Comparative Analysis of Nutritional Components and Flavor Substances between Dali Yangpao and Purple Walnut Kernels
-
摘要: 为研究大理漾泡、紫皮核桃仁营养元素及风味物质的差异,以两种核桃仁为原料,分别测定其氨基酸、脂肪酸、基本营养素、矿物质元素含量,采用气相色谱质谱联用法(GC-MS)检测两种核桃仁之间的挥发性成分。结果表明,紫皮核桃仁总氨基酸、必需氨基酸和鲜味氨基酸含量分别高于漾泡核桃仁,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);两种核桃仁中均检出3种饱和脂肪酸,其中漾泡核桃仁的棕榈酸含量(4.17%)高于紫皮(2.69%);均检出5种不饱和脂肪酸,其中,紫皮核桃仁的油酸、花生一烯酸和亚麻酸含量均高于漾泡核桃仁(P<0.05),棕榈一烯酸和亚油酸含量低于漾泡核桃仁,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);紫皮核桃仁脂肪、蛋白质、碳水化合物含量均高于漾泡核桃(P<0.05);共检出9种矿物质元素,紫皮核桃中P、Zn、Fe、Cu、Na、K元素含量高于漾泡核桃(P<0.05);从漾泡、紫皮核桃仁中分别鉴定出30种、33种挥发性风味物质,其中醇类、醛类、酮类化合物是紫皮核桃的主要风味物质,而漾泡核桃的主要风味物质是醇类和烯烃类化合物(19.948%、3.819%)。两种核桃中醇类化合物峰面积占比最高,对气味贡献较大,尤其己醇峰面积占比最高,可赋予核桃淡青的嫩枝叶气息以及酒香、果香和脂肪气息。以上结果表明两种核桃都具有较高的营养价值,紫皮核桃略胜一筹。Abstract: The aim of study was to analyze the differences in nutritional elements and flavor substances between the Dali Yangpao and purple walnut kernels, two kinds of walnut kernels were used as raw materials, the content of amino acids, fatty acids, essential nutrients and mineral elements were determined separately, and the volatile components between the two walnut kernels were detected by gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The results showed that compared to those of the Yangpao walnut kernels, the purple walnut kernels had a higher content of total amino acid, essential amino acid, and umami amino acid (P<0.05). Three kinds of saturated fatty acids were detected in both walnut kernels, the palmitic acid content of Yangpao walnut kernels (4.17%) was higher than that of purple walnut kernels (2.69%). Five kinds of unsaturated fatty acids were detected in both walnut kernels, compared to those of the Yangpao walnut kernels, the purple walnut kernels had a higher content of oleic acid, arachidonic acid, and linolenic acid, but purple walnut kernels had a lower content of palmitoleic acid and linoleic acid (P<0.05). Compared to those of the Yangpao walnut kernels, the purple walnut kernels had a higher content of fat, protein, and carbohydrate (P<0.05). A total of 9 mineral elements were detected in both walnut kernels, and the P, Zn, Fe, Cu, Na, and K elements content of Yangpao walnut kernels was higher than those of purple walnut kernels (P<0.05). 30 and 33 volatile flavor compounds were identified from Yangpao and purple walnut kernels, respectively. Alcohols, aldehydes, and ketones were the main flavor substances of purple walnut, while Yangpao walnut's main flavor substances were alcohols and olefin compounds (19.948%, 3.819%). The peak area of alcohol compounds, especially hexanol, accounted for the highest proportion in Yangpao and purple walnut kernels, respectively. The above results indicate that purple walnut kernels have higher nutritional value and flavor substances.
-
Keywords:
- walnut kernel /
- amino acids /
- fatty acids /
- mineral elements /
- flavor substances
-
核桃(Juglans spp)又称为胡桃、宪果、羌桃,是胡桃科核桃属植物,是一种综合开发利用价值很高的木本油料树种及干果树种。我国是核桃种植面积及产量大国,物种资源丰富达380多种,广泛分布在20多个省份,主要集中在云南、四川、新疆、贵州等省份。由于云南地形地貌复杂、气候条件特殊、土壤类型多种多样,造成核桃种质资源丰富,品种繁多[1]。漾濞泡核桃仁色黄白、口感香醇,是云南省主栽良种。紫仁核桃属云南核桃晚实特异类群,因核仁皮色为紫色而得名,其核仁颜色特殊,是我国极其宝贵的核桃种质资源,可作为育种材料开发和利用[2]。
香味是影响食品质量和消费者感知的一个关键因素,不同品种的核桃会导致核桃仁的营养成分及相关性风味物质产生差异。目前关于云南核桃营养成分测定分析的研究较多,但鲜有结合核桃仁的挥发性风味物质研究核桃品质异同的研究。胡祥等[3]测定了云南核桃‘龙佳’的基本营养成分、脂肪、氨基酸含量;袁奖娟等[4]对云南三种有色泡核桃仁基本营养成分、矿物质元素、脂肪酸及多酚类物质进行了测定;耿树香等[5]对22个云南主栽品种核桃的蛋白质及脂肪的含量进行测定,刘娇等[6]对漾泡核桃的坚果品质比较进行综合评价。云南核桃的栽培品种较多,目前的报道尚未对大理漾泡、大理紫皮核桃的营养成分进行研究分析。本研究通过对大理漾泡、大理紫皮核桃的氨基酸、脂肪酸、矿物质含量及相关性风味物质进行测定分析,为大理核桃营养品质评价、综合开发利用、桃核的深加工利用以及产业发展提供一定的理论依据和市场竞争力。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与设备
漾泡核桃仁300 g、紫皮核桃仁300 g 均采自大理漾濞,选取核桃仁色泽金黄、肉质饱满、无霉变、无虫害、无杂质的果仁为实验材料;三氯乙酸、氯化钠、冰乙酸、盐酸、柠檬酸(分析纯) 四川西陇科学有限公司;18种氨基酸标准品(纯度≥99%) 购自美国Sanland公司;牛血清蛋白 上海蓝季科技发展有限公司
