Isolation and Identification of Bacteriocin-producing Bacillus subtilis S1-2 from Soybean Paste and Its Stability Study
-
摘要: 本研究首先从东北传统豆酱中分离筛选出一株具有良好抑菌作用的菌株,结合16S rDNA与持家基因gyrA测序分析等方法对菌株鉴定。其次,利用乙酸乙酯萃取法对其所产细菌素进行粗提,使用葡聚糖凝胶Sephadex-G50和高效液相色谱(HPLC)技术进一步纯化,结合SDS-PAGE和液相色谱-质谱联用(LC-MS/MS)技术进行鉴定。最后通过最小浓度实验与生长抑制曲线分析了细菌素对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制效果,并探究了细菌素对热、酸碱和蛋白酶的稳定性。结果表明,枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)菌株S1-2对金黄色葡萄球菌和单增李斯特氏菌抑菌效果最好,该菌株产生的细菌素经分离纯化鉴定为subtilosin A,分子量约为3 kDa,对金黄色葡萄球菌和单增李斯特氏菌有明显的抑制效果,对金黄色葡萄球菌的最小抑制浓度为0.625 mg/mL。该细菌素在20~80 ℃抑菌活性稳定,且在100~120 ℃仍表现出抑菌活性;对酸碱耐受性较高,经过pH为1、10的强酸强碱处理后仍表现出抑菌活性,在pH6.0~8.0的范围内表现出最高的抑菌活性;能够被蛋白酶K、胃蛋白酶、胰蛋白酶水解。综上,枯草芽孢杆菌S1-2与其产生的细菌素subtilosin A在食品生物防腐中具有较强的研究和应用潜力。Abstract: In this study, a strain with good antibacterial effect was screened and identified from traditional soybean paste in Northeast China. The strain was identified using methods such as 16S rDNA and housekeeping gene gyrA sequencing analysis. Its bacteriocins were crude extracted using ethyl acetate extraction, further purified using dextran gel Sephadex-G50 and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) techniques, combined with SDS-PAGE and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) for identification. The antibacterial effect of the bacteriocin on Staphylococcus aureus was analyzed by determining the minimum concentration and growth inhibition curve. Additionally, the stability of the bacteriocins was investigated by exploring its thermal stability, pH tolerance, and resistance to proteases. Results showed that the Bacillus subtilis S1-2 strain had the best antibacterial effect on Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes. The bacteriocin produced by the strain was identified as subtilosin A, with molecular weight of approximately 3 kDa, and demonstrated a significant inhibitory effect on Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes. The minimum inhibitory concentration against Staphylococcus aureus was 0.625 mg/mL. Furthermore, the bacteriocin exhibited stable antibacterial activity between 20~80 ℃ and even between 100~120 ℃. It showed the highest antibacterial activity in the pH range of 6.0~8.0, as well as good acid and alkali tolerance with pH values of 1 and 10. Furthermore, it could be hydrolyzed by proteinase K, pepsin, and trypsin. In conclusion, Bacillus subtilis S1-2 and its bacteriocin subtilosin A have great potential in food preservation due to their strong antibacterial activities.
-
Keywords:
- Bacillus subtilis /
- bacteriocin /
- separation and purification /
- antibacterial
-
芽孢杆菌(Bacillus)因其培养条件简单、生长周期短等特性,在食品、医药、农业、林业、畜牧业等行业应用广泛[1]。芽孢杆菌作为益生菌不仅能够分泌蛋白酶等常用酶,还可以分泌脂肽、细菌素等抑菌物质,在酸奶、豆酱、纳豆等传统发酵食品的制作中有悠久的应用历史[2−3]。早在上个世纪,研究者就发现了芽孢杆菌能分泌多种抗菌活性物质[4],包括脂肽类、细菌素以及其他小分子物质,能抑制细菌、真菌,甚至病毒[5]。
细菌素是优秀的天然防腐剂,抑菌谱较窄但对近缘致病菌有针对性,易于分解不致生态环境污染[6]。近年来,已有大量关于芽孢杆菌细菌素的报道。芽孢杆菌属能产生多类细菌素,包括subtilin、mersacidin、subtilosin A等[7]。细菌素subtilosin A的合成基因簇已有较详细的研究,纪帅奇等[8]通过全基因组测序结合生信分析挖掘出一株枯草芽孢杆菌的细菌素subtilosin A的完整合成基因簇。此外,subtilosin A已确认为套索肽,但其三级结构尚未确定,Ishida等[9]使用拉曼光谱法初步探究了subtilosin A中AlbEF复合物的环化机制。由此可见,目前芽孢杆菌细菌素研究已有一定深度,但在细菌素结构与稳定性等方面有缺失,芽孢杆菌细菌素的稳定性研究能够为芽孢杆菌细菌素的结构研究提供有力支持。
