginseng by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(4): 240−246. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200214-140
[23] RODRÍGUEZ Ó, GOMES W F, RODRIGUES S, et al. Effect of indirect cold plasma treatment on cashew apple juice (Anacardium occidentale L.)[J]. LWT-Food Science Technology,2017,84:457−463. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.06.010
[24] 赵玉娟. 人参叶多酚的提取及应用研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2020. [ZHAO Y J. Extraction and application of polyphenols from ginseng leaves[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2020.] ZHAO Y J. Extraction and application of polyphenols from ginseng leaves[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2020.
[25] 孙艳, 张志伟, 王世清. 常压低温等离子体对黄瓜表面大肠杆菌杀菌效果及品质的影响[J]. 粮油食品科技,2018,26(1):61−67. [SUN Y, ZHANG Z W, WANG S Q. Effect of atmospheric low temperature plasma on the bactericidal effect and quality of cucumber surface[J]. Science and Technology of Cereals,Oils and Foods,2018,26(1):61−67.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7561.2018.01.013 SUN Y, ZHANG Z W, WANG S Q. Effect of atmospheric low temperature plasma on the bactericidal effect and quality of cucumber surface[J]. Science and Technology of Cereals,Oils and Foods, 2018, 26(1): 61−67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7561.2018.01.013
[26] 李玄. 花椒果皮黄酮多酚类物质提取及抗氧化抑菌活性研究[D]. 咸阳:西北农林科技大学, 2018. [LI X. Extraction of flavonoid polyphenols from prickly ash peel and study on antioxidant and antibacterial activities[D]. Xianyang:Northwest A&F University, 2018.] LI X. Extraction of flavonoid polyphenols from prickly ash peel and study on antioxidant and antibacterial activities[D]. Xianyang: Northwest A&F University, 2018.
[27] SCHOLTZ V, PAZLAROVA J, SOUSKOVA H, et al. Nonthermal plasma-A tool for decontamination and disinfection[J]. Biotechnology Advances,2015,33(6):1108−1119. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.01.002
[28] 孟宁基. 于低温等离子体技术应用的糙米食用品质特性及其改善研究[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨商业大学, 2020. [MENG N J. Study on edible quality characteristics and improvement of brown rice using low temperature plasma technology[D]. Harbin:Harbin University of Commerce, 2020.] MENG N J. Study on edible quality characteristics and improvement of brown rice using low temperature plasma technology[D]. Harbin: Harbin University of Commerce, 2020.
[29] 贾茹羽. 氯化钠结合包装材料对鲜切姜粉保鲜效果的研究[D]. 泰安:山东农业大学, 2019. [JIA R Y. Study on fresh-keeping effect of sodium chloride combined with packaging materials on fresh-cut ginger powder[D]. Taian:Shandong Agricultural University, 2019.] JIA R Y. Study on fresh-keeping effect of sodium chloride combined with packaging materials on fresh-cut ginger powder[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2019.
[30] AN K, ZHAO D, WANG Z, et al. Comparison of different drying methods on Chinese ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe):Changes in volatiles, chemical profile, antioxidant properties, and microstructure[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,197(Part B):1292−1300.
[31] 吴颍颍, 盛占武, 郑晓燕, 等. 不同预处理方法对油茶籽种皮成分、结构和抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 热带作物学报,2021,42(2):553−561. [WU Y Y, SHENG Z W, ZHENG X Y, et al. Effects of different pretreatment methods on composition, structure and antioxidant activity of Camellia seed coat[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2021,42(2):553−561.] WU Y Y, SHENG Z W, ZHENG X Y, et al. Effects of different pretreatment methods on composition, structure and antioxidant activity of Camellia seed coat[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2021, 42(2): 553−561.
[32] 赵萌萌, 党斌, 张文刚, 等. 超微粉碎对青稞麸皮粉微观结构及功能特性的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(8):278−286. [ZHAO M M, DANG B, ZHANG W G, et al. Effect of ultrafine grinding on microstructure and functional properties of barley bran powder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2020,36(8):278−286.] ZHAO M M, DANG B, ZHANG W G, et al. Effect of ultrafine grinding on microstructure and functional properties of barley bran powder[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(8): 278−286.
[33] 李家旺, 刘艳, 司民真. 三种山姜干粉的红外光谱对比分析[J]. 光散射学报,2016,28(1):56−61. [LI J W, LIU Y, SI M Z, et al. Comparative analysis of infrared spectrum of three kinds of dried Rhizoma mongolica powder[J]. The Journal of Light Scattering,2016,28(1):56−61.] LI J W, LIU Y, SI M Z, et al. Comparative analysis of infrared spectrum of three kinds of dried Rhizoma mongolica powder[J]. The Journal of Light Scattering, 2016, 28(1): 56−61.
[34] WANG X Q, ZHOU R W, GROOT G, et al. Spectral characteristics of cotton seeds treated by a dielectric barrier discharge plasma[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):5601. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04963-4
[35] DONG S, GAO A, XU H, et al. Effects of dielectric barrier discharges (DBD) cold plasma treatment on physicochemicaland structural properties of zein powders[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2017(10):434−444.
