Screening, Enrichment and Structural Identification of Bitter Almond Antibacterial Peptides
-
摘要: 为探究苦杏仁抑菌肽的制备、富集及结构分析,本实验以苦杏仁为原料,在脱脂后提蛋白,使用酶法制备苦杏仁蛋白抑菌肽,优化制备工艺,检测抑菌肽的抑菌活性,进一步纯化富集,分离出抑菌活性最强的抑菌肽组分并对其进行结构分析。结果表明,木瓜蛋白酶酶解物对于革兰氏阳性菌尤其是金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌作用最强。优化苦杏仁抑菌肽的制备工艺最佳条件为:酶解温度为74 ℃,酶底比为2.5%,pH为7。得到抑菌肽的蛋白浓度为19.21%,并测得最低抑菌浓度为3.13 mg/mL。利用超滤和凝胶过滤色谱(Sephadex G-25)对抑菌肽进行分离纯化,从中筛选出肽组分A-II-b对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制活性最强。将凝胶过滤条件优化为:样品浓度9.38 mg/mL,洗脱速度0.68 mL/min、洗脱剂为纯水。在此条件下测得肽组分A-II-b的峰面积比为13.15%。采用液相色谱-质谱联用技术对肽组分A-II-b进行结构分析,将结果导入Uniprot数据库与APD3数据库进行匹配,筛选出7种分子量在1500~2500 Da的潜在具有抗菌活性的苦杏仁肽序列,分别是ALPDEVLQNAFRIS、ESWNPRDPQFQWAGVA、VAYWSYNNGEQPLVA、FLDLSNDQNQLQLDQVPR、GENDNRNQIIRVR、RNLQGENDNRNQIIRVR和RALPDEVLQNAFRIS。本研究促进了杏仁活性肽的深度开发和资源再利用,同时也为其作为抑菌肽的研究和进一步开发利用提供理论依据。Abstract: To explore the preparation, enrichment, and structural analysis of bitter almond antimicrobial peptides, in this experiment, the protein was extracted from the defatted bitter almonds, and the protein was hydrolyzed by enzymes to prepare bitter almond protein antibacterial peptides. The preparation process was optimized, and the resulting peptides' antibacterial activity was detected. The peptides were further purified and enriched. The components with the strongest antibacterial activity were isolated, and their structure was analyzed. The results showed that the papain hydrolysate had the strongest bacteriostatic effect on Gram-positive bacteria, especially Staphylococcus aureus. The optimal conditions for the preparation of bitter almond antibacterial peptides were as follows: The enzymatic hydrolysis temperature was 74℃, the enzyme-to-substrate ratio was 2.5%, and the pH was 7. The protein concentration of the antibacterial peptides was 19.21%, and the minimum inhibitory concentration was 3.13 mg/mL. The antibacterial peptides were isolated and purified by ultrafiltration and gel filtration chromatography (Sephadex G-25). Peptide component A-II-b was screened out to have the strongest inhibitory activity against Staphylococcus aureus. The gel filtration conditions were optimized with a sample concentration of 9.38 mg/mL, an elution rate of 0.68 mL/min, and pure water as the eluent. Under these conditions, the peak area ratio of peptide component A-II-b was 13.15%. The structure of peptide component A-II-b was analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, and the results were imported into the UniProt database and the APD3 database for matching. Seven kinds of bitter almond peptides with potential antibacterial activity with molecular weights of 1500~2500 Da were screened out, including ALPDEVLQNAFRIS, ESWNPRDPQFQWAGVA, VAYWSYNNGEQPLVA, FLDLSNDQNQLDQVPR, GENDNRNQIIRVR, RNLQGENDNRNQIIRVR, and RALPDEVLQNAFRIS. This study promoted the in-depth development and resource reuse of almond active peptides and also provided a theoretical basis for their research and further development and utilization as an antibacterial peptide.
-
在20世纪初,第一种合成抗菌剂砷凡纳明问世[1]。随着抗菌药物的深入开发和广泛使用,这些药物的局限性也逐渐显露出来。其中最主要的是抗生素的生物利用率低,部分抗生素具有毒性以及过度依赖抗生素药物带来的抗微生物耐药性(Antimicrobial resistance,AMR)危机[2]。除了传统的小分子药物外,世卫组织还建议研究非传统和替代疗法,重点关注不同的细菌靶标的抗菌肽和噬菌体疗法[3]。