豆类发酵食品的发酵过程需要芽孢杆菌的参与来分解豆类蛋白,是芽孢杆菌的资源库[10−13]。本研究从东北地区传统发酵豆酱样品中筛选并鉴定出一株抑菌活性较强的枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)S1-2为试验菌株,设计试验对细菌素进行纯化鉴定、稳定性质以及抑菌机制方面的研究分析,旨在挖掘和探索枯草芽孢杆菌S1-2及其细菌素在食品生物防腐中的应用潜力和价值。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
豆酱样品采自辽中地区农家自然发酵的豆酱,发酵天数为49 d;枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)S1-2、金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)ATCC 25923、大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)ATCC 25922、单增李斯特氏菌(Listeria monocytogenes)ATCC 19115、鼠伤寒沙门氏菌(Salmonella typhimurium)ATCC14028 均为沈阳农业大学食品学院微生物菌种库提供;LB培养基 北京奥博星生物技术有限公司;乙酸乙酯、盐酸、氢氧化钠、乙腈、三氟乙酸 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;蛋白酶K(40 U/mg)、胃蛋白酶(250 U/mg)、胰蛋白酶(250 U/mg) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司。
YT-PCR仪 山东云唐智能科技有限责任公司;Eon酶标仪 美国Biotek公司;Dionex P680半制备反相高效液相色谱 美国Dionex公司;DYY-6C电泳仪 北京六一生物科技有限公司;Regeulus 8100冷场发射扫描电子显微镜 日本日立高科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 豆酱中芽孢杆菌的分离筛选和鉴定
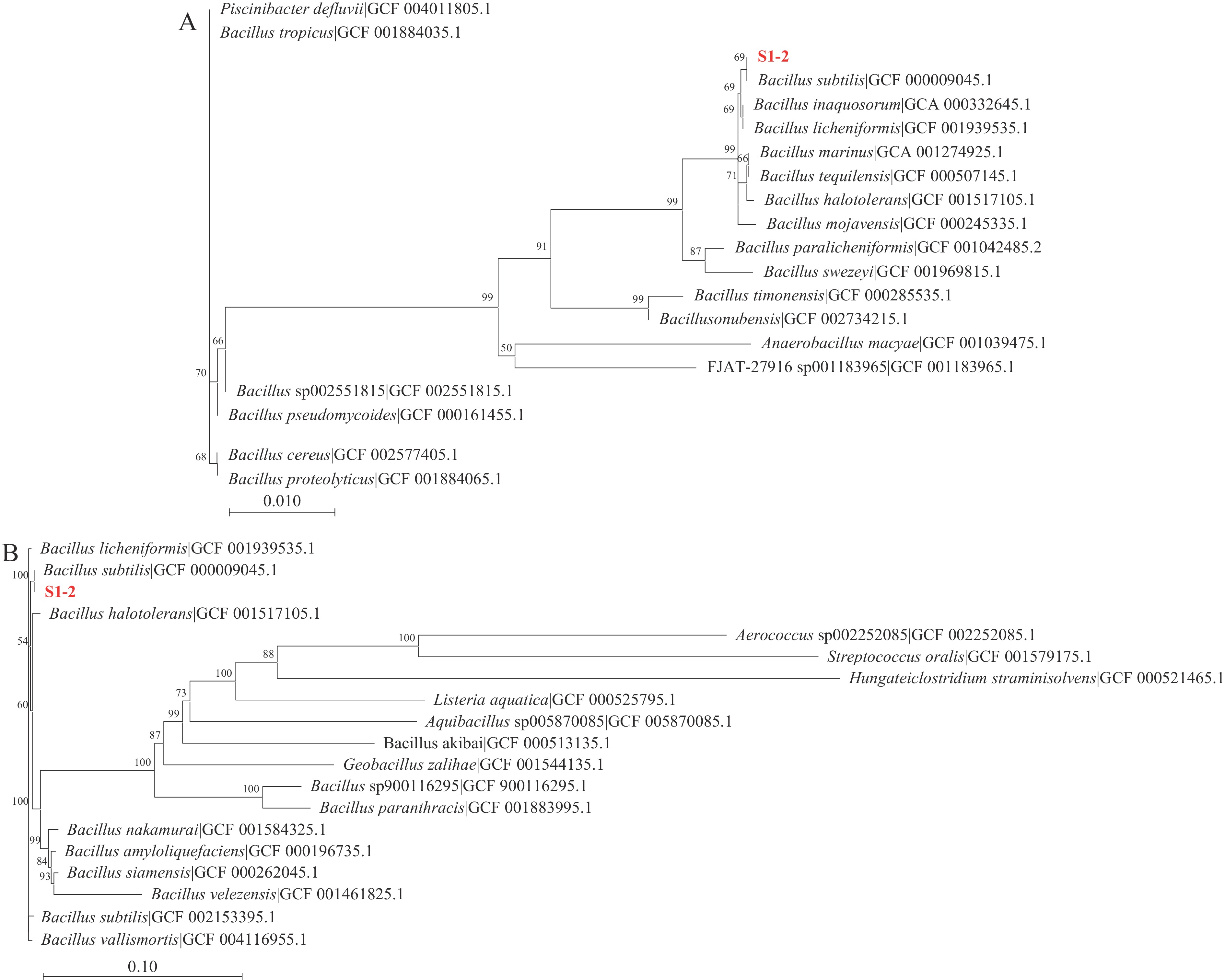
参考Arbulu等[14]的方法,取豆酱样品于试管,经85 ℃水浴加热20 min后稀释,涂布于LB固体培养基培养后挑取单菌落培养,同时进行革兰氏染色与孔雀石绿染色试验,选取细长杆状菌体采用琼脂打孔法,打孔直径为5 mm,以金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、单增李斯特氏菌、沙门氏菌作为指示菌进行抑菌试验,观察抑菌圈并测定抑菌圈直径。参考刘晓萌等[15]的方法,对比抑菌效果后选取较好的菌株活化并提取DNA,用引物对27F(5'-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3')/1492R(5'-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3')和42F(5'-CAGTCAGGAAATGCGTACGTCCTT-3')/1066R(5'-CAAGGTAATGCTCCAGGCATTGCT-3')分别对16S rDNA与持家基因gyrA进行PCR扩增,PCR反应程序:94 ℃ 5 min;94 ℃ 30 s,50 ℃ 1 min,72 ℃ 2 min,30 个循环;72 ℃延伸10 min。送至上海美吉生物医药科技有限公司进行测序。在NCBI数据库(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/)中选择同源性较高的19株模式菌株的序列通过MEGA 11.0软件构建系统发育树。
1.2.2 芽孢杆菌细菌素的分离纯化
离心菌液得到上清液,采用乙酸乙酯萃取法初步分离得到粗样[16],再通过抑菌试验验证抑菌活性,通过考马斯亮蓝法验证蛋白质含量[17],于4 ℃保存备用。选用葡聚糖凝胶Sephadex-G50进行纯化,在280 nm处测定有抑菌效果的峰通过HPLC纯化。采用Tricine-SDS-PAGE来鉴定细菌素的分子量,将目的条带委托上海厚基生物科技公司通过LC-MS/MS进行鉴定。
1.2.3 芽孢杆菌S1-2细菌素的抑菌活性
按照张炜等[18]的方法测定细菌素对指示菌的最小抑菌浓度(MIC)。将金黄色葡萄球菌指示菌按照2%接种量接种于液体LB培养基中,加入细菌素,使浓度达到10.000、5.000、2.500、1.250、0.625、0.313和0.156 mg/mL,设置空白对照,培养24 h观察指示菌生长状况。加入细菌素使浓度达到0.8×MIC,设置乙酸乙酯对照组和与空白对照组,在24 h内每2 h检测600 nm处的吸光值,绘制生长曲线[19]。
1.2.4 芽孢杆菌S1-2细菌素对热、酸、碱、蛋白酶的稳定性研究
取经HPLC纯化后的样品冻干溶解于磷酸盐(PBS)缓冲液,分装于1.5 mL离心管中,每管加入1 mL,进行温度、pH、蛋白酶的单因素实验测试细菌素稳定性;温度单因素实验设置为将细菌素分别置于20、40、60、80、100、120 ℃条件下处理20 min;pH单因素实验设置为将细菌素样品使用NaOH或HCl将pH调整至1~10的整数混匀静置1 h后调至7.0,之后使用无菌水定容;蛋白酶单因素实验设置为使用20 mg/mL的蛋白酶K酶液、胰蛋白酶液、胃蛋白酶液与样品1:20混合并置于37 ℃处理2 h后,置于70 ℃处理10 min使酶灭活。三组单因素均以金黄色葡萄球菌作为指示菌,采用琼脂打孔法进行抑菌活性测定,测量抑菌圈直径。
1.3 数据处理
试验均设置空白对照与三组平行实验。实验数据通过Excel 2021整理,结果用平均值±标准偏差表示,采用SPSS 17.0软件对数据进行显著性分析,P<0.05表示差异显著,利用Graphpad Prism 9.0进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 枯草芽孢杆菌S1-2的分离筛选和鉴定
芽孢杆菌在豆酱中含量丰富[20−21]。根据革兰氏染色与菌落形态观察,本次试验共筛选分离出6株菌株疑似芽孢杆菌,分别命名为SP、S1、S1-2、S1-3、S2、S2-3并进行了抑菌试验比对它们的抑菌效果,抑菌直径结果如表1所示。
表 1 芽孢杆菌对指示菌的抑菌圈直径(mm)Table 1. Diameter of the antibacterial zone of Bacillus against indicator bacteria (mm)菌株 金黄色葡萄球菌 单增李斯特菌 大肠杆菌 沙门氏菌 SP 9.23±0.25 10.7±0.16 6.01±0.02 6.09±0.03 S1 8.03±0.12 10.13±0.14 6.44±0.02 6.41±0.07 S1-2 12.31±0.42 14.06±0.23 7.23±0.03 7.18±0.06 S1-3 6.88±0.20 6.32±0.25 6.72±0.08 6.76±0.05 S2 7.21±0.14 7.41±0.21 − − S2-3 5.23±0.17 6.74±0.32 − − 注:“−”表示无抑制效果。 由表1可以看出,6株菌均有一定的抑菌效果,且对革兰氏阳性菌的抑菌效果远高于革兰氏阴性菌,其中菌株S1-2抑菌效果较为突出,菌株S2-3则表现较差。因此选取菌株S1-2进行PCR初步鉴定后送样进行16S rDNA测序。测序结果显示菌株S1-2与枯草芽孢杆菌同源性为100%,与其他一些芽孢杆菌的同源性也达到了99%以上。为进一步验证种属鉴定结果的准确性,又对持家基因gyrA进行测序与比对[22],测序结果仍显示菌株S1-2与枯草芽孢杆菌同源性为100%,确定菌株S1-2为枯草芽孢杆菌。最终基于16S rDNA与gyrA序列在NCBI数据库选择在种属水平上最接近的20株模式菌(图1)。
