Effects of Xylitol on Physicochemical Properties of Glutinous Rice Flour and Quality of Glutinous Rice Dumplings
-
摘要: 将不同添加量(0%~25%)的木糖醇添加至糯米粉中构建木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系,探讨木糖醇对糯米粉的糊化特性、热力学特性、凝胶质构、流变学特性和消化特性等性质以及对其制成的汤圆品质的影响。结果表明:木糖醇的添加使共混体系的糊化温度、峰值黏度和终值黏度有所提高,体系的短程有序程度降低,体系表现为假塑性流体,具有剪切稀化行为。与对照组相比,木糖醇添加量为10%时,共混体系的回生值和凝胶硬度最小,分别为405 cP和14.952 g,体系抗性淀粉含量为29.88%,表现出较好的抗回生性。但高浓度木糖醇(15%~25%)促进体系发生短期回生,增加其回生值和弹性。另外,木糖醇的添加显著降低了汤圆的冻藏水分损失率和汤汁透过率,其中添加10%的木糖醇制成的汤圆具有更高的硬度、弹性、回复性以及咀嚼性,食用品质最好。本研究为木糖醇改善糯米粉品质以及糯米粉产品开发提供参考。Abstract: Xylitol with different content (0%~25%) was added to glutinous rice flour to construct a xylitol-glutinous rice flour blend system to investigate the effects of xylitol on the gelatinization properties, thermodynamic properties, gel texture, rheology properties and digestion properties of glutinous rice flour, as well as on the quality of rice dumpling made from xylitol-glutinous rice flour. The results showed that the addition of xylitol increased the gelatinization temperature, peak viscosity and final viscosity of the xylitol-glutinous rice flour, while reduced the degree of short-range order of xylitol-glutinous rice flour. The xylitol-glutinous rice flour system behaved as a pseudoplastic fluid with shear thinning behavior. Compared with the control group, when the addition of xylitol was 10%, the xylitol-glutinous rice flour blend system had the smallest retrogradation value and gel hardness, which were 405 cP and 14.952 g, respectively. At this time, the content of resistant starch in the system was 29.88%, showing good retrogradation resistance. However, high content of xylitol (15%~25%) promoted the short-term regeneration of the xylitol-glutinous rice flour blend system, increasing its regeneration value and elasticity. Furthermore, the addition of xylitol significantly reduced the water loss rate and juice permeability of rice dumpling made of xylitol glutinous rice flour. Rice dumpling made of glutinous rice flour with 10% xylitol had high hardness, elasticity, resilience and chewability, and its eating quality was the best. This study provides a theoretical and technical references for the improvement of the quality of glutinous rice flour through xylitol and the product development of glutinous rice flour.
-
Keywords:
- xylitol /
- glutinous rice flour /
- physicochemical properties /
- rice dumplings
-
糯米作为我国主要的粮食作物之一,富含淀粉、蛋白质、脂肪、钙、磷、铁以及维生素等多种营养物质。糯米粉粉质均匀细腻,被广泛应用于传统糕点的制作[1]。由于糯米粉中几乎完全是支链淀粉,直链淀粉含量较少,导致其保水能力较弱,无延展性,显著影响糯米制品的加工以及感官品质[2]。因此,包括糯米制品在内的一些淀粉基食品中常使用糖类为添加剂,以通过影响淀粉的糊化和回生特性来优化加工工艺及理化性质[3]。张瑜等[4]研究发现在海藻糖和糯米粉复合体系中,随海藻糖添加量的增加,糯米粉糊化温度升高,糊化黏度呈现先增大后减小的趋势。马红静[5]研究表明添加小分子糖的糯米淀粉糊化焓值增大,老化作用受到抑制。但是目前糖醇类对糯米粉理化性质的研究较少。
木糖醇(Xylitol)是一种五羟基多元醇,分子式为C5H12O5,分子量为152.15,常态下为白色结晶,易溶于水,具有保水性,热稳定性好,理化性质与蔗糖最为相似,甜度和蔗糖相同但热量低于蔗糖[6]。木糖醇因其特殊的理化性质和生理功能,在食品加工中被广泛应用。木糖醇的添加既不增加血糖值,也可以在一定程度上延长食品的保质期[7]。近年来国内外关于添加木糖醇对淀粉理化指标的影响也有许多研究。邢燕等[8]研究木糖醇对小麦淀粉糊化性质和回生特性的影响,发现随着木糖醇添加量增加,小麦淀粉糊化温度升高,峰值黏度、回生值增加,木糖醇促进了小麦淀粉的老化。Baek等[9]研究木糖醇、山梨糖醇等对于玉米淀粉凝胶热力学稳定性的影响,结果表明,糖醇延迟了淀粉的糊化,促进了支链淀粉的重结晶。Allan等[10]、Xing等[11]用差示扫描量热仪分析糖和糖醇对淀粉糊化温度的影响,发现木糖醇、麦芽糖醇、葡萄糖等甜味剂均能提高淀粉糊的糊化温度。目前关于木糖醇对糯米粉理化性质影响的研究未见报道。
因此,本实验将木糖醇以不同添加量加入到糯米粉中,通过探究木糖醇的加入对糯米粉糊化特性、热力学特性、凝胶质构、流变学特性、消化特性等性质以及对汤圆品质的影响,以期更全面地了解木糖醇对糯米粉理化性质的影响规律,为木糖醇改善糯米粉品质以及糯米粉产品开发提供相应理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