7890A高效气相色谱仪 美国安捷伦公司;Biochrom 30全自动氨基酸分析仪 宁波欧普仪器有限公司;KDY-9810型凯氏定氮仪 北京市通润源机电技术有限责任公司;Optima电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪 美国PE公司;UV 752N紫外-可见分光光度计 上海仪电分析仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 游离氨基酸含量测定
参考Li等[7]的方法并作适当修改。准确称取50 mg核桃样品,加入20 mL超纯水,匀浆,然后加入20 mL 5%的三氯乙酸溶液,充分混匀后于4 ℃静置12 h,过滤,取滤液定容至50 mL,摇匀后过0.22 µm滤膜,待氨基酸自动分析仪检测。
1.2.2 脂肪酸组成的测定
脂肪酸根据GB 5009.168-2016《食品中脂肪酸的测定》对核桃仁中的脂肪酸含量进行测定[8]。
1.2.3 核桃仁风味化合物测定
核桃仁风味化合物采用GC-MS测定。称取核桃仁5 g(精确到0.01 g),加入10 mL蒸馏水,研磨后过滤匀浆,制得样品溶液备用。取3.0 mL样品置于20 mL顶空瓶中,将老化后的50/30 μm CAR/PDMS/DVB萃取头插入样品瓶顶空部分,于60 ℃吸附30 min,吸附后的萃取头取出后插入气相色谱进样口,于250 ℃解吸3 min,同时启动仪器采集数据。
GC条件:进样口温度:265 ℃,载气流速:1.0 μL/min;程序升温:40 ℃保持2 min,以5 ℃/min升温至120 ℃,保持6 min,最后以10 ℃/min升温至25 ℃,保持6 min。
MS条件:放射电流,电子能量70 eV,离子温度200 ℃,传输线温度250 ℃,探测器电压:1000 V。
定性、定量方法:用气相色谱-质谱联用仪分析鉴定核桃样品溶液,得到总离子色谱图。经计算机NIST Library谱库检索,择相似度大于800的物质予以确认,按各组分峰面积进行数据分析处理。
1.2.4 主要营养物质及矿物质元素测定
碳水化合物含量测定:参照GB/T 10782-2006《食品中总糖含量测定》;蛋白质含量的测定:参照GB 5009.5-2016《食品中蛋白质的测定》[9];脂肪含量的测定:参照GB 5009.6-2016《食品中脂肪的测定》[10];灰分的测定:参照GB 5009.4-2016《食品中灰分的测定》;磷含量的测定:参照GB 5009.87-2016《食品中磷的测定》[11];锌含量的测定:参照 GB 5009.14-2016《食品中锌的测定》[12];铁含量的测定:参照GB 5009.90-2016《食品中铁的测定》[13];镁含量的测定:参照GB 5009.241-2017《食品中镁的测定》[14];钙含量的测定:参照GB 5009.92-2016《食品中钙含量的测定》[15];铜含量的测定:参照GB 5009.90-2016《食品中铜含量的测定》[16];钠、钾含量的测定:参照GB 5009.91-2017《食品中钾、钠的测定》[17]。
1.3 数据处理
所有试验重复三次,数据用平均值±标准差(±s)表示,采用SPSS软件进行方差分析,显著性水平为P<0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 漾泡、紫皮核桃仁的游离氨基酸组成分析
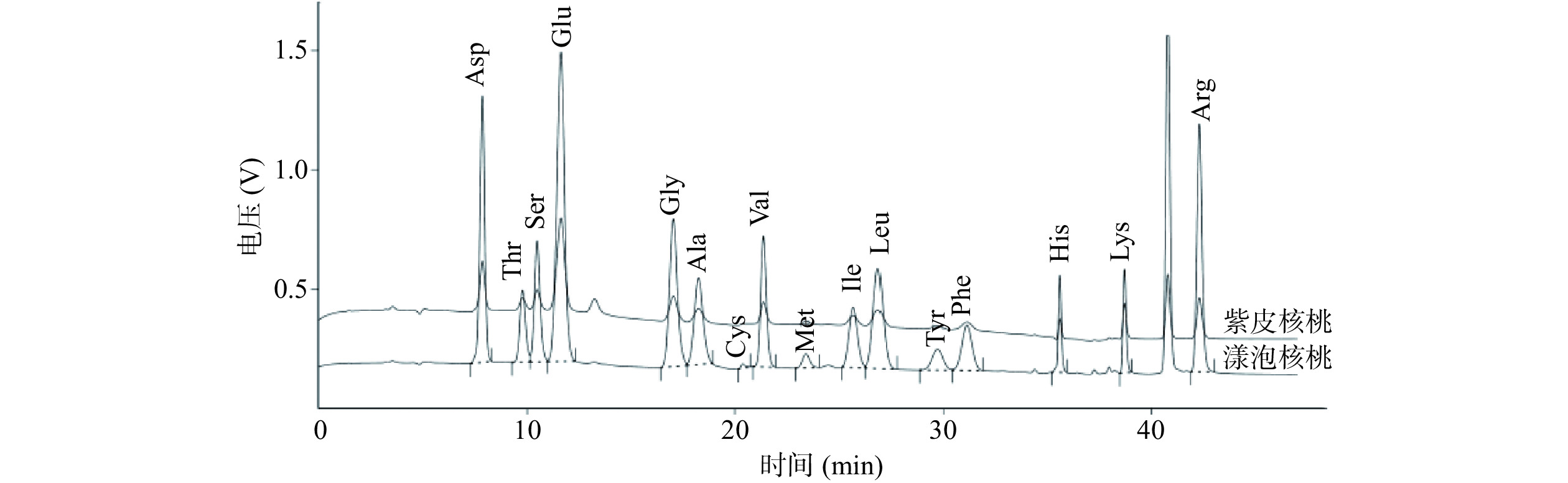
游离氨基酸的含量、组成及阈值共同决定了产品的滋味强度[18]。根据氨基酸不同的结构特性,主要将其分为鲜味、甜味和苦味氨基酸,呈味氨基酸含量越高可使呈味更加浓厚、丰富[19]。漾泡和紫皮核桃的17种游离氨基酸色谱图见图1,含量见表1。漾泡核桃仁中总游离氨基酸的含量(868.70 mg/kg)显著低于紫皮核桃仁(2471.30 mg/kg)(P<0.05)。两种核桃仁中都包含天冬氨酸、谷氨酸、甘氨酸和丙氨酸4种鲜味氨基酸[20],鲜味氨基酸的组成和含量的多少决定了核桃仁的鲜美程度,本研究中紫皮核桃仁的总鲜味氨基酸含量(948.30 mg/kg)显著高于漾泡核桃仁(540.22 mg/kg)(P<0.05)。紫皮核桃中谷氨酸含量(578.00 mg/kg)最高,其次是精氨酸(447.90 mg/kg)和丙氨酸(196.20 mg/kg);漾泡核桃谷氨酸含量(222.50 mg/kg)最高,其次为天门冬氨酸(113.36 mg/kg)、精氨酸(88.50 mg/kg)。紫皮核桃的四种鲜味氨基酸含量均显著高于漾泡核桃(P<0.05)。
表 1 核桃仁游离氨基酸含量(mg/kg)Table 1. Free amino acid content of walnut kernel (mg/kg)滋味描述 项目名称 样品名称 漾泡核桃 紫皮核桃 鲜味 Asp天门冬氨酸 113.36±0.42a 120.90±1.72b 甜味 *Thr苏氨酸 74.80±1.52a 183.30±0.59b 甜味 Ser丝氨酸 42.20±1.33a 151.30±0.86b 鲜味 Glu谷氨酸 222.50±1.90a 578.00±2.99b 鲜味 Gly甘氨酸 28.60±1.96a 53.20±1.68b 鲜味 Ala丙氨酸 62.40±1.34a 196.20±1.96b 甜味 Gys胱氨酸 32.10±0.30b 28.70±0.13a 苦味 *Val缬氨酸 39.00±1.99a 124.10±1.13b 甜味 *Mft蛋氨酸 15.70±0.56a 26.00±0.59b 苦味 *Ile异亮氨酸 16.00±0.36a 71.50±0.79b 苦味 *Leu亮氨酸 25.80±0.20a 116.70±2.07b 无味 Tyr酪氨酸 19.80±0.39a 80.30±0.59b 苦味 *Phe苯丙氨酸 22.10±0.25a 81.30±0.70b 甜味 His组氨酸 28.60±1.90a 97.40±1.70b 苦味 *Lys赖氨酸 16.40±0.25a 48.90±1.33b 苦味 Arg精氨酸 88.50±1.90a 447.90±3.55b 甜味 Pro脯氨酸 20.80±1.89a 65.60±0.92b − 必需氨基酸含量 209.80±1.89a 651.80±7.20b − 非必需氨基酸 657.50±5.23a 1707.90±0.59b − 鲜味氨基酸含量 540.22±5.62a 948.30±8.35b − 游离氨基酸总量(%) 868.70±18.46a 2471.30±23.30b 注:*表示该氨基酸为人体必需氨基酸;同一行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 根据FAO/WHO提出的标准,必需氨基酸与非必需氨基酸比值(EAA/NEAA)越接近FAO/WHO氨基酸模式要求60%左右时,说明该蛋白质营养价值越高[21]。漾泡、紫皮核桃仁中FAO/WHO值分别为31.90%、38.16%,2种核桃与FAO/WHO标准值有一定的差距,但紫皮核桃高于漾泡核桃,由此表明紫皮核桃蛋白质营养价值高于漾泡核桃。
2.2 漾泡、紫皮核桃仁脂肪酸组成及含量
表2可见,漾泡、紫皮核桃仁中均检出8种脂肪酸,包括3种饱和脂肪酸和5种不饱和脂肪酸。漾泡、紫皮核桃仁饱和脂肪酸中棕榈酸含量最高(4.17%、2.69%),硬脂酸次之(1.32%、1.12%),花生酸含量最低(0.04325%、0.0386%),漾泡核桃仁的棕榈酸含量高于紫皮(P<0.05)。不饱和脂肪酸5种,单不饱和脂肪酸3种,包括棕榈一烯酸(0.0911%、0.0389%)、油酸(16.10%、21.40%)、花生一烯酸(0.0711%、0.0793%),紫皮核桃仁的油酸、花生一烯酸含量高于漾泡核桃仁(P<0.05),棕榈一烯酸含量低于漾泡核桃仁(P<0.05);多不饱和脂肪酸2种,亚油酸(37.00%、27.80%)、亚麻酸(4.00%、5.58%),漾泡核桃仁亚油酸含量高于紫皮核桃仁(P<0.05),亚麻酸含量低于紫皮核桃仁(P<0.05)。