2.2 细菌素的鉴定
2.2.1 抑菌活性试验
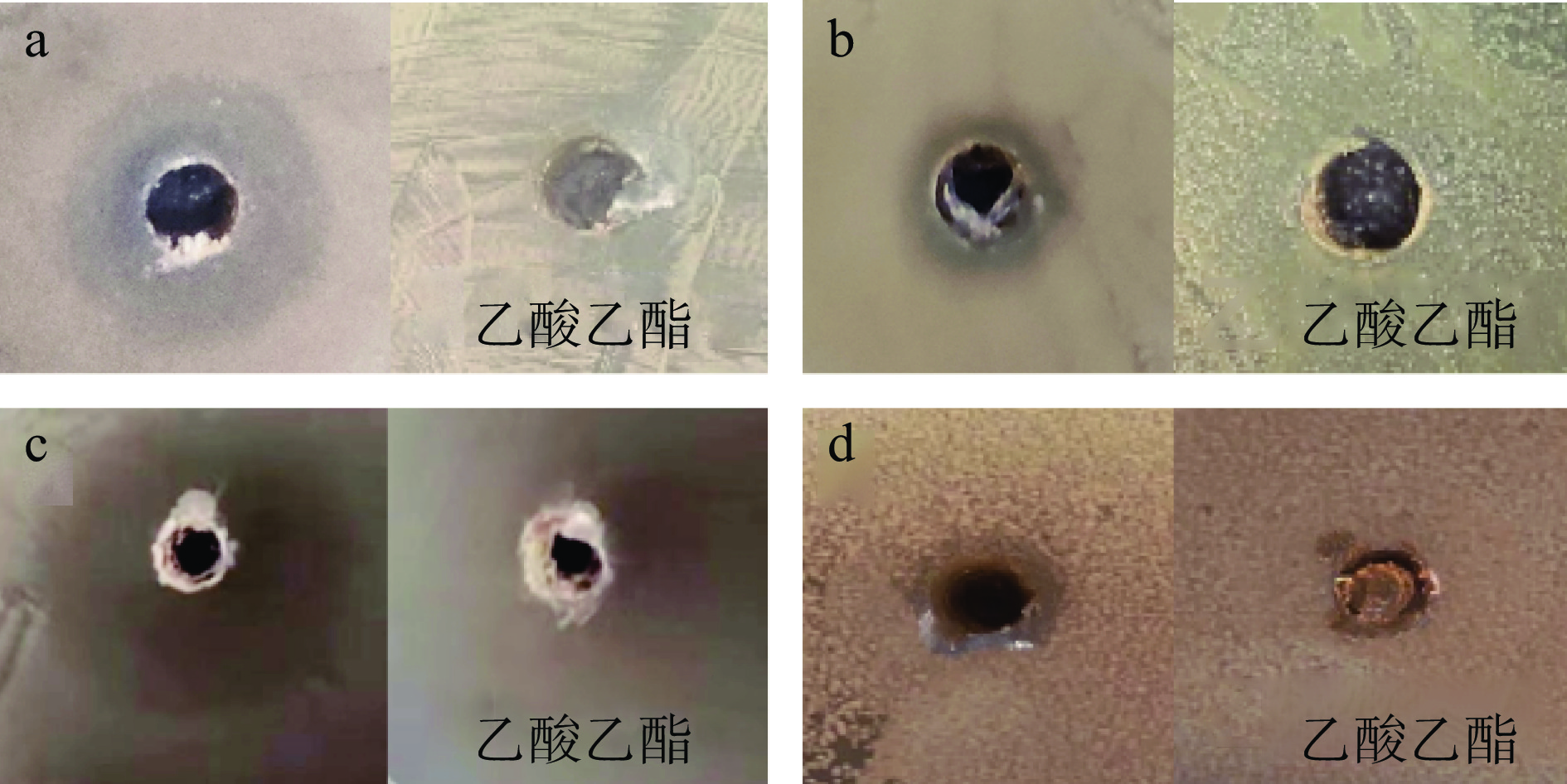
使用琼脂打孔法,对纯化后的细菌素进行抑菌的广谱性研究,实验结果如图2所示。
经测量,细菌素对金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、单增李斯特氏菌、沙门氏菌抑菌圈直径结果分别为:14.06±0.48、8.61±0.10、19.97±0.54、9.23±0.08 mm。抑菌试验结果表明,枯草芽孢杆菌S1-2产生的细菌素对大肠杆菌和沙门氏菌的抑菌效果不明显,对金黄色葡萄球菌和单增李斯特氏菌的抑菌效果明显,乙酸乙酯对四种致病菌均无抑制作用,排除了乙酸乙酯未除尽对细菌素抑菌活性造成影响的可能。由此可初步推断,该细菌素可对革兰氏阳性菌有突出的抗菌能力,对革兰氏阴性菌的抑菌效果不明显,有待进一步研究。此外,本次试验抑菌圈直径远大于菌种初筛时的抑菌试验结果,表明抑菌物质浓度显著提高,即得到了纯化。
2.2.2 SDS-PAGE结果分析
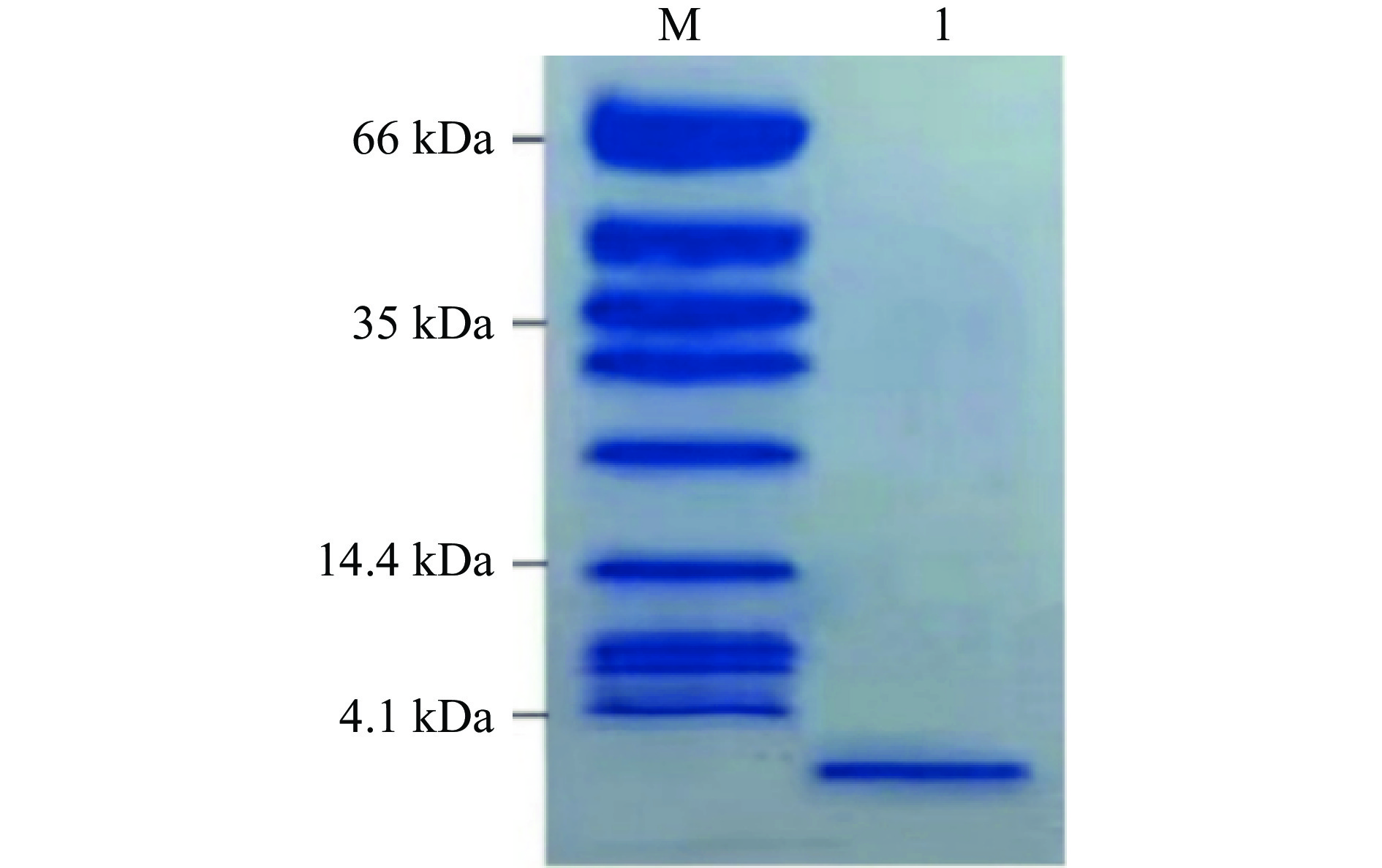
由于一般的SDS-PAGE在低分子区内条带容易弥散且分辨率低[23],而细菌素的分子量不确定且I类细菌素分子量通常小于5 kDa,本试验采用了Tricine-SDS-PAGE,电泳结果如图3所示。
电泳结果显示,经过HPLC纯化后的蛋白样品,在4.1 kDa下方有一条明显条带,由此可知,该条带的分子量小于4.1 kDa。这也说明在经过两步纯化后,细菌素的纯度提升,从而可以更精准的定位细菌素分子量的大小。
2.2.3 LC-MS/MS结果分析
将经Tricine-SDS-PAGE验证,纯化浓缩后的蛋白在4.1 kDa以下单一条带切下,进行LC-MS/MS鉴定。质谱测试原始文件用软件MaxQuant1.5.5.1检索枯草芽孢杆菌的数据库,得到蛋白质鉴定结果如表2所示。
表 2 LC-MS/MS的部分蛋白鉴定结果Table 2. Partial protein identification results of LC-MS/MS蛋白质名称 评分 序列覆盖度(%) 分子量(kDa) Single-stranded DNA-binding protein 323.31 5.3 18.63 Thioredoxin 323.31 11.5 11.393 Uncharacterized protein YjfA 269.95 16.4 16.202 Uncharacterized protein YjdB 171.94 12.394 18.3 Tautomerase 114.18 14.5 7.1451 Subtilosin A 72.102 17.8 3.314 Subtilisin E 49.614 11.9 8.6586 Acyl carrier protein 41.417 19.5 8.5914 根据LC-MS/MS鉴定结果,将鉴定出的蛋白依据Score值、序列的覆盖率、相对分子质量进行综合分析,推测该抗菌物质为Ⅱa类细菌素subtilosin A。文献指出,subtilosin A的分子量约为3 kDa[24],这也印证了Tricine-SDS-PAGE的结果。
2.3 细菌素的抑菌活性
2.3.1 细菌素对金黄色葡萄球菌的最小抑菌浓度
最小抑菌浓度试验结果如表3所示,细菌素浓度为0.625 mg/mL时溶液介于浑浊与澄清,因此细菌素对金黄色葡萄球菌的最小抑制浓度为0.625 mg/mL。
表 3 细菌素对金黄色葡萄球菌的最小抑菌浓度Table 3. Minimum inhibitory concentrations of bacteriocin against Staphylococcus aureus细菌素浓度(mg/mL) 10 5 2.5 1.25 0.625 0.312 0.156 金黄色葡萄球菌 − − − − + ++ ++ 注:“++”指液体浑浊;“+”指液体介于浑浊与澄清;“−”指液体澄清。 2.3.2 金黄色葡萄球菌生长抑制曲线分析
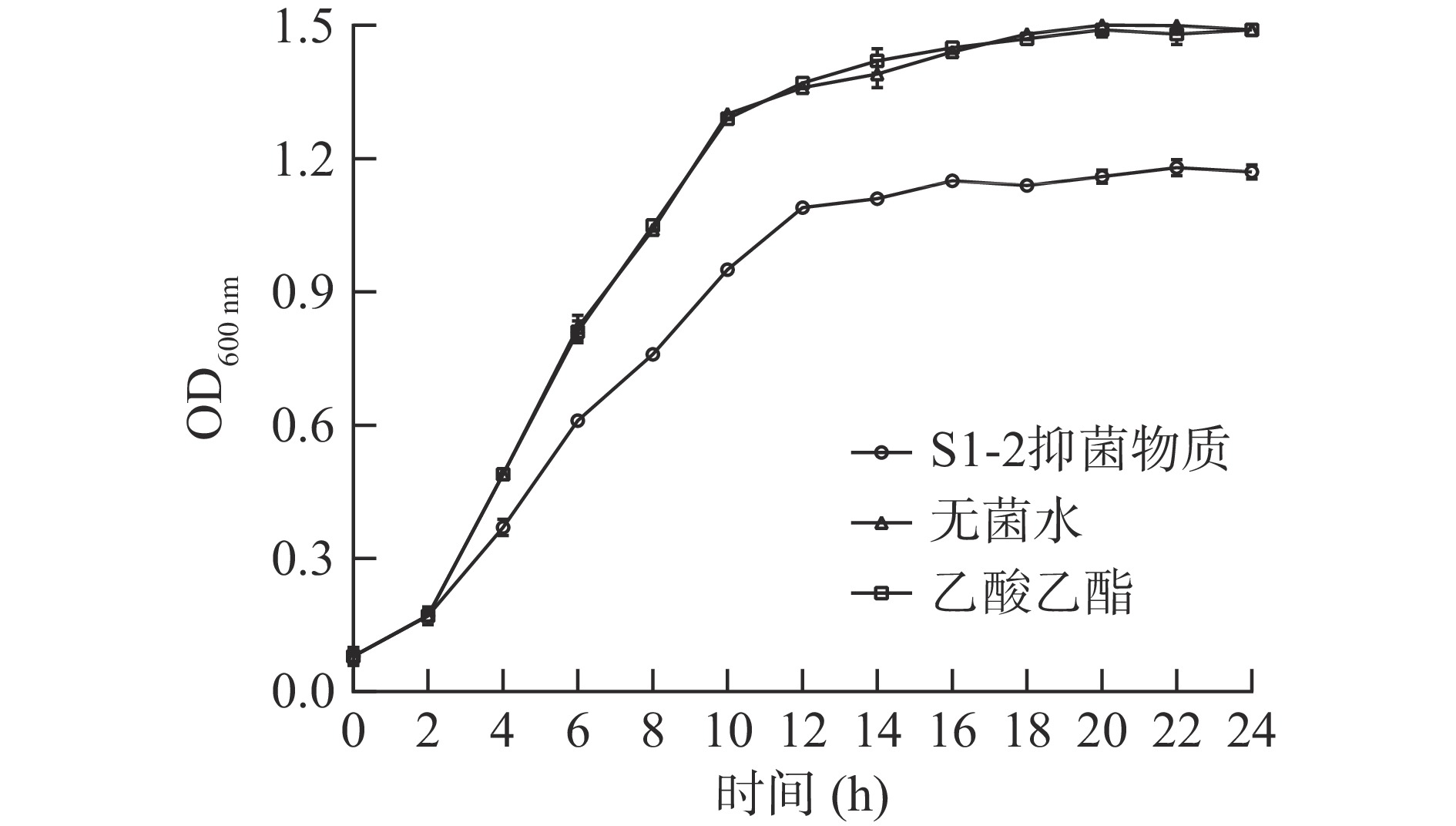
菌液在600 nm处的吸光度(OD600 nm)可以用来表征并比较菌液中细菌数目变化,从而间接反映细菌素对菌体影响情况[25]。结果如图4所示。
由图4可以看出,乙酸乙酯处理组金黄色葡萄球菌生长曲线与无菌水处理组相比无明显变化,表明萃取溶剂对金黄色葡萄球菌生长无影响,这也与抑菌试验中乙酸乙酯对病原指示菌无抑菌效果相对应。而加入细菌素的试验组与对照组相比,从4 h开始,不同时间段菌液OD600 nm明显降低,表明细菌素对金黄色葡萄球菌菌体的生长有较好的抑制作用。
2.4 细菌素稳定性的研究
2.4.1 温度对细菌素抑菌活性的影响
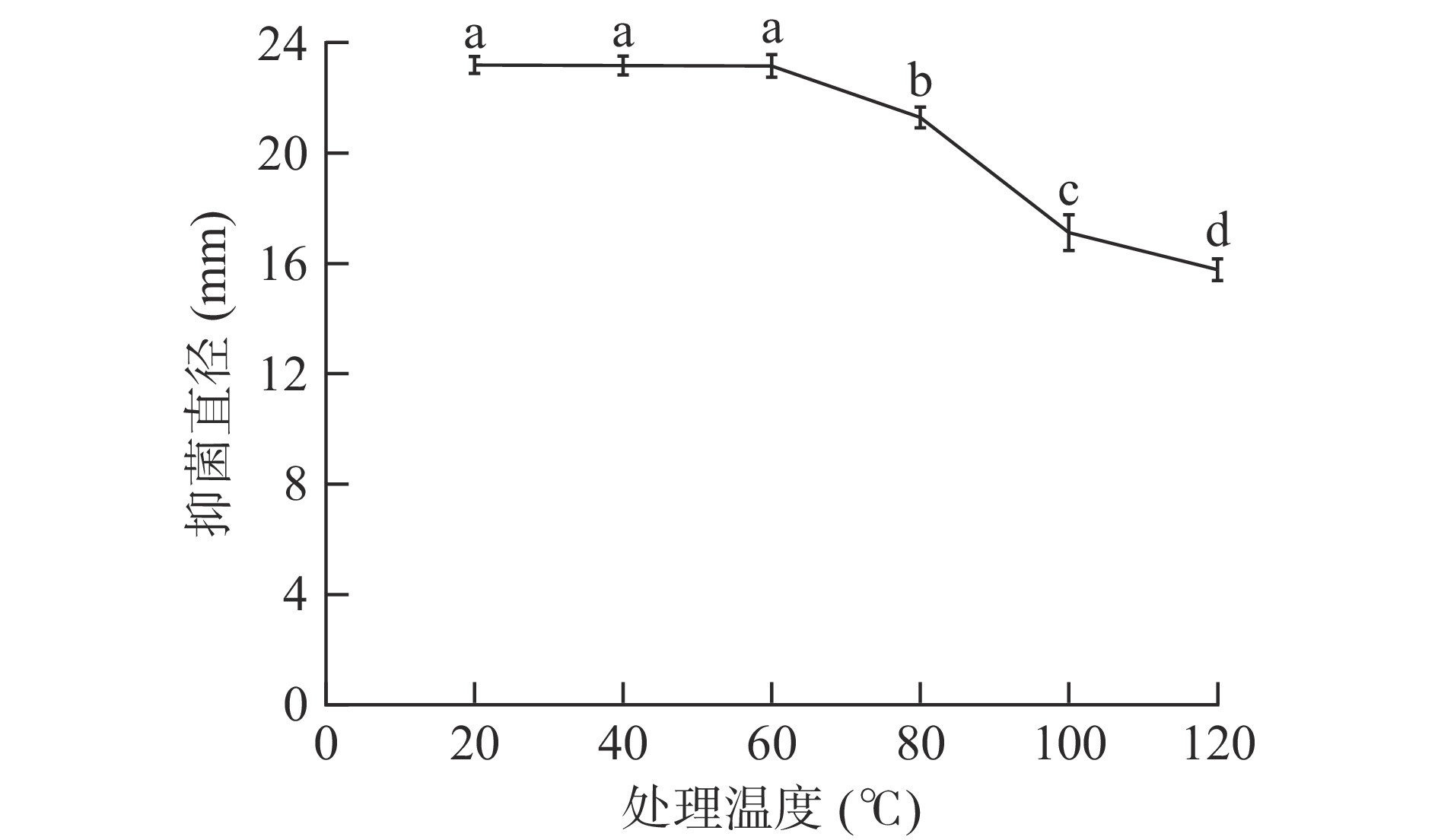
以20 ℃作为温度处理组空白对照,结果如图5所示。
由图5可以看出,细菌素对热不敏感。在20~60 ℃温度范围内,抑菌直径基本保持不变,表明细菌素的抑菌活性受温度影响较小,温度稳定性较好;当温度上升至80 ℃时,抑菌活性出现下降趋势,与对照组相比,抑菌活性下降了15%;在处理100 ℃与120 ℃时,虽然抑菌直径大小明显下降,但也会大致维持在15 mm左右的水平,抑菌活性仍然存在。
2.4.2 pH对细菌素抑菌活性的影响
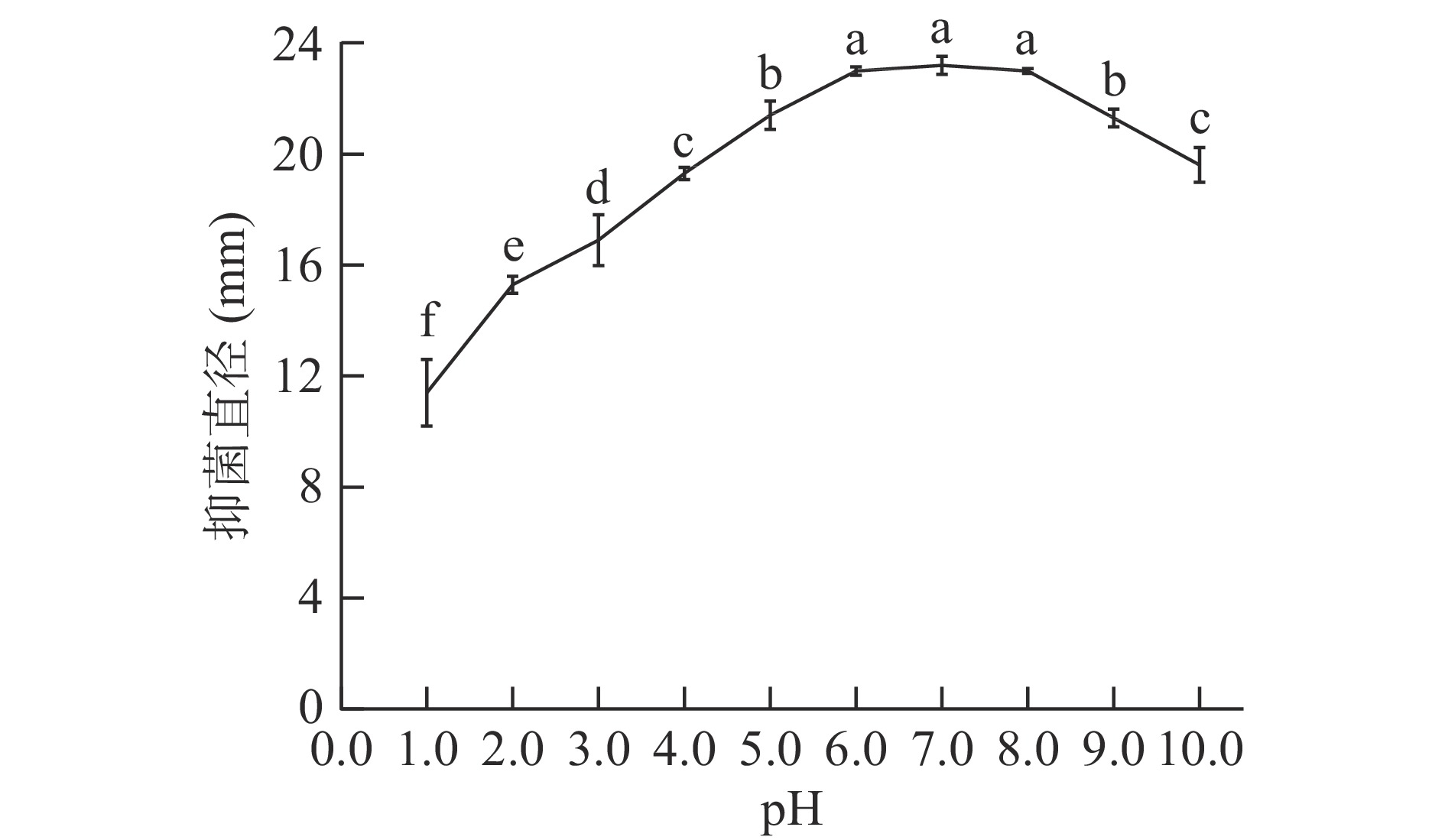
以pH为7.0的细菌素处理组作为空白对照,观察细菌素经过不同pH处理后对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制效果,结果如图6所示。
由图6可以看出,细菌素对酸性和碱性都具有良好的稳定性。与对照组(pH7.0)相比,pH在6.0~8.0范围内,抑菌活性基本无变化;当pH小于4.0时,抑菌直径明显下降;当pH为1.0时,抑菌直径下降至pH为7.0的49.13%,但仍表现出一定的抗菌能力;特别地,细菌素对于碱的耐性要优于酸。总之,细菌素pH耐受范围较宽,具有良好的酸碱稳定性。因此,在实际应用中,环境酸碱性的改变对细菌素的活性影响较小。
2.4.3 蛋白酶对细菌素抑菌活性的影响
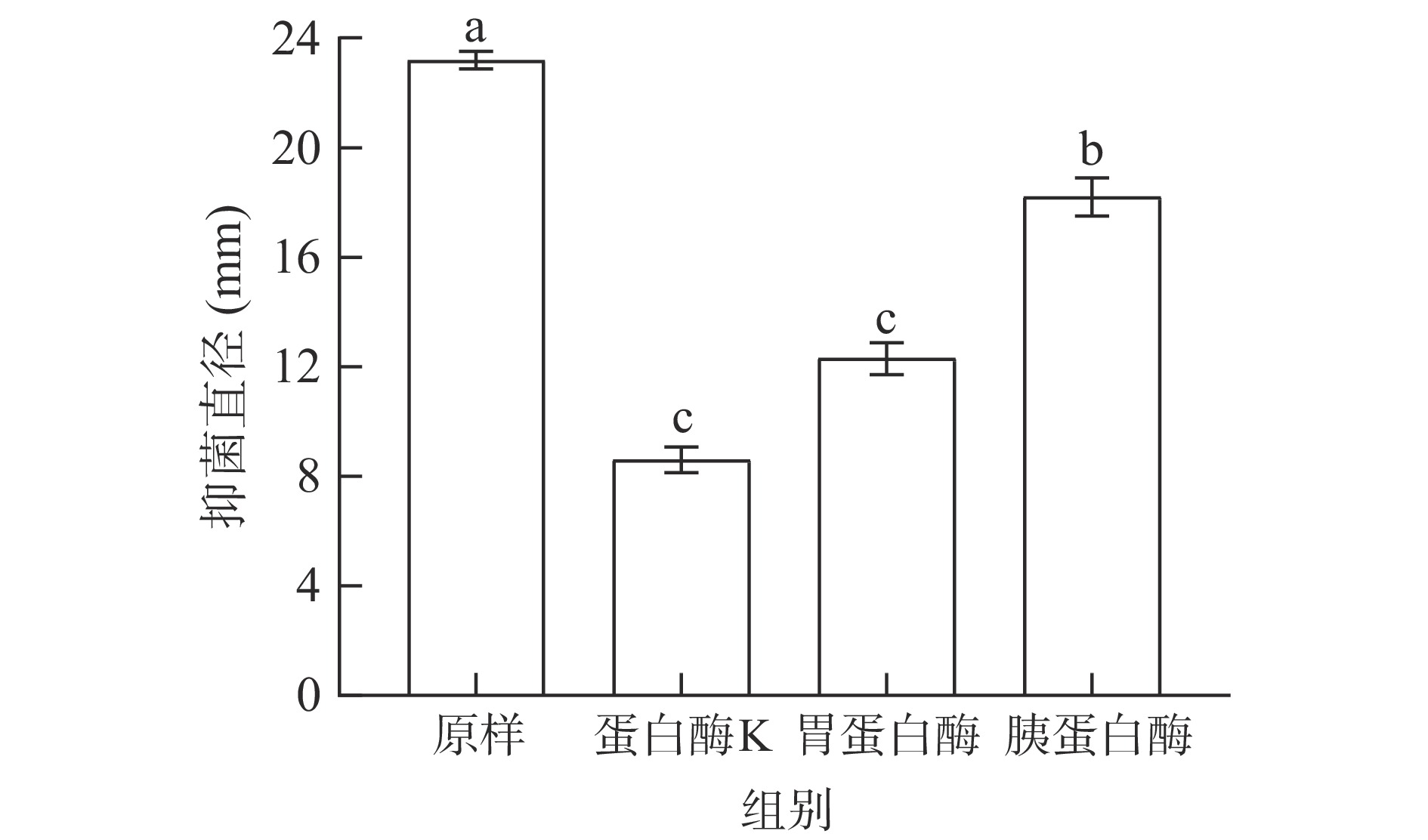
细菌素经蛋白酶K、胃蛋白酶、胰蛋白酶处理后的抑菌效果如图7所示。
经蛋白酶K处理后的抑菌直径与对照组相比,活性明显下降,说明细菌素会被蛋白酶K分解。而胃蛋白酶处理后,抑菌直径下降至53.02%;胰蛋白酶处理后活性下降至78.45%。这表明该抑菌物质可被蛋白酶K分解,且被人产生的胃蛋白酶及胰蛋白酶分解,由于脂肽基本不受蛋白酶影响[26],排除了该抑菌物质为脂肽的可能性,印证了该抑菌物质是细菌素。试验结果可以推测,该细菌素可以应用于食品防腐剂领域,因为其可被消化系统产生的酶分解,不会对人体自身的肠道菌群造成负担,从而不会危害人体健康。
3. 讨论与结论
芽孢杆菌在代谢过程中会分泌一种或多种抑菌活性物质,细菌素作为其次级代谢产物之一,具有抑菌范围广、理化性质稳定、安全性优良等优点,成为抗生素类抑菌制剂的理想替代品,因此,芽孢杆菌成为食品及医学行业的重要研究对象[27]。
