Effects of Different Addition of Agaricus bisporus Powders on Rheological and Textural Properties of Yogurt
-
摘要: 为研究双孢蘑菇粉对酸奶理化性质的影响,以酸奶为原料,探究将不同质量分数(0.0%、1.5%、3.0%、4.5%、6.0%和7.5%)的双孢蘑菇粉(Agaricus bisporus powder,ABP)添加到酸奶中,并对在不同ABP添加量下的酸奶流变学和质构特性进行研究。结果表明:当ABP添加量为1.5%时,酸奶的动态黏弹性、表观黏度、稠度、硬度和内聚性对比对照组均有所降低;而当ABP添加量高于1.5%时,酸奶的动态黏弹性、表观黏度、稠度、硬度和内聚性会随ABP添加量的增加而增大;扫描电镜结果表明,ABP添加量为0.0%和1.5%的酸奶表现为具有较多空隙的酪蛋白纤维状网络结构,并且随着ABP添加量的增加,纤维网络中的空隙逐渐被ABP颗粒所填充,形成致密连续的空间结构,使酸奶的硬度、粘稠度和稳定性得到增强。综合分析可知,当ABP的添加量为1.5%~3.0%时,可使酸奶具有较好的流变性和质构特性。本研究结果为双孢蘑菇风味乳制品的研究和开发提供了理论和数据支持。Abstract: In order to investigate the effect of ABP (Agaricus bisporus powder) on the physicochemical properties of yogurt, ABP with different mass fractions (0.0%, 1.5%, 3.0%, 4.5%, 6.0% and 7.5%) was added to yogurt while using yogurt as the raw material, and the rheological and textural properties of yogurt were investigated at different ABP additions. The findings demonstrated that with the addition of ABP at 1.5%, the dynamic viscoelasticity, apparent viscosity, consistency, hardness, and cohesiveness of yogurt were decreased compared with the control group, while the dynamic viscoelasticity, apparent viscosity, consistency, hardness and cohesiveness of yogurt increased with a higher addition of ABP at over 1.5%. Moreover, the scanning electron microscopy results suggested that yogurt with ABP addition at 0.0% and 1.5% showed casein fibrillar network structure with more voids, and with the increase of ABP addition, the voids in the fibrous network were gradually filled by ABP particles, thus forming a dense and continuous spatial structure, which ultimately enhanced the hardness, consistency, and stability of the yogurt. According to the comprehensive analysis, the addition of ABP at 1.5%~3.0% will result in better rheological and textural properties of yogurt. In conclusion, these findings could provide theoretical and data support for the research and development of Agaricus bisporus-flavored dairy products.
-
Keywords:
- yogurt /
- Agaricus bisporus /
- rheology /
- texture
-