表 2 核桃仁脂肪酸组成(%)Table 2. Fatty acid composition of walnut kernel (%)脂肪酸组成 漾泡核桃 紫皮核桃 棕榈酸C16:0 4.17±0.25a 2.69±0.09b 硬脂酸C18:0 1.32±0.13a 1.12±0.24a 花生酸C20:0 0.0435±0.003a 0.0386±0.002a 饱和脂肪酸含量(SFA) 5.53±0.37a 3.84±0.30b 棕榈一烯酸C16:1 0.0911±0.01a 0.0389±0.002b 油酸C18:1 16.10±0.21b 21.40±0.24a 花生一烯酸C20:1 0.0711±0.001b 0.0793±0.002a 单不饱和脂肪酸含量(MUFA) 16.26±0.22b 21.51±0.24a 亚油酸C18:2 37.00±0.24a 27.80±0.18b 亚麻酸C18:3 4.00±0.12b 5.58±0.05a 多不饱和脂肪酸含量(PUFA) 41.00±0.13a 33.38±0.12b 脂肪酸总含量 62.79±0.27a 58.75±0.40b 注:同一行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 多不饱和脂肪酸与饱和脂肪酸相对含量的比值是判定脂肪酸性质的一个重要指标,当其值>2时,表明植物的油脂具有降血脂功能,其值越大降血脂功能越强[22−23]。本研究中漾泡、紫皮核桃仁的多不饱和脂肪酸/饱和脂肪酸的值分别为7.41、8.67,漾泡核桃仁低于紫皮,说明紫皮核桃仁油脂降血脂的能力高于漾泡核桃仁,与李瑞等[24]报道的云南17种核桃仁相比其值接近甚至高于个别品种。
2.3 漾泡、紫皮核桃仁主要营养物质及矿物质元素分析
营养物质对于维持人体生命健康和生命活动具有重要意义,由表3可知漾泡、紫皮两种核桃仁富含脂肪(68.4、69.7 g/100 g)、蛋白质(19.5、23.1 g/100 g)、碳水化合物(7.4、9.2 g/100 g)三大产能营养素,其中紫皮核桃仁的蛋白质和碳水化合物含量均高于漾泡核桃仁(P<0.05)。核桃蛋白是优质蛋白,本研究中漾泡、紫皮核桃仁蛋白质含量均高于耿香树等[5]研究中的22种核桃蛋白质含量。此外,漾泡核桃仁中灰分含量高于紫皮核桃仁,可能与核桃种植地环境、气候等众多因素有关。
表 3 核桃仁的主要营养成分及矿物质元素含量测定Table 3. Determination of main nutrients and mineral element content of walnut kernel项目名称 样品名称 漾泡核桃 紫皮核桃 碳水化合物(g/100 g) 7.40±0.07a 9.20±0.04b 蛋白质(g/100 g) 19.50±0.28a 23.10±0.17b 脂肪(g/100 g) 68.40±0.28a 69.70±0.28a 灰分(g/100 g) 3.10±0.08b 2.70±0.10a 磷P(mg/kg) 4460±4.04a 4590±2.96b 锌Zn(mg/kg) 21.20±0.26a 34.40±0.34b 铁Fe(mg/kg) 23.80±0.06a 26.60±0.47b 镁Mg(mg/kg) 1760±4.33b 1700±13.74a 钙Ca(mg/kg) 855±3.52b 671±3.60a 铜Cu(mg/kg) 16.80±0.20a 20.50±0.29b 钠Na(mg/kg) 1.65±0.01a 2.33±0.05b 钾K(mg/kg) 1280±2.51a 2140±6.33b 矿物质元素总含量(mg/kg) 8418.45±6.01a 9184.83±20.60b 注:同一行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 矿物质元素是维持机体生理活动不可或缺的营养元素,人体不能自身合成,需要从外界获取[25]。由于核桃仁富含丰富的矿物质元素,可作为人们摄取矿物质元素的重要来源。由表3可知,紫皮核桃仁中P、Zn、Fe、Cu、Na、K元素含量均高于漾泡核桃(P<0.05),Mg、Ca元素含量均低于漾泡核桃仁。
2.4 漾泡、紫皮核桃仁挥发性成分的GC-MS测定结果
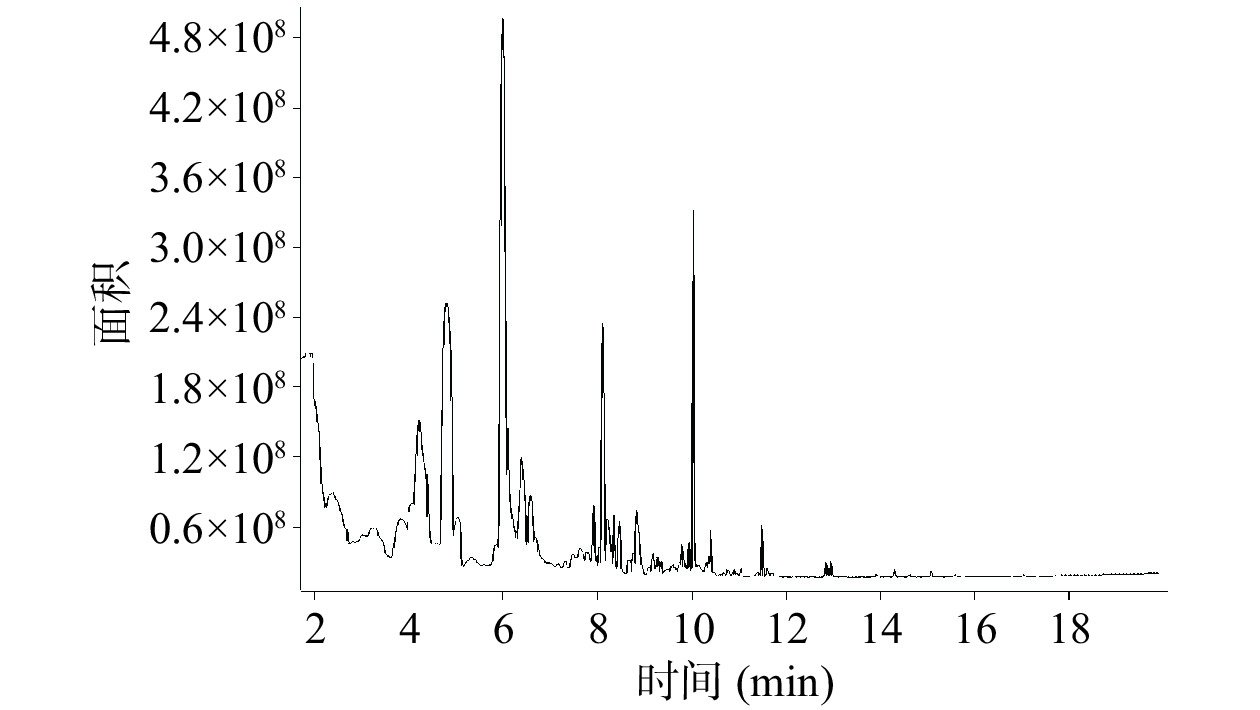
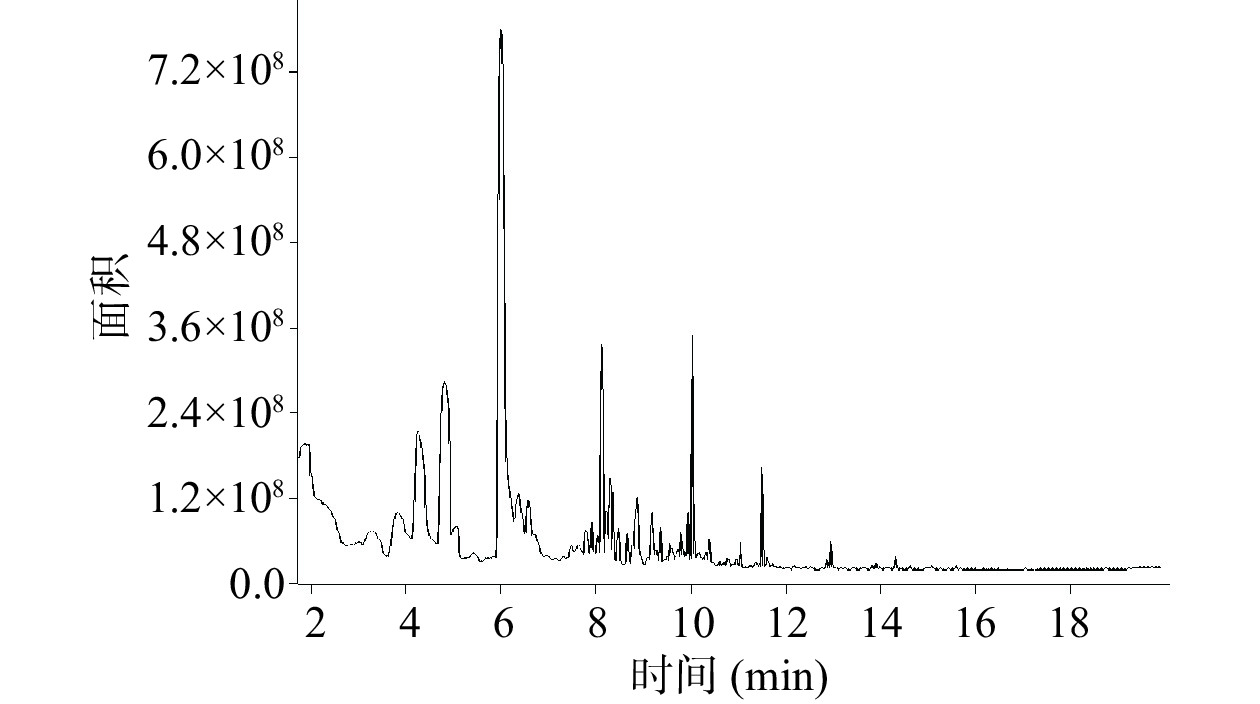
按照GC-MS法的条件试验,对核桃样品溶液顶空收集物质进行了GC-MS分析,图2、图3为漾泡、紫皮核桃总离子色谱图,通过计算机检索和人工解析,扣除由萃取头带来的硅氧烷类杂质峰,对漾泡、紫皮核桃仁的30种、33种化合物进行分析。
由表4可得,漾泡核桃仁中检测出29种挥发性风味成分,主要包括:醇类2种(19.93%)、烯烃类11种(5.08%)、醛类4种(4.11%)、酯类3种(2.25%)、酮类4种(1.43%)、酸类1种(0.31%)芳香烃类5种(0.225%),紫皮核桃仁中共检测出32种挥发性风味成分,主要包括醇类2种(27.36%)、醛类8种(17.33%)、酮类7种(8.69%)、酯类8种(2.67%)、烯烃类5种(0.853%)、酸类1种(0.10%)、芳香烃类1种(0.057%),两种核桃仁在挥发性风味成分的种类及峰面积占比上均有着明显的差异。
表 4 漾泡、紫皮核桃仁挥发性风味化合物Table 4. Volatile flavor compounds of the Yangpao, purple walnut kernels分类 化合物 分子式 CAS 风味[26] 保留时间(min) 漾泡核桃 保留时间(min) 紫皮核桃 相似度 峰面积(%) 相似度 峰面积(%) 脂类化合物 月桂酸甲酯 C8H10 111-82-0 酒香的香气 − − − 5.85848 952 0.066 乙酸丁酯 C7H14O2 590-01-2 果香、甜香、香蕉、热带和热带水果 − − -- 6.68375 916 1.495 己酸甲酯 C7H14O2 106-70-7 果味脂肪 − − − 6.9629 808 0.117 丁酸丁酯 C8H16O2 109-21-7 有苹果香味 8.21051 937 2.206 8.2107 942 0.875 辛酸乙酯 C10H20O2 106-32-1 类似白兰地的香气,并有甜味 − − − 11.4197 849 0.057 丙位辛内酯 C8H14O2 104-50-7 呈桃、椰子似甜果香气和燕麦面包香味 − − − 12.3547 868 0.026 丙酸香叶酯 C13H22O2 105-90-8 呈甜葡萄和玫瑰似香甜气 7.9566 903 0.039 − − − 元氰菊酯 C12H10 92-52-4 略带甜味 14.1709 844 0.001 − − − 己酸戊酯 C11H22O2 540-07-8 呈香蕉和菠萝似香气 − − − 12.7588 911 0.016 甘油二乙酸酯 C7H12O5 25395-31-7 非常轻微的酒精味 − − − 13.4425 891 0.017 醛类化合物 糠醛 C5H4O2 98-01-1 有杏仁的气味 5.3687 823 0.498 − − − 己醛 C5H12O 66-25-1 苹果香气 − − − 4.8031 819 11.471 庚醛 C7H14O 111-71-7 杏仁、坚果香气 − − − 6.5774 940 2.145 (E)-2庚烯醛 C7H12O 18829-55-5 强烈的绿色、甜、新鲜的果味 − − − 7.5604 846 0.098 (E)-2-辛烯醛 C8H14O 2548-87-0 甜绿色柑橘皮、辛辣黄瓜
油性脂肪性9.2872 890 0.237 9.2885 852 0.244 正辛醛 C8H16O 124-13-0 绿色,带有淡淡的柑橘味 8.3585 960 0.659 8.3594 968 0.989 壬醛 C9H18O 124-19-6 有油脂气味、甜橙气息 10.0344 959 2.656 10.0351 957 2.253 癸醛 C10H20O 112-31-2 香气青辛微甜,有似甜橙油与柠檬油以及玫瑰样和蜡香的后韵 11.6008 952 0.062 11.6005 957 0.114 月桂醛 C12H24O 112-54-9 带有甜的花香和柑橘香气 − − − 14.4403 754 0.011 醇类化合物 己醇 C6H14O 111-27-3 有淡青的嫩枝叶气息,微带酒香、果香和脂肪气息 7.0285 956 19.905 6.0012 956 27.355 月桂醇 C12H26O 112-53-8 具有弱而持久的油脂气味、花香味 − − − 12.8298 813 0.006 2-乙基1-丁醇 C6H14O 97-95-0 有淡青的嫩枝叶气息,微带酒香、果香和脂肪气息 10.4783 844 0.024 − − − 酮类化合物 2-庚酮 C7H14O 110-43-0 类似香蕉的香气及轻微的药香气味 6.3498 936 0.830 6.3488 944 3.955 甲基庚烯酮 C8H14O 110-93-0 具有水果香气和绿色植物香气 8.0314 866 0.239 8.0325 837 0.292 辛酮 C8H16O 106-68-3 蘑菇、干酪和发霉果味 − − − 8.0446 899 0.398 2-辛酮 C8H16O 111-13-7 苹果香气 − − − 8.1185 874 3.647 苯乙酮 C8H8O 