抗菌肽(Antimicrobial peptides,AMPs)又称宿主防御肽,是生物机体用来抵抗入侵病原体的天然免疫屏障[4]。它们广泛存在于动物的免疫细胞中,如吞噬细胞、各种脏器的粘膜、皮肤以及植物的花、果、叶,甚至存在于微生物自身体系中[5−7]。与传统的抗生素不同,除了不易产生耐药性和交叉抗性外[4],还具有对环境友好,对人类和动物无害的特点,对细菌、病毒、真菌以及原生动物等都表现出广泛的抑制作用[8−9]。不同抗菌肽在与细胞作用时表现的作用方式和作用机制也各不相同。带正电荷的抗菌肽结合细胞膜中带负电荷的磷脂是一种杀菌机制;抗菌肽结合细胞壁或胞内组分的非膜靶点也可杀死病原体[10]。关于抗菌肽的作用机理有两种观点:膜靶向机制和非膜靶向机制。研究人员采用了聚集体模型、环状孔模型、桶板模型和毯式模型等不同作用模型对两种作用机制作进一步阐述[4]。
我国杏资源非常丰富,主要分布在东北、华北、西北地区,是“三北”生态脆弱区发展经济林产业的适生树种[11],其中新疆杏栽培历史悠久,培植了诸多优质的品种[12]。作为传统的中药原料,苦杏仁能够显著降低血清中胆固醇、动脉粥样硬化指数[13],且杏仁油具有提高免疫力、预防心血管疾病等多种生理功能。苦杏仁市场需求呈不断上升趋势,尤其是在食品[14]、医药[15]、化工[16]等领域。杏仁皮多酚类化合物具有抗菌抗病毒活性[17],崔海燕等[18]对其主要活性成分进行了研究。Salih等[19]从杏仁中提取苦杏仁苷并研究其对绿脓杆菌、沙雷氏菌等病原菌的抑制作用。王丽芳等[20]提取龙井茶叶粗提物,研究茶叶抗菌肽对细菌的作用机制,刘东伟等[21]将压榨提油后的核桃粕酶解制备核桃粕蛋白,发现核桃粕蛋白对金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌均有抑制效果,对于杏仁蛋白的抗菌效果目前暂无研究。前期研究发现苦杏仁蛋白具有抗菌性,本实验以榨油后的杏仁粕为研究对象并探究其蛋白的抑菌特性,优化水解及纯化条件,富集其中的抗菌肽组分并解析其结构,以期为苦杏仁活性肽的开发和杏仁副产品的再利用提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
苦杏仁 新疆乌鲁木齐市沙依巴克区北园春市场采购;金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌和沙门氏菌 北京永泽浩嘉生物技术发展中心购入;碱性蛋白酶(酶活:200 U/mg)、酸性蛋白酶(酶活:50 U/mg)、中性蛋白酶(酶活:100 U/mg)、复合蛋白酶(酶活:120 U/mg)、胰蛋白酶(酶活:130 U/mg)、木瓜蛋白酶(酶活:800 U/mg)、葡聚糖凝胶G-25、考马斯亮蓝G250 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;LB肉汤、琼脂粉 北京奥博星生物技术有限责任公司;其余化学试剂均为分析纯 天津鑫铂特化工有限公司。
ZYJ-7090单螺杆榨油机 东莞市方太电器有限公司;SF-GL-16A高速冷冻离心机 上海菲恰尔分析仪器有限公司;ALpha 2-4 LSCplus冻干机 德国Christ公司;UV-1200型紫外可见分光光度计 上海美谱达仪器有限公司;灭菌锅LDZF-50L-I 上海申安医疗器械厂;HD-21-1核酸蛋白检测仪、HL-2S恒流泵、HD-A电脑采集器 上海沪西分析仪器厂;Agilent Zorbax 300SB-C18 美国安捷伦公司;超分辨液质联用仪Q Exactive HF-X 美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 苦杏仁蛋白的制备
挑选颗粒饱满的苦杏仁热烫去皮后,在60 ℃烘干2 h去除表面水分,使用榨油机对杏仁进行初步脱脂,工艺设置为温度50 ℃,榨轴转速30 r/min。冷榨后的杏仁粕用石油醚按照1:10的比例浸提12 h进行进一步脱脂处理,重复2次,在60 ℃条件下烘干5 h后过60目筛,得脱脂杏仁粉,于4 ℃保存。
采用碱溶酸沉法[22]提取脱脂苦杏仁粉中的杏仁蛋白,以1:25比例加入蒸馏水,NaOH调pH至10.0,连续搅拌浸提60 min,4000 r/min转速下离心20 min,沉淀物重复碱提1次,合并上清液加HCl调至pH4.4,4000 r/min转速下离心20 min弃去上清液,用蒸馏水洗涤沉淀3~5次,冷冻干燥后得到苦杏仁粗蛋白。
1.2.2 蛋白酶的筛选
选择碱性蛋白酶、酸性蛋白酶、中性蛋白酶、复合蛋白酶、胰蛋白酶、木瓜蛋白酶在各自最适条件下对苦杏仁蛋白进行水解,并测试其酶解物对枯草芽孢杆菌、大肠杆菌金黄色葡萄球菌及沙门氏菌的抑制效果,以水解度和抑菌圈直径为衡量指标,筛选出一种较优的蛋白酶用于后续苦杏仁抑菌肽的制备。不同蛋白酶适宜酶解条件如表1所示。
表 1 不同蛋白酶适宜酶解条件Table 1. Suitable enzymatic conditions for different proteases蛋白酶种类 加酶量(U/g) 底物比(%) pH 温度(℃) 时间(h) 碱性蛋白酶 5000 4.0 9.0 55 4 酸性蛋白酶 5000 4.0 3.5 40 4 中性蛋白酶 5000 4.0 7.0 55 4 复合蛋白酶 5000 4.0 7.0 50 4 胰蛋白酶 5000 4.0 7.0 40 4 木瓜蛋白酶 5000 4.0 7.5 60 4 1.2.3 水解度测定
蛋白含量的测定采用考马斯亮蓝法[23],水解度的测定采用甲醛滴定法[24],按下式计算水解度DH:
DH(%)=(V1−V0)×V×C×14.01×5.181000×M×pro×100 式中:V1为酶解液消耗的NaOH溶液体积(mL);V0为蛋白溶液消耗的NaOH溶液体积(mL);V为所用离子水体积(mL);C为滴定消耗的NaOH溶液浓度(mol/L);M为所加蛋白质质量(g);pro为蛋白质浓度(%)。
1.2.4 抑菌活性的测定
采用滤纸片法测定抑菌活性[25]。在整个实验过程中,为保持微生物活力,所有待测菌株需每2周在琼脂培养基上传代培养,并于4 ℃保存。待测菌在使用前,在37 ℃ LB液体培养基中摇床培养18 h。吸取菌悬液在5000 r/min转速下离心15 min,用无菌生理盐水连续稀释调整至105 CFU/mL菌落形成单位。
在超净工作台内,吸取活化完成的试验菌液100 μL均匀涂于LB平板培养基上。使用打孔器制作直径6 mm的滤纸圆片,在苦杏仁酶解液中浸泡2 h,将浸泡过的滤纸片贴于平板培养基上,37 ℃条件下培养12 h,采用十字交叉法测量抑菌圈直径。试验重复3次,以水作空白对照。
1.2.5 最小抑菌浓度测定
采用二倍稀释法测定最小抑菌浓度[26]。将由酶解制备的苦杏仁抑菌肽样品做浓度递减稀释,分别为100、50、25、12.5、6.25、3.125、1.5625、0.78125 mg/mL,对所选指示菌进行抑菌试验,具体操作同1.2.4,以抑菌圈大于8 mm为依据确定最小抑菌浓度,重复3次,取平均值。
1.2.6 单因素实验
以苦杏仁蛋白水解度及酶解物抑菌活性为评价指标,考察酶解时间、pH、酶底比、酶解温度和底物比对抑菌肽酶解及抑菌性的影响,每组实验重复3次,结果取平均值。
酶解时间:固定酶解pH6.5,酶底比为3%,温度为60 ℃,底物比为4%,以水解度和抑菌圈直径的大小为评价指标,考查不同酶解时间(1、2、3、4、5 h)对杏仁蛋白酶解的影响。
酶解pH:选择酶解时间3 h,酶底比为3%,温度为60 ℃,底物比为4%,以水解度和抑菌圈直径的大小为评价指标,考查不同酶解pH(4.5、5.5、6.5、7.5、8.5 h)对杏仁蛋白酶解的影响。