酸奶是一类深受广大消费者喜爱的发酵乳制品,全球酸奶市场于2019年已超过860亿美元,预计到2023年将突破1000亿美元大关[1]。市售的酸奶产品普遍具有较好的风味、口感和丰富的营养价值,富含乳酸菌等益生菌,可改善肠道菌群平衡[2]。研究表明,长期摄入酸奶等发酵乳制品有益于改善人体健康状况,在提高机体免疫力、维护胃肠道和心血管健康方面具有积极意义[3]。
酸奶是一类结构复杂、质地均匀的流体,由于在发酵过程中其内部酪蛋白胶束的聚集作用形成了一定强度的网状结构,因而表现出黏弹性等半固体的性质[4]。酸奶的流变性是酸奶在外力作用下表现出的流动和变形随温度、时间和力的变化而变化的特性,与酸奶内部形成的酪蛋白网络结构密切相关,常用于描述酸奶产品的质地与口感以衡量其优劣性,对于酸奶在消费者中的可接受度至关重要[5]。酸奶的质构特性是乳制和非乳制酸奶结构和质量的指标[6];质构是通过触觉和运动美学感知食物结构和表面特性。同视觉、嗅觉和触觉一样,口腔感觉是另一种动态的、有价值的感觉,它影响着消费者的喜好[7]。综上可知,酸奶的质构和流变特性,对酸奶的品质及感官影响较大。
双孢蘑菇(Agaricus bisporus)又名口蘑,是世界上种植和消费最为广泛的食用菌品种,其质地脆嫩,口感鲜美,富含膳食纤维、多种必需氨基酸和维生素,且含有甾醇、酚类等多种生物活性物质[8]。研究表明,双孢蘑菇提取物具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗癌等多种生理功效[9]。因此,双孢蘑菇兼具较好的食用价值和药用价值,在功能食品开发领域具有较好的前景。然而,近年来对双孢蘑菇的研究主要集中于对其所含生物活性成分[10]、栽培育种技术[11]和贮藏保鲜技术[12]等领域,而添加双孢蘑菇对食品理化性质的影响方面的研究也主要集中于对肉制品的改良。Feng等[13]通过向羊奶酸奶中添加枣浆,改善了酸奶的硬度、黏附性及保水性,在削弱山羊风味的同时,提升了感官接受度;Malihe等[14]将亚麻籽添加到酸奶中,提升了酸奶样品的硬度、黏性、咀嚼性、内聚性和弹性,通过感官评定确定了添加2.63%的亚麻籽可制作出令人满意的功能性酸奶产品;Muhammad等[15]通过添加不同量的芋头淀粉,研究了芋头淀粉对酸奶品质的影响,最终确定了2%的芋头淀粉可以提高酸奶的香气、口感、保水能力等;Vakili等[16]向酸奶中添加香菜籽粉和益生菌改善了酸奶的营养和功能特性;而双孢蘑菇作为一种功能因子,将其添加到酸奶中,期望可以对酸奶的食用品质和营养功效得到提升;而且目前有关双孢蘑菇对乳制品质构、流变特性及结构的影响的研究鲜有报道。
本课题组在前期研究中,对添加ABP制作的冻干型双孢蘑菇风味酸奶的制作工艺及双孢蘑菇的处理方式以及相关的营养基本指标进行了研究。本文将ABP作为一种潜在的功能成分,研究其添加量对酸奶流变学、质构特性及微观结构的影响,以期优化双孢蘑菇风味酸奶的食用品质。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
双孢蘑菇 由钟祥兴利食品股份有限公司提供,洗净后切片、100 ℃蒸汽漂烫3 min、沥干并进行真空冷冻干燥,机械粉碎后过100目筛,密封,4 ℃冷藏备用;蒙牛风味酸奶 原味,内蒙古蒙牛乳业股份有限公司。
FD5-2.5型真空冷冻干燥机 美国GOLDSIM公司;JYL-F700型电动打蛋器 九阳股份有限公司;DHR-2型流变仪 测试夹具为40 mm平行板,间距1 mm,美国TA仪器有限公司;TA.XT.Plus物性测定仪 英国SMS公司;SU8100扫描电子显微镜 日本HITACHI公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 酸奶样品的制备
采用相同规格的容器盛装酸奶样品,以酸奶100.0 g为基准,分别添加比例为0.0%、1.5%、3.0%、4.5%、6.0%和7.5%的ABP,用电动打蛋器充分搅打混匀后,4 ℃静置待测。
1.2.2 动态流变学测定
1.2.2.1 应变扫描与线性黏弹区的确定
考察不同添加量ABP对应变扫描时酸奶样品的储能模量G′的影响,以确定线性黏弹区的范围,并选择合适的应变γ0%。参考Juan等[1]的方法并略作改动,具体试验参数为:振荡-振幅模式;温度:4 ℃;平衡时间:5 min;扫描频率:1 Hz;应变:0.01%~100%;每数量级采点数为8。
1.2.2.2 频率扫描
考察不同添加量ABP对频率扫描时酸奶样品的储能模量G′和损耗模量G′′的影响。参考Pachekrepapol等[17]的方法并略作改动,具体试验参数为:振荡-频率模式;温度:4 ℃;平衡时间:5 min;应变:0.75%;扫描频率:0.01~10.00 Hz;每数量级采点数为8。
1.2.2.3 温度扫描