98-86-2 呈强烈金合欢似甜香气 − − − 9.4473 930 0.057 壬酮 C9H18O 821-55-6 呈水果、花、油脂和药草似香气 9.7985 935 0.255 9.7988 931 0.336 烟叶酮 C13H18O 13215-88-8 烟草辣味 − − − 16.6233 800 0.005 异佛尔酮 C9H14O 78-59-1 有薄荷香味 10.357 938 0.107 − − − 酸类化合物 戊酸 C5H10O2 109-52-4 具有难闻的臭袜子气味 7.8143 855 0.314 7.8333 825 0.103 烯烃类化合物 苯乙烯 C8H8 100-42-5 甜的芭蕉花;塑料气味 6.4115 815 4.098 − − − 枯稀 C9H12 98-82-8 特色的芳香性气味 − − − 7.9456 935 0.094 α-蒎烯 C10H16 80-56-8 强烈的木质和松质气味 7.1704 884 0.073 − − − 2-莰烯 C10H16 464-17-5 樟脑香气 − − − 7.1704 941 0.655 3-蒈烯 C10H16 13466-78-9 松木气息 8.4825 903 0.560 − − − γ-萜烯 C10H16 99-85-4 具有柑橘和柠檬香气 9.3060 812 0.051 − − − 对α-二甲基苯乙烯 C10H12 1195-32-0 辛辣,香辣气味 9.8394 897 0.007 − − − α-铜烯 C15H24 3856-25-5 − 14.1046 809 0.006 − − − 桧烯 C15H24 475-20-7 具有木香及似鸢尾香气 14.6268 915 0.024 − − − α-蒎烯 C15H22 644-30-4 木质雪松,鲜香 15.4154 906 0.010 14.1495 924 0.013 β-红没药烯 C15H24 495-61-4 具有温暖的木香、柑橘香、花香、果香、青香,和甜润的香脂香气 15.7474 876 0.013 − − − P-伞花烃 C10H14 535-77-3 − − − − 9.6355 893 0.079 长叶环烯 C15H24 1137-12-8 − − − − 14.627 877 0.012 芳香烃类
化合物萘 C10H8 91-20-3 辛辣、焦油味 11.4033 968 0.056 11.4033 955 0.057 1,2,4,5-四甲
基苯C10H14 95-93-2 − 10.2561 862 0.136 − − − 1,2-二甲氧
基-苯C8H10O2 91-16-7 甜奶油香草酚类 10.6396 823 0.001 − − − 1-甲基萘 C11H10 90-12-0 类似萘的气味 13.0343 938 0.010 − − − 对二甲基苯
二酚C8H10O2 150-78-7 呈甜苜蓿似香气和酚味 10.9735 859 0.022 − − − 注:“−”表示未检出;相对峰面积<0.01%未列入表中。 对不同种类的风味物质进行分析:醇类化合物前体物质为多不饱和脂肪酸,可与某些酸形成酯类物质,因此可赋予油脂清新的花草香气[27]。本试验检测到漾泡、紫皮核桃仁的醇类化合物峰面积占比最大,其中己醇含量最高,分别占19.91%、27.35%,己醇可赋予核桃淡青的嫩枝叶气息、酒香、果香和脂肪气息;醛类化合物主要来自于油脂的氧化,具有脂肪香味[28]。紫皮核桃中醛类化合物组成丰富且峰面积占比大,为7种(17.08%),漾泡中4种(3.82%)。己醛(苹果香气)、庚醛(坚果香气)、(E)-2-庚烯醛(鲜甜的果味)、月桂醛(带有甜的花香和柑橘香气)在紫皮核桃仁中检出,是紫皮核桃的主要特征性风味;多数的酮类物质具有独特的清香、奶油香味或果香气味,能使食物整体风味更加饱满[29]。
紫皮核桃仁中酮类物质的种类及峰面积均高于漾泡核桃仁,分别为7种(8.69%)、4种(1.43%),辛酮、2-辛酮、苯乙酮、异佛尔酮在紫皮核桃仁中存在,其中2-辛酮含量较高能赋予核桃仁苹果香气;烯烃类化合物气味强烈,呈味阈值也较低,大多具有辛香、木香、柑橘香、樟脑香、柠檬香及热带果香等香气。紫皮核桃仁中检测到的烯烃类物质只有P-伞花烃、长叶环烯、2-莰烯、枯稀四种,而漾泡核桃仁中烯烃类化合物组成较为丰富有7种(1.15%);酯类化合物一般具有酒香、花香和典型的水果香气,是很重要的呈香物质,通常是由脂质代谢或酸类及醇类物质的酯化反应生成[30]。两种核桃仁的酯类化合物峰面积接近,但所含种类差异较大,大理紫皮8种(2.67%)、漾泡3种(2.25%),月桂酸甲酯、乙酸丁酯、己酸甲酯、辛酸乙酯、丙位辛内酯、己酸戊酯、甘油二乙酸酯等在紫皮核桃仁中检出,能赋予紫皮核桃仁果香、酒香及脂肪的香气;芳香烃类化合物主要来源于脂肪酸烷氧自由基的均裂,但由于其阈值普遍较高[31]。在漾泡、紫皮核桃仁总峰面积中占比较小,分别为(0.22%、0.057%)可认为对核桃的风味贡献较小。
3. 讨论与结论
通过对大理紫皮、漾泡两种核桃仁的基本营养成分及挥发性风味物质进行分析,可以得出两种核桃仁所含的氨基酸种类、矿物质元素、脂肪酸组成一致,但在含量方面两者存在较大差异,紫皮核桃仁的游离氨基酸、蛋白质、碳水化合物、矿物质元素含量(2471.3 mg/kg、23.1 g/100 g、9.2 g/100 g、9184.83 mg/kg)高于漾泡核桃仁(868.7 mg/kg、19.5 g/100 g、7.4 g/100 g、8418.45 mg/kg)(P<0.05),鲜味氨基酸的组成和含量的多少决定了核桃仁的鲜美程度,紫皮核桃仁鲜味氨基酸含量(948.30 mg/kg)显著(P<0.05)高于漾泡核桃仁(540.22 mg/kg);漾泡、紫皮核桃仁的蛋白质含量(19.5、23.1 g/100 g)、碳水化合物(7.4、9.2 g/100 g)高于苏为耿等[32]报道的龙佳、香宁、胜霜、漾濞等品种中的含量,两种核桃仁蛋白含量较高可考虑将其做成蛋白饮品。
脂肪酸的组成及含量是衡量核桃仁品质和营养价值的重要指标,其中不饱和脂肪酸对风味物质的产生有很大的影响,对人体健康也有重要影响,在本试验结果中,漾泡和紫皮核桃仁不饱和脂肪酸占比为(41.00%、33.38%),不饱和脂肪酸中油酸含量(16.1%、21.4%)、亚油酸含量(37.00%、27.80%)、亚麻酸含量(4.00%、5.58%),与耿树香等[4]报道的云南主栽的40种核桃脂肪酸含量存在一定差异,可能是由于核桃的种植地域、环境气候及果实成熟度、存储条件等差异造成脂肪酸含量的不同。
从大理漾泡、紫皮核桃仁中分别鉴定出29、32种挥发性风味物质,两种核桃仁中有共同的香气成分(丁酸丁酯、(E)-2辛烯醛、正辛醛、壬醛、癸醛、2-庚酮、甲基庚烯酮、壬酮、己醇、戊酸、α-蒎烯、萘)能赋予核桃仁果香及油脂香气,己醛、庚醛、(E)-2-庚烯醛、月桂醛、2-辛酮、乙酸丁酯、2-莰烯是紫皮核桃仁的主要风味物质,赋予紫皮核桃仁甜的花果香气。糠醛、壬酮、苯乙烯、3-蒈烯、1,2,4,5-四甲基苯、1-甲基萘是漾泡核桃的主要风味物质,赋予漾泡核桃仁油脂、木质香及香辣气味。以上结果表明两种核桃都具有较高的营养价值,紫皮核桃略胜一筹。旨在通过本实验的测定,为大理的核桃营养价值,风味物质的研究提供一定的数据支持。
-
表 1 核桃仁游离氨基酸含量(mg/kg)
Table 1 Free amino acid content of walnut kernel (mg/kg)
滋味描述 项目名称 样品名称 漾泡核桃 紫皮核桃 鲜味 Asp天门冬氨酸 113.36±0.42a 120.90±1.72b 甜味 *Thr苏氨酸 74.80±1.52a 183.30±0.59b 甜味 Ser丝氨酸 42.20±1.33a 151.30±0.86b 鲜味 Glu谷氨酸 222.50±1.90a 578.00±2.99b 鲜味 Gly甘氨酸 28.60±1.96a 53.20±1.68b 鲜味 Ala丙氨酸 62.40±1.34a 196.20±1.96b 甜味 Gys胱氨酸 32.10±0.30b 28.70±0.13a 苦味 *Val缬氨酸 39.00±1.99a 124.10±1.13b 甜味 *Mft蛋氨酸 15.70±0.56a 26.00±0.59b 苦味 *Ile异亮氨酸 16.00±0.36a 71.50±0.79b 苦味 *Leu亮氨酸 25.80±0.20a 116.70±2.07b 无味 Tyr酪氨酸 19.80±0.39a 80.30±0.59b 苦味 *Phe苯丙氨酸 22.10±0.25a 81.30±0.70b 甜味 His组氨酸 28.60±1.90a 97.40±1.70b 苦味 *Lys赖氨酸 16.40±0.25a 48.90±1.33b 苦味 Arg精氨酸 88.50±1.90a 447.90±3.55b 甜味 Pro脯氨酸 20.80±1.89a 65.60±0.92b − 必需氨基酸含量 209.80±1.89a 651.80±7.20b − 非必需氨基酸 657.50±5.23a 1707.90±0.59b − 鲜味氨基酸含量 540.22±5.62a 948.30±8.35b − 游离氨基酸总量(%) 868.70±18.46a 2471.30±23.30b 注:*表示该氨基酸为人体必需氨基酸;同一行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 2 核桃仁脂肪酸组成(%)