糯米粉(淀粉74.8%,水分12.2%,蛋白质8.1%,灰分0.4%,粗脂肪0.8%) 益海嘉里金龙鱼有限公司;木糖醇 山东福田药业有限公司;猪胰α-淀粉酶(10 U/mg) 美国Sigma公司;糖化酶(10万U/mL) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;3,5-二硝基水杨酸(DNS) 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;淀粉总量检测试剂盒 爱尔兰Megazyme公司。
RVA快速黏度测定仪 澳大利亚Newport Scientific有限公司;DSC Q2000差示扫描量热仪 美国TA公司;TMS-Pro物性测定仪 美国FTC公司;Kinexus pro+旋转流变仪 英国马尔文仪器公司;Frontier傅里叶红外光谱仪 铂金埃尔默有限公司;Alpha 1-4 LSCbasic CHRIST冷冻干燥机 北京博劢行仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系的制备
称取10 g糯米粉,加入装有20 mL去离子水的离心管中,室温搅拌均匀,木糖醇按照5%、10%、15%、20%和25%的添加量(以糯米粉质量计)加入到糯米粉溶液中,振荡使木糖醇充分溶解,制备木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系溶液样品。以不添加木糖醇的糯米粉为对照。
另外,按以上方法配制10%(w/w)的木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系,于沸水浴中糊化20 min,冷却至室温后,得到共混体系糊化样品。将得到的糊化样品放入冷冻干燥机中进行冻干处理并研磨,过100 目筛,筛下物即为共混体系冻干样品。
1.2.2 热力学特性的测定
采用差示扫描量热仪(Differential Scanning Calorimetry,DSC)分析共混体系热稳定性,准确称取10 mg由1.2.1制备的木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系溶液样品于铝盒内,于4 ℃冰箱中过夜放置24 h,测试前回温1 h,升温速率10 ℃/min,温度范围20~100 ℃[12]。
1.2.3 糊化特性的测定
取1.2.1制备的10%(w/w)的木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系溶液样品,参照GB/T 24853-2010的测试方法,使用RVA进行黏度测定,设置程序如下:以960 r/min 的速度在35 ℃下保持1 min;降速到160 r/min并保持恒定,以5 ℃/min的速率升温至95 ℃,95 ℃下保持10 min;随后以5 ℃/min的速率降温至50 ℃,50 ℃下保温10 min。
1.2.4 凝胶质构的测定
将1.2.1制备的共混体系糊化样品置于样品盒中(内径2 cm,高度3 cm),在4 ℃冷藏24 h后形成凝胶样品,采用物性测定仪分析其质构特性。测试条件:TPA模式,探头P/0.5,测试前速率1.0 mm/s、测试中速率1.0 mm/s、测试后速率1.0 mm/s,触发力0.05 N,形变量50%[13]。
1.2.5 流变学特性的测定
将1.2.1制备的共混体系糊化样品转移至40 mm的平板夹具上,测试间距为1.0 mm,25 ℃条件下进行振幅扫描检测线性粘弹区,最终确定应变力为1%。Flow Ramp模式,测定木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系的表观黏度和剪切应力随剪切速率(0~100 s−1)的变化关系并根据公式(1)对数据进行拟合。
τ=K⋅γn (1) 式中:τ表示剪切应力,Pa;K表示稠度系数;γ表示剪切速率,s−1;n表示流体指数
1.2.6 分子短程有序度表征
称取1.2.1制备的共混体系冻干粉末与纯溴化钾按质量比1:200进行混合,置于玛瑙研钵中研磨约5 min,并用真空压片机压片,进行傅里叶红外光谱仪扫描测定。测定参数:扫描波数范围400~4000 cm−1,分辨率4 cm−1。用OMNIC分析软件对结果进行傅里叶自去卷积处理,分析短程有序度[14]。
1.2.7 消化特性的测定
参考Englyst等[15]方法,称取200 mg经1.2.1制备的共混体系冻干粉末分散于15 mL 0.2 mol/L醋酸钠缓冲液(pH5.2)中,并在37 ℃恒温水浴中孵育10 min。之后加入10 mL消化酶溶液(含290 U猪胰α-淀粉酶和1500 U糖化酶),以160 r/min搅拌下37 ℃孵育。当水解20和120 min后分别取出0.5 mL消化液,并置于沸水浴中15 min以彻底灭酶。将消化液以8000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液用DNS法进行葡萄糖含量测定。样品中总淀粉含量采用Megazyme淀粉总量检测试剂盒测定。快消化淀粉(RDS)、慢消化淀粉(SDS)和抗性淀粉(RS)的含量按以下公式(2)~(4)计算:
RDS(%)=(G20−FG)×0.9TS×100 (2) SDS(%)=(G120−G20)×0.9TS×100 (3) RS(%)=TS−(RDS+SDS)TS×100 (4) 式中:G20和G120分别表示20和120 min内释放的葡萄糖含量,mg;FG表示淀粉中游离葡萄糖含量,mg;0.9为葡萄糖换算为淀粉的系数;TS指样品中总淀粉的含量,mg。
1.2.8 汤圆的制作
称取50 g糯米粉,将木糖醇分别按照糯米粉的0%、5%、10%、15%、20%和25%(w/w,以干基计)加入40.0 g冷水中,充分溶解后加入糯米粉中,和面搅拌均匀成团后准确称取3 g粉团,手工搓圆成型,速冻后放入−18 ℃冰箱,冷冻保藏5 d[16]。
1.2.9 汤圆冻藏水分损失率的测定
准确测定汤圆冻藏前后的质量,水分损失率[16]的计算公式(5)如下:
冻藏水分损失率(%)=M1−M2M1×100 (5) 式中,M1为冻藏前速冻汤圆的质量,g;M2为冻藏后速冻汤圆的质量,g。
1.2.10 汤圆汤汁透过率的测定
取6个冻藏后的不同木糖醇添加量的汤圆,放入盛有300 mL沸水的锅中加盖煮制3 min,再开盖继续煮制2 min后捞出。将汤汁倒入烧杯中,室温下冷却后,加入去离子水至500 mL。用紫外分光光度计于620 nm波长处测定汤汁透过率,去离子水为空白对照[17]。
1.2.11 汤圆质构特性的分析
用物性测定仪测定煮制后的汤圆。测试条件:选用P/50探头,测前速度为1 mm/s,测试速度为1 mm/s,测后速度为1 mm/s,形变量50%,探头压缩部位为汤圆的中心部位[17]。
1.3 数据处理
采用Origin 9.2软件绘图,SPSS软件对实验数据进行差异显著性分析,P<0.05,差异显著。实验数据均以3次实验结果的平均数±标准误差表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉热力学特性的影响
淀粉糊化需要消耗热量,因此利用DSC测定糯米粉糊化时的温度和热焓值变化。木糖醇添加量对糯米粉热力学特性的影响如表1所示。未添加木糖醇的糯米粉的糊化温度范围为61.63~69.07 ℃,随木糖醇添加量的增加,糯米粉的起始糊化温度和终止温度均逐渐升高,峰值温度由原来的66.41 ℃增加到71.85 ℃。木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系的糊化温度升高,可能是由于在淀粉颗粒的无定形区域中,糖醇和淀粉链之间形成了稳定的氢键,糖醇与糯米粉颗粒之间竞争水分,降低了糯米粉分子在糊化过程中与水分子的结合能力,抑制了糯米粉的膨胀,阻碍了糊化过程,导致淀粉糊化温度升高[18]。