有机溶剂萃取法是硫酸铵沉淀法的有效替代,该粗提方法的粗提液蛋白质含量合适,抑菌效果明显,且乙酸乙酯可以通过蒸馏完全去除,对后续的纯化过程影响极小。本研究曾使用硫酸铵沉淀法作为粗提方法,粗提物却未表现出抑菌活性,可能为硫酸铵浓度不当,或有机溶剂萃取法回收率更高从而能更好的提取此菌株的抑菌物质,有待进一步验证[28−30]。后续的纯化过程依据了细菌素的分子量选用了葡聚糖凝胶Sephadex-G50进行分离纯化,以280 nm处测定的吸光度分批检验出具有抑菌效果的峰值[30],并通过HPLC进一步纯化,经Tricine-SDS-PAGE试验与LC-MS/MS鉴定表明最终得到的细菌素为subtilosin A。
subtilosin A对常见食源性革兰氏阳性致病菌有明显的抑制效果,对常见食源性革兰氏阴性致病菌效果不明显。大量文献表明subtilosin A的抑菌机制为结合与攻击细菌的细胞膜[31],但据Algburi等[32]的观点,subtilosin A还有通过抑制细菌群体感应阻止生物膜形成等其他抑菌机理,具体抑菌机制与相关通路仍需通过其他手段进一步探明。
食品加工和贮藏过程中,温度和pH会因工艺条件、时间和环境等因素而发生变化[33−34],食品中使用的细菌素对热、酸、碱等条件的稳定性至关重要。环状细菌素因其高pH和热稳定性而闻名[35],subtilosin A作为套索肽具有环状结构,有与环状细菌素相似的特性:在20~60 ℃温度范围内的抑菌效果基本不受影响,在100~120 ℃下抑菌能力虽然下降但仍表现出良好活性,对高温有耐受性,有望应用在乳制品等需要高温处理的食品;该细菌素最适pH处于6.0~8.0偏中性的范围,耐酸碱条件范围较宽,具有良好的酸碱稳定性,且根据Nalisa等[24]的研究,即使是长时间的酸处理也无法使subtilosin A失活;与Epparti等[36]的试验结果一致,酶处理稳定性试验表明,该细菌素可被蛋白酶K分解,也可以被消化系统产生的胰蛋白酶与胃蛋白酶分解,不会对人体自身的肠道菌群造成负担,有应用于食品防腐剂领域的潜力。
本试验对传统发酵食品豆酱的菌种筛选中表现出突出抑菌活性的菌株S1-2进行了进一步研究。根据16S rDNA与持家基因gyrA测序结果确认该菌株为枯草芽孢杆菌,后续的试验鉴定该菌株能够产生细菌素subtilosin A并测定了该细菌素的抑菌活性与稳定性,证明了枯草芽孢杆菌S1-2与其所产细菌素的应用潜力。
-
表 1 芽孢杆菌对指示菌的抑菌圈直径(mm)
Table 1 Diameter of the antibacterial zone of Bacillus against indicator bacteria (mm)
菌株 金黄色葡萄球菌 单增李斯特菌 大肠杆菌 沙门氏菌 SP 9.23±0.25 10.7±0.16 6.01±0.02 6.09±0.03 S1 8.03±0.12 10.13±0.14 6.44±0.02 6.41±0.07 S1-2 12.31±0.42 14.06±0.23 7.23±0.03 7.18±0.06 S1-3 6.88±0.20 6.32±0.25 6.72±0.08 6.76±0.05 S2 7.21±0.14 7.41±0.21 − − S2-3 5.23±0.17 6.74±0.32 − − 注:“−”表示无抑制效果。 表 2 LC-MS/MS的部分蛋白鉴定结果
Table 2 Partial protein identification results of LC-MS/MS
蛋白质名称 评分 序列覆盖度(%) 分子量(kDa) Single-stranded DNA-binding protein 323.31 5.3 18.63 Thioredoxin 323.31 11.5 11.393 Uncharacterized protein YjfA 269.95 16.4 16.202 Uncharacterized protein YjdB 171.94 12.394 18.3 Tautomerase 114.18 14.5 7.1451 Subtilosin A 72.102 17.8 3.314 Subtilisin E 49.614 11.9 8.6586 Acyl carrier protein 41.417 19.5 8.5914 表 3 细菌素对金黄色葡萄球菌的最小抑菌浓度
Table 3 Minimum inhibitory concentrations of bacteriocin against Staphylococcus aureus
细菌素浓度(mg/mL) 10 5 2.5 1.25 0.625 0.312 0.156 金黄色葡萄球菌 − − − − + ++ ++ 注:“++”指液体浑浊;“+”指液体介于浑浊与澄清;“−”指液体澄清。 -
[1] 吴孔阳, 娄亚芳, 杨同香, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌功能及相关机制研究进展[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医,2020,611(23):55−58. [WU K Y, LOU Y F, YANG T X, et al. Research progress on the function and related mechanisms of Bacillus subtilis and its applications[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2020,611(23):55−58.] WU K Y, LOU Y F, YANG T X, et al . Research progress on the function and related mechanisms of Bacillus subtilis and its applications[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2020 ,611 (23 ):55 −58 .[2] RUIZ S S, BUENO T, DE O A, et al. Bacillus subtilis natto as a potential probiotic in animal nutrition[J]. Crit Rev Biotechnol,2021,41(3):355−369. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2020.1858019
[3] KIMURA K, YOKOYAMA S. Trends in the application of Bacillus in fermented foods[J]. Curr Opin Biotechnol,2019,56:36−42. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2018.09.001
[4] 张莹, 李章胜, 毛碧增. 生防芽孢杆菌分泌的拮抗物质的研究进展[J]. 浙江农业科学,2016,57(12):1960−1967. [ZHANG Y, LI Z S, MAO B Z. Research progress on antagonistic substances secreted by biocontrol Bacillus[J]. Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,2016,57(12):1960−1967.] ZHANG Y, LI Z S, MAO B Z . Research progress on antagonistic substances secreted by biocontrol Bacillus[J]. Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,2016 ,57 (12 ):1960 −1967 .[5] DE V R D, SCHMITZ K S, BOVIER F T, et al. Intranasal fusion inhibitory lipopeptide prevents direct-contact SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets[J]. Science,2021,371(6536):1379−1382. doi: 10.1126/science.abf4896