酶底比:设置酶解时间3 h,酶解pH6.5,温度为60 ℃,底物比为4%,以水解度和抑菌圈直径的大小为评价指标,考查不同酶底比(1%、2%、3%、4%、5%)对杏仁蛋白酶解的影响。
酶解温度:选择酶解时间3 h,酶解pH6.5,酶底比为3%,底物比为4%,以水解度和抑菌圈直径的大小为评价指标,考查不同酶解温度(40、50、60、70、80 h)对杏仁蛋白酶解的影响。
底物比:确定酶解时间3 h,酶解pH6.5,酶底比为3%,温度为60 ℃,以水解度和抑菌圈直径的大小为评价指标,考查不同底物比(2%、3%、4%、5%、6%)对杏仁蛋白酶解的影响。
1.2.7 响应面法优化酶解工艺
通过单因素实验,研究酶解时间、pH、酶底比、酶解温度、底物比对苦杏仁蛋白水解程度以及酶解物抑菌效果的影响,采用Plackett-Burman设计试验,因素水平设计见表2,筛选3个影响酶解物抑菌效果的主要因素,并用响应面法中的Box-Behnken设计三因素三水平试验,因素水平设计见表3,确定苦杏仁蛋白酶解制备抑菌肽的最优工艺条件。
表 2 Plackett-Burman试验设计因素及水平Table 2. Factors and levels of Plackett-Burman test水平 因素 A-时间(h) B-pH C-酶底比(%) D-酶解温度(℃) E-底物比(%) −1 3 6.5 1 60 2 1 5 8.5 3 80 4 表 3 响应面试验因素水平设计Table 3. Factors and levels of response surface test因子 水平 −1 0 1 A-温度(℃) 60 70 80 B-酶底比(%) 2 3 4 C-pH 6.5 7.5 8.5 1.2.8 抑菌肽的超滤分离
参考徐杨林等[27]的方法。将酶解制备的苦杏仁抑菌肽与去离子水进行1:20溶解,在常温条件下经不同分子截留量的超滤膜将酶解液分离成大于30 kDa(A-Ⅰ)、30~10 kDa(A-Ⅱ)、10~3 kDa(A-Ⅲ)和小于3 kDa(A-Ⅳ)的四组不同分子量的滤液,通过二次循环收集截留液,冻干后−20 ℃保存备用,并用滤纸片法测定各部分酶解物的抑菌活性,重复3次,取平均值。
1.2.9 Sephadex G-25层析纯化条件的优化
经超滤后得到抑菌效果较好的肽粉,用超纯水溶解为不同浓度肽液准备上样。借鉴胡二坤等[28]的实验方法,采用280 nm紫外检测波长,在Sephadex G-25柱上(1.6 cm×60 cm)层析分离,考察上样浓度、洗脱速度、洗脱剂3个因素对苦杏仁抑菌肽的分离效果的影响。用自动接收器接收样品,冷冻干燥后测量各级组分的抑菌圈直径大小。
1.2.9.1 上样浓度的选择
设置洗脱速度为0.68 mL/min,以纯水为洗脱液,上样量为2 mL,探究样品浓度为50、25、12.5、9.38、6.25 mg/mL时的纯化效果。
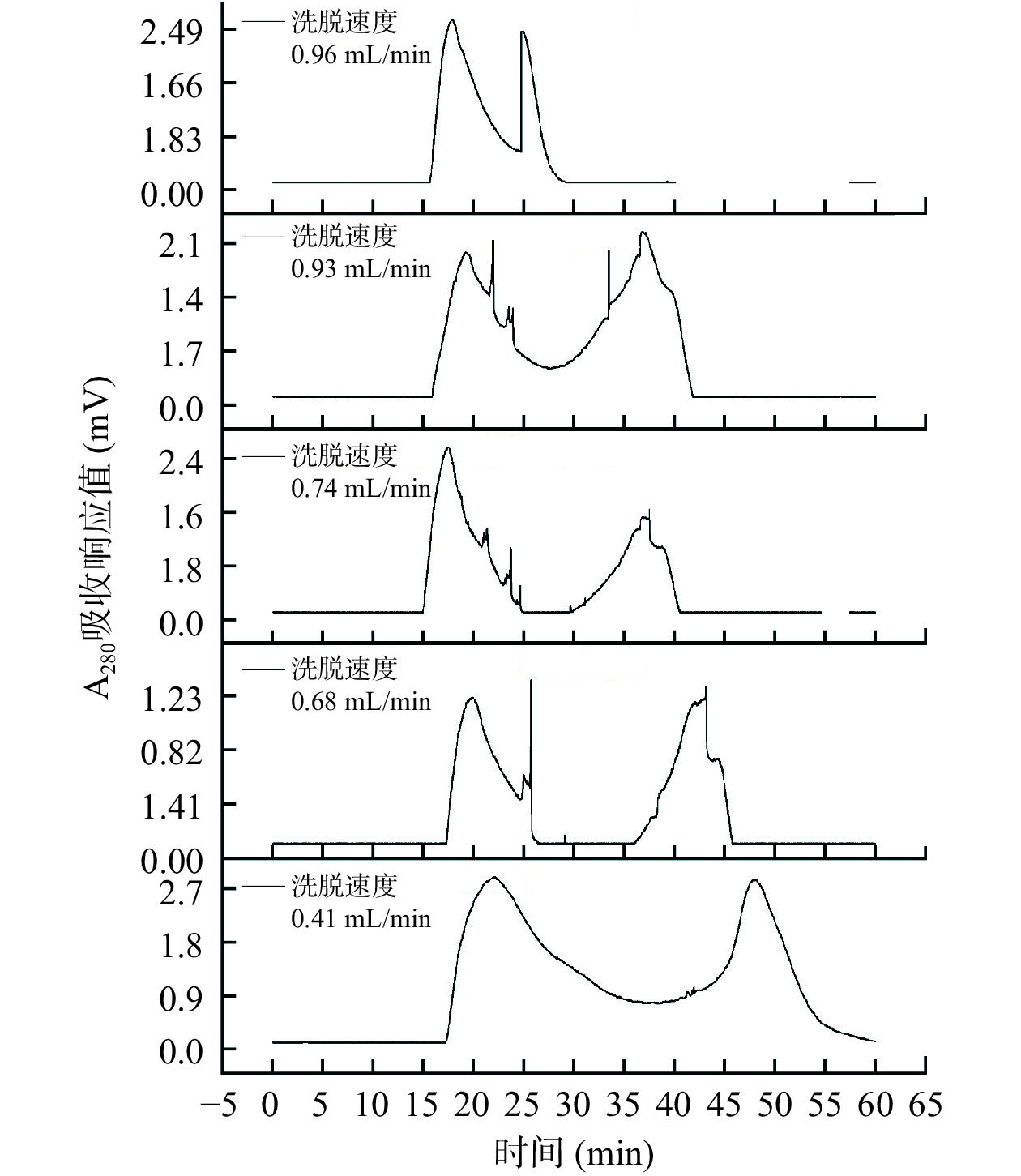
1.2.9.2 洗脱速度的选择
设置样品浓度为9.38 mg/mL,以纯水为洗脱液,上样量为2 mL,探究样品洗脱速度在0.96、0.93、0.74、0.68、0.41 mL/min时的纯化效果。
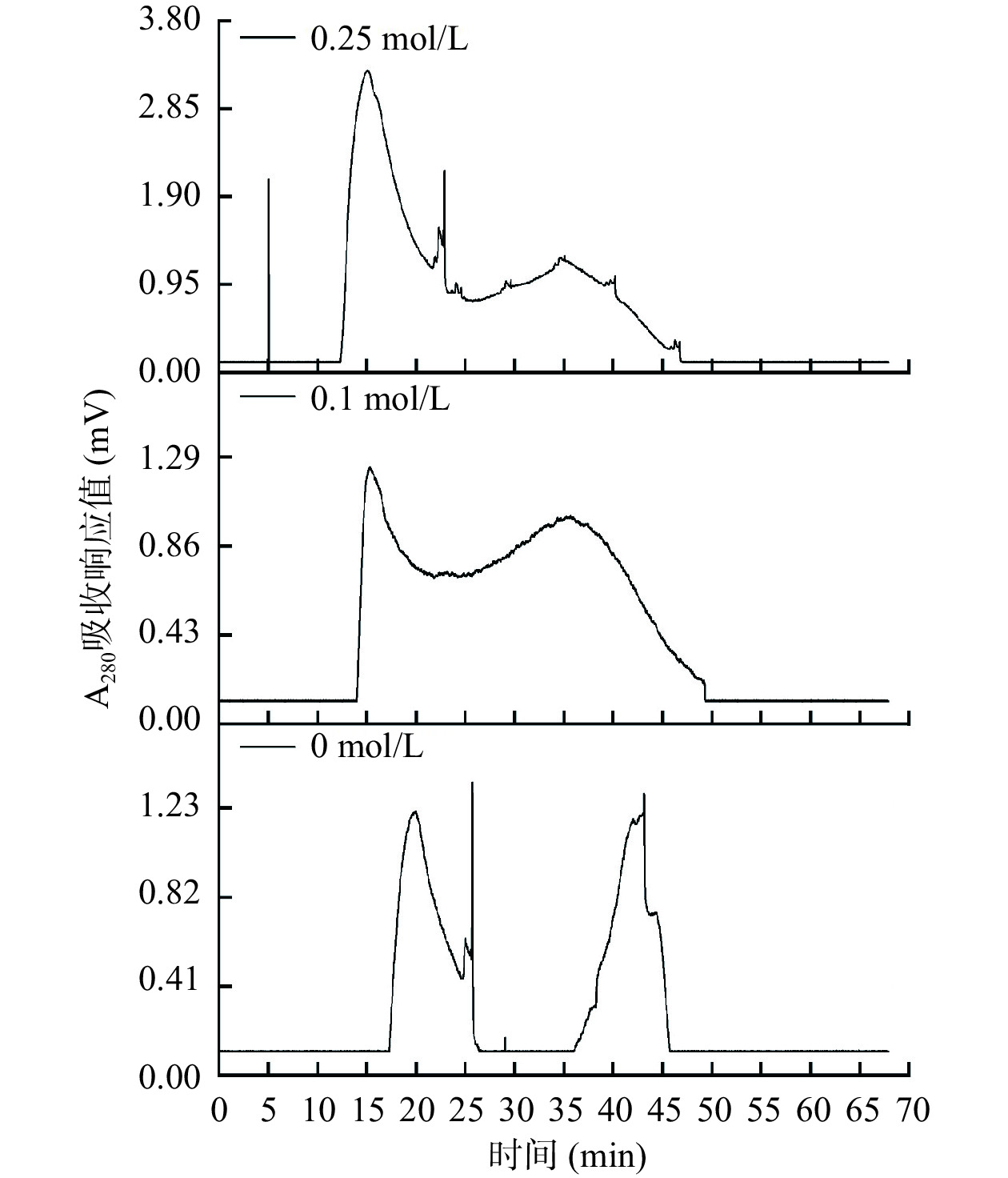
1.2.9.3 洗脱剂的选择
设置样品浓度为9.38 mg/mL,洗脱速度为0.68 mL/min,上样量为2 mL,探究样品洗脱剂含NaCl量为0.25、0.1、0 mol/L时的纯化效果。
1.2.10 LC-MS/MS鉴定肽结构
多肽的一级结构通过LC-MS/MS测定[29],凝胶层析得到的组分脱盐后用纯水溶解,配成质量浓度为1 mg/mL的溶液。
液相条件:液相色谱柱(0.15 mm×150 mm,RP-C18,Column Technology Inc);A液为0.1%甲酸水溶液,B液为0.1%甲酸-乙腈水溶液(乙腈为84%)。以95%的A液进行平衡,样品用0.45 μm的滤膜过滤,再经过液相色谱柱梯度洗脱分离。
质谱鉴定:酶解产物经毛细管高效液相色谱分离后用质谱仪进行质谱分析,分析时长:60 min;检测方式:正离子。按照每次全扫描后采集10个碎片图谱(MS2 scan)的方法采集多肽和多肽碎片的质荷比。该质谱图经软件MaxQuant 1.5.5.1检索相应的蛋白数据库,最后得到蛋白质鉴定及定量分析结果,使用在线软件APD3推断出抗菌肽段。
1.3 数据处理
每个样品重复3次实验,数据为平均值±标准偏差数据,使用Excel 2019统计数据、SPSS 26进行差异检验及方差分析,用Origin 2021绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同蛋白酶种类的筛选及抑菌效果验证
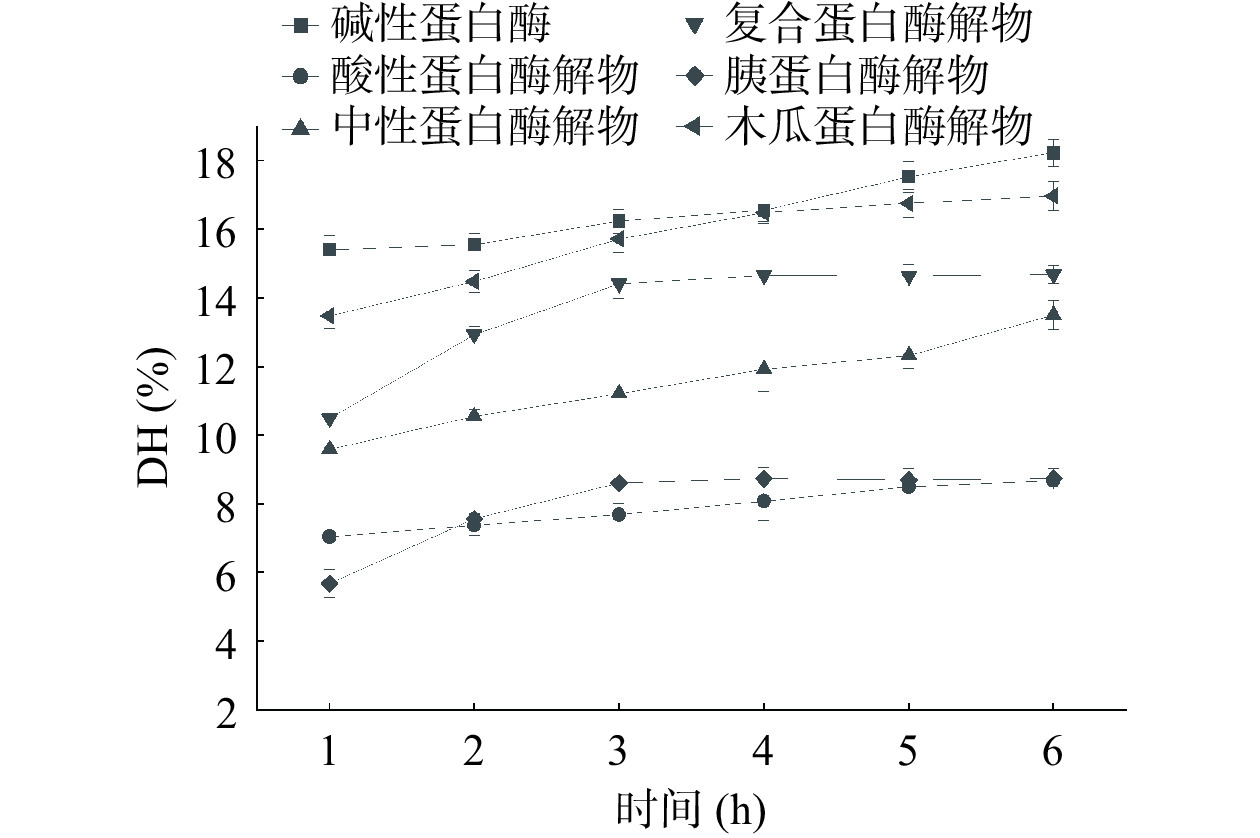
不同蛋白酶水解苦杏仁蛋白的水解度如图1所示,水解初期,水解程度随着水解时间的增长越来越高,反应进行一段时间后,水解程度趋于稳定,这是由于底物以及酶切位点开始变少,反应也逐渐变得平稳。碱性蛋白酶的水解度在本实验的六种蛋白酶中最高,木瓜蛋白酶的水解度比碱性蛋白酶略低一些,在水解反应4 h之后,水解度趋于平缓,达到16.98%±0.42%。而复合蛋白酶在水解反应3 h之后的水解度趋于平缓,最高不到15%,相当于木瓜蛋白酶水解1 h时的水解度;中性蛋白酶的水解度虽然与时间近似正比,但在水解反应6 h之后仍然未超过14%,除此之外,胰蛋白酶和酸性蛋白酶的水解能力接近,在水解反应6 h之后,它们的水解度甚至小于10%。在本试验中,6种蛋白酶水解苦杏仁蛋白的水解度排序为:碱性蛋白酶>木瓜蛋白酶>复合蛋白酶>中性蛋白酶>胰蛋白酶>酸性蛋白酶。不同种类的蛋白酶即使在条件类似的水解度下,苦杏仁蛋白的水解度会有差异,是因为不同的蛋白酶的水解位点不同[4]。
不同种类的蛋白酶水解苦杏仁蛋白所得酶解物的抑菌效果如表4所示,木瓜蛋白酶和酸性蛋白酶的酶解物对2种革兰氏阳性菌均有抑制活性,且木瓜蛋白酶酶解物对2种细菌抑菌圈直径都大于8.0 mm,尤其是金黄色葡萄球菌,抑菌圈直径接近20 mm,表现出较强的抑菌效果。空白对照组没有出现抑菌圈,说明水对金黄色葡萄球菌的生长并未产生任何抑菌的作用。苦杏仁蛋白的酶解物对金黄色葡萄球菌有明显的抑制作用,这可能与木瓜蛋白酶具有在较短时间内切割疏水区域氨基酸的特异性识别切割特征有关[30]。以抑菌效果为主,综合考虑抑菌圈直径和水解度2个因素,本实验选用木瓜蛋白酶作为后续制备抑菌肽的蛋白酶,并以金黄色葡萄球菌作为指示菌,对酶解法制备苦杏仁抑菌肽的工艺进行优化。
表 4 不同蛋白酶酶解物的抑菌活性Table 4. Antibacterial activities of different protease hydrolysates蛋白酶种类 革兰氏阳性菌 革兰氏阴性菌 空白对照 枯草芽孢杆菌 金黄色葡萄球菌 大肠杆菌 沙门氏菌 碱性蛋白酶 − − − + − 酸性蛋白酶 + ++ − − − 中性蛋白酶 − − + − − 复合蛋白酶 − − − + − 胰蛋白酶 − − − + − 木瓜蛋白酶 ++ ++ − − − 注:“−”表示无抑菌圈,“+”表示有抑菌圈但直径≤8.0 mm,“++”表示有抑菌圈但直径>8.0 mm。 2.2 木瓜蛋白酶酶解制备苦杏仁抑菌肽单因素实验
前期的实验中木瓜蛋白酶表现出最好的酶解效果和抑菌效果,为了便于后续实验的开展,实验选定时间、pH、酶底比、温度、底物比5个单因素,研究它们对苦杏仁蛋白水解度及酶解物抑菌活性的影响。
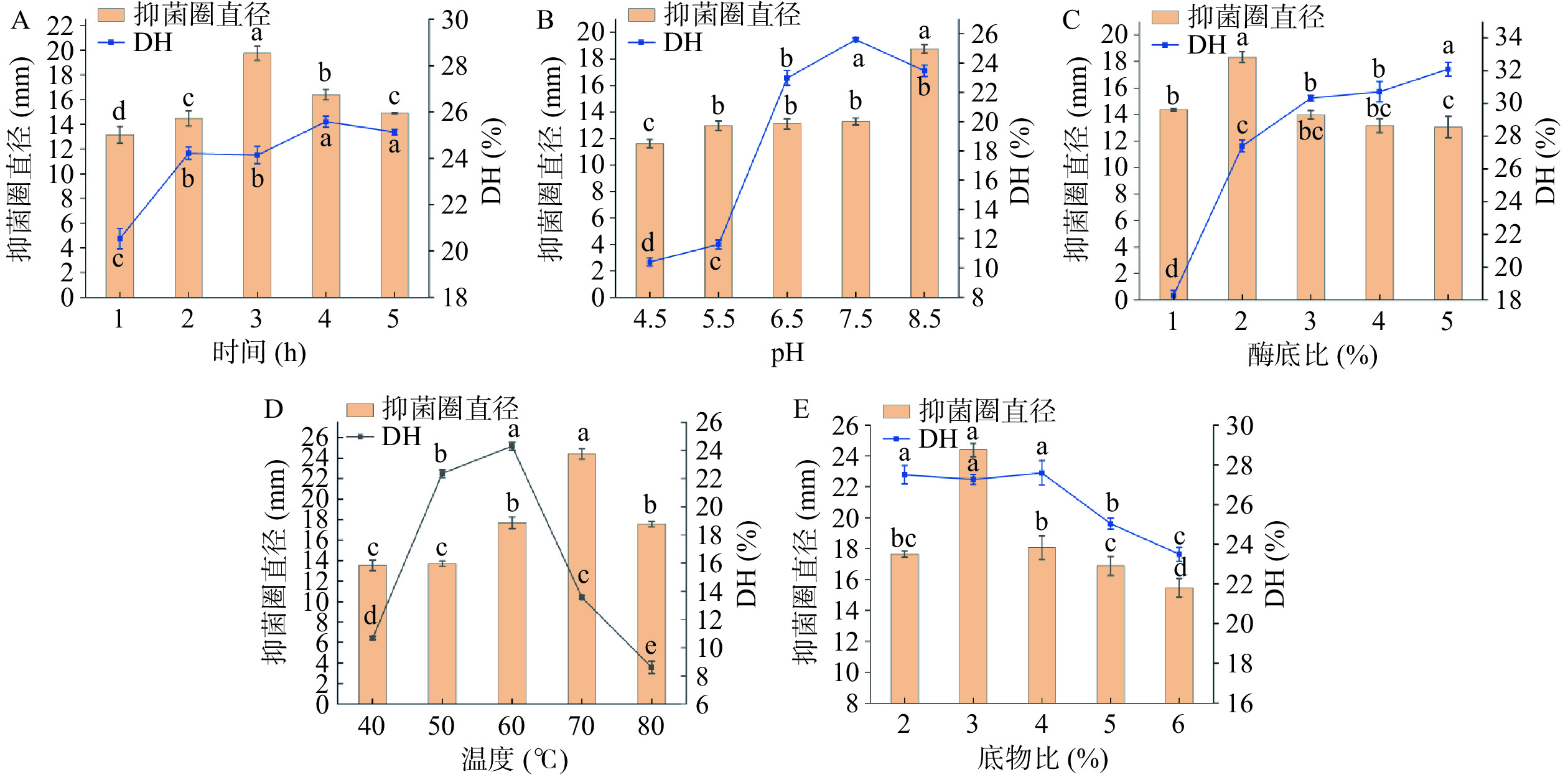