表 1 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉热力学特性的影响Table 1. Effect of addition of xylitol on thermodynamic properties of glutinous rice flour添加量(%) 起始温度(℃) 峰值温度(℃) 终止温度(℃) 糊化焓值(J/g) 0 61.63±0.54a 66.41±0.58a 69.07±1.18a 8.46±0.16a 5 63.26±0.43ab 67.75±0.78ab 70.66±0.41b 8.65±0.63a 10 63.58±0.97b 68.89±0.17bc 72.53±0.74c 10.38±0.60b 15 63.74±0.45b 67.21±0.85ab 72.94±0.39cd 11.67±0.87b 20 64.03±0.66b 70.05±0.70cd 74.20±0.35de 11.25±0.91b 25 64.24±0.82b 71.85±1.05d 74.71±0.18e 10.84±0.33b 注:同列不同小写字母表示存在差异显著(P<0.05);表2~表6同。 糯米粉的糊化焓值随木糖醇添加量的增加呈现先增大后减小的趋势,在添加量为15%时,糊化焓值达到最大值。原因可能是糖醇与糯米粉相互作用时,一部分木糖醇随水渗透到糯米粉颗粒内的无定形区域与其形成较稳定的复合物,并破坏控制支链淀粉双螺旋的氢键,使糯米粉在糊化过程中需要更多的能量[19];而当糖醇添加量过高时,淀粉颗粒外部可利用的自由水含量降低,造成淀粉未糊化完全,因而糊化所需能量减少[20]。
2.2 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉糊化特性的影响
淀粉的糊化性能主要与淀粉颗粒的溶胀和破裂有关[21]。利用快速黏度仪分析木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系在加热和冷却过程中黏度的变化。如表2所示,随木糖醇添加量的增加,体系的峰值黏度和终值黏度逐渐增加,谷值黏度和崩解值无显著差异(P>0.05),说明木糖醇的添加对糯米粉整体黏度影响不大。这与南冲等[22]的研究结果相似。
表 2 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉黏度的影响Table 2. Effect of addition of xylitol on viscosity of glutinous rice flour添加量
(%)峰值黏度
(cP)谷值黏度
(cP)崩解值
(cP)终值黏度
(cP)回生值
(cP)0 3484±10.61a 1954±4.24a 1530±6.36a 2369±2.83a 415±1.41ab 5 3498±4.95ab 1964±13.44a 1534±16.97a 2376±5.66ab 413±5.66ab 10 3498±12.73ab 1970±19.80a 1535±7.70a 2378±16.97ab 405±4.24a 15 3497±14.44ab 1966±9.19a 1531±15.56a 2385±11.31ab 420±2.12bc 20 3518±17.68b 1965±19.09a 1533±9.90a 2401±12.02ab 429±2.83cd 25 3520±12.02b 1965±16.97a 1552±6.36a 2404±17.68b 436±5.66d 淀粉糊冷却期间黏度上升越快,越容易发生短期回生,回生值为终值黏度与谷值黏度的差值,反映了淀粉短期回生程度。当木糖醇添加量为10%时,共混体系的回生值最低,表明其回生抑制效果最好。这可能是因为木糖醇的存在阻碍淀粉与淀粉间氢键的形成,减弱了糯米粉分子的聚集程度,抑制糯米粉分子的重排,从而对淀粉的短期回生有一定的延缓作用[23]。添加15%~25%木糖醇时,回生值逐渐增大。原因可能是高浓度木糖醇分散于体系中,导致淀粉颗粒周围可用水减少,木糖醇分子在糯米粉颗粒周围形成水合层,增加了游离出来的直链淀粉浓度,增强淀粉链间的相互作用,促进淀粉发生短期回生[24]。
2.3 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉凝胶质构的影响
糊化后的糯米粉经4 ℃冷藏24 h后会形成具有一定弹性和强度的半透明凝胶。淀粉凝胶是亚稳态和非平衡体系,凝胶的质地特性主要受短期直链淀粉凝胶化的影响,其特性对凝胶体的加工、成型以及淀粉基食品的感官品质具有较大的影响[25]。糯米粉中主要是支链淀粉,直链淀粉含量较少。由表3可知,木糖醇的添加对糯米粉凝胶质构有显著影响(P<0.05)。在添加量为10%时,与对照相比,共混体系的凝胶硬度降低了16.11%、胶黏性降低了15.75%以及弹性降低了3.48%,内聚性达到最大值。因此,添加10%的木糖醇能够降低凝胶硬度,减少淀粉回生程度。之后随添加量的增加,体系的凝胶硬度增大,胶黏性和弹性也表现出相似的变化规律。这些变化可能是因为木糖醇含有一定数量的羟基,加强了淀粉链、糖醇和水之间的联系,随着木糖醇添加量的增加,促进了糯米粉分子的聚集,形成牢固的凝胶网络结构,使凝胶强度增加[26]。当木糖醇添加量为25%时,体系的相对凝胶结构减弱。原因可能是木糖醇在糯米粉分子间缔合和形成凝胶结构方面受羟基含量以及相容性的影响,较高的木糖醇浓度减弱了凝胶网络结构[27]。
表 3 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉凝胶质构的影响Table 3. Effect of addition of xylitol on gel texture of glutinous rice flour添加量(%) 硬度(g) 胶黏性 内聚性 弹性 0 17.82±0.39c 0.44±0.03b 0.50±0.01a 9.05±0.13b 5 16.14±0.37b 0.41±0.02b 0.52±0.01b 9.03±0.23b 10 14.95±0.41a 0.37±0.01a 0.53±0.01b 8.73±0.15a 15 19.13±0.99d 0.44±0.04b 0.52±0.01b 9.87±0.18c 20 19.31±0.39d 0.49±0.02c 0.52±0.01b 9.89±0.20c 25 16.70±0.77b 0.42±0.03b 0.52±0.01b 9.94±0.08c 2.4 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉流变特性的影响
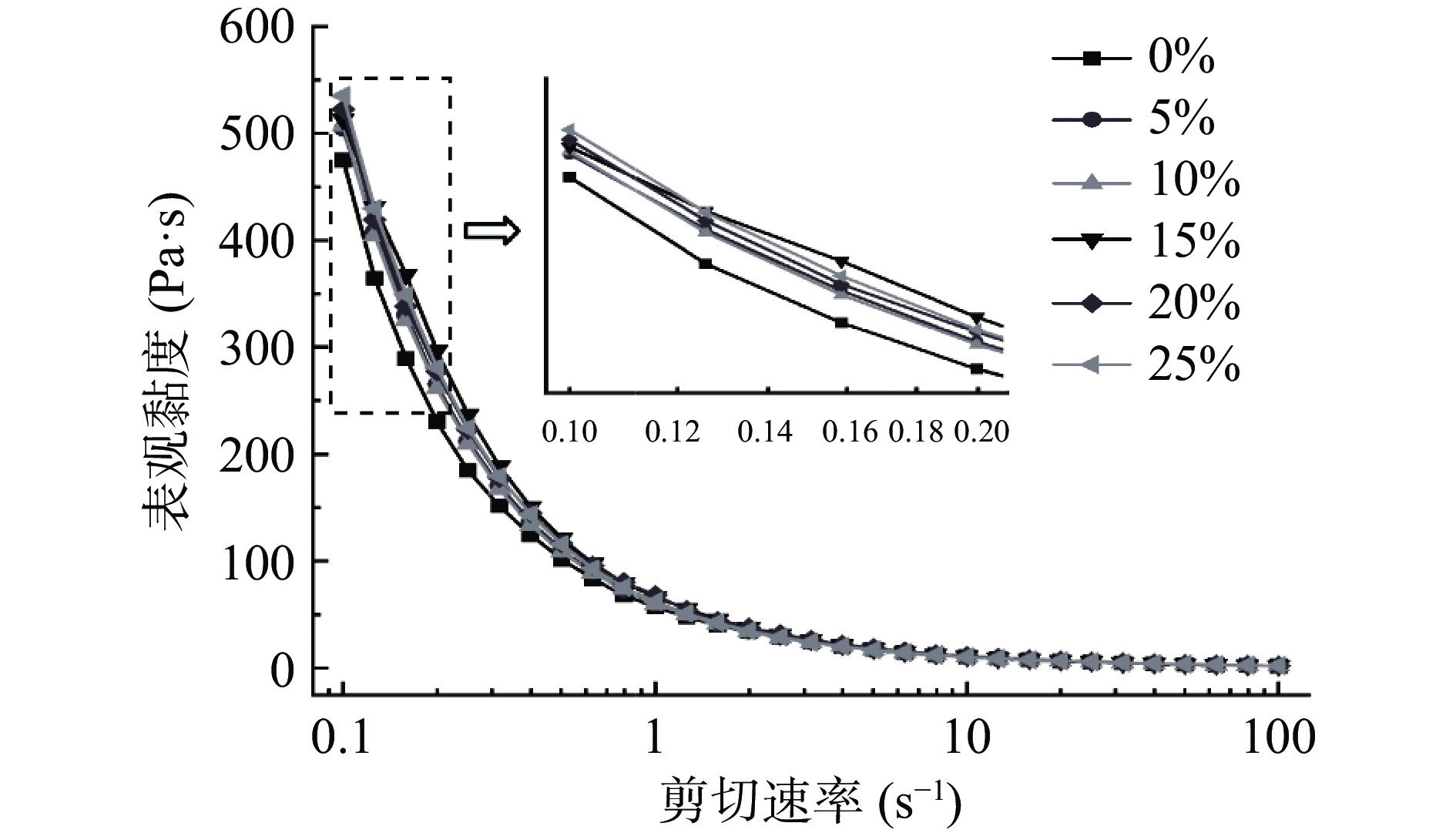
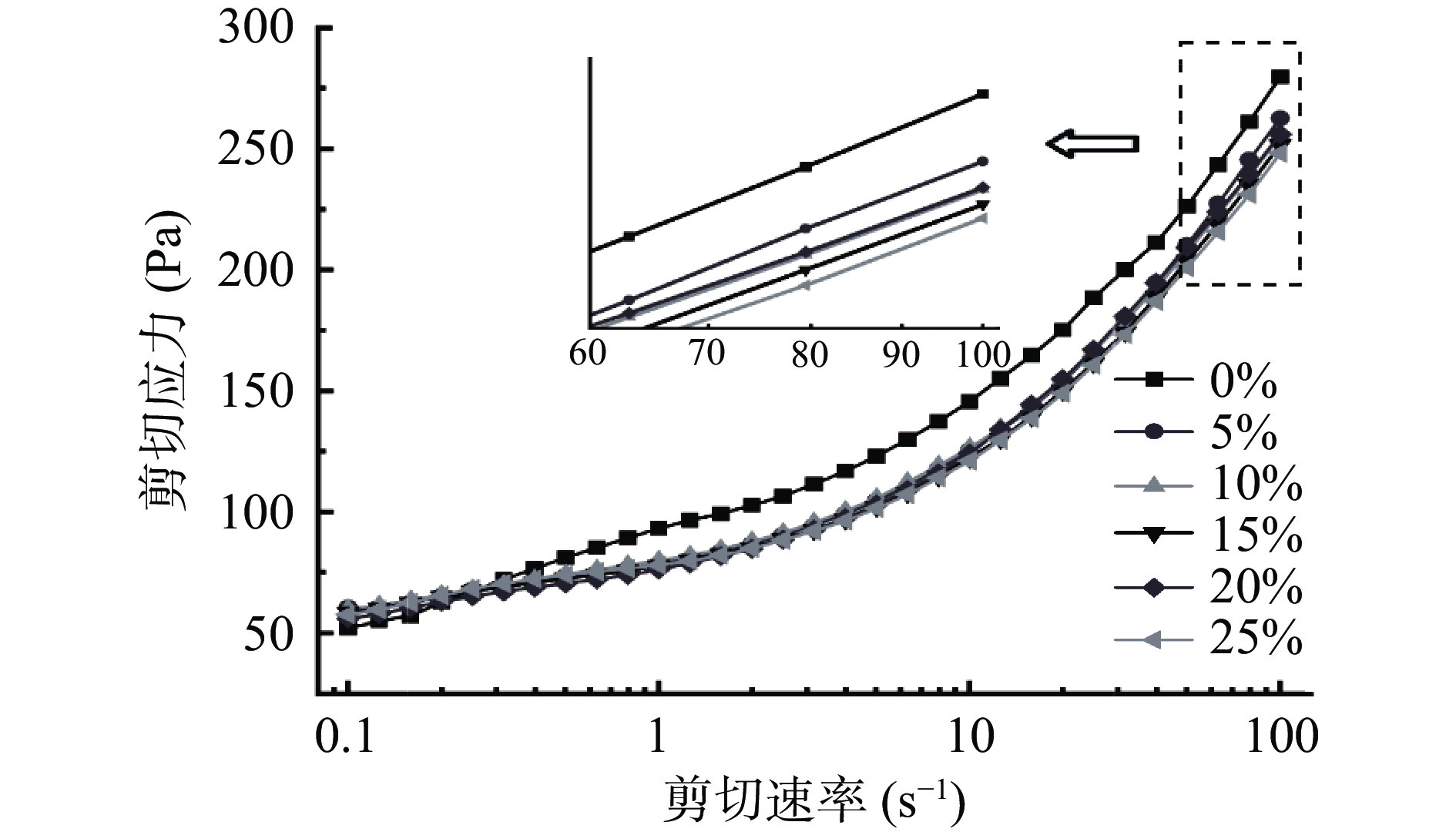
图1表示加入不同添加量的木糖醇经糊化后的共混体系在不同剪切速率下表观黏度的变化情况。由图可知,所有样品均随着剪切速率的升高,黏度逐渐下降,继而趋于平缓,说明所有样品具有假塑性流体黏度和剪切速率变化关系特征[28]。在低剪切速率下,与对照组相比,共混体系黏度增加且具有相对弱的流动特性。这可能是由于随着木糖醇的添加,糖醇和糯米粉之间形成氢键并与糯米粉竞争水分子,抑制了淀粉链的运动,从而增加了共混体系的表观粘度。此现象与RVA测定的黏度变化规律基本一致。另外,如图2所示,对照以及木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系的剪切应力随着剪切速率的增加而增大。在相同剪切速率下,木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系的剪切应力比对照的剪切应力小,且随木糖醇添加量的增加逐渐降低。原因可能是当共混体系受到剪切作用时,淀粉分子间氢键断裂,凝胶结构被破坏,淀粉回生程度减弱,因此,在高剪切速率下,样品具有相对较差的耐剪切能力[29]。