[6] SIMONS A, ALHANOUT K, DUVAL R E. Bacteriocins, antimicrobial peptides from bacterial origin:Overview of their biology and their impact against multidrug-resistant bacteria[J]. Microorganisms,2020,8(5):639. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8050639
[7] 范修强, 喻家晓, 刘峰, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌细菌素研究进展[J]. 湖南畜牧兽医,2022(6):47−50. [FAN X Q, YU J X, LIU F, et al. Research progress on bacteriocins of Bacillus subtilis[J]. Hunan Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2022(6):47−50.] FAN X Q, YU J X, LIU F, et al . Research progress on bacteriocins of Bacillus subtilis[J]. Hunan Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2022 (6 ):47 −50 .[8] 纪帅奇, 乌日娜, 张淘崴, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌SNBS-3全基因组测序及其抑菌物质预测分析[J]. 食品科学,2024,45(2):57−63. [JI S Q, WU R N, ZHANG T W, et al. Whole-genome sequencing and prediction of antibacterial substances of Bacillus subtilis SNBS-3[J]. Food Science,2024,45(2):57−63.] JI S Q, WU R N, ZHANG T W, et al . Whole-genome sequencing and prediction of antibacterial substances of Bacillus subtilis SNBS-3[J]. Food Science,2024 ,45 (2 ):57 −63 .[9] ISHIDA K, NAKAMURA A, KOJIMA S. Crystal structure of the AlbEF complex involved in subtilosin A biosynthesis[J]. Structure,2022,30(12):1637−1646. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2022.10.002
[10] 樊敏, 杨萍, 胡萍, 等. 贵州豆豉粑中微生物多样性研究[J]. 中国酿造,2019,38(3):81−88. [FAN M, YANG P, HU P, et al. Study on microbial diversity in Guizhou fermented soybean cake[J]. China Brewing,2019,38(3):81−88.] FAN M, YANG P, HU P, et al . Study on microbial diversity in Guizhou fermented soybean cake[J]. China Brewing,2019 ,38 (3 ):81 −88 .[11] 侯星, 易弋, 张兴猛, 等. 发酵食品中微生物的功能特性[J]. 中国调味品,2019,44(1):191−194,197. [HOU X, YI Y, ZHANG X M, et al. Functional characteristics of microorganisms in fermented foods[J]. China Condiment,2019,44(1):191−194,197.] HOU X, YI Y, ZHANG X M, et al . Functional characteristics of microorganisms in fermented foods[J]. China Condiment,2019 ,44 (1 ):191 −194,197 .[12] 王露露, 李斌, 彭雪菲, 等. 纳豆及其制品的安全性研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(8):325−333. [WANG L L, LI B, PENG X F, et al. Safety evaluation of natto and its products[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2022,22(8):325−333.] WANG L L, LI B, PENG X F, et al . Safety evaluation of natto and its products[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2022 ,22 (8 ):325 −333 .[13] 乌日娜, 薛亚婷, 张平, 等. 豆酱微生物宏蛋白质组提取及分析[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(14):17−23. [WU R N, XUE Y T, ZHANG P, et al. Extraction and analysis of microbial metaproteome in soybean paste[J]. Food Science,2017,38(14):17−23.] WU R N, XUE Y T, ZHANG P, et al . Extraction and analysis of microbial metaproteome in soybean paste[J]. Food Science,2017 ,38 (14 ):17 −23 .[14] ARBULU S, JIMÉNEZ J J, GÚTIEZ L, et al. Cloning and expression of synthetic genes encoding native, hybrid- and bacteriocin-derived chimeras from mature class IIa bacteriocins, by Pichia pastoris (syn. Komagataella spp.)[J]. Food Res Int,2019,121:888−899. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.01.015