由图2A可知,随着酶解时间的不断增加,水解度随着酶解时间增加整体呈现上升趋势。而酶解物对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌活性逐渐增强,在3 h处达到最大,为19.76±0.58 mm,之后抑菌圈直径呈减小趋势。这是由于具有抑菌活性的氨基酸序列因酶解时间的延长而不断地暴露出来[31]。由图2B可知,pH能直接影响酶的活力。pH在4.5~7.5时,酶解物的抑菌活性变化不大,但水解度迅速增大,当pH进一步增加时,水解度却逐渐降低,而抑菌活性增强,抑菌圈直径达到最大值18.75±0.33 mm。可能是由于pH过低、过高都能使酶蛋白变性而失活,同时pH的改变能影响酶活性中心上必需基团的解离程度,在合适的pH范围中,酶分子与底物蛋白能更容易地结合,进而使得酶解物的抑菌活性增强[32]。由图2C可知,随着酶添加量的增加,抑菌圈的直径增大,当酶底比达到2%时,抑菌活性最强,抑菌圈直径达到18.33±0.4 mm;推测酶量的增加使水解产物具有抑菌活性的多肽片段增加[33]。再增加酶添加量,酶解物的抑菌活性反而略有下降,而水解程度随着酶添加量的增加呈不断增强的趋势。可能是酶将苦杏仁蛋白水解成单个氨基酸或更小的无抑菌活性的小肽[34]。由图2D可知,随着酶解温度升高,抑菌活性和水解度都呈先增后减的趋势,抑菌活性在温度为70 ℃时达到最大,抑菌圈直径为24.42±0.51 mm。这是由于温度升高,能提高水解速度,有利于抑菌多肽的生成。当温度过高的时候,结构遭到破坏的酶分子将丧失或部分丧失活性[35]。从图2E可以看出,底物浓度在2%~4%时,对水解程度的影响不大,在底物浓度达4%后水解度略有下降。抑菌活性随底物浓度的增加呈先增后减趋势,当底物浓度达到3%时,酶解物的抑菌活性最强,抑菌圈直径达到24.39±0.43 mm,可能是因为当底物浓度低时有足够的酶去酶解底物,随着底物浓度的增加,没有剩余的酶蛋白与之结合,且底物蛋白溶液黏度过高不利于底物蛋白与酶蛋白的接触[36]。
2.3 Plackett-Burrman设计筛选主效因素
由表5可知,方差分析模型的P值为0.0038,复决定系数R2=0.9139,校正决定系数R2Adj=0.8422,表明此回归模型相关性好。酶底比、温度对苦杏仁抑菌肽的制备影响极显著(P<0.01),pH对苦杏仁抑菌肽的制备影响显著(P<0.05),而其它两个因素则不显著。显著性大小依次为:酶底比>温度>pH>时间>底物比。因此选择具有显著影响的3个因素,即酶底比、温度、pH作为下一步响应面模型的考察因素。
表 5 Plackett-Burman模型方差分析Table 5. Analysis of variance of Plackett-Burman model项目 平方和 Df 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 309.37 5 61.87 12.74 0.0038 ** A-时间 10.79 1 10.79 2.22 0.1866 B-pH 54.87 1 54.87 11.3 0.0152 * C-酶底比 151.51 1 151.51 31.2 0.0014 ** D-温度 91.3 1 91.3 18.8 0.0049 ** E-底物比 0.9 1 0.9 0.18 0.6825 残差 29.14 6 4.86 总和 338.51 11 R2=0.9139 R2Adj=0.8422 注:**表示P<0.01,*表示P<0.05。 2.4 响应面法优化试验
对Plackett-Burrman设计筛选出的3个主效开展N=15的三因素三水平的Box-Behnken设计试验,试验结果见表5。利用Design Expert 8.0软件对试验数据进行多元回归拟合,得到酶解苦杏仁蛋白的多项式回归模型如下:
Y=17.44+0.47A−0.42B−0.85C−0.22AB+0.058AC−0.35BC−0.64A2−0.44B2−0.59C2
由表6可知,模型F值为8.14,P值0.0163<0.01,说明该回归模型可靠。模型失拟项的P值为0.895,不显著,校正决定系数R2Adj值为0.8211,表明某产量82.11%的变异分布在方程中,其相关系数R2=0.9361,表明产量的实测值与预测值之间具有较好的拟合度,该模型可用于预测对苦杏仁抑菌肽制备的实际情况。
表 6 二次响应面回归模型方差分析Table 6. ANOVA for response surface quadratic model analysis of variance table方差来源 平方和 Df 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 12.62 9 1.40 8.14 0.0163 * A-温度 1.77 1 1.77 10.24 0.0240 * B-酶底比 1.42 1 1.42 8.24 0.0350 * C-pH 5.73 1 5.73 33.21 0.0022 ** AB 0.20 1 0.20 1.15 0.3330 AC 0.013 1 0.013 0.077 0.7930 BC 0.48 1 0.48 2.76 0.1575 A2 1.49 1 1.49 8.65 0.0322 * B2 0.71 1 0.71 4.11 0.0984 C2 1.28 1 1.28 7.41 0.0417 * 残差 0.86 5 0.17 失拟项 0.19 3 0.063 0.19 0.8970 误差 0.67 2 0.34 总和 13.50 14 R2=0.9361 R2Adj=0.8211 R2Pre=0.6632 注:**表示P<0.01,*表示P<0.05。 在该模型中,回归系数的显著性检验显示,一次项A、B对酶解液抑菌性的影响均达到显著水平(P<0.05),C达到极显著水平(P<0.01)。比较A、B、C 3个因素的F值大小可得,各因素对苦杏仁蛋白提取率影响的大小顺序为:pH(C)>温度(A)>酶底比(B)。二次项(A2、C2)对试验结果的影响显著(P<0.05);交互项(AB、AC、BC)对酶解物的抑菌效果影响均不显著(P>0.05)。根据软件程序预测,可得苦杏仁抑菌肽最大抑菌圈直径为17.86 mm,对应的最佳方案为:酶解温度为74.04 ℃,酶底比为2.65%,pH为6.9。
2.5 最佳水解条件的确定和验证
鉴于实验的可操作性,将苦杏仁抑菌肽的制备工艺参数修正为:酶解温度为74 ℃,酶底比为2.5%,pH为7。在此条件下,实际测得的平均抑菌圈直径为18.14±0.26 mm,与理论预测值相比相对误差在1.6%左右。经测定,此条件下酶解物中蛋白质浓度为19.21%,水解度为26.21%,因此采用修正后的方法得到的提取参数准确可靠,具有实用价值。
2.6 最低抑菌浓度的测定
由表7可知,苦杏仁抑菌肽对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制效果活性较高,最低抑菌浓度为3.13 mg/mL,结果表示浓度较低时仍有抑菌效果,具有较高的开发价值。
表 7 不同浓度的苦杏仁抑菌肽对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制效果Table 7. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of bitter almond antibacterial peptide on Staphylococcus aureus苦杏仁抑菌肽质量浓度(mg/mL) 抑菌圈直径(mm) 100 22.19±0.55 50 18.11±0.45 25 15.52±0.67 12.5 13.19±0.84 6.25 10.39±0.57 3.13 8.19±0.81 1.56 6.25±0.68 2.7 苦杏仁抑菌肽的超滤分离