Table 2 Fatty acid composition of walnut kernel (%)
脂肪酸组成 漾泡核桃 紫皮核桃 棕榈酸C16:0 4.17±0.25a 2.69±0.09b 硬脂酸C18:0 1.32±0.13a 1.12±0.24a 花生酸C20:0 0.0435±0.003a 0.0386±0.002a 饱和脂肪酸含量(SFA) 5.53±0.37a 3.84±0.30b 棕榈一烯酸C16:1 0.0911±0.01a 0.0389±0.002b 油酸C18:1 16.10±0.21b 21.40±0.24a 花生一烯酸C20:1 0.0711±0.001b 0.0793±0.002a 单不饱和脂肪酸含量(MUFA) 16.26±0.22b 21.51±0.24a 亚油酸C18:2 37.00±0.24a 27.80±0.18b 亚麻酸C18:3 4.00±0.12b 5.58±0.05a 多不饱和脂肪酸含量(PUFA) 41.00±0.13a 33.38±0.12b 脂肪酸总含量 62.79±0.27a 58.75±0.40b 注:同一行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 3 核桃仁的主要营养成分及矿物质元素含量测定
Table 3 Determination of main nutrients and mineral element content of walnut kernel
项目名称 样品名称 漾泡核桃 紫皮核桃 碳水化合物(g/100 g) 7.40±0.07a 9.20±0.04b 蛋白质(g/100 g) 19.50±0.28a 23.10±0.17b 脂肪(g/100 g) 68.40±0.28a 69.70±0.28a 灰分(g/100 g) 3.10±0.08b 2.70±0.10a 磷P(mg/kg) 4460±4.04a 4590±2.96b 锌Zn(mg/kg) 21.20±0.26a 34.40±0.34b 铁Fe(mg/kg) 23.80±0.06a 26.60±0.47b 镁Mg(mg/kg) 1760±4.33b 1700±13.74a 钙Ca(mg/kg) 855±3.52b 671±3.60a 铜Cu(mg/kg) 16.80±0.20a 20.50±0.29b 钠Na(mg/kg) 1.65±0.01a 2.33±0.05b 钾K(mg/kg) 1280±2.51a 2140±6.33b 矿物质元素总含量(mg/kg) 8418.45±6.01a 9184.83±20.60b 注:同一行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 4 漾泡、紫皮核桃仁挥发性风味化合物
Table 4 Volatile flavor compounds of the Yangpao, purple walnut kernels
分类 化合物 分子式 CAS 风味[26] 保留时间(min) 漾泡核桃 保留时间(min) 紫皮核桃 相似度 峰面积(%) 相似度 峰面积(%) 脂类化合物 月桂酸甲酯 C8H10 111-82-0 酒香的香气 − − − 5.85848 952 0.066 乙酸丁酯 C7H14O2 590-01-2 果香、甜香、香蕉、热带和热带水果 − − -- 6.68375 916 1.495 己酸甲酯 C7H14O2 106-70-7 果味脂肪 − − − 6.9629 808 0.117 丁酸丁酯 C8H16O2 109-21-7 有苹果香味 8.21051 937 2.206 8.2107 942 0.875 辛酸乙酯 C10H20O2 106-32-1 类似白兰地的香气,并有甜味 − − − 11.4197 849 0.057 丙位辛内酯 C8H14O2 104-50-7 呈桃、椰子似甜果香气和燕麦面包香味 − − − 12.3547 868 0.026 丙酸香叶酯 C13H22O2 105-90-8 呈甜葡萄和玫瑰似香甜气 7.9566 903 0.039 − − − 元氰菊酯 C12H10 92-52-4 略带甜味 14.1709 844 0.001 − − − 己酸戊酯 C11H22O2 540-07-8 呈香蕉和菠萝似香气 − − − 12.7588 911 0.016 甘油二乙酸酯 C7H12O5 25395-31-7 非常轻微的酒精味 − − − 13.4425 891 0.017 醛类化合物 糠醛 C5H4O2 98-01-1 有杏仁的气味 5.3687 823 0.498 − − − 己醛 C5H12O 66-25-1 苹果香气 − − − 4.8031 819 11.471 庚醛 C7H14O 111-71-7 杏仁、坚果香气 − − − 6.5774 940 2.145 (E)-2庚烯醛 C7H12O 18829-55-5 强烈的绿色、甜、新鲜的果味 − − − 7.5604 846 0.098 (E)-2-辛烯醛 C8H14O 2548-87-0 甜绿色柑橘皮、辛辣黄瓜
油性脂肪性9.2872 890 0.237 9.2885 852 0.244 正辛醛 C8H16O 124-13-0 绿色,带有淡淡的柑橘味 8.3585 960 0.659 8.3594 968 0.989 壬醛 C9H18O 124-19-6 有油脂气味、甜橙气息 10.0344 959 2.656 10.0351 957 2.253 癸醛 C10H20O 112-31-2 香气青辛微甜,有似甜橙油与柠檬油以及玫瑰样和蜡香的后韵 11.6008 952 0.062 11.6005 957 0.114 月桂醛 C12H24O 112-54-9 带有甜的花香和柑橘香气 − − − 14.4403 754 0.011 醇类化合物 己醇 C6H14O 111-27-3 有淡青的嫩枝叶气息,微带酒香、果香和脂肪气息 7.0285 956 19.905 6.0012 956 27.355 月桂醇 C12H26O 112-53-8 具有弱而持久的油脂气味、花香味 − − − 12.8298 813 0.006 2-乙基1-丁醇 C6H14O 97-95-0 有淡青的嫩枝叶气息,微带酒香、果香和脂肪气息 10.4783 844 0.024 − − − 酮类化合物 2-庚酮 C7H14O 110-43-0 类似香蕉的香气及轻微的药香气味 6.3498 936 0.830 6.3488 944 3.955 甲基庚烯酮 C8H14O 110-93-0 具有水果香气和绿色植物香气 8.0314 866 0.239 8.0325 837 0.292 辛酮 C8H16O 106-68-3 蘑菇、干酪和发霉果味 − − − 8.0446 899 0.398 2-辛酮 C8H16O 111-13-7 苹果香气 − − − 8.1185 874 3.647 苯乙酮 C8H8O 98-86-2 呈强烈金合欢似甜香气 − − − 9.4473 930 0.057 壬酮 C9H18O 821-55-6 呈水果、花、油脂和药草似香气 9.7985 935 0.255 9.7988 931 0.336 烟叶酮 C13H18O 13215-88-8 烟草辣味 − − − 16.6233 800 0.005 异佛尔酮 C9H14O 78-59-1 有薄荷香味 10.357 938 0.107 − − − 酸类化合物 戊酸 C5H10O2 109-52-4 具有难闻的臭袜子气味 7.8143 855 0.314 7.8333 825 0.103 烯烃类化合物 苯乙烯 C8H8 100-42-5 甜的芭蕉花;塑料气味 6.4115 815 4.098 − − − 枯稀 C9H12 98-82-8 特色的芳香性气味 − − − 7.9456 935 0.094 α-蒎烯 C10H16 80-56-8 强烈的木质和松质气味 7.1704 884 0.073 − − − 2-莰烯 C10H16 464-17-5 樟脑香气 − − − 7.1704 941 0.655 3-蒈烯 C10H16 13466-78-9 松木气息 8.4825 903 0.560 − − − γ-萜烯 C10H16 99-85-4 具有柑橘和柠檬香气 9.3060 812 0.051 − − − 对α-二甲基苯乙烯 C10H12 1195-32-0 辛辣,香辣气味 9.8394 897 0.007 − − − α-铜烯 C15H24 3856-25-5 − 14.1046 809 0.006 − − − 桧烯 C15H24 475-20-7 具有木香及似鸢尾香气 14.6268 915 0.024 − − − α-蒎烯 C15H22 644-30-4 木质雪松,鲜香 15.4154 906 0.010 14.1495 924 0.013 β-红没药烯 C15H24 495-61-4 具有温暖的木香、柑橘香、花香、果香、青香,和甜润的香脂香气 15.7474 876 0.013 − − − P-伞花烃 C10H14 535-77-3 − − − − 9.6355 893 0.079 长叶环烯 C15H24 1137-12-8 − − − − 14.627 877 0.012 芳香烃类