[15] 刘晓萌, 张云鹏, 仉磊, 等. 3株降解玉米赤霉烯酮芽孢杆菌的快速鉴定[J]. 中国粮油学报,2022,37(9):34−39. [LIU X M, ZHANG Y P, ZHANG L, et al. Rapid identification of three Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strains capable of degrading zearalenone in maize[J]. Journal of Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2022,37(9):34−39.] LIU X M, ZHANG Y P, ZHANG L, et al . Rapid identification of three Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strains capable of degrading zearalenone in maize[J]. Journal of Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2022 ,37 (9 ):34 −39 .[16] 王伟, 陈渊戈, 迟海, 等. 牡蛎中产广谱细菌素芽孢杆菌的筛选及鉴定[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(3):282−290. [WANG W, CHEN Y G, CHI H, et al. Screening and identification of Bacillus producing broad-spectrum bacteriocins from oysters[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2021,21(3):282−290.] WANG W, CHEN Y G, CHI H, et al . Screening and identification of Bacillus producing broad-spectrum bacteriocins from oysters[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2021 ,21 (3 ):282 −290 .[17] 张建飞. 一株产细菌素粪链球菌N9301的分离鉴定及生物学特性研究[J]. 饲料研究,2022,45(8):78−82. [ZHANG J F. Isolation and biological characteristics of Enterococcus faecalis N9301 producing bacteriocin[J]. Feed Research,2022,45(8):78−82.] ZHANG J F . Isolation and biological characteristics of Enterococcus faecalis N9301 producing bacteriocin[J]. Feed Research,2022 ,45 (8 ):78 −82 .[18] 张炜, 杭柏林, 司素锦, 等. 抗菌肽BSN-37的抑菌活性及其稳定性分析[J]. 中国畜牧兽医,2019,46(1):287−295. [ZHANG W, HANG B L, SI S J, et al. Analysis of antibacterial activity and stability of antibacterial peptide BSN-37[J]. Chinese Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2019,46(1):287−295.] ZHANG W, HANG B L, SI S J, et al . Analysis of antibacterial activity and stability of antibacterial peptide BSN-37[J]. Chinese Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2019 ,46 (1 ):287 −295 .[19] ABDEL-MOHSEIN H S, SASAKI T, TADA C, et al. Characterization and partial purification of a bacteriocin-like substance produced by thermophilic Bacillus licheniformis H1 isolated from cow manure compost[J]. Anim Sci J,2011,82(2):340−351. doi: 10.1111/j.1740-0929.2010.00835.x
[20] 崔梦君, 张振东, 万舒曼, 等. 农家豆瓣酱细菌多样性及其对品质影响的评价[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(5):68−73. [CUI M J, ZHANG Z D, WAN S M, et al. Evaluation of bacterial diversity and its impact on the quality of homemade bean paste[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(5):68−73.] CUI M J, ZHANG Z D, WAN S M, et al . Evaluation of bacterial diversity and its impact on the quality of homemade bean paste[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020 ,46 (5 ):68 −73 .[21] 安飞宇, 姜静, 武俊瑞, 等. 自然发酵豆酱的滋味特性与微生物多样性分析[J]. 中国食品学报,2020,20(7):207−215. [AN F Y, JIANG J, WU J R, et al. Flavor characteristics and microbial diversity analysis of naturally fermented soybean paste[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2020,20(7):207−215.] AN F Y, JIANG J, WU J R, et al . Flavor characteristics and microbial diversity analysis of naturally fermented soybean paste[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2020 ,20 (7 ):207 −215 .[22] TORRES M J, PETROSELLI G, DAZ M, et al. Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis CBMDC3f with antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive foodborne pathogenic bacteria:UV-MALDI-TOF MS analysis of its bioactive compounds[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol,2015,31(6):929−940. doi: 10.1007/s11274-015-1847-9