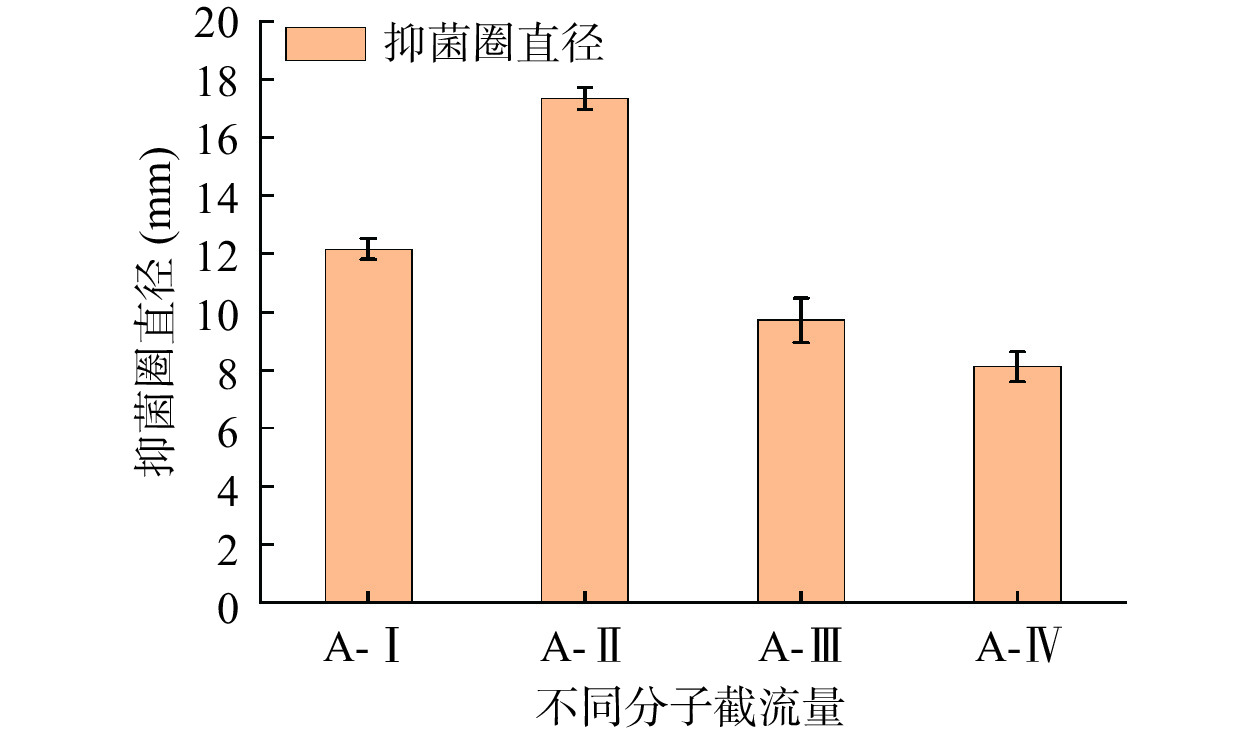
将酶解制备的苦杏仁抑菌肽用截留量不同的滤膜过滤后,共得到A-Ⅰ、A-Ⅱ、A-Ⅲ和A-Ⅳ四个组分,测得各组分的抑菌活性如图3所示,组分A-Ⅱ的抑菌圈直径最高达到17.34±0.38 mm,表明该组分的抑菌效果较强。其余3个组分A-Ⅰ、A-Ⅲ和A-Ⅳ的抑菌圈直径分别为12.17±0.36、9.71±0.77、8.11±0.51 mm。因此,选择组分A-Ⅱ对其进行进一步凝胶层析分离。
2.8 纯化条件优化
在按照1.2.9.1条件进行纯化时,上样浓度对纯化效果的影响结果如图4所示。
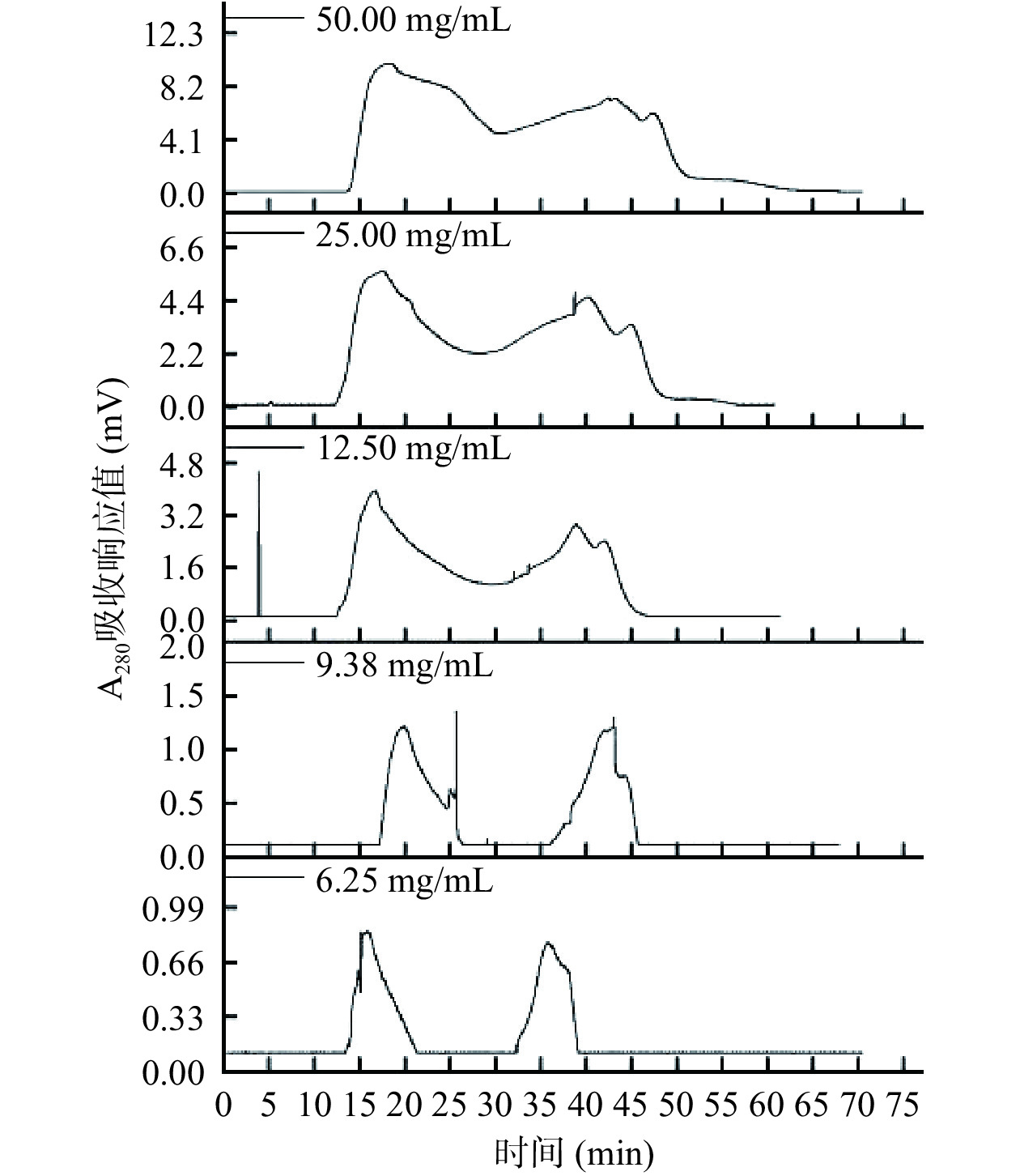
通过图4可知,上样浓度过高,不仅导致组分A-Ⅱ分离时间变长,还导致样品扩散,引起临近峰重叠,分离效果不理想。上样浓度偏低,实验效率低且峰形不尖锐,含量低的部分组分无法分离。过高浓度和过低浓度均只分离出3个组分,选择上样浓度9.38 mg/mL进行层析时,分离出4个组分,样品得到较好的分离,且组分与组分之间较明显。
在按照1.2.9.2条件进行纯化时,洗脱速度对纯化效果的影响结果如图5所示。
通过图5可知,洗脱速度太快,会使组分A-Ⅱ被洗脱液冲洗下来时还未分离彻底,分离出2个峰。洗脱速度过慢,出峰慢且样品由于长时间存留发生扩散,会导致分离效果不佳和峰拖尾,也只分离出2个峰。当洗脱速度为0.68 mL/min时分离出4个组分,峰相对尖锐,且分离效果较佳。
在按照1.2.9.3条件进行纯化时,洗脱剂对纯化效果的影响结果如图6所示。
由图6可知,洗脱剂为0.25 mol/L或0.1 mol/L的NaCl溶液时,分离所得的组分吸光值较高,可能是NaCl具有防止蛋白在凝胶中吸附的作用[37],但分离效果欠佳,前者得到3个峰,而后者只分离出2个单峰。而只用纯水作为洗脱液时,分离效果较含NaCl的效果明显,但所得组分的吸光值较低,部分组分因吸附未被洗脱出来。因此,实验采用不含NaCl的超纯水为洗脱液时,凝胶过滤色谱分离各组分的效果最佳。
2.9 纯化肽的抑菌效果研究
由SephadexG-25纯化的肽对革兰氏阳性菌的抑制效果较好,尤其是金黄色葡萄球菌,分离出的4个组分中,组分A-Ⅱ-b的抑菌效果最强。综上所述,组分A-Ⅱ-b的抑菌活性较强,为了提高该组分的产量,确定凝胶层析的纯化工艺为样品浓度9.38 mg/mL,洗脱速度0.68 mL/min、洗脱剂为纯水的条件为最佳凝胶过滤条件。使用HD-A软件对最佳纯化条件分离的4个目标峰进行分析,得出A-Ⅱ-a、A-Ⅱ-b、A-Ⅱ-c和A-Ⅱ-d的峰面积比分别为38.38%、13.15%、40.52%、7.96%。多次重复试验,收集各组分,将各组分经真空浓缩和冷冻干燥后制成粉末,备用。
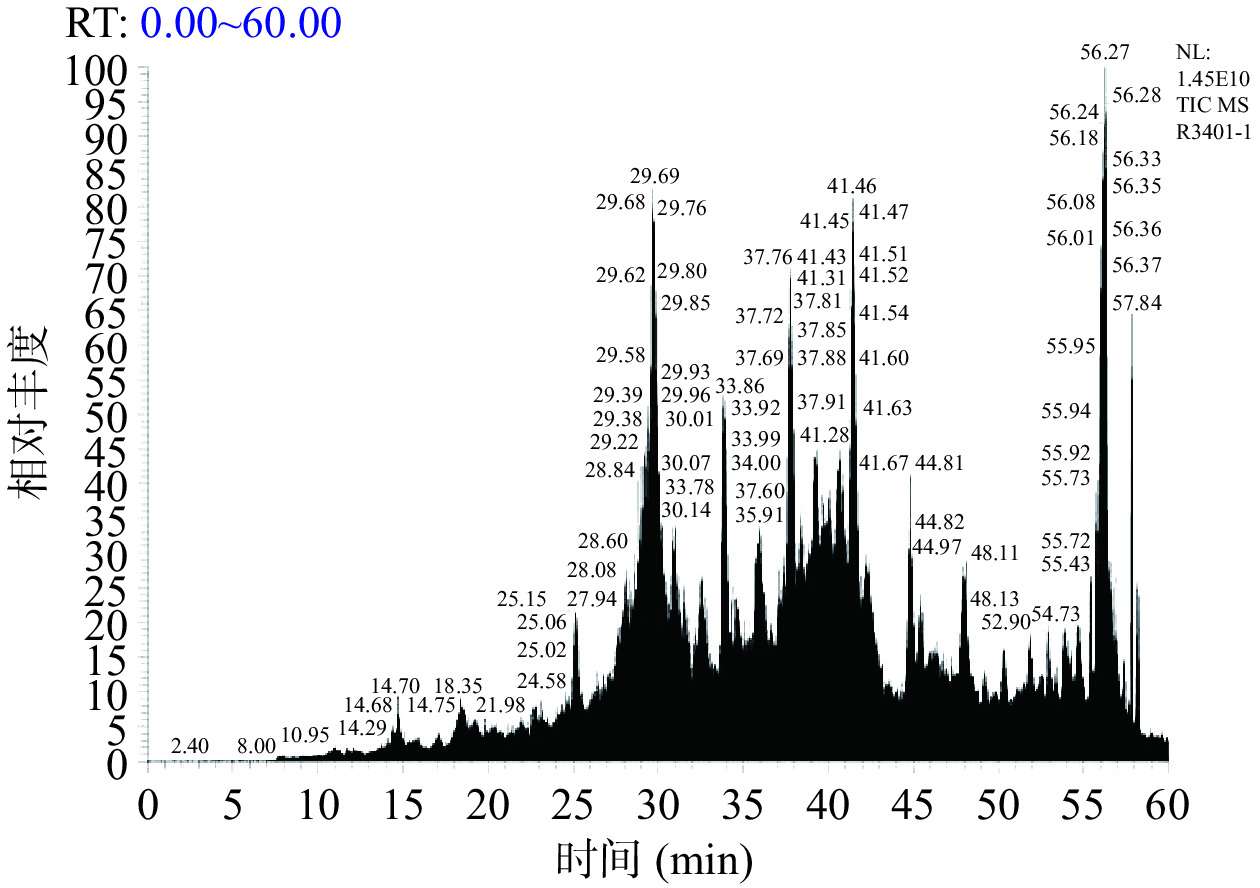
2.10 LC-MS/MS鉴定分析
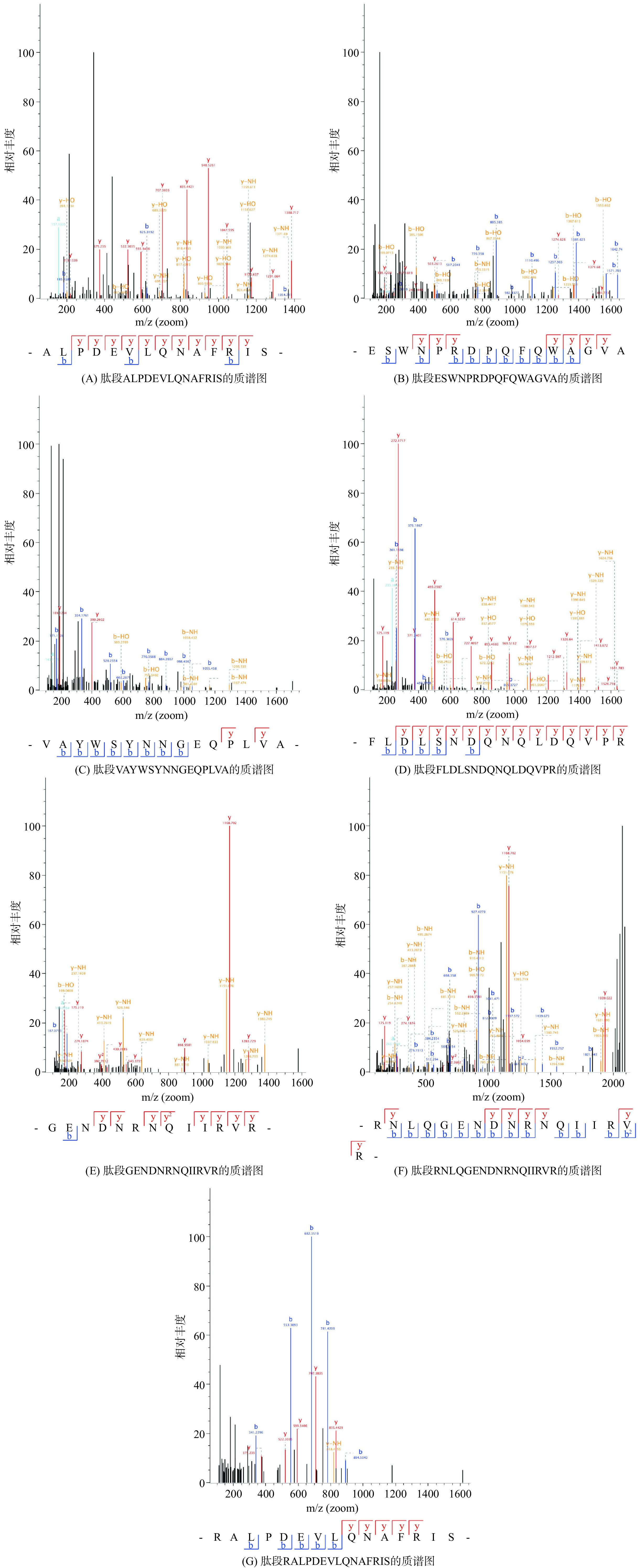
采用液相色谱-质谱联用技术对抑菌效果最强组分A-Ⅱ-b的肽段序列进行鉴定分析,筛选潜在的抑菌肽段。组分A-Ⅱ-b的总离子流图如图7所示。将对重现性最好,相对峰面积也较高的肽段,质谱检测到的b,y离子匹配图(图8)与数据库(uniprot-taxonomy Anabantaria 2023)进行匹配,得到每个肽的准确氨基酸序列。在抗菌肽数据库(APD3)中进行同源性分析并筛选出潜在的抗菌肽,结果如表8所示。经筛选发现7种肽段序列与APD数据库中已报道抑菌肽具有一定的的同源相似度。多肽序列平均为10~20个氨基酸序列长度,分子量在1500~2500 Da的抑菌肽段含有大量的碱性氨基酸残基与疏水性残基,使用在线软件APD3对肽段序列的电荷数和疏水率进行计算,其净电荷数从−1~+2,疏水率范围从23%~50%。这与以往学者的研究结果基本一致[36],由此,推断出这7种苦杏仁肽序列具有潜在的抗菌活性。具有疏水性基团和带正电荷是AMPs的显著特征。抗菌肽通常因为富含精氨酸、赖氨酸残基而形成高度明确的阳离子结构域[36]。疏水作用体现在AMPs通过静电吸引被微生物膜吸附后,疏水残基开始与脂质双分子层的疏水段相互作用,最终导致微生物膜的破坏[38]。
表 8 LC–MS/MS鉴定组分A-Ⅱ-b抑菌肽段Table 8. Antimicrobial peptides identified by LC-MS/MS from A-II-a fraction肽段序列 肽段长度 肽段分子量 留存时间(min) 电荷数 疏水率(%) 同类肽 相似率(%) ALPDEVLQNAFRIS 14 1571.8308 54.583 −1 50 AP02858 40 ESWNPRDPQFQWAGVA 16 1886.87 51.562 −1 38 AP01233 38.89 VAYWSYNNGEQPLVA 15 1709.8049 51.35 −1 40 AP03430 35.29 FLDLSNDQNQLDQVPR 16 1900.9279 48.447 −2 31 AP01899 35.29 GENDNRNQIIRVR 13 1582.8288 16.668 +1 23 AP00344 38.1 RNLQGENDNRNQIIRVR 17 2094.1155 17.997 +2 24 AP00008 38.89 RALPDEVLQNAFRIS 15 1727.9319 50.787 0 47 AP02858 40 3. 结论
本实验中以脱脂苦杏仁为原料提蛋白,使用多种酶法水解提取多肽并检验其抑菌活性。由实验结果得出木瓜蛋白酶水解蛋白的程度较高且酶解物的抑菌活性较强,尤其是对革兰氏阳性菌的抑制效果。使用金黄色葡萄球菌作为后续实验的指示菌。优化木瓜蛋白酶酶解制备苦杏仁抑菌肽的工艺为:酶解温度为74 ℃,酶底比为2.5%,pH为7。在此条件下酶解3 h得该抑菌肽的蛋白浓度为19.21%,对金黄色葡萄球菌的最低抑菌浓度为3.13 mg/mL,产生的抑菌圈直径达到18.14±0.26 mm。
通过超滤分离将苦杏仁抑菌肽分出4个组分并对其抑菌活性进行检测,筛选出活性较好的一个组分做进一步凝胶层析纯化处理。使用SephadexG-25进行纯化洗脱出4个峰A-Ⅱ-a、A-Ⅱ-b、A-Ⅱ-c和A-Ⅱ-d,其中A-Ⅱ-b对革兰氏阳性菌的抑制活性最强。采用LC-MS/MS进行分析,质谱检测到的b,y-离子匹配图与蛋白数据库进行匹配,得到每个肽的准确氨基酸序列。在抗菌肽数据库(APD3)中进行同源性对比分析,筛选推断出七种潜在具有抑菌活性的杏仁活性肽,分别是ALPDEVLQNAFRIS、ESWNPRDPQFQWAGVA、VAYWSYNNGEQPLVA、FLDLSNDQNQLDQVPR、GENDNRNQIIRVR、RNLQGENDNRNQIIRVR、RALPDEVLQNAFRIS。
抑菌活性的研究是对对苦杏仁活性肽功能特性的进一步完善,有利于扩大苦杏仁蛋白的应用,对杏仁资源的深度开发也具有一定的指导意义。在面临耐药性和筛选新的抗生素较为困难的如今,杏仁抑菌肽的研究对培育新一代的抗菌药物注入新的动力,提供新的思路,具有较大的市场及应用潜力。
-
表 1 不同蛋白酶适宜酶解条件
Table 1 Suitable enzymatic conditions for different proteases