化合物萘 C10H8 91-20-3 辛辣、焦油味 11.4033 968 0.056 11.4033 955 0.057 1,2,4,5-四甲
基苯C10H14 95-93-2 − 10.2561 862 0.136 − − − 1,2-二甲氧
基-苯C8H10O2 91-16-7 甜奶油香草酚类 10.6396 823 0.001 − − − 1-甲基萘 C11H10 90-12-0 类似萘的气味 13.0343 938 0.010 − − − 对二甲基苯
二酚C8H10O2 150-78-7 呈甜苜蓿似香气和酚味 10.9735 859 0.022 − − − 注:“−”表示未检出;相对峰面积<0.01%未列入表中。 -
[1] 张雨, 毛云玲, 冯倩, 等. 滇东北地区铁核桃种群优良单株的选择[J]. 经济林研究,2010,28(1):62−68. [ZHANG Yu, MAO Yunling, FENG Qian, et al. Superior tree selection from Juglans siggillata L. populations in Northeastern Yunnan[J]. Research on Economic Forest,2010,28(1):62−68.] ZHANG Yu, MAO Yunling, FENG Qian, et al. Superior tree selection from Juglans siggillata L. populations in Northeastern Yunnan[J]. Research on Economic Forest, 2010, 28(1): 62−68.
[2] 裴东, 鲁新政. 中国核桃种质资源[M]. 北京:中国林业出版社, 2011:1−9. [PEI Dong, LU Xinzheng. Chinese walnut germplasm resources[M]. Beijing:China Forestry Press, 2011:1−9.] PEI Dong, LU Xinzheng. Chinese walnut germplasm resources[M]. Beijing: China Forestry Press, 2011: 1−9.
[3] 胡祥, 刘云, 徐涵, 等. ‘龙佳’核桃品质分析及蛋白质提取工艺优化[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(2):225−231. [HU Xiang, LIU Yun, XU Han, et al. Quality analysis and protein extraction process optimization of Juglans Sigillata ‘Longjia’[J]. Food Technology,2021,46(2):225−231.] HU Xiang, LIU Yun, XU Han, et al. Quality analysis and protein extraction process optimization of Juglans Sigillata ‘Longjia’[J]. Food Technology, 2021, 46(2): 225−231.
[4] 袁奖娟, 郝佳波, 刘云, 等. 云南3种有色泡核桃仁营养成分及仁衣中多酚类物质分析[J]. 中国油脂,2023,48(5):120−123. [YUAN Shengjuan, HAO Jiabo, LIU Yun, et al. Analysis of nutritional components in kernels and polyphenols in coat of three colored Juglans sigillata in Yunnan[J]. Chinese Fats,2023,48(5):120−123.] YUAN Shengjuan, HAO Jiabo, LIU Yun, et al. Analysis of nutritional components in kernels and polyphenols in coat of three colored Juglans sigillata in Yunnan[J]. Chinese Fats, 2023, 48(5): 120−123.
[5] 耿树香, 宁德鲁, 韩明珠, 等. 云南核桃主要栽培品种蛋白质及脂肪酸综合评价分析[J]. 中国油脂,2019,44(10):116−120,141. [GENG Shuxiang, NING Delu, HAN Mingzhu, et al. Comprehensive evaluation on protein and fatty acid of main cultivars of walnut in Yunnan province[J]. Chinese Grease,2019,44(10):116−120,141.] GENG Shuxiang, NING Delu, HAN Mingzhu, et al. Comprehensive evaluation on protein and fatty acid of main cultivars of walnut in Yunnan province[J]. Chinese Grease, 2019, 44(10): 116−120,141.
[6] 刘娇, 范志远, 贠新华, 等. 云南主栽核桃品种坚果品质比较及综合评价[J]. 西南林业大学学报(自然科学),2018,38(5):97−102. [LIU Jiao, FAN Zhiyuan, YUN Xinhua, et al. Comparison and comprehensive evaluation of nut quality of main Juglans sigillata varieties in Yunnan[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Science),2018,38(5):97−102.] LIU Jiao, FAN Zhiyuan, YUN Xinhua, et al. Comparison and comprehensive evaluation of nut quality of main Juglans sigillata varieties in Yunnan[J]. Journal of Southwest Forestry University (Natural Science), 2018, 38(5): 97−102.
[7] LI J L, TU Z C, SHA X M, et al. Effect of frying on fatty acid profile, free amino acids and volatile compounds of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) Fillets[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 2017, 41(4).