[23] 付文鹏, 杨永寿, 肖培云. 动物源活性蛋白多肽的分离纯化方法研究进展[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2019,31(5):916−921. [FU W P, YANG Y S, XIAO P Y. Research progress on isolation and purification methods of bioactive peptides from animal sources[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2019,31(5):916−921.] FU W P, YANG Y S, XIAO P Y . Research progress on isolation and purification methods of bioactive peptides from animal sources[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2019 ,31 (5 ):916 −921 .[24] NALISA K, SURASAK S, PEERAPOL S, et al. Antibacterial activity and genotypic-phenotypic characteristics of bacteriocin-producing Bacillus subtilis KKU213:Potential as a probiotic strain[J]. Microbiological Research,2015,170:36−50. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2014.09.004
[25] 王文婧, 殷文政, 冀昌龙. 产抑菌活性物质菌株的筛选及其抑菌机理的研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2016,32(12):151−157. [WANG W J, YIN W Z, JI C L. Screening of bacterial strains producing antibacterial substances and study on their antibacterial mechanisms[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2016,32(12):151−157.] WANG W J, YIN W Z, JI C L . Screening of bacterial strains producing antibacterial substances and study on their antibacterial mechanisms[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2016 ,32 (12 ):151 −157 .[26] 陆晓岑, 杜明洋, 周维佳, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌BA015对无乳链球菌的拮抗作用及其物质分析[J]. 大连海洋大学学报,2021,36(1):103−109. [LU X C, DU M Y, ZHOU W J, et al. Antagonistic effects of Bacillus subtilis BA015 on Streptococcus agalactiae and analysis of its secreted substances[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University,2021,36(1):103−109.] LU X C, DU M Y, ZHOU W J, et al . Antagonistic effects of Bacillus subtilis BA015 on Streptococcus agalactiae and analysis of its secreted substances[J]. Journal of Dalian Ocean University,2021 ,36 (1 ):103 −109 .[27] 张德锋, 高艳侠, 王亚军, 等. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌的分类、拮抗功能及其应用研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报,2020,47(11):3634−3649. [ZHANG D F, GAO Y X, WANG Y J, et al. Research progress on classification, antagonistic function and application of Bacillus cereus[J]. Microbiology China,2020,47(11):3634−3649.] ZHANG D F, GAO Y X, WANG Y J, et al . Research progress on classification, antagonistic function and application of Bacillus cereus[J]. Microbiology China,2020 ,47 (11 ):3634 −3649 .[28] 徐新星, 曾轩, 李培中, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌CF-3抑菌蛋白的分离与鉴定[J]. 现代食品科技,2016,32(12):145−150,92. [XU X X, ZENG X, LI P Z, et al. Isolation and identification of antibacterial protein from Bacillus subtilis CF-3[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2016,32(12):145−150,92.] XU X X, ZENG X, LI P Z, et al . Isolation and identification of antibacterial protein from Bacillus subtilis CF-3[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2016 ,32 (12 ):145 −150,92 .