蛋白酶种类 加酶量(U/g) 底物比(%) pH 温度(℃) 时间(h) 碱性蛋白酶 5000 4.0 9.0 55 4 酸性蛋白酶 5000 4.0 3.5 40 4 中性蛋白酶 5000 4.0 7.0 55 4 复合蛋白酶 5000 4.0 7.0 50 4 胰蛋白酶 5000 4.0 7.0 40 4 木瓜蛋白酶 5000 4.0 7.5 60 4 表 2 Plackett-Burman试验设计因素及水平
Table 2 Factors and levels of Plackett-Burman test
水平 因素 A-时间(h) B-pH C-酶底比(%) D-酶解温度(℃) E-底物比(%) −1 3 6.5 1 60 2 1 5 8.5 3 80 4 表 3 响应面试验因素水平设计
Table 3 Factors and levels of response surface test
因子 水平 −1 0 1 A-温度(℃) 60 70 80 B-酶底比(%) 2 3 4 C-pH 6.5 7.5 8.5 表 4 不同蛋白酶酶解物的抑菌活性
Table 4 Antibacterial activities of different protease hydrolysates
蛋白酶种类 革兰氏阳性菌 革兰氏阴性菌 空白对照 枯草芽孢杆菌 金黄色葡萄球菌 大肠杆菌 沙门氏菌 碱性蛋白酶 − − − + − 酸性蛋白酶 + ++ − − − 中性蛋白酶 − − + − − 复合蛋白酶 − − − + − 胰蛋白酶 − − − + − 木瓜蛋白酶 ++ ++ − − − 注:“−”表示无抑菌圈,“+”表示有抑菌圈但直径≤8.0 mm,“++”表示有抑菌圈但直径>8.0 mm。 表 5 Plackett-Burman模型方差分析
Table 5 Analysis of variance of Plackett-Burman model
项目 平方和 Df 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 309.37 5 61.87 12.74 0.0038 ** A-时间 10.79 1 10.79 2.22 0.1866 B-pH 54.87 1 54.87 11.3 0.0152 * C-酶底比 151.51 1 151.51 31.2 0.0014 ** D-温度 91.3 1 91.3 18.8 0.0049 ** E-底物比 0.9 1 0.9 0.18 0.6825 残差 29.14 6 4.86 总和 338.51 11 R2=0.9139 R2Adj=0.8422 注:**表示P<0.01,*表示P<0.05。 表 6 二次响应面回归模型方差分析
Table 6 ANOVA for response surface quadratic model analysis of variance table
方差来源 平方和 Df 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 12.62 9 1.40 8.14 0.0163 * A-温度 1.77 1 1.77 10.24 0.0240 * B-酶底比 1.42 1 1.42 8.24 0.0350 * C-pH 5.73 1 5.73 33.21 0.0022 ** AB 0.20 1 0.20 1.15 0.3330 AC 0.013 1 0.013 0.077 0.7930 BC 0.48 1 0.48 2.76 0.1575 A2 1.49 1 1.49 8.65 0.0322 * B2 0.71 1 0.71 4.11 0.0984 C2 1.28 1 1.28 7.41 0.0417 * 残差 0.86 5 0.17 失拟项 0.19 3 0.063 0.19 0.8970 误差 0.67 2 0.34 总和 13.50 14 R2=0.9361 R2Adj=0.8211 R2Pre=0.6632 注:**表示P<0.01,*表示P<0.05。 表 7 不同浓度的苦杏仁抑菌肽对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制效果
Table 7 Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of bitter almond antibacterial peptide on Staphylococcus aureus
苦杏仁抑菌肽质量浓度(mg/mL) 抑菌圈直径(mm) 100 22.19±0.55 50 18.11±0.45 25 15.52±0.67 12.5 13.19±0.84 6.25 10.39±0.57 3.13 8.19±0.81 1.56 6.25±0.68 表 8 LC–MS/MS鉴定组分A-Ⅱ-b抑菌肽段
Table 8 Antimicrobial peptides identified by LC-MS/MS from A-II-a fraction
肽段序列 肽段长度 肽段分子量 留存时间(min) 电荷数 疏水率(%) 同类肽 相似率(%) ALPDEVLQNAFRIS 14 1571.8308 54.583 −1 50 AP02858 40 ESWNPRDPQFQWAGVA 16 1886.87 51.562 −1 38 AP01233 38.89 VAYWSYNNGEQPLVA 15 1709.8049 51.35 −1 40 AP03430 35.29 FLDLSNDQNQLDQVPR 16 1900.9279 48.447 −2 31 AP01899 35.29 GENDNRNQIIRVR 13 1582.8288 16.668 +1 23 AP00344 38.1 RNLQGENDNRNQIIRVR 17 2094.1155 17.997 +2 24 AP00008 38.89 RALPDEVLQNAFRIS 15 1727.9319 50.787 0 47 AP02858 40 -
[1] LLOYD N C, MORGAN H W, NICHOLSON B K, et al. The composition of Ehrlich's Salvarsan:resolution of a century-old debate[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2005,44(6):941−944. doi: 10.1002/anie.200461471
[2] FALAGAS M E, KASIAKOU S K. Toxicity of polymyxins:A systematic review of the evidence from old and recent studies[J]. Critical Care,2006,10(1):43−69.
[3] KAYE D. FDA Updates warnings for fluoroquinolone antibiotics on risks of mental health and low blood sugar adverse reactions[J]. Clinical Infectious Diseases,2018(8):67−86.