[8] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.168-2016食品中脂肪酸的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.168-2016 Determination of fatty acids in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2016.] China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.168-2016 Determination of fatty acids in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[9] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.5-2016食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.5-2016 Determination of protein in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2016.] China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.5-2016 Determination of protein in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[10] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.6-2016食品中脂肪的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.6-2016 Determination of fat in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2016.] China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.6-2016 Determination of fat in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[11] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.87-2016食品中磷的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.87-2016 Determination of phos-phorus in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2016.] China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.87-2016 Determination of phos-phorus in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[12] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.14-2016 食品中锌的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.14-2016 Determination of zinc in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2016.] China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.14-2016 Determination of zinc in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[13] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.90-2016食品中铁的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.90-2016 Determination of iron in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2016.] China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.90-2016 Determination of iron in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[14] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.241-2017食品中镁的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2017. [China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.241-2017 Determination of magne-sium in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2017.] China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.241-2017 Determination of magne-sium in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2017.
[15] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.92-2016食品中钙的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.92-2016 Determination of calcium in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2016.] China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.92-2016 Determination of calcium in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[16] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.13-2017食品中铜的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2017. [China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.13-2017 Determination of copper in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2017.] China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.13-2017 Determination of copper in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2017.
[17] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.91-2017食品中钾、钠的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2017. [China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.91-2017 Determination of potassi-um and sodium in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2017.] China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.91-2017 Determination of potassi-um and sodium in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2017.