[29] 吴光伟, 韩建春. 鼠李糖乳杆菌(ATTC 53103)产细菌素的研究[J]. 东北农业大学学报,2009,40(8):81−85. [WU G W, HAN J C. Study on bacteriocin production of Lactobacillus rhamnosus (ATTC 53103)[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University,2009,40(8):81−85.] WU G W, HAN J C . Study on bacteriocin production of Lactobacillus rhamnosus (ATTC 53103)[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University,2009 ,40 (8 ):81 −85 .[30] 兰宝锋, 王睿, 何双, 等. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌抑菌物质粗提取的优化及分析[J]. 中国酿造,2022,41(6):195−199. [LAN B F, WANG R, HE S, et al. Optimization and analysis of crude extraction of inhibitory substances from Bacillus Amycolatopsis[J]. China Brewing,2022,41(6):195−199.] LAN B F, WANG R, HE S, et al . Optimization and analysis of crude extraction of inhibitory substances from Bacillus Amycolatopsis[J]. China Brewing,2022 ,41 (6 ):195 −199 .[31] THENNARASU S, LEE D K, POON A, et al. Membrane permeabilization, orientation, and antimicrobial mechanism of subtilosin A[J]. Chem Phys Lipids,2005,137(1−2):38−51. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2005.06.003
[32] ALGBURI A, ZEHM S, NETREBOV V, et al. Subtilosin prevents biofilm formation by inhibiting bacterial quorum sensing[J]. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins,2017,9(1):81−90. doi: 10.1007/s12602-016-9242-x
[33] 谭婉静, 张笑薇, 白泓, 等. 丁香油与月桂酸对金黄色葡萄球菌的协同抑制作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2022,38(2):278−285,265. [TAN W J, ZHANG X W, BAI H, et al. Synergistic inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus by clove oil and lauric acid[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2022,38(2):278−285,265.] TAN W J, ZHANG X W, BAI H, et al . Synergistic inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus by clove oil and lauric acid[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2022 ,38 (2 ):278 −285,265 .[34] LIU G R, NIE R, LIU Y S, et al. Combined antimicrobial effect of bacteriocins with other hurdles of physicochemic and microbiome to prolong shelf life of food:A review[J]. Sci Total Environ,2022,825:154058. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154058
[35] GABRIELSEN C, BREDE D A, NES I F, et al. Circular bacteriocins:Biosynthesis and mode of action[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol,2014,80(22):6854−6862. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02284-14
[36] EPPARTI P, ELIGAR S M, SATTUR A P, et al. Characterization of dual bacteriocins producing Bacillus subtilis SC3.7 isolated from fermented food[J]. LWT,2022,154:112854. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112854
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 任卫威,张宇航,郑玉成,陈文贤,林宏政,徐梦婷,陈谢勇,陈百文,叶乃兴. 不同香型安溪黄金桂风味品质解析. 食品科学. 2025(05): 263-271 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李元朝,黎勤吉,郭玉琼,郝志龙,金珊. 枸杞茶感官审评方法的建立及其主要呈香物质的探索. 食品工业科技. 2025(04): 30-41 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 周晶晶,张雯萍,李光发,谢荣富,何吉杭,郝韵智,李秋明,余欣茹,林宏政,孙云. 九龙大白茶白茶风味品质的分析. 食品科学. 2025(06): 201-210 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘学艳,杨文光,徐婷,罗正飞,王绍梅,龚正礼. 并堆工艺对云南白茶品质影响的研究. 中国茶叶. 2025(03): 25-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