考察不同添加量ABP对温度扫描时酸奶样品的储能模量G′和损耗模量G′′的影响。参考Gao等[18]的方法并略作改动,具体试验参数为:振荡-温度斜坡模式;平衡时间:5 min;应变:0.75%;扫描频率:1 Hz;温度:4~30 ℃,升温速度为6 ℃/min;每10 s采点数为1。
1.2.3 静态流变学测定
1.2.3.1 表观黏度的测定
考察不同添加量ABP对酸奶样品表观黏度的影响。参考Tan等[19]的方法并略作改动,具体试验参数为:流动-斜坡模式;温度:4 ℃;平衡时间:5 min;剪切速率:0.01~100 s−1;测试时间:120 s;每4 s采点数为1。
1.2.3.2 触变特性的测定
考察不同添加量ABP对酸奶样品黏度和剪切应力的影响。参考Pérez等[20]的方法并略作改动,具体试验参数为:流动-斜坡模式;温度:4 ℃;平衡时间:5 min;剪切速率:0.01~100 s−1(升速)和100~0.01 s−1(降速);测试时间:120 s;每4 s采点数为1。
采用奥斯特瓦尔德-德沃尔幂律模型(Ostwald-de Waele power law model)拟合上行流动曲线[21],如公式所示:
式中:σ为剪切应力(Pa),K为稠度系数(Pa·sn),γ为剪切速率(s−1),n为流动特征指数。
1.2.4 质构特性
采用TA.XT.plus质构仪测定酸奶的硬度、内聚性、浓稠度、黏性和糊口性[22]等指标。参考Yin等[23]的方法并略作改动,将各组酸奶样品静置至室温后进行质构特性的测定。质构仪参数为:探头型号A/BE-40,测前速度1.0 mm/s,测试速度2.0 mm/s,测后速度10.0 mm/s,测定距离20 mm,触发类型:Auto-5 g。每个样品重复测定3次。
1.2.5 微观结构的测定
挑取各组酸奶样品的中心部分,于−80 ℃冰箱冷冻过夜后进行真空冷冻干燥,镀金后用扫描电子显微镜观察[24]。
1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS 19.0软件中的ANOVA模块的LSD和Duncan方法对实验数据进行差异显著性分析,采用Exponent 6.1.18.0软件对质构测定结果进行处理和分析,采用Origin 9.0.0和Excel 2019软件进行图形绘制。实验结果以平均值±标准差表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 动态流变学测定
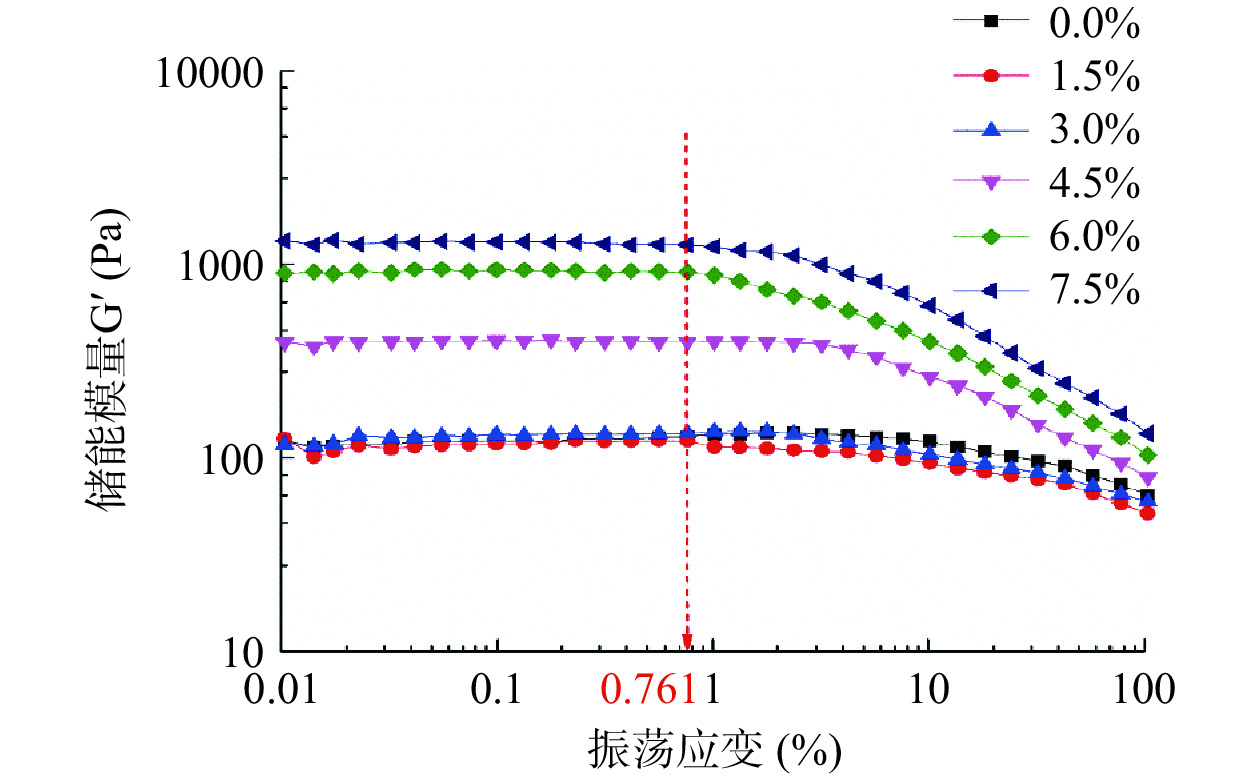
图1为各组酸奶样品的振荡应变扫描结果,由图可知,各组样品的储能模量G′在应变为0.01%~0.761%时均未随应变的增大发生显著变化,即处于样品的线性黏弹区内;而在应变值为0.761%后G′开始随着应变的增加而明显减小,表明已过渡到非线性黏弹区。本研究在线性黏弹区内选择应变为0.75%进行后续动态流变学试验。
2.1.1 应变扫描
储能(弹性)模量G'表示物质受到力的作用时的变形程度,损耗(黏性)模量G''表示物质受到力的作用时阻碍物质流动的特性。表1为应变在临界应变(0.761%)时各组酸奶的储能模量和损耗模量。由表可知,G′始终大于G′′,表明各组酸奶样品均表现为弹性特征占主导地位,具有类似凝胶的特征[25];当ABP添加量为1.5%时,酸奶的G′和G′′均略低于空白组(添加量0.0%),即酸奶的黏弹性均有所降低;当ABP添加量高于1.5%时,酸奶的G′和G′′均高于空白组,且随ABP添加量的增大而显著增大(P<0.05),储能模量G′的增长幅度较损耗模量G′′更为明显,表明ABP的添加量超过1.5%时,可提高酸奶的黏弹性,且对弹性的影响大于对黏性的影响。
表 1 ABP添加量对酸奶临界应变时的储能模量G′和损耗模量G′′的影响Table 1. Effects of ABP addition on storage modulus G′ and loss modulus G′′ of yogurt under the critical strain2.1.2 频率扫描
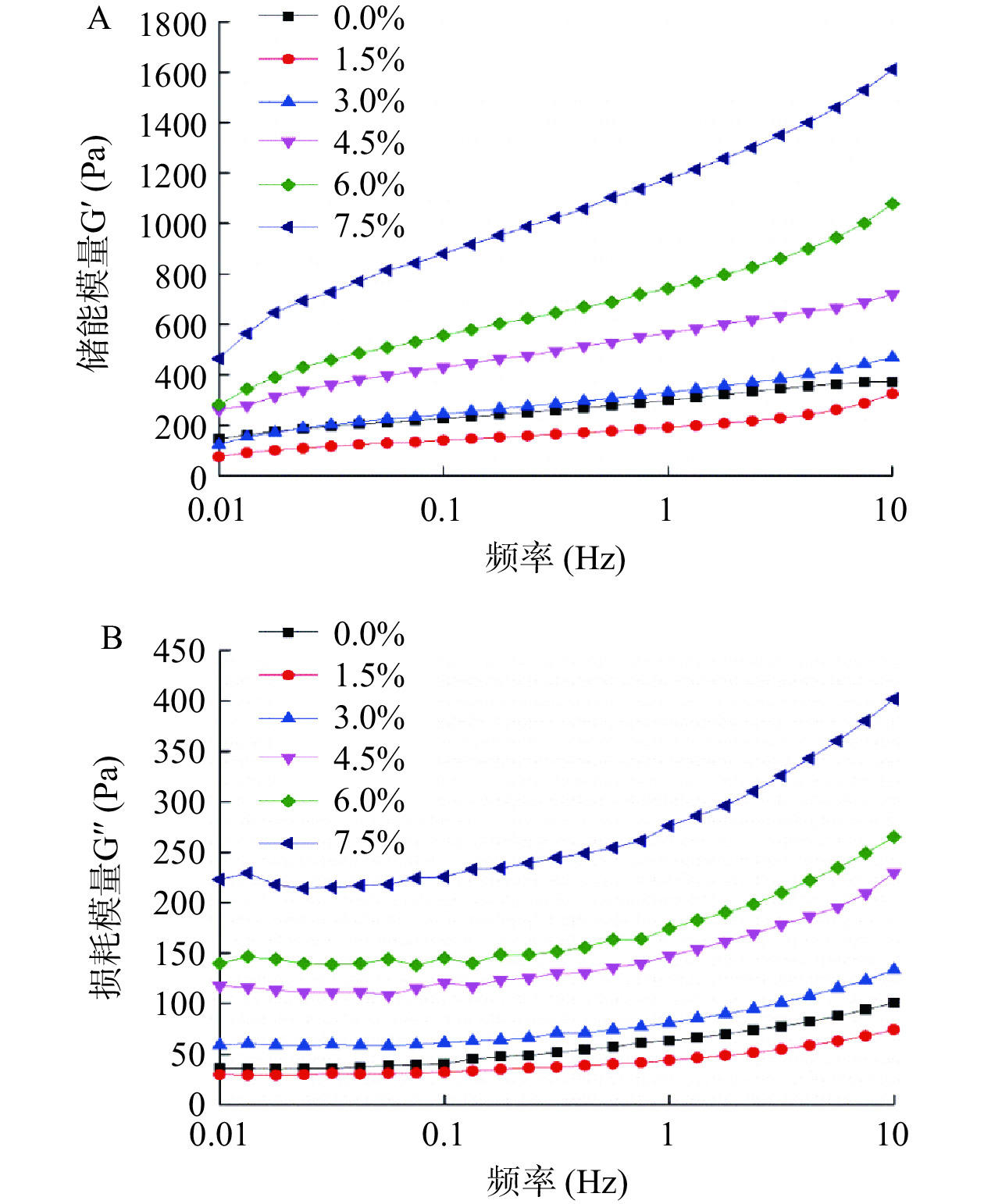