为进一步分析共混体系剪切行为,采用幂律方程进行拟合,计算得到相应的流变学参数,包括稠度系数(K)、流动特征指数(n)和决定系数(R2),拟合后的相关参数见表4。决定系数R2均大于0.95(R2=0.953~0.993),表明木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系的静态流变学特性符合幂律模型。K值是稠度系数,K值越大,表明样品越黏稠[30]。对照组的K值最大为89.95,共混体系K值均小于对照组,说明添加木糖醇的体系对流动和剪切应力的抵抗能力减弱,在一定剪切速率下木糖醇使体系稠度降低,原因可能是在共混体系中,木糖醇的存在阻碍淀粉与淀粉间氢键的形成,减弱了淀粉分子的聚集程度,抑制了淀粉分子的重排[31]。糯米粉以及共混体系的流体特征指数n均小于l,范围在0.20~0.23之间,说明所有样品均表现出剪切稀化现象[32]。剪切稀化实质是相互缠绕的淀粉分子链在剪切力的作用下重新排列的过程[33]。流体指数n越小,假塑性越强。添加木糖醇后的糯米粉的流体指数均小于对照组,体系剪切稀化程度增加,表明添加木糖醇增强了体系的假塑性行为。木糖醇的添加量为25%时,n值最小,表明共混体系在此添加量下具有较高的凝胶稳定性,倾向于形成更高的顺向伸展状态,更稳定的胶态体系[34]。
表 4 木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系静态流变曲线拟合参数Table 4. Static rheological curve fitting parameters of xylitol-glutinous rice flour blend system添加量(%) 稠度系数K 流动特性指数n 决定系数R2 0 89.95±0.10d 0.23±0.00d 0.993 5 83.75±0.66c 0.21±0.00b 0.954 10 84.53±0.90c 0.21±0.00ab 0.961 15 82.47±0.09b 0.21±0.00ab 0.955 20 81.26±0.15a 0.22±0.00c 0.962 25 82.60±0.12b 0.20±0.00a 0.953 2.5 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉分子短程有序度的影响
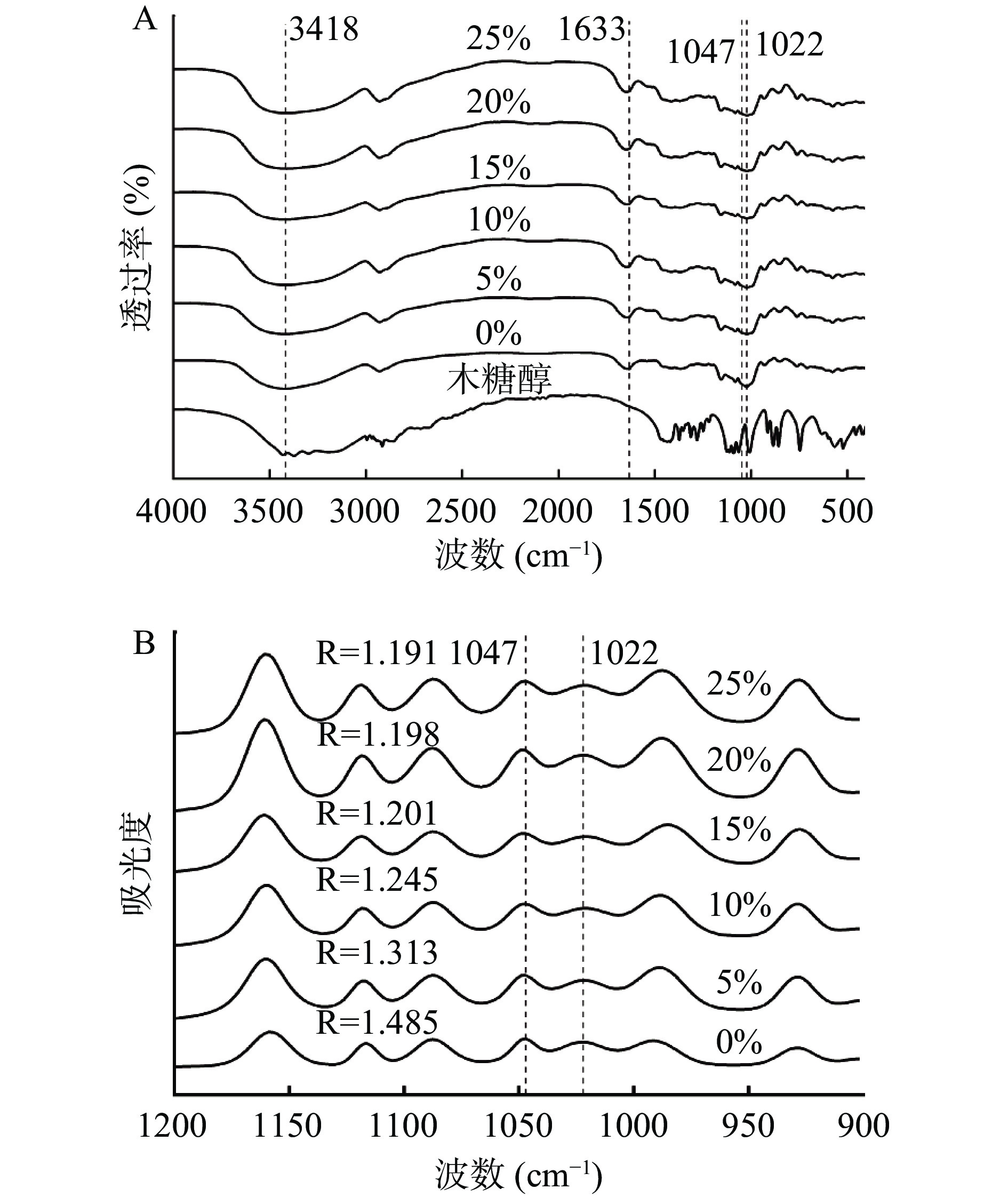
图3A表示对照组、木糖醇以及木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系在400~4000 cm−1处的红外光谱图。如图所示,添加木糖醇的共混体系的红外吸收峰形状和位置与糯米粉基本相似,添加木糖醇后未出现新的特征吸收峰,说明木糖醇的加入并未和糯米粉形成新的基团。样品在3000~3700 cm−1范围内形成一个宽的吸收峰主要与O-H伸缩振动有关,而1633 cm−1处的吸收峰则常用来表示O-H的弯曲振动[35]。由图可知,木糖醇的添加导致共混体系在3418和1633 cm−1处的吸收峰强度均增强,对于高浓度木糖醇的共混体系,强度增加明显,由此说明共混体系中的作用键可能是氢键。冀晓龙等[36]研究中也报道氢键最有可能是非淀粉多糖与淀粉相互作用的主要作用力。
红外光谱在900~1200 cm−1范围内主要与C-C和C-O键的伸展有关,1047 cm−1吸收峰对应于淀粉聚集态结构中的有序结构,是淀粉结晶区的结构特征;1022 cm−1附近的吸收峰则是淀粉非结晶区的结构特征,1047 cm−1和1022 cm−1的峰强度比值R反映淀粉分子的短程有序程度,其比值越大,有序度越高[37]。图3B表示了共混体系在1047 cm−1和1022 cm−1处的峰强度比值。糯米粉的短程有序度为1.485,且随添加量的增加,体系的1047 cm−1和1022 cm−1的比值逐渐减小,结构越来越趋于无序。这一现象可能是由于糯米粉糊化后木糖醇通过氢键与糯米粉分子相结合,阻碍糯米粉分子链间或内部的氢键连接,从而导致糯米粉颗粒内部螺旋结构的不规则排列或解旋,使糯米粉的短程有序度降低[38]。
2.6 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉消化特性的影响
木糖醇对糯米粉消化特性的影响结果见表5。淀粉颗粒表面积和内部结构均影响体外消化特性,糯米粉经过完全糊化后冷冻干燥,几乎失去结晶结构与分子有序结构,破损度较高,颗粒表面积较大且容易酶解。由表可知,对照组的RDS、SDS和RS的含量分别为62.92%、20.78%和16.30%。木糖醇的添加导致体系的RDS和SDS的含量降低,RS含量增加,表明木糖醇能够在一定程度上抑制糯米粉的消化,且在添加量为10%时,RS含量达到峰值,显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。共混体系的RS含量增加可能是由于木糖醇增加了共混体系中的羟基基团,部分木糖醇渗透到糯米粉颗粒中通过氢键相互作用,另一部分在糯米粉颗粒周围形成水合层包裹作用阻碍了消化酶与淀粉之间的接触位点,从而对淀粉颗粒形成保护,抑制酶解,最终表现为RS含量增加[39]。
表 5 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉消化特性的影响Table 5. Effect of addition of xylitol on digestive characteristics of glutinous rice flour添加量(%) RDS(%) SDS(%) RS(%) 0 62.92±0.29c 20.78±0.29c 16.30±0.58a 5 60.45±0.29b 15.43±0.30b 24.12±0.52b 10 58.80±0.26a 11.32±0.29a 29.88±0.58d 15 59.01±0.52a 14.40±1.03b 26.59±1.16c 20 59.63±0.29ab 14.81±0.08b 25.56±0.87bc 25 59.83±0.58ab 15.02±0.87b 25.15±1.46bc 2.7 木糖醇对汤圆冻藏水分损失率的影响
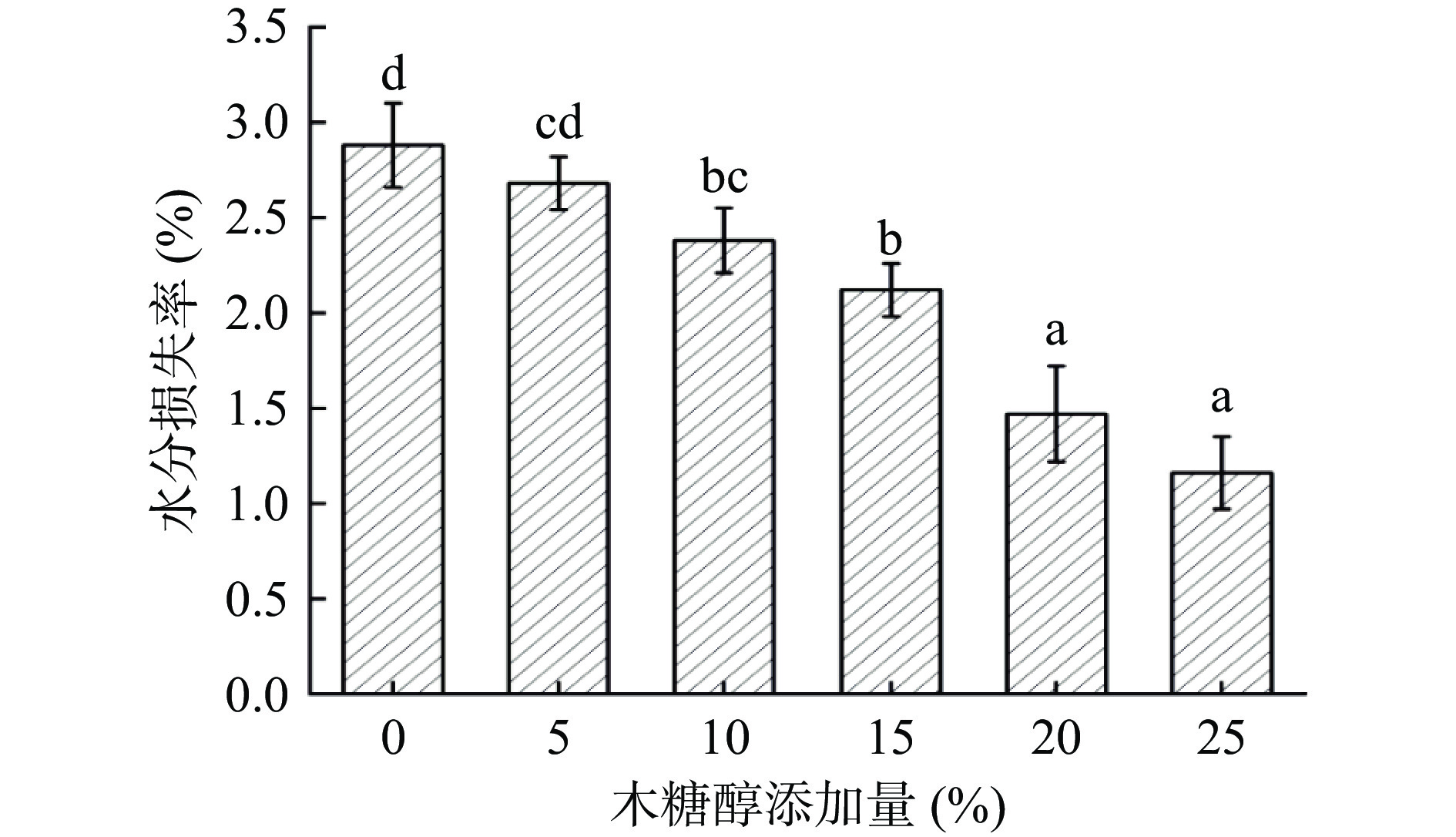
汤圆在冷冻过程中表面冰晶升华造成水分损失,汤圆的失水率是反映其在冷冻过程中的稳定性的重要指标[40]。不同木糖醇添加量的速冻汤圆水分损失率变化如图4所示。由图可知,不添加木糖醇汤圆的水分损失率为2.88%,随着木糖醇添加量的增加,速冻汤圆的水分损失率显著下降(P<0.05),当木糖醇添加量为25%时,水分损失率仅为1.16%。这可能是因为木糖醇的加入增强了体系的水合能力,对水分子束缚力变大,使汤圆内部结构更加致密,一定程度上可使得汤圆在冷冻过程中水分损失降低[41]。
![]() 图 4 不同木糖醇添加量汤圆的水分损失率注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著P<0.05,图5同。Figure 4. Water loss rate of glutinous rice dumplings with different amount of xylitol
图 4 不同木糖醇添加量汤圆的水分损失率注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著P<0.05,图5同。Figure 4. Water loss rate of glutinous rice dumplings with different amount of xylitol2.8 木糖醇对汤圆汤汁透过率的影响
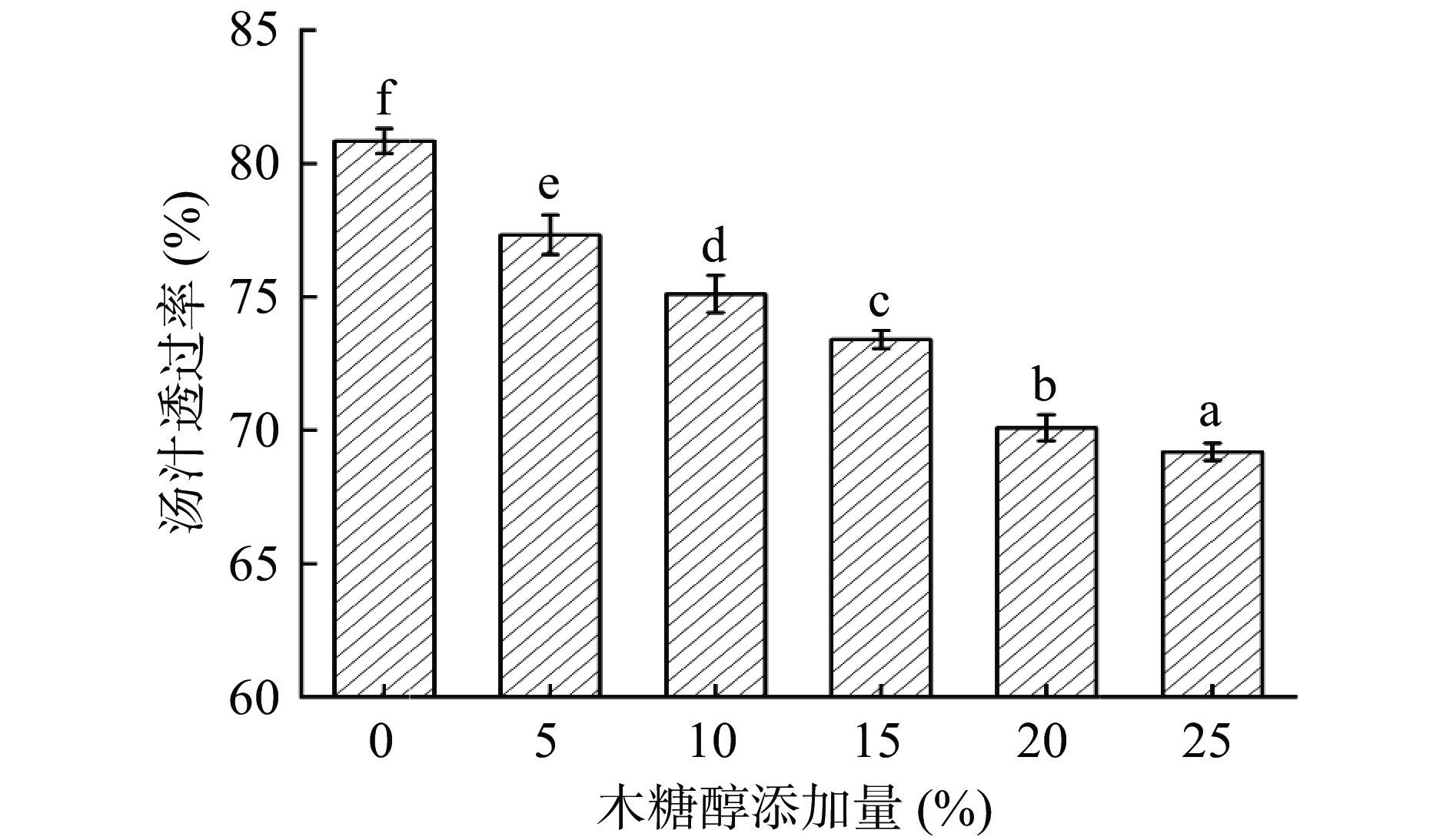