[4] 宋伟光. 棉籽蛋白抗菌肽分离鉴定, 构效关系研究以及中试规模制备[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2020. [SONG W G. Separation and identification of antimicrobial peptide from cottonseed protein, study of conformational relationship and pilot scale preparation[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2020.] SONG W G. Separation and identification of antimicrobial peptide from cottonseed protein, study of conformational relationship and pilot scale preparation[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2020.
[5] BARDAN A, NIZET V, GALLO R L, et al. Antimicrobial peptides and the skin[J]. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy,2004,4(4):543−549. doi: 10.1517/14712598.4.4.543
[6] ZHANG Z X , LI P Y , ZHENG X Y , et al. Research progress of plant antimicrobial peptides[J]. Research on Microenvironment and Microecology,2022,4(1):24−27.
[7] CHOUDHURY A, ORTIZ P, CM K. In vitro inhibition of H. pylori in a preferential manner using bioengineered L. lactis releasing guided Antimicrobial peptides[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory,2021,1(1):44−52.
[8] YEAMAN M R, YOUNT N Y. Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance[J]. Pharmacological Reviews,2003,55(1):27−55. doi: 10.1124/pr.55.1.2
[9] REDDY K V, YEDERY R D, ARANHA C. Antimicrobial peptides:Premises and promises[J]. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents,2004,24(6):536−547. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2004.09.005
[10] ANJA P , KLAUS B , WEINDL G. Antimicrobial peptides and their therapeutic potential for bacterial skin infections and Wounds[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2018, 9(6):268−281.
[11] 张加延, 何跃. 我国"三北"杏树产业带的发展现状[C]//全国李杏资源研究与利用学术研讨会. 北京:中国园艺学会, 2007(1):33-35. [ZHANG J Y, HE Y. Development status of the apricot industry zone in China's "Three Norths"[C]//National symposium on research and utilization of plum and apricot resources. Beijing:Chinese Horticultural Society, 2007(1):33-35.] ZHANG J Y, HE Y. Development status of the apricot industry zone in China's "Three Norths"[C]//National symposium on research and utilization of plum and apricot resources. Beijing: Chinese Horticultural Society, 2007(1): 33-35.
[12] 靳本太, 张怡, 张爱萍. 库车市小白杏产业的文献综述研究[J]. 中国市场,2023,4(13):66−69. [JIN B T, ZHANG Y, ZHANG A P. Literature review study on the small white apricot industry in Kucha City[J]. China Market,2023,4(13):66−69.] JIN B T, ZHANG Y, ZHANG A P. Literature review study on the small white apricot industry in Kucha City[J]. China Market, 2023, 4(13): 66−69.
[13] CHAHIBAKHSH N, HOSSEINI E, LSLAM M S, et al. Bitter almond gum reduces body mass index, serum triglyceride, hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance in overweight subjects with hyperlipidemia[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2019,55(7):343−351.
[14] WANG S, ZENG X F, YANG Q, et al. Antimicrobial Peptides as potential alternatives to antibiotics in food animal industry[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2016,17(5):603. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050603
[15] CAI S Y, SHI J Y, LUO T J. Study on the underlying mechanism of almond and platycodon in treating acute bronchitis based on network pharmacology[J]. Journal of Hainan Medical College: English Edition,2021,27(4):51−57.