频率扫描是研究酸奶流变性最常用的方法之一,对酸奶的凝胶结构不会产生实质性的破坏,可研究酸奶逐渐加载荷时的黏弹性响应,同时也可以间接地反映酸奶的口感[26]。图2A和2B是不同组的酸奶样品在频率扫描中的G′和G′′的变化图。由图可知,各组酸奶样品的G′均表现出频率依赖性,各组酸奶的G′随频率的增加而上升;随着频率的增加,各组酸奶的G′′会首先出现小幅的下降,随后出现一个基本不随频率变化的平台区,最后随频率的增加而逐渐增大,这与吴伟都等[27]的研究结果一致,可能是由于低频振荡时的应力较小,低于样品的屈服应力,故只发生小幅的形变而不流动;随着频率的升高,应力超过了屈服应力,样品发生流动,平台期结束。另一方面,当ABP添加量为1.5%时,酸奶的G′和G′′均低于空白组,说明较低添加量的ABP可使酸奶变稀;当ABP添加量为3.0%时,酸奶的G′和G′′均略高于空白组,随着ABP添加量的增大,酸奶的G′和G′′逐渐增大,说明当ABP添加量高于1.5%时,ABP对酸奶起到了增稠的作用,ABP添加量越高,酸奶越不容易流动,呈现出类似固体的性质,但添加量过高、硬度过大反而对酸奶的口感不利[28]。酸奶中添加不同含量的ABP流变学频率扫描研究表明,添加1.5%~3.0%的ABP能够起到改善酸奶的流动性及质地,降低酸奶的黏结性的作用,且对酸奶品质影响较小。
2.1.3 温度扫描
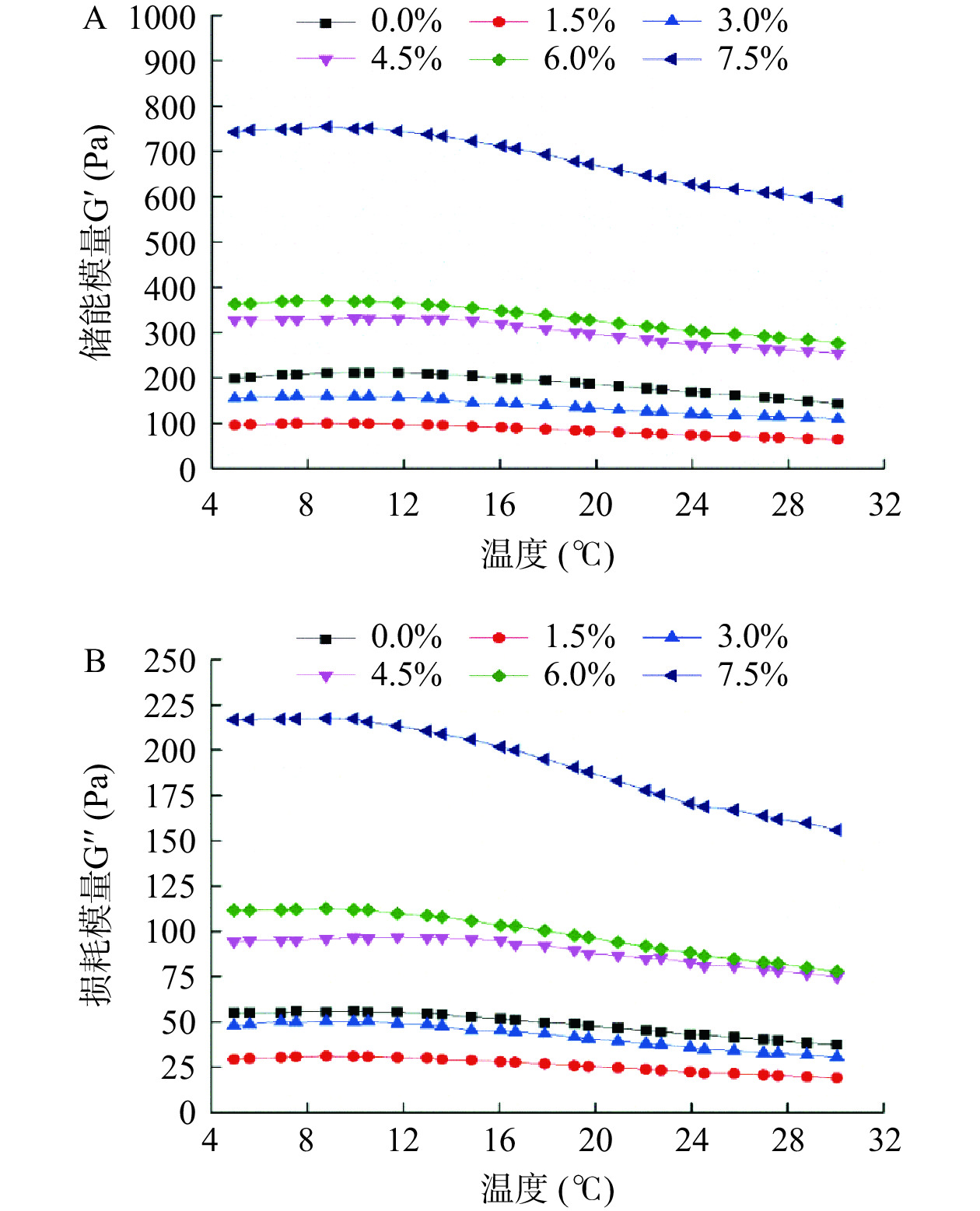
温度的变化会导致酸奶内部组织结构发生一定的变化,故温度扫描的结果可在一定程度上反映产品的稳定性和对温度的耐受能力,可为实际生产提供一定的理论依据[29]。图3A和3B是不同组的酸奶样品在4~30 ℃的温度扫描中储能模量G′和损耗模量G′′的变化图。由图可知,在升温过程中G′一直大于G′′,说明体系依然以弹性为主。从模量随温度的变化情况看,酸奶中ABP添加量越高,酸奶的G′和G′′的下降速率越快,而ABP添加量较低的酸奶在升温过程中模量变化较小,对温度的耐受性较好,能更好地保持其性状的稳定。温度为4~10 ℃时,各组酸奶样品均表现出较好的稳定性,G′和G′′值均随温度的升高基本保持不变;随着温度继续上升,各组酸奶样品的G′和G′′值均表现出一定的下降趋势,这可能是由于分子间的布朗运动加剧降低了流动阻力,或是酪蛋白分子间氢键发生断裂导致分子间的相互作用力下降,从而使黏弹性下降[30]。由动态流变学的温度扫描结果可知,从酸奶稳定性角度进行考量,可以添加1.5%~4.5%的ABP,对酸奶的营养品质进行改善,且添加量在此区间的酸奶具有良好的耐热性,不会影响酸奶的稳定性。
2.2 静态流变学测定
2.2.1 表观黏度
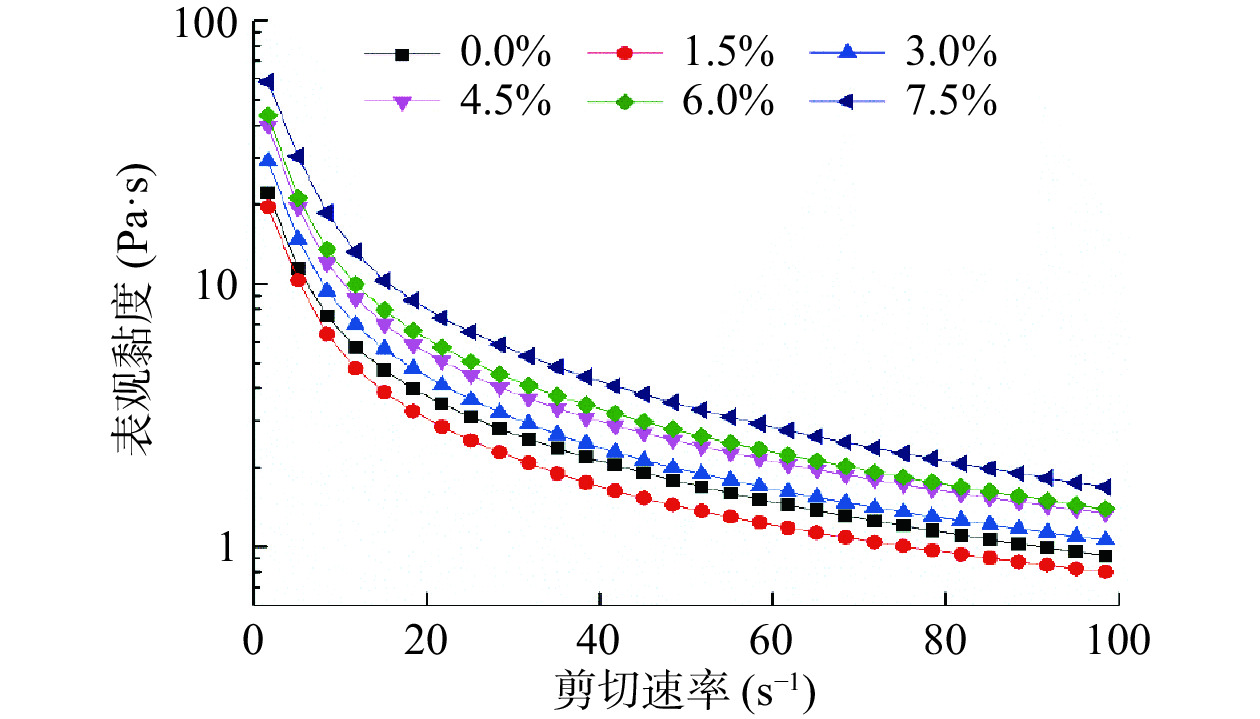
表观黏度可从侧面反映样品的结构及稳定性,是感官评价的重要组成部分[31]。图4是各组酸奶样品的黏度曲线图。由图可知,各组酸奶的表观黏度均随剪切速率的增大而逐渐降低,表现出剪切稀化现象,这是因为随着剪切速率的增大,样品中由蛋白质、糖类和脂肪等物质构成的空间网状结构被破坏,分子间相互作用力降低,表现为黏度下降[32]。同一剪切速率条件下,各实验组酸奶的表观黏度随ABP添加量的增加而逐渐增大;而添加量为1.5%的酸奶的表观黏度反而低于空白组酸奶,说明较低添加量的ABP会削弱酸奶中原有的网络结构,而添加量高于1.5%时,可能是由于ABP的加入增大了体系中膳食纤维的含量,具有较强水合能力,从而使酸奶的黏度不断增大[33]。因此,从静态流变学的观点来看,考虑酸奶的稳定性,ABP的添加量在1.5%~4.5%较为合理。
2.2.2 触变特性及幂律方程拟合
触变特性可以反映酸奶在不断变化的剪切速率下的黏度变化及结构变化规律。图5是各组酸奶样品在不同剪切速率下的流动曲线,由图可知,各组酸奶样品的剪切应力均随剪切速率的增加而增大,然后随剪切速率的降低而减小;各组酸奶样品的升速曲线和降速曲线均不重合,表现出一定的滞后现象从而形成触变环,符合触变性流体的显著特征。这是因为剪切作用会导致酸奶中的凝胶结构发生破坏,需要经过一定的时间才能回复到原有的体系状态,故出现这种剪切变稀的现象[23]。
ABP添加量对酸奶流变学参数的影响如表2所示。其中,触变环面积的大小反映了酸奶样品在经外力剪切后回复原来状态的快慢程度,触变环面积越大,表明样品的触变性越大,体系经外力剪切作用后黏度的变化越大,在剪切作用停止后,样品内部结构重新组合和回复的速度越慢。这也反映出,酸奶经长时间的剪切后再静止是一个重新稠化的过程,具有较小触变环面积的物料更易于保型,有利于产品的加工制作[34]。由表2可知,各实验组酸奶触变环的面积随ABP添加量的增大而显著增大,当添加量为1.5%时,酸奶的触变环面积最小(943.48±3.04 Pa/s),显著(P<0.05)低于空白组酸奶;而添加量高于1.5%时,酸奶的触变环面积均显著高于空白组(P<0.05),说明添加1.5% ABP时,酸奶的凝胶网络结构回复最快,而ABP添加量高于1.5%时,由于酸奶与菇粉颗粒之间形成了相对更为致密稳定的空间结构,故经剪切行为破坏后重构过程更长,回复速度较慢[35]。由上可知,不同添加量的ABP对酸奶受外力剪切后的回复性有着不同的影响,考虑实际生产及样品的稳定性,ABP的添加量在1.5%~3.0%之间较为合适。