汤圆汤汁透过率是指汤圆在煮制过程中糯米粉向水中逐渐溶解扩散的程度大小,可反映汤圆的蒸煮品质[42]。糯米粉糊化后的吸水膨胀能力越强,汤圆煮制后汤汁的透过率越好。添加木糖醇后汤圆汤汁透过率变化如图5所示,未添加木糖醇的汤圆经煮制后,其汤汁透过率为80.85%,木糖醇的添加使汤圆蒸煮后的汤汁透过率显著降低(P<0.05)。这可能是由于木糖醇的加入减弱了糯米粉的吸水膨胀能力,糊化后增加了糯米粉在汤圆煮制过程中的溶出,降低了汤圆的汤汁透过率。
2.9 木糖醇对汤圆质构的影响
为进一步评价汤圆的品质,对煮制后的汤圆进行质构特性测定,表6是不同木糖醇添加量的汤圆的质构特性参数。由表可知,当木糖醇添加量从5%增加到25%时,汤圆的内聚性没有显著变化(P<0.05),但其他质构参数表现出不同的结果。随木糖醇的添加,汤圆的硬度、弹性、回复性和咀嚼性呈现先增大后减小的趋势(P<0.05)。添加10%的木糖醇制成的汤圆具有更高的硬度、弹性、回复性以及咀嚼性,即食用品质最好,这可能是由于加入低浓度的木糖醇使汤圆的结构更致密,咀嚼时需要消耗更多的能量。此外,由高浓度木糖醇(15%~25%)制成的汤圆结构强度较弱、弹性较低以及咀嚼性较差,可能是由于木糖醇阻碍了糯米粉分子链间氢键连接,阻碍了糯米粉形成三维网状结构,降低了链间的缔合度,从而使其内部的紧密度、抗剪切和回复能力下降[43]。综上所述,以添加10%左右的木糖醇制作的汤圆品质良好,适合食用。
表 6 不同木糖醇添加量汤圆的质构特性参数Table 6. Texture characteristic parameters of glutinous rice dumplings with different amount of xylitol添加量
(%)硬度(g) 内聚性 弹性 回复性 咀嚼性 0 343.72±11.26ab 0.65±0.01a 4.32±0.16a 0.34±0.01ab 9.88±0.39ab 5 355.93±5.50bc 0.65±0.01a 4.50±0.18a 0.34±0.01ab 10.11±0.47b 10 375.23±4.21d 0.67±0.01a 4.87±0.12b 0.35±0.02b 12.02±0.28c 15 367.38±2.33cd 0.66±0.02a 4.31±0.18a 0.32±0.02a 9.28±0.35a 20 343.10±6.17ab 0.65±0.01a 4.28±0.38a 0.32±0.00a 9.26±0.74a 25 340.82±9.07a 0.65±0.01a 4.22±0.09a 0.32±0.02a 9.13±0.18a 3. 结论
本文以热力学特性、糊化特性、凝胶质构、流变学特性和消化特性等表征木糖醇对糯米粉性质的影响,并以汤圆的水分损失率、汤汁透过率以及质构等特性分析木糖醇对糯米汤圆制品食用品质的影响。结果表明:木糖醇的添加使共混体系的糊化温度、峰值黏度和终值黏度有所提高,体系的短程有序程度降低,体系表现为假塑性流体,具有剪切稀化行为。与对照组相比,木糖醇添加量为10%时,共混体系的回生值和凝胶硬度最小,体系抗性淀粉含量显著增加(P<0.05),表现出较好的抗回生性。但高浓度木糖醇(15%~25%)促进体系发生短期回生,增加其回生值和弹性。另外,木糖醇的添加显著降低了汤圆的冻藏水分损失率和汤汁透过率,其中添加10%的木糖醇制成的汤圆具有更高的硬度、弹性、回复性以及咀嚼性,食用品质最好。木糖醇对糯米粉理化性质的影响规律表明,当木糖醇添加量为10%时,能够减缓糯米粉的回生和增强抗消化特性以及制作的汤圆品质最优,为木糖醇改善糯米粉品质以及糯米粉产品开发提供了相应的理论参考。
-
图 4 不同木糖醇添加量汤圆的水分损失率
注:图中不同小写字母表示差异显著P<0.05,图5同。
Figure 4. Water loss rate of glutinous rice dumplings with different amount of xylitol
表 1 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉热力学特性的影响
Table 1 Effect of addition of xylitol on thermodynamic properties of glutinous rice flour
添加量(%) 起始温度(℃) 峰值温度(℃) 终止温度(℃) 糊化焓值(J/g) 0 61.63±0.54a 66.41±0.58a 69.07±1.18a 8.46±0.16a 5 63.26±0.43ab 67.75±0.78ab 70.66±0.41b 8.65±0.63a 10 63.58±0.97b 68.89±0.17bc 72.53±0.74c 10.38±0.60b 15 63.74±0.45b 67.21±0.85ab 72.94±0.39cd 11.67±0.87b 20 64.03±0.66b 70.05±0.70cd 74.20±0.35de 11.25±0.91b 25 64.24±0.82b 71.85±1.05d 74.71±0.18e 10.84±0.33b 注:同列不同小写字母表示存在差异显著(P<0.05);表2~表6同。 表 2 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉黏度的影响
Table 2 Effect of addition of xylitol on viscosity of glutinous rice flour
添加量
(%)峰值黏度
(cP)谷值黏度
(cP)崩解值
(cP)终值黏度
(cP)回生值
(cP)0 3484±10.61a 1954±4.24a 1530±6.36a 2369±2.83a 415±1.41ab 5 3498±4.95ab 1964±13.44a 1534±16.97a 2376±5.66ab 413±5.66ab 10 3498±12.73ab 1970±19.80a 1535±7.70a 2378±16.97ab 405±4.24a 15 3497±14.44ab 1966±9.19a 1531±15.56a 2385±11.31ab 420±2.12bc 20 3518±17.68b 1965±19.09a 1533±9.90a 2401±12.02ab 429±2.83cd 25 3520±12.02b 1965±16.97a 1552±6.36a 2404±17.68b 436±5.66d 表 3 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉凝胶质构的影响
Table 3 Effect of addition of xylitol on gel texture of glutinous rice flour
添加量(%) 硬度(g) 胶黏性 内聚性 弹性 0 17.82±0.39c 0.44±0.03b 0.50±0.01a 9.05±0.13b 5 16.14±0.37b 0.41±0.02b 0.52±0.01b 9.03±0.23b 10 14.95±0.41a 0.37±0.01a 0.53±0.01b 8.73±0.15a 15 19.13±0.99d 0.44±0.04b 0.52±0.01b 9.87±0.18c 20 19.31±0.39d 0.49±0.02c 0.52±0.01b 9.89±0.20c 25 16.70±0.77b 0.42±0.03b 0.52±0.01b 9.94±0.08c 表 4 木糖醇-糯米粉共混体系静态流变曲线拟合参数
Table 4 Static rheological curve fitting parameters of xylitol-glutinous rice flour blend system