[16] KLIMASZEWSKA A O M. Application of newly synthesized sulfobetaine based on sweet almond oil in bath liquids for sensitive skin[J]. Tenside Surfactants Detergents:Journal for Theory, Technology and Application of Surfactants, 2021, 58(2):106-113.
[17] WILLIAMS R J, SPENCER J P E, RICE-EVANS C. Flavonoids:Antioxidants or signaling molecules[J]. Free Radic Biol Med,2004,36(7):838−849.
[18] 崔海燕, 张霞, 贾晓艳, 等. 高速逆流色谱法分离纯化山楂中的多酚类化合物[C]//西安:陕西药物分析学术研讨会,2009:205−210. [CUI H Y, ZHANG X, JIA X Y, et al. Separation and purification of polyphenols in hawthorn by high-speed countercurrent chromatography[C]//Xi'an:Shaanxi Symposium on Pharmaceutical Analysis,2009:205−210.] CUI H Y, ZHANG X, JIA X Y, et al. Separation and purification of polyphenols in hawthorn by high-speed countercurrent chromatography[C]//Xi'an: Shaanxi Symposium on Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2009: 205−210.
[19] SALIH A A, ZEID A N, RAYA R J, et al. Antibacterial activity of apricot kernel extract containing amygdalin[J]. Agricultural and Food Sciences,2010,51(4):571-576.
[20] 王丽芳, 叶良, 谢忠稳, 等. 茶叶抗菌肽粗提物的抑菌活性及其对冷却肉保鲜的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报,2022,34(10):2268−2276. [WANG L F, YE L, XIE Z W, et al. Antibacterial activity of tea antimicrobial peptide crude extract and its effect on the preservation of chilled meat[J]. Zhejiang Agricultural Journal,2022,34(10):2268−2276.] WANG L F, YE L, XIE Z W, et al. Antibacterial activity of tea antimicrobial peptide crude extract and its effect on the preservation of chilled meat[J]. Zhejiang Agricultural Journal, 2022, 34(10): 2268−2276.
[21] 刘东伟, 袁玮琼, 柳梅, 等. 核桃粕蛋白抑菌肽的制备工艺及纯化[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(2):185−191. [LIU D W, YUAN W Q, LIU M, et al. Preparation and purification of antibacterial peptide from walnut meal protein[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2021,42(2):185−191.] LIU D W, YUAN W Q, LIU M, et al. Preparation and purification of antibacterial peptide from walnut meal protein[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2021, 42(2): 185−191.
[22] 张爱莉, 曹丙林, 张良, 等. 苦杏仁多肽的制备及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 许昌学院学报,2022,41(5):45−49. [ZHANG A L, CAO B L, ZHANG L, et al. Preparation of bitter almond polypeptides and their antioxidant activity[J]. Journal of Xuchang College,2022,41(5):45−49.] ZHANG A L, CAO B L, ZHANG L, et al. Preparation of bitter almond polypeptides and their antioxidant activity[J]. Journal of Xuchang College, 2022, 41(5): 45−49.
[23] 薛蕾, 李大文, 尉芹, 等. 苦杏仁蛋白的功能特性[J]. 食品科学,2013,34(7):70−75. [XUE L, LI D W, YU Q, et al. Functional properties of bitter almond protein[J]. Food Science,2013,34(7):70−75.] XUE L, LI D W, YU Q, et al. Functional properties of bitter almond protein[J]. Food Science, 2013, 34(7): 70−75.
[24] 刘丽红, 雷清华. 茚三酮比色法与甲醛滴定法测定棉籽粕蛋白水解度的比较[J]. 化学工程与装备,2012(11):160−163. [LIU L H, LEI Q H. Comparison of ninhydrin colorimetric method and formaldehyde titration method for the determination of protein hydrolysis of cottonseed meal[J]. Chemical Engineering and Equipment,2012(11):160−163.] LIU L H, LEI Q H. Comparison of ninhydrin colorimetric method and formaldehyde titration method for the determination of protein hydrolysis of cottonseed meal[J]. Chemical Engineering and Equipment, 2012(11): 160−163.
[25] 李桂峰, 赵国建, 肖春玲, 等. 金针菇蛋白酶解制备抑菌肽的工艺优化及功能评价[J]. 中国食品学报,2012,12(10):107−112. [LI G F, ZHAO G J, XIAO C L, et al. Process optimization and functional evaluation of enzymatic preparation of antibacterial peptides from golden mushroom proteins[J]. Chinese Journal of Food,2012,12(10):107−112.] LI G F, ZHAO G J, XIAO C L, et al. Process optimization and functional evaluation of enzymatic preparation of antibacterial peptides from golden mushroom proteins[J]. Chinese Journal of Food, 2012, 12(10): 107−112.
[26] 张海霞, 包良. 紫色马铃薯花青素的抑菌性及其对草莓保鲜效果的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(24):293−298. [ZHANG H X, BAO L. Research on the antibacterial property of purple potato anthocyanins and its effect on strawberry preservation[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2021,42(24):293−298.] ZHANG H X, BAO L. Research on the antibacterial property of purple potato anthocyanins and its effect on strawberry preservation[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2021, 42(24): 293−298.
[27] 徐杨林, 严宏孟, 高蕾, 等. 苦杏仁醇溶蛋白酶解抗氧化肽的制备工艺优化[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(6):201−210. [XU Y L, YAN H M, GAO L, et al. Optimization of the preparation process of antioxidant peptide from bitter almond by enzymatic proteolysis[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(6):201−210.] XU Y L, YAN H M, GAO L, et al. Optimization of the preparation process of antioxidant peptide from bitter almond by enzymatic proteolysis[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2021, 37(6): 201−210.
[28] 胡二坤, 郭兴凤, 郑慧. 凝胶过滤色谱分离纯化鱼蛋白酶解产物[J]. 食品工业,2020,41(12):240−243. [HU E K, GUO X F, ZHENG H. Separation and purification of fish protein enzymatic products by gel filtration chromatography[J]. Food Industry,2020,41(12):240−243.] HU E K, GUO X F, ZHENG H. Separation and purification of fish protein enzymatic products by gel filtration chromatography[J]. Food Industry, 2020, 41(12): 240−243.
[29] 力俊琛. 鸽血抗氧化肽的分离、结构鉴定及体外抗氧化活性评价[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学, 2022. [LI J S. Isolation, structural characterization and in vitro evaluation of antioxidant peptides from pigeon blood[D]. Urumqi:Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2022.] LI J S. Isolation, structural characterization and in vitro evaluation of antioxidant peptides from pigeon blood[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2022.
[30] 段志强. 大豆肽的制备及其在食品中的应用[D]. 上海:华东师范大学, 2015. [DUAN Z Q. Preparation of soybean peptide and its application in food[D]. Shanghai:East China Normal University, 2015.] DUAN Z Q. Preparation of soybean peptide and its application in food[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2015.
[31] LI G H, LE G W, SHI Y H, et al. Angiotensin I–converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins and their physiological and pharmacological effects[J]. Nutrition Research,2004,24(7):469−486. doi: 10.1016/S0271-5317(04)00058-2
[32] 王全林, 刘志洪, 蔡汝秀, 等. 血红蛋白的过氧化物酶催化特性研究[J]. 化学学报,2003(1):34−39. [WANG Q L, LIU Z H, CAI R X, et al. Catalytic properties of hemoglobin by peroxidase[J]. Journal of Chemistry,2003(1):34−39.] WANG Q L, LIU Z H, CAI R X, et al. Catalytic properties of hemoglobin by peroxidase[J]. Journal of Chemistry, 2003(1): 34−39.
[33] 乔杨波, 庄蕾, 黄伟华, 等. 植物蛋白多肽的研究进展[J]. 中国调味品,2021,46(5):175−178. [QIAO Y B, ZHUANG L, HUANG W H, et al. Research progress of plant protein peptides[J]. China Seasoning,2021,46(5):175−178.] QIAO Y B, ZHUANG L, HUANG W H, et al. Research progress of plant protein peptides[J]. China Seasoning, 2021, 46(5): 175−178.
[34] 龚吉军, 李振华, 李忠海, 等. 响应曲面法优化油茶粕抗菌肽制备条件[J]. 中国食品学报,2012,12(9):137−143. [GONG J J, LI Z H, LI Z H, et al. Optimization of antibacterial peptide preparation conditions for oil tea meal by response surface method[J]. Chinese Journal of Food,2012,12(9):137−143.] GONG J J, LI Z H, LI Z H, et al. Optimization of antibacterial peptide preparation conditions for oil tea meal by response surface method[J]. Chinese Journal of Food, 2012, 12(9): 137−143.
[35] 苏治国. 伴大豆球蛋白抗菌肽的制备及其对鸭免疫功能的影响[D]. 扬州:扬州大学, 2009. [SU Z G. Preparation of antimicrobial peptide associated with soybean globulin and its effect on the immune function of ducks[D]. Yangzhou:Yangzhou University, 2009.] SU Z G. Preparation of antimicrobial peptide associated with soybean globulin and its effect on the immune function of ducks[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2009.
[36] 康媛媛, 孟珺, 王艳阳, 等. 抗菌肽功能特性与作用机制的研究进展[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(1):265−270. [KANG Y Y, MENG J, WANG Y Y, et al. Research progress of functional properties and mechanism of action of antimicrobial peptides[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(1):265−270.] KANG Y Y, MENG J, WANG Y Y, et al. Research progress of functional properties and mechanism of action of antimicrobial peptides[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2021, 46(1): 265−270.
[37] 于娜. 卵黄多肽的分离纯化及降血脂活性研究[D]. 沈阳:沈阳农业大学, 2012. [YU N. Isolation and purification of yolk peptide and its hypolipidemic activity[D]. Shenyang:Shenyang Agricultural University, 2012.] YU N. Isolation and purification of yolk peptide and its hypolipidemic activity[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2012.
[38] 段雨秀. 仿天然抗菌肽的抗菌聚谷氨酸类衍生物的合成及其构效关系[D]. 长春:东北师范大学, 2022. [DUAN Y X. Synthesis of antimicrobial polyglutamic acid derivatives mimicking natural antimicrobial peptides and their conformational relationships[D]. Changchun:Northeast Normal University, 2022.] DUAN Y X. Synthesis of antimicrobial polyglutamic acid derivatives mimicking natural antimicrobial peptides and their conformational relationships[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2022.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 张涛,周芷夷,邓文奇,张婷,马杰,王艺诺,于俊飞,周建中. 苦杏仁多肽/壳聚糖复合膜的制备及其对奶酪的保鲜效果. 食品与发酵工业. 2025(06): 232-238 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