表 2 ABP添加量对酸奶样品流变学参数的影响Table 2. Effects of ABP addition on rheological parameters of yogurt samplesABP添加量(%) 触变环面积(Pa/s) n K (Pa·sn) R2 0.0 1489.96±5.16e 0.16±0.01a 44.78±1.54e 0.9407 1.5 943.48±3.04f 0.17±0.01a 36.87±0.86e 0.9720 3.0 1739.64±11.82d 0.13±0.01b 58.23±1.58d 0.9375 4.5 2222.58±19.95c 0.13±0.01b 74.55±1.71c 0.9517 6.0 2979.49±22.49b 0.10±0.01bc 88.43±2.83b 0.8700 7.5 4435.15±63.30a 0.09±0.01c 117.90±3.95a 0.8177 各组酸奶上行流动曲线的幂律方程拟合参数如表2所示,其中流动特征指数n表示样品的流动特性与牛顿流体特性的接近程度,稠度指数K反映了样品的黏稠度[36]。由表可知,除添加量为6.0%和7.5%的两组样品外,其余4组样品的拟合方程的相关系数均达到0.93以上,表现出较好的拟合度;各组酸奶的流动特征指数n均小于1,在0.09~0.17范围内,为假塑性流体,与其黏度曲线剪切稀化的结果相符。当ABP添加量为1.5%时,样品的K值和n值均与空白组无显著差异(P>0.05),即ABP添加量较低时对酸奶的稠度无显著影响;而当添加量高于1.5%时,随着ABP添加量的增加,酸奶的流动特征指数n逐渐降低,而稠度指数K显著增大(P<0.05),说明ABP添加量越大,酸奶的流动性越小、稠度越大,与黏度曲线的变化趋势相符,这与Hanou等[37]的研究结果一致,可能是酸奶中的总固形物含量的增加促进了粒子间相互作用的增加所致。因此,从酸奶的流动性及黏稠度进行考量,ABP的添加量不应超过3.0%,否则会降低酸奶的流动性,导致酸奶过稠,可能会对酸奶的口感产生不良的影响。
2.3 质构特性
ABP添加量对酸奶质构特性的影响如表3所示,结果也证实了ABP的添加对酸奶流变学特性的影响。由表3可知,酸奶的硬度、内聚性、浓稠度、黏性均随ABP添加量的增大呈先减小后增大的趋势。当添加量为1.5%时,酸奶的硬度、内聚性、浓稠度、黏性和糊口性最小;添加量为3.0%的酸奶与空白组酸奶在各项质构指标上均无显著性差异(P>0.05);而随着添加量的增大,酸奶的硬度、内聚性、浓稠度和黏性均呈上升趋势,说明ABP添加量较低时,会对酸奶内部结构的稳定性产生一定的负面影响,使酸奶呈稀软的状态,而随着ABP添加量的增大,体系中逐渐形成了较强的空间结构,使酸奶变得黏稠而稳定,但由于在口中更难以化开,致使口感变差。根据不同ABP添加量下的酸奶质构特性结果表明,ABP的添加量在1.5%~4.5%较为适宜。
表 3 ABP添加量对酸奶样品质构特性的影响Table 3. Effects of ABP addition on textural properties of yogurt samplesABP添加量(%) 硬度(g) 内聚性(g) 浓稠度(g) 黏性(g·sec) 糊口性 0.0 45.22±1.18c 31.06±0.11c 37.22±1.55bc 67.69±11.06ab 0.69±0.02a 1.5 39.77±0.43d 26.36±1.71d 31.76±3.89c 46.70±10.75c 0.66±0.04a 3.0 45.45±0.43c 30.30±0.11c 39.33±0.49b 58.94±3.94bc 0.67±0.00a 4.5 46.55±0.48bc 32.19±1.07bc 40.22±0.17b 66.78±2.37ab 0.69±0.02a 6.0 49.16±2.36b 34.81±0.91b 42.82±1.85b 71.96±1.76ab 0.71±0.02a 7.5 55.90±2.14a 39.28±1.45a 49.44±3.34a 81.26±4.03a 0.70±0.01a 2.4 微观结构
不同ABP添加量的酸奶的扫描电镜图如图6所示。图6A为空白组酸奶放大5000倍的SEM照片,可以观察到酸奶内部结构主要表现为由较多不规则纤维状酪蛋白胶束连接而成的立体网络结构,结构内部存在较多形状、大小无明显规则的空隙,结构外部存在较多的自由末端。图B、C、D、E和F分别为添加1.5%、3.0%、4.5%、6.0%和7.5% ABP的酸奶样品扫描电镜图,由图可知,ABP颗粒填充了酪蛋白网络结构内部的空隙,或是附着在网络结构外部的自由末端并不断堆积;当ABP添加量为1.5%时,酸奶的结构中能够观察到与对照组类似的较多纤维状的酪蛋白结构和空隙的存在,而ABP添加量为3.0%时可观察到结构中的空隙已有一定减少;随着ABP添加量的不断增加,酸奶的网络结构变得更为紧密和牢固,逐渐形成致密且连续的空间结构,使酸奶的稳定性和黏度逐渐增强[38]。