-
期刊类型引用(26)
1. 王红,彭励,宋乐,冯璐,李振凯,李彦青,高跳. 银柴胡多糖超声辅助提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2024(01): 185-191 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 赵小亮,鲁雲,康兴兴,龙则宇,郑晓杰. 雁荡山铁皮石斛多糖的提取、结构表征与体外抗氧化活性. 浙江农业学报. 2024(08): 1898-1908 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘丽宅,张鑫,金香淑,王蕾,赵云辉,王多伽,刘笑笑. 响应面法优化猪肉TPA质构测试条件. 东北农业科学. 2024(05): 100-108 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张艳,刘雪松,薛沾枚,冯万宇,张备,张蕾,沈思思,武晓东,张国华,江波涛. 麻杏石甘汤处方药材研究进展. 现代畜牧科技. 2023(01): 5-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘宇,戴沅霖,马越,董淑君,张斌,郑振佳. 金银花粗多糖提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性评价. 食品工业科技. 2023(07): 188-196 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 王珏,张华,王丹,唐宇,常兵. 乳化液膜法处理石油石化废水的研究. 油气田环境保护. 2023(02): 6-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 曹建蕾. 响应面法优化枸杞多糖的超声辅助提取工艺. 安徽化工. 2023(03): 105-109+113 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 徐瑾钰,彭小伟,阚欢,赵平,全伟,刘云. 滇皂角米多糖提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性. 食品研究与开发. 2023(14): 112-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 邹湘月,李章保,李霞,叶添梅,邵元元,米雅兰,艾均文,李飞鸣. 90份桑树种质资源桑叶品质的综合评价. 蚕业科学. 2023(04): 313-323 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 董巍,王文豹,王晓丽,付双,野津. 超声法辅助提取内蒙古甘草多糖工艺及其抗氧化活性研究. 现代食品. 2023(16): 91-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 高昆,林洪源. 山西省道地中药材研究进展. 山西农业科学. 2023(12): 1457-1467 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 杨奕凡,高雁,刘亚男,霍向东,娄恺,关波,陈开旭,曾军. 甘草渣中活性成分的提取及其在动物生产中的应用. 饲料研究. 2023(23): 140-143 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 余捷,李亚娜,夏瑾瑾,闫普普,刘佳丽,郭利伟,杨小林,刘国平,易提林. 复合酶辅助提取荷叶多糖工艺优化及其体外抗氧化活性. 食品研究与开发. 2023(24): 115-121 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 杨元华,范馨予,高红艳. 响应面法优化白番红花球茎多糖提取工艺及其抗氧化活性研究. 伊犁师范大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(04): 36-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 刘玉洁,董丽婷,罗灿,陈劭舒,夏凤腾,王征. 枯草芽孢杆菌LY-05发酵玉竹产水溶性多糖工艺优化及其抗氧化活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2022(03): 212-221 .  本站查看
本站查看
16. 张艳,孟维珊,陈曦,刘雪松,薛沾枚,王爽,杨旭东,朱庆贺,罗天瑶,张备,黄红,徐婷婷,史同瑞. 中兽药处方桂枝汤药材研究进展. 现代畜牧科技. 2022(05): 17-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 姚月华,唐宁,应熙锐,应朝阳,程永强. 红萍多糖结构特征、流变特性及抗氧化活性. 食品与机械. 2022(03): 154-159+172 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 张艳,刘雪松,薛沾枚,张备,尹珺伊,张军,王岩,张蕾,沈思思,史同瑞. 兽用理中汤处方药材研究进展. 中国草食动物科学. 2022(03): 51-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 李幼娟,李立郎,陈发菊,王丽,葛丽娟,文平,国光梅,杨小生. 天麻酒渗漉工艺优化及其对小鼠肝组织的影响. 中国酿造. 2022(07): 116-121 .  百度学术
百度学术
20. 则拉莱·司玛依,帕尔哈提·柔孜,吾哈丽妮萨·麦麦提托合提,古丽米热·阿巴拜克日,邓杰,杨晓君. 三种甘草种子蛋白的提取方法、结构及抗氧化活性比较研究. 食品与发酵工业. 2022(18): 227-234 .  百度学术
百度学术
21. 陈文彬,王雪莹,张才,马彦博,程源斌,王国永,孔涛,廖成水. 甘草多糖对肉鸡生长性能和免疫功能的影响. 饲料研究. 2022(18): 34-40 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 赵泽林,张丽艳,晋海军,李军,唐晓琴,董贺,周芳丽,马四补. 响应面法优化油炙淫羊藿炮制工艺及抗氧化活性分析. 亚太传统医药. 2022(12): 76-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 罗灿,刘玉洁,陈劭舒,夏凤腾,李怡成,王征. 灵芝菌液体发酵玉竹产水溶性多糖的工艺优化和抗氧化性研究. 中国酿造. 2022(11): 180-186 .  百度学术
百度学术
24. 董贺,李军,晋海军,唐晓琴,赵泽林,孙恒灿,张丽艳. 响应面法优化大蝎子草水溶性总黄酮提取工艺及其水提液抗氧化活性分析. 贵州科学. 2022(06): 31-36 .  百度学术
百度学术
25. 朱玉婷,文欣,向俊,郭锦材,荆辉华,李灿,陈同强. 植物乳杆菌胞外多糖的单糖组成及抗氧化活性. 乳业科学与技术. 2022(06): 7-11 .  百度学术
百度学术
26. 宋玲玲,王君明,弓明珠,张月月,张振凌,王彦嵋,巫晓慧,郭旭. 炮制对雷公藤诱导的睾丸生殖毒性的减毒作用机制研究. 时珍国医国药. 2021(11): 2664-2667 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)






 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