[18] RABIE M, PERES C, MALCATA F X. Evolution of amino acids and biogenic amines throughout storage in sausages made of horse, beef and turkey meats[J]. Meat Sci,2014,96(1):82−87. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2013.05.042
[19] 赵洪雷, 冯媛, 徐永霞, 等. 海鲈鱼肉蒸制过程中品质及风味特性的变化[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(20):145−151. [ZHAO Honglei, FENG Yuan, XU Yongxia, et al. Changes in quality and flavor characteristics of sea bass muscle during steaming[J]. Food Science,2021,42(20):145−151.] ZHAO Honglei, FENG Yuan, XU Yongxia, et al. Changes in quality and flavor characteristics of sea bass muscle during steaming[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(20): 145−151.
[20] 《食品添加剂手册第四版》新书出版[J]. 食品工业, 2013(7):227. [21] 常君, 张潇丹, 姚小华, 等. 不同品种薄壳山核桃氨基酸组成及营养价值评价[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版),2021,43(4):44−52. [CHANG Jun, ZHANG Xiaodan, YAO Xiaohua, et al. Amino acid composition and nutritional value evaluation of different varieties of pecan (Carya illinoensis K. Koch)[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition),2021,43(4):44−52.] CHANG Jun, ZHANG Xiaodan, YAO Xiaohua, et al. Amino acid composition and nutritional value evaluation of different varieties of pecan (Carya illinoensis K. Koch)[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 43(4): 44−52.
[22] 陈逸鹏, 郑凯航, 何计国, 等. 几类市售坚果产品中油脂的脂肪酸分析[J]. 食品科技,2015,40(1):191−195. [CHEN Yipeng, ZHENG Kaihang, HE Jiguo, et al. Fatty acid analysis of oils and fats in several types of commercially available nut products[J]. Food Technology,2015,40(1):191−195.] CHEN Yipeng, ZHENG Kaihang, HE Jiguo, et al. Fatty acid analysis of oils and fats in several types of commercially available nut products[J]. Food Technology, 2015, 40(1): 191−195.
[23] 王雪, 闫素梅. 多不饱和脂肪酸对动物脂类代谢的调节作用与机制[J]. 动物营养学报,2019,31(6):2471−2478. [WANG Xue, YAN Sumei. Regulation and mechanism of lipid metabolism by polyunsaturated fatty acids of animals[J]. The Journal of Animal Nutrition,2019,31(6):2471−2478.] WANG Xue, YAN Sumei. Regulation and mechanism of lipid metabolism by polyunsaturated fatty acids of animals[J]. The Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2019, 31(6): 2471−2478.
[24] 李瑞, 刘云, 阚欢, 等. 云南17种核桃仁主要营养成分测定及脂肪酸研究[J]. 包装工程,2019,40(7):19−25. [LI Rui, LIU Yun, KAN Huan, et al. Determination of main nutrient components and fatty acids in 17 kinds of walnut kernels in Yunnan[J]. Packaging Engineering,2019,40(7):19−25.] LI Rui, LIU Yun, KAN Huan, et al. Determination of main nutrient components and fatty acids in 17 kinds of walnut kernels in Yunnan[J]. Packaging Engineering, 2019, 40(7): 19−25.
[25] 周红, 张萍, 李彦荣. 新疆野核桃坚果营养成分测定及分析[J]. 果树学报,2019,36(5):621−628. [ZHOU Hong, ZHANG Ping, LI Yanrong. Analysis of nutritive components of different types of Xinjiang wild wal-nuts[J]. Journal of Fruit Trees,2019,36(5):621−628.] ZHOU Hong, ZHANG Ping, LI Yanrong. Analysis of nutritive components of different types of Xinjiang wild wal-nuts[J]. Journal of Fruit Trees, 2019, 36(5): 621−628.
[26] TGSC Information System[A/OL]. http://www.thegoods-centscompany.com/search3.phpqFlavor=78-70-6&submit.x=8&submit.y=9.
[27] 龙杰, 吴昕烨, 毕金峰, 等. HS-SPME-GC-MS结合电子鼻探究渗透脱水联合干燥方式对桃脆片挥发性风味物质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(18):241−251. [LONG Jie, WU Xinye, BI Jinfeng, et al. HS-SPME-GC-MS combined with electronic nose to explore the effects of osmotic dehydration coupled with drying methodson the volatile compounds of peach chips[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2022,43(18):241−251.] LONG Jie, WU Xinye, BI Jinfeng, et al. HS-SPME-GC-MS combined with electronic nose to explore the effects of osmotic dehydration coupled with drying methodson the volatile compounds of peach chips[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2022, 43(18): 241−251.
[28] 罗章, 马美湖, 孙术国, 等. 不同加热处理对牦牛肉风味组成和质构特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2012,33(15):148−154. [LUO Zhang, MA Meihu, SUN Shuguo, et al. Effects of different heat treatments on flavor and texture characteristics of cooked yak meat[J]. Food Science,2012,33(15):148−154.] LUO Zhang, MA Meihu, SUN Shuguo, et al. Effects of different heat treatments on flavor and texture characteristics of cooked yak meat[J]. Food Science, 2012, 33(15): 148−154.
[29] 常海军, 周文斌, 朱建飞. 重庆城口香肠挥发性风味成分的分离与鉴定[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(6):146−152. [CHANG Haijun, ZHOU Wenbin, ZHU Jianfei. lsolation and ldentification of volatile compounds of Chongqing Chengkou sausage[J]. Food Science,2016,37(6):146−152.] CHANG Haijun, ZHOU Wenbin, ZHU Jianfei. lsolation and ldentification of volatile compounds of Chongqing Chengkou sausage[J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(6): 146−152.
[30] SUN W Z, ZHAO Q Z, ZHAO H F, et al. Volatile compounds of cantonese sausage released at different stages of processing and storage[J]. Food Chemistry,2010,121(2):319−325. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.12.031
[31] 孙瑞璐, 刘天月, 罗海玲, 等. 兴安多羔羊肉营养成分与风味物质研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2022,53(10):386−395. [SUN Ruilu, LIU Tianyue, LUO Hailing, et al. Investigation on nutrition and flavor of Xing' an lamb meat[J]. Journal of Agricultural Machinery,2022,53(10):386−395.] SUN Ruilu, LIU Tianyue, LUO Hailing, et al. Investigation on nutrition and flavor of Xing' an lamb meat[J]. Journal of Agricultural Machinery, 2022, 53(10): 386−395.
[32] 苏为耿, 蒲成伟, 阚欢, 等. 云南6种核桃栽培品种果实特性与营养成分分析[J]. 粮食与油脂,2018,31(4):68−71. [SU Weigeng, PU Chengwei, KAN Huan, et al. Analysis of fruit characteristics and nutrient composition of six walnut cultivars in Yunnan[J]. Food and Oil,2018,31(4):68−71.] SU Weigeng, PU Chengwei, KAN Huan, et al. Analysis of fruit characteristics and nutrient composition of six walnut cultivars in Yunnan[J]. Food and Oil, 2018, 31(4): 68−71.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 蒋立文,张浩东,覃业优,胡嘉亮,刘洋. 渥堆期间水分对浏阳豆豉微生物及品质风味的影响. 食品与机械. 2024(05): 11-20+136 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张晓磊,周汉琛,刘亚芹,王辉,雷攀登. 基于代谢组学分析低温烘焙对白化品种绿茶风味品质的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(17): 352-362 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 王秋霜,秦丹丹,方开星,姜晓辉,王青,李波,李红建,倪尔冬,潘晨东,吴华玲. 基于非靶向代谢组学分析印度不同产地红茶关键香气代谢物. 食品研究与开发. 2024(21): 152-163 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 沙艮,张田芳,陈秋月,王藤,陈思琴,伯年国,李丽梅,李若愚,雷鑫,段红星,马燕,赵明. 大理茶鲜叶制成红茶的品质分析. 食品研究与开发. 2024(23): 18-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