3. 结论
本实验对不同ABP添加量的酸奶的流变学和质构特性进行研究,结果表明,与空白组酸奶相比,1.5% ABP酸奶具有较低的动态黏弹性、表观黏度、稠度、硬度和内聚性,酪蛋白网络结构中具有较多无规则空隙;随着ABP添加量的增加,酪蛋白网络结构中的空隙逐渐被ABP颗粒所填充,网络结构逐渐变得致密而连续,使酸奶的硬度、黏稠度和稳定性不断增强,这也侧面反映酸奶品质随ABP的添加而表现出下降的趋势。综合以上结果,ABP的添加量为1.5%~3.0%时,可使酸奶具有较好的流变性和质构特性。本实验的研究结果为双孢蘑菇风味乳制品的制作提供了参考依据。
-
表 1 ABP添加量对酸奶临界应变时的储能模量G′和损耗模量G′′的影响
Table 1 Effects of ABP addition on storage modulus G′ and loss modulus G′′ of yogurt under the critical strain
表 2 ABP添加量对酸奶样品流变学参数的影响
Table 2 Effects of ABP addition on rheological parameters of yogurt samples
ABP添加量(%) 触变环面积(Pa/s) n K (Pa·sn) R2 0.0 1489.96±5.16e 0.16±0.01a 44.78±1.54e 0.9407 1.5 943.48±3.04f 0.17±0.01a 36.87±0.86e 0.9720 3.0 1739.64±11.82d 0.13±0.01b 58.23±1.58d 0.9375 4.5 2222.58±19.95c 0.13±0.01b 74.55±1.71c 0.9517 6.0 2979.49±22.49b 0.10±0.01bc 88.43±2.83b 0.8700 7.5 4435.15±63.30a 0.09±0.01c 117.90±3.95a 0.8177 表 3 ABP添加量对酸奶样品质构特性的影响
Table 3 Effects of ABP addition on textural properties of yogurt samples
ABP添加量(%) 硬度(g) 内聚性(g) 浓稠度(g) 黏性(g·sec) 糊口性 0.0 45.22±1.18c 31.06±0.11c 37.22±1.55bc 67.69±11.06ab 0.69±0.02a 1.5 39.77±0.43d 26.36±1.71d 31.76±3.89c 46.70±10.75c 0.66±0.04a 3.0 45.45±0.43c 30.30±0.11c 39.33±0.49b 58.94±3.94bc 0.67±0.00a 4.5 46.55±0.48bc 32.19±1.07bc 40.22±0.17b 66.78±2.37ab 0.69±0.02a 6.0 49.16±2.36b 34.81±0.91b 42.82±1.85b 71.96±1.76ab 0.71±0.02a 7.5 55.90±2.14a 39.28±1.45a 49.44±3.34a 81.26±4.03a 0.70±0.01a -
[1] JUAN O A, ANGELA P M, OSCAR V C, et al. Rheological, texture, structural, and functional properties of Greek-style yogurt fortified with cheese whey-spent coffee ground powder[J]. LWT,2020,129:109523. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109523
[2] SHIMA P G, MOHAMMAD A K, MEHDI N, et al. Impact of sturgeon gelatin hydrolysates (SGH) on physicochemical and microbiological properties of fat-free set-type yogurt[J]. LWT,2021,148:111665. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111665
[3] DENNIS A S, ROBERT W H. Yogurt, cultured fermented milk, and health:A systematic review[J]. Nutrition Reviews, 2020:599−614.