添加量(%) 稠度系数K 流动特性指数n 决定系数R2 0 89.95±0.10d 0.23±0.00d 0.993 5 83.75±0.66c 0.21±0.00b 0.954 10 84.53±0.90c 0.21±0.00ab 0.961 15 82.47±0.09b 0.21±0.00ab 0.955 20 81.26±0.15a 0.22±0.00c 0.962 25 82.60±0.12b 0.20±0.00a 0.953 表 5 木糖醇添加量对糯米粉消化特性的影响
Table 5 Effect of addition of xylitol on digestive characteristics of glutinous rice flour
添加量(%) RDS(%) SDS(%) RS(%) 0 62.92±0.29c 20.78±0.29c 16.30±0.58a 5 60.45±0.29b 15.43±0.30b 24.12±0.52b 10 58.80±0.26a 11.32±0.29a 29.88±0.58d 15 59.01±0.52a 14.40±1.03b 26.59±1.16c 20 59.63±0.29ab 14.81±0.08b 25.56±0.87bc 25 59.83±0.58ab 15.02±0.87b 25.15±1.46bc 表 6 不同木糖醇添加量汤圆的质构特性参数
Table 6 Texture characteristic parameters of glutinous rice dumplings with different amount of xylitol
添加量
(%)硬度(g) 内聚性 弹性 回复性 咀嚼性 0 343.72±11.26ab 0.65±0.01a 4.32±0.16a 0.34±0.01ab 9.88±0.39ab 5 355.93±5.50bc 0.65±0.01a 4.50±0.18a 0.34±0.01ab 10.11±0.47b 10 375.23±4.21d 0.67±0.01a 4.87±0.12b 0.35±0.02b 12.02±0.28c 15 367.38±2.33cd 0.66±0.02a 4.31±0.18a 0.32±0.02a 9.28±0.35a 20 343.10±6.17ab 0.65±0.01a 4.28±0.38a 0.32±0.00a 9.26±0.74a 25 340.82±9.07a 0.65±0.01a 4.22±0.09a 0.32±0.02a 9.13±0.18a -
[1] LI Y, DING G, YOKOYAMA W, et al. Characteristics of annealed glutinous rice flour and its formation of fast-frozen dumplings[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2018,79:106−112. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2017.09.016
[2] 李温静, 尹玉云. 浅谈糯米淀粉的性状及应用[J]. 粮食与食品工业,2017,24(3):29−34. [LI W J, YIN Y Y. Brief introduction on characteristics and applications of glutinous rice starch[J]. Grain and Food Industry,2017,24(3):29−34.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5026.2017.03.010 LI W J, YIN Y Y . Brief introduction on characteristics and applications of glutinous rice starch[J]. Grain and Food Industry,2017 ,24 (3 ):29 −34 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5026.2017.03.010[3] LIN S D U N, LEE C C, MAU J L, et al. Effect of erythritol on quality characteristics of reduced‐calorie danish cookies[J]. Journal of Food Quality,2010,33:14−26. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4557.2010.00307.x
[4] 张喻, 章丽琳, 张琼, 等. 海藻糖添加量对糯米粉理化性质影响研究[J]. 食品与机械,2016,32(9):28−30,43. [ZHANG Y, ZHANG L L, ZHANG Q, et al. The impacts of trehalose on the characteristics of glutinous rice powders[J]. Food & Machinery,2016,32(9):28−30,43.] ZHANG Y, ZHANG L L, ZHANG Q, et al . The impacts of trehalose on the characteristics of glutinous rice powders[J]. Food & Machinery,2016 ,32 (9 ):28 −30,43 .[5] 马红静. 小分子糖对糯米淀粉糊化特性和质构特性的影响研究[D]. 郑州:河南农业大学, 2016. [MA H J. Study on the effect of low molecular weight sugars on pasting and texture properties of waxy rice starch [D]. Zhengzhou:Henan University of Technology, 2016.] MA H J. Study on the effect of low molecular weight sugars on pasting and texture properties of waxy rice starch [D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2016.
[6] 葛茵, 向沙沙, 张亚林, 等. 木糖醇益生功能研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(5):267−272. [GE Y, XIANG S S, ZHANG Y L, et al. Research progress on probiotic function of xylitol[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(5):267−272.] GE Y, XIANG S S, ZHANG Y L, et al . Research progress on probiotic function of xylitol[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021 ,47 (5 ):267 −272 .[7] KOMMINENI A, AMAMCHARLA J, METZGER L E. Effect of xylitol on the functional properties of low-fat process cheese[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2012,95(11):6252−6259. doi: 10.3168/jds.2012-5376