[4] LESME H, RANNOU C, FAMELART M H, et al. Yogurts enriched with milk proteins:Texture properties, aroma release and sensory perception[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2020,98:140−149.
[5] GILBERT A, TURGEON S L. Studying stirred yogurt microstructure and its correlation to physical properties:A review[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,121:106970. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106970
[6] ANNU M, LOKESH K, LUCA S, et al. Exploring the textural dynamics of dairy and plant-based yoghurts:A comprehensive study[J]. Food Research International,2023,171:113058. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113058
[7] DAVIDE G, CLAUSEN M P, JAEGER S R. Understanding barriers to consumption of plant-based foods and beverages:Insights from sensory and consumer science[J]. Current Opinion in Food Science,2022,48:100919. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2022.100919
[8] CAI Ming, ZHONG Huazhao, MA Qinghua, et al. Physicochemical and microbial quality of Agaricus bisporus packaged in nano-SiO2/TiO2 loaded polyvinyl alcohol films[J]. Food Control,2022,131:108452. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108452
[9] USMAN M, MURTAZA G, DITTA A. Nutritional, medicinal, and cosmetic value of bioactive compounds in button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus):A Review[J]. Applied Sciences,2021,11:5943. doi: 10.3390/app11135943
[10] BLUMFIELD M, ABBOTT K, DUVE E, et al. Examining the health effects and bioactive components in Agaricus bisporus mushrooms:A scoping review[J]. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2020,84:108453. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108453
[11] WANG Qian, JUAN Jiaxiang, XIAO Tingting, et al. The physical structure of compost and C and N utilization during composting and mushroom growth in Agaricus bisporus cultivation with rice, wheat, and reed straw-based composts[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2021,105(9):3811−3823. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11284-0
[12] CHANG C K, CHENG K C, HOU C Y, et al. Development of active packaging to extend the shelf life of Agaricus bisporus by using plasma technology[J]. Polymers,2021,13:2120. doi: 10.3390/polym13132120
[13] FENG Cuijiao, WANG Bini, ZHAO Aiqing, et al. Quality characteristics and antioxidant activities of goat milk yogurt with added jujube pulp[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,277:238−245. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.10.104
[14] MALIHE M, ALI H, AMIR G D, et al. Texture and sensory characterization of functional yogurt supplemented with flaxseed during cold storage[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2019,7(3):907−917.
[15] MUHAMMAD S, MUHAMMAD A, FARHANA N, et al. Functional exploration of taro starch (Colocasia esculenta) supplemented yogurt[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2023,11(6):2697−2707.
[16] VAKILI N S, TOORAJ M, JAVAD A, et al. Physicochemical, sensory and microbiological characteristics of coriander seed powder yogurt[J]. AMB Express,2023,13(1):66−76. doi: 10.1186/s13568-023-01572-5
[17] PACHEKREPAPOL U, SOMBOONCHAI N, KRIMJAI W. Physicochemical, rheological, and microbiological properties of lactose-free functional yogurt supplemented with fructooligosaccharides[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 2020:e15017.
[18] GAO Kun, LIU Yanxiang, TAN Bin, et al. An insight into the rheology and texture assessment:The influence of sprouting treatment on the whole wheat flour[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,125:107248. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107248
[19] TAN P Y, TAN T B, CHANG H W, et al. Effects of storage and yogurt matrix on the stability of tocotrienols encapsulated in chitosan-alginate microcapsules[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,241:79−85. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.08.075
[20] PÉREZ J, ARTEAGA M, ANDRADE R, et al. Effect of yam (Dioscorea spp.) starch on the physicochemical, rheological, and sensory properties of yogurt[J]. Heliyon,2021,7:e05987. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e05987
[21] BURAN İ, AKAL C, OZTURKOGLU-BUDAK S, et al. Rheological, sensorial and volatile profiles of synbiotic kefirs produced from cow and goat milk containing varied probiotics in combination with fructooligosaccharide[J]. LWT,2021,148:111591. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111591
[22] LESME H, RANNOU C, LOISEL C, et al. Controlled whey protein aggregates to modulate the texture of fat-free set-type yoghurts[J]. International Dairy Journal,2019,92:28−36. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2019.01.004
[23] YIN Mengdi, YANG Dongying, LAI Shaojuan, et al. Rheological properties of xanthan-modified fish gelatin and its potential to replace mammalian gelatin in low-fat stirred yogurt[J]. LWT,2021,147:111643. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111643
[24] 刘立鹏, 李雪晴, 李红娟, 等. 脱脂乳的不同热处理工艺对酸奶质构和微观结构的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2017,43(3):26−30. [LIU Lipeng, LI Xueqing, LI Hongjuan, et al. Effect of different heat treatment processes of skim milk on texture and microstructure of yogurt[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2017,43(3):26−30.] LIU Lipeng, LI Xueqing, LI Hongjuan, et al. Effect of different heat treatment processes of skim milk on texture and microstructure of yogurt[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2017, 43(3): 26−30.
[25] ZAINI H B M, SINTANG M D B, PINDI W. The roles of banana peel powders to alter technological functionality, sensory and nutritional quality of chicken sausage[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2020,8:5497−5507.
[26] JUAN P P O, SÁNCHEZ-HERRERA L M, ORTIZ-BASURTO R I. Effect of concentration, temperature, pH, co-solutes on the rheological properties of Hyptis suaveolens L. mucilage dispersions[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,87:297−306. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.08.004
[27] 吴伟都, 欧凯, 朱慧, 等. 流变仪测定搅拌型酸乳黏弹特性的研究[J]. 食品科技,2019,44(2):314−318. [WU Weidu, OU Kai, ZHU Hui, et al. Determination of visco-elasticity properties of stirred yoghurt with rheometer[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,44(2):314−318.] WU Weidu, OU Kai, ZHU Hui, et al. Determination of visco-elasticity properties of stirred yoghurt with rheometer[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2019, 44(2): 314−318.
[28] 付丽, 刘旖旎, 陈丹雅, 等. 乳清蛋白粉对凝固型酸奶品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(13):39−45. [FU Li, LIU Yini, CHEN Danya, et al. Effect of whey protein powder on the quality of solidified yogurt[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(13):39−45.] FU Li, LIU Yini, CHEN Danya, et al. Effect of whey protein powder on the quality of solidified yogurt[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(13): 39−45.
[29] 白英, 张建丽, 刘立杰, 等. 贮藏期发酵剂对发酵乳流变特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(10):179−184,202. [BAI Ying, ZHANG Jianli, LIU Lijie, et al. Effect of culture on the rheological properties of fermented milk during refrigeration[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(10):179−184,202.] BAI Ying, ZHANG Jianli, LIU Lijie, et al. Effect of culture on the rheological properties of fermented milk during refrigeration[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2016, 37(10): 179−184,202.
[30] 赵雯, 张健, 姜芸云, 等. 不同种类脂肪替代物对软冰淇淋浆料流变特性及产品品质和口感的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(12):1−8. [ZHAO Wen, ZHANG Jian, JIANG Yunyun, et al. Effect of fat replacers on rheological properties of soft ice cream mixes and quality and moutufeel of ice cream[J]. Food Science,2018,39(12):1−8.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201812001 ZHAO Wen, ZHANG Jian, JIANG Yunyun, et al. Effect of fat replacers on rheological properties of soft ice cream mixes and quality and moutufeel of ice cream[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(12): 1−8. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201812001
[31] 谭允冰, 赵强忠. 大豆蛋白酶解产物对不同发酵剂酸奶品质的影响[J]. 现代食品科技,2017,33(8):103−109. [TAN Yunbing, ZHAO Qiangzhong. Influences of soy protein hydrolysate on the quality of yoghurts fermented by different starter cultures[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2017,33(8):103−109.] TAN Yunbing, ZHAO Qiangzhong. Influences of soy protein hydrolysate on the quality of yoghurts fermented by different starter cultures[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2017, 33(8): 103−109.
[32] 刘玉兰, 舒垚, 孙国昊, 等. 花生品种对花生酱风味及综合品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(9):15−21. [LIU Yulan, SHU Yao, SUN Guohao, et al. Effects of different varieties of peanuts on the flavor and quality of peanut butter[J]. Food Science,2021,42(9):15−21.] LIU Yulan, SHU Yao, SUN Guohao, et al. Effects of different varieties of peanuts on the flavor and quality of peanut butter[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(9): 15−21.
[33] 陈若辰, 戴涛涛, 陈明舜, 等. 高压射流磨处理对全组分燕麦浆的营养成分及理化性质影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(13):92−97,111. [CHEN Ruochen, DAI Taotao, CHEN Mingshun, et al. Effects of high-pressure jet mill treatment on nutritional composition and physicochemical properties of whole grain oat slurry[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(13):92−97,111.] CHEN Ruochen, DAI Taotao, CHEN Mingshun, et al. Effects of high-pressure jet mill treatment on nutritional composition and physicochemical properties of whole grain oat slurry[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(13): 92−97,111.
[34] 刘婷婷, 杨嘉丹, 曹宸瑀, 等. 银耳多糖与结冷胶复配体系的流变及凝胶特性[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(17):72−78. [LIU Tingting, YANG Jiadan, CAO Chenyu, et al. Rheological and gelling properties of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide and gellan gum mixtures[J]. Food Science,2019,40(17):72−78.] doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190122-257 LIU Tingting, YANG Jiadan, CAO Chenyu, et al. Rheological and gelling properties of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide and gellan gum mixtures[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(17): 72−78. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190122-257
[35] 李浩, 张浩, 赵城彬, 等. 纤维素和聚葡萄糖对玉米淀粉凝胶糊化及流变特性的影响[J]. 食品工业,2018,39(8):59−64. [LI Hao, ZHANG Hao, ZHAO Chengbin, et al. Effect of cellulose and polydextrose on gelatinization and rheological properties of corn starch[J]. The Food Industry,2018,39(8):59−64.] LI Hao, ZHANG Hao, ZHAO Chengbin, et al. Effect of cellulose and polydextrose on gelatinization and rheological properties of corn starch[J]. The Food Industry, 2018, 39(8): 59−64.
[36] BHARDWAJ M, SANDHU K S, SAXENA D C. Experimental and modeling studies of the flow, dynamic and creep recovery properties of pearl millet starch as affected by concentration and cultivar type[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,135:544−552. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.192
[37] HANOU S, BOUKHEMIS M, BENATALLAH L, et al. Research article:Effect of ginger powder addition on fermentation kinetics, rheological properties and bacterial viability of dromedary yogurt[J]. Advance Journal of Food Science & Technology,2016,10(9):667−673.
[38] 吴飞. 大麦粉对酸奶的增稠作用及其机制研究[D]. 镇江:江苏大学, 2017. [WU Fei. Study on thickening properties of barley flour in yoghurt and its mechanism[D]. Zhenjiang:Jiangsu University, 2017.] WU Fei. Study on thickening properties of barley flour in yoghurt and its mechanism[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2017.





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