[8] 邢燕, 熊柳, 孙庆杰. 木糖醇对小麦淀粉和复配粉糊化及回生特性影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2013,28(4):32−36. [XING Y, XIONG L, SUN Q J. The influence of xylitol on the gelatinization and retrogradation properties of wheat starch and blended flour[J]. Chinese Journal of Grain and Oil,2013,28(4):32−36.] XING Y, XIONG L, SUN Q J . The influence of xylitol on the gelatinization and retrogradation properties of wheat starch and blended flour[J]. Chinese Journal of Grain and Oil,2013 ,28 (4 ):32 −36 .[9] BAEK M H, YOO B, LIM S T. Effects of sugars and sugar alcohols on thermal transition and cold stability of corn starch gel[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2004,18(1):133−142. doi: 10.1016/S0268-005X(03)00058-4
[10] ALLAN M C, RAJWA B, MAUER L J. Effects of sugars and sugar alcohols on the gelatinization temperature of wheat starch[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018(84):593−607.
[11] XING Q, HOU C, ZHANG Z, et al. Comparative study on the physicochemical properties of pea, chickpea, and wheat starch gels in the presence of sweeteners[J]. Starch-Starke,2017,69(9-10):1600287.
[12] WOODBURY T J, GRUSH E, ALLAN M C, et al. The effects of sugars and sugar alcohols on the pasting and granular swelling of wheat starch[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,126:107433. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107433
[13] EVAGELIOU V, GEROLEMOU A, ZIKAS A, et al. Effect of salts and sugars on the clarity of gellan gels[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2011,46(5):1001−1006.
[14] 王宏伟, 肖乃勇, 马颖. 超声处理时间对小麦淀粉聚集态结构及理化性能的影响[J]. 轻工学报,2019,34(5):10−19. [WANG H W, XIAO N Y, MA Y. Effect of ultrasonic treatment time on aggregation structure and physicochemical properties of wheat starch[J]. Journal of Light Industry,2019,34(5):10−19.] WANG H W, XIAO N Y, MA Y . Effect of ultrasonic treatment time on aggregation structure and physicochemical properties of wheat starch[J]. Journal of Light Industry,2019 ,34 (5 ):10 −19 .[15] ENGLYST H N, VEENSTRA J, HUDSON G J. Measurement of rapidly available glucose (RAG) in plant foods:A potential in vitro predictor of the glycaemic response[J]. British Journal of Nutrition,1996,75(3):327−337. doi: 10.1079/BJN19960137
[16] 顾娟, 郇美丽, 李义, 等. 蜡质玉米淀粉对糯米粉及速冻汤圆品质的影响[J]. 粮食与饲料工业,2022,401(1):39−43,48. [GU J, HUAN M L, LI Y, et al. Effect of waxy maize starch on the quality of glutinous rice flour and quick-frozen tang-yuan[J]. Cereal & Feed Industry,2022,401(1):39−43,48.] GU J, HUAN M L, LI Y, et al . Effect of waxy maize starch on the quality of glutinous rice flour and quick-frozen tang-yuan[J]. Cereal & Feed Industry,2022 ,401 (1 ):39 −43,48 .[17] 马骏骅, 陆益钡, 王燕, 等. 不同冷冻温度对汤圆粉团品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(23):29−36. [MA J Y, LU Y B, WANG Y, et al. Effects of different freezing temperatures on the quality of rice dumpling dough[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(23):29−36.] MA J Y, LU Y B, WANG Y, et al . Effects of different freezing temperatures on the quality of rice dumpling dough[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023 ,44 (23 ):29 −36 .[18] RENZETTI S, HOEK I , SMAN R. Mechanisms controlling wheat starch gelatinization and pasting behaviour in presence of sugars and sugar replacers:Role of hydrogen bonding and plasticizer molar volume[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2021, 119:106880.
[19] ZHOU H, WANG J, LI J, et al. Pasting properties of Angelica dahurica starches in the presence of NaCl, Na2CO3, NaOH, glucose, fructose and sucrose[J]. Starch-Stärke,2011,63(6):323−332.
[20] 杨恒. 糖醇对辣条品质的影响及抗老化机制研究[D]. 武汉:武汉轻工大学, 2021. [YANG H. Effect of polyols on the quality and anti-retrogradation of spicy wheat gluten sticks[D]. Wuhan:Wuhan Polytechnic University, 2021.] YANG H. Effect of polyols on the quality and anti-retrogradation of spicy wheat gluten sticks[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Polytechnic University, 2021.
[21] MATTHEW C A, MARYCLAIRE C, LISA J M. Effects of sugars and sugar alcohols on the gelatinization temperatures of wheat, potato, and corn starches[J]. Foods,2020,9(6):757. doi: 10.3390/foods9060757
[22] 南冲, 熊柳, 孙庆杰, 等. 糖醇对甘薯淀粉理化性质的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2013,28(2):22−26,32. [NAN C, XIONG L, SUN Q J, et al. Effects of sugar alcohols on physicochemical properties of sweet potato starch[J]. Chinese Journal of Grain and Oil,2013,28(2):22−26,32.] doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2013.02.005 NAN C, XIONG L, SUN Q J, et al . Effects of sugar alcohols on physicochemical properties of sweet potato starch[J]. Chinese Journal of Grain and Oil,2013 ,28 (2 ):22 −26,32 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2013.02.005[23] 林楠, 肖瑜, 杨新标, 等. 麦芽糖对糯性谷物淀粉糊化和流变性质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(10):1−7. [LIN N, XIAO Y, YANG X B, et al. Effect of maltose on gelatinization and rheological properties of waxy cereal starches[J]. Food Science,2021,42(10):1−7.] LIN N, XIAO Y, YANG X B, et al . Effect of maltose on gelatinization and rheological properties of waxy cereal starches[J]. Food Science,2021 ,42 (10 ):1 −7 .[24] ALLAN M C, MAUER L J. Effects of twenty sugars and sugar alcohols on the retrogradation of eheat starch gels[J]. Foods,2022,11(19):3008. doi: 10.3390/foods11193008
[25] GUNARATNE A, RANAWEERA S, CORKE H. Thermal, pasting, and gelling properties of wheat and potato starches in the presence of sucrose, glucose, glycerol, and hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2007,70(1):112−122. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.03.011
[26] 于靖, 熊柳, 孙庆杰, 等. 三种糖醇对高粱淀粉糊化特性和凝胶结构的影响[J]. 现代食品科技,2014,30(10):102−107. [YU J, XIONG L, SUN Q J, et al. Effects of three sugar alcohols on the gelatinization characteristics and gel structure of sorghum starch[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2014,30(10):102−107.] YU J, XIONG L, SUN Q J, et al . Effects of three sugar alcohols on the gelatinization characteristics and gel structure of sorghum starch[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2014 ,30 (10 ):102 −107 .[27] SUN Q, NAN C, DAI L, et al. Effect of sugar alcohol on physicochemical properties of wheat starch[J]. Starch-Stärke,2014,66(9-10):22−26,32.
[28] WANG H, ZHANG J, WANG R, et al. Improving quality attributes of sweet dumplings by germination:Effect of glutinous rice flour microstructure and physicochemical properties[J]. Food Bioscience,2021,44(Pt.B):101445.
[29] 王艳. 亲水胶体对汤圆品质的影响规律及其互作机制研究[D]. 郑州:郑州轻工业大学, 2022. [WANG Y. Effects of hydrocolloids on the quality properties of glutinous dumplings and their interaction mechanism[D]. Zhengzhou:Zhengzhou University of Light Industry, 2022.] WANG Y. Effects of hydrocolloids on the quality properties of glutinous dumplings and their interaction mechanism[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University of Light Industry, 2022.
[30] CHEN L, TONG Q, REN F, et al. Pasting and rheological properties of rice starch as affected by pullulan[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2014,66:325−331. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.02.052
[31] LU J, LUO Z, XIAO Z. Effect of lysine and glycine on pasting and rheological properties of maize starch[J]. Food Research International,2012,49(1):612−617. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.06.038
[32] Al-ATTAR H, AHMED J, THOMAS L. Rheological, pasting and textural properties of corn flour as influenced by the addition of rice and lentil flour[J]. LWT,2022,160:113231. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113231
[33] MA M, WEN Y, QIU C, et al. Milling affects rheological and gel textural properties of rice flour[J]. Cereal Chemistry,2020,97(2):205−215. doi: 10.1002/cche.10236
[34] YANG D, GAO S, YANG H. Effects of sucrose addition on the rheology and structure of iota-carrageenan[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,99:105317. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105317
[35] KACZMARSKA K, GRABOWSKA B, SPYCHAJ T, et al. Effect of microwave treatment on structure of binders based on sodium carboxymethyl starch:FT-IR, FT-Raman and XRD investigations[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2018,199:387−393. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2018.03.047
[36] 冀晓龙, 尹明松, 赵阳, 等. 菊粉-小麦淀粉复配体系理化特性及相互作用[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(3):135−140. [JI X L, YIN M S, ZHAO Y, et al. Physicochemical properties of inulin-wheat starch blended systems and the interactions between the components[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(3):135−140.] JI X L, YIN M S, ZHAO Y, et al . Physicochemical properties of inulin-wheat starch blended systems and the interactions between the components[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022 ,48 (3 ):135 −140 .[37] 肖乃勇. 发芽对糙糯米淀粉特性的影响规律及其在汤圆制品中的应用[D]. 郑州:郑州轻工业大学, 2020. [XIAO N Y. Effect of germination on characteristics of starch isolated from waxy brown rice and its application in glutinous dumplings[D]. Zhengzhou:Zhengzhou University of Light Industry, 2020.] XIAO N Y. Effect of germination on characteristics of starch isolated from waxy brown rice and its application in glutinous dumplings[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University of Light Industry, 2020.
[38] WANG S, LUO H, ZHANG J, et al. Alkali-induced changes in functional properties and in vitro digestibility of wheat starch:The role of surface proteins and lipids[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2014,62(16):3636−3643. doi: 10.1021/jf500249w
[39] CHEN L, REN F, ZHANG Z, et al. Effect of pullulan on the short-term and long-term retrogradation of rice starch[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,115:415−421. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.09.006
[40] 黄忠民, 赵蒙姣, 黄婉婧, 等. 不同冻结方式对汤圆品质特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(6):44−48. [HUANG Z M, ZHAO M J, HUANG W J, et al. Effect of freezing methods on the quality characteristics of tang-yuan[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(6):44−48.] HUANG Z M, ZHAO M J, HUANG W J, et al . Effect of freezing methods on the quality characteristics of tang-yuan[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019 ,40 (6 ):44 −48 .[41] LIN Z, GENG D H, QIN W, et al. Effects of damaged starch on glutinous rice flour properties and sweet dumpling qualities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,181:390−397. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.160
[42] ZHANG H, WU F, XU D, et al. Effects of milling methods on the properties of glutinous rice flour and sweet dumplings[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2021,58:1848−1857. doi: 10.1007/s13197-020-04696-9
[43] 翟羽恒. 果胶对糯米淀粉特性的影响及在汤圆中的应用[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2022. [ZHAI Y H. Effect of pectin on the characteristics of waxy rice starch and its application in glutinous rice dumplings[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2022.] ZHAI Y H. Effect of pectin on the characteristics of waxy rice starch and its application in glutinous rice dumplings[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2022.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



